Intracranial Dural Arteriovenous Fistulas: A Brief Review on Classification and General Features
|
|
|
- Felix Owens
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Review rticle Intracranial ural rteriovenous istulas: rief Review on lassification and General eatures ltay SNR Talat KIRIfi epartment of Neurosurgery, School of Medicine, Istanbul University, stanbul, Turkey STRT Intracranial dural arteriovenous malformations are unique and rare pathological entities. They may present with a wide spectrum of clinical pictures and the natural disease course is also variable. The main determinant in prognosis and indication for and response to treatment is the venous architecture of the fistula. In this paper, two widely accepted classifications of dural arteriovenous fistulas, namely, a classification according to venous drainage and another one according to anatomic location will be discussed with relevant clinical and therapeutic implications. KY WORS: ural arteriovenous fistula, classification, endovascular treatment, surgery INTROUTION ural arteriovenous fistulas are abnormal arteriovenous connections within the dura and are usually located within the walls of a dural sinus or an adjacent cortical vein (3). In a sense, they may represent an arteriovenous malformation with the nidus inside the dura mater. The terminology concerning this malformation has been somewhat controversial. Many authors have preferred the term 'dural arteriovenous malformation' (VM) because it suggests a congenital etiology and also covers the frequently complex angioarchitecture involving many arterial feeders. Others have used 'dural arteriovenous fistula' (V) implying an acquired nature for which there is cumulating evidence that will be discussed later in this text (5). In this paper, the term V will be used. V comprise 10-15% of all intracranial arteriovenous malformations. There is a female preponderance with symptoms usually developing during middle to late adulthood (11). The initiating events which lead to development of a V are not clear, but there are many papers reporting association with trauma, infection, recent surgery and dural sinus thrombosis (6,9,14,20). On the other hand, in many patients with this disorder, none of the stated causative factors can be probed from patient history (14). The causative factors listed above are quite common but Vs are rare lesions. Lasjaunias and erenstein have suggested 'an underlying dural weakness' facilitating dural shunts in some individuals, when other people faced with the same insults do not develop V (3). Received : ccepted : orrespondence ddress ltay SNR stanbul Üniversitesi T p akültesi Nöroflirürji ölümü Sehremini 34390, Istanbul, TURKY Phone : ax : mail : altayser@superonline.com 57
2 There are several theories attempting to explain the underlying mechanism leading to development of a V. Propagation of existing micro arteriovenous fistulas in the dura and formation of new ones under the impact of an angiogenetic/fibroblastic factor are among the suggested pathways. lso, venous hypertension that develops upstream a venous occlusion may account for the opening or enhancement of arteriovenous shunts (3). Natural disease course in Vs is also variable with some cases regressing spontaneously, as in some angiographically documented cases of carotid cavernous fistulas. Other Vs may progress into aggressive lesions leading to severe clinical pictures with recruitment of arterial supply from additional vessels and hypertrophy of existing ones (19). s the angioarchitecture of Vs were documented more precisely and many cases were followed up over time, it was clearly stated by many authors that Vs were 'venous' lesions, meaning that natural history, symptomatology as well as prognosis of the disease were dependant on venous features (5,8). There have been many attempts to classify Vs, and presently two main classification schemes have gained acceptance: classification according to venous drainage pattern which has many important implications for prognosis and another one classifying Vs according to location that is more practical and used more frequently in daily practice. oth classification systems will be acknowledged in this paper. Symptoms and signs of Vs are reportedly headache, pulsatile tinnitus and/or bruit while some cases with an aggressive clinical course may present with signs of raised intracranial pressure due to intracranial hemorrhage or infarction (2,17). fter a thorough neurological evaluation, these patients usually undergo a neuroradiological examination, which is a head T or MRI with or without angiographical sequences. Venous thrombosis, parenchymal changes or the presence of enlarged vascular structures near cortical brain surfaces may suggest the diagnosis of V; however the mainstay of diagnosis is catheter angiography. Vs can be supplied by any and all meningeal branches of external and internal carotid and vertebral arteries and rarely by cortical vessels. Various angiographical findings will be discussed in the following sections of the text. Vs can vary from very simple to extremely complex vascular lesions and the natural history of different subtypes of this disease can therefore be very divergent. Therapeutic approaches are also manifold; conservative follow up, carotid-jugular compression, arterial or venous embolization, surgery and combinations. complete and correct understanding of arterial supply, nidus architecture/location and venous drainage pattern of a V is very important in therapeutic decisionmaking (11) lassification according to venous drainage pattern s stated earlier in this text, venous drainage pattern of Vs is very important. s the high arteriovenous shunting in Vs continues, there is progressive pathology on the venous side. high flow vascular malformation draining into intracranial veins and dural sinuses, especially in the presence of additional disturbing factors such as venous occlusion and reflux into cortical veins, results in intracranial venous hypertension which is a crucial factor predisposing to an aggressive disease course. The following classification scheme originally forwarded by jinjian and Merland (later modified by ognard) is established on venous drainage (Table I) (10,13). Table I: lassification of V according to venous drainage TYP Type I Type II Type III Type IV Type V VNOUS RING rainage into a dural sinus, with normal antegrade flow rainage into a dural sinus, with reflux into II a: (other) sinuses II b: cortical veins II a+b: sinuses + cortical veins rainage into cortical veins rainage into cortical veins with cortical ectasia rainage into spinal perimedullary veins Type I V Type I Vs are clinically benign lesions. They drain antegradely into a dural sinus with normal flow and architecture (igure 1 -). Intracranial 58
3 Type II V Type II Vs also drain into sinuses like type I, but reflux into other sinuses and/or cortical veins complicate the disease (igure 2 -). The reason for reflux may be a stenosis or occlusion in the venous system downstream the venous drainage of the fistula or extremely high flow in the shunt exceeding the drainage ability of the local veins. The intracranial circulation is affected in varying degrees depending on the severity of the reflux and the symptoms are therefore due to raised intracranial pressure. Headache, decreased visual acuity and diplopia may ensue. igure 1 -: In type I V, the fistula drains into the dural sinus with normal antegrade flow as depicted in the graphics (-). In a middle aged female patient with right-sided pulsatile tinnitus, there is a V supplied by right occipital artery, draining into the right sigmoid sinus (-). The antegrade flow in the sinus is undisturbed as shown in the selective injection during transarterial embolization (). Postembolization angiogram shows no residual fistula flow and the symptom has disappeared(). venous flow is also undisturbed. The symptoms may be tinnitus, retroauricular pain and ocular signs and are usually due to increased flow in the sinus. Since type I Vs are clinically and angiographically benign lesions, decision to treat must be made individually and therapy must be risk-free. The intention of treatment may be control of the functional symptoms when they are disturbing for the patient. onservative follow-up, carotid jugular compression to decrease flow and induce thrombosis of the fistula or transarterial embolization of the arterial feeders with the same purpose are the options for treatment (11). igure 2 -: In type II V, there is reflux into the other dural sinuses or cortical veins due to occlusion downstream of the fistula site as shown in the picture (-). In a 47-year-old female admitted with headache, S has shown a multicentric V (located in both the superior sagittal and both transverse-sigmoid sinus junctions). ngiographically there was retrograde flow in both dural sinuses and cortical veins, compatible with type II a+b fistula (-). (the red arrow in d depicts retrograde flow in the cortical vein) 59
4 In type II a V, treatment must be performed especially if there are signs of raised intracranial pressure. The goal of therapy is flow reduction and downgrading of the fistula. Transarterial embolization is the treatment of choice. It is most frequently performed by selective catheterization of arterial feeders of the fistula and embolization with particle or liquid agents. In type II b and a+b Vs, reflux into cortical veins is more likely to cause an increase in intracranial pressure. In this type of fistula there is a 10% risk of raised IP and 29% risk of neurological sequel. onsequently, treatment must be performed and result in a definite cure of the lesion. The lesion may be cured by endovascular occlusion of the defective segment of the dural sinus responsible for the arteriovenous shunts, or surgery may be performed after transarterial devascularization of the fistula (5,11) Type III and IV V These types of V are located more frequently in the anterior cranial fossa and the tentorium. The presence of varicosities on the draining cortical veins increases the risk of bleeding and neurological deficit from 40 to 65% and from 76 to 96%, respectively. Location of these Vs and high percentage of bleeding and neurological deficit calls for prompt and definitive treatment. (igure 3 - and igure 4 -). The patient in igure 8 with a tentorial V is a typical example of Type III and IV V. There is direct drainage into the pial veins (with varicosities). The usually complex angiographical features of these lesions usually complicate both endovascular and surgical treatment. ombination of transarterial embolization and surgery or transarterial and transvenous embolization may be performed. omplete cure of the fistula should be aimed since inadequate or incomplete treatment may cause (re)bleeding (3, 5, 11). igure 3 -: Type III V drains directly into the cortical veins as depicted in the graphics. igure 4 -: In type IV V there are varicosities in the cortical veins draining the fistula. Type V V These Vs drain into spinal veins. The underlying physiopathological mechanisms of the disease may generally be attributed to spinal venous hypertension. linical symptoms are due to the resultant myelopathy (igure 5 -G). This type of fistula has the same risk of neurological deficit and haemorrhage as in types III and IV Vs and must be treated in the same fashion (7,21). In a patient with progressive myelopathy, type V V must be included in the differential diagnosis, enlargement and edema of the involved segment of the spinal cord and congested perimedullary vessels in crosssectional imaging should be considered suggestive while catheter angiography must be performed for definitive diagnosis. lassification according to location When classified according to location, transversesigmoid sinus Vs make up the majority of Vs. avernous sinus Vs (10-16%), tentorial Vs (8-12%), superior sagittal sinus Vs (8%) and anterior cranial fossa Vs (5%) and rare locations (torcula, foramen magnum, deep venous fistula) are other types of Vs (11). Transverse - sigmoid sinus V V located in the transverse-sigmoid system make up the majority of Vs. There are usually multiple arterial feeders originating from external carotid artery branches or dural branches of the internal carotid artery (I), vertebral artery (V) and posterior cerebral artery (P) (igure 6 -). Venous drainage may be in as in any type discussed in the above classification of Vs. Vs located in the foramen magnum are considered a specific subtype of this group; however, they are much rarer than their counterparts located in the transverse- 60
5 igure 6 -: 50-year-old man was admitted with signs of raised intracranial pressure: igures (-) show occlusion of both sigmoid and disturbed flow in the right transverse sinuses. There is prominent cortical reflux together with a V located in both transverse-sigmoid areas. Transarterial embolization failed to cure the fistula and transvenous approach was unsuccessful. The fistulous sinuses were embolized during surgery with excellent angiographical (-) and clinical cure. t one-year followup, the patient was in good clinical condition; control S could not be performed since the patient refused any further invasive test. igure 5 -: 55-year-old male presented with ataxia and disability in walking. ervical MR revealed edema in the brain stem as well as enlarged perimedullary vessels (-). S with the presumptive diagnosis of spinal vascular malformation revealed a type V V, supplied by the occipital artery and meningeal branches of the vertebral artery and draining into spinal perimedullary veins (-). fter transarterial embolization there was no residual fistula and the symptoms resolved (-G). (the red arrow shows fistula location and the blue arrow points to perimedullary venous drainage).() sigmoid area. rain MR studies must be carefully examined for parenchymal edema suggesting venous hypertension, hydrocephalus, or intracerebral or subarachnoid hemorrhage. hoice of treatment depends on the type of venous drainage (16). avernous sinus V avernous sinus Vs are usually encountered in females and association with pregnancy, sphenoiditis and trauma have been reported. The G symptoms depend on the type of venous drainage and are usually ocular (proptosis, chemosis, diplopia). Loss of visual acuity is also common and variable in degree. ccording to the classification by arrow and colleagues, cavernous sinus fistula type are direct and high flow arteriovenous fistula usually secondary to trauma, whereas type,, are dural Vs supplied by meningeal branches of and I (igure 7 -) (4,18). Venous drainage may be 'anterior', involving the ophthalmic veins where the symptoms are usually ocular, or it may be 'posterior' via the petrosal veins, where the risk of hemorrhage and neurological deficit is higher. The more frequent ocular sign and symptoms are generally reversible if not longstanding. Suggested methods of treatment are compression, transarterial embolization, transvenous embolization and surgery. Tentorium cerebelli V V located at the tentorium cerebelli are usually type III and IV fistulas and therefore almost always present with haemorrhage, neurological deficit, seizure or myelopathy. Treatment must definitely be performed and result in total cure. The main feeders are meningohypophyseal and inferolateral trunks of I. There is perimesencephalic venous drainage with venous ectasia. The arterial feeders from I may not be 61
6 igure 7 : arrow classification of carotid cavernous fistula. In type, there is laceration in the wall of I due to trauma or aneurysmal rupture. Type, and fistulas are dural type. igure 7 -: In a middle-aged female with exophthalmus, S has shown a type fistula with supply from both () and I (). Venous drainage is both anterior into ophthalmic veins and posterior into the occipital cortical veins. injection after embolization of the feeders (). (the red arrow: ophthalmic vein, blue arrow: cortical veins) embolized safely. Therefore, endovascular treatment has limited use in this type of malformation. In the authors' opinion, the best treatment is surgical clipping of the draining vein and resection of the involved dura segment (12). In very complicated cases, radiosurgery combined with serial embolizations have been suggested as useful (igure 8 -G). G igure 8 -G: In this patient with tentorial V, the fistula site is marked by the perimesencephalic venous pouch (red arrow). fter transarterial embolization of the feeders, a venous approach has been attempted but the draining vein has ruptured with SH (blue arrow). fter surgical clipping of the draining vein, there is complete obliteration of the V(G). Superior sagittal sinus V This type of V usually presents with intracranial bleeding or dementia (12). Since the lesion is located in the midline, there are bilateral feeders from dural branches of I and. The fistula site is frequently in the middle or posterior third of the superior sagittal sinus ndovascular 62
7 treatment via the arterial route is usually successful in this fistula nterior cranial fossa V This type of fistula is usually a type III or IV V. They are supplied by ethmoidal arteries and drain into the frontal cortical or olfactory vein. The frequency of venous dilatation is predisposes to intracranial bleeding. The aim of treatment is total cure and, surgical clipping of the draining vein can safely succeed (1,15). ONLUSION The scope of this review does not allow an extensive discussion of the Vs. Vs are intriguing lesions that may present with a varying clinical course. Natural disease course of Vs located in the anterior cranial fossa, superior sagittal sinus and tentorium cerebelli may be aggressive with a high risk of intracranial haemorrhage. No matter what the natural disease course may be, the following issues are crucial for optimal clinical management of Vs: The key feature in both diagnostic and therapeutic decision-making is the venous drainage pattern of the lesion. Indication for treatment as well as choice of therapeutic alternative must be individualized for each patient as the existing classification schemes are not perfect and subject to change over time. The risks and benefits of therapy must be treatment carefully in each patient and considered together with the possible natural course or present complications of the disease as dictated by the venous features previously emphasized in this text. RRNS 1. brahams JM, agley LJ, lamm S, Hurst RW, Sinson GP: lternative management considerations for ethmoidal dural arteriovenous fistulas. Surg Neurol. 58; 410-6, wad I, Little J, krawi W, hl J: Intracranial dural arteriovenous malformations: factors predisposing to an aggressive neurological course. J Neurosurg 72; , wad I, arrow L: ural arteriovenous malformations, first edition, Illinois, US: merican ssociation of Neurological Surgeons Publications, arrow L, Spector RH, raun I, et al: lassification and treatment of spontaneous carotid-cavernous fistulas. J Neurosurg 62; , erenstein, Lasjaunias P, ter rugge K.G: Surgical Neuroangiography, second edition, erlin Heidelberg: Springer, 2004; rainin M, Samec P: Venous hemodynamics of arteriovenous fistulas in the posterior cranial fossa. Neuroradiology 25; , runereau L, Gobin YP, Meder J, et al: Intracranial dural arteriovenous fistulas with spinal venous drainage: Relationship between clinical presentation and angiographic findings. JNR 17; , yrne JV: erebrovascular malformations. ur Radiol. 15; , haudhary M, Sachdev V, ho S: ural arteriovenous malformations of the major venous sinuses: an acquired lesion. JNR 3; 13-19, ognard, Gobin YP, Pierot L, et al: erebral dural arteriovenous fistulas: clinical and angiographic correlation with a revised classification of venous drainage. Radiology 194; , ognard, Houdart, asasco, Jhaveri HS, hapot R, Merland JJ: ndovascular therapy and long term results for intracranial dural arteriovenous fistulae. onnors JJ, Wojak J (ed.s), Interventional Neuroradiology, first edition, Philadelphia, US: Saunders ompany, 1999: avies M, Ter rugge KG, Willinsky R, Wallace M: The natural history and management of intracranial dural arteriovenous fistulae. Part II: ggressive lesions. Interventional Neuroradiol 3: , jinjian R, Merland JJ, Theron J: Superselective arteriography of the external carotid artery. New York: Springer Verlag, 1978; Graeh, olman : Radiological and pathological aspects of dural arteriovenous fistulas. J Neurosurg 64; , Im SH, Oh W, Han H: Surgical management of an unruptured dural arteriovenous fistula of the anterior cranial fossa: natural history for 7 years. Surg Neurol. 62; 72-5, Lasjaunias P, urrows P, Planet : evelopmental venous anomalies: the so called venous angiomas. Neurosurg Rev 9; , Lasjaunias P, hiu M, terrugge KT: Neurological manifestations of intracranial dural sinus arteriovenous malformations. J Neurosurg 64; , Peeters LM; Kroger R: ural and direct cavernous sinus fistulas. JR 132; , Steiger HJ, Hanggi, Schmid-lsaesser R: ranial and spinal dural arteriovenous malformations and fistulas: an update. cta Neurochir Suppl. 94; , Watanabe, Takahara Y, Ibuchi Y, Miukami K: Two cases of dural arteriovenous malformation occurring after intracranial surgery. Neuroradiology 26; , Woo HH, Masaryk TJ, Rasmussen P: Treatment of dural arteriovenous malformations and fistulae. Neurosurg lin N m. 16; ,
A.J. Hauer Intracranial dural arteriovenous fistulae
 A.J. Hauer 27-06-2018 Intracranial dural arteriovenous fistulae Dural arteriovenous fistulae (davfs) epidemiology Pathological anastomoses (within the dural leaflets) between meningeal arteries and dural
A.J. Hauer 27-06-2018 Intracranial dural arteriovenous fistulae Dural arteriovenous fistulae (davfs) epidemiology Pathological anastomoses (within the dural leaflets) between meningeal arteries and dural
Transverse-Sigmoid Sinus Dural Arteriovenous Malformations
 Transverse-Sigmoid Sinus Dural Arteriovenous Malformations Kenan I. Amautovic, M.D., and Ali F. Krisht, M.D. '-...--- Learning Objectives: After reading this article, the participant should: 1. Have an
Transverse-Sigmoid Sinus Dural Arteriovenous Malformations Kenan I. Amautovic, M.D., and Ali F. Krisht, M.D. '-...--- Learning Objectives: After reading this article, the participant should: 1. Have an
Intracranial dural arteriovenous fistulas (DAVFs) with retrograde
 ORIGINAL RESEARCH W.J. van Rooij M. Sluzewski G.N. Beute Dural Arteriovenous Fistulas with Cortical Venous Drainage: Incidence, Clinical Presentation, and Treatment BACKGROUND AND PURPOSE: Our purpose
ORIGINAL RESEARCH W.J. van Rooij M. Sluzewski G.N. Beute Dural Arteriovenous Fistulas with Cortical Venous Drainage: Incidence, Clinical Presentation, and Treatment BACKGROUND AND PURPOSE: Our purpose
Dural Arteriovenous Malformations and Fistulae (DAVM S DAVF S)
 Jorge Guedes Campos NEUROIMAGING DEPARTMENT HOSPITAL SANTA MARIA UNIVERSITY OF LISBON PORTUGAL DEFINITION region of arteriovenous shunting confined to a leaflet of packymeninges often adjacent to a major
Jorge Guedes Campos NEUROIMAGING DEPARTMENT HOSPITAL SANTA MARIA UNIVERSITY OF LISBON PORTUGAL DEFINITION region of arteriovenous shunting confined to a leaflet of packymeninges often adjacent to a major
Three Cases of Dural Arteriovenous Fistula of the Anterior Condylar Vein within the Hypoglossal Canal
 AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 20:2016 2020, November/December 1999 Case Report Three Cases of Dural Arteriovenous Fistula of the Anterior Condylar Vein within the Hypoglossal Canal Robert Ernst, Robert Bulas,
AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 20:2016 2020, November/December 1999 Case Report Three Cases of Dural Arteriovenous Fistula of the Anterior Condylar Vein within the Hypoglossal Canal Robert Ernst, Robert Bulas,
Spontaneous Closure of Dural Arteriovenous Fistulas: Report of Three Cases and Review of the Literature
 AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 22:992 996, May 2001 Case Report Spontaneous Closure of Dural Arteriovenous Fistulas: Report of Three Cases and Review of the Literature Alain Luciani, Emmanuel Houdart, Charbel Mounayer,
AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 22:992 996, May 2001 Case Report Spontaneous Closure of Dural Arteriovenous Fistulas: Report of Three Cases and Review of the Literature Alain Luciani, Emmanuel Houdart, Charbel Mounayer,
Selective disconnection of cortical venous reflux as treatment for cranial dural arteriovenous fistulas
 J Neurosurg 101:31 35, 2004 Selective disconnection of cortical venous reflux as treatment for cranial dural arteriovenous fistulas J. MARC C. VAN DIJK, M.D., PH.D., KAREL G. TERBRUGGE, M.D., ROBERT A.
J Neurosurg 101:31 35, 2004 Selective disconnection of cortical venous reflux as treatment for cranial dural arteriovenous fistulas J. MARC C. VAN DIJK, M.D., PH.D., KAREL G. TERBRUGGE, M.D., ROBERT A.
Complex dural arteriovenous fistulas. Results of combined endovascular and neurosurgical treatment in 16 patients
 J Neurosurg 71:352-358,1989 Complex dural arteriovenous fistulas Results of combined endovascular and neurosurgical treatment in 16 patients STANLEY L. BARNWELL, M.D., PH.D., VAN V. HALBACH, M.D., RANDALL
J Neurosurg 71:352-358,1989 Complex dural arteriovenous fistulas Results of combined endovascular and neurosurgical treatment in 16 patients STANLEY L. BARNWELL, M.D., PH.D., VAN V. HALBACH, M.D., RANDALL
A Case of Carotid-Cavernous Fistula
 A Case of Carotid-Cavernous Fistula By : Mohamed Elkhawaga 2 nd Year Resident of Ophthalmology Alexandria University A 19 year old male patient came to our outpatient clinic, complaining of : -Severe conjunctival
A Case of Carotid-Cavernous Fistula By : Mohamed Elkhawaga 2 nd Year Resident of Ophthalmology Alexandria University A 19 year old male patient came to our outpatient clinic, complaining of : -Severe conjunctival
CASE OF THE WEEK PROFESSOR YASSER METWALLY
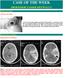 CLINICAL PICTURE CLINICAL PICTURE: CASE OF THE WEEK PROFESSOR YASSER METWALLY A 29 years old male patients presented with proptosis, ecchymoses of the left eye with both subjective and objective bruit
CLINICAL PICTURE CLINICAL PICTURE: CASE OF THE WEEK PROFESSOR YASSER METWALLY A 29 years old male patients presented with proptosis, ecchymoses of the left eye with both subjective and objective bruit
Dural arteriovenous fistulas (DAVFs) are abnormal. Long-term angiographic results of endovascularly cured intracranial dural arteriovenous fistulas
 clinical article J Neurosurg 124:1123 1127, 2016 Long-term angiographic results of endovascularly cured intracranial dural arteriovenous fistulas Sudheer Ambekar, MD, Brandon G. Gaynor, MD, Eric C. Peterson,
clinical article J Neurosurg 124:1123 1127, 2016 Long-term angiographic results of endovascularly cured intracranial dural arteriovenous fistulas Sudheer Ambekar, MD, Brandon G. Gaynor, MD, Eric C. Peterson,
Cryptogenic Enlargement Of Bilateral Superior Ophthalmic Veins
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Radiology Volume 18 Number 1 Cryptogenic Enlargement Of Bilateral Superior Ophthalmic Veins K Kragha Citation K Kragha. Cryptogenic Enlargement Of Bilateral Superior Ophthalmic
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Radiology Volume 18 Number 1 Cryptogenic Enlargement Of Bilateral Superior Ophthalmic Veins K Kragha Citation K Kragha. Cryptogenic Enlargement Of Bilateral Superior Ophthalmic
Brain AVM with Accompanying Venous Aneurysm with Intracerebral and Intraventricular Hemorrhage
 Cronicon OPEN ACCESS EC PAEDIATRICS Case Report Brain AVM with Accompanying Venous Aneurysm with Intracerebral and Intraventricular Hemorrhage Dimitrios Panagopoulos* Neurosurgical Department, University
Cronicon OPEN ACCESS EC PAEDIATRICS Case Report Brain AVM with Accompanying Venous Aneurysm with Intracerebral and Intraventricular Hemorrhage Dimitrios Panagopoulos* Neurosurgical Department, University
Vascular Malformations
 Vascular Malformations LTC Robert Shih Chief of Neuroradiology Walter Reed Medical Center Special thanks to LTC Alice Smith (retired) Disclosures: None. This presentation reflects the personal views of
Vascular Malformations LTC Robert Shih Chief of Neuroradiology Walter Reed Medical Center Special thanks to LTC Alice Smith (retired) Disclosures: None. This presentation reflects the personal views of
Untangling Cerebral Dural Arteriovenous Fistulas
 Untangling Cerebral Dural Arteriovenous Fistulas Bradley A. Gross, MD Assistant Professor, Dept of Neurosurgery, University of Pittsburgh September 2017 davfs Definition Clinical Presentation Natural History
Untangling Cerebral Dural Arteriovenous Fistulas Bradley A. Gross, MD Assistant Professor, Dept of Neurosurgery, University of Pittsburgh September 2017 davfs Definition Clinical Presentation Natural History
Transvenous Embolization of Cavernous Sinus Dural Arteriovenous Fistulas with Shunts Involving the Laterocavernous Sinus
 Journal of Neuroendovascular Therapy 2017; 11: 1 7 Online November 9, 2016 DOI: 10.5797/jnet.oa.2016-0062 Transvenous Embolization of Cavernous Sinus Dural Arteriovenous Fistulas with Shunts Involving
Journal of Neuroendovascular Therapy 2017; 11: 1 7 Online November 9, 2016 DOI: 10.5797/jnet.oa.2016-0062 Transvenous Embolization of Cavernous Sinus Dural Arteriovenous Fistulas with Shunts Involving
What Is an Arteriovenous malformation (AVM)?
 American Society of Neuroradiology What Is an Arteriovenous malformation (AVM)? From the Cerebrovascular Imaging and Intervention Committee of the American Heart Association Cardiovascular Council Randall
American Society of Neuroradiology What Is an Arteriovenous malformation (AVM)? From the Cerebrovascular Imaging and Intervention Committee of the American Heart Association Cardiovascular Council Randall
Fluoroscopy-guided Combined (Surgical/Endovascular) Treatment of Dural Arteriovenous Fistula
 Journal of Cerebrovascular and Endovascular Neurosurgery pissn 2234-8565, eissn 2287-3139, http://dx.doi.org/10.7461/jcen.2017.19.2.106 Case Report Fluoroscopy-guided Combined (Surgical/Endovascular) Treatment
Journal of Cerebrovascular and Endovascular Neurosurgery pissn 2234-8565, eissn 2287-3139, http://dx.doi.org/10.7461/jcen.2017.19.2.106 Case Report Fluoroscopy-guided Combined (Surgical/Endovascular) Treatment
Tentorial Dural Arteriovenous Fistulas: A Single-Center Cohort of 12 Patients
 Journal of Cerebrovascular and Endovascular Neurosurgery pissn 2234-8565, eissn 2287-3139, http://dx.doi.org/10.7461/jcen.2017.19.4.284 Original Article Tentorial Dural Arteriovenous Fistulas: A Single-Center
Journal of Cerebrovascular and Endovascular Neurosurgery pissn 2234-8565, eissn 2287-3139, http://dx.doi.org/10.7461/jcen.2017.19.4.284 Original Article Tentorial Dural Arteriovenous Fistulas: A Single-Center
EMBOLIZATION OF ARTERIOVENOUS FISTULA AFTER RADIOSURGERY FOR MULTIPLE CEREBRAL ARTERIOVENOUS MALFORMATIONS
 Arteriovenous fistula after radiosurgery for multiple CAVM EMBOLIZATION OF ARTERIOVENOUS FISTULA AFTER RADIOSURGERY FOR MULTIPLE CEREBRAL ARTERIOVENOUS MALFORMATIONS Chao-Bao Luo, Wan-Yuo Guo, Michael
Arteriovenous fistula after radiosurgery for multiple CAVM EMBOLIZATION OF ARTERIOVENOUS FISTULA AFTER RADIOSURGERY FOR MULTIPLE CEREBRAL ARTERIOVENOUS MALFORMATIONS Chao-Bao Luo, Wan-Yuo Guo, Michael
Percutaneous Embolization of Arteriovenous Fistulas of the External Carotid Artery
 937 Percutaneous Embolization of rteriovenous Fistulas of the External Carotid rtery lex erenstein 1 John Scote In Sup Choi 1 Mark Persky3 Nineteen arteriovenous fistulas of the external carotid branches
937 Percutaneous Embolization of rteriovenous Fistulas of the External Carotid rtery lex erenstein 1 John Scote In Sup Choi 1 Mark Persky3 Nineteen arteriovenous fistulas of the external carotid branches
PTA 106 Unit 1 Lecture 3
 PTA 106 Unit 1 Lecture 3 The Basics Arteries: Carry blood away from the heart toward tissues. They typically have thicker vessels walls to handle increased pressure. Contain internal and external elastic
PTA 106 Unit 1 Lecture 3 The Basics Arteries: Carry blood away from the heart toward tissues. They typically have thicker vessels walls to handle increased pressure. Contain internal and external elastic
Venous Stroke with Intracranial Dural Arteriovenous Fistula
 Case Reports 24 Venous Stroke with Intracranial Dural Arteriovenous Fistula Tzung-Wen Chiang 1,2, Shung-Lon Lai 1, Leang-Kai Chang 2, Yung-Yee Chang 1, Min-Yu Lan 1, Yeh-Lin Kuo 3, Chen-Chung Lu 3, and
Case Reports 24 Venous Stroke with Intracranial Dural Arteriovenous Fistula Tzung-Wen Chiang 1,2, Shung-Lon Lai 1, Leang-Kai Chang 2, Yung-Yee Chang 1, Min-Yu Lan 1, Yeh-Lin Kuo 3, Chen-Chung Lu 3, and
The superior ophthalmic vein approach for the treatment of carotid-cavernous fistulas: our first experience
 230 Chiriac et al - Superior ophthalmic vein approach The superior ophthalmic vein approach for the treatment of carotid-cavernous fistulas: our first experience A. Chiriac, N. Dobrin 1, Georgiana Ion
230 Chiriac et al - Superior ophthalmic vein approach The superior ophthalmic vein approach for the treatment of carotid-cavernous fistulas: our first experience A. Chiriac, N. Dobrin 1, Georgiana Ion
Dural arteriovenous fistula discovered in patient presenting with recent head trauma
 ISSN 1507-6164 DOI: 10.12659/AJCR.889610 Received: 2013.07.25 Accepted: 2013.08.08 Published: 2013.10.28 Dural arteriovenous fistula discovered in patient presenting with recent head trauma Authors Contribution:
ISSN 1507-6164 DOI: 10.12659/AJCR.889610 Received: 2013.07.25 Accepted: 2013.08.08 Published: 2013.10.28 Dural arteriovenous fistula discovered in patient presenting with recent head trauma Authors Contribution:
Dementia Resulting from Dural Arteriovenous Fistulas: The Pathologic Findings of Venous Hypertensive Encephalopathy
 AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 19:1267 1273, August 1998 Dementia Resulting from Dural Arteriovenous Fistulas: The Pathologic Findings of Venous Hypertensive Encephalopathy Robert W. Hurst, Linda J. Bagley, Steven
AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 19:1267 1273, August 1998 Dementia Resulting from Dural Arteriovenous Fistulas: The Pathologic Findings of Venous Hypertensive Encephalopathy Robert W. Hurst, Linda J. Bagley, Steven
Paraplegia in a chiropractic patient secondary to atraumatic dural arteriovenous fistula with perimedullary hypertension: case report
 Foreman et al. Chiropractic & Manual Therapies 2013, 21:23 http://www.chiromt.com/content/21/1/23 CHIROPRACTIC & MANUAL THERAPIES CASE REPORT Paraplegia in a chiropractic patient secondary to atraumatic
Foreman et al. Chiropractic & Manual Therapies 2013, 21:23 http://www.chiromt.com/content/21/1/23 CHIROPRACTIC & MANUAL THERAPIES CASE REPORT Paraplegia in a chiropractic patient secondary to atraumatic
Cerebrovascular Malformations in the Elderly Indications for Treatment
 Cerebrovascular Malformations in the Elderly Indications for Treatment Johanna T. Fifi, MD, FAHA, FSVIN Director of Endovascular Ischemic Stroke Assistant Professor of Neurology, Neurosurgery, and Radiology
Cerebrovascular Malformations in the Elderly Indications for Treatment Johanna T. Fifi, MD, FAHA, FSVIN Director of Endovascular Ischemic Stroke Assistant Professor of Neurology, Neurosurgery, and Radiology
MASSIVE EPISTAXIS IN A NEONATE: A SYMPTOM OF VEIN OF GALEN MALFORMATION!
 CASE REPORT MASSIVE EPISTAXIS IN A NEONATE: A SYMPTOM OF VEIN OF GALEN MALFORMATION! Shagufta Wahab 1, Rizwan Ahmad Khan 2, Manjari Thapa Manger 3 1. Radiodiagnosis, Aligarh Muslim University, Aligarh,
CASE REPORT MASSIVE EPISTAXIS IN A NEONATE: A SYMPTOM OF VEIN OF GALEN MALFORMATION! Shagufta Wahab 1, Rizwan Ahmad Khan 2, Manjari Thapa Manger 3 1. Radiodiagnosis, Aligarh Muslim University, Aligarh,
Dural arteriovenous shunts (DAVSs), also called dural
 Natural History of Dural Arteriovenous Shunts Michael Söderman, MD, PhD; Ladislav Pavic, MD, PhD; Göran Edner, MD; Staffan Holmin, MD, PhD; Tommy Andersson, MD, PhD Background and Purpose Dural arteriovenous
Natural History of Dural Arteriovenous Shunts Michael Söderman, MD, PhD; Ladislav Pavic, MD, PhD; Göran Edner, MD; Staffan Holmin, MD, PhD; Tommy Andersson, MD, PhD Background and Purpose Dural arteriovenous
Dural arteriovenous fistulas (DAVFs) are
 TOPIC DURAL FISTULAS DURAL FISTULAS Advances in Surgical Approaches to Dural Fistulas Patrick P. Youssef, MD Albert Jess Schuette, MD C. Michael Cawley, MD Daniel L. Barrow, MD Department of Neurosurgery,
TOPIC DURAL FISTULAS DURAL FISTULAS Advances in Surgical Approaches to Dural Fistulas Patrick P. Youssef, MD Albert Jess Schuette, MD C. Michael Cawley, MD Daniel L. Barrow, MD Department of Neurosurgery,
DIAGNOSTIC NEURORADIOLOGY
 Neuroradiology (2008) 50:1013 1023 DOI 10.1007/s00234-008-0433-3 DIAGNOSTIC NEURORADIOLOGY The anterior medullary anterior pontomesencephalic venous system and its bridging veins communicating to the dural
Neuroradiology (2008) 50:1013 1023 DOI 10.1007/s00234-008-0433-3 DIAGNOSTIC NEURORADIOLOGY The anterior medullary anterior pontomesencephalic venous system and its bridging veins communicating to the dural
Endovascular Treatment of Cavernous Sinus Dural Arteriovenous Fistulas by Direct Puncture of Facial Vein
 J Radiol Sci 2011; 36: 129-134 Endovascular Treatment of Cavernous Sinus Dural Arteriovenous Fistulas by Direct Puncture of Facial Vein Shih-Wei Hsu 1 Yeh-Lin Kuo 1 Min-Hsiung Cheng 2 Department of Diagnostic
J Radiol Sci 2011; 36: 129-134 Endovascular Treatment of Cavernous Sinus Dural Arteriovenous Fistulas by Direct Puncture of Facial Vein Shih-Wei Hsu 1 Yeh-Lin Kuo 1 Min-Hsiung Cheng 2 Department of Diagnostic
A Shunt of the Diploic Vein of the Orbital Roof Accompanying a Cavernous Sinus Dural Arteriovenous Fistula: A Case Report
 Journal of Neuroendovascular Therapy 2018; 12: 38 42 Online September 11, 2017 DOI: 10.5797/jnet.cr.2017-0056 A Shunt of the Diploic Vein of the Orbital Roof Accompanying a Cavernous Sinus Dural Arteriovenous
Journal of Neuroendovascular Therapy 2018; 12: 38 42 Online September 11, 2017 DOI: 10.5797/jnet.cr.2017-0056 A Shunt of the Diploic Vein of the Orbital Roof Accompanying a Cavernous Sinus Dural Arteriovenous
Fatal progression of posttraumatic dural arteriovenous fistulas refractory to multimodal therapy
 See the Letter to the Editor and the Response in this issue in Neurosurgical Forum, pp 858 861. J Neurosurg 94:831 835, 2001 Fatal progression of posttraumatic dural arteriovenous fistulas refractory to
See the Letter to the Editor and the Response in this issue in Neurosurgical Forum, pp 858 861. J Neurosurg 94:831 835, 2001 Fatal progression of posttraumatic dural arteriovenous fistulas refractory to
Cranial dural arteriovenous fistula: transarterial Onyx embolization experience and technical nuances
 Division of Neurological Surgery, Barrow Neurological Institute, St. Joseph s Hospital and Medical Center, Phoenix, Arizona, USA Correspondence to Dr C G McDougall, Division of Neurological Surgery, Barrow
Division of Neurological Surgery, Barrow Neurological Institute, St. Joseph s Hospital and Medical Center, Phoenix, Arizona, USA Correspondence to Dr C G McDougall, Division of Neurological Surgery, Barrow
High-Flow, Small-Hole Arteriovenous Fistulas: Treatment with Electrodetachable Coils
 High-Flow, Small-Hole Arteriovenous Fistulas: Treatment with Electrodetachable Coils Guido Guglielmi, Fernando Viñuela, Gary Duckwiler, Jacques Dion, and Alfredo Stocker Summary: We present one case of
High-Flow, Small-Hole Arteriovenous Fistulas: Treatment with Electrodetachable Coils Guido Guglielmi, Fernando Viñuela, Gary Duckwiler, Jacques Dion, and Alfredo Stocker Summary: We present one case of
Dural Arteriovenous Fistula of the Cavernous Sinus Presenting with Progressive Venous Congestion of the Pons and Cerebrum: Report of one case
 Dural Arteriovenous Fistula of the Cavernous Sinus Presenting with Progressive Venous Congestion of the Pons and Cerebrum: Report of one case Soo-Bin Yim, M.D., Jong-Sung Kim, M.D., Yang Kwon,M.D.*, Choong-Gon
Dural Arteriovenous Fistula of the Cavernous Sinus Presenting with Progressive Venous Congestion of the Pons and Cerebrum: Report of one case Soo-Bin Yim, M.D., Jong-Sung Kim, M.D., Yang Kwon,M.D.*, Choong-Gon
MR Imaging of Spinal Cord Arteriovenous Malformations at 0.5 T: Study of 34 Cases
 833 MR Imaging of Spinal Cord Arteriovenous Malformations at 0.5 T: Study of 34 Cases D. Dormont 1 F. Gelbert 2 E. Assouline 2 D. Reizine 2 A. Helias 2 M. C. Riche 2 J. Chiras 1 J. Sories 1 J. J. Merland
833 MR Imaging of Spinal Cord Arteriovenous Malformations at 0.5 T: Study of 34 Cases D. Dormont 1 F. Gelbert 2 E. Assouline 2 D. Reizine 2 A. Helias 2 M. C. Riche 2 J. Chiras 1 J. Sories 1 J. J. Merland
Dural arteriovenous fistulas of the cavernous sinus - clinical case and treatment
 166 Chiriac et al Dural arteriovenous fistulas of the cavernous sinus Dural arteriovenous fistulas of the cavernous sinus - clinical case and treatment A. Chiriac, N. Dobrin*, St.M. Iencean, I. Poeata
166 Chiriac et al Dural arteriovenous fistulas of the cavernous sinus Dural arteriovenous fistulas of the cavernous sinus - clinical case and treatment A. Chiriac, N. Dobrin*, St.M. Iencean, I. Poeata
Carotid Cavernous Fistula
 Chief Complaint: Double vision. Carotid Cavernous Fistula Alex W. Cohen, MD, PhD; Richard Allen, MD, PhD May 14, 2010 History of Present Illness: A 46 year old female patient presented to the Oculoplastics
Chief Complaint: Double vision. Carotid Cavernous Fistula Alex W. Cohen, MD, PhD; Richard Allen, MD, PhD May 14, 2010 History of Present Illness: A 46 year old female patient presented to the Oculoplastics
Spontaneous occlusion of a cerebral arteriovenous malformation after subtotal endovascular embolisation
 206 Chiriac et al Spontaneous occlusion of a cerebral arteriovenous malformation Spontaneous occlusion of a cerebral arteriovenous malformation after subtotal endovascular embolisation A. Chiriac, N. Dobrin*,
206 Chiriac et al Spontaneous occlusion of a cerebral arteriovenous malformation Spontaneous occlusion of a cerebral arteriovenous malformation after subtotal endovascular embolisation A. Chiriac, N. Dobrin*,
SDAVFs are rare acquired vascular lesions predominantly
 CLINICAL REPORT W.J. van Rooij R.J. Nijenhuis J.P. Peluso M. Sluzewski G.N. Beute B. van der Pol Spinal Dural Fistulas without Swelling and Edema of the Cord as Incidental Findings SUMMARY: SDAVFs cause
CLINICAL REPORT W.J. van Rooij R.J. Nijenhuis J.P. Peluso M. Sluzewski G.N. Beute B. van der Pol Spinal Dural Fistulas without Swelling and Edema of the Cord as Incidental Findings SUMMARY: SDAVFs cause
Peripheral Spinal Cord Hypointensity on T2-weighted MR Images: A Reliable Imaging Sign of Venous Hypertensive Myelopathy
 AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 21:781 786, April 2000 Peripheral Spinal Cord Hypointensity on T2-weighted MR Images: A Reliable Imaging Sign of Venous Hypertensive Myelopathy Robert W. Hurst and Robert I. Grossman
AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 21:781 786, April 2000 Peripheral Spinal Cord Hypointensity on T2-weighted MR Images: A Reliable Imaging Sign of Venous Hypertensive Myelopathy Robert W. Hurst and Robert I. Grossman
Cerebellar Hemorrhage due to a Direct Carotid Cavernous Fistula after Surgery for Maxillary Cancer
 Case Report J Korean Neurosurg Soc 60 (1) : 89-93, 2017 https://doi.org/10.3340/jkns.2015.1206.001 pissn 2005-3711 eissn 1598-7876 Cerebellar Hemorrhage due to a Direct Carotid Cavernous Fistula after
Case Report J Korean Neurosurg Soc 60 (1) : 89-93, 2017 https://doi.org/10.3340/jkns.2015.1206.001 pissn 2005-3711 eissn 1598-7876 Cerebellar Hemorrhage due to a Direct Carotid Cavernous Fistula after
General Data. Gender: Female Birthday and age: 1932/11/03, 73 y/o Occupation: house keeper Date of Admission: 2005/03/30
 General Data Gender: Female Birthday and age: 1932/11/03, 73 y/o Occupation: house keeper Date of Admission: 2005/03/30 Chief Complain Dizziness and light headache for recent 1 year. Present illness Hypertension
General Data Gender: Female Birthday and age: 1932/11/03, 73 y/o Occupation: house keeper Date of Admission: 2005/03/30 Chief Complain Dizziness and light headache for recent 1 year. Present illness Hypertension
Dural Arteriovenous Fistulas: the value of Carotid Ultrasonography.
 Dural Arteriovenous Fistulas: the value of Carotid Ultrasonography. Poster No.: C-2199 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: J. P. Filipe, T. Parreira, C. Andrade, R. Santos, E. Azevedo;
Dural Arteriovenous Fistulas: the value of Carotid Ultrasonography. Poster No.: C-2199 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: J. P. Filipe, T. Parreira, C. Andrade, R. Santos, E. Azevedo;
Borden type3 superior sagittal sinus dural arteriovenous fistula, angiographic features and endovascular treatment.
 Borden type3 superior sagittal sinus dural arteriovenous fistula, angiographic features and endovascular treatment. Poster No.: C-1939 Congress: ECR 2013 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: T. Dotsu 1, H.
Borden type3 superior sagittal sinus dural arteriovenous fistula, angiographic features and endovascular treatment. Poster No.: C-1939 Congress: ECR 2013 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: T. Dotsu 1, H.
Dural arteriovenous fistulas (dural AVFs) constitute 10%
 ORIGINAL RESEARCH N. Horie M. Morikawa N. Kitigawa K. Tsutsumi M. Kaminogo I. Nagata 2D Thick-Section MR Digital Subtraction Angiography for the Assessment of Dural Arteriovenous Fistulas BACKGROUND AND
ORIGINAL RESEARCH N. Horie M. Morikawa N. Kitigawa K. Tsutsumi M. Kaminogo I. Nagata 2D Thick-Section MR Digital Subtraction Angiography for the Assessment of Dural Arteriovenous Fistulas BACKGROUND AND
PEER-REVIEW REPORTS. various signs and symptoms such as headaches, tinnitus, bruit, neurologic deficits, venous hypertensive encephalopathy with
 Multimodality Treatment of Intracranial Dural Arteriovenous Fistulas in the Onyx Era: a Single Center Experience Sabareesh K. Natarajan 1, Basavaraj Ghodke 1,2, Louis J. Kim 1,2, Danial K. Hallam 1,2,
Multimodality Treatment of Intracranial Dural Arteriovenous Fistulas in the Onyx Era: a Single Center Experience Sabareesh K. Natarajan 1, Basavaraj Ghodke 1,2, Louis J. Kim 1,2, Danial K. Hallam 1,2,
Vascular and Parameningeal Infections of the Head and Neck
 Vascular and Parameningeal Infections of the Head and Neck Kevin B. Laupland, MD, MSc, FRCPC Associate Professor Departments of Medicine, Critical Care Medicine, Pathology and Laboratory Medicine, and
Vascular and Parameningeal Infections of the Head and Neck Kevin B. Laupland, MD, MSc, FRCPC Associate Professor Departments of Medicine, Critical Care Medicine, Pathology and Laboratory Medicine, and
Differences between CS-DAVF and TCCF to reveal and redefine CS-DAVF
 Pan et al. Chinese Neurosurgical Journal (2018) 4:26 https://doi.org/10.1186/s41016-018-0121-z CHINESE MEDICAL ASSOCIATION COMMENTARY Differences between CS-DAVF and TCCF to reveal and redefine CS-DAVF
Pan et al. Chinese Neurosurgical Journal (2018) 4:26 https://doi.org/10.1186/s41016-018-0121-z CHINESE MEDICAL ASSOCIATION COMMENTARY Differences between CS-DAVF and TCCF to reveal and redefine CS-DAVF
Intracranial Dural Arteriovenous Fistulas: Clinical Characteristics and Management Based on Location and Hemodynamics
 Journal of Cerebrovascular and Endovascular Neurosurgery ISSN -8565, EISSN 87-9, http://dx.doi.org/0.76/jcen.0...9 Original Article Intracranial Dural Arteriovenous Fistulas: Clinical Characteristics and
Journal of Cerebrovascular and Endovascular Neurosurgery ISSN -8565, EISSN 87-9, http://dx.doi.org/0.76/jcen.0...9 Original Article Intracranial Dural Arteriovenous Fistulas: Clinical Characteristics and
Vascular Malformations of the Brain: A Review of Imaging Features and Risks
 Vascular Malformations of the Brain: A Review of Imaging Features and Risks Comprehensive Neuroradiology: Best Practices October 27-30, 2016 Sudhakar R. Satti, MD Associate Director Neurointerventional
Vascular Malformations of the Brain: A Review of Imaging Features and Risks Comprehensive Neuroradiology: Best Practices October 27-30, 2016 Sudhakar R. Satti, MD Associate Director Neurointerventional
Dural arteriovenous fistulas (DAVFs) are acquired abnormal
 ORIGINAL RESEARCH R.G. Nogueira G. Dabus J.D. Rabinov C.J. Eskey C.S. Ogilvy J.A. Hirsch J.C. Pryor Preliminary Experience with Onyx Embolization for the Treatment of Intracranial Dural Arteriovenous Fistulas
ORIGINAL RESEARCH R.G. Nogueira G. Dabus J.D. Rabinov C.J. Eskey C.S. Ogilvy J.A. Hirsch J.C. Pryor Preliminary Experience with Onyx Embolization for the Treatment of Intracranial Dural Arteriovenous Fistulas
Vein of Galen Aneurysms
 Interventional Neuroradiology 7 (Suppll): 99103, 2001 Vein of Galen Aneurysms Experience with Eleven Cases. KOIYAA, H. NAKAJIA,. NISHIKAWA, K. YAANAKA, Y. IWAI, T. YASUI, T. ORIKAWA*, S. KITANO*, H. SAKAOTO*,A.
Interventional Neuroradiology 7 (Suppll): 99103, 2001 Vein of Galen Aneurysms Experience with Eleven Cases. KOIYAA, H. NAKAJIA,. NISHIKAWA, K. YAANAKA, Y. IWAI, T. YASUI, T. ORIKAWA*, S. KITANO*, H. SAKAOTO*,A.
BACKGROUND AND PURPOSE:
 AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 26:1715 1722, August 2005 Dural Sinus Compartment in Dural Arteriovenous Shunts: A New Angioarchitectural Feature Allowing Superselective Transvenous Dural Sinus Occlusion Treatment
AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 26:1715 1722, August 2005 Dural Sinus Compartment in Dural Arteriovenous Shunts: A New Angioarchitectural Feature Allowing Superselective Transvenous Dural Sinus Occlusion Treatment
Dural Arteriovenous Fistulas of the Posterior Fossa Draining into Subarachnoid Veins
 Dural Arteriovenous Fistulas of the Posterior Fossa Draining into Subarachnoid Veins Laurent Pierot, 1 Jacques Chiras, 1 Jean-Frans:ois Meder, 2 Michele Rose, 1 Maurice Rivierez, 3 and Claude Marsault
Dural Arteriovenous Fistulas of the Posterior Fossa Draining into Subarachnoid Veins Laurent Pierot, 1 Jacques Chiras, 1 Jean-Frans:ois Meder, 2 Michele Rose, 1 Maurice Rivierez, 3 and Claude Marsault
Dural arteriovenous fistulas (DAVFs) constitute 10% to
 Color Doppler Flow Imaging of the Superior Ophthalmic Vein in Dural Arteriovenous Fistulas Shoichiro Kawaguchi, MD; Toshisuke Sakaki, MD; Ryunosuke Uranishi, MD Background and Purpose This article evaluates
Color Doppler Flow Imaging of the Superior Ophthalmic Vein in Dural Arteriovenous Fistulas Shoichiro Kawaguchi, MD; Toshisuke Sakaki, MD; Ryunosuke Uranishi, MD Background and Purpose This article evaluates
Historical perspective
 SPINAL AVM Introduction Vascular malformations of spinal cord are a rare clinical entity, representing 5% of all primary spinal cord lesions, with arteriovenous malformations(avm) & cavernous malformations
SPINAL AVM Introduction Vascular malformations of spinal cord are a rare clinical entity, representing 5% of all primary spinal cord lesions, with arteriovenous malformations(avm) & cavernous malformations
Course of apparent diffusion coefficient values in cerebral edema of dural arteriovenous
 Title Page Title: Course of apparent diffusion coefficient values in cerebral edema of dural arteriovenous fistula before and after treatment Authors: Shigeyuki Sakamoto, Shinji Ohba, Masaaki Shibukawa,
Title Page Title: Course of apparent diffusion coefficient values in cerebral edema of dural arteriovenous fistula before and after treatment Authors: Shigeyuki Sakamoto, Shinji Ohba, Masaaki Shibukawa,
Principles Arteries & Veins of the CNS LO14
 Principles Arteries & Veins of the CNS LO14 14. Identify (on cadaver specimens, models and diagrams) and name the principal arteries and veins of the CNS: Why is it important to understand blood supply
Principles Arteries & Veins of the CNS LO14 14. Identify (on cadaver specimens, models and diagrams) and name the principal arteries and veins of the CNS: Why is it important to understand blood supply
Intracranial dural arteriovenous fistulas (DAVF) have long
 ORIGINAL RESEARCH K. Noguchi M. Kubo N. Kuwayama Y. Kamisaki G. Tomizawa K. Kameda H. Kawabe S. Ogawa N. Watanabe S. Endo H. Seto Intracranial Dural Arteriovenous Fistulas with Retrograde Cortical Venous
ORIGINAL RESEARCH K. Noguchi M. Kubo N. Kuwayama Y. Kamisaki G. Tomizawa K. Kameda H. Kawabe S. Ogawa N. Watanabe S. Endo H. Seto Intracranial Dural Arteriovenous Fistulas with Retrograde Cortical Venous
Dural Arteriovenous Fistula in Children: Endovascular Treatment and Outcomes in Seven Cases
 AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 22:1217 1225, June/July 2001 Dural Arteriovenous Fistula in Children: Endovascular Treatment and Outcomes in Seven Cases Patricia K. Kincaid, Gary R. Duckwiler, Y. Pierre Gobin, and
AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 22:1217 1225, June/July 2001 Dural Arteriovenous Fistula in Children: Endovascular Treatment and Outcomes in Seven Cases Patricia K. Kincaid, Gary R. Duckwiler, Y. Pierre Gobin, and
Combining endovascular and neurosurgical treatments of high-risk dural arteriovenous fistulas in the lateral sinus and the confluence of the sinuses
 Neurosurg Focus 5 (4):Article 10, 1998 Combining endovascular and neurosurgical treatments of high-risk dural arteriovenous fistulas in the lateral sinus and the confluence of the sinuses Katsuya Goto,
Neurosurg Focus 5 (4):Article 10, 1998 Combining endovascular and neurosurgical treatments of high-risk dural arteriovenous fistulas in the lateral sinus and the confluence of the sinuses Katsuya Goto,
Pediatric Neurointervention: Vein of Galen Malformations
 Pediatric Neurointervention: Vein of Galen Malformations Johanna T. Fifi, M.D. Assistant Professor of Neurology, Neurosurgery, and Radiology Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai November 9 th, 2014
Pediatric Neurointervention: Vein of Galen Malformations Johanna T. Fifi, M.D. Assistant Professor of Neurology, Neurosurgery, and Radiology Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai November 9 th, 2014
Ultrasound diagnostics of a spontaneous arteriovenous fistula of the head and neck
 Case report Cite as: Zakharkina MV, Chechetkin O, Krotenkova MV, Konovalov RN: Ultrasound diagnostics of a spontaneous arteriovenous fistula of the head and neck.. Submitted: 29.03.2017 ccepted: 24.05.2017
Case report Cite as: Zakharkina MV, Chechetkin O, Krotenkova MV, Konovalov RN: Ultrasound diagnostics of a spontaneous arteriovenous fistula of the head and neck.. Submitted: 29.03.2017 ccepted: 24.05.2017
Enhancement of Cranial US: Utility of Supplementary Acoustic Windows and Doppler Harriet J. Paltiel, MD
 Enhancement of Cranial US: Utility of Supplementary Acoustic Windows and Doppler Harriet J. Paltiel, MD Boston Children s Hospital Harvard Medical School None Disclosures Conventional US Anterior fontanelle
Enhancement of Cranial US: Utility of Supplementary Acoustic Windows and Doppler Harriet J. Paltiel, MD Boston Children s Hospital Harvard Medical School None Disclosures Conventional US Anterior fontanelle
Therapeutic Embolization of the Dural Arteriovenous Malformation Involving the Jugular Bulb
 J Korean Med Sci 2001; 16: 527-31 ISSN 1011-8934 Copyright The Korean Academy of Medical Sciences Therapeutic Embolization of the Dural Arteriovenous Malformation Involving the Jugular Bulb Pulsatile tinnitus
J Korean Med Sci 2001; 16: 527-31 ISSN 1011-8934 Copyright The Korean Academy of Medical Sciences Therapeutic Embolization of the Dural Arteriovenous Malformation Involving the Jugular Bulb Pulsatile tinnitus
Brain Arteriovenous Malformations Endovascular Therapy and Associated Therapeutic Protocols Jorge Guedes Cabral de Campos
 Endovascular Therapy and Associated Therapeutic Protocols Jorge Guedes Cabral de Campos Neuroradiology Department Hospital de Santa Maria University of Lisbon CEREBRAL AVM CLINICAL / EPIDEMIOLOGY Brain
Endovascular Therapy and Associated Therapeutic Protocols Jorge Guedes Cabral de Campos Neuroradiology Department Hospital de Santa Maria University of Lisbon CEREBRAL AVM CLINICAL / EPIDEMIOLOGY Brain
Brain Meninges, Ventricles and CSF
 Brain Meninges, Ventricles and CSF Lecture Objectives Describe the arrangement of the meninges and their relationship to brain and spinal cord. Explain the occurrence of epidural, subdural and subarachnoid
Brain Meninges, Ventricles and CSF Lecture Objectives Describe the arrangement of the meninges and their relationship to brain and spinal cord. Explain the occurrence of epidural, subdural and subarachnoid
Endovascular Treatment of Cerebral Arteriovenous Malformations. Bs. Nguyễn Ngọc Pi Doanh- Bs Đặng Ngọc Dũng Khoa Ngoại Thần Kinh
 Endovascular Treatment of Cerebral Arteriovenous Malformations Bs. Nguyễn Ngọc Pi Doanh- Bs Đặng Ngọc Dũng Khoa Ngoại Thần Kinh Stroke Vascular Malformations of the Brain Epidemiology: - Incidence: 0.1%,
Endovascular Treatment of Cerebral Arteriovenous Malformations Bs. Nguyễn Ngọc Pi Doanh- Bs Đặng Ngọc Dũng Khoa Ngoại Thần Kinh Stroke Vascular Malformations of the Brain Epidemiology: - Incidence: 0.1%,
Spontaneous Obliteration of Pial Arteriovenous Malformations: A Review of 27 Cases
 AJNR Am J Neuroradiol :, March 00 Spontaneous Obliteration of Pial Arteriovenous Malformations: A Review of ases Maneesh. Patel, Timothy J. Hodgson, Andras A. Kemeny, and David M. Forster BAKGROUND AND
AJNR Am J Neuroradiol :, March 00 Spontaneous Obliteration of Pial Arteriovenous Malformations: A Review of ases Maneesh. Patel, Timothy J. Hodgson, Andras A. Kemeny, and David M. Forster BAKGROUND AND
HEAD AND NECK IMAGING. James Chen (MS IV)
 HEAD AND NECK IMAGING James Chen (MS IV) Anatomy Course Johns Hopkins School of Medicine Sept. 27, 2011 OBJECTIVES Introduce cross sectional imaging of head and neck Computed tomography (CT) Review head
HEAD AND NECK IMAGING James Chen (MS IV) Anatomy Course Johns Hopkins School of Medicine Sept. 27, 2011 OBJECTIVES Introduce cross sectional imaging of head and neck Computed tomography (CT) Review head
point of dural arteriovenous fistul
 NAOSITE: Nagasaki University's Ac Title Author(s) Citation Efficacy of DynaCT digital angiogra point of dural arteriovenous fistul Hiu, Takeshi; Kitagawa, Naoki; Mori Horie, Nobutaka; Morofuji, Yoichi;
NAOSITE: Nagasaki University's Ac Title Author(s) Citation Efficacy of DynaCT digital angiogra point of dural arteriovenous fistul Hiu, Takeshi; Kitagawa, Naoki; Mori Horie, Nobutaka; Morofuji, Yoichi;
HEAD/NECK VESSELS. Objectives
 Objectives Arterial Supply to Head and Neck Arteries to Head Surrounding Brain Common carotid arteries Arteries to Head Surrounding Brain External carotid arteries Arteries to Head Surrounding Brain External
Objectives Arterial Supply to Head and Neck Arteries to Head Surrounding Brain Common carotid arteries Arteries to Head Surrounding Brain External carotid arteries Arteries to Head Surrounding Brain External
Neurosurgical decision making in structural lesions causing stroke. Dr Rakesh Ranjan MS, MCh, Dip NB (Neurosurgery)
 Neurosurgical decision making in structural lesions causing stroke Dr Rakesh Ranjan MS, MCh, Dip NB (Neurosurgery) Subarachnoid Hemorrhage Every year, an estimated 30,000 people in the United States experience
Neurosurgical decision making in structural lesions causing stroke Dr Rakesh Ranjan MS, MCh, Dip NB (Neurosurgery) Subarachnoid Hemorrhage Every year, an estimated 30,000 people in the United States experience
41 year old female with headache. Elena G. Violari MD and Leo Wolansky MD
 41 year old female with headache Elena G. Violari MD and Leo Wolansky MD ? Dural Venous Sinus Thrombosis with Hemorrhagic Venous Infarct Acute intraparenchymal hematoma measuring ~3 cm in diameter centered
41 year old female with headache Elena G. Violari MD and Leo Wolansky MD ? Dural Venous Sinus Thrombosis with Hemorrhagic Venous Infarct Acute intraparenchymal hematoma measuring ~3 cm in diameter centered
Treatment of Slow-Flow (Type I) Perimedullary Spinal Arteriovenous Fistulas with Special Reference to Embolization
 AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 26:2582 2586, November/December 2005 Case Report Treatment of Slow-Flow (Type I) Perimedullary Spinal Arteriovenous Fistulas with Special Reference to Embolization Ismail Oran, Mustafa
AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 26:2582 2586, November/December 2005 Case Report Treatment of Slow-Flow (Type I) Perimedullary Spinal Arteriovenous Fistulas with Special Reference to Embolization Ismail Oran, Mustafa
Role of Three-Dimensional Rotational Angiography in the Treatment of Spinal Dural Arteriovenous Fistulas
 Open Access Case Report DOI: 10.7759/cureus.1932 Role of Three-Dimensional Rotational Angiography in the Treatment of Spinal Dural Arteriovenous Fistulas Yigit Ozpeynirci 1, Bernd Schmitz 2, Melanie Schick
Open Access Case Report DOI: 10.7759/cureus.1932 Role of Three-Dimensional Rotational Angiography in the Treatment of Spinal Dural Arteriovenous Fistulas Yigit Ozpeynirci 1, Bernd Schmitz 2, Melanie Schick
Endovascular treatment with transvenous approach for embolization of carotid cavernous fistula
 169 Case Report Endovascular treatment with transvenous approach for embolization of carotid cavernous fistula Benny Young, Agusmanan Bojeng Department of Radiology, University Malaysia Sarawak, Faculty
169 Case Report Endovascular treatment with transvenous approach for embolization of carotid cavernous fistula Benny Young, Agusmanan Bojeng Department of Radiology, University Malaysia Sarawak, Faculty
Advanced Vascular Imaging: Pulsatile Tinnitus. Disclosures. Pulsatile Tinnitus: Differential Diagnosis. Pulsatile Tinnitus
 Advanced Vascular Imaging: Pulsatile Tinnitus Patrick Turski MD, Zach Clark MD, Tabby Kennedy MD The Objectives of this presentation are to: Review the differential diagnosis of pulsatile tinnitus Discuss
Advanced Vascular Imaging: Pulsatile Tinnitus Patrick Turski MD, Zach Clark MD, Tabby Kennedy MD The Objectives of this presentation are to: Review the differential diagnosis of pulsatile tinnitus Discuss
Methods. Treatment options for intracranial arteriovenous malformations
 AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 25:1139 1143, August 2004 Complete Obliteration of Intracranial Arteriovenous Malformation with Endovascular Cyanoacrylate Embolization: Initial Success and Rate of Permanent Cure
AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 25:1139 1143, August 2004 Complete Obliteration of Intracranial Arteriovenous Malformation with Endovascular Cyanoacrylate Embolization: Initial Success and Rate of Permanent Cure
7/5/2016. Neonatal high-output cardiac failure. Case 1 POSTNATAL STRATEGIES FOR CEREBRAL ATERIOVENOUS MALFORMATIONS
 John Deveikis, M.D. POSTNATAL STRATEGIES FOR CEREBRAL ATERIOVENOUS MALFORMATIONS JULY, 2016 Neonatal high-output cardiac failure Tachypnea, tachycardia, hypotension, failure to thrive When congenital heart
John Deveikis, M.D. POSTNATAL STRATEGIES FOR CEREBRAL ATERIOVENOUS MALFORMATIONS JULY, 2016 Neonatal high-output cardiac failure Tachypnea, tachycardia, hypotension, failure to thrive When congenital heart
Patients are referred to neurosurgeons specialized. Pure arterial malformation of the posterior cerebral artery: importance of its recognition
 J Neurosurg 119:655 660, 2013 AANS, 2013 Pure arterial malformation of the posterior cerebral artery: importance of its recognition Case report Nancy McLaughlin, M.D., Ph.D., 1 Radoslav Raychev, M.D.,
J Neurosurg 119:655 660, 2013 AANS, 2013 Pure arterial malformation of the posterior cerebral artery: importance of its recognition Case report Nancy McLaughlin, M.D., Ph.D., 1 Radoslav Raychev, M.D.,
Dural Arteriovenous Malformations: A Review of the Literature and a Presentation of the JHN Series
 JHN Journal Volume 5 Issue 2 Article 2 12-2010 Dural Arteriovenous Malformations: A Review of the Literature and a Presentation of the JHN Series Ed Marchan edward.marchan@jefferson.edu Stavropoula Tjoumakaris
JHN Journal Volume 5 Issue 2 Article 2 12-2010 Dural Arteriovenous Malformations: A Review of the Literature and a Presentation of the JHN Series Ed Marchan edward.marchan@jefferson.edu Stavropoula Tjoumakaris
Classical CNS Disease Patterns
 Classical CNS Disease Patterns Inflammatory Traumatic In response to the trauma of having his head bashed in GM would have experienced some of these features. NOT TWO LITTLE PEENY WEENY I CM LACERATIONS.
Classical CNS Disease Patterns Inflammatory Traumatic In response to the trauma of having his head bashed in GM would have experienced some of these features. NOT TWO LITTLE PEENY WEENY I CM LACERATIONS.
I-iodoamphetamine single photon emission computed tomography
 clinical article J Neurosurg 123:110 117, 2015 Cerebral hemodynamic disturbance in dural arteriovenous fistula with retrograde leptomeningeal venous drainage: a prospective study using 123 I-iodoamphetamine
clinical article J Neurosurg 123:110 117, 2015 Cerebral hemodynamic disturbance in dural arteriovenous fistula with retrograde leptomeningeal venous drainage: a prospective study using 123 I-iodoamphetamine
Methods. Yahya Paksoy, Bülent Oğuz Genç, and Emine Genç. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 24: , August 2003
 AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 24:1364 1368, August 2003 Retrograde Flow in the Left Inferior Petrosal Sinus and Blood Steal of the Cavernous Sinus Associated with Central Vein Stenosis: MR Angiographic Findings
AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 24:1364 1368, August 2003 Retrograde Flow in the Left Inferior Petrosal Sinus and Blood Steal of the Cavernous Sinus Associated with Central Vein Stenosis: MR Angiographic Findings
Combining endovascular and neurosurgical treatments of high-risk dural arteriovenous fistulas in the lateral sinus and the confluence of the sinuses
 J Neurosurg 90:289 299, 1999 Combining endovascular and neurosurgical treatments of high-risk dural arteriovenous fistulas in the lateral sinus and the confluence of the sinuses KATSUYA GOTO, M.D., PH.D.,
J Neurosurg 90:289 299, 1999 Combining endovascular and neurosurgical treatments of high-risk dural arteriovenous fistulas in the lateral sinus and the confluence of the sinuses KATSUYA GOTO, M.D., PH.D.,
Transvenous Embolization of Dural Fistulas Involving the Transverse and Sigmoid Sinuses
 385 Transvenous Embolization of Dural Fistulas Involving the Transverse and Sigmoid Sinuses Van V. Halbach 1 Randall T. Higashida 1 Grant B. Hieshima 1 C. Mark Mehringer 2 Carl W. Hardin 1 Received February
385 Transvenous Embolization of Dural Fistulas Involving the Transverse and Sigmoid Sinuses Van V. Halbach 1 Randall T. Higashida 1 Grant B. Hieshima 1 C. Mark Mehringer 2 Carl W. Hardin 1 Received February
Multiple Dural Arteriovenous Fistulas
 Multiple Dural Arteriovenous Fistulas Satoshi USHIKOSHI, Yoichi KIKUCHI*, Kiyohiro HOUKIN**, Hisatoshi SAITO, and Hiroshi ABE** Sapporo Azabu Neurosurgical Hospital, Sapporo; Departments of *Radiology
Multiple Dural Arteriovenous Fistulas Satoshi USHIKOSHI, Yoichi KIKUCHI*, Kiyohiro HOUKIN**, Hisatoshi SAITO, and Hiroshi ABE** Sapporo Azabu Neurosurgical Hospital, Sapporo; Departments of *Radiology
T HE blood supply of cerebral arteriovenous malformations is often extensive
 NOVEMBER, 1974 ROENTGENOGRAPHIC ANALYSIS OF ARTERIOVENOUS MALFORMATIONS OF THE OCCIPITAL LOBE* By B. TODD TROOST, M.D.,t and THOMAS H. NEWTON, M.D4 T HE blood supply of cerebral arteriovenous malformations
NOVEMBER, 1974 ROENTGENOGRAPHIC ANALYSIS OF ARTERIOVENOUS MALFORMATIONS OF THE OCCIPITAL LOBE* By B. TODD TROOST, M.D.,t and THOMAS H. NEWTON, M.D4 T HE blood supply of cerebral arteriovenous malformations
Cerebral DAVF is an acquired abnormal arterialto-venous
 Neurosurg Focus 32 (5):E10, 2012 Dural arteriovenous fistulas presenting with brainstem dysfunction: diagnosis and surgical treatment Charles Kulwin, M.D., Bradley N. Bohnstedt, M.D., John A. Scott, M.D.,
Neurosurg Focus 32 (5):E10, 2012 Dural arteriovenous fistulas presenting with brainstem dysfunction: diagnosis and surgical treatment Charles Kulwin, M.D., Bradley N. Bohnstedt, M.D., John A. Scott, M.D.,
Evolutionary History of Multiple Dural Fistula
 683722HICXXX10.1177/2324709616683722Journal of Investigative Medicine High Impact Case ReportsMartinez-Burbano et al case-report2016 Case Report Evolutionary History of Multiple Dural Fistula Journal of
683722HICXXX10.1177/2324709616683722Journal of Investigative Medicine High Impact Case ReportsMartinez-Burbano et al case-report2016 Case Report Evolutionary History of Multiple Dural Fistula Journal of
Treatment of Dural Arteriovenous Malformations Involving the Superior Sagittal Sinus
 337 Treatment of Dural Arteriovenous Malformations Involving the Superior Sagittal Sinus Van V. Halbach1 Randall T. Higashida 1 Grant B. Hieshima 1 Mark Rosenblum 2 Les Cahan 3 We report the diagnosis
337 Treatment of Dural Arteriovenous Malformations Involving the Superior Sagittal Sinus Van V. Halbach1 Randall T. Higashida 1 Grant B. Hieshima 1 Mark Rosenblum 2 Les Cahan 3 We report the diagnosis
Transarterial Embolization with Berenstein Liquid Coils and N-butyl Cyanoacrylate in a Vein of Galen Aneurysmal Malformation: a Case Report
 Transarterial Embolization with erenstein Liquid oils and N-butyl yanoacrylate in a Vein of Galen neurysmal Malformation: a ase Report Ming-hua Li, MD Wen-bin Li, MD hun Fang, MD u-lang Gao, MD 12-week-old
Transarterial Embolization with erenstein Liquid oils and N-butyl yanoacrylate in a Vein of Galen neurysmal Malformation: a ase Report Ming-hua Li, MD Wen-bin Li, MD hun Fang, MD u-lang Gao, MD 12-week-old
New Concept in Cavernous Sinus Dural Arteriovenous Fistula Correlation With Presenting Symptom and Venous Drainage Patterns
 New Concept in Cavernous Sinus Dural Arteriovenous Fistula Correlation With Presenting Symptom and Venous Drainage s Dae Chul Suh, MD; Jeong Hyun Lee, MD; Sang Joon Kim, MD; Sun Ju Chung, MD; Choong Gon
New Concept in Cavernous Sinus Dural Arteriovenous Fistula Correlation With Presenting Symptom and Venous Drainage s Dae Chul Suh, MD; Jeong Hyun Lee, MD; Sang Joon Kim, MD; Sun Ju Chung, MD; Choong Gon
Endovascular Embolization of Intracranial Dural AV Fistula- Benign?
 Endovascular Embolization of Intracranial Dural AV Fistula- Benign? Suneeta Gollapudy, M.D. Assistant Professor of Anesthesiology Director, Division of Neuroanesthesia Director, Division of PACU Rotation(
Endovascular Embolization of Intracranial Dural AV Fistula- Benign? Suneeta Gollapudy, M.D. Assistant Professor of Anesthesiology Director, Division of Neuroanesthesia Director, Division of PACU Rotation(
Dural Arteriovenous Fistula Following Translabyrinthine Resection of Cerebellopontine Angle Tumors: Report of Two Cases
 Dural Arteriovenous Fistula Following Translabyrinthine Resection of Cerebellopontine Angle Tumors: Report of Two Cases Peter M.M.C. Li, M.D., 1 Nancy J. Fischbein, M.D., 1,2 Huy M. Do, M.D., 2,3 and Nikolas
Dural Arteriovenous Fistula Following Translabyrinthine Resection of Cerebellopontine Angle Tumors: Report of Two Cases Peter M.M.C. Li, M.D., 1 Nancy J. Fischbein, M.D., 1,2 Huy M. Do, M.D., 2,3 and Nikolas
