The natriuretic peptides (NP) are valuable biomarkers
|
|
|
- Ethel Eaton
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Natriuretic Peptides Atrial Natriuretic Peptide Affects Cardiac Remodeling, Function, Heart Failure, and Survival in a Mouse Model of Dilated Cardiomyopathy Dong Wang, Inna P. Gladysheva, Tai-Hwang M. Fan, Ryan Sullivan, Aiilyan K. Houng, Guy L. Reed Abstract Dilated cardiomyopathy is a frequent cause of heart failure and death. Atrial natriuretic peptide (ANP) is a biomarker of dilated cardiomyopathy, but there is controversy whether ANP modulates the development of heart failure. Therefore, we examined whether ANP affects heart failure, cardiac remodeling, function, and survival in a well-characterized, tragenic model of dilated cardiomyopathy. Mice with dilated cardiomyopathy with normal ANP levels survived longer than mice with partial ANP (P<.) or full ANP deficiency (P<.). In dilated cardiomyopathy mice, ANP protected agait the development of heart failure as indicated by reduced lung water, alveolar congestion, pleural effusio, etc. ANP improved systolic function and reduced cardiomegaly. Pathological cardiac remodeling was diminished in mice with normal ANP as indicated by decreased ventricular interstitial and perivascular fibrosis. Mice with dilated cardiomyopathy and normal ANP levels had better systolic function (P<.) than mice with dilated cardiomyopathy and ANP deficiency. Dilated cardiomyopathy was associated with diminished cardiac tracripts for NP receptors A and B in mice with normal ANP and ANP deficiency, but tracripts for NP receptor C and C-type natriuretic peptide were selectively altered in mice with dilated cardiomyopathy and ANP deficiency. Taken together, these data indicate that ANP has potent effects in experimental dilated cardiomyopathy that reduce the development of heart failure, prevent pathological remodeling, preserve systolic function, and reduce mortality. Despite the apparent overlap in physiological function between the NPs, these data suggest that the role of ANP in dilated cardiomyopathy and heart failure is not compeated physiologically by other NPs. (Hyperteion. 4;63:54-59.) Online Data Supplement Downloaded from by on January 9, 9 Key Words: atrial natriuretic peptide cardiomyopathy, dilated heart failure natriuretic peptides The natriuretic peptides (NP) are valuable biomarkers for detecting and monitoring heart failure (HF). Atrial NP (ANP) and B-type NP (BNP), the major cardiac synthesized NPs, have potent natriuretic, diuretic, vasodilator, and renin- and aldosterone-suppressing activities. In volume- or pressure-overload mouse models, genetic deletion of ANP results in exaggerated cardiac hypertrophy and fibrosis.,3 However, the effects of ANP on dilated cardiomyopathy (DCM), a distinctly different process, are unknown. In patients with DCM rising ANP levels are correlated with increasing severity of cardiac dysfunction. 4 Yet, despite high ANP levels, patients with HF paradoxically retain salt and water, which suggests that ANP may have limited effect on modulating the pathophysiology of HF. 4 Clinical studies have not provided conclusive iights as infusio of ANP either improve cgmp levels or have no effects. 5,6 Thus, it is unclear whether ANP is a modulator or simply a biomarker of the development and progression of HF in DCM. We assessed the role of ANP in modulating the progression of HF in a well-established tragenic mouse model of DCM characterized by progressive HF and death caused by the specific action of a cardiac-targeted, dominant-negative camp respoe element-binding protein tracription factor. 7,8 Methods Experimental details are found in the online-only Data Supplement. Results ANP Affects Mortality in Mice With DCM To examine whether ANP affects the development and progression of DCM, we monitored the survival of DCM mice with normal ANP levels and ANP deficiency because of gene deletion (Figure ). By comparing DCM mice with normal ANP levels ( ), mice with partial ANP deficiency (DCM ANP+/ ) had an accelerated mortality (median survival 6 versus 96 days; P<.). Mice with complete deficiency of Received August 5, 3; first decision August 8, 3; revision accepted November 3, 3. From the Departments of Medicine (D.W., I.P.G., T.-H.M.F., A.K.H., G.L.R.) and Comparative Medicine (R.S.), University of Tennessee Health Science Center, Memphis. The online-only Data Supplement is available with this article at /-/DC. Correspondence to Guy L. Reed, Department of Medicine, University of Tennessee Health Science Center, Coleman, D334, 956 Court Ave, Memphis, TN glreed@uthsc.edu 3 American Heart Association, Inc. Hyperteion is available at DOI:.6/HYPERTENSIONAHA
2 Wang et al ANP Modulates Heart Failure in Cardiomyopathy 5 Downloaded from by on January 9, 9 Survival (%) p<. ANP+/- DCM p<. ANP-/- p<. DCM Age (days) 4 Figure. Dilated cardiomyopathy (DCM) mice with partial or complete atrial natriuretic peptide (ANP) deficiency have an accelerated mortality. Kaplan Meier survival curves of DCM ANP / (n=46), DCM ANP /+ (n=67), and (n=6) mice were assessed by log-rank test. P<., P<.. ANP (DCM ANP / ) had a significantly reduced survival (median survival, 84 days) when compared with DCM ANP+/ mice with partial ANP deficiency (P<.) or DCM mice with normal ANP levels (P<.). These data indicate that mortality in DCM mice was modulated by ANP levels in a gene-dose related fashion. ANP Modulates the Development of HF If ANP modulates survival in DCM mice, the presence or the absence of ANP may affect the development and progression of HF. Chest radiographs showed that mice had cardiomegaly (enlarged heart silhouettes) and mild lung edema without pleural effusio (Figure S in the online-only Data Supplement). In contrast, DCM ANP / mice had cardiomegaly with pronounced bilateral lung edema and pleural effusion (Figure S). A postmortem analysis of DCM ANP / mice showed severe lung congestion and pleural effusio. DCM ANP / mice had greater lung fluid accumulation as indicated by higher total lung wet weight (P<.5) and the lung wet weight:body weight ratio (lung A BW & LW (g) C BW LW LW/BW B LW / BW D Alveolar congestion % Figure. Enhanced heart dysfunction and pulmonary congestion in DCM ANP / mice. A, Lung wet weight (LW), body weight (BW), and LW:BW ratio (n= 3 in each group). B and C, Histological evaluation of lung congestion by H&E stain. B, mice have mild interstitial edema, whereas DCM ANP / mice show severe interstitial and intra-alveolar edema (pink area, asterisks). C, DCM ANP / mice have more punctate hemorrhagic lesio in alveolar capillaries than in mice. Scale bars, μm. D, Quantitative analysis of total alveolar congestion area per field. Results are mea of averages of randomly selected fields from 3 to 4 mice in each group. P<., P<., P<.5, P>.5. ANP indicates atrial natriuretic peptide; and DCM, dilated cardiomyopathy. wet weight/body weight, P<.5) than mice (n= 3 each group; Figure A). Lung histology analysis showed that DCM ANP / mice had more severe congestion in the interstitial and intra-alveolar space (Figure B, pink area, asterisks) and spotty hemorrhagic lesio in alveolar capillaries (Figure C). The total alveolar area filled with congestion was significantly increased in DCM ANP / mice when compared with mice (P<.; n=3 4 each group; Figure D). Renal function may affect salt and water retention associated with pleural effusio and pulmonary edema; creatinine levels were statistically higher in the DCM ANP / mice (P<.) although blood urea nitrogen and creatinine levels were within the normal range in both groups (Figure S). ANP Levels Affect Progression of Left Ventricular Dysfunction The increased lung congestion or pulmonary edema found in DCM ANP / mice may signify severe left ventricle (LV) dysfunction. Therefore, cardiac function was assessed by echocardiography. When compared with mice, DCM ANP / mice showed greater LV dilation in both diastole (P<.) and systole (P<.; Figure 3A 3C), suggesting that DCM ANP / mice had worse heart dilatation. There was no significant difference between DCM ANP / and mice in myocardial measures, such as thickness of the interventricular septum or posterior wall (P>.5; Figure 3D and 3E). However, DCM ANP / mice had marked decreases in LV systolic function as assessed by ejection fraction (P<.) and fractional shortening (P<.) when compared with mice (Figure 3F and 3G). ANP Affects Cardiac Remodeling Autopsy and histological studies showed that DCM ANP / mice had more severe heart enlargement than littermate controls (Figure 4A). In comparison with mice, left atrial enlargement was more marked in DCM ANP / mice. Heart weight (P<.) and heart weight:body weight ratio was significantly greater in DCM ANP / mice than in mice (P<.5; n= 3 each group; Figure 4B). Because eccentric hypertrophy may be a feature of DCM, we examined whether ANP deficiency affected cardiomyocyte hypertrophy by wheat germ agglutinin staining. 7 The cardiomyocyte cross-sectional area was significantly increased in DCM ANP / versus mice (P<.; Figure 4C and 4D). Fibrosis often plays a critical role in pathological remodeling in cardiomyopathy. When compared with mice, DCM ANP / mouse hearts had more exteive interstitial fibrosis between bundles of myocytes (Figure 4E and 4F; P<.). DCM ANP / mouse hearts showed areas coistent with fibrotic scarring in the LV (Figure 4E, arrow head), which have been associated with focal cardiomyocyte degeneration. Perivascular fibrosis was also more marked in DCM ANP / versus hearts (Figure 4G and 4H; P<.). There was exteive perivascular fibrosis in the cardiac vei and in different sized arteries (conductive arteries, prearterioles, and arterioles) 9 in the heart of DCM ANP / mice (Figure 4I). In addition, DCM ANP / mice hearts had
3 56 Hyperteion March 4 A B 6 C D LVID,d E F G LVPW,d 4 LVID, s EF % IVS,d FS % Figure 3. Echocardiographic findings in and DCM ANP / mice. A, Representative M-mode images. B, Left ventricular internal dimeion in diastole (LVIDd). C, left ventricular internal dimeion in systole (LVIDs). D, Interventricular septal thickness in diastole (IVSd). E, Left ventricular posterior wall thickness in diastole (LVPWd). F, Ejection fraction (EF %). G, Fractional shortening (FS %). P<., P>.5, n=9 each group. ANP indicates atrial natriuretic peptide; and DCM, dilated cardiomyopathy. Downloaded from by on January 9, 9 more severe atrial fibrosis, especially of the left atrium, than mice (Figure 4A). Effects of ANP Deficiency on NP Cardiac Gene Expression and cgmp Levels We have previously shown that ANP levels were increased in mice in comparison with mice without DCM. 8 As expected there were no detectable tracripts for ANP in DCM ANP / mice (Figure 5A). There was a trend toward increased BNP expression in DCM ANP / mice, but the expression levels were not statistically different from mice (Figure 5B; P=.67). Cardiac tracripts for C-type natriuretic peptide (CNP) were significantly lower in DCM ANP / mice than in mice (Figure 5C; P<.) although both showed a trend to lower expression than wild-type (WT) mice. Cardiac expression of the NP receptors (NPR) A and B was significantly decreased in both and DCM ANP / mice when compared with WT mice (NPRA, P<. versus WT; NPRB, P<.5 versus WT; n=5 each group), but they A D G E cross-sectional area X 3 (AU) B BW & HW (g) BW HW HW/BW I did not differ from each other (P>.5; n=5 each group; Figure 5D and 5E). Similarly, cardiac expression of NPRC was lower in mice (P<. versus WT) but not in DCM ANP / mice (P>.5 versus WT; Figure 5F). However, cardiac levels of NPRC were higher in DCM ANP / mice versus mice (P<.; n=5 each group; Figure 5F). There was no significant difference between mice and DCM ANP / in plasma levels of angiotein II, renin activity, or aldosterone (Figures S3 S5); however, levels of cortisol were 33% higher in DCM ANP / mice (Figure S6; P<.5). Blood levels of cgmp were significantly higher in versus DCM ANP / mice (Figure S7; P<.) coistent with higher cardiac tracripts of ANP. Discussion Chronic HF is increasing in prevalence. Both ANP and BNP are potent biomarkers for predicting mortality in patients with chronic HF. High levels of ANP are correlated with progressive HF, but it remai unclear whether ANP is protective.5..5 HW / BW C F 5 H IF % PF ratio to LA3 Figure 4. Pathological cardiac remodeling in DCM ANP / mice. A, Representative longitudinal sectio of hearts from and DCM ANP / mice ( weeks old). Severe 4-chamber dilation was frequently observed in DCM ANP / mice. Scale bars, mm. B, Heart weight (HW), body weight (BW), and HW/BW ratio (n= 3 in each group). C and D, Representative wheat germ agglutinin stain ( ) and quantitation of cardiomyocyte cross-sectional area. Results are averages of to cardiomyocytes from 4 to 6 mice each group. E and G, Representative Masson trichrome stain showing interstitial fibrosis (IF) and perivascular fibrosis (PF). F and H, Quantitative analysis of IF (% of total area) and PF (PF, ratio to lumen area). A total of to fields (4 ) or to arteries (4 ) from left ventricle per heart were measured. Results are mea of averages of 3 to 6 mice for each group. I, Intee PF involving cardiac vei and various sizes of coronary arteries. C, E, G, and I, Scale bars, μm. Dashed lines represent normal reference value from wild-type mice. P<., P>.5. ANP indicates atrial natriuretic peptide; and DCM, dilated cardiomyopathy.
4 Wang et al ANP Modulates Heart Failure in Cardiomyopathy 57 Downloaded from by on January 9, 9 A B C ANP expression D NPRA expression BNP expression E NPRB expression or merely serves as a biomarker in HF, particularly in conditio such as DCM. 4 The paradox of high ANP levels and progressive HF has been attributed to () incomplete processing of pro-anp to the active form; () the inability of current immunologic assays to distinguish between functional ANP and dysfunctional or nonfunctional ANP-related peptides; (3) NPRA/NPRB downregulation or clearance; (4) diminished kidney respoiveness and other mechanisms. Experimental data indicate that ANP plays a key role in modulating the hypertrophic respoe of cardiomyocytes in normal hearts to increased pressure overload (eg, traverse aortic cotriction) and in volume overload (aortocaval fistula).,3 Human studies have largely focused on short-term treatment of patients with impaired systolic function and show that brief ANP infusio do improve natriuresis in some but not all in subjects; however, there are no data that they modify cardiac structure, function, or survival. 5 Thus, to our knowledge these are the first data to show that ANP plays a key role in the progression of preexisting DCM by modifying systolic function, cardiac fibrosis, HF, and mortality. ANP has an antihypertrophic effect on cardiomyocytes both in vitro and in vivo. We found that ANP deficiency significantly affected cardiac remodeling. DCM ANP / mice hearts were greater in mass and in mass normalized to body weight. There was an increase in cardiomyocyte cross-sectional area in DCM ANP / versus mice. In contrast to models of pressure overload, the increased cardiomyocyte hypertrophy in this study was not associated with protective or compeatory effects because DCM ANP / mice showed greater impairment of systolic function, with lower ejection fractio, and greater ventricular dilation, with larger LV internal diameter in diastole and LV internal diameter in systole. Moreover, DCM ANP / mice did not show typical hypertrophic increases in the interventricular septum or posterior wall when compared with mice. Thus, the increased cardiac mass and worsened systolic function may be because of the fact that DCM ANP / mice developed more exteive interstitial and perivascular fibrosis in the ventricles and atria than that found in mice or in ANP / mice (data not shown). CNP expression F NPRC expression _ WT Figure 5. Changes in natriuretic peptides (NPs) and NP receptors (NPR) in wild-type (WT),, and DCM ANP / mice. A C, Relative cardiac expression of atrial NP (ANP), B-type NP (BNP), and C-type NP (CNP). D F, Relative cardiac expression of NPRA, NPRB, and NPRC. Tracripts are mea of averages of triplicate measures in 5 mice in each group assessed by quantitative reverse tracriptase polymerase chain reaction. P<., P<., P>.5. ANP inhibits cardiac fibroblast-mediated collagen synthesis and may protect hearts from pathological remodeling. As such, ANP deficiency may have additive or synergistic effects on promoting fibrosis in the setting of a preexisting cardiomyopathy, such as DCM. Although plasma renin activity, angiotein II, and aldosterone levels were not significantly different between DCM ANP / and mice, ANP may still affect aldosterone and angiotein II induced fibrosis at the tissue level. 3,4 The finding of elevated cortisol levels in the DCM ANP / mice underscores the potential pathogenic role of enhanced mineralocorticoid receptor activity in fibrosis. 3 Exteive interstitial fibrosis can cause ventricular stiffness, abnormal electric behavior of the myocardium, and fatal arrythmias. There is also a clear link between interstitial fibrosis and ventricular dysfunction. 6 DCM ANP / hearts also showed exteive fibrosis in the left atrium, which is also associated with HF. 7 There were areas of microscopic scar formation noted in DCM ANP / hearts that may indicate cardiomyocyte loss. 8 There was also exteive perivascular fibrosis of coronary vessels, particularly small coronary arteries and arterioles in DCM ANP / mice (Figure 4I). Severe perivascular fibrosis can lead to structural remodeling and luminal narrowing of intramural coronary arteries and arterioles, which may be associated with impaired coronary blood flow. 9 In patients with DCM, coronary microvascular dysfunction has been associated with advanced HF and increased risk of death. In addition to acting on cardiac tissue through autocrine and paracrine mechanisms, ANP enhances natriuresis and modulates renal function. Although ANP-deficient mice have normal blood pressures under normal salt diets, they may develop hyperteion under high-salt diets mediated by angiotein II. Because these mice were not on high-salt diets, and there were not significant differences in angiotein II levels between the groups, this may not have contributed to the adverse outcomes in DCM ANP / mice. In the present study, no physiologically significant differences were observed between DCM ANP / versus mice in indices of renal function, sodium, or electrolyte levels. Still DCM ANP / mice showed objective evidence of more severe HF as indicated by chest radiography, increased lung fluid, and exteive alveolar congestion. We analyzed cardiac tracripts to determine how ANP deficiency in DCM affected other key members of the NP system (ANP, BNP, CNP and their receptors NPRA, NPRB, and NPRC) which are thought to be regulated by LV wall stress in HF., Tracript analyses of hearts showed that ANP levels were significantly increased, BNP levels trended toward elevation, and CNP levels were unchanged to decreased when compared with WT controls. In contrast, in DCM ANP / mice, tracripts for ANP were undetectable, there was a trend toward increased BNP tracripts, and CNP tracripts were significantly diminished. The NPs exert their biological effects through specific receptors, NPRA (ANP and BNP) and NPRB (CNP), that increase intracellular cgmp. 3 NPRA downregulation occurs in HF and impairs the beneficial effects of NPs.,4 We found that NPRA and NPRB were significantly and comparably downregulated in mice and DCM ANP / mice versus WT littermates. Unexpectedly, NPRC
5 58 Hyperteion March 4 Downloaded from by on January 9, 9 levels were higher in DCM ANP / mice than in mice. NPRC is coidered a physiological clearance receptor for all 3 NPs, 5 which suggests that NP clearance may be accelerated and contributed to functionally reduced level of NPs in DCM ANP / mice although definitive data are lacking. Taken together, the changes in tracript expression do not reflect an obvious pattern of coordination between members of the NP system to compeate for the loss of ANP activity. This failure of compeation is further supported by the finding that plasma cgmp levels were lower in DCM ANP / mice when compared with mice (Figure 5H). Although it has been difficult to assign unique molecular functio to ANP and BNP at a cellular level, DCM ANP / mice showed severe structural and functional impairments, indicating that ANP plays an essential role that was not compeated by the activity or function of other members of the NP system. CNP tracripts were particularly diminished in DCM ANP / mice. This may reflect the direct effect of ANP deficiency because ANP enhances the production and secretion of CNP in cell culture. 6 CNP is not stored in granules, and activity seems dependent on tracriptional regulation. CNP potently inhibits cardiac fibroblast proliferation and collagen synthesis and has been shown to play a significant role in modulating fibrosis in vivo. 7,8 CNP also regulates the coronary circulation or microcirculation, 9 which suggests that it may affect myocardial blood supply in DCM ANP / mice. Thus, low CNP levels may also have affected cardiac function and remodeling in the DCM ANP / mice. 7 In conclusion, these data suggest that ANP affects cardiac remodeling, function, HF progression, and survival in the setting of DCM. Surprisingly, ANP deficiency is not adequately complemented by changes in the activity of other components of the NP system. Further studies are necessary to understand the functional inter-relatiohips of the NP and NPRs and how they act coordinately in processes, such as cardiomyopathy. Perspectives ANP is a biomarker for predicting mortality in patients with chronic HF. Still is unclear whether ANP functionally modulates the development of HF, especially in the setting of DCM. DCM mice with partial or complete ANP deficiency have a gene-dose dependent accelerated mortality. ANP deficiency is associated with cardiac dilatation, hypertrophy, fibrosis, and impaired heart function. These data suggest that in addition to its value as a biomarker, ANP affects the progression of cardiac fibrosis, systolic dysfunction, HF, and death in DCM. Acknowledgments We gratefully acknowledge the initial contributio of Rachel McNamee. Sources of Funding This study was supported by grants: National Ititutes of Health (HL58496 and HL7856 [Principal Investigator, G.L. Reed]; HL36 [Principal Investigator, I.P. Gladysheva]); Scientist Development Grant from the American Heart Association ( N, I.P. Gladysheva). None. Disclosures References. Nishikimi T, Maeda N, Matsuoka H. The role of natriuretic peptides in cardioprotection. Cardiovasc Res. 6;69: Mori T, Chen YF, Feng JA, Hayashi T, Oparil S, Perry GJ. Volume overload results in exaggerated cardiac hypertrophy in the atrial natriuretic peptide knockout mouse. Cardiovasc Res. 4;6: Franco V, Chen YF, Oparil S, Feng JA, Wang D, Hage F, Perry G. Atrial natriuretic peptide dose-dependently inhibits pressure overload-induced cardiac remodeling. Hyperteion. 4;44: Gottlieb SS, Kukin ML, Ahern D, Packer M. Prognostic importance of atrial natriuretic peptide in patients with chronic heart failure. J Am Coll Cardiol. 989;3: Hata N, Seino Y, Tsutamoto T, Hiramitsu S, Kaneko N, Yoshikawa T, Yokoyama H, Tanaka K, Mizuno K, Nejima J, Kinoshita M. Effects of carperitide on the long-term prognosis of patients with acute decompeated chronic heart failure: the PROTECT multicenter randomized controlled study. Circ J. 8;7: Kohzuki M, Hodsman GP, Harrison RW, Western PS, Johton CI. Atrial natriuretic peptide infusion in chronic heart failure in the rat. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol. 989;3 Suppl 6:S43 S Fentzke RC, Korcarz CE, Lang RM, Lin H, Leiden JM. Dilated cardiomyopathy in tragenic mice expressing a dominant-negative CREB tracription factor in the heart. J Clin Invest. 998;: Gladysheva IP, Wang D, McNamee RA, Houng AK, Mohamad AA, Fan TM, Reed GL. Corin overexpression improves cardiac function, heart failure, and survival in mice with dilated cardiomyopathy. Hyperteion. 3;6: Camici PG, Crea F. Coronary microvascular dysfunction. N Engl J Med. 7;356: von Haehling S, Jankowska EA, Morgenthaler NG, et al. Comparison of midregional pro-atrial natriuretic peptide with n-terminal pro-b-type natriuretic peptide in predicting survival in patients with chronic heart failure. J Am Coll Cardiol. 7;5: Ibebuogu UN, Gladysheva IP, Houng AK, Reed GL. Decompeated heart failure is associated with reduced corin levels and decreased cleavage of pro-atrial natriuretic peptide. Circ Heart Fail. ;4:4.. Redondo J, Bishop JE, Wilki MR. Effect of atrial natriuretic peptide and cyclic GMP phosphodiesterase inhibition on collagen synthesis by adult cardiac fibroblasts. Br J Pharmacol. 998;4: Messaoudi S, Azibani F, Delcayre C, Jaisser F. Aldosterone, mineralocorticoid receptor, and heart failure. Mol Cell Endocrinol. ; 35: Holtwick R, Baba HA, Ehler E, Risse D, Vobeta M, Gehrmann J, Pierkes M, Kuhn M. Left but not right cardiac hypertrophy in atrial natriuretic peptide receptor-deficient mice is prevented by angiotein type receptor antagonist losartan. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol. ;4: Mandinov L, Eberli FR, Seiler C, Hess OM. Diastolic heart failure. Cardiovasc Res. ;45: Hamid T, Gu Y, Ortines RV, Bhattacharya C, Wang G, Xuan YT, Prabhu SD. Divergent tumor necrosis factor receptor-related remodeling respoes in heart failure: role of nuclear factor-kappab and inflammatory activation. Circulation. 9;9: Kostin S, Klein G, Szalay Z, Hein S, Bauer EP, Schaper J. Structural correlate of atrial fibrillation in human patients. Cardiovasc Res. ;54: Hanna N, Cardin S, Leung TK, Nattel S. Differences in atrial versus ventricular remodeling in dogs with ventricular tachypacing-induced congestive heart failure. Cardiovasc Res. 4;63: Dai Z, Aoki T, Fukumoto Y, Shimokawa H. Coronary perivascular fibrosis is associated with impairment of coronary blood flow in patients with non-ischemic heart failure. J Cardiol. ;6: Neglia D, Michelassi C, Trivieri MG, Sambuceti G, Giorgetti A, Pratali L, Gallopin M, Salvadori P, Sorace O, Carpeggiani C, Poddighe R, L Abbate A, Parodi O. Prognostic role of myocardial blood flow impairment in idiopathic left ventricular dysfunction. Circulation. ;: Melo LG, Veress AT, Chong CK, Ackermann U, Sonnenberg H. Salt-seitive hyperteion in ANP knockout mice is prevented by AT receptor antagonist losartan. Am J Physiol. 999;77(3 Pt ):R64 R63.. Potter LR, Abbey-Hosch S, Dickey DM. Natriuretic peptides, their receptors, and cyclic guanosine monophosphate-dependent signaling functio. Endocr Rev. 6;7: Garbers DL, Lowe DG. Guanylyl cyclase receptors. J Biol Chem. 994;69: Tsutamoto T, Kanamori T, Morigami N, Sugimoto Y, Yamaoka O, Kinoshita M. Possibility of downregulation of atrial natriuretic peptide
6 Wang et al ANP Modulates Heart Failure in Cardiomyopathy 59 receptor coupled to guanylate cyclase in peripheral vascular beds of patients with chronic severe heart failure. Circulation. 993;87: Koller KJ, Goeddel DV. Molecular biology of the natriuretic peptides and their receptors. Circulation. 99;86: Nazario B, Hu RM, Pedram A, Pri B, Levin ER. Atrial and brain natriuretic peptides stimulate the production and secretion of C-type natriuretic peptide from bovine aortic endothelial cells. J Clin Invest. 995;95: Horio T, Tokudome T, Maki T, Yoshihara F, Suga S, Nishikimi T, Kojima M, Kawano Y, Kangawa K. Gene expression, secretion, and autocrine action of C-type natriuretic peptide in cultured adult rat cardiac fibroblasts. Endocrinology. 3;44: Soeki T, Kishimoto I, Okumura H, Tokudome T, Horio T, Mori K, Kangawa K. C-type natriuretic peptide, a novel antifibrotic and antihypertrophic agent, prevents cardiac remodeling after myocardial infarction. J Am Coll Cardiol. 5;45: Wright RS, Wei CM, Kim CH, Kinoshita M, Matsuda Y, Aarhus LL, Burnett JC Jr, Miller WL. C-type natriuretic peptide-mediated coronary vasodilation: role of the coronary nitric oxide and particulate guanylate cyclase systems. J Am Coll Cardiol. 996;8:3 38. Novelty and Significance What Is New? In experimental dilated cardiomyopathy we found the following:. partial or complete atrial natriuretic peptide (ANP) deficiency accelerates mortality.. ANP deficiency worse heart function and worse heart failure. ANP deficiency adversely affects cardiac remodeling by increasing both interstitial and perivascular fibrosis. ANP deficiency affects cardiac tracript expression of other NPs and receptors but is not functionally compeated by other members of the NP family. What Is Relevant? Beyond its role in natriuresis and vascular dilation, ANP seems to affect cardiac function, remodeling, heart failure development, and survival in dilated cardiomyopathy Summary In addition to its value as a biomarker, ANP seems to play a critical, irreplaceable role in modulating cardiac function, myocardial fibrosis, heart failure, and survival in experimental dilated cardiomyopathy. Downloaded from by on January 9, 9
J Jpn Coll Angiol, 2009, 49:
 Online publication October 6, 2009 48 2 20 J Jpn Coll Angiol, 2009, 49: 293 297 atrial natriuretic peptide, brain natriuretic peptide, guanylyl cyclase-a receptor, cardiac remodeling, cardiac hypertrophy
Online publication October 6, 2009 48 2 20 J Jpn Coll Angiol, 2009, 49: 293 297 atrial natriuretic peptide, brain natriuretic peptide, guanylyl cyclase-a receptor, cardiac remodeling, cardiac hypertrophy
Pathophysiology and Diagnosis of Heart Failure
 Pathophysiology and Diagnosis of Heart Failure Francesco Paneni, MD, PhD, FESC Cardiology Unit Karolinska University Hospital Stockholm, Sweden Cardiology University Hospital Zurich Switzerland francesco.paneni@gmail.com
Pathophysiology and Diagnosis of Heart Failure Francesco Paneni, MD, PhD, FESC Cardiology Unit Karolinska University Hospital Stockholm, Sweden Cardiology University Hospital Zurich Switzerland francesco.paneni@gmail.com
Supplemental Figure I
 Supplemental Figure I Kl ( mmol/l)-induced Force orta M (mn) 1 (mn) 1 Supplemental Figure I. Kl-induced contractions. and, Kl ( mmol/l)-induced contractions of the aorta () and those of mesenteric arteries
Supplemental Figure I Kl ( mmol/l)-induced Force orta M (mn) 1 (mn) 1 Supplemental Figure I. Kl-induced contractions. and, Kl ( mmol/l)-induced contractions of the aorta () and those of mesenteric arteries
E10.5 E18.5 P2 10w 83w NF1 HF1. Sham ISO. Bmi1. H3K9me3. Lung weight (g)
 Myociyte cross-sectional Relative mrna levels Relative levels Relative mrna levels Supplementary Figures and Legends a 8 6 4 2 Ezh2 E1.5 E18.5 P2 1w 83w b Ezh2 p16 amhc b-actin P2 43w kd 37 86 16 wt mouse
Myociyte cross-sectional Relative mrna levels Relative levels Relative mrna levels Supplementary Figures and Legends a 8 6 4 2 Ezh2 E1.5 E18.5 P2 1w 83w b Ezh2 p16 amhc b-actin P2 43w kd 37 86 16 wt mouse
Copyright 2011, 2007 by Mosby, Inc., an affiliate of Elsevier Inc. Normal Cardiac Anatomy
 Mosby,, an affiliate of Elsevier Normal Cardiac Anatomy Impaired cardiac pumping Results in vasoconstriction & fluid retention Characterized by ventricular dysfunction, reduced exercise tolerance, diminished
Mosby,, an affiliate of Elsevier Normal Cardiac Anatomy Impaired cardiac pumping Results in vasoconstriction & fluid retention Characterized by ventricular dysfunction, reduced exercise tolerance, diminished
c Ischemia (30 min) Reperfusion (8 w) Supplementary Figure bp 300 bp Ischemia (30 min) Reperfusion (4 h) Dox 20 mg/kg i.p.
 a Marker Ripk3 +/ 5 bp 3 bp b Ischemia (3 min) Reperfusion (4 h) d 2 mg/kg i.p. 1 w 5 w Sacrifice for IF size A subset for echocardiography and morphological analysis c Ischemia (3 min) Reperfusion (8
a Marker Ripk3 +/ 5 bp 3 bp b Ischemia (3 min) Reperfusion (4 h) d 2 mg/kg i.p. 1 w 5 w Sacrifice for IF size A subset for echocardiography and morphological analysis c Ischemia (3 min) Reperfusion (8
In Vivo Animal Models of Heart Disease. Why Animal Models of Disease? Timothy A Hacker, PhD Department of Medicine University of Wisconsin-Madison
 In Vivo Animal Models of Heart Disease Timothy A Hacker, PhD Department of Medicine University of Wisconsin-Madison Why Animal Models of Disease? Heart Failure (HF) Leading cause of morbidity and mortality
In Vivo Animal Models of Heart Disease Timothy A Hacker, PhD Department of Medicine University of Wisconsin-Madison Why Animal Models of Disease? Heart Failure (HF) Leading cause of morbidity and mortality
Heart Failure (HF) Treatment
 Heart Failure (HF) Treatment Heart Failure (HF) Complex, progressive disorder. The heart is unable to pump sufficient blood to meet the needs of the body. Its cardinal symptoms are dyspnea, fatigue, and
Heart Failure (HF) Treatment Heart Failure (HF) Complex, progressive disorder. The heart is unable to pump sufficient blood to meet the needs of the body. Its cardinal symptoms are dyspnea, fatigue, and
Heart Failure in Women: Dr Goh Ping Ping Cardiologist Asian Heart & Vascular Centre
 Heart Failure in Women: More than EF? Dr Goh Ping Ping Cardiologist Asian Heart & Vascular Centre Overview Review pathophysiology as it relates to diagnosis and management Rational approach to workup:
Heart Failure in Women: More than EF? Dr Goh Ping Ping Cardiologist Asian Heart & Vascular Centre Overview Review pathophysiology as it relates to diagnosis and management Rational approach to workup:
Definition of Congestive Heart Failure
 Heart Failure Definition of Congestive Heart Failure A clinical syndrome of signs & symptoms resulting from the heart s inability to supply adequate tissue perfusion. CHF Epidemiology Affects 4.7 million
Heart Failure Definition of Congestive Heart Failure A clinical syndrome of signs & symptoms resulting from the heart s inability to supply adequate tissue perfusion. CHF Epidemiology Affects 4.7 million
Protocol Identifier Subject Identifier Visit Description. [Y] Yes [N] No. [Y] Yes [N] N. If Yes, admission date and time: Day Month Year
![Protocol Identifier Subject Identifier Visit Description. [Y] Yes [N] No. [Y] Yes [N] N. If Yes, admission date and time: Day Month Year Protocol Identifier Subject Identifier Visit Description. [Y] Yes [N] No. [Y] Yes [N] N. If Yes, admission date and time: Day Month Year](/thumbs/76/74263761.jpg) PAST MEDICAL HISTORY Has the subject had a prior episode of heart failure? o Does the subject have a prior history of exposure to cardiotoxins, such as anthracyclines? URGENT HEART FAILURE VISIT Did heart
PAST MEDICAL HISTORY Has the subject had a prior episode of heart failure? o Does the subject have a prior history of exposure to cardiotoxins, such as anthracyclines? URGENT HEART FAILURE VISIT Did heart
Left atrial function. Aliakbar Arvandi MD
 In the clinic Left atrial function Abstract The left atrium (LA) is a left posterior cardiac chamber which is located adjacent to the esophagus. It is separated from the right atrium by the inter-atrial
In the clinic Left atrial function Abstract The left atrium (LA) is a left posterior cardiac chamber which is located adjacent to the esophagus. It is separated from the right atrium by the inter-atrial
hemodynamic stress. A. Echocardiographic quantification of cardiac dimensions and function in
 SUPPLEMENTAL FIGURE LEGENDS Supplemental Figure 1. Fbn1 C1039G/+ hearts display normal cardiac function in the absence of hemodynamic stress. A. Echocardiographic quantification of cardiac dimensions and
SUPPLEMENTAL FIGURE LEGENDS Supplemental Figure 1. Fbn1 C1039G/+ hearts display normal cardiac function in the absence of hemodynamic stress. A. Echocardiographic quantification of cardiac dimensions and
The Who, How and When of Advanced Heart Failure Therapies. Disclosures. What is Advanced Heart Failure?
 The Who, How and When of Advanced Heart Failure Therapies 9 th Annual Dartmouth Conference on Advances in Heart Failure Therapies Dartmouth-Hitchcock Medical Center Lebanon, NH May 20, 2013 Joseph G. Rogers,
The Who, How and When of Advanced Heart Failure Therapies 9 th Annual Dartmouth Conference on Advances in Heart Failure Therapies Dartmouth-Hitchcock Medical Center Lebanon, NH May 20, 2013 Joseph G. Rogers,
Patterns of Left Ventricular Remodeling in Chronic Heart Failure: The Role of Inadequate Ventricular Hypertrophy
 Abstract ESC 82445 Patterns of Left Ventricular Remodeling in Chronic Heart Failure: The Role of Inadequate Ventricular Hypertrophy FL. Dini 1, P. Capozza 1, P. Fontanive 2, MG. Delle Donne 1, V. Santonato
Abstract ESC 82445 Patterns of Left Ventricular Remodeling in Chronic Heart Failure: The Role of Inadequate Ventricular Hypertrophy FL. Dini 1, P. Capozza 1, P. Fontanive 2, MG. Delle Donne 1, V. Santonato
Outline. Pathophysiology: Heart Failure. Heart Failure. Heart Failure: Definitions. Etiologies. Etiologies
 Outline Pathophysiology: Mat Maurer, MD Irving Assistant Professor of Medicine Definitions and Classifications Epidemiology Muscle and Chamber Function Pathophysiology : Definitions An inability of the
Outline Pathophysiology: Mat Maurer, MD Irving Assistant Professor of Medicine Definitions and Classifications Epidemiology Muscle and Chamber Function Pathophysiology : Definitions An inability of the
Entresto Development of sacubitril/valsartan (LCZ696) for the treatment of heart failure with reduced ejection fraction
 Cardio-Metabolic Franchise Entresto Development of sacubitril/valsartan (LCZ696) for the treatment of heart failure with reduced ejection fraction Randy L Webb, PhD Rutgers Workshop October 21, 2016 Heart
Cardio-Metabolic Franchise Entresto Development of sacubitril/valsartan (LCZ696) for the treatment of heart failure with reduced ejection fraction Randy L Webb, PhD Rutgers Workshop October 21, 2016 Heart
LCZ696 A First-in-Class Angiotensin Receptor Neprilysin Inhibitor
 The Angiotensin Receptor Neprilysin Inhibitor LCZ696 in Heart Failure with Preserved Ejection Fraction The Prospective comparison of ARNI with ARB on Management Of heart failure with preserved ejection
The Angiotensin Receptor Neprilysin Inhibitor LCZ696 in Heart Failure with Preserved Ejection Fraction The Prospective comparison of ARNI with ARB on Management Of heart failure with preserved ejection
Pathophysiology of Coronary Microvascular Dysfunction
 Pathophysiology of Coronary Microvascular Dysfunction Cheol Woong Yu, MD, PhD Cardiology Department Division of Internal Medicine Korea University Anam Hospital. Etiologies of Chest Pain without obstructive
Pathophysiology of Coronary Microvascular Dysfunction Cheol Woong Yu, MD, PhD Cardiology Department Division of Internal Medicine Korea University Anam Hospital. Etiologies of Chest Pain without obstructive
Restrictive Cardiomyopathy
 ESC Congress 2011, Paris Imaging Unusual Causes of Cardiomyopathy Restrictive Cardiomyopathy Kazuaki Tanabe, MD, PhD Professor of Medicine Chair, Division of Cardiology Izumo, Japan I Have No Disclosures
ESC Congress 2011, Paris Imaging Unusual Causes of Cardiomyopathy Restrictive Cardiomyopathy Kazuaki Tanabe, MD, PhD Professor of Medicine Chair, Division of Cardiology Izumo, Japan I Have No Disclosures
Topic Page: congestive heart failure
 Topic Page: congestive heart failure Definition: congestive heart f ailure from Merriam-Webster's Collegiate(R) Dictionary (1930) : heart failure in which the heart is unable to maintain an adequate circulation
Topic Page: congestive heart failure Definition: congestive heart f ailure from Merriam-Webster's Collegiate(R) Dictionary (1930) : heart failure in which the heart is unable to maintain an adequate circulation
Value of echocardiography in chronic dyspnea
 Value of echocardiography in chronic dyspnea Jahrestagung Schweizerische Gesellschaft für /Schweizerische Gesellschaft für Pneumologie B. Kaufmann 16.06.2016 Chronic dyspnea Shortness of breath lasting
Value of echocardiography in chronic dyspnea Jahrestagung Schweizerische Gesellschaft für /Schweizerische Gesellschaft für Pneumologie B. Kaufmann 16.06.2016 Chronic dyspnea Shortness of breath lasting
Disclosure of Relationships
 Disclosure of Relationships Over the past 12 months Dr Ruilope has served as Consultant and Speakers Bureau member of Astra-Zeneca, Bayer, Daiichi-Sankyo, Menarini, Novartis, Otsuka, Pfizer, Relypsa, Servier
Disclosure of Relationships Over the past 12 months Dr Ruilope has served as Consultant and Speakers Bureau member of Astra-Zeneca, Bayer, Daiichi-Sankyo, Menarini, Novartis, Otsuka, Pfizer, Relypsa, Servier
Antialdosterone treatment in heart failure
 Update on the Treatment of Chronic Heart Failure 2012 Antialdosterone treatment in heart failure 전남의대윤현주 Chronic Heart Failure Prognosis of Heart failure Cecil, Text book of Internal Medicine, 22 th edition
Update on the Treatment of Chronic Heart Failure 2012 Antialdosterone treatment in heart failure 전남의대윤현주 Chronic Heart Failure Prognosis of Heart failure Cecil, Text book of Internal Medicine, 22 th edition
Risk Stratification in Heart Failure: The Role of Emerging Biomarkers
 Risk Stratification in Heart Failure: The Role of Emerging Biomarkers David G. Grenache, PhD Associate Professor of Pathology, University of Utah Medical Director, ARUP Laboratories Salt Lake City, UT
Risk Stratification in Heart Failure: The Role of Emerging Biomarkers David G. Grenache, PhD Associate Professor of Pathology, University of Utah Medical Director, ARUP Laboratories Salt Lake City, UT
DECLARATION OF CONFLICT OF INTEREST
 DECLARATION OF CONFLICT OF INTEREST ESC Congress 2011 Pathophysiology of HFPEF Vascular Remodeling & Pulmonary Hypertension Carolyn S.P. Lam MBBS, MRCP, MS Case Presentation 81 yo woman with dyspnoea &
DECLARATION OF CONFLICT OF INTEREST ESC Congress 2011 Pathophysiology of HFPEF Vascular Remodeling & Pulmonary Hypertension Carolyn S.P. Lam MBBS, MRCP, MS Case Presentation 81 yo woman with dyspnoea &
Heart Failure. Cardiac Anatomy. Functions of the Heart. Cardiac Cycle/Hemodynamics. Determinants of Cardiac Output. Cardiac Output
 Cardiac Anatomy Heart Failure Professor Qing ZHANG Department of Cardiology, West China Hospital www.blaufuss.org Cardiac Cycle/Hemodynamics Functions of the Heart Essential functions of the heart to cover
Cardiac Anatomy Heart Failure Professor Qing ZHANG Department of Cardiology, West China Hospital www.blaufuss.org Cardiac Cycle/Hemodynamics Functions of the Heart Essential functions of the heart to cover
Bio-Molecular Markers for Cardiovascular Disease: Significance of Natriuretic Peptides and Adrenomedullin
 REVIEW Korean Circ J 2008;38:507-513 Print ISSN 1738-5520 / On-line ISSN 1738-5555 Copyright c 2008 The Korean Society of Cardiology Bio-Molecular Markers for Cardiovascular Disease: Significance of Natriuretic
REVIEW Korean Circ J 2008;38:507-513 Print ISSN 1738-5520 / On-line ISSN 1738-5555 Copyright c 2008 The Korean Society of Cardiology Bio-Molecular Markers for Cardiovascular Disease: Significance of Natriuretic
Index of subjects. effect on ventricular tachycardia 30 treatment with 101, 116 boosterpump 80 Brockenbrough phenomenon 55, 125
 145 Index of subjects A accessory pathways 3 amiodarone 4, 5, 6, 23, 30, 97, 102 angina pectoris 4, 24, 1l0, 137, 139, 140 angulation, of cavity 73, 74 aorta aortic flow velocity 2 aortic insufficiency
145 Index of subjects A accessory pathways 3 amiodarone 4, 5, 6, 23, 30, 97, 102 angina pectoris 4, 24, 1l0, 137, 139, 140 angulation, of cavity 73, 74 aorta aortic flow velocity 2 aortic insufficiency
Pathophysiology: Heart Failure
 Pathophysiology: Heart Failure Mat Maurer, MD Irving Assistant Professor of Medicine Outline Definitions and Classifications Epidemiology Muscle and Chamber Function Pathophysiology Heart Failure: Definitions
Pathophysiology: Heart Failure Mat Maurer, MD Irving Assistant Professor of Medicine Outline Definitions and Classifications Epidemiology Muscle and Chamber Function Pathophysiology Heart Failure: Definitions
Effect of Short-term Maximal Exercise on BNP Plasma Levels in. Healthy Individuals
 1 Effect of Short-term Maximal Exercise on BNP Plasma Levels in Healthy Individuals Jan Krupicka, MD, Tomas Janota, MD, Zdislava Kasalova, MD, Jaromir Hradec, MD 3rd Department of Internal Medicine, 1st
1 Effect of Short-term Maximal Exercise on BNP Plasma Levels in Healthy Individuals Jan Krupicka, MD, Tomas Janota, MD, Zdislava Kasalova, MD, Jaromir Hradec, MD 3rd Department of Internal Medicine, 1st
HFpEF. April 26, 2018
 HFpEF April 26, 2018 (J Am Coll Cardiol 2017;70:2476 86) HFpEF 50% or more (40-71%) of patients with CHF have preserved LV systolic function. HFpEF is an increasingly frequent hospital discharge. Outcomes
HFpEF April 26, 2018 (J Am Coll Cardiol 2017;70:2476 86) HFpEF 50% or more (40-71%) of patients with CHF have preserved LV systolic function. HFpEF is an increasingly frequent hospital discharge. Outcomes
ΒΙΟΔΕΙΚΤΕΣ ΣΤΗΝ ΚΑΡΔΙΑΚΗ ΑΝΕΠΑΡΚΕΙΑ. ΔΗΜΗΤΡΙΟΣ ΤΟΥΣΟΥΛΗΣ Καθηγητής Καρδιολογίας
 ΕΘΝΙΚΟ ΚΑΙ ΚΑΠΟΔΙΣΤΡΙΑΚΟ ΠΑΝΕΠΙΣΤΗΜΙΟ ΑΘΗΝΩΝ ΙΑΤΡΙΚΗ ΣΧΟΛΗ Ά ΚΑΡΔΙΟΛΟΓΙΚΗ ΚΛΙΝΙΚΗ Διευθυντής: Καθηγητής Δημήτριος Τούσουλης ΒΙΟΔΕΙΚΤΕΣ ΣΤΗΝ ΚΑΡΔΙΑΚΗ ΑΝΕΠΑΡΚΕΙΑ ΔΗΜΗΤΡΙΟΣ ΤΟΥΣΟΥΛΗΣ Καθηγητής Καρδιολογίας
ΕΘΝΙΚΟ ΚΑΙ ΚΑΠΟΔΙΣΤΡΙΑΚΟ ΠΑΝΕΠΙΣΤΗΜΙΟ ΑΘΗΝΩΝ ΙΑΤΡΙΚΗ ΣΧΟΛΗ Ά ΚΑΡΔΙΟΛΟΓΙΚΗ ΚΛΙΝΙΚΗ Διευθυντής: Καθηγητής Δημήτριος Τούσουλης ΒΙΟΔΕΙΚΤΕΣ ΣΤΗΝ ΚΑΡΔΙΑΚΗ ΑΝΕΠΑΡΚΕΙΑ ΔΗΜΗΤΡΙΟΣ ΤΟΥΣΟΥΛΗΣ Καθηγητής Καρδιολογίας
HEART FAILURE PHARMACOLOGY. University of Hawai i Hilo Pre- Nursing Program NURS 203 General Pharmacology Danita Narciso Pharm D
 HEART FAILURE PHARMACOLOGY University of Hawai i Hilo Pre- Nursing Program NURS 203 General Pharmacology Danita Narciso Pharm D 1 LEARNING OBJECTIVES Understand the effects of heart failure in the body
HEART FAILURE PHARMACOLOGY University of Hawai i Hilo Pre- Nursing Program NURS 203 General Pharmacology Danita Narciso Pharm D 1 LEARNING OBJECTIVES Understand the effects of heart failure in the body
Diagnosis is it really Heart Failure?
 ESC Congress Munich - 25-29 August 2012 Heart Failure with Preserved Ejection Fraction From Bench to Bedside Diagnosis is it really Heart Failure? Prof. Burkert Pieske Department of Cardiology Med.University
ESC Congress Munich - 25-29 August 2012 Heart Failure with Preserved Ejection Fraction From Bench to Bedside Diagnosis is it really Heart Failure? Prof. Burkert Pieske Department of Cardiology Med.University
Role of CMR in heart failure and cardiomyopathy
 Role of CMR in heart failure and cardiomyopathy Hajime Sakuma Department of Radiology, Mie University Late gadolinium enhancement (LGE) LGE MRI can demonstrate site of necrosis, fibrosis or deposition
Role of CMR in heart failure and cardiomyopathy Hajime Sakuma Department of Radiology, Mie University Late gadolinium enhancement (LGE) LGE MRI can demonstrate site of necrosis, fibrosis or deposition
BNP mrna expression in DR and DS rat left ventricles (n = 5). (C) Plasma norepinephrine
 Kanazawa, et al. Supplementary figure legends Supplementary Figure 1 DS rats had congestive heart failure. (A) DR and DS rat hearts. (B) QRT-PCR analysis of BNP mrna expression in DR and DS rat left ventricles
Kanazawa, et al. Supplementary figure legends Supplementary Figure 1 DS rats had congestive heart failure. (A) DR and DS rat hearts. (B) QRT-PCR analysis of BNP mrna expression in DR and DS rat left ventricles
Proceedings of the 34th World Small Animal Veterinary Congress WSAVA 2009
 www.ivis.org Proceedings of the 34th World Small Animal Veterinary Congress WSAVA 2009 São Paulo, Brazil - 2009 Next WSAVA Congress : Reprinted in IVIS with the permission of the Congress Organizers MANAGEMENT
www.ivis.org Proceedings of the 34th World Small Animal Veterinary Congress WSAVA 2009 São Paulo, Brazil - 2009 Next WSAVA Congress : Reprinted in IVIS with the permission of the Congress Organizers MANAGEMENT
Tcf21 MCM ; R26 mtmg Sham GFP Col 1/3 TAC 8W TAC 2W. Postn MCM ; R26 mtmg Sham GFP Col 1/3 TAC 8W TAC 2W
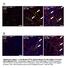 A Tcf21 MCM ; R26 mtmg Sham GFP Col 1/3 Tcf21 MCM ; R26 mtmg TAC 2W Tcf21 MCM ; R26 mtmg TAC 8W B Postn MCM ; R26 mtmg Sham GFP Col 1/3 Postn MCM ; R26 mtmg TAC 2W Postn MCM ; R26 mtmg TAC 8W Supplementary
A Tcf21 MCM ; R26 mtmg Sham GFP Col 1/3 Tcf21 MCM ; R26 mtmg TAC 2W Tcf21 MCM ; R26 mtmg TAC 8W B Postn MCM ; R26 mtmg Sham GFP Col 1/3 Postn MCM ; R26 mtmg TAC 2W Postn MCM ; R26 mtmg TAC 8W Supplementary
Effects of Cilostazol in Patients With Bradycardiac Atrial Fibrillation
 J Cardiol 2001 ; 37: 27 33 Effects of Cilostazol in Patients With Bradycardiac Atrial Fibrillation 1 2 1 Masato Kouki KISHIDA, MD WATANABE, MD Abstract Objectives. Cilostazol, an antithrombotic agent,
J Cardiol 2001 ; 37: 27 33 Effects of Cilostazol in Patients With Bradycardiac Atrial Fibrillation 1 2 1 Masato Kouki KISHIDA, MD WATANABE, MD Abstract Objectives. Cilostazol, an antithrombotic agent,
Diastolic Heart Failure (HFpEF) Felix J. Rogers, DO, FACOI April 29, 2018
 Diastolic Heart Failure (HFpEF) Felix J. Rogers, DO, FACOI April 29, 2018 Case presentation MSO, an 81 year old woman was admitted to HFWH because of progressive dyspnea and difficult to control hypertension
Diastolic Heart Failure (HFpEF) Felix J. Rogers, DO, FACOI April 29, 2018 Case presentation MSO, an 81 year old woman was admitted to HFWH because of progressive dyspnea and difficult to control hypertension
Circulation. Blood Pressure and Antihypertensive Medications. Venous Return. Arterial flow. Regulation of Cardiac Output.
 Circulation Blood Pressure and Antihypertensive Medications Two systems Pulmonary (low pressure) Systemic (high pressure) Aorta 120 mmhg Large arteries 110 mmhg Arterioles 40 mmhg Arteriolar capillaries
Circulation Blood Pressure and Antihypertensive Medications Two systems Pulmonary (low pressure) Systemic (high pressure) Aorta 120 mmhg Large arteries 110 mmhg Arterioles 40 mmhg Arteriolar capillaries
Cardiorenal Syndrome Prof. Dr. Bülent ALTUN Hacettepe University Faculty of Medicine Department of Internal Medicine Division of Nephrology
 Cardiorenal Syndrome Prof. Dr. Bülent ALTUN Hacettepe University Faculty of Medicine Department of Internal Medicine Division of Nephrology Heart and Kidney The kidney yin dominates water, The heart yang
Cardiorenal Syndrome Prof. Dr. Bülent ALTUN Hacettepe University Faculty of Medicine Department of Internal Medicine Division of Nephrology Heart and Kidney The kidney yin dominates water, The heart yang
DOWNLOAD PDF ABC OF HEART FAILURE
 Chapter 1 : The ABCs of managing systolic heart failure: Past, present, and future Heart failure is a multisystem disorder which is characterised by abnormalities of cardiac, skeletal muscle, and renal
Chapter 1 : The ABCs of managing systolic heart failure: Past, present, and future Heart failure is a multisystem disorder which is characterised by abnormalities of cardiac, skeletal muscle, and renal
Overview & Update on the Utilization of the Natriuretic Peptides in Heart Failure
 June 28, 2016 Overview & Update on the Utilization of the Natriuretic Peptides in Heart Failure Linda C. Rogers, PhD, DABCC, FACB. Agenda Overview of the Natriuretic Peptides and Efficacy studies Similarities
June 28, 2016 Overview & Update on the Utilization of the Natriuretic Peptides in Heart Failure Linda C. Rogers, PhD, DABCC, FACB. Agenda Overview of the Natriuretic Peptides and Efficacy studies Similarities
Ventricular Tachycardia Ablation. Saverio Iacopino, MD, FACC, FESC
 Ventricular Tachycardia Ablation Saverio Iacopino, MD, FACC, FESC ü Ventricular arrhythmias, both symptomatic and asymptomatic, are common, but syncope and SCD are infrequent initial manifestations of
Ventricular Tachycardia Ablation Saverio Iacopino, MD, FACC, FESC ü Ventricular arrhythmias, both symptomatic and asymptomatic, are common, but syncope and SCD are infrequent initial manifestations of
CT for Myocardial Characterization of Cardiomyopathy. Byoung Wook Choi, Yonsei University Severance Hospital, Seoul, Korea
 CT for Myocardial Characterization of Cardiomyopathy Byoung Wook Choi, Yonsei University Severance Hospital, Seoul, Korea Cardiomyopathy Elliott P et al. Eur Heart J 2008;29:270-276 The European Society
CT for Myocardial Characterization of Cardiomyopathy Byoung Wook Choi, Yonsei University Severance Hospital, Seoul, Korea Cardiomyopathy Elliott P et al. Eur Heart J 2008;29:270-276 The European Society
Ejection Fraction in Patients With Chronic Heart Failure. Diastolic Heart Failure or Heart Failure with Preserved Ejection Fraction
 Diastolic Heart Failure or Heart Failure with Preserved Ejection Fraction Keith Miller MD Diastolic Heart Failure Risk Factors Common Risk Factors Aging Female gender Obesity Hypertension Diabetes mellitus
Diastolic Heart Failure or Heart Failure with Preserved Ejection Fraction Keith Miller MD Diastolic Heart Failure Risk Factors Common Risk Factors Aging Female gender Obesity Hypertension Diabetes mellitus
The Causes of Heart Failure
 The Causes of Heart Failure Andy Birchall HFSN Right heart failure LVSD - HFREF Valve regurgitation or stenosis Dropsy CCF congestive cardiac failure Cor pulmonale Pulmonary hypertension HFPEF LVF Definitions
The Causes of Heart Failure Andy Birchall HFSN Right heart failure LVSD - HFREF Valve regurgitation or stenosis Dropsy CCF congestive cardiac failure Cor pulmonale Pulmonary hypertension HFPEF LVF Definitions
Lnformation Coverage Guidance
 Lnformation Coverage Guidance Coverage Indications, Limitations, and/or Medical Necessity Abstract: B-type natriuretic peptide (BNP) is a cardiac neurohormone produced mainly in the left ventricle. It
Lnformation Coverage Guidance Coverage Indications, Limitations, and/or Medical Necessity Abstract: B-type natriuretic peptide (BNP) is a cardiac neurohormone produced mainly in the left ventricle. It
Athlete s Heart vs. Cardiomyopathy
 Athlete s Heart vs. Cardiomyopathy Linda D. Gillam, MD, MPH, FASE Chair, Department of Cardiovascular Medicine Medical Director, Cardiovascular Service Line Former Team Cardiologist to the New York Jets
Athlete s Heart vs. Cardiomyopathy Linda D. Gillam, MD, MPH, FASE Chair, Department of Cardiovascular Medicine Medical Director, Cardiovascular Service Line Former Team Cardiologist to the New York Jets
Comparison with plasma angiotensin II and endothelin-1
 European Heart Journal (1999) 2, 1799 187 Article No. euhj.1999.1746, available online at http://www.idealibrary.com on Plasma brain natriuretic peptide level as a biochemical marker of morbidity and mortality
European Heart Journal (1999) 2, 1799 187 Article No. euhj.1999.1746, available online at http://www.idealibrary.com on Plasma brain natriuretic peptide level as a biochemical marker of morbidity and mortality
Fetal gene upregulation by 1-wk TAC is significantly increased in mice lacking RGS2.
 3562-RG-1 Supplementary Figure 1 Fetal gene upregulation by 1-wk is significantly increased in mice lacking RGS2. ANP(Nppa) /BNP(Nppb) A-type and B-type natriuretic peptide; β-mhc (Myh7) beta myosin heavy
3562-RG-1 Supplementary Figure 1 Fetal gene upregulation by 1-wk is significantly increased in mice lacking RGS2. ANP(Nppa) /BNP(Nppb) A-type and B-type natriuretic peptide; β-mhc (Myh7) beta myosin heavy
Pearls in Acute Heart Failure Management
 Pearls in Acute Heart Failure Management Best Practices Juan M. Aranda Jr., M.D. Professor of Medicine Medical Director of Heart Failure/ Transplant Program University of Florida College of Medicine Disclosures:
Pearls in Acute Heart Failure Management Best Practices Juan M. Aranda Jr., M.D. Professor of Medicine Medical Director of Heart Failure/ Transplant Program University of Florida College of Medicine Disclosures:
LV geometric and functional changes in VHD: How to assess? Mi-Seung Shin M.D., Ph.D. Gachon University Gil Hospital
 LV geometric and functional changes in VHD: How to assess? Mi-Seung Shin M.D., Ph.D. Gachon University Gil Hospital LV inflow across MV LV LV outflow across AV LV LV geometric changes Pressure overload
LV geometric and functional changes in VHD: How to assess? Mi-Seung Shin M.D., Ph.D. Gachon University Gil Hospital LV inflow across MV LV LV outflow across AV LV LV geometric changes Pressure overload
Diagnosis & Management of Heart Failure. Abena A. Osei-Wusu, M.D. Medical Fiesta
 Diagnosis & Management of Heart Failure Abena A. Osei-Wusu, M.D. Medical Fiesta Learning Objectives: 1) Become familiar with pathogenesis of congestive heart failure. 2) Discuss clinical manifestations
Diagnosis & Management of Heart Failure Abena A. Osei-Wusu, M.D. Medical Fiesta Learning Objectives: 1) Become familiar with pathogenesis of congestive heart failure. 2) Discuss clinical manifestations
The right heart: the Cinderella of heart failure
 The right heart: the Cinderella of heart failure Piotr Ponikowski, MD, PhD, FESC Medical University, Centre for Heart Disease Clinical Military Hospital Wroclaw, Poland none Disclosure Look into the Heart
The right heart: the Cinderella of heart failure Piotr Ponikowski, MD, PhD, FESC Medical University, Centre for Heart Disease Clinical Military Hospital Wroclaw, Poland none Disclosure Look into the Heart
Rapid Publication. Cardiac Secretion of Adrenomedullin in Human Heart Failure. Abstract. Methods. Introduction
 Rapid Publication Cardiac Secretion of Adrenomedullin in Human Heart Failure Michihisa Jougasaki, Richard J. Rodeheffer, Margaret M. Redfield, Kazuhiro Yamamoto, Chi-Ming Wei, Linda J. McKinley, and John
Rapid Publication Cardiac Secretion of Adrenomedullin in Human Heart Failure Michihisa Jougasaki, Richard J. Rodeheffer, Margaret M. Redfield, Kazuhiro Yamamoto, Chi-Ming Wei, Linda J. McKinley, and John
Australian Journal of Basic and Applied Sciences, 9(36) December 2015, Pages: ISSN: Journal home page:
 ISSN:1991-8178 Australian Journal of Basic and Applied Sciences Journal home page: www.ajbasweb.com Role of Biochemical Tests Artery Disease (ANP, BNP) in the Evaluation of Patients with Coronary 1 Saad
ISSN:1991-8178 Australian Journal of Basic and Applied Sciences Journal home page: www.ajbasweb.com Role of Biochemical Tests Artery Disease (ANP, BNP) in the Evaluation of Patients with Coronary 1 Saad
Heart failure (HF) is a syndrome of abnormal salt and water
 Heart Corin Overexpression Improves Cardiac Function, Heart Failure, and Survival in Mice With Dilated Cardiomyopathy Inna P. Gladysheva,* Dong Wang,* Rachel A. McNamee, Aiilyan K. Houng, Almois A. Mohamad,
Heart Corin Overexpression Improves Cardiac Function, Heart Failure, and Survival in Mice With Dilated Cardiomyopathy Inna P. Gladysheva,* Dong Wang,* Rachel A. McNamee, Aiilyan K. Houng, Almois A. Mohamad,
During exercise the heart rate is 190 bpm and the stroke volume is 115 ml/beat. What is the cardiac output?
 The Cardiovascular System Part III: Heart Outline of class lecture After studying part I of this chapter you should be able to: 1. Be able to calculate cardiac output (CO) be able to define heart rate
The Cardiovascular System Part III: Heart Outline of class lecture After studying part I of this chapter you should be able to: 1. Be able to calculate cardiac output (CO) be able to define heart rate
Blood Pressure Regulation 2. Faisal I. Mohammed, MD,PhD
 Blood Pressure Regulation 2 Faisal I. Mohammed, MD,PhD 1 Objectives Outline the intermediate term and long term regulators of ABP. Describe the role of Epinephrine, Antidiuretic hormone (ADH), Renin-Angiotensin-Aldosterone
Blood Pressure Regulation 2 Faisal I. Mohammed, MD,PhD 1 Objectives Outline the intermediate term and long term regulators of ABP. Describe the role of Epinephrine, Antidiuretic hormone (ADH), Renin-Angiotensin-Aldosterone
Blood Pressure Regulation 2. Faisal I. Mohammed, MD,PhD
 Blood Pressure Regulation 2 Faisal I. Mohammed, MD,PhD 1 Objectives Outline the intermediate term and long term regulators of ABP. Describe the role of Epinephrine, Antidiuretic hormone (ADH), Renin-Angiotensin-Aldosterone
Blood Pressure Regulation 2 Faisal I. Mohammed, MD,PhD 1 Objectives Outline the intermediate term and long term regulators of ABP. Describe the role of Epinephrine, Antidiuretic hormone (ADH), Renin-Angiotensin-Aldosterone
Cor pulmonale. Dr hamid reza javadi
 1 Cor pulmonale Dr hamid reza javadi 2 Definition Cor pulmonale ;pulmonary heart disease; is defined as dilation and hypertrophy of the right ventricle (RV) in response to diseases of the pulmonary vasculature
1 Cor pulmonale Dr hamid reza javadi 2 Definition Cor pulmonale ;pulmonary heart disease; is defined as dilation and hypertrophy of the right ventricle (RV) in response to diseases of the pulmonary vasculature
Supplemental Table 1. Echocardiography Control (n=4)
 Supplemental Table 1. Echocardiography (n=4) Mlc2v cre/+ ; DNMAML (n=4) LVIDd, mm 3.9±0.3 4.3±0.3 LVIDs, mm 2.6±0.4 2.9±0.2 d, mm 0.72±0.06 0.75±0.1 LVPWd, mm 0.72±0.06 0.77±0.11 FS, % 33±6 33±1 EF, %
Supplemental Table 1. Echocardiography (n=4) Mlc2v cre/+ ; DNMAML (n=4) LVIDd, mm 3.9±0.3 4.3±0.3 LVIDs, mm 2.6±0.4 2.9±0.2 d, mm 0.72±0.06 0.75±0.1 LVPWd, mm 0.72±0.06 0.77±0.11 FS, % 33±6 33±1 EF, %
Οξεία καρδιακή ανεπάρκεια: Ποιες παράμετροι συμβάλλουν στη διαστρωμάτωση κινδύνου των ασθενών;
 Οξεία καρδιακή ανεπάρκεια: Ποιες παράμετροι συμβάλλουν στη διαστρωμάτωση κινδύνου των ασθενών; Γ. Φιλιππάτος, MD, FACC, FESC, FCCP Επ. Καθηγητής Καρδιολογίας Πανεπ. Αθηνών Clinical Outcomes in Patients
Οξεία καρδιακή ανεπάρκεια: Ποιες παράμετροι συμβάλλουν στη διαστρωμάτωση κινδύνου των ασθενών; Γ. Φιλιππάτος, MD, FACC, FESC, FCCP Επ. Καθηγητής Καρδιολογίας Πανεπ. Αθηνών Clinical Outcomes in Patients
LEFT BUNDLE BRANCH BLOCK- BENIGN OR A HARBINGER OF HEART FAILURE? PROGNOSTIC INDICATOR?
 LEFT BUNDLE BRANCH BLOCK- BENIGN OR A HARBINGER OF HEART FAILURE? PROGNOSTIC INDICATOR? Juan Cinca Department and Chair of Cardiology Hospital de la Santa Creu i Sant Pau Universitat Autònoma de Barcelona
LEFT BUNDLE BRANCH BLOCK- BENIGN OR A HARBINGER OF HEART FAILURE? PROGNOSTIC INDICATOR? Juan Cinca Department and Chair of Cardiology Hospital de la Santa Creu i Sant Pau Universitat Autònoma de Barcelona
C57BL/6 Mice are More Appropriate. than BALB/C Mice in Inducing Dilated Cardiomyopathy with Short-Term Doxorubicin Treatment
 Original Article C57BL/6 Mice are More Appropriate Acta Cardiol Sin 2012;28:236 240 Heart Failure & Cardiomyopathy C57BL/6 Mice are More Appropriate than BALB/C Mice in Inducing Dilated Cardiomyopathy
Original Article C57BL/6 Mice are More Appropriate Acta Cardiol Sin 2012;28:236 240 Heart Failure & Cardiomyopathy C57BL/6 Mice are More Appropriate than BALB/C Mice in Inducing Dilated Cardiomyopathy
Review of Cardiac Imaging Modalities in the Renal Patient. George Youssef
 Review of Cardiac Imaging Modalities in the Renal Patient George Youssef ECHO Left ventricular hypertrophy (LVH) assessment Diastolic dysfunction Stress ECHO Cardiac CT angiography Echocardiography - positives
Review of Cardiac Imaging Modalities in the Renal Patient George Youssef ECHO Left ventricular hypertrophy (LVH) assessment Diastolic dysfunction Stress ECHO Cardiac CT angiography Echocardiography - positives
Drugs Used in Heart Failure. Assistant Prof. Dr. Najlaa Saadi PhD pharmacology Faculty of Pharmacy University of Philadelphia
 Drugs Used in Heart Failure Assistant Prof. Dr. Najlaa Saadi PhD pharmacology Faculty of Pharmacy University of Philadelphia Heart Failure Heart failure (HF), occurs when cardiac output is inadequate to
Drugs Used in Heart Failure Assistant Prof. Dr. Najlaa Saadi PhD pharmacology Faculty of Pharmacy University of Philadelphia Heart Failure Heart failure (HF), occurs when cardiac output is inadequate to
Paul M McKie, Alessandro Cataliotti, Guido Boerrigter, Horng C Chen, Fernando L Martin, and John C Burnett Jr
 Cardiorenal Enhancing and Aldosterone Suppressing Actions of a Novel Designer Natriuretic Peptide in Experimental Hypertension with Ventricular Pressure Overload Paul M McKie, Alessandro Cataliotti, Guido
Cardiorenal Enhancing and Aldosterone Suppressing Actions of a Novel Designer Natriuretic Peptide in Experimental Hypertension with Ventricular Pressure Overload Paul M McKie, Alessandro Cataliotti, Guido
Πνευμονική υπέρταση και περικαρδιακή συλλογή. Τρόποι αντιμετώπισης
 Πνευμονική υπέρταση και περικαρδιακή συλλογή. Τρόποι αντιμετώπισης Γεώργιος Λάζαρος Καρδιολόγος, Διευθυντής ΕΣΥ Α Πανεπιστημιακή Καρδιολογική Κλινική Ιπποκράτειο Γ.Ν. Αθηνών Pericardial syndromes o Acute
Πνευμονική υπέρταση και περικαρδιακή συλλογή. Τρόποι αντιμετώπισης Γεώργιος Λάζαρος Καρδιολόγος, Διευθυντής ΕΣΥ Α Πανεπιστημιακή Καρδιολογική Κλινική Ιπποκράτειο Γ.Ν. Αθηνών Pericardial syndromes o Acute
Left ventricular hypertrophy: why does it happen?
 Nephrol Dial Transplant (2003) 18 [Suppl 8]: viii2 viii6 DOI: 10.1093/ndt/gfg1083 Left ventricular hypertrophy: why does it happen? Gerard M. London Department of Nephrology and Dialysis, Manhes Hospital,
Nephrol Dial Transplant (2003) 18 [Suppl 8]: viii2 viii6 DOI: 10.1093/ndt/gfg1083 Left ventricular hypertrophy: why does it happen? Gerard M. London Department of Nephrology and Dialysis, Manhes Hospital,
Myocardial Infarction
 Myocardial Infarction MI = heart attack Defined as necrosis of heart muscle resulting from ischemia. A very significant cause of death worldwide. of these deaths, 33% -50% die before they can reach the
Myocardial Infarction MI = heart attack Defined as necrosis of heart muscle resulting from ischemia. A very significant cause of death worldwide. of these deaths, 33% -50% die before they can reach the
Study of grading of severity of Heart Failure in patients with Dilated Cardiomyopathy
 Original article: Study of grading of severity of Heart Failure in patients with Dilated Cardiomyopathy Dr Satyajeet Shantaram Nighute *, Dr Govind S. Shiddapur, Dr Madhulika Mahashaabde, Dr Chintan K.
Original article: Study of grading of severity of Heart Failure in patients with Dilated Cardiomyopathy Dr Satyajeet Shantaram Nighute *, Dr Govind S. Shiddapur, Dr Madhulika Mahashaabde, Dr Chintan K.
Exercise in Adverse Cardiac Remodeling: of Mice and Men
 Exercise in Adverse Cardiac Remodeling: of Mice and Men 17-01-2013 Dirk J Duncker Experimental Cardiology, Cardiology, Thoraxcenter Cardiovascular Research Institute COEUR Erasmus MC, University Medical
Exercise in Adverse Cardiac Remodeling: of Mice and Men 17-01-2013 Dirk J Duncker Experimental Cardiology, Cardiology, Thoraxcenter Cardiovascular Research Institute COEUR Erasmus MC, University Medical
4/11/2017. Cardiomyopathy. John Steuter, MD Bryan Heart. Disclosures. No Conflicts. Cardiomyopathy. WHO Classification
 Cardiomyopathy John Steuter, MD Bryan Heart Disclosures No Conflicts Cardiomyopathy WHO Classification Anatomy & physiology of the LV 1. Dilated Enlarged Systolic dysfunction 2. Hypertrophic Thickened
Cardiomyopathy John Steuter, MD Bryan Heart Disclosures No Conflicts Cardiomyopathy WHO Classification Anatomy & physiology of the LV 1. Dilated Enlarged Systolic dysfunction 2. Hypertrophic Thickened
Copeptin in heart failure: Associations with clinical characteristics and prognosis
 Copeptin in heart failure: Associations with clinical characteristics and prognosis D. Berliner, N. Deubner, W. Fenske, S. Brenner, G. Güder, B. Allolio, R. Jahns, G. Ertl, CE. Angermann, S. Störk for
Copeptin in heart failure: Associations with clinical characteristics and prognosis D. Berliner, N. Deubner, W. Fenske, S. Brenner, G. Güder, B. Allolio, R. Jahns, G. Ertl, CE. Angermann, S. Störk for
ARIC HEART FAILURE HOSPITAL RECORD ABSTRACTION FORM. General Instructions: ID NUMBER: FORM NAME: H F A DATE: 10/13/2017 VERSION: CONTACT YEAR NUMBER:
 ARIC HEART FAILURE HOSPITAL RECORD ABSTRACTION FORM General Instructions: The Heart Failure Hospital Record Abstraction Form is completed for all heart failure-eligible cohort hospitalizations. Refer to
ARIC HEART FAILURE HOSPITAL RECORD ABSTRACTION FORM General Instructions: The Heart Failure Hospital Record Abstraction Form is completed for all heart failure-eligible cohort hospitalizations. Refer to
Advanced imaging of the left atrium - strain, CT, 3D, MRI -
 Advanced imaging of the left atrium - strain, CT, 3D, MRI - Monica Rosca, MD Carol Davila University of Medicine and Pharmacy, Bucharest, Romania Declaration of interest: I have nothing to declare Case
Advanced imaging of the left atrium - strain, CT, 3D, MRI - Monica Rosca, MD Carol Davila University of Medicine and Pharmacy, Bucharest, Romania Declaration of interest: I have nothing to declare Case
Therapeutic Targets and Interventions
 Therapeutic Targets and Interventions Ali Valika, MD, FACC Advanced Heart Failure and Pulmonary Hypertension Advocate Medical Group Midwest Heart Foundation Disclosures: 1. Novartis: Speaker Honorarium
Therapeutic Targets and Interventions Ali Valika, MD, FACC Advanced Heart Failure and Pulmonary Hypertension Advocate Medical Group Midwest Heart Foundation Disclosures: 1. Novartis: Speaker Honorarium
Probe. Hind III Q,!?R'!! /0!!!!D1"?R'! vector. Homologous recombination
 Supple-Zhang Page 1 Wild-type locus Targeting construct Targeted allele Exon Exon3 Exon Probe P1 P P3 FRT FRT loxp loxp neo vector amh I Homologous recombination neo P1 P P3 FLPe recombination Q,!?R'!!
Supple-Zhang Page 1 Wild-type locus Targeting construct Targeted allele Exon Exon3 Exon Probe P1 P P3 FRT FRT loxp loxp neo vector amh I Homologous recombination neo P1 P P3 FLPe recombination Q,!?R'!!
Serum Cardiac Troponin T in Cardiac Amyloidosis: Serial Observations in Five Patients
 Tohoku J. Exp. Med., 2006, 208, 163-167 ctnt in Cardiac Amyloidosis 163 Serum Cardiac Troponin T in Cardiac Amyloidosis: Serial Observations in Five Patients Case Report TAKAO KATO, YUKIHITO SATO, KAZUYA
Tohoku J. Exp. Med., 2006, 208, 163-167 ctnt in Cardiac Amyloidosis 163 Serum Cardiac Troponin T in Cardiac Amyloidosis: Serial Observations in Five Patients Case Report TAKAO KATO, YUKIHITO SATO, KAZUYA
Biomarkers in cardiovascular disease. Felix J. Rogers, DO, FACOI April 29, 2018
 Biomarkers in cardiovascular disease Felix J. Rogers, DO, FACOI April 29, 2018 Biomarkers NIH: A biomarker is a characteristic that is objectively measured and evaluated as an indicator of normal biological
Biomarkers in cardiovascular disease Felix J. Rogers, DO, FACOI April 29, 2018 Biomarkers NIH: A biomarker is a characteristic that is objectively measured and evaluated as an indicator of normal biological
Diagnosis of heart failure in dogs with mitral valve disease
 Vet Times The website for the veterinary profession https://www.vettimes.co.uk Diagnosis of heart failure in dogs with mitral valve disease Author : PHILLIP SPEER Categories : Vets Date : March 31, 2014
Vet Times The website for the veterinary profession https://www.vettimes.co.uk Diagnosis of heart failure in dogs with mitral valve disease Author : PHILLIP SPEER Categories : Vets Date : March 31, 2014
Heart Failure. Subjective SOB (shortness of breath) Peripheral edema. Orthopnea (2-3 pillows) PND (paroxysmal nocturnal dyspnea)
 Pharmacology I. Definitions A. Heart Failure (HF) Heart Failure Ezra Levy, Pharm.D. HF Results when one or both ventricles are unable to pump sufficient blood to meet the body s needs There are 2 types
Pharmacology I. Definitions A. Heart Failure (HF) Heart Failure Ezra Levy, Pharm.D. HF Results when one or both ventricles are unable to pump sufficient blood to meet the body s needs There are 2 types
Cardiomyopathy. Jeff Grubbe MD FACP, Chief Medical Director, Allstate Life & Retirement
 Cardiomyopathy Jeff Grubbe MD FACP, Chief Medical Director, Allstate Life & Retirement Nebraska Home Office Life Underwriters Association March 20, 2018 1 Cardiomyopathy A myocardial disorder in which
Cardiomyopathy Jeff Grubbe MD FACP, Chief Medical Director, Allstate Life & Retirement Nebraska Home Office Life Underwriters Association March 20, 2018 1 Cardiomyopathy A myocardial disorder in which
Sleep Apnea and Heart Failure
 Sleep Apnea and Heart Failure Micha T. Maeder, MD Cardiology Division Kantonsspital St. Gallen Switzerland micha.maeder@kssg.ch Sleep Disordered Breathing (SDB) in HFrEF 700 HFrEF patients (LVEF
Sleep Apnea and Heart Failure Micha T. Maeder, MD Cardiology Division Kantonsspital St. Gallen Switzerland micha.maeder@kssg.ch Sleep Disordered Breathing (SDB) in HFrEF 700 HFrEF patients (LVEF
2/15/2017. Disclosures. Heart Failure = Big Problem. Heart Failure Update Reducing Hospitalizations and Improving Patient Outcomes 02/18/2017
 Heart Failure Update Reducing Hospitalizations and Improving Patient Outcomes 02/18/2017 Julio A. Barcena, M.D. South Miami Heart Specialists Disclosures I have no relevant commercial relationships to
Heart Failure Update Reducing Hospitalizations and Improving Patient Outcomes 02/18/2017 Julio A. Barcena, M.D. South Miami Heart Specialists Disclosures I have no relevant commercial relationships to
Dr. Khairy Abdel Dayem. Professor of Cardiology Ain-Shams University
 Dr. Khairy Abdel Dayem Professor of Cardiology Ain-Shams University RALES Randomized Aldactone Evaluation Study 1. NEJM 1999 2. Bertram Pitt 3. 1660 Class III and IV HF patients 4. EF 35% 5. 841 placebo
Dr. Khairy Abdel Dayem Professor of Cardiology Ain-Shams University RALES Randomized Aldactone Evaluation Study 1. NEJM 1999 2. Bertram Pitt 3. 1660 Class III and IV HF patients 4. EF 35% 5. 841 placebo
A study of Brain Natriuretic Peptide levels in acute cardiac failure
 Original Research Article A study of Brain Natriuretic Peptide levels in acute cardiac failure Bhavik Prajapati 1*, Anirudh Kulkarni 2 1 Assistant Professor, Department of Medicine, SMS Multispecialty
Original Research Article A study of Brain Natriuretic Peptide levels in acute cardiac failure Bhavik Prajapati 1*, Anirudh Kulkarni 2 1 Assistant Professor, Department of Medicine, SMS Multispecialty
Selected age-associated changes in the cardiovascular system
 Selected age-associated changes in the cardiovascular system Tamara Harris, M.D., M.S. Chief, Interdisciplinary Studies of Aging Acting Co-Chief, Laboratory of Epidemiology and Population Sciences Intramural
Selected age-associated changes in the cardiovascular system Tamara Harris, M.D., M.S. Chief, Interdisciplinary Studies of Aging Acting Co-Chief, Laboratory of Epidemiology and Population Sciences Intramural
Diastolic Heart Failure. Edwin Tulloch-Reid MBBS FACC Consultant Cardiologist Heart Institute of the Caribbean December 2012
 Diastolic Heart Failure Edwin Tulloch-Reid MBBS FACC Consultant Cardiologist Heart Institute of the Caribbean December 2012 Disclosures Have spoken for Merck, Sharpe and Dohme Sat on a physician advisory
Diastolic Heart Failure Edwin Tulloch-Reid MBBS FACC Consultant Cardiologist Heart Institute of the Caribbean December 2012 Disclosures Have spoken for Merck, Sharpe and Dohme Sat on a physician advisory
Images have been removed from the PowerPoint slides in this handout due to copyright restrictions.
 Heart Failure Heart Failure Introduction and History AHA 2015 Statistics About 6 million Americans 870,000 new cases each year 1 in 9 deaths related to HF Almost 1 million hospitalizations each year (cost
Heart Failure Heart Failure Introduction and History AHA 2015 Statistics About 6 million Americans 870,000 new cases each year 1 in 9 deaths related to HF Almost 1 million hospitalizations each year (cost
Echocardiography for the Electrophysiologist: Day-to-day practice. Emmanuel Fares, MD
 Echocardiography for the Electrophysiologist: Day-to-day practice Emmanuel Fares, MD EP and pacing service, Department of Cardiovascular Medicine, Cairo University Agenda Role of echo in arrhythmia management:
Echocardiography for the Electrophysiologist: Day-to-day practice Emmanuel Fares, MD EP and pacing service, Department of Cardiovascular Medicine, Cairo University Agenda Role of echo in arrhythmia management:
Influence of Paroxysmal Atrial Fibrillation Attack on Brain Natriuretic Peptide Secretion
 Influence of Paroxysmal Atrial Fibrillation Attack on Brain Natriuretic Peptide Secretion Keizo Kazuhiko TSUCHIDA,MD TANABE, MD Abstract Objectives. Plasma brain natriuretic peptide BNP concentration is
Influence of Paroxysmal Atrial Fibrillation Attack on Brain Natriuretic Peptide Secretion Keizo Kazuhiko TSUCHIDA,MD TANABE, MD Abstract Objectives. Plasma brain natriuretic peptide BNP concentration is
Squeeze, Squeeze, Squeeze: The Importance of Right Ventricular Function and PH
 Squeeze, Squeeze, Squeeze: The Importance of Right Ventricular Function and PH Javier Jimenez MD PhD FACC Director, Advanced Heart Failure and Pulmonary Hypertension Miami Cardiac & Vascular Institute
Squeeze, Squeeze, Squeeze: The Importance of Right Ventricular Function and PH Javier Jimenez MD PhD FACC Director, Advanced Heart Failure and Pulmonary Hypertension Miami Cardiac & Vascular Institute
Supplementary material 1. Definitions of study endpoints (extracted from the Endpoint Validation Committee Charter) 1.
 Rationale, design, and baseline characteristics of the SIGNIFY trial: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial of ivabradine in patients with stable coronary artery disease without clinical
Rationale, design, and baseline characteristics of the SIGNIFY trial: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial of ivabradine in patients with stable coronary artery disease without clinical
Ischemic Heart Failure
 15 th Cardiology Congress of Northern Greece Thessaloniki, May 26-28, 2016 Ischemic Heart Failure Filippos Triposkiadis, MD, FESC, FACC Professor of Cardiology Director, Department of Cardiology Larissa
15 th Cardiology Congress of Northern Greece Thessaloniki, May 26-28, 2016 Ischemic Heart Failure Filippos Triposkiadis, MD, FESC, FACC Professor of Cardiology Director, Department of Cardiology Larissa
