IVORY EXOSTOSIS OF THE SKULL
|
|
|
- Samson Grant
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 POSTGRAD. MED. J. (1965), 41, 277 IVORY EXOSTOSIS OF THE SKULL PETER G. BULLOUGH, M.B., Ch.B., The Nuffield Department of Orthopcedic Surgery, University of Oxford. THE IVORY exostosis, or, as it is sometimes called, the ivory osteoma, is a bump of dense bone most often seen on the cranial vault (Fig. 1) or in relation to one or other of the nasal sinuses (Fig. 2). In keeping with its usual origin from a bone preformed in membrane it is not capped by cartilage as is the osteochondroma or exostosis which is commonly seen arising from a long bone. In hospital practice ivory exostoses are very rare, though probably there are many cases which are non-symptomatic. Smith (1952), reporting from Duke University found a total of forty cases in 176,000 surgical specimens examined in their pathology department over a twenty year period. The purpose of this paper is to discuss the clinical presentation and the pathology of the exostoses of twenty-one patients treated surgically over the last twelve years in Oxford. In seven the tumour arose from the cranial vault and in fourteen was related to a nasal sinus. In the first group there were no symptoms and usually the lesions were removed for cosmetic effect. In the second group the patients complained of stabbing frontal headaches, bulging of the eye (Fig. 3), recurrent infection of the sinuses and alteration in vision. The left frontal sinus was affected much more frequently (ten cases) than the other nasal sinuses. Most of the patients were between twenty and forty years of age; the youngest was twelve years and the oldest 68 years. In the first group presenting with cranial lesions six were female, whereas in those presenting with lesions of a sinus ten were male. The following selected cases illustrate the salient features of these two types of lesion. Case Reports Case No. 1 An eighteen-year-old white female who worked as a shorthand typist. About two years prior to admission her hairdresser had noticed a lump on the right side of her head. Since then she had "worried" about it and she thought that possibly it was growing larger. There were no other symptoms. FIG. 1.-X-ray of an exostosis of the parietal bone in a forty-year-old woman. FIG. 2.-X-ray of an exostosis of the left frontal sinus in a twenty-nine-year-old man.
2 278 POSTGRADUATE MEDICAL JOURNAL May, Clinical photograph of a twenty-six-year-old FIG. woman complaining of recurrent rhinitis and diplopia. A large exostosis was removed from the right frontal sinus. FIG. 4.-Macro-photograph of an exostosis removed from the right parietal bone of an eighteen-yearold girl. (H. & E. x4). On examination there was slight tenderness over the bump, the skin moved freely over it and X-ray examination revealed an ivory osteoma of the parietal bone. Histologic examination revealed dense cortical bone but no other abnormality (Fig. 4). Case No. 2 A seventeen-year-old white male working as a farm labourer. Five years prior to admission he first noticed bulging of the left eye and at about the same time he started to experience stabbing pains over the left eye. His local doctor diagnosed the condition as migraine and treated him with phenobarbitone. After six months the pains ceased and did not return until two months prior to admission. He had never had fits Ȯn examination the left eye was protuberant by five millimetres. All the movements of the left were slightly limited and there eye was diplopia at the extremes of gaze in all directions. An X-ray picture of the skull showed a radio-opaque lesion of the left ethmoid sinus encroaching on the left orbit. At operation the tumour had eroded the orbital plate and the outer layer of the dura mater so that the arachnoid was in contact with the tumour. The histology of the lesion is illustrated in Figs FIG. 5.-Photograph of the tumour removed from the left frontal sinus of a fifty-year-old man with recurrent sinusitis. FIG. 6.-Macrophotograph of an exostosis removed from the left ethmoid sinus of a seventeen-yearold boy complaining of headaches and bulging of the left eye for approximately five years. (H. & E. x4).
3 May, 1965 BULLOUGH: Ivory Exostosis of the Skull ;*at-" ^x*krt^ *; :-i-. b: o,:.. : - t,,,,"" r. - ": > * ':'. * -... (a) (b) FIGS. 7a & b.-photomicrograph of the edge of the lesion shown in Fig. 5. There is a very mild chronic inflammatory infiltrate beneath the respiratory epithelium lining the sinus. Fig. 7b taken of the same field by polarized light shows the non-lamellar patttern of the collagen in the bone matrix. (H. & E. x400). Case No. 3 A thirty-five-year-old white farmer. Two months prior to admission he noticed that in order to keep the sun out of his eyes it had become necessary to tip his hat more and more. At the same time he had noticed some slight pain around the eye. At the eye hospital he was told that there was a slight displacement of the eye. Study of photographs taken two years before the onset of symptoms showed in retrospect that even then there had been some displacement. On examination it was found that there was a hard, non-tender, bony lump in the supero-medial part of the right orbit. The proptometer reading was fifteen millimetres on the right and thirteen millimetres on the left. The X-ray picture showed a lobulated radio-opaque mass filling the right frontal sinus. At operation the lesion had eroded through the dura mater. Histologic examination revealed an essentially similar picture to the previous case except that the laying down of lamellar bone in the central part of the lesion had proceeded somewhat further. He was admitted to hospital for a second time six months later with almost complete ptosis of the right eyelid and pain over the eye. An X-ray picture revealed that a good deal of the lesion still remained in the sinus and he was re-explored and the rest of the lesion removed. FIG. lesion shown in Fig. 6. There is active osteo- 8.-Photomicrograph of the central area of the clastic resorption of the non-lamellar bone in the upper right hand corner of the picture and replacement by vascular fibrous tissue in which lamellar bone trabeculae are being formed. (H. & E. xloo).
4 280 POSTGRADUATE MEDICAL JOURNAL May, 1965 Discussion FIGS. 9a & b.-photomicrograph at higher power of the right hand corner of Fig. 8 showing the osteoclastic resorption and in 9b taken by polarized light to demonstrate the nonlamellar character of the bone. (H. & E. x400). In this series the two principal complications of the tumours occurring in the nasal sinuses were erosion of the bone, particularly the supraorbital plate, and subsequent erosion of the dura mater, and secondly, blockage of the nasal duct. The first sometimes resulted in severe bleeding and difficulties in approach at the time of operation, the second in recurrent attacks of sinusitis and sometimes the formation of a mucocele. Hudolin, Riessner, Kadrnka and Knezevicm (1961) have reported a case of a large osteoma arising from the frontal sinus and extending into the anterior cranial fossa in a patient who presented clinically with severe mental derangement, headaches, incontinence, epilepsy and chronic alcoholism. She was considerably improved after the removal of the lesion. The differences in clinical presentation depending upon the site of the lesion are to be expected, but morphologically there are also marked dissimilarities. (hi The lesions which occur on the vault of the skull are generally smaller, usually about one centimetre in diameter, and are smooth and regular in outline (Fig. 4). They are formed of non-lamellar woven bone. When examined in situ they are poorly vascularized and appear very pale against the surrounding skull. The tumours occurring in relation to the sinuses (Fig. 5) are larger, irregular in outline and hyperemic. They consist largely of primitive woven bone (Fig. 6). At the edge of the lesion there is evidence of active production of woven bone which is recognised histologically by the large closely packed osteocytes and the irregular pattern of the collagen (Figs. 7a and 7b). Away from the periphery of the tumour most of the osteocytes are dead. In the central area there is active resorption of the bone with the subsequent deposition of adult lamellar bone (Figs. 8, 9a and 9b, 10). Taken as an isolated histologic field Fig. 8 has the appearances of Paget's disease in the active phase and indeed at the periphery of the
5 May, 1965 BULLOUGH: Ivory Fxostosis of the Skull 281 'jj( C5 ; t-hi wwes-i A l ' FIG. 10.-Photomicrograph at higher power of the trabeculk being laid down in the vascular fibrous tissue illustrated in Fig. 8 to show the lamellar character of the bone being formed. (H. & E. x400). hypervascular fibrous zone there is even a mosaic appearance. It is because of this appearance that the lesion has been interpreted as fibrous dysplasia, localised leontiasis ossea *and Pagetoid bone. But in fact the histologic appearances are consistent with what we know of the remodelling and replacement of woven bone by lamellar bone in other situations, for example, myositis ossificans circumscripta, or fracture callus (Collins and Curran, 1959). The hyperactive periosteum lays down a bump of woven or non-lamellar bone which acts as a calcified scaffold upon which the vascularized fibrous tissue can build the lamellar bone. The lesion therefore follows a general rule that lamellar bone is only laid down on a pre-existing calcified framework, either calcified cartilage, calcified woven bone, or foci of dystrophic calcification. In the ivory exostosis of the cranial vault the growth is probably very slow and the substitution of the woven bone by lamellar bone occurs at a steady pace. Thus these lesions show mostly a lamellar pattern with only occasional fragments of non-lamellar bone. On the other hand the lesions occurring in relation to the sinuses have a more rapid growth and depending on the speed of growth and the age of the lesion will show different proportions of the two types of bone. Because of their position the lesions of the sinuses will also tend to draw attention to themselves much sooner than the calvaral lesions. Both types of the tumour probably have their origin in stimulation of the periosteum which lays down a non-lamellar type of bone. The stimulation is probably due to a developmental abnormality, trauma or possibly infection. Maxwell (1946) has suggested that the tumours found in relation to the paranasal sinuses are the result of a chronic proliferative osteomyelitis secondary to sinus infection. In the cases reported here, however,- infection did not seem to be a predisposing factor and this was also the experience of Andrew (1956). Summary 1. Twenty-one cases of exostosis of the skull are presented. Fourteen cases were found in relation to one or other of the paranasal sinuses, most frequently the left frontal sinus, and seven were on the cranial vault. 2. Depending upon the site the clinical presentation of the tumour differs. 3. The pathological appearance of the lesions also differs, both on gross and microscopic examination. 4. Despite the superficial dissimilarities evidence is presented to support the view that the exostosis of the cranial vault and of the paranasal sinuses are basically similar. REFERENCES ANDREW, J. (1956): Osteomata of the Paranasal Sinuses, Brit. J. Surg., 43, 489. COLLINS, D. H., and CURRAN, R. C. (1959): Pathological Ossification and Osseous Metaplasia in Man in 'Modern Trends in Pathology'; Chapter 15; London: Butterworth. HUDOLIN, V., RIESSNER, D., KADRNKA, S., and KNEZEVICM (1%1): Osteoma in the Anterior Cranial Fossa, J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiat., 24, 80. MAXWELL, J. H. (1946): Chronic Proliferative Osteomyelitis of the Skull, Ann. Otol. (St. Louis), 55, 719. SMITH, A. G., and ZAVALETA, A. (1952): Osteoma, Ossifying Fibroma, and Fibrous Dysplasia of Facial and Cranial Bones, A.M.A. Arch. Path., 54, 507.
Citation Hong Kong Practitioner, 1996, v. 18 n. 12, p
 Title Radiological conference. Frontal sinus osteoma complicated by pneumocephalus Author(s) Fung, WT; Peh, WCG Citation Hong Kong Practitioner, 1996, v. 18 n. 12, p. 658-662 Issued Date 1996 URL http://hdl.handle.net/10722/44655
Title Radiological conference. Frontal sinus osteoma complicated by pneumocephalus Author(s) Fung, WT; Peh, WCG Citation Hong Kong Practitioner, 1996, v. 18 n. 12, p. 658-662 Issued Date 1996 URL http://hdl.handle.net/10722/44655
FORMATION OF BONE. Intramembranous Ossification. Bone-Lec-10-Prof.Dr.Adnan Albideri
 FORMATION OF BONE All bones are of mesodermal origin. The process of bone formation is called ossification. We have seen that formation of most bones is preceded by the formation of a cartilaginous model,
FORMATION OF BONE All bones are of mesodermal origin. The process of bone formation is called ossification. We have seen that formation of most bones is preceded by the formation of a cartilaginous model,
Chapter 6: Skeletal System: Bones and Bone Tissue
 Chapter 6: Skeletal System: Bones and Bone Tissue I. Functions A. List and describe the five major functions of the skeletal system: 1. 2. 3.. 4. 5.. II. Cartilage A. What do chondroblasts do? B. When
Chapter 6: Skeletal System: Bones and Bone Tissue I. Functions A. List and describe the five major functions of the skeletal system: 1. 2. 3.. 4. 5.. II. Cartilage A. What do chondroblasts do? B. When
BIOH111. o Cell Module o Tissue Module o Integumentary system o Skeletal system o Muscle system o Nervous system o Endocrine system
 BIOH111 o Cell Module o Tissue Module o Integumentary system o Skeletal system o Muscle system o Nervous system o Endocrine system Endeavour College of Natural Health endeavour.edu.au 1 TEXTBOOK AND REQUIRED/RECOMMENDED
BIOH111 o Cell Module o Tissue Module o Integumentary system o Skeletal system o Muscle system o Nervous system o Endocrine system Endeavour College of Natural Health endeavour.edu.au 1 TEXTBOOK AND REQUIRED/RECOMMENDED
FIBROUS CORTICAL DEFECT AND NON-OSSIFYING FIBROMA
 POSTGRAD. MED. J. (1965), 41, 672. FIBROUS CORTICAL DEFECT AND NON-OSSIFYING FIBROMA PETER G. BULLOUGH, M.B., Ch.B. JON WALIFY, F.R.C.S. Nuffield Department of Orthopaedic University of Oxford, Surgery,
POSTGRAD. MED. J. (1965), 41, 672. FIBROUS CORTICAL DEFECT AND NON-OSSIFYING FIBROMA PETER G. BULLOUGH, M.B., Ch.B. JON WALIFY, F.R.C.S. Nuffield Department of Orthopaedic University of Oxford, Surgery,
Skeletal System. Chapter 6.1 Human Anatomy & Physiology
 Skeletal System Chapter 6.1 Human Anatomy & Physiology Overview of Skeletal System Bones Joints Skeletal System Cartilage Tendons (bone to muscle) Ligaments (bone to bone) Function of the Skeletal System
Skeletal System Chapter 6.1 Human Anatomy & Physiology Overview of Skeletal System Bones Joints Skeletal System Cartilage Tendons (bone to muscle) Ligaments (bone to bone) Function of the Skeletal System
BONE TISSUE. Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Associate Professor of Anatomy and Histology
 BONE TISSUE Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Associate Professor of Anatomy and Histology BONE FUNCTION Support Protection (protect internal organs) Movement (provide leverage system for skeletal muscles, tendons, ligaments
BONE TISSUE Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Associate Professor of Anatomy and Histology BONE FUNCTION Support Protection (protect internal organs) Movement (provide leverage system for skeletal muscles, tendons, ligaments
The Skeletal System:Bone Tissue
 The Skeletal System:Bone Tissue Dynamic and ever-changing throughout life Skeleton composed of many different tissues cartilage, bone tissue, epithelium, nerve, blood forming tissue, adipose, and dense
The Skeletal System:Bone Tissue Dynamic and ever-changing throughout life Skeleton composed of many different tissues cartilage, bone tissue, epithelium, nerve, blood forming tissue, adipose, and dense
CHAPTER 6 LECTURE OUTLINE
 CHAPTER 6 LECTURE OUTLINE I. INTRODUCTION A. Bone is made up of several different tissues working together: bone, cartilage, dense connective tissue, epithelium, various blood forming tissues, adipose
CHAPTER 6 LECTURE OUTLINE I. INTRODUCTION A. Bone is made up of several different tissues working together: bone, cartilage, dense connective tissue, epithelium, various blood forming tissues, adipose
in compact bone, large vertical canals carrying blood vessels and nerves. in compact bone, large horizontal canals carrying blood vessels and nerves.
 Carl Christensen, PhD Skeletal System (Bones`) Bio. 2304 Human Anatomy 1. Identify a term for each of the following: shaft of a long bone ends of a long bone ossified remnant of the "growth plate" connective
Carl Christensen, PhD Skeletal System (Bones`) Bio. 2304 Human Anatomy 1. Identify a term for each of the following: shaft of a long bone ends of a long bone ossified remnant of the "growth plate" connective
Dr. Heba Kalbouneh. Saba Alfayoumi. Heba Kalbouneh
 11 Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Saba Alfayoumi Heba Kalbouneh 2- Bone Bone tissue is also classified into primary bone and secondary bone. In the beginning, the first bone that is deposited by the osteoblasts is
11 Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Saba Alfayoumi Heba Kalbouneh 2- Bone Bone tissue is also classified into primary bone and secondary bone. In the beginning, the first bone that is deposited by the osteoblasts is
SKELETAL TISSUES CHAPTER 7 INTRODUCTION TO THE SKELETAL SYSTEM TYPES OF BONES
 SKELETAL TISSUES CHAPTER 7 By John McGill Supplement Outlines: Beth Wyatt Original PowerPoint: Jack Bagwell INTRODUCTION TO THE SKELETAL SYSTEM STRUCTURE Organs: Bones Related Tissues: Cartilage and Ligaments
SKELETAL TISSUES CHAPTER 7 By John McGill Supplement Outlines: Beth Wyatt Original PowerPoint: Jack Bagwell INTRODUCTION TO THE SKELETAL SYSTEM STRUCTURE Organs: Bones Related Tissues: Cartilage and Ligaments
1/5 (ID:15UK )
 1/5 (ID:15UK02000531) Introduction Osteochondromas are benign bone tumors of mesenchymal and non mesenchymal types (1). Their presentation as intracranial mass is a very rare phenomenon (2). The incidence
1/5 (ID:15UK02000531) Introduction Osteochondromas are benign bone tumors of mesenchymal and non mesenchymal types (1). Their presentation as intracranial mass is a very rare phenomenon (2). The incidence
BONE LABORATORY DEMONSTRATIONS. These demonstrations are found on the bulletin boards outside the MCO Bookstore.
 BONE LABORATORY DEMONSTRATIONS These demonstrations are found on the bulletin boards outside the MCO Bookstore. COMPACT & TRABECULAR BONE - LM When viewed under the polarizing light microscope, the layering
BONE LABORATORY DEMONSTRATIONS These demonstrations are found on the bulletin boards outside the MCO Bookstore. COMPACT & TRABECULAR BONE - LM When viewed under the polarizing light microscope, the layering
Skeletal System. The skeletal System... Components
 Skeletal System The skeletal System... What are the general components of the skeletal system? What does the skeletal system do for you & how does it achieve these functions? Components The skeletal system
Skeletal System The skeletal System... What are the general components of the skeletal system? What does the skeletal system do for you & how does it achieve these functions? Components The skeletal system
Bones. The division of bones anatomically is : long, short, irregular, flat and sesamoid.
 Bones Osteocytes : Are responsible for maintenance of bones Present in lacunae, and send processes. Unable to divide. The division of bones anatomically is : long, short, irregular, flat and sesamoid.
Bones Osteocytes : Are responsible for maintenance of bones Present in lacunae, and send processes. Unable to divide. The division of bones anatomically is : long, short, irregular, flat and sesamoid.
NOTES: Skeletal System (Ch 5, part 1)
 NOTES: Skeletal System (Ch 5, part 1) Individual bones are the organs of the skeletal system. A bone contains very active tissues. BONE STRUCTURE: *Bone structure reflects its function. Parts of a long
NOTES: Skeletal System (Ch 5, part 1) Individual bones are the organs of the skeletal system. A bone contains very active tissues. BONE STRUCTURE: *Bone structure reflects its function. Parts of a long
Musculoskeletal System (Part A-1) Module 7 -Chapter 10 Overview. Functions
 Musculoskeletal System (Part A-1) Module 7 -Chapter 10 Overview Susie Turner, M.D. 1/8/13 Muscles Attachments Bones Bone types Surface features of bones Divisions of the skeletal system Joints or Articulations
Musculoskeletal System (Part A-1) Module 7 -Chapter 10 Overview Susie Turner, M.D. 1/8/13 Muscles Attachments Bones Bone types Surface features of bones Divisions of the skeletal system Joints or Articulations
Copyright 2004 Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. 2. Bone Structure. Copyright 2004 Lippincott Williams & Wilkins
 Chapter 7 The Skeleton: Bones and Joints The Skeleton Skeletal system is made up of bones and joints and supporting connective tissue. 1. Bone Functions 1. To store calcium salts 2. To protect delicate
Chapter 7 The Skeleton: Bones and Joints The Skeleton Skeletal system is made up of bones and joints and supporting connective tissue. 1. Bone Functions 1. To store calcium salts 2. To protect delicate
Functions of the Skeletal System. Chapter 6: Osseous Tissue and Bone Structure. Classification of Bones. Bone Shapes
 Chapter 6: Osseous Tissue and Bone Structure Functions of the Skeletal System 1. Support 2. Storage of minerals (calcium) 3. Storage of lipids (yellow marrow) 4. Blood cell production (red marrow) 5. Protection
Chapter 6: Osseous Tissue and Bone Structure Functions of the Skeletal System 1. Support 2. Storage of minerals (calcium) 3. Storage of lipids (yellow marrow) 4. Blood cell production (red marrow) 5. Protection
Know all the bones of the skull, lateral view and frontal view. From the worksheets, one of the earlier ones in this unit.
 Study Guide for Skeleton unit. Here are many of the questions minus the answers and minus the matching. Matching will be vocab on bone fractures and vocab on bones of the axial skeleton and their common
Study Guide for Skeleton unit. Here are many of the questions minus the answers and minus the matching. Matching will be vocab on bone fractures and vocab on bones of the axial skeleton and their common
2 PROCESSES OF BONE OSSIFICATION
 2 PROCESSES OF BONE OSSIFICATION ENDOCHONDRAL OSSIFICATION 6 STEPS 1. CARTILAGE ENLARGES, BY APPOSITIONAL GROWTH; CHONDROCYTES AT CENTER OF CARTILAGE GROW IN SIZE; MATRIX REDUCES IN SIZE & SPICULES CALCIFY;
2 PROCESSES OF BONE OSSIFICATION ENDOCHONDRAL OSSIFICATION 6 STEPS 1. CARTILAGE ENLARGES, BY APPOSITIONAL GROWTH; CHONDROCYTES AT CENTER OF CARTILAGE GROW IN SIZE; MATRIX REDUCES IN SIZE & SPICULES CALCIFY;
Chapter 6 Skeletal System
 Chapter 6 Skeletal System Functions of the skeletal system/bone 1. Support skeletal system is the internal framework of the body 2. Protection protects internal organs 3. Movement muscles & bones work
Chapter 6 Skeletal System Functions of the skeletal system/bone 1. Support skeletal system is the internal framework of the body 2. Protection protects internal organs 3. Movement muscles & bones work
OSSEOUS TISSUE & BONE STRUCTURE PART I: OVERVIEW & COMPONENTS
 OSSEOUS TISSUE & BONE STRUCTURE PART I: OVERVIEW & COMPONENTS The Skeletal System Skeletal system includes: bones of the skeleton, cartilages, ligaments, and connective tissues What are the functions of
OSSEOUS TISSUE & BONE STRUCTURE PART I: OVERVIEW & COMPONENTS The Skeletal System Skeletal system includes: bones of the skeleton, cartilages, ligaments, and connective tissues What are the functions of
BY Dr Farooq Khan Aman Ullah khan
 Lecture 01 General Anatomy & Classification of Bone BY Dr Farooq Khan Aman Ullah khan Dated: 22.012.2017 Skeleton The hard, supporting framework of the body is called the skeleton. Skeleton includes bones
Lecture 01 General Anatomy & Classification of Bone BY Dr Farooq Khan Aman Ullah khan Dated: 22.012.2017 Skeleton The hard, supporting framework of the body is called the skeleton. Skeleton includes bones
Case Report An Uncommon Osseous Frontal Sinus Tumor: Monostotic Paget s Disease
 Case Reports in Otolaryngology Volume 2013, Article ID 650428, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2013/650428 Case Report An Uncommon Osseous Frontal Sinus Tumor: Monostotic Paget s Disease Varant Labajian,
Case Reports in Otolaryngology Volume 2013, Article ID 650428, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2013/650428 Case Report An Uncommon Osseous Frontal Sinus Tumor: Monostotic Paget s Disease Varant Labajian,
Chapter 7: Head & Neck
 Chapter 7: Head & Neck Osteology I. Overview A. Skull The cranium is composed of irregularly shaped bones that are fused together at unique joints called sutures The skull provides durable protection from
Chapter 7: Head & Neck Osteology I. Overview A. Skull The cranium is composed of irregularly shaped bones that are fused together at unique joints called sutures The skull provides durable protection from
NEUROCRANIUM VISCEROCRANIUM VISCEROCRANIUM VISCEROCRANIUM
 LECTURE 4 SKULL NEUROCRANIUM VISCEROCRANIUM VISCEROCRANIUM VISCEROCRANIUM CRANIUM NEUROCRANIUM (protective case around brain) VISCEROCRANIUM (skeleton of face) NASOMAXILLARY COMPLEX MANDIBLE (DESMOCRANIUM)
LECTURE 4 SKULL NEUROCRANIUM VISCEROCRANIUM VISCEROCRANIUM VISCEROCRANIUM CRANIUM NEUROCRANIUM (protective case around brain) VISCEROCRANIUM (skeleton of face) NASOMAXILLARY COMPLEX MANDIBLE (DESMOCRANIUM)
Skeletal Tissues Dr. Ali Ebneshahidi
 Skeletal Tissues Dr. Ali Ebneshahidi Functions of Bones 1. Support and protection: Bones give shape to body structure. Bones provide support to body weight. Certain bones protect vital internal organs
Skeletal Tissues Dr. Ali Ebneshahidi Functions of Bones 1. Support and protection: Bones give shape to body structure. Bones provide support to body weight. Certain bones protect vital internal organs
Sheets 16&17. Dr. Heba Kalbouneh. Dr. Heba Kalbouneh. Dr. Heba Kalbouneh
 Sheets 16&17 Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Ossification (formation of bone) - Osteoblasts are responsible for producing the extracellular matrix of the bone and these osteoblasts
Sheets 16&17 Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Ossification (formation of bone) - Osteoblasts are responsible for producing the extracellular matrix of the bone and these osteoblasts
Fig Articular cartilage. Epiphysis. Red bone marrow Epiphyseal line. Marrow cavity. Yellow bone marrow. Periosteum. Nutrient foramen Diaphysis
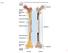 Fig. 7.1 Articular cartilage Epiphysis Red bone marrow Epiphyseal line Marrow cavity Yellow bone marrow Nutrient foramen Diaphysis Site of endosteum Compact bone Spongy bone Epiphyseal line Epiphysis Articular
Fig. 7.1 Articular cartilage Epiphysis Red bone marrow Epiphyseal line Marrow cavity Yellow bone marrow Nutrient foramen Diaphysis Site of endosteum Compact bone Spongy bone Epiphyseal line Epiphysis Articular
Anatomy & Physiology Skeletal System
 I. Functions of the Skeletal System A. the body Anatomy & Physiology Skeletal System B. of vital organs C. Provide for movement D. storage (calcium & phosphate) E. cell formation II. Bone Structure A.
I. Functions of the Skeletal System A. the body Anatomy & Physiology Skeletal System B. of vital organs C. Provide for movement D. storage (calcium & phosphate) E. cell formation II. Bone Structure A.
 www.oralradiologists.com CONE BEAM CT REPORT CASE XXXX Patient information Patient Name: - Referring Doctor: - Patient DOB: - Scan Date: [Start date] Reason for Exam: Maxillary facial pain Doctor Notes:
www.oralradiologists.com CONE BEAM CT REPORT CASE XXXX Patient information Patient Name: - Referring Doctor: - Patient DOB: - Scan Date: [Start date] Reason for Exam: Maxillary facial pain Doctor Notes:
Primary Tumors of Ribs
 Primary Tumors of Ribs Frank E. Schmidt, M.D., and Max J. Trummer, Capt, MC, USN ABSTRACT An analysis of 50 consecutive patients with primary rib tumors operated on at the U.S. Naval Hospital, San Diego,
Primary Tumors of Ribs Frank E. Schmidt, M.D., and Max J. Trummer, Capt, MC, USN ABSTRACT An analysis of 50 consecutive patients with primary rib tumors operated on at the U.S. Naval Hospital, San Diego,
Skull and Axial Skeleton
 Published on Second Faculty of Medicine, Charles University (http://www.lf2.cuni.cz ) Skull and Axial Skeleton Description of the test The examination of the skull skeleton is in oral format. It consists
Published on Second Faculty of Medicine, Charles University (http://www.lf2.cuni.cz ) Skull and Axial Skeleton Description of the test The examination of the skull skeleton is in oral format. It consists
Degenerative Lesions Of The Patellofemoral Joint: An Autopsy Study
 Degenerative Lesions Of The Patellofemoral Joint: An Autopsy Study Laura Cutignola-Kelley Norman A. Johanson Abstract: 30 knee joints were collected from individuals who were between 55 and 85 at the time
Degenerative Lesions Of The Patellofemoral Joint: An Autopsy Study Laura Cutignola-Kelley Norman A. Johanson Abstract: 30 knee joints were collected from individuals who were between 55 and 85 at the time
Ossification = Osteogenesis
 Ossification = Osteogenesis Ossification = Osteogenesis Parts of the fetal skeleton form during the first few weeks after conception By the end of the 8 th week, the skeletal pattern is formed : cartilage
Ossification = Osteogenesis Ossification = Osteogenesis Parts of the fetal skeleton form during the first few weeks after conception By the end of the 8 th week, the skeletal pattern is formed : cartilage
FRONTO-ETHMOIDAL MUCOCOELE AS A CAUSE OF UNILATERAL PROPTOSIS*t
 Brit. J. Ophthal. (1968) 52, 833 FRONTO-ETHMOIDAL MUCOCOELE AS A CAUSE OF UNILATERAL PROPTOSIS*t BY P. W. R. M. ALBERTI, H. F. MARSHALL, AND J. I. MUNRO BLACK Royal Victoria Infirmary, Newcastle upon Tyne
Brit. J. Ophthal. (1968) 52, 833 FRONTO-ETHMOIDAL MUCOCOELE AS A CAUSE OF UNILATERAL PROPTOSIS*t BY P. W. R. M. ALBERTI, H. F. MARSHALL, AND J. I. MUNRO BLACK Royal Victoria Infirmary, Newcastle upon Tyne
Histopathology: healing
 Histopathology: healing These presentations are to help you identify, and to test yourself on identifying, basic histopathological features. They do not contain the additional factual information that
Histopathology: healing These presentations are to help you identify, and to test yourself on identifying, basic histopathological features. They do not contain the additional factual information that
Biology. Dr. Khalida Ibrahim
 Biology Dr. Khalida Ibrahim BONE TISSUE Bone tissue is a specialized form of connective tissue and is the main element of the skeletal tissues. It is composed of cells and an extracellular matrix in which
Biology Dr. Khalida Ibrahim BONE TISSUE Bone tissue is a specialized form of connective tissue and is the main element of the skeletal tissues. It is composed of cells and an extracellular matrix in which
Bone Development. Two Types of OssificaDon 10/18/14. Osteogenesis ( ) bone Dssue formadon Stages. Bones and Skeletal Tissues: Part B
 Bone Development 6 Bones and Skeletal Tissues: Part B Osteogenesis ( ) bone Dssue formadon Stages Bone formadon begins in the 2nd month of development Postnatal bone growth undl early adulthood Bone remodeling
Bone Development 6 Bones and Skeletal Tissues: Part B Osteogenesis ( ) bone Dssue formadon Stages Bone formadon begins in the 2nd month of development Postnatal bone growth undl early adulthood Bone remodeling
Osteology. Dr. Carmen E. Rexach Anatomy 35 Mt San Antonio College
 Osteology Dr. Carmen E. Rexach Anatomy 35 Mt San Antonio College Functions of the Skeletal System: Support Movement Protection Hemopoiesis Electrolyte balance (Ca ++ /PO -3 4 ) Acid-base balance Storage
Osteology Dr. Carmen E. Rexach Anatomy 35 Mt San Antonio College Functions of the Skeletal System: Support Movement Protection Hemopoiesis Electrolyte balance (Ca ++ /PO -3 4 ) Acid-base balance Storage
Bio 103 Skeletal System 45
 45 Lecture Outline: SKELETAL SYSTEM [Chapters 7, 8] Introduction A. Components B. Functions 1. 2. 3. 4. Classification and Parts A. Bone Shapes 1. Long: 2. Short: 3. Flat: 4. Irregular: 5. Sesamoid: B.
45 Lecture Outline: SKELETAL SYSTEM [Chapters 7, 8] Introduction A. Components B. Functions 1. 2. 3. 4. Classification and Parts A. Bone Shapes 1. Long: 2. Short: 3. Flat: 4. Irregular: 5. Sesamoid: B.
Skeletal Tissues. Dr. Ali Ebneshahidi
 Skeletal Tissues Dr. Ali Ebneshahidi Functions of Bones 1. Support and protection : Bones give shape to body structure. Bones provide support to body weight. Certain bones protect vital internal organs
Skeletal Tissues Dr. Ali Ebneshahidi Functions of Bones 1. Support and protection : Bones give shape to body structure. Bones provide support to body weight. Certain bones protect vital internal organs
The sebaceous glands (glands of Zeis) open directly into the eyelash follicles, ciliary glands (glands of Moll) are modified sweat glands that open
 The Orbital Region The orbits are a pair of bony cavities that contain the eyeballs; their associated muscles, nerves, vessels, and fat; and most of the lacrimal apparatus upper eyelid is larger and more
The Orbital Region The orbits are a pair of bony cavities that contain the eyeballs; their associated muscles, nerves, vessels, and fat; and most of the lacrimal apparatus upper eyelid is larger and more
THIEME. Scalp and Superficial Temporal Region
 CHAPTER 2 Scalp and Superficial Temporal Region Scalp Learning Objectives At the end of the dissection of the scalp, you should be able to identify, understand and correlate the clinical aspects: Layers
CHAPTER 2 Scalp and Superficial Temporal Region Scalp Learning Objectives At the end of the dissection of the scalp, you should be able to identify, understand and correlate the clinical aspects: Layers
Figure ) The area that causes the lengthwise growth of a long bone is indicated by letter. Diff: 2 Page Ref:
 Essentials of Anatomy and Physiology, 9e (Marieb) Chapter 5 The Skeletal System Short Answer Figure 5.1 Using Figure 5.1, identify the following: 1) Spongy bone is indicated by letter. Diff: 1 Page Ref:
Essentials of Anatomy and Physiology, 9e (Marieb) Chapter 5 The Skeletal System Short Answer Figure 5.1 Using Figure 5.1, identify the following: 1) Spongy bone is indicated by letter. Diff: 1 Page Ref:
For more information about how to cite these materials visit
 Author(s): University of Michigan Medical School, Department of Cell and Developmental Biology License: Unless otherwise noted, the content of this course material is licensed under a Creative Commons
Author(s): University of Michigan Medical School, Department of Cell and Developmental Biology License: Unless otherwise noted, the content of this course material is licensed under a Creative Commons
BONE REMODELLING. Tim Arnett. University College London. Department of Anatomy and Developmental Biology
 BONE REMODELLING Tim Arnett Department of Anatomy and Developmental Biology University College London The skeleton, out of sight and often out of mind, is a formidable mass of tissue occupying about 9%
BONE REMODELLING Tim Arnett Department of Anatomy and Developmental Biology University College London The skeleton, out of sight and often out of mind, is a formidable mass of tissue occupying about 9%
Course Description 343 DDS- Clinical Oral and Maxillofacial Radiology II ( )
 King Saud University College of Dentistry Dept. of Oral Medicine & Diagnostic Sciences Division of Oral & Maxillofacial Radiology Course Description 343 DDS- Clinical Oral and Maxillofacial Radiology II
King Saud University College of Dentistry Dept. of Oral Medicine & Diagnostic Sciences Division of Oral & Maxillofacial Radiology Course Description 343 DDS- Clinical Oral and Maxillofacial Radiology II
Primary bone tumors > metastases from other sites Primary bone tumors widely range -from benign to malignant. Classified according to the normal cell
 Primary bone tumors > metastases from other sites Primary bone tumors widely range -from benign to malignant. Classified according to the normal cell counterpart and line of differentiation. Among the
Primary bone tumors > metastases from other sites Primary bone tumors widely range -from benign to malignant. Classified according to the normal cell counterpart and line of differentiation. Among the
Fracture frontal bone and its management
 From the SelectedWorks of Balasubramanian Thiagarajan March 1, 2013 Fracture frontal bone and its management Balasubramanian Thiagarajan Available at: https://works.bepress.com/drtbalu/14/ ISSN: 2250-0359
From the SelectedWorks of Balasubramanian Thiagarajan March 1, 2013 Fracture frontal bone and its management Balasubramanian Thiagarajan Available at: https://works.bepress.com/drtbalu/14/ ISSN: 2250-0359
Bony orbit Roof The orbital plate of the frontal bone Lateral wall: the zygomatic bone and the greater wing of the sphenoid
 Bony orbit Roof: Formed by: The orbital plate of the frontal bone, which separates the orbital cavity from the anterior cranial fossa and the frontal lobe of the cerebral hemisphere Lateral wall: Formed
Bony orbit Roof: Formed by: The orbital plate of the frontal bone, which separates the orbital cavity from the anterior cranial fossa and the frontal lobe of the cerebral hemisphere Lateral wall: Formed
THE JAWS AND TEETH IN PAGET'S DISEASE OF BONE
 J. clin. Path. (1955), 8, 195. THE JAWS AND TEETH IN PAGET'S DISEASE OF BONE BY R. B. LUCAS From the Department of Pathology, Royal Dental Hospital of the London School of Dental Surgery (RECEIVED FOR
J. clin. Path. (1955), 8, 195. THE JAWS AND TEETH IN PAGET'S DISEASE OF BONE BY R. B. LUCAS From the Department of Pathology, Royal Dental Hospital of the London School of Dental Surgery (RECEIVED FOR
Bursa Formation and Synovial Chondrometaplasia Associated with Osteochondromas
 Bursa Formation and Synovial Chondrometaplasia Associated with Osteochondromas ANITA M. BORGES, M. D., ANDREW G. HUVOS, M. D., AND JULIUS SMITH, M. D. Borges, Anita M., Huvos, Andrew G., and Smith, Julius:
Bursa Formation and Synovial Chondrometaplasia Associated with Osteochondromas ANITA M. BORGES, M. D., ANDREW G. HUVOS, M. D., AND JULIUS SMITH, M. D. Borges, Anita M., Huvos, Andrew G., and Smith, Julius:
What are the parts of the skeletal system? Chapter 6- Part I Bones and Skeletal Tissues. Growth of Cartilage. Bones come in many shapes
 Chapter 6- Part I Bones and Skeletal Tissues Components of the skeletal system Classification of Bone (bone shapes) Functions of bone Bone structure Microscopic structure of bone and bone cells What are
Chapter 6- Part I Bones and Skeletal Tissues Components of the skeletal system Classification of Bone (bone shapes) Functions of bone Bone structure Microscopic structure of bone and bone cells What are
PROTECTION OF THE BLOOD CLOT IN HEALING CIRCUMSCRIBED BONE DEFECTS
 PROTECTION OF THE BLOOD CLOT IN HEALING CIRCUMSCRIBED BONE DEFECTS A. H. MELCHER, LONDON, ENGLAND and C. J. DREYER. JOHANNESBURG, SOUTH AFRICA From the University of the Witwatersrand and the Councilfor
PROTECTION OF THE BLOOD CLOT IN HEALING CIRCUMSCRIBED BONE DEFECTS A. H. MELCHER, LONDON, ENGLAND and C. J. DREYER. JOHANNESBURG, SOUTH AFRICA From the University of the Witwatersrand and the Councilfor
Peggers Super Summaries Basic Sciences Bone
 Bone Overview & Turnover BONES Function o Support o Protection o Assisting movement o Storage of minerals o Production of red blood cells from marrow Types o Cancellous o Compact with Haversian systems
Bone Overview & Turnover BONES Function o Support o Protection o Assisting movement o Storage of minerals o Production of red blood cells from marrow Types o Cancellous o Compact with Haversian systems
Chapter 6 Bones and Bone Tissue Chapter Outline
 Chapter 6 Bones and Bone Tissue Chapter Outline Module 6.1: Introduction to Bones as Organs (Figures 6.1, 6.2, 6.3, 6.4) A. The skeletal system includes the bones, joints, and their associated supporting
Chapter 6 Bones and Bone Tissue Chapter Outline Module 6.1: Introduction to Bones as Organs (Figures 6.1, 6.2, 6.3, 6.4) A. The skeletal system includes the bones, joints, and their associated supporting
-the emphasis on this section is the structure and function of bone tissue and on the dynamics of its formation and remodeling throughout life.
 Biology 325 Fall 2004 BONES AND SKELETAL TISSUES Introduction -skeleton contains cartilage and bones -the emphasis on this section is the structure and function of bone tissue and on the dynamics of its
Biology 325 Fall 2004 BONES AND SKELETAL TISSUES Introduction -skeleton contains cartilage and bones -the emphasis on this section is the structure and function of bone tissue and on the dynamics of its
OpenStax-CNX module: m Bone Structure * Ildar Yakhin. Based on Bone Structure by OpenStax. Abstract
 OpenStax-CNX module: m63474 1 Bone Structure * Ildar Yakhin Based on Bone Structure by OpenStax This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License 4.0 By
OpenStax-CNX module: m63474 1 Bone Structure * Ildar Yakhin Based on Bone Structure by OpenStax This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License 4.0 By
b. Adult bones produce 2.5 million RBCs each second.
 Ch 6 Skeletal System I. Functions of the Skeletal System A. The skeletal system consists of: 1. bones, cartilage, tendons and ligaments B. Living bone is not Gr. dried up 1. It is dynamic and adaptable
Ch 6 Skeletal System I. Functions of the Skeletal System A. The skeletal system consists of: 1. bones, cartilage, tendons and ligaments B. Living bone is not Gr. dried up 1. It is dynamic and adaptable
Module 2:! Functional Musculoskeletal Anatomy A! Semester 1! !!! !!!! Hard Tissues, Distal Upper Limb & Neurovascular Supply of Upper Limb!
 Functional Musculoskeletal Anatomy A Module 2: Hard Tissues, Distal Upper Limb & Neurovascular Supply of Upper Limb Semester 1 1 18. Bone Tissue & Growth of Bones 18.1 Describe the structure of bone tissue
Functional Musculoskeletal Anatomy A Module 2: Hard Tissues, Distal Upper Limb & Neurovascular Supply of Upper Limb Semester 1 1 18. Bone Tissue & Growth of Bones 18.1 Describe the structure of bone tissue
MALIGNANT SALIVARY GLAND TUMOURS OF THE
 Brit. J. Ophthal. (1963) 47, 279. MALIGNANT SALIVARY GLAND TUMOURS OF THE NASAL SINUSES AND EXOPHTHALMOS* BY ALY MORTADA Department of Ophthalmology, Faculty of Medicine Cairo University, Egypt TUMOURS
Brit. J. Ophthal. (1963) 47, 279. MALIGNANT SALIVARY GLAND TUMOURS OF THE NASAL SINUSES AND EXOPHTHALMOS* BY ALY MORTADA Department of Ophthalmology, Faculty of Medicine Cairo University, Egypt TUMOURS
LARGE OSTEOMA OF THE FRONTAL SINUS. By THOMAS GIBSON, M.B., F.R.C.S.Ed. From the Department of Plastic Surgery, Ballochmyle Hospital.
 LARGE OSTEOMA OF THE FRONTAL SINUS A METHOD OF REMOVAL TO MINIMISE SCARRING AND PREVENT DEFORMITY By THOMAS GIBSON, M.B., F.R.C.S.Ed. From the Department of Plastic Surgery, Ballochmyle Hospital and FORBES
LARGE OSTEOMA OF THE FRONTAL SINUS A METHOD OF REMOVAL TO MINIMISE SCARRING AND PREVENT DEFORMITY By THOMAS GIBSON, M.B., F.R.C.S.Ed. From the Department of Plastic Surgery, Ballochmyle Hospital and FORBES
KEY CONCEPTS Unit 6 THE SKELETAL SYSTEM
 ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY 1 (101-805 - AB) PAUL ANDERSON 2011 KEY CONCEPTS Unit 6 THE SKELETAL SYSTEM A Overview of The Skeletal System 1. Definition: Anatomically the SKELETAL SYSTEM consists of bones, cartilages,
ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY 1 (101-805 - AB) PAUL ANDERSON 2011 KEY CONCEPTS Unit 6 THE SKELETAL SYSTEM A Overview of The Skeletal System 1. Definition: Anatomically the SKELETAL SYSTEM consists of bones, cartilages,
Course Description 343 DDS- Clinical Oral and Maxillofacial Radiology II ( )
 King Saud University College of Dentistry Dept. of Oral Medicine & Diagnostic Sciences Division of Oral & Maxillofacial Radiology Course Description 343 DDS- Clinical Oral and Maxillofacial Radiology II
King Saud University College of Dentistry Dept. of Oral Medicine & Diagnostic Sciences Division of Oral & Maxillofacial Radiology Course Description 343 DDS- Clinical Oral and Maxillofacial Radiology II
Course Description 343 DDS- Clinical Oral and Maxillofacial Radiology II ( )
 King Saud University College of Dentistry Dept. of Oral Medicine & Diagnostic Sciences Division of Oral & Maxillofacial Radiology Course Description 343 DDS- Clinical Oral and Maxillofacial Radiology II
King Saud University College of Dentistry Dept. of Oral Medicine & Diagnostic Sciences Division of Oral & Maxillofacial Radiology Course Description 343 DDS- Clinical Oral and Maxillofacial Radiology II
V. CENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTEM TRAUMA
 V. CENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTEM TRAUMA I. Concussion - Is a clinical syndrome of altered consiousness secondary to head injury - Brought by a change in the momentum of the head when a moving head suddenly arrested
V. CENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTEM TRAUMA I. Concussion - Is a clinical syndrome of altered consiousness secondary to head injury - Brought by a change in the momentum of the head when a moving head suddenly arrested
Chapter 5 The Skeletal System
 Chapter 5 The Skeletal System The Skeletal System Parts of the skeletal system Bones (skeleton) Joints Cartilages Ligaments (bone to bone)(tendon=bone to muscle) Divided into two divisions Axial skeleton:
Chapter 5 The Skeletal System The Skeletal System Parts of the skeletal system Bones (skeleton) Joints Cartilages Ligaments (bone to bone)(tendon=bone to muscle) Divided into two divisions Axial skeleton:
Inherited & developmental disorders:
 Inherited & developmental disorders: Osteogenesis Imperfecta: Excessive fragility of bone Defect in synthesis of type I collagen Inadequate formation of bone generalized osteoporosis Slender and fracture
Inherited & developmental disorders: Osteogenesis Imperfecta: Excessive fragility of bone Defect in synthesis of type I collagen Inadequate formation of bone generalized osteoporosis Slender and fracture
POST-INJURY INTERVALS 1
 POST-INJURY INTERVALS 1 Introduction 1 Contusion dating 2 Skin 2 Brain 5 Hypoxic/ischemic injury and increased intracranial pressure 18 Brain incidentals (non-injurious) 21 Sexual violence 27 INTRODUCTION
POST-INJURY INTERVALS 1 Introduction 1 Contusion dating 2 Skin 2 Brain 5 Hypoxic/ischemic injury and increased intracranial pressure 18 Brain incidentals (non-injurious) 21 Sexual violence 27 INTRODUCTION
OPERATIVE CORRECTION BY OSTEOTOMY OF RECESSED MALAR MAXILLARY COMPOUND IN A CASE OF OXYCEPHALY
 OPERATIVE CORRECTION BY OSTEOTOMY OF RECESSED MALAR MAXILLARY COMPOUND IN A CASE OF OXYCEPHALY By Sir HAROLD GILLIES, C.B.E., F.R.C.S., and STEWART H. HARRISON, F.R.C.S., L.D.S., R.C.S. From the Plastic
OPERATIVE CORRECTION BY OSTEOTOMY OF RECESSED MALAR MAXILLARY COMPOUND IN A CASE OF OXYCEPHALY By Sir HAROLD GILLIES, C.B.E., F.R.C.S., and STEWART H. HARRISON, F.R.C.S., L.D.S., R.C.S. From the Plastic
CASE REPORTS. Inflammatory Polyp of the Bronchus. V. K. Saini, M.S., and P. L. Wahi, M.D.
 CASE REPORTS V. K. Saini, M.S., and P. L. Wahi, M.D. I n 1932 Jackson and Jackson [l] first reported a number of clinical cases under the title Benign Tumors of the Trachea and Bronchi with Especial Reference
CASE REPORTS V. K. Saini, M.S., and P. L. Wahi, M.D. I n 1932 Jackson and Jackson [l] first reported a number of clinical cases under the title Benign Tumors of the Trachea and Bronchi with Especial Reference
Bone/Osteoid Producing Lesions
 Chapter 2 Bone/Osteoid Producing Lesions Introduction There are many lesions that are associated with reactive new bone formation; this chapter predominantly covers those in which deposition of osteoid/bone
Chapter 2 Bone/Osteoid Producing Lesions Introduction There are many lesions that are associated with reactive new bone formation; this chapter predominantly covers those in which deposition of osteoid/bone
Neurosurgical Techniques
 Neurosurgical Techniques EBEN ALEXANDER, JR., M.D., EDITOR Supratentorial Skull Flaps GuY L. ODOM, M.D., AND BARNES WOODHALL,!V[.D. Department of Surgery, Division of Neurosurgery, Duke University Medical
Neurosurgical Techniques EBEN ALEXANDER, JR., M.D., EDITOR Supratentorial Skull Flaps GuY L. ODOM, M.D., AND BARNES WOODHALL,!V[.D. Department of Surgery, Division of Neurosurgery, Duke University Medical
Epidemiology 3002). Epidemiology and Pathophysiology
 Epidemiology Maxillofacial trauma or injuries are commonly encountered in the practice of emergency medicine and are presenting one of the most challenging problems to the attending surgeons or physicians
Epidemiology Maxillofacial trauma or injuries are commonly encountered in the practice of emergency medicine and are presenting one of the most challenging problems to the attending surgeons or physicians
Bone Tissue- Chapter 5 5-1
 Bone Tissue- Chapter 5 5-1 Bone Functions Support Protection Assistance in movement Mineral storage and release Blood cell production Triglyceride storage 5-2 Bone Chemistry Water (25%) Organic Constituent
Bone Tissue- Chapter 5 5-1 Bone Functions Support Protection Assistance in movement Mineral storage and release Blood cell production Triglyceride storage 5-2 Bone Chemistry Water (25%) Organic Constituent
The Skeletal System Vertebral column Sacrum. Osseous tissue For the body and soft organs. Magnesium, sodium, fluoride Levers for muscle action
 10/1/2016 Cranium Facial s Skull Clavicle Scapula Sternum Rib Humerus Vertebra Radius Ulna Carpals Thoracic cage (ribs and sternum) The Skeletal System Vertebral column Sacrum Phalanges Metacarpals Femur
10/1/2016 Cranium Facial s Skull Clavicle Scapula Sternum Rib Humerus Vertebra Radius Ulna Carpals Thoracic cage (ribs and sternum) The Skeletal System Vertebral column Sacrum Phalanges Metacarpals Femur
Copy and Return to Teacher. The Skeletal System
 Copy and Return to Teacher The Skeletal System The Skeletal System Parts of the skeletal system o Bones (skeleton) o Joints o Cartilages o Ligaments Divided into two divisions o Axial skeleton o Appendicular
Copy and Return to Teacher The Skeletal System The Skeletal System Parts of the skeletal system o Bones (skeleton) o Joints o Cartilages o Ligaments Divided into two divisions o Axial skeleton o Appendicular
Department of Plastic Surgery, Royal Melbourne Hospital, Australia
 ARTICULAR CARTILAGE LOSS IN LONG-STANDING IMMOBILISATION OF INTERPHALANGEAL JOINTS By P. L. FIELD, F.R.C.S., and J. T. HUESTON,/Vi.S., F.R.C.S., F.R.A.C.S. Department of Plastic Surgery, Royal Melbourne
ARTICULAR CARTILAGE LOSS IN LONG-STANDING IMMOBILISATION OF INTERPHALANGEAL JOINTS By P. L. FIELD, F.R.C.S., and J. T. HUESTON,/Vi.S., F.R.C.S., F.R.A.C.S. Department of Plastic Surgery, Royal Melbourne
Ethan M. Braunstein, M.D. 1, Steven A. Goldstein, Ph.D. 2, Janet Ku, M.S. 2, Patrick Smith, M.D. 2, and Larry S. Matthews, M.D. 2
 Skeletal Radiol (1986) 15:27-31 Skeletal Radiology Computed tomography and plain radiography in experimental fracture healing Ethan M. Braunstein, M.D. 1, Steven A. Goldstein, Ph.D. 2, Janet Ku, M.S. 2,
Skeletal Radiol (1986) 15:27-31 Skeletal Radiology Computed tomography and plain radiography in experimental fracture healing Ethan M. Braunstein, M.D. 1, Steven A. Goldstein, Ph.D. 2, Janet Ku, M.S. 2,
Rama Nada. - Mousa Al-Abbadi. 1 P a g e
 - 1 - Rama Nada - - Mousa Al-Abbadi 1 P a g e Bones, Joints and Soft tissue tumors Before we start: the first 8 minutes was recalling to Dr.Mousa s duties, go over them in the slides. Wherever you see
- 1 - Rama Nada - - Mousa Al-Abbadi 1 P a g e Bones, Joints and Soft tissue tumors Before we start: the first 8 minutes was recalling to Dr.Mousa s duties, go over them in the slides. Wherever you see
Chapter 5. The Skeletal System. Osseous Tissue and Skeletal Structure. Lecture Presentation by Steven Bassett Southeast Community College
 Chapter 5 The Skeletal System Osseous Tissue and Skeletal Structure Lecture Presentation by Steven Bassett Southeast Community College Introduction The skeletal system is made of: Skeletal bones Cartilage
Chapter 5 The Skeletal System Osseous Tissue and Skeletal Structure Lecture Presentation by Steven Bassett Southeast Community College Introduction The skeletal system is made of: Skeletal bones Cartilage
SARCOMA FOLLOWING X-RAY THERAPY FOR GRAVES' DISEASE
 SARCOMA FOLLOWING X-RAY THERAPY FOR GRAVES' DISEASE By P. H. JAYES, M.B., B.S., F.R.C.S., and R. H. DALE, M.B., B.Chir., F.R.C.S.Ed. From the Plastic Surgery and Jaw Injuries Centre, East Grinstead IT
SARCOMA FOLLOWING X-RAY THERAPY FOR GRAVES' DISEASE By P. H. JAYES, M.B., B.S., F.R.C.S., and R. H. DALE, M.B., B.Chir., F.R.C.S.Ed. From the Plastic Surgery and Jaw Injuries Centre, East Grinstead IT
BIOL 2457 CHAPTER 6 SI 1. irregular ectopic: sutural (Wormian) The is between the shaft and end. It contains cartilage that is
 BIOL 2457 CHAPTER 6 SI 1 1. List 5 functions of bones: 2. Classify bones according to shape: give descriptions and examples: long short flat irregular ectopic: sutural (Wormian) ectopic: sesamoid 3. The
BIOL 2457 CHAPTER 6 SI 1 1. List 5 functions of bones: 2. Classify bones according to shape: give descriptions and examples: long short flat irregular ectopic: sutural (Wormian) ectopic: sesamoid 3. The
Osseous Tissue and Bone Structure
 C h a p t e r 6 Osseous Tissue and Bone Structure PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Jason LaPres Lone Star College - North Harris Copyright 2009 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Pearson Benjamin
C h a p t e r 6 Osseous Tissue and Bone Structure PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Jason LaPres Lone Star College - North Harris Copyright 2009 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Pearson Benjamin
SKELETAL SYSTEM I NOTE: LAB ASSIGNMENTS for this topic will run over 3 Weeks. A SEPARATE WORKSHEET WILL BE PROVIDED.
 BIO 211; Anatomy and Physiology I REFERENCE: CHAPTER 07 1 Dr. Lawrence Altman Naugatuck Valley Community College LECTURE TOPICS OUTLINE SKELETAL SYSTEM I NOTE: LAB ASSIGNMENTS for this topic will run over
BIO 211; Anatomy and Physiology I REFERENCE: CHAPTER 07 1 Dr. Lawrence Altman Naugatuck Valley Community College LECTURE TOPICS OUTLINE SKELETAL SYSTEM I NOTE: LAB ASSIGNMENTS for this topic will run over
Bone. Development. Tim Arnett. University College London. Department of Anatomy and Developmental Biology
 Bone Development Tim Arnett Department of Anatomy and Developmental Biology University College London Bone development Outline Bone composition matrix + mineral Bone formation - intramembranous & endochondral
Bone Development Tim Arnett Department of Anatomy and Developmental Biology University College London Bone development Outline Bone composition matrix + mineral Bone formation - intramembranous & endochondral
Superior View of the Skull (Norma Verticalis) Anteriorly the frontal bone articulates with the two parietal bones AT THE CORONAL SUTURE
 Superior View of the Skull (Norma Verticalis) Anteriorly the frontal bone articulates with the two parietal bones AT THE CORONAL SUTURE 1 The two parietal bones articulate in the midline AT THE SAGITTAL
Superior View of the Skull (Norma Verticalis) Anteriorly the frontal bone articulates with the two parietal bones AT THE CORONAL SUTURE 1 The two parietal bones articulate in the midline AT THE SAGITTAL
Mucocele of paranasal sinuses
 From the SelectedWorks of Balasubramanian Thiagarajan March 7, 2012 Mucocele of paranasal sinuses Balasubramanian Thiagarajan Available at: https://works.bepress.com/drtbalu/57/ Mucoceles of paranasal
From the SelectedWorks of Balasubramanian Thiagarajan March 7, 2012 Mucocele of paranasal sinuses Balasubramanian Thiagarajan Available at: https://works.bepress.com/drtbalu/57/ Mucoceles of paranasal
Cranium Facial bones. Sternum Rib
 Figure 7.1 The human skeleton. Skull Thoracic cage (ribs and sternum) Cranium Facial bones Sternum Rib Bones of pectoral girdle Vertebral column Sacrum Vertebra Bones of pelvic girdle (a) Anterior view
Figure 7.1 The human skeleton. Skull Thoracic cage (ribs and sternum) Cranium Facial bones Sternum Rib Bones of pectoral girdle Vertebral column Sacrum Vertebra Bones of pelvic girdle (a) Anterior view
Experience with malignant tumours of the maxillary sinus in the Department of Otolaryngology Universiti Kebangsaan Malaysia, Kuala Lumpur
 Med. J. Malaysia Vol. 44 No. 1 March 1989 Experience with malignant tumours of the maxillary sinus in the Department of Otolaryngology Universiti Kebangsaan Malaysia, Kuala Lumpur S. Lokman, MD (UKMalaysia)
Med. J. Malaysia Vol. 44 No. 1 March 1989 Experience with malignant tumours of the maxillary sinus in the Department of Otolaryngology Universiti Kebangsaan Malaysia, Kuala Lumpur S. Lokman, MD (UKMalaysia)
Chapter 5 The Skeletal System:Bone Tissue. Functions of Bone. Bones
 Chapter 5 The Skeletal System:Bone Tissue Dynamic and ever-changing throughout life Skeleton composed of many different tissues cartilage, bone tissue, epithelium, nerve, blood forming tissue, adipose,
Chapter 5 The Skeletal System:Bone Tissue Dynamic and ever-changing throughout life Skeleton composed of many different tissues cartilage, bone tissue, epithelium, nerve, blood forming tissue, adipose,
Malignant growth Maxilla management an analysis
 ISSN: 2250-0359 Volume 3 Issue 2 2013 Malignant growth Maxilla management an analysis *Balasubramanian Thiagarajan *Geetha Ramamoorthy *Stanley Medical College Abstract: Malignant tumors involving maxilla
ISSN: 2250-0359 Volume 3 Issue 2 2013 Malignant growth Maxilla management an analysis *Balasubramanian Thiagarajan *Geetha Ramamoorthy *Stanley Medical College Abstract: Malignant tumors involving maxilla
Cartilage & bone. Red: important. Black: in male female slides. Gray: notes extra. Editing File
 Cartilage & bone Red: important. Black: in male female slides. Gray: notes extra. Editing File OBJECTIVES describe the microscopic structure, distribution and growth of the different types of Cartilage
Cartilage & bone Red: important. Black: in male female slides. Gray: notes extra. Editing File OBJECTIVES describe the microscopic structure, distribution and growth of the different types of Cartilage
Plastic Surgeon, Middlesbrough General Hospital, Stockton Children's Hospital, Newcastle Regional Hospital Board
 THE NASAL TIP IN BILATERAL HARE LIP By J. POTTER, F.R.C.S.Ed. Plastic Surgeon, Middlesbrough General Hospital, Stockton Children's Hospital, Newcastle Regional Hospital Board IN the problem of the bilateral
THE NASAL TIP IN BILATERAL HARE LIP By J. POTTER, F.R.C.S.Ed. Plastic Surgeon, Middlesbrough General Hospital, Stockton Children's Hospital, Newcastle Regional Hospital Board IN the problem of the bilateral
From the Department of Orthopaedics and Traumatology, University of Helsinki
 AN OPERATION FOR PARTIAL CLOSURE OF AN EPIPHYSIAL PLATE IN CHILDREN, AND ITS EXPERIMENTAL BASIS A. LANGENSKI#{246}LD, HELSINKI, FINLAND From the Department of Orthopaedics and Traumatology, University
AN OPERATION FOR PARTIAL CLOSURE OF AN EPIPHYSIAL PLATE IN CHILDREN, AND ITS EXPERIMENTAL BASIS A. LANGENSKI#{246}LD, HELSINKI, FINLAND From the Department of Orthopaedics and Traumatology, University
