Quantitative Assessment of Optic Disc Elevation in Idiopathic Intracranial Hypertension
|
|
|
- Duane Nicholson
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Med. J. Cairo Univ., Vol. 81, No. 1, September: , Quantitative Assessment of Optic Disc Elevation in Idiopathic Intracranial Hypertension AHMAD M.M. SHALABY, M.D.*; MOHAMMAD A. NASR, M.D.**; NEVIN M. SHALABY, M.D.***; ASMAA M. EBRAHEIM, M.D.*** and REHAM SHAMLOUL, M.D.*** The Departments of Ophthalmology*, Ophthalmic Diagnostic & Laser Unit (DL U)**, Kasr Al Aini Teaching Hospital and Neurology***, Faculty of Medicine, Cairo University Abstract Introduction: Quantification of optic disc elevation in papilledema may predict CSF opening pressure. Objective: To correlate height of papilledema in idiopathic intracranial hypertension (IIH) to cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) opening pressure and visual function and monitor its rate of resolution. Design: Cross-sectional ecological study. Patients and Methods: Twenty female patients with IIH with a mean age of 29.8±5.8 years and mean body mass index (BMI) of 37.3±5.5Kg/m 2 underwent general and neuroophthalmological assessment, brain CT/MRI and magnetic resonance venography (MRV), visual field testing, lumbar puncture (LP) with measuring of CSF opening pressure, and optical coherence tomography (OCT) to measure degree of optic disc elevation at presentation, 3 and 7 days post LP and after 3 and 6 weeks, with clinical follow-up. Results: Mean optic disc elevation from retinal surface to summit pre-lp was 469±216.5tim and mean CSF opening pressure was ±93.85mmH 2 0; they did not correlate with each other. Visual field losses and visual acuity (VA) did not correlate with optic disc height, but correlated positively with CSF opening pressure. The mean optic disc elevation was significantly lower 3 days post-lp and after 6 weeks from treatment compared to pre-lp. Repeated therapeutic LP showed a higher rate of resolution relative to acetazolamide alone. Conclusion: The height of papilledema in IIH is not indicative of CSF opening pressure or visual function. OCT is a beneficial tool for monitoring resolution of papilledema and hence therapeutic efficacy through measuring disc height. Resolution of papilledema is attained within 6 weeks with proper therapeutic measures. Key Words: Optic disc elevation Idiopathic intracranial hypertension. Correspondence to: Dr. Ahmad M.M. Shalaby, The Department of Ophthalmology, Faculty of Medicine, Cairo University Introduction A HALLMARK of idiopathic intracranial hypertension (IIH), is papilledema which is nearly always bilateral, although may be asymmetrical ill. Unfortunately, identification of papilledema in the neurological clinic requires experienced ophthalmoscopic examination. Evaluation is qualitative and subjective and up to 6% of IIH patients do not present with clinical papilledema [2]. Monitoring of IIH using visual field testing provides functional information concerning the degree of optic nerve damage and the change of papilledema over time, therefore provides a useful structural measure of the clinical course and effect of treatment [3]. Optical coherence tomography (OCT) is a promising objective examination modality for optic disc evaluation in IIH with superior sensitivity compared to direct ophthalmoscopy, and fundus photography. Moreover, it improves the identification of subtle disc swellings and measures changes over time [4]. The technique of OCT has been developed for noninvasive cross-sectional imaging in biological systems. OCT produces a two-dimensional image of optical scattering from internal tissue microstructures in a way similar to ultrasonic pulse-echo imaging. OCT has longitudinal and lateral spatial resolutions of a few micrometers [5] (Fig. 1). The rational of this study was based on two main themes; the first is that lumbar puncture may be painful, technically difficult to perform, and may cause a low-pressure headache ill. So, trying to find a means to predict the CSF opening pressure indirectly warrants investigation. Another point is about the frequently raised question: When papilledema is expected to resolve? This study aims at correlating the height of papilledema in IIH patients 643
2 644 Quantitative Assessment of Optic Disc Elevation to CSF opening pressure and visual function, and monitoring the rate of resolution of papilledema utilizing OCT. Subjects and Methods The study included 40 papilledemic eyes of 20 female patients with IIH, according to modified Dandy criteria [2], who were recruited from Kasr Al-Aini Neurology outpatient clinic during Their age ranged from years with a mean of 29.8±5.8 years. Patients were excluded if they had ventricular enlargement or mass lesion on brain imaging, evidence of venous sinus thrombosis on MRV or abnormal CSF chemistry. Patients were compared according to certain characteristics including history of intake of hormonal contraception (estro-progestinic drugs), and disease duration, where they were divided into two groups of <1 year and >1 year duration. The study was performed following all the guidelines for experimental investigations required by the Ethics Committee of Faculty of Medicine, Cairo University. All patients underwent: Clinical assessment including history taking and general medical examination including measuring blood pressure as well as weight and height to calculate BMI in Kg/m 2. Proper neurological examination was done to exclude deficits that may indicate focal brain lesions. Thorough neuro-ophthalmological examination was carried out for 40 eyes which were evaluated for best corrected visual acuity using Snellen chart, ocular motility, pupillary reactions, intraocular pressure and degree of papilledema using indirect ophthalmoscopy. Papilledema was graded into grades I, II, III, IV, and V according to Frisen [6]. Visual field testing was done using the Humphrey automated perimetry where the full threshold test 24-2 test strategy was used. It evaluates the mean deviation and pattern standard deviation (PSD) of retinal sensitivity (MD) in each eye, and the size of the blind spot. The PSD was used to evaluate the deterioration; the higher the PSD the more is the visual field deterioration ill. OCT to measure the degree of optic disc elevation (papilledema height) was carried out in the Ophthalmic Diagnostic and Laser Unit, Kasr Al-Aini Hospital using OCT/SLO (OTI, Toronto, Ontario) device. OCT was performed at initial presentation before performing lumbar puncture, 3days and 7 days after lumbar puncture and then by the end of the 3rd and 6th weeks. Disc elevation was measured from the retinal surface to summit in the superior, inferior, nasal and temporal quadrants, and then the mean disc elevation in the four quadrants was calculated. Brain Imaging by CT/MRI and MRV was done for all patients. Spinal tap was carried out for all patients. The procedure was explained to the patient. LP was done under complete aseptic conditions, the area was carefully prepared. The location of the needle was identified between the two spinous processes of L4 and L5 levels. A 20- gauge needle was used, CSF opening pressure was measured in the left lateral decubitus using a manometer, and CSF samples were obtained. Frequency of lumbar puncture and amount of CSF withdrawn was determined for each patient individually. Clinical follow-up for symptomatic improvement and fundus picture was done after 1 week, 3, 6 and 8 weeks. Treatment modality was reported and the dose of medical treatment and amount of CSF withdrawn were recorded. Statistical analysis: Descriptive analyses were conducted to examine frequencies; mean was used as measure of central tendency with standard deviation as measure of dispersion. Pearson correlation was used to study the relation between qualitative variables. To test the significance of difference between quantitative and qualitative variable t-test was used. Paired t- test was used to compare pre and post variables of the same patient. Results Patients and headache characteristics: The mean BMI for the patients was 37.3±5.5 Kg/m 2. The mean duration of the syndrome was 23.7±32.7 months, where 12 patients (24 eyes, 60%) reported <1 year duration and 8 patients (16 eyes, 40%) reported >1 year duration (one of them had a duration of 9 years). Eight patients only (16 eyes, 40%) received estro-progestinic drugs for hormonal contraception at a certain time in their lives for periods ranging from 4-24 months, but none of them was using it at time of presentation. History of menstrual irregularities was given by 10 patients (20 eyes, 50%), hormonal assay for whom was not done, being outside the scope of our study. Grade I papilledema was observed in 15 eyes (37.5%), grade II in 24 eyes (60%) and grade V in 1 eye (2.5%). Corrected visual acuity was 6/6 in 13 eyes (32.5%), 6/9 in 13 eyes (32.5%), 6/18 in 8 eyes (20%), 6/24 in 3 eyes (7.5%), 6/36 in 2 eyes (5%) and counting fingers at 50cm in 1 eye (2.5%) which had post papilledemic optic atrophy. The pattern standard deviation (PSD) of visual field testing of both eyes ranged from DB with a mean of 3.79±2.1 DB.
3 Ahmad M.M. Shalaby, et al. 645 Headache was the presenting symptom in all patients (100%), the main visual symptoms were blurring of vision in 18 patients (36 eyes, 90%) and transient visual obscurations in 10 patients (20 eyes, 50%), diplopia was reported by 2 patients (4 eyes, 10%), but no limitation of ocular motility was observed by time of examination, and diminution of VA was reported by one patient (2 eyes, 5%). Other associated symptoms included intracranial noises (10 patients; 50%); nausea (8 patients; 40%); phonophobia (3 patients; 15%); fatigue (4 patients; 20%); dizziness (3 patients; 15%) and photophobia (1 patient, 5%). The treatment modalities used were acetazolamide which was received by all patients (100%) at a mean dose of 1475±543mg, repeated therapeutic LP, carried out for 8 patients (40%) after the primary LP done with OCT, where the mean amount of CSF withdrawn was 140.8±40.7mm and lumboperitoneal shunt was done for 1 patient (5%). Corticosteroids were reserved to those who complained of diminution of VA, and in our series the only patient who had this complaint was diabetic. Pre-LP findings: Regarding the findings of OCT, the mean optic disc diameter of both eyes was 1.68±0.16mm, of the right eye 1.67±0.11mm, and of the left eye was 1.68±0.21mm with no significant difference between both eyes (p=0.9). The mean optic disc elevation from retinal surface to summit pre-lp was 469±216.5gm. It ranged from p,m in clinically diagnosed grade I papilledema and from gm in grade II. The right optic disc diameter showed inverse correlation with degree of disc elevation but this was far from statistical significance (r=-0.17, p=0.63) and no correlation was observed between optic disc diameter of both eyes and mean degree of disc elevation (r=0.24, 0.27). Pattern standard deviation (PSD) of retinal sensitivity did not correlate with either mean degree of disc elevation (r=-0.13, p=0.58) or optic disc diameter (r=0.26, p=0.25). No correlation was found between degree of disc elevation and VA (r=0.14, p=0.5), age (r=-0.27, p=0.21), BMI (r=-0.21, p=0.35). Mean optic disc elevation did not differ between patients with and without menstrual irregularities (p=0.63). However, patients who received hormonal contraception had higher mean disc elevation compared to those who did not receive (p=0.04). Regarding results of visual field testing in relation to patients and disease characteristics, PSD of retinal sensitivity correlated positively with BMI (r=0.46, p=0.04), and age of the patients but this latter relation did not reach statistical significance (x=0.43, p=0.05). No correlation was found between visual field deterioration and VA (r=0.36, p=0.11) or disease duration (r=-0.25, p=0.28). Post-LP findings: The CSF opening pressure ranged from mmH 2 0 with a mean of mmH 2 0; 10 patients had a CSF opening pressure of mmH20. No statistically significant correlation was found between mean degree of disc elevation and CSF opening pressure neither in the whole patient group (r=0.09, p=0.69) nor in the recently diagnosed ones alone (<1 year duration) (r=0.04, p=0.78). Also, the height of each disc sector individually (upper, lower, nasal and temporal) did not correlate with CSF opening pressure (p>0.05). CSF opening pressure did not correlate with optic disc diameter (r=0.28, p=0.20), however, it correlated positively with PSD of retinal sensitivity on visual field testing (r=0.49,p=0.02) and negatively with VA (r=-0.43, p=0.03). Mean CSF opening pressure did not differ between patients who received hormonal contraception compared to those who did not (p=0.7). A statistically significant correlation was found between CSF opening pressure and age of the patients (r=0.7, p=0.0001). CSF opening pressure tended to correlate positively with BMI but it hardly reached statistical significance (x=0.40, p=0.05). No correlation was found between opening pressure and disease duration (r=-0.06, p=0.79). The mean amount of CSF withdrawn on initial LP was 130.3±50.3mm. Disc elevation correlated inversely with amount of CSF withdrawn, however, this relation did not reach statistical significance (r=-0.21, p=0.42). The mean optic disc elevation was significantly lower 3 days after the initial LP (p0.01) (Fig. 2) and after 6 weeks from treatment (whether medical alone or accompanied with repeated LPs) (p0.02) compared to pre-lp measurement (Fig. 3). The disc elevation was also lower after 7 days and 3 weeks than pre-lp, yet the difference was not statistically significant (p0.06 and 0.71 respectively). Table (1) and Fig. (4) show the mean optic disc height pre-lp and serially after therapy. Patients who underwent repeated therapeutic LPs (n=8) showed a higher rate of papilledema resolution (percent of change of disc height) compared to those who underwent single diagnostic LP (received medical treatment only), however the difference did not reach statistical significance (p=0.07) (Fig. 5).
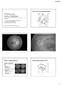
4 646 Quantitative Assessment of Optic Disc Elevation Fig. (1): An OCT tomogram of a normal retina NFL: Nerve fiber layer, RPE: Retinal pigmentary epithelium. Fig. (2): OCT 3 days post-lp. Fig. (3): Retinal OCT Pre-LP " 50 0 Pre-LP 3 days Post-LP Mean Disc Thickness) 7 7 days 3 weeks 6 weeks Post-LP Fig. (4): Serial mean optic disc height (um) by OCT during the follow-up period Single LP Repeated LP Fig. (5): Percentage of resolution of papilledema in patients who underwent single diagnostic LP compared to those who underwent repeated therapeutic LPs. Table (1): Mean optic disc height by OCT on serial measurements. Timing Mean (SD) Gm) p-value (In relation to Pre-LP measurement) Pre-LP 469 (216.5) 3 Days after initial LP 326 (190.5) 0.01 * 7 Days after initial LP (202) weeks after initial LP 440 (224.9) weeks after initial LP 340 (172.6) 0.02* * Statistically significant. Discussion This study was directed to investigate the relation of CSF opening pressure to optic disc height in papilledema of IIH patients as well as to followup the rate of resolution of papilledema. The CSF opening pressure did not correlate with the mean degree of optic disc elevation even in the recently diagnosed patients (<1 year; to avoid possibility of gliosis of optic nerve head with long standing papilledema) [7]. This lack of significant correlation was also observed clinically; some patients with early papilledema had high CSF opening pressure
5 Ahmad M.M. Shalaby, et al. 647 and conversely others with evident mushrooming of optic disc exhibited modest pressure elevations. This agrees with what has been mentioned in literature that IIH could occur without papilledema; in a previous study 10% of 62 patients with headache had elevated CSF opening pressure but none of the patients had papilledema [8], implying that high CSF pressure does not necessarily have to be fully transmitted to the optic nerve head. This can be explained on the basis of anatomic and histological considerations; the lamina cribrosa is related to the direct transmission of elevated CSF pressure, a more posterior lamina cribrosa position is related to greater ophthalmoscopically non apparent edema [7]. Also, the prelaminar region of the optic nerve contains bundles of axons within astrocytic channels the processes of which form loose supportive glial tissue which does not bind the axon bundles tightly together, therefore fibers are easily separated and the disc swells easily in papilledema [9]. Radius and Gonzales [10] have confirmed a regional variation in the distribution of supportive glial and connective tissue between nerves of different individuals. These anatomic considerations can also contribute to asymmetrical bilateral papilledema. One study 1111 utilizing a comparable technique, which is laser scanning tomography (LST), could find significant linear correlation of the papilla height with the CSF opening pressure. This difference can be largely attributed to the use of various techniques. Though LST allows a 2.5-dimensional assessment of the papilla and its volume, yet OCT utilized in this study, has a superior axial resolution [12]. Another possible factor was that none of the patients in the other study had a CSF opening pressure higher than 400mm water, while in our study 10 patients had a CSF opening pressure of mm water. A further concern might be a potential ceiling effect, despite an increasing CSF opening pressure over 400mm water, the papilla volume and height would not be expected to reveal infinite linear correlation, but would instead converge to a limiting value of papilla volume and papilla height which seems logical for anatomic reasons [9]. On the other hand, Skau et al. [4], using OCT, reported that increased peripapillary retinal thickness measurements is closely associated with increased CSF opening pressure in newly diagnosed IIH patients. However, in patients with long-term IIH, OCT is of limited value in predicting intracranial pressure. The patient sample in that study was double the sample we studied. Also the OCT utilized, though a time domain one as the OCT we used; is a faster and more advanced machine and the authors used different measurement technique. We also investigated the effect of optic disc diameter as well as body mass index on degree of optic disc elevation, and we observed an inverse correlation between right disc diameter and disc height, but this was far from statistical significance. BMI had no influence on disc height though it tended to correlate positively with CSF opening pressure (p=0.05). This goes in accordance with Whiteley et al. [13] who stated that body mass index had a small but clinically insignificant influence on CSF opening pressure. No correlation was found between visual field losses and height of papilledema in the current work. Studies evaluating the correlation between degree of papilledema and visual field loss have reported different and, at least inpart, conflicting results. Although a qualitative correlation between high-grade papilledema and perimetric loss has been found by some investigators [14], Gael et al. [is], in accordance with our results did not find any quantitative correlation between Heidelberg retina tomograph measurements of disc swelling and automated field sensitivity. Mulholland et al. [16] reported that, in individual patients with IIH, changes in disc volume were qualitatively correlated with corresponding perimetric sensitivity changes in the short term. However, no quantitative correlations were reported, either in cross-sectional or longitudinal measurements. In this work, the VA did not correlate with degree of disc elevation. There is no evidence of whether functional damage is related mostly to the ophthalmoscopically apparent or non-apparent edema [7]. However, in another study vision tended to be worse in the eye with the high-grade papilledema [17]. Both visual field losses and visual acuity were worse with higher CSF pressure (p.02 and 0.03 respectively). Previous CT and MRI studies in patients with chronically high CSF pressure have postulated that the true edema has only a contributing role in disc elevation, indicating a bulging of the terminal optic sheath subarachnoid space into the posterior aspect of the globe at the optic nerve head as a major factor [18], thus another factor, in addition to edema, contributes to further compression of optic nerve axons in cases of high CSF pressure and hence worsening of visual function. In this work, more visual field losses were observed in patients with higher BMI who tended to have higher CSF opening pressure. An interesting finding was that patients who received hormonal contraception had statistically significant higher mean disc elevation compared to those who did not (p=0.04), however, they did not differ in CSF opening pressure. Yanoff and
6 648 Quantitative Assessment of Optic Disc Elevation Fine7 mentioned that in addition to blockade of the optic nerve axoplasmic flow at the level of lamina choroidalis and lamina scleralis through increased intracranial pressure, hormonal contraception induces local phenomenon at the lamina cribrosa, but they did not specify such phenomenon. A theoretically attractive concept, to explain this, can be the increasing incorporation of progesterone into estrogen contraceptive pills [19], it is known that high levels of estrogen and progesterone cause increased connective tissue laxity, as during pregnancy [20], this increased laxity may involve the optic nerve supportive tissue inducing more looseness of axon bundles and allowing easier separation and more swelling in cases of papilledema. However, all the patients in the current study were not on hormonal contraception at time of presentation or shortly before, and investigating such relation warrants further research as it is beyond the scope of this study. Another interesting finding was the presence of a statistically significant correlation between CSF opening pressure and age of the patients (r=0.7, p=0.0001). Although absorption of cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) occurs through arachnoid granulations and extracranial lymphatics, outflow resistance is increased in IIH; therefore, intracranial pressure must increase for CSF to be absorbed [21]. An MRI imaging-based study [22] showed that there was increased CSF production in aged subjects as compared with production in young subjects. Hence our result could be expected. The second objective in our study was to assess quantitatively the rate of resolution of papilledema following the primary LP and medical treatment. To serve this aim, patients were followed with OCT 3 days and 1 week after spinal tap and after 3 and 6 weeks. Disc elevation correlated inversely with amount of CSF withdrawn; however, this correlation did not reach statistical significance. Generally, the disc height showed fluctuation in the follow-up period (in comparison to pre-lp findings) to be at the lowest level 3 days post-lp (p=0.01); then a slight rise occurred after 7 days (p=0.06); a further significant rise occurred by 3 weeks which almost approached the pre-lp level (p=0.7), which can be attributed to: The reluctance of patients in receiving their medications due to improvement of symptoms and/or appearance of acral paresthesia caused by acetazolamide; under dosage of medical treatment; variable rate of reformation of CSF and the need for repeated lumbar punctures. At this point, strict instructions were given to patients to receive their medication regularly, potassium supplements were added, doses were readjusted, and repeated therapeutic LPs were done for selected patients, so by 6th week another remarkable decline in disc height was observed (p=0.02). The 8 patients who underwent repeated LP showed better resolution of papilledema than those who only performed the initial LP. This implies that OCT can serve in assessment of the efficacy of line of treatment used, thus can contribute to modification of dosage of medical treatment or recommends another line of treatment, this in agreement with Mulholland et al. [16] who used a comparable technique (confocal scanning laser tomography) to confirm therapeutic failure by detecting stable or increasing disc volume. Confocal scanning laser tomography can quantify the magnitude and monitor the resolution of papilledema in IIH. Studies of optic nerve head topography may provide further insight into optic nerve compliance with elevated intracranial pressure [4]. Patients were followed-up to 6 weeks. Papilledema showed evident resolution by the 6th week with our treatment policy. One patient presented with post-papilledemic optic atrophy and a VA of counting fingers at 50cm in right eye and deterioration of VA and grade II papilledema in the left eye underwent lumboperitoneal shunt, though the papilla height was comparable in both eyes, yet no improvement of VA in the right eye, while the left eye VA improved to 6/6 and fundus picture was almost normal after 1 month. This implies that disc height does not predict prognosis. Conclusion: The height of optic disc in papilledema of IIH patients does not necessarily reflect the CSF opening pressure or visual function; however, serial measurement of this height by OCT can be a useful tool for monitoring the therapeutic efficacy via observing the degree of decline or rise and accordingly helps adjusting treatment plan. Repeated therapeutic LPs result in a more rapid resolution of papilledema than acetazolamide alone. With proper plan of therapy the resolution of papilledema can be attained over 6 (provided the course is not malignant). OCT cannot replace the fundamental role of visual field testing. References 1- KANSKI J.J.: Clinical Ophthalmology, A systematic Approach. 5th ed. Butterworth Heinemann, Elsevier Science Limited, DIGRE K.B., NAKAMOTO B.K., WORNER J.E.A., LANGERBERG W.J., BAGGALEY S.K. and KATZ B.J.: A comparison of idiopathic intracranial hypertension with and without papilledema. Headache, 49: , 2009.
7 Ahmad M.M. Shalaby, et al FRIEDMAN D.I. and JACOBSON D.M.: Idiopathic Intracranial Hypertension. J. Neuro-Ophthalmol., 24: , SKAU M., YRI H., SANDER B., GERDS S., MILEA D. and JENES R.: Diagnostic value of optical coherencetomography for intracranial pressure in idiopathic intracranial hypertension. Graefe's Arch. Clin. Exp. Ophthalmol., 251 (2): , RUTLEDGE B.K., PULIAFITO C.A. and DUKER J.S.: Optical coherence tomography of macular lesions associated with optic nerve head pits. Ophthalmology, 103: 1047, FRISEN L.: J. Neurol. Neurosurg Psychiatry, 45: 13-18, YANOFF M. and FINE B.S.: Ocular pathology, Vol. 2. Optic disc edema, p th ed. Morton E. Smith, Mosby Inc., VIEIRA D.S., MASRUHA M.R., GOKALVES A.L., ZUKERMAN E., SENNE SOARES C.A., NAFFAH- MAZZACORATTI MDA G. and PERES M.F.: Idiopathic intracranial hypertension with and without papilloedema in a consecutive series of patients with chronic migraine. Cephalalgia. Jun., 28 (6): , BRON A.J., TRIPATHI R.C. and TRIPATHI B.J.: Wolff s Anatomy of the Eye and Orbit, The visual pathway. p th ed. Chapman & Hall Medical, RADIUS R.L. and GONZALES M.: Anatomy of the lamina cribrosa in human eyes. Arch Ophthalmol., Vol: 99, 478, Cited in: Bron A.J., Tripathi R.C., Tripathi B.J. Wolff s Anatomy of the Eye and Orbit, The visual pathway. p th ed. Chapman & Hall Medical, HECKMANN J.G., WEBER M., JONEMANN A.G., NEUNDORFER B. and MARDIN C.Y.: Laser scanning tomography of the optic nerve vs CSF opening pressure inidiopathic intracranial hypertension. Neurology Apr., 13; 62 (7): , YEOW T.W., YANG V.X.D., CHAHWAN A., GORDON M.L., QI B., VITKIN I.A., WILSON B.C. and GOLDEN- BERG A.A.: Micromachined 2-D scanner for 3-D optical coherence tomography. Sensors and Actuators A., 117 (2): , WHITELEY W., AL-SHAHI M.A., WARLOW C.P., ZEIDLER M. and LUECK C.J.: CSF opening pressure: Reference interval and the effect of body mass index. Neurology, 67: 1-1, SMITH T.J. and BAKER R.S.: Perimetric findings in pseudotumor cerebri using automated techniques. Ophthalmology, 93: , GOBEL W., LOEB W.E. and GRAIN H.J.: Quantitative and objective follow-up of papillary swelling with the Heidelberg Retina Tomograph. Ophthalmology, 94: , MULHOLLAND D.A., CRAIG J.J. and RANKIN S.J.A.: Use of scanning laser ophthalmoscopy to monitor papilloedema in idiopathic intracranial hypertension. Br. J. Ophthalmol., 82: , WALL M. and WHITE W.N.: Asymmetric papilledema in idiopathic intracranial hypertension: Prospective interocular comparison of sensory visual function. Invest. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci., 39: , JINKINS J.R., ATHALE S., XIONG L., YUH W.T.C., ROTHMAN M.I. and NGUYEN P.T.: MR of optic papilla protrusion in patients with high intracranial pressure Am. J. Neuroradiol., 17: (Abst), CIANCI A. and DE LEO V.: Individualization of lowdose oral contraceptives. Pharmacological principles and practical indications for oral contraceptives. Minerva Ginecol. Aug., 59 (4): (Abst), HEWETT T.E.: Neuromuscular and hormonal factors associated with knee injuries in female athletes. Strategies for intervention. Sports Med. May, 29 (5): , WALL M.: Idiopathic intracranial hypertension (pseudotumor cerebri). Curt Neurol. Neurosci. Rep. Mar., 8 (2): (Abst), GIDEON P., THOMSEN C., STAHLBERG F. and HEN- RIKSEN 0.: Cerebrospinal fluid production and dynamics in normal aging: A MRI phase-mapping study. Acta. Neurol. Scand, 89: , 1994.
Use of scanning laser ophthalmoscopy to monitor papilloedema in idiopathic intracranial hypertension
 Br J Ophthalmol 998;8:35 3 Ophthalmology, Royal Victoria Hospital, Belfast D A Mulholland S J A Rankin Neurology, Royal Victoria Hospital, Belfast J J Craig Correspondence to: Mr David A Mulholland, Ophthalmology,
Br J Ophthalmol 998;8:35 3 Ophthalmology, Royal Victoria Hospital, Belfast D A Mulholland S J A Rankin Neurology, Royal Victoria Hospital, Belfast J J Craig Correspondence to: Mr David A Mulholland, Ophthalmology,
Papilledema. Golnaz Javey, M.D. and Jeffrey J. Zuravleff, M.D.
 Papilledema Golnaz Javey, M.D. and Jeffrey J. Zuravleff, M.D. Papilledema specifically refers to optic nerve head swelling secondary to increased intracranial pressure (IICP). Optic nerve swelling from
Papilledema Golnaz Javey, M.D. and Jeffrey J. Zuravleff, M.D. Papilledema specifically refers to optic nerve head swelling secondary to increased intracranial pressure (IICP). Optic nerve swelling from
IDIOPATHIC INTRACRANIAL HYPERTENSION
 IDIOPATHIC INTRACRANIAL HYPERTENSION ASSESSMENT OF VISUAL FUNCTION AND PROGNOSIS FOR VISUAL OUTCOME Doctor of Philosophy thesis Anglia Ruskin University, Cambridge Fiona J. Rowe Department of Orthoptics,
IDIOPATHIC INTRACRANIAL HYPERTENSION ASSESSMENT OF VISUAL FUNCTION AND PROGNOSIS FOR VISUAL OUTCOME Doctor of Philosophy thesis Anglia Ruskin University, Cambridge Fiona J. Rowe Department of Orthoptics,
Typical idiopathic intracranial hypertension Optic nerve appearance and brain MRI findings. Jonathan A. Micieli, MD Valérie Biousse, MD
 Typical idiopathic intracranial hypertension Optic nerve appearance and brain MRI findings Jonathan A. Micieli, MD Valérie Biousse, MD A 24 year old African American woman is referred for bilateral optic
Typical idiopathic intracranial hypertension Optic nerve appearance and brain MRI findings Jonathan A. Micieli, MD Valérie Biousse, MD A 24 year old African American woman is referred for bilateral optic
Neuro-Ocular Grand Rounds
 Neuro-Ocular Grand Rounds Anthony B. Litwak,OD, FAAO VA Medical Center Baltimore, Maryland Dr. Litwak is on the speaker and advisory boards for Alcon and Zeiss Meditek COMMON OPTIC NEUROPATHIES THAT CAN
Neuro-Ocular Grand Rounds Anthony B. Litwak,OD, FAAO VA Medical Center Baltimore, Maryland Dr. Litwak is on the speaker and advisory boards for Alcon and Zeiss Meditek COMMON OPTIC NEUROPATHIES THAT CAN
MOHAMED LOTFY, M.D.*; MOATAZ A. EL-AWADY, M.D.**; ASHRAF E. ZAGHLOUL, M.D.** and TAREK NEHAD, M.D.***
 Med. J. Cairo Univ., Vol. 84, No. 2, December: 301-306, 2016 www.medicaljournalofcairouniversity.net Effect of Therapeutic Lumbar Puncture on the Visual Outcome and the Further Need for Surgery in Patients
Med. J. Cairo Univ., Vol. 84, No. 2, December: 301-306, 2016 www.medicaljournalofcairouniversity.net Effect of Therapeutic Lumbar Puncture on the Visual Outcome and the Further Need for Surgery in Patients
Prevalence of venous sinus stenosis in Pseudotumor cerebri(ptc) using digital subtraction angiography (DSA)
 Prevalence of venous sinus stenosis in Pseudotumor cerebri(ptc) using digital subtraction angiography (DSA) Dr.Mohamed hamdy ibrahim MBBC,MSc,MD, PhD Neurology Degree Kings lake university (USA). Fellow
Prevalence of venous sinus stenosis in Pseudotumor cerebri(ptc) using digital subtraction angiography (DSA) Dr.Mohamed hamdy ibrahim MBBC,MSc,MD, PhD Neurology Degree Kings lake university (USA). Fellow
Optical coherence tomography of the retinal nerve fibre layer in mild papilloedema and pseudopapilloedema
 294 SCIENTIFIC REPORT Optical coherence tomography of the retinal nerve fibre layer in mild papilloedema and pseudopapilloedema E Z Karam, T R Hedges... Aims: To determine the degree to which optical coherence
294 SCIENTIFIC REPORT Optical coherence tomography of the retinal nerve fibre layer in mild papilloedema and pseudopapilloedema E Z Karam, T R Hedges... Aims: To determine the degree to which optical coherence
NANOS Patient Brochure
 NANOS Patient Brochure Pseudotumor Cerebri Copyright 2016. North American Neuro-Ophthalmology Society. All rights reserved. These brochures are produced and made available as is without warranty and for
NANOS Patient Brochure Pseudotumor Cerebri Copyright 2016. North American Neuro-Ophthalmology Society. All rights reserved. These brochures are produced and made available as is without warranty and for
Index. Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type.
 Index Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A Acetazolamide, in idiopathic intracranial hypertension, 49 52, 60 Angiography, computed tomography, in cranial nerve palsy, 103 107 digital
Index Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A Acetazolamide, in idiopathic intracranial hypertension, 49 52, 60 Angiography, computed tomography, in cranial nerve palsy, 103 107 digital
Pearls, Pitfalls and Advances in Neuro-Ophthalmology
 Pearls, Pitfalls and Advances in Neuro-Ophthalmology Nancy J. Newman, MD Emory University Atlanta, GA Consultant for Gensight Biologics, Santhera Data Safety Monitoring Board for Quark AION Study Medical-legal
Pearls, Pitfalls and Advances in Neuro-Ophthalmology Nancy J. Newman, MD Emory University Atlanta, GA Consultant for Gensight Biologics, Santhera Data Safety Monitoring Board for Quark AION Study Medical-legal
BMB Disclosures. Papilledema can be a. Neurological Emergency, Causing Preventable Blindness
 Reasonable Doubt: Can High Intracranial Pressure Occur Without Papilledema? 15 February 2013 Jonathan C. Horton hortonj@vision.ucsf.edu http://www.ucsf.edu/hortonlab BMB Disclosures Financial Disclosures
Reasonable Doubt: Can High Intracranial Pressure Occur Without Papilledema? 15 February 2013 Jonathan C. Horton hortonj@vision.ucsf.edu http://www.ucsf.edu/hortonlab BMB Disclosures Financial Disclosures
Neuro-Ocular Grand Rounds Anthony B. Litwak,OD, FAAO VA Medical Center Baltimore, Maryland
 Neuro-Ocular Grand Rounds Anthony B. Litwak,OD, FAAO VA Medical Center Baltimore, Maryland Dr. Litwak is on the speaker and advisory boards for Alcon and Zeiss Meditek COMMON OPTIC NEUROPATHIES THAT CAN
Neuro-Ocular Grand Rounds Anthony B. Litwak,OD, FAAO VA Medical Center Baltimore, Maryland Dr. Litwak is on the speaker and advisory boards for Alcon and Zeiss Meditek COMMON OPTIC NEUROPATHIES THAT CAN
OCT in the Diagnosis and Follow-up of Glaucoma
 OCT in the Diagnosis and Follow-up of Glaucoma Karim A Raafat MD. Professor Of Ophthalmology Cairo University Hmmmm! Do I have Glaucoma or not?! 1 Visual Function 100% - N Gl Structure : - 5000 axon /
OCT in the Diagnosis and Follow-up of Glaucoma Karim A Raafat MD. Professor Of Ophthalmology Cairo University Hmmmm! Do I have Glaucoma or not?! 1 Visual Function 100% - N Gl Structure : - 5000 axon /
What is IIH? Idiopathic Intracranial Hypertension (IIH)
 What is IIH? Idiopathic Intracranial Hypertension (IIH) What is Idiopathic Intracranial Hypertension? Idiopathic intracranial hypertension (IIH), also known as benign intracranial hypertension or pseudotumour
What is IIH? Idiopathic Intracranial Hypertension (IIH) What is Idiopathic Intracranial Hypertension? Idiopathic intracranial hypertension (IIH), also known as benign intracranial hypertension or pseudotumour
Idiopathic Intracranial Hypertension (Pseudotumor Cerebri) David I. Kaufman, D.O. Michigan State University Department of Neurology and Ophthalmology
 Idiopathic Intracranial Hypertension (Pseudotumor Cerebri) David I. Kaufman, D.O. Michigan State University Department of Neurology and Ophthalmology 26 year old 5 3, 300 pound female with papilledema,
Idiopathic Intracranial Hypertension (Pseudotumor Cerebri) David I. Kaufman, D.O. Michigan State University Department of Neurology and Ophthalmology 26 year old 5 3, 300 pound female with papilledema,
THE SWOLLEN DISC. Valerie Biousse, MD Emory University School of Medicine Atlanta, GA
 THE SWOLLEN DISC Valerie Biousse, MD Emory University School of Medicine Atlanta, GA Updated from: Neuro-Ophthalmology Illustrated. Biousse V, Newman NJ. Thieme, New-York,NY. 2 nd Ed, 2016. Edema of the
THE SWOLLEN DISC Valerie Biousse, MD Emory University School of Medicine Atlanta, GA Updated from: Neuro-Ophthalmology Illustrated. Biousse V, Newman NJ. Thieme, New-York,NY. 2 nd Ed, 2016. Edema of the
Management of Pseudo Tumor Cerebri by Frequent Tapping VS lumboperitoneal Shunt
 The Egyptian Journal of Hospital Medicine (July 2018) Vol. 72 (5), Page 4556-4560 Management of Pseudo Tumor Cerebri by Frequent Tapping VS lumboperitoneal Shunt Ali K. Ali, Maamoun M. Abo Shousha, Mohammed
The Egyptian Journal of Hospital Medicine (July 2018) Vol. 72 (5), Page 4556-4560 Management of Pseudo Tumor Cerebri by Frequent Tapping VS lumboperitoneal Shunt Ali K. Ali, Maamoun M. Abo Shousha, Mohammed
Case Series. The efficacy of optic nerve ultrasonography for differentiating papilloedema from pseudopapilloedema in eyes with swollen optic discs
 Case Series The efficacy of optic nerve ultrasonography for differentiating papilloedema from pseudopapilloedema in eyes with swollen optic discs Meira Neudorfer, Maytal Siegman Ben-Haim, Igal Leibovitch
Case Series The efficacy of optic nerve ultrasonography for differentiating papilloedema from pseudopapilloedema in eyes with swollen optic discs Meira Neudorfer, Maytal Siegman Ben-Haim, Igal Leibovitch
Greater than expected prevalence of pseudotumor cerebri: a prospective study
 Surgery for Obesity and Related Diseases 9 (2013) 77 82 Original article Greater than expected prevalence of pseudotumor cerebri: a prospective study Isam N. Hamdallah, M.D., Hazem N. Shamseddeen, M.D.,
Surgery for Obesity and Related Diseases 9 (2013) 77 82 Original article Greater than expected prevalence of pseudotumor cerebri: a prospective study Isam N. Hamdallah, M.D., Hazem N. Shamseddeen, M.D.,
Khalil Zahra, M.D Neuro-interventional radiology
 Khalil Zahra, M.D Neuro-interventional radiology 1 Disclosure None 2 Outline Etiology and pathogensis Imaging techniques and Features Literature review Treatment modalities Endovascular techniques Long
Khalil Zahra, M.D Neuro-interventional radiology 1 Disclosure None 2 Outline Etiology and pathogensis Imaging techniques and Features Literature review Treatment modalities Endovascular techniques Long
Intracranial hypertension and headache. Daniel Tibussek, MD
 Intracranial hypertension and headache. Daniel Tibussek, MD none Disclosures Overview Case Clinical presentation of pediatric PTC Nomenclature, Definition What is intracranial hypertension? Diagnostic
Intracranial hypertension and headache. Daniel Tibussek, MD none Disclosures Overview Case Clinical presentation of pediatric PTC Nomenclature, Definition What is intracranial hypertension? Diagnostic
Idiopathic Intracranial Hypertension
 Idiopathic Intracranial Hypertension Dr. Mar'n Su+onBrown MD. FRCPC Neuro-Ophthalmology, Neurology Div of Neurology, Island Health Clinical Assistant Professor, Div of Neurology, UBC Stroke Rapid Assessment
Idiopathic Intracranial Hypertension Dr. Mar'n Su+onBrown MD. FRCPC Neuro-Ophthalmology, Neurology Div of Neurology, Island Health Clinical Assistant Professor, Div of Neurology, UBC Stroke Rapid Assessment
11/10/2017. Headache and Increased Pressure: A tale of 2 cases. Kathleen Digre MD University of Utah TWO CASES. 23 yo medical practice manager
 Headache and Increased Pressure: A tale of 2 cases Kathleen Digre MD University of Utah TWO CASES 23 yo medical practice manager September 2016 began developing intense frontal headaches first intermittent
Headache and Increased Pressure: A tale of 2 cases Kathleen Digre MD University of Utah TWO CASES 23 yo medical practice manager September 2016 began developing intense frontal headaches first intermittent
Retinal Nerve Fiber Layer Measurements in Myopia Using Optical Coherence Tomography
 Original Article Philippine Journal of OPHTHALMOLOGY Retinal Nerve Fiber Layer Measurements in Myopia Using Optical Coherence Tomography Dennis L. del Rosario, MD and Mario M. Yatco, MD University of Santo
Original Article Philippine Journal of OPHTHALMOLOGY Retinal Nerve Fiber Layer Measurements in Myopia Using Optical Coherence Tomography Dennis L. del Rosario, MD and Mario M. Yatco, MD University of Santo
Cases of visual impairment caused by cerebral venous sinus occlusion-induced intracranial hypertension in the absence of headache
 Zhao et al. BMC Neurology (2018) 18:159 https://doi.org/10.1186/s12883-018-1156-7 CASE REPORT Open Access Cases of visual impairment caused by cerebral venous sinus occlusion-induced intracranial hypertension
Zhao et al. BMC Neurology (2018) 18:159 https://doi.org/10.1186/s12883-018-1156-7 CASE REPORT Open Access Cases of visual impairment caused by cerebral venous sinus occlusion-induced intracranial hypertension
Chapter 2 Long Duration Flight Data
 Chapter 2 Long Duration Flight Data Astronaut s bodies suffer in microgravity. Without effective countermeasures, muscles atrophy, bones shed calcium, and eyesight deteriorates. We ve known about this
Chapter 2 Long Duration Flight Data Astronaut s bodies suffer in microgravity. Without effective countermeasures, muscles atrophy, bones shed calcium, and eyesight deteriorates. We ve known about this
Retinal nerve fiber layer thickness in Indian eyes with optical coherence tomography
 Original articles in Indian eyes with optical coherence tomography Malik A, Singh M, Arya SK, Sood S, Ichhpujani P Department of Ophthalmology Government Medical College and Hospital, Sector 32, Chandigarh,
Original articles in Indian eyes with optical coherence tomography Malik A, Singh M, Arya SK, Sood S, Ichhpujani P Department of Ophthalmology Government Medical College and Hospital, Sector 32, Chandigarh,
Macular Ganglion Cell Complex Measurement Using Spectral Domain Optical Coherence Tomography in Glaucoma
 Med. J. Cairo Univ., Vol. 83, No. 2, September: 67-72, 2015 www.medicaljournalofcairouniversity.net Macular Ganglion Cell Complex Measurement Using Spectral Domain Optical Coherence Tomography in Glaucoma
Med. J. Cairo Univ., Vol. 83, No. 2, September: 67-72, 2015 www.medicaljournalofcairouniversity.net Macular Ganglion Cell Complex Measurement Using Spectral Domain Optical Coherence Tomography in Glaucoma
The headache profile of idiopathic intracranial hypertension
 The headache profile of idiopathic intracranial hypertension Michael Wall CEPHALALGIA Wall M. The headache profile of idiopathic intracranial hypertension. Cephalalgia 1990;10:331-5. Oslo. ISSN 0333-1024
The headache profile of idiopathic intracranial hypertension Michael Wall CEPHALALGIA Wall M. The headache profile of idiopathic intracranial hypertension. Cephalalgia 1990;10:331-5. Oslo. ISSN 0333-1024
I diopathic intracranial hypertension (IIH) presents commonly
 206 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Visual failure without headache in idiopathic intracranial hypertension M Lim, M Kurian, A Penn, D Calver, J-P Lin... See end of article for authors affiliations... Correspondence
206 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Visual failure without headache in idiopathic intracranial hypertension M Lim, M Kurian, A Penn, D Calver, J-P Lin... See end of article for authors affiliations... Correspondence
Glaucoma: Diagnostic Modalities
 Glaucoma: Diagnostic Modalities - Dr. Barun Kumar Nayak, Dr. Sarika Ramugade Glaucoma is a leading cause of blindness in the world, especially in older people. Early detection and treatment by ophthalmologist
Glaucoma: Diagnostic Modalities - Dr. Barun Kumar Nayak, Dr. Sarika Ramugade Glaucoma is a leading cause of blindness in the world, especially in older people. Early detection and treatment by ophthalmologist
S uperior segmental optic hypoplasia (SSOH), also termed
 910 CLINICAL SCIENCE Optical coherence tomography of superior segmental optic hypoplasia K Unoki, N Ohba, W F Hoyt... See end of article for authors affiliations... Correspondence to: Kazuhiko Unoki, MD,
910 CLINICAL SCIENCE Optical coherence tomography of superior segmental optic hypoplasia K Unoki, N Ohba, W F Hoyt... See end of article for authors affiliations... Correspondence to: Kazuhiko Unoki, MD,
Optical coherence tomography in diabetic macular edema: patterns and related risk factors
 Original article Optical coherence tomography in diabetic macular edema: patterns and related risk factors Mohammadreza Ahmadpour-Baghdadabad Masoudreza Manaviat Ahmad Shojaoddiny-Ardekani Yazd Diabetes
Original article Optical coherence tomography in diabetic macular edema: patterns and related risk factors Mohammadreza Ahmadpour-Baghdadabad Masoudreza Manaviat Ahmad Shojaoddiny-Ardekani Yazd Diabetes
Coexistence of migraine and idiopathic intracranial hypertension without papilledema
 / GX'~C1~.. Coexistence of migraine and idiopathic intracranial hypertension without papilledema Ninan T. Mathew, MD; K. Ravishankar, MD; and Luis C. Sanin, MD!
/ GX'~C1~.. Coexistence of migraine and idiopathic intracranial hypertension without papilledema Ninan T. Mathew, MD; K. Ravishankar, MD; and Luis C. Sanin, MD!
Idiopathic Intracranial Hypertension in Pregnant Women
 Azza A. Ghali et al. Idiopathic Intracranial Hypertension in Pregnant Women Azza Abass Ghali, Ehab El-Seidy, Tarek Ragaiey Hussein 2, Manal Mostfa 3 Departments of Neuropsychiatry, Ophthalmology 2, Obstetrics
Azza A. Ghali et al. Idiopathic Intracranial Hypertension in Pregnant Women Azza Abass Ghali, Ehab El-Seidy, Tarek Ragaiey Hussein 2, Manal Mostfa 3 Departments of Neuropsychiatry, Ophthalmology 2, Obstetrics
Translating data and measurements from stratus to cirrus OCT in glaucoma patients and healthy subjects
 Romanian Journal of Ophthalmology, Volume 60, Issue 3, July-September 2016. pp:158-164 GENERAL ARTICLE Translating data and measurements from stratus to cirrus OCT in glaucoma patients and healthy subjects
Romanian Journal of Ophthalmology, Volume 60, Issue 3, July-September 2016. pp:158-164 GENERAL ARTICLE Translating data and measurements from stratus to cirrus OCT in glaucoma patients and healthy subjects
Study of clinical significance of optical coherence tomography in diagnosis & management of diabetic macular edema
 Original Research Article Study of clinical significance of optical coherence tomography in diagnosis & management of diabetic macular edema Neha Kantilal Desai 1,*, Somesh Vedprakash Aggarwal 2, Sonali
Original Research Article Study of clinical significance of optical coherence tomography in diagnosis & management of diabetic macular edema Neha Kantilal Desai 1,*, Somesh Vedprakash Aggarwal 2, Sonali
Ganglion cell complex scan in the early prediction of glaucoma
 Original article in the early prediction of glaucoma Ganekal S Nayana Super Specialty Eye Hospital and Research Center, Davangere, Karnataka, India Abstract Objective: To compare the macular ganglion cell
Original article in the early prediction of glaucoma Ganekal S Nayana Super Specialty Eye Hospital and Research Center, Davangere, Karnataka, India Abstract Objective: To compare the macular ganglion cell
New Concepts in Glaucoma Ben Gaddie, OD Moderator Murray Fingeret, OD Louis Pasquale, MD
 New Concepts in Glaucoma Ben Gaddie, OD Moderator Murray Fingeret, OD Louis Pasquale, MD New Concepts in Glaucoma Optical Coherence Tomography: Is it necessary and needed to diagnose and monitor glaucoma?
New Concepts in Glaucoma Ben Gaddie, OD Moderator Murray Fingeret, OD Louis Pasquale, MD New Concepts in Glaucoma Optical Coherence Tomography: Is it necessary and needed to diagnose and monitor glaucoma?
Optic Nerve Anomalies
 Optic Nerve Anomalies Raman Bhakhri, OD, FAAO Southern California College of Optometry Marshall B. Ketchum University Goals for today Review some of the optic nerve anomalies that can be seen in practice
Optic Nerve Anomalies Raman Bhakhri, OD, FAAO Southern California College of Optometry Marshall B. Ketchum University Goals for today Review some of the optic nerve anomalies that can be seen in practice
Question 1: Comment on the optic nerve appearance of each eye.
 Case 2 - Right Optic Nerve Head Drusen (ONHD) A 41 year old female was referred by her optometrist for a workup for unilateral optic disc drusen, OCT, and visual field changes. The patient was otherwise
Case 2 - Right Optic Nerve Head Drusen (ONHD) A 41 year old female was referred by her optometrist for a workup for unilateral optic disc drusen, OCT, and visual field changes. The patient was otherwise
Delayed Correction of Hypotony Maculopathy in a Patient with Glaucoma and Thyroid-Related Orbitopathy
 Published online: October 14, 2015 2015 The Author(s) Published by S. Karger AG, Basel 1663 2699/15/0063 0356$39.50/0 This article is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International
Published online: October 14, 2015 2015 The Author(s) Published by S. Karger AG, Basel 1663 2699/15/0063 0356$39.50/0 This article is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International
Andrew J. Barkmeier, MD; Benjamin P. Nicholson, MA; Levent Akduman, MD
 c l i n i c a l s c i e n c e Effectiveness of Laser Photocoagulation in Clinically Significant Macular Edema With Focal Versus Diffuse Parafoveal Thickening on Optical Coherence Tomography Andrew J. Barkmeier,
c l i n i c a l s c i e n c e Effectiveness of Laser Photocoagulation in Clinically Significant Macular Edema With Focal Versus Diffuse Parafoveal Thickening on Optical Coherence Tomography Andrew J. Barkmeier,
Glaucoma Past, Present and Future
 Glaucoma Past, Present and Future Paul A. Weber, M.D. Professor Emeritus Department of Ophthalmology and Visual Science- Havener Eye Institute The Ohio State University Before we talk about glaucoma, I
Glaucoma Past, Present and Future Paul A. Weber, M.D. Professor Emeritus Department of Ophthalmology and Visual Science- Havener Eye Institute The Ohio State University Before we talk about glaucoma, I
PITFALLS IN PAPILLOEDEMA
 PITFALLS IN PAPILLOEDEMA SRC 2013 Why care about papilloedema? Dr Neil Shuey FRACP MBBS(Hons) MScOptom St Vincent s Hospital, Melbourne Royal Victorian Eye & Ear Hospital Disclosures: Travel grants Biogen
PITFALLS IN PAPILLOEDEMA SRC 2013 Why care about papilloedema? Dr Neil Shuey FRACP MBBS(Hons) MScOptom St Vincent s Hospital, Melbourne Royal Victorian Eye & Ear Hospital Disclosures: Travel grants Biogen
Neuro Ocular Grand Rounds Anthony B. Litwak, OD, FAAO VA Medical Center Baltimore, MD
 Neuro Ocular Grand Rounds Anthony B. Litwak, OD, FAAO VA Medical Center Baltimore, MD 58 YOWM! C/O I think there is something wrong with my vision, but I m not sure what it is.! +PMH for HTN, atrial fibrillation,
Neuro Ocular Grand Rounds Anthony B. Litwak, OD, FAAO VA Medical Center Baltimore, MD 58 YOWM! C/O I think there is something wrong with my vision, but I m not sure what it is.! +PMH for HTN, atrial fibrillation,
Michelle L. Ischayek D.O. Emergency Medicine Resident Aria Health
 Michelle L. Ischayek D.O. Emergency Medicine Resident Aria Health History 15 year old African female with CC of Headache. Onset: 2 weeks ago Location: Frontal Character: Sharp & Throbbing Radiation: None
Michelle L. Ischayek D.O. Emergency Medicine Resident Aria Health History 15 year old African female with CC of Headache. Onset: 2 weeks ago Location: Frontal Character: Sharp & Throbbing Radiation: None
p f .'''a.".: ;i.l i PAPILLOEDEMA brain. The ophthalmoscope may be looked upon as the Plate i is that of papilloedema of the optic nerve.
 382 * s. ii d:.'. ; z. j:.'''a.".: : ;i.l i 4 PAPILLOEDEMA FIG. I.-Papilloedema or 'choked disc' due to raised intracranial tension. In this instance the papilloedema was due to a frontal lobe tumour.
382 * s. ii d:.'. ; z. j:.'''a.".: : ;i.l i 4 PAPILLOEDEMA FIG. I.-Papilloedema or 'choked disc' due to raised intracranial tension. In this instance the papilloedema was due to a frontal lobe tumour.
Role Of Various Factors In The Treatment Of Optic Neuritis----A Study Abstract Aim: Materials & Methods Discussion: Conclusion: Key words
 IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 15, Issue 9 Ver. X (September). 2016), PP 51-57 www.iosrjournals.org Role Of Various Factors In The Treatment
IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 15, Issue 9 Ver. X (September). 2016), PP 51-57 www.iosrjournals.org Role Of Various Factors In The Treatment
Case #1: 68 M with floaters OS
 Case #1: 68 M with floaters OS Point-of-Care Ocular Sonography for the Emergency Department Nate Teismann MD Dept of Emergency Medicine, UCSF Topics in EM 2012 Acute onset of dark spots in L eye 2 days
Case #1: 68 M with floaters OS Point-of-Care Ocular Sonography for the Emergency Department Nate Teismann MD Dept of Emergency Medicine, UCSF Topics in EM 2012 Acute onset of dark spots in L eye 2 days
Alan G. Kabat, OD, FAAO (901)
 THE SWOLLEN OPTIC DISC: EMERGENCY OR ANOMALY? Alan G. Kabat, OD, FAAO (901) 252-3691 Memphis, Tennessee alan.kabat@alankabat.com Course description: The swollen disc presents a diagnostic dilemma. While
THE SWOLLEN OPTIC DISC: EMERGENCY OR ANOMALY? Alan G. Kabat, OD, FAAO (901) 252-3691 Memphis, Tennessee alan.kabat@alankabat.com Course description: The swollen disc presents a diagnostic dilemma. While
Criteria for early CLINICAL STUDY. N Fujimoto 1, N Saeki 2, O Miyauchi 1
 (2002) 16, 731 738 2002 Nature Publishing Group All rights reserved 0950-222X/02 $25.00 www.nature.com/eye N Fujimoto 1, N Saeki 2, O Miyauchi 1 Criteria for early and E Adachi-Usami 1 detection of temporal
(2002) 16, 731 738 2002 Nature Publishing Group All rights reserved 0950-222X/02 $25.00 www.nature.com/eye N Fujimoto 1, N Saeki 2, O Miyauchi 1 Criteria for early and E Adachi-Usami 1 detection of temporal
A Case of Carotid-Cavernous Fistula
 A Case of Carotid-Cavernous Fistula By : Mohamed Elkhawaga 2 nd Year Resident of Ophthalmology Alexandria University A 19 year old male patient came to our outpatient clinic, complaining of : -Severe conjunctival
A Case of Carotid-Cavernous Fistula By : Mohamed Elkhawaga 2 nd Year Resident of Ophthalmology Alexandria University A 19 year old male patient came to our outpatient clinic, complaining of : -Severe conjunctival
Ocular Pathology I 6234_16385 Rm HBSB 203-E 1:00-3:00pm. Tonya G. Ketcham, OD, PhD , RM 2113
 Ocular Pathology I 6234_16385 Rm HBSB 203-E 1:00-3:00pm Tonya G. Ketcham, OD, PhD tketcham@optometry.uh.edu 3-1799, RM 2113 Course Syllabus Course Description To describe normal anomalies and pathologic
Ocular Pathology I 6234_16385 Rm HBSB 203-E 1:00-3:00pm Tonya G. Ketcham, OD, PhD tketcham@optometry.uh.edu 3-1799, RM 2113 Course Syllabus Course Description To describe normal anomalies and pathologic
12/2/16. Ways to differentiate:
 Nate Lighthizer, O.D., F.A.A.O. Assistant Dean for Clinical Care Services Director of CE Chief of Specialty Care Clinics Chief of Electrodiagnostics Clinic Oklahoma College of Optometry lighthiz@nsuok.edu
Nate Lighthizer, O.D., F.A.A.O. Assistant Dean for Clinical Care Services Director of CE Chief of Specialty Care Clinics Chief of Electrodiagnostics Clinic Oklahoma College of Optometry lighthiz@nsuok.edu
Differences between Non-arteritic Anterior Ischemic Optic Neuropathy and Open Angle Glaucoma with Altitudinal Visual Field Defect
 pissn: 1011-8942 eissn: 2092-9382 Korean J Ophthalmol 2015;29(6):418-423 http://dx.doi.org/10.3341/kjo.2015.29.6.418 Original Article Differences between Non-arteritic Anterior Ischemic Optic Neuropathy
pissn: 1011-8942 eissn: 2092-9382 Korean J Ophthalmol 2015;29(6):418-423 http://dx.doi.org/10.3341/kjo.2015.29.6.418 Original Article Differences between Non-arteritic Anterior Ischemic Optic Neuropathy
Case Report Optic Disk Pit with Sudden Central Visual Field Scotoma
 Case Reports in Ophthalmological Medicine Volume 2016, Article ID 1423481, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2016/1423481 Case Report Optic Disk Pit with Sudden Central Visual Field Scotoma Nikol Panou
Case Reports in Ophthalmological Medicine Volume 2016, Article ID 1423481, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2016/1423481 Case Report Optic Disk Pit with Sudden Central Visual Field Scotoma Nikol Panou
Reproducibility of Nerve Fiber Layer Thickness Measurements by Use of Optical Coherence Tomography
 Reproducibility of Nerve Fiber Layer Thickness Measurements by Use of Optical Coherence Tomography Eytan Z. Blumenthal, MD, 1 Julia M. Williams, BS, 1 Robert N. Weinreb, MD, 1 Christopher A. Girkin, MD,
Reproducibility of Nerve Fiber Layer Thickness Measurements by Use of Optical Coherence Tomography Eytan Z. Blumenthal, MD, 1 Julia M. Williams, BS, 1 Robert N. Weinreb, MD, 1 Christopher A. Girkin, MD,
MEDICAL POLICY. Proprietary Information of Excellus Health Plan, Inc. A nonprofit independent licensee of the BlueCross BlueShield Association
 MEDICAL POLICY SUBJECT: OPHTHALMOLOGIC TECHNIQUES PAGE: 1 OF: 7 If the member's subscriber contract excludes coverage for a specific service it is not covered under that contract. In such cases, medical
MEDICAL POLICY SUBJECT: OPHTHALMOLOGIC TECHNIQUES PAGE: 1 OF: 7 If the member's subscriber contract excludes coverage for a specific service it is not covered under that contract. In such cases, medical
Is it Papilloedema? John Ross Ainsworth Orthoptic staff Birmingham Children s Hospital Birmingham and Midland Eye Centre University of Birmingham
 Is it Papilloedema? John Ross Ainsworth Orthoptic staff Birmingham Children s Hospital Birmingham and Midland Eye Centre University of Birmingham Aims Children/young people A bit about hypoplasia / NFL
Is it Papilloedema? John Ross Ainsworth Orthoptic staff Birmingham Children s Hospital Birmingham and Midland Eye Centre University of Birmingham Aims Children/young people A bit about hypoplasia / NFL
SOUTH-EAST EUROPEAN JOURNAL of OPHTHALMOLOGY 2015; 1 (1) 34 40
 Review article SOUTH-EAST EUROPEAN JOURNAL of OPHTHALMOLOGY 2015; 1 (1) 34 40 Retinal nerve fiber layer versus peripapillary capillary density assessment A powerful tool for detecting optic nerve head
Review article SOUTH-EAST EUROPEAN JOURNAL of OPHTHALMOLOGY 2015; 1 (1) 34 40 Retinal nerve fiber layer versus peripapillary capillary density assessment A powerful tool for detecting optic nerve head
Choroidal Mapping; a Novel Approach for Evaluating Choroidal Thickness and Volume
 Imaging Technique Choroidal Mapping; a Novel Approach for Evaluating Choroidal Thickness and Volume Jila Noori 1, MD; Mohammad Riazi Esfahani 1,2, MD Fedra Hajizadeh 2, MD; Mohammad-Mehdi Zaferani 1, MD
Imaging Technique Choroidal Mapping; a Novel Approach for Evaluating Choroidal Thickness and Volume Jila Noori 1, MD; Mohammad Riazi Esfahani 1,2, MD Fedra Hajizadeh 2, MD; Mohammad-Mehdi Zaferani 1, MD
Visual and Anatomical Outcomes of Vitreous Surgery for Large Macular Holes
 March 2009 Raju K.V. et al. - Closed Globe Injuries 31 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Visual and Anatomical Outcomes of Vitreous Surgery for Large Macular Holes Dr. Mahesh G. MS DO DNB FRCSEd, Dr. A. Giridhar MS, Dr.
March 2009 Raju K.V. et al. - Closed Globe Injuries 31 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Visual and Anatomical Outcomes of Vitreous Surgery for Large Macular Holes Dr. Mahesh G. MS DO DNB FRCSEd, Dr. A. Giridhar MS, Dr.
Point-of-care Ocular Ultrasound to Detect Optic Disc Swelling
 ORIGINAL RESEARCH CONTRIBUTION Point-of-care Ocular Ultrasound to Detect Optic Disc Swelling Nathan Teismann, MD, Patrick Lenaghan, MD, Rachel Nolan, John Stein, MD, and Ari Green, MD Abstract Objectives:
ORIGINAL RESEARCH CONTRIBUTION Point-of-care Ocular Ultrasound to Detect Optic Disc Swelling Nathan Teismann, MD, Patrick Lenaghan, MD, Rachel Nolan, John Stein, MD, and Ari Green, MD Abstract Objectives:
Spontaneous Cerebrospinal Fluid Rhinorrhea as the Presenting Symptom of Idiopathic Intracranial Hypertension: A Case Series
 CASE REPORT Spontaneous Cerebrospinal Fluid Rhinorrhea as the Presenting Symptom of Idiopathic Intracranial Hypertension: A Case Series Hossein Ghalaenovi 1, Maziar Azar 1, Morteza Taheri 1, Mahdi Safdarian
CASE REPORT Spontaneous Cerebrospinal Fluid Rhinorrhea as the Presenting Symptom of Idiopathic Intracranial Hypertension: A Case Series Hossein Ghalaenovi 1, Maziar Azar 1, Morteza Taheri 1, Mahdi Safdarian
Learn Connect Succeed. JCAHPO Regional Meetings 2017
 Learn Connect Succeed JCAHPO Regional Meetings 2017 NO FINANCIAL DISCLOSURES Technician s Role in Neuro-Ophthalmology Workup Beth Koch COT, ROUB Cleveland 9/16/2017 What Tests Are You Expected To Perform?
Learn Connect Succeed JCAHPO Regional Meetings 2017 NO FINANCIAL DISCLOSURES Technician s Role in Neuro-Ophthalmology Workup Beth Koch COT, ROUB Cleveland 9/16/2017 What Tests Are You Expected To Perform?
Structural examina.on: Imaging
 ManaMa: Glaucoma Structural examina.on: Imaging Luís Abegão Pinto, MD, PhD Department of Ophthalmology CHLC Lisbon Faculty of Medicine, Lisbon University 1 11-10- 2013 Structural changes Qualitative changes
ManaMa: Glaucoma Structural examina.on: Imaging Luís Abegão Pinto, MD, PhD Department of Ophthalmology CHLC Lisbon Faculty of Medicine, Lisbon University 1 11-10- 2013 Structural changes Qualitative changes
CLINICAL SCIENCES. Repeatability and Reproducibility of Fast Macular Thickness Mapping With Stratus Optical Coherence Tomography
 CLINICAL SCIENCES Repeatability and Reproducibility of Fast Macular Thickness Mapping With Stratus Optical Coherence Tomography Antonio Polito, MD; Michele Del Borrello, MD; Miriam Isola, MHS; Nicola Zemella,
CLINICAL SCIENCES Repeatability and Reproducibility of Fast Macular Thickness Mapping With Stratus Optical Coherence Tomography Antonio Polito, MD; Michele Del Borrello, MD; Miriam Isola, MHS; Nicola Zemella,
Comparative evaluation of time domain and spectral domain optical coherence tomography in retinal nerve fiber layer thickness measurements
 Original article Comparative evaluation of time domain and spectral domain optical coherence tomography in retinal nerve fiber layer thickness measurements Dewang Angmo, 1 Shibal Bhartiya, 1 Sanjay K Mishra,
Original article Comparative evaluation of time domain and spectral domain optical coherence tomography in retinal nerve fiber layer thickness measurements Dewang Angmo, 1 Shibal Bhartiya, 1 Sanjay K Mishra,
Parafoveal Scanning Laser Polarimetry for Early Glaucoma Detection
 Yamanashi Med. J. 18(1), 15~ 20, 2003 Original Article Parafoveal Scanning Laser Polarimetry for Early Glaucoma Detection Satoshi KOGURE, Yoshiki TODA, Hiroyuki IIJIMA and Shigeo TSUKAHARA Department of
Yamanashi Med. J. 18(1), 15~ 20, 2003 Original Article Parafoveal Scanning Laser Polarimetry for Early Glaucoma Detection Satoshi KOGURE, Yoshiki TODA, Hiroyuki IIJIMA and Shigeo TSUKAHARA Department of
Relationship Between Structure
 Original Article Relationship Between Structure and Function of the Optic Nerve Head-Glaucoma versus Normal Dr Savita Bhat, Dr Anna Elias, Dr Siddharth Pawar, Dr S.J. Saikumar, Dr Alpesh Rajput, superior,
Original Article Relationship Between Structure and Function of the Optic Nerve Head-Glaucoma versus Normal Dr Savita Bhat, Dr Anna Elias, Dr Siddharth Pawar, Dr S.J. Saikumar, Dr Alpesh Rajput, superior,
Optic Disk Pit with Sudden Central Visual Field Scotoma
 Optic Disk Pit with Sudden Central Visual Field Scotoma The Harvard community has made this article openly available. Please share how this access benefits you. Your story matters. Citation Published Version
Optic Disk Pit with Sudden Central Visual Field Scotoma The Harvard community has made this article openly available. Please share how this access benefits you. Your story matters. Citation Published Version
University Hospital Basel. Optical Coherence Tomography Emerging Role in the Assessment of MS PD Dr. Konstantin Gugleta
 University Hospital Basel Optical Coherence Tomography Emerging Role in the Assessment of MS PD Dr. Konstantin Gugleta 15th State of the Art SMSS, Lucerne January 2013 Retinal Nerve Fiber Layer 1.200.000
University Hospital Basel Optical Coherence Tomography Emerging Role in the Assessment of MS PD Dr. Konstantin Gugleta 15th State of the Art SMSS, Lucerne January 2013 Retinal Nerve Fiber Layer 1.200.000
Total improvement after surgery for obstructive sleep apnea syndrome in a patient with concurrent malignant idiopathic intracranial hypertension
 CASE REPORT Total improvement after surgery for obstructive sleep apnea syndrome in a patient with concurrent malignant idiopathic intracranial hypertension Halil Onder, MD, 1 Onur Ergun, MD, 2 Mehmet
CASE REPORT Total improvement after surgery for obstructive sleep apnea syndrome in a patient with concurrent malignant idiopathic intracranial hypertension Halil Onder, MD, 1 Onur Ergun, MD, 2 Mehmet
OCCLUSIVE VASCULAR DISORDERS OF THE RETINA
 OCCLUSIVE VASCULAR DISORDERS OF THE RETINA Learning outcomes By the end of this lecture the students would be able to Classify occlusive vascular disorders (OVD) of the retina. Correlate the clinical features
OCCLUSIVE VASCULAR DISORDERS OF THE RETINA Learning outcomes By the end of this lecture the students would be able to Classify occlusive vascular disorders (OVD) of the retina. Correlate the clinical features
Relationship between the GDx VCC and Stratus OCT in Primary Open Angle Glaucoma
 Relationship between the GDx VCC and Stratus OCT in Primary Open Angle Glaucoma Reza Zarei, MD 1 Mohammad Soleimani, MD 2 Sasan Moghimi, MD 3 Mohammad Yaser Kiarudi, MD 2 Mahmoud Jabbarvand, MD 1 Yadollah
Relationship between the GDx VCC and Stratus OCT in Primary Open Angle Glaucoma Reza Zarei, MD 1 Mohammad Soleimani, MD 2 Sasan Moghimi, MD 3 Mohammad Yaser Kiarudi, MD 2 Mahmoud Jabbarvand, MD 1 Yadollah
Neovascular Glaucoma Associated with Cilioretinal Artery Occlusion Combined with Perfused Central Retinal Vein Occlusion
 Neovascular Glaucoma Associated with Cilioretinal Artery Occlusion Combined with Perfused Central Retinal Vein Occlusion Man-Seong Seo,* Jae-Moon Woo* and Jeong-Jin Seo *Department of Ophthalmology, Chonnam
Neovascular Glaucoma Associated with Cilioretinal Artery Occlusion Combined with Perfused Central Retinal Vein Occlusion Man-Seong Seo,* Jae-Moon Woo* and Jeong-Jin Seo *Department of Ophthalmology, Chonnam
T he lamina cribrosa is a sieve-like membrane in the
 1299 EXTENDED REPORT Three dimensional analysis of the lamina cribrosa in glaucoma J Morgan-Davies, N Taylor, A R Hill, P Aspinall, CJ O Brien, A Azuara-Blanco... See end of article for authors affiliations...
1299 EXTENDED REPORT Three dimensional analysis of the lamina cribrosa in glaucoma J Morgan-Davies, N Taylor, A R Hill, P Aspinall, CJ O Brien, A Azuara-Blanco... See end of article for authors affiliations...
Optic Disc: Anatomy, Variants, Unusual discs. Kathleen B. Digre, MD Professor Neurology, Ophthalmology
 Optic Disc: Anatomy, Variants, Unusual discs Kathleen B. Digre, MD Professor Neurology, Ophthalmology THE OPHTHALMOSCOPE DIRECT OPHTHALMOSCOPY Jan Purkinje 1823 Hermann von Helmholtz 1851 Hand held ophthalmoscope
Optic Disc: Anatomy, Variants, Unusual discs Kathleen B. Digre, MD Professor Neurology, Ophthalmology THE OPHTHALMOSCOPE DIRECT OPHTHALMOSCOPY Jan Purkinje 1823 Hermann von Helmholtz 1851 Hand held ophthalmoscope
OPTIC NERVE SWELLING IN CHILDHOOD
 OPTIC NERVE SWELLING IN CHILDHOOD Melissa W. Ko, MD, FAAN One of the main findings on a pediatric neurologic examination that can instill fear and lead to an urgent referral to neuro-ophthalmology is the
OPTIC NERVE SWELLING IN CHILDHOOD Melissa W. Ko, MD, FAAN One of the main findings on a pediatric neurologic examination that can instill fear and lead to an urgent referral to neuro-ophthalmology is the
Optical Coherence Tomograpic Features in Idiopathic Retinitis, Vasculitis, Aneurysms and Neuroretinitis (IRVAN)
 Columbia International Publishing Journal of Ophthalmic Research (2014) Research Article Optical Coherence Tomograpic Features in Idiopathic Retinitis, Vasculitis, Aneurysms and Neuroretinitis (IRVAN)
Columbia International Publishing Journal of Ophthalmic Research (2014) Research Article Optical Coherence Tomograpic Features in Idiopathic Retinitis, Vasculitis, Aneurysms and Neuroretinitis (IRVAN)
EXPERIMENTAL AND THERAPEUTIC MEDICINE 6: , 2013
 268 Comparison of optic nerve morphology in eyes with glaucoma and eyes with non-arteritic anterior ischemic optic neuropathy by Fourier domain optical coherence tomography YUXIN YANG 1, HAITAO ZHANG 1,
268 Comparison of optic nerve morphology in eyes with glaucoma and eyes with non-arteritic anterior ischemic optic neuropathy by Fourier domain optical coherence tomography YUXIN YANG 1, HAITAO ZHANG 1,
Noel de Jesus Atienza, MD, MSc and Joseph Anthony Tumbocon, MD
 Original Article Philippine Journal of OPHTHALMOLOGY Diagnostic Accuracy of the Optical Coherence Tomography in Assessing Glaucoma Among Filipinos. Part 1: Categorical Outcomes Based on a Normative Database
Original Article Philippine Journal of OPHTHALMOLOGY Diagnostic Accuracy of the Optical Coherence Tomography in Assessing Glaucoma Among Filipinos. Part 1: Categorical Outcomes Based on a Normative Database
MEDICAL POLICY. Proprietary Information of YourCare Healthcare
 MEDICAL POLICY PAGE: 1 OF: 7 If the member's subscriber contract excludes coverage for a specific service it is not covered under that contract. In such cases, medical policy criteria are not applied.
MEDICAL POLICY PAGE: 1 OF: 7 If the member's subscriber contract excludes coverage for a specific service it is not covered under that contract. In such cases, medical policy criteria are not applied.
Summary HTA HTA-Report Summary Validity and cost-effectiveness of methods for screening of primary open angle glau- coma
 Summary HTA HTA-Report Summary Validity and cost-effectiveness of methods for screening of primary open angle glaucoma Antony K, Genser D, Fröschl B DAHTA@DIMDI Waisenhausgasse 36-38a D-50676 Köln Tel.:
Summary HTA HTA-Report Summary Validity and cost-effectiveness of methods for screening of primary open angle glaucoma Antony K, Genser D, Fröschl B DAHTA@DIMDI Waisenhausgasse 36-38a D-50676 Köln Tel.:
* Şükrü Bayraktar, MD, Zerrin Bayraktar, MD, and Ömer Faruk Yilmaz, MD
 Journal of Glaucoma 10:163 169 2001 Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, Inc. Influence of Scan Radius Correction for Ocular Magnification and Relationship Between Scan Radius With Retinal Nerve Fiber Layer
Journal of Glaucoma 10:163 169 2001 Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, Inc. Influence of Scan Radius Correction for Ocular Magnification and Relationship Between Scan Radius With Retinal Nerve Fiber Layer
Clinically Significant Macular Edema (CSME)
 Clinically Significant Macular Edema (CSME) 1 Clinically Significant Macular Edema (CSME) Sadrina T. Shaw OMT I Student July 26, 2014 Advisor: Dr. Uwaydat Clinically Significant Macular Edema (CSME) 2
Clinically Significant Macular Edema (CSME) 1 Clinically Significant Macular Edema (CSME) Sadrina T. Shaw OMT I Student July 26, 2014 Advisor: Dr. Uwaydat Clinically Significant Macular Edema (CSME) 2
53 year old woman attends your practice for routine exam. She has no past medical history or family history of note.
 Case 1 Normal Tension Glaucoma 53 year old woman attends your practice for routine exam. She has no past medical history or family history of note. Table 1. Right Eye Left Eye Visual acuity 6/6 6/6 Ishihara
Case 1 Normal Tension Glaucoma 53 year old woman attends your practice for routine exam. She has no past medical history or family history of note. Table 1. Right Eye Left Eye Visual acuity 6/6 6/6 Ishihara
Magnetic Resonance Derived CSF Production Rate as a Predictor of Orbital Abnormalities after Exposure to Microgravity
 Magnetic Resonance Derived CSF Production Rate as a Predictor of Orbital Abnormalities after Exposure to Microgravity Courtesy of NASA Disclosure Information 84th Annual AsMA Scientific Meeting Larry A.
Magnetic Resonance Derived CSF Production Rate as a Predictor of Orbital Abnormalities after Exposure to Microgravity Courtesy of NASA Disclosure Information 84th Annual AsMA Scientific Meeting Larry A.
Misdiagnosed Vogt-Koyanagi-Harada (VKH) disease and atypical central serous chorioretinopathy (CSC)
 HPTER 12 Misdiagnosed Vogt-Koyanagi-Harada (VKH) disease and atypical central serous chorioretinopathy (S) linical Features VKH disease is a bilateral granulomatous panuveitis often associated with exudative
HPTER 12 Misdiagnosed Vogt-Koyanagi-Harada (VKH) disease and atypical central serous chorioretinopathy (S) linical Features VKH disease is a bilateral granulomatous panuveitis often associated with exudative
NERVE FIBER LAYER THICKNESS IN NORMALS AND GLAUCOMA PATIENTS
 Nerve fiber layer thickness in normals and glaucoma patients 403 NERVE FIBER LAYER THICKNESS IN NORMALS AND GLAUCOMA PATIENTS HIROTAKA SUZUMURA, KAYOKO HARASAWA, AKIKO KOBAYASHI and NARIYOSHI ENDO Department
Nerve fiber layer thickness in normals and glaucoma patients 403 NERVE FIBER LAYER THICKNESS IN NORMALS AND GLAUCOMA PATIENTS HIROTAKA SUZUMURA, KAYOKO HARASAWA, AKIKO KOBAYASHI and NARIYOSHI ENDO Department
Learn Connect Succeed. JCAHPO Regional Meetings 2015
 Learn Connect Succeed JCAHPO Regional Meetings 2015 OPTIC NEUROPATHY AS EASY AS 1,2,3,4 OPTIC NERVE ANATOMY M. Tariq Bhatti, MD Departments of Ophthalmology and Neurology Duke Eye Center and Duke University
Learn Connect Succeed JCAHPO Regional Meetings 2015 OPTIC NEUROPATHY AS EASY AS 1,2,3,4 OPTIC NERVE ANATOMY M. Tariq Bhatti, MD Departments of Ophthalmology and Neurology Duke Eye Center and Duke University
Dr/ Marwa Abdellah EOS /16/2018. Dr/ Marwa Abdellah EOS When do you ask Fluorescein angiography for optic disc diseases???
 When do you ask Fluorescein angiography for optic disc diseases??? 1 NORMAL OPTIC DISC The normal optic disc on fluorescein angiography is fluorescent due to filling of vessels arising from the posterior
When do you ask Fluorescein angiography for optic disc diseases??? 1 NORMAL OPTIC DISC The normal optic disc on fluorescein angiography is fluorescent due to filling of vessels arising from the posterior
Headache Assessment In Primary Eye Care
 Headache Assessment In Primary Eye Care Spencer Johnson, O.D., F.A.A.O. Northeastern State University Oklahoma College of Optometry johns137@nsuok.edu Course Objectives Review headache classification Understand
Headache Assessment In Primary Eye Care Spencer Johnson, O.D., F.A.A.O. Northeastern State University Oklahoma College of Optometry johns137@nsuok.edu Course Objectives Review headache classification Understand
GLAUCOMA SUMMARY BENCHMARKS FOR PREFERRED PRACTICE PATTERN GUIDELINES
 SUMMARY BENCHMARKS FOR PREFERRED PRACTICE PATTERN GUIDELINES Introduction These are summary benchmarks for the Academy s Preferred Practice Pattern (PPP) guidelines. The Preferred Practice Pattern series
SUMMARY BENCHMARKS FOR PREFERRED PRACTICE PATTERN GUIDELINES Introduction These are summary benchmarks for the Academy s Preferred Practice Pattern (PPP) guidelines. The Preferred Practice Pattern series
Pseudotumor Cerebri Secondary to Minocycline Intake
 Pseudotumor Cerebri Secondary to Minocycline Intake Earl Robert G. Ang, MD, J. C. Chava Zimmerman, MD, and Elissa Malkin, DO, MPH Background: Pseudotumor cerebri, or idiopathic intracranial hypertension,
Pseudotumor Cerebri Secondary to Minocycline Intake Earl Robert G. Ang, MD, J. C. Chava Zimmerman, MD, and Elissa Malkin, DO, MPH Background: Pseudotumor cerebri, or idiopathic intracranial hypertension,
VMA at the macula resulting in VMT
 Ocriplasmina for pharmacologic treatment in VMT Teresio Avitabile 1 Introduction PVD is a normal, physiologic process that occurs with aging; however, in some cases, PVD is incomplete Incomplete PVD localized
Ocriplasmina for pharmacologic treatment in VMT Teresio Avitabile 1 Introduction PVD is a normal, physiologic process that occurs with aging; however, in some cases, PVD is incomplete Incomplete PVD localized
An Organized Approach to the Patient with Papilledema and IIH
 An Organized Approach to the Patient with Papilledema and IIH Leonard V. Messner, OD, FAAO James L. Fanelli, OD, FAAO Please silence all mobile devices and remove items from chairs so others can sit. Unauthorized
An Organized Approach to the Patient with Papilledema and IIH Leonard V. Messner, OD, FAAO James L. Fanelli, OD, FAAO Please silence all mobile devices and remove items from chairs so others can sit. Unauthorized
Non-arteritic anterior ischemic optic neuropathy (NAION) with segmental optic disc edema. Jonathan A. Micieli, MD Valérie Biousse, MD
 Non-arteritic anterior ischemic optic neuropathy (NAION) with segmental optic disc edema Jonathan A. Micieli, MD Valérie Biousse, MD A 75 year old white woman lost vision in the inferior part of her visual
Non-arteritic anterior ischemic optic neuropathy (NAION) with segmental optic disc edema Jonathan A. Micieli, MD Valérie Biousse, MD A 75 year old white woman lost vision in the inferior part of her visual
