EVALUATION OF CHRONIC HEADACHE BY COMPUTED TOMOGRAPHY: A RETROSPECTIVE STUDY
|
|
|
- Myles Bruce
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 EVALUATION OF CHRONIC HEADACHE BY COMPUTED TOMOGRAPHY: A RETROSPECTIVE STUDY Abstract: Anish Subedee Objective: To find out the proportion of intracranial abnormalities in patients with chronic headache without neurologic abnormality with the use of computed tomography (CT) and to compare the results with similar studies done previously. Materials and methods: CT images of 56 patients with chronic/recurrent headache and normal neurological findings were reviewed retrospectively. In 38 of 56 patients, both plain and contrast enhanced CT were done. Patients were divided into three groups according to the CT findings: those with no abnormality, those with minor abnormality (that did not alter patient management) and those with clinically significant abnormality. Proportion of patients in each group was found out and results were compared with previous studies with similar study design. Z test was used to evaluate whether the difference in proportions of patients in our study and previous study was statistically significant or not. Results: Of the 56 patients, 50 had normal CT (89.28 %), four had minor abnormality (7.14%) that did not alter patient management and two had significant lesions (3.57%). Contrast enhanced CT did not improve lesion detection. The minor findings detected were sub-ependymal calcifications of Tuberous sclerosis, calcified neurocysticercosis and old lacunar infarctions in external capsule. Clinically significant lesions detected were small ring enhancing lesion (neurocysticercosis or tuberculoma) and pineal cyst. Results of this study were compared with previous study with similar study design. The Z test showed that the difference in proportions in these studies was not statistically significant (p = for minor findings and p = for significant findings). Conclusion: The proportion of intracranial abnormalities detected by CT in this study was similar to that of previous studies. The use of intravenous contrast material administration did not improve its yield. This corroborates the evidence that the ability of CT scan in detecting significant intracranial pathology is poor in patients with chronic headache without neurologic abnormality. Key words: Chronic headache, CT Introduction: Headache is an almost universal experience and one of the most common symptoms in medical practice. It varies from an infrequent and trivial nuisance to a pointer to serious disease (1). Population based estimates suggest that about 4% of adults have daily or near daily headache (2). Although majority of the patients who present with chronic or recurrent headache have no neurologic abnormality, many patients undergo evaluation with computed tomography (CT) and more recently, Journal of Nobel Medical College (2012), Vol.1 No.2 57
2 magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) to exclude important abnormalities (3). The studies that have been done so far show that CT is of extremely low yield in patients who undergo imaging for chronic headache without neurologic abnormality (4-6). MR imaging, which is more sensitive than CT in detecting intracranial abnormality (7), has also been found to be unrewarding in evaluation of chronic or recurrent headache without neurological abnormality (3).Yet patient s demand for thorough and high-tech evaluation coupled with the low threshold among doctors for requesting these investigations has accelerated the use of CT and MRI despite the evidences against their use. Due to unavailability and higher cost of MRI, CT is requested more frequently in our set up. However no data exist in our country about the use of CT for evaluation of chronic headache and normal neurological finding. Thus, the purpose of this study was to evaluate the ability of CT in evaluation of chronic headache without neurologic abnormality. Specifically, this study aimed to find out the proportion of intracranial abnormalities in this group of patient and compare the results with similar studies done previously. Materials and methods: Setting: The study was carried out at department of radiology in Chitwan Medical College Teaching Hospital, Bharatpur, Nepal. The clinical data and the CT images of the patients undergoing cranial CT scan for the evaluation of chronic headache were retrospectively reviewed. Clinical information was collected from the requisition form supplied by the referring doctor. CT images were reviewed from the digital archive of the department. All the patients with the chief complaint of chronic / recurrent / long standing headache were included in the study. Exclusion criteria were as follows: Inadequately filled requisition forms Presence of other neurologic symptoms like trauma, seizures. Abnormal neurological finding in clinical examination. Patients with diagnosed CNS abnormality Of the consecutive 515 head CT scans done between and , only 56 scans were included in the study. CT scan: All the patients underwent scan with same 16 slice CT scanner (Bright speed, GE). Helical scan of the cranium from base of the skull to the vertex was done with collimation of 5 mm and multi-planar reconstruction at 0.6mm thickness when desirable. Although no definite departmental protocols were present for indication of intravenous contrast material administration, both plain and contrast enhanced scans were done in 38 patients when referring doctor or radiologist recommended its use. All the images were interpreted by the same radiologist and the imaging results were divided into three groups: i) those with no abnormality (normal scans) ii) those with minor abnormality (that did not alter patient management) iii) those with clinically significant abnormality (which may result in chronic/recurrent headache) Journal of Nobel Medical College (2012), Vol.1 No.2 58
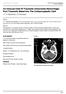
3 Results: Of the total 789 CT scans done during the study period, 515 scans (65.27%) were that of head and only 56 patients were included in the study. Of the 56 patients, 16 were male and 40 were female and the age range was 5-72 years. Of the 56 patients, 50 had normal CT (89.28 %), 4 had minor abnormality (7.14%) that did not alter patient management and 2 had significant lesions (3.57%). Of the patients with minor findings, one had sub-ependymal calcifications of Tuberous Sclerosis, two had calcified neurocysticercosis and one had old lacunar infarctions in b/l external capsule. Two minor findings were seen in male and two in female group. Of the significant findings detected, one was a small ring enhancing lesion (either neurocysticercosis or tuberculoma) in a 12 years girl and another was a pineal cyst measuring 14 mm in diameter in a 30 years female. The results of present study were compared with previous study with similar study design using CT for evaluation of headache. Dumas MD et al (6) had found that of the 402 CT scans 14 (3.48%) revealed minor findings and 4 (0.99%) revealed significant findings. Z test was used to evaluate whether the difference in proportions of patients in our study and the study of Dumas MD et al was statistically significant or not. For minor findings, the Z value was 1.47 (p =0.0708) and for significant findings Z value was 0.83 (p =0.2033). The difference in proportions in these studies was not significant. Age and sex wise distribution of the disease was not evaluated for statistical significance because of very small number of observations in individual group. Among the 56 patients, 38 patients had been investigated with both plain and contrast enhanced CT scans. Of these, none of patients showed additional advantage of contrast enhanced over plain CT. Statistical significance was not evaluated because of small number of patients and number of observations in one of the column being zero. Table 1: Age distribution: Age No. of patients < >60 3 Journal of Nobel Medical College (2012), Vol.1 No.2 59
4 Fig 1: Sub-ependymal calcifications in Tuberous Sclerosis Discussion: In evaluation of chronic headache without neurological abnormality, balancing patient s concern and available evidences regarding use of neuroimaging has been a tight rope walk for clinicians. In practice however tendency towards liberal use of imaging is prevalent. American Academy of Fig 2: Pineal cyst Neurology in 2000 had published practice guidelines for imaging in headache (8). Neuroimaging recommendations for nonacute headache are as follows: Consider neuroimaging in: Patients with an unexplained abnormal finding on the neurologic examination (Grade B) Journal of Nobel Medical College (2012), Vol.1 No.2 60
5 Patients with atypical headache features or headaches that do not fulfill the strict definition of migraine or other primary headache disorder (or have some additional risk factor, such as immune deficiency), when a lower threshold for neuroimaging may be applied (Grade C) Neuroimaging is not usually warranted in patients with migraine and a normal neurologic examination (Grade B). No evidence-based recommendations are established for the following: Presence or absence of neurologic symptoms (Grade C) Tension-type headache (Grade C) The US headache consortium (9) later said that the evidences were insufficient to define the role of neuroimaging in evaluation of chronic or recurrent headaches without neurological abnormality. However it made similar recommendations as that of American Academy of Neurology and further recommended larger study involving more than 1000 patients to settle the issue. Various studies have been done to evaluate the ability of neuro-imaging in detecting abnormalities in patients with chronic or recurrent headache without neurological abnormality. Definition of minor and significant abnormality however was not uniform among the studies performed earlier. Only two studies were found having study design similar to our study, one using CT and another using MR imaging for evaluation of headache. Hence the results of present study were compared only with the study of Dumas et al who had used CT for evaluation of headache. The present study found that 7.14% of patients had minor abnormality and 3.57% had significant abnormality mandating change in line of management. Presence of pineal cyst was taken as significant on the basis of a study conducted at Germany (10) in 51 patients with pineal cysts which showed significant causal relationship between pineal cyst and headache. Comparison of proportions of patients with minor and significant abnormality with prior study showed no significant statistical difference (6). Other studies also showed results similar to our study. According to a meta-analysis (9), significant clinical abnormalities detected in CT scans in patients with unspecified headache ranged from 0.0% to 6.7% in ten studies. Though MR imaging is considered more sensitive than CT, one study done in Japan concluded that MR is an unrewarding technique in evaluation of patients with chronic or recurrent headache and neurologic findings (3). Value of intravenous contrast material administration in this group of patient has also been evaluated previously by different authors (11,12). None of the studies have shown value of contrast material administration in this group of patient which is similar to our findings. Moreover contrast administration means additional cost to the patient along with the risk of adverse drug reactions as well. Some of the previous studies have tried to evaluate the cost effectiveness of CT scan in this group of patient (6,13). Both show very high cost per single significant finding. CT scan is one of the expensive investigations in our country also. Its use in evaluation of a Journal of Nobel Medical College (2012), Vol.1 No.2 61
6 problem which is universal in magnitude especially when the diagnostic yield is so little should be seriously re-evaluated in underdeveloped country like Nepal. Many patients seek attention for their headache because of the anxiety that they are having significant intracranial disease. It has been argued that the relief patient feels that he/she does not have any significant intracranial disease is a worthwhile outcome. However anxiety relief is subjective and difficult to measure. Furthermore, patients prone to anxiety may not feel completely relieved even after undergoing CT scan. There were few important limitations of this study. First, lack of records of neurological evaluation was an important limitation which might have misled us in patient selection. Our study being retrospective in nature, and most of the patients coming from out patient department, record of complete neurological evaluation could not be obtained. Second, small number of patients in the study was another limitation. The number of patients in individual sub group, in which patients were categorized according to their imaging findings, was subsequently very small. Conclusion: In the patients with chronic/recurrent headache without neurologic abnormality, CT detected minor abnormalities in 7.14% and significant abnormalities in 3.57% of patients. The use of intravenous contrast material administration did not improve its yield. This result is consistent with findings of previous studies. This further corroborates the evidence that the ability of CT scan in detecting significant intracranial pathology is poor in this group of patients. However large studies need to be done to establish the role of CT scan in evaluation of the patients with chronic headache. References: 1. Clarke CRA. Neurological Disease. In: Kumar P, Clark M, editors. Clinical Medicine. Sixth ed. Elsevier Limited; p Goadsby PJ, Raskin NH. Headache. In: Fauci AS, Braunwald EB, Casper DL et al, editors. Harrison s Principles of Internal Medicine. 17 th ed. McGraw Hill Medical; p Tsushima Y, Endo K. MR imaging in the evaluation of chronic or recurrent headache. Radiology 2005; 235: Practice parameter: the utility of neuroimaging in the evaluation of headache in patients with normal neurological examinations (summary statement). Report of the Quality Standards Subcommittee of the American Academy of Neurology. Neurology 1994; 44: Frishberg BM. The utility of neuroimaging in the evaluation of headache in patients with normal neurologic examinations. Neurology 1994; 44: Dumas MD, Pexman JH, Kreeft JH. Computed tomography evaluation of patients with chronic headache. [pulished correction appears in Can Med Assoc J. 1995; 152:158]. CMAJ 1994; 151: Haughton VM, Rimm AA, Sobocinski KA, et al. A blinded clinical comparison of MR imaging and CT in neuroradiology. Radiology1986; 160: Practice parameter: Evidence-based guidelines for migraine headache (an evidence based review). Report of the Quality Standards Subcommittee of the American Academy of Neurology. Neurology 1994; 44: Frishberg BM, Rosenberg JH, Matchar DB, et al. Evidence-based guideline in the primary care setting: neuroimaging in patients with nonacute headache. U.S. Headache Consortium Web site. Available at: Seifert CL, Woeller A, Valet M, et al. Headaches and pineal cyst: a case control study. Headache 2008 Mar; 48(3): Jordan JE, Ramirez GF, Bradley WG, Chen DY, Lightfoote JB, Song A. Economic and outcomes assessment of magnetic resonance Journal of Nobel Medical College (2012), Vol.1 No.2 62
7 imaging in the evaluation of headache. J Natl Med Assoc 2000; 92: Osborn RE, Alder DC, Mitchell CS. MR imaging of the brain in patients with migraine headaches. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 1991; 12: Kahn CE Jr, Sanders GD, Lyons EA et al. Computed tomography for non-traumatic headache: current utilization and cost effectiveness. Can Assoc Radiol J Jun; 44(3): Correspondence Address: Anish Subedee, Lecturer and Consultant Radiologist, Department of Radiology, Nobel medical College Teaching Hospital, Biratnagar-5, Nepal. anish_subedee@yahoo.com Journal of Nobel Medical College (2012), Vol.1 No.2 63
Pediatric Imaging Spine MRI and Spine CT Test Request Tip Sheet
 Pediatric Imaging Spine MRI and Spine CT MRI is almost always preferred over CT scan; if ordering CT, CLEARLY document why MRI is not appropriate. In cases of back pain without red flags, six weeks of
Pediatric Imaging Spine MRI and Spine CT MRI is almost always preferred over CT scan; if ordering CT, CLEARLY document why MRI is not appropriate. In cases of back pain without red flags, six weeks of
Pediatric Imaging Spine MRI and Spine CT Test Request Tip Sheet
 Pediatric Imaging Spine MRI and Spine CT MRI is almost always preferred over CT scan; if ordering CT, CLEARLY document why MRI is not appropriate. In cases of ongoing back pain, six weeks of conservative
Pediatric Imaging Spine MRI and Spine CT MRI is almost always preferred over CT scan; if ordering CT, CLEARLY document why MRI is not appropriate. In cases of ongoing back pain, six weeks of conservative
2018 OPTIONS FOR INDIVIDUAL MEASURES: REGISTRY ONLY. MEASURE TYPE: Efficiency
 Quality ID #419: Overuse Of Neuroimaging For Patients With Primary Headache And A Normal Neurological Examination National Quality Strategy Domain: Efficiency and Cost Reduction 2018 OPTIONS FOR INDIVIDUAL
Quality ID #419: Overuse Of Neuroimaging For Patients With Primary Headache And A Normal Neurological Examination National Quality Strategy Domain: Efficiency and Cost Reduction 2018 OPTIONS FOR INDIVIDUAL
Spine MRI and Spine CT Test Request Tip Sheet
 Spine MRI and Spine CT MRI is almost always preferred over CT scan; if ordering CT, CLEARLY document why MRI is not appropriate. In cases of back pain without red flags, six weeks of multimodality supervised
Spine MRI and Spine CT MRI is almost always preferred over CT scan; if ordering CT, CLEARLY document why MRI is not appropriate. In cases of back pain without red flags, six weeks of multimodality supervised
Spine MRI and Spine CT Test Request Tip Sheet
 Spine MRI and Spine CT With/Without Contrast CT, MRI Studies should NOT be ordered simultaneously as dual studies (i.e., with and without contrast). Radiation exposure is doubled and both views are rarely
Spine MRI and Spine CT With/Without Contrast CT, MRI Studies should NOT be ordered simultaneously as dual studies (i.e., with and without contrast). Radiation exposure is doubled and both views are rarely
Correlation of Computed Tomography findings with Glassgow Coma Scale in patients with acute traumatic brain injury
 Journal of College of Medical Sciences-Nepal, 2014, Vol-10, No-2 ABSTRACT OBJECTIVE To correlate Computed Tomography (CT) findings with Glasgow Coma Scale (GCS) in patients with acute traumatic brain injury
Journal of College of Medical Sciences-Nepal, 2014, Vol-10, No-2 ABSTRACT OBJECTIVE To correlate Computed Tomography (CT) findings with Glasgow Coma Scale (GCS) in patients with acute traumatic brain injury
Spine MRI and Spine CT Test Request Tip Sheet
 Spine MRI and Spine CT With/Without Contrast CT, MRI The study considered best for a specific clinical scenario should be ordered. The second study should be done ONLY if the first study does not provide
Spine MRI and Spine CT With/Without Contrast CT, MRI The study considered best for a specific clinical scenario should be ordered. The second study should be done ONLY if the first study does not provide
Spine MRI and Spine CT Test Request Tip Sheet
 Spine MRI and Spine CT With/Without Contrast CT, MRI The study considered best for a specific clinical scenario should be ordered. The second study should be done ONLY if the first study does not provide
Spine MRI and Spine CT With/Without Contrast CT, MRI The study considered best for a specific clinical scenario should be ordered. The second study should be done ONLY if the first study does not provide
Neuroimaging in Migraine Critically Appraised Topic (CAT)
 Neuroimaging in Migraine Critically Appraised Topic (CAT) PICOT Question: Does a head CT scan compared to no head CT scan change the management of a child with migraine? Clinical bottom line based on literature
Neuroimaging in Migraine Critically Appraised Topic (CAT) PICOT Question: Does a head CT scan compared to no head CT scan change the management of a child with migraine? Clinical bottom line based on literature
Original Article. Emergency Department Evaluation of Ventricular Shunt Malfunction. Is the Shunt Series Really Necessary? Raymond Pitetti, MD, MPH
 Original Article Emergency Department Evaluation of Ventricular Shunt Malfunction Is the Shunt Series Really Necessary? Raymond Pitetti, MD, MPH Objective: The malfunction of a ventricular shunt is one
Original Article Emergency Department Evaluation of Ventricular Shunt Malfunction Is the Shunt Series Really Necessary? Raymond Pitetti, MD, MPH Objective: The malfunction of a ventricular shunt is one
with susceptibility-weighted imaging and computed tomography perfusion abnormalities in diagnosis of classic migraine
 Emerg Radiol (2012) 19:565 569 DOI 10.1007/s10140-012-1051-2 CASE REPORT Susceptibility-weighted imaging and computed tomography perfusion abnormalities in diagnosis of classic migraine Christopher Miller
Emerg Radiol (2012) 19:565 569 DOI 10.1007/s10140-012-1051-2 CASE REPORT Susceptibility-weighted imaging and computed tomography perfusion abnormalities in diagnosis of classic migraine Christopher Miller
Magnetic Resonance Imaging. Basics of MRI in practice. Generation of MR signal. Generation of MR signal. Spin echo imaging. Generation of MR signal
 Magnetic Resonance Imaging Protons aligned with B0 magnetic filed Longitudinal magnetization - T1 relaxation Transverse magnetization - T2 relaxation Signal measured in the transverse plane Basics of MRI
Magnetic Resonance Imaging Protons aligned with B0 magnetic filed Longitudinal magnetization - T1 relaxation Transverse magnetization - T2 relaxation Signal measured in the transverse plane Basics of MRI
ORIGINAL ARTICLE. CT ASSESSMENT OF BRAIN VENTRICULAR SIZE BASED ON AGE AND SEX: A STUDY OF 112 CASES Vinoo Jacob 1, A.S.
 CT ASSESSMENT OF BRAIN VENTRICULAR SIZE BASED ON AGE AND SEX: A STUDY OF 112 CASES Vinoo Jacob 1, A.S. Krishna Kumar 2 HOW TO CITE THIS ARTICLE: Vinoo Jacob, A.S. Krishna Kumar. CT Assessment of Brain
CT ASSESSMENT OF BRAIN VENTRICULAR SIZE BASED ON AGE AND SEX: A STUDY OF 112 CASES Vinoo Jacob 1, A.S. Krishna Kumar 2 HOW TO CITE THIS ARTICLE: Vinoo Jacob, A.S. Krishna Kumar. CT Assessment of Brain
Detectability of unruptured intracranial aneurysms on thinslice non-contrast-enhanced CT
 Detectability of unruptured intracranial aneurysms on thinslice non-contrast-enhanced CT Poster No.: C-9 Congress: ECR 5 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: M. Nakadate, Y. Iwasa, M. Kishino, U. Tateishi;
Detectability of unruptured intracranial aneurysms on thinslice non-contrast-enhanced CT Poster No.: C-9 Congress: ECR 5 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: M. Nakadate, Y. Iwasa, M. Kishino, U. Tateishi;
An analysis of MRI findings in patients referred with fits
 An analysis of MRI findings in patients referred with fits Pallewatte AS 1, Alahakoon S 1, Senanayake G 1, Bulathsinghela BC 1 1 National Hospital of Sri Lanka, Colombo, Sri Lanka Abstract Introduction:
An analysis of MRI findings in patients referred with fits Pallewatte AS 1, Alahakoon S 1, Senanayake G 1, Bulathsinghela BC 1 1 National Hospital of Sri Lanka, Colombo, Sri Lanka Abstract Introduction:
Admission criteria to the Danish Brain Cancer Program are moderately associated with magnetic resonance imaging findings
 Dan Med J 60/3 March 2013 danish medical JOURNAL 1 Admission criteria to the Danish Brain Cancer Program are moderately associated with magnetic resonance imaging findings Thomas Winther Hill, Mie Kiszka
Dan Med J 60/3 March 2013 danish medical JOURNAL 1 Admission criteria to the Danish Brain Cancer Program are moderately associated with magnetic resonance imaging findings Thomas Winther Hill, Mie Kiszka
The Role of Magnetic Resonance Imaging and Computed Tomography of the Brain in First Episode of Psychosis
 The Role of Magnetic Resonance Imaging and Computed Tomography of the Brain in First Episode of Psychosis Poster No.: C-0816 Congress: ECR 2012 Type: Authors: Scientific Exhibit N. Khandanpour 1, N. Hoggard
The Role of Magnetic Resonance Imaging and Computed Tomography of the Brain in First Episode of Psychosis Poster No.: C-0816 Congress: ECR 2012 Type: Authors: Scientific Exhibit N. Khandanpour 1, N. Hoggard
UTILIZATION MANAGEMENT POLICY AND PROCEDURE MANUAL
 University of Florida, Pediatric Integrated Care System UTILIZATION MANAGEMENT POLICY AND PROCEDURE MANUAL Policy: Program(s): Approval Criteria for Neuroimaging of Headaches Title XIX and Title XXI Effective
University of Florida, Pediatric Integrated Care System UTILIZATION MANAGEMENT POLICY AND PROCEDURE MANUAL Policy: Program(s): Approval Criteria for Neuroimaging of Headaches Title XIX and Title XXI Effective
Subject: Brain CT. Original Effective Date: 11/7/2017. Policy Number: MCR: 600. Revision Date(s): Review Date:
 Subject: Brain CT Policy Number: MCR: 600 Revision Date(s): MHW Original Effective Date: 11/7/2017 Review Date: DISCLAIMER This Molina Clinical Review (MCR) is intended to facilitate the Utilization Management
Subject: Brain CT Policy Number: MCR: 600 Revision Date(s): MHW Original Effective Date: 11/7/2017 Review Date: DISCLAIMER This Molina Clinical Review (MCR) is intended to facilitate the Utilization Management
Hemodynamic patterns of status epilepticus detected by susceptibility weighted imaging (SWI)
 Hemodynamic patterns of status epilepticus detected by susceptibility weighted imaging (SWI) Poster No.: C-1086 Congress: ECR 014 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: J. AELLEN, E. Abela, R. Kottke, E. Springer,
Hemodynamic patterns of status epilepticus detected by susceptibility weighted imaging (SWI) Poster No.: C-1086 Congress: ECR 014 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: J. AELLEN, E. Abela, R. Kottke, E. Springer,
11. HEADACHE 1. Pablo Lapuerta, MD, Steven Asch, MD, MPH, and Kenneth Clark, MD, MPH
 11. HEADACHE 1 Pablo Lapuerta, MD, Steven Asch, MD, MPH, and Kenneth Clark, MD, MPH We identified articles on the evaluation and management of headache by conducting a MEDLINE search of English language
11. HEADACHE 1 Pablo Lapuerta, MD, Steven Asch, MD, MPH, and Kenneth Clark, MD, MPH We identified articles on the evaluation and management of headache by conducting a MEDLINE search of English language
Presence and severity of carotid siphon calcification on computed tomography images in mild cognitive impairment
 Presence and severity of carotid siphon calcification on computed tomography images in mild cognitive impairment Poster No.: C-2117 Congress: ECR 2013 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: S. Rutkauskas, S.
Presence and severity of carotid siphon calcification on computed tomography images in mild cognitive impairment Poster No.: C-2117 Congress: ECR 2013 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: S. Rutkauskas, S.
CT angiography and its role in the investigation of intracranial haemorrhage
 CT angiography and its role in the investigation of intracranial haemorrhage RD Magazine, 39, 458, 29-30 Dr M Igra Radiology SPR Leeds General Infirmary Dr I Djoukhadar Research fellow Wolfson Molecular
CT angiography and its role in the investigation of intracranial haemorrhage RD Magazine, 39, 458, 29-30 Dr M Igra Radiology SPR Leeds General Infirmary Dr I Djoukhadar Research fellow Wolfson Molecular
ANNOUNCING THE NEW STONY BROOK UNIVERSITY OUTPATIENT IMAGING CENTER
 ANNOUNCING THE NEW STONY BROOK UNIVERSITY OUTPATIENT IMAGING CENTER PROVIDING THE MOST ADVANCED DIAGNOSTICS FOR THE HIGHEST QUALITY OF CARE Call Our Dedicated Line: (631) 638-2121 When you need the benefit
ANNOUNCING THE NEW STONY BROOK UNIVERSITY OUTPATIENT IMAGING CENTER PROVIDING THE MOST ADVANCED DIAGNOSTICS FOR THE HIGHEST QUALITY OF CARE Call Our Dedicated Line: (631) 638-2121 When you need the benefit
Prevalence of venous sinus stenosis in Pseudotumor cerebri(ptc) using digital subtraction angiography (DSA)
 Prevalence of venous sinus stenosis in Pseudotumor cerebri(ptc) using digital subtraction angiography (DSA) Dr.Mohamed hamdy ibrahim MBBC,MSc,MD, PhD Neurology Degree Kings lake university (USA). Fellow
Prevalence of venous sinus stenosis in Pseudotumor cerebri(ptc) using digital subtraction angiography (DSA) Dr.Mohamed hamdy ibrahim MBBC,MSc,MD, PhD Neurology Degree Kings lake university (USA). Fellow
Introduction, use of imaging and current guidelines. John O Brien Professor of Old Age Psychiatry University of Cambridge
 Introduction, use of imaging and current guidelines John O Brien Professor of Old Age Psychiatry University of Cambridge Why do we undertake brain imaging in AD and other dementias? Exclude other causes
Introduction, use of imaging and current guidelines John O Brien Professor of Old Age Psychiatry University of Cambridge Why do we undertake brain imaging in AD and other dementias? Exclude other causes
ASKLEPIOS Course. July 20 21, 2018 Bangkok/Thailand
 This ASKLEPIOS course is implemented with great support and partnership of Guerbet and RCRT Education in partnership Course information This ESOR course aims to discuss the most important topics in neuroradiology.
This ASKLEPIOS course is implemented with great support and partnership of Guerbet and RCRT Education in partnership Course information This ESOR course aims to discuss the most important topics in neuroradiology.
Case 7391 Intraventricular Lesion
 Case 7391 Intraventricular Lesion Bastos Lima P1, Marques C1, Cabrita F2, Barbosa M2, Rebelo O3, Rio F1. 1Neuroradiology, 2Neurosurgery, 3Neuropathology, Coimbra University Hospitals, Portugal. University
Case 7391 Intraventricular Lesion Bastos Lima P1, Marques C1, Cabrita F2, Barbosa M2, Rebelo O3, Rio F1. 1Neuroradiology, 2Neurosurgery, 3Neuropathology, Coimbra University Hospitals, Portugal. University
HEADACHE 1 Pablo Lapuerta, M.D., and Steven Asch, M.D., M.P.H.
 - 253-13. HEADACHE 1 Pablo Lapuerta, M.D., and Steven Asch, M.D., M.P.H. We identified articles on the evaluation and management of headache by conducting a MEDLINE search of English language articles
- 253-13. HEADACHE 1 Pablo Lapuerta, M.D., and Steven Asch, M.D., M.P.H. We identified articles on the evaluation and management of headache by conducting a MEDLINE search of English language articles
A Study on Clinical and Etiological Factors of New-Onset Seizures in Adults
 Original Article Print ISSN: 2321-6379 Online ISSN: 2321-595X A Study on Clinical and Etiological Factors of New-Onset Seizures in Adults P. S. V. Ramana Murthy Associate Professor, Department of General
Original Article Print ISSN: 2321-6379 Online ISSN: 2321-595X A Study on Clinical and Etiological Factors of New-Onset Seizures in Adults P. S. V. Ramana Murthy Associate Professor, Department of General
Role of the Radiologist
 Diagnosis and Treatment of Blunt Cerebrovascular Injuries NORDTER Consensus Conference October 22-24, 2007 Clint W. Sliker, M.D. University of Maryland Medical Center R Adams Cowley Shock Trauma Center
Diagnosis and Treatment of Blunt Cerebrovascular Injuries NORDTER Consensus Conference October 22-24, 2007 Clint W. Sliker, M.D. University of Maryland Medical Center R Adams Cowley Shock Trauma Center
Ring-shaped Lateral Ventricular Nodules Detected with Brain MR Imaging
 Magn Reson Med Sci, Vol. 12, No. 2, pp. 105 110, 2013 2013 Japanese Society for Magnetic Resonance in Medicine doi:10.2463/mrms.2012-0044 MAJOR PAPER Ring-shaped Lateral Ventricular Nodules Detected with
Magn Reson Med Sci, Vol. 12, No. 2, pp. 105 110, 2013 2013 Japanese Society for Magnetic Resonance in Medicine doi:10.2463/mrms.2012-0044 MAJOR PAPER Ring-shaped Lateral Ventricular Nodules Detected with
CT and MR findings of systemic lupus erythematosus involving the brain: Differential diagnosis based on lesion distribution
 CT and MR findings of systemic lupus erythematosus involving the brain: Differential diagnosis based on lesion distribution Poster No.: C-2723 Congress: ECR 2010 Type: Educational Exhibit Topic: Neuro
CT and MR findings of systemic lupus erythematosus involving the brain: Differential diagnosis based on lesion distribution Poster No.: C-2723 Congress: ECR 2010 Type: Educational Exhibit Topic: Neuro
Computed tomography. Department of Radiology, University Medical School, Szeged
 Computed tomography Department of Radiology, University Medical School, Szeged voxel +1-4 +2 +5 +3 +1 0-2 pixel -2 0 +1-4 -6 +5 +2 +1 Department of Radiology, University Medical School, Szeged
Computed tomography Department of Radiology, University Medical School, Szeged voxel +1-4 +2 +5 +3 +1 0-2 pixel -2 0 +1-4 -6 +5 +2 +1 Department of Radiology, University Medical School, Szeged
Radiology. General radiology department. X-ray
 The radiology directorate provides a diagnostic, interventional and therapeutic service for its local population, and a tertiary service for the region. It also provides support to some national work such
The radiology directorate provides a diagnostic, interventional and therapeutic service for its local population, and a tertiary service for the region. It also provides support to some national work such
COMPUTED TOMOGRAPHY COURSE
 CT Radiography RAD 421 4 th year semester 2 Course Lecture Tutorial Practical Credit hours CT Radiography 2-1 2 Course Description The course explores the basic physical and technical principles of CT
CT Radiography RAD 421 4 th year semester 2 Course Lecture Tutorial Practical Credit hours CT Radiography 2-1 2 Course Description The course explores the basic physical and technical principles of CT
The Low Sensitivity of Fluid-Attenuated Inversion-Recovery MR in the Detection of Multiple Sclerosis of the Spinal Cord
 The Low Sensitivity of Fluid-Attenuated Inversion-Recovery MR in the Detection of Multiple Sclerosis of the Spinal Cord Mark D. Keiper, Robert I. Grossman, John C. Brunson, and Mitchell D. Schnall PURPOSE:
The Low Sensitivity of Fluid-Attenuated Inversion-Recovery MR in the Detection of Multiple Sclerosis of the Spinal Cord Mark D. Keiper, Robert I. Grossman, John C. Brunson, and Mitchell D. Schnall PURPOSE:
5 Diagnosis. Timely diagnosis. Back to contents
 5 5 Diagnosis Back to contents Study Advisory Group questions: Are there delays in diagnosis? Is there variation in how the cerebral palsies are described? signs can fluctuate, to avoid over-diagnosis
5 5 Diagnosis Back to contents Study Advisory Group questions: Are there delays in diagnosis? Is there variation in how the cerebral palsies are described? signs can fluctuate, to avoid over-diagnosis
Child Neurology Elective PL1 Rotation
 PL1 Rotation The neurology elective is available to first year residents in either a 2 or 4 week block rotation. The experience will include performing inpatient consultations, attending outpatient clinics
PL1 Rotation The neurology elective is available to first year residents in either a 2 or 4 week block rotation. The experience will include performing inpatient consultations, attending outpatient clinics
CT & MRI Evaluation of Brain Tumour & Tumour like Conditions
 CT & MRI Evaluation of Brain Tumour & Tumour like Conditions Dr. Anjana Trivedi 1, Dr. Jay Thakkar 2, Dr. Maulik Jethva 3, Dr. Ishita Virda 4 1 M.D. Radiology, Professor and Head, P.D.U. Medical College
CT & MRI Evaluation of Brain Tumour & Tumour like Conditions Dr. Anjana Trivedi 1, Dr. Jay Thakkar 2, Dr. Maulik Jethva 3, Dr. Ishita Virda 4 1 M.D. Radiology, Professor and Head, P.D.U. Medical College
Natural Evolution of Lumbar Spinal Stenosis
 Natural Evolution of Lumbar Spinal Stenosis William R. Sears, MB BS FRACS Wentworth Spine Clinic, Sydney, Australia MUST KNOW An understanding of the natural evolution of lumbar spinal stenosis (LSS) is
Natural Evolution of Lumbar Spinal Stenosis William R. Sears, MB BS FRACS Wentworth Spine Clinic, Sydney, Australia MUST KNOW An understanding of the natural evolution of lumbar spinal stenosis (LSS) is
DIAGNOSTIC TECHNIQUES. Background:
 e-issn 1643-3750 DOI: 10.12659/MSM.890719 Received: 2014.03.19 Accepted: 2014.05.15 Published: 2014.09.02 Multi-Slice Computed Tomography 5-Minute Delayed Scan is Superior to Immediate Scan after Contrast
e-issn 1643-3750 DOI: 10.12659/MSM.890719 Received: 2014.03.19 Accepted: 2014.05.15 Published: 2014.09.02 Multi-Slice Computed Tomography 5-Minute Delayed Scan is Superior to Immediate Scan after Contrast
PEDIATRIC MILD TRAUMATIC HEAD INJURY
 PEDIATRIC MILD TRAUMATIC HEAD INJURY October 2011 Quality Improvement Resources Illinois Emergency Medical Services for Children is a collaborative program between the Illinois Department of Public Health
PEDIATRIC MILD TRAUMATIC HEAD INJURY October 2011 Quality Improvement Resources Illinois Emergency Medical Services for Children is a collaborative program between the Illinois Department of Public Health
Original Article. Evaluation of The Role and Utility of Neuroimaging In New Onset Seizures Presenting To The Emergency Department
 Original Article Evaluation of The Role and Utility of Neuroimaging In New Onset Seizures Presenting To The Emergency Department Lalit Kumar 1, Vipin Kumar 2, Hardeep Singh Gill 3 *, G Avasthi 4, Gagandeep
Original Article Evaluation of The Role and Utility of Neuroimaging In New Onset Seizures Presenting To The Emergency Department Lalit Kumar 1, Vipin Kumar 2, Hardeep Singh Gill 3 *, G Avasthi 4, Gagandeep
By: Abdulrahman A. Al-Humaizi Rhinology Fellow, F1
 05.04.2016 By: Abdulrahman A. Al-Humaizi Rhinology Fellow, F1 Objectives Introduction Materials and methods Results Discussion Algorithm Conclusion Introduction Risk of meningitis, which has been reported
05.04.2016 By: Abdulrahman A. Al-Humaizi Rhinology Fellow, F1 Objectives Introduction Materials and methods Results Discussion Algorithm Conclusion Introduction Risk of meningitis, which has been reported
C2 COMPLETION INSTRUCTIONS
 The C2 Form is completed for each screening exam at T0, T1, and T2. The C2 Form is to be completed by each of the following ACRIN-NLST study staff: the research associate (study coordinator), CT technologist,
The C2 Form is completed for each screening exam at T0, T1, and T2. The C2 Form is to be completed by each of the following ACRIN-NLST study staff: the research associate (study coordinator), CT technologist,
Redgrave JN, Coutts SB, Schulz UG et al. Systematic review of associations between the presence of acute ischemic lesions on
 6. Imaging in TIA 6.1 What type of brain imaging should be used in suspected TIA? 6.2 Which patients with suspected TIA should be referred for urgent brain imaging? Evidence Tables IMAG1: After TIA/minor
6. Imaging in TIA 6.1 What type of brain imaging should be used in suspected TIA? 6.2 Which patients with suspected TIA should be referred for urgent brain imaging? Evidence Tables IMAG1: After TIA/minor
WEB device for treating brain (intracranial) aneurysms
 WEB device for treating brain (intracranial) aneurysms This leaflet explains more about the WEB device, including the benefits, risks and any alternatives and what you can expect when you come to hospital.
WEB device for treating brain (intracranial) aneurysms This leaflet explains more about the WEB device, including the benefits, risks and any alternatives and what you can expect when you come to hospital.
Original Article Evaluation of Diagnostic Value of CT Scan and MRI in Brain Tumors and Comparison with Biopsy
 Original Article Evaluation of Diagnostic Value of CT Scan and MRI in Brain Tumors and Comparison with Biopsy Taghipour Zahir SH MD 1, Rezaei sadrabadi M MD 2, Dehghani F MD 3 1- Department of Clinical
Original Article Evaluation of Diagnostic Value of CT Scan and MRI in Brain Tumors and Comparison with Biopsy Taghipour Zahir SH MD 1, Rezaei sadrabadi M MD 2, Dehghani F MD 3 1- Department of Clinical
Transcranial ultrasound diagnosis of intracranial lesions in children with headaches Wang H S, Kuo M F, Huang S C, Chou M L, Hung P C, Lin K L
 Transcranial ultrasound diagnosis of intracranial lesions in children with headaches Wang H S, Kuo M F, Huang S C, Chou M L, Hung P C, Lin K L Record Status This is a critical abstract of an economic evaluation
Transcranial ultrasound diagnosis of intracranial lesions in children with headaches Wang H S, Kuo M F, Huang S C, Chou M L, Hung P C, Lin K L Record Status This is a critical abstract of an economic evaluation
X-RAY Contents lists available at
 ISSN 1115-7976 X-RAY Contents lists available at Journal of Association of Radiographers of Nigeria Journal homepage: www.jarn-xray.org X-RAYS Vol. 21 Value of Conventional Skull X-Rays Examination in
ISSN 1115-7976 X-RAY Contents lists available at Journal of Association of Radiographers of Nigeria Journal homepage: www.jarn-xray.org X-RAYS Vol. 21 Value of Conventional Skull X-Rays Examination in
Masses of the Corpus Callosum
 Masses of the Corpus Callosum Kesav Raghavan, HMS Year III Dr. Agenda Corpus Callosum Development and Anatomy Our Patient: Clinical Presentation Differential Diagnosis of Masses in the Corpus Callosum
Masses of the Corpus Callosum Kesav Raghavan, HMS Year III Dr. Agenda Corpus Callosum Development and Anatomy Our Patient: Clinical Presentation Differential Diagnosis of Masses in the Corpus Callosum
CURRICULUM VITAE Intern in Medicine, Beth Israel Hospital, Harvard Medical School, Boston, MA
 Bruce D. Kohrman, M.D. 12305 SW 69 th Place Miami, Florida 33156 Telephone: (305) 903-8678 Fax: (305) 661-1672 CURRICULUM VITAE EDUCATION 1977 - B.S. Stanford University, Stanford, CA 1982 - M.D. Case
Bruce D. Kohrman, M.D. 12305 SW 69 th Place Miami, Florida 33156 Telephone: (305) 903-8678 Fax: (305) 661-1672 CURRICULUM VITAE EDUCATION 1977 - B.S. Stanford University, Stanford, CA 1982 - M.D. Case
Blunt Carotid Injury- CT Angiography is Adequate For Screening. Kelly Knudson, M.D. UCHSC April 3, 2006
 Blunt Carotid Injury- CT Angiography is Adequate For Screening Kelly Knudson, M.D. UCHSC April 3, 2006 CT Angiography vs Digital Subtraction Angiography Blunt carotid injury screening is one of the very
Blunt Carotid Injury- CT Angiography is Adequate For Screening Kelly Knudson, M.D. UCHSC April 3, 2006 CT Angiography vs Digital Subtraction Angiography Blunt carotid injury screening is one of the very
Adult Neurology Residency Training Program McGill University Objectives of Training and Training Requirements. For Outpatient Neurology Clinics
 Neurology Residency Program Department of Neurology & Neurosurgery Postal address: Montreal Neurological Institute 3801 University Street Montreal, PQ, Canada H3A 2B4 Tel.: (514) 398-1904 Fax: (514) 398-4621
Neurology Residency Program Department of Neurology & Neurosurgery Postal address: Montreal Neurological Institute 3801 University Street Montreal, PQ, Canada H3A 2B4 Tel.: (514) 398-1904 Fax: (514) 398-4621
recommendations of the Royal College of
 Archives of Emergency Medicine, 1993, 10, 138-144 Skull X-ray after head injury: the recommendations of the Royal College of Surgeons Working Party Report in practice R. E. MACLAREN, H. I. GHOORAHOO &
Archives of Emergency Medicine, 1993, 10, 138-144 Skull X-ray after head injury: the recommendations of the Royal College of Surgeons Working Party Report in practice R. E. MACLAREN, H. I. GHOORAHOO &
Tension-type Headaches
 Stress-related Diseases Tension-type Headaches JMAJ 45(5): 202 206, 2002 Koji TSUBOI Professor, Department of Psychosomatic Medicine, School of Medicine, Toho University Abstract: Tension-type headaches
Stress-related Diseases Tension-type Headaches JMAJ 45(5): 202 206, 2002 Koji TSUBOI Professor, Department of Psychosomatic Medicine, School of Medicine, Toho University Abstract: Tension-type headaches
CT Based Study of Frontal Horn Ratio And Ventricular Index in South Indian Population
 IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 16, Issue 7 Ver. VI (July. 2017), PP 55-59 www.iosrjournals.org CT Based Study of Frontal Horn Ratio
IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 16, Issue 7 Ver. VI (July. 2017), PP 55-59 www.iosrjournals.org CT Based Study of Frontal Horn Ratio
Acute Disseminated Encephalomyelitis Presenting as Rhombencephalitis: An Atypical Case Presentation
 pissn 2384-1095 eissn 2384-1109 imri 2015;19:186-190 http://dx.doi.org/10.13104/imri.2015.19.3.186 Acute Disseminated Encephalomyelitis Presenting as Rhombencephalitis: An Atypical Case Presentation Joonseok
pissn 2384-1095 eissn 2384-1109 imri 2015;19:186-190 http://dx.doi.org/10.13104/imri.2015.19.3.186 Acute Disseminated Encephalomyelitis Presenting as Rhombencephalitis: An Atypical Case Presentation Joonseok
PREVALENCE BY HEADACHE TYPE
 CLINICAL CLUES AND CLINICAL RULES: PRIMARY VS SECONDARY HEADACHE * Based on a presentation by David W. Dodick, MD ABSTRACT Headache is a common condition, accounting for many specialist office visits annually.
CLINICAL CLUES AND CLINICAL RULES: PRIMARY VS SECONDARY HEADACHE * Based on a presentation by David W. Dodick, MD ABSTRACT Headache is a common condition, accounting for many specialist office visits annually.
NEURORADIOLOGY Part I
 NEURORADIOLOGY Part I Vörös Erika University of Szeged Department of Radiology SZEGED BRAIN IMAGING METHODS Plain film radiography Ultrasonography (US) Computer tomography (CT) Magnetic resonance imaging
NEURORADIOLOGY Part I Vörös Erika University of Szeged Department of Radiology SZEGED BRAIN IMAGING METHODS Plain film radiography Ultrasonography (US) Computer tomography (CT) Magnetic resonance imaging
A Study of Measurements of Spinal Canal at the Level of Lower Three Lumbar Vertebra by 16 Slice CT Scanner in Nepalese Population
 Journal of College of Medical Sciences-Nepal, Vol-10, No 4, Oct-Dec 014 ISSN: 2091-0657 (Print); 2091-0673 (Online) Open Access A Study of Measurements of Spinal Canal at the Level of Lower Three Lumbar
Journal of College of Medical Sciences-Nepal, Vol-10, No 4, Oct-Dec 014 ISSN: 2091-0657 (Print); 2091-0673 (Online) Open Access A Study of Measurements of Spinal Canal at the Level of Lower Three Lumbar
MEDICAL POLICY EFFECTIVE DATE: 12/18/08 REVISED DATE: 12/17/09, 03/17/11, 05/19/11, 05/24/12, 05/23/13, 05/22/14
 MEDICAL POLICY SUBJECT: CT (COMPUTED TOMOGRAPHY) PAGE: 1 OF: 5 If the member's subscriber contract excludes coverage for a specific service it is not covered under that contract. In such cases, medical
MEDICAL POLICY SUBJECT: CT (COMPUTED TOMOGRAPHY) PAGE: 1 OF: 5 If the member's subscriber contract excludes coverage for a specific service it is not covered under that contract. In such cases, medical
Purpose. Methods and Materials. Results
 Prevalence and significance of hypoattenuating hepatic lesions deemed too small to characterise: How are we following up these lesions and what are the outcomes? Poster No.: C-014 Congress: ECR 2009 Type:
Prevalence and significance of hypoattenuating hepatic lesions deemed too small to characterise: How are we following up these lesions and what are the outcomes? Poster No.: C-014 Congress: ECR 2009 Type:
Normal Variations and Artifacts in MR Venography that may cause Pitfalls in the Diagnosis of Cerebral Venous Sinus Thrombosis.
 Normal Variations and Artifacts in MR Venography that may cause Pitfalls in the Diagnosis of Cerebral Venous Sinus Thrombosis. Poster No.: R-0005 Congress: 2015 ASM Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: A.
Normal Variations and Artifacts in MR Venography that may cause Pitfalls in the Diagnosis of Cerebral Venous Sinus Thrombosis. Poster No.: R-0005 Congress: 2015 ASM Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: A.
Current Imaging Diagnosis of the Breast Tumors
 Breast Cancer Current Imaging Diagnosis of the Breast Tumors JMAJ 45(6): 258 264, 2002 Tokiko ENDO Director of the Department of Radiology, National Nagoya Hospital Abstract: Breast masses include the
Breast Cancer Current Imaging Diagnosis of the Breast Tumors JMAJ 45(6): 258 264, 2002 Tokiko ENDO Director of the Department of Radiology, National Nagoya Hospital Abstract: Breast masses include the
Intracranial hypotension secondary to spinal CSF leak: diagnosis
 Intracranial hypotension secondary to spinal CSF leak: diagnosis Spinal cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) leak is an important and underdiagnosed cause of new onset headache that is treatable. Cerebrospinal fluid
Intracranial hypotension secondary to spinal CSF leak: diagnosis Spinal cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) leak is an important and underdiagnosed cause of new onset headache that is treatable. Cerebrospinal fluid
Headache Syndrome. Karen Alvarez, D.O Nemours Children s Specialty Care Jacksonville, FL
 Headache Syndrome Karen Alvarez, D.O Nemours Children s Specialty Care Jacksonville, FL What is a headache? A headache or cephalgia is defined as pain anywhere in the region of head or neck Where does
Headache Syndrome Karen Alvarez, D.O Nemours Children s Specialty Care Jacksonville, FL What is a headache? A headache or cephalgia is defined as pain anywhere in the region of head or neck Where does
MRIofthe Central Nervous System
 K. Mori (Ed.) MRIofthe Central Nervous System A Pathology Atlas With the Collaboration of M. Kurisaka A. Moriki A. Sawada With 116 Case Studies and 372 Figures Springer-Verlag Tokyo Berlin Heidelberg New
K. Mori (Ed.) MRIofthe Central Nervous System A Pathology Atlas With the Collaboration of M. Kurisaka A. Moriki A. Sawada With 116 Case Studies and 372 Figures Springer-Verlag Tokyo Berlin Heidelberg New
The AAO- HNS s position statement on Point- of- Care Imaging in Otolaryngology states that the AAO- HNS,
 AAO- HNS Statement on Diagnostic Imaging Reimbursement for Otolaryngologist Head and Neck Surgeons (September 2014) The American Academy of Otolaryngology Head and Neck Surgery (AAO- HNS), with approximately
AAO- HNS Statement on Diagnostic Imaging Reimbursement for Otolaryngologist Head and Neck Surgeons (September 2014) The American Academy of Otolaryngology Head and Neck Surgery (AAO- HNS), with approximately
Analysis of Low-Value Health Services in the Minnesota All Payer Claims Database
 TECHNICAL SPECIFICATIONS AND METHODS SUPPLEMENT Analysis of Low-Value Health Services in the Minnesota All Payer Claims Database MAY 2017 Minnesota Department of Health Health Economics Program 85 E. 7th
TECHNICAL SPECIFICATIONS AND METHODS SUPPLEMENT Analysis of Low-Value Health Services in the Minnesota All Payer Claims Database MAY 2017 Minnesota Department of Health Health Economics Program 85 E. 7th
Outline. Neuroradiology. Diffusion Imaging in. Clinical Applications of. Basics of Diffusion Imaging. Basics of Diffusion Imaging
 Clinical Applications of Diffusion Imaging in Neuroradiology No disclosures Stephen F. Kralik Assistant Professor of Radiology Indiana University School of Medicine Department of Radiology and Imaging
Clinical Applications of Diffusion Imaging in Neuroradiology No disclosures Stephen F. Kralik Assistant Professor of Radiology Indiana University School of Medicine Department of Radiology and Imaging
Comparison of RECIST version 1.0 and 1.1 in assessment of tumor response by computed tomography in advanced gastric cancer
 Original Article Comparison of RECIST version 1.0 and 1.1 in assessment of tumor response by computed tomography in advanced gastric cancer Gil-Su Jang 1 *, Min-Jeong Kim 2 *, Hong-Il Ha 2, Jung Han Kim
Original Article Comparison of RECIST version 1.0 and 1.1 in assessment of tumor response by computed tomography in advanced gastric cancer Gil-Su Jang 1 *, Min-Jeong Kim 2 *, Hong-Il Ha 2, Jung Han Kim
Goals & Objectives CanMeds VGH Neuroradiology MRI VGH 899 West 12th Ave., Vancouver, BC V5Z 1M9
 Goals & Objectives CanMeds VGH Neuroradiology MRI VGH 899 West 12th Ave., Vancouver, BC V5Z 1M9 Total: # Periods/modules/Rotations Level: PGY 2 5 Rotation Supervisor: Jason Shewchuk Residents receive a
Goals & Objectives CanMeds VGH Neuroradiology MRI VGH 899 West 12th Ave., Vancouver, BC V5Z 1M9 Total: # Periods/modules/Rotations Level: PGY 2 5 Rotation Supervisor: Jason Shewchuk Residents receive a
Subtraction CT Angiography with Controlled- Orbit Helical Scanning for Detection of Intracranial Aneurysms
 AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 19:291 295, February 1998 Subtraction CT Angiography with Controlled- Orbit Helical Scanning for Detection of Intracranial Aneurysms Satoshi Imakita, Yoshitaka Onishi, Tokihiro Hashimoto,
AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 19:291 295, February 1998 Subtraction CT Angiography with Controlled- Orbit Helical Scanning for Detection of Intracranial Aneurysms Satoshi Imakita, Yoshitaka Onishi, Tokihiro Hashimoto,
Case report. Open Access. Abstract
 Open Access Case report Acute posterior neck pain in adult: a case series Yasuhiro Homma*, Akira Itoi, Tomoya Muta, Yoshio Shimamura, Kiyohito Naito, Atsuhiko Mogami, Osamu Obayashi, Colin G Murphy and
Open Access Case report Acute posterior neck pain in adult: a case series Yasuhiro Homma*, Akira Itoi, Tomoya Muta, Yoshio Shimamura, Kiyohito Naito, Atsuhiko Mogami, Osamu Obayashi, Colin G Murphy and
Imaging of Demyelinating Processes
 Acta Radiológica Portuguesa, Vol.XXI, nº 82, pág. 81-88, Abr.-Jun., 2009 Imaging of Demyelinating Processes Alice Boyd Smith, MD Chief, Neuroradiology - Department of Radiologic Pathology, Armed Forces
Acta Radiológica Portuguesa, Vol.XXI, nº 82, pág. 81-88, Abr.-Jun., 2009 Imaging of Demyelinating Processes Alice Boyd Smith, MD Chief, Neuroradiology - Department of Radiologic Pathology, Armed Forces
An Unusual Kind Of Traumatic Intracranial Hemorrhage: Post Traumatic Bleed Into The Schizencephalic Cleft
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Radiology Volume 8 Number 2 An Unusual Kind Of Traumatic Intracranial Hemorrhage: Post Traumatic Bleed Into The Schizencephalic J T, V Rajendran, E Devarajan Citation
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Radiology Volume 8 Number 2 An Unusual Kind Of Traumatic Intracranial Hemorrhage: Post Traumatic Bleed Into The Schizencephalic J T, V Rajendran, E Devarajan Citation
CURRICULUM VITAE REZA PORDELL, M.D.
 REZA, M.D. Education Undergraduate: Medical Doctor: College of Arts and Sciences, Iran Shiraz Medical School, Shiraz, Iran Post-Doctoral Training Internship: Surgical Resident: Orthopedic Resident: Greater
REZA, M.D. Education Undergraduate: Medical Doctor: College of Arts and Sciences, Iran Shiraz Medical School, Shiraz, Iran Post-Doctoral Training Internship: Surgical Resident: Orthopedic Resident: Greater
Managing Patient Dose in Computed Tomography (CT) INTERNATIONAL COMMISSION ON RADIOLOGICAL PROTECTION
 Managing Patient Dose in Computed Tomography (CT) International Commission on Radiological Protection Information abstracted from ICRP Publication 87 Available at www.icrp.org Task Group: M.M. Rehani,
Managing Patient Dose in Computed Tomography (CT) International Commission on Radiological Protection Information abstracted from ICRP Publication 87 Available at www.icrp.org Task Group: M.M. Rehani,
128-slice dual-source CT coronary angiography using highpitch scan protocols in 102 patients
 128-slice dual-source CT coronary angiography using highpitch scan protocols in 102 patients Poster No.: C-0634 Congress: ECR 2010 Type: Scientific Exhibit Topic: Cardiac Authors: Y. H. Choe, J. W. Lee,
128-slice dual-source CT coronary angiography using highpitch scan protocols in 102 patients Poster No.: C-0634 Congress: ECR 2010 Type: Scientific Exhibit Topic: Cardiac Authors: Y. H. Choe, J. W. Lee,
The determination of eligible population for this measure requires administrative claims data.
 Overuse of Imaging Measure 6: Ratio of Magnetic Resonance Imaging Scans to Computed Tomography Scans for the Evaluation of Children with Atraumatic Headache Description This measure assesses the ratio
Overuse of Imaging Measure 6: Ratio of Magnetic Resonance Imaging Scans to Computed Tomography Scans for the Evaluation of Children with Atraumatic Headache Description This measure assesses the ratio
MRI and CT of the CNS
 MRI and CT of the CNS Dr.Maha ELBeltagy Assistant Professor of Anatomy Faculty of Medicine The University of Jordan 2018 Computed Tomography CT is used for the detection of intracranial lesions. CT relies
MRI and CT of the CNS Dr.Maha ELBeltagy Assistant Professor of Anatomy Faculty of Medicine The University of Jordan 2018 Computed Tomography CT is used for the detection of intracranial lesions. CT relies
BERGEN COMMUNITY COLLEGE Division of Science and Health Radiography Program. STUDENT COURSE of STUDY and SYLLABUS for LECTURE Spring 2016
 A. COURSE INFORMATION Course Title: Specialty Imaging and Therapeutic Modalities Course Code: RAD 275 Section: 001 Credits: 1.0 (1 hour per week for 15 weeks= 15 lecture hours) Pre-requisites: Co-requisites:
A. COURSE INFORMATION Course Title: Specialty Imaging and Therapeutic Modalities Course Code: RAD 275 Section: 001 Credits: 1.0 (1 hour per week for 15 weeks= 15 lecture hours) Pre-requisites: Co-requisites:
factor for identifying unstable thoracolumbar fractures. There are clinical and radiological criteria
 NMJ-Vol :2/ Issue:1/ Jan June 2013 Case Report Medical Sciences Progressive subluxation of thoracic wedge compression fracture with unidentified PLC injury Dr.Thalluri.Gopala krishnaiah* Dr.Voleti.Surya
NMJ-Vol :2/ Issue:1/ Jan June 2013 Case Report Medical Sciences Progressive subluxation of thoracic wedge compression fracture with unidentified PLC injury Dr.Thalluri.Gopala krishnaiah* Dr.Voleti.Surya
University of Minnesota Diagnostic Radiology Residency Curriculum, Department of Radiology Rotation Duty Sheet - UMNE
 Department of Radiology Rotation Duty Sheet - UMNE ROTATION DUTY SHEET FOR: UMNE The resident will review Duty Sheet regularly throughout the rotation. Please review documents posted on moodle about detailed
Department of Radiology Rotation Duty Sheet - UMNE ROTATION DUTY SHEET FOR: UMNE The resident will review Duty Sheet regularly throughout the rotation. Please review documents posted on moodle about detailed
SUPPLEMENTAL MATERIAL
 SUPPLEMENTAL MATERIAL Table I. Studies from literature their sample size and results Study Woodcock et al. 1999 1 Sample size Selection patients of 64 Referred for conventional diagnostic angiogram Ptak
SUPPLEMENTAL MATERIAL Table I. Studies from literature their sample size and results Study Woodcock et al. 1999 1 Sample size Selection patients of 64 Referred for conventional diagnostic angiogram Ptak
Imaging the post-operative spine - are we united in where we stand?
 Imaging the post-operative spine - are we united in where we stand? Poster No.: C-2424 Congress: ECR 2015 Type: Authors: Keywords: DOI: Scientific Exhibit J. Kumaraguru, N. Kandasamy, D. A. Elias, J. M.
Imaging the post-operative spine - are we united in where we stand? Poster No.: C-2424 Congress: ECR 2015 Type: Authors: Keywords: DOI: Scientific Exhibit J. Kumaraguru, N. Kandasamy, D. A. Elias, J. M.
Spinal injury is very common in Ireland: 19 per 100,000 (1). It poses a significant disease burden.
 MRI in traumatic spinal cord injury: a single national spinal centre experience and study of imaging features with clinical correlation with ASIA score and outcome Poster No.: C-1235 Congress: ECR 2011
MRI in traumatic spinal cord injury: a single national spinal centre experience and study of imaging features with clinical correlation with ASIA score and outcome Poster No.: C-1235 Congress: ECR 2011
ISSN X (Print) Research Article
 Scholars Journal of Applied Medical Sciences (SJAMS) Sch. J. App. Med. Sci., 2014; 2(5D):1760-1764 Scholars Academic and Scientific Publisher (An International Publisher for Academic and Scientific Resources)
Scholars Journal of Applied Medical Sciences (SJAMS) Sch. J. App. Med. Sci., 2014; 2(5D):1760-1764 Scholars Academic and Scientific Publisher (An International Publisher for Academic and Scientific Resources)
Purpose. Page 2 of 11
 Medical Imaging in Emergency Medicine: Assessing the Use of Serial Imaging to Screen for Delayed Intracranial Haemorrhage in Patients on Anticoagulant and Antiplatelet Therapy Poster No.: R-0143 Congress:
Medical Imaging in Emergency Medicine: Assessing the Use of Serial Imaging to Screen for Delayed Intracranial Haemorrhage in Patients on Anticoagulant and Antiplatelet Therapy Poster No.: R-0143 Congress:
International Journal of Research in Health Sciences ISSN: Available online at: Case Study
 International Journal of Research in Health Sciences ISSN: 2321-7251 Available online at: http://www.ijrhs.org/ Case Study Foreign body granuloma mimicking a soft tissue neoplasm *Rohan Sawant, Abhishek
International Journal of Research in Health Sciences ISSN: 2321-7251 Available online at: http://www.ijrhs.org/ Case Study Foreign body granuloma mimicking a soft tissue neoplasm *Rohan Sawant, Abhishek
Reassessment: Neuroimaging in the Emergency Patient Presenting with Seizure
 Reassessment: Neuroimaging in the Emergency Patient Presenting with Seizure This evidence-based report provides clinicians with information to identify which seizure patients in the emergency department
Reassessment: Neuroimaging in the Emergency Patient Presenting with Seizure This evidence-based report provides clinicians with information to identify which seizure patients in the emergency department
Dense Breasts, Get Educated
 Dense Breasts, Get Educated What are Dense Breasts? The normal appearances to breasts, both visually and on mammography, varies greatly. On mammography, one of the important ways breasts differ is breast
Dense Breasts, Get Educated What are Dense Breasts? The normal appearances to breasts, both visually and on mammography, varies greatly. On mammography, one of the important ways breasts differ is breast
Research Article Analysis of Repeated CT Scan Need in Blunt Head Trauma
 Hindawi Publishing Corporation Emergency Medicine International Volume 2013, Article ID 916253, 5 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2013/916253 Research Article Analysis of Repeated CT Scan Need in Blunt
Hindawi Publishing Corporation Emergency Medicine International Volume 2013, Article ID 916253, 5 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2013/916253 Research Article Analysis of Repeated CT Scan Need in Blunt
Health Learning Partnership 13 th September Neuroimaging. Headache Dementia Incidentalomas DR MARCUS BRADLEY CONSULTANT NEURORADIOLOGIST
 Health Learning Partnership 13 th September 2017 Neuroimaging DR MARCUS BRADLEY CONSULTANT NEURORADIOLOGIST Headache Dementia Incidentalomas Dr Marcus Bradley Consultant Neuroradiologist Interventional
Health Learning Partnership 13 th September 2017 Neuroimaging DR MARCUS BRADLEY CONSULTANT NEURORADIOLOGIST Headache Dementia Incidentalomas Dr Marcus Bradley Consultant Neuroradiologist Interventional
CLINICAL PRESENTATION AND RADIOLOGY QUIZ QUESTION
 Donald L. Renfrew, MD Radiology Associates of the Fox Valley, 333 N. Commercial Street, Suite 100, Neenah, WI 54956 6/23/2012 Radiology Quiz of the Week # 78 Page 1 CLINICAL PRESENTATION AND RADIOLOGY
Donald L. Renfrew, MD Radiology Associates of the Fox Valley, 333 N. Commercial Street, Suite 100, Neenah, WI 54956 6/23/2012 Radiology Quiz of the Week # 78 Page 1 CLINICAL PRESENTATION AND RADIOLOGY
Neuroimaging Guidelines in Nonacute Headaches
 Continuing Medical Education 137 Neuroimaging Guidelines in Nonacute Headaches Treatment Guideline Subcommittee of the Taiwan Headache Society Abstract- The Treatment Guideline Subcommittee of the Taiwan
Continuing Medical Education 137 Neuroimaging Guidelines in Nonacute Headaches Treatment Guideline Subcommittee of the Taiwan Headache Society Abstract- The Treatment Guideline Subcommittee of the Taiwan
FOR CMS (MEDICARE) MEMBERS ONLY NATIONAL COVERAGE DETERMINATION (NCD) FOR MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING:
 National Imaging Associates, Inc. Clinical guidelines SINUS MRI Original Date: November 2007 Page 1 of 5 CPT Codes: 70540, 70542, 70543 Last Review Date: July 2014 NCD 220.2 MRI Last Effective Date: July
National Imaging Associates, Inc. Clinical guidelines SINUS MRI Original Date: November 2007 Page 1 of 5 CPT Codes: 70540, 70542, 70543 Last Review Date: July 2014 NCD 220.2 MRI Last Effective Date: July
CT perfusion in Moyamoya disease
 CT perfusion in Moyamoya disease Poster No.: C-1726 Congress: ECR 2015 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: K. C. Lam, C. P. Tsang, K. K. Wong, R. LEE ; HK, Hong Kong/HK Keywords: Hemodynamics / Flow dynamics,
CT perfusion in Moyamoya disease Poster No.: C-1726 Congress: ECR 2015 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: K. C. Lam, C. P. Tsang, K. K. Wong, R. LEE ; HK, Hong Kong/HK Keywords: Hemodynamics / Flow dynamics,
