A New Minimally Invasive Technique for Cauterizing the Maxillary Artery and Its Application in the Treatment of Cluster Headache
|
|
|
- Wesley French
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 A New Minimally Invasive Technique for Cauterizing the Maxillary Artery and Its Application in the Treatment of Cluster Headache Elliot Shevel, BDS, DipMFOS, MBBCh* Purpose: To describe a new, relatively atraumatic method of cauterizing the maxillary artery and its effectiveness in treating cluster headache. Materials and Methods: Five patients with cluster headache were treated with arterial ligation of certain terminal branches of the external carotid artery. A new, atraumatic method of cauterizing the maxillary artery is described. Results: The success rate and postoperative morbidity are presented. In four out of five patients the cluster attacks ceased immediately following surgery. Conclusion: A new intraoral technique for maxillary artery cauterization and the effectiveness of cauterization of the terminal branches of the external carotid artery in the treatment of cluster headache are described. Although the sample is small, the results are encouraging, and may offer permanent relief of cluster headache pain. Ó 2013 American Association of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgeons J Oral Maxillofac Surg 71: , 2013 *Medical Director, The Headache Clinic, Johannesburg, South Africa. Address correspondence and reprint requests to Dr Shevel: The Headache Clinic, 45 Empire Road, Johannesburg 2193, South Africa; drshevel@headclin.com Ó 2013 American Association of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgeons /12/01659-X$36.00/0 Cluster headache (CH), formerly called cluster migraine, is the most frequent of the trigeminal autonomic cephalalgias. It is one of the most painful conditions known and as such has been referred to as suicide headache. CH occurs with a lifetime prevalence of 124 per 100,000 and is 4.3 times more common in men than in women. 1 Diagnostic criteria for CH have been established by the International Headache Society, which recognizes the episodic and chronic forms. 2 Episodic CH occurs 6 times more commonly than chronic CH. 1 The pain in CH is strictly unilateral and most often is localized to the region supplied by the maxillary artery (MA), namely the periorbital, retro-orbital, and orofacial areas, and may be of a toothache-like nature. 3 The pain is accompanied by at least 1 of the following autonomic symptoms, all of which are ipsilateral to the pain: conjunctival injection, lacrimation, nasal congestion, rhinorrhea, forehead and facial sweating, miosis, ptosis, and eyelid edema. 2 These features of CH are thought to be related to the parasympathetic and sympathetic innervation of the sphenopalatine ganglion (SPG). 4 The third section of the MA courses through the infratemporal fossa (Fig 1), 5 and the anatomic location of the SPG is in the region supplied by this portion of the MA. Surgical cauterization of the terminal branches of the external carotid artery has proved effective in patients with migraine who respond to rescue treatment with triptans. 6 The most effective rescue treatment for CH is with triptans. Although some patients can adequately control CH using prophylactic medication, many episodes are refractory and, in some cases, medication cannot be used because of undesirable side effects. 7 In those patients who respond favorably to vasoconstrictor rescue medications such as the ergots or triptans, it appeared feasible that permanent closure by cauterization of the involved arteries could be a solution to the problem. This form of treatment has been used successfully for chronic migraine in which vascular involvement has been positively diagnosed. 6 The tenderness to palpation of the retromaxillary tissues on the painful side during a cluster period and particularly the exquisite tenderness during an attack suggest the presence of inflammation, possibly sterile neurogenic inflammation, in the vicinity of the MA. It is postulated that the autonomic symptoms that occur 677
2 678 NEW TREATMENT OF CLUSTER HEADACHE FIGURE 1. Computed tomographic angiogram showing the maxillary artery coursing through the pterygopalatine fossa. during CH may be the result of the effect of neurogenic inflammation on the autonomic elements in the SPG. The decrease in pain during an attack from compression of the MA strongly suggests that it is involved in the pain of CH. There are several other indications for cauterizing the MA. During maxillary (Le Fort I, II, or III) or midfacial osteotomy, profuse bleeding is possible and complications such as postoperative hemorrhage, false aneurysm, and arteriovenous fistula have been reported In cases of intractable posterior epistaxis, if posterior nasal packing fails, ligation, cauterization, or embolization of the MA may be necessary The atraumatic method of cauterizing the MA through an intraoral approach described here also may prove useful for these applications. MAXILLARY ARTERY The course of the MA in the infratemporal fossa is variable, but it can be determined accurately with a 3-dimensional computed tomographic angiogram (Fig 1). A Doppler flowmeter (Parks Doppler Model 811B with pencil probe (Parks Medical Electronics, Aloha, Oregon) (Fig 2) is used during surgery to confirm its exact location (Fig 3). A local anesthetic solution is injected into the retromaxillary tissues, above and below the Doppler probe, with the needle parallel to the Doppler probe. The needle is advanced until it strikes the base of the skull to ensure full-depth anesthesia. Pinholes are then made in the mucosa above and below the Doppler probe with a 15-gauge needle. Each pinhole is then widened using a blunt tapering metal probe (Fig 2), which is advanced until the basal surface of the greater wing of the sphenoid bone at the cranial base is encountered. The direction in which this probe is advanced must be parallel to the direction of the Doppler probe when the artery is heard (Fig 3). This ensures that there is a preformed channel on either side of the MA, into which the tips of the bipolar cautery probe (Erbe 25-cm 0.4-mm Bayonet Non-Stick (ERBE USA, Inc., Marietta, Georgia) (Fig 2) are advanced, one on either side of the artery (Fig 4). The cautery probe is then advanced, also at the same Materials and Methods Ethical approval was obtained from the research ethics committee of the South African Medical Association. Under sedation and with local anesthesia, the superficial temporal artery main trunk, its frontal branch, and the occipital arteries were cauterized bilaterally as described elsewhere. 6 Although CH is unilateral, these arteries are cauterized bilaterally because of the extensive anastomoses between the left and right sides. 14 The MA is cauterized only on the painful side. The procedure is carried out in a day facility. FIGURE 2. Blunt tapering probe (Parks Doppler pencil probe; Erbe 25-cm 0.4-mm Bayonet Non-Stick).
3 ELLIOT SHEVEL 679 after which the probe is removed, and the Doppler is reapplied to the mucosa. The procedure is completed when the MA blood flow can no longer be heard with the Doppler probe. The procedure is generally atraumatic and, because it is carried out through pinholes, no sutures are necessary. Blunt instruments are used to prevent accidental puncture of the MA. Postoperative antibiotic cover for 5 days with amoxicillin 500 mg every 8 hours and metronidazole 400 mg every 8 hours is recommended. FIGURE 3. Doppler probe locating the maxillary artery. angle as the Doppler probe, into the enlarged pinholes, stopping every 2 to 3 mm to clamp the ends together and listen with the Doppler until the MA is silenced by the clamped cautery probe. A coagulation pulse of 40 W is activated for approximately 4 seconds, FIGURE 4. Bipolar cautery probe in situ. PATIENTS Five patients, 4 with episodic CH and 1 with chronic CH, underwent the procedure from June 2010 to July All selected patients had proved refractory to preventive treatments, but they were responsive to vasoconstrictors if taken before the pain became severe. Involvement of the terminal branches of the external carotid artery was confirmed clinically in all 5 patients. On clinical examination interictally, the cluster shadow decreased with digital compression of the superficial temporal, frontal, and occipital arteries bilaterally. MA involvement in the pain was confirmed interictally by finger pressure applied to the retromaxillary tissues. The affected side is always more tender than the contralateral side in patients with CH. In 2 patients who were examined during a cluster attack, finger pressure to the retromaxillary tissues not only was exceedingly painful on the affected side compared with the contralateral side, but also decreased the severity of the cluster pain temporarily, presumably because of compression of the MA. Patient 1 was a 43-year-old man with refractory rightside CH. He had been diagnosed by a neurologist elsewhere 10 years previously with chronic CH and had been treated with various medications, including topiramate and prednisone, without relief. Oxygen therapy had helped to abort some attacks for some years, but was no longer effective. The attacks could be aborted at times by sumatriptan injection if it was administered early in the attack before the pain became severe. The attacks were irregular, with a frequency of 3 to 4 a day and a maximum duration of 1 hour. The attacks were accompanied by a burning sensation of the right nares and irritation of the maxillary gingivae on the right side. The surgery was carried out on June 24, The clusters stopped immediately after surgery, and by September 1, 2012, there had been no further attacks. Patient 2 was a 63-year-old man who had been diagnosed by a neurologist elsewhere in 2005 with rightside episodic CH. He had reported a temporary improvement of 1 week with topiramate and prednisone and responded well to sumatriptan injections if administered before the pain became severe. The
4 680 NEW TREATMENT OF CLUSTER HEADACHE FIGURE 5. Computed tomographic angiogram showing the occipital, superficial temporal, and frontal arteries. surgery was carried out on August 19, The clusters stopped immediately, and on follow-up on September 1, 2012, he reported that he had to date had no further attacks. Patient 3 was a 59-year-old man who had left-side episodic CHs for 8 years; his clusters occurred regularly every year in April. There had been no response to topiramate and prednisone, but the attacks were controlled with sumatriptan injections if used before the pain became severe. All his attacks occurred at night, although, more frequently than not, he was awoken by the attack and the drug was not helpful. The surgery was carried out on May 4, The clusters stopped immediately after surgery, and on August 23, 2012, he reported that he had had no further attacks. Patient 4 was a 55-year-old man with right-side episodic CH that began 16 years previously. He was into the second week of his cluster, which usually lasted 4 to 6 weeks. There were 2 attacks per day. He had used verapamil, prednisone, oxygen, and sumatriptan injections. Only the sumatriptan provided relief if he used it before the pain became severe, but not when he was woken by the pain. The surgery was carried out on June 20, The clusters stopped immediately after surgery, and by September 1, 2012, there had been no further attacks.
5 ELLIOT SHEVEL 681 Patient 5 was a 48-year-old woman with left-side episodic CH of 8 years standing. She had just started her present cluster. Her cluster had in the past lasted 3 to 8 weeks. She was experiencing 4 to 5 attacks every 24 hours at the time of surgery. She had previously used prednisone, topiramate, and oxygen, without any benefit. Most attacks responded well to sumatriptan injections. The surgery was carried out on July 18, 2011, but the CH attacks continued unchanged. All patients underwent preoperative computed tomographic angiography to determine the precise subcutaneous positions of the superficial temporal, frontal, and occipital arteries (Fig 5), the course of the MA in the infratemporal fossa (Fig 1), and the possible presence of anatomic variations. POSTOPERATIVE MORBIDITY There may be localized swelling and limitation of movement for up to 2 weeks, for which nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs are prescribed. In 1 patient the pain and swelling were more severe, with limitation of mouth opening for 4 weeks. This complication rate compares with 14% for embolization and 26% with transantral ligation. 13 The statistics and postoperative morbidity for this procedure may prove to be inaccurate because they are based on a small number of cases. Results Four of the 5 patients have reported no further cluster attacks since the surgery. Patient 4 had a cluster attack start during the procedure and reported immediate cessation of his pain the moment the MA was cauterized. The failure rate of 20% may be ascribed to the fact that it is a blind procedure and to the difficulty of access in some patients. This compares with a 20% failure rate with embolization and a 12% rate with transantral ligation. 13 Discussion In the treatment of CH, the possibility must always be borne in mind that the cluster stopped spontaneously, not because of the intervention, but because of the natural progression of the disease. This could not have been the case with patient 1 who had chronic CH. Also, the fact that the attacks stopped immediately after the surgery in 4 of 5 cases makes it statistically highly unlikely that all 4 happened to obtain spontaneous relief directly after surgery. What is also significant is that patient 4 had an attack that started during the surgery. Without prompting and without being aware of what stage the surgery had reached, he reported that the pain ceased at the moment the MA was clamped and cauterized. The autonomic features of CH are thought to be related to parasympathetic activity in the SPG. Lacrimation, nasal congestion, and rhinorrhea are manifestations of parasympathetic activation. Sympathetic fibers transit the SPG, and some cluster attacks manifest a partial Horner syndrome, suggesting sympathetic paresis. 4 The exquisite tenderness to palpation of the retromaxillary tissues during a cluster attack indicates the presence of inflammation, possibly sterile neurogenic inflammation in the vicinity of the MA. It is postulated that the autonomic symptoms that occur during CH, namely conjunctival injection, lacrimation, nasal congestion, miosis, ptosis, and eyelid edema, may be the result of the effect of neurogenic inflammation on the autonomic elements in the SPG. In conclusion, a new atraumatic technique for cauterizing the MA has been described. Four of 5 patients with CH were successfully treated using this technique. Although the sample was small, this appears to be a promising new treatment for CH. References 1. Fischera M, Marziniak M, Gralow I, et al: The incidence and prevalence of cluster headache: A meta-analysis of population-based studies. Cephalalgia 28:614, Olesen J: The international classification of headache disorders. Cephalalgia 24:1, Gaul C, Christmann N, Schroder D, et al: Differences in clinical characteristics and frequency of accompanying migraine features in episodic and chronic cluster headache. Cephalalgia 32:571, Jenkins B, Tepper SJ: Neurostimulation for primary headache disorders, part 1: Pathophysiology and anatomy, history of neuromodulation in headache treatment, and review of peripheral neuromodulation in primary headaches. Headache 51:1254, Morton AL, Khan A: Internal maxillary artery variability in the pterygopalatine fossa. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 104:204, Shevel E: Vascular surgery for chronic migraine. Therapy 4:451, Oomen K, Wijck A, Hordijk G, et al: Microvascular decompression of the pterygopalatine ganglion in patients with refractory cluster headache. Cephalalgia 31:1236, Lanigan DT, West RA: Aseptic necrosis of the mandible: Report of two cases. J Oral Maxillofac Surg 48:296, Lanigan DT, Hey JH, West RA: Major vascular complications of orthognathic surgery: Hemorrhage associated with Le Fort I osteotomies. J Oral Maxillofac Surg 48:561, Choi J, Park HS: The clinical anatomy of the maxillary artery in the pterygopalatine fossa. J Oral Maxillofac Surg 61:72, Seno S, Arikata M, Sakurai H, et al: Endoscopic ligation of the sphenopalatine artery and the maxillary artery for the treatment of intractable posterior epistaxis. Am J Rhinol Allergy 23:197, Pothier DD, Mackeith S, Youngs R: Sphenopalatine artery ligation: Technical note. J Laryngol Otol 119:810, Cullen MM, Tami TA: Comparison of internal maxillary artery ligation versus embolization for refractory posterior epistaxis. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 118:636, Marty F, Montandon D, Gumener R, et al: Subcutaneous tissue in the scalp: Anatomical, physiological, and clinical study. Ann Plast Surg 16:368, 1986
Headache Master School Japan-Osaka 2016 II. Management of refractory headaches Case Presentation 2. SUNCT/SUNA: concept, management and prognosis
 Headache Master School Japan-Osaka 2016 II. Management of refractory headaches Case Presentation 2. SUNCT/SUNA: concept, management and prognosis Noboru Imai(Department of Neurology, Japanese Red Cross
Headache Master School Japan-Osaka 2016 II. Management of refractory headaches Case Presentation 2. SUNCT/SUNA: concept, management and prognosis Noboru Imai(Department of Neurology, Japanese Red Cross
Corporate Medical Policy
 Corporate Medical Policy File Name: Origination: Last CAP Review: Next CAP Review: Last Review: occipital_nerve_stimulation 8/2010 5/2017 5/2018 5/2017 Description of Procedure or Service Occipital nerve
Corporate Medical Policy File Name: Origination: Last CAP Review: Next CAP Review: Last Review: occipital_nerve_stimulation 8/2010 5/2017 5/2018 5/2017 Description of Procedure or Service Occipital nerve
THE MAXILLARY ARTERY IS THE
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Anatomical Variability of the Maxillary Artery Findings From 100 Asian Cadaveric Dissections Jin Kook Kim, MD; Jae Hoon Cho, MD; Yeo-Jin Lee, MD; Chang-Hoon Kim, MD; Jung Ho Bae, MD; Jeung-Gweon
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Anatomical Variability of the Maxillary Artery Findings From 100 Asian Cadaveric Dissections Jin Kook Kim, MD; Jae Hoon Cho, MD; Yeo-Jin Lee, MD; Chang-Hoon Kim, MD; Jung Ho Bae, MD; Jeung-Gweon
Tears of Pain SUNCT and SUNA A/PROFESSOR ARUN AGGARWAL RPAH PAIN MANAGEMENT CENTRE
 Tears of Pain SUNCT and SUNA A/PROFESSOR ARUN AGGARWAL RPAH PAIN MANAGEMENT CENTRE IHS Classification 1989 (updated 2004) Primary Headaches 4 categories Migraine Tension-type Cluster and other trigeminal
Tears of Pain SUNCT and SUNA A/PROFESSOR ARUN AGGARWAL RPAH PAIN MANAGEMENT CENTRE IHS Classification 1989 (updated 2004) Primary Headaches 4 categories Migraine Tension-type Cluster and other trigeminal
Implantation of a sphenopalatine ganglion stimulation device for chronic cluster headache
 NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CARE EXCELLENCE Interventional procedure consultation document Implantation of a sphenopalatine ganglion stimulation device for chronic cluster headache Cluster headaches
NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CARE EXCELLENCE Interventional procedure consultation document Implantation of a sphenopalatine ganglion stimulation device for chronic cluster headache Cluster headaches
Disclosures. Objectives 6/2/2017
 Classification: Migraine and Trigeminal Autonomic Cephalalgias Lauren Doyle Strauss, DO, FAHS Assistant Professor, Child Neurology Assistant Director, Child Neurology Residency @StraussHeadache No disclosures
Classification: Migraine and Trigeminal Autonomic Cephalalgias Lauren Doyle Strauss, DO, FAHS Assistant Professor, Child Neurology Assistant Director, Child Neurology Residency @StraussHeadache No disclosures
Cluster headache (CH): epidemiology, classification and clinical picture
 Cluster headache (CH): epidemiology, classification and clinical picture Toomas Toomsoo, M.D. Head of the Center of Neurology East Tallinn Central Hospital 1 INTRODUCTION Cluster headache - known as trigeminal
Cluster headache (CH): epidemiology, classification and clinical picture Toomas Toomsoo, M.D. Head of the Center of Neurology East Tallinn Central Hospital 1 INTRODUCTION Cluster headache - known as trigeminal
Chapter 2 Diagnosis of Trigeminal Autonomic Cephalalgias
 Chapter 2 Diagnosis of Trigeminal Autonomic Cephalalgias Mark J. Stillman Introduction The trigeminal autonomic cephalalgias (TACs) refer to a specific group of primary headaches characterized by unilaterality,
Chapter 2 Diagnosis of Trigeminal Autonomic Cephalalgias Mark J. Stillman Introduction The trigeminal autonomic cephalalgias (TACs) refer to a specific group of primary headaches characterized by unilaterality,
Peripheral Extracranial Neurostimulation for the treatment of Primary Headache and Migraine:
 Chapter 19 Peripheral Extracranial Neurostimulation for the treatment of Primary Headache and Migraine: Introduction 1) The occipital nerve is involved in pain syndromes originating from nerve trauma,
Chapter 19 Peripheral Extracranial Neurostimulation for the treatment of Primary Headache and Migraine: Introduction 1) The occipital nerve is involved in pain syndromes originating from nerve trauma,
Original Policy Date
 MP 7.01.105 Occipital Nerve Stimulation Medical Policy Section Surgery Issue 12/2013 Original Policy Date 12/2013 Last Review Status/Date Reviewed with literature search/12/2013 Return to Medical Policy
MP 7.01.105 Occipital Nerve Stimulation Medical Policy Section Surgery Issue 12/2013 Original Policy Date 12/2013 Last Review Status/Date Reviewed with literature search/12/2013 Return to Medical Policy
Chronic Daily Headaches
 Chronic Daily Headaches ANWARUL HAQ, MD, MRCP(UK), FAHS DIRECTOR BAYLOR HEADACHE CENTER, DALLAS, TEXAS DISCLOSURES: None OBJECTIVES AT THE CONCLUSION OF THIS ACTIVITY, PARTICIPANTS WILL BE ABLE TO: define
Chronic Daily Headaches ANWARUL HAQ, MD, MRCP(UK), FAHS DIRECTOR BAYLOR HEADACHE CENTER, DALLAS, TEXAS DISCLOSURES: None OBJECTIVES AT THE CONCLUSION OF THIS ACTIVITY, PARTICIPANTS WILL BE ABLE TO: define
Trigeminal Autonomic Cephalalgias. Disclosures. Objectives 6/20/2018. Rashmi Halker Singh, MD FAHS UCNS Review Course June 2018
 Trigeminal Autonomic Cephalalgias Rashmi Halker Singh, MD FAHS UCNS Review Course June 2018 Disclosures Honoraria from Allergan and Amgen for advisory board, Current Neurology and Neuroscience Reports
Trigeminal Autonomic Cephalalgias Rashmi Halker Singh, MD FAHS UCNS Review Course June 2018 Disclosures Honoraria from Allergan and Amgen for advisory board, Current Neurology and Neuroscience Reports
North Oaks Trauma Symposium Friday, November 3, 2017
 + Evaluation and Management of Facial Trauma D Antoni Dennis, MD North Oaks ENT an Allergy November 3, 2017 + Financial Disclosure I do not have any conflicts of interest or financial interest to disclose
+ Evaluation and Management of Facial Trauma D Antoni Dennis, MD North Oaks ENT an Allergy November 3, 2017 + Financial Disclosure I do not have any conflicts of interest or financial interest to disclose
The Role of Allergies and Sinus Disorders in Headache & Facial Pain
 The Role of Allergies and Sinus Disorders in Headache & Facial Pain Vincent T. Martin, MD Professor of Medicine Co-director of the Headache & Facial Pain Center University of Cincinnati College of Medicine
The Role of Allergies and Sinus Disorders in Headache & Facial Pain Vincent T. Martin, MD Professor of Medicine Co-director of the Headache & Facial Pain Center University of Cincinnati College of Medicine
Clinical Commissioning Policy Statement: Sphenopalatine Ganglion Stimulation for Refractory Chronic Cluster Headache (Adults)
 Clinical Commissioning Policy Statement: Sphenopalatine Ganglion Stimulation for Refractory Chronic Cluster Headache (Adults) NHS England Reference: 170083P 1 Contents 1. Plain Language Summary... 3 2.
Clinical Commissioning Policy Statement: Sphenopalatine Ganglion Stimulation for Refractory Chronic Cluster Headache (Adults) NHS England Reference: 170083P 1 Contents 1. Plain Language Summary... 3 2.
MEDICAL POLICY I. POLICY II. PRODUCT VARIATIONS TOP III. DESCRIPTION/BACKGROUND POLICY TITLE SPHENOPALATINE GANGLION BLOCK POLICY NUMBER MP-4.
 Original Issue Date (Created): 2/1/2018 Most Recent Review Date (Revised): 7/5/2018 Effective Date: 9/1/2018 POLICY PRODUCT VARIATIONS DESCRIPTION/BACKGROUND RATIONALE DEFINITIONS BENEFIT VARIATIONS DISCLAIMER
Original Issue Date (Created): 2/1/2018 Most Recent Review Date (Revised): 7/5/2018 Effective Date: 9/1/2018 POLICY PRODUCT VARIATIONS DESCRIPTION/BACKGROUND RATIONALE DEFINITIONS BENEFIT VARIATIONS DISCLAIMER
*in general the blood supply of the nose comes from branches of the internal and external carotid arteries.
 In the previous lecture we talked about the anatomy of the nasal cavity, today we will talk about its blood supply, venous drainage, innervations, and finally about the paranasal sinuses. When we describe
In the previous lecture we talked about the anatomy of the nasal cavity, today we will talk about its blood supply, venous drainage, innervations, and finally about the paranasal sinuses. When we describe
Bony orbit Roof The orbital plate of the frontal bone Lateral wall: the zygomatic bone and the greater wing of the sphenoid
 Bony orbit Roof: Formed by: The orbital plate of the frontal bone, which separates the orbital cavity from the anterior cranial fossa and the frontal lobe of the cerebral hemisphere Lateral wall: Formed
Bony orbit Roof: Formed by: The orbital plate of the frontal bone, which separates the orbital cavity from the anterior cranial fossa and the frontal lobe of the cerebral hemisphere Lateral wall: Formed
Policy #: 411 Latest Review Date: January 2014
 Name of Policy: Occipital Nerve Stimulation Policy #: 411 Latest Review Date: January 2014 Category: Surgery Policy Grade: B Background/Definitions: As a general rule, benefits are payable under Blue Cross
Name of Policy: Occipital Nerve Stimulation Policy #: 411 Latest Review Date: January 2014 Category: Surgery Policy Grade: B Background/Definitions: As a general rule, benefits are payable under Blue Cross
Headache Assessment In Primary Eye Care
 Headache Assessment In Primary Eye Care Spencer Johnson, O.D., F.A.A.O. Northeastern State University Oklahoma College of Optometry johns137@nsuok.edu Course Objectives Review headache classification Understand
Headache Assessment In Primary Eye Care Spencer Johnson, O.D., F.A.A.O. Northeastern State University Oklahoma College of Optometry johns137@nsuok.edu Course Objectives Review headache classification Understand
Is OnabotulinumtoxinA Good for Other Head and Face Pain? Disclosures BoNT/A for non- CM Botulinum neurotoxin (BoNT) in clinical use for headache >20
 1 2 3 4 5 6 Is OnabotulinumtoxinA Good for Other Head and Face Pain? Disclosures BoNT/A for non- CM Botulinum neurotoxin (BoNT) in clinical use for headache >20 years Efficacy of BoNT type A (onabotulinumtoxina,
1 2 3 4 5 6 Is OnabotulinumtoxinA Good for Other Head and Face Pain? Disclosures BoNT/A for non- CM Botulinum neurotoxin (BoNT) in clinical use for headache >20 years Efficacy of BoNT type A (onabotulinumtoxina,
Temporal fossa Infratemporal fossa Pterygopalatine fossa Terminal branches of external carotid artery Pterygoid venous plexus
 Outline of content Temporal fossa Infratemporal fossa Pterygopalatine fossa Terminal branches of external carotid artery Pterygoid venous plexus Boundary Content Communication Mandibular division of trigeminal
Outline of content Temporal fossa Infratemporal fossa Pterygopalatine fossa Terminal branches of external carotid artery Pterygoid venous plexus Boundary Content Communication Mandibular division of trigeminal
Regional nerve block of the upper eyelid in oculoplastic surg e r y
 E u ropean Journal of Ophthalmology / Vol. 16 no. 4, 2006 / pp. 5 0 9-5 1 3 Regional nerve block of the upper eyelid in oculoplastic surg e r y A.R. ISMAIL, T. ANTHONY, D.J. MORDANT, H. MacLEAN Portsmouth
E u ropean Journal of Ophthalmology / Vol. 16 no. 4, 2006 / pp. 5 0 9-5 1 3 Regional nerve block of the upper eyelid in oculoplastic surg e r y A.R. ISMAIL, T. ANTHONY, D.J. MORDANT, H. MacLEAN Portsmouth
Charlin S Syndrome Following a Routine Septorhinoplasty
 Kavyani et al. 103 Case Report Charlin S Syndrome Following a Routine Septorhinoplasty Ali Kavyani1*, Ali Manafi2 1. 2. Department of Plastic Surgery, School of Medicine, Shiraz University of Medical Sciences,
Kavyani et al. 103 Case Report Charlin S Syndrome Following a Routine Septorhinoplasty Ali Kavyani1*, Ali Manafi2 1. 2. Department of Plastic Surgery, School of Medicine, Shiraz University of Medical Sciences,
Trigeminal Autonomic. Trigeminal Autonomic Cephalalgias (TACs) María-Carmen Wilson,MD
 Trigeminal Autonomic Cephalalgias (TACs) María-Carmen Wilson,MD Director, Headache and Facial Pain Program Ochsner, North Shore Region Trigeminal Autonomic Cephalgias gwith autonomic features gcluster
Trigeminal Autonomic Cephalalgias (TACs) María-Carmen Wilson,MD Director, Headache and Facial Pain Program Ochsner, North Shore Region Trigeminal Autonomic Cephalgias gwith autonomic features gcluster
Transcutaneous stimulation of the cervical branch of the vagus nerve for cluster headache and migraine
 NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CARE EXCELLENCE Interventional procedure consultation document Transcutaneous stimulation of the cervical branch of the vagus nerve for cluster headache and migraine Cluster
NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CARE EXCELLENCE Interventional procedure consultation document Transcutaneous stimulation of the cervical branch of the vagus nerve for cluster headache and migraine Cluster
PTERYGOPALATINE FOSSA
 PTERYGOPALATINE FOSSA Outline Anatomical Structure and Boundaries Foramina and Communications with other spaces and cavities Contents Pterygopalatine Ganglion Especial emphasis on certain arteries and
PTERYGOPALATINE FOSSA Outline Anatomical Structure and Boundaries Foramina and Communications with other spaces and cavities Contents Pterygopalatine Ganglion Especial emphasis on certain arteries and
The Surgical Treatment of Migraine Headaches
 The Surgical Treatment of Migraine Headaches Being migraine-free for 11 years has been a dream come true. I live my life now with a freedom that I hadn t known for more than 23 years. Kathy Where is the
The Surgical Treatment of Migraine Headaches Being migraine-free for 11 years has been a dream come true. I live my life now with a freedom that I hadn t known for more than 23 years. Kathy Where is the
Headache. Section 1. Migraine headache. Clinical presentation
 Section 1 Headache Migraine headache 1 Clinical presentation It is important to recognize just how significant a problem migraine headache is. It has been estimated that migraine affects 11% of the United
Section 1 Headache Migraine headache 1 Clinical presentation It is important to recognize just how significant a problem migraine headache is. It has been estimated that migraine affects 11% of the United
3-Deep fascia: is absent (except over the parotid gland & buccopharngeal fascia covering the buccinator muscle)
 The Face 1-Skin of the Face The skin of the face is: Elastic Vascular (bleed profusely however heal rapidly) Rich in sweat and sebaceous glands (can cause acne in adults) It is connected to the underlying
The Face 1-Skin of the Face The skin of the face is: Elastic Vascular (bleed profusely however heal rapidly) Rich in sweat and sebaceous glands (can cause acne in adults) It is connected to the underlying
Cluster headache associated with acute maxillary sinusitis.
 Cluster headache associated with acute maxillary sinusitis. Edvardsson, Bengt Published in: SpringerPlus DOI: 10.1186/2193-1801-2-509 2013 Link to publication Citation for published version (APA): Edvardsson,
Cluster headache associated with acute maxillary sinusitis. Edvardsson, Bengt Published in: SpringerPlus DOI: 10.1186/2193-1801-2-509 2013 Link to publication Citation for published version (APA): Edvardsson,
Atypical presentations of cluster headache
 Blackwell Science, LtdOxford, UKCHACephalalgia0333-1024Blackwell Science, 200222Original ArticleAtypical presentations in cluster headachetd Rozen Atypical presentations of cluster headache TD Rozen Department
Blackwell Science, LtdOxford, UKCHACephalalgia0333-1024Blackwell Science, 200222Original ArticleAtypical presentations in cluster headachetd Rozen Atypical presentations of cluster headache TD Rozen Department
Omran Saeed. Luma Taweel. Mohammad Almohtaseb. 1 P a g e
 2 Omran Saeed Luma Taweel Mohammad Almohtaseb 1 P a g e I didn t include all the photos in this sheet in order to keep it as small as possible so if you need more clarification please refer to slides In
2 Omran Saeed Luma Taweel Mohammad Almohtaseb 1 P a g e I didn t include all the photos in this sheet in order to keep it as small as possible so if you need more clarification please refer to slides In
Occipital Nerve Stimulation with the Bion Microstimulator for the Treatment of Medically Refractory Chronic Cluster Headache
 Pain Physician 2011; 14:435-440 ISSN 1533-3159 Case Report Occipital Nerve Stimulation with the Bion Microstimulator for the Treatment of Medically Refractory Chronic Cluster Headache Natalie H. Strand
Pain Physician 2011; 14:435-440 ISSN 1533-3159 Case Report Occipital Nerve Stimulation with the Bion Microstimulator for the Treatment of Medically Refractory Chronic Cluster Headache Natalie H. Strand
Temporal region. temporal & infratemporal fossae. Zhou Hong Ying Dept. of Anatomy
 Temporal region temporal & infratemporal fossae Zhou Hong Ying Dept. of Anatomy Temporal region is divided by zygomatic arch into temporal & infratemporal fossae. Temporal Fossa Infratemporal fossa Temporal
Temporal region temporal & infratemporal fossae Zhou Hong Ying Dept. of Anatomy Temporal region is divided by zygomatic arch into temporal & infratemporal fossae. Temporal Fossa Infratemporal fossa Temporal
Dr. Sami Zaqout, IUG Medical School
 The skull The skull is composed of several separate bones united at immobile joints called sutures. Exceptions? Frontal bone Occipital bone Vault Cranium Sphenoid bone Zygomatic bones Base Ethmoid bone
The skull The skull is composed of several separate bones united at immobile joints called sutures. Exceptions? Frontal bone Occipital bone Vault Cranium Sphenoid bone Zygomatic bones Base Ethmoid bone
Occipital Nerve Stimulation Corporate Medical Policy
 Occipital Nerve Stimulation Corporate Medical Policy File name: Occipital Nerve Stimulation File code: UM.SPSVC.14 Origination: 2011 Last Review: 11/2017 Next Review: 11/2018 Effective Date: 05/01/2018
Occipital Nerve Stimulation Corporate Medical Policy File name: Occipital Nerve Stimulation File code: UM.SPSVC.14 Origination: 2011 Last Review: 11/2017 Next Review: 11/2018 Effective Date: 05/01/2018
23 How Cluster Headache and Other Trigeminal Autonomic Cephalalgias Present
 23 How Cluster Headache and Other Trigeminal Autonomic Cephalalgias Present Henrik Winther Schytz 1. Cristina Tassorelli 2. Messoud Ashina 1 1 Glostrup Hospital, University of Copenhagen, Glostrup, Copenhagen,
23 How Cluster Headache and Other Trigeminal Autonomic Cephalalgias Present Henrik Winther Schytz 1. Cristina Tassorelli 2. Messoud Ashina 1 1 Glostrup Hospital, University of Copenhagen, Glostrup, Copenhagen,
CLUSTER HEADACHES: THE WORST PAIN POSSIBLE? QUESTIONS:
 CLUSTER HEADACHES: THE WORST PAIN POSSIBLE? QUESTIONS: 1. Have any of you heard of cluster headaches? 2. Do you know someone who suffers from cluster headaches? 1 WHAT ARE CLUSTER HEADACHES? A neurological
CLUSTER HEADACHES: THE WORST PAIN POSSIBLE? QUESTIONS: 1. Have any of you heard of cluster headaches? 2. Do you know someone who suffers from cluster headaches? 1 WHAT ARE CLUSTER HEADACHES? A neurological
For the following questions, indicate the letter that corresponds to the SINGLE MOST APPROPRIATE ANSWER
 GROSS ANATOMY EXAMINATION May 15, 2000 For the following questions, indicate the letter that corresponds to the SINGLE MOST APPROPRIATE ANSWER 1. Pain associated with an infection limited to the middle
GROSS ANATOMY EXAMINATION May 15, 2000 For the following questions, indicate the letter that corresponds to the SINGLE MOST APPROPRIATE ANSWER 1. Pain associated with an infection limited to the middle
Core Curriculum Syllabus Emergencies in Otolaryngology-Head and Neck Surgery FACIAL FRACTURES
 Core Curriculum Syllabus Emergencies in Otolaryngology-Head and Neck Surgery A. General Considerations FACIAL FRACTURES Look for other fractures like skull and/or cervical spine fractures Test function
Core Curriculum Syllabus Emergencies in Otolaryngology-Head and Neck Surgery A. General Considerations FACIAL FRACTURES Look for other fractures like skull and/or cervical spine fractures Test function
The trigeminal autonomic cephalalgias (TACs) are a group of. Cluster Headache and Other Trigeminal Autonomic Cephalalgias By Mark Burish, MD, PhD
 Downloaded from https://journals.lww.com/continuum by SruuCyaLiGD/095xRqJ2PzgDYuM98ZB494KP9rwScvIkQrYai2aioRZDTyulujJ/fqPksscQKqke3QAnIva1ZqwEKekuwNqyUWcnSLnClNQLfnPrUdnEcDXOJLeG3sr/HuiNevTSNcdMFp1i4FoTX9EXYGXm/fCfrbTavvQSUHUH4eazE11ptLzgCyEpzDoF
Downloaded from https://journals.lww.com/continuum by SruuCyaLiGD/095xRqJ2PzgDYuM98ZB494KP9rwScvIkQrYai2aioRZDTyulujJ/fqPksscQKqke3QAnIva1ZqwEKekuwNqyUWcnSLnClNQLfnPrUdnEcDXOJLeG3sr/HuiNevTSNcdMFp1i4FoTX9EXYGXm/fCfrbTavvQSUHUH4eazE11ptLzgCyEpzDoF
Sphenoid rhinosinusitis associated with abducens nerve palsy Case report
 Romanian Journal of Rhinology, Volume 8, No. 30, April-June 2018 CASE REPORT Sphenoid rhinosinusitis associated with abducens nerve palsy Case report Lucian Lapusneanu 1, Marlena Radulescu 1, Florin Ghita
Romanian Journal of Rhinology, Volume 8, No. 30, April-June 2018 CASE REPORT Sphenoid rhinosinusitis associated with abducens nerve palsy Case report Lucian Lapusneanu 1, Marlena Radulescu 1, Florin Ghita
Occipital Nerve Stimulation
 Occipital Nerve Stimulation Policy Number: 7.01.125 Last Review: 5/2018 Origination: 5/2006 Next Review: 5/2019 Policy Blue Cross and Blue Shield of Kansas City (Blue KC) will not provide coverage for
Occipital Nerve Stimulation Policy Number: 7.01.125 Last Review: 5/2018 Origination: 5/2006 Next Review: 5/2019 Policy Blue Cross and Blue Shield of Kansas City (Blue KC) will not provide coverage for
Cryptogenic Enlargement Of Bilateral Superior Ophthalmic Veins
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Radiology Volume 18 Number 1 Cryptogenic Enlargement Of Bilateral Superior Ophthalmic Veins K Kragha Citation K Kragha. Cryptogenic Enlargement Of Bilateral Superior Ophthalmic
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Radiology Volume 18 Number 1 Cryptogenic Enlargement Of Bilateral Superior Ophthalmic Veins K Kragha Citation K Kragha. Cryptogenic Enlargement Of Bilateral Superior Ophthalmic
Headache and Facial Pain. Mohammed ALEssa MBBS, FRCSC Assistant Professor Consultant Otolaryngology,Head & Neck Surgical Oncology
 Headache and Facial Pain Mohammed ALEssa MBBS, FRCSC Assistant Professor Consultant Otolaryngology,Head & Neck Surgical Oncology Introduction It is the most common neurologic complain The diagnosis usually
Headache and Facial Pain Mohammed ALEssa MBBS, FRCSC Assistant Professor Consultant Otolaryngology,Head & Neck Surgical Oncology Introduction It is the most common neurologic complain The diagnosis usually
Maxillofacial and Ocular Injuries
 Maxillofacial and Ocular Injuries Objectives At the conclusion of this presentation the participant will be able to: Identify the key anatomical structures of the face and eye and the impact of force on
Maxillofacial and Ocular Injuries Objectives At the conclusion of this presentation the participant will be able to: Identify the key anatomical structures of the face and eye and the impact of force on
Miller S, Matharu MS. Managing patients with cluster headache in primary care
 Miller S, Matharu MS. Managing patients with cluster headache in primary care Miller S, Matharu MS. Managing patients with cluster headache in primary care. Practitioner 2013;257 (1764):15-20 Dr Sarah
Miller S, Matharu MS. Managing patients with cluster headache in primary care Miller S, Matharu MS. Managing patients with cluster headache in primary care. Practitioner 2013;257 (1764):15-20 Dr Sarah
Clinical case. Clinical case 3/15/2018 OVERVIEW. Refractory headaches and update on novel treatment. Refractory headache.
 OVERVIEW Refractory headaches and update on novel treatment Definition of refractory headache Treatment approach Medications Neuromodulation In the pipeline Juliette Preston, MD OHSU Headache Center Refractory
OVERVIEW Refractory headaches and update on novel treatment Definition of refractory headache Treatment approach Medications Neuromodulation In the pipeline Juliette Preston, MD OHSU Headache Center Refractory
Anatomic Relations Summary. Done by: Sohayyla Yasin Dababseh
 Anatomic Relations Summary Done by: Sohayyla Yasin Dababseh Anatomic Relations Lecture 1 Part-1 - The medial wall of the nose is the septum. - The vestibule lies directly inside the nostrils (Nares). -
Anatomic Relations Summary Done by: Sohayyla Yasin Dababseh Anatomic Relations Lecture 1 Part-1 - The medial wall of the nose is the septum. - The vestibule lies directly inside the nostrils (Nares). -
Mark W. Green, MD, FAAN
 Mark W. Green, MD, FAAN Professor of Neurology, Anesthesiology, and Rehabilitation Medicine Director of Headache and Pain Medicine Icahn School of Medicine at Mt Sinai New York Pain-sensitive structures
Mark W. Green, MD, FAAN Professor of Neurology, Anesthesiology, and Rehabilitation Medicine Director of Headache and Pain Medicine Icahn School of Medicine at Mt Sinai New York Pain-sensitive structures
10/13/17. Christy M. Jackson, MD Director, Dalessio Headache Center Scripps Clinic, La Jolla Clinical Professor, Neurosciences UCSD
 Christy M. Jackson, MD Director, Dalessio Headache Center Scripps Clinic, La Jolla Clinical Professor, Neurosciences UCSD } Depomed Consultant 2014 to present } Avanir Consultant 2014 to present } Amgen
Christy M. Jackson, MD Director, Dalessio Headache Center Scripps Clinic, La Jolla Clinical Professor, Neurosciences UCSD } Depomed Consultant 2014 to present } Avanir Consultant 2014 to present } Amgen
Anterior Ethmoidal Nerve Overview
 Anterior Ethmoidal Nerve Overview Name Anterior Ethmoidal Nerve Latin Nervus Ethmoidalis anterior Etymology Pain Differential Diagnosis - Enrico Dellacà M.D Ph.D. Nerve from Latin nervus meaning sinew,
Anterior Ethmoidal Nerve Overview Name Anterior Ethmoidal Nerve Latin Nervus Ethmoidalis anterior Etymology Pain Differential Diagnosis - Enrico Dellacà M.D Ph.D. Nerve from Latin nervus meaning sinew,
Maxilla, ORBIT and infratemporal fossa. Neophytos C Demetriades MD, DDS, MSc Associate professor European University of Cyprus School of Medicine
 Maxilla, ORBIT and infratemporal fossa Neophytos C Demetriades MD, DDS, MSc Associate professor European University of Cyprus School of Medicine MAXILLA Superior, middle, and inferior meatus Frontal sinus
Maxilla, ORBIT and infratemporal fossa Neophytos C Demetriades MD, DDS, MSc Associate professor European University of Cyprus School of Medicine MAXILLA Superior, middle, and inferior meatus Frontal sinus
Infratemporal fossa: Tikrit University college of Dentistry Dr.Ban I.S. head & neck Anatomy 2 nd y.
 Infratemporal fossa: This is a space lying beneath the base of the skull between the lateral wall of the pharynx and the ramus of the mandible. It is also referred to as the parapharyngeal or lateral pharyngeal
Infratemporal fossa: This is a space lying beneath the base of the skull between the lateral wall of the pharynx and the ramus of the mandible. It is also referred to as the parapharyngeal or lateral pharyngeal
The Clinical Profile of Sumatriptan: Cluster Headache Key Words
 Paper Eur Neurol 1994;34(suppl 2):35-39 P.J. Peter J. Goadsby Department of Neurology, The Prince Henry Hospital, Little Bay, Sydney, NSW, Australia The Clinical Profile of Sumatriptan: Cluster Headache
Paper Eur Neurol 1994;34(suppl 2):35-39 P.J. Peter J. Goadsby Department of Neurology, The Prince Henry Hospital, Little Bay, Sydney, NSW, Australia The Clinical Profile of Sumatriptan: Cluster Headache
Parotid Gland. Parotid Gland. Largest of 3 paired salivary glands (submandibular; sublingual) Ramus of Mandible. Medial pterygoid.
 Parotid region Parotid Gland Largest of 3 paired salivary glands (submandibular; sublingual) Ramus of Mandible Medial pterygoid Cross section of mandible Masseter D S SCM Parotid Gland Mastoid Process
Parotid region Parotid Gland Largest of 3 paired salivary glands (submandibular; sublingual) Ramus of Mandible Medial pterygoid Cross section of mandible Masseter D S SCM Parotid Gland Mastoid Process
Post-Operative Cluster Headache Following Carotid Endarterectomy
 Review Received: October 31, 2016 Accepted: January 11, 2017 Published online: February 3, 2017 Post-Operative Cluster Headache Following Carotid Endarterectomy Thijs H.T. Dirkx Peter J. Koehler Department
Review Received: October 31, 2016 Accepted: January 11, 2017 Published online: February 3, 2017 Post-Operative Cluster Headache Following Carotid Endarterectomy Thijs H.T. Dirkx Peter J. Koehler Department
SCHOOL OF ANATOMICAL SCIENCES Mock Run Questions. 4 May 2012
 SCHOOL OF ANATOMICAL SCIENCES Mock Run Questions 4 May 2012 1. With regard to the muscles of the neck: a. the platysma muscle is supplied by the accessory nerve. b. the stylohyoid muscle is supplied by
SCHOOL OF ANATOMICAL SCIENCES Mock Run Questions 4 May 2012 1. With regard to the muscles of the neck: a. the platysma muscle is supplied by the accessory nerve. b. the stylohyoid muscle is supplied by
Commen Nose Diseases
 Commen Nose Diseases Symptoms List: Nasal obstruction. Nasal discharge: Anterior (Rhinorrhea). Posterior (Postnasal discharge). Epistaxis. Hyposmia and Anosmia. Headache. Snoring. Nasal Obstruction Definition:
Commen Nose Diseases Symptoms List: Nasal obstruction. Nasal discharge: Anterior (Rhinorrhea). Posterior (Postnasal discharge). Epistaxis. Hyposmia and Anosmia. Headache. Snoring. Nasal Obstruction Definition:
Corporate Medical Policy
 Corporate Medical Policy File Name: Origination: Last CAP Review: Next CAP Review: Last Review: surgical_deactivation_of_migraine_headache_trigger_sites 10/2012 5/2017 5/2018 5/2017 Description of Procedure
Corporate Medical Policy File Name: Origination: Last CAP Review: Next CAP Review: Last Review: surgical_deactivation_of_migraine_headache_trigger_sites 10/2012 5/2017 5/2018 5/2017 Description of Procedure
Mohammad Hisham Al-Mohtaseb. Lina Mansour. Reyad Jabiri. 0 P a g e
 2 Mohammad Hisham Al-Mohtaseb Lina Mansour Reyad Jabiri 0 P a g e This is only correction for the last year sheet according to our record. If you already studied this sheet just read the yellow notes which
2 Mohammad Hisham Al-Mohtaseb Lina Mansour Reyad Jabiri 0 P a g e This is only correction for the last year sheet according to our record. If you already studied this sheet just read the yellow notes which
Anatomy and Physiology. Bones, Sutures, Teeth, Processes and Foramina of the Human Skull
 Anatomy and Physiology Chapter 6 DRO Bones, Sutures, Teeth, Processes and Foramina of the Human Skull Name: Period: Bones of the Human Skull Bones of the Cranium: Frontal bone: forms the forehead and the
Anatomy and Physiology Chapter 6 DRO Bones, Sutures, Teeth, Processes and Foramina of the Human Skull Name: Period: Bones of the Human Skull Bones of the Cranium: Frontal bone: forms the forehead and the
Trigeminal Nerve (V)
 Trigeminal Nerve (V) Lecture Objectives Discuss briefly how the face is developed. Follow up the course of trigeminal nerve from its point of central connections, exit and down to its target areas. Describe
Trigeminal Nerve (V) Lecture Objectives Discuss briefly how the face is developed. Follow up the course of trigeminal nerve from its point of central connections, exit and down to its target areas. Describe
GNK485 The eye and related structures. Prof MC Bosman 2012
 GNK485 The eye and related structures Prof MC Bosman 2012 Surface anatomy Bony orbit Eyeball and Lacrimal apparatus Extra-ocular muscles Movements of the eye Innervation Arterial supply and venous drainage
GNK485 The eye and related structures Prof MC Bosman 2012 Surface anatomy Bony orbit Eyeball and Lacrimal apparatus Extra-ocular muscles Movements of the eye Innervation Arterial supply and venous drainage
Supraorbital nerve stimulation Cefaly Device - FDA Approved for migraine prevention (also being investigated as acute therapy)
 NEUROSTIMULATION/NEUROMODULATION UPDATE Meyer and Renee Luskin Andrew Charles, M.D. Professor Luskin Chair in Migraine and Headache Studies Director, UCLA Goldberg Migraine Program David Geffen School
NEUROSTIMULATION/NEUROMODULATION UPDATE Meyer and Renee Luskin Andrew Charles, M.D. Professor Luskin Chair in Migraine and Headache Studies Director, UCLA Goldberg Migraine Program David Geffen School
Sinus Surgery. Middle Meatus
 Sinus Surgery Introduction Sinus surgery is a very common and safe operation. Your doctor may recommend that you have sinus surgery. The decision whether or not to have sinus surgery is also yours. This
Sinus Surgery Introduction Sinus surgery is a very common and safe operation. Your doctor may recommend that you have sinus surgery. The decision whether or not to have sinus surgery is also yours. This
Epidemiology 3002). Epidemiology and Pathophysiology
 Epidemiology Maxillofacial trauma or injuries are commonly encountered in the practice of emergency medicine and are presenting one of the most challenging problems to the attending surgeons or physicians
Epidemiology Maxillofacial trauma or injuries are commonly encountered in the practice of emergency medicine and are presenting one of the most challenging problems to the attending surgeons or physicians
COMPLICATIONS IN ENDOSCOPIC SINUS SURGERY
 COMPLICATIONS IN ENDOSCOPIC SINUS SURGERY John M. DelGaudio, MD Professor and Vice Chair Chief of Rhinology and Sinus Surgery Department of Otolaryngology-Head and Neck Surgery Emory University School
COMPLICATIONS IN ENDOSCOPIC SINUS SURGERY John M. DelGaudio, MD Professor and Vice Chair Chief of Rhinology and Sinus Surgery Department of Otolaryngology-Head and Neck Surgery Emory University School
The orbit-1. Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Assistant Professor of Anatomy and Histology
 The orbit-1 Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Assistant Professor of Anatomy and Histology Orbital plate of frontal bone Orbital plate of ethmoid bone Lesser wing of sphenoid Greater wing of sphenoid Lacrimal bone Orbital
The orbit-1 Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Assistant Professor of Anatomy and Histology Orbital plate of frontal bone Orbital plate of ethmoid bone Lesser wing of sphenoid Greater wing of sphenoid Lacrimal bone Orbital
ANASTAMOSIS FOR BRAIN STEM ISCHEMIA/Khodadad et al.
 ANASTAMOSIS FOR BRAIN STEM ISCHEMIA/Khodadad et al. visualization of the posterior inferior cerebellar artery. The patient, now 11 months post-operative, has shown further neurological improvement since
ANASTAMOSIS FOR BRAIN STEM ISCHEMIA/Khodadad et al. visualization of the posterior inferior cerebellar artery. The patient, now 11 months post-operative, has shown further neurological improvement since
Outpatient Headache Care Guideline
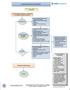 1 Outpatient Care Guideline Inclusion criteria: children > 3 yrs with headaches Is urgent emergency department, neuroimaging, or Neurology consultation indicated? Referral to ED if: New severe headache
1 Outpatient Care Guideline Inclusion criteria: children > 3 yrs with headaches Is urgent emergency department, neuroimaging, or Neurology consultation indicated? Referral to ED if: New severe headache
Oral and Maxillofacial Surgeons and the seriously injured patient. Barts and The London NHS Trust
 Oral and Maxillofacial Surgeons and the seriously injured patient Barts and The London NHS Trust How do you assess this? Primary Survey A B C D E Airway & Cervical Spine Breathing & Ventilation Circulation
Oral and Maxillofacial Surgeons and the seriously injured patient Barts and The London NHS Trust How do you assess this? Primary Survey A B C D E Airway & Cervical Spine Breathing & Ventilation Circulation
ANGIOGRAPHY IN PATIENTS WITH INTRACTABLE EPISTAXIS*
 %OL. ii6, No. I ANGIOGRAPHY IN PATIENTS WITH INTRACTABLE EPISTAXIS* By MARC N. COEL, M.l).,f and EDWARD A. JANON, M.D. NGIOG RAPHY has become increasingly important in the evaluation and treatment of bleeding
%OL. ii6, No. I ANGIOGRAPHY IN PATIENTS WITH INTRACTABLE EPISTAXIS* By MARC N. COEL, M.l).,f and EDWARD A. JANON, M.D. NGIOG RAPHY has become increasingly important in the evaluation and treatment of bleeding
Allergic fungal rhinosinusitis: detection of fungal DNA in sinus aspirate using polymerase chain reaction
 1- Allergic fungal rhinosinusitis: detection of fungal DNA in sinus aspirate using polymerase chain reaction Abstract Objective: This study investigated allergic fungal rhinosinusitis cases, and aimed
1- Allergic fungal rhinosinusitis: detection of fungal DNA in sinus aspirate using polymerase chain reaction Abstract Objective: This study investigated allergic fungal rhinosinusitis cases, and aimed
Overview INTRODUCTION 3/15/2018. Headache Emergencies. Other way to differentiate between them? Is there an easy way to differentiate between them?
 Overview Headache Emergencies Primary versus Secondary headache disorder Red flags 4 cases of unusual headache emergencies Disclaimer: we will not talk about brain bleed as patients usually go the ED.
Overview Headache Emergencies Primary versus Secondary headache disorder Red flags 4 cases of unusual headache emergencies Disclaimer: we will not talk about brain bleed as patients usually go the ED.
Embriologically, The head is formed from the first two cervical segments (except the mandible, which is formed by the third). The first and second
 Embriologically, The head is formed from the first two cervical segments (except the mandible, which is formed by the third). The first and second cervical vertebra are also derived from these two segments.
Embriologically, The head is formed from the first two cervical segments (except the mandible, which is formed by the third). The first and second cervical vertebra are also derived from these two segments.
A synopsis of: Diagnosis and Management of Headaches in Adults: A national clinical guideline. Scottish intercollegiate Guidelines Network SIGN
 A synopsis of: Diagnosis and Management of Headaches in Adults: A national clinical guideline Scottish intercollegiate Guidelines Network SIGN November 2008. PETER FRAMPTON MSc MCOptom BAppSc (Optom)(AUS)
A synopsis of: Diagnosis and Management of Headaches in Adults: A national clinical guideline Scottish intercollegiate Guidelines Network SIGN November 2008. PETER FRAMPTON MSc MCOptom BAppSc (Optom)(AUS)
PTA 106 Unit 1 Lecture 3
 PTA 106 Unit 1 Lecture 3 The Basics Arteries: Carry blood away from the heart toward tissues. They typically have thicker vessels walls to handle increased pressure. Contain internal and external elastic
PTA 106 Unit 1 Lecture 3 The Basics Arteries: Carry blood away from the heart toward tissues. They typically have thicker vessels walls to handle increased pressure. Contain internal and external elastic
Hemicrania continua-like headache associated with carotid dissection may respond to indomethacin
 Thomas Jefferson University Jefferson Digital Commons Department of Neurology Faculty Papers Department of Neurology January 2007 Hemicrania continua-like headache associated with carotid dissection may
Thomas Jefferson University Jefferson Digital Commons Department of Neurology Faculty Papers Department of Neurology January 2007 Hemicrania continua-like headache associated with carotid dissection may
Trigeminal Nerve Anatomy. Dr. Mohamed Rahil Ali
 Trigeminal Nerve Anatomy Dr. Mohamed Rahil Ali Trigeminal nerve Largest cranial nerve Mixed nerve Small motor root and large sensory root Motor root Nucleus of motor root present in the pons and medulla
Trigeminal Nerve Anatomy Dr. Mohamed Rahil Ali Trigeminal nerve Largest cranial nerve Mixed nerve Small motor root and large sensory root Motor root Nucleus of motor root present in the pons and medulla
MIGRAINOUS NEURALGIA BY E. A. NIEMAN* and L. J. HURWITZ
 J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiat., 1961, 24, 369. OCULAR SYMPATHETIC PALSY IN PERIODIC MIGRAINOUS NEURALGIA BY E. A. NIEMAN* and L. J. HURWITZ From the National Hospital, Queen Square, London Harris (1921,
J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiat., 1961, 24, 369. OCULAR SYMPATHETIC PALSY IN PERIODIC MIGRAINOUS NEURALGIA BY E. A. NIEMAN* and L. J. HURWITZ From the National Hospital, Queen Square, London Harris (1921,
Sphenopalatine Ganglion Block or Other Intranasal Blockage for Headache
 Sphenopalatine Ganglion Block or Other Intranasal Blockage for Headache Policy Number: 7.01.159 Last Review: 1/1/18 Origination: 7/2017 Next Review: 7/1/18 Policy Blue Cross and Blue Shield of Kansas City
Sphenopalatine Ganglion Block or Other Intranasal Blockage for Headache Policy Number: 7.01.159 Last Review: 1/1/18 Origination: 7/2017 Next Review: 7/1/18 Policy Blue Cross and Blue Shield of Kansas City
Medical Policy An independent licensee of the Blue Cross Blue Shield Association
 Sphenopalatine Ganglion Block for Headache Page 1 of 12 Medical Policy An independent licensee of the Blue Cross Blue Shield Association Title: Sphenopalatine Ganglion Block for Headache Professional Institutional
Sphenopalatine Ganglion Block for Headache Page 1 of 12 Medical Policy An independent licensee of the Blue Cross Blue Shield Association Title: Sphenopalatine Ganglion Block for Headache Professional Institutional
By Nathan Hall Associate Editor
 By Nathan Hall Associate Editor 34 Practical Neurology March 2005 These new rules may change the definition of head pain, but some practitioners may find the new guidelines themselves to be a source of
By Nathan Hall Associate Editor 34 Practical Neurology March 2005 These new rules may change the definition of head pain, but some practitioners may find the new guidelines themselves to be a source of
TRAUMA TO THE FACE AND MOUTH
 Dr.Yahya A. Ali 3/10/2012 F.I.C.M.S TRAUMA TO THE FACE AND MOUTH Bailey & Love s 25 th edition Injuries to the orofacial region are common, but the majority are relatively minor in nature. A few are major
Dr.Yahya A. Ali 3/10/2012 F.I.C.M.S TRAUMA TO THE FACE AND MOUTH Bailey & Love s 25 th edition Injuries to the orofacial region are common, but the majority are relatively minor in nature. A few are major
MAXILLA, ORBIT & PTERYGOPALATINE FOSSA. Neophytos C Demetriades MD, DDS, MSc Associate professor European University of Cyprus School of Medicine
 MAXILLA, ORBIT & PTERYGOPALATINE FOSSA Neophytos C Demetriades MD, DDS, MSc Associate professor European University of Cyprus School of Medicine Maxilla MAXILLA Superior, middle, and inferior meatus Frontal
MAXILLA, ORBIT & PTERYGOPALATINE FOSSA Neophytos C Demetriades MD, DDS, MSc Associate professor European University of Cyprus School of Medicine Maxilla MAXILLA Superior, middle, and inferior meatus Frontal
Surgical Correction of Crow s Feet Deformity With Radiofrequency Current
 INTERNATIONAL CONTRIBUTION Oculoplastic Surgery Surgical Correction of Crow s Feet Deformity With Radiofrequency Current Min-Hee Ryu, MD; David Kahng, MD; and Yongho Shin, MD, PhD Aesthetic Surgery Journal
INTERNATIONAL CONTRIBUTION Oculoplastic Surgery Surgical Correction of Crow s Feet Deformity With Radiofrequency Current Min-Hee Ryu, MD; David Kahng, MD; and Yongho Shin, MD, PhD Aesthetic Surgery Journal
Parotid Gland, Temporomandibular Joint and Infratemporal Fossa
 M1 - Anatomy Parotid Gland, Temporomandibular Joint and Infratemporal Fossa Jeff Dupree Sanger 9-057 jldupree@vcu.edu Parotid gland: wraps around the mandible positioned between the mandible and the sphenoid
M1 - Anatomy Parotid Gland, Temporomandibular Joint and Infratemporal Fossa Jeff Dupree Sanger 9-057 jldupree@vcu.edu Parotid gland: wraps around the mandible positioned between the mandible and the sphenoid
ORIGINAL ARTICLE. Le Fort I Osteotomy and Skull Base Tumors. Tyler M. Lewark, MD; Gregory C. Allen, MD; Khalid Chowdhury, MD, FRCSC; Kenny H.
 Le Fort I Osteotomy and Skull Base Tumors A Pediatric Experience ORIGINAL ARTICLE Tyler M. Lewark, MD; Gregory C. Allen, MD; Khalid Chowdhury, MD, FRCSC; Kenny H. Chan, MD Background: The Le Fort I maxillary
Le Fort I Osteotomy and Skull Base Tumors A Pediatric Experience ORIGINAL ARTICLE Tyler M. Lewark, MD; Gregory C. Allen, MD; Khalid Chowdhury, MD, FRCSC; Kenny H. Chan, MD Background: The Le Fort I maxillary
Index. Prim Care Clin Office Pract 31 (2004) Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type.
 Prim Care Clin Office Pract 31 (2004) 441 447 Index Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A Abscess, brain, headache in, 388 Acetaminophen for migraine, 406 407 headache from, 369
Prim Care Clin Office Pract 31 (2004) 441 447 Index Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A Abscess, brain, headache in, 388 Acetaminophen for migraine, 406 407 headache from, 369
Veins of the Face and the Neck
 Veins of the Face and the Neck Facial Vein The facial vein is formed at the medial angle of the eye by the union of the supraorbital and supratrochlear veins. connected through the ophthalmic veins with
Veins of the Face and the Neck Facial Vein The facial vein is formed at the medial angle of the eye by the union of the supraorbital and supratrochlear veins. connected through the ophthalmic veins with
They are updated regularly as new NICE guidance is published. To view the latest version of this NICE Pathway see:
 bring together everything NICE says on a topic in an interactive flowchart. are interactive and designed to be used online. They are updated regularly as new NICE guidance is published. To view the latest
bring together everything NICE says on a topic in an interactive flowchart. are interactive and designed to be used online. They are updated regularly as new NICE guidance is published. To view the latest
1. EPINEPHRINE 2. PREDNISONE 3. BENADRYL 4. HYALURONIDASE 5. BABY ASPIRIN 6. NITROPASTE 7. VIAGRA 8. CANNULAS. Must Haves for Injection Safety
 1. EPINEPHRINE 2. PREDNISONE 3. BENADRYL 4. HYALURONIDASE 5. BABY ASPIRIN 6. NITROPASTE 7. VIAGRA 8. CANNULAS Must Haves for Injection Safety Facial artery: This artery stems from the external carotid
1. EPINEPHRINE 2. PREDNISONE 3. BENADRYL 4. HYALURONIDASE 5. BABY ASPIRIN 6. NITROPASTE 7. VIAGRA 8. CANNULAS Must Haves for Injection Safety Facial artery: This artery stems from the external carotid
What Is an Arteriovenous malformation (AVM)?
 American Society of Neuroradiology What Is an Arteriovenous malformation (AVM)? From the Cerebrovascular Imaging and Intervention Committee of the American Heart Association Cardiovascular Council Randall
American Society of Neuroradiology What Is an Arteriovenous malformation (AVM)? From the Cerebrovascular Imaging and Intervention Committee of the American Heart Association Cardiovascular Council Randall
