HEADACHE. Primary vs Secondary Headaches SNOOP4. Classification of Primary Headaches. Novel Approaches to Diagnosis and Treatment.
|
|
|
- Jasper Harrell
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 HEADACHE Novel Approaches to Diagnosis and Treatment Primary vs Secondary Headaches SNOOP4 S - systemic signs and symptoms (fever, weight loss) or secondary risk factors (HIV, cancer) N - neurological signs and symptoms O - onset, < one minute (thunder clap headache) O - older (GCA, glaucoma) P - previous headache history (new or changed) P - postural or positional P - precipitated by valsalva or exertion P - papilledema Classification of Primary Headaches Migraine Tension-type headache Cluster headache and other trigeminal autonomic cephalalgias Other primary headaches
2 Migraine ICHD-3 Diagnostic Criteria At least 5 headaches lasting 4-72 hours (untreated or unsuccessfully treated) with at least two of the following characteristics: unilateral location pulsating quality moderate or severe pain intensity aggravation by or causing avoidance of routine physical activity Migraine and Tension-type Headache Two ends of the continuum of benign recurrent headache or separate disorders? and one of: nausea and/or vomiting photophobia and phonophobia Factors Supporting the Continuum of Benign Recurrent Headache 1. Most patients with frequent headaches exhibit the whole spectrum. 2. Triptans work for tension-type headaches (TTH). 3. Preventive medications (antidepressants, AEDs) work for TTH. 4. Neck pain is a common feature of migraine. 5. Patients with tension-type headache may experience migraine auras. 6. Plasma serotonin levels are decreased during migraine and TTH 7. The same increased number of T2 hyperintensities are seen on MRI.
3 Allodynia (The Difference Between TTH and Migraine?) Pain due to a stimulus which does not normally provoke pain. Reflects peripheral and central sensitization. Pulsatile pain (throbbing headache) Photophobia Phonophobia Osmophobia Does It Matter? Yes Ignoring anti-migraine treatment for chronic or frequent, episodic TTH gets you nowhere and leads to medication overuse. For occasional, severe TTH, refractory to OTC analgesics, try a triptan. No Occasional, mild, TTH can usually be effectively treated with OTC analgesics. Cutaneous allodynia (scalp tenderness) Migraine Demography Thirty-six million Americans, about 12 % of the population Keep in mind a couple of developing consensuses: Try to avoid the diagnosis of chronic TTH. Think of chronic (formerly called transformed ) migraine. Look for medication overuse. If some of a patients headaches are migraine, all of them are migraine. One in four households affected Women:men = 3:1 30% of women affected at sometime in their lives All ages affected; most common late teens through 40s 3% of people have chronic migraine
4 Migraine Comorbidity Vascular Disease Women with migraine with aura have a 91% increased risk of myocardial infarction and a 108% increased risk of stroke. Fibromyalgia 76% of patients with fibromyalgia have chronic headache; 35% of patients with chronic migraine have fibromyalgia. Depression, insomnia and anxiety are common, especially with chronic migraine and MOH. Migraine Disability Estimated 88 hours of lost productivity per year. QOL < to patients with CHF, recent MI, diabetes, hypertension, depression, and osteoarthritis. Normals Osteoarthritis Depression Migraine
5 Neurovascular (Neuronal) Theory Migraine is, largely, genetically determined. Cortex (esp. occipital cortex) hyperexcitable at baseline. Cortical spreading depression. Activation of the trigeminovascular system. Migraine Genetics 70% of migraineurs have an affected first degree relative. Risk of migraine is increased 4-fold in relatives of patients with migraine with aura. The gene for 3 variants of hemiplegic migraine has been discovered. Impaired brainstem modulation of pain. Cortical Spreading Depression Wave of neuronal excitation followed by inhibition. Self propagating at rate of 2-6 mm/min. Responsible for migraine aura: visual sensory motor Occurs in migraine without aura (cognitive dysfunction). Activates trigeminovascular system.
6 Trigeminovascular Activation Activation of trigeminovasular system releases: substance P calcitonin gene related peptide (CGRP) neurokinin A nitric oxide Causes sterile inflammation. Leads to peripheral and, ultimately, central sensitization. Probably not sufficient to cause pain of migraine.
7 Migraine Center rcbf persistently increased in brainstem. Locus ceruleus, dorsal raphe nuclei, PAG. Modulates thalamic processing of pain. Serotonin Onset of migraine characterized by increased serotonergic activity f/b serotonin depletion. Serotonin depletion during migraine headaches facilitates cortical hyperexcitability, CSD and trigeminovascular activation. 5-HT1D receptors present on trigeminal neurons and trigeminal nucleus caudalis. 5-HT1B receptors present on meningeal blood vessels. Triptans are 5-HT1B/D receptor agonists. Dopamine Prodrome symptoms reflect dopamine pathway stimulation: yawning cognitive impairment mood changes: euphoria, depression, irritability physical symptoms: diarrhea, thirst Dopamine blocking antiemetics (droperidol, prochlorperazine, metochlopramide): abort headache, if given during prodrome relieve nausea and vomiting relieve headache in up to 75%
8 P i h l bl k What Is Migraine? A hereditary susceptibility of the brain to decrease modulation of afferent impulses, thus permitting and augmenting the perception of head pain, sensitivity to light, sounds, and smells, vascular pulsation and scalp tenderness. Peter Goadsby 2009 Migraine (Acute Treatment) Dark, quiet room, ice OTC analgesics: NSAIDS, APAP, ASA (caveat - MOH) Dopamine blocking antiemetics (metoclopramide, prochlorperazine) Triptans Avoid opioids and butalbital (MOH) Ergotamine tartrate Dihydroergotamine Triptans Effective and well tolerated. Should be taken early. Consider nasal spray. May provoke typical triptan side effects. Avoid in patients with risk for CAD. Should not give within 24 hours of ergotamine or dihydroergotamine.
9 Serotonin Syndrome and Triptans FDA warning (2006): There is the potential for life-threatening serotonin syndrome in patients taking 5-hydroxytryptamine receptor agonists (triptans) and selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs) or selective serotonin/norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors (SNRIs) concomitantly. Based on 29 anecdotal cases. Most did not meet established criteria for serotonin syndrome. Frequency not clearly increased with concomitant treatment. Triptans are selective 5 HT1B/D/F agonists. Serotonin syndrome mediated by 5 HT2A receptors. AHS Position Paper (2010): The currently available evidence does not support limiting the use of triptans with SSRIs or SNRIs, or the use of triptan monotherapy, due to concerns for serotonin syndrome. However, given the seriousness of serotonin syndrome, caution is certainly warranted and clinicians should be vigilant to serotonin toxicity symptoms and signs to insure prompt treatment. Peripheral Nerve Blocks May provide prompt, definitive relief of headache for days, weeks or months. Safe and well tolerated. Greater occipital, supraorbital, supratrochlear, auriculotemporal nerves are treated, depending on headache pattern. Lidocaine or bupivacaine; corticosteroids can be used for GON. Useful for status migrainosus, chronic migraine, and cluster headache. Prolonged analgesia likely due to effects on central pain modulation. Migraine Prevention Lifestyle Regular Sleep - too much or too little can trigger migraine Regular meals - fasting a common trigger Regular exercise Manage stress - caveat: holiday or weekend headache Stop smoking Attain or maintain ideal weight Avoid bright light, loud noises and strong or unpleasant smells Caffeine - too much or withdrawal can cause headaches Avoid dietary triggers: red wine, beer, aged cheese,nuts, processed meats (hot dogs, sausage), MSG Elimination diet (?) - data are mixed Avoid medication overuse Medication Overuse Headache (Transformed Migraine) Most common cause of migraine progression Can result from overuse of any symptomatic treatment Rule of thumb: > 2-3/week for 3 months Butalbital 5/month Opiates 8/month Triptans 10/month ASA/APAP/caffeine 10/month ASA, APAP, NSAID 15/month Headaches increase in frequency and don t respond to preventive treatment
10 Migraine Prevention Prescription Meds FDA approved: Propranolol Timolol Divalproex Sodium Topiramate Methysergide Botulinum Toxin Type A (chronic migraine only) Consensus: Other Beta Blockers (nadolol, atenolol, metoprolol) Amitriptyline, Nortriptyline Calcium Channel Blockers (amlodipine, verapamil) Possibly Effective: Gabapentin, ACE inhibitors, ARBs, SNRIs, methylergonovine, cyproheptadine Beta Blockers FDA approved: propranolol, timolol Likely effective: nadolol, metoprolol, atenolol Mechanism of action: reduction of firing rates in PAG and locus coeruleus neurons possible effects on brain 5 HT receptors and 5 HT synthesis Side Effects: reduced exercise tolerance, lethargy, depression, hypotension, bradycardia Contraindications: asthma, congestive heart failure, diabetes Dose: propranolol LA mg daily timolol 10 mg BID initially, then mg daily Topiramate Mechanism of Action: Blocking voltage dependent sodium channels? Side Effects: Cognitive impairment, paresthesias, acute glaucoma(1/50,000), metabolic acidosis, nephrolithiasis. Sodium Divalproex Dose: mg nightly, maybe more
11 Migraine Prevention Nutraceuticals Butterbur Melatonin Feverfew (MIG-99) Magnesium Riboflavin (Vit B2) CoQ10 Butterbur Petasites Hybridus Safety and effectiveness establish in three RCTs. Efficacy equal to the FDA approved migraine preventives. Mechanism: anti-inflammatory v blockade of presynaptic VG Ca channels. Must be free of pyrrolizidine alkaloids (PA Free). Minor GI side effects (increased burping). Melatonin Feverfew (Tanacetum parthenium) Likely effective for migraine. Slightly more effective than amitriptyline in one RCT. Minimal side effects (excessive daytime sleepiness?) Dose: 3 mg hs. Anti-inflammatory. Efficacy less robust than Butterbur and Melatonin. Potency varies widely among different preparations (> 400%). Best data for MIG-99: 6.25 mg tid
12 Riboflavin Magnesium (Vitamin B2) RCTs have demonstrated mixed results. Magnesium levels reduced in menstrual migraine and migraine with aura. RCT results have been mixed. May decrease post synaptic excitation. May cause diarrhea. Dose: 600 mg of Magnesium Citrate daily. May improve mitochondrial function. Rare reports of diarrhea and polyuria. May turn urine bright yellow. Coenzyme Q 10 (CoQ10) In a small RCT was moderately effective. May improve mitochondrial function. Rare side effects: nausea, anorexia, dyspepsia, diarrhea, and rash. Dose: 100 mg tid Alternative/Complimentary Therapy Chiropractic Treatment Acupuncture Stress management / CBT Biofeedback
13 Chronic Migraine Headache occurring on 15 or more days per month for more than 3 months, which has the features of migraine headache on at least 8 days per month. Formerly called transformed migraine. 80% of patients with chronic migraine overuse symptomatic medication (MOH). Anxiety and depression are frequent; 80% have depression. Treatment: stop medication overuse lifestyle changes: regular sleep, diet/weight loss, stress reduction preventive medication peripheral nerve blocks Botox Menstrual Associated Migraine Caused by drop in estrogen levels prior to menses. Pure menstrual migraine => migraines confined to -2 to +3 days of the period. Menstrual related migraine => HAs on other days. Acute treatment the same as that given for any migraine patient. Short term prophylaxis start 2 days before headaches typically begin and continue for a week: naproxen triptans frovatriptan, naratriptan, zolmitriptan estrogen Continuous prophylatic treatment: hormonal long duration oral contraceptive treatment non-hormonal the same as for all migraine patients Migraine-Associated Vertigo Varied symptoms: vertigo - episodic true vertigo or positional imbalance movement associated disequilibrium lightheadedness Occurs in up to 38% of patients with migraine Before, during or in the absence of headache Variable duration: Cause: some cortical patients spreading have depression a rocking sensation lasting weeks neuropeptide induced increased firing rate of vestibular endothelium
14 Cluster Headache Occur daily to several times daily for wks to mos f/b wks to mos without headache. Last 30 to 180 min. Occur about the same time every day, often 02:00 to 03:00. Unilateral, side locked, retro-orbital. Associated with ptosis, miosis, conjunctival injection, rhinorrhea, tearing. Unlike migraine, patients with cluster headache are restless. Other headaches can occur in clusters, but they aren t cluster headaches. Dx of cluster migraine is erroneous and leads to confusion. Treatment of Cluster Headache Acute Treatment: Sumatriptan injection or nasal spray Oxygen DHE 45 Octreotide injection Intranasal lidocaine Preventive Treatment: Calcium channel blockers Lithium Corticosteroids Occipital nerve block and stimulation Ergots Melatonin Topamax Sodium divalproex Hypnic Headache Benign recurring headache beginning age Dull, aching, moderate severity Like cluster headache, related to circadian rhythm Occur nightly between 1 and 3 AM Triggered by decreased brainstem antinociceptive activity during REM sleep Treatment: melatonin lithium calcium channel blockers indomethacin ergots gabapentin acetazolamide caffeine at bedtime Reversible Cerebral Vasoconstriction Syndrome Thunderclap headache presentation Results in segmental spasm of cerebral arteries Fluctuating focal neurological symptoms and signs Often occurs peripartum, associated with eclampsia/preeclampsia Some cases of coital headache can be associated with RCVS Vasoactive drugs may trigger RCVS: cannabis SSRIs OTC decongestants Spontaneously resolves over days to weeks Calcium channel blockers may attenuate spasms
15 Paroxysmal Hemicrania - Hemicrania Continua Persistent side locked headache disorders. Both associated with autonomic features: ipsilateral ptosis, miosis, excessive lacrimationnasal congestion, conjunctival injection. PH - headaches last 2-30 minutes occur 5-40 times a day. If you are considering CH in a woman think PH. HC - headaches are continuous. Unlike migraine, patients with HC are restless. Both respond to indomethacin. Migraine in Children Common Presentation similar to adult migraine unilateral headache less common children may have trouble describing aura Headache tends to resolve with sleep Acute treatment: cool, dark, quiet, room - encourage sleep OTC analgesics - NSAIDs, APAP, not ASA (Reye s syndrome) Triptans - consider nasal sprays Avoid opioids and butalbital Avoid MOH Preventive treatment: encourage regular sleep, meals, and exercise exercise, recreation, rest avoid environmental and dietary triggers nutraceuticals - butterbur, melatonin, feverfew, B2, magnesium, CoQ10 beta blockers - watch for lethargy, depression, decreased exercise tolerance cyproheptadine - really is associated with sedation and weight gain in children topiramate and divalproex sodium are last resorts Periodic Syndromes (migraine equivalents) Cyclic vomiting recurrent episodes of vomiting lasting 6-48 hours begins in toddlers - headache may not show up until adolescence often there is a family history of migraine Recurrent vertigo vertigo, trouble with balance, nausea lasting minutes starts in childhood - headache usually shows up later Episodic confusion confusion, agitation, delirium, aphasia, memory loss older children sometimes provoked by minor head trauma resolves with sleep Paroxysmal torticollis of infancy episodes of head tilt lasting hours to days a/w headache, nausea, and vomiting Abdominal migraine episodes of abdominal pain lasting hours and relieved with sleep headaches may occur between attacks or may occur later Migraine Pathophysiology Vascular Theory Vasoconstriction induced ischemia causes aura Vasodilation causes throbbing headache Problems Ischemia not sufficient to cause aura Headache begins during initial cerebral hypoperfusion Doesn t explain prodrome Some preventive medications have no effect on CBF
16 Cough, Exertion, Coital Headache Triggered by sudden increase in ICP Abrupt onset, severe, brief 10% associated with structural abnormalities Chiari malformation other craniocervical junction abnormalities tumors aneurysms Cranial MRI/MRA required Indomethacin,? other NSAIDS, beta blockers often help Surgery may be required for structural causes Thunderclap Headache Headache that builds to its maximum intensity in less than one minute. Often associated with cough, exertion, and coital headache. May occur spontaneously. Usually benign. Can be associated with: subarachnoid hemorrhage - sentinel bleed pituitary apoplexy arterial dissection colloid cyst of the 3rd ventricle stroke cerebral venous sinus thrombosis severe hypertension - PRES reversible cerebral vasoconstriction syndrome Cranial MRI, head and neck MRA, MRV, LP may be needed.
Index. Prim Care Clin Office Pract 31 (2004) Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type.
 Prim Care Clin Office Pract 31 (2004) 441 447 Index Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A Abscess, brain, headache in, 388 Acetaminophen for migraine, 406 407 headache from, 369
Prim Care Clin Office Pract 31 (2004) 441 447 Index Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A Abscess, brain, headache in, 388 Acetaminophen for migraine, 406 407 headache from, 369
Strategies in Migraine Care
 Strategies in Migraine Care Julie L. Roth, MD Rhode Island Hospital Assistant Professor, Neurology The Warren Alpert Medical School of Brown University March 28, 2015 Financial Disclosures None. Objectives
Strategies in Migraine Care Julie L. Roth, MD Rhode Island Hospital Assistant Professor, Neurology The Warren Alpert Medical School of Brown University March 28, 2015 Financial Disclosures None. Objectives
ADVANCES IN MIGRAINE MANAGEMENT
 ADVANCES IN MIGRAINE MANAGEMENT Joanna Girard Katzman, M.D.MSPH Assistant Professor, Dept. of Neurology Project ECHO, Chronic Pain Program University of New Mexico Outline Migraine throughout the decades
ADVANCES IN MIGRAINE MANAGEMENT Joanna Girard Katzman, M.D.MSPH Assistant Professor, Dept. of Neurology Project ECHO, Chronic Pain Program University of New Mexico Outline Migraine throughout the decades
HMFP Comprehensive Headache Center Department of Anesthesia, Critical Care and Pain Medicine Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center Instructor in
 HMFP Comprehensive Headache Center Department of Anesthesia, Critical Care and Pain Medicine Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center Instructor in Anesthesia and Neurology Harvard Medical School Limited time
HMFP Comprehensive Headache Center Department of Anesthesia, Critical Care and Pain Medicine Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center Instructor in Anesthesia and Neurology Harvard Medical School Limited time
A synopsis of: Diagnosis and Management of Headaches in Adults: A national clinical guideline. Scottish intercollegiate Guidelines Network SIGN
 A synopsis of: Diagnosis and Management of Headaches in Adults: A national clinical guideline Scottish intercollegiate Guidelines Network SIGN November 2008. PETER FRAMPTON MSc MCOptom BAppSc (Optom)(AUS)
A synopsis of: Diagnosis and Management of Headaches in Adults: A national clinical guideline Scottish intercollegiate Guidelines Network SIGN November 2008. PETER FRAMPTON MSc MCOptom BAppSc (Optom)(AUS)
MIGRAINE UPDATE. Objectives & Disclosures. Learn techniques used to diagnose headaches. Become familiar with medications used for headache treatment.
 MIGRAINE UPDATE Karen L. Bremer, MD November 16, 2018 Objectives & Disclosures Learn techniques used to diagnose headaches. Become familiar with medications used for headache treatment. Disclosure: I am
MIGRAINE UPDATE Karen L. Bremer, MD November 16, 2018 Objectives & Disclosures Learn techniques used to diagnose headaches. Become familiar with medications used for headache treatment. Disclosure: I am
Goals. Primary Headache Syndromes. One-Year Prevalence of Common Headache Disorders
 Goals One-Year Prevalence of Common Headache Disorders Impact of primary headache syndromes Non pharmacologic Rx of migraine individualized to patient triggers Complementary and alternative Rx of migraine
Goals One-Year Prevalence of Common Headache Disorders Impact of primary headache syndromes Non pharmacologic Rx of migraine individualized to patient triggers Complementary and alternative Rx of migraine
Case Presentation. Case Presentation. Case Presentation. Truths about Headaches (2017) Most headaches were muscle-tension headaches
 Agenda Case presentation Migraine Morphology Primary and Premonitory Phase Secondary Headache Aura Headache Primer on Pain Medication Overuse Headache Case Presentation RT is a 25 year old woman with daily
Agenda Case presentation Migraine Morphology Primary and Premonitory Phase Secondary Headache Aura Headache Primer on Pain Medication Overuse Headache Case Presentation RT is a 25 year old woman with daily
Faculty Disclosure. Karen L. Bremer, MD. Dr. Bremer has listed no financial interest/arrangement that would be considered a conflict of interest.
 Faculty Disclosure Karen L. Bremer, MD Dr. Bremer has listed no financial interest/arrangement that would be considered a conflict of interest. HEADACHE UPDATE Karen L. Bremer, MD November 10, 2017 karen.bremer@creighton.edu
Faculty Disclosure Karen L. Bremer, MD Dr. Bremer has listed no financial interest/arrangement that would be considered a conflict of interest. HEADACHE UPDATE Karen L. Bremer, MD November 10, 2017 karen.bremer@creighton.edu
Headache. Section 1. Migraine headache. Clinical presentation
 Section 1 Headache Migraine headache 1 Clinical presentation It is important to recognize just how significant a problem migraine headache is. It has been estimated that migraine affects 11% of the United
Section 1 Headache Migraine headache 1 Clinical presentation It is important to recognize just how significant a problem migraine headache is. It has been estimated that migraine affects 11% of the United
ปวดศ รษะมา 5 ป ก นยาแก ปวดก ย งไม ข น นพ.พาว ฒ เมฆว ช ย โรงพยาบาลนครราชส มา
 ปวดศ รษะมา 5 ป ก นยาแก ปวดก ย งไม ข น นพ.พาว ฒ เมฆว ช ย โรงพยาบาลนครราชส มา 1 CONTENT 1 2 3 Chronic Daily Headache Medical Overused Headache Management Headaches are one of the most common symptoms List
ปวดศ รษะมา 5 ป ก นยาแก ปวดก ย งไม ข น นพ.พาว ฒ เมฆว ช ย โรงพยาบาลนครราชส มา 1 CONTENT 1 2 3 Chronic Daily Headache Medical Overused Headache Management Headaches are one of the most common symptoms List
Tears of Pain SUNCT and SUNA A/PROFESSOR ARUN AGGARWAL RPAH PAIN MANAGEMENT CENTRE
 Tears of Pain SUNCT and SUNA A/PROFESSOR ARUN AGGARWAL RPAH PAIN MANAGEMENT CENTRE IHS Classification 1989 (updated 2004) Primary Headaches 4 categories Migraine Tension-type Cluster and other trigeminal
Tears of Pain SUNCT and SUNA A/PROFESSOR ARUN AGGARWAL RPAH PAIN MANAGEMENT CENTRE IHS Classification 1989 (updated 2004) Primary Headaches 4 categories Migraine Tension-type Cluster and other trigeminal
Chronic Daily Headaches
 Chronic Daily Headaches ANWARUL HAQ, MD, MRCP(UK), FAHS DIRECTOR BAYLOR HEADACHE CENTER, DALLAS, TEXAS DISCLOSURES: None OBJECTIVES AT THE CONCLUSION OF THIS ACTIVITY, PARTICIPANTS WILL BE ABLE TO: define
Chronic Daily Headaches ANWARUL HAQ, MD, MRCP(UK), FAHS DIRECTOR BAYLOR HEADACHE CENTER, DALLAS, TEXAS DISCLOSURES: None OBJECTIVES AT THE CONCLUSION OF THIS ACTIVITY, PARTICIPANTS WILL BE ABLE TO: define
Clinical case. Clinical case 3/15/2018 OVERVIEW. Refractory headaches and update on novel treatment. Refractory headache.
 OVERVIEW Refractory headaches and update on novel treatment Definition of refractory headache Treatment approach Medications Neuromodulation In the pipeline Juliette Preston, MD OHSU Headache Center Refractory
OVERVIEW Refractory headaches and update on novel treatment Definition of refractory headache Treatment approach Medications Neuromodulation In the pipeline Juliette Preston, MD OHSU Headache Center Refractory
Update on Diagnosis and Management of Migraines
 Update on Diagnosis and Management of Migraines Joel J. Heidelbaugh, MD, FAAFP, FACG Clinical Professor Departments of Family Medicine and Urology University of Michigan Learning Objectives To distinguish
Update on Diagnosis and Management of Migraines Joel J. Heidelbaugh, MD, FAAFP, FACG Clinical Professor Departments of Family Medicine and Urology University of Michigan Learning Objectives To distinguish
MIGRAINE A MYSTERY HEADACHE
 MIGRAINE A MYSTERY HEADACHE The migraine is a chronic neurological disease that is characterized by moderate to severe episodes of headache that is mostly associated with other central nervous system (CNS)
MIGRAINE A MYSTERY HEADACHE The migraine is a chronic neurological disease that is characterized by moderate to severe episodes of headache that is mostly associated with other central nervous system (CNS)
WHY IS MIGRAINE IMPORTANT
 WHY IS MIGRAINE IMPORTANT Migraine is a complex disorder characterized by recurrent episodes of headache, most often unilateral and in some cases associated with visual or sensory symptoms collectively
WHY IS MIGRAINE IMPORTANT Migraine is a complex disorder characterized by recurrent episodes of headache, most often unilateral and in some cases associated with visual or sensory symptoms collectively
OH, MY ACHING HEAD! I HAVE NO DISCLOSURES OR CONFLICTS OF INTERESTS TO DECLARE MANAGING HEADACHE IN THE OUTPATIENT SETTING SECONDARY HEADACHES
 1 JUSTIN A. OSSMAN, MD CHATTANOOGA FAMILY MEDICINE UPDATE OH, MY ACHING HEAD! MANAGING HEADACHE IN THE OUTPATIENT SETTING 2 I HAVE NO DISCLOSURES OR CONFLICTS OF INTERESTS TO DECLARE OBJECTIVES International
1 JUSTIN A. OSSMAN, MD CHATTANOOGA FAMILY MEDICINE UPDATE OH, MY ACHING HEAD! MANAGING HEADACHE IN THE OUTPATIENT SETTING 2 I HAVE NO DISCLOSURES OR CONFLICTS OF INTERESTS TO DECLARE OBJECTIVES International
Treatment of Primary Headache Syndromes
 Presenter Disclosure Information 2:45 3:45pm Treatment of Primary Headache Syndromes SPEAKER Gerald W. Smetana, MD The following relationships exist related to this presentation: Gerald W.Smetana, MD,
Presenter Disclosure Information 2:45 3:45pm Treatment of Primary Headache Syndromes SPEAKER Gerald W. Smetana, MD The following relationships exist related to this presentation: Gerald W.Smetana, MD,
How do we treat migraine? New SIGN Guidelines
 How do we treat migraine? New SIGN Guidelines Managing your migraine Migraine Trust, Edinburgh 2018 Callum Duncan Consultant Neurologist Aberdeen Royal Infirmary Chair SIGN Guideline 155 Premonitory Mood
How do we treat migraine? New SIGN Guidelines Managing your migraine Migraine Trust, Edinburgh 2018 Callum Duncan Consultant Neurologist Aberdeen Royal Infirmary Chair SIGN Guideline 155 Premonitory Mood
I have no financial relationships to disclose. I will not discuss investigational use of medication in my presentation.
 I have no financial relationships to disclose. I will not discuss investigational use of medication in my presentation. In 1962, Bille published landmark epidemiologic survey of headache among 9,000 school
I have no financial relationships to disclose. I will not discuss investigational use of medication in my presentation. In 1962, Bille published landmark epidemiologic survey of headache among 9,000 school
Headache A Practical Approach
 Headache A Practical Approach Integrated Pain Symposium December 1, 2017 Alyssa Lettich. MD Neurosciences Institute/Neurosciences Clinical Program Medical Director Headache and Pain Development Teams Disclosures:
Headache A Practical Approach Integrated Pain Symposium December 1, 2017 Alyssa Lettich. MD Neurosciences Institute/Neurosciences Clinical Program Medical Director Headache and Pain Development Teams Disclosures:
A case of a patient with chronic headache. Focus on Migraine. None related to the presentation Grants to conduct clinical trials from: Speaker bureau:
 Chronic Daily Headache Bassel F. Shneker, MD, MBA Associate Professor Vice Chair, OSU Neurology The Ohio State University Wexner Medical Center Financial Disclosures None related to the presentation Grants
Chronic Daily Headache Bassel F. Shneker, MD, MBA Associate Professor Vice Chair, OSU Neurology The Ohio State University Wexner Medical Center Financial Disclosures None related to the presentation Grants
10/31/2017 PRIMARY CARE AND HEADACHE DISCLOSURES WHERE DO THOSE WITH HEADACHE SEEK MEDICAL CARE? Primary Care 67%
 PRIMARY CARE AND HEADACHE Sonja Potrebic MD PhD Regional Headache Specialist Kaiser LAMC 1 WHERE DO THOSE WITH HEADACHE SEEK MEDICAL CARE? Column1 Primary Care 67% Primary Care Headache Specialty Other
PRIMARY CARE AND HEADACHE Sonja Potrebic MD PhD Regional Headache Specialist Kaiser LAMC 1 WHERE DO THOSE WITH HEADACHE SEEK MEDICAL CARE? Column1 Primary Care 67% Primary Care Headache Specialty Other
Migraine Management. Jane Melling Headache nurse Mater Misericordiae Hospital
 Migraine Management Jane Melling Headache nurse Mater Misericordiae Hospital Migraine facts Among the most common disorders of the nervous system 3 rd most prevalent medical disorder on the planet (lancet
Migraine Management Jane Melling Headache nurse Mater Misericordiae Hospital Migraine facts Among the most common disorders of the nervous system 3 rd most prevalent medical disorder on the planet (lancet
Controlling Migraine Pain
 Migraine Stats Controlling Migraine Pain Alan Zacharias, M.D. Associated Neurologists, Boulder Community Health 303-622-3365 Women 15% Men 5% Usually starts in 2 nd and 3 rd Decade Major Impact on days
Migraine Stats Controlling Migraine Pain Alan Zacharias, M.D. Associated Neurologists, Boulder Community Health 303-622-3365 Women 15% Men 5% Usually starts in 2 nd and 3 rd Decade Major Impact on days
Can I send this headache patient home? Dr Nicola Giffin Consultant Neurologist Bath, Nov 2017
 Can I send this headache patient home? Dr Nicola Giffin Consultant Neurologist Bath, Nov 2017 SAH v benign thunderclap headaches Other pathologies not apparent on CT Severe primary headaches: management
Can I send this headache patient home? Dr Nicola Giffin Consultant Neurologist Bath, Nov 2017 SAH v benign thunderclap headaches Other pathologies not apparent on CT Severe primary headaches: management
HEADACHE: Benign or Severe Dr Gobinda Chandra Roy
 HEADACHE: Benign or Severe Dr Gobinda Chandra Roy Associate Professor, Department of Medicine, Shaheed Suhrawardy Medical College and Hospital Outlines 1. Introduction 2. Classification of headache 3.
HEADACHE: Benign or Severe Dr Gobinda Chandra Roy Associate Professor, Department of Medicine, Shaheed Suhrawardy Medical College and Hospital Outlines 1. Introduction 2. Classification of headache 3.
6/4/2018. Headache. Headaches. Headache. Migraine Headaches. Headache. Red Flag signs and symptoms. Imaging CT without contrast.
 Presented by M.D. Shepherd, M.D. OH MY ACHING HEAD! Estimated that one half of the adult population is affected by a headache disorder International Society Classification Primary : Tension s 40% of the
Presented by M.D. Shepherd, M.D. OH MY ACHING HEAD! Estimated that one half of the adult population is affected by a headache disorder International Society Classification Primary : Tension s 40% of the
Clinical Learning Days November 10, 2017
 Migraine Clinical Learning Days November 10, 2017 Alyssa Lettich. MD Neurosciences Institute/Neurosciences Clinical Program Medical Director Headache Disclosures: none Learning Objectives: At the conclusion
Migraine Clinical Learning Days November 10, 2017 Alyssa Lettich. MD Neurosciences Institute/Neurosciences Clinical Program Medical Director Headache Disclosures: none Learning Objectives: At the conclusion
Disclosures. Objectives 6/2/2017
 Classification: Migraine and Trigeminal Autonomic Cephalalgias Lauren Doyle Strauss, DO, FAHS Assistant Professor, Child Neurology Assistant Director, Child Neurology Residency @StraussHeadache No disclosures
Classification: Migraine and Trigeminal Autonomic Cephalalgias Lauren Doyle Strauss, DO, FAHS Assistant Professor, Child Neurology Assistant Director, Child Neurology Residency @StraussHeadache No disclosures
Headache Pain Generators
 Objectives 1. Define the major categories of headache. 2. Take a history directed at characterizing a headache pattern in an individual patient and identify the cause or triggers of the headache. 3. Understand
Objectives 1. Define the major categories of headache. 2. Take a history directed at characterizing a headache pattern in an individual patient and identify the cause or triggers of the headache. 3. Understand
Current Migraine Treatment Therapy. Daniel Kassicieh, DO, FAAN
 Current Migraine Treatment Therapy Daniel Kassicieh, DO, FAAN Migraine a Disease Process Migraines are a chronic disease process similar to many other chronic medical conditions Migraine has a low mortality
Current Migraine Treatment Therapy Daniel Kassicieh, DO, FAAN Migraine a Disease Process Migraines are a chronic disease process similar to many other chronic medical conditions Migraine has a low mortality
Ishaq Abu Arafeh Consultant Paediatrician Royal Hospital for Children, Glasgow Forth Valley Royal Hospital, Larbert
 Ishaq Abu Arafeh Consultant Paediatrician Royal Hospital for Children, Glasgow Forth Valley Royal Hospital, Larbert Childhood headache: Is it really difficult to manage? It shouldn t be... But it can be...
Ishaq Abu Arafeh Consultant Paediatrician Royal Hospital for Children, Glasgow Forth Valley Royal Hospital, Larbert Childhood headache: Is it really difficult to manage? It shouldn t be... But it can be...
Migraine Migraine Age Specific Prevalence in the United States. Headache International Headache Society Classification
 28 Primary Care Medicine Principles and Practice 29 October 28 Professor Peter J. Goadsby Peter.Goadsby@headache.ucsf.edu Department of Neurology Headache International Headache Society Classification
28 Primary Care Medicine Principles and Practice 29 October 28 Professor Peter J. Goadsby Peter.Goadsby@headache.ucsf.edu Department of Neurology Headache International Headache Society Classification
Headache. Headache Case. Migraine Headache. Eric Kraus, MD. Types» Without aura (common)» With aura (classic)
 Headache Eric Kraus, MD Headache Case This 23 year-old female has headaches behind the right eye that cause her to lay down in a quiet room. They have a throbbing quality and she may vomit. Migraine Headache
Headache Eric Kraus, MD Headache Case This 23 year-old female has headaches behind the right eye that cause her to lay down in a quiet room. They have a throbbing quality and she may vomit. Migraine Headache
Managing Headache in Acute Medicine. Ben Lovell Consultant Physician in Acute Medicine University College London Hospital
 Managing Headache in Acute Medicine Ben Lovell Consultant Physician in Acute Medicine University College London Hospital Some ED headache stats Arrive by ambulance 31% Median age 39 Worst ever headache
Managing Headache in Acute Medicine Ben Lovell Consultant Physician in Acute Medicine University College London Hospital Some ED headache stats Arrive by ambulance 31% Median age 39 Worst ever headache
Jessica Ailani MD FAHS Director, Georgetown Headache Center Associate Professor Neurology Medstar Georgetown University Hospital
 Jessica Ailani MD FAHS Director, Georgetown Headache Center Associate Professor Neurology Medstar Georgetown University Hospital Honorarium from Current Pain and Headache Reports; Section Editor Unusual
Jessica Ailani MD FAHS Director, Georgetown Headache Center Associate Professor Neurology Medstar Georgetown University Hospital Honorarium from Current Pain and Headache Reports; Section Editor Unusual
MEASURE #4: Overuse of Barbiturate Containing Medications for Primary Headache Disorders Headache
 MEASURE #4: Overuse of Barbiturate Containing Medications for Primary Headache Disorders Headache Measure Description Percentage of patients age 18 years old and older with a diagnosis of primary headache
MEASURE #4: Overuse of Barbiturate Containing Medications for Primary Headache Disorders Headache Measure Description Percentage of patients age 18 years old and older with a diagnosis of primary headache
Prevention and Treatment of Migraines CAITLIN BARNES, PHARM.D. CANDIDATE AMBULATORY CARE JOE CAMMILLERI, PHARM.D. NATOHYA MALLORY, PHARM.D.
 Prevention and Treatment of Migraines CAITLIN BARNES, PHARM.D. CANDIDATE AMBULATORY CARE JOE CAMMILLERI, PHARM.D. NATOHYA MALLORY, PHARM.D. Objectives Present patient case Review epidemiology/pathophysiology
Prevention and Treatment of Migraines CAITLIN BARNES, PHARM.D. CANDIDATE AMBULATORY CARE JOE CAMMILLERI, PHARM.D. NATOHYA MALLORY, PHARM.D. Objectives Present patient case Review epidemiology/pathophysiology
Headache. Susan Hickenbottom MD, MS February 24, 2015
 Headache Susan Hickenbottom MD, MS February 24, 2015 Epidemiology One of most common complaints in primary care 90% of US population 50% at least one severe 25% recurrent disabling attacks 5% chronic daily
Headache Susan Hickenbottom MD, MS February 24, 2015 Epidemiology One of most common complaints in primary care 90% of US population 50% at least one severe 25% recurrent disabling attacks 5% chronic daily
2) Headache - Dr. Hawar
 2) Headache - Dr. Hawar Headache is caused by traction, displacement, inflammation, vascular spasm, or distention of the painsensitive structures in the head or neck. Isolated involvement of the bony skull,
2) Headache - Dr. Hawar Headache is caused by traction, displacement, inflammation, vascular spasm, or distention of the painsensitive structures in the head or neck. Isolated involvement of the bony skull,
July 2012 Target Population. Adult patients 18 years or older in primary care settings.
 Guideline for Primary Care Management of Headache in Adults July 2012 Target Population Adult patients 18 years or older in primary care settings. Exclusions: This guideline does not provide recommendations
Guideline for Primary Care Management of Headache in Adults July 2012 Target Population Adult patients 18 years or older in primary care settings. Exclusions: This guideline does not provide recommendations
What You Should Know About Your HEADACHE. Learn more about headache types, triggers, and treatments, when to get help, and how to help yourself
 What You Should Know About Your HEADACHE Learn more about headache types, triggers, and treatments, when to get help, and how to help yourself Introduction The purpose of this brochure is to give you a
What You Should Know About Your HEADACHE Learn more about headache types, triggers, and treatments, when to get help, and how to help yourself Introduction The purpose of this brochure is to give you a
Headache and Facial Pain. Mohammed ALEssa MBBS, FRCSC Assistant Professor Consultant Otolaryngology,Head & Neck Surgical Oncology
 Headache and Facial Pain Mohammed ALEssa MBBS, FRCSC Assistant Professor Consultant Otolaryngology,Head & Neck Surgical Oncology Introduction It is the most common neurologic complain The diagnosis usually
Headache and Facial Pain Mohammed ALEssa MBBS, FRCSC Assistant Professor Consultant Otolaryngology,Head & Neck Surgical Oncology Introduction It is the most common neurologic complain The diagnosis usually
Pediatric Grand Rounds UT Health San Antonio 2/10/2017
 Jose Luis Aceves, M.D. has no relationships with commercial companies to disclose. Jose Luis Aceves, M.D. Clinical Associate Professor Department of Pediatrics at UTHSCSA At the end of this presentation
Jose Luis Aceves, M.D. has no relationships with commercial companies to disclose. Jose Luis Aceves, M.D. Clinical Associate Professor Department of Pediatrics at UTHSCSA At the end of this presentation
Headaches in Pregnancy Before, During, and After
 Headaches in Pregnancy Before, During, and After Robert Kaniecki, MD Director, UPMC Headache Center Assistant Professor of Neurology University of Pittsburgh Headaches and Pregnancy Pre-pregnancy counseling
Headaches in Pregnancy Before, During, and After Robert Kaniecki, MD Director, UPMC Headache Center Assistant Professor of Neurology University of Pittsburgh Headaches and Pregnancy Pre-pregnancy counseling
Migraine Controversies in Women s Health. Professor Peter J. Goadsby 5 December Department of Neurology
 Migraine 2008 Controversies in Women s Health 5 December 2008 Professor Peter J. Goadsby Peter.Goadsby@headache.ucsf.edu Department of Neurology Headache International Headache Society Classification Primary
Migraine 2008 Controversies in Women s Health 5 December 2008 Professor Peter J. Goadsby Peter.Goadsby@headache.ucsf.edu Department of Neurology Headache International Headache Society Classification Primary
Headaches in Children and Adolescents. Paul Shillito
 Headaches in Children and Adolescents Paul Shillito Topics For Discussion What s different about childhood migraine Chronic daily headache (CDH) Tumours and other things to worry about Management of childhood
Headaches in Children and Adolescents Paul Shillito Topics For Discussion What s different about childhood migraine Chronic daily headache (CDH) Tumours and other things to worry about Management of childhood
Pause for thought. Dr Jane Anderson Consultant Neurologist
 Pause for thought Dr Jane Anderson Consultant Neurologist Which is the top cause of years lived with disability worldwide? 1. COPD 2. Low Back pain 3. Diabetes 4. Migraine with medication overuse headache
Pause for thought Dr Jane Anderson Consultant Neurologist Which is the top cause of years lived with disability worldwide? 1. COPD 2. Low Back pain 3. Diabetes 4. Migraine with medication overuse headache
Primary Care Adult Headache Management Pathway (formerly North West Headache Management Guideline for Adults) Version 1.0
 Primary Care Adult Headache Management Pathway (formerly rth West Headache Management Guideline for Adults) Version 1.0 1 VERSION CONTROL Version Date Amendments made Version 1.0 October 2018 Reformatted
Primary Care Adult Headache Management Pathway (formerly rth West Headache Management Guideline for Adults) Version 1.0 1 VERSION CONTROL Version Date Amendments made Version 1.0 October 2018 Reformatted
Trigeminal Autonomic Cephalalgias. Disclosures. Objectives 6/20/2018. Rashmi Halker Singh, MD FAHS UCNS Review Course June 2018
 Trigeminal Autonomic Cephalalgias Rashmi Halker Singh, MD FAHS UCNS Review Course June 2018 Disclosures Honoraria from Allergan and Amgen for advisory board, Current Neurology and Neuroscience Reports
Trigeminal Autonomic Cephalalgias Rashmi Halker Singh, MD FAHS UCNS Review Course June 2018 Disclosures Honoraria from Allergan and Amgen for advisory board, Current Neurology and Neuroscience Reports
Outpatient Headache Care Guideline
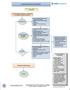 1 Outpatient Care Guideline Inclusion criteria: children > 3 yrs with headaches Is urgent emergency department, neuroimaging, or Neurology consultation indicated? Referral to ED if: New severe headache
1 Outpatient Care Guideline Inclusion criteria: children > 3 yrs with headaches Is urgent emergency department, neuroimaging, or Neurology consultation indicated? Referral to ED if: New severe headache
Çiçek Wöber-Bingöl HEADACHE UNIT FOR CHILDREN AND ADOLESCENCE
 Headache in children and adolescents Çiçek Wöber-Bingöl HEADACHE UNIT FOR CHILDREN AND ADOLESCENCE Dept. of Psychiatry of Childhood and Adolescence Medical University of Vienna, Vienna, Austria Impact
Headache in children and adolescents Çiçek Wöber-Bingöl HEADACHE UNIT FOR CHILDREN AND ADOLESCENCE Dept. of Psychiatry of Childhood and Adolescence Medical University of Vienna, Vienna, Austria Impact
Headache evaluation and management after concussion. Assistant Professor
 Headache evaluation and management after concussion Juliette Preston, M.D. Assistant Professor OHSU Headache Center OVERVIEW Introduction Definition Acute post-traumatic headache Red flags Persistent post-traumatic
Headache evaluation and management after concussion Juliette Preston, M.D. Assistant Professor OHSU Headache Center OVERVIEW Introduction Definition Acute post-traumatic headache Red flags Persistent post-traumatic
Migraine Management. Dr Helen Brown Director of Neurology and Stroke The Princess Alexandra Hospital
 Migraine Management Dr Helen Brown Director of Neurology and Stroke The Princess Alexandra Hospital Referral Criteria for Migraine Migraine Management Migraine Diagnosis Spot on Health Migraine pathway
Migraine Management Dr Helen Brown Director of Neurology and Stroke The Princess Alexandra Hospital Referral Criteria for Migraine Migraine Management Migraine Diagnosis Spot on Health Migraine pathway
Headache Mary D. Hughes, MD Neuroscience Associates
 Headache Mary D. Hughes, MD Neuroscience Associates Case 1 22 year old female presents with recurrent headaches. She has had headaches for the past 3 years. They start on the right side of her head and
Headache Mary D. Hughes, MD Neuroscience Associates Case 1 22 year old female presents with recurrent headaches. She has had headaches for the past 3 years. They start on the right side of her head and
Adult with headache. Problem-specific video guides to diagnosing patients and helping them with management and prevention
 Adult with headache Problem-specific video guides to diagnosing patients and helping them with management and prevention London Strategic Clinical Networks London Neuroscience Strategic Clinical Network
Adult with headache Problem-specific video guides to diagnosing patients and helping them with management and prevention London Strategic Clinical Networks London Neuroscience Strategic Clinical Network
Migraine Treatment What you need to know
 Migraine Treatment What you need to know DR NICOLE LIMBERG ST ANDREWS PLACE SPRING HILL www.migrainespecialist.com.au Migraine what is it? Primary neurobiological condition Waves of reduced brain activity
Migraine Treatment What you need to know DR NICOLE LIMBERG ST ANDREWS PLACE SPRING HILL www.migrainespecialist.com.au Migraine what is it? Primary neurobiological condition Waves of reduced brain activity
Preventive treatment of migraine. Rebecca Burch, MD Brigham and Women s Faulkner Hospital Harvard Medical School Boston, MA
 Preventive treatment of migraine Rebecca Burch, MD Brigham and Women s Faulkner Hospital Harvard Medical School Boston, MA No disclosures Disclosures Many preventive treatments for migraine are not FDA-approved
Preventive treatment of migraine Rebecca Burch, MD Brigham and Women s Faulkner Hospital Harvard Medical School Boston, MA No disclosures Disclosures Many preventive treatments for migraine are not FDA-approved
Headache Assessment In Primary Eye Care
 Headache Assessment In Primary Eye Care Spencer Johnson, O.D., F.A.A.O. Northeastern State University Oklahoma College of Optometry johns137@nsuok.edu Course Objectives Review headache classification Understand
Headache Assessment In Primary Eye Care Spencer Johnson, O.D., F.A.A.O. Northeastern State University Oklahoma College of Optometry johns137@nsuok.edu Course Objectives Review headache classification Understand
GENERAL APPROACH AND CLASSIFICATION OF HEADACHES
 GENERAL APPROACH AND CLASSIFICATION OF HEADACHES CLASSIFICATION Headache is one of the most common medical complaints. Most of the population will have experienced headache, and over 5% will seek medical
GENERAL APPROACH AND CLASSIFICATION OF HEADACHES CLASSIFICATION Headache is one of the most common medical complaints. Most of the population will have experienced headache, and over 5% will seek medical
MEASURE #3: PREVENTIVE MIGRAINE MEDICATION PRESCRIBED Headache
 MEASURE #3: PREVENTIVE MIGRAINE MEDICATION PRESCRIBED Headache Measure Description Percentage of patients age 18 years old and older diagnosed with migraine headache whose migraine frequency is 4 migraine
MEASURE #3: PREVENTIVE MIGRAINE MEDICATION PRESCRIBED Headache Measure Description Percentage of patients age 18 years old and older diagnosed with migraine headache whose migraine frequency is 4 migraine
Disclosures. Triptans for Kids 5/16/13
 5/16/13 Disclosures Triptans for Kids Amy A. Gelfand, MD GelfandA@neuropeds.ucsf.edu Departments of Neurology and Pediatrics UCSF Child Neurology and Headache Center I receive grant funding from: NIH/NINDS
5/16/13 Disclosures Triptans for Kids Amy A. Gelfand, MD GelfandA@neuropeds.ucsf.edu Departments of Neurology and Pediatrics UCSF Child Neurology and Headache Center I receive grant funding from: NIH/NINDS
11/10/2017. THE BRIDGE Course Objectives. THE BRIDGE Course Objectives
 THE BRIDGE Course Objectives Describe clinical characteristics associated with migraine diagnosis in adult and pediatric populations. Identify barriers and risk factors impacting the clinical course of
THE BRIDGE Course Objectives Describe clinical characteristics associated with migraine diagnosis in adult and pediatric populations. Identify barriers and risk factors impacting the clinical course of
HEADACHES THE RED FLAGS
 HEADACHES THE RED FLAGS FAYYAZ AHMED CONSULTANT NEUROLOGIST HON. SENIOR LECTURER HULL YORK MEDICAL SCHOOL SECONDARY VS PRIMARY HEADACHES COMMON SECONDARY HEADACHES UNCOMMON BUT SERIOUS SECONDARY HEADACHES
HEADACHES THE RED FLAGS FAYYAZ AHMED CONSULTANT NEUROLOGIST HON. SENIOR LECTURER HULL YORK MEDICAL SCHOOL SECONDARY VS PRIMARY HEADACHES COMMON SECONDARY HEADACHES UNCOMMON BUT SERIOUS SECONDARY HEADACHES
Understanding. Migraine. Amy, diagnosed in 1989, with her family.
 Understanding Migraine Amy, diagnosed in 1989, with her family. What Is a Migraine? A migraine is a recurring moderate to severe headache. The pain usually occurs on one side of the head. It is typically
Understanding Migraine Amy, diagnosed in 1989, with her family. What Is a Migraine? A migraine is a recurring moderate to severe headache. The pain usually occurs on one side of the head. It is typically
An Overview of MOH. ALAN M. Rapoport, M.D. Clinical Professor of Neurology The David Geffen School of Medicine at UCLA Los Angeles, California
 An Overview of MOH IHS ASIAN HA MASTERS SCHOOL MARCH 24, 2013 ALAN M. Rapoport, M.D. Clinical Professor of Neurology The David Geffen School of Medicine at UCLA Los Angeles, California President-Elect
An Overview of MOH IHS ASIAN HA MASTERS SCHOOL MARCH 24, 2013 ALAN M. Rapoport, M.D. Clinical Professor of Neurology The David Geffen School of Medicine at UCLA Los Angeles, California President-Elect
Reflections on NICE Headache Guideline. Dr Kay Kennis GPwSI in Headache, Bradford
 Reflections on NICE Headache Guideline Dr Kay Kennis GPwSI in Headache, Bradford Overview The process of guideline development illustrated with the headache guideline Reflections on the process Key recommendations
Reflections on NICE Headache Guideline Dr Kay Kennis GPwSI in Headache, Bradford Overview The process of guideline development illustrated with the headache guideline Reflections on the process Key recommendations
ARxCH. Annual Review of Changes in Healthcare. Calcitonin Gene-Related Peptide Receptors and the Prevention of Migraines. Abstract
 Calcitonin Gene-Related Peptide Receptors and the Prevention of Migraines Brian Schuler, PharmD Candidate 2018 1 1 University of Findlay College of Pharmacy Abstract Migraines are the third most prevalent
Calcitonin Gene-Related Peptide Receptors and the Prevention of Migraines Brian Schuler, PharmD Candidate 2018 1 1 University of Findlay College of Pharmacy Abstract Migraines are the third most prevalent
Management of headache
 Management of headache TJ Steiner Imperial College London Based on European principles of management of common headache disorders TJ Steiner, K Paemeleire, R Jensen, D Valade, L Savi, MJA Lainez, H-C Diener,
Management of headache TJ Steiner Imperial College London Based on European principles of management of common headache disorders TJ Steiner, K Paemeleire, R Jensen, D Valade, L Savi, MJA Lainez, H-C Diener,
4/12/2018. ECHO Ontario Chronic Pain Migraine. Migraine Definition and Epidemiology. Migraine - Undertreatment. Migraine - Diagnostic Classification
 Andrew J Smith, MDCM ECHO Ontario Chronic Pain Migraine Staff Physician, Neurology, Pain and Addiction Medicine Centre for Addiction and Mental Health Migraine Learning Objectives At the end of this session,
Andrew J Smith, MDCM ECHO Ontario Chronic Pain Migraine Staff Physician, Neurology, Pain and Addiction Medicine Centre for Addiction and Mental Health Migraine Learning Objectives At the end of this session,
Lynda J. Krasenbaum, MSN, ANP BC. Associate Director New York Headache Center
 Diagnosing Headache in Adults and Adolescents Lynda J. Krasenbaum, MSN, ANP BC Associate Director New York Headache Center New York, New York Learning Objectives Understand the diagnostic challenges of
Diagnosing Headache in Adults and Adolescents Lynda J. Krasenbaum, MSN, ANP BC Associate Director New York Headache Center New York, New York Learning Objectives Understand the diagnostic challenges of
23, 2005 RESIDENT PHYSICIAN:
 TITLE: Migraine SOURCE: Grand Rounds Presentation, UTMB, Dept. of Otolaryngology DATE: March 23, 2005 RESIDENT PHYSICIAN: Jeffrey Buyten, MD FACULTY PHYSICIAN: David C. Teller, MD SERIES EDITORS: Francis
TITLE: Migraine SOURCE: Grand Rounds Presentation, UTMB, Dept. of Otolaryngology DATE: March 23, 2005 RESIDENT PHYSICIAN: Jeffrey Buyten, MD FACULTY PHYSICIAN: David C. Teller, MD SERIES EDITORS: Francis
Daniel Kassicieh, DO, FAAN
 Daniel Kassicieh, DO, FAAN Migraine a Disease Process Migraine is a chronic disease process similar to many other chronic medical conditions Migraine has a low mortality but high morbidity 38 million Americans
Daniel Kassicieh, DO, FAAN Migraine a Disease Process Migraine is a chronic disease process similar to many other chronic medical conditions Migraine has a low mortality but high morbidity 38 million Americans
Headache. Anna Morenkova, MD, PhD Assistant Professor Department of Neurology UC Irvine
 Headache Anna Morenkova, MD, PhD Assistant Professor Department of Neurology UC Irvine SOURCE OF HEAD PAIN (NOCICEPTIVE STRUCTURES) Intracranial Extracranial arteries of circle of Willis dura, dural arteries
Headache Anna Morenkova, MD, PhD Assistant Professor Department of Neurology UC Irvine SOURCE OF HEAD PAIN (NOCICEPTIVE STRUCTURES) Intracranial Extracranial arteries of circle of Willis dura, dural arteries
By Nathan Hall Associate Editor
 By Nathan Hall Associate Editor 34 Practical Neurology March 2005 These new rules may change the definition of head pain, but some practitioners may find the new guidelines themselves to be a source of
By Nathan Hall Associate Editor 34 Practical Neurology March 2005 These new rules may change the definition of head pain, but some practitioners may find the new guidelines themselves to be a source of
CHRONIC HEADACHES IN CHILDHOOD
 CHRONIC HEADACHES IN CHILDHOOD EDWIN LIU, MD PEDIATRIC NEUROLOGISTS OF PALM BEACH PEDIATRIC SLEEP CENTERS OF FLORIDA ASSISTANT CLINICAL PROFESSOR FSU ASSISTANT CLINICAL PROFESSOR NOVA SOUTHEASTERN PEDIATRIC
CHRONIC HEADACHES IN CHILDHOOD EDWIN LIU, MD PEDIATRIC NEUROLOGISTS OF PALM BEACH PEDIATRIC SLEEP CENTERS OF FLORIDA ASSISTANT CLINICAL PROFESSOR FSU ASSISTANT CLINICAL PROFESSOR NOVA SOUTHEASTERN PEDIATRIC
Headache Management in Primary Care Dr Niranjanan Nirmalananthan Consultant Neurologist
 Headache Management in Primary Care Dr Niranjanan Nirmalananthan Consultant Neurologist Wednesday 10 th of April 2019 Summary Why does it matter? Classification and diagnosis Who to refer / scan? Serious
Headache Management in Primary Care Dr Niranjanan Nirmalananthan Consultant Neurologist Wednesday 10 th of April 2019 Summary Why does it matter? Classification and diagnosis Who to refer / scan? Serious
My patient s pain in the head, is a pain in Greg Jicha, M.D., Ph.D.
 My patient s pain in the head, is a pain in the @%$*&# Greg Jicha, M.D., Ph.D. Kentucky Neurologic Institute University of Kentucky, Lexington, KY Migraine is More Common than Asthma & Diabetes Combined
My patient s pain in the head, is a pain in the @%$*&# Greg Jicha, M.D., Ph.D. Kentucky Neurologic Institute University of Kentucky, Lexington, KY Migraine is More Common than Asthma & Diabetes Combined
Dubai Standards of Care (Migraine)
 Dubai Standards of Care 2018 (Migraine) Preface Migraine is one of the most common problem dealt with in daily practice. In Dubai, the management of migraine is done through various different strategies.
Dubai Standards of Care 2018 (Migraine) Preface Migraine is one of the most common problem dealt with in daily practice. In Dubai, the management of migraine is done through various different strategies.
Migraine, Tension, and Cluster Headache: Primary Care for Primary Headaches. Jonathon M. Firnhaber, MD, FAAFP
 Migraine, Tension, and Cluster Headache: Primary Care for Primary Headaches Jonathon M. Firnhaber, MD, FAAFP Learning objectives 1. Utilize evidence-based strategies to diagnose patients presenting with
Migraine, Tension, and Cluster Headache: Primary Care for Primary Headaches Jonathon M. Firnhaber, MD, FAAFP Learning objectives 1. Utilize evidence-based strategies to diagnose patients presenting with
Greg Book. September 25, 2007 Olin Neuropsychiatry Research Center
 Migraine Pathogenesis Greg Book September 25, 2007 Olin Neuropsychiatry Research Center Migraine Migraine i affects approximately 19.2% of females and 6.6% of males in the United States. (Patel, Bigal
Migraine Pathogenesis Greg Book September 25, 2007 Olin Neuropsychiatry Research Center Migraine Migraine i affects approximately 19.2% of females and 6.6% of males in the United States. (Patel, Bigal
Medical Policy An independent licensee of the Blue Cross Blue Shield Association
 CGRP Page 1 of 8 Medical Policy An independent licensee of the Blue Cross Blue Shield Association Title: CGRP (calcitonin gene-related peptide) Prime Therapeutics will review Prior Authorization requests
CGRP Page 1 of 8 Medical Policy An independent licensee of the Blue Cross Blue Shield Association Title: CGRP (calcitonin gene-related peptide) Prime Therapeutics will review Prior Authorization requests
Faculty Disclosures. Learning Objectives. Acute Treatment Strategies
 WWW.AMERICANHEADACHESOCIETY.ORG Acute Treatment Strategies Content developed by: Lawrence C. Newman, MD, FAHS Donna Gutterman, PharmD Faculty Disclosures LAWRENCE C. NEWMAN, MD, FAHS Dr. Newman has received
WWW.AMERICANHEADACHESOCIETY.ORG Acute Treatment Strategies Content developed by: Lawrence C. Newman, MD, FAHS Donna Gutterman, PharmD Faculty Disclosures LAWRENCE C. NEWMAN, MD, FAHS Dr. Newman has received
Lynne Kerr, MD May 2014
 Lynne Kerr, MD May 2014 Headache is one of top 5 health problems in children 2 nd most common diagnosis in the peds neurology outpatient clinic 14 year old girl severe headache Headaches 1-2 times/month
Lynne Kerr, MD May 2014 Headache is one of top 5 health problems in children 2 nd most common diagnosis in the peds neurology outpatient clinic 14 year old girl severe headache Headaches 1-2 times/month
Subject: CGRP Inhibitors
 ARCHIVED (NOT ACTIVE RETIRED) Archived: 08/01/18 09-J2000-98 Original Effective Date: 06/15/18 Reviewed: 05/09/18 Revised: 08/01/18 Next Review: ARCHIVED (NOT ACTIVE RETIRED) Subject: CGRP Inhibitors THIS
ARCHIVED (NOT ACTIVE RETIRED) Archived: 08/01/18 09-J2000-98 Original Effective Date: 06/15/18 Reviewed: 05/09/18 Revised: 08/01/18 Next Review: ARCHIVED (NOT ACTIVE RETIRED) Subject: CGRP Inhibitors THIS
ONZETRA XSAIL (sumatriptan) nasal powder
 ONZETRA XSAIL (sumatriptan) nasal powder Coverage for services, procedures, medical devices and drugs are dependent upon benefit eligibility as outlined in the member's specific benefit plan. This Pharmacy
ONZETRA XSAIL (sumatriptan) nasal powder Coverage for services, procedures, medical devices and drugs are dependent upon benefit eligibility as outlined in the member's specific benefit plan. This Pharmacy
How could I be having migraine when I don't have a headache?
 Migraine Your doctor thinks you may have migraine. Classic migraine attacks start with visual symptoms (often zig-zag colored lights or flashes of light expanding to one side over 10-30 minutes) followed
Migraine Your doctor thinks you may have migraine. Classic migraine attacks start with visual symptoms (often zig-zag colored lights or flashes of light expanding to one side over 10-30 minutes) followed
10/17/2017 CHRONIC MIGRAINES BOTOX: TO INJECT OR NOT INJECT? IN CHRONIC MIGRAINE PROPHYLAXIS OBJECTIVES PATIENT CASE EPIDEMIOLOGY EPIDEMIOLOGY
 BOTOX: TO INJECT OR NOT INJECT? IN CHRONIC MIGRAINE PROPHYLAXIS OBJECTIVES JENNIFER SHIN, PHARMD PGY2 AMBULATORY CARE PHARMACY RESIDENT COMMUNITYCARE HEALTH CENTERS PHARMACOTHERAPY ROUNDS OCTOBER 20, 2017
BOTOX: TO INJECT OR NOT INJECT? IN CHRONIC MIGRAINE PROPHYLAXIS OBJECTIVES JENNIFER SHIN, PHARMD PGY2 AMBULATORY CARE PHARMACY RESIDENT COMMUNITYCARE HEALTH CENTERS PHARMACOTHERAPY ROUNDS OCTOBER 20, 2017
Emerging Challenges in Primary Care: Brainstorm: A Symposium on Migraine Treatment and Management
 Emerging Challenges in Primary Care: 2017 Brainstorm: A Symposium on Migraine Treatment and Management 1 Faculty Jeff Unger, MD, ABFM, FACE Director, Unger Primary Care Medical Group Rancho Cucamonga,
Emerging Challenges in Primary Care: 2017 Brainstorm: A Symposium on Migraine Treatment and Management 1 Faculty Jeff Unger, MD, ABFM, FACE Director, Unger Primary Care Medical Group Rancho Cucamonga,
Regulatory Status FDA approved indication: Migranal Nasal Spray is indicated for the acute treatment of migraine headaches with or without aura (1).
 Federal Employee Program 1310 G Street, N.W. Washington, D.C. 20005 202.942.1000 Fax 202.942.1125 5.70.60 Subject: Migranal Nasal Spray Page: 1 of 5 Last Review Date: November 30, 2018 Migranal Nasal Spray
Federal Employee Program 1310 G Street, N.W. Washington, D.C. 20005 202.942.1000 Fax 202.942.1125 5.70.60 Subject: Migranal Nasal Spray Page: 1 of 5 Last Review Date: November 30, 2018 Migranal Nasal Spray
Headache Syndrome. Karen Alvarez, D.O Nemours Children s Specialty Care Jacksonville, FL
 Headache Syndrome Karen Alvarez, D.O Nemours Children s Specialty Care Jacksonville, FL What is a headache? A headache or cephalgia is defined as pain anywhere in the region of head or neck Where does
Headache Syndrome Karen Alvarez, D.O Nemours Children s Specialty Care Jacksonville, FL What is a headache? A headache or cephalgia is defined as pain anywhere in the region of head or neck Where does
2008 Migraine Update Migraine Update Migraine Update. Epidemiology. Yousef Mohammad MD., MSc. Epidemiology
 2008 Migraine Update Yousef Mohammad MD., MSc Assistant Professor of Neurology Ohio State University Medical Center 2008 Migraine Update Epidemiology 2008 Migraine Update Epidemiology Abortive Treatment
2008 Migraine Update Yousef Mohammad MD., MSc Assistant Professor of Neurology Ohio State University Medical Center 2008 Migraine Update Epidemiology 2008 Migraine Update Epidemiology Abortive Treatment
Headaches. Mini Medical School. November 10, A. Laine Green MSc, MD FRCP(C) Assistant Professor Department of Medicine (Neurology)
 Headaches. Mini Medical School. November 10, 2016 A. Laine Green MSc, MD FRCP(C) Assistant Professor Department of Medicine (Neurology) Artist Agnes Cecile Disclosures I have received an honorarium from
Headaches. Mini Medical School. November 10, 2016 A. Laine Green MSc, MD FRCP(C) Assistant Professor Department of Medicine (Neurology) Artist Agnes Cecile Disclosures I have received an honorarium from
Back Pain. John W. Engstrom, MD December 15, Disclosures. A Primary Care Approach to Headache. Headache Goals
 Disclosures Nothing to declare --- or --- Significant ownership interests Consulting, speaker bureaus, honorarium, grants Link to Harrison s Chapter on Headache: http://ucsfneuroresidency.com/public_html/educati
Disclosures Nothing to declare --- or --- Significant ownership interests Consulting, speaker bureaus, honorarium, grants Link to Harrison s Chapter on Headache: http://ucsfneuroresidency.com/public_html/educati
Long-Term Care Updates
 Long-Term Care Updates September 2017 By Lindsay Slowiczek, PharmD Migraines are often considered to be a condition affecting younger or middle-aged patients, during which patients experience episodic,
Long-Term Care Updates September 2017 By Lindsay Slowiczek, PharmD Migraines are often considered to be a condition affecting younger or middle-aged patients, during which patients experience episodic,
Why does my child hurt? How can we reduce the burden of headache? What is the burden of headache?
 How can we reduce the burden of headache? Disclosure: Independent learning grant from Pfizer Jennifer Bickel, MD FAAN Chief, Headache Section Associate Professor of Pediatrics Division of Neurology The
How can we reduce the burden of headache? Disclosure: Independent learning grant from Pfizer Jennifer Bickel, MD FAAN Chief, Headache Section Associate Professor of Pediatrics Division of Neurology The
Headaches in the Pediatric Emergency Dept
 Headaches in Children February 23, 2011 Jinny Tavee, MD Associate Professor Neuromuscular Center Cleveland Clinic Foundation Cleveland, OH 1 Headaches in the Pediatric Emergency Dept Burton Gutierrez Kan
Headaches in Children February 23, 2011 Jinny Tavee, MD Associate Professor Neuromuscular Center Cleveland Clinic Foundation Cleveland, OH 1 Headaches in the Pediatric Emergency Dept Burton Gutierrez Kan
Headaches in Children
 How common are headaches? What is the impact? Very common! 20% of kids from preschool through teenage report frequent or severe headaches in any given year 2 Headaches are more common in children who have
How common are headaches? What is the impact? Very common! 20% of kids from preschool through teenage report frequent or severe headaches in any given year 2 Headaches are more common in children who have
