Concealed Accessory Pathway in Late Presentation Wolff-Parkinson-White Syndrome
|
|
|
- Matilda Marianna Shields
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 CASE REPORT Concealed Accessory Pathway in Late Presentation Wolff-Parkinson-White Syndrome Stephanie Rose1, Richard Armstrong2, David Moore2 Third year medicine, Trinity College Dublin Department of Cardiology, Adelaide and Meath Hospital, Dublin, incorporating the National Children s Hospital 1 2 Background During normal electrical conduction of the heart, an electrical impulse begins at the sino-atrial (SA) node and spreads across the right and left atria before passing through the atrioventricular (AV) node. It then passes down to the ventricles via the right and left bundle branches (of His) and finally the Purkinje fibres. This pattern of electrical conductance creates the familiar tracing on an electrocardiogram (ECG) of a P-wave (representative of atrial depolarisation), followed by a flat section, the P-R interval; representing a delay as the electrical activity passes through the AV node, followed by a QRS wave representing ventricular depolarisation. patients with functional bundle branch block, a short P-R interval and arrhythmias (Wolff et al., 1930). To date, the authors now lend their names to a syndrome that encompasses ECG changes revealing of an accessory pathway (AP) of conduction within the heart and tachycardia. If the specific ECG changes associated with an AP occur without tachycardia, this is termed WPW pattern. In approximately 0.1% to 0.3% of the population (Ehtisham et al., 2005; Rodday et al., 2012), myocardial fibres connect the atria to the ipsilateral ventricles across the mitral or tricuspid annuli (Wolff et al., 1930). This acts as a concealed AP for conduction that bypasses the AV node (Figure 2A). Unlike the normal AV nodal function, conduction is not delayed when traveling down these accessory pathways and thus pre-excitation or premature partial-depolarisation of the ventricles occurs, thereby, reducing the P-R interval. This produces the characteristic slurred and slow rising initial up-stroke of the QRS complex, or delta wave, immediately after the termination of the p-wave (Figures 1 & 3). As described in our case, ECG changes may only occur when the AP becomes electrically active during tachycardia. The P-R interval is normally 0.12 to 0.20 seconds in duration and the QRS complex is normally less than 0.12 seconds (Figure 1). This is important to note as in Wolff-Parkinson-White (WPW) syndrome, characteristic ECG changes may show a shortened P-R interval and widened QRS complex. These ECG changes may or may not be present at baseline. In 1930, Louis Wolff, John Parkinson, and Paul Dudley White published an article in the American Heart Journal describing TSMJ 2016 Figure 1. Normal Electrocardiogram (ECG) tracing and Delta wave.
2 SA Node AVN Accessory pathway Accessory pathway Figure 2. (A) A physiological mechanism of conduction in WPW with accessory pathway conduction (atrioventricular) resulting in the delta wave. (B) Orthodromic conduction in WPW syndrome occurring down AVN and retrogradely up accessory pathway. (C) Antidromic conduction where accessory pathway conducts anterogradely (atrioventricular) and the impulse returns to the atria via the AVN. (D) mechanism of AF in WPW syndrome. Therefore there are no ECG changes at baseline and this can be described as a concealed AP (Kulig et al., 2010). If ECG changes are present at baseline this is described as a manifest pathway. These APs (Figure 2) may permit atrioventricular re-entrant tachycardia (AVRT), whereby electrical conduction travels as a circuit from the atrium to the ventricles and back to the atrium resulting in repeated AV nodal stimulation, inducing tachycardia. This accounts for 95% of re-entrant tachycardias in WPW patients (Blomström-Lundqvist et al., 2003). Most commonly, the electrical impulse travels to the ventricles via the AV node and back to the atria via the AP in a retrograde manner. This is classified as orthodromic reciprocating tachycardia, and no delta wave is seen on ECG investigation (Figure 2B). If the electrical impulse anterogradely travels to the ventricles via the AP and returns via the AV node, this is classified as antidromic reciprocating tachycardia (Figure 2C). This occurs in only 5-10% of cases (Blomström-Lundqvist et al., 2003). Lastly, the AP may lead to atrial fibrillation (Figure 2D). These arrhythmia experienced in WPW patients are potentially fatal and a summary of risk factors, signs and symptoms, ECG findings, and investigations can be found in Table 1. Case Presentation Here we describe a case of a concealed accessory pathway in a 64 year old lady who presented to cardiology in 2015 with acute chest pain, palpitations and shortness of breath on a background of heavy smoking (10 pack years), high cholesterol, type 2 diabetes mellitus and aortic regurgitation. On admission, the patient was apyrexial with a blood pressure of 118/67, a pulse rate of 100/ min and respiration rate of 15. The initial symptom of chest pain occurred at 11am in the morning following mild to moderate exertion whilst painting indoors on a ladder. The pain was continuous, dull and described as a central tightness across the chest radiating to the left neck and shoulder. Her subjective pain score was 8/10. The pain worsened on inspiration and there were no alleviating factors. Other presenting symptoms were pre-syncope, weakness, and numbness on the left side of the tongue. The patient had slowly walked for nearly an hour to her General Practitioner who called an ambulance and administered sublingual glyceryl trinitrate without symptomatic relief. Of note, the patient s previous medical history revealed two previous admissions to A&E for chest pain in 2006/2007 which had been excluded as cardiac in origin by the cardiology team following negative blood tests, a normal 24 hour Holter ECG, and two non-revealing stress tests achieving 96% of her target heart rate. TSMJ
3 CASE REPORT Table 1. Summary of most common structural risk factors, signs and symptoms, ECG findings (not always present) and possible investigations in WPW syndrome Risk Factor Ebstein s Anomaly; The most commonly occurring congenital defect associated with WPW syndrome. It involves malformation of the tricuspid valve and may lead to cyanosis, dyspnoea, fatigue, arrhythmias, and congestive heart failure. Signs and symptoms Palpitations Dizziness Dyspnoea Atrial Flutter Atrial Fibrillation Syncope or presyncope 12 lead ECG findings indicative of WPW syndrome Shortened P-R interval of <0.12 s A prolonged QRS complex >0.11 s Delta Waves (bidirectional AP) No delta waves (retrograde AP) Additional Investigations Echocardiogram Treadmill test Pharmacological testing with procainamide or ajmaline may define duration of anterograde effective refractive period of the accessory pathway. Tachycardia Sudden cardiac death Electrophysiological Study ECG Findings The appearance of the 12 lead ECG on admission revealed a wide QRS complex and regular monomorphic ventricular tachycardia (VT) (Figure 3). The patient was diagnosed by the clinician on-call as having monomorphic unstable VT and emergency direct current (DC) cardioversion was delivered as a synchronised shock. The patient was then converted to sinus rhythm (Figure 4). A differential diagnosis for wide complex tachyarrhythmias is given in Table 2 and in this clinical situation, the Brugada Criteria (Figure 5) provides a flow chart to the clinician that may be used to ascertain whether or not the tachyarrhythmia is ventricular or supraventricular in origin. Investigations Throughout the patient s admission, blood tests were non-revealing for any indication of ischaemia or other pathology. A coronary angiogram was performed to rule out coronary artery disease. As represented in Figures 6 and 7, very mild arterial disease within the right and left coronary arteries was found, mainly at the bifurcations and not in keeping with the signs and symptoms experienced by the patient. Both the coronary angiogram and transthoracic echocardiogram did not reveal any structural abnormalities. Following coronary angiography, delta wave ECG changes were detected, allowing for Table 2. Differential Diagnosis of Wide Complex Tachyarrhythmias Supraventricular Tachycardia With Bundle Branch Block Supraventricular Tachycardia With Atrioventricular Conduction Over an Accessory Pathway Ventricular Tachycardia Bundle branch block can occur with any supraventricular arrhythmia May occur during atrial flutter, atrial fibrillation, atrioventricular nodal reciprocating tachycardia (AVNRT), atrioventricular reciprocating tachycardia (AVRT), and atrial tachycardia May be diagnosed using Brugada Criteria 14 TSMJ 2016
4 Figure 3. ECG on admission: Wide complex regular tachyarrhythmia showing delta waves (arrows) and right bundle branch block pattern. Appearance of possible fusion of wide and narrow complex tachycardia Regular monomorphic tachycardia
5 Normal P-QRS complexes Example of the appearance of a delta wave in red Figure 4. ECG following direct current cardioversion (DCC). Delta waves are not present on the post-dcc ECG which is highly suggestive of a concealed accessory pathway. ABSENCE OF R-S COMPLEX IN ALL PRAECORDIAL Figure 5. Based on Brugada Criteria (1991). Clinical guideline LEADS V1-6? for a definitive diagnosis of wide complex tachyarrhythmias. In particular this flowchart aids in the differentiation between ventricular and supraventricular tachyarrhythmias. R-S INTERVAL > 100 ms IN PRAECORDIAL LEAD? ATRIO-VENTRICULAR DISSOCIATION? MORPHOLOGY CRITERIA FOR VT PRSENT IN BOTH PRAECORDIAL LEADS V1-2 AND V6? SVT WITH ABERRANT CONDUCTION 16 TSMJ 2016 definitive diagnosis of WPW syndrome. The patient was subsequently sent for electrophysiology in a separate procedure that was successful in locating and ablating a left sided accessory pathway. Discussion WPW patients may be asymptomatic or they may experience palpitations, chest pain, syncope, headache, dizziness, nausea, dyspnoea, impaired vision, arrhythmias or even sudden cardiac death in less than 0.1% of cases (Kulig et al., 2010). In a recent 8-year prospective study of 2,169 WPW syndrome patients in Italy, a greater proportion of asymptomatic patients
6 CASE REPORT Right Coronary Artery syndrome should be fully evaluated due to the risk of lethal arrhythmias (Blomström-Lundqvist et al., 2003). Posterior Descending Artery Posterior Left Ventricular Artery Figure 6. Angiogram of right coronary arteries from patient. Circles indicate areas of mild disease (continuity is slightly irregular in the areas of the bifurcations, as circled, but there is no obvious occlusion or stenosis). experienced malignant arrhythmias (MA) and ventricular fibrillation (VF) than symptomatic patients. However, this was pertained to be due to symptomatic patients receiving ablation, leading to better long term outcomes. None of the 1168 patients who underwent ablation suffered MA or VF post-operatively compared to 93 of the 1001 non-ablated patients (Pappone et al., 2014). Fortunately, our patient eventually presented with symptoms and ECG changes in keeping with the WPW syndrome diagnosis, which allowed her previously concealed AP to be located and ablated. Left Main Coronary Artery Left Circumflex Artery Interesting aspects of this case include the concealment of her ECG findings as baseline and the age of the patient at presentation. Concealed APs may occur in approximately one third of accessory pathway tachycardias and are an important prognostic feature, as accurate diagnosis and ablation should lead to a permanent cure of tachycardia and prevents potentially lethal future arrhythmias (Ross and Uther, 1984). Patients with WPW syndrome may present at any age; however, it more commonly occurs in young people and decreases with age due to loss of pre-excitation (Jung et al., 2011). Our patient was 64 years old when she presented with detectable evidence of cardiac arrhythmia and positive ECG findings. It is therefore important to consider WPW syndrome as a differential diagnosis for cardiac arrhythmias with tachycardia irrespective of age or previously normal ECGs. Left Anterior Descending Artery Diagonal Artery Obtuse Marginal (1) In a larger 15 year prospective cohort study of 22,500 healthy aviation personnel undergoing systematic ECG screening, the WPW pattern was seen in 0.25% of subjects, and only 1.8% of those had documented arrhythmia diagnostic of WPW syndrome (Davidoff et al., 1981). For the general population, the risk is considered to be small and screening for WPW syndrome is not recommended at present. However all patients found to have WPW Obtuse Marginal (2) Figure 7. Angiogram of left coronary arteries from patient. Circles indicate areas of mild disease (continuity is slightly irregular in the areas of the bifurcations, as circled, but there is no obvious occlusion or stenosis). TSMJ
7 CASE REPORT Additionally, the patient presented acutely unwell with ECG findings of complex ventricular tachycardia. The treating clinician suspected the possibility of a fusion of wide and narrow complex tachycardia (Figure 3) and provisionally made a diagnosis of ventricular tachycardia. In actual fact, this was a p-wave followed by a wide complex QRS-complex wave, indicating supraventricular tachycardia. This was only confirmed post coronary angiogram having made a definitive diagnosis of WPW syndrome based on the ECG findings taken throughout the procedure. The history of this patient was an important clue in helping ascertain a correct diagnosis. A patient with ventricular tachycardia is likely to be extremely unstable and unlikely to walk to her local GP over the course of an hour. However, at the time of presentation the patient was acutely unwell and did not reveal these details until after DC cardioversion. Certain guidelines (Frankel et al., 2015) will advocate the use of IV adenosine before DC cardioversion in the management of our case. Adenosine is an antiarrhythmic with a half-life of less than 10 seconds and its effects are therefore self-limiting. It is, however, contraindicated in WPW with atrial fibrillation due to the risk of precipitating ventricular flutter and increasing the likelihood of sudden cardiac death. In 18 TSMJ 2016 these cases, ibutilide, procainamide, or flecainide are the preferred drug choices as they are capable of slowing conduction along the AP (Blomström-Lundqvist et al., 2003). Adenosine used in the presence of unstable ventricular tachycardia may lead to further deterioration and is therefore contraindicated. As the clinician on call had made the provisional diagnosis of VT during initial presentation, this case highlights the importance of treating the case as ventricular tachycardia until proven otherwise. Conclusion This case describes an atypical acute presentation of a concealed AP in a female patient with WPW syndrome, presenting unusually late in life. The ECG appearance was that of a wide QRS complex, regular monomorphic VT, and new delta-waves presenting during an acute episode of tachycardia and post coronary angiogram. This case highlights the need to be vigilant in history taking, ECG analysis, and formulating a differential diagnosis in order to provide the best treatment for our patients. References Blomström-Lundqvist, C., Scheinman, M. M., Aliot, E. M., Alpert, J. S., Calkins, H., Camm, A. J.,... & Trappe, H. J. (2003). ACC/AHA/ESC guidelines for the management of patients with supraventricular arrhythmias executive summary. Journal of the American College of Cardiology, 42(8), Brugada, P., Brugada, J., Mont, L., Smeets, J. L. R. M., & Andries, E. W. (1991). A new approach to the differential diagnosis of a regular tach- ycardia with a wide QRS complex. Circulation, 83(5), Davidoff, R., C. L. Schamroth, and D. P. Myburgh. The Wolff-Parkinson-White pattern in health aircrew. Aviation, space, and environmental medicine 52.9 (1981): Ehtisham, J., & Watkins, H. (2005). Is Wolff-Parkinson-White Syndrome a Genetic Disease?. Journal of cardiovascular electrophysiology, 16(11), Frankel D, Das M, Zipes D, Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome. BMJ Best Practice last update: March 27th BMJ Publishing Group Limited Jung, H. J., Ju, H. Y., Hyun, M. C., Lee, S. B., & Kim, Y. H. (2011). Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome in young people, from childhood to young adulthood: relationships between age and clinical and electrophysiological findings. Korean journal of pediatrics, 54(12), Keating, L., Morris, F. P., & Brady, W. J. (2003). Electrocardiographic features of Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome. Emergency medicine journal, 20(5), Kulig, J., & Koplan, B. A. (2010). Wolff-Parkinson-White Syndrome and Accessory Pathways. Circulation, 122(15), e480-e483. Pappone, C., Vicedomini, G., Manguso, F., Saviano, M., Baldi, M., Pappone, A.,... & Vitale, R. (2014). WPW syndrome in the era of catheter ablation: insights from a registry study of 2169 patients. Circulation, CIRCULATIONAHA-114. Rodday, A. M., Triedman, J. K., Alexander, M. E., Cohen, J. T., Ip, S., Newburger, J. W.,... & Leslie, L. K. (2012). Electrocardiogram screening for disorders that cause sudden cardiac death in asymptomatic children: a meta-analysis. Pediatrics, 129(4), e999-e1010. Ross, D. L., & Uther, J. B. (1984). Diagnosis of concealed accessory pathways in supraventricular tachycardia. Pacing and Clinical Electrophysiology, 7(6), Wolff, L., Parkinson, J., & White, P. D. (1930). Bundle-branch block with short PR interval in healthy young people prone to paroxysmal tachycardia. American Heart Journal, 5(6),
Emergency Medical Training Services Emergency Medical Technician Paramedic Program Outlines Outline Topic: WPW Revised: 11/2013
 Emergency Medical Training Services Emergency Medical Technician Paramedic Program Outlines Outline Topic: WPW Revised: 11/2013 Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome (WPW) is a syndrome of pre-excitation of the
Emergency Medical Training Services Emergency Medical Technician Paramedic Program Outlines Outline Topic: WPW Revised: 11/2013 Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome (WPW) is a syndrome of pre-excitation of the
Chapter 16: Arrhythmias and Conduction Disturbances
 Complete the following. Chapter 16: Arrhythmias and Conduction Disturbances 1. Cardiac arrhythmias result from abnormal impulse, abnormal impulse, or both mechanisms together. 2. is the ability of certain
Complete the following. Chapter 16: Arrhythmias and Conduction Disturbances 1. Cardiac arrhythmias result from abnormal impulse, abnormal impulse, or both mechanisms together. 2. is the ability of certain
1 Cardiology Acute Care Day 22 April 2013 Arrhythmia Tutorial Course Material
 1 Cardiology Acute Care Day 22 April 2013 Arrhythmia Tutorial Course Material Arrhythmia recognition This tutorial builds on the ECG lecture and provides a framework for approaching any ECG to allow the
1 Cardiology Acute Care Day 22 April 2013 Arrhythmia Tutorial Course Material Arrhythmia recognition This tutorial builds on the ECG lecture and provides a framework for approaching any ECG to allow the
Sustained tachycardia with wide QRS
 Sustained tachycardia with wide QRS Courtesy from Prof. Antonio Américo Friedmann. Electrocardiology Service of University of Faculty of São Paulo. Opinions from colleagues Greetings to everyone, In a
Sustained tachycardia with wide QRS Courtesy from Prof. Antonio Américo Friedmann. Electrocardiology Service of University of Faculty of São Paulo. Opinions from colleagues Greetings to everyone, In a
Paroxysmal Supraventricular Tachycardia PSVT.
 Atrial Tachycardia; is the name for an arrhythmia caused by a disorder of the impulse generation in the atrium or the AV node. An area in the atrium sends out rapid signals, which are faster than those
Atrial Tachycardia; is the name for an arrhythmia caused by a disorder of the impulse generation in the atrium or the AV node. An area in the atrium sends out rapid signals, which are faster than those
TACHYARRHYTHMIAs. Pawel Balsam, MD, PhD
 TACHYARRHYTHMIAs Pawel Balsam, MD, PhD SupraVentricular Tachycardia Atrial Extra Systole Sinus Tachycardia Focal A. Tachycardia AVRT AVNRT Atrial Flutter Atrial Fibrillation Ventricular Tachycardia Ventricular
TACHYARRHYTHMIAs Pawel Balsam, MD, PhD SupraVentricular Tachycardia Atrial Extra Systole Sinus Tachycardia Focal A. Tachycardia AVRT AVNRT Atrial Flutter Atrial Fibrillation Ventricular Tachycardia Ventricular
Supraventricular Tachycardia (SVT)
 Supraventricular Tachycardia (SVT) Bruce Stambler, MD Piedmont Heart Atlanta, GA Supraventricular Tachycardia Objectives Types and mechanisms AV nodal reentrant tachycardia (AVNRT) AV reciprocating tachycardia
Supraventricular Tachycardia (SVT) Bruce Stambler, MD Piedmont Heart Atlanta, GA Supraventricular Tachycardia Objectives Types and mechanisms AV nodal reentrant tachycardia (AVNRT) AV reciprocating tachycardia
WPW syndrome and AVRT
 WPW syndrome and AVRT Myung-Yong Lee, MD, PhD Division of Cardiology Department of Internal Medicine School of Medicine Dankook University, Cheonan, Korea Supraventricular tachycardia (SVT) Paroxysmal
WPW syndrome and AVRT Myung-Yong Lee, MD, PhD Division of Cardiology Department of Internal Medicine School of Medicine Dankook University, Cheonan, Korea Supraventricular tachycardia (SVT) Paroxysmal
You Don t Want to Miss This One! Focus on can t miss EKG tracings
 You Don t Want to Miss This One! Focus on can t miss EKG tracings Renaissance St. Louis Grand Hotel Convention Center October 23, 2014 David K. Tan, M.D., EMT-T, FAAEM EMS Section Chief, Division of Emergency
You Don t Want to Miss This One! Focus on can t miss EKG tracings Renaissance St. Louis Grand Hotel Convention Center October 23, 2014 David K. Tan, M.D., EMT-T, FAAEM EMS Section Chief, Division of Emergency
Case-Based Practical ECG Interpretation for the Generalist
 Case-Based Practical ECG Interpretation for the Generalist Paul D. Varosy, MD, FACC, FAHA, FHRS Director of Cardiac Electrophysiology VA Eastern Colorado Health Care System Associate Professor of Medicine
Case-Based Practical ECG Interpretation for the Generalist Paul D. Varosy, MD, FACC, FAHA, FHRS Director of Cardiac Electrophysiology VA Eastern Colorado Health Care System Associate Professor of Medicine
ECG Interpretation Made Easy
 ECG Interpretation Made Easy Dr. A Tageldien Abdellah, MSc MD EBSC Lecturer of Cardiology- Hull University Hull York Medical School 2007-2008 ECG Interpretation Made Easy Synopsis Benefits Objectives Process
ECG Interpretation Made Easy Dr. A Tageldien Abdellah, MSc MD EBSC Lecturer of Cardiology- Hull University Hull York Medical School 2007-2008 ECG Interpretation Made Easy Synopsis Benefits Objectives Process
Huseng Vefali MD St. Luke s University Health Network Department of Cardiology
 Huseng Vefali MD St. Luke s University Health Network Department of Cardiology Learning Objectives Establish Consistent Approach to Interpreting ECGs Review Essential Cases for Paramedics and first responders
Huseng Vefali MD St. Luke s University Health Network Department of Cardiology Learning Objectives Establish Consistent Approach to Interpreting ECGs Review Essential Cases for Paramedics and first responders
Asymptomatic WPW Syndrome; Observation or Ablation? 전남대학교병원순환기내과 박형욱
 Asymptomatic WPW Syndrome; Observation or Ablation? 전남대학교병원순환기내과 박형욱 Let It Be? Vs. Just Do It? Natural history of asymptomatic WPW Incidence of sudden cardiac death in natural history studies involving
Asymptomatic WPW Syndrome; Observation or Ablation? 전남대학교병원순환기내과 박형욱 Let It Be? Vs. Just Do It? Natural history of asymptomatic WPW Incidence of sudden cardiac death in natural history studies involving
We are IntechOpen, the world s leading publisher of Open Access books Built by scientists, for scientists. International authors and editors
 We are IntechOpen, the world s leading publisher of Open Access books Built by scientists, for scientists 3,500 108,000 1.7 M Open access books available International authors and editors Downloads Our
We are IntechOpen, the world s leading publisher of Open Access books Built by scientists, for scientists 3,500 108,000 1.7 M Open access books available International authors and editors Downloads Our
Supraventricular Tachycardia: From Fetus to Adult. Mohamed Hamdan, MD
 Supraventricular Tachycardia: From Fetus to Adult Mohamed Hamdan, MD Learning Objectives Define type of SVT by age Describe clinical approach Describe prenatal and postnatal management of SVT 2 SVT Across
Supraventricular Tachycardia: From Fetus to Adult Mohamed Hamdan, MD Learning Objectives Define type of SVT by age Describe clinical approach Describe prenatal and postnatal management of SVT 2 SVT Across
Nathan Cade, MD Brandon Fainstad, MD Andrew Prouse, MD
 Nathan Cade, MD Brandon Fainstad, MD Andrew Prouse, MD OBJECTIVES 1. Identify the basic electrophysiology of the four causes of wide complex tachycardia. 2. Develop a simple framework for acute management
Nathan Cade, MD Brandon Fainstad, MD Andrew Prouse, MD OBJECTIVES 1. Identify the basic electrophysiology of the four causes of wide complex tachycardia. 2. Develop a simple framework for acute management
Asymptomatic patient with WPW
 Asymptomatic patient with WPW Dimosthenis Avramidis, MD. Arrythmiologist Mitera Children s Hospital Athens Greece Scientific Associate 1st Cardiology Dpt Evangelismos Hospital Athens Greece Preexcitation
Asymptomatic patient with WPW Dimosthenis Avramidis, MD. Arrythmiologist Mitera Children s Hospital Athens Greece Scientific Associate 1st Cardiology Dpt Evangelismos Hospital Athens Greece Preexcitation
a lecture series by SWESEMJR
 Arrhythmias Automaticity- the ability to depolarize spontaneously. Pacemakers: Sinoatrial node: 70 bpm AV-nodal area: 40 bpm His-Purkinje: 20-40 bpm it Mechanisms of arrhythmias 1. Increased automaticity
Arrhythmias Automaticity- the ability to depolarize spontaneously. Pacemakers: Sinoatrial node: 70 bpm AV-nodal area: 40 bpm His-Purkinje: 20-40 bpm it Mechanisms of arrhythmias 1. Increased automaticity
Arrhythmia 341. Ahmad Hersi Professor of Cardiology KSU
 Arrhythmia 341 Ahmad Hersi Professor of Cardiology KSU Objectives Epidemiology and Mechanisms of AF Evaluation of AF patients Classification of AF Treatment and Risk stratification of AF Identify other
Arrhythmia 341 Ahmad Hersi Professor of Cardiology KSU Objectives Epidemiology and Mechanisms of AF Evaluation of AF patients Classification of AF Treatment and Risk stratification of AF Identify other
Supraventricular Tachycardia (SVT)
 Supraventricular Tachycardia (SVT) Daniel Frisch, MD Cardiology Division, Electrophysiology Section Thomas Jefferson University Hospital daniel.frisch@jefferson.edu Short RP Are these the Mid same RP tachycardias?
Supraventricular Tachycardia (SVT) Daniel Frisch, MD Cardiology Division, Electrophysiology Section Thomas Jefferson University Hospital daniel.frisch@jefferson.edu Short RP Are these the Mid same RP tachycardias?
Pediatrics ECG Monitoring. Pediatric Intensive Care Unit Emergency Division
 Pediatrics ECG Monitoring Pediatric Intensive Care Unit Emergency Division 1 Conditions Leading to Pediatric Cardiology Consultation 12.7% of annual consultation Is arrhythmias problems Geggel. Pediatrics.
Pediatrics ECG Monitoring Pediatric Intensive Care Unit Emergency Division 1 Conditions Leading to Pediatric Cardiology Consultation 12.7% of annual consultation Is arrhythmias problems Geggel. Pediatrics.
UNDERSTANDING ELECTROPHYSIOLOGY STUDIES
 UNDERSTANDING ELECTROPHYSIOLOGY STUDIES Testing and Treating Your Heart s Electrical System A Problem with Your Heart Rhythm The speed and pattern of a heartbeat is called the heart rhythm. The rhythm
UNDERSTANDING ELECTROPHYSIOLOGY STUDIES Testing and Treating Your Heart s Electrical System A Problem with Your Heart Rhythm The speed and pattern of a heartbeat is called the heart rhythm. The rhythm
Antiarrhythmic Drugs
 Antiarrhythmic Drugs DR ATIF ALQUBBANY A S S I S T A N T P R O F E S S O R O F M E D I C I N E / C A R D I O L O G Y C O N S U L T A N T C A R D I O L O G Y & I N T E R V E N T I O N A L E P A C H D /
Antiarrhythmic Drugs DR ATIF ALQUBBANY A S S I S T A N T P R O F E S S O R O F M E D I C I N E / C A R D I O L O G Y C O N S U L T A N T C A R D I O L O G Y & I N T E R V E N T I O N A L E P A C H D /
Patient Resources: Arrhythmias and Congenital Heart Disease
 Patient Resources: Arrhythmias and Congenital Heart Disease Overview Arrhythmias (abnormal heart rhythms) can develop in patients with congenital heart disease (CHD) due to thickening/weakening of their
Patient Resources: Arrhythmias and Congenital Heart Disease Overview Arrhythmias (abnormal heart rhythms) can develop in patients with congenital heart disease (CHD) due to thickening/weakening of their
Repetitive narrow QRS tachycardia in a 61-year-old female patient with recent palpitations
 Journal of Geriatric Cardiology (2018) 15: 193 198 2018 JGC All rights reserved; www.jgc301.com Case Report Open Access Repetitive narrow QRS tachycardia in a 61-year-old female patient with recent palpitations
Journal of Geriatric Cardiology (2018) 15: 193 198 2018 JGC All rights reserved; www.jgc301.com Case Report Open Access Repetitive narrow QRS tachycardia in a 61-year-old female patient with recent palpitations
PhD FRCP MESC MEAPCI. Consultant Cardiologist SVT - Supra Ventricular Tachycardia. Coronary Arteries
 SVT - Supra Ventricular Tachycardia Coronary Arteries Overview LMS Supraventricular tachycardia is defined as an abnormally fast heartbeat. It's a describes a group of arrhythmias which all originate from
SVT - Supra Ventricular Tachycardia Coronary Arteries Overview LMS Supraventricular tachycardia is defined as an abnormally fast heartbeat. It's a describes a group of arrhythmias which all originate from
Self-assessment corner
 Postgrad Med J 1995; 71: 181-185 C) The Fellowship of Postgraduate Medicine, 1995 Self-assessment corner Department of Cardiology, Royal Liverpool University Hospital, Liverpool L7 8XP, UK SS Mushahwar
Postgrad Med J 1995; 71: 181-185 C) The Fellowship of Postgraduate Medicine, 1995 Self-assessment corner Department of Cardiology, Royal Liverpool University Hospital, Liverpool L7 8XP, UK SS Mushahwar
The most common. hospitalized patients. hypotension due to. filling time Rate control in ICU patients may be difficult as many drugs cause hypotension
 Arrhythmias in the critically ill ICU patients: Approach for rapid recognition & management Objectives Be able to identify and manage: Atrial fibrillation with a rapid ventricular response Atrial flutter
Arrhythmias in the critically ill ICU patients: Approach for rapid recognition & management Objectives Be able to identify and manage: Atrial fibrillation with a rapid ventricular response Atrial flutter
Paramedic Rounds. Tachyarrhythmia's. Sean Sutton Dallas Wood
 Paramedic Rounds Tachyarrhythmia's Sean Sutton Dallas Wood Objectives At the end of this session, the paramedic will be able to: State the key components of the cardiac conduction pathway, along with the
Paramedic Rounds Tachyarrhythmia's Sean Sutton Dallas Wood Objectives At the end of this session, the paramedic will be able to: State the key components of the cardiac conduction pathway, along with the
Ventricular Preexcitation (Wolff-Parkinson-White Syndrome and Its Variants) 柯文欽醫師 國泰綜合醫院心臟內科主治醫師 臺北醫學大學講師
 Ventricular Preexcitation (Wolff-Parkinson-White Syndrome and Its Variants) 柯文欽醫師 國泰綜合醫院心臟內科主治醫師 臺北醫學大學講師 The Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine 1924 "for his discovery of the mechanism of the electrocardiogram"
Ventricular Preexcitation (Wolff-Parkinson-White Syndrome and Its Variants) 柯文欽醫師 國泰綜合醫院心臟內科主治醫師 臺北醫學大學講師 The Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine 1924 "for his discovery of the mechanism of the electrocardiogram"
(living in the fast lane)
 (living in the fast lane) Presented by M.D. Cardiology IT S A group of ECG and Electrophysiological abnormalities in which The atrial impulses are conducted partly or completely, PREMATURELY, to the ventricles
(living in the fast lane) Presented by M.D. Cardiology IT S A group of ECG and Electrophysiological abnormalities in which The atrial impulses are conducted partly or completely, PREMATURELY, to the ventricles
Dysrhythmias 11/7/2017. Disclosures. 3 reasons to evaluate and treat dysrhythmias. None. Eliminate symptoms and improve hemodynamics
 Dysrhythmias CYDNEY STEWART MD, FACC NOVEMBER 3, 2017 Disclosures None 3 reasons to evaluate and treat dysrhythmias Eliminate symptoms and improve hemodynamics Prevent imminent death/hemodynamic compromise
Dysrhythmias CYDNEY STEWART MD, FACC NOVEMBER 3, 2017 Disclosures None 3 reasons to evaluate and treat dysrhythmias Eliminate symptoms and improve hemodynamics Prevent imminent death/hemodynamic compromise
Wolff-Parkinson-White Syndrome
 Wolff-Parkinson-White Syndrome www.consultant360.com /articles/wolff-parkinson-white-syndrome A 37-year-old woman presented to the office with intermittent dizziness, palpitations, and multiple syncopal
Wolff-Parkinson-White Syndrome www.consultant360.com /articles/wolff-parkinson-white-syndrome A 37-year-old woman presented to the office with intermittent dizziness, palpitations, and multiple syncopal
Electrophysiological recognition of an atrio-ventricular mahaim fibre pathway
 Interventional Cardiology Electrophysiological recognition of an atrio-ventricular mahaim fibre pathway Mahaim fibres are cardiac accessory bundles which can cause dangerous tachyarrhythmias. Despite their
Interventional Cardiology Electrophysiological recognition of an atrio-ventricular mahaim fibre pathway Mahaim fibres are cardiac accessory bundles which can cause dangerous tachyarrhythmias. Despite their
Evaluation and Initial Treatment of Supraventricular Tachycardia
 T h e n e w e ngl a nd j o u r na l o f m e dic i n e clinical practice Evaluation and Initial Treatment of Supraventricular Tachycardia Mark S. Link, M.D. This Journal feature begins with a case vignette
T h e n e w e ngl a nd j o u r na l o f m e dic i n e clinical practice Evaluation and Initial Treatment of Supraventricular Tachycardia Mark S. Link, M.D. This Journal feature begins with a case vignette
Atrial Fibrillation and Common Supraventricular Tachycardias. Sunil Kapur MD
 Atrial Fibrillation and Common Supraventricular Tachycardias Sunil Kapur MD Cardiac Electrophysiology Brigham and Women s Hospital Instructor, Harvard Medical School No disclosures Cardiac Conduction:
Atrial Fibrillation and Common Supraventricular Tachycardias Sunil Kapur MD Cardiac Electrophysiology Brigham and Women s Hospital Instructor, Harvard Medical School No disclosures Cardiac Conduction:
the ECG, 6 mg of intravenous adenosine was administered as a fast bolus through a large bore intravenous cannula in
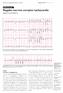 (arrows). Electrocardiography Series Singapore Med.1 2011, 52(3) 146 CME Article Regular narrow complex tachycardia Singh D, Teo S G, Poh K K V Hr JL1 11 VL VF WA, Fig. I ECG shows regular narrow complex
(arrows). Electrocardiography Series Singapore Med.1 2011, 52(3) 146 CME Article Regular narrow complex tachycardia Singh D, Teo S G, Poh K K V Hr JL1 11 VL VF WA, Fig. I ECG shows regular narrow complex
Declaration of conflict of interest NONE
 Declaration of conflict of interest NONE Transatlantic Electrophysiology Lessons for and from Iberoamerica European Society of Cardiology Mexican Society of Cardiology Wolff-Parkinson-White Syndrome in
Declaration of conflict of interest NONE Transatlantic Electrophysiology Lessons for and from Iberoamerica European Society of Cardiology Mexican Society of Cardiology Wolff-Parkinson-White Syndrome in
PATIENT WITH ARRHYTHMIA IN DENTIST S OFFICE. Małgorzata Kurpesa, MD., PhD. Chair&Department of Cardiology
 PATIENT WITH ARRHYTHMIA IN DENTIST S OFFICE Małgorzata Kurpesa, MD., PhD. Chair&Department of Cardiology Medical University of Łódź The heart is made up of four chambers Left Atrium Right Atrium Left Ventricle
PATIENT WITH ARRHYTHMIA IN DENTIST S OFFICE Małgorzata Kurpesa, MD., PhD. Chair&Department of Cardiology Medical University of Łódź The heart is made up of four chambers Left Atrium Right Atrium Left Ventricle
EHRA Accreditation Exam - Sample MCQs Invasive cardiac electrophysiology
 EHRA Accreditation Exam - Sample MCQs Invasive cardiac electrophysiology Dear EHRA Member, Dear Colleague, As you know, the EHRA Accreditation Process is becoming increasingly recognised as an important
EHRA Accreditation Exam - Sample MCQs Invasive cardiac electrophysiology Dear EHRA Member, Dear Colleague, As you know, the EHRA Accreditation Process is becoming increasingly recognised as an important
Arrhythmias (I) Supraventricular Tachycardias. Disclosures
 Arrhythmias (I) Supraventricular Tachycardias Amy Leigh Miller, MD, PhD Cardiovascular Electrophysiology, Brigham & Women s Hospital Disclosures None Short R-P Tachycardia REGULAR with 1:1 P/R relationship
Arrhythmias (I) Supraventricular Tachycardias Amy Leigh Miller, MD, PhD Cardiovascular Electrophysiology, Brigham & Women s Hospital Disclosures None Short R-P Tachycardia REGULAR with 1:1 P/R relationship
Step by step approach to EKG rhythm interpretation:
 Sinus Rhythms Normal sinus arrhythmia Small, slow variation of the R-R interval i.e. variation of the normal sinus heart rate with respiration, etc. Sinus Tachycardia Defined as sinus rhythm with a rate
Sinus Rhythms Normal sinus arrhythmia Small, slow variation of the R-R interval i.e. variation of the normal sinus heart rate with respiration, etc. Sinus Tachycardia Defined as sinus rhythm with a rate
Arrhythmia Management Joshua M. Cooper, MD, FHRS, FACC
 Arrhythmia Management Joshua M. Cooper, MD, FHRS, FACC Professor of Medicine Director of Cardiac Electrophysiology Temple University Health System Plumbing Electrical System Bradyarrhythmias Sinus Node
Arrhythmia Management Joshua M. Cooper, MD, FHRS, FACC Professor of Medicine Director of Cardiac Electrophysiology Temple University Health System Plumbing Electrical System Bradyarrhythmias Sinus Node
Differential diagnosis and pacing in maneuvers narrow QRS tachycardia. Richard Schilling
 Differential diagnosis and pacing in maneuvers narrow QRS tachycardia Richard Schilling Differential diagnosis of narrow complex QRS tachycardia Anything that activates the ventricle normally via the His
Differential diagnosis and pacing in maneuvers narrow QRS tachycardia Richard Schilling Differential diagnosis of narrow complex QRS tachycardia Anything that activates the ventricle normally via the His
Case #1. 73 y/o man with h/o HTN and CHF admitted with dizziness and SOB Treated for CHF exacerbation with Lasix Now HR 136
 Tachycardias Case #1 73 y/o man with h/o HTN and CHF admitted with dizziness and SOB Treated for CHF exacerbation with Lasix Now HR 136 Initial Assessment Check Telemetry screen if pt on tele Telemetry
Tachycardias Case #1 73 y/o man with h/o HTN and CHF admitted with dizziness and SOB Treated for CHF exacerbation with Lasix Now HR 136 Initial Assessment Check Telemetry screen if pt on tele Telemetry
Clinical Cardiac Electrophysiology
 Clinical Cardiac Electrophysiology Certification Examination Blueprint Purpose of the exam The exam is designed to evaluate the knowledge, diagnostic reasoning, and clinical judgment skills expected of
Clinical Cardiac Electrophysiology Certification Examination Blueprint Purpose of the exam The exam is designed to evaluate the knowledge, diagnostic reasoning, and clinical judgment skills expected of
PEDIATRIC SVT MANAGEMENT
 PEDIATRIC SVT MANAGEMENT 1 INTRODUCTION Supraventricular tachycardia (SVT) can be defined as an abnormally rapid heart rhythm originating above the ventricles, often (but not always) with a narrow QRS
PEDIATRIC SVT MANAGEMENT 1 INTRODUCTION Supraventricular tachycardia (SVT) can be defined as an abnormally rapid heart rhythm originating above the ventricles, often (but not always) with a narrow QRS
2) Heart Arrhythmias 2 - Dr. Abdullah Sharif
 2) Heart Arrhythmias 2 - Dr. Abdullah Sharif Rhythms from the Sinus Node Sinus Tachycardia: HR > 100 b/m Causes: o Withdrawal of vagal tone & Sympathetic stimulation (exercise, fight or flight) o Fever
2) Heart Arrhythmias 2 - Dr. Abdullah Sharif Rhythms from the Sinus Node Sinus Tachycardia: HR > 100 b/m Causes: o Withdrawal of vagal tone & Sympathetic stimulation (exercise, fight or flight) o Fever
Pediatrics. Arrhythmias in Children: Bradycardia and Tachycardia Diagnosis and Treatment. Overview
 Pediatrics Arrhythmias in Children: Bradycardia and Tachycardia Diagnosis and Treatment See online here The most common form of cardiac arrhythmia in children is sinus tachycardia which can be caused by
Pediatrics Arrhythmias in Children: Bradycardia and Tachycardia Diagnosis and Treatment See online here The most common form of cardiac arrhythmia in children is sinus tachycardia which can be caused by
Arrhythmias_for_6_c..docx. Олена Костянтинівна Редько
 Arrhythmias_for_6_c..docx Олена Костянтинівна Редько 2015 Ключові терміни: 3 Зміст Ключові терміни: Arrhythmias 3 3 Ключові терміни: 4 Arrhythmias Ключові терміни: An irregular heart rhythm, Atrial flutter,
Arrhythmias_for_6_c..docx Олена Костянтинівна Редько 2015 Ключові терміни: 3 Зміст Ключові терміни: Arrhythmias 3 3 Ключові терміни: 4 Arrhythmias Ключові терміни: An irregular heart rhythm, Atrial flutter,
«Aσθενής με ασυμπτωματικό WPW και παροξυσμική κολπική μαρμαρυγή» Χάρης Κοσσυβάκης Επιμελητής A Καρδιολογικό Τμήμα Γ.Ν.Α. «Γ.
 «Aσθενής με ασυμπτωματικό WPW και παροξυσμική κολπική μαρμαρυγή» Χάρης Κοσσυβάκης Επιμελητής A Καρδιολογικό Τμήμα Γ.Ν.Α. «Γ. ΓΕΝΝΗΜΑΤΑΣ» the primary mechanism of SCD in patients with WPW is the rapid conduction
«Aσθενής με ασυμπτωματικό WPW και παροξυσμική κολπική μαρμαρυγή» Χάρης Κοσσυβάκης Επιμελητής A Καρδιολογικό Τμήμα Γ.Ν.Α. «Γ. ΓΕΝΝΗΜΑΤΑΣ» the primary mechanism of SCD in patients with WPW is the rapid conduction
Definition, Diagnosis and Treatment of Tachycardia
 3 Definition, Diagnosis and Treatment of Tachycardia Anand Deshmukh The Cardiac Center of Creighton University, Omaha, Nebraska USA 1. Introduction 1.1 Anatomy of the human cardiac conduction system 1.1.1
3 Definition, Diagnosis and Treatment of Tachycardia Anand Deshmukh The Cardiac Center of Creighton University, Omaha, Nebraska USA 1. Introduction 1.1 Anatomy of the human cardiac conduction system 1.1.1
Cardiology Flash Cards
 Cardiology Flash Cards EKG in a nut shell www.brain101.info Conduction System www.brain101.info 2 Analyzing EKG Step by step Steps in Analyzing ECG'S 1. Rhythm: - Regular _ Sinus, Junctional or Ventricular.
Cardiology Flash Cards EKG in a nut shell www.brain101.info Conduction System www.brain101.info 2 Analyzing EKG Step by step Steps in Analyzing ECG'S 1. Rhythm: - Regular _ Sinus, Junctional or Ventricular.
Arrhythmic Complications of MI. Teferi Mitiku, MD Assistant Clinical Professor of Medicine University of California Irvine
 Arrhythmic Complications of MI Teferi Mitiku, MD Assistant Clinical Professor of Medicine University of California Irvine Objectives Brief overview -Pathophysiology of Arrhythmia ECG review of typical
Arrhythmic Complications of MI Teferi Mitiku, MD Assistant Clinical Professor of Medicine University of California Irvine Objectives Brief overview -Pathophysiology of Arrhythmia ECG review of typical
Intraoperative and Postoperative Arrhythmias: Diagnosis and Treatment
 Intraoperative and Postoperative Arrhythmias: Diagnosis and Treatment Karen L. Booth, MD, Lucile Packard Children s Hospital Arrhythmias are common after congenital heart surgery [1]. Postoperative electrolyte
Intraoperative and Postoperative Arrhythmias: Diagnosis and Treatment Karen L. Booth, MD, Lucile Packard Children s Hospital Arrhythmias are common after congenital heart surgery [1]. Postoperative electrolyte
ECGs and Arrhythmias: Family Medicine Board Review 2009
 Rate Rhythm Intervals Hypertrophy ECGs and Arrhythmias: Family Medicine Board Review 2009 Axis Jess (Fogler) Waldura, MD University of California, San Francisco walduraj@nccc.ucsf.edu Ischemia Overview
Rate Rhythm Intervals Hypertrophy ECGs and Arrhythmias: Family Medicine Board Review 2009 Axis Jess (Fogler) Waldura, MD University of California, San Francisco walduraj@nccc.ucsf.edu Ischemia Overview
Dr.Binoy Skaria 13/07/15
 Dr.Binoy Skaria binoyskaria@hotmail.com binoy.skaria@heartofengland.nhs.uk 13/07/15 Acknowledgement Medtronic, Google images & Elsevier for slides Natalie Ryan, Events Manager, HEFT- for organising the
Dr.Binoy Skaria binoyskaria@hotmail.com binoy.skaria@heartofengland.nhs.uk 13/07/15 Acknowledgement Medtronic, Google images & Elsevier for slides Natalie Ryan, Events Manager, HEFT- for organising the
SIMPLY ECGs. Dr William Dooley
 SIMPLY ECGs Dr William Dooley Content Basic ECG interpretation pattern Some common (examined) abnormalities Presenting ECGs in context Setting up an ECG Setting up an ECG 1 V1-4 th Right intercostal space
SIMPLY ECGs Dr William Dooley Content Basic ECG interpretation pattern Some common (examined) abnormalities Presenting ECGs in context Setting up an ECG Setting up an ECG 1 V1-4 th Right intercostal space
ARTICLE. Supraventricular Tachycardia in Infancy. Catherine D. DeAngelis, MD. In most infants, SVT is due to an accessory atrioventricular
 Supraventricular Tachycardia in Infancy Evaluation, Management, and Follow-up Susan P. Etheridge, MD; Victoria E. Judd, MD ARTICLE Background: Supraventricular tachycardia (SVT) occurs frequently in infancy.
Supraventricular Tachycardia in Infancy Evaluation, Management, and Follow-up Susan P. Etheridge, MD; Victoria E. Judd, MD ARTICLE Background: Supraventricular tachycardia (SVT) occurs frequently in infancy.
LONG RP TACHYCARDIA MAPPING AND RF ABLATION
 LONG RP TACHYCARDIA MAPPING AND RF ABLATION Dr. Hayam Eldamanhoury Ain shams univeristy Arrhythmia is a too broad topic SVT is broadly defined as narrow complex ( unless aberrant conduction ) Requires
LONG RP TACHYCARDIA MAPPING AND RF ABLATION Dr. Hayam Eldamanhoury Ain shams univeristy Arrhythmia is a too broad topic SVT is broadly defined as narrow complex ( unless aberrant conduction ) Requires
A Lessening In the Cardiac Electrical Systole and a Wolff-Parkinson-White Pattern Together in the same Electrocardiographic Tracing
 Cronicon OPEN ACCESS CARDIOLOGY Case Report A Lessening In the Cardiac Electrical Systole and a Wolff-Parkinson-White Pattern Together in the same Electrocardiographic Francisco R. Breijo-Marquez* Department
Cronicon OPEN ACCESS CARDIOLOGY Case Report A Lessening In the Cardiac Electrical Systole and a Wolff-Parkinson-White Pattern Together in the same Electrocardiographic Francisco R. Breijo-Marquez* Department
Case Report Wide-QRS Tachycardia Inducible by Both Atrial and Ventricular Pacing
 Hellenic J Cardiol 2008; 49: 446-450 Case Report Wide-QRS Tachycardia Inducible by Both Atrial and Ventricular Pacing ELEFTHERIOS GIAZITZOGLOU, DEMOSTHENES G. KATRITSIS Department of Cardiology, Athens
Hellenic J Cardiol 2008; 49: 446-450 Case Report Wide-QRS Tachycardia Inducible by Both Atrial and Ventricular Pacing ELEFTHERIOS GIAZITZOGLOU, DEMOSTHENES G. KATRITSIS Department of Cardiology, Athens
Basic Electrophysiology Protocols
 Indian Journal of Cardiology ISSN-0972-1622 2012 by the Indian Society of Cardiology Vol. 15, (3-4), 27-37 [ 27 Review Article Shomu Bohora Assistant Professor, Deptt. of Cardiology, U.N. Mehta Institute
Indian Journal of Cardiology ISSN-0972-1622 2012 by the Indian Society of Cardiology Vol. 15, (3-4), 27-37 [ 27 Review Article Shomu Bohora Assistant Professor, Deptt. of Cardiology, U.N. Mehta Institute
Chapter 9. Learning Objectives. Learning Objectives 9/11/2012. Cardiac Arrhythmias. Define electrical therapy
 Chapter 9 Cardiac Arrhythmias Learning Objectives Define electrical therapy Explain why electrical therapy is preferred initial therapy over drug administration for cardiac arrest and some arrhythmias
Chapter 9 Cardiac Arrhythmias Learning Objectives Define electrical therapy Explain why electrical therapy is preferred initial therapy over drug administration for cardiac arrest and some arrhythmias
UNDERSTANDING YOUR ECG: A REVIEW
 UNDERSTANDING YOUR ECG: A REVIEW Health professionals use the electrocardiograph (ECG) rhythm strip to systematically analyse the cardiac rhythm. Before the systematic process of ECG analysis is described
UNDERSTANDING YOUR ECG: A REVIEW Health professionals use the electrocardiograph (ECG) rhythm strip to systematically analyse the cardiac rhythm. Before the systematic process of ECG analysis is described
Arrhythmias. A/Prof Drew Richardson. The Canberra Hospital May MB BS (Hons) FACEM Grad CertHE MD
 Arrhythmias A/Prof Drew Richardson MB BS (Hons) FACEM Grad CertHE MD The Canberra Hospital May 2013 Objectives Recognise the features of the common nonlethal arrhythmias Describe the emergency treatment
Arrhythmias A/Prof Drew Richardson MB BS (Hons) FACEM Grad CertHE MD The Canberra Hospital May 2013 Objectives Recognise the features of the common nonlethal arrhythmias Describe the emergency treatment
Core Content In Urgent Care Medicine
 Palpitations/Arrhythmias Ebrahim Barkoudah, MD Clinical Instructor in Internal Medicine Harvard Medical School Assistant in Internal Medicine & Pediatrics Massachusetts General Hospital MGH Chelsea Chelsea,
Palpitations/Arrhythmias Ebrahim Barkoudah, MD Clinical Instructor in Internal Medicine Harvard Medical School Assistant in Internal Medicine & Pediatrics Massachusetts General Hospital MGH Chelsea Chelsea,
Rhythm Control: Is There a Role for the PCP? Blake Norris, MD, FACC BHHI Primary Care Symposium February 28, 2014
 Rhythm Control: Is There a Role for the PCP? Blake Norris, MD, FACC BHHI Primary Care Symposium February 28, 2014 Financial disclosures Consultant Medtronic 3 reasons to evaluate and treat arrhythmias
Rhythm Control: Is There a Role for the PCP? Blake Norris, MD, FACC BHHI Primary Care Symposium February 28, 2014 Financial disclosures Consultant Medtronic 3 reasons to evaluate and treat arrhythmias
How To Think About Rhythms and Conduction
 How To Think About Rhythms and Conduction Frank Yanowitz, MD Professor of Medicine (Cardiology) University of Utah School of Medicine Medical Director, IHC ECG Services Intermountain Healthcare http://ecg.utah.edu
How To Think About Rhythms and Conduction Frank Yanowitz, MD Professor of Medicine (Cardiology) University of Utah School of Medicine Medical Director, IHC ECG Services Intermountain Healthcare http://ecg.utah.edu
APPROACH TO TACHYARRYTHMIAS
 APPROACH TO TACHYARRYTHMIAS PROF.DR.MD.ZAKIR HOSSAIN PROFESSOR AND HEAD DEPARTMENT OF MEDICINE SZMCH TACHYARRYTHMIA Cardiac arrythmia is a disturbance of electrical rhythm of heart. Cardac arrythmia with
APPROACH TO TACHYARRYTHMIAS PROF.DR.MD.ZAKIR HOSSAIN PROFESSOR AND HEAD DEPARTMENT OF MEDICINE SZMCH TACHYARRYTHMIA Cardiac arrythmia is a disturbance of electrical rhythm of heart. Cardac arrythmia with
Pre-excitation on the ECG what next? Kevin M W Leong Specialty Registrar in Cardiology
 Pre-excitation on the ECG what next? Kevin M W Leong Specialty Registrar in Cardiology Nicholas F Kelland Consultant in Cardiology and Electrophysiology Northern General Hospital Sheffield Teaching Hospitals
Pre-excitation on the ECG what next? Kevin M W Leong Specialty Registrar in Cardiology Nicholas F Kelland Consultant in Cardiology and Electrophysiology Northern General Hospital Sheffield Teaching Hospitals
Cardiovascular Nursing Practice: A Comprehensive Resource Manual and Study Guide for Clinical Nurses 2 nd Edition
 Cardiovascular Nursing Practice: A Comprehensive Resource Manual and Study Guide for Clinical Nurses 2 nd Edition Table of Contents Volume 1 Chapter 1: Cardiovascular Anatomy and Physiology Basic Cardiac
Cardiovascular Nursing Practice: A Comprehensive Resource Manual and Study Guide for Clinical Nurses 2 nd Edition Table of Contents Volume 1 Chapter 1: Cardiovascular Anatomy and Physiology Basic Cardiac
ECGs on the acute admission ward. - Cardiology Update -
 ECGs on the acute admission ward - Cardiology Update - Dr Simon Fynn Consultant Cardiologist Papworth Hospital, Cambridge RCP London Oct 2017 ECG 1 1. AF with BBB 2. Pre-excited AF 3. SVT with BBB 4.
ECGs on the acute admission ward - Cardiology Update - Dr Simon Fynn Consultant Cardiologist Papworth Hospital, Cambridge RCP London Oct 2017 ECG 1 1. AF with BBB 2. Pre-excited AF 3. SVT with BBB 4.
EKG Abnormalities. Adapted from:
 EKG Abnormalities Adapted from: http://www.bem.fi/book/19/19.htm Some key terms: Arrhythmia-an abnormal rhythm or sequence of events in the EKG Flutter-rapid depolarizations (and therefore contractions)
EKG Abnormalities Adapted from: http://www.bem.fi/book/19/19.htm Some key terms: Arrhythmia-an abnormal rhythm or sequence of events in the EKG Flutter-rapid depolarizations (and therefore contractions)
ECG S: A CASE-BASED APPROACH December 6,
 ECG S: A CASE-BASED APPROACH December 6, 2018 1 Faculty Disclosure Faculty: Lorne Gula MD, FRCPC Professor, Western University Cardiologist, Hearth Rhythm Specialist Director, Electrophysiology Laboratory,
ECG S: A CASE-BASED APPROACH December 6, 2018 1 Faculty Disclosure Faculty: Lorne Gula MD, FRCPC Professor, Western University Cardiologist, Hearth Rhythm Specialist Director, Electrophysiology Laboratory,
Common Codes for ICD-10
 Common Codes for ICD-10 Specialty: Cardiology *Always utilize more specific codes first. ABNORMALITIES OF HEART RHYTHM ICD-9-CM Codes: 427.81, 427.89, 785.0, 785.1, 785.3 R00.0 Tachycardia, unspecified
Common Codes for ICD-10 Specialty: Cardiology *Always utilize more specific codes first. ABNORMALITIES OF HEART RHYTHM ICD-9-CM Codes: 427.81, 427.89, 785.0, 785.1, 785.3 R00.0 Tachycardia, unspecified
Special health. guide. Hugh Calkins, M.D., and Ronald Berger, M.D., Ph.D. Guide to Understanding. Atrial Fibrillation WITH
 Hugh Calkins, M.D., and Ronald Berger, M.D., Ph.D. Guide to Understanding Atrial Fibrillation WITH Table of Contents Atrial Fibrillation: An Introduction... 1 How AF Affects the Heart... 2 Who Gets AF?...
Hugh Calkins, M.D., and Ronald Berger, M.D., Ph.D. Guide to Understanding Atrial Fibrillation WITH Table of Contents Atrial Fibrillation: An Introduction... 1 How AF Affects the Heart... 2 Who Gets AF?...
Management of Arrhythmias The General Practitioners role
 Management of Arrhythmias The General Practitioners role Rohan Gunawardena MD, FRCP, FCCP, FACC Consultant Cardiac Electrophysiologist National Hospital of Sri Lanka Arrhythmias not common Palpitations
Management of Arrhythmias The General Practitioners role Rohan Gunawardena MD, FRCP, FCCP, FACC Consultant Cardiac Electrophysiologist National Hospital of Sri Lanka Arrhythmias not common Palpitations
The pill-in-the-pocket strategy for paroxysmal atrial fibrillation
 The pill-in-the-pocket strategy for paroxysmal atrial fibrillation KONSTANTINOS P. LETSAS, MD, FEHRA LABORATORY OF CARDIAC ELECTROPHYSIOLOGY EVANGELISMOS GENERAL HOSPITAL OF ATHENS ARRHYTHMIAS UPDATE,
The pill-in-the-pocket strategy for paroxysmal atrial fibrillation KONSTANTINOS P. LETSAS, MD, FEHRA LABORATORY OF CARDIAC ELECTROPHYSIOLOGY EVANGELISMOS GENERAL HOSPITAL OF ATHENS ARRHYTHMIAS UPDATE,
4. The two inferior chambers of the heart are known as the atria. the superior and inferior vena cava, which empty into the left atrium.
 Answer each statement true or false. If the statement is false, change the underlined word to make it true. 1. The heart is located approximately between the second and fifth ribs and posterior to the
Answer each statement true or false. If the statement is false, change the underlined word to make it true. 1. The heart is located approximately between the second and fifth ribs and posterior to the
Update on Palpitations and AF February 28 th 2018
 Update on Palpitations and AF February 28 th 2018 Dr Mrinal Andrew Saha MA(Cantab) MBBS FRCP PhD Consultant Interventional Cardiologist GHNHSFT Dr Mrinal Saha Appointed 2010 Special interests: Angioplasty,
Update on Palpitations and AF February 28 th 2018 Dr Mrinal Andrew Saha MA(Cantab) MBBS FRCP PhD Consultant Interventional Cardiologist GHNHSFT Dr Mrinal Saha Appointed 2010 Special interests: Angioplasty,
ECGs: Everything a finalist needs to know. Dr Amy Coulden As part of the Simply Finals series
 ECGs: Everything a finalist needs to know Dr Amy Coulden As part of the Simply Finals series Aims and objectives To be able to interpret basic ECG abnormalities To be able to recognise commonly tested
ECGs: Everything a finalist needs to know Dr Amy Coulden As part of the Simply Finals series Aims and objectives To be able to interpret basic ECG abnormalities To be able to recognise commonly tested
ECGs and Arrhythmias: Family Medicine Board Review 2012
 Overview ECGs and Arrhythmias: Family Medicine Board Review 2012 Jess Waldura, MD University of California, San Francisco walduraj@nccc.ucsf.edu Bundle branch blocks Quick review of ischemia Arrhythmias
Overview ECGs and Arrhythmias: Family Medicine Board Review 2012 Jess Waldura, MD University of California, San Francisco walduraj@nccc.ucsf.edu Bundle branch blocks Quick review of ischemia Arrhythmias
WPW in Athletes Should we treat all? age? RAMI FOGELMAN SCHNEIDER CHILDREN MEDICAL CENTER OF ISRAEL
 WPW in Athletes Should we treat all? age? RAMI FOGELMAN SCHNEIDER CHILDREN MEDICAL CENTER OF ISRAEL W.P.W Clues in sinus rhythm No Q in Lt chest leads (WPW 88%, control 5%) PR < 100msec (WPW 80%, control
WPW in Athletes Should we treat all? age? RAMI FOGELMAN SCHNEIDER CHILDREN MEDICAL CENTER OF ISRAEL W.P.W Clues in sinus rhythm No Q in Lt chest leads (WPW 88%, control 5%) PR < 100msec (WPW 80%, control
Palpitations and Management of Arrhythmias. Palpitations. Differential Diagnosis. Differential Diagnosis. Differential Diagnosis
 Palpitations and Management of Arrhythmias Fernando Vega, M.D. 7/8/2011 Fernando Vega, M.D. 1 7/8/2011 Fernando Vega, M.D. 2 Palpitations A sensory symptom An unpleasant awareness of the forceful, rapid
Palpitations and Management of Arrhythmias Fernando Vega, M.D. 7/8/2011 Fernando Vega, M.D. 1 7/8/2011 Fernando Vega, M.D. 2 Palpitations A sensory symptom An unpleasant awareness of the forceful, rapid
CATHETER ABLATION FOR TACHYCARDIAS
 190 CATHETER ABLATION FOR TACHYCARDIAS MASOOD AKHTAR, M.D. T ACHY ARRHYTHMIAS constitute a major cause of mortality and morbidity. The most serious manifestation of cardiac arrhythmia is sudden cardiac
190 CATHETER ABLATION FOR TACHYCARDIAS MASOOD AKHTAR, M.D. T ACHY ARRHYTHMIAS constitute a major cause of mortality and morbidity. The most serious manifestation of cardiac arrhythmia is sudden cardiac
Chapter 26. Media Directory. Dysrhythmias. Diagnosis/Treatment of Dysrhythmias. Frequency in Population Difficult to Predict
 Chapter 26 Drugs for Dysrythmias Slide 33 Slide 35 Media Directory Propranolol Animation Amiodarone Animation Upper Saddle River, New Jersey 07458 All rights reserved. Dysrhythmias Abnormalities of electrical
Chapter 26 Drugs for Dysrythmias Slide 33 Slide 35 Media Directory Propranolol Animation Amiodarone Animation Upper Saddle River, New Jersey 07458 All rights reserved. Dysrhythmias Abnormalities of electrical
Clinical Policy: Holter Monitors Reference Number: CP.MP.113
 Clinical Policy: Reference Number: CP.MP.113 Effective Date: 05/18 Last Review Date: 04/18 Coding Implications Revision Log Description Ambulatory electrocardiogram (ECG) monitoring provides a view of
Clinical Policy: Reference Number: CP.MP.113 Effective Date: 05/18 Last Review Date: 04/18 Coding Implications Revision Log Description Ambulatory electrocardiogram (ECG) monitoring provides a view of
WOLFF PARKINSON WHITE SYNDROME. Katarzyna Bigaj PGY-1
 WOLFF PARKINSON WHITE SYNDROME Katarzyna Bigaj PGY-1 Preexcitation is defined as a premature activation of the ventricular myocardium by an impulse that travels by an anomalous path and avoids physiologic
WOLFF PARKINSON WHITE SYNDROME Katarzyna Bigaj PGY-1 Preexcitation is defined as a premature activation of the ventricular myocardium by an impulse that travels by an anomalous path and avoids physiologic
Dos and Don t in Cardiac Arrhythmia. Case 1 -ECG. Case 1. Management. Emergency Admissions. Reduction of TE risk -CHADS 2 score. Hospital Admissions
 Emergency Admissions Dos and Don t in Cardiac Arrhythmia Tom Wong, MD, FESC Consultant Cardiologist, Honorary Senior Lecturer Royal Brompton & Harefield Hospitals National Heart and Lung Institute, Imperial
Emergency Admissions Dos and Don t in Cardiac Arrhythmia Tom Wong, MD, FESC Consultant Cardiologist, Honorary Senior Lecturer Royal Brompton & Harefield Hospitals National Heart and Lung Institute, Imperial
Debate: Asymptomatic Patients with Ventricular Preexcitation Require EP Testing for Risk Stratification. Carlo Pappone, MD, PhD, FACC
 Debate: Asymptomatic Patients with Ventricular Preexcitation Require EP Testing for Risk Stratification Carlo Pappone, MD, PhD, FACC The Wolff-Parkinson-White Syndrome Demographics Δ waves detectable on
Debate: Asymptomatic Patients with Ventricular Preexcitation Require EP Testing for Risk Stratification Carlo Pappone, MD, PhD, FACC The Wolff-Parkinson-White Syndrome Demographics Δ waves detectable on
Tachycardia-induced heart failure - Does it exist?
 Tachycardia-induced heart failure - Does it exist? PD Dr Etienne Delacrétaz Clinique Cecil et Hôpital de Fribourg SSC Cardiology meeting 2015 Zürich Rapid atrial fibrillation is a common cause of heart
Tachycardia-induced heart failure - Does it exist? PD Dr Etienne Delacrétaz Clinique Cecil et Hôpital de Fribourg SSC Cardiology meeting 2015 Zürich Rapid atrial fibrillation is a common cause of heart
Skin supplied by T1-4 (medial upper arm and neck) T5-9- epigastrium Visceral afferents from skin and heart are the same dorsal root ganglio
 Cardio 2 ECG... 3 Cardiac Remodelling... 11 Valvular Diseases... 13 Hypertension... 18 Aortic Coarctation... 24 Erythropoiesis... 27 Haemostasis... 30 Anaemia... 36 Atherosclerosis... 44 Angina... 48 Myocardial
Cardio 2 ECG... 3 Cardiac Remodelling... 11 Valvular Diseases... 13 Hypertension... 18 Aortic Coarctation... 24 Erythropoiesis... 27 Haemostasis... 30 Anaemia... 36 Atherosclerosis... 44 Angina... 48 Myocardial
Cardiac Arrhythmias. For Pharmacists
 Cardiac Arrhythmias For Pharmacists Agenda Overview of the normal Classification Management Therapy Conclusion Cardiac arrhythmias Overview of the normal Arrhythmia: definition From the Greek a-, loss
Cardiac Arrhythmias For Pharmacists Agenda Overview of the normal Classification Management Therapy Conclusion Cardiac arrhythmias Overview of the normal Arrhythmia: definition From the Greek a-, loss
December 2018 Tracings
 Tracings Tracing 1 Tracing 4 Tracing 1 Answer Tracing 4 Answer Tracing 2 Tracing 5 Tracing 2 Answer Tracing 5 Answer Tracing 3 Tracing 6 Tracing 3 Answer Tracing 6 Answer Questions? Contact Dr. Nelson
Tracings Tracing 1 Tracing 4 Tracing 1 Answer Tracing 4 Answer Tracing 2 Tracing 5 Tracing 2 Answer Tracing 5 Answer Tracing 3 Tracing 6 Tracing 3 Answer Tracing 6 Answer Questions? Contact Dr. Nelson
National Coverage Determination (NCD) for Cardiac Pacemakers (20.8)
 Page 1 of 12 Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services National Coverage Determination (NCD) for Cardiac Pacemakers (20.8) Tracking Information Publication Number 100-3 Manual Section Number 20.8 Manual
Page 1 of 12 Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services National Coverage Determination (NCD) for Cardiac Pacemakers (20.8) Tracking Information Publication Number 100-3 Manual Section Number 20.8 Manual
CLINICAL CARDIAC ELECTROPHYSIOLOGY Maintenance of Certification (MOC) Examination Blueprint
 CLINICAL CARDIAC ELECTROPHYSIOLOGY Maintenance of Certification (MOC) Examination Blueprint ABIM invites diplomates to help develop the Clinical Cardiac Electrophysiology MOC exam blueprint Based on feedback
CLINICAL CARDIAC ELECTROPHYSIOLOGY Maintenance of Certification (MOC) Examination Blueprint ABIM invites diplomates to help develop the Clinical Cardiac Electrophysiology MOC exam blueprint Based on feedback
A Narrow QRS Complex Tachycardia With An Apparently Concentric Retrograde Atrial Activation Sequence
 www.ipej.org 125 Case Report A Narrow QRS Complex Tachycardia With An Apparently Concentric Retrograde Atrial Activation Sequence Miguel A. Arias MD, PhD; Eduardo Castellanos MD, PhD; Alberto Puchol MD;
www.ipej.org 125 Case Report A Narrow QRS Complex Tachycardia With An Apparently Concentric Retrograde Atrial Activation Sequence Miguel A. Arias MD, PhD; Eduardo Castellanos MD, PhD; Alberto Puchol MD;
Hatim Al Lawati. MD, FRCPC, DABIM(CV), FACC
 Hatim Al Lawati. MD, FRCPC, DABIM(CV), FACC Consultant Interventional Cardiology & Structural Heart Disease Department of Medicine Sultan Qaboos University Hospital hatim.al.lawati@gmail.com April 2017
Hatim Al Lawati. MD, FRCPC, DABIM(CV), FACC Consultant Interventional Cardiology & Structural Heart Disease Department of Medicine Sultan Qaboos University Hospital hatim.al.lawati@gmail.com April 2017
Ablation Update and Case Studies. Lawrence Nair, MD, FACC Director of Electrophysiology Presbyterian Heart Group
 Ablation Update and Case Studies Lawrence Nair, MD, FACC Director of Electrophysiology Presbyterian Heart Group Disclosures No financial relationships to disclose Objectives At the conclusion of this activity,
Ablation Update and Case Studies Lawrence Nair, MD, FACC Director of Electrophysiology Presbyterian Heart Group Disclosures No financial relationships to disclose Objectives At the conclusion of this activity,
