Long-Term Effects of Enzyme Replacement Therapy on Fabry Cardiomyopathy Evidence for a Better Outcome With Early Treatment
|
|
|
- Lynne Morgan
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Long-Term Effects of Enzyme Replacement Therapy on Fabry Cardiomyopathy Evidence for a Better Outcome With Early Treatment Frank Weidemann, MD*; Markus Niemann*; Frank Breunig, MD; Sebastian Herrmann; Meinrad Beer, MD; Stefan Störk, MD; Wolfram Voelker, MD; Georg Ertl, MD; Christoph Wanner, MD; Jörg Strotmann, MD Background Enzyme replacement therapy with recombinant -galactosidase A reduces left ventricular hypertrophy and improves regional myocardial function in patients with Fabry disease during short-term treatment. Whether enzyme replacement therapy is effective in all stages of Fabry cardiomyopathy during long-term follow-up is unknown. Methods and Results We studied 32 Fabry patients over a period of 3 years regarding disease progression and clinical outcome under enzyme replacement therapy. Regional myocardial fibrosis was assessed by magnetic resonance imaging late-enhancement technique. Echocardiographic myocardial mass was calculated with the Devereux formula, and myocardial function was quantified by ultrasonic strain-rate imaging. In addition, exercise capacity was measured by bicycle stress test. All measurements were repeated at yearly intervals. At baseline, 9 patients demonstrated at least 2 fibrotic left ventricular segments (severe myocardial fibrosis), 11 had 1 left ventricular segment affected (mild fibrosis), and 12 were without fibrosis. In patients without fibrosis, enzyme replacement therapy resulted in a significant reduction in left ventricular mass ( g at baseline, g at 3 years; P for trend 0.001), an improvement in myocardial function (systolic radial strain rate, and seconds 1, respectively; P for trend 0.045), and a higher exercise capacity obtained by bicycle stress exercise ( and W, respectively; P for trend 0.014). In contrast, patients with mild or severe fibrosis showed a minor reduction in left ventricular hypertrophy and no improvement in myocardial function or exercise capacity. Conclusions These data suggest that treatment of Fabry cardiomyopathy with recombinant -galactosidase A should best be started before myocardial fibrosis has developed to achieve long-term improvement in myocardial morphology and function and exercise capacity. (Circulation. 2009;119: ) Key Words: cardiomyopathy echocardiography Fabry disease hypertrophy treatment Fabry disease is a relatively rare X-linked lysosomal storage disorder caused by -galactosidase A deficiency. The enzymatic deficit results in progressive intracellular accumulation of globotriaosylceramide in different tissues. Cardiac involvement is frequent, presenting with left ventricular (LV) hypertrophy as the most common finding, and many patients die of heart failure. 1 Clinical Perspective p 529 Enzyme replacement therapy (ERT) with recombinant -galactosidase A cleared microvascular deposits of globotriaosylceramide in biopsies of kidney, skin, and heart of most Fabry patients. 2,3 We have shown a reduction in LV mass and an improvement in LV function after 1 year of ERT in 16 Fabry patients. 4 However, the response to ERT was not consistent in this small cohort of Fabry patients. In addition, it remained unclear whether the effect of ERT could persist over longer periods of time. In a more recent study in a larger group of patients, we identified the coexistence of LV hypertrophy, myocardial fibrosis, and severely reduced regional LV function as a surrogate of advanced Fabry cardiomyopathy. 5 It is conceivable that such severe morphological manifestation is irreversible and that the course of cardiomyopathy at this stage is unresponsive to therapy of the underlying disease. The hypothesis of the present study was that patients at an early stage of the disease showing no or little myocardial fibrosis may consistently benefit from ERT over a period of 3 years. This hypothesis was tested in a cohort that was relatively large for this rare disease. Fibrosis was quantified by magnetic resonance imaging (MRI). Received May 27, 2008; accepted November 14, From the Department of Medicine, Divisions of Cardiology and Nephrology (F.W., M.N., F.B., S.H., S.S., W.V., G.E., C.W., J.S.) and Department of Radiology (M.B.), University Hospital, Wuerzburg, Germany. *The first 2 authors contributed equally to this work. Correspondence to Frank Weidemann, Medizinische Klinik und Poliklinik I, Universitätsklinik Würzburg, Josef-Schneider Str 2, Bau 4, Würzburg, Germany. weidemann_f@medizin.uni-wuerzburg.de 2009 American Heart Association, Inc. Circulation is available at DOI: /CIRCULATIONAHA
2 Weidemann et al Enzyme Replacement Improves Fabry Cardiomyopathy 525 Methods Study Population Thirty-two patients with genetically confirmed Fabry disease 42 7 years of age were observed over a period of 3 years. None of the Fabry patients had received ERT at study entry. A subgroup of these patients (n 16) who were under ERT for 1 year was already reported. 4 The data from the Fabry group were compared with those from 20 age-matched healthy control subjects. The study conformed with the principles outlined in the Declaration of Helsinki. Informed consent was obtained from all patients. Patients were treated with recombinant -galactosidase A (dosage of 1 mg/kg body weight) intravenously every 2 weeks (infusion time, 2 to 4 hours) for a period of 3 years. 4 Patients underwent MRI, standard echocardiographic, color Doppler myocardial imaging studies, and bicycle stress tests at baseline and after 1, 2, and 3 years. MRI Studies Routine cine MRI with gadolinium was carried out in all patients with Fabry disease as part of the standard assessment. The lateenhancement (LE) technique (8-mm slice thickness, breath hold, short heart axis) was applied to detect changes in tissue integrity in the LV myocardium. 6 Images were acquired with an inversion recovery sequence (field of view, mm 2 ; matrix, ). Short-axis views at the basal, mid, and apical segments were used for the semiquantitative assessment of the appearance of LE in every LV segment (LE, yes or no) according to the standardized 16-segment model. 7 With this LE technique, every LV segment was evaluated for the occurrence of intramyocardial fibrosis. All MRI data were analyzed by researchers blinded to the time point. Standard Echocardiographic Measurements LV end-diastolic and end-systolic dimensions and end-diastolic thickness of the posterior wall (PWT) and septum were measured with standard M-mode echocardiographic methods and parasternal LV long-axis images (3.5 MHz; GE Vingmed Vivid 7, Horten, Norway). Myocardial mass was calculated with the Devereux formula. Ejection fraction was calculated with the modified Simpson method. Blood pool pulsed Doppler of the mitral valve inflow was used to extract the ratio of early to late diastolic flow velocity (E/A ratio) and the deceleration time. Color Doppler Myocardial Imaging Real-time 2-dimensional color Doppler myocardial imaging data were recorded from the interventricular septum and the LV lateral wall with standard apical 4-chamber views to evaluate longitudinal function (3.5 MHz; GE Vingmed Vivid 7). To assess radial function of the posterior wall, parasternal long-axis views were used. Color Doppler myocardial imaging data were analyzed with dedicated software (Echopac, GE Ultrasound, Horten, Norway). Radial strainrate curves of the midbasal posterior wall were extracted, as well as longitudinal strain-rate curves of the midapical septum and the basal midlateral wall. These longitudinal segments were chosen on the basis of experience gained in earlier studies on Fabry cardiomyopathy: The midapical septum is always without fibrosis, whereas the basal midlateral wall is the segment in which fibrosis usually starts. 5,6,8 From the resulting strain-rate curves, peak systolic strain rate (SR SYS ) was derived. All echocardiographic data were analyzed by researchers blinded to the time point and degree of fibrosis. Bicycle Stress Test Symptom-limited (fatigue or dyspnea) exercise was performed on a bicycle ergometer with a 25-W 3-minute step protocol starting at 50 W. The heart rate was continuously monitored, and a 12-lead ECG and blood pressure were recorded at every step. Criteria for termination were achievement of maximal heart rate, severe chest pain or dyspnea, horizontal or downsloping ST-segment depression 2 mm, systolic blood pressure 220 mm Hg, diastolic blood pressure 120 mm Hg, reduction in systolic blood pressure 30 mm Hg, and supraventricular or ventricular tachyarrhythmia. Table 1. Baseline Characteristics of Fabry Patients and Control Subjects Fabry Patients (n 32) Control Subject (n 20) P Age, y Sex, M/F 27/6 15/ Weight, kg Height, cm HR, bpm Systolic BP, mm Hg LVEDD, mm PWT, mm Arterial hypertension, n Ventricular arrhythmia, n Atrial fibrillation, n Angina pectoris, n Dyspnea, n HR indicates heart rate; LVEDD, LV end-diastolic diameter. Values are mean SD when appropriate. Probability values refer to t test and 2 test as appropriate. Patient Groups Patients were assigned to 1 of 3 groups according to the amount of fibrosis in the MRI. 5,6,8 Patients without detectable fibrosis were categorized as the no fibrosis group. Patients with fibrosis in no more than 1 LV segment were categorized as the mild fibrosis group, and patients with 2 fibrotic LV segments were categorized as the severe fibrosis group. Data Analysis Data are presented as mean SD. Differences between control subjects and patients were tested with the unpaired Student t test or 2 test as appropriate. Multiple comparisons between different groups were performed using ANOVA with Duncan s posthoc test. Changes over time were analyzed with a general linear model for repeated measurements. The overall effect was assessed in a multivariable analysis after testing for sphericity to check the circular covariance assumption. If sphericity was not present, the Huyhn- Feldt correction factor was applied to correct the degrees of freedom, and the resulting probability value was then reported. Sidak s t test was applied to account for multiple testing in analyses assessing between-subject effects. All tests were performed 2 sided. A value of P 0.05 was considered statistically significant. SPSS version (SPSS Inc, Chicago, Ill) was used. The authors had full access to and take full responsibility for the integrity of the data. All authors have read and agree to the manuscript as written. Results The baseline characteristics of the control subjects and Fabry patients are presented in Table 1. Fourteen patients had a history of hypertension. All were under hypertensive medication and therefore were almost normotensive at study entry. The types of antihypertensive medication and the number of patients receiving antihypertensive medication were very uniformly distributed in all 3 groups. The major clinical limitation at baseline was dyspnea. Two patients died during follow-up of heart failure as a consequence of the underlying disease.
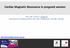
3 526 Circulation February 3, 2009 Table 2. Baseline Echocardiographic Data of the Fabry Subgroups No Fibrosis (n 12) Mild Fibrosis (n 11) Severe Fibrosis (n 9) Age, y * 50 7* LVEDD, mm LVESD, mm PWT, mm Septum, mm LV mass, g * Ejection fraction, % E/A DT, ms LVEDD indicates LV end-diastolic diameter; LVESD, LV end-systolic diameter; and DT, deceleration time. Values are mean SD. *P 0.05 vs no fibrosis group (ANOVA with Duncan s posthoc test). Figure 1. MRI of 3 typical Fabry patients at baseline. Top, Short-axis view of a patient showing no LE (LE indicates fibrosis). Middle, Short-axis view of a patient with mild fibrosis (only 1 LE-positive segment). Bottom, Short-axis views on the basal and mid-lv levels showing 2 LE-positive segments (severe fibrosis). Arrows indicate LE-positive segments. MRI Studies At baseline, 12 patients were LE negative, 11 patients had only 1 LE-positive segment, and 9 patients had LE in 1 segment (Figure 1). In general, LE was detected in basal or mid segments of the posterolateral walls. Only in the severe fibrosis group were fibrotic segments also found in the basal third of the other LV walls. None of the patients had an LE-positive segment in the apical septum. There was no change in the LE pattern after 3 years of ERT. Standard Echocardiographic Measurements Comparison Between the Complete Fabry Cohort and Control Subjects Fabry patients had a longer deceleration time ( ms) compared with control subjects ( ms; P 0.01), but the E/A ratio did not differ (Fabry, ; control subjects, ). Patients showed a normal ejection fraction at baseline (62 1%), not different from control subjects (64 1%), and no change during ERT (Fabry, 64 1%). End-diastolic thicknesses of the LV posterior wall and septum were significantly higher in patients compared with control subjects (PWT: Fabry, mm; control subjects, mm; septum: Fabry, mm; control subjects, mm; both P 0.001). In Fabry patients, myocardial mass at study entry averaged g, which was significantly higher compared with the control subjects ( g; P 0.001). The standard echocardiographic measurements of the Fabry subgroups are shown in Table 2, and the changes in these parameters during ERT are given in Table 3. In all 3 subgroups, PWT and LV myocardial mass decreased significantly after 3 years of ERT. Radial and Longitudinal Function In the complete Fabry cohort, radial SR SYS averaged seconds 1, which was significantly lower than in control Table 3. Changes in Echocardiographic Data of the Fabry Subgroups of Fibrosis During 3 Years of ERT Fibrosis Baseline 1 Year 2 Years 3 Years P LVEDD No * Mild Severe PWT, No * mm Mild Severe Septum, No * mm Mild Severe LV No * mass, g Mild Severe LVEDD indicates LV end-diastolic diameter; LVESD, left ventricular end-systolic diameter. *Probability value for the test of the overall effect (n 32) of ERT over time (general linear model: within-subject effect). Probability value for the comparison of fibrosis groups (ie, no fibrosis vs mild fibrosis and no fibrosis vs severe fibrosis; general linear model with Sidak s posthoc test for between-subject effect).
4 Weidemann et al Enzyme Replacement Improves Fabry Cardiomyopathy 527 Figure 2. Change in LV radial peak systolic strain rate of the posterior wall during 3 years of ERT according to the degree of myocardial fibrosis. Note that there is a linear increase in radial function in patients with no fibrosis (P 0.005). P for comparison of trend between no fibrosis and mild fibrosis; P for comparison of trend between no fibrosis and severe fibrosis (general linear model with Sidak s posthoc test); P for the overall effect of ERT over time. BS indicates baseline; 1, 1 year of ERT; 2, 2 years of ERT; and 3, 3 years of ERT. subjects (SR SYS seconds 1 ; P 0.001). The lowest radial SR SYS was seen in the severe fibrosis group. Figure 2 displays the change in radial SR SYS during the 3 years of treatment in the various subgroups. Radial SR SYS increased in the no fibrosis group (normal values after 3 years of ERT) and rather decreased in the severe fibrosis group (Figure 2). Septal longitudinal SR SYS in Fabry patients ( seconds 1 ) was similar to that of controls ( seconds 1 ) and among the 3 Fabry groups at baseline. Septal longitudinal SR SYS increased in the 3 Fabry groups (significantly for the no fibrosis group, P 0.045; Figure 3). Lateral longitudinal SR SYS was lower in Fabry patients ( seconds 1 ) compared with the control subjects ( seconds 1 ; P 0.001) and was lowest in the 2 groups with fibrosis. There was a nonsignificant decrease in lateral SR SYS in patients with severe fibrosis during 3 years of ERT (Figure 3). The 2 patients who died during follow-up (1 after 1 year and another after 2 years) had low radial and longitudinal strain-rate values at baseline and were in the severe fibrosis group. Interestingly, both patients showed a decrease in lateral longitudinal systolic strain rate of 0.5 seconds 1 between the last 2 assessments (displaying a systolic strain rate of 0.3 seconds 1 in the last assessment). Bicycle Stress Test The exercise capacity was lower in the Fabry severe fibrosis group compared with the other 2 groups. Figure 4 displays the change in exercise capacity in the 3 Fabry groups during follow-up. Only patients of the no fibrosis group showed an improvement after 3 years of ERT (baseline, W; 3 years, W; P for trend 0.014). Discussion The clearance of globotriaosylceramide from various tissues during ERT in Fabry disease has been well documented. 2 This long-term observation evaluates the impact of ERT on the Fabry cardiomyopathy in relation to the baseline disease stages. The data presented here suggest that early treatment is Figure 3. Change in LV longitudinal function during 3 years of ERT in the 3 different groups. Top, The longitudinal peak systolic strain rate of the septum increases during ERT (P 0.045) in patients with no fibrosis. Bottom, The longitudinal peak systolic strain rate of the lateral wall is lower in patients with fibrosis; there is no significant change during ERT (all P 0.3). Abbreviations as in Figure 2. desirable to achieve long-term improvement in myocardial morphology, function, and exercise capacity. ERT in Fabry Disease The safety of ERT was documented in 2 initial studies. 2,3 Furthermore, Eng et al 2 demonstrated in a placebo-controlled, double-blind study that ERT resulted in histological clearance Figure 4. Change in exercise capacity during 3 years of ERT in the 3 different groups. A mild but significant improvement in exercise capacity could be demonstrated for patients with no fibrosis (P 0.014). Abbreviations as in Figure 2.
5 528 Circulation February 3, 2009 of the deposits of globotriaosylceramide from cardiomyocytes. Subsequently, clinical short-term follow-up studies in relatively small Fabry cohorts or registries have documented that ERT leads to a regression of LV hypertrophy and an improvement in myocardial function. 4,9,10 The present investigation shows that the long-term ERT effects on Fabry cardiomyopathy are related to the extent of myocardial fibrosis at baseline, when therapy is started. We and others have shown that Fabry patients at an early stage of the disease have virtually no myocardial fibrosis. 5,8 These patients with no detectable fibrosis and mild hypertrophy at baseline showed a normalization of LV wall thickness and mass during ERT in the present study. Parallel to cardiac morphology, LV radial and longitudinal septal function improved to normal. Subsequently, the patients with no fibrosis also improved in exercise capacity, which might be at least partly related to the positive effects of ERT on the Fabry cardiomyopathy. Thus, in the largest group of our Fabry patients (those in the beginning of disease progression), cardiac and exercise improvement during long-term ERT was proven. The effect of ERT critically depended on the stage of the disease at baseline. In patients with localized myocardial fibrosis in only 1 LV segment, a reduction in LV hypertrophy could be achieved during ERT that was associated with a stabilization of LV function and exercise capacity. Patients in a more advanced stage with fibrosis in several LV segments still showed some reduction in hypertrophy but hardly any benefit in terms of LV function during long-term ERT. Monitoring the Effects of ERT The change in LV mass was used in several studies to monitor ERT effects. 4,9,10 The present study proved LV mass to be in principle a useful parameter to monitor the cardiac effects of ERT. However, fibrosis spreading to the posterior wall may mimic a reduction in hypertrophy in more advanced stages of the cardiomyopathy. Thus, PWT, which is an echocardiographic standard parameter to monitor changes in LV hypertrophy, is probably not useful for monitoring ERT. 11 Strain-rate imaging based on tissue Doppler is superior to global parameters like ejection fraction in monitoring and quantifying LV function in patients with Fabry disease. 4,5,12,13 The increase in peak systolic strain rate appears to be more specific for regional contractility and rather independent of wall thickness. 14 The present study shows that an increase in radial strain rate after 1 year of ERT may predict long-term improvement in regional myocardial function. A decrease in longitudinal lateral function is an ominous sign in advanced stages and predicts an adverse outcome. Interestingly, both patients who died during ERT showed a decrease in longitudinal lateral strain rate of 0.5 seconds 1 in the last year of life. Most patients in our study sample who were treated with ERT reported an improvement in exercise capacity. The improvement could, however, be objectified only in the group of patients at an early stage of the disease. The reason might be that the mechanisms limiting exercise capacity are complex in Fabry patients and include cardiovascular factors, neuropathic pain, and hypohydrosis. Clinical Impact and Limitations The present study shows that an assessment of the baseline conditions before ERT is necessary. Knowledge of the presence or absence of myocardial fibrosis is crucial with respect to the treatment expectations. A recent phase IV ERT study focusing on renal function showed more benefit in patients starting with better renal function. 15 We showed this finding here for Fabry cardiomyopathy, suggesting that the earlier the treatment is started, the better the long-term outcome is. Conclusions In patients with Fabry disease, early is probably superior to late treatment to achieve long-term improvements in cardiac morphology and function and exercise capacity. Disclosures Dr Wanner is a member of the European Advisory Board of the Fabry Registry sponsored by Genzyme Corp and has received travel assistance, speaking fees, and research support. Drs Weidemann, Breunig, and Strotmann have received speaking fees from Genzyme Corp. The other authors report no conflicts. References 1. Desnick RJ, Brady R, Barranger J, Collins AJ, Germain DP, Goldman M, Grabowski G, Packman S, Wilcox WR. Fabry disease, an underrecognized multisystemic disorder: expert recommendations for diagnosis, management, and enzyme replacement therapy. Ann Intern Med. 2003;138: Eng CM, Guffon N, Wilcox WR, Germain DP, Lee P, Waldek S, Caplan L, Linthorst GE, Desnick RJ. Safety and efficacy of recombinant human alpha-galactosidase A: replacement therapy in Fabry s disease. N Engl J Med. 2001;345: Schiffmann R, Kopp JB, Austin HA 3rd, Sabnis S, Moore DF, Weibel T, Balow JE, Brady RO. Enzyme replacement therapy in Fabry disease: a randomized controlled trial. JAMA. 2001;285: Weidemann F, Breunig F, Beer M, Sandstede J, Turschner O, Voelker W, Ertl G, Knoll A, Wanner C, Strotmann JM. Improvement of cardiac function during enzyme replacement therapy in patients with Fabry disease: a prospective strain rate imaging study. Circulation. 2003;108: Weidemann F, Breunig F, Beer M, Sandstede J, Stork S, Voelker W, Ertl G, Knoll A, Wanner C, Strotmann JM. The variation of morphological and functional cardiac manifestation in Fabry disease: potential implications for the time course of the disease. Eur Heart J. 2005;26: Beer M, Weidemann F, Breunig F, Knoll A, Koeppe S, Machann W, Hahn D, Wanner C, Strotmann J, Sandstede J. Impact of enzyme replacement therapy on cardiac morphology and function and late enhancement in Fabry s cardiomyopathy. Am J Cardiol. 2006;97: Cerqueira MD, Weissman NJ, Dilsizian V, Jacobs AK, Kaul S, Laskey WK, Pennell DJ, Rumberger JA, Ryan T, Verani MS. Standardized myocardial segmentation and nomenclature for tomographic imaging of the heart: a statement for healthcare professionals from the Cardiac Imaging Committee of the Council on Clinical Cardiology of the American Heart Association. Circulation. 2002;105: Moon JC, Sachdev B, Elkington AG, McKenna WJ, Mehta A, Pennell DJ, Leed PJ, Elliott PM. Gadolinium enhanced cardiovascular magnetic resonance in Anderson-Fabry disease: evidence for a disease specific abnormality of the myocardial interstitium. Eur Heart J. 2003;24: Beck M, Ricci R, Widmer U, Dehout F, de Lorenzo AG, Kampmann C, Linhart A, Sunder-Plassmann G, Houge G, Ramaswami U, Gal A, Mehta A. Fabry disease: overall effects of agalsidase alfa treatment. Eur J Clin Invest. 2004;34: Hughes DA, Elliott PM, Shah J, Zuckerman J, Coghlan G, Brookes J, Mehta AB. Effects of enzyme replacement therapy on the cardiomyopathy of Anderson-Fabry disease: a randomised, double-blind, placebocontrolled clinical trial of agalsidase alfa. Heart. 2008;94:
6 Weidemann et al Enzyme Replacement Improves Fabry Cardiomyopathy Eng CM, Germain DP, Banikazemi M, Warnock DG, Wanner C, Hopkin RJ, Bultas J, Lee P, Sims K, Brodie SE, Pastores GM, Strotmann JM, Wilcox WR. Fabry disease: guidelines for the evaluation and management of multi-organ system involvement. Genet Med. 2006;8: Pieroni M, Chimenti C, Ricci R, Sale P, Russo MA, Frustaci A. Early detection of Fabry cardiomyopathy by tissue Doppler imaging. Circulation. 2003;107: Weidemann F, Niemann M, Herrmann S, Kung M, Stork S, Waller C, Beer M, Breunig F, Wanner C, Voelker W, Ertl G, Bijnens B, Strotmann JM. A new echocardiographic approach for the detection of nonischaemic fibrosis in hypertrophic myocardium. Eur Heart J. 2007;28: Weidemann F, Jamal F, Sutherland GR, Claus P, Kowalski M, Hatle L, De Scheerder I, Bijnens B, Rademakers FE. Myocardial function defined by strain rate and strain during alterations in inotropic states and heart rate. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2002;283:H792 H Banikazemi M, Bultas J, Waldek S, Wilcox WR, Whitley CB, McDonald M, Finkel R, Packman S, Bichet DG, Warnock DG, Desnick RJ. Agalsidase-beta therapy for advanced Fabry disease: a randomized trial. Ann Intern Med. 2007;146: CLINICAL PERSPECTIVE Enzyme replacement therapy with recombinant -galactosidase A clears microvascular deposits of globotriaosylceramide in biopsies of kidney, skin, and heart of most Fabry patients. Clinically, it could be demonstrated that enzyme replacement therapy reduces left ventricular hypertrophy and improves regional myocardial function in patients with Fabry cardiomyopathy during short-term treatment. Whether enzyme replacement therapy is effective in all stages of Fabry cardiomyopathy during long-term follow-up is unknown. The present study shows that a baseline assessment of cardiac morphology and function before the start of enzyme replacement therapy is necessary. Thus, knowledge of the presence or absence of myocardial fibrosis (which is typical for a late stage of this disease) is crucial with respect to treatment expectations. Myocardial fibrosis can be visualized directly with the magnetic resonance imaging late-enhancement technique. In addition, the functional consequences of fibrosis can be quantified by ultrasonic strain-rate imaging. Only Fabry patients with no fibrosis before enzyme replacement therapy show a sustained improvement in regional myocardial function and exercise capacity in the long term. Thus, in Fabry disease, early is probably superior to late treatment to improve cardiac morphology, function, and exercise capacity.
Annalisa Sechi 1*, Gaetano Nucifora 2, Gianluca Piccoli 3, Andrea Dardis 1 and Bruno Bembi 1
 Sechi et al. BMC Cardiovascular Disorders 2014, 14:86 CASE REPORT Open Access Myocardial fibrosis as the first sign of cardiac involvement in a male patient with Fabry disease: report of a clinical case
Sechi et al. BMC Cardiovascular Disorders 2014, 14:86 CASE REPORT Open Access Myocardial fibrosis as the first sign of cardiac involvement in a male patient with Fabry disease: report of a clinical case
Fabry Disease: A rare condition emerging from the darkness
 Fabry Disease: A rare condition emerging from the darkness Running Title: Fabry Disease: A rare condition emerging from the darkness Professor Perry Elliott MBBS; MD; FRCP; FESC; FACC Chair of Cardiovascular
Fabry Disease: A rare condition emerging from the darkness Running Title: Fabry Disease: A rare condition emerging from the darkness Professor Perry Elliott MBBS; MD; FRCP; FESC; FACC Chair of Cardiovascular
Little is known about the degree and time course of
 Differential Changes in Regional Right Ventricular Function Before and After a Bilateral Lung Transplantation: An Ultrasonic Strain and Strain Rate Study Virginija Dambrauskaite, MD, Lieven Herbots, MD,
Differential Changes in Regional Right Ventricular Function Before and After a Bilateral Lung Transplantation: An Ultrasonic Strain and Strain Rate Study Virginija Dambrauskaite, MD, Lieven Herbots, MD,
Mechanisms of False Positive Exercise Electrocardiography: Is False Positive Test Truly False?
 Mechanisms of False Positive Exercise Electrocardiography: Is False Positive Test Truly False? Masaki Izumo a, Kengo Suzuki b, Hidekazu Kikuchi b, Seisyo Kou b, Keisuke Kida b, Yu Eguchi b, Nobuyuki Azuma
Mechanisms of False Positive Exercise Electrocardiography: Is False Positive Test Truly False? Masaki Izumo a, Kengo Suzuki b, Hidekazu Kikuchi b, Seisyo Kou b, Keisuke Kida b, Yu Eguchi b, Nobuyuki Azuma
Global left ventricular circumferential strain is a marker for both systolic and diastolic myocardial function
 Global left ventricular circumferential strain is a marker for both systolic and diastolic myocardial function Toshinari Onishi 1, Samir K. Saha 2, Daniel Ludwig 1, Erik B. Schelbert 1, David Schwartzman
Global left ventricular circumferential strain is a marker for both systolic and diastolic myocardial function Toshinari Onishi 1, Samir K. Saha 2, Daniel Ludwig 1, Erik B. Schelbert 1, David Schwartzman
FABRY DISEASE: Phenotypic Spectrum Genotype/Phenotype Correlations Enzyme Replacement Therapy (ERT) R. J. Desnick, Ph.D., M.D.
 FABRY DISEASE: Phenotypic Spectrum Genotype/Phenotype Correlations Enzyme Replacement Therapy (ERT) R. J. Desnick, Ph.D., M.D. Director, International Center for Fabry Disease Dean for Genetic & Genomic
FABRY DISEASE: Phenotypic Spectrum Genotype/Phenotype Correlations Enzyme Replacement Therapy (ERT) R. J. Desnick, Ph.D., M.D. Director, International Center for Fabry Disease Dean for Genetic & Genomic
Velocity Vector Imaging as a new approach for cardiac magnetic resonance: Comparison with echocardiography
 Velocity Vector Imaging as a new approach for cardiac magnetic resonance: Comparison with echocardiography Toshinari Onishi 1, Samir K. Saha 2, Daniel Ludwig 1, Erik B. Schelbert 1, David Schwartzman 1,
Velocity Vector Imaging as a new approach for cardiac magnetic resonance: Comparison with echocardiography Toshinari Onishi 1, Samir K. Saha 2, Daniel Ludwig 1, Erik B. Schelbert 1, David Schwartzman 1,
Cardiac Magnetic Resonance in pregnant women
 Cardiac Magnetic Resonance in pregnant women Chen SSM, Leeton L, Dennis AT Royal Women s Hospital and The University of Melbourne, Parkville, Australia alicia.dennis@thewomens.org.au Quantification of
Cardiac Magnetic Resonance in pregnant women Chen SSM, Leeton L, Dennis AT Royal Women s Hospital and The University of Melbourne, Parkville, Australia alicia.dennis@thewomens.org.au Quantification of
Fabry Disease and the Kidneys
 Department of Human Genetics Division of Medical Genetics Lysosomal Storage Disease Center www.genetics.emory.edu Fabry Disease and the Kidneys What is Fabry Disease? Fabry disease (FD) is an X-linked
Department of Human Genetics Division of Medical Genetics Lysosomal Storage Disease Center www.genetics.emory.edu Fabry Disease and the Kidneys What is Fabry Disease? Fabry disease (FD) is an X-linked
Appendix II: ECHOCARDIOGRAPHY ANALYSIS
 Appendix II: ECHOCARDIOGRAPHY ANALYSIS Two-Dimensional (2D) imaging was performed using the Vivid 7 Advantage cardiovascular ultrasound system (GE Medical Systems, Milwaukee) with a frame rate of 400 frames
Appendix II: ECHOCARDIOGRAPHY ANALYSIS Two-Dimensional (2D) imaging was performed using the Vivid 7 Advantage cardiovascular ultrasound system (GE Medical Systems, Milwaukee) with a frame rate of 400 frames
Clinical benefit of enzyme replacement therapy in Fabry disease
 original article http://www.kidney-international.org & 2006 International Society of Nephrology Clinical benefit of enzyme replacement therapy in Fabry disease F Breunig 1, F Weidemann 2, J Strotmann 2,
original article http://www.kidney-international.org & 2006 International Society of Nephrology Clinical benefit of enzyme replacement therapy in Fabry disease F Breunig 1, F Weidemann 2, J Strotmann 2,
Global and Regional Myocardial Function Quantification by Two-Dimensional Strain Application in Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy
 Journal of the American College of Cardiology Vol. 47, No. 6, 2006 2006 by the American College of Cardiology Foundation ISSN 0735-1097/06/$32.00 Published by Elsevier Inc. doi:10.1016/j.jacc.2005.10.061
Journal of the American College of Cardiology Vol. 47, No. 6, 2006 2006 by the American College of Cardiology Foundation ISSN 0735-1097/06/$32.00 Published by Elsevier Inc. doi:10.1016/j.jacc.2005.10.061
Effectiveness of agalsidase alfa enzyme replacement in Fabry disease: cardiac outcomes after 10 years treatment
 Kampmann et al. Orphanet Journal of Rare Diseases (205) 0:25 DOI 0.86/s02-05-08-2 RESEARCH Open Access Effectiveness of agalsidase alfa enzyme replacement in Fabry disease: cardiac outcomes after 0 years
Kampmann et al. Orphanet Journal of Rare Diseases (205) 0:25 DOI 0.86/s02-05-08-2 RESEARCH Open Access Effectiveness of agalsidase alfa enzyme replacement in Fabry disease: cardiac outcomes after 0 years
Highlights from EuroEcho 2009 Echo in cardiomyopathies
 Highlights from EuroEcho 2009 Echo in cardiomyopathies Bogdan A. Popescu University of Medicine and Pharmacy, Bucharest, Romania ESC Congress 2010 Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy To determine the differences
Highlights from EuroEcho 2009 Echo in cardiomyopathies Bogdan A. Popescu University of Medicine and Pharmacy, Bucharest, Romania ESC Congress 2010 Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy To determine the differences
Coronary artery disease (CAD) risk factors
 Background Coronary artery disease (CAD) risk factors CAD Risk factors Hypertension Insulin resistance /diabetes Dyslipidemia Smoking /Obesity Male gender/ Old age Atherosclerosis Arterial stiffness precedes
Background Coronary artery disease (CAD) risk factors CAD Risk factors Hypertension Insulin resistance /diabetes Dyslipidemia Smoking /Obesity Male gender/ Old age Atherosclerosis Arterial stiffness precedes
Echocardiographic and Doppler Assessment of Cardiac Functions in Patients of Non-Insulin Dependent Diabetes Mellitus
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE JIACM 2002; 3(2): 164-8 Echocardiographic and Doppler Assessment of Cardiac Functions in Patients of Non-Insulin Dependent Diabetes Mellitus Rajesh Rajput*, Jagdish**, SB Siwach***, A
ORIGINAL ARTICLE JIACM 2002; 3(2): 164-8 Echocardiographic and Doppler Assessment of Cardiac Functions in Patients of Non-Insulin Dependent Diabetes Mellitus Rajesh Rajput*, Jagdish**, SB Siwach***, A
Impaired Regional Myocardial Function Detection Using the Standard Inter-Segmental Integration SINE Wave Curve On Magnetic Resonance Imaging
 Original Article Impaired Regional Myocardial Function Detection Using the Standard Inter-Segmental Integration Ngam-Maung B, RT email : chaothawee@yahoo.com Busakol Ngam-Maung, RT 1 Lertlak Chaothawee,
Original Article Impaired Regional Myocardial Function Detection Using the Standard Inter-Segmental Integration Ngam-Maung B, RT email : chaothawee@yahoo.com Busakol Ngam-Maung, RT 1 Lertlak Chaothawee,
Dr. Dermot Phelan MB BCh BAO PhD European Society of Cardiology 2012
 Relative Apical Sparing of Longitudinal Strain Using 2- Dimensional Speckle-Tracking Echocardiography is Both Sensitive and Specific for the Diagnosis of Cardiac Amyloidosis. Dr. Dermot Phelan MB BCh BAO
Relative Apical Sparing of Longitudinal Strain Using 2- Dimensional Speckle-Tracking Echocardiography is Both Sensitive and Specific for the Diagnosis of Cardiac Amyloidosis. Dr. Dermot Phelan MB BCh BAO
Cardiomyopathy in Fabry s disease
 Cardiomyopathy in Fabry s disease Herzinsuffizienzlunch Basel, 11.09.2018 Christiane Gruner Kardiologie, UniversitätsSpital Zürich Content Background / epidemiology Differential diagnosis Clinical presentations
Cardiomyopathy in Fabry s disease Herzinsuffizienzlunch Basel, 11.09.2018 Christiane Gruner Kardiologie, UniversitätsSpital Zürich Content Background / epidemiology Differential diagnosis Clinical presentations
Index of subjects. effect on ventricular tachycardia 30 treatment with 101, 116 boosterpump 80 Brockenbrough phenomenon 55, 125
 145 Index of subjects A accessory pathways 3 amiodarone 4, 5, 6, 23, 30, 97, 102 angina pectoris 4, 24, 1l0, 137, 139, 140 angulation, of cavity 73, 74 aorta aortic flow velocity 2 aortic insufficiency
145 Index of subjects A accessory pathways 3 amiodarone 4, 5, 6, 23, 30, 97, 102 angina pectoris 4, 24, 1l0, 137, 139, 140 angulation, of cavity 73, 74 aorta aortic flow velocity 2 aortic insufficiency
Fabry disease (FD) is a rare X-linked lysosomal storage
 High-Sensitivity Troponin: A Clinical Blood Biomarker for Staging Cardiomyopathy in Fabry Disease Nora Seydelmann, MD; Dan Liu, MD; Johannes Kr amer, MD; Christiane Drechsler, MD; Kai Hu, MD; Peter Nordbeck,
High-Sensitivity Troponin: A Clinical Blood Biomarker for Staging Cardiomyopathy in Fabry Disease Nora Seydelmann, MD; Dan Liu, MD; Johannes Kr amer, MD; Christiane Drechsler, MD; Kai Hu, MD; Peter Nordbeck,
Carlos Eduardo Suaide Silva, Luiz Darcy Cortez Ferreira, Luciana Braz Peixoto, Claudia Gianini Monaco, Manuel Adán Gil, Juarez Ortiz
 Silva et al Original Article Arq Bras Cardiol Study of the Myocardial Contraction and Relaxation Velocities through Doppler Tissue Imaging Echocardiography. A New Alternative in the Assessment of the Segmental
Silva et al Original Article Arq Bras Cardiol Study of the Myocardial Contraction and Relaxation Velocities through Doppler Tissue Imaging Echocardiography. A New Alternative in the Assessment of the Segmental
Value of echocardiography in chronic dyspnea
 Value of echocardiography in chronic dyspnea Jahrestagung Schweizerische Gesellschaft für /Schweizerische Gesellschaft für Pneumologie B. Kaufmann 16.06.2016 Chronic dyspnea Shortness of breath lasting
Value of echocardiography in chronic dyspnea Jahrestagung Schweizerische Gesellschaft für /Schweizerische Gesellschaft für Pneumologie B. Kaufmann 16.06.2016 Chronic dyspnea Shortness of breath lasting
Heart disease. Other symptoms too? FABRY DISEASE IN PATIENTS WITH UNEXPLAINED HEART CONDITIONS
 Heart disease Other symptoms too? FABRY DISEASE IN PATIENTS WITH UNEXPLAINED HEART CONDITIONS You have been given this brochure because your heart condition may be linked to Fabry disease, which is a rare,
Heart disease Other symptoms too? FABRY DISEASE IN PATIENTS WITH UNEXPLAINED HEART CONDITIONS You have been given this brochure because your heart condition may be linked to Fabry disease, which is a rare,
Advanced Multi-Layer Speckle Strain Permits Transmural Myocardial Function Analysis in Health and Disease:
 Advanced Multi-Layer Speckle Strain Permits Transmural Myocardial Function Analysis in Health and Disease: Clinical Case Examples Jeffrey C. Hill, BS, RDCS Echocardiography Laboratory, University of Massachusetts
Advanced Multi-Layer Speckle Strain Permits Transmural Myocardial Function Analysis in Health and Disease: Clinical Case Examples Jeffrey C. Hill, BS, RDCS Echocardiography Laboratory, University of Massachusetts
Feasibility and limitations of 2D speckle tracking echocardiography
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE 204 A prospective study in daily clinical practice Feasibility and limitations of 2D speckle tracking echocardiography Lina Melzer, Anja Faeh-Gunz, Barbara Naegeli, Burkhardt Seifert*,
ORIGINAL ARTICLE 204 A prospective study in daily clinical practice Feasibility and limitations of 2D speckle tracking echocardiography Lina Melzer, Anja Faeh-Gunz, Barbara Naegeli, Burkhardt Seifert*,
Nancy Goldman Cutler, MD Beaumont Children s Hospital Royal Oak, Mi
 Nancy Goldman Cutler, MD Beaumont Children s Hospital Royal Oak, Mi Identify increased LV wall thickness (WT) Understand increased WT in athletes Understand hypertrophic cardiomyopathy (HCM) Enhance understanding
Nancy Goldman Cutler, MD Beaumont Children s Hospital Royal Oak, Mi Identify increased LV wall thickness (WT) Understand increased WT in athletes Understand hypertrophic cardiomyopathy (HCM) Enhance understanding
Quantitation of right ventricular dimensions and function
 SCCS Basics of cardiac assessment Quantitation of right ventricular dimensions and function Tomasz Kukulski, MD PhD Dept of Cardiology, Congenital Heart Disease and Electrotherapy Silesian Medical University
SCCS Basics of cardiac assessment Quantitation of right ventricular dimensions and function Tomasz Kukulski, MD PhD Dept of Cardiology, Congenital Heart Disease and Electrotherapy Silesian Medical University
MEDVISO WHITE PAPER ON STRAIN ANALYSIS IN TAGGED MR IMAGES
 Purpose of document The purpose of this document is to document validation of the Strain analysis module in Segment software packages. Intended audience The intended audiences of this document are: Engineering
Purpose of document The purpose of this document is to document validation of the Strain analysis module in Segment software packages. Intended audience The intended audiences of this document are: Engineering
LV FUNCTION ASSESSMENT: WHAT IS BEYOND EJECTION FRACTION
 LV FUNCTION ASSESSMENT: WHAT IS BEYOND EJECTION FRACTION Jamilah S AlRahimi Assistant Professor, KSU-HS Consultant Noninvasive Cardiology KFCC, MNGHA-WR Introduction LV function assessment in Heart Failure:
LV FUNCTION ASSESSMENT: WHAT IS BEYOND EJECTION FRACTION Jamilah S AlRahimi Assistant Professor, KSU-HS Consultant Noninvasive Cardiology KFCC, MNGHA-WR Introduction LV function assessment in Heart Failure:
Association and diagnostic utility of diastolic dysfunction and myocardial fibrosis in patients with Fabry disease
 Open access To cite: Liu D, Oder D, Salinger T, et al. Association and diagnostic utility of diastolic dysfunction and myocardial fibrosis in patients with Fabry disease. Open Heart 2018;5:e000803. doi:10.1136/
Open access To cite: Liu D, Oder D, Salinger T, et al. Association and diagnostic utility of diastolic dysfunction and myocardial fibrosis in patients with Fabry disease. Open Heart 2018;5:e000803. doi:10.1136/
RIGHT VENTRICULAR SIZE AND FUNCTION
 RIGHT VENTRICULAR SIZE AND FUNCTION Edwin S. Tucay, MD, FPCC, FPCC, FPSE Philippine Society of Echocardiography Quezon City, Philippines Echo Mission, BRTTH, Legaspi City, July 1-2, 2016 NO DISCLOSURE
RIGHT VENTRICULAR SIZE AND FUNCTION Edwin S. Tucay, MD, FPCC, FPCC, FPSE Philippine Society of Echocardiography Quezon City, Philippines Echo Mission, BRTTH, Legaspi City, July 1-2, 2016 NO DISCLOSURE
HFPEF Echo with Strain vs. MRI T1 Mapping
 HFPEF Echo with Strain vs. MRI T1 Mapping Erik Schelbert, MD MS Director, Cardiovascular Magnetic Resonance Assistant Professor of Medicine Heart & Vascular Institute University of Pittsburgh Disclosures
HFPEF Echo with Strain vs. MRI T1 Mapping Erik Schelbert, MD MS Director, Cardiovascular Magnetic Resonance Assistant Professor of Medicine Heart & Vascular Institute University of Pittsburgh Disclosures
Left atrial function. Aliakbar Arvandi MD
 In the clinic Left atrial function Abstract The left atrium (LA) is a left posterior cardiac chamber which is located adjacent to the esophagus. It is separated from the right atrium by the inter-atrial
In the clinic Left atrial function Abstract The left atrium (LA) is a left posterior cardiac chamber which is located adjacent to the esophagus. It is separated from the right atrium by the inter-atrial
Heart Failure in Women: Dr Goh Ping Ping Cardiologist Asian Heart & Vascular Centre
 Heart Failure in Women: More than EF? Dr Goh Ping Ping Cardiologist Asian Heart & Vascular Centre Overview Review pathophysiology as it relates to diagnosis and management Rational approach to workup:
Heart Failure in Women: More than EF? Dr Goh Ping Ping Cardiologist Asian Heart & Vascular Centre Overview Review pathophysiology as it relates to diagnosis and management Rational approach to workup:
PRELIMINARY STUDIES OF LEFT VENTRICULAR WALL THICKNESS AND MASS OF NORMOTENSIVE AND HYPERTENSIVE SUBJECTS USING M-MODE ECHOCARDIOGRAPHY
 Malaysian Journal of Medical Sciences, Vol. 9, No. 1, January 22 (28-33) ORIGINAL ARTICLE PRELIMINARY STUDIES OF LEFT VENTRICULAR WALL THICKNESS AND MASS OF NORMOTENSIVE AND HYPERTENSIVE SUBJECTS USING
Malaysian Journal of Medical Sciences, Vol. 9, No. 1, January 22 (28-33) ORIGINAL ARTICLE PRELIMINARY STUDIES OF LEFT VENTRICULAR WALL THICKNESS AND MASS OF NORMOTENSIVE AND HYPERTENSIVE SUBJECTS USING
Fabry disease is a rare X-linked metabolic disorder caused by
 ARTICLE Agalsidase beta treatment is associated with improved quality of life in patients with Fabry disease: Findings from the Fabry Registry Torquil Watt, MD 1, Alessandro P. Burlina, MD 2, Chiara Cazzorla,
ARTICLE Agalsidase beta treatment is associated with improved quality of life in patients with Fabry disease: Findings from the Fabry Registry Torquil Watt, MD 1, Alessandro P. Burlina, MD 2, Chiara Cazzorla,
Tissue Doppler and Strain Imaging
 Tissue Doppler and Strain Imaging Steven J. Lester MD, FRCP(C), FACC, FASE Relevant Financial Relationship(s) None Off Label Usage None 1 Objective way with which to quantify the minor amplitude and temporal
Tissue Doppler and Strain Imaging Steven J. Lester MD, FRCP(C), FACC, FASE Relevant Financial Relationship(s) None Off Label Usage None 1 Objective way with which to quantify the minor amplitude and temporal
HYPERTROPHY: Behind the curtain. V. Yotova St. Radboud Medical University Center, Nijmegen
 HYPERTROPHY: Behind the curtain V. Yotova St. Radboud Medical University Center, Nijmegen Disclosure of interest: none Relative wall thickness (cm) M 0.22 0.42 0.43 0.47 0.48 0.52 0.53 F 0.24 0.42 0.43
HYPERTROPHY: Behind the curtain V. Yotova St. Radboud Medical University Center, Nijmegen Disclosure of interest: none Relative wall thickness (cm) M 0.22 0.42 0.43 0.47 0.48 0.52 0.53 F 0.24 0.42 0.43
Influence of RAAS inhibition on outflow tract obstruction in hypertrophic cardiomyopathy
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE 5 RAAS inhibitors should be avoided if possible in patients with obstructive HCM Influence of RAAS inhibition on outflow tract obstruction in hypertrophic cardiomyopathy Katrin Witzel,
ORIGINAL ARTICLE 5 RAAS inhibitors should be avoided if possible in patients with obstructive HCM Influence of RAAS inhibition on outflow tract obstruction in hypertrophic cardiomyopathy Katrin Witzel,
Left Ventricular Dyssynchrony in Patients Showing Diastolic Dysfunction without Overt Symptoms of Heart Failure
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE DOI: 10.3904/kjim.2010.25.3.246 Left Ventricular Dyssynchrony in Patients Showing Diastolic Dysfunction without Overt Symptoms of Heart Failure Jae Hoon Kim, Hee Sang Jang, Byung Seok
ORIGINAL ARTICLE DOI: 10.3904/kjim.2010.25.3.246 Left Ventricular Dyssynchrony in Patients Showing Diastolic Dysfunction without Overt Symptoms of Heart Failure Jae Hoon Kim, Hee Sang Jang, Byung Seok
ONLINE DATA SUPPLEMENT. Impact of Obstructive Sleep Apnea on Left Ventricular Mass and. Diastolic Function
 ONLINE DATA SUPPLEMENT Impact of Obstructive Sleep Apnea on Left Ventricular Mass and Diastolic Function Mitra Niroumand Raffael Kuperstein Zion Sasson Patrick J. Hanly St. Michael s Hospital University
ONLINE DATA SUPPLEMENT Impact of Obstructive Sleep Apnea on Left Ventricular Mass and Diastolic Function Mitra Niroumand Raffael Kuperstein Zion Sasson Patrick J. Hanly St. Michael s Hospital University
Mechanisms of heart failure with normal EF Arterial stiffness and ventricular-arterial coupling. What is the pathophysiology at presentation?
 Mechanisms of heart failure with normal EF Arterial stiffness and ventricular-arterial coupling What is the pathophysiology at presentation? Ventricular-arterial coupling elastance Central arterial pressure
Mechanisms of heart failure with normal EF Arterial stiffness and ventricular-arterial coupling What is the pathophysiology at presentation? Ventricular-arterial coupling elastance Central arterial pressure
Fabry Disease in Latin America: Data from the Fabry Registry
 JIMD Reports DOI 10.1007/8904_2012_165 RESEARCH REPORT Fabry Disease in Latin America: Data from the Fabry Registry J. Villalobos J.M. Politei A.M. Martins G. Cabrera H. Amartino R. Lemay S. Ospina S.
JIMD Reports DOI 10.1007/8904_2012_165 RESEARCH REPORT Fabry Disease in Latin America: Data from the Fabry Registry J. Villalobos J.M. Politei A.M. Martins G. Cabrera H. Amartino R. Lemay S. Ospina S.
Københavns Universitet
 university of copenhagen Københavns Universitet Total average diastolic longitudinal displacement by colour tissue doppler imaging as an assessment of diastolic function de Knegt, Martina Chantal; Biering-Sørensen,
university of copenhagen Københavns Universitet Total average diastolic longitudinal displacement by colour tissue doppler imaging as an assessment of diastolic function de Knegt, Martina Chantal; Biering-Sørensen,
Early Regional Myocardial Dysfunction in Young Patients With Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy
 Early Regional Myocardial Dysfunction in Young Patients With Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy Luc Mertens, MD, PhD, Javier Ganame, MD, PhD, Piet Claus, PhD, Nathalie Goemans, MD, Daisy Thijs, MSc, Bénédicte
Early Regional Myocardial Dysfunction in Young Patients With Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy Luc Mertens, MD, PhD, Javier Ganame, MD, PhD, Piet Claus, PhD, Nathalie Goemans, MD, Daisy Thijs, MSc, Bénédicte
Coronary Microvascular Dysfunction in Male Patients With Anderson-Fabry Disease and the Effect of Treatment With Alpha Galactosidase A
 Heart Online First, published on August 5, 2005 as 10.1136/hrt.2004.054015 1 Coronary Microvascular Dysfunction in Male Patients With Anderson-Fabry Disease and the Effect of Treatment With Alpha Galactosidase
Heart Online First, published on August 5, 2005 as 10.1136/hrt.2004.054015 1 Coronary Microvascular Dysfunction in Male Patients With Anderson-Fabry Disease and the Effect of Treatment With Alpha Galactosidase
The Impact of Autonomic Neuropathy on Left Ventricular Function in Normotensive Type 1 Diabetic Patients: a Tissue Doppler Echocardiographic Study
 Diabetes Care Publish Ahead of Print, published online November 13, 2007 The Impact of Autonomic Neuropathy on Left Ventricular Function in Normotensive Type 1 Diabetic Patients: a Tissue Doppler Echocardiographic
Diabetes Care Publish Ahead of Print, published online November 13, 2007 The Impact of Autonomic Neuropathy on Left Ventricular Function in Normotensive Type 1 Diabetic Patients: a Tissue Doppler Echocardiographic
Managing Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy with Imaging. Gisela C. Mueller University of Michigan Department of Radiology
 Managing Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy with Imaging Gisela C. Mueller University of Michigan Department of Radiology Disclosures Gadolinium contrast material for cardiac MRI Acronyms Afib CAD Atrial fibrillation
Managing Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy with Imaging Gisela C. Mueller University of Michigan Department of Radiology Disclosures Gadolinium contrast material for cardiac MRI Acronyms Afib CAD Atrial fibrillation
Left Ventricular Function In Subclinical Hypothyroidism
 Clinical Proceedings. 2016;12(1):13-19 Original Article Left Ventricular Function In Subclinical Hypothyroidism NK Thulaseedharan, P Geetha, TM Padmaraj Department of Internal Medicine, Govt. Medical College
Clinical Proceedings. 2016;12(1):13-19 Original Article Left Ventricular Function In Subclinical Hypothyroidism NK Thulaseedharan, P Geetha, TM Padmaraj Department of Internal Medicine, Govt. Medical College
좌심실수축기능평가 Cardiac Function
 Basic Echo Review Course 좌심실수축기능평가 Cardiac Function Seonghoon Choi Cardiology Hallym university LV systolic function Systolic function 좌심실수축기능 - 심근의수축으로심실에서혈액을대동맥으로박출하는기능 실제임상에서 LV function 의의미 1Diagnosis
Basic Echo Review Course 좌심실수축기능평가 Cardiac Function Seonghoon Choi Cardiology Hallym university LV systolic function Systolic function 좌심실수축기능 - 심근의수축으로심실에서혈액을대동맥으로박출하는기능 실제임상에서 LV function 의의미 1Diagnosis
Evalua&on)of)Le-)Ventricular)Diastolic) Dysfunc&on)by)Echocardiography:) Role)of)Ejec&on)Frac&on)
 Evalua&on)of)Le-)Ventricular)Diastolic) Dysfunc&on)by)Echocardiography:) Role)of)Ejec&on)Frac&on) N.Koutsogiannis) Department)of)Cardiology) University)Hospital)of)Patras)! I have no conflicts of interest
Evalua&on)of)Le-)Ventricular)Diastolic) Dysfunc&on)by)Echocardiography:) Role)of)Ejec&on)Frac&on) N.Koutsogiannis) Department)of)Cardiology) University)Hospital)of)Patras)! I have no conflicts of interest
Myocardial Strain Imaging in Cardiac Diseases and Cardiomyopathies.
 Myocardial Strain Imaging in Cardiac Diseases and Cardiomyopathies. Session: Cardiomyopathy Tarun Pandey MD, FRCR. Associate Professor University of Arkansas for Medical Sciences Disclosures No relevant
Myocardial Strain Imaging in Cardiac Diseases and Cardiomyopathies. Session: Cardiomyopathy Tarun Pandey MD, FRCR. Associate Professor University of Arkansas for Medical Sciences Disclosures No relevant
Tissue Doppler and Strain Imaging. Steven J. Lester MD, FRCP(C), FACC, FASE
 Tissue Doppler and Strain Imaging Steven J. Lester MD, FRCP(C), FACC, FASE Relevant Financial Relationship(s) None Off Label Usage None a. Turn the wall filters on and turn down the receiver gain. b. Turn
Tissue Doppler and Strain Imaging Steven J. Lester MD, FRCP(C), FACC, FASE Relevant Financial Relationship(s) None Off Label Usage None a. Turn the wall filters on and turn down the receiver gain. b. Turn
Evaluation of Left Ventricular Diastolic Dysfunction by Doppler and 2D Speckle-tracking Imaging in Patients with Primary Pulmonary Hypertension
 ESC Congress 2011.No 85975 Evaluation of Left Ventricular Diastolic Dysfunction by Doppler and 2D Speckle-tracking Imaging in Patients with Primary Pulmonary Hypertension Second Department of Internal
ESC Congress 2011.No 85975 Evaluation of Left Ventricular Diastolic Dysfunction by Doppler and 2D Speckle-tracking Imaging in Patients with Primary Pulmonary Hypertension Second Department of Internal
Imaging. Impact of Myocardial Fibrosis in Patients With Symptomatic Severe Aortic Stenosis
 Imaging Impact of Myocardial Fibrosis in Patients With Symptomatic Severe Aortic Stenosis Frank Weidemann, MD*; Sebastian Herrmann*; Stefan Störk, MD; Markus Niemann, MD; Stefan Frantz, MD; Volkmar Lange,
Imaging Impact of Myocardial Fibrosis in Patients With Symptomatic Severe Aortic Stenosis Frank Weidemann, MD*; Sebastian Herrmann*; Stefan Störk, MD; Markus Niemann, MD; Stefan Frantz, MD; Volkmar Lange,
Relationship Between Serum Biochemical Markers of Myocardial Fibrosis and Diastolic Function at Rest and With Exercise in Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE DOI 10.4070 / kcj.2009.39.12.519 Print ISSN 1738-5520 / On-line ISSN 1738-5555 Copyright c 2009 The Korean Society of Cardiology Open Access Relationship Between Serum Biochemical Markers
ORIGINAL ARTICLE DOI 10.4070 / kcj.2009.39.12.519 Print ISSN 1738-5520 / On-line ISSN 1738-5555 Copyright c 2009 The Korean Society of Cardiology Open Access Relationship Between Serum Biochemical Markers
Stage I: Rule-Out Dashboard
 Stage I: Rule-Out Dashboard GENE/GENE PANEL: GLA DISORDER: Fabry disease HGNC ID: 4296 OMIM ID: 301500 ACTIONABILITY PENETRANCE 1. Is there a qualifying resource, such as a practice guideline or systematic
Stage I: Rule-Out Dashboard GENE/GENE PANEL: GLA DISORDER: Fabry disease HGNC ID: 4296 OMIM ID: 301500 ACTIONABILITY PENETRANCE 1. Is there a qualifying resource, such as a practice guideline or systematic
Noninvasive monitoring of regional myocardial
 ORIGINAL ARTICLES Sequential Changes of Myocardial Function During Acute Myocardial Infarction, in the Early and Chronic Phase After Coronary Intervention Described by Ultrasonic Strain Rate Imaging Frank
ORIGINAL ARTICLES Sequential Changes of Myocardial Function During Acute Myocardial Infarction, in the Early and Chronic Phase After Coronary Intervention Described by Ultrasonic Strain Rate Imaging Frank
How NOT to miss Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy? Adaya Weissler-Snir, MD University Health Network, University of Toronto
 How NOT to miss Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy? Adaya Weissler-Snir, MD University Health Network, University of Toronto Introduction Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy is the most common genetic cardiomyopathy,
How NOT to miss Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy? Adaya Weissler-Snir, MD University Health Network, University of Toronto Introduction Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy is the most common genetic cardiomyopathy,
Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy
 Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy From Genetics to ECHO Alexandra A Frogoudaki Second Cardiology Department ATTIKON University Hospital Athens University Athens, Greece EUROECHO 2010, Copenhagen, 11/12/2010
Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy From Genetics to ECHO Alexandra A Frogoudaki Second Cardiology Department ATTIKON University Hospital Athens University Athens, Greece EUROECHO 2010, Copenhagen, 11/12/2010
Tissue Doppler and Strain Imaging
 Tissue Doppler and Strain Imaging Steven J. Lester MD, FRCP(C), FACC, FASE Relevant Financial Relationship(s) None Off Label Usage None 1 Objective way with which to quantify the minor amplitude and temporal
Tissue Doppler and Strain Imaging Steven J. Lester MD, FRCP(C), FACC, FASE Relevant Financial Relationship(s) None Off Label Usage None 1 Objective way with which to quantify the minor amplitude and temporal
Cardiovascular Images
 Cardiovascular Images Pulmonary Embolism Diagnosed From Right Heart Changes Seen After Exercise Stress Echocardiography Brian C. Case, MD; Micheas Zemedkun, MD; Amarin Sangkharat, MD; Allen J. Taylor,
Cardiovascular Images Pulmonary Embolism Diagnosed From Right Heart Changes Seen After Exercise Stress Echocardiography Brian C. Case, MD; Micheas Zemedkun, MD; Amarin Sangkharat, MD; Allen J. Taylor,
PART II ECHOCARDIOGRAPHY LABORATORY OPERATIONS ADULT TRANSTHORACIC ECHOCARDIOGRAPHY TESTING
 PART II ECHOCARDIOGRAPHY LABORATORY OPERATIONS ADULT TRANSTHORACIC ECHOCARDIOGRAPHY TESTING STANDARD - Primary Instrumentation 1.1 Cardiac Ultrasound Systems SECTION 1 Instrumentation Ultrasound instruments
PART II ECHOCARDIOGRAPHY LABORATORY OPERATIONS ADULT TRANSTHORACIC ECHOCARDIOGRAPHY TESTING STANDARD - Primary Instrumentation 1.1 Cardiac Ultrasound Systems SECTION 1 Instrumentation Ultrasound instruments
WHAT DO ELECTROPHYSIOLOGISTS WANT TO KNOW FROM ECHOCARDIOGRAPHERS BEFORE, DURING&AFTER CARDIAC RESYNCHRONIZATION THERAPY?
 WHAT DO ELECTROPHYSIOLOGISTS WANT TO KNOW FROM ECHOCARDIOGRAPHERS BEFORE, DURING&AFTER CARDIAC RESYNCHRONIZATION THERAPY? Mary Ong Go, MD, FPCP, FPCC, FACC OUTLINE What is CRT Who needs CRT What does the
WHAT DO ELECTROPHYSIOLOGISTS WANT TO KNOW FROM ECHOCARDIOGRAPHERS BEFORE, DURING&AFTER CARDIAC RESYNCHRONIZATION THERAPY? Mary Ong Go, MD, FPCP, FPCC, FACC OUTLINE What is CRT Who needs CRT What does the
Assessment of right ventricular function by tissue Doppler in relation to plasma NT-proBNP concentration in patients with dilated cardiomyopathy
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Cardiology Journal 2007, Vol. 14, No. 2, pp. 167 173 Copyright 2007 Via Medica ISSN 1507 4145 Assessment of right ventricular function by tissue Doppler in relation to plasma NT-proBNP
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Cardiology Journal 2007, Vol. 14, No. 2, pp. 167 173 Copyright 2007 Via Medica ISSN 1507 4145 Assessment of right ventricular function by tissue Doppler in relation to plasma NT-proBNP
Hemodynamic Assessment. Assessment of Systolic Function Doppler Hemodynamics
 Hemodynamic Assessment Matt M. Umland, RDCS, FASE Aurora Medical Group Milwaukee, WI Assessment of Systolic Function Doppler Hemodynamics Stroke Volume Cardiac Output Cardiac Index Tei Index/Index of myocardial
Hemodynamic Assessment Matt M. Umland, RDCS, FASE Aurora Medical Group Milwaukee, WI Assessment of Systolic Function Doppler Hemodynamics Stroke Volume Cardiac Output Cardiac Index Tei Index/Index of myocardial
DOI: /j x
 DOI: 10.1111/j.1540-8175.2010.01149.x C 2010, Wiley Periodicals, Inc. Comparison of Left Ventricular Contractility in Pressure and Volume Overload: A Strain Rate Study in the Clinical Model of Aortic Stenosis
DOI: 10.1111/j.1540-8175.2010.01149.x C 2010, Wiley Periodicals, Inc. Comparison of Left Ventricular Contractility in Pressure and Volume Overload: A Strain Rate Study in the Clinical Model of Aortic Stenosis
Imaging in Heart Failure: A Multimodality Approach. Thomas Ryan, MD
 Imaging in Heart Failure: A Multimodality Approach Thomas Ryan, MD Heart Failure HFrEF HFpEF EF50% Lifetime risk 20% Prevalence 6M Americans Societal costs - $30B 50% 5-year survival 1 Systolic
Imaging in Heart Failure: A Multimodality Approach Thomas Ryan, MD Heart Failure HFrEF HFpEF EF50% Lifetime risk 20% Prevalence 6M Americans Societal costs - $30B 50% 5-year survival 1 Systolic
Role of CMR in heart failure and cardiomyopathy
 Role of CMR in heart failure and cardiomyopathy Hajime Sakuma Department of Radiology, Mie University Late gadolinium enhancement (LGE) LGE MRI can demonstrate site of necrosis, fibrosis or deposition
Role of CMR in heart failure and cardiomyopathy Hajime Sakuma Department of Radiology, Mie University Late gadolinium enhancement (LGE) LGE MRI can demonstrate site of necrosis, fibrosis or deposition
Assessment of LV systolic function
 Tutorial 5 - Assessment of LV systolic function Assessment of LV systolic function A knowledge of the LV systolic function is crucial in the undertanding of and management of unstable hemodynamics or a
Tutorial 5 - Assessment of LV systolic function Assessment of LV systolic function A knowledge of the LV systolic function is crucial in the undertanding of and management of unstable hemodynamics or a
ECHOCARDIOGRAPHY DATA REPORT FORM
 Patient ID Patient Study ID AVM - - Date of form completion / / 20 Initials of person completing the form mm dd yyyy Study period Preoperative Postoperative Operative 6-month f/u 1-year f/u 2-year f/u
Patient ID Patient Study ID AVM - - Date of form completion / / 20 Initials of person completing the form mm dd yyyy Study period Preoperative Postoperative Operative 6-month f/u 1-year f/u 2-year f/u
Masked Hypertension and Aortic Coarctation: Impact on Ventricular Function and Morphology
 Masked Hypertension and Aortic Coarctation: Impact on Ventricular Function and Morphology Giovanni Di Salvo MD, PhD, MMSc, FESC BACKGROUND MASKED HYPERTENSION Masked hypertension (MH) consists of an elevated
Masked Hypertension and Aortic Coarctation: Impact on Ventricular Function and Morphology Giovanni Di Salvo MD, PhD, MMSc, FESC BACKGROUND MASKED HYPERTENSION Masked hypertension (MH) consists of an elevated
Jong-Won Ha*, Jeong-Ah Ahn, Jae-Yun Moon, Hye-Sun Suh, Seok-Min Kang, Se-Joong Rim, Yangsoo Jang, Namsik Chung, Won-Heum Shim, Seung-Yun Cho
 Eur J Echocardiography (2006) 7, 16e21 CLINICAL/ORIGINAL PAPERS Triphasic mitral inflow velocity with mid-diastolic flow: The presence of mid-diastolic mitral annular velocity indicates advanced diastolic
Eur J Echocardiography (2006) 7, 16e21 CLINICAL/ORIGINAL PAPERS Triphasic mitral inflow velocity with mid-diastolic flow: The presence of mid-diastolic mitral annular velocity indicates advanced diastolic
CT for Myocardial Characterization of Cardiomyopathy. Byoung Wook Choi, Yonsei University Severance Hospital, Seoul, Korea
 CT for Myocardial Characterization of Cardiomyopathy Byoung Wook Choi, Yonsei University Severance Hospital, Seoul, Korea Cardiomyopathy Elliott P et al. Eur Heart J 2008;29:270-276 The European Society
CT for Myocardial Characterization of Cardiomyopathy Byoung Wook Choi, Yonsei University Severance Hospital, Seoul, Korea Cardiomyopathy Elliott P et al. Eur Heart J 2008;29:270-276 The European Society
Segmental Tissue Doppler Image-Derived Tei Index in Patients With Regional Wall Motion Abnormalities
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE DOI 10.4070 / kcj.2010.40.3.114 Print ISSN 1738-5520 / On-line ISSN 1738-5555 Copyright c 2010 The Korean Society of Cardiology Open Access Segmental Tissue Doppler Image-Derived Tei Index
ORIGINAL ARTICLE DOI 10.4070 / kcj.2010.40.3.114 Print ISSN 1738-5520 / On-line ISSN 1738-5555 Copyright c 2010 The Korean Society of Cardiology Open Access Segmental Tissue Doppler Image-Derived Tei Index
Conflict of interest: none declared
 The value of left ventricular global longitudinal strain assessed by three-dimensional strain imaging in the early detection of anthracycline-mediated cardiotoxicity C. Mornoş, A. Ionac, D. Cozma, S. Pescariu,
The value of left ventricular global longitudinal strain assessed by three-dimensional strain imaging in the early detection of anthracycline-mediated cardiotoxicity C. Mornoş, A. Ionac, D. Cozma, S. Pescariu,
Fabry disease is an X-linked lysosomal storage disorder,
 Stroke in Fabry Disease Frequently Occurs Before Diagnosis and in the Absence of Other Clinical Events Natural History Data From the Fabry Registry Katherine Sims, MD; Juan Politei, MD; Maryam Banikazemi,
Stroke in Fabry Disease Frequently Occurs Before Diagnosis and in the Absence of Other Clinical Events Natural History Data From the Fabry Registry Katherine Sims, MD; Juan Politei, MD; Maryam Banikazemi,
The impacts of pericardial effusion on the heart function of infants and young children with respiratory syncytial virus infection
 The impacts of pericardial effusion on the heart function of infants and young children with respiratory syncytial virus infection Author(s): Muslim M. Al Saadi, Abdullah S. Al Jarallah Vol. 13, No. 1
The impacts of pericardial effusion on the heart function of infants and young children with respiratory syncytial virus infection Author(s): Muslim M. Al Saadi, Abdullah S. Al Jarallah Vol. 13, No. 1
Tissue Doppler Imaging in Congenital Heart Disease
 Tissue Doppler Imaging in Congenital Heart Disease L. Youngmin Eun, M.D. Department of Pediatrics, Division of Pediatric Cardiology, Kwandong University College of Medicine The potential advantage of ultrasound
Tissue Doppler Imaging in Congenital Heart Disease L. Youngmin Eun, M.D. Department of Pediatrics, Division of Pediatric Cardiology, Kwandong University College of Medicine The potential advantage of ultrasound
Fabry meets Markov: evaluating biochemistry, disease course and costs in support of health care policy Rombach, S.M.
 UvA-DARE (Digital Academic Repository) Fabry meets Markov: evaluating biochemistry, disease course and costs in support of health care policy Rombach, S.M. Link to publication Citation for published version
UvA-DARE (Digital Academic Repository) Fabry meets Markov: evaluating biochemistry, disease course and costs in support of health care policy Rombach, S.M. Link to publication Citation for published version
Myocardial Fibrosis in Heart Failure
 Myocardial Fibrosis in Heart Failure Dr Leah Iles, MBChB, FRACP The Alfred Hospital and Baker IDI Heart and Diabetes Research Institute, Vic, Australia DECLARATION OF CONFLICT OF INTEREST Nothing to declare
Myocardial Fibrosis in Heart Failure Dr Leah Iles, MBChB, FRACP The Alfred Hospital and Baker IDI Heart and Diabetes Research Institute, Vic, Australia DECLARATION OF CONFLICT OF INTEREST Nothing to declare
Two-Dimensional Ultrasonic Strain Rate Measurement of the Human Heart in Vivo
 Two-Dimensional Ultrasonic Strain Rate Measurement of the Human Heart in Vivo Jan D hooge 1, Fadi Jamal 2, Bart Bijnens 2, Jan Thoen 3, Frans Van de Werf 2, George R. Sutherland 2, and Paul Suetens 1 1
Two-Dimensional Ultrasonic Strain Rate Measurement of the Human Heart in Vivo Jan D hooge 1, Fadi Jamal 2, Bart Bijnens 2, Jan Thoen 3, Frans Van de Werf 2, George R. Sutherland 2, and Paul Suetens 1 1
Clinical Utilization and Function of Tissue Doppler Imaging in Detecting Congenital Cardiomyopathies
 618221JDMXXX10.1177/8756479315618221Journal of Diagnostic Medical SonographyAlexander research-article2015 Literature Review Clinical Utilization and Function of Tissue Doppler Imaging in Detecting Congenital
618221JDMXXX10.1177/8756479315618221Journal of Diagnostic Medical SonographyAlexander research-article2015 Literature Review Clinical Utilization and Function of Tissue Doppler Imaging in Detecting Congenital
Left atrial mechanical function and stiffness in patients with atrial septal aneurysm: A speckle tracking study
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Cardiology Journal 2015, Vol. 22, No. 5, 535 540 DOI: 10.5603/CJ.a2015.0033 Copyright 2015 Via Medica ISSN 1897 5593 Left atrial mechanical function and stiffness in patients with atrial
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Cardiology Journal 2015, Vol. 22, No. 5, 535 540 DOI: 10.5603/CJ.a2015.0033 Copyright 2015 Via Medica ISSN 1897 5593 Left atrial mechanical function and stiffness in patients with atrial
Restrictive Cardiomyopathy
 ESC Congress 2011, Paris Imaging Unusual Causes of Cardiomyopathy Restrictive Cardiomyopathy Kazuaki Tanabe, MD, PhD Professor of Medicine Chair, Division of Cardiology Izumo, Japan I Have No Disclosures
ESC Congress 2011, Paris Imaging Unusual Causes of Cardiomyopathy Restrictive Cardiomyopathy Kazuaki Tanabe, MD, PhD Professor of Medicine Chair, Division of Cardiology Izumo, Japan I Have No Disclosures
Incorporating the New Echo Guidelines Into Everyday Practice
 Incorporating the New Echo Guidelines Into Everyday Practice Clinical Case RIGHT VENTRICULAR FAILURE Gustavo Restrepo MD President Elect Interamerican Society of Cardiology Director Fellowship Training
Incorporating the New Echo Guidelines Into Everyday Practice Clinical Case RIGHT VENTRICULAR FAILURE Gustavo Restrepo MD President Elect Interamerican Society of Cardiology Director Fellowship Training
Tissue Doppler Derived Longitudinal Strain and Strain Rate During the First 3 Days of Life in Healthy Term Neonates
 0031-3998/09/6503-0357 PEDIATRIC RESEARCH Copyright 2009 International Pediatric Research Foundation, Inc. Vol. 65, No. 3, 2009 Printed in U.S.A. Tissue Doppler Derived Longitudinal Strain and Strain Rate
0031-3998/09/6503-0357 PEDIATRIC RESEARCH Copyright 2009 International Pediatric Research Foundation, Inc. Vol. 65, No. 3, 2009 Printed in U.S.A. Tissue Doppler Derived Longitudinal Strain and Strain Rate
Strain/Untwisting/Diastolic Suction
 What Is Diastole and How to Assess It? Strain/Untwisting/Diastolic Suction James D. Thomas, M.D., F.A.C.C. Cardiovascular Imaging Center Department of Cardiology Cleveland Clinic Foundation Cleveland,
What Is Diastole and How to Assess It? Strain/Untwisting/Diastolic Suction James D. Thomas, M.D., F.A.C.C. Cardiovascular Imaging Center Department of Cardiology Cleveland Clinic Foundation Cleveland,
Assessment of Regional Atrial Function in Patients with Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathies Using Tissue Doppler Imaging
 Pediatr Cardiol (2008) 29:301 308 DOI 10.1007/s00246-007-9112-0 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Assessment of Regional Atrial Function in Patients with Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathies Using Tissue Doppler Imaging Ragiab
Pediatr Cardiol (2008) 29:301 308 DOI 10.1007/s00246-007-9112-0 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Assessment of Regional Atrial Function in Patients with Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathies Using Tissue Doppler Imaging Ragiab
PRESENTER DISCLOSURE INFORMATION. There are no potential conflicts of interest regarding current presentation
 PRESENTER DISCLOSURE INFORMATION There are no potential conflicts of interest regarding current presentation Better synchrony and diastolic function for septal versus apical right ventricular permanent
PRESENTER DISCLOSURE INFORMATION There are no potential conflicts of interest regarding current presentation Better synchrony and diastolic function for septal versus apical right ventricular permanent
Assessment of left ventricular function by different speckle-tracking software
 European Journal of Echocardiography (2010) 11, 417 421 doi:10.1093/ejechocard/jep226 Assessment of left ventricular function by different speckle-tracking software Ana Manovel*, David Dawson, Benjamin
European Journal of Echocardiography (2010) 11, 417 421 doi:10.1093/ejechocard/jep226 Assessment of left ventricular function by different speckle-tracking software Ana Manovel*, David Dawson, Benjamin
A New Method to Rapidly Evaluate LVEF from a Contractility Polar Map. Lebeau et al.
 A New Method to Rapidly Evaluate LVEF from a Contractility Polar Map Lebeau et al. Good afternoon It is my pleasure to present to you a new method to rapidly evaluate LVEF from a contractility polar map
A New Method to Rapidly Evaluate LVEF from a Contractility Polar Map Lebeau et al. Good afternoon It is my pleasure to present to you a new method to rapidly evaluate LVEF from a contractility polar map
Medication Policy Manual. Topic: Fabrazyme, agalsidase beta Date of Origin: February 17, 2015
 Medication Policy Manual Policy No: dru391 Topic: Fabrazyme, agalsidase beta Date of Origin: February 17, 2015 Committee Approval Date: March 13, 2015 Next Review Date: March 2016 Effective Date: July
Medication Policy Manual Policy No: dru391 Topic: Fabrazyme, agalsidase beta Date of Origin: February 17, 2015 Committee Approval Date: March 13, 2015 Next Review Date: March 2016 Effective Date: July
A STUDY OF LEFT VENTRICULAR DIASTOLIC DYSFUNCTION IN HYPERTENSION Ravi Keerthy M 1
 A STUDY OF LEFT VENTRICULAR DIASTOLIC DYSFUNCTION IN HYPERTENSION Ravi Keerthy M 1 HOW TO CITE THIS ARTICLE: Ravi Keerthy M. A Study of Left Ventricular Diastolic Dysfunction in Hypertension. Journal of
A STUDY OF LEFT VENTRICULAR DIASTOLIC DYSFUNCTION IN HYPERTENSION Ravi Keerthy M 1 HOW TO CITE THIS ARTICLE: Ravi Keerthy M. A Study of Left Ventricular Diastolic Dysfunction in Hypertension. Journal of
Stephen Glen ISCHAEMIC HEART DISEASE AND LEFT VENTRICULAR FUNCTION
 Stephen Glen ISCHAEMIC HEART DISEASE AND LEFT VENTRICULAR FUNCTION Overview Coronary arteries Terminology to describe contractility Measuring ventricular function Systolic dysfunction Practice cases- LV
Stephen Glen ISCHAEMIC HEART DISEASE AND LEFT VENTRICULAR FUNCTION Overview Coronary arteries Terminology to describe contractility Measuring ventricular function Systolic dysfunction Practice cases- LV
Clinical material and methods. Departments of 1 Cardiology and 2 Anatomy, Gaziantep University, School of Medicine, Gaziantep, Turkey
 Interatrial Block and P-Terminal Force: A Reflection of Mitral Stenosis Severity on Electrocardiography Murat Yuce 1, Vedat Davutoglu 1, Cayan Akkoyun 1, Nese Kizilkan 2, Suleyman Ercan 1, Murat Akcay
Interatrial Block and P-Terminal Force: A Reflection of Mitral Stenosis Severity on Electrocardiography Murat Yuce 1, Vedat Davutoglu 1, Cayan Akkoyun 1, Nese Kizilkan 2, Suleyman Ercan 1, Murat Akcay
The Imaging Diagnosis of Less Advanced Cases of Cardiac Amyloidosis: The Relative Apical Sparing Pattern
 CASE REPORT The Imaging Diagnosis of Less Advanced Cases of Cardiac Amyloidosis: The Relative Apical Sparing Pattern Koya Ono 1, Go Ishimaru 2, Miho Hayashi 3,YuanBae 4, Takashi Ito 4, Toshiyuki Izumo
CASE REPORT The Imaging Diagnosis of Less Advanced Cases of Cardiac Amyloidosis: The Relative Apical Sparing Pattern Koya Ono 1, Go Ishimaru 2, Miho Hayashi 3,YuanBae 4, Takashi Ito 4, Toshiyuki Izumo
Exercise Test: Practice and Interpretation. Jidong Sung Division of Cardiology Samsung Medical Center Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine
 Exercise Test: Practice and Interpretation Jidong Sung Division of Cardiology Samsung Medical Center Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine 2 Aerobic capacity and survival Circulation 117:614, 2008
Exercise Test: Practice and Interpretation Jidong Sung Division of Cardiology Samsung Medical Center Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine 2 Aerobic capacity and survival Circulation 117:614, 2008
Fabry RADAR 2007 The Fabry Registry Aggregate Data Annual Report
 Fabry RADAR 2007 The Fabry Registry Aggregate Data Annual Report A program supported by Genzyme Fabr/GL/P341/05/07 2007 Genzyme Corporation. All rights reserved. Table of Contents I. II. III. IV. V. VI.
Fabry RADAR 2007 The Fabry Registry Aggregate Data Annual Report A program supported by Genzyme Fabr/GL/P341/05/07 2007 Genzyme Corporation. All rights reserved. Table of Contents I. II. III. IV. V. VI.
