'circular shunt'1. CASE 1 Shortly after birth a 36-hour-old, full-term infant girl showed cyanosis and dyspnoea. Physical
|
|
|
- Constance Lewis
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Pulmonary atresia with left ventricularright atrial communication: basis for 'circular shunt'1 Thorax (1966), 21, 83. KENNETH L. JUE, GEORGE NOREN, AND JESSE E. EDWARDS From the Departments of Paediatrics and Pathology, University of Minnesota, the Department of Paediatrics, Hennepin County General Hospital, Minneapolis, and the Department of Pathology, The Charles T. Miller Hospital, St. Paul, Minnesota In the usual instance of an intracardiac right-toleft shunt the blood participating in the shunt traverses a capillary bed before it returns to the chamber from which it originated. In an uncommon instance some of the shunted blood returns to the chamber of origin through intracardiac channels, yielding a phenomenon which may be termed a 'circular' shunt. This term was first used with reference to a case reported from our group by Shone, Anderson, Elliott, Amplatz, Lillehei, and Edwards (1962). In that case it was assumed that some of the right atrial blood had been shunted in a right-to-left direction into the left atrium. Some of this blood then escaped from the left ventricle through a small ventricular septal defect into the right ventricle. Then, in the presence of pulmonary stenosis and of tricuspid insufficiency, some of the blood which had originated in the right atrium returned to that chamber to complete a 'circular' shunt in which each of the four cardiac chambers had participated. We have studied two additional cases which fulfil the foregoing definition of a 'circular' shunt. In each there was pulmonary valvular atresia in association with a left ventricular-right atrial communication. In the first, the left ventricularright atrial communication was of the classical variety. In the second, this communication resulted from a combination of Ebstein's malformation of the tricuspid valve and a ventricular septal defect in which the defect opened into that part of the right ventricle which lay proximal to the attachments of the malformed tricuspid valve. 'This study was supported by Research Grant HE-5694 and Training Grant 5 Ti HE 5570 of the National Institutes of Health. United States Public Health Service. 83 CASE REPORTS CASE 1 Shortly after birth a 36-hour-old, full-term infant girl showed cyanosis and dyspnoea. Physical examination revealed a cyanotic and tachypnoeic infant with respiratory retraction of the subcostal areas and of the suprasternal notches. No cardiac murmurs were heard, and the cardiac sounds were thought to be normal. The lower edge of the liver lay 4 cm. below the right costal margin and that of the spleen at the left costal margin. Chest radiographs showed mild cardiomegaly and diminished pulmonary vascular markings (Fig. 1). The electrocardiogram was interpreted as showing a normal axis for age, right atrial enlargement, and left ventricular preponderance (Fig. 2). A forward angiocardiogram, taken at the University of Minnesota Hospitals when the infant was 23 hours old, was interpreted as representing pulmonary atresia with an intact ventricular septum (Fig. 3). A deteriorating condition, despite intensive medical management, led to the transfer of the patient to the Hennepin County General Hospital for surgical treatment under hyperbaric conditions. Under these conditions, with halothane anaesthesia and with the aid of inflow occlusion, valvulotomy of the atretic pulmonary valve was performed. The child failed to improve and died on the operating table. Pathologically, the findings were related to the heart. The main ventricular mass was formed by the left ventricle. The pulmonary trunk was narrow and normally related to the aorta, which was wider than normal. The ductus arteriosus was patent. The pulmonary valve, which had been atretic, was found, for the most part, to have been removed during the surgical procedure. The right ventricle showed the features commonly seen in pulmonary valvular atresia, since its chamber was hypoplastic and its wall was relatively thick. No septal defect led into this chamber. In concert with the hypoplastic nature of the right ventricle, the tricuspid valve was hypoplastic although the individual leaflets could be identified.
2 84 FIG. 2. Case 1. Electrocardiogram. Peaked P waves in lead II, indicating right atrial enlargement. Normal electrical axis in the frontal plane. Left ventricular preponderance. Kenneth L. Jue, George Noren, and Jesse E. Edwards FIG. 1. Case 1. Frontal radiograph of thorax. Marked decrease of pulmonary vascular markings. The pulmonary arterial segment is concave. WgIgL4IFt U T[TT mt t ~~Tl r 1W 7;X fx lllilli W11 T1 avr avl avp IIIW EE Thorax: first published as /thx on 1 January Downloaded from V4R A communication, 2 mm. in diameter (Fig. 4), was found between the left ventricle and the right atrium. Trhe left ventricular opening of this communication lay in the ventricular septum below the junction of the right and posterior aortic cusps. The right atrial opening lay in the septal wall immediately superior to the septal leaflet of the tricuspid valve. The right atrial cavity was enlarged and the foramen ovale was patent. In the left side of the heart the aortic and mitral valves were normal and the left ventricular chamber was somewhat enlarged. VI V2 V4 V6 CASE 2 A 7-day-old, cyanotic infant girl was referred to the University of Minnesota Hospitals for evaluation. Physical examination revealed a cyanotic infant in no distress. No thrill was palpable. A grade II (on a basis of I to IV) pansystolic murmur was best heard in the second and third intercostal spaces along the left sternal border. The second cardiac sound was single (with marked diminution of the pulmonic component). No diastolic murmurs or ejection clicks were heard. An electrocardiogram was interpreted as showing a normal axis for age, right atrial hypertrophy, and on 13 November 2018 by guest. Protected by
3 Pulmonary atresia with left ventricular-right atrial communication C.. -~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~A FIG. 3. Case 1. Venous angiocardiogram: (a) and (b) early phases offrontal and lateral views, respectively. Contrast material extends from the opacified right atrium (R.A.) (in frontal view) into the left atrium (L.A.), and from the latter chamber into the left ventricle (L. V.); (c) and (d) late phases of study in frontal and lateral views, respectively. Opacification of the left atrium (L.A.), left ventricle (L. V.), and aorta (A.). The aorta is markedly dilated. The pulmonary trunk (P.T.), which is hypoplastic, has been opacified through a patent ductus arteriosus. In the frontal view (c) the arrow indicates the position of an opacified right ventricle. left ventricular hypertrophy (Fig. 5). Chest radiographs showed a concentrically enlarged and globular heart (Fig. 6). The pulmonary arterial segment was flat but not distinctly concave. The peripheral pulmonary vascular markings were markedly diminished. A venous angiocardiogram from a saphenous vein (Fig. 7) was interpreted as being compatible with pulmonary atresia, an intact ventricular septum, and a hypoplastic right ventricle. When 4 weeks of age the patient developed congestive cardiac failure, but responded well to medical management. With the infant in an apparently optimal physical condition, an endto-end anastomosis between the pulmonary trunk and the innominate artery was performed. Marked re- 85
4 86 ' Kenneth L. Jue, George Noren, and Jesse E. Edwards FIG. 4. Case 1. Gross specimen of heart. (a) Interior of left ventricle (L.V.) and the ascending aorta (A.A.). Immediately inferior to the level of the aortic valve (A. V.) is a defect (containing probe). This leads from the left ventricle into the right atrium, beyond. (b) Right atrium (R.A.) and right ventricle (R.V.). The right ventricular chamber is hypoplastic. The pulmonary valve is atretic. Above the tricuspid valve (T.V.) is a defect (containing probe) representing a communication between the left ventricle (beyond) and the right atrium. The foramen ovale (F.O.) is patent. i-, -..H- IT4'1 W;t fffsi Et~~~~~~~~;i '1 Thorax: first published as /thx on 1 January Downloaded from I IT m avr avl avtv..,,!,... i Vl V2 V4 V6 FIG. 5. Case 2. Electrocardiogram. In frontal plane normal electrical axis for age. Right atrial enlargement (peaked P waves in leads V, and V3) and left ventricular hypertrophy. on 13 November 2018 by guest. Protected by
5 Pulmonary atresia with left ventricular-right atrial communication FIG. 6. Case 2. Frontal chest radiograph. Decreased pulmonary vascular markings, left ventricular enlargement, and lack of prominence of pulmonary arterial segment. FIG. 7. Case 2. Venous angiocardiogram. (a) Early phase in left anterior oblique view. Right-to-left shunt at the atrial level. R.A. = right atrium; L.A. = left atrium. (b) Late phase in left anterior oblique view. Opacification of right atrium (R.A.), left atrium (L.A.), and left ventricle. The aorta (A.) is markedly dilated and the pulmonary trunk (P. T.), which has been opacified through a patent ductus arteriosus, is correspondingly hypoplastic. H 87
6 88 Kenneth L. Jue, George Noren, and Jesse E. Edwards FIG. 8. Case 2. Pulmonary atresia associated with an Ebstein-like malformation of the tricuspid valve and a small defect of the ventricular septum yielding a communication between the left ventricle and the right atrium. (Illustrations from Elliott et al. (1963). Reproduced with permission.) (a) Interior of right atrium (R.A.) and right ventricle (R. V.). The tricuspid valve is displaced downward from the annulus fibrosus (dotted line) as part of an Ebstein's malformation. The probe lies in the communication between the left ventricle and the 'atrialized' portion of the right ventricle which lies above the tricuspid valve. (b) View of tricuspid valve (T. V.) and adjacent structures. Tricuspid valve is inserted below the annulus fibrosus (dotted line). Probe in defect. (c) Left ventricle and aorta (A.). Probe lies in the defect which leads to the 'atrialized' portion of the right ventricle beyond. spiratory distress developed 24 hours after the operation and the infant died soon afterwards. At necropsy the heart was found to be slightly enlarged and the great vessels normally related. The ductus arteriosus was patent and the pulmonary trunk hypoplastic. The main ventricular mass was formed by the left ventricle. The right atrium was dilated and hypertrophied. The pulmonary valve was atretic and the right ventricle hypoplastic. The tricuspid valve showed an Ebstein's malformation in which its septal and posterior leaflets were attached to the right ventricular wall below the annulus of the valve. A narrow ventricular septal defect (Fig. 8), measuring about 1' mm. in diameter, was present. From the left ventricular side the defect lay immediately inferior to the right aortic cusp. From the right ventricular side the defect was found to open into that part of the right ventricle which lay proximal to the malformed tricuspid valve; that is, the defect communicated with the 'atrialized' portion of the right ventricle. This case was included in the report of Elliott, Adams, and Edwards (1963) on pulmonary atresia with intact ventricular septum. In that report emphasis was placed on polypoid, loose, fibrous tissue attached to the rim of the defect. It is suggested that this tissue, in company with nearby tricuspid valvular tissue, might have closed the defect during systole. The right atrium was grossly enlarged and the foramen ovale was patent. COMMENT In each of the cases presented there was a communication, though narrow, between the left ventricle and the right atrium in the presence of pulmonary atresia. Although venous angiocardiography had been performed in each patient, the left ventricular-right atrial communication was not identified. This may have resulted from a rapid circulation time, so that during the levophase of the study opaque material was still present in the right atrium. A left ventriculogram might have demonstrated the left ventricular-right atrial communication. In spite of this, one may assume that some blood passed from the left ventricle to the right atrium. If one refers to the diagrams of the basic abnormalities in each of the two cases reported (Fig. 9), several features are apparent. The first is that in the presence of pulmonary atresia and without a communication between the two propelling ventricles, blood in the right atrium is shunted into the left atrium
7 Pulmonary atresia with left ventricular-right atrial communication a FIG. 9. Diagram of the central circulation in the two cases reported. (a) Case 1. Pulmonary valvular atresia associated with left ventricular-right atrial communication. A circular shunt is engendered by the presence ofpulmonary atresia, the left ventricular-right atrial communication, and the patent foramen ovale. Of the blood in the right atrium which shunts into the left atrium and then flows into the left ventricle, some is recirculated into the right atrium through the left ventricular-right atrial communication. (b) Case 2. Pulmonary valvular atresia associated with Ebstein's malformation of the tricuspid valve and a communication between the left ventricle and the 'atrialized' portion of the right ventricle. As in case 1, of the blood originating in the right atrium and then shunting into the left atrium and the left ventricle, some, in turn, is delivered through the abnormal communication into the right atrium to complete the 'circular' shunt. through the foramen ovale. This blood then reaches the left ventricle, from which chamber some of the blood which had originated in the right atrium returns directly to this chamber. In this way the definition of a 'circular' shunt is fulfilled. It is recognized that, in the situation peculiar to each of the two cases presented, the propelling right ventricle does not participate as a conduit in carrying right atrial blood back to the right atrium. This is in contrast with the 'circular' shunt in the case of Shone et al. (1962). In each of our cases the small size of the left ventricular-right atrial communication probably precluded the 'circular' shunt from being of large volume. As indicated, Elliott et al. (1963) suggested that the defect in case 2 might have been closed during systole by the accessory tissue in relation to the defect. The two cases are instructive because the same findings may be present in other cases in which, under basically similar conditions, the left ventricular-right atrial communication is wider than in the two cases here presented. The co-existence of a left ventricular-right atrial communication with pulmonary atresia has previously been noted (Lauer, Fink, Petry, Dunn, and Diehl, 1964). SUMMARY A 'circular' shunt is defined as a condition in which blood originating in one cardiac chamber is shunted through the heart to return to the original chamber without having passed through a capillary bed. In each of two cases of pulmonary atresia a left ventricular-right atrial communication was associated. In one the later communication was of the classical variety. In the other, an Ebstein's malformation of the tricuspid valve was present. In this instance a ventricular septal defect entered 89
8 90 Kenneth L. Jue, George Noren, and Jesse E. Edwards the right ventricle proximal to the valve and in blood would fulfil the definition of a 'circular' this way accounted for the left ventricular-right shunt. atrial communication. REFERENCES In each case, on the basis of the pulmonary Elliott, L. P., Adams, P., Jr., and Edwards, J. E. (1963). Pulmonary atresia, a right-to-left transatrial shunt occurred. atresia with intact ventricular septum. Brit. Heart J., 25, 489. Lauer, R. M., Fink, H. P., Petry, E. L., Dunn, M. I., and Diehl, A. M. It is assumed that some of the blood which had (1964). Angiographic demonstration of intramyocardial sinusoids originated in the right atrium was returned to the in pulmonary-valve atresia with intact ventricular septum and hypoplastic right ventricle. New Engl. J. Med., 271, 68. right atrium after passing through the left atrium Shone, J. D., Anderson, R. C., Elliott, L. P., Amplatz, K., Lillehei, and the left ventricle. This peculiar course of the AC. W., and Edwards, J. E. (1962). Clinical pathologic conference. Thorax: first published as /thx on 1 January Downloaded from on 13 November 2018 by guest. Protected by
COMBINED CONGENITAL SUBAORTIC STENOSIS AND INFUNDIBULAR PULMONARY STENOSIS*
 COMBINED CONGENITAL SUBAORTIC STENOSIS AND INFUNDIBULAR PULMONARY STENOSIS* BY HENRY N. NEUFELD,t PATRICK A. ONGLEY, AND JESSE E. EDWARDS From the Sections of Pa?diatrics and Pathological Anatomy, Mayo
COMBINED CONGENITAL SUBAORTIC STENOSIS AND INFUNDIBULAR PULMONARY STENOSIS* BY HENRY N. NEUFELD,t PATRICK A. ONGLEY, AND JESSE E. EDWARDS From the Sections of Pa?diatrics and Pathological Anatomy, Mayo
HISTORY. Question: What category of heart disease is suggested by the fact that a murmur was heard at birth?
 HISTORY 23-year-old man. CHIEF COMPLAINT: Decreasing exercise tolerance of several years duration. PRESENT ILLNESS: The patient is the product of an uncomplicated term pregnancy. A heart murmur was discovered
HISTORY 23-year-old man. CHIEF COMPLAINT: Decreasing exercise tolerance of several years duration. PRESENT ILLNESS: The patient is the product of an uncomplicated term pregnancy. A heart murmur was discovered
Congenital Heart Defects
 Normal Heart Congenital Heart Defects 1. Patent Ductus Arteriosus The ductus arteriosus connects the main pulmonary artery to the aorta. In utero, it allows the blood leaving the right ventricle to bypass
Normal Heart Congenital Heart Defects 1. Patent Ductus Arteriosus The ductus arteriosus connects the main pulmonary artery to the aorta. In utero, it allows the blood leaving the right ventricle to bypass
Communication of Mitral Valve with Both Ventricles Associated with Double Outlet Right Ventricle
 Communication of Mitral Valve with Both Ventricles Associated with Double Outlet Right Ventricle By RAJENTDRA TANDON, M.D., JAMES H. MOLLR, MD, AND JESSE E. EDWARDS, M.D. SUMMARY A rare case of an infant
Communication of Mitral Valve with Both Ventricles Associated with Double Outlet Right Ventricle By RAJENTDRA TANDON, M.D., JAMES H. MOLLR, MD, AND JESSE E. EDWARDS, M.D. SUMMARY A rare case of an infant
right-sided circular shunt
 British HeartJournal, I974, 36, I06I-I065. Contributions of intramyocardial sinusoids in pulmonary atresia and intact ventricular septum to a right-sided circular shunt Robert M. Freedom and Donald P.
British HeartJournal, I974, 36, I06I-I065. Contributions of intramyocardial sinusoids in pulmonary atresia and intact ventricular septum to a right-sided circular shunt Robert M. Freedom and Donald P.
CONGENITAL HEART DISEASE (CHD)
 CONGENITAL HEART DISEASE (CHD) DEFINITION It is the result of a structural or functional abnormality of the cardiovascular system at birth GENERAL FEATURES OF CHD Structural defects due to specific disturbance
CONGENITAL HEART DISEASE (CHD) DEFINITION It is the result of a structural or functional abnormality of the cardiovascular system at birth GENERAL FEATURES OF CHD Structural defects due to specific disturbance
THE SOUNDS AND MURMURS IN TRANSPOSITION OF THE
 Brit. Heart J., 25, 1963, 748. THE SOUNDS AND MURMURS IN TRANSPOSITION OF THE GREAT VESSELS BY BERTRAND WELLS From The Hospital for Sick Children, Great Ormond Street, London W. C.J Received April 18,
Brit. Heart J., 25, 1963, 748. THE SOUNDS AND MURMURS IN TRANSPOSITION OF THE GREAT VESSELS BY BERTRAND WELLS From The Hospital for Sick Children, Great Ormond Street, London W. C.J Received April 18,
HISTORY. Question: What category of heart disease is suggested by this history? CHIEF COMPLAINT: Heart murmur present since early infancy.
 HISTORY 18-year-old man. CHIEF COMPLAINT: Heart murmur present since early infancy. PRESENT ILLNESS: Although normal at birth, a heart murmur was heard at the six week check-up and has persisted since
HISTORY 18-year-old man. CHIEF COMPLAINT: Heart murmur present since early infancy. PRESENT ILLNESS: Although normal at birth, a heart murmur was heard at the six week check-up and has persisted since
Anatomy & Physiology
 1 Anatomy & Physiology Heart is divided into four chambers, two atrias & two ventricles. Atrioventricular valves (tricuspid & mitral) separate the atria from ventricles. they open & close to control flow
1 Anatomy & Physiology Heart is divided into four chambers, two atrias & two ventricles. Atrioventricular valves (tricuspid & mitral) separate the atria from ventricles. they open & close to control flow
Chapter 2 Cardiac Interpretation of Pediatric Chest X-Ray
 Chapter 2 Cardiac Interpretation of Pediatric Chest X-Ray Ra-id Abdulla and Douglas M. Luxenberg Key Facts The cardiac silhouette occupies 50 55% of the chest width on an anterior posterior chest X-ray
Chapter 2 Cardiac Interpretation of Pediatric Chest X-Ray Ra-id Abdulla and Douglas M. Luxenberg Key Facts The cardiac silhouette occupies 50 55% of the chest width on an anterior posterior chest X-ray
HISTORY. Question: What type of heart disease is suggested by this history? CHIEF COMPLAINT: Decreasing exercise tolerance.
 HISTORY 15-year-old male. CHIEF COMPLAINT: Decreasing exercise tolerance. PRESENT ILLNESS: A heart murmur was noted in childhood, but subsequent medical care was sporadic. Easy fatigability and slight
HISTORY 15-year-old male. CHIEF COMPLAINT: Decreasing exercise tolerance. PRESENT ILLNESS: A heart murmur was noted in childhood, but subsequent medical care was sporadic. Easy fatigability and slight
Notes by Sandra Dankwa 2009 HF- Heart Failure DS- Down Syndrome IE- Infective Endocarditis ET- Exercise Tolerance. Small VSD Symptoms -asymptomatic
 Congenital Heart Disease: Notes. Condition Pathology PC Ix Rx Ventricular septal defect (VSD) L R shuntsdefect anywhere in the ventricle, usually perimembranous (next to the tricuspid valve) 30% 1)small
Congenital Heart Disease: Notes. Condition Pathology PC Ix Rx Ventricular septal defect (VSD) L R shuntsdefect anywhere in the ventricle, usually perimembranous (next to the tricuspid valve) 30% 1)small
Large Arteries of Heart
 Cardiovascular System (Part A-2) Module 5 -Chapter 8 Overview Arteries Capillaries Veins Heart Anatomy Conduction System Blood pressure Fetal circulation Susie Turner, M.D. 1/5/13 Large Arteries of Heart
Cardiovascular System (Part A-2) Module 5 -Chapter 8 Overview Arteries Capillaries Veins Heart Anatomy Conduction System Blood pressure Fetal circulation Susie Turner, M.D. 1/5/13 Large Arteries of Heart
Heart and Lungs. LUNG Coronal section demonstrates relationship of pulmonary parenchyma to heart and chest wall.
 Heart and Lungs Normal Sonographic Anatomy THORAX Axial and coronal sections demonstrate integrity of thorax, fetal breathing movements, and overall size and shape. LUNG Coronal section demonstrates relationship
Heart and Lungs Normal Sonographic Anatomy THORAX Axial and coronal sections demonstrate integrity of thorax, fetal breathing movements, and overall size and shape. LUNG Coronal section demonstrates relationship
Large veins of the thorax Brachiocephalic veins
 Large veins of the thorax Brachiocephalic veins Right brachiocephalic vein: formed at the root of the neck by the union of the right subclavian & the right internal jugular veins. Left brachiocephalic
Large veins of the thorax Brachiocephalic veins Right brachiocephalic vein: formed at the root of the neck by the union of the right subclavian & the right internal jugular veins. Left brachiocephalic
CongHeartDis.doc. Андрій Миколайович Лобода
 CongHeartDis.doc Андрій Миколайович Лобода 2015 Зміст 3 Зміст Зміст 4 A child with tetralogy of Fallot is most likely to exhibit: -Increased pulmonary blood flow -Increased pressure in the right ventricle
CongHeartDis.doc Андрій Миколайович Лобода 2015 Зміст 3 Зміст Зміст 4 A child with tetralogy of Fallot is most likely to exhibit: -Increased pulmonary blood flow -Increased pressure in the right ventricle
List of Videos. Video 1.1
 Video 1.1 Video 1.2 Video 1.3 Video 1.4 Video 1.5 Video 1.6 Video 1.7 Video 1.8 The parasternal long-axis view of the left ventricle shows the left ventricular inflow and outflow tract. The left atrium
Video 1.1 Video 1.2 Video 1.3 Video 1.4 Video 1.5 Video 1.6 Video 1.7 Video 1.8 The parasternal long-axis view of the left ventricle shows the left ventricular inflow and outflow tract. The left atrium
HISTORY. Question: How do you interpret the patient s history? CHIEF COMPLAINT: Dyspnea of two days duration. PRESENT ILLNESS: 45-year-old man.
 HISTORY 45-year-old man. CHIEF COMPLAINT: Dyspnea of two days duration. PRESENT ILLNESS: His dyspnea began suddenly and has been associated with orthopnea, but no chest pain. For two months he has felt
HISTORY 45-year-old man. CHIEF COMPLAINT: Dyspnea of two days duration. PRESENT ILLNESS: His dyspnea began suddenly and has been associated with orthopnea, but no chest pain. For two months he has felt
2) VSD & PDA - Dr. Aso
 2) VSD & PDA - Dr. Aso Ventricular Septal Defect (VSD) Most common cardiac malformation 25-30 % Types of VSD: According to position perimembranous, inlet, muscular. According to size small, medium, large.
2) VSD & PDA - Dr. Aso Ventricular Septal Defect (VSD) Most common cardiac malformation 25-30 % Types of VSD: According to position perimembranous, inlet, muscular. According to size small, medium, large.
Mitral incompetence after repair of ostium
 Thorax (1965), 20, 40. Mitral incompetence after repair of ostium primum septal defects A. R. C. DOBELL, D. R. MURPHY, G. M. KARN, AND A. MARTINEZ-CARO From the Department of Cardiovascular Surgery, the
Thorax (1965), 20, 40. Mitral incompetence after repair of ostium primum septal defects A. R. C. DOBELL, D. R. MURPHY, G. M. KARN, AND A. MARTINEZ-CARO From the Department of Cardiovascular Surgery, the
Ch.15 Cardiovascular System Pgs {15-12} {15-13}
 Ch.15 Cardiovascular System Pgs {15-12} {15-13} E. Skeleton of the Heart 1. The skeleton of the heart is composed of rings of dense connective tissue and other masses of connective tissue in the interventricular
Ch.15 Cardiovascular System Pgs {15-12} {15-13} E. Skeleton of the Heart 1. The skeleton of the heart is composed of rings of dense connective tissue and other masses of connective tissue in the interventricular
Case 47 Clinical Presentation
 93 Case 47 C Clinical Presentation 45-year-old man presents with chest pain and new onset of a murmur. Echocardiography shows severe aortic insufficiency. 94 RadCases Cardiac Imaging Imaging Findings C
93 Case 47 C Clinical Presentation 45-year-old man presents with chest pain and new onset of a murmur. Echocardiography shows severe aortic insufficiency. 94 RadCases Cardiac Imaging Imaging Findings C
Stenosis of Pulmonary Veins
 Stenosis of Pulmonary Veins Report of a Patient Corrected Surgically Yasunaru Kawashima, M.D., Takeshi Ueda, M.D., Yasuaki Naito, M.D, Eiji Morikawa, M.D., and Hisao Manabe, M.D. ABSTRACT A 15-year-old
Stenosis of Pulmonary Veins Report of a Patient Corrected Surgically Yasunaru Kawashima, M.D., Takeshi Ueda, M.D., Yasuaki Naito, M.D, Eiji Morikawa, M.D., and Hisao Manabe, M.D. ABSTRACT A 15-year-old
Persistence of Fetal Ductus Function after Birth The Ductus Arteriosus as an Avenue of Escape
 Persistence of Fetal Ductus Function after Birth The Ductus Arteriosus as an Avenue of Escape By HERBERT L. ABRAMS, M.D. Within recent years there has been increasing interest in the presence of reversed
Persistence of Fetal Ductus Function after Birth The Ductus Arteriosus as an Avenue of Escape By HERBERT L. ABRAMS, M.D. Within recent years there has been increasing interest in the presence of reversed
Cervical aortic arch with aortic obstruction:
 Thorax, 1980, 35, 26-30 Cervical aortic arch with aortic obstruction: report of two cases ROBERTO TIRABOSCHI, GIANCARLO CRUPI, GIUSEPPE LOCATELLI, SIEW YEN HO, AND LUCIO PARENZAN From the Department of
Thorax, 1980, 35, 26-30 Cervical aortic arch with aortic obstruction: report of two cases ROBERTO TIRABOSCHI, GIANCARLO CRUPI, GIUSEPPE LOCATELLI, SIEW YEN HO, AND LUCIO PARENZAN From the Department of
Notes: 1)Membranous part contribute in the formation of small portion in the septal cusp.
 Embryology 9 : Slide 16 : There is a sulcus between primitive ventricular and bulbis cordis that will disappear gradually and lead to the formation of one chamber which is called bulboventricular chamber.
Embryology 9 : Slide 16 : There is a sulcus between primitive ventricular and bulbis cordis that will disappear gradually and lead to the formation of one chamber which is called bulboventricular chamber.
Adult Congenital Heart Disease: What All Echocardiographers Should Know Sharon L. Roble, MD, FACC Echo Hawaii 2016
 1 Adult Congenital Heart Disease: What All Echocardiographers Should Know Sharon L. Roble, MD, FACC Echo Hawaii 2016 DISCLOSURES I have no disclosures relevant to today s talk 2 Why should all echocardiographers
1 Adult Congenital Heart Disease: What All Echocardiographers Should Know Sharon L. Roble, MD, FACC Echo Hawaii 2016 DISCLOSURES I have no disclosures relevant to today s talk 2 Why should all echocardiographers
By Dickens ATURWANAHO & ORIBA DAN LANGOYA MAKchs, MBchB CONGENTAL HEART DISEASE
 By Dickens ATURWANAHO & ORIBA DAN LANGOYA MAKchs, MBchB CONGENTAL HEART DISEASE Introduction CHDs are abnormalities of the heart or great vessels that are present at birth. Common type of heart disease
By Dickens ATURWANAHO & ORIBA DAN LANGOYA MAKchs, MBchB CONGENTAL HEART DISEASE Introduction CHDs are abnormalities of the heart or great vessels that are present at birth. Common type of heart disease
human anatomy 2016 lecture thirteen Dr meethak ali ahmed neurosurgeon
 Heart The heart is a hollow muscular organ that is somewhat pyramid shaped and lies within the pericardium in the mediastinum. It is connected at its base to the great blood vessels but otherwise lies
Heart The heart is a hollow muscular organ that is somewhat pyramid shaped and lies within the pericardium in the mediastinum. It is connected at its base to the great blood vessels but otherwise lies
Paediatric Cardiology. Acyanotic CHD. Prof F F Takawira
 Paediatric Cardiology Acyanotic CHD Prof F F Takawira Aetiology Chromosomal Down syndrome, T13, T18 Genetic syndromes (gene defects) Velo-Cardio-facial (22 del) Genetic syndromes (undefined aetiology)
Paediatric Cardiology Acyanotic CHD Prof F F Takawira Aetiology Chromosomal Down syndrome, T13, T18 Genetic syndromes (gene defects) Velo-Cardio-facial (22 del) Genetic syndromes (undefined aetiology)
Doppler-echocardiographic findings in a patient with persisting right ventricular sinusoids
 Zurich Open Repository and Archive University of Zurich Main Library Strickhofstrasse 39 CH-8057 Zurich www.zora.uzh.ch Year: 1990 Doppler-echocardiographic findings in a patient with persisting right
Zurich Open Repository and Archive University of Zurich Main Library Strickhofstrasse 39 CH-8057 Zurich www.zora.uzh.ch Year: 1990 Doppler-echocardiographic findings in a patient with persisting right
Patent ductus arteriosus PDA
 Patent ductus arteriosus PDA Is connecting between the aortic end just distal to the origin of the LT sub clavian artery& the pulmonary artery at its bifurcation. Female/male ratio is 2:1 and it is more
Patent ductus arteriosus PDA Is connecting between the aortic end just distal to the origin of the LT sub clavian artery& the pulmonary artery at its bifurcation. Female/male ratio is 2:1 and it is more
Congenital heart disease. By Dr Saima Ali Professor of pediatrics
 Congenital heart disease By Dr Saima Ali Professor of pediatrics What is the most striking clinical finding in this child? Learning objectives By the end of this lecture, final year student should be able
Congenital heart disease By Dr Saima Ali Professor of pediatrics What is the most striking clinical finding in this child? Learning objectives By the end of this lecture, final year student should be able
ULTRASOUND OF THE FETAL HEART
 ULTRASOUND OF THE FETAL HEART Cameron A. Manbeian, MD Disclosure Statement Today s faculty: Cameron Manbeian, MD does not have any relevant financial relationships with commercial interests or affiliations
ULTRASOUND OF THE FETAL HEART Cameron A. Manbeian, MD Disclosure Statement Today s faculty: Cameron Manbeian, MD does not have any relevant financial relationships with commercial interests or affiliations
Paediatrics Revision Session Cardiology. Emma Walker 7 th May 2016
 Paediatrics Revision Session Cardiology Emma Walker 7 th May 2016 Cardiovascular Examination! General:! Make it fun!! Change how you act depending on their age! Introduction! Introduce yourself & check
Paediatrics Revision Session Cardiology Emma Walker 7 th May 2016 Cardiovascular Examination! General:! Make it fun!! Change how you act depending on their age! Introduction! Introduce yourself & check
Atrial Septal Defects
 Supplementary ACHD Echo Acquisition Protocol for Atrial Septal Defects The following protocol for echo in adult patients with atrial septal defects (ASDs) is a guide for performing a comprehensive assessment
Supplementary ACHD Echo Acquisition Protocol for Atrial Septal Defects The following protocol for echo in adult patients with atrial septal defects (ASDs) is a guide for performing a comprehensive assessment
Uptofate Study Summary
 CONGENITAL HEART DISEASE Uptofate Study Summary Acyanotic Atrial septal defect Ventricular septal defect Patent foramen ovale Patent ductus arteriosus Aortic coartation Pulmonary stenosis Cyanotic Tetralogy
CONGENITAL HEART DISEASE Uptofate Study Summary Acyanotic Atrial septal defect Ventricular septal defect Patent foramen ovale Patent ductus arteriosus Aortic coartation Pulmonary stenosis Cyanotic Tetralogy
When is Risky to Apply Oxygen for Congenital Heart Disease 부천세종병원 소아청소년과최은영
 When is Risky to Apply Oxygen for Congenital Heart Disease 부천세종병원 소아청소년과최은영 The Korean Society of Cardiology COI Disclosure Eun-Young Choi The author have no financial conflicts of interest to disclose
When is Risky to Apply Oxygen for Congenital Heart Disease 부천세종병원 소아청소년과최은영 The Korean Society of Cardiology COI Disclosure Eun-Young Choi The author have no financial conflicts of interest to disclose
Giovanni Di Salvo MD, PhD, FESC Second University of Naples Monaldi Hospital
 Giovanni Di Salvo MD, PhD, FESC Second University of Naples Monaldi Hospital VSD is one of the most common congenital cardiac abnormalities in the newborn. It can occur as an isolated finding or in combination
Giovanni Di Salvo MD, PhD, FESC Second University of Naples Monaldi Hospital VSD is one of the most common congenital cardiac abnormalities in the newborn. It can occur as an isolated finding or in combination
Pathophysiology: Left To Right Shunts
 Pathophysiology: Left To Right Shunts Daphne T. Hsu, MD dh17@columbia.edu Learning Objectives Learn the relationships between pressure, blood flow, and resistance Review the transition from fetal to mature
Pathophysiology: Left To Right Shunts Daphne T. Hsu, MD dh17@columbia.edu Learning Objectives Learn the relationships between pressure, blood flow, and resistance Review the transition from fetal to mature
/b O. Figure 4.1 Tracing of a normal dorsoventral angiocardiogram. The. veins (PV) enter the left atrium (LA) well within the
 /b O " Figure 4.1 Tracing of a normal dorsoventral angiocardiogram. The pu~nonary veins (PV) enter the left atrium (LA) well within the limits of the cardiac silhouette; the left atri~m does not contribute
/b O " Figure 4.1 Tracing of a normal dorsoventral angiocardiogram. The pu~nonary veins (PV) enter the left atrium (LA) well within the limits of the cardiac silhouette; the left atri~m does not contribute
Anatomy of left ventricular outflow tract'
 Anatomy of left ventricular outflow tract' ROBERT WALMSLEY British Heart Journal, 1979, 41, 263-267 From the Department of Anatomy and Experimental Pathology, The University, St Andrews, Scotland SUMMARY
Anatomy of left ventricular outflow tract' ROBERT WALMSLEY British Heart Journal, 1979, 41, 263-267 From the Department of Anatomy and Experimental Pathology, The University, St Andrews, Scotland SUMMARY
Adult Echocardiography Examination Content Outline
 Adult Echocardiography Examination Content Outline (Outline Summary) # Domain Subdomain Percentage 1 2 3 4 5 Anatomy and Physiology Pathology Clinical Care and Safety Measurement Techniques, Maneuvers,
Adult Echocardiography Examination Content Outline (Outline Summary) # Domain Subdomain Percentage 1 2 3 4 5 Anatomy and Physiology Pathology Clinical Care and Safety Measurement Techniques, Maneuvers,
Absent Pulmonary Valve Syndrome
 Absent Pulmonary Valve Syndrome Fact sheet on Absent Pulmonary Valve Syndrome In this condition, which has some similarities to Fallot's Tetralogy, there is a VSD with narrowing at the pulmonary valve.
Absent Pulmonary Valve Syndrome Fact sheet on Absent Pulmonary Valve Syndrome In this condition, which has some similarities to Fallot's Tetralogy, there is a VSD with narrowing at the pulmonary valve.
The sinus venosus represent the venous end of the heart It receives 3 veins: 1- Common cardinal vein body wall 2- Umbilical vein from placenta 3-
 1 2 The sinus venosus represent the venous end of the heart It receives 3 veins: 1- Common cardinal vein body wall 2- Umbilical vein from placenta 3- Vitelline vein from yolk sac 3 However!!!!! The left
1 2 The sinus venosus represent the venous end of the heart It receives 3 veins: 1- Common cardinal vein body wall 2- Umbilical vein from placenta 3- Vitelline vein from yolk sac 3 However!!!!! The left
Pathophysiology: Left To Right Shunts
 Pathophysiology: Left To Right Shunts Daphne T. Hsu, MD dh17@columbia.edu Learning Objectives Learn the relationships between pressure, blood flow, and resistance Review the transition from fetal to mature
Pathophysiology: Left To Right Shunts Daphne T. Hsu, MD dh17@columbia.edu Learning Objectives Learn the relationships between pressure, blood flow, and resistance Review the transition from fetal to mature
LECTURE 5. Anatomy of the heart
 LECTURE 5. Anatomy of the heart Main components of the CVS: Heart Blood circulatory system arterial compartment haemomicrocirculatory (=microvascular) compartment venous compartment Lymphatic circulatory
LECTURE 5. Anatomy of the heart Main components of the CVS: Heart Blood circulatory system arterial compartment haemomicrocirculatory (=microvascular) compartment venous compartment Lymphatic circulatory
THE HEART. A. The Pericardium - a double sac of serous membrane surrounding the heart
 THE HEART I. Size and Location: A. Fist-size weighing less than a pound (250 to 350 grams). B. Located in the mediastinum between the 2 nd rib and the 5 th intercostal space. 1. Tipped to the left, resting
THE HEART I. Size and Location: A. Fist-size weighing less than a pound (250 to 350 grams). B. Located in the mediastinum between the 2 nd rib and the 5 th intercostal space. 1. Tipped to the left, resting
Coarctation of the aorta
 T H E P E D I A T R I C C A R D I A C S U R G E R Y I N Q U E S T R E P O R T Coarctation of the aorta In the normal heart, blood flows to the body through the aorta, which connects to the left ventricle
T H E P E D I A T R I C C A R D I A C S U R G E R Y I N Q U E S T R E P O R T Coarctation of the aorta In the normal heart, blood flows to the body through the aorta, which connects to the left ventricle
Appendix II: ECHOCARDIOGRAPHY ANALYSIS
 Appendix II: ECHOCARDIOGRAPHY ANALYSIS Two-Dimensional (2D) imaging was performed using the Vivid 7 Advantage cardiovascular ultrasound system (GE Medical Systems, Milwaukee) with a frame rate of 400 frames
Appendix II: ECHOCARDIOGRAPHY ANALYSIS Two-Dimensional (2D) imaging was performed using the Vivid 7 Advantage cardiovascular ultrasound system (GE Medical Systems, Milwaukee) with a frame rate of 400 frames
PROSTHETIC VALVE BOARD REVIEW
 PROSTHETIC VALVE BOARD REVIEW The correct answer D This two chamber view shows a porcine mitral prosthesis with the typical appearance of the struts although the leaflets are not well seen. The valve
PROSTHETIC VALVE BOARD REVIEW The correct answer D This two chamber view shows a porcine mitral prosthesis with the typical appearance of the struts although the leaflets are not well seen. The valve
Diagnostic approach to heart disease
 Diagnostic approach to heart disease Initial work up History Physical exam Chest radiographs ECG Special studies Echocardiography Cardiac catheterization Echocardiography principles Technique of producing
Diagnostic approach to heart disease Initial work up History Physical exam Chest radiographs ECG Special studies Echocardiography Cardiac catheterization Echocardiography principles Technique of producing
Tricuspid and Pulmonic Valve Disease
 Chapter 31 Tricuspid and Pulmonic Valve Disease David A. Tate Acquired disease of the right-sided cardiac valves is much less common than disease of the leftsided counterparts, possibly because of the
Chapter 31 Tricuspid and Pulmonic Valve Disease David A. Tate Acquired disease of the right-sided cardiac valves is much less common than disease of the leftsided counterparts, possibly because of the
ECHOCARDIOGRAPHIC APPROACH TO CONGENITAL HEART DISEASE: THE UNOPERATED ADULT
 ECHOCARDIOGRAPHIC APPROACH TO CONGENITAL HEART DISEASE: THE UNOPERATED ADULT Karen Stout, MD, FACC Divisions of Cardiology University of Washington Medical Center Seattle Children s Hospital NO DISCLOSURES
ECHOCARDIOGRAPHIC APPROACH TO CONGENITAL HEART DISEASE: THE UNOPERATED ADULT Karen Stout, MD, FACC Divisions of Cardiology University of Washington Medical Center Seattle Children s Hospital NO DISCLOSURES
7.3,u (74), packed cell volume 63 per cent (37),
 TRANSPOSITION OF THE AORTA AND PULMONARY ARTERY DEMONSTRATED BY ANGIOCARDIOGRAPHY BY J. F. GOODWIN, R. STEINER, AND E. J. WAYNE From the Department of Pharmacology and Therapeutics, University of Sheffield
TRANSPOSITION OF THE AORTA AND PULMONARY ARTERY DEMONSTRATED BY ANGIOCARDIOGRAPHY BY J. F. GOODWIN, R. STEINER, AND E. J. WAYNE From the Department of Pharmacology and Therapeutics, University of Sheffield
2. The heart sounds are produced by a summed series of mechanical events, as follows:
 Heart Sounds. Phonocardiography 1 Objectives 1. Phonocardiography - Definition 2. What produces the heart sounds 3. Where to listen for the heart sounds 4. How to record a phonocardiogram 5. Normal heart
Heart Sounds. Phonocardiography 1 Objectives 1. Phonocardiography - Definition 2. What produces the heart sounds 3. Where to listen for the heart sounds 4. How to record a phonocardiogram 5. Normal heart
PROGRESS IN CARDIOVASCULAR SURGERY. Congenital Mitral Stenosis and Mitral Insufficiency
 PROGRESS IN CARDIOVASCULAR SURGERY Congenital Mitral Stenosis and Mitral Insufficiency GEORGE W. B. STARKEY, M.D.* Boston, Massachusetts CONGENITAL MITRAL STENOSIS AND mitral insufficiency are rare, particularly
PROGRESS IN CARDIOVASCULAR SURGERY Congenital Mitral Stenosis and Mitral Insufficiency GEORGE W. B. STARKEY, M.D.* Boston, Massachusetts CONGENITAL MITRAL STENOSIS AND mitral insufficiency are rare, particularly
Two Cases Report of Scimitar Syndrome: The Classical one with Subaortic Membrane and the Scimitar Variant
 Bahrain Medical Bulletin, Vol.22, No.1, March 2000 Two Cases Report of Scimitar Syndrome: The Classical one with Subaortic Membrane and the Scimitar Variant F Hakim, MD* A Madani, MD* A Abu Haweleh, MD,MRCP*
Bahrain Medical Bulletin, Vol.22, No.1, March 2000 Two Cases Report of Scimitar Syndrome: The Classical one with Subaortic Membrane and the Scimitar Variant F Hakim, MD* A Madani, MD* A Abu Haweleh, MD,MRCP*
Anomalous muscle bundle of the right ventricle
 British Heart Journal, 1978, 40, 1040-1045 Anomalous muscle bundle of the right ventricle Its recognition and surgical treatment M. D. LI, J. C. COLES, AND A. C. McDONALD From the Department of Paediatrics,
British Heart Journal, 1978, 40, 1040-1045 Anomalous muscle bundle of the right ventricle Its recognition and surgical treatment M. D. LI, J. C. COLES, AND A. C. McDONALD From the Department of Paediatrics,
CJ Shuster A&P2 Lab Addenum Beef Heart Dissection 1. Heart Dissection. (taken from Johnson, Weipz and Savage Lab Book)
 CJ Shuster A&P2 Lab Addenum Beef Heart Dissection 1 Heart Dissection. (taken from Johnson, Weipz and Savage Lab Book) Introduction When you have finished examining the model, you are ready to begin your
CJ Shuster A&P2 Lab Addenum Beef Heart Dissection 1 Heart Dissection. (taken from Johnson, Weipz and Savage Lab Book) Introduction When you have finished examining the model, you are ready to begin your
Congenital diverticulum of the heart arising from the
 Br Heart J 1986;56:380-4 Congenital diverticulum of the heart arising from the coronary sinus ELIO DI SEGNI,* ANNETTE SIEGAL,t MICHAEL KATZENSTEINt From the Department of *Cardiology and of tpathology,
Br Heart J 1986;56:380-4 Congenital diverticulum of the heart arising from the coronary sinus ELIO DI SEGNI,* ANNETTE SIEGAL,t MICHAEL KATZENSTEINt From the Department of *Cardiology and of tpathology,
Hypoplastic Left Heart Syndrome: Echocardiographic Assessment
 Hypoplastic Left Heart Syndrome: Echocardiographic Assessment Craig E Fleishman, MD, FACC, FASE Director, Non-invasive Cardiac Imaging The Hear Center at Arnold Palmer Hospital for Children, Orlando SCAI
Hypoplastic Left Heart Syndrome: Echocardiographic Assessment Craig E Fleishman, MD, FACC, FASE Director, Non-invasive Cardiac Imaging The Hear Center at Arnold Palmer Hospital for Children, Orlando SCAI
Surgical Treatment of Congenital Heart Disease
 Surgical Treatment of Congenital Heart Disease The Evaluation of Diagnostic Data JAMES V. MALONEY, JR., M.D., and PIERCE J. FLYNN, M.D., Los Angeles THE TASK OF THE CARDIOLOGIST in diagnosing congenital
Surgical Treatment of Congenital Heart Disease The Evaluation of Diagnostic Data JAMES V. MALONEY, JR., M.D., and PIERCE J. FLYNN, M.D., Los Angeles THE TASK OF THE CARDIOLOGIST in diagnosing congenital
Ebstein s anomaly is a congenital malformation of the right
 Cone Reconstruction of the Tricuspid Valve for Ebstein s Anomaly: Anatomic Repair Joseph A. Dearani, MD, Emile Bacha, MD, and José Pedro da Silva, MD Division of Cardiovascular Surgery, Mayo Clinic, Rochester,
Cone Reconstruction of the Tricuspid Valve for Ebstein s Anomaly: Anatomic Repair Joseph A. Dearani, MD, Emile Bacha, MD, and José Pedro da Silva, MD Division of Cardiovascular Surgery, Mayo Clinic, Rochester,
Assessing Cardiac Anatomy With Digital Subtraction Angiography
 485 JACC Vol. 5, No. I Assessing Cardiac Anatomy With Digital Subtraction Angiography DOUGLAS S., MD, FACC Cleveland, Ohio The use of intravenous digital subtraction angiography in the assessment of patients
485 JACC Vol. 5, No. I Assessing Cardiac Anatomy With Digital Subtraction Angiography DOUGLAS S., MD, FACC Cleveland, Ohio The use of intravenous digital subtraction angiography in the assessment of patients
Pediatric Echocardiography Examination Content Outline
 Pediatric Echocardiography Examination Content Outline (Outline Summary) # Domain Subdomain Percentage 1 Anatomy and Physiology Normal Anatomy and Physiology 10% 2 Abnormal Pathology and Pathophysiology
Pediatric Echocardiography Examination Content Outline (Outline Summary) # Domain Subdomain Percentage 1 Anatomy and Physiology Normal Anatomy and Physiology 10% 2 Abnormal Pathology and Pathophysiology
CMS Limitations Guide - Radiology Services
 CMS Limitations Guide - Radiology Services Starting October 1, 2015, CMS will update their existing medical necessity limitations on tests and procedures to correspond to ICD-10 codes. This limitations
CMS Limitations Guide - Radiology Services Starting October 1, 2015, CMS will update their existing medical necessity limitations on tests and procedures to correspond to ICD-10 codes. This limitations
Anatomy lab -1- Imp note: papillary muscle Trabeculae Carneae chordae tendineae
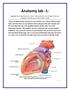 Anatomy lab -1- Imp note: the arrangement of this sheet is different than the lab recording, it has been arranged in a certain way to make it easier to study. When you open the left ventricle you can see
Anatomy lab -1- Imp note: the arrangement of this sheet is different than the lab recording, it has been arranged in a certain way to make it easier to study. When you open the left ventricle you can see
Idiopathic hypertrophic obstructive cardiomyopathy causing severe right ventricular outflow tract
 British Heart Journal, I973, 35, II09-III5. Idiopathic hypertrophic obstructive cardiomyopathy causing severe right ventricular outflow tract obstruction in infancy P. A. Barr, J. M. Celermajer, J. D.
British Heart Journal, I973, 35, II09-III5. Idiopathic hypertrophic obstructive cardiomyopathy causing severe right ventricular outflow tract obstruction in infancy P. A. Barr, J. M. Celermajer, J. D.
PATENT DUCTUS ARTERIOSUS (PDA)
 PATENT DUCTUS ARTERIOSUS (PDA) It is a channel that connect the pulmonary artery with the descending aorta (isthumus part). It results from the persistence of patency of the fetal ductus arteriosus after
PATENT DUCTUS ARTERIOSUS (PDA) It is a channel that connect the pulmonary artery with the descending aorta (isthumus part). It results from the persistence of patency of the fetal ductus arteriosus after
Hemodynamic Assessment. Assessment of Systolic Function Doppler Hemodynamics
 Hemodynamic Assessment Matt M. Umland, RDCS, FASE Aurora Medical Group Milwaukee, WI Assessment of Systolic Function Doppler Hemodynamics Stroke Volume Cardiac Output Cardiac Index Tei Index/Index of myocardial
Hemodynamic Assessment Matt M. Umland, RDCS, FASE Aurora Medical Group Milwaukee, WI Assessment of Systolic Function Doppler Hemodynamics Stroke Volume Cardiac Output Cardiac Index Tei Index/Index of myocardial
Truncus arteriosus communis with intact ventricular septum1
 British Heart Journal, 1979, 42, 97-102 Truncus arteriosus communis with intact ventricular septum1 IAN CARR, SAROJA BHARATI, V. S. KUSNOOR, AND MAURICE LEV From the Divisions of Pediatric Cardiology and
British Heart Journal, 1979, 42, 97-102 Truncus arteriosus communis with intact ventricular septum1 IAN CARR, SAROJA BHARATI, V. S. KUSNOOR, AND MAURICE LEV From the Divisions of Pediatric Cardiology and
The Chest X-ray for Cardiologists
 Mayo Clinic & British Cardiovascular Society at the Royal College of Physicians, London : 21-23-October 2013 Cases-Controversies-Updates 2013 The Chest X-ray for Cardiologists Michael Rubens Royal Brompton
Mayo Clinic & British Cardiovascular Society at the Royal College of Physicians, London : 21-23-October 2013 Cases-Controversies-Updates 2013 The Chest X-ray for Cardiologists Michael Rubens Royal Brompton
the Cardiovascular System I
 the Cardiovascular System I By: Dr. Nabil A Khouri MD, MsC, Ph.D MEDIASTINUM 1. Superior Mediastinum 2. inferior Mediastinum Anterior mediastinum. Middle mediastinum. Posterior mediastinum Anatomy of
the Cardiovascular System I By: Dr. Nabil A Khouri MD, MsC, Ph.D MEDIASTINUM 1. Superior Mediastinum 2. inferior Mediastinum Anterior mediastinum. Middle mediastinum. Posterior mediastinum Anatomy of
The Heart. The Heart A muscular double pump. The Pulmonary and Systemic Circuits
 C H A P T E R 19 The Heart The Heart A muscular double pump circuit takes blood to and from the lungs Systemic circuit vessels transport blood to and from body tissues Atria receive blood from the pulmonary
C H A P T E R 19 The Heart The Heart A muscular double pump circuit takes blood to and from the lungs Systemic circuit vessels transport blood to and from body tissues Atria receive blood from the pulmonary
Surface anatomy of Cardiovascular system
 Surface anatomy of Cardiovascular system Prof. Abdulameer Al-Nuaimi E-mail: a.al-nuaimi@sheffield.ac.uk E. mail: abdulameerh@yahoo.com The lines cover the front, side, and back of the thorax Midsternal
Surface anatomy of Cardiovascular system Prof. Abdulameer Al-Nuaimi E-mail: a.al-nuaimi@sheffield.ac.uk E. mail: abdulameerh@yahoo.com The lines cover the front, side, and back of the thorax Midsternal
Residual Right=to-Left Shunt Following Repair of Atrial Septal Defect
 Residual Right=to-Left Shunt Following Repair of Atrial Septal Defect Susan J. Desnick, Ph.D., M.D., William A. Neal, M.D., Demetre M. Nicoloff, M.D., and James H. Moller, M.D. ABSTRACT Information about
Residual Right=to-Left Shunt Following Repair of Atrial Septal Defect Susan J. Desnick, Ph.D., M.D., William A. Neal, M.D., Demetre M. Nicoloff, M.D., and James H. Moller, M.D. ABSTRACT Information about
Echocardiography Conference
 Echocardiography Conference David Stultz, MD Cardiology Fellow, PGY-6 September 20, 2005 Atrial Septal Aneurysm Bulging of Fossa Ovalis Associated commonly with Atrial septal defect or small perforations
Echocardiography Conference David Stultz, MD Cardiology Fellow, PGY-6 September 20, 2005 Atrial Septal Aneurysm Bulging of Fossa Ovalis Associated commonly with Atrial septal defect or small perforations
Clinical significance of cardiac murmurs: Get the sound and rhythm!
 Clinical significance of cardiac murmurs: Get the sound and rhythm! Prof. dr. Gunther van Loon, DVM, PhD, Ass Member ECVDI, Dip ECEIM Dept. of Large Animal Internal Medicine Ghent University, Belgium Murmurs
Clinical significance of cardiac murmurs: Get the sound and rhythm! Prof. dr. Gunther van Loon, DVM, PhD, Ass Member ECVDI, Dip ECEIM Dept. of Large Animal Internal Medicine Ghent University, Belgium Murmurs
Aortography in Fallot's Tetralogy and Variants
 Brit. Heart J., 1969, 31, 146. Aortography in Fallot's Tetralogy and Variants SIMON REES AND JANE SOMERVILLE From The Institute of Cardiology and National Heart Hospital, London W.J In patients with Fallot's
Brit. Heart J., 1969, 31, 146. Aortography in Fallot's Tetralogy and Variants SIMON REES AND JANE SOMERVILLE From The Institute of Cardiology and National Heart Hospital, London W.J In patients with Fallot's
- what other structures, besides the heart, does the mediastinum contain?
 Basic A & P II Dr. L. Bacha Chapter Outline (Martini & Nath 2010) An Introduction to the Cardiovascular System - read the paragraphs under this heading on page 580 The Heart is a Four Chambered Organ describe
Basic A & P II Dr. L. Bacha Chapter Outline (Martini & Nath 2010) An Introduction to the Cardiovascular System - read the paragraphs under this heading on page 580 The Heart is a Four Chambered Organ describe
Pulmonary valve echo motion in pulmonary
 British HeartJournal, I975, 37, ii84-ii90. Pulmonary valve echo motion in pulmonary regurgitation' Arthur E. Weyman, James C. Dillon, Harvey Feigenbaum, and Sonia Chang From the Department of Medicine,
British HeartJournal, I975, 37, ii84-ii90. Pulmonary valve echo motion in pulmonary regurgitation' Arthur E. Weyman, James C. Dillon, Harvey Feigenbaum, and Sonia Chang From the Department of Medicine,
PART II ECHOCARDIOGRAPHY LABORATORY OPERATIONS ADULT TRANSTHORACIC ECHOCARDIOGRAPHY TESTING
 PART II ECHOCARDIOGRAPHY LABORATORY OPERATIONS ADULT TRANSTHORACIC ECHOCARDIOGRAPHY TESTING STANDARD - Primary Instrumentation 1.1 Cardiac Ultrasound Systems SECTION 1 Instrumentation Ultrasound instruments
PART II ECHOCARDIOGRAPHY LABORATORY OPERATIONS ADULT TRANSTHORACIC ECHOCARDIOGRAPHY TESTING STANDARD - Primary Instrumentation 1.1 Cardiac Ultrasound Systems SECTION 1 Instrumentation Ultrasound instruments
Patent Ductus Arteriosus (PDA)
 Patent Ductus Arteriosus (PDA) How does the heart work? The heart is the organ responsible for pumping blood to and from all tissues of the body. The heart is divided into right and left sides. The job
Patent Ductus Arteriosus (PDA) How does the heart work? The heart is the organ responsible for pumping blood to and from all tissues of the body. The heart is divided into right and left sides. The job
ISUOG Basic Training. Obtaining & Interpreting Heart Views Correctly Alfred Abuhamad, USA. Basic training. Editable text here
 ISUOG Basic Training Obtaining & Interpreting Heart Views Correctly Alfred Abuhamad, USA Learning Objectives 6, 7 & 8 At the end of the lecture you will be able to: describe how to assess cardiac situs
ISUOG Basic Training Obtaining & Interpreting Heart Views Correctly Alfred Abuhamad, USA Learning Objectives 6, 7 & 8 At the end of the lecture you will be able to: describe how to assess cardiac situs
IMAGES. in PAEDIATRIC CARDIOLOGY. Abstract. Case
 IMAGES in PAEDIATRIC CARDIOLOGY Images PMCID: PMC3232604 Isolated subpulmonary membrane causing critical neonatal pulmonary stenosis with concordant atrioventricular and ventriculoarterial connections
IMAGES in PAEDIATRIC CARDIOLOGY Images PMCID: PMC3232604 Isolated subpulmonary membrane causing critical neonatal pulmonary stenosis with concordant atrioventricular and ventriculoarterial connections
Cardiac Ausculation in the Elderly
 Cardiac Ausculation in the Elderly 박성하 신촌세브란스병원심장혈관병원심장내과 Anatomy Surface projection of the Heart and Great Vessels Evaluating pulsation Superior vena cava Rt. pulmonary artery Right atrium Right ventricle
Cardiac Ausculation in the Elderly 박성하 신촌세브란스병원심장혈관병원심장내과 Anatomy Surface projection of the Heart and Great Vessels Evaluating pulsation Superior vena cava Rt. pulmonary artery Right atrium Right ventricle
Two semilunar valves. Two atrioventricular valves. Valves of the heart. Left atrioventricular or bicuspid valve Mitral valve
 The Heart 3 Valves of the heart Two atrioventricular valves Two semilunar valves Right atrioventricular or tricuspid valve Left atrioventricular or bicuspid valve Mitral valve Aortic valve Pulmonary valve
The Heart 3 Valves of the heart Two atrioventricular valves Two semilunar valves Right atrioventricular or tricuspid valve Left atrioventricular or bicuspid valve Mitral valve Aortic valve Pulmonary valve
Cardiac ultrasound protocols
 Cardiac ultrasound protocols IDEXX Telemedicine Consultants Two-dimensional and M-mode imaging planes Right parasternal long axis four chamber Obtained from the right side Displays the relative proportions
Cardiac ultrasound protocols IDEXX Telemedicine Consultants Two-dimensional and M-mode imaging planes Right parasternal long axis four chamber Obtained from the right side Displays the relative proportions
Fig.1 Normal appearance of RV in SAX:
 Tutorial 7 - Assessment of the right heart Assessment of the Right heart The right heart assessment clinically and echocardiographically is not a very important part of mainstream cardiology. In the ICU,
Tutorial 7 - Assessment of the right heart Assessment of the Right heart The right heart assessment clinically and echocardiographically is not a very important part of mainstream cardiology. In the ICU,
Lab Activity 23. Cardiac Anatomy. Portland Community College BI 232
 Lab Activity 23 Cardiac Anatomy Portland Community College BI 232 Cardiac Muscle Histology Branching cells Intercalated disc: contains many gap junctions connecting the adjacent cell cytoplasm, creates
Lab Activity 23 Cardiac Anatomy Portland Community College BI 232 Cardiac Muscle Histology Branching cells Intercalated disc: contains many gap junctions connecting the adjacent cell cytoplasm, creates
Individual Pulmonary Vein Atresia in Adults: Report of Two Cases
 Case Report DOI: 10.3348/kjr.2011.12.3.395 pissn 1229-6929 eissn 2005-8330 Korean J Radiol 2011;12(3):395-399 Individual Pulmonary Vein Atresia in Adults: Report of Two Cases Hyoung Nam Lee, MD, Young
Case Report DOI: 10.3348/kjr.2011.12.3.395 pissn 1229-6929 eissn 2005-8330 Korean J Radiol 2011;12(3):395-399 Individual Pulmonary Vein Atresia in Adults: Report of Two Cases Hyoung Nam Lee, MD, Young
Heart sounds and murmurs. Dr. Szathmári Miklós Semmelweis University First Department of Medicine 15. Oct
 Heart sounds and murmurs Dr. Szathmári Miklós Semmelweis University First Department of Medicine 15. Oct. 2013. Conditions for auscultation of the heart Quiet room Patient comfortable Chest fully exposed
Heart sounds and murmurs Dr. Szathmári Miklós Semmelweis University First Department of Medicine 15. Oct. 2013. Conditions for auscultation of the heart Quiet room Patient comfortable Chest fully exposed
Middle mediastinum---- heart & pericardium. Dep. of Human Anatomy Zhou Hongying
 Middle mediastinum---- heart & pericardium Dep. of Human Anatomy Zhou Hongying eaglezhyxzy@163.com Subdivisions of the mediastinum Contents of Middle mediastinum Heart Pericardium: a serous sac enclosing
Middle mediastinum---- heart & pericardium Dep. of Human Anatomy Zhou Hongying eaglezhyxzy@163.com Subdivisions of the mediastinum Contents of Middle mediastinum Heart Pericardium: a serous sac enclosing
Data Collected: June 17, Reported: June 30, Survey Dates 05/24/ /07/2010
 Job Task Analysis for ARDMS Pediatric Echocardiography Data Collected: June 17, 2010 Reported: Analysis Summary For: Pediatric Echocardiography Exam Survey Dates 05/24/2010-06/07/2010 Invited Respondents
Job Task Analysis for ARDMS Pediatric Echocardiography Data Collected: June 17, 2010 Reported: Analysis Summary For: Pediatric Echocardiography Exam Survey Dates 05/24/2010-06/07/2010 Invited Respondents
J Somerville and V Grech. The chest x-ray in congenital heart disease 2. Images Paediatr Cardiol Jan-Mar; 12(1): 1 8.
 IMAGES in PAEDIATRIC CARDIOLOGY Images Paediatr Cardiol. 2010 PMCID: PMC3228330 The chest x-ray in congenital heart disease 2 J Somerville and V Grech Paediatric Department, Mater Dei Hospital, Malta Corresponding
IMAGES in PAEDIATRIC CARDIOLOGY Images Paediatr Cardiol. 2010 PMCID: PMC3228330 The chest x-ray in congenital heart disease 2 J Somerville and V Grech Paediatric Department, Mater Dei Hospital, Malta Corresponding
FUNCTIONALLY SINGLE VENTRICLE
 MORPHOLOGICAL DETERMINANTS VI TRAN EuroEcho, Budapest, 7 th December 2011 DECLARATION OF CONFLICT OF INTEREST: I have nothing to declare What is the functionally single ventricle? The heart that is incapable
MORPHOLOGICAL DETERMINANTS VI TRAN EuroEcho, Budapest, 7 th December 2011 DECLARATION OF CONFLICT OF INTEREST: I have nothing to declare What is the functionally single ventricle? The heart that is incapable
Atrial Septal Defect Closure. Stephen Brecker Director, Cardiac Catheterisation Labs
 Stephen Brecker Director, Cardiac Catheterisation Labs ADVANCED ANGIOPLASTY Incorporating The Left Main 5 Plus Course Conflicts of Interest The following companies have supported educational courses held
Stephen Brecker Director, Cardiac Catheterisation Labs ADVANCED ANGIOPLASTY Incorporating The Left Main 5 Plus Course Conflicts of Interest The following companies have supported educational courses held
Index. radiologic.theclinics.com. Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type.
 Index Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A ALCAPA. See Anomalous left coronary artery from the pulmonary artery. Angiosarcoma computed tomographic assessment of, 809 811 Anomalous
Index Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A ALCAPA. See Anomalous left coronary artery from the pulmonary artery. Angiosarcoma computed tomographic assessment of, 809 811 Anomalous
