Disclosure of Commercial Interest
|
|
|
- Charity Lucy Craig
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Evidence Based Imaging: Getting the Right Study for Your Patient Johanne E. Dillon, MD, FAAP Pediatric Radiology UK HealthCare Assistant Professor of Radiology and Pediatrics University of Kentucky College of Medicine Medical Director of Radiology, Shriners Hospitals for Children Medical Center Lexington and Erich C. Maul, DO, MPH Division Chief, Pediatric Hospital Medicine UK HealthCare Associate Professor of Pediatrics University of Kentucky College of Medicine July 21, 2017 Disclosure of Commercial Interest Neither we 1
2 Disclosure of Commercial Interest nor our immediate family members have any relevant financial relationships with the manufacturers of any commercial products and/or providers of commercial services discussed in this CME activity. Disclosure of Commercial Interest We do not intend to discuss any unapproved or investigative use of a commercial product or device in this presentation. 2
3 Learning Objectives At the end of this presentation, learners will be able to Discuss the ALARA principle and principles of evidencebased imaging and how they relate to radiation safety and best practices Locate and use the American College of Radiology (ACR) Appropriateness Criteria to your patient s advantage Learning Objectives Evaluate when an imaging study is indicated and when none is needed When indicated, choose the most appropriate study for the workup of Vomiting in an infant up to 3 months of age Suspected malrotation/midgut volvulus 3
4 Learning Objectives Distinguish among modified barium swallow (MBS), contrast swallow, e.g., barium swallow, upper GI series (UGI), and small bowel follow through (SBFT) Indicate when barium should be used and when water soluble contrast is needed Learning Objectives When indicated, choose the most appropriate study for the work up of Head trauma (which may or may not be accidental) Suspected nonaccidental trauma (NAT) 4
5 Learning Objectives Identify fractures that are common in (NAT) When indicated, choose the most appropriate study for the work up of the limping child, ages 0 5 years Restate a useful mnemonic for classifying a common type of pediatric specific fracture ALARA The ALARA Principle As Low As Reasonably Achievable 5
6 The ALARA Principle AS LOW AS REASONABLY ACHIEVABLE: Exactly where we need to keep ionizing radiation exposure in children What s REASONABLY ACHIEVABLE? Reasonably Achievable Sometimes a study with no ionizing radiation will answer your clinical question Ultrasound MRI Sometimes no imaging examination is needed 6
7 IMAGE GENTLY Campaign Launched in January 2008 by Society for Pediatric Radiology (SPR) Pledge taken by tens of thousands of medical professionals CT protocols can be downloaded free of charge If you wish, you can go online and take the Image Gently pledge 7
8 Imaging Modalities CT, Fluoro, MRI, US, X rays (Radiographs) Let s review which imaging modalities use ionizing radiation and which do not Imaging Modalities and Ionizing Radiation YES NO CT Fluoroscopy Nuclear medicine MRI Ultrasound X rays (radiographs) 8
9 RADIATION SAFETY NOT having a physics lecture today CUNooz.com Ionizing Radiation Absorbed dose (mgy) Effective dose (msv) 9
10 Ionizing Radiation 1 Background radiation 3 msv/yr (millisieverts per year) 67% from Radon exposure Occupational exposure msv/yr Above background exposure Ionizing Radiation What s the big deal? Theoretical cancer risk Based on cumulative dose 10
11 Ionizing Radiation Exposure and Cancer Several studies show association between risk of cancer and increased use of CT scans 2 Head Chest Abd/Pelvis Total Dose (msv) Projected Cancers Decrease #scansby 33% Decrease dose from 75%ile to median Ionizing Radiation Exposure and Cancer Association Causality 11
12 Evidence Based Imaging (EBI) The right thing to do Pediatric radiologists know how to do it and are happy to help anyone who wants to learn more Together, we can do this! Evidence Based Imaging (EBI) Sounds good (but we need to define it) 12
13 Evidence Based Imaging (EBI) clinical information + physician s/clinician s experience + patient s/parent s/caregiver s expectations + best available evidence most appropriate imaging study Evidence Based Imaging (EBI) clinical information + physician s/clinician s experience + patient s/parent s/caregiver s expectations + best available evidence most appropriate imaging study 13
14 Pediatric Evidence Based Imaging The American College of Radiology (ACR) Appropriateness Criteria Quality initiative Decision support tool to help you order the right imaging study, the first time ACR Appropriateness Criteria For a given clinical scenario, e.g., vomiting in infants up to 3 months of age, the ACR rates the appropriateness of an imaging study and stratifies it with regard to radiation dose 14
15 ACR Appropriateness Criteria Appropriateness Rating Scale 1, 2, and 3: Usually not appropriate 4, 5, and 6: May be appropriate 7, 8, and 9: Usually appropriate The American College of Radiology (ACR) Appropriateness Criteria Radiation Dose 0 15
16 ACR Appropriateness Criteria No cost data dreamstime.com Flickr.com Imaging Studies Relative Costs $ MRI > CT > US > X rays (Radiographs) What about Fluoroscopy ( Fluoro )? $ CT > Fluoro > X rays 16
17 Imaging Studies Relative Costs And what about Nuclear Medicine? Differences in cost among various Nuclear Medicine examinations can be considerable, e.g., PET scan, $1300 Bone scan, $375 Cost of Imaging Studies 1,3 Mean Radiation (msv) CXR Equivalents Charges (US$) CXR KUB/Abdomen Head CT without contrast Chest CT without contrast Abd/Pelvis with contrast DMSA or MAG MRI brain without contrast Ultrasound of (insert organ here) Adapted from References 1 and 3 17
18 Co$t$ of Imaging Studies Don t forget hidden and non monetary costs Sedation Patient and family stress Unintended consequences LOCATE ACR Appropriateness Criteria Get your device Open your browser Type ACR appr in the search bar 18
19 ACR Appropriateness Criteria Multiple Sections Breast Interventional Radiology Cardiac Gastrointestinal Radiation Oncology Musculoskeletal Neurologic Pediatric Thoracic Urologic Vascular 19
20 Back Pain ACR Appropriateness Criteria Pediatric Topics Developmental dysplasia of the hip Fever without source or Unknown Origin Head trauma Headache Hematuria 20
21 ACR Appropriateness Criteria Pediatric Topics Limping child age 0 to 5 years Seizures Sinusitis Suspected physical abuse Urinary tract infection Vomiting in infants up to 3 months of age ACR Appropriateness Criteria Phone app from my personal phone 21
22 ACR Appropriateness Criteria Pediatric Topics PHONE APP BEST PRACTICES ALARA Principle Safety prioritized Patient centered/relationship centered Quality focused 22
23 BEST PRACTICES Don t order unnecessary studies, especially if they use ionizing radiation Babygram ordered when you actually need chest x ray or abdominal x ray but not both BOTTOM LINE: Avoid ordering imaging of anatomy that does not need to be evaluated BEST PRACTICES REDUCING EXPOSURE: GONADAL SHIELDS Ask your radiologists if they using gonadal shields in every examination for which they are appropriate 23
24 BEST PRACTICES REDUCING EXPOSURE: CONING OUT /COLLIMATION Check to see if appropriate collimation is used in studies at your institution For example, pelvis is coned out if you don t need to see it HISTORY: We need it! deadline.com practicallyhistorical.net SkoolShop.com deltaradio.net GrenadaChamberofCommerce mysql.com 24
25 Least Favorite ICD 10 Entity Other injury, unspecified body part * *We don t know what happened. We don t know where it happened. We just know something happened. Clinical Scenarios Let s start with the vomiting infant! 25
26 Vomiting Infant Vomiting vs. regurgitation Bilious vs. bloody vs. neither Solid H&P will yield the path to take CASE 1 4 day old infant with vomiting Benign prenatal course Spontaneous vaginal delivery at 40 weeks, discharged to home, breastfeeding at 48 hours As you re examining the child, he has an episode of bright green emesis all over you! 26
27 4 day old infant with bilious vomiting Do you need imaging? Yes! What s your strategy? VOMITING Choice of Imaging Studies Abdominal x rays Abdominal ultrasound Upper GI series Contrast enema Contrast swallow Modified Barium Swallow CT MRI 27
28 VOMITING Choice of Imaging Studies Abdominal x rays Abdominal ultrasound Upper GI series Contrast enema Contrast swallow Modified Barium Swallow CT MRI ACR Appropriateness Criteria Vomiting in an infant up to 3 months of age 4 Variants 28
29 ACR (American College of Radiology) Appropriateness Criteria American College of Radiology Date of origin: 1995 ACR Appropriateness Criteria Last review date: 201 Clinical Condition: Vomiting in Infants Up to 3 Months of Age Variant 1: Bilious vomiting in neonate up to 1 week old Radiologic Procedure Rating RRL* Comments X-ray abdomen 9 Initial x-ray will help determine further workup strategy. X-ray upper GI series 8 X-ray contrast enema 7 US abdomen (UGI tract) 4 Rating Scale: 1,2,3 Usually not appropriate; 4,5,6 May be appropriate; 7,8,9 Usually appropriate 0 *Relative Radiation Level Bilious emesis in neonate up to 1 week old 9 Abdominal x ray 8 Upper GI series X ray is important Evaluate for obstruction, proximal vs. distal Look for free air 7 Contrast enema 4 Abdominal ultrasound 29
30 ACR (American College of Radiology) Appropriateness Criteria Clinical Condition: Vomiting in Infants Up to 3 Months of Age Variant 2: Bilious vomiting in infant 1 week to 3 months old Radiologic Procedure Rating Comments RRL* X-ray upper GI series X-ray abdomen US abdomen (UGI tract) Tc-99m sulfur colloid reflux scintigraphy O Rating Scale: 1,2,3 Usually not appropriate; 4,5,6 May be appropriate; 7,8,9 Usually appropriate *Relative Radiation Level Bilious emesis in infant 1 wk to 3 mo old 9 Upper GI series 5 Abdominal x ray 3 Abdominal ultrasound 1 Nuclear medicine sulfur colloid reflux scintigraphy 30
31 ACR (American College of Radiology) Appropriateness Criteria Clinical Condition: Vomiting in Infants Up to 3 Months of Age Variant 3: Intermittent nonbilious vomiting since birth Radiologic Procedure Rating RRL* X-ray upper GI series US abdomen (UGI tract) 6 4 Comments 0 Tc-99m sulfur colloid reflux scintigraphy 3 May seldom provided useful information about gastric emptying and GER X-ray abdomen Rating Scale: 1,2,3 Usually not appropriate; 4,5,6 May be appropriate; 7,8,9 Usually appropriate 1 *Relative Radiation Level Intermittent nonbilious vomiting since birth The Spitter 6 Upper GI series 4 Abdominal ultrasound 3 Nuclear medicine gastric emptying study 1 Abdominal x ray Adapted from Reference 8 31
32 ACR (American College of Radiology) Appropriateness Criteria Clinical Condition: Vomiting in Infants Up to 3 Months of Age Variant 4: New-onset projectile nonbilious vomiting Radiologic Procedure Rating Comments RRL* US abdomen (UGI tract). X-ray upper GI series X-ray abdomen Tc-99m sulfur colloid reflux scintigraphy Rating Scale: 1,2,3 Usually not appropriate; 4,5,6 May be appropriate; 7,8,9 Usually appropriate *Relative Radiation Level New onset projectile nonbilious vomiting 9 Abdominal (pyloric) ultrasound 6 Upper GI series 2 Abdominal ultrasound 1 Nuclear medicine sulfur colloid reflux scintigraphy 32
33 Tables are followed by evidence Expert Panel on Pediatric Imaging: Dorothy Bulas, MD1; Siobhán L. McGrane, MD2; Brian D. Coley, MD3; Boaz Karmazyn, MD4; Lori L. Barr, MD5; Larry A. Binkovitz, MD6; Christopher E. Dory, MD7; Matthew Garber, MD8; Laura L. Hayes, MD9; Marc S. Keller, MD10; Abhaya V. Kulkarni, MD11; James S. Meyer, MD12; Sarah S. Milla, MD13; John S. Myseros, MD14; Charles Paidas, MD.15 Summary of Literature Review Introduction/Background Vomiting, or the forceful extrusion of gastric contents, is never normal in the neonate and usually occurs because of complete or partial obstruction somewhere along the course of the gastrointestinal (GI) tract between the stomach and cecum [1]. However, there may be difficulty in differentiating clinically between vomiting and regurgitation. StraightDopeDad 33
34 Oropharynx and Esophagus Common Clinical Concerns Difficulty swallowing Gagging Coughing? Aspiration Odynophagia? Esophageal stricture? Esophageal perforation/tear Fluoroscopy ( Fluoro ) studies Modified barium swallow Contrast swallow Barium Water soluble contrast Upper GI (UGI) series Small bowel follow through (SBFT) Contrast enema (barium or water soluble contrast) 34
35 Fluoroscopy Studies Which one to choose? Let s proceed in logical anatomic fashion Start with studies that evaluate more proximal problems and proceed to studies that evaluate more distally Modified Barium Swallow Performed in conjunction with our colleagues in Speech Pathology Primarily video (few, if any, static images) Focuses on mechanics of swallowing Best test to evaluate for aspiration! 35
36 Modified Barium Swallow (MBS) Does not evaluate for gastroesophageal (GE) reflux May not be able to be done immediately before or after upper GI series Why? Depends on requesting clinician s priorities What does that mean? If your primary concern is the mechanics of swallowing and/or aspiration, then Modified Barium Swallow is the 1 st test that should be done 36
37 What about concern for malrotation? If you re more concerned about the possibility of malrotation and midgut volvulus than aspiration, then UGI series should be done prior to Modified Barium Swallow Contrast Swallow If need to evaluate ESOPHAGUS for ulcer, perforation, or tear: Not modified barium swallow you re not primarily interested in swallowing mechanics and/or evaluating for aspiration You need a CONTRAST SWALLOW 37
38 Contrast Swallow Mouth to gastric fundus only Contrast Swallow Which contrast? Barium? Water soluble contrast? And if water soluble contrast, which one? 38
39 Contrast Swallow Mouth to gastric fundus only Best test if need to evaluate esophagus only, e.g., if concern for esophageal tear NO BARIUM if concern for PERFORATION/LEAK Use water soluble contrast if possibility of perforation/leak; same is true for abdomen Water Soluble Contrast For pediatric patients, NO high osmolality watersoluble contrast, either orally or by NG/OG tube or G tube NO EXCEPTIONS 39
40 Contrast Swallow Water soluble contrast Low osmolality water soluble contrast only NO High Osmolality Water Soluble Contrast Why not? If aspirated, high osmolality contrast can cause flash pulmonary edema 40
41 Contrast Swallow Barium or Water soluble Contrast Does NOT evaluate well for GE REFLUX Only evaluates from mouth to gastric fundus, not entire stomach If concern for abnormality involving Esophagus and Stomach Stomach only Stomach and Duodenum Duodenum only UGI series is the best choice for your patient because it evaluates Esophagus Stomach Duodenum (YES, DUODENUM is included) 41
42 Duodenum You DO NOT need a small bowel follow through (SBFT) to evaluate the duodenum Get an UGI series UGI Series From mouth to ligament of Treitz/ duodenojejunal junction 42
43 Upper GI Series Patient should be NPO! Upper GI Series Patient has an NG tube 43
44
45 UGI Series To exclude malrotation, must establish normal position of ligament of Treitz Contrast must progress through duodenum To left of spine s left pedicles Up to level of duodenal bulb Not either/or, it s both/and If not both/and, we have to call malrotation Left Pedicles 45
46 Evaluate for Malrotation and Midgut Volvulus Best test: UGI series Upper GI Series 46
47 47
48 Upper GI Series Radiologist called malrotation, no midgut volvulus Surgeons asked radiologist to repeat UGI Series WHY? 48
49 Repeat UGI Series Repeat UGI Series 49
50 Repeat UGI Series No malrotation What was wrong with the 1 st UGI series? Upper GI Series (UGI) First 2 Images, what s the problem? 50
51 UGI Series UGI Series Stomach is massively gas distended Difficult to determine rotation in this setting Stomach is exerting mass effect on duodenum May prevent contrast from passing to left of left pedicles and up to level of bulb Malrotation may or may not be present 51
52 UGI Series In this case, on repeat UGI series, there was no evidence of malrotation Take home point: Markedly distended stomach may contribute to appearance of malrotation when it is not present May need to drop NG/OG tube prior to UGI Abdominal Pain 52
53 Chronic Recurrent Abdominal Pain Abdominal Pain in Another Patient 53
54 Next Patient, Also Abdominal Pain Jejunum and Ileum Small bowel follow through (SBFT) Includes the terminal ileum (TI) MR Enterography (MRE) 54
55 Colon and Rectum Contrast enema Barium Water soluble contrast CT colonography MRI Summary of Fluoroscopy Studies From Proximal to Distal MBS: Mechanics of swallow, evaluates for aspiration Contrast swallow: Mouth to gastric fundus (does not evaluate well for GE reflux) UGI series: Mouth to duodenojejunal junction/ligament of Treitz, includes duodenum SBFT: Entire small bowel, including terminal ileum (usually see proximal colon) Contrast enema: Rectum and colon (usually reflux contrast into distal small bowel) 55
56 Evaluate for Intussusception Evaluation should begin with abdominal x rays No agreement on utility of x rays, except for excluding free air Most children with intussusception have abnormal abdominal x rays Intussusception: Diagnosis In addition to x rays, WHAT ELSE? ULTRASOUND! 56
57 Intussusception: Diagnosis WHY ULTRASOUND? Sensitivity: % In hands that are experienced, sensitivity of ultrasound is essentially 100% Specificity: % False positives Fecal content Inflammatory bowel disease Intramural hematoma Intussusception 57
58 Intussusception free fluid Intussusception free fluid 58
59 Intussusception fluid within the intussusception Intussusception intussuscepted bowel contains blood flow 59
60 Intussusception intussuscepted bowel contains blood flow Intussusception intussuscepted bowel, no internal blood flow 60
61 CASE 2 Head trauma You are helping staff your Community Hospital Emergency Department when EMS calls and says they are coming to your facility with an 18 monthold boy who wandered into the street and was struck by a car. Cervical spine precautions have been taken and they say they have been unable to awaken him with a sternal rub. When the child arrives he now has open eyes but is not interactive with his mother Should this child get a head CT? What if he was hit by a car but never had altered mental status? What if he was 8 years old and not 18 months? PECARN Head Trauma Prediction Rules <2 years old GCS <15, skull fracture palpated, altered mental status CT head without contrast (TBI 4.4%) Scalp hematoma anywhere but frontal, loss of consciousness for more than 5 seconds, parents state abnormal behavior or severe mechanism of injury (fall >3 ft, motor vehicle collision with ejection, rollover or fatality, pedestrian or bicycle against a vehicle without a helmet or hit in the head with a high impact object CT head without contrast versus observation (TBI 0.9%) No to all means observation (TBI<0.02%) Adapted from Reference 7 61
62 PECARN Head Trauma Prediction Rules 2 years and older GCS <15, signs of basilar skull fracture, altered mental status CT head without contrast(tbi 4.3%) Vomiting, LOC, severe headache, severe mechanism of injury (fall >5 ft, motor vehicle collision with ejection, rollover or fatality, pedestrian or bicycle against a vehicle without a helmet or hit in the head with a high impact object CT head without contrast versus observation (TBI 0.8%) No to all means observation (TBI<0.05%) Adapted from Reference 7 Clinical Condition: Head Trauma Child ACR Appropriateness Criteria Head Trauma Variant 1: Minor head injury (GCS >13) 2 years of age, without neurologic signs or highrisk factors, e.g., altered mental status, clinical evidence of basilar skull fracture. Excluding nonaccidental trauma. 3 CT head without IV contrast. This is a known low yield procedure 2 MRI head without IV contrast 1 All 11 studies: X ray head, CT head without and with IV contrast, CT head with IV contrast, CTA head with IV contrast, MRI head without and with IV contrast, MRA head without IV contrast, MRA head without and with IV contrast, cerebral arteriography, head ultrasound, FDG PET/CT head, and Tc 99m HMPAO SPECT head 62
63 ACR Appropriateness Criteria Head Trauma Clinical Condition: Head Trauma Child Variant 2: Minor head injury (GCS >13) <2 years of age, no neurologic signs or high risk factors, e.g., altered mental status, clinical evidence of basilar skull fracture. Excluding nonaccidental trauma. 3 X ray head. Refer to variant 4 if concern for nonaccidental trauma 3 CT head without IV contrast 3 MRI head without IV contrast Low yield in absence of signs of symptoms 2 MRA head without IV contrast 2 CTA head with IV contrast 1 All 6 studies: MRI head without and with IV contrast, MRA head without and with IV contrast, cerebral arteriography, head ultrasound, FDG PET/CT head, and Tc 99m HMPAO SPECT head Clinical Condition: Head Trauma Child ACR Appropriateness Criteria Head Trauma Variant 3: Moderate or severe head injury (GCS <13) or minor head trauma with high risk factors, e.g., altered mental status, clinical evidence of basilar skull fracture. Excluding nonaccidental trauma. 9 CT head without IV contrast 7 MRI head without IV contrast 4 MRA head without IV contrast. Consider if vascular injury is suspected. 4 CTA head with IV contrast. MRA is preferred. CTA may be used for problem solving. 3 MRA head without and with IV contrast 2 All 5 studies: X ray head, CT head without and with IV contrast, CT head with IV contrast, MRI head without and with IV contrast, and cerebral arteriography 1 All 3 studies: Head ultrasound, FDG PET/CT head, and Tc 99m HMPAO SPECT head 63
64 Clinical Condition: Head Trauma Child Variant 4: Suspected nonaccidental trauma ACR Appropriateness Criteria Head Trauma 9 CT head without IV contrast 8 MRI head without IV contrast 7 X ray head 3 MRA head without IV contrast. Consider if vascular injury is suspected. May be performed in conjunction with neck imaging. 3 Head ultrasound 2 All 4 studies: MRI head without and with IV contrast, MRA head without and with IV contrast, CT head without and with IV contrast, and CT head with IV contrast 1 All 4 studies: Cerebral arteriography, CTA head with IV contrast (MRA is preferred to CTA but CTA may be used for problem solving), FDG PET/CT head, and Tc 99m HMPAO SPECT head Clinical Condition: Head Trauma Child ACR Appropriateness Criteria Head Trauma Variant 5: Subacute head injury with cognitive and/or neurologic signs 8 MRI head without IV contrast. MRI is preferred, but imaging should not be delayed if it is not readily available 7 CT head without IV contrast 3 MRA head without IV contrast. Consider if vascular injury is suspected. 2 All 5 studies: MRI head without and with IV contrast (not indicated unless there is concern for infection), MRA head without and with IV contrast, CT head without and with IV contrast, CTA head with IV contrast, and cerebral arteriography 1 All 5 studies: X ray head, CT head with IV contrast, head ultrasound, FDG PET/CT head, and Tc 99m HMPAO SPECT head 64
65 CASE 3 11 week old with nonbilious vomiting and fussiness WHAT DO YOU SEE? How does the bowel gas pattern look? Normal or not? What else should we look at? 65
6/23/2017. What do you see? skull fracture
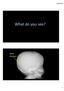 What do you see? skull fracture 1 Head CT On soft tissue windows, posterior soft tissues swelling and hemorrhage, no definite evidence of fracture Head CT On bone windows, fracture now seen subjacent to
What do you see? skull fracture 1 Head CT On soft tissue windows, posterior soft tissues swelling and hemorrhage, no definite evidence of fracture Head CT On bone windows, fracture now seen subjacent to
Back to Basics: What Imaging Test should I order? Jeanne G. Hill, M.D. Pediatric Radiology Medical University of South Carolina
 Back to Basics: What Imaging Test should I order? Jeanne G. Hill, M.D. Pediatric Radiology Medical University of South Carolina Disclosure Neither I nor any member of my immediate family has a relevant
Back to Basics: What Imaging Test should I order? Jeanne G. Hill, M.D. Pediatric Radiology Medical University of South Carolina Disclosure Neither I nor any member of my immediate family has a relevant
Overview. Imaging Indications. Paediatric Radiation Safety 2015/03/12. Paediatric radiation safety General guidelines Protocols
 Overview Paediatric radiation safety General guidelines Protocols Paediatric Radiation Safety Paediatric patients are unique Children are more susceptible to radiation induced cancer than adults Younger
Overview Paediatric radiation safety General guidelines Protocols Paediatric Radiation Safety Paediatric patients are unique Children are more susceptible to radiation induced cancer than adults Younger
Pediatric Radiology Update
 Pediatric Radiology Update Douglas Rivard, DO Vice Chairman, Radiology Dept Children s Mercy Hospital Asst Professor of Radiology University of Missouri-Kansas City Objectives Review radiation biology
Pediatric Radiology Update Douglas Rivard, DO Vice Chairman, Radiology Dept Children s Mercy Hospital Asst Professor of Radiology University of Missouri-Kansas City Objectives Review radiation biology
Vomiting in children: The good coordination between radiologists and pediatricians is the key to success
 Vomiting in children: The good coordination between radiologists and pediatricians is the key to success C. Santos Montón 1, M. T. Garzon Guiteria 2, A. Hortal Benito-Sendín 1, K. El Karzazi 1, P. Sanchez
Vomiting in children: The good coordination between radiologists and pediatricians is the key to success C. Santos Montón 1, M. T. Garzon Guiteria 2, A. Hortal Benito-Sendín 1, K. El Karzazi 1, P. Sanchez
Head injury in children
 Head injury in children Michael Kim, MD Department of Emergency Medicine University of Wisconsin- Madison #1 cause of death and disability Bimodal distribution 62,000 hospitalization 564,000 ED visits
Head injury in children Michael Kim, MD Department of Emergency Medicine University of Wisconsin- Madison #1 cause of death and disability Bimodal distribution 62,000 hospitalization 564,000 ED visits
Abdominal Pain in Pediatric Patients Image Gently
 Abdominal Pain in Pediatric Patients Image Gently Susan D. John, M.D. Baptist Health Emergency Radiology 2017 Disclosure I have no financial relationships with a commercial entity producing healthcarerelated
Abdominal Pain in Pediatric Patients Image Gently Susan D. John, M.D. Baptist Health Emergency Radiology 2017 Disclosure I have no financial relationships with a commercial entity producing healthcarerelated
Radiological Tests: Which One is Most Appropriate for My Patient?
 Radiological Tests: Which One is Most Appropriate for My Patient? Robert Hartman, M.D. 2016 MFMER slide-1 Disclosures No Disclosures 2016 MFMER slide-2 Objectives Discuss tools to aid in the ordering of
Radiological Tests: Which One is Most Appropriate for My Patient? Robert Hartman, M.D. 2016 MFMER slide-1 Disclosures No Disclosures 2016 MFMER slide-2 Objectives Discuss tools to aid in the ordering of
RADIOLOGY REQUEST MANUAL. (615)
 RADIOLOGY REQUEST MANUAL www.vanderbiltchildrens.com RADIOLOGY REQUEST MANUAL EXAM PROTOCOL QUESTIONS? Please call: DIAGNOSTIC RADIOLOGY (X-RAY) Pager (615) 835-1714 CT (615) 936-4920 MRI (615) 936-4933
RADIOLOGY REQUEST MANUAL www.vanderbiltchildrens.com RADIOLOGY REQUEST MANUAL EXAM PROTOCOL QUESTIONS? Please call: DIAGNOSTIC RADIOLOGY (X-RAY) Pager (615) 835-1714 CT (615) 936-4920 MRI (615) 936-4933
Imaging Children with Acute Abdominal Pain -- Role/Protocols of US, CT, MR
 Imaging Children with Acute Abdominal Pain -- Role/Protocols of US, CT, MR Kimberly E. Applegate, MD, MS Emory University Financial disclosures: AIM (American Imaging Management) radiation protection advisory
Imaging Children with Acute Abdominal Pain -- Role/Protocols of US, CT, MR Kimberly E. Applegate, MD, MS Emory University Financial disclosures: AIM (American Imaging Management) radiation protection advisory
n Make tremendous difference in patients lives: n Diagnosing or excluding disease and injury n Evaluating response to therapy
 Imaging: Choosing the Appropriate Exam Rob Milman, MD Austin Radiological Association What is a Radiologist? A physician who specializes in diagnosing and treating disease and injury by using medical imaging
Imaging: Choosing the Appropriate Exam Rob Milman, MD Austin Radiological Association What is a Radiologist? A physician who specializes in diagnosing and treating disease and injury by using medical imaging
Steven Aaron Ross, M.D. Pediatric Radiologist El Paso Imaging Consultants El Paso Children s Hospital
 Steven Aaron Ross, M.D. Pediatric Radiologist El Paso Imaging Consultants El Paso Children s Hospital I will prescribe regimens for the good of my patients according to my ability and my judgment and never
Steven Aaron Ross, M.D. Pediatric Radiologist El Paso Imaging Consultants El Paso Children s Hospital I will prescribe regimens for the good of my patients according to my ability and my judgment and never
Pediatric Imaging Spine MRI and Spine CT Test Request Tip Sheet
 Pediatric Imaging Spine MRI and Spine CT MRI is almost always preferred over CT scan; if ordering CT, CLEARLY document why MRI is not appropriate. In cases of back pain without red flags, six weeks of
Pediatric Imaging Spine MRI and Spine CT MRI is almost always preferred over CT scan; if ordering CT, CLEARLY document why MRI is not appropriate. In cases of back pain without red flags, six weeks of
2017 OPTIONS FOR INDIVIDUAL MEASURES: REGISTRY ONLY. MEASURE TYPE: Efficiency
 Measure #416: Emergency Medicine: Emergency Department Utilization of CT for Minor Blunt Head Trauma for Patients Aged 2 Through 17 Years - National Quality Strategy Domain: Efficiency and Cost Reduction
Measure #416: Emergency Medicine: Emergency Department Utilization of CT for Minor Blunt Head Trauma for Patients Aged 2 Through 17 Years - National Quality Strategy Domain: Efficiency and Cost Reduction
PEDIATRIC EMERGENCY DEPARTMENT CLINICAL GUIDELINE: GI SURGICAL EMERGENCIES: VOMITING
 GI SURGICAL EMERGENCIES: VOMITING PYLORIC STENOSIS Population: Infants: onset between 2-5 weeks of age 1 in 250 births Male: female ratio 4:1 Familial incidence History: No vomiting in the first few weeks
GI SURGICAL EMERGENCIES: VOMITING PYLORIC STENOSIS Population: Infants: onset between 2-5 weeks of age 1 in 250 births Male: female ratio 4:1 Familial incidence History: No vomiting in the first few weeks
of Trauma Assembly 27 th Page 1
 Eastern Association for the Surgery of Trauma 27 th Annual Scientific Assembly Sunrise Session 08 To Scan or Not To Scan Thatt is the Question January 16, 2014 Waldorf Astoria Naples Naples, Floridaa Page
Eastern Association for the Surgery of Trauma 27 th Annual Scientific Assembly Sunrise Session 08 To Scan or Not To Scan Thatt is the Question January 16, 2014 Waldorf Astoria Naples Naples, Floridaa Page
2016 PQRS OPTIONS FOR INDIVIDUAL MEASURES: CLAIMS, REGISTRY
 Measure #416: Emergency Medicine: Emergency Department Utilization of CT for Minor Blunt Head Trauma for Patients Aged 2 through 17 Years - National Quality Strategy Domain: Efficiency and Cost Reduction
Measure #416: Emergency Medicine: Emergency Department Utilization of CT for Minor Blunt Head Trauma for Patients Aged 2 through 17 Years - National Quality Strategy Domain: Efficiency and Cost Reduction
Basic Abdominal and Pelvic Imaging Concepts. David L. Smith, MD Assistant Professor of Radiology
 Basic Abdominal and Pelvic Imaging Concepts David L. Smith, MD Assistant Professor of Radiology Basic Imaging Concepts Contrast Resolution vs Spacial Resolution Spacial Resolution......refers to the ability
Basic Abdominal and Pelvic Imaging Concepts David L. Smith, MD Assistant Professor of Radiology Basic Imaging Concepts Contrast Resolution vs Spacial Resolution Spacial Resolution......refers to the ability
created by high-voltage devices Examples include medical and dental x-rays, light, microwaves and nuclear energy
 What is radiation? Radiation is energy emitted from a source, that travels through space and can penetrate matter. Listed below are two types that we are exposed to and contribute to our overall radiation
What is radiation? Radiation is energy emitted from a source, that travels through space and can penetrate matter. Listed below are two types that we are exposed to and contribute to our overall radiation
PREAMBLE GENERAL DIAGNOSTIC RADIOLOGY
 PREAMBLE The General Diagnostic Radiology category is intended to cover the body of knowledge a practicing board certified Diagnostic Radiologist should know. Since the range of content relevant to the
PREAMBLE The General Diagnostic Radiology category is intended to cover the body of knowledge a practicing board certified Diagnostic Radiologist should know. Since the range of content relevant to the
Pediatric Imaging Spine MRI and Spine CT Test Request Tip Sheet
 Pediatric Imaging Spine MRI and Spine CT MRI is almost always preferred over CT scan; if ordering CT, CLEARLY document why MRI is not appropriate. In cases of ongoing back pain, six weeks of conservative
Pediatric Imaging Spine MRI and Spine CT MRI is almost always preferred over CT scan; if ordering CT, CLEARLY document why MRI is not appropriate. In cases of ongoing back pain, six weeks of conservative
Hirschprung s. Meconium plug R/S >1 R/S <1
 NEONATAL ABDOMINAL EMERGENCIES LOW OBSTRUCTION HIGH OBSTRUCTION INTESTINAL OBSTRUCTION High obstruction - proximal to mid-ileumileum Few dilated, air filled bowel loops Complete obstruction diagnosed by
NEONATAL ABDOMINAL EMERGENCIES LOW OBSTRUCTION HIGH OBSTRUCTION INTESTINAL OBSTRUCTION High obstruction - proximal to mid-ileumileum Few dilated, air filled bowel loops Complete obstruction diagnosed by
Interesting Pediatric ultrasound cases. Presented by: Falguni Patel (RDMS, RVT)
 Interesting Pediatric ultrasound cases Presented by: Falguni Patel (RDMS, RVT) Role of ultrasound to rule out Appendicitis Overview: Ultrasound is relatively inexpensive, safe and quick solution to rule
Interesting Pediatric ultrasound cases Presented by: Falguni Patel (RDMS, RVT) Role of ultrasound to rule out Appendicitis Overview: Ultrasound is relatively inexpensive, safe and quick solution to rule
Bilateral rib fractures 2 on right and 1 on left In different stages of healing, with left fracture older than right fractures
 More history: Seen by PCP yesterday because of vomiting and fussinesss. Called by ED today because Mom presents with same complaints. ED found nothing but got an abdominal x ray. ED now wants kid admitted
More history: Seen by PCP yesterday because of vomiting and fussinesss. Called by ED today because Mom presents with same complaints. ED found nothing but got an abdominal x ray. ED now wants kid admitted
Residents should be able to understand the role of imaging-guidance to facilitate common radiological procedures.
 Educational Goals & Objectives Internists provide continuing care for patients with a myriad of medical and psychosocial problems. During many patient encounters, the focus is on the diagnosis and treatment
Educational Goals & Objectives Internists provide continuing care for patients with a myriad of medical and psychosocial problems. During many patient encounters, the focus is on the diagnosis and treatment
Debra Pennington, MD Director of Imaging Dell Children s Medical Center
 Debra Pennington, MD Director of Imaging Dell Children s Medical Center 1 Gray (Gy) is 1 J of radiation energy/ 1 kg matter (physical quantity absorbed dose) Diagnostic imaging doses in mgy (.001 Gy)
Debra Pennington, MD Director of Imaging Dell Children s Medical Center 1 Gray (Gy) is 1 J of radiation energy/ 1 kg matter (physical quantity absorbed dose) Diagnostic imaging doses in mgy (.001 Gy)
 Page 1 of 5 Patient Safety: Radiation Dose in X-Ray and CT Exams What are x-rays and what do they do? X-rays are forms of radiant energy, like light or radio waves. Unlike light, x-rays can penetrate the
Page 1 of 5 Patient Safety: Radiation Dose in X-Ray and CT Exams What are x-rays and what do they do? X-rays are forms of radiant energy, like light or radio waves. Unlike light, x-rays can penetrate the
Chapter 14: Training in Radiology. DDSEP Chapter 1: Question 12
 DDSEP Chapter 1: Question 12 A 52-year-old white male presents for evaluation of sudden onset of abdominal pain and shoulder pain. His past medical history is notable for a history of coronary artery disease,
DDSEP Chapter 1: Question 12 A 52-year-old white male presents for evaluation of sudden onset of abdominal pain and shoulder pain. His past medical history is notable for a history of coronary artery disease,
Effective Utilization of Imaging. John V. Roberts, M.D. Premier Radiology Abdominal Imaging
 Effective Utilization of Imaging John V. Roberts, M.D. Premier Radiology Abdominal Imaging Safety Contrast and Radiation What to order Abdomen/Pelvis Brain/Spine Chest Musculoskeletal Ob/Gyn Head and Neck
Effective Utilization of Imaging John V. Roberts, M.D. Premier Radiology Abdominal Imaging Safety Contrast and Radiation What to order Abdomen/Pelvis Brain/Spine Chest Musculoskeletal Ob/Gyn Head and Neck
Radiology. Undergraduate Radiology Curriculum
 Radiology Undergraduate Radiology Curriculum April 2012 INTRODUCTION This curriculum is intended to form a framework for undergraduate learning and teaching in radiology. It refers to the relevant competencies
Radiology Undergraduate Radiology Curriculum April 2012 INTRODUCTION This curriculum is intended to form a framework for undergraduate learning and teaching in radiology. It refers to the relevant competencies
R-SCAN: Engaging Clinicians in Value-based Care
 R-SCAN: Engaging Clinicians in Value-based Care Nancy Fredericks, MBA R-SCAN Director rscan.org What is R-SCAN? A collaborative between referring clinicians and radiologists to improve patient care R-SCAN
R-SCAN: Engaging Clinicians in Value-based Care Nancy Fredericks, MBA R-SCAN Director rscan.org What is R-SCAN? A collaborative between referring clinicians and radiologists to improve patient care R-SCAN
Contrast Materials Patient Safety: What are contrast materials and how do they work?
 Contrast Materials Patient Safety: What are contrast materials and how do they work? Which imaging exams use contrast materials? How safe are contrast materials? How should I prepare for my imaging procedure
Contrast Materials Patient Safety: What are contrast materials and how do they work? Which imaging exams use contrast materials? How safe are contrast materials? How should I prepare for my imaging procedure
Patti Edwards, Senior Radiographer, West Herts Hospitals, UK. February Radiation Safety
 Patti Edwards, Senior Radiographer, West Herts Hospitals, UK. February 2008. Radiation Safety Sub -headings Background Radiation Effects of Radiation Safe Levels Effective Doses ALARA Principle Radiation
Patti Edwards, Senior Radiographer, West Herts Hospitals, UK. February 2008. Radiation Safety Sub -headings Background Radiation Effects of Radiation Safe Levels Effective Doses ALARA Principle Radiation
Objectives. Pediatric Mortality. Another belly pain. Gastroenteritis. Spewing & Pooing Child 4/18/16
 Gastro-tastrophies A Review of Pediatric GI Emergencies Objectives Discuss common presentations of Pediatric Abdominal Pain complaints Discuss work up and physical exam findings Discuss care, management
Gastro-tastrophies A Review of Pediatric GI Emergencies Objectives Discuss common presentations of Pediatric Abdominal Pain complaints Discuss work up and physical exam findings Discuss care, management
Suspected Foreign Body Ingestion
 Teresa Liang Suspected Foreign Body Ingestion 1. General Presentation Background: Of more than 100,000 cases of foreign body ingestion reported each year in the United States, 80% occur in children, with
Teresa Liang Suspected Foreign Body Ingestion 1. General Presentation Background: Of more than 100,000 cases of foreign body ingestion reported each year in the United States, 80% occur in children, with
Reviewing the recent literature to answer clinical questions: Should I change my practice?
 Reviewing the recent literature to answer clinical questions: Should I change my practice? JILL MILLER, MD PEM ATTENDING CHKD ASSISTANT PROFESSOR PEDIATRICS, EVMS Objectives Review the literature to answer
Reviewing the recent literature to answer clinical questions: Should I change my practice? JILL MILLER, MD PEM ATTENDING CHKD ASSISTANT PROFESSOR PEDIATRICS, EVMS Objectives Review the literature to answer
Managing Patient Dose in Computed Tomography (CT) INTERNATIONAL COMMISSION ON RADIOLOGICAL PROTECTION
 Managing Patient Dose in Computed Tomography (CT) International Commission on Radiological Protection Information abstracted from ICRP Publication 87 Available at www.icrp.org Task Group: M.M. Rehani,
Managing Patient Dose in Computed Tomography (CT) International Commission on Radiological Protection Information abstracted from ICRP Publication 87 Available at www.icrp.org Task Group: M.M. Rehani,
Spine MRI and Spine CT Test Request Tip Sheet
 Spine MRI and Spine CT With/Without Contrast CT, MRI The study considered best for a specific clinical scenario should be ordered. The second study should be done ONLY if the first study does not provide
Spine MRI and Spine CT With/Without Contrast CT, MRI The study considered best for a specific clinical scenario should be ordered. The second study should be done ONLY if the first study does not provide
3/30/18. Common Radiology Studies in Pediatric Surgery. Disclosure Information. Objectives
 Common Radiology Studies in Pediatric Surgery A Scenario Based Approach to Interpretation for the Pediatric Nurse and Provider presented by Elizabeth A. Paton, DNP, RN-BC, PNP-A, PPCNP-BC, CPEN, FAEN Disclosure
Common Radiology Studies in Pediatric Surgery A Scenario Based Approach to Interpretation for the Pediatric Nurse and Provider presented by Elizabeth A. Paton, DNP, RN-BC, PNP-A, PPCNP-BC, CPEN, FAEN Disclosure
Spine MRI and Spine CT Test Request Tip Sheet
 Spine MRI and Spine CT With/Without Contrast CT, MRI Studies should NOT be ordered simultaneously as dual studies (i.e., with and without contrast). Radiation exposure is doubled and both views are rarely
Spine MRI and Spine CT With/Without Contrast CT, MRI Studies should NOT be ordered simultaneously as dual studies (i.e., with and without contrast). Radiation exposure is doubled and both views are rarely
Course specification
 Al-Azhar University Faculty of Medicine for Men Course specification For Master of Radiodiagnosis ( 2014 2015 ) University : Al-Azhar Faculty : Medicine for men Course specification - Programmers on which
Al-Azhar University Faculty of Medicine for Men Course specification For Master of Radiodiagnosis ( 2014 2015 ) University : Al-Azhar Faculty : Medicine for men Course specification - Programmers on which
Spine MRI and Spine CT Test Request Tip Sheet
 Spine MRI and Spine CT With/Without Contrast CT, MRI The study considered best for a specific clinical scenario should be ordered. The second study should be done ONLY if the first study does not provide
Spine MRI and Spine CT With/Without Contrast CT, MRI The study considered best for a specific clinical scenario should be ordered. The second study should be done ONLY if the first study does not provide
X-rays How safe are they?
 X-rays How safe are they? Patient information Thirty years ago, X-rays were the only way to see what was going on inside your body. Now other methods of medical imaging are available, some using different
X-rays How safe are they? Patient information Thirty years ago, X-rays were the only way to see what was going on inside your body. Now other methods of medical imaging are available, some using different
Flouroscopy CT. Principal Modality (2): Case Report # [] Date accepted: 14 May 2015
![Flouroscopy CT. Principal Modality (2): Case Report # [] Date accepted: 14 May 2015 Flouroscopy CT. Principal Modality (2): Case Report # [] Date accepted: 14 May 2015](/thumbs/85/92263701.jpg) Radiological Category: Emergency Principal Modality (1): Principal Modality (2): Flouroscopy CT Case Report # [] Submitted by: Haider Virani, M.D. Faculty reviewer: Naga Chinapuvvula, MD Date accepted:
Radiological Category: Emergency Principal Modality (1): Principal Modality (2): Flouroscopy CT Case Report # [] Submitted by: Haider Virani, M.D. Faculty reviewer: Naga Chinapuvvula, MD Date accepted:
performed to help sway the clinician in what the appropriate diagnosis is, which can substantially alter the treatment of management.
 Hello, I am Maura Polansky at the University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center. I am a Physician Assistant in the Department of Gastrointestinal Medical Oncology and the Program Director for Physician
Hello, I am Maura Polansky at the University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center. I am a Physician Assistant in the Department of Gastrointestinal Medical Oncology and the Program Director for Physician
Imaging techniques in the diagnosis, staging and follow up of GI cancers. Moderators: Banke Agarwal, MD and Paul Schultz, MD
 Imaging techniques in the diagnosis, staging and follow up of GI cancers Moderators: Banke Agarwal, MD and Paul Schultz, MD Panelists Axel Grothey, MD Professor of Oncology Division of Medical Oncology
Imaging techniques in the diagnosis, staging and follow up of GI cancers Moderators: Banke Agarwal, MD and Paul Schultz, MD Panelists Axel Grothey, MD Professor of Oncology Division of Medical Oncology
Occult and Overt GI Bleeding: Small Bowel Imaging. Outline of Talk
 Occult and Overt GI Bleeding: Small Bowel Imaging Lauren B. Gerson MD, MSc Director of Clinical Research, GI Fellowship Program California Pacific Medical Center San Francisco, CA Outline of Talk Definition
Occult and Overt GI Bleeding: Small Bowel Imaging Lauren B. Gerson MD, MSc Director of Clinical Research, GI Fellowship Program California Pacific Medical Center San Francisco, CA Outline of Talk Definition
Spine MRI and Spine CT Test Request Tip Sheet
 Spine MRI and Spine CT MRI is almost always preferred over CT scan; if ordering CT, CLEARLY document why MRI is not appropriate. In cases of back pain without red flags, six weeks of multimodality supervised
Spine MRI and Spine CT MRI is almost always preferred over CT scan; if ordering CT, CLEARLY document why MRI is not appropriate. In cases of back pain without red flags, six weeks of multimodality supervised
RADPrimer Curriculum Breast Topics Covered Basic Intermediate 225
 Breast Anatomy & Normal Variants 11 Breast Imaging Modalities 13 BI RADS Lexicon 3 Mammography: Masses 9 Mammography: Calcifications 17 Mammography: Additional Findings 8 Ultrasound Features 10 Ultrasound
Breast Anatomy & Normal Variants 11 Breast Imaging Modalities 13 BI RADS Lexicon 3 Mammography: Masses 9 Mammography: Calcifications 17 Mammography: Additional Findings 8 Ultrasound Features 10 Ultrasound
McHenry Western Lake County EMS System Paramedic, EMT-B and PHRN Optional Continuing Education 2018 #10 Acute GI Bleeds
 McHenry Western Lake County EMS System Paramedic, EMT-B and PHRN Optional Continuing Education 2018 #10 Acute GI Bleeds Gastrointestinal bleeding is a very common problem in emergency medicine. Between
McHenry Western Lake County EMS System Paramedic, EMT-B and PHRN Optional Continuing Education 2018 #10 Acute GI Bleeds Gastrointestinal bleeding is a very common problem in emergency medicine. Between
A novel plain abdominal radiograph sign to diagnose malrotation with volvulus
 A novel plain abdominal radiograph sign to diagnose malrotation with volvulus Nataraja RM 1, Mahomed AA 1* 1. Department of Paediatric Surgery, Royal Alexandra Hospital for Sick Children, Brighton,UK *
A novel plain abdominal radiograph sign to diagnose malrotation with volvulus Nataraja RM 1, Mahomed AA 1* 1. Department of Paediatric Surgery, Royal Alexandra Hospital for Sick Children, Brighton,UK *
Radiology of the abdomen Lecture -1-
 Radiology of the abdomen Lecture -1- Objectives To know radiology modalities used in abdomen imaging mainly GI tract. To know advantages and disadvantages of each modality. To know indications and contraindications
Radiology of the abdomen Lecture -1- Objectives To know radiology modalities used in abdomen imaging mainly GI tract. To know advantages and disadvantages of each modality. To know indications and contraindications
3/14/2014 USED TO BE SIMPLE.. TO IMMOBILIZE OR NOT TO IMMOBILIZE.THAT IS THE QUESTION THE PROBLEM OLD THINKING
 USED TO BE SIMPLE.. TO IMMOBILIZE OR NOT TO IMMOBILIZE.THAT IS THE QUESTION Immobilization following injury used to be a simple decision--but no one was thinking. Up to 5 million people per year receive
USED TO BE SIMPLE.. TO IMMOBILIZE OR NOT TO IMMOBILIZE.THAT IS THE QUESTION Immobilization following injury used to be a simple decision--but no one was thinking. Up to 5 million people per year receive
Introduction to WVU Radiology
 Introduction to WVU Radiology Lana Winkler, MD Assistant Professor Department of Radiology Section of Cardiothoracic Imaging Special thanks to Jeffery P. Hogg, MD Radiology Orientation Objectives Why is
Introduction to WVU Radiology Lana Winkler, MD Assistant Professor Department of Radiology Section of Cardiothoracic Imaging Special thanks to Jeffery P. Hogg, MD Radiology Orientation Objectives Why is
Index. Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type.
 Index Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A Abdominal injuries clinical presentation of, 23 24 Abdominal trauma evaluation for pediatric surgeon, 59 74 background of, 60 colon and
Index Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A Abdominal injuries clinical presentation of, 23 24 Abdominal trauma evaluation for pediatric surgeon, 59 74 background of, 60 colon and
European evidence-based consensus on the use of imaging techniques in inflammatory bowel disease diagnosis and management
 European evidence-based consensus on the use of imaging techniques in inflammatory bowel disease diagnosis and management J. Martin-Comin Hospital U. Bellvitge Hospitalet de Llobregat Spain THE EUROPEAN
European evidence-based consensus on the use of imaging techniques in inflammatory bowel disease diagnosis and management J. Martin-Comin Hospital U. Bellvitge Hospitalet de Llobregat Spain THE EUROPEAN
Imaging for Pediatric Trauma and the Acute Patient What to Order When
 Imaging for Pediatric Trauma and the Acute Patient What to Order When Paula Shultz, MD Pediatric Radiologist Central Oregon Radiology Associates November 8, 2013 5 yr old male involved in multicar accident,
Imaging for Pediatric Trauma and the Acute Patient What to Order When Paula Shultz, MD Pediatric Radiologist Central Oregon Radiology Associates November 8, 2013 5 yr old male involved in multicar accident,
Radiology Rotation Educational Goals & Objectives for Internal Medicine
 Radiology Rotation Educational Goals & Objectives for Internal Medicine Internists provide continuing care for patients with a myriad of medical and psychosocial problems. During many patient encounters,
Radiology Rotation Educational Goals & Objectives for Internal Medicine Internists provide continuing care for patients with a myriad of medical and psychosocial problems. During many patient encounters,
Tracheoesophageal Fistula and Esophageal Atresia
 Patient and Family Education Tracheoesophageal Fistula and Esophageal Atresia What is tracheoesophageal fistula? The word fistula means abnormal connection. Tracheoesophageal fistula (TEF) is a condition
Patient and Family Education Tracheoesophageal Fistula and Esophageal Atresia What is tracheoesophageal fistula? The word fistula means abnormal connection. Tracheoesophageal fistula (TEF) is a condition
Managing Radiation Risk in Pediatric CT Imaging
 Managing Radiation Risk in Pediatric CT Imaging Mahadevappa Mahesh, MS, PhD, FAAPM, FACR, FACMP, FSCCT. Professor of Radiology and Cardiology Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine Chief Physicist
Managing Radiation Risk in Pediatric CT Imaging Mahadevappa Mahesh, MS, PhD, FAAPM, FACR, FACMP, FSCCT. Professor of Radiology and Cardiology Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine Chief Physicist
Avoidable Imaging Learning Collaborative: 2008 Mild Traumatic Brain Injury Clinical Policy Success Story BWH Head and PE CTs with Clinical Decision
 Avoidable Imaging Learning Collaborative: 2008 Mild Traumatic Brain Injury Clinical Policy Success Story BWH Head and PE CTs with Clinical Decision Support Using the Canadian CT Head Rule to Reduce Unnecessary
Avoidable Imaging Learning Collaborative: 2008 Mild Traumatic Brain Injury Clinical Policy Success Story BWH Head and PE CTs with Clinical Decision Support Using the Canadian CT Head Rule to Reduce Unnecessary
Neonatal intestinal obstruction: how to make etiological diagnosis?
 Neonatal intestinal obstruction: how to make etiological diagnosis? Poster No.: C-1414 Congress: ECR 2013 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: W. Mnari, M. Zguidi, A. Zrig, M. Maatouk, B. Hmida, R. Salem,
Neonatal intestinal obstruction: how to make etiological diagnosis? Poster No.: C-1414 Congress: ECR 2013 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: W. Mnari, M. Zguidi, A. Zrig, M. Maatouk, B. Hmida, R. Salem,
SALZBURG WEILL CORNELL/NYPH SEMINAR. Diagnostic Imaging 3-Year Curriculum. YEAR 1 (i.e. 2015, 2018, 2021, 2024)
 SALZBURG WEILL CORNELL/NYPH SEMINAR Diagnostic Imaging 3-Year Curriculum YEAR 1 (i.e. 2015, 2018, 2021, 2024) Course Directors: David W. Trost, MD, Franz Kainberger, MD Faculty: Gerd Bodner, MD, Marius
SALZBURG WEILL CORNELL/NYPH SEMINAR Diagnostic Imaging 3-Year Curriculum YEAR 1 (i.e. 2015, 2018, 2021, 2024) Course Directors: David W. Trost, MD, Franz Kainberger, MD Faculty: Gerd Bodner, MD, Marius
Neonatal intestinal obstruction: how to make etiological diagnosis?
 Neonatal intestinal obstruction: how to make etiological diagnosis? Poster No.: C-1414 Congress: ECR 2013 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: W. MNARI, M. Zguidi, A. Zrig, M. MAATOUK, B. Hmida, R. Salem,
Neonatal intestinal obstruction: how to make etiological diagnosis? Poster No.: C-1414 Congress: ECR 2013 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: W. MNARI, M. Zguidi, A. Zrig, M. MAATOUK, B. Hmida, R. Salem,
Therapeutic Enema for Intussusception
 Scan for mobile link. Therapeutic Enema for Intussusception Therapeutic enema is used to help identify and diagnose intussusception, a serious disorder in which one part of the intestine slides into another
Scan for mobile link. Therapeutic Enema for Intussusception Therapeutic enema is used to help identify and diagnose intussusception, a serious disorder in which one part of the intestine slides into another
2018 OPTIONS FOR INDIVIDUAL MEASURES: REGISTRY ONLY. MEASURE TYPE: Efficiency
 Quality ID #333: Adult Sinusitis: Computerized Tomography (CT) for Acute Sinusitis (Overuse) National Quality Strategy Domain: Efficiency and Cost Reduction 2018 OPTIONS FOR INDIVIDUAL MEASURES: REGISTRY
Quality ID #333: Adult Sinusitis: Computerized Tomography (CT) for Acute Sinusitis (Overuse) National Quality Strategy Domain: Efficiency and Cost Reduction 2018 OPTIONS FOR INDIVIDUAL MEASURES: REGISTRY
Esophageal Cancer. What is esophageal cancer?
 Scan for mobile link. Esophageal Cancer Esophageal cancer occurs when cancer cells develop in the esophagus. The two main types are squamous cell carcinoma and adenocarcinoma. Esophageal cancer may not
Scan for mobile link. Esophageal Cancer Esophageal cancer occurs when cancer cells develop in the esophagus. The two main types are squamous cell carcinoma and adenocarcinoma. Esophageal cancer may not
Gastroschisis Sequelae and Management
 Gastroschisis Sequelae and Management Mary Finn Gillian Lieberman, MD Primary Care Radiology Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center Harvard Medical School April 2014 Outline I. Definition and Epidemiology
Gastroschisis Sequelae and Management Mary Finn Gillian Lieberman, MD Primary Care Radiology Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center Harvard Medical School April 2014 Outline I. Definition and Epidemiology
Early in Life. Noboru Takamura, M.D., Ph.D.
 Health Risks of Radiation Exposure Early in Life Noboru Takamura, M.D., Ph.D. Diagnostic Radiologic Procedures In recent years, the largest source of general population exposure to radiation has shifted
Health Risks of Radiation Exposure Early in Life Noboru Takamura, M.D., Ph.D. Diagnostic Radiologic Procedures In recent years, the largest source of general population exposure to radiation has shifted
BENEFITS OF CT AND HOW LEADING ACADEMIC INSTITUTIONS ARE COMMUNICATING RISK TO PATIENTS. James A. Brink, MD Massachusetts General Hospital
 BENEFITS OF CT AND HOW LEADING ACADEMIC INSTITUTIONS ARE COMMUNICATING RISK TO PATIENTS James A. Brink, MD Massachusetts General Hospital BENEFITS OF CT Standard Axial Imaging Superb Anatomic Depiction
BENEFITS OF CT AND HOW LEADING ACADEMIC INSTITUTIONS ARE COMMUNICATING RISK TO PATIENTS James A. Brink, MD Massachusetts General Hospital BENEFITS OF CT Standard Axial Imaging Superb Anatomic Depiction
Case Whirlpool sign in midgut volvulus
 Case 11454 Whirlpool sign in midgut volvulus Emad El-din Althamer 1, Shagufta Jabeen 2, Nada Al-Assaf 1, Akram Jawad 1, Muhammad Hassan 1, Muhammad Fatani 1, Rumayan Al-Rumyan 1, A Aziz Mosabihi 1, Ahmeduddin
Case 11454 Whirlpool sign in midgut volvulus Emad El-din Althamer 1, Shagufta Jabeen 2, Nada Al-Assaf 1, Akram Jawad 1, Muhammad Hassan 1, Muhammad Fatani 1, Rumayan Al-Rumyan 1, A Aziz Mosabihi 1, Ahmeduddin
Good morning! July 24, 2014
 Good morning! July 24, 2014 Prep #1 A 2-year-old boy presents to your office with a 2-day history of swelling of the right eye. He has been otherwise well. There are scattered insect bites on his body,
Good morning! July 24, 2014 Prep #1 A 2-year-old boy presents to your office with a 2-day history of swelling of the right eye. He has been otherwise well. There are scattered insect bites on his body,
X-ray (Radiography) - Lower GI Tract
 Scan for mobile link. X-ray (Radiography) - Lower GI Tract Lower gastrointestinal tract radiography or lower GI uses a form of real-time x-ray called fluoroscopy and a barium-based contrast material to
Scan for mobile link. X-ray (Radiography) - Lower GI Tract Lower gastrointestinal tract radiography or lower GI uses a form of real-time x-ray called fluoroscopy and a barium-based contrast material to
Radiology of GI system diseases
 GI Cycle - Lecture 12 436 Teams Radiology of GI system diseases Objectives 1. 2. 3. To know common GIT Pathologies presentation. To understand step wise approach in requesting GIT Radiology Investigations.
GI Cycle - Lecture 12 436 Teams Radiology of GI system diseases Objectives 1. 2. 3. To know common GIT Pathologies presentation. To understand step wise approach in requesting GIT Radiology Investigations.
Radiation Dose in Pediatric Imaging
 Radiation Dose in Pediatric Imaging A Brief History of Radiology Dose: Why Does It Matter? Measuring Exposure and Dose Deterministic Effects Stochastic Effects Common Exams: What is the Risk? Reducing
Radiation Dose in Pediatric Imaging A Brief History of Radiology Dose: Why Does It Matter? Measuring Exposure and Dose Deterministic Effects Stochastic Effects Common Exams: What is the Risk? Reducing
Emergent Pediatric Ultrasound. Katharine Dennis, RDMS/RVT Tiffany Schultz, RDMS UNC Health Care Dept of General Ultrasound
 Emergent Pediatric Ultrasound Katharine Dennis, RDMS/RVT Tiffany Schultz, RDMS UNC Health Care Dept of General Ultrasound Introduction Learning Objectives Review common pediatric emergent ultrasound exams
Emergent Pediatric Ultrasound Katharine Dennis, RDMS/RVT Tiffany Schultz, RDMS UNC Health Care Dept of General Ultrasound Introduction Learning Objectives Review common pediatric emergent ultrasound exams
Colorectal Cancer Screening
 Scan for mobile link. Colorectal Cancer Screening What is colorectal cancer screening? Screening examinations are tests performed to identify disease in individuals who lack any signs or symptoms. The
Scan for mobile link. Colorectal Cancer Screening What is colorectal cancer screening? Screening examinations are tests performed to identify disease in individuals who lack any signs or symptoms. The
CLINICAL RADIATION SCIENCES (CLRS)
 Clinical Radiation Sciences (CLRS) 1 CLINICAL RADIATION SCIENCES (CLRS) CLRS 101. Introduction to Clinical Radiologic Sciences. 1 Hour. Semester course; 1 lecture hour. 1 credit. Presentation and discussion
Clinical Radiation Sciences (CLRS) 1 CLINICAL RADIATION SCIENCES (CLRS) CLRS 101. Introduction to Clinical Radiologic Sciences. 1 Hour. Semester course; 1 lecture hour. 1 credit. Presentation and discussion
Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease in Infants and Children
 Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease in Infants and Children 4 Marzo 2017 Drssa Chiara Leoni Drssa Valentina Giorgio pediatriagastro@gmail.com valentinagiorgio1@gmail.com Definitions: GER GER is the passage
Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease in Infants and Children 4 Marzo 2017 Drssa Chiara Leoni Drssa Valentina Giorgio pediatriagastro@gmail.com valentinagiorgio1@gmail.com Definitions: GER GER is the passage
CT Radiation Risks and Dose Reduction
 CT Radiation Risks and Dose Reduction Walter L. Robinson, M.S. D.A.B.S.N.M., D.A.B.M.P., D.A.B.R. Consultant Certified Medical Radiation Health & Diagnostic Imaging Physicist Medical Radiation and Children
CT Radiation Risks and Dose Reduction Walter L. Robinson, M.S. D.A.B.S.N.M., D.A.B.M.P., D.A.B.R. Consultant Certified Medical Radiation Health & Diagnostic Imaging Physicist Medical Radiation and Children
Radiology. Undergraduate Radiology Sample Questions
 Radiology Undergraduate Radiology Sample Questions April 2012 The following examples are offered of questions that might be used to assess undergraduate radiology. There are 3 different styles: An OSCE
Radiology Undergraduate Radiology Sample Questions April 2012 The following examples are offered of questions that might be used to assess undergraduate radiology. There are 3 different styles: An OSCE
73725x2 MRA Pelvis Runoff (to ankle) CTA Abdomen with & without CTA Cardiac Brain without 70551
 CT CT Myelogram MRI Abdomen without 74150 Cervical 62302 Abdomen / MRCP 74181 Abdomen with 74160 Thoracic 62303 Abdomen / MRCP with & without 74183 Abdomen with & without 74170 Lumbar 62304 Abdomen / Pelvis
CT CT Myelogram MRI Abdomen without 74150 Cervical 62302 Abdomen / MRCP 74181 Abdomen with 74160 Thoracic 62303 Abdomen / MRCP with & without 74183 Abdomen with & without 74170 Lumbar 62304 Abdomen / Pelvis
Objectives: Resources:
 Objectives: Realize the impact of Age : - Where/who are the history sources Recognize and interpret the : - Important symptoms - Important signs Resources: Davidson s. Slides Surgical recall. Raslan s
Objectives: Realize the impact of Age : - Where/who are the history sources Recognize and interpret the : - Important symptoms - Important signs Resources: Davidson s. Slides Surgical recall. Raslan s
Upper Gastrointestinal (GI) Tract X-ray (Radiography)
 Upper Gastrointestinal (GI) Tract X-ray (Radiography) What is Upper Gastrointestinal (GI) Tract Radiography? What are some common uses of the procedure? How should I prepare? What does the equipment look
Upper Gastrointestinal (GI) Tract X-ray (Radiography) What is Upper Gastrointestinal (GI) Tract Radiography? What are some common uses of the procedure? How should I prepare? What does the equipment look
Chapter 16 Worksheet Code It
 Name: Class: Date: ID: A Chapter 16 Worksheet 3 2 1 Code It True/False Indicate whether the statement is true or false. 1. CT scans generate three-dimensional images. 2. An ultrasound produces images of
Name: Class: Date: ID: A Chapter 16 Worksheet 3 2 1 Code It True/False Indicate whether the statement is true or false. 1. CT scans generate three-dimensional images. 2. An ultrasound produces images of
Benghazi University Faculty of Medicine Radiology
 Benghazi University Faculty of Medicine Radiology 1 1- General Information: Program on which the course is given: Bachelor of Medicine and Surgery. Departments: Medicine Course Title& Code: Radiology Total
Benghazi University Faculty of Medicine Radiology 1 1- General Information: Program on which the course is given: Bachelor of Medicine and Surgery. Departments: Medicine Course Title& Code: Radiology Total
 P R E S E N T S Dr. Mufa T. Ghadiali is skilled in all aspects of General Surgery. His General Surgery Services include: General Surgery Advanced Laparoscopic Surgery Surgical Oncology Gastrointestinal
P R E S E N T S Dr. Mufa T. Ghadiali is skilled in all aspects of General Surgery. His General Surgery Services include: General Surgery Advanced Laparoscopic Surgery Surgical Oncology Gastrointestinal
GI Grand Rounds. A A Lifetime of Abdominal Pain 12/9/2004 Tim Edwards
 GI Grand Rounds A A Lifetime of Abdominal Pain 12/9/2004 Tim Edwards PMH Aug 25, 1992 4 year old male presents to a pediatric gastroenterologist for primary complaint of anorexia, intermittent abdominal
GI Grand Rounds A A Lifetime of Abdominal Pain 12/9/2004 Tim Edwards PMH Aug 25, 1992 4 year old male presents to a pediatric gastroenterologist for primary complaint of anorexia, intermittent abdominal
A Trip Through the GI Tract: Common GI Diseases and Complaints. Jennifer Curtis, MD
 A Trip Through the GI Tract: Common GI Diseases and Complaints Jennifer Curtis, MD Colon Cancer How does it develop? Most cancers arise from polyps Over time these can turn into cancer Combination of genetic
A Trip Through the GI Tract: Common GI Diseases and Complaints Jennifer Curtis, MD Colon Cancer How does it develop? Most cancers arise from polyps Over time these can turn into cancer Combination of genetic
Overview of Abusive Head Trauma: What Everyone Needs to Know. 11 th Annual Keeping Children Safe Conference Boise, ID October 17, 2012
 Overview of Abusive Head Trauma: What Everyone Needs to Know 11 th Annual Keeping Children Safe Conference Boise, ID October 17, 2012 Deborah Lowen, MD Associate Professor Pediatrics Director, Child Abuse
Overview of Abusive Head Trauma: What Everyone Needs to Know 11 th Annual Keeping Children Safe Conference Boise, ID October 17, 2012 Deborah Lowen, MD Associate Professor Pediatrics Director, Child Abuse
CASE CONFERENCE GASTRIC VOLVULUS PIKOM, MD NONGLUK, MD; RADIOLOGIST
 CASE CONFERENCE GASTRIC VOLVULUS PIKOM, MD NONGLUK, MD; RADIOLOGIST IDENTIFICATION DATA ผ ป วยเด กชายไทย อาย 13 ว น เช อชาต ไทย ส ญชาต ไทย ภ ม ล าเนา จ งหว ด อ ท ยธาน เข าร บการร กษาท รพ.มหาว ทยาล ยนเรศวรว
CASE CONFERENCE GASTRIC VOLVULUS PIKOM, MD NONGLUK, MD; RADIOLOGIST IDENTIFICATION DATA ผ ป วยเด กชายไทย อาย 13 ว น เช อชาต ไทย ส ญชาต ไทย ภ ม ล าเนา จ งหว ด อ ท ยธาน เข าร บการร กษาท รพ.มหาว ทยาล ยนเรศวรว
VOMITING. Tan Lay Zye
 VOMITING Tan Lay Zye Vomiting is a common symptom. It is a complex reflex behavioural response involving forceful expulsion of the stomach contents through oral cavity. Contents Emetic reflex Causes of
VOMITING Tan Lay Zye Vomiting is a common symptom. It is a complex reflex behavioural response involving forceful expulsion of the stomach contents through oral cavity. Contents Emetic reflex Causes of
PEDIATRIC MILD TRAUMATIC HEAD INJURY
 PEDIATRIC MILD TRAUMATIC HEAD INJURY October 2011 Quality Improvement Resources Illinois Emergency Medical Services for Children is a collaborative program between the Illinois Department of Public Health
PEDIATRIC MILD TRAUMATIC HEAD INJURY October 2011 Quality Improvement Resources Illinois Emergency Medical Services for Children is a collaborative program between the Illinois Department of Public Health
3/5/2015. Don t Electrocute Me!: Common Misconceptions in Imaging and Radiation Safety (and What to Do About Them)
 Don t Electrocute Me!: Common Misconceptions in Imaging and Radiation Safety (and What to Do About Them) Rebecca Milman Marsh, Ph.D. University of Colorado Department of Radiology Who in the Facility Works
Don t Electrocute Me!: Common Misconceptions in Imaging and Radiation Safety (and What to Do About Them) Rebecca Milman Marsh, Ph.D. University of Colorado Department of Radiology Who in the Facility Works
What is Your Diagnosis?
 What is Your Diagnosis? Izabela Ragan, Class of 2014 Signalment Species: Canine Breed: English Bulldog Sex: Male castrated Date of birth: 04/14/11 Presenting Complaint Dog was presented for vomiting and
What is Your Diagnosis? Izabela Ragan, Class of 2014 Signalment Species: Canine Breed: English Bulldog Sex: Male castrated Date of birth: 04/14/11 Presenting Complaint Dog was presented for vomiting and
Course specification
 Al-Azhar University Faculty of Medicine for Men Course specification For Doctorate of Radiodiagnosis ( 2014 2015 ) University : Al-Azhar Faculty : Medicine for Men Course specification - Programmers on
Al-Azhar University Faculty of Medicine for Men Course specification For Doctorate of Radiodiagnosis ( 2014 2015 ) University : Al-Azhar Faculty : Medicine for Men Course specification - Programmers on
Volvulus of the Gastrointestinal Tract: x-ray and CT imaging
 Volvulus of the Gastrointestinal Tract: x-ray and CT imaging Poster No.: C-0076 Congress: ECR 2013 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: E. Papadaki, S. Paschalidou, S. GIANNOU ; Rethymno, CR/ 1 2 2 3 1 3
Volvulus of the Gastrointestinal Tract: x-ray and CT imaging Poster No.: C-0076 Congress: ECR 2013 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: E. Papadaki, S. Paschalidou, S. GIANNOU ; Rethymno, CR/ 1 2 2 3 1 3
COMPETENCY REQUIREMENTS for the CERTIFICATION EXAMINATION
 COMPETENCY REQUIREMENTS for the 10/2013 CERTIFICATION BOARD FOR RADIOLOGY PRACTITIONER ASSISTANTS CERTIFICATION EXAMINATION Note: The competency requirements contained in this document will be in effect
COMPETENCY REQUIREMENTS for the 10/2013 CERTIFICATION BOARD FOR RADIOLOGY PRACTITIONER ASSISTANTS CERTIFICATION EXAMINATION Note: The competency requirements contained in this document will be in effect
Imaging Appropriateness: What s out there
 Imaging Appropriateness: What s out there Anish Kirpalani, MD FRCPC Staff Radiologist & Co-Director of MRI Department of Medical Imaging St. Michael's Hospital and University of Toronto Outline Why are
Imaging Appropriateness: What s out there Anish Kirpalani, MD FRCPC Staff Radiologist & Co-Director of MRI Department of Medical Imaging St. Michael's Hospital and University of Toronto Outline Why are
