Endocarditis caused by anaerobes and microaerophilic
|
|
|
- Clarissa Sybil Barker
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 C a s e R e p o r t Clostridium perfringens: A Rare Cause of Infective Endocarditis and Aortic Root Abscess Ramanna Merla, MD, MPH Nischita K. Reddy, MD, MPH Yochai Birnbaum, MD Suimin Qiu, MD, PhD Masood Ahmad, MD Shaul Atar, MD Endocarditis caused by anaerobes and microaerophilic bacteria accounts for 7% to 10% of all cases of infective endocarditis; however, if anaerobic streptococcal endocarditis is excluded, this number decreases to 1.3%. 1 Anaerobic organisms that can cause endocarditis include Streptococcus, Bacteroides, Fusobacterium, Clostridium, and Propionibacterium species. 1 Isolating Clostridium species with blood cultures can be difficult, and the majority of positive cultures are obtained postsurgically or postmortem from tissue specimens. Thus, physicians must maintain a high index of suspicion even if cultures are negative, utilize modalities such as transthoracic and transesophageal echocardiography to further delineate complications of endocarditis, and promptly initiate appropriate antibiotic treatment if anaerobic endocarditis is suspected. This article presents the case of a woman who, despite numerous negative aerobic and anaerobic blood cultures, was found to have infective endocarditis caused by C. perfringens after culture of aortic valve tissue obtained from emergent aortic root and valve replacement returned positive. CASE PRESENTATION Initial Presentation and History A 48-year-old woman with idiopathic pulmonary arterial hypertension undergoing treatment with oral bosentan and warfarin and intravenous (IV) epoprostenol administered through a right internal jugular Hickman catheter presented to the emergency department with a 10-day history of progressive shortness of breath and diarrhea. Past medical history was unremarkable except for total abdominal hysterectomy for nonmalignant reasons 8 years ago. Physical Examination The patient was febrile (101.5 F) with a blood pressure of 109/51 mm Hg. On examination, a pronounced pulmonary component of the second heart sound and bibasilar crackles with rhonchi were noted. Rectal examination revealed brown guaiac-positive stool. No stigmata of endocarditis, such as Janeway s lesions, Osler s nodes, or Roth s spots, were noted. Laboratory testing revealed a white blood cell count of 12,100 cells/µl with a left shift, hemoglobin level of 9.4 g/dl, serum creatinine level of 2.29 mg/dl, fractional excretion of sodium of less than 1%, and an international normalized ratio of 9.7. Chest radiograph revealed interstitial edema with cardiomegaly. A ventilation-perfusion scan indicated a low probability of pulmonary embolism. A transthoracic echocardiogram (TTE) showed thickened aortic valve leaflets and moderate to severe aortic regurgitation. Stool samples were negative for C. difficile toxin, ova, parasites, and presence of leukocytes. Stool cultures were also negative. Urinalysis was unremarkable, and urine culture was negative. Warfarin was discontinued, and the patient was given IV hydration for prerenal azotemia. IV vancomycin, ceftriaxone, and gentamicin were initiated for suspected infective endocarditis. Clinical Course The following day, the patient remained febrile and Drs. Merla and Reddy are residents in internal medicine, Department of Internal Medicine; Dr. Birnbaum is a professor of medicine, biochemistry, and molecular biology; Dr. Qiu is an assistant professor, Department of Pathology; Dr. Ahmad is a professor of medicine; and Dr. Atar is an associate professor of medicine; all are at the University of Texas Medical Branch at Galveston, Galveston, TX. Hospital Physician June
2 Figure 1. Electrocardiogram demonstrating first-degree atrioventricular block and T-wave inversion in the inferolateral leads. developed acute hypoxia and hypotension, and her hemoglobin dropped to 7.9 g/dl. New holodiastolic and midsystolic ejection murmurs were heard over the aortic area. The patient was given noninvasive oxygen supplementation and aggressive fluid resuscitation, transfused with packed red blood cells, and placed on vasopressor therapy. She had no evidence of overt gastrointestinal bleeding. Schistocytes and polychromasia were seen on peripheral blood smear. Because aerobic and anaerobic blood cultures performed prior to the initiation of antibiotics and 3 sets performed later in the clinical course were negative, antibiotic coverage for culture-negative endocarditis was continued. Wide pulse pressures of /38 45 mm Hg and a firstdegree atrioventricular block with T-wave inversion in the inferolateral leads developed (Figure 1). Cultures for slow-growing fastidious species such as Hemophilus, Actinobacillus, Cardiobacterium, Eikenella, and Kingella and serologic testing for Brucella, Bartonella, Coxiella, and Legionella species were negative. A transesophageal echocardiogram (TEE) demonstrated a 3-leaflet aortic valve with detachment of the noncoronary cusp from the aortic wall (Figure 2). The cusp was protruding into the aortic outflow tract. Color Doppler interrogation revealed severe aortic regurgitation with a jet emerging behind the noncoronary cusp. The posterior wall of the ascending aorta immediately above the aortic annulus was echolucent. The finding of a detached aortic valve and severe aortic regurgitation raised the possibility of acute aortic dissection. Emergent surgery revealed large vegetation and a perforated noncoronary cusp. An aortic root abscess that extended underneath the detached cusp was partially elevating the cusp from the aortic wall (Figure 2). Homograft aortic root replacement and coronary artery bypass grafting of a saphenous vein to the left anterior descending artery was performed. The patient s Hickman catheter was removed. A Gram stain of the aortic valve leaflet showed gram-positive coccobacillary organisms with inflammatory exudates (Figure 3). To cover for invasive nocardiosis, IV trimethoprim/ sulfamethoxazole was started. Aerobic cultures from valvular tissue as well as from the Hickman catheter tip failed to show any growth; however, anaerobic cultures of valvular tissue grew C. perfringens (Figure 3C). The patient was treated with IV metronidazole and imipenem/cilastin for 5 weeks, and all other antibiotics were discontinued. TTE performed prior to discharge showed a left ventricular ejection fraction of 45% to 50%, with a normally functioning homograft aortic valve. The patient continued to do well 1 year postsurgery. DISCUSSION In all cases of suspected infective endocarditis, the initial assessment should include a thorough history 24 Hospital Physician June
3 A B C Figure 2. A transesophageal echocardiogram performed in the case patient, with (A) a short-axis view of the aortic valve showing a severe diastolic jet of aortic regurgitation (arrow) and a posteriorly located aortic root abscess (asterisk); (B) a long-axis view of the aortic root and left ventricular outflow, showing severe aortic regurgitation (arrow) with a portion of the aortic root abscess (asterisk) at the base of the noncoronary aortic cusp; and (C) a long-axis view of the aortic root and left ventricular outflow, showing an aortic root abscess (asterisk) and large vegetation (V) with perforation of the noncoronary cusp (arrow). The large abscess cavity partially elevates the noncoronary cusp from the underlying aortic wall. A B C Figure 3. (A) Hematoxylin and eosin stain demonstrating distortion of the valvular architecture by inflammatory vegetations, which contain fibrinous exudates and platelets and collections of polymorphonuclear neutrophils. (B) Tissue Gram stain showing gram-positive bacterial colonies with inflammatory exudates on the surface of the infected valve. (C) Colony Gram stain showing Clostridium perfringens, which appears as gram-positive bacilli with heterogeneous incorporation of the stain into the spores. and physical examination, including a history of prior cardiac lesions, a search for potential sources of bacteremia (eg, indwelling catheter, IV drug use), and a careful cardiac evaluation. Modified Duke criteria for diagnosis of infective endocarditis are outlined in Table 1 and Table 2. The case patient met 2 major clinical criteria, specifically new-onset murmur and a finding of valvular vegetation on echocardiography. Additionally, infective endocarditis was confirmed by the positive histologic examination and culture of valvular tissue. In this case, we suspect that the indwelling Hickman catheter may have been the portal of entry of C. perfringens. The patient had possible signs of clostridial sepsis, including fever, shock (which required vasopressors for circulatory support), and schistocytes on peripheral blood smear (which may have indicated intravascular hemolysis). Gastrointestinal and urinary sources of infection were ruled out with cultures. This case underscores the importance of using TEE in the diagnosis of infective endocarditis, as it is superior to TTE for detecting valvular vegetations, valvular perforation, and perivalvular abscess. 2 4 Empiric treatment for culture-negative endocarditis was started and then tapered to metronidazole and imipenem/cilastin once C. perfringens was confirmed as the cause. CULTURE-NEGATIVE ENDOCARDITIS Culture-negative endocarditis constitutes less than 5% to 12% of all cases of endocarditis. 5,6 Factors influencing negative blood cultures include antibiotic administration prior to obtaining cultures, a slow-growing fastidious bacteria or fungi that has limited proliferation in conventional blood cultures, and the presence of right-sided endocarditis or permanent pacemakers. 5,7 Hospital Physician June
4 Table 1. Modified Duke Criteria for Diagnosis of Infective Endocarditis Definite infective endocarditis Pathologic criteria (1) Microorganisms demonstrated by culture or histologic examination of a vegetation, a vegetation that has embolized, or an intracardiac abscess specimen; or (2) Pathologic lesions; vegetation or intracardiac abscess confirmed by histologic examination showing active endocarditis Clinical criteria* (1) 2 major criteria; or (2) 1 major criterion and 3 minor criteria; or (3) 5 minor criteria Possible infective endocarditis (1) 1 major criterion and 1 minor criterion; or (2) 3 minor criteria Rejected (1) Firm alternate diagnosis explaining evidence of infective endocarditis; or (2) Resolution of infective endocarditis syndrome with antibiotic therapy for 4 days; or (3) No pathologic evidence of infective endocarditis at surgery or autopsy with antibiotic therapy for 4 days; or (4) Does not meet criteria for possible infective endocarditis, as above Adapted with permission from Li JS, Sexton DJ, Mick N, et al. Proposed modifications to the Duke criteria for the diagnosis of infective endocarditis. Clin Infect Dis 2000;30: The University of Chicago Press. *See Table 2 for definitions of major and minor criteria. In patients who meet modified Duke criteria for infective endocarditis but have negative blood cultures, it is imperative to evaluate for unusual organisms using a combination of serologic tests, specialized cultures, histopathology, and polymerase chain reaction. 5,6 Organisms identified with these additional tests in blood culture negative infective endocarditis include Coxiella burnetii, Bartonella species, Tropheryma whippelii, Abiotrophia elegans, Mycoplasma hominis, L. pneumophila, S. bovis, Rhodococcus species, and Histoplasma species. 5,6 With the use of these methods, effective cases of culture-negative endocarditis can be decreased to 1%. 5 Clostridial Endocarditis C. perfringens is a rare cause of infective endocarditis. Only 21 cases of clostridial endocarditis have been reported in the literature, predominantly caused by C. perfringens Likely portals of entry include the skin, oropharynx, and gastrointestinal and genitourinary Table 2. Definitions of Major and Minor Criteria in the Modified Duke Criteria for Diagnosis of Infective Endocarditis (IE) Major criteria Blood culture positive for IE Typical microorganisms consistent with IE from 2 separate blood cultures: Viridans streptococci, Streptococcus bovis, HACEK group, Staphylococcus aureus; or Community-acquired enterococci, in the absence of a primary focus; or Microorganisms consistent with IE from persistently positive blood cultures, defined as follows: At least 2 positive cultures of blood samples drawn > 12 h apart; or All of 3 or a majority of 4 separate cultures of blood (with first and last sample drawn at least 1 h apart) Single positive blood culture for Coxiella burnetii or antiphase I IgG antibody titer > 1:800 Evidence of endocardial involvement Echocardiogram positive for IE (TEE recommended in patients with prosthetic valves, rating of at least possible IE by clinical criteria, or complicated IE [paravalvular abscess]; TTE is first test in other patients), defined as follows: Oscillating intracardiac mass on valve or supporting structures, in the path of regurgitant jets, or on implanted material in the absence of an alternative anatomic explanation; or Abscess; or New partial dehiscence of prosthetic valve New valvular regurgitation (worsening or changing of preexisting murmur not sufficient) Minor criteria Predisposition, predisposing heart condition, or injection drug use Fever, temperature > 38 C (100.4 F) Vascular phenomena, major arterial emboli, septic pulmonary infarcts, mycotic aneurysm, intracranial hemorrhage, conjunctival hemorrhages, and Janeway s lesions Immunologic phenomena: glomerulonephritis, Osler s nodes, Roth s spots, and rheumatoid factor Microbiologic evidence: positive blood culture but does not meet a major criterion as noted above* or serologic evidence of active infection with organism consistent with IE Echocardiographic minor criteria eliminated Adapted with permission from Li JS, Sexton DJ, Mick N, et al. Proposed modifications to the Duke criteria for the diagnosis of infective endocarditis. Clin Infect Dis 2000;30: The University of Chicago Press. HACEK = Haemophilus parainfluenzae, H. influenzae, H. aphrophilus, H. paraphrophilus, Actinobacillus actinomycetemcomitans, Cardiobacterium hominis, Eikenella corrodens, and Kingella species; TEE = transesophageal echocardiography; TTE = transthoracic echocardiography. *Excludes single positive cultures for coagulase-negative staphylococci and organisms that do not cause endocarditis. 26 Hospital Physician June
5 systems. 11 Although some studies have found no predisposing factors for the development of infective endocarditis, 8 patients with IV drug use, 12 carcinoma of the colon or cervix, and preexisting valvular disease, including those with prosthetic valves and rheumatic heart disease, may be at increased risk. 11 Valvular disease is present in approximately 50% of patients with clostridial endocarditis. 9,11 Nkoua et al 13 isolated C. perfringens from a patient with postpartum infective endocarditis and a patient with illicit postabortive infective endocarditis. Clostridial endocarditis has also been reported after penetrating cardiac trauma. 14 Diagnosis of clostridial endocarditis is similar to that of endocarditis caused by other organisms and involves demonstration of a valvular lesion on echocardiography. Fever is a presenting symptom in the majority of patients with infective endocarditis, and embolic phenomena occur in approximately 50% of cases. 11 A spectrum of shock, intravascular hemolysis, and jaundice (known as clostridial sepsis ) has been observed in one third of patients with clostridial endocarditis. 11 Clostridia are not frequently isolated from blood cultures. Use of aerobic and anaerobic culture methods may increase the yield of detection of clostridial or culture-negative endocarditis. 15 Clostridia have been predominantly cultured from endovascular tissue specimens obtained either postsurgically or at autopsy. Anaerobic endocarditis appears to cause large vegetations, as was the case in our patient. In 14 cases with a well-documented clinical history, 4 involved prosthetic valves, while others involved the tricuspid valve, the aortic and mitral valves, the aortic wall at the junction with Dacron prosthesis, and the left ventricular wall below the mitral annulus. 15 Empiric treatment for culture-negative endocarditis includes vancomycin, fluoroquinolone/ceftriaxone, and gentamicin. 1,16 IV penicillin G is the treatment of choice for clostridial endocarditis, but metronidazole has been considered for prolonged bacteremia or in treatment failures. Mortality rates have been reported to be as high as 47% despite appropriate antibiotic treatment. 10 SUMMARY It is imperative to perform blood cultures prior to the initiation of antibiotics in patients with suspected endocarditis. When blood cultures are negative and the probability of infective endocarditis is still high, specialized cultures, serologic testing, polymerase chain reaction, and tissue histopathology and culture can be performed to identify a causative organism, which subsequently allows for targeted antibiotic therapy. Despite a sound diagnostic approach and numerous cultures to identify the causative organism, in some cases the organism cannot be isolated and broad-spectrum antibiotic coverage then becomes important. HP Corresponding author: Yochai Birnbaum, MD, Division of Cardiology, The University of Texas Medical Branch, John Sealy Annex, 301 University Boulevard, Galveston, TX ; yobirnba@utmb.edu. REFERENCES 1. Fowler VG, Scheld MW, Bayer AS. Endocarditis and intravascular infections. In: Mandell GL, Douglas RG, Bennett JE, Dolin R, editors. Mandell, Douglas, and Bennett s principles and practice of infectious diseases. 6th ed. New York: Elsevier/Churchill Livingstone; 2005: Shapiro SM, Young E, De Guzman S, et al. Transesophageal echocardiography in diagnosis of infective endocarditis. Chest 1994;105: Schulz R, Werner GS, Fuchs JB, et al. Clinical outcome and echocardiographic findings of native and prosthetic valve endocarditis in the 1990 s. Eur Heart J 1996;17: Daniel WG, Mügge A, Martin RP, et al. Improvement in the diagnosis of abscesses associated with endocarditis by transesophageal echocardiography. N Engl J Med 1991;324: Houpikian P, Raoult D. Blood culture negative endocarditis in a reference center: etiologic diagnosis of 348 cases. Medicine (Baltimore) 2005;84: Lamas CC, Eykyn SJ. Blood culture negative endocarditis: analysis of 63 cases presenting over 25 years. Heart 2003;89: Naber CK, Erbel R. Diagnosis of culture negative endocarditis: novel strategies to prove the suspect guilty. Heart 2003;89: Kolander SA, Cosgrove EM, Molavi A. Clostridial endocarditis. Report of a case caused by Clostridium bifermentans and review of the literature. Arch Intern Med 1989;149: Alvarez-Elcoro S, Sifuentes-Osorio J. Clostridium perfringens bacteremia in prosthetic valve endocarditis. Diagnosis by peripheral blood smear. Arch Intern Med 1984;144: Cutrona AF, Waranakunakorn C, Schaub C, Jagetia A. Clostridium innocuum endocarditis. Clin Infect Dis 1995;21: Brouqui P, Raoult D. Endocarditis due to rare and fastidious bacteria. Clin Microbiol Rev 2001;14: Moyano R, Gomez-Mateos JM, Lozano de Leon F, et al. Clostridium bifermentans: an exceptional agent of endocarditis [letter]. Clin Infect Dis 1994; 18: Nkoua JL, Kimbally-Kaky G, Ekoba J, et al. [Infectious endocarditis of gynecoobstetric origin. Apropos of 15 cases.] [Article in French.] J Gynecol Obstet Biol Reprod (Paris) 1993;22: Holland F 2nd, Fernandez L, Jacobs J, Bolooki H. Clostridial endocarditis following penetrating cardiac trauma. Clin Infect Dis 1997;24: Durmaz B, Agel HE, Sonmez E, et al. Infective endocarditis due to Clostridium histolyticum [letter]. Clin Microbiol Infect 2000;6: Baddour LM, Wilson WR, Bayer AS, et al; Committee on Rheumatic Fever, Endocarditis, and Kawasaki Disease; Council on Cardiovascular Disease in the Young; Councils on Clinical Cardiology, Stroke, and Cardiovascular Surgery and Anesthesia; American Heart Association; Infection Diseases Society of America. Infective endocarditis: diagnosis, antimicrobial therapy, and management of complications: a statement for healthcare professionals from the Committee on Rheumatic Fever, Endocarditis, and Kawasaki Disease, Council on Cardiovascular Disease in the Young, and the Councils on Clinical Cardiology, Stroke, and Cardiovascular Surgery and Anesthesia, American Heart Association: endorsed by the Infectious Diseases Society of America [published errata appear in Circulation 2005;112:2373 and 2007;115:e408]. Circulation 2005;111:e Copyright 2008 by Turner White Communications Inc., Wayne, PA. All rights reserved. Hospital Physician June
Daniel C. DeSimone, MD Assistant Professor of Medicine
 Daniel C. DeSimone, MD Assistant Professor of Medicine Faculty photo will be placed here Desimone.Daniel@mayo.edu 2015 MFMER 3543652-1 Infective Endocarditis Mayo School of Continuous Professional Development
Daniel C. DeSimone, MD Assistant Professor of Medicine Faculty photo will be placed here Desimone.Daniel@mayo.edu 2015 MFMER 3543652-1 Infective Endocarditis Mayo School of Continuous Professional Development
Infective Endocarditis Empirical therapy Antibiotic Guidelines. Contents
 Infective Endocarditis Empirical therapy Antibiotic Guidelines Classification: Clinical Guideline Lead Author: Antibiotic Steering Group Additional author(s): as above Authors Division: Division of Clinical
Infective Endocarditis Empirical therapy Antibiotic Guidelines Classification: Clinical Guideline Lead Author: Antibiotic Steering Group Additional author(s): as above Authors Division: Division of Clinical
Challenging clinical situation
 Challenging clinical situation A young patient with prosthetic aortic valve endocarditis Gilbert Habib La Timone Hospital Marseille - France October 25 th 2014 Case report History of the disease Clinical
Challenging clinical situation A young patient with prosthetic aortic valve endocarditis Gilbert Habib La Timone Hospital Marseille - France October 25 th 2014 Case report History of the disease Clinical
NATIONAL HEART FOUNDATION HOSPITAL & RESEARCH INSTITUTE
 Welcome INFECTIVE ENDOCARDITIS: WHERE WE ARE AT 2005? DR MD HABIBUR RAHMAN FCPS(Medicine) NATIONAL HEART FOUNDATION HOSPITAL & RESEARCH INSTITUTE DEFINITION OF INFECTIVE ENDOCARDITIS Infective endocarditis
Welcome INFECTIVE ENDOCARDITIS: WHERE WE ARE AT 2005? DR MD HABIBUR RAHMAN FCPS(Medicine) NATIONAL HEART FOUNDATION HOSPITAL & RESEARCH INSTITUTE DEFINITION OF INFECTIVE ENDOCARDITIS Infective endocarditis
Diagnostic strategy. Dr Pilar Tornos Hospital Vall d Hebron Barcelona
 Diagnostic strategy Dr Pilar Tornos Hospital Vall d Hebron Barcelona Faculty disclosure Pilar Tornos I disclose the following financial relationships: Paid speaker for Recordati, Edwards. Diagnosis of
Diagnostic strategy Dr Pilar Tornos Hospital Vall d Hebron Barcelona Faculty disclosure Pilar Tornos I disclose the following financial relationships: Paid speaker for Recordati, Edwards. Diagnosis of
Dr Babak Tamizi far MD. Assistant Professor Of Internal Medicine Al-Zahra Hospital Isfahan University Of Medical Sciences
 Dr Babak Tamizi far MD. Assistant Professor Of Internal Medicine Al-Zahra Hospital Isfahan University Of Medical Sciences ١ ٢ ٣ A 57-year-old man presents with new-onset fever, shortness of breath, lower
Dr Babak Tamizi far MD. Assistant Professor Of Internal Medicine Al-Zahra Hospital Isfahan University Of Medical Sciences ١ ٢ ٣ A 57-year-old man presents with new-onset fever, shortness of breath, lower
Michael Stander, Pharm.D.
 Michael Stander, Pharm.D. Endocarditis: Goals Epidemiology Presentation of acute and subacute. Diagnosis: What is Dukes Criteria and how do we approach the diagnosis of endocarditis? Treatment: Understand
Michael Stander, Pharm.D. Endocarditis: Goals Epidemiology Presentation of acute and subacute. Diagnosis: What is Dukes Criteria and how do we approach the diagnosis of endocarditis? Treatment: Understand
Heart on Fire: Infective Endocarditis. Objectives. Disclosure 8/27/2018. Mary McGreal DNP, RN, ANP-c, CCRN
 Heart on Fire: Infective Endocarditis Mary McGreal DNP, RN, ANP-c, CCRN Objectives Discuss the incidence of infective endocarditis? Discuss the pathogenesis of infective endocarditis? Discuss clinical
Heart on Fire: Infective Endocarditis Mary McGreal DNP, RN, ANP-c, CCRN Objectives Discuss the incidence of infective endocarditis? Discuss the pathogenesis of infective endocarditis? Discuss clinical
Overview. Clinical Scenario. Endocarditis: Treatment & Prevention. Prophylaxis The Concept. Jeremy D. Young, MD, MPH. Division of Infectious Diseases
 Endocarditis: Treatment & Prevention Jeremy D. Young, MD, MPH Division of Infectious Diseases Clinical Scenario Patient with MVP scheduled to have wisdom teeth extracted. Has systolic murmur with mid-systolic
Endocarditis: Treatment & Prevention Jeremy D. Young, MD, MPH Division of Infectious Diseases Clinical Scenario Patient with MVP scheduled to have wisdom teeth extracted. Has systolic murmur with mid-systolic
Microbiological diagnosis of infective endocarditis; what is new?
 Microbiological diagnosis of infective endocarditis; what is new? Dr Amani El Kholy, MD Professor of Clinical Pathology (Microbiology), Faculty of Medicine, Cairo University ESC 2017 1 Objectives Lab Diagnostic
Microbiological diagnosis of infective endocarditis; what is new? Dr Amani El Kholy, MD Professor of Clinical Pathology (Microbiology), Faculty of Medicine, Cairo University ESC 2017 1 Objectives Lab Diagnostic
Infective Endocarditis
 Infective Endocarditis Definition Historical perspective Classification Epidemiological Features Etiology Pathogenesis Clinical presentation Diagnosis Treatment options Prevention Infective endocarditis
Infective Endocarditis Definition Historical perspective Classification Epidemiological Features Etiology Pathogenesis Clinical presentation Diagnosis Treatment options Prevention Infective endocarditis
An assessment of the current diagnostic criteria for infective endocarditis
 REVIEW An assessment of the current diagnostic criteria for infective endocarditis Albert W Chan MD FRCPC, Heather J Ross MD FRCPC AW Chan, HJ Ross. An assessment of the current diagnostic criteria for
REVIEW An assessment of the current diagnostic criteria for infective endocarditis Albert W Chan MD FRCPC, Heather J Ross MD FRCPC AW Chan, HJ Ross. An assessment of the current diagnostic criteria for
INFECTIOUS endocarditis (IE) is a
 ORIGINAL INVESTIGATION Diagnosis of Infective Endocarditis Sensitivity of the Duke vs von Reyn Criteria Maija Heiro, MD; Jukka Nikoskelainen, MD, PhD; Jaakko J. Hartiala, MD, PhD; Markku K. Saraste, MD;
ORIGINAL INVESTIGATION Diagnosis of Infective Endocarditis Sensitivity of the Duke vs von Reyn Criteria Maija Heiro, MD; Jukka Nikoskelainen, MD, PhD; Jaakko J. Hartiala, MD, PhD; Markku K. Saraste, MD;
SYMPOSIUM 10TH MAY 2007 BELGIUM. Blood culture-negative endocarditis
 SYMPOSIUM 10TH MAY 2007 BELGIUM Blood culture-negative endocarditis Didier RAOULT Didier.raoult@gmail.com Modified Duke criteria for diagnosis of infective endocarditis (IE) Li JS, et al. Proposed modifications
SYMPOSIUM 10TH MAY 2007 BELGIUM Blood culture-negative endocarditis Didier RAOULT Didier.raoult@gmail.com Modified Duke criteria for diagnosis of infective endocarditis (IE) Li JS, et al. Proposed modifications
Endocarditis, including Prophylaxis
 Endocarditis, including Prophylaxis ACOI Board Review 2018 gerald.blackburn@beaumont.org (No Disclosures) Infective Endocarditis Persistant bacteremia (blood cultures drawn >12 hrs apart) w/ organisms
Endocarditis, including Prophylaxis ACOI Board Review 2018 gerald.blackburn@beaumont.org (No Disclosures) Infective Endocarditis Persistant bacteremia (blood cultures drawn >12 hrs apart) w/ organisms
Infective endocarditis (IE) By Assis. Prof. Nader Alaridah MD, PhD
 Infective endocarditis (IE) By Assis. Prof. Nader Alaridah MD, PhD Infective endocarditis (IE) is an inflammation of the endocardium.. inner of the heart muscle & the epithelial lining of heart valves.
Infective endocarditis (IE) By Assis. Prof. Nader Alaridah MD, PhD Infective endocarditis (IE) is an inflammation of the endocardium.. inner of the heart muscle & the epithelial lining of heart valves.
April 16, 09:00-09:15 중앙대학교 윤신원
 April 16, 09:00-09:15 중앙대학교 윤신원 When to perform Echocardiography in IE? Vegetations?(pathologic Whatever the level hallmark) of suspicion Intracardiac abscess? Confirm or R/O at the Earliest opportunity.
April 16, 09:00-09:15 중앙대학교 윤신원 When to perform Echocardiography in IE? Vegetations?(pathologic Whatever the level hallmark) of suspicion Intracardiac abscess? Confirm or R/O at the Earliest opportunity.
BASIC KNOWLEDGE ABOUT INFECTIVE ENDOCARDITIS FOR CLINICIAN
 BASIC KNOWLEDGE ABOUT INFECTIVE ENDOCARDITIS FOR CLINICIAN When should I suspect infective endocarditis? Antibiotic regimen Patient care after completion of treatment Prophylactic Regimens Prosthetic Valve
BASIC KNOWLEDGE ABOUT INFECTIVE ENDOCARDITIS FOR CLINICIAN When should I suspect infective endocarditis? Antibiotic regimen Patient care after completion of treatment Prophylactic Regimens Prosthetic Valve
Echocardiography after stroke - where to look
 Echocardiography after stroke - where to look Vuyisile T. Nkomo, MD,MPH, FACC, FASE Joint Cardiac Imaging Society of South Africa/Mayo Clinic Echocardiography Workshop 2017 2016 MFMER slide-1 Disclosures
Echocardiography after stroke - where to look Vuyisile T. Nkomo, MD,MPH, FACC, FASE Joint Cardiac Imaging Society of South Africa/Mayo Clinic Echocardiography Workshop 2017 2016 MFMER slide-1 Disclosures
PRINCIPLES OF ENDOCARDITIS
 015 // Endocarditis CONTENTS 140 Principles of Endocarditis 141 Native Valve Endocarditis 143 Complications of Native Valve Endocarditis 145 Right Heart Endocarditis 145 Prosthetic Valve Endocarditis 146
015 // Endocarditis CONTENTS 140 Principles of Endocarditis 141 Native Valve Endocarditis 143 Complications of Native Valve Endocarditis 145 Right Heart Endocarditis 145 Prosthetic Valve Endocarditis 146
Sepsis and Infective Endocarditis
 Sepsis and Infective Endocarditis Michal Holub Department of Infectious Diseases First Faculty of Medicine Charles University in Prague and University Military Hospital Bacteremia and Sepsis bacteremia
Sepsis and Infective Endocarditis Michal Holub Department of Infectious Diseases First Faculty of Medicine Charles University in Prague and University Military Hospital Bacteremia and Sepsis bacteremia
A Predictable Outcome of a Preventable Disease. Sanjay Kamboj, MD; Shaminder Gupta, MD; Glenn P. Kelley, MD; Fred Helmcke, MD; and Fred A.
 Clinical Case of the Month A Predictable Outcome of a Preventable Disease Sanjay Kamboj, MD; Shaminder Gupta, MD; Glenn P. Kelley, MD; Fred Helmcke, MD; and Fred A. Lopez, MD Infective endocarditis is
Clinical Case of the Month A Predictable Outcome of a Preventable Disease Sanjay Kamboj, MD; Shaminder Gupta, MD; Glenn P. Kelley, MD; Fred Helmcke, MD; and Fred A. Lopez, MD Infective endocarditis is
Infective Endocarditis
 Frank Lowy Infective Endocarditis 1. Introduction Infective endocarditis (IE) is an infection of the heart valves. A large number of different bacteria are capable of causing this disease. Depending on
Frank Lowy Infective Endocarditis 1. Introduction Infective endocarditis (IE) is an infection of the heart valves. A large number of different bacteria are capable of causing this disease. Depending on
Infective Endocarditis
 Definition Infective Endocarditis Pattaya Riengchan M.D. MAR 16, 2017 Infection of endocardial surface of the heart and implies the physical presence microorganisms in the lesion Heart valves are most
Definition Infective Endocarditis Pattaya Riengchan M.D. MAR 16, 2017 Infection of endocardial surface of the heart and implies the physical presence microorganisms in the lesion Heart valves are most
Infective Endocarditis
 Infective Endocarditis Infective Endocarditis Historical Perspective.. A concretion larger than a pigeon s egg; contained in the left auricle. Burns, 1809 Osler s Gulstonian lectures provided the 1 st
Infective Endocarditis Infective Endocarditis Historical Perspective.. A concretion larger than a pigeon s egg; contained in the left auricle. Burns, 1809 Osler s Gulstonian lectures provided the 1 st
AHA Scientific Statement
 AHA Scientific Statement Infective Endocarditis in Adults: Diagnosis, Antimicrobial Therapy, and Management of Complications A Scientific Statement for Healthcare Professionals From the American Heart
AHA Scientific Statement Infective Endocarditis in Adults: Diagnosis, Antimicrobial Therapy, and Management of Complications A Scientific Statement for Healthcare Professionals From the American Heart
ACCME/Disclosures 4/13/2016 IDPB
 ACCME/Disclosures The USCAP requires that anyone in a position to influence or control the content of CME disclose any relevant financial relationship WITH COMMERCIAL INTERESTS which they or their spouse/partner
ACCME/Disclosures The USCAP requires that anyone in a position to influence or control the content of CME disclose any relevant financial relationship WITH COMMERCIAL INTERESTS which they or their spouse/partner
Diagnosis and management of bacterial endocarditis in 2003 Blaithnead Murtagh, MD, O.H. Frazier, MD, and George V. Letsou, MD
 Diagnosis and management of bacterial endocarditis in 2003 Blaithnead Murtagh, MD, O.H. Frazier, MD, and George V. Letsou, MD The diagnosis of infective endocarditis has been notoriously difficult. Over
Diagnosis and management of bacterial endocarditis in 2003 Blaithnead Murtagh, MD, O.H. Frazier, MD, and George V. Letsou, MD The diagnosis of infective endocarditis has been notoriously difficult. Over
Bacterial Endocarditis
 Objectives Bacterial Endocarditis John C. Rotschafer, Pharm. D. Professor College of Pharmacy University of Minnesota Identify which valves are commonly involved with endocarditis Identify common pathogens
Objectives Bacterial Endocarditis John C. Rotschafer, Pharm. D. Professor College of Pharmacy University of Minnesota Identify which valves are commonly involved with endocarditis Identify common pathogens
Echocardiography in Endocarditis
 Echocardiography in Endocarditis Bicol Hospital, Legazpi City, Philippines July 2016 Gregg S. Pressman MD, FACC, FASE Einstein Medical Center Philadelphia, USA Demographics of IE Incidence is 1.4 12.7/100,000
Echocardiography in Endocarditis Bicol Hospital, Legazpi City, Philippines July 2016 Gregg S. Pressman MD, FACC, FASE Einstein Medical Center Philadelphia, USA Demographics of IE Incidence is 1.4 12.7/100,000
The changing landscape of infective endocarditis (IE)in congenital heart disease (CHD)
 The changing landscape of infective endocarditis (IE)in congenital heart disease (CHD) Rekwan Sittiwangkul,MD Department of Pediatrics. Chiang Mai University Hospital, 24 th March 2018 Infective endocarditis
The changing landscape of infective endocarditis (IE)in congenital heart disease (CHD) Rekwan Sittiwangkul,MD Department of Pediatrics. Chiang Mai University Hospital, 24 th March 2018 Infective endocarditis
The microbial diagnosis of infective endocarditis (IE)
 The microbial diagnosis of infective endocarditis (IE) Pierrette Melin Medical Microbiology pm-chulg sbimc 10.05.2007 1 Introduction for diagnosis Review of microbiological investigation of IE and perspectives
The microbial diagnosis of infective endocarditis (IE) Pierrette Melin Medical Microbiology pm-chulg sbimc 10.05.2007 1 Introduction for diagnosis Review of microbiological investigation of IE and perspectives
Infective Endocarditis for Primary Care Physicians
 Infective Endocarditis for Primary Care Physicians David N Gilbert, MD Disclosures Consultant to: Merck Pfizer Medicine Company Cempra 1 Introduction There are roughly 30,000 new cases of IE in the US
Infective Endocarditis for Primary Care Physicians David N Gilbert, MD Disclosures Consultant to: Merck Pfizer Medicine Company Cempra 1 Introduction There are roughly 30,000 new cases of IE in the US
Diagnosis and Treatment of Bacterial Endocarditis
 Infectious diseases Board Review Manual Statement of Editorial Purpose The Hospital Physician Infectious Diseases Board Review Manual is a study guide for fellows and practicing physicians preparing for
Infectious diseases Board Review Manual Statement of Editorial Purpose The Hospital Physician Infectious Diseases Board Review Manual is a study guide for fellows and practicing physicians preparing for
Infective Endocarditis
 Chapter 32 Infective Endocarditis Lisa B. Hightow and Meera Kelley The term infective endocarditis (IE) refers to infection of the endocardial surface of the heart and implies a physical presence of microganisms
Chapter 32 Infective Endocarditis Lisa B. Hightow and Meera Kelley The term infective endocarditis (IE) refers to infection of the endocardial surface of the heart and implies a physical presence of microganisms
Disclosures. Native Valve Endocarditis and its Complications. Outline. Outline. Basics. Basics 3/23/2017
 Native Valve Endocarditis and its Complications SCVP and Binford Dammin Society of Infectious Disease Pathologists Shared Companion Meeting USCAP 2017 Annual Meeting Disclosures Relevant financial relationships
Native Valve Endocarditis and its Complications SCVP and Binford Dammin Society of Infectious Disease Pathologists Shared Companion Meeting USCAP 2017 Annual Meeting Disclosures Relevant financial relationships
Update on the prevention, diagnosis and management of Infective Endocarditis (IE)
 Update on the prevention, diagnosis and management of Infective Endocarditis (IE) Dr.Ahmed Yahya Mohammed Alarhabi MD, MsC,FcUSM,FACC,MAHA Consultant Interventional Cardiologist Head of Cardiac Center
Update on the prevention, diagnosis and management of Infective Endocarditis (IE) Dr.Ahmed Yahya Mohammed Alarhabi MD, MsC,FcUSM,FACC,MAHA Consultant Interventional Cardiologist Head of Cardiac Center
PROSTHETIC VALVE BOARD REVIEW
 PROSTHETIC VALVE BOARD REVIEW The correct answer D This two chamber view shows a porcine mitral prosthesis with the typical appearance of the struts although the leaflets are not well seen. The valve
PROSTHETIC VALVE BOARD REVIEW The correct answer D This two chamber view shows a porcine mitral prosthesis with the typical appearance of the struts although the leaflets are not well seen. The valve
A Study of Infective Endocarditis in Malta
 Science Journal of Clinical Medicine 2017; 6(6): 98-104 http://www.sciencepublishinggroup.com/j/sjcm doi: 10.11648/j.sjcm.20170606.11 ISSN: 2327-2724 (Print); ISSN: 2327-2732 (Online) A Study of Infective
Science Journal of Clinical Medicine 2017; 6(6): 98-104 http://www.sciencepublishinggroup.com/j/sjcm doi: 10.11648/j.sjcm.20170606.11 ISSN: 2327-2724 (Print); ISSN: 2327-2732 (Online) A Study of Infective
Infections Amenable to OPAT. (Nabin Shrestha + Ajay Mathur)
 3 Infections Amenable to OPAT (Nabin Shrestha + Ajay Mathur) Decisions regarding outpatient treatment of infections vary with the institution, the prescribing physician, the individual patient s condition
3 Infections Amenable to OPAT (Nabin Shrestha + Ajay Mathur) Decisions regarding outpatient treatment of infections vary with the institution, the prescribing physician, the individual patient s condition
ICE: Echo Core Lab-CRF
 APPENDIX 1 ICE: Echo Core Lab-CRF Study #: - Pt Initials: 1. Date of study: / / D D M M M Y Y Y Y 2. Type of Study: TTE TEE 3. Quality of Study: Poor Moderate Excellent Ejection Fraction 4. Ejection Fraction
APPENDIX 1 ICE: Echo Core Lab-CRF Study #: - Pt Initials: 1. Date of study: / / D D M M M Y Y Y Y 2. Type of Study: TTE TEE 3. Quality of Study: Poor Moderate Excellent Ejection Fraction 4. Ejection Fraction
CLINICAL SYNDROMES: COMMUNITY ACQUIRED INFECTIONS
 SECTION 2 CLINICAL SYNDROMES: COMMUNITY ACQUIRED INFECTIONS 118-1 118 Adolf W. Karchmer The prototypic lesion of infective endocarditis, the vegetation (Fig. 118-1), is a mass of platelets, fibrin, microcolonies
SECTION 2 CLINICAL SYNDROMES: COMMUNITY ACQUIRED INFECTIONS 118-1 118 Adolf W. Karchmer The prototypic lesion of infective endocarditis, the vegetation (Fig. 118-1), is a mass of platelets, fibrin, microcolonies
Contents. 1. Introduction. J Antimicrob Chemother 2012; 67: doi: /jac/dkr450 Advance Access publication 14 November 2011
 J Antimicrob Chemother 2012; 67: 269 289 doi:10.1093/jac/dkr450 Advance Access publication 14 November 2011 Guidelines for the diagnosis and antibiotic treatment of endocarditis in adults: a report of
J Antimicrob Chemother 2012; 67: 269 289 doi:10.1093/jac/dkr450 Advance Access publication 14 November 2011 Guidelines for the diagnosis and antibiotic treatment of endocarditis in adults: a report of
Infective endocarditis
 Infective endocarditis This is caused by microbial infection of a heart valve (native or prosthetic), the lining of a cardiac chamber or blood vessel, or a congenital anomaly (e.g. septal defect). The
Infective endocarditis This is caused by microbial infection of a heart valve (native or prosthetic), the lining of a cardiac chamber or blood vessel, or a congenital anomaly (e.g. septal defect). The
Infective Endocarditis عبد المهيمن أحمد
 Infective Endocarditis إعداد : عبد المهيمن أحمد أحمد علي Infective endocarditis Inflammation of the heart valve or endocardium of the heart. The agents are usually bacterial, but other organisms can also
Infective Endocarditis إعداد : عبد المهيمن أحمد أحمد علي Infective endocarditis Inflammation of the heart valve or endocardium of the heart. The agents are usually bacterial, but other organisms can also
VEGETATION NEGATIVE INFECTIVE ENDOCARDITIS A VIEW POINT... Mumbai Dec 2005 Annual scientific sessions
 VEGETATION NEGATIVE INFECTIVE ENDOCARDITIS A VIEW POINT... Mumbai Dec 2005 Annual scientific sessions S.Venkatesan,G.Gnanavelu,G.Karthikeyan,V.Jaganathan,R.Alagesan M.Annamalai,S.Shanmugasundaram, S.Geetha,A.Balaguru.G.Anuradha
VEGETATION NEGATIVE INFECTIVE ENDOCARDITIS A VIEW POINT... Mumbai Dec 2005 Annual scientific sessions S.Venkatesan,G.Gnanavelu,G.Karthikeyan,V.Jaganathan,R.Alagesan M.Annamalai,S.Shanmugasundaram, S.Geetha,A.Balaguru.G.Anuradha
A CASE OF RIGHT SIDED INFECTIVE ENDOCARDITIS WITH REACTIVE KNEE ARTHRITIS AND ACUTE KIDNEY INJURY Suresh Babu S 1, A. K. Badrinath 2, K.
 A CASE OF RIGHT SIDED INFECTIVE ENDOCARDITIS WITH REACTIVE KNEE ARTHRITIS AND ACUTE KIDNEY INJURY Suresh Babu S 1, A. K. Badrinath 2, K. Suresh 3 HOW TO CITE THIS ARTICLE: Suresh Babu S, A. K. Badrinath,
A CASE OF RIGHT SIDED INFECTIVE ENDOCARDITIS WITH REACTIVE KNEE ARTHRITIS AND ACUTE KIDNEY INJURY Suresh Babu S 1, A. K. Badrinath 2, K. Suresh 3 HOW TO CITE THIS ARTICLE: Suresh Babu S, A. K. Badrinath,
Infected cardiac-implantable electronic devices: diagnosis, and treatment
 Infected cardiac-implantable electronic devices: diagnosis, and treatment The incidence of infection following implantation of cardiac implantable electronic devices (CIEDs) is increasing at a faster rate
Infected cardiac-implantable electronic devices: diagnosis, and treatment The incidence of infection following implantation of cardiac implantable electronic devices (CIEDs) is increasing at a faster rate
WRITTEN BY: Thaer Al-qatish & Sarah Awaisheh
 WRITTEN BY: Thaer Al-qatish & Sarah Awaisheh Not all informations in the slides are included in this sheet so please study the slides. 3 kinds of Intracardiac infections: -endocarditis(inflammation of
WRITTEN BY: Thaer Al-qatish & Sarah Awaisheh Not all informations in the slides are included in this sheet so please study the slides. 3 kinds of Intracardiac infections: -endocarditis(inflammation of
Case Report Subacute Staphylococcusepidermidis Bacterial Endocarditis Complicated by Mitral-Aortic Intervalvular Fibrosa Pseudoaneurysm
 Case Reports in Cardiology Volume 2012, Article ID 467210, 4 pages doi:10.1155/2012/467210 Case Report Subacute Staphylococcusepidermidis Bacterial Endocarditis Complicated by Mitral-Aortic Intervalvular
Case Reports in Cardiology Volume 2012, Article ID 467210, 4 pages doi:10.1155/2012/467210 Case Report Subacute Staphylococcusepidermidis Bacterial Endocarditis Complicated by Mitral-Aortic Intervalvular
Infective Endocarditis:
 CME Workshop Infective Endocarditis: Prophylaxis, Diagnosis and Management Presented at a CME program, University of Manitoba, Winnipeg, Manitoba, December 2001. By Davinder S. Jassal, MD; and John M.
CME Workshop Infective Endocarditis: Prophylaxis, Diagnosis and Management Presented at a CME program, University of Manitoba, Winnipeg, Manitoba, December 2001. By Davinder S. Jassal, MD; and John M.
Joshua Budhu M.S, Dorian Wood B.S, Marvin Crawford M.D, Khuram Ashraf M.D, Frederick Doamekpor M.D, Olufunke Akinbobuyi M.D
 Accepted Manuscript Aerococcus Viridans Infectious Endocarditis Complicated by Splenic Infarction Joshua Budhu M.S, Dorian Wood B.S, Marvin Crawford M.D, Khuram Ashraf M.D, Frederick Doamekpor M.D, Olufunke
Accepted Manuscript Aerococcus Viridans Infectious Endocarditis Complicated by Splenic Infarction Joshua Budhu M.S, Dorian Wood B.S, Marvin Crawford M.D, Khuram Ashraf M.D, Frederick Doamekpor M.D, Olufunke
Apport des recommandations européennes
 Apport des recommandations européennes Gilbert Habib Cardiology Department- La Timone Marseille - France Bordeaux le 28 Juin 2011 Infective Endocarditis: a changing disease new high-risk subgroups IVDA
Apport des recommandations européennes Gilbert Habib Cardiology Department- La Timone Marseille - France Bordeaux le 28 Juin 2011 Infective Endocarditis: a changing disease new high-risk subgroups IVDA
IE with cerebral hemorrhage
 IE with cerebral hemorrhage Gilbert Habib / Patrizio Lancellotti La Timone Hospital Marseille - France Palermo, 26 April 2018 Case report: aortic bioprosthetic IE History of the disease 75 year-old man
IE with cerebral hemorrhage Gilbert Habib / Patrizio Lancellotti La Timone Hospital Marseille - France Palermo, 26 April 2018 Case report: aortic bioprosthetic IE History of the disease 75 year-old man
Bacterial Endocarditis
 Disclosures Bacterial Endocarditis Henry F. Chambers, MD Allergan research grant Genentech research grant Infective endocarditis: Outline Native valve endocarditis Prosthetic valve endocarditis Cardiac
Disclosures Bacterial Endocarditis Henry F. Chambers, MD Allergan research grant Genentech research grant Infective endocarditis: Outline Native valve endocarditis Prosthetic valve endocarditis Cardiac
109 Infective Endocarditis
 Página 1 de 30 Copyright 2005 McGraw-Hill Kasper, Dennis L., Fauci, Anthony S., Longo, Dan L., Braunwald, Eugene, Hauser, Stephen L., Jameson, J. Larry, Harrison, T. R., Resnick, W. R., Wintrobe, M. M.,
Página 1 de 30 Copyright 2005 McGraw-Hill Kasper, Dennis L., Fauci, Anthony S., Longo, Dan L., Braunwald, Eugene, Hauser, Stephen L., Jameson, J. Larry, Harrison, T. R., Resnick, W. R., Wintrobe, M. M.,
Outcomes After Surgical Treatment of Native and Prosthetic Valve Infective Endocarditis
 Outcomes After Surgical Treatment of Native and Prosthetic Valve Infective Endocarditis Mahesh B. Manne, MD, MPH, Nabin K. Shrestha, MD, Bruce W. Lytle, MD, Edward R. Nowicki, MD, MS, Eugene Blackstone,
Outcomes After Surgical Treatment of Native and Prosthetic Valve Infective Endocarditis Mahesh B. Manne, MD, MPH, Nabin K. Shrestha, MD, Bruce W. Lytle, MD, Edward R. Nowicki, MD, MS, Eugene Blackstone,
Pr AMEL OMEZZINE LETAIEF CHU FarhatHached Sousse
 Pr AMEL OMEZZINE LETAIEF CHU FarhatHached Sousse cours de collège infectiologie Sousse le27/02/2013 ENDOCARDITIS There is a change in epidemiology Clinical features of IE remains classical Diagnosis of
Pr AMEL OMEZZINE LETAIEF CHU FarhatHached Sousse cours de collège infectiologie Sousse le27/02/2013 ENDOCARDITIS There is a change in epidemiology Clinical features of IE remains classical Diagnosis of
Management of infective endocarditis in children
 Management of infective endocarditis in children Ashutosh Marwah, MD* Savitri Shrivastava, MD DM FAMS FACC* INTRODUCTION Infective endocarditis (IE) continues to remain a serious disease despite advances
Management of infective endocarditis in children Ashutosh Marwah, MD* Savitri Shrivastava, MD DM FAMS FACC* INTRODUCTION Infective endocarditis (IE) continues to remain a serious disease despite advances
The New England Journal of Medicine. Review Articles
 Review Articles Medical Progress INFECTIVE ENDOCARDITIS IN ADULTS ELEFTHERIOS MYLONAKIS, M.D., AND STEPHEN B. CALDERWOOD, M.D. INFECTIVE endocarditis, a microbial infection of the endocardial surface of
Review Articles Medical Progress INFECTIVE ENDOCARDITIS IN ADULTS ELEFTHERIOS MYLONAKIS, M.D., AND STEPHEN B. CALDERWOOD, M.D. INFECTIVE endocarditis, a microbial infection of the endocardial surface of
Case Studies in Complex Endocarditis
 Case Studies in Complex Endocarditis Vera H. Rigolin, MD Professor of Medicine Northwestern University Feinberg School of Medicine Medical Director, Echocardiography Laboratory Northwestern Memorial Hospital
Case Studies in Complex Endocarditis Vera H. Rigolin, MD Professor of Medicine Northwestern University Feinberg School of Medicine Medical Director, Echocardiography Laboratory Northwestern Memorial Hospital
Supplementary Appendix
 Supplementary Appendix This appendix has been provided by the authors to give readers additional information about their work. Supplement to: Kang D-H, Kim Y-J, Kim S-H, et al. Early surgery versus conventional
Supplementary Appendix This appendix has been provided by the authors to give readers additional information about their work. Supplement to: Kang D-H, Kim Y-J, Kim S-H, et al. Early surgery versus conventional
General management of infective endocarditis
 General management of infective endocarditis Team approach in infective endocarditis Gilbert Habib La Timone Hospital Marseille - France Eurovalves Barcelona 2017 The echolab «Heart Team" Infective Endocarditis
General management of infective endocarditis Team approach in infective endocarditis Gilbert Habib La Timone Hospital Marseille - France Eurovalves Barcelona 2017 The echolab «Heart Team" Infective Endocarditis
Hearts afire: Infective endocarditis
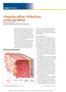 Hearts afire: Infective endocarditis By Kim McCarron, MS, CRNP Clinical Associate Professor Towson University Towson, Md. Editorial Advisory Board Member Nursing made Incredibly Easy! Picturing endocarditis
Hearts afire: Infective endocarditis By Kim McCarron, MS, CRNP Clinical Associate Professor Towson University Towson, Md. Editorial Advisory Board Member Nursing made Incredibly Easy! Picturing endocarditis
HISTORY. Question: How do you interpret the patient s history? CHIEF COMPLAINT: Dyspnea of two days duration. PRESENT ILLNESS: 45-year-old man.
 HISTORY 45-year-old man. CHIEF COMPLAINT: Dyspnea of two days duration. PRESENT ILLNESS: His dyspnea began suddenly and has been associated with orthopnea, but no chest pain. For two months he has felt
HISTORY 45-year-old man. CHIEF COMPLAINT: Dyspnea of two days duration. PRESENT ILLNESS: His dyspnea began suddenly and has been associated with orthopnea, but no chest pain. For two months he has felt
Approach to the Laboratory Diagnosis of Infective Endocarditis SWACM 2018
 Approach to the Laboratory Diagnosis of Infective Endocarditis SWACM 2018 Rachael Liesman, PhD, D(ABMM) Director, Clinical Microbiology Department of Pathology and Laboratory Medicine University of Kansas
Approach to the Laboratory Diagnosis of Infective Endocarditis SWACM 2018 Rachael Liesman, PhD, D(ABMM) Director, Clinical Microbiology Department of Pathology and Laboratory Medicine University of Kansas
Case Report Subacute Staphylococcusepidermidis Bacterial Endocarditis Complicated by Mitral-Aortic Intervalvular Fibrosa Pseudoaneurysm
 Hindawi Publishing Corporation Case Reports in Cardiology Volume 2012, Article ID 467210, 4 pages doi:10.1155/2012/467210 Case Report Subacute Staphylococcusepidermidis Bacterial Endocarditis Complicated
Hindawi Publishing Corporation Case Reports in Cardiology Volume 2012, Article ID 467210, 4 pages doi:10.1155/2012/467210 Case Report Subacute Staphylococcusepidermidis Bacterial Endocarditis Complicated
Echocardiography as a diagnostic and management tool in medical emergencies
 Echocardiography as a diagnostic and management tool in medical emergencies Frank van der Heusen MD Department of Anesthesia and perioperative Care UCSF Medical Center Objective of this presentation Indications
Echocardiography as a diagnostic and management tool in medical emergencies Frank van der Heusen MD Department of Anesthesia and perioperative Care UCSF Medical Center Objective of this presentation Indications
results in stenosis or insufficiency (regurgitation or incompetence), or both.
 results in stenosis or insufficiency (regurgitation or incompetence), or both. The outcome of valvular disease depends on : 1-the valve involved 2-the degree of impairment 3-the cause of its development
results in stenosis or insufficiency (regurgitation or incompetence), or both. The outcome of valvular disease depends on : 1-the valve involved 2-the degree of impairment 3-the cause of its development
Endocarditis in the elderly
 Endocarditis in the elderly Gilbert Habib Département de Cardiologie - Timone Marseille Eurovalves Barcelona 2017 Endocarditis in the octogenarian Gilbert Habib Département de Cardiologie - Timone Marseille
Endocarditis in the elderly Gilbert Habib Département de Cardiologie - Timone Marseille Eurovalves Barcelona 2017 Endocarditis in the octogenarian Gilbert Habib Département de Cardiologie - Timone Marseille
Suggested Reading: Pages Donald P. Levine, M.D. Professor of Medicine Page 1 of 8
 Professor of Medicine Page 1 of 8 ENDOCARDITIS I. General A. infectivie endocarditis (IE) 1. definition: infection of the endocardial surface of the heart; implies the physical presence of microorganisms
Professor of Medicine Page 1 of 8 ENDOCARDITIS I. General A. infectivie endocarditis (IE) 1. definition: infection of the endocardial surface of the heart; implies the physical presence of microorganisms
Research Article. Neilmegh Varada 1, Jonathan Quinonez 2, Andrew Sou 2, Jimmy Chua 2
 Research Article Potential Simultaneous Aortic and Mitral Valve Endocarditis in A Patient With Bio-Prosthetic Porcine Aortic Valve Replacement and Pacemaker Implantation Neilmegh Varada 1, Jonathan Quinonez
Research Article Potential Simultaneous Aortic and Mitral Valve Endocarditis in A Patient With Bio-Prosthetic Porcine Aortic Valve Replacement and Pacemaker Implantation Neilmegh Varada 1, Jonathan Quinonez
Detailed Order Request Checklists for Cardiology
 Next Generation Solutions Detailed Order Request Checklists for Cardiology 8600 West Bryn Mawr Avenue South Tower Suite 800 Chicago, IL 60631 www.aimspecialtyhealth.com Appropriate.Safe.Affordable 2018
Next Generation Solutions Detailed Order Request Checklists for Cardiology 8600 West Bryn Mawr Avenue South Tower Suite 800 Chicago, IL 60631 www.aimspecialtyhealth.com Appropriate.Safe.Affordable 2018
You Won t Believe What I Saw on. Disclosures. Goals. Dimensions 2013 October 18 th Michael Pfeiffer, MD. No Financial Disclosures
 You Won t Believe What I Saw on that ECHO! Dimensions 2013 October 18 th Michael Pfeiffer, MD Disclosures No Financial Disclosures Goals Review unusual and unique echocardiographic images. Briefly present
You Won t Believe What I Saw on that ECHO! Dimensions 2013 October 18 th Michael Pfeiffer, MD Disclosures No Financial Disclosures Goals Review unusual and unique echocardiographic images. Briefly present
MULTIVALVULAR INFECTIVE ENDOCARDITIS CLINICAL FEATURES, ECHOCARDIOGRAPHIC DATA AND OUTCOMES
 Article Original MULTIVALVULAR INFECTIVE ENDOCARDITIS CLINICAL FEATURES, ECHOCARDIOGRAPHIC DATA AND OUTCOMES L. ABID, B. JERBI, I. TRABELSI, A. ZNAZEN*, S. KRICHÈNE, D. ABID, M. AKROUT, S. MALLEK, F. TRIKI,
Article Original MULTIVALVULAR INFECTIVE ENDOCARDITIS CLINICAL FEATURES, ECHOCARDIOGRAPHIC DATA AND OUTCOMES L. ABID, B. JERBI, I. TRABELSI, A. ZNAZEN*, S. KRICHÈNE, D. ABID, M. AKROUT, S. MALLEK, F. TRIKI,
Infective Endocarditis in Elderly Patients
 AGING AND INFECTIOUS DISEASES Thomas T. Yoshikawa, Section Editor INVITED ARTICLE Infective Endocarditis in Elderly Patients Vinod K. Dhawan Charles R. Drew University of Medicine and Science, Martin Luther
AGING AND INFECTIOUS DISEASES Thomas T. Yoshikawa, Section Editor INVITED ARTICLE Infective Endocarditis in Elderly Patients Vinod K. Dhawan Charles R. Drew University of Medicine and Science, Martin Luther
Bacteriemia and sepsis
 Bacteriemia and sepsis Case 1 An 80-year-old man is brought to the emergency room by his son, who noted that his father had become lethargic and has decreased urination over the past 4 days. The patient
Bacteriemia and sepsis Case 1 An 80-year-old man is brought to the emergency room by his son, who noted that his father had become lethargic and has decreased urination over the past 4 days. The patient
Adult Echocardiography Examination Content Outline
 Adult Echocardiography Examination Content Outline (Outline Summary) # Domain Subdomain Percentage 1 2 3 4 5 Anatomy and Physiology Pathology Clinical Care and Safety Measurement Techniques, Maneuvers,
Adult Echocardiography Examination Content Outline (Outline Summary) # Domain Subdomain Percentage 1 2 3 4 5 Anatomy and Physiology Pathology Clinical Care and Safety Measurement Techniques, Maneuvers,
INFECTIVE ENDOCARDITIS IN CHILDREN
 INFECTIVE ENDOCARDITIS IN CHILDREN Rohayati Taib RIPAS Hospital, Bundar Seri Begawan, Brunei Darussalam Infective Endocarditis (IE) is a microbial infection of the endocardium. It encompasses both bacterial
INFECTIVE ENDOCARDITIS IN CHILDREN Rohayati Taib RIPAS Hospital, Bundar Seri Begawan, Brunei Darussalam Infective Endocarditis (IE) is a microbial infection of the endocardium. It encompasses both bacterial
7. Echocardiography Appropriate Use Criteria (by Indication)
 Criteria for Echocardiography 1133 7. Echocardiography Criteria (by ) Table 1. TTE for General Evaluation of Cardiac Structure and Function Suspected Cardiac Etiology General With TTE 1. Symptoms or conditions
Criteria for Echocardiography 1133 7. Echocardiography Criteria (by ) Table 1. TTE for General Evaluation of Cardiac Structure and Function Suspected Cardiac Etiology General With TTE 1. Symptoms or conditions
The Diagnostic Challenge of Infective Endocarditis: Cutaneous Vasculitis Leading to the Diagnosis of Infective Endocarditis
 MEDICAL PRACTICE The Diagnostic Challenge of Infective Endocarditis: Cutaneous Vasculitis Leading to the Diagnosis of Infective Endocarditis Tracey Conti, MD, and Beth Barnet, MD Background: Signs and
MEDICAL PRACTICE The Diagnostic Challenge of Infective Endocarditis: Cutaneous Vasculitis Leading to the Diagnosis of Infective Endocarditis Tracey Conti, MD, and Beth Barnet, MD Background: Signs and
Surgical Indications of Infective Endocarditis in Children
 2016 Annual Spring Scientific Conference of the KSC April 15-16, 2016 Surgical Indications of Infective Endocarditis in Children Cheul Lee, MD Pediatric and Congenital Cardiac Surgery Seoul St. Mary s
2016 Annual Spring Scientific Conference of the KSC April 15-16, 2016 Surgical Indications of Infective Endocarditis in Children Cheul Lee, MD Pediatric and Congenital Cardiac Surgery Seoul St. Mary s
Getting the Point of Injection Safety
 Getting the Point of Injection Safety Barbara Montana, MD, MPH, FACP Medical Director Communicable Disease Service Outbreak of Enterococcus faecalis endocarditis associated with an oral surgery practice
Getting the Point of Injection Safety Barbara Montana, MD, MPH, FACP Medical Director Communicable Disease Service Outbreak of Enterococcus faecalis endocarditis associated with an oral surgery practice
Section 1: Initial Evaluation for Valvular Heart Disease Table 1: Initial Evaluation of an Asymptomatic Patient
 Section 1: Initial Evaluation for Valvular Heart Disease Table 1: Initial Evaluation of an Asymptomatic Patient Indication 1. Unexplained murmur or abnormal heart sounds 2. Reasonable suspicion of valvular
Section 1: Initial Evaluation for Valvular Heart Disease Table 1: Initial Evaluation of an Asymptomatic Patient Indication 1. Unexplained murmur or abnormal heart sounds 2. Reasonable suspicion of valvular
Complicated infective endocarditis: a case series
 Kim et al. Journal of Medical Case Reports (2017) 11:128 DOI 10.1186/s13256-017-1274-7 CASE REPORT Complicated infective endocarditis: a case series Joo Seop Kim 1, Min-Kyung Kang 1*, A. Jin Cho 2, Yu
Kim et al. Journal of Medical Case Reports (2017) 11:128 DOI 10.1186/s13256-017-1274-7 CASE REPORT Complicated infective endocarditis: a case series Joo Seop Kim 1, Min-Kyung Kang 1*, A. Jin Cho 2, Yu
AHA Scientific Statement
 AHA Scientific Statement Infective Endocarditis Diagnosis, Antimicrobial Therapy, and Management of Complications A Statement for Healthcare Professionals From the Committee on Rheumatic Fever, Endocarditis,
AHA Scientific Statement Infective Endocarditis Diagnosis, Antimicrobial Therapy, and Management of Complications A Statement for Healthcare Professionals From the Committee on Rheumatic Fever, Endocarditis,
Case : A 53-Year-Old Man with a Prosthetic Aortic Valve and Recent Onset of Fatigue, Dyspnea, Weight Loss, and Sweats
 case records of the massachusetts general hospital Founded by Richard C. Cabot Nancy Lee Harris, m.d., Editor Eric S. Rosenberg, m.d., Associate Editor Jo-Anne O. Shepard, m.d., Associate Editor Alice
case records of the massachusetts general hospital Founded by Richard C. Cabot Nancy Lee Harris, m.d., Editor Eric S. Rosenberg, m.d., Associate Editor Jo-Anne O. Shepard, m.d., Associate Editor Alice
Prognostic factors in infective endocarditis
 Boston University OpenBU Theses & Dissertations http://open.bu.edu Boston University Theses & Dissertations 2016 Prognostic factors in infective endocarditis Grzybinski, Sarah https://hdl.handle.net/2144/19176
Boston University OpenBU Theses & Dissertations http://open.bu.edu Boston University Theses & Dissertations 2016 Prognostic factors in infective endocarditis Grzybinski, Sarah https://hdl.handle.net/2144/19176
University of Florida Department of Surgery. CardioThoracic Surgery VA Learning Objectives
 University of Florida Department of Surgery CardioThoracic Surgery VA Learning Objectives This service performs coronary revascularization, valve replacement and lung cancer resections. There are 2 faculty
University of Florida Department of Surgery CardioThoracic Surgery VA Learning Objectives This service performs coronary revascularization, valve replacement and lung cancer resections. There are 2 faculty
ISF criteria (International sepsis forum consensus conference of infection in the ICU) Secondary peritonitis
 Appendix with supplementary material. This appendix was part of the submitted manuscript and has been peer reviewed. It is posted as supplied by the authors. Supplementary Tables Table S1. Definitions
Appendix with supplementary material. This appendix was part of the submitted manuscript and has been peer reviewed. It is posted as supplied by the authors. Supplementary Tables Table S1. Definitions
The Challenge of Managing Staphylococcus aureus Bacteremia
 The Challenge of Managing Staphylococcus aureus Bacteremia M A R G A R E T G R A Y B S P F C S H P C L I N I C A L P R A C T I C E M A N A G E R N O R T H / I D P H A R M A C I S T A L B E R T A H E A
The Challenge of Managing Staphylococcus aureus Bacteremia M A R G A R E T G R A Y B S P F C S H P C L I N I C A L P R A C T I C E M A N A G E R N O R T H / I D P H A R M A C I S T A L B E R T A H E A
HISTORY. Question: What category of heart disease is suggested by this history? CHIEF COMPLAINT: Heart murmur present since early infancy.
 HISTORY 18-year-old man. CHIEF COMPLAINT: Heart murmur present since early infancy. PRESENT ILLNESS: Although normal at birth, a heart murmur was heard at the six week check-up and has persisted since
HISTORY 18-year-old man. CHIEF COMPLAINT: Heart murmur present since early infancy. PRESENT ILLNESS: Although normal at birth, a heart murmur was heard at the six week check-up and has persisted since
A study of clinical and etiological profile of infective endocarditis and its correlation with echocardiography in patients of rheumatic heart disease
 International Journal of Advances in Medicine Sarkar A et al. Int J Adv Med. 2017 Oct;4(5):1323-1327 http://www.ijmedicine.com pissn 2349-3925 eissn 2349-3933 Original Research Article DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18203/2349-3933.ijam20174177
International Journal of Advances in Medicine Sarkar A et al. Int J Adv Med. 2017 Oct;4(5):1323-1327 http://www.ijmedicine.com pissn 2349-3925 eissn 2349-3933 Original Research Article DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18203/2349-3933.ijam20174177
FEATURE. Infective Endocarditis: Diagnosis and Treatment. Tony Main (Meds 2011) Faculty Reviewer: Dr. Linrui Guo
 FEATURE Infective Endocarditis: Diagnosis and Treatment Tony Main (Meds 2011) Faculty Reviewer: Dr. Linrui Guo Introduction When one thinks of infectious disease, endocarditis infection of the heart- does
FEATURE Infective Endocarditis: Diagnosis and Treatment Tony Main (Meds 2011) Faculty Reviewer: Dr. Linrui Guo Introduction When one thinks of infectious disease, endocarditis infection of the heart- does
We are IntechOpen, the world s leading publisher of Open Access books Built by scientists, for scientists. International authors and editors
 We are IntechOpen, the world s leading publisher of Open Access books Built by scientists, for scientists 4,100 116,000 120M Open access books available International authors and editors Downloads Our
We are IntechOpen, the world s leading publisher of Open Access books Built by scientists, for scientists 4,100 116,000 120M Open access books available International authors and editors Downloads Our
ASE 2011 Appropriate Use Criteria for Echocardiography
 ASE 2011 Appropriate Use Criteria for Echocardiography Table 1. TTE for General Evaluation of Cardiac Structure and Function 1 2 Suspected Cardiac Etiology General With TTE Symptoms or conditions potentially
ASE 2011 Appropriate Use Criteria for Echocardiography Table 1. TTE for General Evaluation of Cardiac Structure and Function 1 2 Suspected Cardiac Etiology General With TTE Symptoms or conditions potentially
TSDA Boot Camp September 13-16, Introduction to Aortic Valve Surgery. George L. Hicks, Jr., MD
 TSDA Boot Camp September 13-16, 2018 Introduction to Aortic Valve Surgery George L. Hicks, Jr., MD Aortic Valve Pathology and Treatment Valvular Aortic Stenosis in Adults Average Course (Post mortem data)
TSDA Boot Camp September 13-16, 2018 Introduction to Aortic Valve Surgery George L. Hicks, Jr., MD Aortic Valve Pathology and Treatment Valvular Aortic Stenosis in Adults Average Course (Post mortem data)
Infective endocarditis causing mitral valve stenosis a rare but deadly complication: a case report
 Hart and Shroff Journal of Medical Case Reports (2017) 11:44 DOI 10.1186/s13256-017-1197-3 CASE REPORT Open Access Infective endocarditis causing mitral valve stenosis a rare but deadly complication: a
Hart and Shroff Journal of Medical Case Reports (2017) 11:44 DOI 10.1186/s13256-017-1197-3 CASE REPORT Open Access Infective endocarditis causing mitral valve stenosis a rare but deadly complication: a
VALVULAR HEART DISEASE
 VALVULAR HEART DISEASE Stenosis: failure of a valve to open completely, obstructing forward flow. - almost always due to a chronic process (e.g., calcification or valve scarring). Insufficiency : failure
VALVULAR HEART DISEASE Stenosis: failure of a valve to open completely, obstructing forward flow. - almost always due to a chronic process (e.g., calcification or valve scarring). Insufficiency : failure
