the part between the neck and the abdomen Chest X-ray
|
|
|
- Isaac Lang
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 The Two Fridas 1939 by Frida Kahlo Kaan Yücel M.D., Ph.D
2 the part between the neck and the abdomen Chest X-ray
3 1.1. REGIONS/T ERMS Thoracic cavity cavity between neck and abdomen protected by the thoracic wall. Thoracic wall bounds the thoracic cavity. formed by the skin, bones, fasciae, and muscles. Thoracic cage bony portion of the thoracic wall thoracic skeleton
4 1.2. SURFACES OF THE THORAX Posterior surface 12 thoracic vertebræ & posterior parts of the ribs Anterior surface sternum & costal cartilages Lateral surfaces ribs, separated by the intercostal spaces STERNUM & COSTAL CARTILAGES anteriorly 12 THORACIC VERTEBRAE & POST. RIBS posteriorly RIBS & INTERCOSTAL SPACES laterally
5 1.3. BOUNDARIES OF THE THORAX Superior Jugular notch Sternoclavicular joint Superior border of clavicle Acromion Spinous processes of C7 Inferior Xiphoid process Costal arch 12th and 11th ribs Vertebra T12
6 1.4. CONTENTS OF THE THORAX Organs of the cardiovascular, respiratory, digestive, reproductive, immune, and nervous systems
7 thoracic cage (skeleton) muscles between the ribs skin subcutaneous tissue muscles, and fascia covering its anterolateral aspect. The mammary glands of the breasts lie within the subcutaneous tissue of the thoracic wall.
8 2.1. FUNCTIONS OF THE THORACIC WALL 1) Protects vital thoracic and abdominal organs 2) Resists the negative (sub-atmospheric) internal pressures generated by the elastic recoil of the lungs and inspiratory movements. 3) Provides attachment for and support the weight of the upper limbs. 4) Provides the origins of many of the muscles that move and maintain the position of the upper limbs relative to the trunk. 5) Provides attachments for muscles of the abdomen, neck, back, and respiration.
9 3. SKELETON OF THE THORACIC WALL 1) 12 pairs of ribs and associated costal cartilages 2) 12 thoracic vertebrae and the intervertebral (IV) discs interposed between them 3) Sternum
10 4. THORACIC APERTURES Thoracic inlet Thoracic outlet
11 4.1. Superior thoracic aperture doorway between the thoracic cavity and the neck and upper limb bounded: Posteriorly vertebra T1 Laterally 1st pair of ribs and their costal cartilages Anteriorly superior border of the manubrium Trachea Esophagus nerves, and vessels that supply and drain the head, neck, and upper limbs.
12 4.2. Inferior thoracic aperture By closing the inferior thoracic aperture, the diaphragm separates the thoracic and abdominal cavities almost completely. bounded: Posteriorly 12th thoracic vertebra Posterolaterally 11th and 12th pairs of ribs Anterolaterally joined costal cartilages of ribs 7-10 costal margins Anteriorly xiphisternal joint
13 5. MOVEMENTS OF THE THORACIC WALL One of the principal functions of the thoracic wall and the diaphragm is to alter the volume of the thorax and thereby move air in and out of the lungs. During breathing, the dimensions of the thorax change in vertical, lateral, and A-P directions. Diaphragm contracts Depression Diaphragm relaxes Elevation (during passive expiration) Elevation &depression of the ribs
14 DERMATOMES Skin area supplied by a segment of the spinal cord Through its posterior ramus and the lateral and anterior cutaneous branches of its anterior ramus, most thoracic spinal nerves (T2-T12) supply a strip-like dermatome of the trunk extending from the posterior median line to the anterior median line. T2- Sternal angle T4- Nipple T6- Xiphoid process T8- Costal arch T10-Umbliculus T12-Midpoint between umbilicus and symphysis pubis
15 2. BREASTS Reproduction, back pain Aesthetics, and breast cancer Mammary glands & associated skin -connective tissues. modified sweat glands in the superficial fascia anterior to the pectoral muscles and the anterior thoracic wall.
16 2. BREASTS Mammary glands: Series of ducts and associated secretory lobules. Form 15 to 20 lactiferous ducts open nipple. Nipple is surrounded by a circular pigmented area of skin areola (L. small area).
17 FEMALE BREASTS NON-LACTING WOMEN PREDOMINANT COMPONENT: FAT LACTING WOMEN- PREDOMINANT COMPONENT: GLANDULAR TISSUE The breast rests on a bed extends transversely from lateral border of the sternum mid-axillary line vertically from the 2nd through 6th ribs
18 75% (lateral breast quadrants) Axillary lymph nodes Most of the remaining (medial breast quadrants) parasternal lymph nodes or to the opposite breast Lymph from inferior quadrants may pass deeply to abdominal lymph nodes.
19
20 Trapezoidal in A-P dimensions Tipped-over pyramid in 3-D crucial organ of the human body 20
21 Right heart (Suction) poorly- oxygenated(venous) blood from the body superior vena cava & inferior vena cava right atrium right ventricle pulmonary arteries lungs Left heart (Pumping) well- oxygenated (arterial) blood from the lungs pulmonary veins left atrium left ventricle aorta the body 21
22 right and left atria & right and left ventricles Atrium plural atria Receiving chambers Ventricles Discharging chambers cardiac cycle 1. Ventricular filling (diastole) 2. Ventricular emptying (systole) Blood pressure mm/hg 22
23 The fibrous skeleton of the heart Keeps the orifices of the AV & semilunar valves patent prevents them from being overly distended by an increased volume of blood. Provides attachments for the valves & myocardium. Forms an electrical «insulator» separating impulses of the atria & ventricles they contract independently surrounding and providing passage for the initial part of the AV bundle 23
24 coronary sulcus (atrioventricular groove) between atrium & ventricles anterior & posterior interventricular (IV) sulci (grooves) between right and left ventricles 24
25 apex located inferiorly & base located superiorly Apex projects forward, downward and to the left Base faces in a posterior direction 25
26 Anterior (sternocostal) surface o mostly of right ventricle o some of the right atrium on the right o some of the left ventricle on the left Diaphragmatic (inferior) surface o formed mainly by the left ventricle o partly by the right ventricle o related to central tendon of diaphragm. Right pulmonary surface o formed by the right atrium. Left pulmonary surface o left ventricle & a portion of left atrium. 26
27 RIGHT ATRIUM forms the right border of the heart Receives venous blood from the SVC, IVC, and coronary sinus. Through the right atrioventricular orifice, discharges the poorly oxygenated blood it has received into the right ventricle. 27
28 RIGHT VENTRICLE forms largest part of the anterior surface of the heart a small part of the diaphragmatic surface almost the entire inferior border of the heart. 28
29 interventricular septum (IVS) obliquely placed partition between the right and left ventricles, forming part of the walls of each muscular and membranous parts Bulges into the cavity of the right ventricle. Superiorly and posteriorly, a thin membrane, forms the much smaller membranous part of the IVS. 29
30 LEFT ATRIUM right and left pulmonary veins enter here. Tubular, muscular left auricle, Its wall trabeculated with pectinate muscles. A semilunar depression in the interatrial septum Floor of the oval fossa surrounding ridge Valve of the oval fossa forms most of the base of the heart 30
31 LEFT VENTRICLE forms the apex of the heart, left (pulmonary) surface & border, most of the diaphragmatic surface. Compared to the right ventricle Walls 2-3 times thicker Trabeculae carneae finer and more numerous Cavity longer Anterior & posterior papillary muscles larger 31
32 aortic valve semilunar valve between the left ventricle & ascending aorta obliquely placed. 32
33 mitral valve double-leaflet mitral valve Guards the left AV orifice. Has two cusps, anterior and posterior. 33
34 6. SEMILUNAR VALVES Semilunar cusps of the pulmonary valve anterior-right-left Seminular cusps of the aortic valve posterior-right-left concave when viewed superiorly no tendinous cords to support 34
35 VASCULATURE OF THE HEART coronary arteries & cardiac veins embedded in fat course across the surface of the heart just deep to the epicardium. 35
36 supply the myocardium and epicardium first branches of the aorta Anastomoses between the branches of the coronary arteries exist, which enables the development of the collateral circulation. 36
37 STIMULATING, CONDUCTING, & REGULATING SYSTEMS OF HEART 1. sinuatrial (SA) node initiates the heartbeat & coordinates contractions of the four heart chambers 2.atrioventricular (AV) node 3.bundles highly specialized conducting fibers for conducting impulses rapidly to different areas of the heart o Propagation of the impluse o Simultaneous contraction of the cardiac striated muscle cells 37
38 pacemaker of the of the SVC & right atrium near to the superior end of the sulcus terminalis 38
39 pacemaker of the heart stimulated by sympathetic division of the autonomic nervous system to accelerate the heart rate inhibited by parasympathetic division to return to or approach its basal rate. 39
40 a smaller collection of nodal tissue than the SA node in the posteroinferior region of the interatrial septum near the opening of the coronary sinus 40
41 JOURNEY OF THE SIGNAL SA node Passed through the walls of the right atrium Propageted by the cardiac muscle Signal passed from SA node to AV node Distributed to the ventricles through the AV bundle 41
42 AV bundle the only bridge between the atrial and ventricular myocardium passes from the AV node through the fibrous skeleton of the heart and along the membranous part of the junction of membranous & muscular parts of the IVS divides into : right bundle & left bundle. 42
43 right and left bundles proceed on each side of the muscular IVS deep to the endocardium then ramify into subendocardial branches (Purkinje fibers) extend into the walls of the respective ventricles. 43
44 autonomic nervous system, cardiac plexus Cardiac plexus posterior to the ascending aorta and bifurcation of the pulmonary trunk 44
45 autonomic nervous system, cardiac plexus Parasympathetic supply presynaptic fibers of the vagus nerves Slows the heart rate Reduces the force of the contraction Constricts the coronary arteries saving energy 45
46 sympathetic supply presynaptic fibers cell bodies in the intermediolateral cell columns (IMLs) of the superior 5 or 6 thoracic segments postsynaptic sympathetic fibers cell bodies in the cervical and superior thoracic paravertebral ganglia of the sympathetic trunks. causes increased heart rate increased impulse conduction, increased force of contraction, increased blood flow through the coronary vessels increased activity. 46
47 What happens? 9. SEPTAL DEFECTS Atrial Septal Defects (ASD) congenital anomaly of the interatrial septum a hole between the two atria Oxygenated blood from the lungs Left atrium Right atrium More blood in the right heart Results in enlargement of right atrium & ventricle dilation of the pulmonary trunk 47
48 Ventricular Septal Defects (VSD) rank first on all lists of cardiac defects membranous part of the IVS common site of VSDs What happens? Oxygenated blood from the ventricles Left ventricle Right ventricle Results in in pulmonary blood flow severe pulmonary disease (hypertension) cardiac failure 48
49 10. VALVULAR HEART DISEASES Disturb pumping efficiency of the heart. Stenosis (narrowing) or insufficiency Both result in an increased workload for the heart. Valvuloplasty repairing the heart valves 49
50 Scarring and shortening of the cusps results in insufficiency Restricts the outflow of the left ventricle Leads to the hypertrophy of the myocardium During ventricular systole, blood regurgitates back to the left atrium A hurt murmur will be heard. 50
51 Narrowing of the mitral orifice. Restricts the outflow of the left atrium. A murmur will be heard during atrial contraction. 51
52 Narrowing of the pulmonary valve due to the fused cusps. Restricts the outflow of the right ventricle. Leads to the hypertrophy of the myocardium. 52
53 Incomplete closure of the cusps due to thickening of their free margins due to a disease. During diastole, blood regurgitates back to the right ventricle from the pulmonary trunk. Heart murmur could be heard. 53
54 most frequent valve abnormality Blood is unable to flow freely from left ventricle to aorta. A result of degenerative calcification, fusion of the aortic cups as a result. Causes extra work for the heart, resulting in left ventricular hypertrophy. 54
55 During diastole blood regurgitates from aorta back to the left ventricle. A hurt murmur will be heard during diastole. 55
56 a pathologic sound could be heard by stethoscope. produced due to the turbulence caused by the blood passing from a narrow opening into a larger vessel or chamber. 56
57 tricuspid valve behind the right half of the sternum opposite 4th intercostal space mitral valve behind the left half of the sternum opposite 4th costal cartilage pulmonary valve behind the medial end of the 3rd left costal cartilage and adjoining part of the sternum aortic valve behind the left half of the sternum opposite 3rd intercostal space. 57
58 S1 produced by contraction of the ventricles closure of the tricuspid & mitral valves (AV valves) S2 produced by the sharp closure of the aortic & pulmonary valves hear sounds produced at each valve with the minimum of distraction or interference 58
59 tricuspid valve right half of lower end of the body of the sternum mitral valve apex beat fifth left intercostal space, 9 cm from the midline pulmonary valve medial end of the second left intercostal space aortic valve medial end of the second right intercostal space 59
60 PERICARDIUM fibroserous membrane, covers the heart & beginning of its great vessels a closed sac with two layers fibrous pericardium serous pericardium parietal layer visceral layer heart & great vessels. 60
61 fibrous pericardium continuous superiorly w/ tunica adventitia of the great vessels & w/pretracheal layer of deep cervical fascia Continuous inferiorly w/ central tendon of the diaphragm Attached anteriorly to the sternum by sternopericardial ligaments Site of continuity pericardiacophrenic ligament Inner surface lined by parietal layer of the serous pericardium Protects the heart against sudden overfilling. 61
62 pericardial cavity potential space between opposing layers of the parietal & visceral layers of serous pericardium contains a thin film of fluid : pericardial fluid enables the heart to move and beat in a frictionless environment. 62
63 GREAT VESSELS formed by the union of internal jugular & subclavian veins posterior to the sternoclavicular (SC) joints. brachiocephalic veins unite to form the inferior border of the 1st right costal cartilage shunt blood from the head, neck, & upper limbs right atrium. 63
64 Returns blood from all structures superior to the diaphragm except the lungs & heart. Passes inferiorly and ends by entering right atrium of the heart. 64
65 begins at the aortic orifice. only branches coronary arteries, arising from the aortic sinuses. 65
66 curved continuation of the ascending aorta begins posterior to the 2nd right sternocostal (SC) joint at the level of the sternal angle. ligamentum arteriosum remnant of the fetal ductus arteriosus root of the left pulmonary artery inferior surface of the arch of the aorta The usual branches of the arch 1) brachiocephalic trunk 2) left common carotid artery 3) left subclavian artery. 66
67 first and largest branch of the arch of the aorta arises posterior to the manubrium. ascends superolaterally divides into right common carotid & right subclavian arteries. 67
68 second branch of the arch of the aorta arises o posterior to the manubrium, o slightly posterior and to the left of the brachiocephalic trunk. 68
69 third branch of the arch of the aorta arises from the posterior part of the arch posterior to left common carotid artery. ascends lateral to trachea & left common carotid artery. Leaves the thorax and enters the root of the neck. 69
70 responsible for detecting changes in blood chemistry, primarily oxygen content monitor changes in blood pressure 70
71 Abdominal aorta 71
72 72
73 73
74 74
75 75
76 76
77 77
78 78
79 79
80 80
81 81
82 82
83 83
84 84
human anatomy 2016 lecture thirteen Dr meethak ali ahmed neurosurgeon
 Heart The heart is a hollow muscular organ that is somewhat pyramid shaped and lies within the pericardium in the mediastinum. It is connected at its base to the great blood vessels but otherwise lies
Heart The heart is a hollow muscular organ that is somewhat pyramid shaped and lies within the pericardium in the mediastinum. It is connected at its base to the great blood vessels but otherwise lies
Chapter 20 (1) The Heart
 Chapter 20 (1) The Heart Learning Objectives Describe the location and structure of the heart Describe the path of a drop of blood from the superior vena cava or inferior vena cava through the heart out
Chapter 20 (1) The Heart Learning Objectives Describe the location and structure of the heart Describe the path of a drop of blood from the superior vena cava or inferior vena cava through the heart out
Human Anatomy, First Edition
 Human Anatomy, First Edition McKinley & O'Loughlin Chapter 22 : Heart 1 Functions of the Heart Center of the cardiovascular system, the heart. Connects to blood vessels that transport blood between the
Human Anatomy, First Edition McKinley & O'Loughlin Chapter 22 : Heart 1 Functions of the Heart Center of the cardiovascular system, the heart. Connects to blood vessels that transport blood between the
2. right heart = pulmonary pump takes blood to lungs to pick up oxygen and get rid of carbon dioxide
 A. location in thorax, in inferior mediastinum posterior to sternum medial to lungs superior to diaphragm anterior to vertebrae orientation - oblique apex points down and to the left 2/3 of mass on left
A. location in thorax, in inferior mediastinum posterior to sternum medial to lungs superior to diaphragm anterior to vertebrae orientation - oblique apex points down and to the left 2/3 of mass on left
Large veins of the thorax Brachiocephalic veins
 Large veins of the thorax Brachiocephalic veins Right brachiocephalic vein: formed at the root of the neck by the union of the right subclavian & the right internal jugular veins. Left brachiocephalic
Large veins of the thorax Brachiocephalic veins Right brachiocephalic vein: formed at the root of the neck by the union of the right subclavian & the right internal jugular veins. Left brachiocephalic
The Heart. The Heart A muscular double pump. The Pulmonary and Systemic Circuits
 C H A P T E R 19 The Heart The Heart A muscular double pump circuit takes blood to and from the lungs Systemic circuit vessels transport blood to and from body tissues Atria receive blood from the pulmonary
C H A P T E R 19 The Heart The Heart A muscular double pump circuit takes blood to and from the lungs Systemic circuit vessels transport blood to and from body tissues Atria receive blood from the pulmonary
THE CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM. Part 1
 THE CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM Part 1 CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM Blood Heart Blood vessels What is the function of this system? What other systems does it affect? CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM Functions Transport gases,
THE CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM Part 1 CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM Blood Heart Blood vessels What is the function of this system? What other systems does it affect? CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM Functions Transport gases,
Mediastinum and pericardium
 Mediastinum and pericardium Prof. Abdulameer Al-Nuaimi E-mail: a.al-nuaimi@sheffield.ac.uk E. mail: abdulameerh@yahoo.com The mediastinum: is the central compartment of the thoracic cavity surrounded by
Mediastinum and pericardium Prof. Abdulameer Al-Nuaimi E-mail: a.al-nuaimi@sheffield.ac.uk E. mail: abdulameerh@yahoo.com The mediastinum: is the central compartment of the thoracic cavity surrounded by
Identify the lines used in anatomical surface descriptions of the thorax. median line mid-axillary line mid-clavicular line
 L 14 A B O R A T O R Y Thorax THORACIC WALL Identify the lines used in anatomical surface descriptions of the thorax. median line mid-axillary line mid-clavicular line Identify the surface landmarks of
L 14 A B O R A T O R Y Thorax THORACIC WALL Identify the lines used in anatomical surface descriptions of the thorax. median line mid-axillary line mid-clavicular line Identify the surface landmarks of
Dr. Weyrich G07: Superior and Posterior Mediastina. Reading: 1. Gray s Anatomy for Students, chapter 3
 Dr. Weyrich G07: Superior and Posterior Mediastina Reading: 1. Gray s Anatomy for Students, chapter 3 Objectives: 1. Subdivisions of mediastinum 2. Structures in Superior mediastinum 3. Structures in Posterior
Dr. Weyrich G07: Superior and Posterior Mediastina Reading: 1. Gray s Anatomy for Students, chapter 3 Objectives: 1. Subdivisions of mediastinum 2. Structures in Superior mediastinum 3. Structures in Posterior
THE HEART. A. The Pericardium - a double sac of serous membrane surrounding the heart
 THE HEART I. Size and Location: A. Fist-size weighing less than a pound (250 to 350 grams). B. Located in the mediastinum between the 2 nd rib and the 5 th intercostal space. 1. Tipped to the left, resting
THE HEART I. Size and Location: A. Fist-size weighing less than a pound (250 to 350 grams). B. Located in the mediastinum between the 2 nd rib and the 5 th intercostal space. 1. Tipped to the left, resting
LECTURE 5. Anatomy of the heart
 LECTURE 5. Anatomy of the heart Main components of the CVS: Heart Blood circulatory system arterial compartment haemomicrocirculatory (=microvascular) compartment venous compartment Lymphatic circulatory
LECTURE 5. Anatomy of the heart Main components of the CVS: Heart Blood circulatory system arterial compartment haemomicrocirculatory (=microvascular) compartment venous compartment Lymphatic circulatory
CV Anatomy Quiz. Dr Ella Kim Dr Pip Green
 CV Anatomy Quiz Dr Ella Kim Dr Pip Green Q1 The location of the heart is correctly described as A) lateral to the lungs. B) medial to the sternum. C) superior to the diaphragm. D) posterior to the spinal
CV Anatomy Quiz Dr Ella Kim Dr Pip Green Q1 The location of the heart is correctly described as A) lateral to the lungs. B) medial to the sternum. C) superior to the diaphragm. D) posterior to the spinal
Chapter 14. The Cardiovascular System
 Chapter 14 The Cardiovascular System Introduction Cardiovascular system - heart, blood and blood vessels Cardiac muscle makes up bulk of heart provides force to pump blood Function - transports blood 2
Chapter 14 The Cardiovascular System Introduction Cardiovascular system - heart, blood and blood vessels Cardiac muscle makes up bulk of heart provides force to pump blood Function - transports blood 2
Chapter 5: Other mediastinal structures. The Large Arteries. The Aorta. Ascending aorta
 Chapter 5: Other mediastinal structures The Large Arteries The Aorta The aorta is the main arterial trunk of the systemic circulation and in the healthy state its wall contain a large amount of yellow
Chapter 5: Other mediastinal structures The Large Arteries The Aorta The aorta is the main arterial trunk of the systemic circulation and in the healthy state its wall contain a large amount of yellow
DESCRIPTION: This is the part of the trunk, which is located between the root of the neck and the superior border of the abdominal region.
 1 THE THORACIC REGION DESCRIPTION: This is the part of the trunk, which is located between the root of the neck and the superior border of the abdominal region. SHAPE : T It has the shape of a truncated
1 THE THORACIC REGION DESCRIPTION: This is the part of the trunk, which is located between the root of the neck and the superior border of the abdominal region. SHAPE : T It has the shape of a truncated
Ch 19: Cardiovascular System - The Heart -
 Ch 19: Cardiovascular System - The Heart - Give a detailed description of the superficial and internal anatomy of the heart, including the pericardium, the myocardium, and the cardiac muscle. Trace the
Ch 19: Cardiovascular System - The Heart - Give a detailed description of the superficial and internal anatomy of the heart, including the pericardium, the myocardium, and the cardiac muscle. Trace the
Chapter 4: The thoracic cavity and heart. The Heart
 Chapter 4: The thoracic cavity and heart The thoracic cavity is divided into right and left pleural cavities by a central partition, the mediastinum. The mediastinum is bounded behind by the vertebral
Chapter 4: The thoracic cavity and heart The thoracic cavity is divided into right and left pleural cavities by a central partition, the mediastinum. The mediastinum is bounded behind by the vertebral
the Cardiovascular System I
 the Cardiovascular System I By: Dr. Nabil A Khouri MD, MsC, Ph.D MEDIASTINUM 1. Superior Mediastinum 2. inferior Mediastinum Anterior mediastinum. Middle mediastinum. Posterior mediastinum Anatomy of
the Cardiovascular System I By: Dr. Nabil A Khouri MD, MsC, Ph.D MEDIASTINUM 1. Superior Mediastinum 2. inferior Mediastinum Anterior mediastinum. Middle mediastinum. Posterior mediastinum Anatomy of
THE THORACIC WALL. Boundaries Posteriorly by the thoracic part of the vertebral column. Anteriorly by the sternum and costal cartilages
 THE THORACIC WALL Boundaries Posteriorly by the thoracic part of the vertebral column Anteriorly by the sternum and costal cartilages Laterally by the ribs and intercostal spaces Superiorly by the suprapleural
THE THORACIC WALL Boundaries Posteriorly by the thoracic part of the vertebral column Anteriorly by the sternum and costal cartilages Laterally by the ribs and intercostal spaces Superiorly by the suprapleural
Surface anatomy of Cardiovascular system
 Surface anatomy of Cardiovascular system Prof. Abdulameer Al-Nuaimi E-mail: a.al-nuaimi@sheffield.ac.uk E. mail: abdulameerh@yahoo.com The lines cover the front, side, and back of the thorax Midsternal
Surface anatomy of Cardiovascular system Prof. Abdulameer Al-Nuaimi E-mail: a.al-nuaimi@sheffield.ac.uk E. mail: abdulameerh@yahoo.com The lines cover the front, side, and back of the thorax Midsternal
Anatomy of the Heart. Figure 20 2c
 Anatomy of the Heart Figure 20 2c Pericardium & Myocardium Remember, the heart sits in it s own cavity, known as the mediastinum. The heart is surrounded by the Pericardium, a double lining of the pericardial
Anatomy of the Heart Figure 20 2c Pericardium & Myocardium Remember, the heart sits in it s own cavity, known as the mediastinum. The heart is surrounded by the Pericardium, a double lining of the pericardial
HUMAN HEART. Learn the following structures on the heart models.
 HUMAN HEART Learn the following structures on the heart models. The human heart has four chambers that consist of the right atrium, left atrium, right ventricle, and left ventricle. The atria are smaller
HUMAN HEART Learn the following structures on the heart models. The human heart has four chambers that consist of the right atrium, left atrium, right ventricle, and left ventricle. The atria are smaller
Anatomy of the Thorax
 Anatomy of the Thorax A) THE THORACIC WALL Boundaries Posteriorly by the thoracic part of the vertebral column Anteriorly by the sternum and costal cartilages Laterally by the ribs and intercostal spaces
Anatomy of the Thorax A) THE THORACIC WALL Boundaries Posteriorly by the thoracic part of the vertebral column Anteriorly by the sternum and costal cartilages Laterally by the ribs and intercostal spaces
THE HEART OBJECTIVES: LOCATION OF THE HEART IN THE THORACIC CAVITY CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM
 BIOLOGY II CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM ACTIVITY #3 NAME DATE HOUR THE HEART OBJECTIVES: Describe the anatomy of the heart and identify and give the functions of all parts. (pp. 356 363) Trace the flow of blood
BIOLOGY II CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM ACTIVITY #3 NAME DATE HOUR THE HEART OBJECTIVES: Describe the anatomy of the heart and identify and give the functions of all parts. (pp. 356 363) Trace the flow of blood
Salvador Dali - Anthropomorphic Chest of Drawers, 1936
 Salvador Dali - Anthropomorphic Chest of Drawers, 1936 Kaan Yücel M.D., Ph.D. 05.March.2014 the part between the neck and the abdomen Chest X-ray 1.1. REGIONS/T ERMS Thoracic cavity cavity between neck
Salvador Dali - Anthropomorphic Chest of Drawers, 1936 Kaan Yücel M.D., Ph.D. 05.March.2014 the part between the neck and the abdomen Chest X-ray 1.1. REGIONS/T ERMS Thoracic cavity cavity between neck
Lab Activity 23. Cardiac Anatomy. Portland Community College BI 232
 Lab Activity 23 Cardiac Anatomy Portland Community College BI 232 Cardiac Muscle Histology Branching cells Intercalated disc: contains many gap junctions connecting the adjacent cell cytoplasm, creates
Lab Activity 23 Cardiac Anatomy Portland Community College BI 232 Cardiac Muscle Histology Branching cells Intercalated disc: contains many gap junctions connecting the adjacent cell cytoplasm, creates
Middle mediastinum---- heart & pericardium. Dep. of Human Anatomy Zhou Hongying
 Middle mediastinum---- heart & pericardium Dep. of Human Anatomy Zhou Hongying eaglezhyxzy@163.com Subdivisions of the mediastinum Contents of Middle mediastinum Heart Pericardium: a serous sac enclosing
Middle mediastinum---- heart & pericardium Dep. of Human Anatomy Zhou Hongying eaglezhyxzy@163.com Subdivisions of the mediastinum Contents of Middle mediastinum Heart Pericardium: a serous sac enclosing
Heart Anatomy. 7/5/02 Stephen G Davenport 1
 Heart Anatomy Copyright 1999, Stephen G. Davenport, No part of this publication may be reproduced, stored in a retrieval system, or transmitted, in any form without prior written permission. 7/5/02 Stephen
Heart Anatomy Copyright 1999, Stephen G. Davenport, No part of this publication may be reproduced, stored in a retrieval system, or transmitted, in any form without prior written permission. 7/5/02 Stephen
The Thoracic wall including the diaphragm. Prof Oluwadiya KS
 The Thoracic wall including the diaphragm Prof Oluwadiya KS www.oluwadiya.com Components of the thoracic wall Skin Superficial fascia Chest wall muscles (see upper limb slides) Skeletal framework Intercostal
The Thoracic wall including the diaphragm Prof Oluwadiya KS www.oluwadiya.com Components of the thoracic wall Skin Superficial fascia Chest wall muscles (see upper limb slides) Skeletal framework Intercostal
Heart & Pericardium. December, 2015
 Heart & Pericardium December, 2015 2 Pericardium Definition Fibro-serous sac that encloses the heart and the roots of great vessels Function Restrict excessive movements of the heart as a whole Serve as
Heart & Pericardium December, 2015 2 Pericardium Definition Fibro-serous sac that encloses the heart and the roots of great vessels Function Restrict excessive movements of the heart as a whole Serve as
Part 1. Copyright 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. Figure Copyright 2011 Pearson Education, Inc.
 PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Leslie Hendon University of Alabama, Birmingham C H A P T E R The Heart 19 Part 1 The Heart A muscular double pump circuit vessels transport blood to and from the
PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Leslie Hendon University of Alabama, Birmingham C H A P T E R The Heart 19 Part 1 The Heart A muscular double pump circuit vessels transport blood to and from the
STERNUM. Lies in the midline of the anterior chest wall It is a flat bone Divides into three parts:
 STERNUM Lies in the midline of the anterior chest wall It is a flat bone Divides into three parts: 1-Manubrium sterni 2-Body of the sternum 3- Xiphoid process The body of the sternum articulates above
STERNUM Lies in the midline of the anterior chest wall It is a flat bone Divides into three parts: 1-Manubrium sterni 2-Body of the sternum 3- Xiphoid process The body of the sternum articulates above
Chapter 18 - Heart. I. Heart Anatomy: size of your fist; located in mediastinum (medial cavity)
 Chapter 18 - Heart I. Heart Anatomy: size of your fist; located in mediastinum (medial cavity) A. Coverings: heart enclosed in double walled sac called the pericardium 1. Fibrous pericardium: dense connective
Chapter 18 - Heart I. Heart Anatomy: size of your fist; located in mediastinum (medial cavity) A. Coverings: heart enclosed in double walled sac called the pericardium 1. Fibrous pericardium: dense connective
10/14/2018 Dr. Shatarat
 2018 Objectives To discuss mediastina and its boundaries To discuss and explain the contents of the superior mediastinum To describe the great veins of the superior mediastinum To describe the Arch of
2018 Objectives To discuss mediastina and its boundaries To discuss and explain the contents of the superior mediastinum To describe the great veins of the superior mediastinum To describe the Arch of
ANATDMY. lecture # : Date : Lecturer : Maher Hadidi
 ANATDMY 27 lecture # : Date : Lecturer : Maher Hadidi Pericardium A double-walled fibroserous conical-shaped sac, within middle mediastinum. Enclose the heart and roots of its large vessels. Vagus nerves
ANATDMY 27 lecture # : Date : Lecturer : Maher Hadidi Pericardium A double-walled fibroserous conical-shaped sac, within middle mediastinum. Enclose the heart and roots of its large vessels. Vagus nerves
Anatomy notes-thorax.
 Anatomy notes-thorax. Thorax: the part extending from the root of the neck to the abdomen. Parts of the thorax: - Thoracic cage (bones). - Thoracic wall. - Thoracic cavity. ** The thoracic cavity is covered
Anatomy notes-thorax. Thorax: the part extending from the root of the neck to the abdomen. Parts of the thorax: - Thoracic cage (bones). - Thoracic wall. - Thoracic cavity. ** The thoracic cavity is covered
The Cardiovascular System. Chapter 15. Cardiovascular System FYI. Cardiology Closed systemof the heart & blood vessels. Functions
 Chapter 15 Cardiovascular System FYI The heart pumps 7,000 liters (4000 gallons) of blood through the body each day The heart contracts 2.5 billion times in an avg. lifetime The heart & all blood vessels
Chapter 15 Cardiovascular System FYI The heart pumps 7,000 liters (4000 gallons) of blood through the body each day The heart contracts 2.5 billion times in an avg. lifetime The heart & all blood vessels
Diaphragm and intercostal muscles. Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Associate Professor of Anatomy and Histology
 Diaphragm and intercostal muscles Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Associate Professor of Anatomy and Histology Skeletal System Adult Human contains 206 Bones 2 parts: Axial skeleton (axis): Skull, Vertebral column,
Diaphragm and intercostal muscles Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Associate Professor of Anatomy and Histology Skeletal System Adult Human contains 206 Bones 2 parts: Axial skeleton (axis): Skull, Vertebral column,
Cardiovascular Anatomy Dr. Gary Mumaugh
 Cardiovascular Anatomy Dr. Gary Mumaugh Location of Heart Approximately the size of your fist Location o Superior surface of diaphragm o Left of the midline in mediastinum o Anterior to the vertebral column,
Cardiovascular Anatomy Dr. Gary Mumaugh Location of Heart Approximately the size of your fist Location o Superior surface of diaphragm o Left of the midline in mediastinum o Anterior to the vertebral column,
This lab activity is aligned with Visible Body s A&P app. Learn more at visiblebody.com/professors
 1 This lab activity is aligned with Visible Body s A&P app. Learn more at visiblebody.com/professors 2 PRE-LAB EXERCISES: A. Watch the video 29.1 Heart Overview and make the following observations: 1.
1 This lab activity is aligned with Visible Body s A&P app. Learn more at visiblebody.com/professors 2 PRE-LAB EXERCISES: A. Watch the video 29.1 Heart Overview and make the following observations: 1.
Welcome to the Structure & Development Dissector. Section I
 Welcome to the Structure & Development Dissector The vast majority of questions will be drawn from structures present in the checklist; however, we reserve the right to use a structure or two that is not
Welcome to the Structure & Development Dissector The vast majority of questions will be drawn from structures present in the checklist; however, we reserve the right to use a structure or two that is not
Anatomy of the Heart
 Biology 212: Anatomy and Physiology II Anatomy of the Heart References: Saladin, KS: Anatomy and Physiology, The Unity of Form and Function 8 th (2018). Required reading before beginning this lab: Chapter
Biology 212: Anatomy and Physiology II Anatomy of the Heart References: Saladin, KS: Anatomy and Physiology, The Unity of Form and Function 8 th (2018). Required reading before beginning this lab: Chapter
The Heart & Pericardium Dr. Rakesh Kumar Verma Assistant Professor Department of Anatomy KGMU UP Lucknow
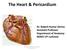 The Heart & Pericardium Dr. Rakesh Kumar Verma Assistant Professor Department of Anatomy KGMU UP Lucknow Fibrous skeleton Dense fibrous connective tissue forms a structural foundation around AV & arterial
The Heart & Pericardium Dr. Rakesh Kumar Verma Assistant Professor Department of Anatomy KGMU UP Lucknow Fibrous skeleton Dense fibrous connective tissue forms a structural foundation around AV & arterial
Cardiovascular system:
 Cardiovascular system: Mediastinum: The mediastinum: lies between the right and left pleura and lungs. It extends from the sternum in front to the vertebral column behind, and from the root of the neck
Cardiovascular system: Mediastinum: The mediastinum: lies between the right and left pleura and lungs. It extends from the sternum in front to the vertebral column behind, and from the root of the neck
Mediastinum It is a thick movable partition between the two pleural sacs & lungs. It contains all the structures which lie
 Dr Jamila EL medany OBJECTIVES At the end of the lecture, students should be able to: Define the Mediastinum. Differentiate between the divisions of the mediastinum. List the boundaries and contents of
Dr Jamila EL medany OBJECTIVES At the end of the lecture, students should be able to: Define the Mediastinum. Differentiate between the divisions of the mediastinum. List the boundaries and contents of
The Cardiovascular System
 The Cardiovascular System The Manila Times College of Subic Prepared by: Stevens B. Badar, RN, MANc THE HEART Anatomy of the Heart Location and Size approx. the size of a person s fist, hollow and cone-shaped,
The Cardiovascular System The Manila Times College of Subic Prepared by: Stevens B. Badar, RN, MANc THE HEART Anatomy of the Heart Location and Size approx. the size of a person s fist, hollow and cone-shaped,
THE VESSELS OF THE HEART
 1 THE VESSELS OF THE HEART The vessels of the heart include the coronary arteries, which supply the heart and the veins and lymph vessels, which drain the heart. THE CORONARY ARTERIES These are the blood
1 THE VESSELS OF THE HEART The vessels of the heart include the coronary arteries, which supply the heart and the veins and lymph vessels, which drain the heart. THE CORONARY ARTERIES These are the blood
Major Function of the Cardiovascular System. Transportation. Structures of the Cardiovascular System. Heart - muscular pump
 Structures of the Cardiovascular System Heart - muscular pump Blood vessels - network of tubes Blood - liquid transport vehicle brachiocephalic trunk superior vena cava right pulmonary arteries right pulmonary
Structures of the Cardiovascular System Heart - muscular pump Blood vessels - network of tubes Blood - liquid transport vehicle brachiocephalic trunk superior vena cava right pulmonary arteries right pulmonary
Right lung. -fissures:
 -Right lung is shorter and wider because it is compressed by the right copula of the diaphragm by the live.. 2 fissure, 3 lobes.. hilum : 2 bronchi ( ep-arterial, hyp-arterial ), one artery mediastinal
-Right lung is shorter and wider because it is compressed by the right copula of the diaphragm by the live.. 2 fissure, 3 lobes.. hilum : 2 bronchi ( ep-arterial, hyp-arterial ), one artery mediastinal
THE DESCENDING THORACIC AORTA
 Intercostal Arteries and Veins Each intercostal space contains a large single posterior intercostal artery and two small anterior intercostal arteries. The anterior intercostal arteries of the lower spaces
Intercostal Arteries and Veins Each intercostal space contains a large single posterior intercostal artery and two small anterior intercostal arteries. The anterior intercostal arteries of the lower spaces
Lecturer: Ms DS Pillay ROOM 2P24 25 February 2013
 Lecturer: Ms DS Pillay ROOM 2P24 25 February 2013 Thoracic Wall Consists of thoracic cage Muscle Fascia Thoracic Cavity 3 Compartments of the Thorax (Great Vessels) (Heart) Superior thoracic aperture
Lecturer: Ms DS Pillay ROOM 2P24 25 February 2013 Thoracic Wall Consists of thoracic cage Muscle Fascia Thoracic Cavity 3 Compartments of the Thorax (Great Vessels) (Heart) Superior thoracic aperture
Vasculature and innervation of the heart. A. Bendelic Human Anatomy Department
 Vasculature and innervation of the heart A. Bendelic Human Anatomy Department Plan: 1. Arterial blood supply of the heart. Coronary arteries 2. Venous drainage of the heart. Cardiac veins 3. Innervation
Vasculature and innervation of the heart A. Bendelic Human Anatomy Department Plan: 1. Arterial blood supply of the heart. Coronary arteries 2. Venous drainage of the heart. Cardiac veins 3. Innervation
DEVELOPMENT OF THE CIRCULATORY SYSTEM L E C T U R E 5
 DEVELOPMENT OF THE CIRCULATORY SYSTEM L E C T U R E 5 REVIEW OF CARDIAC ANATOMY Heart 4 chambers Base and apex Valves Pericardial sac 3 layers: epi, myo, endo cardium Major blood vessels Aorta and its
DEVELOPMENT OF THE CIRCULATORY SYSTEM L E C T U R E 5 REVIEW OF CARDIAC ANATOMY Heart 4 chambers Base and apex Valves Pericardial sac 3 layers: epi, myo, endo cardium Major blood vessels Aorta and its
The Cardiovascular System: The Heart: Part A
 PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Janice Meeking, Mount Royal College CHAPTER 18 The Cardiovascular System: The Heart: Part A Heart Anatomy Approximately the size of a fist Location In the mediastinum
PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Janice Meeking, Mount Royal College CHAPTER 18 The Cardiovascular System: The Heart: Part A Heart Anatomy Approximately the size of a fist Location In the mediastinum
The Heart. Size, Form, and Location of the Heart. 1. Blunt, rounded point; most inferior part of the heart.
 12 The Heart FOCUS: The heart is composed of cardiac muscle cells, which are elongated, branching cells that appear striated. Cardiac muscle cells behave as a single electrical unit, and the highly coordinated
12 The Heart FOCUS: The heart is composed of cardiac muscle cells, which are elongated, branching cells that appear striated. Cardiac muscle cells behave as a single electrical unit, and the highly coordinated
The Mediastinum & Heart
 2018 The Mediastinum & Heart Sameh S. Akkila THE MEDIASTINUM The mediastinum is a septum that lies between the two lungs. It extends from the vertebral column posteriorly to the sternum anteriorly and
2018 The Mediastinum & Heart Sameh S. Akkila THE MEDIASTINUM The mediastinum is a septum that lies between the two lungs. It extends from the vertebral column posteriorly to the sternum anteriorly and
Introduction to Anatomy. Dr. Maher Hadidi. Bayan Yanes. April/9 th /2013
 Introduction to Anatomy Dr. Maher Hadidi Bayan Yanes 27 April/9 th /2013 KEY POINTS: 1) Right side of the heart 2) Papillary muscles 3) Left side of the heart 4) Comparison between right and left sides
Introduction to Anatomy Dr. Maher Hadidi Bayan Yanes 27 April/9 th /2013 KEY POINTS: 1) Right side of the heart 2) Papillary muscles 3) Left side of the heart 4) Comparison between right and left sides
Anatomy of thoracic wall
 Anatomy of thoracic wall Topographic Anatomy of the Thorax 1 Bones of Thoracic wall ribs 1-7"true" ribs -those which attach directly to the sternum true ribs actually attach to the sternum by means of
Anatomy of thoracic wall Topographic Anatomy of the Thorax 1 Bones of Thoracic wall ribs 1-7"true" ribs -those which attach directly to the sternum true ribs actually attach to the sternum by means of
Figure ) The specific chamber of the heart that is indicated by letter A is called the. Diff: 1 Page Ref: 364
 Essentials of Anatomy and Physiology, 9e (Marieb) Chapter 11 The Cardiovascular System Short Answer Figure 11.1 Using Figure 11.1, identify the following: 1) The Purkinje fibers are indicated by label.
Essentials of Anatomy and Physiology, 9e (Marieb) Chapter 11 The Cardiovascular System Short Answer Figure 11.1 Using Figure 11.1, identify the following: 1) The Purkinje fibers are indicated by label.
Approximately the size of your fist Location Superior surface of diaphragm Left of the midline in mediastinum Anterior to the vertebral column,
 Dr. Gary Mumaugh Approximately the size of your fist Location Superior surface of diaphragm Left of the midline in mediastinum Anterior to the vertebral column, posterior to the sternum Posteriorly the
Dr. Gary Mumaugh Approximately the size of your fist Location Superior surface of diaphragm Left of the midline in mediastinum Anterior to the vertebral column, posterior to the sternum Posteriorly the
Dana Alrafaiah. - Moayyad Al-Shafei. -Mohammad H. Al-Mohtaseb. 1 P a g e
 - 6 - Dana Alrafaiah - Moayyad Al-Shafei -Mohammad H. Al-Mohtaseb 1 P a g e Quick recap: Both lungs have an apex, base, mediastinal and costal surfaces, anterior and posterior borders. The right lung,
- 6 - Dana Alrafaiah - Moayyad Al-Shafei -Mohammad H. Al-Mohtaseb 1 P a g e Quick recap: Both lungs have an apex, base, mediastinal and costal surfaces, anterior and posterior borders. The right lung,
Circulation. Circulation = is a process used for the transport of oxygen, carbon! dioxide, nutrients and wastes through-out the body
 Circulation Circulation = is a process used for the transport of oxygen, carbon! dioxide, nutrients and wastes through-out the body Heart = muscular organ about the size of your fist which pumps blood.
Circulation Circulation = is a process used for the transport of oxygen, carbon! dioxide, nutrients and wastes through-out the body Heart = muscular organ about the size of your fist which pumps blood.
Chapter 20: Cardiovascular System: The Heart
 Chapter 20: Cardiovascular System: The Heart I. Functions of the Heart A. List and describe the four functions of the heart: 1. 2. 3. 4. II. Size, Shape, and Location of the Heart A. Size and Shape 1.
Chapter 20: Cardiovascular System: The Heart I. Functions of the Heart A. List and describe the four functions of the heart: 1. 2. 3. 4. II. Size, Shape, and Location of the Heart A. Size and Shape 1.
Cardiovascular System
 Cardiovascular System I. Structure of the Heart A. Average adult heart is 14 cm long and 9 cm wide. B. Lies in the mediastinum. C. Enclosed in the pericardium. 1. Fibrous pericardium- Outer, tough connective
Cardiovascular System I. Structure of the Heart A. Average adult heart is 14 cm long and 9 cm wide. B. Lies in the mediastinum. C. Enclosed in the pericardium. 1. Fibrous pericardium- Outer, tough connective
11/10/2014. Muscular pump Two atria Two ventricles. In mediastinum of thoracic cavity 2/3 of heart's mass lies left of midline of sternum
 It beats over 100,000 times a day to pump over 1,800 gallons of blood per day through over 60,000 miles of blood vessels. During the average lifetime, the heart pumps nearly 3 billion times, delivering
It beats over 100,000 times a day to pump over 1,800 gallons of blood per day through over 60,000 miles of blood vessels. During the average lifetime, the heart pumps nearly 3 billion times, delivering
LAB 12-1 HEART DISSECTION GROSS ANATOMY OF THE HEART
 LAB 12-1 HEART DISSECTION GROSS ANATOMY OF THE HEART Because mammals are warm-blooded and generally very active animals, they require high metabolic rates. One major requirement of a high metabolism is
LAB 12-1 HEART DISSECTION GROSS ANATOMY OF THE HEART Because mammals are warm-blooded and generally very active animals, they require high metabolic rates. One major requirement of a high metabolism is
The Cardiovascular System: The Heart
 PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Meg Flemming Austin Community College C H A P T E R 12 The Cardiovascular System: The Heart Chapter 12 Learning Outcomes 12-1 12-2 Describe the anatomy of the heart,
PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Meg Flemming Austin Community College C H A P T E R 12 The Cardiovascular System: The Heart Chapter 12 Learning Outcomes 12-1 12-2 Describe the anatomy of the heart,
Chapter 14. Circulatory System Images. VT-122 Anatomy & Physiology II
 Chapter 14 Circulatory System Images VT-122 Anatomy & Physiology II The mediastinum Dog heart Dog heart Cat heart Dog heart ultrasound Can see pericardium as distinct bright line Pericardial effusion Fluid
Chapter 14 Circulatory System Images VT-122 Anatomy & Physiology II The mediastinum Dog heart Dog heart Cat heart Dog heart ultrasound Can see pericardium as distinct bright line Pericardial effusion Fluid
10. Thick deposits of lipids on the walls of blood vessels, called, can lead to serious circulatory issues. A. aneurysm B. atherosclerosis C.
 Heart Student: 1. carry blood away from the heart. A. Arteries B. Veins C. Capillaries 2. What is the leading cause of heart attack and stroke in North America? A. alcohol B. smoking C. arteriosclerosis
Heart Student: 1. carry blood away from the heart. A. Arteries B. Veins C. Capillaries 2. What is the leading cause of heart attack and stroke in North America? A. alcohol B. smoking C. arteriosclerosis
Yara saddam & Dana Qatawneh. Razi kittaneh. Maher hadidi
 1 Yara saddam & Dana Qatawneh Razi kittaneh Maher hadidi LECTURE 10 THORAX The thorax extends from the root of the neck to the abdomen. The thorax has a Thoracic wall Thoracic cavity and it is divided
1 Yara saddam & Dana Qatawneh Razi kittaneh Maher hadidi LECTURE 10 THORAX The thorax extends from the root of the neck to the abdomen. The thorax has a Thoracic wall Thoracic cavity and it is divided
MODULE 2: CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM ANTOMY An Introduction to the Anatomy of the Heart and Blood vessels
 MODULE 2: CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM ANTOMY An Introduction to the Anatomy of the Heart and Blood vessels The cardiovascular system includes a pump (the heart) and the vessels that carry blood from the heart
MODULE 2: CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM ANTOMY An Introduction to the Anatomy of the Heart and Blood vessels The cardiovascular system includes a pump (the heart) and the vessels that carry blood from the heart
Figure 10.1A Transparency Master 79
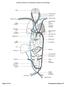 Brain Carotid arteries Jugular vein Right front leg Lungs (inflated) Cranial Right atrium To left front leg Left subclavian Bronchus capillaries Brachiocephalic vein Left atrium Dorsal aorta Right ventricle
Brain Carotid arteries Jugular vein Right front leg Lungs (inflated) Cranial Right atrium To left front leg Left subclavian Bronchus capillaries Brachiocephalic vein Left atrium Dorsal aorta Right ventricle
- what other structures, besides the heart, does the mediastinum contain?
 Basic A & P II Dr. L. Bacha Chapter Outline (Martini & Nath 2010) An Introduction to the Cardiovascular System - read the paragraphs under this heading on page 580 The Heart is a Four Chambered Organ describe
Basic A & P II Dr. L. Bacha Chapter Outline (Martini & Nath 2010) An Introduction to the Cardiovascular System - read the paragraphs under this heading on page 580 The Heart is a Four Chambered Organ describe
The Heart. C h a p t e r. PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Jason LaPres Lone Star College - North Harris
 C h a p t e r 20 The Heart PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Jason LaPres Lone Star College - North Harris Copyright 2009 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Pearson Benjamin Cummings Introduction
C h a p t e r 20 The Heart PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Jason LaPres Lone Star College - North Harris Copyright 2009 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Pearson Benjamin Cummings Introduction
Function: Transportation of. Oxygen Nutrients Waste Hormones gases
 Function: Transportation of Oxygen Nutrients Waste Hormones gases Pericardium: double sac of serous membrane filled with fluid (pericardial fluid to be exact) that surrounds the heart. Parietal pericardium:
Function: Transportation of Oxygen Nutrients Waste Hormones gases Pericardium: double sac of serous membrane filled with fluid (pericardial fluid to be exact) that surrounds the heart. Parietal pericardium:
Blood supply of the Heart & Conduction System. Dr. Nabil Khouri
 Blood supply of the Heart & Conduction System Dr. Nabil Khouri Arterial supply of Heart Right coronary artery Left coronary artery 3 Introduction: Coronary arteries - VASAVASORUM arising from aortic sinuses
Blood supply of the Heart & Conduction System Dr. Nabil Khouri Arterial supply of Heart Right coronary artery Left coronary artery 3 Introduction: Coronary arteries - VASAVASORUM arising from aortic sinuses
slide 23 The lobes in the right and left lungs are divided into segments,which called bronchopulmonary segments
 Done By : Rahmeh Alsukkar Date : 26 /10/2017 slide 23 The lobes in the right and left lungs are divided into segments,which called bronchopulmonary segments Each segmental bronchus passes to a structurally
Done By : Rahmeh Alsukkar Date : 26 /10/2017 slide 23 The lobes in the right and left lungs are divided into segments,which called bronchopulmonary segments Each segmental bronchus passes to a structurally
Ch.15 Cardiovascular System Pgs {15-12} {15-13}
 Ch.15 Cardiovascular System Pgs {15-12} {15-13} E. Skeleton of the Heart 1. The skeleton of the heart is composed of rings of dense connective tissue and other masses of connective tissue in the interventricular
Ch.15 Cardiovascular System Pgs {15-12} {15-13} E. Skeleton of the Heart 1. The skeleton of the heart is composed of rings of dense connective tissue and other masses of connective tissue in the interventricular
The Heart and Cardiovascular System
 The Heart and Cardiovascular System What you will learn The location of the heart 3 layers and covering of the heart Explain the function of the heart as 2 separate pumps Identify the 4 chambers of the
The Heart and Cardiovascular System What you will learn The location of the heart 3 layers and covering of the heart Explain the function of the heart as 2 separate pumps Identify the 4 chambers of the
The Cardiovascular System
 Essentials of Human Anatomy & Physiology Elaine N. Marieb Slides 11.1 11.19 Seventh Edition Chapter 11 The Cardiovascular System Functions of the Cardiovascular system Function of the heart: to pump blood
Essentials of Human Anatomy & Physiology Elaine N. Marieb Slides 11.1 11.19 Seventh Edition Chapter 11 The Cardiovascular System Functions of the Cardiovascular system Function of the heart: to pump blood
Approximately the size of your fist Location. Pericardial physiology
 Heart Anatomy Approximately the size of your fist Location Superior surface of diaphragm Left of the midline Anterior to the vertebral column, posterior to the sternum Wednesday, March 28, 2012 Muscle
Heart Anatomy Approximately the size of your fist Location Superior surface of diaphragm Left of the midline Anterior to the vertebral column, posterior to the sternum Wednesday, March 28, 2012 Muscle
Syllabus: 6 pages (Page 6 lists corresponding figures for Grant's Atlas 11 th & 12 th Eds.)
 PLEURAL CAVITY AND LUNGS Dr. Milton M. Sholley SELF STUDY RESOURCES Essential Clinical Anatomy 3 rd ed. (ECA): pp. 70 81 Syllabus: 6 pages (Page 6 lists corresponding figures for Grant's Atlas 11 th &
PLEURAL CAVITY AND LUNGS Dr. Milton M. Sholley SELF STUDY RESOURCES Essential Clinical Anatomy 3 rd ed. (ECA): pp. 70 81 Syllabus: 6 pages (Page 6 lists corresponding figures for Grant's Atlas 11 th &
The Heart. Happy Friday! #takeoutyournotes #testnotgradedyet
 The Heart Happy Friday! #takeoutyournotes #testnotgradedyet Introduction Cardiovascular system distributes blood Pump (heart) Distribution areas (capillaries) Heart has 4 compartments 2 receive blood (atria)
The Heart Happy Friday! #takeoutyournotes #testnotgradedyet Introduction Cardiovascular system distributes blood Pump (heart) Distribution areas (capillaries) Heart has 4 compartments 2 receive blood (atria)
BOGOMOLETS NATIONAL MEDICAL UNIVERSITY DEPARTMENT OF HUMAN ANATOMY. Guidelines. Module 2 Topic of the lesson Aorta. Thoracic aorta.
 BOGOMOLETS NATIONAL MEDICAL UNIVERSITY DEPARTMENT OF HUMAN ANATOMY Guidelines Academic discipline HUMAN ANATOMY Module 2 Topic of the lesson Aorta. Thoracic aorta. Course 1 The number of hours 3 1. The
BOGOMOLETS NATIONAL MEDICAL UNIVERSITY DEPARTMENT OF HUMAN ANATOMY Guidelines Academic discipline HUMAN ANATOMY Module 2 Topic of the lesson Aorta. Thoracic aorta. Course 1 The number of hours 3 1. The
Read Chapters 21 & 22, McKinley et al
 ACTIVITY 9: BLOOD AND HEART OBJECTIVES: 1) How to get ready: Read Chapters 21 & 22, McKinley et al., Human Anatomy, 5e. All text references are for this textbook. Read dissection instructions BEFORE YOU
ACTIVITY 9: BLOOD AND HEART OBJECTIVES: 1) How to get ready: Read Chapters 21 & 22, McKinley et al., Human Anatomy, 5e. All text references are for this textbook. Read dissection instructions BEFORE YOU
CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM
 CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM Overview Heart and Vessels 2 Major Divisions Pulmonary Circuit Systemic Circuit Closed and Continuous Loop Location Aorta Superior vena cava Right lung Pulmonary trunk Base of heart
CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM Overview Heart and Vessels 2 Major Divisions Pulmonary Circuit Systemic Circuit Closed and Continuous Loop Location Aorta Superior vena cava Right lung Pulmonary trunk Base of heart
Read Me. covering the Heart Anatomy. Labs. textbook. use. car: you
 Heart Anatomy Lab Pre-Lab Exercises Read Me These exercises should be done before coming to lab, after watching the videos covering the Heart Anatomy Labs. Answer the questions in this guide using the
Heart Anatomy Lab Pre-Lab Exercises Read Me These exercises should be done before coming to lab, after watching the videos covering the Heart Anatomy Labs. Answer the questions in this guide using the
CJ Shuster A&P2 Lab Addenum Beef Heart Dissection 1. Heart Dissection. (taken from Johnson, Weipz and Savage Lab Book)
 CJ Shuster A&P2 Lab Addenum Beef Heart Dissection 1 Heart Dissection. (taken from Johnson, Weipz and Savage Lab Book) Introduction When you have finished examining the model, you are ready to begin your
CJ Shuster A&P2 Lab Addenum Beef Heart Dissection 1 Heart Dissection. (taken from Johnson, Weipz and Savage Lab Book) Introduction When you have finished examining the model, you are ready to begin your
PLEURAE and PLEURAL RECESSES
 PLEURAE and PLEURAL RECESSES By Dr Farooq Aman Ullah Khan PMC 26 th April 2018 Introduction When sectioned transversely, it is apparent that the thoracic cavity is kidney shaped: a transversely ovoid space
PLEURAE and PLEURAL RECESSES By Dr Farooq Aman Ullah Khan PMC 26 th April 2018 Introduction When sectioned transversely, it is apparent that the thoracic cavity is kidney shaped: a transversely ovoid space
4. The two inferior chambers of the heart are known as the atria. the superior and inferior vena cava, which empty into the left atrium.
 Answer each statement true or false. If the statement is false, change the underlined word to make it true. 1. The heart is located approximately between the second and fifth ribs and posterior to the
Answer each statement true or false. If the statement is false, change the underlined word to make it true. 1. The heart is located approximately between the second and fifth ribs and posterior to the
OBJECTIVE: To obtain a fundamental knowledge of the root of the neck with respect to structure and function
 The root of the neck Jeff Dupree, Ph.D. e mail: jldupree@vcu.edu OBJECTIVE: To obtain a fundamental knowledge of the root of the neck with respect to structure and function READING ASSIGNMENT: Moore and
The root of the neck Jeff Dupree, Ph.D. e mail: jldupree@vcu.edu OBJECTIVE: To obtain a fundamental knowledge of the root of the neck with respect to structure and function READING ASSIGNMENT: Moore and
Chapter 3: Thorax. Thorax
 Chapter 3: Thorax Thorax Thoracic Cage I. Thoracic Cage Osteology A. Thoracic Vertebrae Basic structure: vertebral body, pedicles, laminae, spinous processes and transverse processes Natural kyphotic shape,
Chapter 3: Thorax Thorax Thoracic Cage I. Thoracic Cage Osteology A. Thoracic Vertebrae Basic structure: vertebral body, pedicles, laminae, spinous processes and transverse processes Natural kyphotic shape,
The Cardiovascular System (Heart)
 The Cardiovascular System The Cardiovascular System (Heart) A closed system of the heart and blood vessels The heart pumps blood Blood vessels allow blood to circulate to all parts of the body The function
The Cardiovascular System The Cardiovascular System (Heart) A closed system of the heart and blood vessels The heart pumps blood Blood vessels allow blood to circulate to all parts of the body The function
The cardiovascular system is composed of the heart and blood vessels that carry blood to and from the body s organs. There are 2 major circuits:
 1 The cardiovascular system is composed of the heart and blood vessels that carry blood to and from the body s organs. There are 2 major circuits: pulmonary and systemic. The pulmonary goes out to the
1 The cardiovascular system is composed of the heart and blood vessels that carry blood to and from the body s organs. There are 2 major circuits: pulmonary and systemic. The pulmonary goes out to the
thoracic cage inlet and outlet landmarks of the anterior chest wall muscles of the thoracic wall sternum joints ribs intercostal spaces diaphragm
 Thoracic Wall Lecture Objectives Describe the shape and outline of the thoracic cage including inlet and outlet. Describe the anatomical landmarks of the anterior chest wall. List various structures making
Thoracic Wall Lecture Objectives Describe the shape and outline of the thoracic cage including inlet and outlet. Describe the anatomical landmarks of the anterior chest wall. List various structures making
Cardiovascular System. Heart Anatomy
 Cardiovascular System Heart Anatomy 1 The Heart Location & general description: Atria vs. ventricles Pulmonary vs. systemic circulation Coverings Walls The heart is found in the mediastinum, the medial
Cardiovascular System Heart Anatomy 1 The Heart Location & general description: Atria vs. ventricles Pulmonary vs. systemic circulation Coverings Walls The heart is found in the mediastinum, the medial
Human Anatomy and Physiology Chapter 19 Worksheet 1- The Heart
 Human Anatomy and Physiology Chapter 19 Worksheet 1- The Heart Name Date Period 1. The "double pump" function of the heart includes the right side, which serves as the circuit pump, while the left side
Human Anatomy and Physiology Chapter 19 Worksheet 1- The Heart Name Date Period 1. The "double pump" function of the heart includes the right side, which serves as the circuit pump, while the left side
Circulatory system. Lecture #2
 Circulatory system Lecture #2 The essential components of the human cardiovascular system: Heart Blood Blood vessels Arteries - blood vessels that conduct arterial blood from heart ventricle to organs
Circulatory system Lecture #2 The essential components of the human cardiovascular system: Heart Blood Blood vessels Arteries - blood vessels that conduct arterial blood from heart ventricle to organs
The Cardiovascular System
 11 PART A The Cardiovascular System PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Jerry L. Cook, Sam Houston University ESSENTIALS OF HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY EIGHTH EDITION ELAINE N. MARIEB The Cardiovascular
11 PART A The Cardiovascular System PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Jerry L. Cook, Sam Houston University ESSENTIALS OF HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY EIGHTH EDITION ELAINE N. MARIEB The Cardiovascular
