1 Fq-ii I - I I...L w. husband on the morning of her admission. Her symptoms
|
|
|
- Shauna Barrett
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
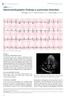
1 . ', ir Electrocardiography Series Singapore Med J 202;53(6) 367 CM EARTCLE Nonischaemic causes of ST segment elevation vandito Kuntjorol, MD, Swee Guan Teo'2, MBBS, MRCP, Kian Keong Poh'2, FRCP, FACC L' pi r ; ii 4,,4 W:,. li Fqii....L...,., Ell.. r..... i,. w,,... n. Fig. ECG shows ST elevation in leads VV6, and avl with biphasic T wave in VV4. Mild ST depression can be seen in lead ll. CASE CLNCAL PRESENTATON A 54 year old woman with a history of dyslipidaemia was admitted with shortness of breath following an upper respiratory tract infection and a stressful argument with her husband on the morning of her admission. Her symptoms progressively worsened and she was subsequently intubated in the emergency department. She was transferred to our hospital due to an abnormal electrocardiogram (ECG). What are the ECG abnormalities seen in Fig.? 'Cardiac Department, National University Heart Centre, Singapore, 2Yong Loo Lin School of Medicine, National University of Singapore, Singapore Correspondence: A/Prof Poh Kian Keong, Senior Consultant and Associate Professor, Cardiac Department, National University Heart Centre, E Kent Ridge Road, NUHS Tower Block, Level 9, Singapore kiankeongpoh@nuhs.edu.sg
2 and!electrocardiography Series ECG NTERPRETATON The ECG shows sinus tachycardia with elevated ST elevation (3 mm) in the anterior and lateral leads (VV6, avl). The T waves in VV4 are biphasic. Mild ST depression is seen in lead. CLNCAL COURSE The patient was rushed to the cardiac catheterisation laboratory for emergency coronary angiography, which showed a nonsignificant 25% stenosis of both the left anterior descending and right coronary arteries. Her left ventriculogram showed apical and mid left ventricular ballooning (Fig. 2). She was diagnosed as suffering from stress induced cardiomyopathy. Supportive measurement with intraaortic balloon pump (ABP) was initiated. Further investigation showed only a mild elevation of the cardiac enzymes, with a peak creatine kinase (CK)MB fraction of.0 ug/l and troponin T of.09 ug/l compared to ST segment elevation myocardial infarction (STEM), where the cardiac enzymes would usually be significantly higher. Echocardiogram showed moderate left ventricular systolic dysfunction. The patient's condition improved and she was weaned off the ABP LV Fig. 2 Left ventriculogram shows apical and mid left ventricular ballooning (arrows) during systole. LV: left ventricle and extubated within the next 48 hours. She was discharged well from the hospital. Repeat echocardiogram done five months later showed normal left ventricular function with an ejection fraction of 60% and no apical ballooning. Fig. 3 ECG shows sinus tachycardia with widespread ST elevation. in lead. PR elevation arrows) is seen in lead avr and reciprocal PR depression CASE 2 CLNCAL PRESENTATON A 59 year old man with a history of prostate cancer (status post prostatectomy) and myelodysplastic syndrome, with recent transformation to acute myeloblastic leukaemia (AML), was admitted with chest pain of three days' duration. The chest pain was worse on deep inspiration, and was accompanied by fever, chills and palpitation. He had normal blood pressure and the heart rate was 20 beats per minute. What are the ECG abnormalities seen in Fig. 3? Singapore Med J 202; 53(6) 368
3 ECG NTERPRETATON There is diffuse ST segment elevation in leads V2V6,, and avf, and reciprocal ST depression in avr. The ST elevation is about 2 mm and is mildly concave. There is PR segment elevation in avr and reciprocal PR segment depression in lead. These abnormalities are consistent with acute pericarditis. CLNCAL COURSE The patient underwent urgent bedside echocardiography, which showed moderate pericardial effusion with no definite features of pericardial tamponade. However, he deteriorated the next day, and repeat echocardiogram showed worsening of the pericardial effusion (Fig. 4). Pericardiocentesis was done and 350 ml of haemoserous fluid was drained. Fluid cytology revealed no malignancy and all cultures sent from the fluid sample were negative. His acute pericarditis and pericardial effusion were most likely exacerbated by the newly diagnosed AML. The patient's condition improved after he was started on chemotherapy for AML. Repeat echocardiogram ten days later vvr Nip: 0 PO 4 47 PE V Re LA E BP TRM Fig. 4 Echocardiogram in apical 4 chamber window shows circumferential pericardial effusion. PE: pericardial effusion; RA: right atrium; RV: right ventricle; LA: left atrium; LV: left ventricle revealed no pericardial effusion. He stayed in the hospital for a total of 30 days for chemotherapy and post chemotherapy care. He was discharged well from the hospital. [: k J L.. L ' :., i,.. r ' 7+! i7,j...i. gliz L LL. Er t,7 '3 ±F i i Fig. 5 ECG shows sinus rhythm with concave ST elevation (arrows) in leads V4V6. There are prominent and asymmetrical upright T waves. No reciprocal ST depression is seen in the inferior leads. CASE 3 CLNCAL PRESENTATON A 58 year old man with hypertension and hyperlipidaemia was electively admitted for transforaminal lumbar inter body fusion of L4L5 with bilateral decompression. The cardiology team was consulted postoperatively to review his ECG. What is the ECG diagnosis in Fig. 5? ECG NTERPRETATON The ECG shows ST segment elevation (concave upwards) associated with tall T waves in leads V3V6. There is no reciprocal depression seen in the inferior leads. This is consistent with a normal variant pattern of the ECG known as 'early repolarisation pattern'. Singapore Med J 202; 53(6) 369
4 Table. Causes of nonischaemic ST segment elevation on ECG. Acute pericarditis Normal variants (early repolarisation pattern) LVH, LBBB (mainly in V V2 or V3) Takotsubo cardiomyopathy Acute pulmonary embolism Post cardioversion Brugada pattern (Coved like ST segment elevation in V V3 ) Type C anti arrhythmic drugs Hypercalcaemia, hyperkalaemia LVH: left ventricular hypertrophy; LBBB: left bundle branch block CLNCAL COURSE The patient was in good condition postoperatively without any active cardiac symptoms. Blood tests revealed normal troponin T, with a slight elevation of total CK level, most likely due to muscle injury post surgery. A repeat ECG showed no significant change. The patient was subsequently discharged from the hospital. Further evaluation with a nuclear stress test a few months later showed normal perfusion with normal left ventricular ejection fraction. DSCUSSON STEM remains the most important cause of ST segment elevation in the ECG, and needs be recognised and treated immediately with urgent coronary revascularisation. However, there are several nonischaemic causes of ST segment elevation on ECG (Table ) that are also important. Stress induced cardiomyopathy is also known as Takotsubo cardiomyopathy, apical ballooning syndrome or broken heart syndrome. This condition is more common in females, mostly postmenopausal, and usually triggered by an acute medical illness or sudden and intense emotional or physical stress (such as death of relatives, particularly if unexpected, domestic abuse, arguments, catastrophic medical diagnoses and natural disasters). Clinical presentation of stress induced cardiomyopathy has many similarities with acute myocardial infarction. The most common symptoms are acute onset of chest pain, commonly accompanied by ST elevation in the ECG in a majority of the patients. Coronary angiogram, which is frequently performed on such patients, usually shows no significant coronary lesions that can contribute to the significant decrease in left ventricular function and apical ballooning of the left ventricle. The mechanisms for these ECG findings are currently unclear. The possible hypothesis is catecholamine excess or micro vascular dysfunction. Echocardiogram usually shows ballooning of the apex and the mid left ventricular cavity with hyperkinesis on the basal walls Despite the severity and acute presentation of this condition, the abnormality is most often transient. Supportive treatment during the illness and heart failure medication during the recovery phase often result in complete recovery of the symptoms and heart function. The second case highlights the other frequent cause of ST elevation. n contrast to the first case, the ST elevation in acute pericarditis has some distinct and specific characteristics, especially in the acute phase. The ST segment elevation rarely exceeds 5 mm and usually retains its normal concavity, unlike in STEM.6 Reciprocal ST depression is absent except in avr. Since the pericardium wraps around the heart, the ST changes are more generalised, and thus present in most leads and do not correspond to anatomical grouping based on coronary vascularisation. Another important clue to the diagnosis of acute pericarditis is the frequent presence of PR segment elevation in avr, with reciprocal PR segment depression in lead. The last case highlights the importance of knowledge that normal variant ECG or 'early repolarisation pattern' can mimic the ST elevation seen in myocardial infarction. This variant occurs in 2%5% of the population, mainly in young adults who are athletically active. The characteristic concave ST elevation and asymmetrical tall upright T wave need to be recognised in order to differentiate this normal variant from STEM. A few recent studies have suggested the association of this syndrome with an increased risk of sudden death from ventricular tachyarrhythmias. However, in these studies, ST elevation was noted to be present mainly in the inferior (and not the lateral leads), and prominent) waves were seen. There are, at present, important ongoing studies on this issue. However, it is currently accepted that early repolarisation pattern is generally a benign ECG finding with an excellent prognosis, although in a few patients, a very low risk of ventricular tachyarrhythmia and sudden death may be present. ACKNOWLEDGEMENT We acknowledge Professor Chia Boon Lock for his advice and help in the writing of this article. ABSTRACT ST segment elevation is one of the most important electrocardiographic features that need to be recognised. Although ST segment elevation myocardial infarction is one of the main causes of this abnormality, there are other nonischaemic causes that are also important. We discuss reversible apical ballooning syndrome or Takotsubo cardiomyopathy, pericarditis and a case of ST segment elevation due to 'early repolarisation pattern'. Keywords: acute pericarditis, early repolarisation, ECG, ST segment elevation, Takotsubo cardiomyopathy Singapore Med J 202; 53(6): REFERENCES. Poh KK, Tan HC, Teo SG. Electrocardiography Series. ECG ST segment elevation in patients with chest pain. Singapore Med J 20; 52: Akashi YJ, Goldstein DS, Barbaro G, Ueyama T. Takotsubo cardiomyopathy: a new form of acute, reversible heart failure. Circulation 2008; 8: Wittstein S, Thiemann DR, Lima JA, et al. Neurohumoral features of myocardial stunning due to sudden emotional stress. N Engl J Med 2005; 352: Dib C, Asirvatham S, Elesber A, et al. Clinical correlates and prognostic significance of electrocardiographic abnormalities in apical ballooning syndrome (Takotsubo/stressinduced cardiomyopathy). Am Heart J 2009; 57:9338. Singapore Med J 202; 53(6) 370
5 5. Poh KK, Chan MY, Chia BL. mages in cardiology: reversible left ventricular apical ballooning after head injury. Clin Cardiol 2005; 28: Massimo. Clinical presentation and diagnostic evaluation of acute pericarditis. n: UpToDate 20 ver 9.3 [online]. Available at: www. uptodate.com. Accessed March 23, Robert OB, Douglas LM, Douglas PZ, Peter L. Braunwald's Heart Disease. A Textbook of Cardiovascular Medicine. 9th ed. Philadelphia: Elsevier Saunders, 202: 367, 559. SNGAPORE MEDCAL COUNCL CATEGORY 3B CME PROGRAMME (Code SMJ 20206A) Question. The following are causes of stress induced (Takotsubo) cardiomyopathy: (a) Severe emotional stress. (b) Acute psychosis. (c) Severe acute illness. (d) Natural disasters. True False Question 2. These statements are true for Takotsubo cardiomyopathy: (a) The ECG changes can be easily differentiated from ST segment elevation myocardial infarction. (b) No treatment is necessary for the acute phase. (c) Most patients will recover and retain normal left ventricular ejection fraction. (d) Performing cardiac catheterisation on these patients is considered unnecessary. Question 3. Causes of nonischaemic ST elevation on ECG include: (a) Hypokalaemia. (b) Acute pulmonary embolism. (c) Left bundle branch block pattern. (d) Brugada ECG pattern. Question 4. The following ECG changes are characteristic for acute pericarditis: (a) The ECG changes are widespread because the pericardium wraps around the heart. (b) PR elevation can be seen in lead avr. (c) PR depression and ST elevation can be seen in lead, causing PR ST segment discordance. (d) ST elevation is usually less than 5 mm. Question 5. The following are true of 'early repolarisation pattern' on ECG: (a) The ST elevation is convex. (b) T wave can mimic those of hyper acute T wave changes in acute myocardial infarction. (c) T wave abnormality is usually asymmetrical. (d) t is more common in older people. Doctor's particulars: Name in full MCR number Specialty: address SUBMSSON NSTRUCTONS: () Log on at the SMJ website: and select the appropriate set of questions. (2) Select your answers and provide your name, address and MCR number. Click on "Submit answers" to submit. RESULTS: () Answers will be published in the SMJ August 202 issue. (2) The MC R numbers of successful candidates will be posted online at by 6 July 202. (3) All online submissions will receive an automatic acknowledgement. (4) Passing mark is 60%. No mark will be deducted for incorrect answers. (5) The SMJ editorial office will submit the list of successful candidates to the Singapore Medical Council. (6) One CME point is awarded for successful candidates. Deadline for submission: (June 202 SMJ 3B CME programme): 2 noon, 9 July 202. Singapore Med J 202; 53(6) 37
CME Article Brugada pattern masking anterior myocardial infarction
 Electrocardiography Series Singapore Med J 2011; 52(9) : 647 CME Article Brugada pattern masking anterior myocardial infarction Seow S C, Omar A R, Hong E C T Cardiology Department, National University
Electrocardiography Series Singapore Med J 2011; 52(9) : 647 CME Article Brugada pattern masking anterior myocardial infarction Seow S C, Omar A R, Hong E C T Cardiology Department, National University
ECGs of structural heart disease: Part I
 Electrocardiography Series Singapore Med J 2011; 52(12) 855 CME Article ECGs of structural heart disease: Part I Poh K K, Teo S G, Tay E L W, Yip J WL Cardiac Department, National University Heart Centre,
Electrocardiography Series Singapore Med J 2011; 52(12) 855 CME Article ECGs of structural heart disease: Part I Poh K K, Teo S G, Tay E L W, Yip J WL Cardiac Department, National University Heart Centre,
15 th Sukaman Memorial Lecture ST Segment Elevation: New Electrocardiographic Insights in 2014
 DOI 10.7603/s40602-016-0006-3 ASEAN Heart Journal http://www.globalsciencejournals.com/journal/40602 Vol. 24, no.1, 98 105 (2016) ISSN: 2315-4551 15 th Sukaman Memorial Lecture ST Segment Elevation: New
DOI 10.7603/s40602-016-0006-3 ASEAN Heart Journal http://www.globalsciencejournals.com/journal/40602 Vol. 24, no.1, 98 105 (2016) ISSN: 2315-4551 15 th Sukaman Memorial Lecture ST Segment Elevation: New
_FT 4. _Ci4 - ;,..., r. _ L.1_4±J-1 +.1_77 di _-_,..i , lt.! -7H :-,-...i-2 Litt drri "94. _Ia. :7...-t. ' ; r., r - .J...
 rr 7 :,Liir 6 E I it i, r i s : al, r I Electrocardiography Series Singapore Med 20, 52() 3 C M E Article ECG ST segment elevation in patients with chest pain Poh K K, Tan H C, Teo S G Cardiac Department,
rr 7 :,Liir 6 E I it i, r i s : al, r I Electrocardiography Series Singapore Med 20, 52() 3 C M E Article ECG ST segment elevation in patients with chest pain Poh K K, Tan H C, Teo S G Cardiac Department,
Electrocardiographic T wave abnormalities
 Singapore Med J 2013; 54(11): 606-610 doi: 10.11622/smedj.2013218 CMEArticle Electrocardiographic T wave abnormalities Weiqin Lin 1, MBBS, MRCP, Swee Guan Teo 2, MBBS (Hons), MRCP, Kian Keong Poh 1,3,
Singapore Med J 2013; 54(11): 606-610 doi: 10.11622/smedj.2013218 CMEArticle Electrocardiographic T wave abnormalities Weiqin Lin 1, MBBS, MRCP, Swee Guan Teo 2, MBBS (Hons), MRCP, Kian Keong Poh 1,3,
the ECG, 6 mg of intravenous adenosine was administered as a fast bolus through a large bore intravenous cannula in
 (arrows). Electrocardiography Series Singapore Med.1 2011, 52(3) 146 CME Article Regular narrow complex tachycardia Singh D, Teo S G, Poh K K V Hr JL1 11 VL VF WA, Fig. I ECG shows regular narrow complex
(arrows). Electrocardiography Series Singapore Med.1 2011, 52(3) 146 CME Article Regular narrow complex tachycardia Singh D, Teo S G, Poh K K V Hr JL1 11 VL VF WA, Fig. I ECG shows regular narrow complex
CMEArticle ECGs of structural heart disease: Part 2
 Singapore Med J 2012; 53(2) : 77 CMEArticle ECGs of structural heart disease: Part 2 Ayyachamy SS 1, MRCP, Teo SG 1, MBBS, MRCP, Tay ELW 1, MRCP, FACC, Yip JWL 1, MBBS, MRCP, Poh KK 1,2, FRCP, FACC Fig.
Singapore Med J 2012; 53(2) : 77 CMEArticle ECGs of structural heart disease: Part 2 Ayyachamy SS 1, MRCP, Teo SG 1, MBBS, MRCP, Tay ELW 1, MRCP, FACC, Yip JWL 1, MBBS, MRCP, Poh KK 1,2, FRCP, FACC Fig.
All About STEMIs. Presented By: Brittney Urvand, RN, BSN, CCCC. Essentia Health Fargo Cardiovascular Program Manager.
 All About STEMIs Presented By: Brittney Urvand, RN, BSN, CCCC Essentia Health Fargo Cardiovascular Program Manager Updated 10/2/2018 None Disclosures Objectives Identify signs and symptoms of a heart attack
All About STEMIs Presented By: Brittney Urvand, RN, BSN, CCCC Essentia Health Fargo Cardiovascular Program Manager Updated 10/2/2018 None Disclosures Objectives Identify signs and symptoms of a heart attack
Acute Coronary Syndromes Unstable Angina Non ST segment Elevation MI (NSTEMI) ST segment Elevation MI (STEMI)
 Leanna R. Miller, RN, MN, CCRN-CSC, PCCN-CMC, CEN, CNRN, CMSRN, NP Education Specialist LRM Consulting Nashville, TN Objectives Evaluate common abnormalities that mimic myocardial infarction. Identify
Leanna R. Miller, RN, MN, CCRN-CSC, PCCN-CMC, CEN, CNRN, CMSRN, NP Education Specialist LRM Consulting Nashville, TN Objectives Evaluate common abnormalities that mimic myocardial infarction. Identify
2/7/ LEAD ECG CASE STUDIES Lisa Riggs MSN, RN, ACNS-BC, CCRN-K CASE #1 WHAT ELSE WOULD YOU ASSESS? WHAT S YOUR DIAGNOSIS?
 12 LEAD ECG CASE STUDIES Lisa Riggs MSN, RN, ACNS-BC, CCRN-K CASE #1 31 y/o male is a direct admit from the physician s office with c/o chest pain and SOA WHAT ELSE WOULD YOU ASSESS? WHAT S YOUR DIAGNOSIS?
12 LEAD ECG CASE STUDIES Lisa Riggs MSN, RN, ACNS-BC, CCRN-K CASE #1 31 y/o male is a direct admit from the physician s office with c/o chest pain and SOA WHAT ELSE WOULD YOU ASSESS? WHAT S YOUR DIAGNOSIS?
ECG Workshop. Nezar Amir
 ECG Workshop Nezar Amir Myocardial Ischemia ECG Infarct ECG in STEMI is dynamic & evolving Common causes of ST shift Infarct Localisation Left main artery occlusion: o diffuse ST-depression with ST elevation
ECG Workshop Nezar Amir Myocardial Ischemia ECG Infarct ECG in STEMI is dynamic & evolving Common causes of ST shift Infarct Localisation Left main artery occlusion: o diffuse ST-depression with ST elevation
Comparison of Clinical Features between Typical and Atypical Takotsubo Cardiomyopathy: A Single Center, Retrospective, Case-Controlled Study
 Brief Report Acta Cardiol Sin 2013;29:88 93 Comparison of Clinical Features between Typical and Atypical Takotsubo Cardiomyopathy: A Single Center, Retrospective, Case-Controlled Study Cheng-Kang Chen,
Brief Report Acta Cardiol Sin 2013;29:88 93 Comparison of Clinical Features between Typical and Atypical Takotsubo Cardiomyopathy: A Single Center, Retrospective, Case-Controlled Study Cheng-Kang Chen,
Myocardial Infarction. Reading Assignment (p66-78 in Outline )
 Myocardial Infarction Reading Assignment (p66-78 in Outline ) Objectives 1. Why do ST segments go up or down in ischemia? 2. STEMI locations and culprit vessels 3. Why 15-lead ECGs? 4. What s up with avr?
Myocardial Infarction Reading Assignment (p66-78 in Outline ) Objectives 1. Why do ST segments go up or down in ischemia? 2. STEMI locations and culprit vessels 3. Why 15-lead ECGs? 4. What s up with avr?
By the end of this lecture, you will be able to: Understand the 12 lead ECG in relation to the coronary circulation and myocardium Perform an ECG
 By the end of this lecture, you will be able to: Understand the 12 lead ECG in relation to the coronary circulation and myocardium Perform an ECG recording Identify the ECG changes that occur in the presence
By the end of this lecture, you will be able to: Understand the 12 lead ECG in relation to the coronary circulation and myocardium Perform an ECG recording Identify the ECG changes that occur in the presence
PERICARDIAL DIAESE. Kaijun Cui Associated professor Sichuan University
 PERICARDIAL DIAESE Kaijun Cui Associated professor Sichuan University CLASSIFICATION acute pericarditis pericardial effusion cardiac tamponade constrictive pericarditis congenitally absent pericardium
PERICARDIAL DIAESE Kaijun Cui Associated professor Sichuan University CLASSIFICATION acute pericarditis pericardial effusion cardiac tamponade constrictive pericarditis congenitally absent pericardium
REtrive. REpeat. RElearn Design by. Test-Enhanced Learning based ECG practice E-book
 Test-Enhanced Learning Test-Enhanced Learning Test-Enhanced Learning Test-Enhanced Learning based ECG practice E-book REtrive REpeat RElearn Design by S I T T I N U N T H A N G J U I P E E R I Y A W A
Test-Enhanced Learning Test-Enhanced Learning Test-Enhanced Learning Test-Enhanced Learning based ECG practice E-book REtrive REpeat RElearn Design by S I T T I N U N T H A N G J U I P E E R I Y A W A
Takotsubo syndrome. Ευτυχία Σμπαρούνη, FACC, FESC
 Takotsubo syndrome Ευτυχία Σμπαρούνη, FACC, FESC Definition Takotsubo Apical ballooning Broken heart syndrome Stress cardiomyopathy Cathecholaminergic cardiomyopathy Epidemiology 1990 first report by Japanese
Takotsubo syndrome Ευτυχία Σμπαρούνη, FACC, FESC Definition Takotsubo Apical ballooning Broken heart syndrome Stress cardiomyopathy Cathecholaminergic cardiomyopathy Epidemiology 1990 first report by Japanese
ECG Cases and Questions. Ashish Sadhu, MD, FHRS, FACC Electrophysiology/Cardiology
 ECG Cases and Questions Ashish Sadhu, MD, FHRS, FACC Electrophysiology/Cardiology 32 yo female Life Insurance Physical 56 yo male with chest pain Terminology Injury ST elevation Ischemia T wave inversion
ECG Cases and Questions Ashish Sadhu, MD, FHRS, FACC Electrophysiology/Cardiology 32 yo female Life Insurance Physical 56 yo male with chest pain Terminology Injury ST elevation Ischemia T wave inversion
ECG ABNORMALITIES D R. T AM A R A AL Q U D AH
 ECG ABNORMALITIES D R. T AM A R A AL Q U D AH When we interpret an ECG we compare it instantaneously with the normal ECG and normal variants stored in our memory; these memories are stored visually in
ECG ABNORMALITIES D R. T AM A R A AL Q U D AH When we interpret an ECG we compare it instantaneously with the normal ECG and normal variants stored in our memory; these memories are stored visually in
Takotsubo Cardiomyopathy
 Advances in Heart Disease 2008 Takotsubo Cardiomyopathy Mary O. Gray, MD, FAHA, FACC Associate Professor of Medicine University of California, San Francisco Staff Cardiologist and Training Faculty Divisions
Advances in Heart Disease 2008 Takotsubo Cardiomyopathy Mary O. Gray, MD, FAHA, FACC Associate Professor of Medicine University of California, San Francisco Staff Cardiologist and Training Faculty Divisions
Mid-ventricular takotsubo: A case report
 Jain et al. 452 CASE REPORT OPEN ACCESS Mid-ventricular takotsubo: A case report Sachin Kumar Amruthlal Jain, Hrishabh Modi, Timothy R Larsen, Shukri David Abstract Introduction: Is mid-ventricular takotsubo
Jain et al. 452 CASE REPORT OPEN ACCESS Mid-ventricular takotsubo: A case report Sachin Kumar Amruthlal Jain, Hrishabh Modi, Timothy R Larsen, Shukri David Abstract Introduction: Is mid-ventricular takotsubo
Pennsylvania Academy of Family Physicians Foundation & UPMC 43rd Refresher Course in Family Medicine CME Conference March 10-13, 2016
 Pennsylvania Academy of Family Physicians Foundation & UPMC 43rd Refresher Course in Family Medicine CME Conference March 10-13, 2016 Disclosures: EKG Workshop Louis Mancano, MD Speaker has no disclosures
Pennsylvania Academy of Family Physicians Foundation & UPMC 43rd Refresher Course in Family Medicine CME Conference March 10-13, 2016 Disclosures: EKG Workshop Louis Mancano, MD Speaker has no disclosures
Case 1. Case 2. Case 3
 Case 1 The correct answer is D. Occasionally, the Brugada syndrome can present similar morphologies to A and also change depending on the lead position but in the Brugada pattern the r is wider and ST
Case 1 The correct answer is D. Occasionally, the Brugada syndrome can present similar morphologies to A and also change depending on the lead position but in the Brugada pattern the r is wider and ST
Tako-Tsubo Cardiomyopathy by Transient Dynamic Left Midventricular Obstruction
 CSE REPORT DOI 10.4070 / kcj.2009.39.1.37 Print ISSN 1738-5520 / On-line ISSN 1738-5555 Copyright c 2009 The Korean Society of Cardiology Tako-Tsubo Cardiomyopathy by Transient Dynamic Left Midventricular
CSE REPORT DOI 10.4070 / kcj.2009.39.1.37 Print ISSN 1738-5520 / On-line ISSN 1738-5555 Copyright c 2009 The Korean Society of Cardiology Tako-Tsubo Cardiomyopathy by Transient Dynamic Left Midventricular
Synephrine-containing dietary supplement precipitating apical ballooning syndrome in a young female
 CASE REPORT Korean J Intern Med 2013;28:356-360 Synephrine-containing dietary supplement precipitating apical ballooning syndrome in a young female Hyemoon Chung 1, Sung Woo Kwon 2, Tae Hoon Kim 3, Ji
CASE REPORT Korean J Intern Med 2013;28:356-360 Synephrine-containing dietary supplement precipitating apical ballooning syndrome in a young female Hyemoon Chung 1, Sung Woo Kwon 2, Tae Hoon Kim 3, Ji
Takotsubo cardiomyopathy-like phenotype in a boy
 Journal of Pediatric Intensive Care 2 (2013) 187 192 DOI 10.3233/PIC-13067 IOS Press Case Report 187 Takotsubo cardiomyopathy-like phenotype in a boy Mohammed Firdouse a, Arnav Garwal a, Claudia Lace De
Journal of Pediatric Intensive Care 2 (2013) 187 192 DOI 10.3233/PIC-13067 IOS Press Case Report 187 Takotsubo cardiomyopathy-like phenotype in a boy Mohammed Firdouse a, Arnav Garwal a, Claudia Lace De
Case Study 50 YEAR OLD MALE WITH UNSTABLE ANGINA
 Case Study 50 YEAR OLD MALE WITH UNSTABLE ANGINA Case History A 50-year-old man with type 1 diabetes mellitus and hypertension presents after experiencing 1 hour of midsternal chest pain that began after
Case Study 50 YEAR OLD MALE WITH UNSTABLE ANGINA Case History A 50-year-old man with type 1 diabetes mellitus and hypertension presents after experiencing 1 hour of midsternal chest pain that began after
Rhythmic chaos: irregularities of computer ECG diagnosis
 Singapore Med J 2017; 58(9): 516-520 doi: 10.11622/smedj.2017088 CMEArticle Rhythmic chaos: irregularities of computer ECG diagnosis Yi-Ting Laureen Wang 1, MBBS, MRCP, Swee-Chong Seow 1,2, MRCP, FACC,
Singapore Med J 2017; 58(9): 516-520 doi: 10.11622/smedj.2017088 CMEArticle Rhythmic chaos: irregularities of computer ECG diagnosis Yi-Ting Laureen Wang 1, MBBS, MRCP, Swee-Chong Seow 1,2, MRCP, FACC,
Normal ECG And ECHO Findings in Athletes
 Normal ECG And ECHO Findings in Athletes Dr.Yahya Kiwan Consultant Interventional Cardiologist Head Of Departement Of Cardiology Canadian Specialist Hospital Sinus Bradycardia The normal heartbeat is initiated
Normal ECG And ECHO Findings in Athletes Dr.Yahya Kiwan Consultant Interventional Cardiologist Head Of Departement Of Cardiology Canadian Specialist Hospital Sinus Bradycardia The normal heartbeat is initiated
Bundle Branch & Fascicular Blocks. Reading Assignment (p53-58 in Outline )
 Bundle Branch & Fascicular Blocks Reading Assignment (p53-58 in Outline ) Objectives 1. QRS analysis of Right and Left BBB 2. Uncomplicated vs complicated BBB 3. Diagnosis of RBBB with LAFB and LPFB 4.
Bundle Branch & Fascicular Blocks Reading Assignment (p53-58 in Outline ) Objectives 1. QRS analysis of Right and Left BBB 2. Uncomplicated vs complicated BBB 3. Diagnosis of RBBB with LAFB and LPFB 4.
Progress. Four weeks later. What becomes of the broken hearted? What do you think her coronary angiogram shows? 18/06/2018.
 What becomes of the broken hearted? Stephen Glen What do you think her coronary angiogram shows? 1. Mid LAD stenosis 2. Ostial LAD stenosis 3. LMS stenosis 4. RCA occlusion 5. Normal Four weeks later CT
What becomes of the broken hearted? Stephen Glen What do you think her coronary angiogram shows? 1. Mid LAD stenosis 2. Ostial LAD stenosis 3. LMS stenosis 4. RCA occlusion 5. Normal Four weeks later CT
Other 12-Lead ECG Findings
 Other 12-Lead ECG Findings Left Atrial Enlargement Left atrial enlargement is illustrated by increased P wave duration in lead II, top ECG, and by the prominent negative P terminal force in lead V1, bottom
Other 12-Lead ECG Findings Left Atrial Enlargement Left atrial enlargement is illustrated by increased P wave duration in lead II, top ECG, and by the prominent negative P terminal force in lead V1, bottom
Ampulla Cardiomyopathy. ( Takotsubo Cardiomyopathy ) in A Patient. with Diabetic Ketoacidosis. A Case Report
 2007 18 120-124 Ampulla Cardiomyopathy ( Takotsubo Cardiomyopathy ) in A Patient with Diabetic Ketoacidosis A Case Report Cheng-Hui Lin, Chun-Chang Chen 1, Ming-Kai Tsai 2, Yi-Chen Wang 1, Shih-Kan Chang
2007 18 120-124 Ampulla Cardiomyopathy ( Takotsubo Cardiomyopathy ) in A Patient with Diabetic Ketoacidosis A Case Report Cheng-Hui Lin, Chun-Chang Chen 1, Ming-Kai Tsai 2, Yi-Chen Wang 1, Shih-Kan Chang
ECG pre-reading manual. Created for the North West Regional EMET training program
 ECG pre-reading manual Created for the North West Regional EMET training program Author:- Dr Juan Carlos Ascencio-Lane juan.ascencio-lane@ths.tas.gov.au 1 Disclaimer This handbook has been created for
ECG pre-reading manual Created for the North West Regional EMET training program Author:- Dr Juan Carlos Ascencio-Lane juan.ascencio-lane@ths.tas.gov.au 1 Disclaimer This handbook has been created for
Can you interpret the ECG under stress?
 Singapore Med J 2018; 59(9): 455-459 https://doi.org/10.11622/smedj.2018108 CMEArticle Can you interpret the ECG under stress? Ching-Hui Sia 1, MBBS, MRCP, Devinder Singh 1,2, MD, MRCP, Joshua Ping-Yun
Singapore Med J 2018; 59(9): 455-459 https://doi.org/10.11622/smedj.2018108 CMEArticle Can you interpret the ECG under stress? Ching-Hui Sia 1, MBBS, MRCP, Devinder Singh 1,2, MD, MRCP, Joshua Ping-Yun
Correspondence should be addressed to Catherine Demers;
 Case Reports in Medicine Volume 2013, Article ID 793193, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2013/793193 Case Report The Ace of Spades: Reverse Takotsubo Cardiomyopathy in the Context of Angiographic Embolization
Case Reports in Medicine Volume 2013, Article ID 793193, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2013/793193 Case Report The Ace of Spades: Reverse Takotsubo Cardiomyopathy in the Context of Angiographic Embolization
Electrocardiography for Healthcare Professionals. Chapter 14 Basic 12-Lead ECG Interpretation
 Electrocardiography for Healthcare Professionals Chapter 14 Basic 12-Lead ECG Interpretation 2012 The Companies, Inc. All rights reserved. Learning Outcomes 14.1 Discuss the anatomic views seen on a 12-lead
Electrocardiography for Healthcare Professionals Chapter 14 Basic 12-Lead ECG Interpretation 2012 The Companies, Inc. All rights reserved. Learning Outcomes 14.1 Discuss the anatomic views seen on a 12-lead
12 th Annual West Virginia ACC Meeting April 8, 2017
 12 th Annual West Virginia ACC Meeting April 8, 2017 Rameez Sayyed, M.D., FACC, FSCAI Associate professor of Medicine Program Director for interventional cardiology Marshall University Joan C. Edwards
12 th Annual West Virginia ACC Meeting April 8, 2017 Rameez Sayyed, M.D., FACC, FSCAI Associate professor of Medicine Program Director for interventional cardiology Marshall University Joan C. Edwards
ECG Basics Sonia Samtani 7/2017 UCI Resident Lecture Series
 ECG Basics Sonia Samtani 7/2017 UCI Resident Lecture Series Agenda I. Introduction II.The Conduction System III.ECG Basics IV.Cardiac Emergencies V.Summary The Conduction System Lead Placement avf Precordial
ECG Basics Sonia Samtani 7/2017 UCI Resident Lecture Series Agenda I. Introduction II.The Conduction System III.ECG Basics IV.Cardiac Emergencies V.Summary The Conduction System Lead Placement avf Precordial
Relax and Learn at the FARM 2012: Session 8: 12 Lead ECG 401: ECG Variants
 Relax and Learn at the FARM 2012: Session 8: 12 Lead ECG 401: ECG Variants A Ship in the Harbor is Safe But that is not what ships are built for. Karen Marzlin DNP, RN, CCNS, CCRN-CMC, CHFN Cardiovascular
Relax and Learn at the FARM 2012: Session 8: 12 Lead ECG 401: ECG Variants A Ship in the Harbor is Safe But that is not what ships are built for. Karen Marzlin DNP, RN, CCNS, CCRN-CMC, CHFN Cardiovascular
Masqueraders of STEMI
 Masqueraders of STEMI Steven M. Costa, M.D. Assistant Professor Department of Medicine Division of Cardiology Scott & White Memorial Hospital and Clinic Texas A&M University Health Science Center Disclosures
Masqueraders of STEMI Steven M. Costa, M.D. Assistant Professor Department of Medicine Division of Cardiology Scott & White Memorial Hospital and Clinic Texas A&M University Health Science Center Disclosures
12 Lead ECG Interpretation
 12 Lead ECG Interpretation Julie Zimmerman, MSN, RN, CNS, CCRN Significant increase in mortality for every 15 minutes of delay! N Engl J Med 2007;357:1631-1638 Who should get a 12-lead ECG? Also include
12 Lead ECG Interpretation Julie Zimmerman, MSN, RN, CNS, CCRN Significant increase in mortality for every 15 minutes of delay! N Engl J Med 2007;357:1631-1638 Who should get a 12-lead ECG? Also include
How to Read an Athlete s ECG. Sanjay Sharma BSc (Hons), MD, FRCP, FESC
 How to Read an Athlete s ECG Sanjay Sharma BSc (Hons), MD, FRCP, FESC Athlete s EKG Vagotonia Sinus bradycardia Sinus arrhythmia First degree AVB ST-elevation Tall T waves Increased chamber size Left ventricular
How to Read an Athlete s ECG Sanjay Sharma BSc (Hons), MD, FRCP, FESC Athlete s EKG Vagotonia Sinus bradycardia Sinus arrhythmia First degree AVB ST-elevation Tall T waves Increased chamber size Left ventricular
3/4/2018. March Martina Frost, PA C Desert Cardiology. Electricity moving towards/away from electrode create downward/upward directions of waves
 March 2018 Martina Frost, PA C Desert Cardiology Electricity moving towards/away from electrode create downward/upward directions of waves Frontal view Limb leads: I, II, III, avl, avf, (avr) Horizontal
March 2018 Martina Frost, PA C Desert Cardiology Electricity moving towards/away from electrode create downward/upward directions of waves Frontal view Limb leads: I, II, III, avl, avf, (avr) Horizontal
Persistent PR segment change in malignant pericardial disease
 Ahluwalia et al. Cardio-Oncology (2016) 2:6 DOI 10.1186/s40959-016-0015-1 RESEARCH Open Access Persistent PR segment change in malignant pericardial disease M. Ahluwalia 1*,R.O Quinn 2,B.Ky 2, D. Callans
Ahluwalia et al. Cardio-Oncology (2016) 2:6 DOI 10.1186/s40959-016-0015-1 RESEARCH Open Access Persistent PR segment change in malignant pericardial disease M. Ahluwalia 1*,R.O Quinn 2,B.Ky 2, D. Callans
MICS OF MYOCARDIAL ISCHEMIA AND INFARCTION REVISED FOR LAS VEGAS
 ECG MIMICS OF MYOCARDIAL ISCHEMIA AND INFARCTION 102.06.05 Tzong-Luen Wang MD, PhD, JM, FESC, FACC Professor. Medical School, Fu-Jen Catholic University Chief, Emergency Department, Shin-Kong Wu Ho-Su
ECG MIMICS OF MYOCARDIAL ISCHEMIA AND INFARCTION 102.06.05 Tzong-Luen Wang MD, PhD, JM, FESC, FACC Professor. Medical School, Fu-Jen Catholic University Chief, Emergency Department, Shin-Kong Wu Ho-Su
A Qadeer Negahban. Cardiologist Barnsley Hospital United Kingdom
 A Qadeer Negahban Cardiologist Barnsley Hospital United Kingdom Tako Tsubo Cardiomyopathy Transient left ventricular (LV) apical ballooning syndrome Broken heart syndrome Stress induced myocardial stunning
A Qadeer Negahban Cardiologist Barnsley Hospital United Kingdom Tako Tsubo Cardiomyopathy Transient left ventricular (LV) apical ballooning syndrome Broken heart syndrome Stress induced myocardial stunning
DR QAZI IMTIAZ RASOOL OBJECTIVES
 PRACTICAL ELECTROCARDIOGRAPHY DR QAZI IMTIAZ RASOOL OBJECTIVES Recording of electrical events in heart Established electrode pattern results in specific tracing pattern Health of heart i. e. Anatomical
PRACTICAL ELECTROCARDIOGRAPHY DR QAZI IMTIAZ RASOOL OBJECTIVES Recording of electrical events in heart Established electrode pattern results in specific tracing pattern Health of heart i. e. Anatomical
Study methodology for screening candidates to athletes risk
 1. Periodical Evaluations: each 2 years. Study methodology for screening candidates to athletes risk 2. Personal history: Personal history of murmur in childhood; dizziness, syncope, palpitations, intolerance
1. Periodical Evaluations: each 2 years. Study methodology for screening candidates to athletes risk 2. Personal history: Personal history of murmur in childhood; dizziness, syncope, palpitations, intolerance
Typical chest pain with normal ECG
 Typical chest pain with normal ECG F. Mut, C. Bentancourt, M. Beretta Nuclear Medicine Service, Asociacion Española Montevideo, Uruguay Clinical history Male 41 y.o. Overweight, hypertension, high cholesterol,
Typical chest pain with normal ECG F. Mut, C. Bentancourt, M. Beretta Nuclear Medicine Service, Asociacion Española Montevideo, Uruguay Clinical history Male 41 y.o. Overweight, hypertension, high cholesterol,
Diploma in Electrocardiography
 The Society for Cardiological Science and Technology Diploma in Electrocardiography The Society makes this award to candidates who can demonstrate the ability to accurately record a resting 12-lead electrocardiogram
The Society for Cardiological Science and Technology Diploma in Electrocardiography The Society makes this award to candidates who can demonstrate the ability to accurately record a resting 12-lead electrocardiogram
Cardiovascular Nursing Practice: A Comprehensive Resource Manual and Study Guide for Clinical Nurses 2 nd Edition
 Cardiovascular Nursing Practice: A Comprehensive Resource Manual and Study Guide for Clinical Nurses 2 nd Edition Table of Contents Volume 1 Chapter 1: Cardiovascular Anatomy and Physiology Basic Cardiac
Cardiovascular Nursing Practice: A Comprehensive Resource Manual and Study Guide for Clinical Nurses 2 nd Edition Table of Contents Volume 1 Chapter 1: Cardiovascular Anatomy and Physiology Basic Cardiac
Echocardiography as a diagnostic and management tool in medical emergencies
 Echocardiography as a diagnostic and management tool in medical emergencies Frank van der Heusen MD Department of Anesthesia and perioperative Care UCSF Medical Center Objective of this presentation Indications
Echocardiography as a diagnostic and management tool in medical emergencies Frank van der Heusen MD Department of Anesthesia and perioperative Care UCSF Medical Center Objective of this presentation Indications
12 Lead ECG. Presented by Rebecca Sevigny BSN, RN Professional Practice & Development Dept.
 12 Lead ECG Presented by Rebecca Sevigny BSN, RN Professional Practice & Development Dept. Two Main Coronary Arteries RCA LCA which branches into Left Anterior Descending Circumflex Artery Two Main Coronary
12 Lead ECG Presented by Rebecca Sevigny BSN, RN Professional Practice & Development Dept. Two Main Coronary Arteries RCA LCA which branches into Left Anterior Descending Circumflex Artery Two Main Coronary
Electrocardiographic findings in pulmonary embolism
 Singapore Med J 2015; 56(10): 533-537 doi: 10.11622/smedj.2015147 Electrocardiography Series CMEArticle Electrocardiographic findings in pulmonary embolism Elaine Boey1, MBBS, MRCP, Swee-Guan Teo2, MRCP,
Singapore Med J 2015; 56(10): 533-537 doi: 10.11622/smedj.2015147 Electrocardiography Series CMEArticle Electrocardiographic findings in pulmonary embolism Elaine Boey1, MBBS, MRCP, Swee-Guan Teo2, MRCP,
Marcin Dada, MD December 03, 2013
 STEMI Imposters Marcin Dada, MD December 03, 2013 Marcin Dada, MD Associate Director, Chest Pain Center Hartford Hospital, Hartford, CT Member, AHA Mission Lifeline Steering Committee Outline of Topics
STEMI Imposters Marcin Dada, MD December 03, 2013 Marcin Dada, MD Associate Director, Chest Pain Center Hartford Hospital, Hartford, CT Member, AHA Mission Lifeline Steering Committee Outline of Topics
General Introduction to ECG. Reading Assignment (p2-16 in PDF Outline )
 General Introduction to ECG Reading Assignment (p2-16 in PDF Outline ) Objectives 1. Practice the 5-step Method 2. Differential Diagnosis: R & L axis deviation 3. Differential Diagnosis: Poor R-wave progression
General Introduction to ECG Reading Assignment (p2-16 in PDF Outline ) Objectives 1. Practice the 5-step Method 2. Differential Diagnosis: R & L axis deviation 3. Differential Diagnosis: Poor R-wave progression
Section V. Objectives
 Section V Landscape of an MI Objectives At the conclusion of this presentation the participant will be able to Outline a systematic approach to 12 lead ECG interpretation Demonstrate the process for determining
Section V Landscape of an MI Objectives At the conclusion of this presentation the participant will be able to Outline a systematic approach to 12 lead ECG interpretation Demonstrate the process for determining
Preface: Wang s Viewpoints
 AHA/ACCF/HRS Recommendations for the Standardization and Interpretation of the Electrocardiogram: Part IV, Ischemia and Infarction Presented by: WANG, TZONG LUEN, MD, PhD, JM, FACC, FESC, FCAPSC Professor,
AHA/ACCF/HRS Recommendations for the Standardization and Interpretation of the Electrocardiogram: Part IV, Ischemia and Infarction Presented by: WANG, TZONG LUEN, MD, PhD, JM, FACC, FESC, FCAPSC Professor,
A patient with non-q wave acute inferior myocardial infarction. Citation Hong Kong Practitioner, 1997, v. 19 n. 4, p
 Title A patient with non-q wave acute inferior myocardial infarction Author(s) Ng, W; Wong, CK; Lau, CP Citation Hong Kong Practitioner, 1997, v. 19 n. 4, p. 199-202 ssued Date 1997 URL http://hdl.handle.net/10722/45037
Title A patient with non-q wave acute inferior myocardial infarction Author(s) Ng, W; Wong, CK; Lau, CP Citation Hong Kong Practitioner, 1997, v. 19 n. 4, p. 199-202 ssued Date 1997 URL http://hdl.handle.net/10722/45037
ELECTROCARDIOGRAPH. General. Heart Rate. Starship Children s Health Clinical Guideline
 General Heart Rate QRS Axis T Wave Axis PR Interval according to Heart Rate & Age P Wave Duration and Amplitude QRS Duration according to Age QT Interval R & S voltages according to Lead & Age R/S ratio
General Heart Rate QRS Axis T Wave Axis PR Interval according to Heart Rate & Age P Wave Duration and Amplitude QRS Duration according to Age QT Interval R & S voltages according to Lead & Age R/S ratio
Recurrent fetal postpartum stress induced cardiomyopathy after normal vaginal delivery
 https://doi.org/10.7180/kmj.2017.32.2.244 KMJ Case Report Recurrent fetal postpartum stress induced cardiomyopathy after normal vaginal delivery Yong-Sun Noh 1, Sung-Ho Her 1, Jong Bum Kwon 2, Chan Joon
https://doi.org/10.7180/kmj.2017.32.2.244 KMJ Case Report Recurrent fetal postpartum stress induced cardiomyopathy after normal vaginal delivery Yong-Sun Noh 1, Sung-Ho Her 1, Jong Bum Kwon 2, Chan Joon
SIMPLY ECGs. Dr William Dooley
 SIMPLY ECGs Dr William Dooley Content Basic ECG interpretation pattern Some common (examined) abnormalities Presenting ECGs in context Setting up an ECG Setting up an ECG 1 V1-4 th Right intercostal space
SIMPLY ECGs Dr William Dooley Content Basic ECG interpretation pattern Some common (examined) abnormalities Presenting ECGs in context Setting up an ECG Setting up an ECG 1 V1-4 th Right intercostal space
Basic electrocardiography reading. R3 lee wei-chieh
 Basic electrocardiography reading R3 lee wei-chieh The Normal Conduction System Lead Placement avf Limb Leads Precordial Leads Interpretation Rate Rhythm Interval Axis Chamber abnormality QRST change What
Basic electrocardiography reading R3 lee wei-chieh The Normal Conduction System Lead Placement avf Limb Leads Precordial Leads Interpretation Rate Rhythm Interval Axis Chamber abnormality QRST change What
Acute heart failure in a patient with lower urinary tract infection Case report of an infection-induced Reverse Takotsubo syndrome
 Acute heart failure in a patient with lower urinary tract infection Case report of an infection-induced Reverse Takotsubo syndrome N.Μoschos, A.Dimitra, E.Tsakiri, D.Stavrianakis, A.Nouli CARDIOLOGY DEPARTMENT
Acute heart failure in a patient with lower urinary tract infection Case report of an infection-induced Reverse Takotsubo syndrome N.Μoschos, A.Dimitra, E.Tsakiri, D.Stavrianakis, A.Nouli CARDIOLOGY DEPARTMENT
ACUTE CORONARY SYNDROME
 12 LEAD ECG INTERPRETATION in ACUTE CORONARY SYNDROME WAYNE W RUPPERT, CVT, CCCC, NREMT-P Cardiovascular Clinical Coordinator Bayfront Health Seven Rivers Crystal River, FL Education Specialist St. Joseph
12 LEAD ECG INTERPRETATION in ACUTE CORONARY SYNDROME WAYNE W RUPPERT, CVT, CCCC, NREMT-P Cardiovascular Clinical Coordinator Bayfront Health Seven Rivers Crystal River, FL Education Specialist St. Joseph
Conus artery occlusion causing isolated right ventricular outflow tract infarction: novel application of cardiac magnetic resonance in anterior STEMI
 Case Report Conus artery occlusion causing isolated right ventricular outflow tract infarction: novel application of cardiac magnetic resonance in anterior STEMI Melissa Lyle 1, Ryan C. Van Woerkom 2,
Case Report Conus artery occlusion causing isolated right ventricular outflow tract infarction: novel application of cardiac magnetic resonance in anterior STEMI Melissa Lyle 1, Ryan C. Van Woerkom 2,
Paediatric ECG Interpretation
 Paediatric ECG Interpretation Dr Sanj Fernando (thanks to http://lifeinthefastlane.com/ecg-library/paediatric-ecginterpretation/) 3 yo boy complaining of abdominal pain and chest pain Child ECG vs Adult
Paediatric ECG Interpretation Dr Sanj Fernando (thanks to http://lifeinthefastlane.com/ecg-library/paediatric-ecginterpretation/) 3 yo boy complaining of abdominal pain and chest pain Child ECG vs Adult
Takotsubo Cardiomyopathy: Pathophysiology and Assessment
 Takotsubo Cardiomyopathy: Pathophysiology and Assessment Roberto M Lang, MD Tako-Tsubo Cardiomyopathy Broken Heart Syndrome Apical Balooning 1. Sato H, Tateishi H, Uchida T, et al. Takotsubo type cardiomyopathy
Takotsubo Cardiomyopathy: Pathophysiology and Assessment Roberto M Lang, MD Tako-Tsubo Cardiomyopathy Broken Heart Syndrome Apical Balooning 1. Sato H, Tateishi H, Uchida T, et al. Takotsubo type cardiomyopathy
A few new tools for better detection and understanding of STEMIs in the field.
 A few new tools for better detection and understanding of STEMIs in the field. Let s talk, prep and placement. Try to shoot for quality, consistency and no artifact! (looking sometimes for 1 or 2 mm changes)
A few new tools for better detection and understanding of STEMIs in the field. Let s talk, prep and placement. Try to shoot for quality, consistency and no artifact! (looking sometimes for 1 or 2 mm changes)
Adel Hasanin Ahmed 1
 Adel Hasanin Ahmed 1 PERICARDIAL DISEASE The pericardial effusion ends anteriorly to the descending aorta and is best visualised in the PLAX. PSAX is actually very useful sometimes for looking at posterior
Adel Hasanin Ahmed 1 PERICARDIAL DISEASE The pericardial effusion ends anteriorly to the descending aorta and is best visualised in the PLAX. PSAX is actually very useful sometimes for looking at posterior
HEART CONDITIONS IN SPORT
 HEART CONDITIONS IN SPORT Dr. Anita Green CHD Risk Factors Smoking Hyperlipidaemia Hypertension Obesity Physical Inactivity Diabetes Risks are cumulative (multiplicative) Lifestyles predispose to RF One
HEART CONDITIONS IN SPORT Dr. Anita Green CHD Risk Factors Smoking Hyperlipidaemia Hypertension Obesity Physical Inactivity Diabetes Risks are cumulative (multiplicative) Lifestyles predispose to RF One
Cardiovascular Images
 Cardiovascular Images Pulmonary Embolism Diagnosed From Right Heart Changes Seen After Exercise Stress Echocardiography Brian C. Case, MD; Micheas Zemedkun, MD; Amarin Sangkharat, MD; Allen J. Taylor,
Cardiovascular Images Pulmonary Embolism Diagnosed From Right Heart Changes Seen After Exercise Stress Echocardiography Brian C. Case, MD; Micheas Zemedkun, MD; Amarin Sangkharat, MD; Allen J. Taylor,
Please check your answers with correct statements in answer pages after the ECG cases.
 ECG Cases ECG Case 1 Springer International Publishing AG, part of Springer Nature 2018 S. Okutucu, A. Oto, Interpreting ECGs in Clinical Practice, In Clinical Practice, https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-90557-0
ECG Cases ECG Case 1 Springer International Publishing AG, part of Springer Nature 2018 S. Okutucu, A. Oto, Interpreting ECGs in Clinical Practice, In Clinical Practice, https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-90557-0
XVth Balkan Congress of Radiology Danubius Hotel Helia, October 2017, Budapest, Hungary
 XVth Balkan Congress of Radiology Danubius Hotel Helia, 12-14 October 2017, Budapest, Hungary Ružica Maksimović MRI in Myocarditis Faculty of Medicine, University of Belgrade, Centre for Radiology and
XVth Balkan Congress of Radiology Danubius Hotel Helia, 12-14 October 2017, Budapest, Hungary Ružica Maksimović MRI in Myocarditis Faculty of Medicine, University of Belgrade, Centre for Radiology and
UPDATE ON THE MANAGEMENTACUTE CORONARY SYNDROME. DR JULES KABAHIZI, Psc (Rwa) Lt Col CHIEF CONSULTANT RMH/KFH 28 JUNE18
 UPDATE ON THE MANAGEMENTACUTE CORONARY SYNDROME DR JULES KABAHIZI, Psc (Rwa) Lt Col CHIEF CONSULTANT RMH/KFH 28 JUNE18 INTRODUCTION The clinical entities that comprise acute coronary syndromes (ACS)-ST-segment
UPDATE ON THE MANAGEMENTACUTE CORONARY SYNDROME DR JULES KABAHIZI, Psc (Rwa) Lt Col CHIEF CONSULTANT RMH/KFH 28 JUNE18 INTRODUCTION The clinical entities that comprise acute coronary syndromes (ACS)-ST-segment
December 2018 Tracings
 Tracings Tracing 1 Tracing 4 Tracing 1 Answer Tracing 4 Answer Tracing 2 Tracing 5 Tracing 2 Answer Tracing 5 Answer Tracing 3 Tracing 6 Tracing 3 Answer Tracing 6 Answer Questions? Contact Dr. Nelson
Tracings Tracing 1 Tracing 4 Tracing 1 Answer Tracing 4 Answer Tracing 2 Tracing 5 Tracing 2 Answer Tracing 5 Answer Tracing 3 Tracing 6 Tracing 3 Answer Tracing 6 Answer Questions? Contact Dr. Nelson
Two Cardiology Zebras ERIC MARTIN MD
 Two Cardiology Zebras ERIC MARTIN MD Disclosures Bayer Gilead Sciences NIH Vascular Dynamics, In. Employer Iowa Heart Center/Mercy Des Moines Zebra # 1 History CC: 52-year-old man seen in consultation
Two Cardiology Zebras ERIC MARTIN MD Disclosures Bayer Gilead Sciences NIH Vascular Dynamics, In. Employer Iowa Heart Center/Mercy Des Moines Zebra # 1 History CC: 52-year-old man seen in consultation
Case Report Inverted (Reverse) Takotsubo Cardiomyopathy following Cerebellar Hemorrhage
 Case Reports in Cardiology, Article ID 781926, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2014/781926 Case Report Inverted (Reverse) Takotsubo Cardiomyopathy following Cerebellar Hemorrhage Sophie Piérard, 1 Marco
Case Reports in Cardiology, Article ID 781926, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2014/781926 Case Report Inverted (Reverse) Takotsubo Cardiomyopathy following Cerebellar Hemorrhage Sophie Piérard, 1 Marco
About T waves
 About T waves - 2014 Dr. Andres R. Pérez Riera The T waves is a positive deflection after each QRS complex. It represents ventricular repolarization The T wave represents the unconcealed potential differences
About T waves - 2014 Dr. Andres R. Pérez Riera The T waves is a positive deflection after each QRS complex. It represents ventricular repolarization The T wave represents the unconcealed potential differences
Current ECG interpretation guidelines in the screening of athletes
 REVIEW ARTICLE 7 How to differentiate physiological adaptation to intensive physical exercise from pathologies Current ECG interpretation guidelines in the screening of athletes Gemma Parry-Williams, Sanjay
REVIEW ARTICLE 7 How to differentiate physiological adaptation to intensive physical exercise from pathologies Current ECG interpretation guidelines in the screening of athletes Gemma Parry-Williams, Sanjay
also aid the clinician in recognizing both the obvious and subtle abnormalities that may help guide therapy.
 Karen Lieberman, MS, CRNP f the many diagnostic tools used to screen for and evaluate cardiac abnormalities, the 12-lead electrocardiogram (ECG) is among the most basic. This inexpensive and noninvasive
Karen Lieberman, MS, CRNP f the many diagnostic tools used to screen for and evaluate cardiac abnormalities, the 12-lead electrocardiogram (ECG) is among the most basic. This inexpensive and noninvasive
Case based learning: CMR in Heart Failure
 Case based learning: CMR in Heart Failure Milind Y Desai, MD FACC FAHA FESC Associate Professor of Medicine Heart and Vascular Institute, Cleveland Clinic Cleveland, OH Disclosures: none Use of Gadolinium
Case based learning: CMR in Heart Failure Milind Y Desai, MD FACC FAHA FESC Associate Professor of Medicine Heart and Vascular Institute, Cleveland Clinic Cleveland, OH Disclosures: none Use of Gadolinium
2. Case Report. 1. Introduction
 Case Reports in Cardiology Volume 2016, Article ID 3251032, 5 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2016/3251032 Case Report Ventricular Septal Perforation after Biventricular Takotsubo Cardiomyopathy Successfully
Case Reports in Cardiology Volume 2016, Article ID 3251032, 5 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2016/3251032 Case Report Ventricular Septal Perforation after Biventricular Takotsubo Cardiomyopathy Successfully
Severe Coronary Vasospasm Complicated with Ventricular Tachycardia
 Severe Coronary Vasospasm Complicated with Ventricular Tachycardia Göksel Acar, Serdar Fidan, Servet İzci and Anıl Avcı Kartal Koşuyolu High Specialty Education and Research Hospital, Cardiology Department,
Severe Coronary Vasospasm Complicated with Ventricular Tachycardia Göksel Acar, Serdar Fidan, Servet İzci and Anıl Avcı Kartal Koşuyolu High Specialty Education and Research Hospital, Cardiology Department,
Isolated right ventricular ballooning syndrome: a new variant of transient cardiomyopathy
 Zurich Open Repository and Archive University of Zurich Main Library Strickhofstrasse 39 CH-8057 Zurich www.zora.uzh.ch Year: 2011 Isolated right ventricular ballooning syndrome: a new variant of transient
Zurich Open Repository and Archive University of Zurich Main Library Strickhofstrasse 39 CH-8057 Zurich www.zora.uzh.ch Year: 2011 Isolated right ventricular ballooning syndrome: a new variant of transient
4/14/15. The Electrocardiogram. In jeopardy more than a century after its introduction by Willem Einthoven? Time for a revival. by Hein J.
 The Electrocardiogram. In jeopardy more than a century after its introduction by Willem Einthoven? Time for a revival. by Hein J. Wellens MD 1 Einthoven, 1905 The ECG! Everywhere available! Easy and rapid
The Electrocardiogram. In jeopardy more than a century after its introduction by Willem Einthoven? Time for a revival. by Hein J. Wellens MD 1 Einthoven, 1905 The ECG! Everywhere available! Easy and rapid
PERMANENT PACEMAKERS AND IMPLANTABLE DEFIBRILLATORS Considerations for intensivists
 PERMANENT PACEMAKERS AND IMPLANTABLE DEFIBRILLATORS Considerations for intensivists Craig A. McPherson, MD, FACC Associate Professor of Medicine Constantine Manthous, MD, FACP, FCCP Associate Clinical
PERMANENT PACEMAKERS AND IMPLANTABLE DEFIBRILLATORS Considerations for intensivists Craig A. McPherson, MD, FACC Associate Professor of Medicine Constantine Manthous, MD, FACP, FCCP Associate Clinical
Original Article Malignant Arrhythmia in Apical Ballooning Syndrome: Risk Factors and Outcomes
 www.ipej.org 182 Original Article Malignant Arrhythmia in Apical Ballooning Syndrome: Risk Factors and Outcomes Chadi Dib, MD 1 ; Abhiram Prasad, MD 1 ; Paul A. Friedman, MD 1 ; Ahmad Elesber, MD 2 ; Charanjit
www.ipej.org 182 Original Article Malignant Arrhythmia in Apical Ballooning Syndrome: Risk Factors and Outcomes Chadi Dib, MD 1 ; Abhiram Prasad, MD 1 ; Paul A. Friedman, MD 1 ; Ahmad Elesber, MD 2 ; Charanjit
TRANSIENT LEFT BUNDLE BRANCH BLOCK -
 Vol. 11, No. 2. June, 1970. SINGAPORE MEDICAL JOURNAL TRANSIENT LEFT BUNDLE BRANCH BLOCK - A CASE REPORT 86 By L.S. Chew (Medical Unit III, General Hospital, Singapore) INTRODUCTION It is generally believed
Vol. 11, No. 2. June, 1970. SINGAPORE MEDICAL JOURNAL TRANSIENT LEFT BUNDLE BRANCH BLOCK - A CASE REPORT 86 By L.S. Chew (Medical Unit III, General Hospital, Singapore) INTRODUCTION It is generally believed
at least 4 8 hours per week
 ECG IN ATHLETS An athlete is defined as an individual who engages in regular exercise or training for sport or general fitness, typically with a premium on performance, and often engaged in individual
ECG IN ATHLETS An athlete is defined as an individual who engages in regular exercise or training for sport or general fitness, typically with a premium on performance, and often engaged in individual
My Patient Needs a Stress Test
 My Patient Needs a Stress Test Amy S. Burhanna,, MD, FACC Coastal Cardiology Cape May Court House, New Jersey Absolute and relative contraindications to exercise testing Absolute Acute myocardial infarction
My Patient Needs a Stress Test Amy S. Burhanna,, MD, FACC Coastal Cardiology Cape May Court House, New Jersey Absolute and relative contraindications to exercise testing Absolute Acute myocardial infarction
Exercise Test: Practice and Interpretation. Jidong Sung Division of Cardiology Samsung Medical Center Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine
 Exercise Test: Practice and Interpretation Jidong Sung Division of Cardiology Samsung Medical Center Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine 2 Aerobic capacity and survival Circulation 117:614, 2008
Exercise Test: Practice and Interpretation Jidong Sung Division of Cardiology Samsung Medical Center Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine 2 Aerobic capacity and survival Circulation 117:614, 2008
12-Lead ECG Interpretation. Kathy Kuznar, RN, ANP
 12-Lead ECG Interpretation Kathy Kuznar, RN, ANP The 12-Lead ECG Objectives Identify the normal morphology and features of the 12- lead ECG. Perform systematic analysis of the 12-lead ECG. Recognize abnormalities
12-Lead ECG Interpretation Kathy Kuznar, RN, ANP The 12-Lead ECG Objectives Identify the normal morphology and features of the 12- lead ECG. Perform systematic analysis of the 12-lead ECG. Recognize abnormalities
Takotsubo Cardiomyopathy Transient Left Ventricular Apical Ballooning Mimicking Acute Myocardial Infarction
 CSE REPORT Takotsubo Cardiomyopathy Transient Left Ventricular pical allooning Mimicking cute Myocardial Infarction Yung-Lung Chen, Tung-Hong Yu, Morgan Fu* Takotsubo cardiomyopathy is characterized by
CSE REPORT Takotsubo Cardiomyopathy Transient Left Ventricular pical allooning Mimicking cute Myocardial Infarction Yung-Lung Chen, Tung-Hong Yu, Morgan Fu* Takotsubo cardiomyopathy is characterized by
Disclosure. 3. ST depression indicative of ischemia is most commonly observed in leads: 1. V1-V2. 2. I and avl 3. V
 Interpreting Stress Induced Ischemia by ECG, Bundle Branch Block & Arrhythmias Disclosure Gregory S Thomas MD, MPH Medical Director, MemorialCare Heart & Vascular Institute, Long Beach Memorial Astellas
Interpreting Stress Induced Ischemia by ECG, Bundle Branch Block & Arrhythmias Disclosure Gregory S Thomas MD, MPH Medical Director, MemorialCare Heart & Vascular Institute, Long Beach Memorial Astellas
Conduction Problems / Arrhythmias. Conduction
 Conduction Problems / Arrhythmias Conduction Wolf-Parkinson White Syndrome (WPW) and Lown-Ganong-Levine (LGL): Atrial impulses bypass the AV node through an accessory pathway or bypass tract (bundle of
Conduction Problems / Arrhythmias Conduction Wolf-Parkinson White Syndrome (WPW) and Lown-Ganong-Levine (LGL): Atrial impulses bypass the AV node through an accessory pathway or bypass tract (bundle of
SIMPLY ECGs. Dr William Dooley
 SIMPLY ECGs Dr William Dooley 1 No anatomy just interpretation 2 Setting up an ECG 3 Setting up an ECG 1 V1-4 th Right intercostal space at sternal border 2 V2-4 th Left intercostal space at sternal border
SIMPLY ECGs Dr William Dooley 1 No anatomy just interpretation 2 Setting up an ECG 3 Setting up an ECG 1 V1-4 th Right intercostal space at sternal border 2 V2-4 th Left intercostal space at sternal border
Urgent VT Ablation in a Patient with Presumed ARVC
 Urgent VT Ablation in a Patient with Presumed ARVC Mr Alex Cambridge, Chief Cardiac Physiologist, St. Barts Hospital, London, UK The patient, a 52 year-old male, attended the ICD clinic without an appointment
Urgent VT Ablation in a Patient with Presumed ARVC Mr Alex Cambridge, Chief Cardiac Physiologist, St. Barts Hospital, London, UK The patient, a 52 year-old male, attended the ICD clinic without an appointment
Abnormal, Autoquant Adenosine Myocardial Perfusion Heart Imaging. ID: GOLD Date: Age: 46 Sex: M John Doe Phone (310)
 Background: Reason: preoperative assessment of CAD, Shortness of Breath Symptom: atypical chest pain Risk factors: hypertension Under influence: a beta blocker Medications: digoxin Height: 66 in. Weight:
Background: Reason: preoperative assessment of CAD, Shortness of Breath Symptom: atypical chest pain Risk factors: hypertension Under influence: a beta blocker Medications: digoxin Height: 66 in. Weight:
