Does Talking and Different Body (Sitting, Supine, Standing) Positions affect Blood Pressure?
|
|
|
- Lorin Gray
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 International Journal of Nursing December 2018, Vol. 5,. 2, pp ISSN (Print) (Online) Copyright The Author(s). All Rights Reserved. Published by American Research Institute for Policy Development DOI: /jns.v5n2a8 URL: Does Talking and Different Body (Sitting, Supine, Standing) Positions affect Blood Pressure? Zühre Yoloğlu 1 & Dr. Bahire Ulus 2 Abstract Thisstudyaimtocompare Blood Pressure (BP) values obtained sitting, talking, supine, and standing positions.the study was planned in a comparative and descriptive design and conducted on 357 hypertensive patients in the cardiology department at a private health center in Istanbul in 2016.The data were collected with a patient identification form and BP Measurements form. BP measurement was done with aneroid sphygmomanometer. Measurements were done on the the patients left and right arms, respectively, sitting, talking, supine and standing position.the blood pressure measurement process lasted about 30 minutes in each patient. The obtained data were analyzed with percentages, repeated measures (in order to determine from which measurement the difference originated) ANOVA and Bonferroni tests.the mean of the sitting position BP, talking and standing SBP was significantly lower than average (p<0.05). There was no significant difference between talking and standing SBP averages (p>0.05). Standing DBP, mean, talking, sitting and supine measured diastolic blood pressure was significantly higher than average (p<0.05). Talking and sitting diastolic BP measured was no significant difference between the averages (p> 0.05).At the end of the study, we concluded that sitting is the most reliable position for the measurement of BP. Keywords: Blood pressure measurement, sitting, talking, supine standing position, 1.Introduction Blood pressure (BP) is measured with two basic techniques; direct and indirect (manual and digital) methods (Pickering et al., 2005). In clinics, indirect, manual BP measurement method is usually preferred for the evaluation of the pressure exerted by the blood on the vessel walls within the systemic arterial circulation (Verberk, Kessels, & Thien, 2011). The measurements are carried out either with mercury or aneroid sphygmomanometers (De Greeff et al., 2010). The most common device used in daily routine by nurses is the aneroid sphygmomanometer (O'brien et al., 2003; Pickering et al., 2008). According to the Turkish Cardiology Association Guideline, these devices should be calibrated with the mercury sphygmomanometer every 6 months (Parati et al., 2008).BP, which is a vital sign, is a hemodynamic event and can be affected by various factors (Pickering et al., 2005).Therefore, the nurses, who are monitoring the blood pressure of the patients, should take the emotional state (Gabbay et al., 2006), fatigue, eating and smoking habits, fullness of the bladder and room temperature into consideration (Chobanian et al., 2003). The BP results are also affected by the type and brand of the device used, the measurer, preferred extremity for the measurement, with of the cuff and the patient s position (Cicolini et al., 2011; Myers, 2006; O'brien et al., 2003).But the position of the patient during the BP measurement is often neglected(netea, Lenders, Smits, Thien, 2003). World Health Organization (WHO) and the International Society of Hypertension emphasize that regarding the routine BP measurements, the patient should be in a relaxed position. The extremity, which will be used for the measurement, should be placed and supported at the level of the heart.in addition, the Turkish Cardiology Association Work Group state that the patient should not talk during the measurement. 1 Acibadem Mehmet Ali Aydinlar University, Atakent Hospital, İstanbul/Turkey 2 Lecturer, Acibadem Mehmet Ali Aydinlar University, Faculty of Health Sciences, Department of Nursing, Istanbul/ Turkey
2 Zühre Yoloğlu & Dr. Bahire Ulus 95 The National Hypertension Treatment and Follow-Up Guideline of Turkish Society of Cardiology state that the environmental factors of the patients (fed state, fatigue, room temperature, and body position) should be checked by the measurer to ensure correct BP measurements. According to the Guideline of the European Society of Cardiology/European Society of Hypertension (ESC/ESH) of 2013, systolic blood pressures (SBP) higher than 140 mmhg and diastolic blood pressures (DBP) higher than 90 mmhg are accepted as hypertension.these levels are considered as limit values for the age and risk groups in adults (Verdecchia & Angeli, 2003). The objective of this study was to determine the differences between the blood pressures in certain conditions (sitting, talking, supine, standing position) in hypertensive patients older than 30 years. 2. Methods The study was planned in a comparative and descriptive design and conducted on 357 hypertensive patients in the cardiology department at a private health center in Istanbul in December 2015/ February The participating patients were selected with a simple randomized sampling. Hypertensive patients, who were older than 30 years, had no psychological disorder, had adequate communication skills, were not pregnant and accepted to participate, were included in the study.all blood pressure measurements were performed with an aneroid sphygmomanometer (Omron) and stethoscope. The obtained data were recorded in the Patient Description Formand Blood Pressure Entry Form. The blood pressure measurements were done while the patient was sitting, talking, supine, standing position.the data were collected according to the below-mentioned steps:clinical blood pressure measurement: The measurements were performed according to the nursing care guideline of the Turkish Society of Cardiology. Thepatientswerelet to rest for 5 minutes before the measurement. Special caution was exercised to assure that the cuff wrapped 80% of the arm and 2/3 of the arm length. The cuff was inflated 20 mmhg higher than the systolic blood pressure while the radial pulse was kept under control. Then the cuff was deflated with a rate of 2 mmhg per second. The appearance and disappearance of the Korotkoff sounds were considered for the determination of the systolic and diastolic blood pressures. Materials: Aneroid sphygmomanometer (Omron) with a cuff width of 15x33cm. Stethoscope. - Referring the patient to a quiet, comfortable room 1st measurement (in the sitting position) - In the sitting position (on a chair with back support), while the patient reclined and his/her feet standing parallel on the floor. - Fulfilling the Patient Description Form - BP measurement left arm 2nd measurement (talking) - Certain questions were asked in order to provoke the patient to talk, while the previous sitting position was preserved. - BP measurement, left arm 3rd measurement (in the supine position) - The patient rests in the supine position - The right arm was supported with a small pillow at the midline level of the sternum - The left arm was supported with a small pillow at the midline level of the sternum - BP measurement, left arm
3 96 International Journal of Nursing, Vol. 5(2), December th measurement (in the standing position) - The patient in the standing position - BP measurement, left arm The blood pressure measurement process lasted about 30 minutes in each patient.the obtained data were analyzed with percentages, repeated measures (in order to determine from which measurement the difference originated) ANOVA and Bonferroni tests. Research Question:Is there any difference between the results of the systolic and diastolic blood pressure measurements in the sitting, speaking, supineand standing positions? 2.1.Ethical Consideration The study was approved by the Ethics Committee of Acibadem University (ATADEK-2015/7) and the institutional permission of the Atakent Hospital Coordinatorship of Acibadem Mehmet Ali Aydinlar University was also obtained. All patients were informed about the objective of the study by the researcher and the patients were included in the study after the informed patient consent was obtained from the patients, who accepted to participate. During the study, the privacy of the patients was taken into consideration and the ethical principles were respected. 3.Results The study population included 357 patients. The mean of the participants was 52±9 years; males were 52.9 %. The majority of the patients were using antihypertensive agents (93.3%). Table 1. Characteristics of Patients Characteristics n % Gender Women Men ,1 52,9 Smoking Alcohol use Drug Use Co-morbid Diseases Family history of Hypertension (Mean 15.8) 41,2 58,8 84,3 (Mean 3.11) 15,7 93,3 6,7 55,2 44, ,3 13,7 Age Mean Min Max Total ,0 Participants of the families 86.3% of had a history of hypertension and they (55.2 %) had more than one chronic disease. Measured blood pressure (BP) averages were evaluated as systolic blood pressure (SBP) and diastolic blood pressure (DBP). The average SBPs were sitting 143,2 ± 13,9;talking 144,4 ± 13,4; supine position 139,2 ± 13,5; standing position145,0 ± 14,1; mmhg and DBPaverage of the measurements were 85,8 ± 8,9; 85,9 ± 9,2 82,5 ± 8,6; 87,0 ± 9,0 mmhg respectively (Table1).
4 Zühre Yoloğlu & Dr. Bahire Ulus 97 The evaluation of the four differences SBP measurements revealed a statistically significant difference between the sitting, talking, supine, standingposition(p<0.05). The SBP level during the talking was significantly different from the standing SBP (p<0.05). We observed that the sitting SBP (1st measurement) was a little bit lower than the other (2nd, 3rd, and 4th) measurements. The evaluation of the measurements showed that there was a significant difference between the groups (p<0.05). However, the difference between the average of the SBP during the talking and the average of the standing SBP was not statistically significant (p>0.05) (Table2). Table 2. Comparison of systolic blood pressure results measured during speech and different body positions Talking Sitting Supine Standing Multiple Comparisons (Post-hoc) Mean (I-J) SS p. a * İnterval Confidence Average 95 % Min. Max. Sitting 1,221 * 0,353 0,004 0,286 2,157 Supine 5,213 * 0,343 0,000 4,302 6,124 Standing -0,627 0,357 0,479-1,575 0,320 Talking -1,221 * 0,353 0,004-2,157-0,286 Supine 3,992 * 0,341 0,000 3,086 4,897 Standing -1,849 * 0,365 0,000-2,817-0,880 Talking -5,213 * 0,343 0,000-6,124-4,302 Sitting -3,992 * 0,341 0,000-4,897-3,086 Standing -5,840 * 0,332 0,000-6,720-4,960 Talking 0,627 0,357 0,479-0,320 1,575 Sitting 1,849 * 0,365 0,000 0,880 2,817 Supine 5,840 * 0,332 0,000 4,960 6,720 * Mean differences are significant at 0.05 level. *a. Multiple comparisons correction method: Bonferroni The mean DBP when supine, talking, sitting and standing position measured diastolic blood pressure were significantly lower than the average (p<0.05). Standing diastolic arterial pressure, mean, talking, sitting and supine position measured DBP was significantly higher than average (p<0.05). Talking and sitting DBP measured was no significant difference between the averages (p>0.05) (Figure 1).However, the average of the standing DBP was significantly higher than the sitting, talking and supine position DBP respectively (p<0.05). Figure 1. Diastolic Blood Pressure measurement ranges
5 98 International Journal of Nursing, Vol. 5(2), December Discussion Hypertension can be diagnosed with a correct and precise measurement of blood pressure (Calhoun et al., 2008). Incorrect and ambiguous BP measurements with non-invasive methods may lead to medical complications and economic losses. The non-invasive BP measurement methods preferred in the monitoring of the hypertensive patients should be used by experienced nurses (O'brien et al., 2003).Although the advantages of the control of the blood pressure in hypertensive patients are well known, the level of the hypertension management in all health centers including the primary care health centers is still unsatisfactory. The main objective of the BP control is to keep the systolic and diastolic blood pressures below 140 mmhg and 90 mmhg respectively (Rushton & Smith, 2016).According to the findings of this study, the diastolic BP measurements were more affected by the patient s body positions than the systolic BP measurements.ersoy, Pınar conducted also a similar study in 2011 and found out that systolic and diastolic BP levels reached the highest values in the supine position and although the systolic BP measurements differed, there was no significant difference between the diastolic BP measurements.lynch (1981) investigated the BP during the speaking and they reported that speaking increased the BP. Greenreportedthatblood pressure changed prominently during the speaking. The results of our studyareconsistentwiththisstudy(aksöyek et al, 1992). Regarding the results of our study, we concluded that the measurement of the BP in the supine position delivered lower values and the standing systolic and diastolic BP levels were higher than the BP levels in other body positions. 5. Conclusion Nurses should ensure that the patients rest at least 5 minutes before the measurement and try to eliminate all factors, which may influence the measurement results. The BP measurement should be performed according to the Nursing Care Guideline of the Turkish Society of Cardiology and it should be kept in mind that measurements in the supine position will lead to relatively lower results.the sitting position should be preferred and measurements in the standing position and during conversation should be avoided. - As different body positions lead to different measurements, the measurements should be performed always in the same position in the hypertensive patients. - As the measurements can deliver different results in sitting, lying, standing positions and during the speaking, the BP measurements should be performed in different body positions in patients with the suspicion of orthostatic hypertension and the patients should not talk during the measurements. - Which body position and extremity are used for the measurement should be also recorded. Acknowledgements This study was conducted a master'sproject submitted to the Acibadem Mehmet Ali Aydinlar University Health Sciences Institute. We sincerely thank the patients of Department of Cardiology of Atakent Hospital of Acibadem Mehmet Ali Aydinlar University. Authorship Statement We confirm that all listed authors meet the authorship criteria, and all authors are in agreement with the content of the manuscript. ZY and BU designed the present study. ZY collected, analysed, and interpreted the data. BU wrote the first draft of the manuscript. ZY and BU revised the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript to be published. Conflict of interest The authors declare no conflict of interest. References Aksöyek, S., Kazazoğlu, A. R., Okay, T., Sancaktar, O. (1992). Comparison of Office Blood Pressures in Supine, Sitting and Standing Positions with Ambulatory Blood Pressures. Turk Kardiyol Dern Ars, 20(5), Calhoun, D. A., Jones, D., Textor, S., Goff, D. C., Murphy, T. P., Toto, R. D., Sica, D. (2008). Resistant hypertension: diagnosis, evaluation, and treatment: a scientific statement from the American Heart Association Professional Education Committee of the Council for High Blood Pressure Research. Circulation, 117(25), e510-e526.
6 Zühre Yoloğlu & Dr. Bahire Ulus 99 Chobanian, A. V., Bakris, G. L., Black, H. R., Cushman, W. C., Green, L. A., Izzo Jr, J. L. Wright Jr, J. T. (2003). Seventh report of the joint national committee on prevention, detection, evaluation, and treatment of high blood pressure. Hypertension, 42(6), Cicolini, G., Pizzi, C., Palma, E., Bucci, M., Schioppa, F., Mezzetti, A., & Manzoli, L. (2011). Differences in blood pressure by body position (supine, Fowler's, and sitting) in hypertensive subjects. American journal of hypertension, 24(10), De Greeff, A., Lorde, I., Wilton, A., Seed, P., Coleman, A., & Shennan, A. (2010). Calibration accuracy of hospitalbased non-invasive blood pressure measuring devices. Journal of human hypertension, 24(1), 58. Gabbay, R. A., Lendel, I., Saleem, T. M., Shaeffer, G., Adelman, A. M., Mauger, D. T., Polomano, R. C. (2006). Nurse case management improves blood pressure, emotional distress and diabetes complication screening. Diabetes research and clinical practice, 71(1), Green, L.A. (2017). It is time to change how we measure blood pressures in the office. Annals Family Med,15 (2) Myers, M. G. (2006). Automated blood pressure measurement in routine clinical practice. Blood pressure monitoring, 11(2), Netea, R., Lenders, J., Smits, P., Thien, T. (2003). Both body and arm position significantly influence blood pressure measurement. Journal of Human Hypertension, 17(7), 459. O'brien, E., Asmar, R., Beilin, L., Imai, Y., Mallion, J.-M., Mancia, G., Palatini, P. (2003). European Society of Hypertension recommendations for conventional, ambulatory and home blood pressure measurement. Journal of hypertension, 21(5), Parati, G., Stergiou, G. S., Asmar, R., Bilo, G., de Leeuw, P., Imai, Y., Mengden, T. (2008). European Society of Hypertension guidelines for blood pressure monitoring at home: a summary report of the Second International Consensus Conference on Home Blood Pressure Monitoring. Journal of hypertension, 26(8), Pickering, T. G., Hall, J. E., Appel, L. J., Falkner, B. E., Graves, J., Hill, M. N., Roccella, E. J. (2005). Recommendations for blood pressure measurement in humans and experimental animals: part 1: blood pressure measurement in humans: a statement for professionals from the Subcommittee of Professional and Public Education of the American Heart Association Council on High Blood Pressure Research. Circulation, 111(5), Pickering, T. G., Miller, N. H., Ogedegbe, G., Krakoff, L. R., Artinian, N. T., Goff, D. (2008). Call to action on use and reimbursement for home blood pressure monitoring: a joint scientific statement from the American Heart Association, American Society of Hypertension, and Preventive Cardiovascular Nurses Association. Hypertension, 52(1), Rushton, M., Smith, J. (2016). How to measure blood pressure manually. Nursing standard (Royal College of Nursing (Great Britain): 1987), 30(21), Verberk, W. J., Kessels, A. G., Thien, T. (2011). Blood pressure measurement method and inter-arm differences: a meta-analysis. American journal of hypertension, 24(11), Verdecchia, P., Angeli, F. (2003). The seventh report of the joint national committee on the prevention, detection, evaluation and treatment of high blood pressure: the weapons are ready. Revista espanola de cardiologia, 56(09),
SARASOTA MEMORIAL HOSPITAL NURSING PROCEDURE. MEASURING BLOOD PRESSURE - MANUAL (equ04)
 SARASOTA MEMORIAL HOSPITAL NURSING PROCEDURE TITLE: ISSUED FOR: MEASURING BLOOD PRESSURE - MANUAL Nursing DATE: REVIEWED: PAGES: 2/80 7/17 1 of 5 RESPONSIBILITY: RN, LPN, Patient Care Technician Multi-skilled
SARASOTA MEMORIAL HOSPITAL NURSING PROCEDURE TITLE: ISSUED FOR: MEASURING BLOOD PRESSURE - MANUAL Nursing DATE: REVIEWED: PAGES: 2/80 7/17 1 of 5 RESPONSIBILITY: RN, LPN, Patient Care Technician Multi-skilled
and bias, which are known to be present in self-home and in professional office BP measurements taken using the auscultatory technique [7].
![and bias, which are known to be present in self-home and in professional office BP measurements taken using the auscultatory technique [7]. and bias, which are known to be present in self-home and in professional office BP measurements taken using the auscultatory technique [7].](/thumbs/86/94636218.jpg) Devices and technology 37 Validation of the A&D UM-11 professional hybrid device for office blood pressure measurement according to the International Protocol George S. Stergiou, Periklis P. Giovas, Charilaos
Devices and technology 37 Validation of the A&D UM-11 professional hybrid device for office blood pressure measurement according to the International Protocol George S. Stergiou, Periklis P. Giovas, Charilaos
1. Department of Gynecology and Obstetrics, St. Joseph's Hospital Berlin Tempelhof, Germany
 Page 1 of 9 Validation of the TONOPORT VI ambulatory blood pressure monitor, according to the European Society of Hypertension International Protocol revision 2010 Michael Abou-Dakn 1, Cornelius Döhmen
Page 1 of 9 Validation of the TONOPORT VI ambulatory blood pressure monitor, according to the European Society of Hypertension International Protocol revision 2010 Michael Abou-Dakn 1, Cornelius Döhmen
Validation of the SEJOY BP-1307 upper arm blood pressure monitor for home. blood pressure monitoring according to the European Society of Hypertension
 Validation of the SEJOY BP-1307 upper arm blood pressure monitor for home blood pressure monitoring according to the European Society of Hypertension International Protocol revision 2010 Short title: Validation
Validation of the SEJOY BP-1307 upper arm blood pressure monitor for home blood pressure monitoring according to the European Society of Hypertension International Protocol revision 2010 Short title: Validation
Validation of the OMRON 705 IT blood pressure measuring device according to the International Protocol of the European Society of Hypertension
 Validation of the OMRON 705 IT blood pressure measuring device according to the International Protocol of the European Society of Hypertension M. EL ASSAAD, J. TOPOUCHIAN, G. LABAKI, R. ASMAR L Institut
Validation of the OMRON 705 IT blood pressure measuring device according to the International Protocol of the European Society of Hypertension M. EL ASSAAD, J. TOPOUCHIAN, G. LABAKI, R. ASMAR L Institut
Copyright: DOI link to paper: Date deposited: This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 2.5 Generic License
 Zheng DC, Liu CY, Amoore J, Mieke S, Murray A. Need for Re-validation of Automated Blood Pressure Devices for use in Unstable Conditions. In: 215 Computing in Cardiology Conference (CinC). 215, Nice, France:
Zheng DC, Liu CY, Amoore J, Mieke S, Murray A. Need for Re-validation of Automated Blood Pressure Devices for use in Unstable Conditions. In: 215 Computing in Cardiology Conference (CinC). 215, Nice, France:
Copyright Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. Unauthorized reproduction of this article is prohibited.
 Devices and technology 261 Validation of the ROSSMAX blood pressure measuring monitor according to the European Society of Hypertension International Protocol for Validation of Blood Pressure Measuring
Devices and technology 261 Validation of the ROSSMAX blood pressure measuring monitor according to the European Society of Hypertension International Protocol for Validation of Blood Pressure Measuring
Taking and recording blood pressure and pulse. City Gate Training Centre all rights reserved
 Taking and recording blood pressure and pulse City Gate Training Centre all rights reserved Course Content: Definition of Blood Pressure Normal Blood Pressure Readings Systolic and Diastolic Blood Pressure
Taking and recording blood pressure and pulse City Gate Training Centre all rights reserved Course Content: Definition of Blood Pressure Normal Blood Pressure Readings Systolic and Diastolic Blood Pressure
a Centre de Médecine Cardiovasculaire, Paris, France, b Lebanese Hospital and Received 7 June 2009 Revised 15 September 2009 Accepted 9 October 2009
 42 Original article Validation of three professional devices measuring office blood pressure according to three different methods: the Omron BP, the Omron HBP T and the Pic Indolor Professional Roland
42 Original article Validation of three professional devices measuring office blood pressure according to three different methods: the Omron BP, the Omron HBP T and the Pic Indolor Professional Roland
DR JIRAR TOPOUCHIAN PROF PAROUNAK ZELVEIAN PROF ROLAND ASMAR. September 8 th, Principal Investigator and Study Chair:
 Page 1 of 10 Validation of the automatic blood pressure measurements device, the OMRON EVOLV (HEM- 7600 T-E) in Pregnancy according to the Modified European Society of Hypertension International Protocol
Page 1 of 10 Validation of the automatic blood pressure measurements device, the OMRON EVOLV (HEM- 7600 T-E) in Pregnancy according to the Modified European Society of Hypertension International Protocol
Data Collection Worksheet
 Data Collection Worksheet 1. Has a doctor or nurse ever said that you have: High blood pressure or hypertension? [ ] No [ ] Yes [ ] Not Sure 1.a. If Yes, then at what age were you first told this? Age
Data Collection Worksheet 1. Has a doctor or nurse ever said that you have: High blood pressure or hypertension? [ ] No [ ] Yes [ ] Not Sure 1.a. If Yes, then at what age were you first told this? Age
THE NEW ARMENIAN MEDICAL JOURNAL DISTRIBUTION, AWARENESS, TREATMENT, AND CONTROL OF ARTERIAL HYPERTENSION IN YEREVAN (ARMENIA)
 THE NEW ARMENIAN MEDICAL JOURNAL Vol.5 (2011), Nо 2, p.29-34 DISTRIBUTION, AWARENESS, TREATMENT, AND CONTROL OF ARTERIAL HYPERTENSION IN YEREVAN (ARMENIA) Zelveian P.H. 1, 2, Podosyan G.A. 2 1 Institute
THE NEW ARMENIAN MEDICAL JOURNAL Vol.5 (2011), Nо 2, p.29-34 DISTRIBUTION, AWARENESS, TREATMENT, AND CONTROL OF ARTERIAL HYPERTENSION IN YEREVAN (ARMENIA) Zelveian P.H. 1, 2, Podosyan G.A. 2 1 Institute
Managing Blood Pressure: It Takes a Team
 Managing Blood Pressure: It Takes a Team Module Two How to Take Blood Pressure October 2011 MODULE TWO: How to Take Blood Pressure Module Two: HOW TO TAKE BLOOD PRESSURE Objectives Demonstrate proper technique
Managing Blood Pressure: It Takes a Team Module Two How to Take Blood Pressure October 2011 MODULE TWO: How to Take Blood Pressure Module Two: HOW TO TAKE BLOOD PRESSURE Objectives Demonstrate proper technique
2. Measure a subject's blood pressure and heart rate both at rest and during exercise.
 Lab Activity 11 The Cardiovascular System Student Learning Objectives After completing this lab, you should be able to: 1. Define, explain and correctly use the key terms. 2. Measure a subject's blood
Lab Activity 11 The Cardiovascular System Student Learning Objectives After completing this lab, you should be able to: 1. Define, explain and correctly use the key terms. 2. Measure a subject's blood
Webinar Logistics. Now What Do I Need To Do? Blood Pressure in Kids January NC Department of Health and Human Services Division of Public Health
 NC Department of Health and Human Services Division of Public Health Now What Do I Need To Do? Blood Pressure in Kids January 2018 Gerri Mattson, MD, MSPH, FAAP Pediatric Medical Consultant Children and
NC Department of Health and Human Services Division of Public Health Now What Do I Need To Do? Blood Pressure in Kids January 2018 Gerri Mattson, MD, MSPH, FAAP Pediatric Medical Consultant Children and
Unreliable oscillometric blood pressure measurement: prevalence, repeatability and characteristics of the phenomenon
 (2009) 23, 794 800 & 2009 Macmillan Publishers Limited All rights reserved 0950-9240/09 $32.00 www.nature.com/jhh ORIGINAL ARTICLE Unreliable oscillometric blood pressure measurement: prevalence, repeatability
(2009) 23, 794 800 & 2009 Macmillan Publishers Limited All rights reserved 0950-9240/09 $32.00 www.nature.com/jhh ORIGINAL ARTICLE Unreliable oscillometric blood pressure measurement: prevalence, repeatability
PLANK 1 Direct Care Staff Trained in Accurate BP Measurement
 Direct Care Staff Trained in Accurate BP Measurement 1. 2. 3. 5. 22 to 26 cm Small adult (12X22 cm) 27 to 34 cm Adult (16X30 cm) 35 to 44 cm Large adult (16X36 cm) 45 to 52 cm Adult thigh (16X42 cm) widths
Direct Care Staff Trained in Accurate BP Measurement 1. 2. 3. 5. 22 to 26 cm Small adult (12X22 cm) 27 to 34 cm Adult (16X30 cm) 35 to 44 cm Large adult (16X36 cm) 45 to 52 cm Adult thigh (16X42 cm) widths
LAB: Blood Pressure Measurable Indicator of the Health of the Circulatory System!
 LAB: Blood Measurable Indicator of the Health of the Circulatory System! Lab Objectives. At the completion of the lab, you should be able to: measure pulse or heart rate (HR) and respiratory rate (RR);
LAB: Blood Measurable Indicator of the Health of the Circulatory System! Lab Objectives. At the completion of the lab, you should be able to: measure pulse or heart rate (HR) and respiratory rate (RR);
LEARNING OUTCOME The students will be able to elicit vital signs correctly on human volunteers/patients
 Vital signs (pulse, blood pressure, temperature, respiratory rate, pain) are physiological parameters that a healthcare professional requires when dealing with patients. Accurate measurement of vital signs
Vital signs (pulse, blood pressure, temperature, respiratory rate, pain) are physiological parameters that a healthcare professional requires when dealing with patients. Accurate measurement of vital signs
Received 10 April 2008 Revised 23 June 2008 Accepted 24 June 2008
 342 Original article Development of an accurate oscillometric blood pressure device for low resource settings Annemarie de Greeff, Hannah Nathan, Nina Stafford, Bing Liu and Andrew H. Shennan Objective
342 Original article Development of an accurate oscillometric blood pressure device for low resource settings Annemarie de Greeff, Hannah Nathan, Nina Stafford, Bing Liu and Andrew H. Shennan Objective
Received 24 February 2015 Revised 29 April 2015 Accepted 20 May 2015
 Original article 1 Clinical practice of ambulatory versus home blood pressure monitoring in hypertensive patients Jorge A. Paolasso, Florencia Crespo, Viviana Arias, Eduardo A. Moreyra, Ariel Volmaro,
Original article 1 Clinical practice of ambulatory versus home blood pressure monitoring in hypertensive patients Jorge A. Paolasso, Florencia Crespo, Viviana Arias, Eduardo A. Moreyra, Ariel Volmaro,
Home blood pressure measurement with oscillometric upper-arm devices
 REVIEW Home blood pressure measurement with oscillometric upper-arm devices R.L. Braam, Th. Thien *# Department of Internal Medicine, University Medical Centre St Radboud, PO Box 9101, 6500 HB Nijmegen,
REVIEW Home blood pressure measurement with oscillometric upper-arm devices R.L. Braam, Th. Thien *# Department of Internal Medicine, University Medical Centre St Radboud, PO Box 9101, 6500 HB Nijmegen,
Comparison of manual versus automated blood pressure measurement in intensive care unit, coronary care unit, and emergency room.
 Comparison of manual versus automated blood pressure measurement in intensive care unit, coronary care unit, and emergency room Abstract Ahmad Mirdamadi (1), Mostafa Etebari (2) Original Article BACKGROUND:
Comparison of manual versus automated blood pressure measurement in intensive care unit, coronary care unit, and emergency room Abstract Ahmad Mirdamadi (1), Mostafa Etebari (2) Original Article BACKGROUND:
Please do not hesitate to contact our dedicated service unit for more details regarding this program at
 The Blue Cross and Blue Shield Federal Employee Program (FEP) and the American Medical Association (AMA) have come together in a collaborative effort to provide physicians with resources designed to improve
The Blue Cross and Blue Shield Federal Employee Program (FEP) and the American Medical Association (AMA) have come together in a collaborative effort to provide physicians with resources designed to improve
Lecture #3 - Blood Pressure Recording Procedure. Equipment
 Lecture #3 - Blood Pressure Recording Procedure CKiD Blood Pressure Training Equipment Mabis Medic-Kit aneroid sphygmomanometer Mabis Medic-Kit assortment of cuff sizes Stethoscope with bell (pediatric
Lecture #3 - Blood Pressure Recording Procedure CKiD Blood Pressure Training Equipment Mabis Medic-Kit aneroid sphygmomanometer Mabis Medic-Kit assortment of cuff sizes Stethoscope with bell (pediatric
AFFORDABLE TECHNOLOGY
 World Health Organization AFFORDABLE TECHNOLOGY BLOOD PRESSURE MEASURING DEVICES FOR LOW RESOURCE SETTINGS CARDIOVASCULAR DISEASES Blood Pressure Measurement in Low Resource Settings Annex 1: Blood Pressure
World Health Organization AFFORDABLE TECHNOLOGY BLOOD PRESSURE MEASURING DEVICES FOR LOW RESOURCE SETTINGS CARDIOVASCULAR DISEASES Blood Pressure Measurement in Low Resource Settings Annex 1: Blood Pressure
greater than 90% of patients having blood pressure measured consistently according to the protocol.
 Clinical methods and pathophysiology 1 Reliability and validity of blood pressure measurement in the Secondary Prevention of Small Subcortical Strokes study Pablo E. Pérgola a, Carole L. White b, John
Clinical methods and pathophysiology 1 Reliability and validity of blood pressure measurement in the Secondary Prevention of Small Subcortical Strokes study Pablo E. Pérgola a, Carole L. White b, John
Methods DEVICES AND TECHNOLOGY
 DEVICES AND TECHNOLOGY Validation of the Omron HEM-907 device for blood pressure measurement Mohamed A. El Assaad, Jirar A. Topouchian, Bernadette M. Darné and Roland G. Asmar Background The aim of this
DEVICES AND TECHNOLOGY Validation of the Omron HEM-907 device for blood pressure measurement Mohamed A. El Assaad, Jirar A. Topouchian, Bernadette M. Darné and Roland G. Asmar Background The aim of this
Home Blood Pressure Log
 Home Blood Pressure Log 2 You or your health care professional may want to monitor your blood pressure at home twice a day for a week or more before appointments to accurately confirm your average blood
Home Blood Pressure Log 2 You or your health care professional may want to monitor your blood pressure at home twice a day for a week or more before appointments to accurately confirm your average blood
The measurement of blood pressure and hypertension. Handout Fenyvesi Tamás III.Department of Medicine
 The measurement of blood pressure and hypertension Handout Fenyvesi Tamás III.Department of Medicine 1 2 History of the blood pressure measurement direct Stephen HALES 1726 horse carotid indirect Riva-Rocci
The measurement of blood pressure and hypertension Handout Fenyvesi Tamás III.Department of Medicine 1 2 History of the blood pressure measurement direct Stephen HALES 1726 horse carotid indirect Riva-Rocci
Comparison of two oscillometric blood pressure monitors in subjects with atrial fibrillation
 ORIGINAL RESEARCH Comparison of two oscillometric blood pressure monitors in subjects with atrial fibrillation Tyler S Lamb BSc Amar Thakrar MD, FRCPC Mahua Ghosh MD, PhD Merne P Wilson MSc Thomas W Wilson
ORIGINAL RESEARCH Comparison of two oscillometric blood pressure monitors in subjects with atrial fibrillation Tyler S Lamb BSc Amar Thakrar MD, FRCPC Mahua Ghosh MD, PhD Merne P Wilson MSc Thomas W Wilson
Blood Pressure Competency Training
 Blood Pressure Competency Training WORKBOOK Table of Contents 3..... Introduction 4..... Background 6..... Equipment Accurate blood pressure What impacts a patient s blood pressure Strategies for proper
Blood Pressure Competency Training WORKBOOK Table of Contents 3..... Introduction 4..... Background 6..... Equipment Accurate blood pressure What impacts a patient s blood pressure Strategies for proper
Ambulatory Services Orientation & Skill Review Skill Performance Checklist: Vital Signs. Name: Date:
 Evaluation Levels Behavior Level 3 Met Performed all skills competently. No behaviors omitted. Level 2 Satisfactory Omitted no more than three (3) non-critical behaviors. Level 1 Unsatisfactory Omitted
Evaluation Levels Behavior Level 3 Met Performed all skills competently. No behaviors omitted. Level 2 Satisfactory Omitted no more than three (3) non-critical behaviors. Level 1 Unsatisfactory Omitted
9/27/2016. Adherence and Monitoring of Hypertensive Patients. Conflicts of Interest. Brought to you though a partnership:
 Adherence and Monitoring of Hypertensive Patients. Conflicts of Interest Speaker has no conflicts of interest to disclose I have had no financial relationship over the past 12 months with any commercial
Adherence and Monitoring of Hypertensive Patients. Conflicts of Interest Speaker has no conflicts of interest to disclose I have had no financial relationship over the past 12 months with any commercial
Importance Of Taking Manual Blood Pressure In Both Arms
 Importance Of Taking Manual Blood Pressure In Both Arms Its importance to health is now well-recognised, in that high blood pressure can lead to Have a look at our slide show on how to take a blood pressure
Importance Of Taking Manual Blood Pressure In Both Arms Its importance to health is now well-recognised, in that high blood pressure can lead to Have a look at our slide show on how to take a blood pressure
Vital Signs. Vital Signs. Pulse. Temperature. Respiration. Blood Pressure
 Vital Signs Jarvis, Chapter 9 Vital Signs Classic Vital Signs TPR/BP Temperature Pulse Respirations Blood Pressure Additional Vital Signs Height Weight BMI (Kg/m2) or (702Xlbs/in2) Supine, orthostatic
Vital Signs Jarvis, Chapter 9 Vital Signs Classic Vital Signs TPR/BP Temperature Pulse Respirations Blood Pressure Additional Vital Signs Height Weight BMI (Kg/m2) or (702Xlbs/in2) Supine, orthostatic
!"#$ Blood Pressure Monitor. Instruction manual page 1 Gebrauchsanweisung Seite 17 Gebruiksaanwijzing pagina 33
 !"#$ Blood Pressure Monitor Instruction manual page 1 Gebrauchsanweisung Seite 17 Gebruiksaanwijzing pagina 33 Mode d emploi page 49 Manuale de instructone pagina 65 Manual de instrucciones pagina 81 Introduction
!"#$ Blood Pressure Monitor Instruction manual page 1 Gebrauchsanweisung Seite 17 Gebruiksaanwijzing pagina 33 Mode d emploi page 49 Manuale de instructone pagina 65 Manual de instrucciones pagina 81 Introduction
Section 03: Pre Exercise Evaluations and Risk Factor Assessment
 Section 03: Pre Exercise Evaluations and Risk Factor Assessment ACSM Guidelines: Chapter 3 Pre Exercise Evaluations ACSM Manual: Chapter 3 Risk Factor Assessments HPHE 4450 Dr. Cheatham Purpose The extent
Section 03: Pre Exercise Evaluations and Risk Factor Assessment ACSM Guidelines: Chapter 3 Pre Exercise Evaluations ACSM Manual: Chapter 3 Risk Factor Assessments HPHE 4450 Dr. Cheatham Purpose The extent
Validation study of the Dinamap ProCare 200 upper arm blood pressure monitor in children and adolescents
 Original article http://dx.doi.org/10.3345/kjp.2011.54.11.463 Korean J Pediatr 2011;54(11):463-469 Validation study of the Dinamap ProCare 200 upper arm blood pressure monitor in children and adolescents
Original article http://dx.doi.org/10.3345/kjp.2011.54.11.463 Korean J Pediatr 2011;54(11):463-469 Validation study of the Dinamap ProCare 200 upper arm blood pressure monitor in children and adolescents
Copyright Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. Unauthorized reproduction of this article is prohibited.
 Devices and technology 16 Validation of two automatic devices for self-measurement of blood pressure according to the International Protocol of the European Society of Hypertension: the Omron M6 (HEM-71-E)
Devices and technology 16 Validation of two automatic devices for self-measurement of blood pressure according to the International Protocol of the European Society of Hypertension: the Omron M6 (HEM-71-E)
Evaluation of the Accutracker I1 noninvasive ambulatory blood pressure recorder according to the AAMI Standard
 Evaluation of the Accutracker I1 noninvasive ambulatory blood pressure recorder according to the AAMI Standard EOIN O'BRIENt, NEIL ATKINS, JAMES SHERIDAN, COLM KILLEEN, RICHARD COSTELLOE, SHANE LYDON and
Evaluation of the Accutracker I1 noninvasive ambulatory blood pressure recorder according to the AAMI Standard EOIN O'BRIENt, NEIL ATKINS, JAMES SHERIDAN, COLM KILLEEN, RICHARD COSTELLOE, SHANE LYDON and
Copyright Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. Unauthorized reproduction of this article is prohibited.
 Devices and technology 57 Comparison of wrist-type and arm-type 24-h blood pressure monitoring devices for ambulatory use Takahiro Komori a, Kazuo Eguchi a, Satoshi Hoshide a, Bryan Williams b and Kazuomi
Devices and technology 57 Comparison of wrist-type and arm-type 24-h blood pressure monitoring devices for ambulatory use Takahiro Komori a, Kazuo Eguchi a, Satoshi Hoshide a, Bryan Williams b and Kazuomi
BLOOD PRESSURE ASSESSMENT
 BLOOD PRESSURE ASSESSMENT Course Principles of Health Science Unit X Vital Signs Course Health Science Unit VI CPR / AED & First Aid Essential Question How do health care skills help to promote health
BLOOD PRESSURE ASSESSMENT Course Principles of Health Science Unit X Vital Signs Course Health Science Unit VI CPR / AED & First Aid Essential Question How do health care skills help to promote health
a Medical Physics Department, Guy s & St Thomas NHS Foundation Trust and b King s College School of Medicine, St Thomas Campus, London, UK
 Devices and technology 27 Validation of the Omron 705IT (HEM-759-E) oscillometric blood pressure monitoring device according to the British Hypertension Society protocol Andrew Coleman a, Paul Freeman
Devices and technology 27 Validation of the Omron 705IT (HEM-759-E) oscillometric blood pressure monitoring device according to the British Hypertension Society protocol Andrew Coleman a, Paul Freeman
Biomedical Instrumentation E. Blood Pressure
 Biomedical Instrumentation E. Blood Pressure Dr Gari Clifford Adapted from slides by Prof. Lionel Tarassenko Blood pressure Blood is pumped around the body by the heart. It makes its way around the body
Biomedical Instrumentation E. Blood Pressure Dr Gari Clifford Adapted from slides by Prof. Lionel Tarassenko Blood pressure Blood is pumped around the body by the heart. It makes its way around the body
PART I: HEART ANATOMY
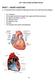 Lab 7: Heart Sounds and Blood Pressure PART I: HEART ANATOMY a) You should be able to identify the following structures on an adult human heart diagram. the 4 chambers the bicuspid (mitral) and tricuspid
Lab 7: Heart Sounds and Blood Pressure PART I: HEART ANATOMY a) You should be able to identify the following structures on an adult human heart diagram. the 4 chambers the bicuspid (mitral) and tricuspid
& Wilkins. a Division of Cardiology, Schulich Heart Centre, b Institute for Clinical and
 Original article 333 Optimum frequency of office blood pressure measurement using an automated sphygmomanometer Martin G. Myers a, Miguel Valdivieso a and Alexander Kiss b,c Objective To determine the
Original article 333 Optimum frequency of office blood pressure measurement using an automated sphygmomanometer Martin G. Myers a, Miguel Valdivieso a and Alexander Kiss b,c Objective To determine the
Clinical Research Coordinator Skills Program
 Clinical Research Coordinator Skills Program Vital Signs This Skill Requires Provider direction Standard Precautions Using purell before and after contact with the patient or the patient s environment
Clinical Research Coordinator Skills Program Vital Signs This Skill Requires Provider direction Standard Precautions Using purell before and after contact with the patient or the patient s environment
Does masked hypertension exist in healthy volunteers and apparently well-controlled hypertensive patients?
 O R I G I N A L A R T I C L E Does masked hypertension exist in healthy volunteers and apparently well-controlled hypertensive patients? I. Aksoy, J. Deinum, J.W.M. Lenders, Th. Thien *# Department of
O R I G I N A L A R T I C L E Does masked hypertension exist in healthy volunteers and apparently well-controlled hypertensive patients? I. Aksoy, J. Deinum, J.W.M. Lenders, Th. Thien *# Department of
STUDIES INVOLVING THE NON-INVASIVE MEASUREMENT OF BLOOD PRESSURE IN THE ARM
 STUDIES INVOLVING THE NON-INVASIVE MEASUREMENT OF BLOOD PRESSURE IN THE ARM 1. SCOPE Blood pressure is a vital sign that is used in many clinical situations, and assesses the pressure of blood as it flows
STUDIES INVOLVING THE NON-INVASIVE MEASUREMENT OF BLOOD PRESSURE IN THE ARM 1. SCOPE Blood pressure is a vital sign that is used in many clinical situations, and assesses the pressure of blood as it flows
Physiology of the Circulatory System modified from
 Physiology of the Circulatory System modified from http://www.ekcsk12.org/science/aplabreview/aplab10.htm Introduction The circulatory system functions to deliver oxygen and nutrients to tissues for growth
Physiology of the Circulatory System modified from http://www.ekcsk12.org/science/aplabreview/aplab10.htm Introduction The circulatory system functions to deliver oxygen and nutrients to tissues for growth
Chapter 29 1/8/2018. Vital Signs. Measuring and Reporting Vital Signs. Key Terms
 Chapter 29 Vital Signs Key Terms Blood pressure Body temperature Diastolic pressure Hypertension Hypotension Pulse Pulse rate Respiration Sphygmomanometer Stethoscope Systolic pressure Vital signs Measuring
Chapter 29 Vital Signs Key Terms Blood pressure Body temperature Diastolic pressure Hypertension Hypotension Pulse Pulse rate Respiration Sphygmomanometer Stethoscope Systolic pressure Vital signs Measuring
Copyright: DOI link to article: Date deposited: This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License
 Pan F, Zheng DC, He PY, Murray A. Does the Position or Contact Pressure of the Stethoscope Make Any Difference to Clinical Blood Pressure Measurements: An Observational Study. Medicine 214, 93(29). Copyright:
Pan F, Zheng DC, He PY, Murray A. Does the Position or Contact Pressure of the Stethoscope Make Any Difference to Clinical Blood Pressure Measurements: An Observational Study. Medicine 214, 93(29). Copyright:
Techniques of Vital Signs. John Gazewood, MD, MSPH Department of Family Medicine
 Techniques of Vital Signs John Gazewood, MD, MSPH Department of Family Medicine Objectives Define normal in several ways. Describe correct technique of measuring vital signs. Describe correct technique
Techniques of Vital Signs John Gazewood, MD, MSPH Department of Family Medicine Objectives Define normal in several ways. Describe correct technique of measuring vital signs. Describe correct technique
Experiment HC-1: Blood Pressure, Peripheral Circulation, and Body Position
 Experiment HC-1: Blood Pressure, Peripheral Circulation, and Body Position Exercise 1: Blood Pressures from the Left Arm Aim: To determine the systolic and diastolic blood pressures in a reclining subject,
Experiment HC-1: Blood Pressure, Peripheral Circulation, and Body Position Exercise 1: Blood Pressures from the Left Arm Aim: To determine the systolic and diastolic blood pressures in a reclining subject,
HOW CONSISTENT ARE THE BLOOD PRESSURE AND PULSE RATE MEASUREMENTS OF THE ELECTRONIC BP APPARATUS AND THE MANUAL SPHYGMOMANOMETER
 HOW CONSISTENT ARE THE BLOOD PRESSURE AND PULSE RATE MEASUREMENTS OF THE ELECTRONIC BP APPARATUS AND THE MANUAL SPHYGMOMANOMETER Naser KA. Teaching Hospital Peradeniya, Peradeniya, Sri Lanka Zawahir S
HOW CONSISTENT ARE THE BLOOD PRESSURE AND PULSE RATE MEASUREMENTS OF THE ELECTRONIC BP APPARATUS AND THE MANUAL SPHYGMOMANOMETER Naser KA. Teaching Hospital Peradeniya, Peradeniya, Sri Lanka Zawahir S
In clinical practice, blood pressure (BP) treatment
 Original Paper Does Hidden Undercuffing Occur Among Obese Patients? Effect of Arm Sizes and Other Predictors of the Difference Between Wrist and Upper Arm Blood Pressures Hardik Doshi, MD; Alan B. Weder,
Original Paper Does Hidden Undercuffing Occur Among Obese Patients? Effect of Arm Sizes and Other Predictors of the Difference Between Wrist and Upper Arm Blood Pressures Hardik Doshi, MD; Alan B. Weder,
MANUAL BLOOD PRESSURE MONITOR BPM 168B Contents Blood Pressure Monitor Intended Use What is blood pressure?
 MANUAL BLOOD PRESSURE MONITOR BPM 168B Contents 01... Blood Pressure Monitor Intended Use 02... 1. What is blood pressure? 02... 2. Why is it useful measure blood pressure at home?... A. WHO blood pressure
MANUAL BLOOD PRESSURE MONITOR BPM 168B Contents 01... Blood Pressure Monitor Intended Use 02... 1. What is blood pressure? 02... 2. Why is it useful measure blood pressure at home?... A. WHO blood pressure
Blood Pressure Measurement During Pregnancy: Auscultatory Versus Oscillatory Methods
 CLINICAL STUDIES Blood Pressure Measurement During Pregnancy: Auscultatory Versus Oscillatory Methods Linda A. Green, RN, MS, Robin D. Froman, RN, PhD, FAAN Objective: To determine the equivalence of auscultatory
CLINICAL STUDIES Blood Pressure Measurement During Pregnancy: Auscultatory Versus Oscillatory Methods Linda A. Green, RN, MS, Robin D. Froman, RN, PhD, FAAN Objective: To determine the equivalence of auscultatory
SECTION 16: BLOOD PRESSURE MEASUREMENT
 CHRONIC KIDNEY DISEASE IN CHILDREN COHORT STUDY SECTION 16: BLOOD PRESSURE MEASUREMENT 16.1 OVERVIEW OF BLOOD PRESSURE MEASUREMENT This section describes the procedures that are to be performed to obtain
CHRONIC KIDNEY DISEASE IN CHILDREN COHORT STUDY SECTION 16: BLOOD PRESSURE MEASUREMENT 16.1 OVERVIEW OF BLOOD PRESSURE MEASUREMENT This section describes the procedures that are to be performed to obtain
science-u.org What affects blood Blood Pressure Directions You Will Need BEST FOR GRADES 5-8 ESTIMATED TIME Minutes
 What affects blood pressure? BEST FOR GRADES 5-8 ESTIMATED TIME 25-60 Minutes You Will Need Sphygmomanometer (blood pressure cuff) Stethoscope Blood pressure cuffs and stethoscopes can be found online
What affects blood pressure? BEST FOR GRADES 5-8 ESTIMATED TIME 25-60 Minutes You Will Need Sphygmomanometer (blood pressure cuff) Stethoscope Blood pressure cuffs and stethoscopes can be found online
Clinical Evaluation of an Oscillometric NIBP Technology During Hemodialysis According to the British Hypertension Society Protocol
 Clinical Evaluation of an Oscillometric NIBP Technology During Hemodialysis According to the British Hypertension Society Protocol Abstract Objectives Existing concerns over the accuracy of automated blood
Clinical Evaluation of an Oscillometric NIBP Technology During Hemodialysis According to the British Hypertension Society Protocol Abstract Objectives Existing concerns over the accuracy of automated blood
Protocol. Automated Ambulatory Blood Pressure Monitoring for the Diagnosis of Hypertension in Patients with Elevated Office Blood Pressure
 Automated Ambulatory Blood Monitoring for the Diagnosis of Hypertension in Patients with Elevated Office Blood (10102) Medical Benefit Effective Date: 07/01/14 Next Review Date: 03/15 Preauthorization
Automated Ambulatory Blood Monitoring for the Diagnosis of Hypertension in Patients with Elevated Office Blood (10102) Medical Benefit Effective Date: 07/01/14 Next Review Date: 03/15 Preauthorization
PATIENT INFORMATION. Medicine To Treat: H ypertension. Patient Awareness and Self-Care
 PATIENT INFORMATION Medicine To Treat: H ypertension Patient Awareness and Self-Care WHAT IS BLOOD PRESSURE AND HIGH BLOOD PRESSURE? Blood pressure is the force generated as your heart pumps blood and
PATIENT INFORMATION Medicine To Treat: H ypertension Patient Awareness and Self-Care WHAT IS BLOOD PRESSURE AND HIGH BLOOD PRESSURE? Blood pressure is the force generated as your heart pumps blood and
Copyright Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. Unauthorized reproduction of this article is prohibited.
 Devices and technology 223 Validation of the A&D UA-705 device for self-measurement of blood pressure according to the British Hypertension Society protocol Paolo Verdecchia, Fabio Angeli, Roberto Gattobigio,
Devices and technology 223 Validation of the A&D UA-705 device for self-measurement of blood pressure according to the British Hypertension Society protocol Paolo Verdecchia, Fabio Angeli, Roberto Gattobigio,
Understanding Blood Pressure. A handy guide to understanding what blood pressure is, how it affects you, and how to measure it at home
 Understanding Blood Pressure A handy guide to understanding what blood pressure is, how it affects you, and how to measure it at home Acknowledgments page Special thanks to the following individuals and
Understanding Blood Pressure A handy guide to understanding what blood pressure is, how it affects you, and how to measure it at home Acknowledgments page Special thanks to the following individuals and
SELF-MEASURED BLOOD PRESSURE MONITORING PROGRAM: ENGAGING PATIENTS IN SELF-MEASUREMENT
 SELF-MEASURED BLOOD PRESSURE MONITORING PROGRAM: ENGAGING PATIENTS IN SELF-MEASUREMENT Self-measured blood pressure monitoring program: Engaging patients in self-measurement This program is designed for
SELF-MEASURED BLOOD PRESSURE MONITORING PROGRAM: ENGAGING PATIENTS IN SELF-MEASUREMENT Self-measured blood pressure monitoring program: Engaging patients in self-measurement This program is designed for
Chapter 15: Measuring Height, Weight, and Vital Signs. Copyright 2012 Wolters Kluwer Health Lippincott Williams & Wilkins
 Chapter 15: Measuring Height, Weight, and Vital Signs Height and Weight Weight Baseline measurement at patient s first visit Measured in kg or lbs Common types of scales Balance beam Dial Digital Height
Chapter 15: Measuring Height, Weight, and Vital Signs Height and Weight Weight Baseline measurement at patient s first visit Measured in kg or lbs Common types of scales Balance beam Dial Digital Height
European Society of Hypertension Practice Guidelines for home blood pressure monitoring
 European Society of Hypertension Practice Guidelines for home blood pressure monitoring G Parati 1, GS Stergiou 2, R Asmar 3, G Bilo 1, P de Leeuw 4, Y Imai 5, K Kario 6, E Lurbe 7, A Manolis 8, T Mengden
European Society of Hypertension Practice Guidelines for home blood pressure monitoring G Parati 1, GS Stergiou 2, R Asmar 3, G Bilo 1, P de Leeuw 4, Y Imai 5, K Kario 6, E Lurbe 7, A Manolis 8, T Mengden
Lab #10 Physiology of the Circulatory System
 Lab #10 Physiology of the Circulatory System Introduction The circulatory system functions to deliver oxygen an nutrients to tissues for growth and metabolism, and to remove metabolic wastes. The heart
Lab #10 Physiology of the Circulatory System Introduction The circulatory system functions to deliver oxygen an nutrients to tissues for growth and metabolism, and to remove metabolic wastes. The heart
Céline Guggiari a, Christophe Büla a, Katia Iglesias b and Bernard Waeber b,c
 Published in Blood Pressure Monitoring 19, issue 11, 32-37, 2014 which should be used for any reference to this work 1 Measurement with an automated oscillometric wrist device with position sensor leads
Published in Blood Pressure Monitoring 19, issue 11, 32-37, 2014 which should be used for any reference to this work 1 Measurement with an automated oscillometric wrist device with position sensor leads
Arm position and blood pressure: a risk factor for hypertension?
 (3) 17, 389 395 & 3 Nature Publishing Group All rights reserved 09-9240/03 $25.00 www.nature.com/jhh ORIGINAL ARTICLE Arm position and blood pressure: a risk factor for hypertension? A Mourad, S Carney,
(3) 17, 389 395 & 3 Nature Publishing Group All rights reserved 09-9240/03 $25.00 www.nature.com/jhh ORIGINAL ARTICLE Arm position and blood pressure: a risk factor for hypertension? A Mourad, S Carney,
High Blood Pressure Blood Pressure Monitoring at Home -- F...
 Return to Web version High Blood Pressure Blood Pressure Monitoring at Home Why should I measure my blood pressure at home and keep a record of it? Measuring your blood pressure at home and keeping a record
Return to Web version High Blood Pressure Blood Pressure Monitoring at Home Why should I measure my blood pressure at home and keep a record of it? Measuring your blood pressure at home and keeping a record
Effect of respiratory pattern on automated clinical blood pressure measurement: an observational study with normotensive subjects
 Herakova et al. Clinical Hypertension (2017) 23:15 DOI 10.1186/s40885-017-0071-3 RESEARCH Effect of respiratory pattern on automated clinical blood pressure measurement: an observational study with normotensive
Herakova et al. Clinical Hypertension (2017) 23:15 DOI 10.1186/s40885-017-0071-3 RESEARCH Effect of respiratory pattern on automated clinical blood pressure measurement: an observational study with normotensive
Assessing Blood Pressure Accuracy of an Aneroid Sphygmomanometer in a National Survey Environment
 original contributions nature publishing group Assessing Blood Pressure Accuracy of an Aneroid Sphygmomanometer in a National Survey Environment Yechiam Ostchega 1, Ronald J. Prineas 2, Tatiana Nwankwo
original contributions nature publishing group Assessing Blood Pressure Accuracy of an Aneroid Sphygmomanometer in a National Survey Environment Yechiam Ostchega 1, Ronald J. Prineas 2, Tatiana Nwankwo
M1 Classic. Digital Blood Pressure Monitor. Instruction manual page 1 SYS. mmhg DIA. mmhg. PULSE/min
 1 Classic Digital Blood Pressure onitor Instruction manual page 1 1 Classic English Introduction The ORON 1 Classic measures your blood pressure and pulse simply and quickly from the arm, without the use
1 Classic Digital Blood Pressure onitor Instruction manual page 1 1 Classic English Introduction The ORON 1 Classic measures your blood pressure and pulse simply and quickly from the arm, without the use
MX3 Plus English. Introduction. Table of contents. 1 How to obtain meaningful blood pressure readings
 X3 Plus English X3 Plus Introduction The ORON X3 Plus measures your blood pressure and pulse simply and quickly from the arm, without the use of an inflation bulb or stethoscope. The measurement values
X3 Plus English X3 Plus Introduction The ORON X3 Plus measures your blood pressure and pulse simply and quickly from the arm, without the use of an inflation bulb or stethoscope. The measurement values
Measuring body temperature, blood pressure, pulse, respiratory rate and oxygen saturation
 Vital Signs Measuring body temperature, blood pressure, pulse, respiratory rate and oxygen saturation Aims To ensure that students are able to demonstrate the safe and correct technique for setting up
Vital Signs Measuring body temperature, blood pressure, pulse, respiratory rate and oxygen saturation Aims To ensure that students are able to demonstrate the safe and correct technique for setting up
Continuous Monitoring of Blood Pressure Based on Heart Pulse Analysis
 Journal of Physics: Conference Series PAPER OPEN ACCESS Continuous Monitoring of Blood Pressure Based on Heart Pulse Analysis To cite this article: Valerie Tan et al 2018 J. Phys.: Conf. Ser. 1049 012062
Journal of Physics: Conference Series PAPER OPEN ACCESS Continuous Monitoring of Blood Pressure Based on Heart Pulse Analysis To cite this article: Valerie Tan et al 2018 J. Phys.: Conf. Ser. 1049 012062
Blood Pressure Protocol Training
 Blood Pressure Protocol Training May 31, 2018 Pat Spier, RN-BC, PCMH-CCE Barb Rice, RN-BC BCBS of North Dakota Fargo, ND 2013 Template and icons provided by The Advisory Board Company. Hypertension Education
Blood Pressure Protocol Training May 31, 2018 Pat Spier, RN-BC, PCMH-CCE Barb Rice, RN-BC BCBS of North Dakota Fargo, ND 2013 Template and icons provided by The Advisory Board Company. Hypertension Education
UNDERSTANDING BLOOD PRESSURE
 UNDERSTANDING BLOOD PRESSURE A HANDY GUIDE TO UNDERSTANDING WHAT BLOOD PRESSURE IS, HOW IT AFFECTS YOU, AND HOW TO MEASURE IT AT HOME Authored by the Texas Department of State Health Services Health Promotion
UNDERSTANDING BLOOD PRESSURE A HANDY GUIDE TO UNDERSTANDING WHAT BLOOD PRESSURE IS, HOW IT AFFECTS YOU, AND HOW TO MEASURE IT AT HOME Authored by the Texas Department of State Health Services Health Promotion
LAB 9: Metabolic Rates
 LAB 9: Metabolic Rates Introduction: The cardiovascular (circulatory) system functions to deliver oxygen and nutrients to tissues for growth and metabolism, and to remove metabolic wastes. The heart pumps
LAB 9: Metabolic Rates Introduction: The cardiovascular (circulatory) system functions to deliver oxygen and nutrients to tissues for growth and metabolism, and to remove metabolic wastes. The heart pumps
Ambulatory BP Monitoring: Getting the Diagnosis of Hypertension Right. Anthony J. Viera, MD, MPH, FAHA Professor and Chair
 Ambulatory BP Monitoring: Getting the Diagnosis of Hypertension Right Anthony J. Viera, MD, MPH, FAHA Professor and Chair Objectives Review limitations of office BP in making a correct diagnosis of hypertension
Ambulatory BP Monitoring: Getting the Diagnosis of Hypertension Right Anthony J. Viera, MD, MPH, FAHA Professor and Chair Objectives Review limitations of office BP in making a correct diagnosis of hypertension
The introduction of oscillometric automated blood pressure
 Atrial Fibrillation Impact of Atrial Fibrillation on the Accuracy of Oscillometric Blood Pressure Monitoring Nikolaos Pagonas,* Sven Schmidt,* Jörg Eysel, Friederike Compton, Clemens Hoffmann, Felix Seibert,
Atrial Fibrillation Impact of Atrial Fibrillation on the Accuracy of Oscillometric Blood Pressure Monitoring Nikolaos Pagonas,* Sven Schmidt,* Jörg Eysel, Friederike Compton, Clemens Hoffmann, Felix Seibert,
1 Department of Medical Physics, Royal Infirmary of Edinburgh, 2 Department of. Received 11 June 2004 Accepted 7 September 2004
 Devices and technology 1 Do SpaceLabs ambulatory non-invasive blood pressure recorders measure blood pressure consistently over several years use? John N. Amoore 1, David Dewar 2, Kathleen Gough 3 and
Devices and technology 1 Do SpaceLabs ambulatory non-invasive blood pressure recorders measure blood pressure consistently over several years use? John N. Amoore 1, David Dewar 2, Kathleen Gough 3 and
A CROSS SECTIONAL STUDY OF RELATIONSHIP OF OBESITY INDICES WITH BLOOD PRESSURE AND BLOOD GLUCOSE LEVEL IN YOUNG ADULT MEDICAL STUDENTS
 Original Article A CROSS SECTIONAL STUDY OF RELATIONSHIP OF OBESITY INDICES WITH BLOOD PRESSURE AND BLOOD GLUCOSE LEVEL IN YOUNG ADULT MEDICAL STUDENTS Renu Lohitashwa, Parwati Patil ABSTRACT Overweight
Original Article A CROSS SECTIONAL STUDY OF RELATIONSHIP OF OBESITY INDICES WITH BLOOD PRESSURE AND BLOOD GLUCOSE LEVEL IN YOUNG ADULT MEDICAL STUDENTS Renu Lohitashwa, Parwati Patil ABSTRACT Overweight
Protocol 4: Measuring Blood Pressure
 Zool 430L Protocols Page 8 of 12 Protocol 4: Measuring Blood Pressure 4.1 Via Auscultation (listening through stethoscope) The estimate of blood pressure is obtained by cutting off blood flow with a known
Zool 430L Protocols Page 8 of 12 Protocol 4: Measuring Blood Pressure 4.1 Via Auscultation (listening through stethoscope) The estimate of blood pressure is obtained by cutting off blood flow with a known
GETTING THE NUMBERS RIGHT: ACCURATE MEASUREMENT OF BLOOD PRESSURE
 GETTING THE NUMBERS RIGHT: ACCURATE MEASUREMENT OF BLOOD PRESSURE Pamela B. Morris, MD, FACC, FAHA, FASPC, FNLA Professor Medicine and Cardiovascular Diseases Director, Seinsheimer Cardiovascular Health
GETTING THE NUMBERS RIGHT: ACCURATE MEASUREMENT OF BLOOD PRESSURE Pamela B. Morris, MD, FACC, FAHA, FASPC, FNLA Professor Medicine and Cardiovascular Diseases Director, Seinsheimer Cardiovascular Health
OHTAC Recommendation: Twenty-Four-Hour Ambulatory Blood Pressure Monitoring in Hypertension. Ontario Health Technology Advisory Committee
 OHTAC Recommendation: Twenty-Four-Hour Ambulatory Blood Pressure Monitoring in Hypertension Ontario Health Technology Advisory Committee May 2012 Background Hypertension in Canada Hypertension occurs when
OHTAC Recommendation: Twenty-Four-Hour Ambulatory Blood Pressure Monitoring in Hypertension Ontario Health Technology Advisory Committee May 2012 Background Hypertension in Canada Hypertension occurs when
Recommendations for Blood Pressure Measurement in Humans and Experimental Ani...
 Recommendations for Blood Pressure Measurement in Humans and Experimental Ani... Página 1 de 41 Published online before print December 20, 2004, doi:10.1161/01.hyp.0000150859.47929.8e (Hypertension. 2005;45:142.)
Recommendations for Blood Pressure Measurement in Humans and Experimental Ani... Página 1 de 41 Published online before print December 20, 2004, doi:10.1161/01.hyp.0000150859.47929.8e (Hypertension. 2005;45:142.)
Clinical research. Introduction. * Corresponding author. Tel: þ ; fax: þ address:
 European Heart Journal (2005) 26, 2026 2031 doi:10.1093/eurheartj/ehi330 Clinical research Use of 2003 European Society of Hypertension European Society of Cardiology guidelines for predicting stroke using
European Heart Journal (2005) 26, 2026 2031 doi:10.1093/eurheartj/ehi330 Clinical research Use of 2003 European Society of Hypertension European Society of Cardiology guidelines for predicting stroke using
Comparison of the Microlife A2 Basic (BP3GQ1-3P) with the Microlife BP3BT0-A and Microlife BP A100 Plus
 Comparison of the Microlife A2 Basic (BP3GQ1-3P) with the Microlife BP3BT0-A and Microlife BP A100 Plus Devices Microlife A2 Basic (BP3GQ1-3P) 9 BP3BT0-A 9 Microlife BP A100 Plus 9 Image 10 10 10 Validation
Comparison of the Microlife A2 Basic (BP3GQ1-3P) with the Microlife BP3BT0-A and Microlife BP A100 Plus Devices Microlife A2 Basic (BP3GQ1-3P) 9 BP3BT0-A 9 Microlife BP A100 Plus 9 Image 10 10 10 Validation
CAMOSUN COLLEGE BIOLOGY 144 (2010) LABS
 LAB 8: CARDIOVASCULAR PHYSIOLOGY PART 1. HEART SOUNDS AND PULSE DETERMINATIONS Introduction Two distinct sounds can be heard during each cardiac cycle. These sounds are commonly described as lub and dup
LAB 8: CARDIOVASCULAR PHYSIOLOGY PART 1. HEART SOUNDS AND PULSE DETERMINATIONS Introduction Two distinct sounds can be heard during each cardiac cycle. These sounds are commonly described as lub and dup
Self Measurement of Blood Pressure for Control of Blood Pressure Levels and Adherence to Treatment
 Self Measurement of Blood Pressure for Control of Blood Pressure Levels and Adherence to Treatment Weimar Kunz Sebba Barroso Souza, Paulo César Brandão Veiga Jardim, Ludmila Porto Brito, Fabrício Alves
Self Measurement of Blood Pressure for Control of Blood Pressure Levels and Adherence to Treatment Weimar Kunz Sebba Barroso Souza, Paulo César Brandão Veiga Jardim, Ludmila Porto Brito, Fabrício Alves
DEVICES AND TECHNOLOGY
 DEVICES AND TECHNOLOGY Validation of a new algorithm for the BPM-100 electronic oscillometric office blood pressure monitor James M. Wright ab, Gurdial S. Mattu a, Thomas L. Perry Jr ab, Mark E. Gelfer
DEVICES AND TECHNOLOGY Validation of a new algorithm for the BPM-100 electronic oscillometric office blood pressure monitor James M. Wright ab, Gurdial S. Mattu a, Thomas L. Perry Jr ab, Mark E. Gelfer
AN INTRODUCTION TO DOPPLER. Sarah Gardner, Clinical lead, Tissue viability service. Oxford Health NHS Foundation Trust.
 AN INTRODUCTION TO DOPPLER Sarah Gardner, Clinical lead, Tissue viability service. Oxford Health NHS Foundation Trust. THE DOPPLER EFFECT The Doppler Principle was described by Physicist and mathematician
AN INTRODUCTION TO DOPPLER Sarah Gardner, Clinical lead, Tissue viability service. Oxford Health NHS Foundation Trust. THE DOPPLER EFFECT The Doppler Principle was described by Physicist and mathematician
Diagnostic accuracy of a home blood pressure monitor to detect atrial fibrillation
 (2009), 1 5 & 2009 Macmillan Publishers Limited All rights reserved 0950-9240/09 $32.00 www.nature.com/jhh ORIGINAL ARTICLE Diagnostic accuracy of a home blood pressure monitor to detect atrial fibrillation
(2009), 1 5 & 2009 Macmillan Publishers Limited All rights reserved 0950-9240/09 $32.00 www.nature.com/jhh ORIGINAL ARTICLE Diagnostic accuracy of a home blood pressure monitor to detect atrial fibrillation
Effect of respiration on Korotkoff sounds and oscillometric cuff pressure pulses during blood pressure measurement
 DOI 10.1007/s11517-014-1150-1 Original Article Effect of respiration on Korotkoff sounds and oscillometric cuff pressure pulses during blood pressure measurement Dingchang Zheng Luigi Yuri Di Marco Alan
DOI 10.1007/s11517-014-1150-1 Original Article Effect of respiration on Korotkoff sounds and oscillometric cuff pressure pulses during blood pressure measurement Dingchang Zheng Luigi Yuri Di Marco Alan
BRIEF COMMUNICATIONS. KEY WORDS: Ambulatory blood pressure monitoring, placebo effect, antihypertensive drug trials.
 AJH 1995; 8:311-315 BRIEF COMMUNICATIONS Lack of Placebo Effect on Ambulatory Blood Pressure Giuseppe Mancia, Stefano Omboni, Gianfranco Parati, Antonella Ravogli, Alessandra Villani, and Alberto Zanchetti
AJH 1995; 8:311-315 BRIEF COMMUNICATIONS Lack of Placebo Effect on Ambulatory Blood Pressure Giuseppe Mancia, Stefano Omboni, Gianfranco Parati, Antonella Ravogli, Alessandra Villani, and Alberto Zanchetti
