Close Association between valvular heart disease and central nervous system manifestations in the antiphospholipid syndrome
|
|
|
- Derick Hunt
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 ARD Online First, published on March 18, 2005 as /ard Close Association between valvular heart disease and central nervous system manifestations in the antiphospholipid syndrome Category: Extended report. Ilan Krause 1,2, Shaul Lev 2, Abigail Fraser 2, Miri Blank 1, Margalit Lorber 3, Ludmilla Stojanovich 4, Josef Rovensky 5, Joab Chapman 6, Yehuda Shoenfeld 1,7 1 Research Center for Autoimmune Diseases, 7 Department of Medicine B and 6 Department of Neurology, Sheba Medical Center, 2 Department of Medicine "E", Rabin Medical Center, Beilinson Campus; Sackler Faculty of Medicine, Tel-Aviv University, Israel. 3 Institute of Allergy, Clinical Immunology and AIDS, Rambam Medical Center and Rappaport Faculty of Medicine, Technion, Israel. 4 Institute of Rheumatology University Hospital, Belgrad, Yugoslavia, 5 National Institute of Rheumatic Diseases, Slovak Republic. Key words: Epilepsy, migraine, cardiac valves, vegetations, systemic lupus erythematosus. Running title: Cardiac and CNS associations in APS Address for correspondence: Y. Shoenfeld, MD, Department of Medicine B, Sheba Medical Center, Tel-Hashomer 52621, Israel. Tel: , Fax: , Shoenfel@post.tau.ac.il The Corresponding Author has the right to grant on behalf of all authors and does grant on behalf of all authors, an exclusive license on a worldwide basis to the BMJ Publishing Group Ltd and its Licensees to permit this article (if accepted) to be published in the Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases editions and any other BMJPGL products to exploit all subsidiary rights, as set out in the licence ( Copyright Article author (or their employer) Produced by BMJ Publishing Group Ltd (& EULAR) under licence.
2 2 ABSTRACT Objectives: Heart valves lesions and central nervous system involvement are among the most common manifestations of the antiphospholipid syndrome (APS). In the present study we evaluated possible inter-relations between these manifestations in a large group of APS patients. Methods: Two hundred eighty four APS patients were retrospectively evaluated, 159 of whom had primary APS (PAPS). Cardiac-CNS associations were determined for the entire study population, and for subgroups of patients with PAPS or APS associated to SLE. Results: Significant associations where found between cardiac vegetations and epilepsy (p<0.02), and between cardiac valves thickening or dysfunction and migraine (p=0.002). Borderline association was found between valvular vegetations and migraine (p=0.09). A significant association was also found between all valvular lesions and stroke/tia. Sub-analyses revealed that patients with PAPS had significant associations between cardiac valves pathology and all CNS manifestations, while patients with APS associated to SLE presented no such associations. Conclusions: Our study point to potential different biological behaviors in PAPS than in APS associated to SLE. According to our results, the presence of cardiac valves pathology may be a risk factor for several CNS involvements in PAPS.
3 3 INTRODUCTION Traditionally described as a syndrome consisting of recurrent fetal loss, vascular thrombosis, and anticardiolipin autoantibodies (1-3), the antiphospholipid syndrome (APS) is now increasingly recognized as a multisystem disease, the clinical expression of which may include cardiac, neurological, renal, gastrointestinal, hematologic or cutaneous manifestations (4, 5). Over the last years a growing number of studies have extended our knowledge on the spectrum of two major target organs involvement in APS, namely the heart and the central nervous system (CNS). Heart valve lesions are the most common cardiac manifestations described in patients with APS (6-10). The introduction of two-dimensional and Doppler echocardiography has revealed a high prevalence of valvular abnormalities, such as thickening, stenosis, regurgitation and vegetations in patients with primary and secondary APS. Their frequency appear to be quite high, with up to 70 percent of APS patients revealing at least one valvular abnormality on echocardiography (4, 11, 12). Although many of these abnormalities are of little clinical consequence, vegetations of the mitral or aortic valves are present in approximately 4 percent of the patients (11), and 4 6% of all APS patients develop severe mitral or aortic regurgitation, necessitating valve replacement surgery in half of theme (8). Regarding the strong association of cardiac valvular disease with APS, it has been recently suggested to include cardiac valve thickening or vegetations among the classification criteria for APS (13) CNS involvement is also one of the most prominent clinical manifestations of APS. Although the mechanism of neurological involvement in APS is thought to be thrombotic in origin, and cerebral ischemia associated with antiphospholipid antibodies (apl) is the most common arterial thrombotic manifestation, a number of other neuropsychiatric manifestations, including optic atrophy, chronic headache, dementia, cognitive dysfunction, psychosis, depression, transverse myelopathy, multiple sclerosis-like disease, chorea and seizures have also been associated with apl (14, 15). Despite the reported heterogeneity in clinical expression of APS, the interrelations between various manifestations of the disease has not yet been studied, and might have been overlooked due to numerous possible combinations of clinical manifestations. Awareness of such associations might give us a better understanding of the disease. Considering the high prevalences of cardiac and CNS manifestations in APS we sought to evaluate possible inter associations between these manifestations in a large group of APS patients. PATIENTS AND METHODS Patients Two hundred eighty four APS patients from seven medical centers in Israel, Yugoslavia and Slovak Republic were included in the study. All patients met the 1997 revised Sapporo criteria for the antiphospholipid syndrome (16). All patients underwent detailed medical interview and routine physical examination by a qualified internist and/or rheumatologist prior to inclusion in the study. Further data were obtained from patients medical files regarding the expression of various clinical manifestations of the disease, demographic parameters and laboratory results. The study was designed to evaluate possible associations between cardiac valves abnormalities and epilepsy or migraine. All patients underwent 2- dimentional and Doppler color flow echocardiographic examination for determination of cardiac valves abnormalities. Valvular thickening was defined as focal areas of increased echogenicity and thickening of cardiac valve s leaflets. For the mitral valve a thickness of above 5 mm was considered abnormal, for other valves abnormal thickness was determined according to standards of the specific medical center. Valvular dysfunction was defined as the presence of stenosis or regurgitation of at least moderate severity. Non-infectious vegetations were defined as echocardiographically identified masses protruding from valvular leaflets, in the presence of sterile blood cultures and without fever. Epilepsy was defined as at least 2
4 4 separate episodes of unprovoked seizures with an interval greater than 24 hours. Seizures could either be simple partial, complex partial or generalized tonic-clonic, and had to be unrelated to metabolic abnormalities or to drug or medication use or withdrawal, and without other provoking factors such as hypoxia or cerebral hypoperfusion. Migraine was defined by a neurologist at the specific medical center, as a recurrent severe unilateral or bilateral headaches, lasting 4-72 hours, with or without aura, after excluding other relevant etiologies such as tension headache or secondary to hypertension. The cardiac-cns associations were determined for the entire study population, and for subgroups of patients with primary APS (PAPS) or APS associated to SLE. Detection of anti-β2gpi antibodies and anti-peptides antibodies The levels of anti-phospholipid antibodies were detected by ELISA. Ninety six wells ELISA plates (Nunc, Kamstrup, Roskilde, Denmark) were coated with cardiolipin (Sigma Chemical Co., St. Louis, Missouri, USA) 50 µg/ml in ethanol or β2gpi 10 µg/ml in PBS. Following blocking with 3% BSA, sera at different dilutions were added, and incubated for 2 hrs at room temperature. Bound antibodies were detected using goat anti-human IgG or IgM conjugated to alkaline phosphatase (Sigma) and appropriate substrate. The color reaction was read in Titertrek ELISA reader (SLT- Labistruments, Austria) at O.D. of 405nm. Extensive washing with PBS followed each step. Statistics Chi-Square test was performed or Fisher s Exact test if appropriate, to analyze statistical significant differences between categorical variables. Two sided p-values of less than 0.05 were considered statistically significant. RESULTS Two hundred eighty four APS patients were studied, 238 of whom (83.8 %) were women and 46 (16.2%) were men. The mean age of the patients was 33.7 ± 11.9 years (range years), mean disease duration was 7.8 ± 5.2 years. Most patients had PAPS (n=159, 56%). APS was associated to SLE in 97 patients (34.2 %). The rates of anti-cl (IgG and/or IgM) and anti-β2gpi (IgG and/or IgM) Abs were 88.0% and 72.2% respectively. Lupus anticoagulants were detected in 77.1% of the study population. The prevalences of the most frequent clinical manifestations among the patients are presented in Table 1. The patients with APS associated to SLE had significantly higher rates of epilepsy, livedo reticularis, thrombocytopenia and autoimmune hemolytic anemia, and lower rates of fetal loss, compared to the patients with PAPS. There were 60 patients with valvular disease, of whom 17 had noninfectious vegetations and 51 had valvular thickening or dysfunction. Some of the patients had several valvular abnormalities. Information about anticoagulant and anti-aggregate treatments was available for 235 patients. One hundred and nine patients received anticoagulant treatment, 66 of them with INR targeted to 3-4 and 43 with INR targeted to 2-3. Fifty-nine patients were treated with anti platelets aggregants. There were no differences in the rates of anti-coagulant or anti-aggregate treatments in patients with valvular disease with or without epilepsy or migraine. The heart-cns associations are detailed in Table 2. When analyzing the whole group of APS patients (Table 2a), significant associations where found between cardiac vegetations and epilepsy (p<0.02), and between cardiac valves thickening or dysfunction, as well as overall valvular abnormalities (vegetations and/or valvular dysfunction) and migraine (p=0.002 for both). Borderline association was found between valvular vegetations and migraine (p=0.09). Sub analyses revealed striking differences between patients with PAPS (Table 2b) and SLE patients with APS (Table 2c). While PAPS patients had significant associations between cardiac valves vegetations and epilepsy, and between any valvular abnormality (vegetations, dysfunction or both) and migraine, patients with APS associated to SLE presented no such
5 5 associations. We also evaluated a possible connection between cardiac valves abnormalities and the occurrence of CVA or TIA. As shown in Table 3, significant associations were found between valvular disease and past episodes of CVA/TIA (Table 3a). Furthermore, these associations were confined to PAPS patients, but not to patients with APS associated to SLE Table 3b and 3c, respectively). DISCUSSION In the present study we point to significant associations between cardiac valves lesions and CNS manifestations in a large group of APS patients. The presence of valvular vegetations was found to be associated with epilepsy and migraine, while valvular thickening or dysfunction (as well as overall valvular abnormalities) were significantly associated with the presence of migraine. Furthermore, cardiac valves vegetations and/or dysfunction were strongly associated with a high rate of CVA or TIA. The rate of cardiac valve abnormalities in our study population was 21.1%, being somewhat more common in SLE patients (27.8%) than in PAPS (18.2%, NS). The prevalence of valvular pathology in our study is in the range reported in previous studies (7), ranging usually between 32-38% of APS patients (8, 9, 11, 17, 18), although lower and higher prevalences have also been reported (9). Recently, Zavaleta et al (12) reported a rate of 70.8% of valvular lesions in APS patients, detected by transesophageal echocardiography. New valvular lesions or progression of existing lesions were detected in 9 out of 12 patients during a 5-year follow-up (12). Epilepsy was diagnosed in 9.9% of the patients in our study, and migraine in 18.0%, which are in line with previously reported rates (19, 20). In the current study we did not have information on the sequence of events. Thus further prospective studies are needed to evaluate whether cardiac valvular disease is a risk factor for CNS manifestations, or vice versa. A possible link between heart pathology and various CNS involvements in APS has not yet been investigated. The only cardiac-cns association in APS to be reported thus fur has been on valvular vegetations as a possible risk factor for cerebral emboli (21-23). The results of our study support this observation. To the best of our knowledge a relationship between valvular vegetations or dysfunctions and other CNS manifestations has not yet been reported. The pathogenesis of valvular as well as cerebral abnormalities in APS is not entirely clear. It has been postulated that apl directly cause valvular or endothelial injury unrelated to severity of the disease, with apl deposition on the valves resembling immune complexes deposition in the dermo-epidermal junction or in the kidney basement membrane in patients with SLE (9, 10, 24). Antibody deposition and complement components initiating valve damage have been described (6), along with increased endothelial cell expression of α3β1 integrin (25). On the other hand, some histologic studies suggest that fibrin deposits are the major findings, not inflammation (26). It had also been suggested that anticoagulation may improve cardiac valve lesions, yet other studies did not find benefit of anticoagulant or antiaggregate therapy (13). In our study we did not find a relation between anti-coagulant/antiaggregate treatments and the rates of valvular pathology. As to CNS involvement, the specific role of apl remains one of the least understood aspects of this syndrome. The link between apl and epilepsy has been supported by several studies (27, 28), but no direct evidence yet exists that apl per se are pathogenic or are direct mediators in the development of thrombotic or other neurological complications in human patients. Laboratory findings which indicate that apl directly binds to brain tissue, inhibit astrocytes proliferation in vitro or depolarize brain nerve terminals may provide a basis for understanding the pathogenesis of epilepsy and other neurological complications in APS (29, 30). The pathophysiology of migraine is complex, and includes genetic, metabolic, vascular and emotional components. Cuadrado et al (31) reported on five APS patients with intractable headaches treated with a 7-day course of anticoagulation. All five patients had a marked improvement of the headaches following
6 6 the treatment. It was speculated that low-dose anticoagulant therapy might be tried in APS patients with migraine (31). Our study was not designed to evaluate the role of therapy on CNS or cardiac manifestations in APS, yet we observed similar rates of migraine in patients treated, or untreated, with either anticoagulant or anti-aggregate therapies. The linkage between cardiac valves and CNS pathologies, found in our study, may point to a common pathogenic mechanism mediated, for example, by localized apl-associated tissue damage. Further studies are required to evaluate these mechanisms. Of special interest is the opposite cardiac-cns relationships found between PAPS patients and those with APS associated to SLE. Whereas PAPS patients showed significant association between cardiac valves pathology and CNS manifestations, such associations were not found in patients with APS associated to SLE. Possible disparities in clinical presentation between patients with primary and secondary APS has not yet been thoroughly investigated. In their retrospective study, Asherson et al reported on a lower female/male sex ratio, and lower rates of livedo reticularis and chorea in PAPS than that found in patients with SLE (32). Vianna et al found Similar clinical and laboratory profiles in patients with PAPS or APS associated to SLE, with the exceptions of autoimmune hemolytic anemia, endocardial valve disease, neutropenia, and low C4 levels, all which occurred more frequently in SLE patients (11). The different valvular-cns connections found in our study may imply for distinct pathogenic mechanisms underlying cardiac and/or cerebral involvements in APS patients, depending on their background autoimmune condition. In conclusion, we report on close associations between cardiac valve pathology and several CNS manifestations- epilepsy, migraine and CVA/TIA in APS patients. Our study also point to potential distinct biological behaviors in PAPS and APS associated to SLE. According to our results, the presence of cardiac valves pathology may be a risk factor for several CNS involvements in PAPS.
7 7 REFERENCES 1. Alarcon Segovia D, Deleze M, Oria CV, et al. Antiphospholipid antibodies and the antiphospholipid syndrome in systemic lupus erythematosus. A prospective analysis of 500 consecutive patients. Medicine (Baltimore). 1989; 68: Hughes GR, Harris NN, Gharavi AE. The anticardiolipin syndrome. J Rheumatol. 1986; 13: Alarcon Segovia D. The antiphospholipid story. J Rheumatol. 2003; 30: Levine JS, Branch DW, Rauch J. The antiphospholipid syndrome. N Engl J Med. 2002; 346: Shoenfeld Y. Systemic antiphospholipid syndrome. Lupus. 2003; 12: Lev S, Shoenfeld Y. Cardiac valvulopathy in the antiphospholipid syndrome. Clin Rev Allergy Immunol. 2002; 23: Cervera R. Recent advances in antiphospholipid antibody-related valvulopathies. J Autoimmun. 2000; 15: Nesher G, Ilany J, Rosenmann D, Abraham AS. Valvular dysfunction in antiphospholipid syndrome: prevalence, clinical features, and treatment. Semin Arthritis Rheum. 1997; 27: Hojnik M, George J, Ziporen L, Shoenfeld Y. Heart valve involvement (Libman- Sacks endocarditis) in the antiphospholipid syndrome. Circulation. 1996; 93: Ziporen L, Goldberg I, Arad M, et al. Libman-Sacks endocarditis in the antiphospholipid syndrome: immunopathologic findings in deformed heart valves. Lupus. 1996; 5: Vianna JL, Khamashta MA, Ordi Ros J, et al. Comparison of the primary and secondary antiphospholipid syndrome: a European Multicenter Study of 114 patients. Am J Med. 1994; 96: Zavaleta NE, Montes RM, Soto ME, Vanzzini NA, Amigo MC. Primary antiphospholipid syndrome: a 5-year transesophageal echocardiographic followup study. J Rheumatol. 2004; 31: Petri MA. Classification criteria for antiphospholipid syndrome: the case for cardiac valvular disease. J Rheumatol. 2004; 31: Sanna G, Bertolaccini ML, Cuadrado MJ, Khamashta MA, Hughes GR. Central nervous system involvement in the antiphospholipid (Hughes) syndrome. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2003; 42: Hughes GR. Migraine, memory loss, and "multiple sclerosis ". Neurological features of the antiphospholipid (Hughes') syndrome. Postgrad Med J. 2003; 79: Wilson WA, Gharavi AE, Koike T, et al. International consensus statement on preliminary classification criteria for definite antiphospholipid syndrome: report of an international workshop. Arthritis Rheum. 1999; 42: Galve E, Ordi J, Barquinero J, Evangelista A, Vilardell M, Soler Soler J. Valvular heart disease in the primary antiphospholipid syndrome. Ann Intern Med. 1992; 116: Cervera R, Khamashta MA, Font J, et al. High prevalence of significant heart valve lesions in patients with the 'primary' antiphospholipid syndrome. Lupus. 1991; 1: Cervera R, Piette JC, Font J, et al. Antiphospholipid syndrome: clinical and immunologic manifestations and patterns of disease expression in a cohort of 1,000 patients. Arthritis Rheum. 2002; 46: Shoenfeld Y, Lev S, Blatt I, et al. Features associated with epilepsy in the antiphospholipid syndrome. J Rheumatol. 2004; 31: Pope JM, Canny CL, Bell DA. Cerebral ischemic events associated with endocarditis, retinal vascular disease, and lupus anticoagulant. Am J Med. 1991; 90:
8 8 22. Barbut D, Borer JS, Gharavi A, et al. Prevalence of anticardiolipin antibody in isolated mitral or aortic regurgitation, or both, and possible relation to cerebral ischemic events. Am J Cardiol. 1992; 70: Pamuk ON, Cakir N, Soy M, Aktoz M, Celik Y, Akdemir O. Mitral valve vegetation and cerebral emboli in a primary antiphospholipid syndrome patient who had hepatitis C virus infection: report of a case and review of the literature. Clin Rheumatol. 2003; 22: Amital H, Langevitz P, Levy Y, et al. Valvular deposition of antiphospholipid antibodies in the antiphospholipid syndrome: a clue to the origin of the disease. Clin Exp Rheumatol. 1999; 17: Afek A, Shoenfeld Y, Manor R, et al. Increased endothelial cell expression of alpha3beta1 integrin in cardiac valvulopathy in the primary (Hughes) and secondary antiphospholipid syndrome. Lupus. 1999; 8: Garcia Torres R, Amigo MC, de la Rosa A, Moron A, Reyes PA. Valvular heart disease in primary antiphospholipid syndrome (PAPS): clinical and morphological findings. Lupus. 1996; 5: Peltola JT, Haapala A, Isojarvi JI, et al. Antiphospholipid and antinuclear antibodies in patients with epilepsy or new-onset seizure disorders. Am J Med. 2000; 109: Chapman J, Rand JH, Brey RL, et al. Non-stroke neurological syndromes associated with antiphospholipid antibodies: evaluation of clinical and experimental studies. Lupus. 2003; 12: Sun KH, Liu WT, Tsai CY, Liao TS, Lin WM, Yu CL. Inhibition of astrocyte proliferation and binding to brain tissue of anticardiolipin antibodies purified from lupus serum. Ann Rheum Dis. 1992; 51: Chapman J, Cohen Armon M, Shoenfeld Y, Korczyn AD. Antiphospholipid antibodies permeabilize and depolarize brain synaptoneurosomes. Lupus. 1999; 8: Cuadrado MJ, Khamashta MA, Hughes GR. Migraine and stroke in young women. QJM. 2000; 93: Asherson RA, Khamashta MA, Ordi Ros J, et al. The "primary" antiphospholipid syndrome: major clinical and serological features. Medicine (Baltimore). 1989; 68:
9 9 Table 1: Clinical manifestations in the study population, patients with PAPS or SLE with APS (%). Clinical manifestations Entire APS population (n=284) Primary APS (n=159) SLE with APS (n=97) P Value Deep venous thrombosis NS Arterial thrombosis NS Recurrent pregnancy loss <0.03 TIA/CVA NS Myocardial infarction NS Epilepsy <0.03 Migraine NS Cardiac valve vegetations NS Cardiac valve thickening NS Overall cardiac valve abnormalities NS Livedo reticularis <0.005 Thrombocytopenia <0.005 Autoimmune hemolytic anemia <0.02
10 10 Table 2: Percentage of cardiac valves abnormalities in APS patients with and without CNS manifestations (epilepsy and migraine), A: the whole study population (n=284), B: patients with PAPS (n=159), C: patients with SLE and APS (n=97). With Without P Value With Without P Value A- Whole study population Epilepsy Epilepsy Migraine Migraine Cardiac valves vegetations < Valvular thickening and/or dysfunction NS Overall Cardiac valves abnormalities NS B- PAPS Cardiac valves vegetations < <0.04 Valvular thickening and/or dysfunction NS <0.01 Overall Cardiac valves abnormalities NS C- APS associated to SLE Cardiac valves vegetations NS NS Valvular thickening and/or dysfunction NS NS Overall Cardiac valves abnormalities NS NS
11 11 Table 3: Cardiac valves abnormalities (%) in APS patients with and without CVA/TIA, A: the whole study population (n=284), B: patients with PAPS (n=159), C: patients with SLE and APS (n=97). With Without P Value A- Whole study population CVA/TIA CVA/TIA Cardiac valves vegetations <0.04 Valvular thickening and/or dysfunction <0.01 Overall Cardiac valves abnormalities <0.001 B- PAPS Cardiac valves vegetations NS Valvular thickening and/or dysfunction Overall Cardiac valves abnormalities <0.02 C- APS associated to SLE Cardiac valves vegetations NS Valvular thickening and/or dysfunction NS Overall Cardiac valves abnormalities NS
Manifestation of Antiphospholipid Syndrome among Saudi patients :examining the applicability of sapporo Criteria
 Manifestation of Antiphospholipid Syndrome among Saudi patients :examining the applicability of sapporo Criteria Farjah H AlGahtani Associate professor,md,mph Leukemia,Lymphoma in adolescent,thromboembolic
Manifestation of Antiphospholipid Syndrome among Saudi patients :examining the applicability of sapporo Criteria Farjah H AlGahtani Associate professor,md,mph Leukemia,Lymphoma in adolescent,thromboembolic
Antiphospholipid Syndrome Handbook
 Antiphospholipid Syndrome Handbook Maria Laura Bertolaccini, Oier Ateka-Barrutia, and Munther A. Khamashta Antiphospholipid Syndrome Handbook Maria Laura Bertolaccini, MD, PhD Lupus Research Unit The Rayne
Antiphospholipid Syndrome Handbook Maria Laura Bertolaccini, Oier Ateka-Barrutia, and Munther A. Khamashta Antiphospholipid Syndrome Handbook Maria Laura Bertolaccini, MD, PhD Lupus Research Unit The Rayne
Livedo reticularis is a marker for predicting multi-system thrombosis in antiphospholipid syndrome
 Livedo reticularis is a marker for predicting multi-system thrombosis in antiphospholipid syndrome E. Toubi 1, I. Krause 2,3, A. Fraser 3, S. Lev 3, L. Stojanovich 4, J. Rovensky 5, M. Blank 2, Y. Shoenfeld
Livedo reticularis is a marker for predicting multi-system thrombosis in antiphospholipid syndrome E. Toubi 1, I. Krause 2,3, A. Fraser 3, S. Lev 3, L. Stojanovich 4, J. Rovensky 5, M. Blank 2, Y. Shoenfeld
Lupus anticoagulant and anticardiolipin antibodies in SLE with secondary Antiphospholipid Antibody Syndrome
 Turk J Hematol 2007; 24:69-74 Turkish Society of Hematology RESEARCH ARTICLE Lupus anticoagulant and anticardiolipin antibodies in SLE with secondary Antiphospholipid Antibody Syndrome Shveta Garg, Annamma
Turk J Hematol 2007; 24:69-74 Turkish Society of Hematology RESEARCH ARTICLE Lupus anticoagulant and anticardiolipin antibodies in SLE with secondary Antiphospholipid Antibody Syndrome Shveta Garg, Annamma
Sindrome da anticorpi antifosfolipidi: clinica e terapia. Vittorio Pengo Clinical Cardiology, Padova, Italy
 Sindrome da anticorpi antifosfolipidi: clinica e terapia Vittorio Pengo Clinical Cardiology, Padova, Italy Revised Classification Criteria for the Antiphospholipid Syndrome J Thromb Haemost 2006;4:295-306
Sindrome da anticorpi antifosfolipidi: clinica e terapia Vittorio Pengo Clinical Cardiology, Padova, Italy Revised Classification Criteria for the Antiphospholipid Syndrome J Thromb Haemost 2006;4:295-306
Antiphospholipid Syndrome
 Antiphospholipid Syndrome EliA Cardiolipin and EliA β2-glycoprotein I Fully Automated Testing for Antiphospholipid Syndrome (APS) Testing for APS according to classification criteria determination of anti-β2-glycoprotein
Antiphospholipid Syndrome EliA Cardiolipin and EliA β2-glycoprotein I Fully Automated Testing for Antiphospholipid Syndrome (APS) Testing for APS according to classification criteria determination of anti-β2-glycoprotein
Anti β 2. -Glycoprotein I and Antiphosphatidylserine Antibodies Are Predictors of Arterial Thrombosis in Patients With Antiphospholipid Syndrome
 Coagulation and Transfusion Medicine / PREDICTIVE VALUE OF ANTIPHOSPHOLIPID ANTIBODIES Anti β -Glycoprotein I and Antiphosphatidylserine Antibodies Are Predictors of Arterial Thrombosis in Patients With
Coagulation and Transfusion Medicine / PREDICTIVE VALUE OF ANTIPHOSPHOLIPID ANTIBODIES Anti β -Glycoprotein I and Antiphosphatidylserine Antibodies Are Predictors of Arterial Thrombosis in Patients With
Association between non-thrombotic neurological and cardiac manifestations in patients with antiphospholipid syndrome
 Association between non-thrombotic neurological and cardiac manifestations in patients with antiphospholipid syndrome L. Stojanovich 1, M. Kontic 2, D. Smiljanic 3, A. Djokovic 1, B. Stamenkovic 4 D. Marisavljevic
Association between non-thrombotic neurological and cardiac manifestations in patients with antiphospholipid syndrome L. Stojanovich 1, M. Kontic 2, D. Smiljanic 3, A. Djokovic 1, B. Stamenkovic 4 D. Marisavljevic
Disclosures. Sneddon Syndrome: Untangling the Web. Case Presentation. MRI head w/ and w/o contrast. Further Workup. Further Workup 10/26/2017
 Sneddon Syndrome: Untangling the Web Sadhana Murali, MD, PGY-4 University of Wisconsin-Madison WNS Conference October 27-28, 2017 Disclosures I have no relevant financial relationships with any commercial
Sneddon Syndrome: Untangling the Web Sadhana Murali, MD, PGY-4 University of Wisconsin-Madison WNS Conference October 27-28, 2017 Disclosures I have no relevant financial relationships with any commercial
Neurological involvement in antiphospholipid antibodies syndrome (APS)
 European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences Neurological involvement in antiphospholipid antibodies syndrome (APS) A. AMOROSO, A.P. MITTERHOFER, G.M. FERRI, S. GALLUZZO, M. VADACCA, A. AFELTRA
European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences Neurological involvement in antiphospholipid antibodies syndrome (APS) A. AMOROSO, A.P. MITTERHOFER, G.M. FERRI, S. GALLUZZO, M. VADACCA, A. AFELTRA
Situaciones estresantes en el lupus
 Situaciones estresantes en el lupus Munther A Khamashta MD FRCP PhD Director: Lupus Research Unit Barcelona, Noviembre 2008 What is Lupus? Lupus is a neurological disease and sometimes affects other organs
Situaciones estresantes en el lupus Munther A Khamashta MD FRCP PhD Director: Lupus Research Unit Barcelona, Noviembre 2008 What is Lupus? Lupus is a neurological disease and sometimes affects other organs
Prevalence of antiphospholipid auto antibodies in patients with thrombosis
 EUROPEAN ACADEMIC RESEARCH Vol. IV, Issue 6/ September 2016 ISSN 2286-4822 www.euacademic.org Impact Factor: 3.4546 (UIF) DRJI Value: 5.9 (B+) Prevalence of antiphospholipid auto antibodies in patients
EUROPEAN ACADEMIC RESEARCH Vol. IV, Issue 6/ September 2016 ISSN 2286-4822 www.euacademic.org Impact Factor: 3.4546 (UIF) DRJI Value: 5.9 (B+) Prevalence of antiphospholipid auto antibodies in patients
Mortality in the Catastrophic Antiphospholipid Syndrome
 ARTHRITIS & RHEUMATISM Vol. 54, No. 8, August 2006, pp 2568 2576 DOI 10.1002/art.22018 2006, American College of Rheumatology Mortality in the Catastrophic Antiphospholipid Syndrome Causes of Death and
ARTHRITIS & RHEUMATISM Vol. 54, No. 8, August 2006, pp 2568 2576 DOI 10.1002/art.22018 2006, American College of Rheumatology Mortality in the Catastrophic Antiphospholipid Syndrome Causes of Death and
Central nervous system involvement in the antiphospholipid (Hughes) syndrome
 Rheumatology 2003;42:200 213 doi:10.1093/rheumatology/keg080, available online at www.rheumatology.oupjournals.org Review Central nervous system involvement in the antiphospholipid (Hughes) syndrome G.
Rheumatology 2003;42:200 213 doi:10.1093/rheumatology/keg080, available online at www.rheumatology.oupjournals.org Review Central nervous system involvement in the antiphospholipid (Hughes) syndrome G.
Neuropsychiatric SLE (NPSLE) Dr. MTL NYO FCP(SA), Cert Rheum (Phys) Division of Rheumatology Department of Internal Medicine DGMAH / SMU
 Neuropsychiatric SLE (NPSLE) Dr. MTL NYO FCP(SA), Cert Rheum (Phys) Division of Rheumatology Department of Internal Medicine DGMAH / SMU NPSLE represents a diagnostic and therapeutic challenge Wide range
Neuropsychiatric SLE (NPSLE) Dr. MTL NYO FCP(SA), Cert Rheum (Phys) Division of Rheumatology Department of Internal Medicine DGMAH / SMU NPSLE represents a diagnostic and therapeutic challenge Wide range
Case Report Lower Limb Ischemia: Aortoiliac Thrombosis Related to Antiphospholipid Syndrome (APS) Case Report and Review of the Literature
 Case Reports in Surgery Volume 2013, Article ID 536971, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2013/536971 Case Report Lower Limb Ischemia: Aortoiliac Thrombosis Related to Antiphospholipid Syndrome (APS) Case
Case Reports in Surgery Volume 2013, Article ID 536971, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2013/536971 Case Report Lower Limb Ischemia: Aortoiliac Thrombosis Related to Antiphospholipid Syndrome (APS) Case
Anticardiolipin Antibodies in Patients With Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
 CM&R Rapid Release. Published online ahead of print February 26, 2009 as doi:10.3121/cmr.2008.828 Original Research Anticardiolipin Antibodies in Patients With Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus José María Calvo-Romero,
CM&R Rapid Release. Published online ahead of print February 26, 2009 as doi:10.3121/cmr.2008.828 Original Research Anticardiolipin Antibodies in Patients With Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus José María Calvo-Romero,
The Antiphospholipid Syndrome
 The Antiphospholipid Syndrome 1 / 6 2 / 6 3 / 6 The Antiphospholipid Syndrome Antiphospholipid antibody syndrome (commonly called antiphospholipid syndrome or APS) is an autoimmune disease present mostly
The Antiphospholipid Syndrome 1 / 6 2 / 6 3 / 6 The Antiphospholipid Syndrome Antiphospholipid antibody syndrome (commonly called antiphospholipid syndrome or APS) is an autoimmune disease present mostly
Systemic lupus erythematosus in 50 year olds
 Postgrad Med J (1992) 68, 440-444 The Fellowship of Postgraduate Medicine, 1992 Systemic lupus erythematosus in 50 year olds I. Domenech, 0. Aydintug, R. Cervera, M. Khamashta, A. Jedryka-Goral, J.L. Vianna
Postgrad Med J (1992) 68, 440-444 The Fellowship of Postgraduate Medicine, 1992 Systemic lupus erythematosus in 50 year olds I. Domenech, 0. Aydintug, R. Cervera, M. Khamashta, A. Jedryka-Goral, J.L. Vianna
T he antiphospholipid syndrome (APS) is a thrombophilic
 1639 EXTENDED REPORT ntiphospholipid antibody tests: spreading the net M L ertolaccini, S Gomez, J F P Pareja, Theodoridou, G Sanna, G R V Hughes, M Khamashta... See end of article for authors affiliations...
1639 EXTENDED REPORT ntiphospholipid antibody tests: spreading the net M L ertolaccini, S Gomez, J F P Pareja, Theodoridou, G Sanna, G R V Hughes, M Khamashta... See end of article for authors affiliations...
Antiphospholipid Syndrome Handbook
 Antiphospholipid Syndrome Handbook Maria Laura Bertolaccini, Oier Ateka-Barrutia, and Munther A. Khamashta Antiphospholipid Syndrome Handbook Maria Laura Bertolaccini, MD, PhD Lupus Research Unit The Rayne
Antiphospholipid Syndrome Handbook Maria Laura Bertolaccini, Oier Ateka-Barrutia, and Munther A. Khamashta Antiphospholipid Syndrome Handbook Maria Laura Bertolaccini, MD, PhD Lupus Research Unit The Rayne
ORIGINAL PAPERS. Marek Cieśla 1, B D, Ewa Wypasek 1, 2, B D 1, 2, A, E, F. Abstract
 ORIGINAL PAPERS Adv Clin Exp Med 2014, 23, 5, 729 733 ISSN 1899 5276 Copyright by Wroclaw Medical University Marek Cieśla 1, B D, Ewa Wypasek 1, 2, B D 1, 2, A, E, F, Anetta Undas IgA Antiphospholipid
ORIGINAL PAPERS Adv Clin Exp Med 2014, 23, 5, 729 733 ISSN 1899 5276 Copyright by Wroclaw Medical University Marek Cieśla 1, B D, Ewa Wypasek 1, 2, B D 1, 2, A, E, F, Anetta Undas IgA Antiphospholipid
DISCLOSURE. Echocardiography in Systemic Diseases: Questions. Relevant Financial Relationship(s) None. Off Label Usage None 5/7/2018
 Echocardiography in Systemic Diseases: Questions Sunil Mankad, MD, FACC, FCCP, FASE Associate Professor of Medicine Mayo Clinic College of Medicine Director, Transesophageal Echocardiography Associate
Echocardiography in Systemic Diseases: Questions Sunil Mankad, MD, FACC, FCCP, FASE Associate Professor of Medicine Mayo Clinic College of Medicine Director, Transesophageal Echocardiography Associate
Thrombophilia. Dr. A Sarrafnejad PhD Dep. Immunology School of public health TUMS
 Autoimmune Thrombophilia Dr. A Sarrafnejad PhD Dep. Immunology School of public health TUMS Saraf@sina.tums.ac.ir Acquired Thrombophilia HIT PNH Cyckle cell Anemia Myeloproliferative lf Diseases Thrombocytosis
Autoimmune Thrombophilia Dr. A Sarrafnejad PhD Dep. Immunology School of public health TUMS Saraf@sina.tums.ac.ir Acquired Thrombophilia HIT PNH Cyckle cell Anemia Myeloproliferative lf Diseases Thrombocytosis
Name and Intended Use
 Name and Intended Use Anti-Prothrombin IgG/IgM is an indirect solid phase enzyme immunoassay (ELISA) for the quantitative measurement of IgG and IgM class autoantibodies against Prothrombin in human serum
Name and Intended Use Anti-Prothrombin IgG/IgM is an indirect solid phase enzyme immunoassay (ELISA) for the quantitative measurement of IgG and IgM class autoantibodies against Prothrombin in human serum
Key words: antiphospholipid syndrome, trombosis, pathogenesis
 26. XI,. 4/2011,.,..,..,., -..,,. 2GPI. -,.,,., -,, -, -,,,,, IL-1, IL-2, IL-6, IL-8, IL-12, IL-10, TNF, INF-. :,, N. Stoilov, R. Rashkov and R. Stoilov. ANTIPHOSPHOLIPID SYNDROME HISTORICAL DATA, ETI-
26. XI,. 4/2011,.,..,..,., -..,,. 2GPI. -,.,,., -,, -, -,,,,, IL-1, IL-2, IL-6, IL-8, IL-12, IL-10, TNF, INF-. :,, N. Stoilov, R. Rashkov and R. Stoilov. ANTIPHOSPHOLIPID SYNDROME HISTORICAL DATA, ETI-
Thrombotic Risk Factors In Primary Antiphospholipid Syndrome A 5-Year Prospective Study
 Thrombotic Risk Factors In Primary Antiphospholipid Syndrome A 5-Year Prospective Study Maurizio Turiel, MD; Piercarlo Sarzi-Puttini, MD; Rossana Peretti, MD; Edoardo Rossi, MD; Fabiola Atzeni, MD; Wendy
Thrombotic Risk Factors In Primary Antiphospholipid Syndrome A 5-Year Prospective Study Maurizio Turiel, MD; Piercarlo Sarzi-Puttini, MD; Rossana Peretti, MD; Edoardo Rossi, MD; Fabiola Atzeni, MD; Wendy
AMPLIADO SÍNDROME ANTIFOSFOLÍPIDO SÍNDROME DE SJÖGREN María José Cuadrado Lozano Clínica Universidad de Navarra-Madrid
 AMPLIADO SÍNDROME ANTIFOSFOLÍPIDO SÍNDROME DE SJÖGREN María José Cuadrado Lozano Clínica Universidad de Navarra-Madrid PLASMABLAST PROLIFERATION IS ASSOCIATED WITH TLR7 POLYMORPHISMS AND UPREGULATION OF
AMPLIADO SÍNDROME ANTIFOSFOLÍPIDO SÍNDROME DE SJÖGREN María José Cuadrado Lozano Clínica Universidad de Navarra-Madrid PLASMABLAST PROLIFERATION IS ASSOCIATED WITH TLR7 POLYMORPHISMS AND UPREGULATION OF
Daniel Egan, MD April 13, 2012
 Daniel Egan, MD April 13, 2012 Aug 2006 (at age 15): Acute unprovoked DVT in left common femoral vein Factor V Leiden heterozygous Positive lupus inhibitor Lovenox BID 2 weeks later: increased clot burden,
Daniel Egan, MD April 13, 2012 Aug 2006 (at age 15): Acute unprovoked DVT in left common femoral vein Factor V Leiden heterozygous Positive lupus inhibitor Lovenox BID 2 weeks later: increased clot burden,
Are there still any valid indications for thrombophilia screening in DVT?
 Carotid artery stenosis and risk of stroke Are there still any valid indications for thrombophilia screening in DVT? Armando Mansilha MD, PhD, FEBVS Faculty of Medicine of University of Porto Munich, 2016
Carotid artery stenosis and risk of stroke Are there still any valid indications for thrombophilia screening in DVT? Armando Mansilha MD, PhD, FEBVS Faculty of Medicine of University of Porto Munich, 2016
Images in Cardiovascular Medicine
 Images in Cardiovascular Medicine Numerous Small Vegetations Revealing Libman-Sacks Endocarditis in Catastrophic Antiphospholipid Syndrome Hideo Yamamoto, MD; Tamaki Iwade, MD; Ryuji Nakano, MD; Masahiro
Images in Cardiovascular Medicine Numerous Small Vegetations Revealing Libman-Sacks Endocarditis in Catastrophic Antiphospholipid Syndrome Hideo Yamamoto, MD; Tamaki Iwade, MD; Ryuji Nakano, MD; Masahiro
Case Report Antiphospholipid Syndrome: Multiple Manifestations in a Single Patient A High Suspicion Is Still Needed
 Hindawi Case Reports in Medicine Volume 2017, Article ID 5797041, 4 pages https://doi.org/10.1155/2017/5797041 Case Report Antiphospholipid Syndrome: Multiple Manifestations in a Single Patient A High
Hindawi Case Reports in Medicine Volume 2017, Article ID 5797041, 4 pages https://doi.org/10.1155/2017/5797041 Case Report Antiphospholipid Syndrome: Multiple Manifestations in a Single Patient A High
Antiphospholipid Syndrome ( APS)
 Antiphospholipid Syndrome ( APS) Edward John Walter Bowie, MD Mayo Medical School the first to identify APS as an acquired thrombophilia Graham Robert Vivian Hughes MD FRCP Unit Rayne Institute St Thomas
Antiphospholipid Syndrome ( APS) Edward John Walter Bowie, MD Mayo Medical School the first to identify APS as an acquired thrombophilia Graham Robert Vivian Hughes MD FRCP Unit Rayne Institute St Thomas
Review Article Rheumatic Fever Associated with Antiphospholipid Syndrome: Systematic Review
 Immunology Research, Article ID 614591, 6 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2014/614591 Review Article Rheumatic Fever Associated with Antiphospholipid Syndrome: Systematic Review Felipe da Silva 1 and Jozélio
Immunology Research, Article ID 614591, 6 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2014/614591 Review Article Rheumatic Fever Associated with Antiphospholipid Syndrome: Systematic Review Felipe da Silva 1 and Jozélio
Efficacy and Safety of Belimumab in the treatment of Systemic Lupus Erythematosus: a Prospective Multicenter Study.
 1. Title Efficacy and Safety of Belimumab in the treatment of Systemic Lupus Erythematosus: a Prospective Multicenter Study. 2. Background Systemic Lupus Erythematosus (SLE) is a chronic, autoimmune and
1. Title Efficacy and Safety of Belimumab in the treatment of Systemic Lupus Erythematosus: a Prospective Multicenter Study. 2. Background Systemic Lupus Erythematosus (SLE) is a chronic, autoimmune and
IMMUNOWELL CARDIOLIPIN ANTIBODY (IGM) TEST
 IMMUNOWELL CARDIOLIPIN ANTIBODY (IGM) TEST Product No. 3100 For In Vitro Diagnostic Use SEE CALIBRATION VALUES, TABLE 2, PAGE 3 INTENDED USE The ImmunoWELL Cardiolipin Antibody (IgM) Test is an enzyme
IMMUNOWELL CARDIOLIPIN ANTIBODY (IGM) TEST Product No. 3100 For In Vitro Diagnostic Use SEE CALIBRATION VALUES, TABLE 2, PAGE 3 INTENDED USE The ImmunoWELL Cardiolipin Antibody (IgM) Test is an enzyme
Case Report Embolic Stroke as the Initial Manifestation of Systemic Lupus Erythematosus
 Case Reports in Rheumatology Volume 2015, Article ID 373201, 5 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2015/373201 Case Report Embolic Stroke as the Initial Manifestation of Systemic Lupus Erythematosus Reshma
Case Reports in Rheumatology Volume 2015, Article ID 373201, 5 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2015/373201 Case Report Embolic Stroke as the Initial Manifestation of Systemic Lupus Erythematosus Reshma
Assessment of Cardiac Structure and Left Atrial Appendage Functions in Primary Antiphospholipid Syndrome A Transesophageal Echocardiographic Study
 Assessment of Cardiac Structure and Left Atrial Appendage Functions in Primary Antiphospholipid Syndrome A Transesophageal Echocardiographic Study Dogan Erdogan, MD; M. Taner Goren, MD; Reyhan Diz-Kucukkaya,
Assessment of Cardiac Structure and Left Atrial Appendage Functions in Primary Antiphospholipid Syndrome A Transesophageal Echocardiographic Study Dogan Erdogan, MD; M. Taner Goren, MD; Reyhan Diz-Kucukkaya,
Systemic Lupus Erythematosus among Jordanians: A Single Rheumatology Unit Experience
 Systemic Lupus Erythematosus among Jordanians: A Single Rheumatology Unit Experience Ala M. AlHeresh MD* ABSTRACT Objectives: To study the characteristics of Systemic Lupus Erythematosus in Jordan and
Systemic Lupus Erythematosus among Jordanians: A Single Rheumatology Unit Experience Ala M. AlHeresh MD* ABSTRACT Objectives: To study the characteristics of Systemic Lupus Erythematosus in Jordan and
A Case of Massive Pulmonary Embolism in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus without Antiphospholipid Antibody
 Journal of Rheumatic Diseases Vol. 22, No. 2, April, 2015 http://dx.doi.org/10.4078/jrd.2015.22.2.106 Case Report A Case of Massive Pulmonary Embolism in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus without Antiphospholipid
Journal of Rheumatic Diseases Vol. 22, No. 2, April, 2015 http://dx.doi.org/10.4078/jrd.2015.22.2.106 Case Report A Case of Massive Pulmonary Embolism in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus without Antiphospholipid
Lupus as a risk factor for cardiovascular disease
 Lupus as a risk factor for cardiovascular disease SØREN JACOBSEN Department Rheumatology, Rigshospitalet Søren Jacobsen Main sponsors: Gigtforeningen Novo Nordisk Fonden Rigshospitalet Disclaimer: Novo
Lupus as a risk factor for cardiovascular disease SØREN JACOBSEN Department Rheumatology, Rigshospitalet Søren Jacobsen Main sponsors: Gigtforeningen Novo Nordisk Fonden Rigshospitalet Disclaimer: Novo
Clinical and immunological characteristics of antiphospholipid syndrome in an Asian population: a retrospective study
 Asian Pacific Journal of Allergy and Immunology ORIGINAL ARTICLE Clinical and immunological characteristics of antiphospholipid syndrome in an Asian population: a retrospective study Kanon Jatuworapruk,
Asian Pacific Journal of Allergy and Immunology ORIGINAL ARTICLE Clinical and immunological characteristics of antiphospholipid syndrome in an Asian population: a retrospective study Kanon Jatuworapruk,
SYSTEMIC LUPUS ERYTHEMATOSUS: CURRENT CONCEPTS AND CLINICAL PEARLS. Dr Sheila Vasoo Consultant Division of Rheumatology NUHS
 SYSTEMIC LUPUS ERYTHEMATOSUS: CURRENT CONCEPTS AND CLINICAL PEARLS Dr Sheila Vasoo Consultant Division of Rheumatology NUHS Listen to the Patient Concepts Diagnosis Immunopathogenesis Clinical Pearls Disease
SYSTEMIC LUPUS ERYTHEMATOSUS: CURRENT CONCEPTS AND CLINICAL PEARLS Dr Sheila Vasoo Consultant Division of Rheumatology NUHS Listen to the Patient Concepts Diagnosis Immunopathogenesis Clinical Pearls Disease
The adjunctive role of antiphospholipid antibodies in systemic lupus erythematosus cardiac involvement
 The adjunctive role of antiphospholipid antibodies in systemic lupus erythematosus cardiac involvement A. Amoroso 1, F. Cacciapaglia 2, S. De Castro 3, A. Battagliese 3, G. Coppolino 2, S. Galluzzo 2,
The adjunctive role of antiphospholipid antibodies in systemic lupus erythematosus cardiac involvement A. Amoroso 1, F. Cacciapaglia 2, S. De Castro 3, A. Battagliese 3, G. Coppolino 2, S. Galluzzo 2,
T he general consensus is that autoimmune
 2 EDITORIAL Antiphospholipid syndrome... Infectious origin of the antiphospholipid syndrome* Y Shoenfeld, M Blank, R Cervera, J Font, E Raschi, P-L Meroni... From a systemic disease towards the infectious
2 EDITORIAL Antiphospholipid syndrome... Infectious origin of the antiphospholipid syndrome* Y Shoenfeld, M Blank, R Cervera, J Font, E Raschi, P-L Meroni... From a systemic disease towards the infectious
LUPUS CAN DO EVERYTHING, BUT NOT EVERYTHING IS LUPUS LUPUS 101 SLE SUBSETS AUTOIMMUNE DISEASE 11/4/2013 HOWARD HAUPTMAN, MD IDIOPATHIC DISCOID LUPUS
 LUPUS 101 LUPUS CAN DO EVERYTHING, BUT NOT EVERYTHING IS LUPUS HOWARD HAUPTMAN, MD IDIOPATHIC DISCOID LUPUS SLE SUBSETS SUBACUTE CUTANEOUS LUPUS DRUG INDUCED LUPUS NEONATAL LUPUS LATE ONSET LUPUS ANTI-PHOSPHOLIPID
LUPUS 101 LUPUS CAN DO EVERYTHING, BUT NOT EVERYTHING IS LUPUS HOWARD HAUPTMAN, MD IDIOPATHIC DISCOID LUPUS SLE SUBSETS SUBACUTE CUTANEOUS LUPUS DRUG INDUCED LUPUS NEONATAL LUPUS LATE ONSET LUPUS ANTI-PHOSPHOLIPID
Antiphospholipid antibodies are a heterogeneous family
 Seasonal Distribution of Antiphospholipid Antibodies Thanh-Ha Luong, MD; Jacob H. Rand, MD; Xiao-Xuan Wu, MD; James H. Godbold, PhD; Mayra Gascon-Lema, MS; Stanley Tuhrim, MD Background and Purpose The
Seasonal Distribution of Antiphospholipid Antibodies Thanh-Ha Luong, MD; Jacob H. Rand, MD; Xiao-Xuan Wu, MD; James H. Godbold, PhD; Mayra Gascon-Lema, MS; Stanley Tuhrim, MD Background and Purpose The
Definition Chronic autoimmune disease The body s immune system starts attacking itself Can affect most organs and tissues in the body Brain, lungs, he
 LIVING WITH SYSTEMIC LUPUS ERYTHEMATOSUS Stacy Kennedy, M.D.,M.B.A. Rowan Diagnostic Clinic Salisbury, N.C. May 11, 2013 Agenda What is lupus Who is affected Causes of lupus Symptoms and organ involvement
LIVING WITH SYSTEMIC LUPUS ERYTHEMATOSUS Stacy Kennedy, M.D.,M.B.A. Rowan Diagnostic Clinic Salisbury, N.C. May 11, 2013 Agenda What is lupus Who is affected Causes of lupus Symptoms and organ involvement
Supplemental Figures and Legends
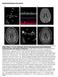 Supplemental Figures and Legends Online Figure 1. 18 year old female with SLE and acute homonymous hemianopsia, confusional state, and cognitive dysfunction. A. This TEE four chamber view demonstrates
Supplemental Figures and Legends Online Figure 1. 18 year old female with SLE and acute homonymous hemianopsia, confusional state, and cognitive dysfunction. A. This TEE four chamber view demonstrates
Summary of the 11th International Congress on Antiphospholipid Antibodies, Sydney, Australia, November 2004
 Journal of Reproductive Immunology 66 (2005) 85 90 Meeting report Summary of the 11th International Congress on Antiphospholipid Antibodies, Sydney, Australia, November 2004 The 11th International Congress
Journal of Reproductive Immunology 66 (2005) 85 90 Meeting report Summary of the 11th International Congress on Antiphospholipid Antibodies, Sydney, Australia, November 2004 The 11th International Congress
Patient with Musculo-skeletal Complaints - Summary
 Patient with Musculo-skeletal Complaints - Summary 1. Soft Tissue Rheumatism or Arthritis 2. Arthritis Monoarticular Polyarticular - :- (Asymmetrical) (Symetrical) :- -Crystals, Gout - Infective acute
Patient with Musculo-skeletal Complaints - Summary 1. Soft Tissue Rheumatism or Arthritis 2. Arthritis Monoarticular Polyarticular - :- (Asymmetrical) (Symetrical) :- -Crystals, Gout - Infective acute
APPENDIX A NORTH AMERICAN SYMPTOMATIC CAROTID ENDARTERECTOMY TRIAL
 APPENDIX A Primary Findings From Selected Recent National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke-Sponsored Clinical Trials That Have shaped Modern Stroke Prevention Philip B. Gorelick 178 NORTH
APPENDIX A Primary Findings From Selected Recent National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke-Sponsored Clinical Trials That Have shaped Modern Stroke Prevention Philip B. Gorelick 178 NORTH
9/25/2013 SYSTEMIC LUPUS ERYTHEMATOSUS (SLE)
 SYSTEMIC LUPUS ERYTHEMATOSUS (SLE) 1 Other Types of Lupus Discoid Lupus Erythematosus Lupus Pernio --- Sarcoidosis Lupus Vulgaris --- Tuberculosis of the face Manifestations of SLE Fever Rashes Arthritis
SYSTEMIC LUPUS ERYTHEMATOSUS (SLE) 1 Other Types of Lupus Discoid Lupus Erythematosus Lupus Pernio --- Sarcoidosis Lupus Vulgaris --- Tuberculosis of the face Manifestations of SLE Fever Rashes Arthritis
AN INTERESTING CASE OF RESPIRATORY DISTRESS. Dr.V.Akila Devi DNB PG Southern Railway Headquarters Hospital Chennai
 AN INTERESTING CASE OF RESPIRATORY DISTRESS Dr.V.Akila Devi DNB PG Southern Railway Headquarters Hospital Chennai 11 month old female infant 1 st born to parents of NC marriage referred from Kolkatta H/O:
AN INTERESTING CASE OF RESPIRATORY DISTRESS Dr.V.Akila Devi DNB PG Southern Railway Headquarters Hospital Chennai 11 month old female infant 1 st born to parents of NC marriage referred from Kolkatta H/O:
Antiphospholipid Antibody Syndrome: Management Issues for the Hematologist
 Antiphospholipid Antibody Syndrome: Management Issues for the Hematologist Wisconsin Institute of Discovery Karen Rossi/Bristol-Myers Squibb Morey A. Blinder, MD Washington University, St. Louis, MO March
Antiphospholipid Antibody Syndrome: Management Issues for the Hematologist Wisconsin Institute of Discovery Karen Rossi/Bristol-Myers Squibb Morey A. Blinder, MD Washington University, St. Louis, MO March
Central Nervous System (CNS) and Lupus: Learn from the Experts. Betty Diamond, M.D. Feinstein Institute for Medical Research
 Central Nervous System (CNS) and Lupus: Learn from the Experts Betty Diamond, M.D. Feinstein Institute for Medical Research Stages in SLE Pathogenesis Crow MK, Arth Res & Tx. 2009 ACR Criteria for the
Central Nervous System (CNS) and Lupus: Learn from the Experts Betty Diamond, M.D. Feinstein Institute for Medical Research Stages in SLE Pathogenesis Crow MK, Arth Res & Tx. 2009 ACR Criteria for the
DRG Anti-Phospholipid Screen IgG/IgM ELISA (EIA-3591) USA: RUO Revised 1 Aug rm (Vers. 5.1)
 This kit is intended for Research Use Only. Not for use in diagnostic procedures. Please use only the valid version of the package insert provided with the kit. 1. NAME AND INTENDED USE The Anti-Phospholipid
This kit is intended for Research Use Only. Not for use in diagnostic procedures. Please use only the valid version of the package insert provided with the kit. 1. NAME AND INTENDED USE The Anti-Phospholipid
THE antiphospholipid-antibody syndrome is a
 Vol. 332. 15 MANAGEMENT OF THROMBOSIS IN THE ANTIPHOSPHOLIPID-ANTIBODY SYNDROME 993 THE MANAGEMENT OF THROMBOSIS IN THE ANTIPHOSPHOLIPID-ANTIBODY SYNDROME MUNTHER A. KHAMASHTA, M.D., MARIA JOSE CUADRADO,
Vol. 332. 15 MANAGEMENT OF THROMBOSIS IN THE ANTIPHOSPHOLIPID-ANTIBODY SYNDROME 993 THE MANAGEMENT OF THROMBOSIS IN THE ANTIPHOSPHOLIPID-ANTIBODY SYNDROME MUNTHER A. KHAMASHTA, M.D., MARIA JOSE CUADRADO,
CEREBRO VASCULAR ACCIDENTS
 CEREBRO VASCULAR S MICHAEL OPONG-KUSI, DO MBA MORTON CLINIC, TULSA, OK, USA 8/9/2012 1 Cerebrovascular Accident Third Leading cause of deaths (USA) 750,000 strokes in USA per year. 150,000 deaths in USA
CEREBRO VASCULAR S MICHAEL OPONG-KUSI, DO MBA MORTON CLINIC, TULSA, OK, USA 8/9/2012 1 Cerebrovascular Accident Third Leading cause of deaths (USA) 750,000 strokes in USA per year. 150,000 deaths in USA
UNDERSTANDING SYSTEMIC LUPUS ERYTHEMATOSUS
 UNDERSTANDING SYSTEMIC LUPUS ERYTHEMATOSUS Stacy Kennedy, M.D.,M.B.A. October 20, 2012 Agenda What is lupus Who is affected Causes of lupus Symptoms and organ involvement Diagnosis Treatment Pregnancy
UNDERSTANDING SYSTEMIC LUPUS ERYTHEMATOSUS Stacy Kennedy, M.D.,M.B.A. October 20, 2012 Agenda What is lupus Who is affected Causes of lupus Symptoms and organ involvement Diagnosis Treatment Pregnancy
å ORIGINAL ARTICLE å Distribution and Clinical Significance of Lupus Anticoagulant and Anticardiolipin Antibody in 349 Patients with
 å ORIGINAL ARTICLE å Distribution and Clinical Significance of Lupus Anticoagulant and Anticardiolipin Antibody in 349 Patients with Systemic Lupus Erythematosus Chiho Ninomiya, Osamu Taniguchi, Toshihiko
å ORIGINAL ARTICLE å Distribution and Clinical Significance of Lupus Anticoagulant and Anticardiolipin Antibody in 349 Patients with Systemic Lupus Erythematosus Chiho Ninomiya, Osamu Taniguchi, Toshihiko
The New England Journal of Medicine AN ECHOCARDIOGRAPHIC STUDY OF VALVULAR HEART DISEASE ASSOCIATED WITH SYSTEMIC LUPUS ERYTHEMATOSUS
 AN ECHOCARDIOGRAPHIC STUDY OF HEART ASSOCIATED WITH SYSTEMIC LUPUS ERYTHEMATOSUS CARLOS A. ROLDAN, M.D., BRUCE K. SHIVELY, M.D., AND MICHAEL H. CRAWFORD, M.D. ABSTRACT Background Valvular heart disease
AN ECHOCARDIOGRAPHIC STUDY OF HEART ASSOCIATED WITH SYSTEMIC LUPUS ERYTHEMATOSUS CARLOS A. ROLDAN, M.D., BRUCE K. SHIVELY, M.D., AND MICHAEL H. CRAWFORD, M.D. ABSTRACT Background Valvular heart disease
Complete heart block and severe aortic stenosis in a patient with Rheumatoid
 Complete heart block and severe aortic stenosis in a patient with Rheumatoid Arthtritis: A case report. Ioannis Moyssakis M.D, FESC, FACC 1 Nikolaos Lionakis,M.D 1 Ioannis Vlahodimitris,M.D 1 Vassilios
Complete heart block and severe aortic stenosis in a patient with Rheumatoid Arthtritis: A case report. Ioannis Moyssakis M.D, FESC, FACC 1 Nikolaos Lionakis,M.D 1 Ioannis Vlahodimitris,M.D 1 Vassilios
Vague Neurological Conditions
 Vague Neurological Conditions Dr. John Lefebre, MD, FRCPC Chief Regional Medical Director Europe, India, South Africa, Middle East and Turkey Canada 2014 2 3 4 Agenda Dr. John Lefebre, M.D., FRCPC 1. TIA
Vague Neurological Conditions Dr. John Lefebre, MD, FRCPC Chief Regional Medical Director Europe, India, South Africa, Middle East and Turkey Canada 2014 2 3 4 Agenda Dr. John Lefebre, M.D., FRCPC 1. TIA
ANTIPHOSPHOLIPID ANTIBODIES IN 57 CHILDREN AND ADOLESCENTS WITH SYSTEMIC LUPUS ERYTHEMATOSUS
 REV. HOSP. CLÍN. FAC. MED. S. PAULO 58(3):157-162, 2003 ANTIPHOSPHOLIPID ANTIBODIES IN 57 CHILDREN AND ADOLESCENTS WITH SYSTEMIC LUPUS ERYTHEMATOSUS Lúcia Maria de Arruda Campos, Maria Helena B. Kiss,
REV. HOSP. CLÍN. FAC. MED. S. PAULO 58(3):157-162, 2003 ANTIPHOSPHOLIPID ANTIBODIES IN 57 CHILDREN AND ADOLESCENTS WITH SYSTEMIC LUPUS ERYTHEMATOSUS Lúcia Maria de Arruda Campos, Maria Helena B. Kiss,
Clinical and immunological characteristics of Polish patients with systemic lupus erythematosus
 Original papers Clinical and immunological characteristics of Polish patients with systemic lupus erythematosus Martyna Tomczyk-Socha 1, B E, Hanna Sikorska-Szaflik 2, B E, Marek Frankowski 3, B D, Karolina
Original papers Clinical and immunological characteristics of Polish patients with systemic lupus erythematosus Martyna Tomczyk-Socha 1, B E, Hanna Sikorska-Szaflik 2, B E, Marek Frankowski 3, B D, Karolina
ANTIPHOSPHOLIPID (HUGHES) SYNDROME
 1 ANTIPHOSPHOLIPID (HUGHES) SYNDROME INTRODUCTION In 1983, Hughes et al describe a syndrome characterized by arterial and venous thrombosis, recurrent foetal wastage, and thrombocytopenia, which were seen
1 ANTIPHOSPHOLIPID (HUGHES) SYNDROME INTRODUCTION In 1983, Hughes et al describe a syndrome characterized by arterial and venous thrombosis, recurrent foetal wastage, and thrombocytopenia, which were seen
February 2016, Volume: 8, Issue: 2, Pages: , DOI:
 Electronic Physician (ISSN: 2008-5842) http://www.ephysician.ir February 2016, Volume: 8, Issue: 2, Pages: 1874-1879, DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.19082/1874 Pulmonary embolism in an adolescent girl with
Electronic Physician (ISSN: 2008-5842) http://www.ephysician.ir February 2016, Volume: 8, Issue: 2, Pages: 1874-1879, DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.19082/1874 Pulmonary embolism in an adolescent girl with
Current View of the Treatment of Antiphospholipid Syndrome
 GROUPE HOSPITALIER PITIE SALPETRIERE Current View of the Treatment of Antiphospholipid Syndrome Pr Zahir AMOURA Department of Internal Medicine French National Reference center for SLE and APS Hôpital
GROUPE HOSPITALIER PITIE SALPETRIERE Current View of the Treatment of Antiphospholipid Syndrome Pr Zahir AMOURA Department of Internal Medicine French National Reference center for SLE and APS Hôpital
PSYCHIATRIC MANIFESTATIONS IN PEDIATRIC SLE PATIENTS AT SIRIRAJ HOSPITAL BANGKOK, THAILAND
 PSYCHIATRIC MANIFESTATIONS IN PEDIATRIC SLE PATIENTS AT SIRIRAJ HOSPITAL BANGKOK, THAILAND Sasitorn Chantaratin, Prae Wongtangman, Sudrat Sirisakpanit and Vitharon Boon-yasidhi Division of Child and Adolescent
PSYCHIATRIC MANIFESTATIONS IN PEDIATRIC SLE PATIENTS AT SIRIRAJ HOSPITAL BANGKOK, THAILAND Sasitorn Chantaratin, Prae Wongtangman, Sudrat Sirisakpanit and Vitharon Boon-yasidhi Division of Child and Adolescent
SUPPLEMENTARY MATERIALS
 SUPPLEMENTARY MATERIALS Supplementary Table 1. Demographic and clinical characteristics of the primary Sjögren's syndrome patient cohort Number % Females/males 73/5 93.6/6.4 Age, median (range) years 65
SUPPLEMENTARY MATERIALS Supplementary Table 1. Demographic and clinical characteristics of the primary Sjögren's syndrome patient cohort Number % Females/males 73/5 93.6/6.4 Age, median (range) years 65
Rheumatic heart disease
 Rheumatic heart disease What will we discuss today? Etiology and epidemiology of rheumatic heart disease Pathogenesis of rheumatic heart disease Morphological changes in rheumatic heart disease Clinical
Rheumatic heart disease What will we discuss today? Etiology and epidemiology of rheumatic heart disease Pathogenesis of rheumatic heart disease Morphological changes in rheumatic heart disease Clinical
ECHOGENIC FETAL HEART WITHOUT HEART BLOCK AND MATERNAL ANTI- Ro/ La ANTIBODIES POSITIVITY A LESS KNOWN ASSOCIATION
 ECHOGENIC FETAL HEART WITHOUT HEART BLOCK AND MATERNAL ANTI- Ro/ La ANTIBODIES POSITIVITY A LESS KNOWN ASSOCIATION DR PUNDALIK BALIGA FELLOW IN FETAL MEDICINE MEDISCAN SYSTEMS, CHENNAI CASE 1 30 year old
ECHOGENIC FETAL HEART WITHOUT HEART BLOCK AND MATERNAL ANTI- Ro/ La ANTIBODIES POSITIVITY A LESS KNOWN ASSOCIATION DR PUNDALIK BALIGA FELLOW IN FETAL MEDICINE MEDISCAN SYSTEMS, CHENNAI CASE 1 30 year old
antiphospholipid antibody binding to platelet membranes*
 Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases, 1988; 47, 849-854 Immune mediated mechanism for thrombosis: antiphospholipid antibody binding to platelet membranes* MUNTHER A KHAMASHTA,1 E NIGEL HARRIS,2 AZZUDIN E GHARAVI,3
Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases, 1988; 47, 849-854 Immune mediated mechanism for thrombosis: antiphospholipid antibody binding to platelet membranes* MUNTHER A KHAMASHTA,1 E NIGEL HARRIS,2 AZZUDIN E GHARAVI,3
THE FRAMINGHAM STUDY Protocol for data set vr_soe_2009_m_0522 CRITERIA FOR EVENTS. 1. Cardiovascular Disease
 THE FRAMINGHAM STUDY Protocol for data set vr_soe_2009_m_0522 CRITERIA FOR EVENTS 1. Cardiovascular Disease Cardiovascular disease is considered to have developed if there was a definite manifestation
THE FRAMINGHAM STUDY Protocol for data set vr_soe_2009_m_0522 CRITERIA FOR EVENTS 1. Cardiovascular Disease Cardiovascular disease is considered to have developed if there was a definite manifestation
Neurological manifestations of antiphospholipid syndrome
 DOI: 10.1111/j.1365-2362.2010.02263.x REVIEW Neurological manifestations of antiphospholipid syndrome Carlos E. M. Rodrigues *, Jozélio F. Carvalho * and Yehuda Shoenfeld,1 * University of São Paulo, São
DOI: 10.1111/j.1365-2362.2010.02263.x REVIEW Neurological manifestations of antiphospholipid syndrome Carlos E. M. Rodrigues *, Jozélio F. Carvalho * and Yehuda Shoenfeld,1 * University of São Paulo, São
Redgrave JN, Coutts SB, Schulz UG et al. Systematic review of associations between the presence of acute ischemic lesions on
 6. Imaging in TIA 6.1 What type of brain imaging should be used in suspected TIA? 6.2 Which patients with suspected TIA should be referred for urgent brain imaging? Evidence Tables IMAG1: After TIA/minor
6. Imaging in TIA 6.1 What type of brain imaging should be used in suspected TIA? 6.2 Which patients with suspected TIA should be referred for urgent brain imaging? Evidence Tables IMAG1: After TIA/minor
SLE and the Antiphospholipid Syndrome
 SLE and the Antiphospholipid Syndrome Susan Y. Ritter MD, PhD Associate Physician Division of Rheumatology, Immunology and Allergy Department of Medicine Brigham and Women s Hospital Instructor in Medicine
SLE and the Antiphospholipid Syndrome Susan Y. Ritter MD, PhD Associate Physician Division of Rheumatology, Immunology and Allergy Department of Medicine Brigham and Women s Hospital Instructor in Medicine
Should infants with perinatal thrombosis be screened for thrombophilia and treated by anticoagulants?
 Should infants with perinatal thrombosis be screened for thrombophilia and treated by anticoagulants? Shoshana Revel-Vilk, MD MSc Pediatric Hematology Center, Pediatric Hematology/Oncology Department,
Should infants with perinatal thrombosis be screened for thrombophilia and treated by anticoagulants? Shoshana Revel-Vilk, MD MSc Pediatric Hematology Center, Pediatric Hematology/Oncology Department,
Systemic Lupus Erythematosus
 Systemic Lupus Erythematosus Marc C. Hochberg, MD, MPH Professor of Medicine and Head, Division of Rheumatology University of Maryland School of Medicine CASE: HISTORY A 26-year-old woman is seen for migratory
Systemic Lupus Erythematosus Marc C. Hochberg, MD, MPH Professor of Medicine and Head, Division of Rheumatology University of Maryland School of Medicine CASE: HISTORY A 26-year-old woman is seen for migratory
Dementia associated with the antiphospholipid syndrome: clinical and radiological characteristics of 30 patients
 Rheumatology 2005;44:95 99 Advance Access publication 14 eptember 2004 Concise Report Dementia associated with the antiphospholipid syndrome: clinical and radiological characteristics of 30 patients J.
Rheumatology 2005;44:95 99 Advance Access publication 14 eptember 2004 Concise Report Dementia associated with the antiphospholipid syndrome: clinical and radiological characteristics of 30 patients J.
Antiphospholipid. Syndrome. Ricard Cervera Margarita Rodríguez-Mahou
 Antiphospholipid Syndrome Ricard Cervera Margarita Rodríguez-Mahou Antiphospholipid Syndrome Ricard Cervera Department of Autoimmune Diseases Barcelona Hospital Margarita Rodríguez-Mahou Autoimmunity
Antiphospholipid Syndrome Ricard Cervera Margarita Rodríguez-Mahou Antiphospholipid Syndrome Ricard Cervera Department of Autoimmune Diseases Barcelona Hospital Margarita Rodríguez-Mahou Autoimmunity
Conflict of Interest. Systemic Lupus Erythematosus and the Antiphospholipid Syndrome Bonnie L. Bermas, MD Brigham and Women s Hospital.
 Systemic Lupus Erythematosus and the Antiphospholipid Syndrome Bonnie L. Bermas, MD Brigham and Women s Hospital Conflict of Interest Disclosures: None Overview Diagnostic Classification Criteria of SLE
Systemic Lupus Erythematosus and the Antiphospholipid Syndrome Bonnie L. Bermas, MD Brigham and Women s Hospital Conflict of Interest Disclosures: None Overview Diagnostic Classification Criteria of SLE
PURPOSE SCIENTIFIC QUESTIONS. How the prevalence of the nine different apl varies among the different age groups of patients with SLE?
 Project plan The prevalence of IgG, IgM, and IgA antibodies against cardiolipin, β2-glycoprotein I and domain I of β2-glycoprotein I in a large cohort of patients with Systemic Lupus Erythematosus and
Project plan The prevalence of IgG, IgM, and IgA antibodies against cardiolipin, β2-glycoprotein I and domain I of β2-glycoprotein I in a large cohort of patients with Systemic Lupus Erythematosus and
Thrombophilia: To test or not to test
 Kenneth Bauer, MD Harvard Medical School, Boston, MA Professor of Medicine VA Boston Healthcare System Chief, Hematology Section Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center, Boston, MA Director, Thrombosis Clinical
Kenneth Bauer, MD Harvard Medical School, Boston, MA Professor of Medicine VA Boston Healthcare System Chief, Hematology Section Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center, Boston, MA Director, Thrombosis Clinical
Thrombophilia. Diagnosis and Management. Kevin P. Hubbard, DO, FACOI
 Thrombophilia Diagnosis and Management Kevin P. Hubbard, DO, FACOI Clinical Professor of Medicine Kansas City University of Medicine and Biosciences-College of Osteopathic Medicine Kansas City, Missouri
Thrombophilia Diagnosis and Management Kevin P. Hubbard, DO, FACOI Clinical Professor of Medicine Kansas City University of Medicine and Biosciences-College of Osteopathic Medicine Kansas City, Missouri
Systemic lupus erythematosus
 Postgraduate Medical Journal (1988) 64, 517-521 Systemic lupus erythematosus Graham R.V. Hughes Lupus Research Laboratory, St Thomas' Hospital, London SE] 7EH, UK. Summary: Systemic lupus erythematosus
Postgraduate Medical Journal (1988) 64, 517-521 Systemic lupus erythematosus Graham R.V. Hughes Lupus Research Laboratory, St Thomas' Hospital, London SE] 7EH, UK. Summary: Systemic lupus erythematosus
Lupus Anticoagulants (LA), Antiphospholipid (APL) Antibodies & APL Syndrome: Review & Update. Antiphospholipid. Antiphospholipid
 , Antiphospholipid (APL) Antibodies & APL Syndrome: Review & Update William L. Nichols, MD Mayo Clinic College of Medicine Rochester, Minnesota USA Disclosures & Objectives (Nichols) Disclosures Relevant
, Antiphospholipid (APL) Antibodies & APL Syndrome: Review & Update William L. Nichols, MD Mayo Clinic College of Medicine Rochester, Minnesota USA Disclosures & Objectives (Nichols) Disclosures Relevant
Antiphospholipid antibodies
 CARDIOLOGY PATIENT PAGE CARDIOLOGY PATIENT PAGE Antiphospholipid Antibodies Caron P. Misita, PharmD; Stephan Moll, MD Antiphospholipid antibodies (APLAs) are proteins that may be present in the blood and
CARDIOLOGY PATIENT PAGE CARDIOLOGY PATIENT PAGE Antiphospholipid Antibodies Caron P. Misita, PharmD; Stephan Moll, MD Antiphospholipid antibodies (APLAs) are proteins that may be present in the blood and
ORIGINAL INVESTIGATION. Association With Clinical, Laboratory, and Brain Magnetic Resonance Imaging Findings
 ORIGINAL INVESTIGATION Cognitive Deficits in Patients With Antiphospholipid Syndrome Association With Clinical, Laboratory, and Brain Magnetic Resonance Imaging Findings Maria G. Tektonidou, MD; Natassa
ORIGINAL INVESTIGATION Cognitive Deficits in Patients With Antiphospholipid Syndrome Association With Clinical, Laboratory, and Brain Magnetic Resonance Imaging Findings Maria G. Tektonidou, MD; Natassa
Review Article. Overview of Systemic Lupus Erythematosus in Hong Kong Chinese: Part 1. Clinical Manifestations and Genetics.
 Review Article Overview of Systemic Lupus Erythematosus in Hong Kong Chinese: Part 1. Clinical Manifestations and Genetics Chi-Chiu Mok Abstract: Keywords: Systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) is a heterogenous
Review Article Overview of Systemic Lupus Erythematosus in Hong Kong Chinese: Part 1. Clinical Manifestations and Genetics Chi-Chiu Mok Abstract: Keywords: Systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) is a heterogenous
Antiphospholipid Syndrome and Vascular Ischemic (Occlusive) Diseases: An Overview
 Yonsei Med J 48(6):901-926, 2007 DOI 10.3349/ymj.2007.48.6.901 Antiphospholipid Syndrome and Vascular Ischemic (Occlusive) Diseases: An Overview Penka A. Atanassova Department of Neurology, Medical University,
Yonsei Med J 48(6):901-926, 2007 DOI 10.3349/ymj.2007.48.6.901 Antiphospholipid Syndrome and Vascular Ischemic (Occlusive) Diseases: An Overview Penka A. Atanassova Department of Neurology, Medical University,
ANTICARDIOLIPIN ANTIBODIES IN PATIENTS WITH SYSTEMIC LUPUS ERYTHEMATOSUS
 382 ANTICARDIOLIPIN ANTIBODIES IN PATIENTS WITH SYSTEMIC LUPUS ERYTHEMATOSUS GUNNAR STURFELT, OLA NIVED, RENEE NORBERG, RIGMOR THORSTENSSON, and KATARINA KROOK We studied a group of 59 unselected patients
382 ANTICARDIOLIPIN ANTIBODIES IN PATIENTS WITH SYSTEMIC LUPUS ERYTHEMATOSUS GUNNAR STURFELT, OLA NIVED, RENEE NORBERG, RIGMOR THORSTENSSON, and KATARINA KROOK We studied a group of 59 unselected patients
DOWNLOAD OR READ : POSITIVE OPTIONS FOR ANTIPHOSPHOLIPID SYNDROME APS SELF HELP AND TREATMENT PDF EBOOK EPUB MOBI
 DOWNLOAD OR READ : POSITIVE OPTIONS FOR ANTIPHOSPHOLIPID SYNDROME APS SELF HELP AND TREATMENT PDF EBOOK EPUB MOBI Page 1 Page 2 positive options for antiphospholipid syndrome aps self help and treatment
DOWNLOAD OR READ : POSITIVE OPTIONS FOR ANTIPHOSPHOLIPID SYNDROME APS SELF HELP AND TREATMENT PDF EBOOK EPUB MOBI Page 1 Page 2 positive options for antiphospholipid syndrome aps self help and treatment
Research Article Seizures in Primary Antiphospholipid Syndrome: The Relevance of Smoking to Stroke
 Hindawi Publishing Corporation Clinical and Developmental Immunology Volume 2012, Article ID 981519, 7 pages doi:10.1155/2012/981519 Research Article Seizures in Primary Antiphospholipid Syndrome: The
Hindawi Publishing Corporation Clinical and Developmental Immunology Volume 2012, Article ID 981519, 7 pages doi:10.1155/2012/981519 Research Article Seizures in Primary Antiphospholipid Syndrome: The
Acta Medica Okayama. Catastrophic secondary antiphospholipid syndrome with peripheral nervous system involvement: a case report.
 Acta Medica Okayama Volume 58, Issue 2 2004 Article 7 APRIL 2004 Catastrophic secondary antiphospholipid syndrome with peripheral nervous system involvement: a case report. Nilgun Erten Bulent Saka M Akif
Acta Medica Okayama Volume 58, Issue 2 2004 Article 7 APRIL 2004 Catastrophic secondary antiphospholipid syndrome with peripheral nervous system involvement: a case report. Nilgun Erten Bulent Saka M Akif
Correlation between Systemic Lupus Erythematosus Disease Activity Index, C3, C4 and Anti-dsDNA Antibodies
 Original Article Correlation between Systemic Lupus Erythematosus Disease Activity Index, C3, C4 and Anti-dsDNA Antibodies Col K Narayanan *, Col V Marwaha +, Col K Shanmuganandan #, Gp Capt S Shankar
Original Article Correlation between Systemic Lupus Erythematosus Disease Activity Index, C3, C4 and Anti-dsDNA Antibodies Col K Narayanan *, Col V Marwaha +, Col K Shanmuganandan #, Gp Capt S Shankar
Insights into the DX of Pediatric SLE
 Insights into the DX of Pediatric SLE Dr. John H. Yost Pediatric Rheumatology Children s Hospital at Dartmouth Assistant Professor of Medicine Geisel School of Medicine at Dartmouth john.h.yost@hitchcock.org
Insights into the DX of Pediatric SLE Dr. John H. Yost Pediatric Rheumatology Children s Hospital at Dartmouth Assistant Professor of Medicine Geisel School of Medicine at Dartmouth john.h.yost@hitchcock.org
Patrick R Wood, MD Fellow, Rheumatology University of Colorado
 Patrick R Wood, MD Fellow, Rheumatology University of Colorado Discuss an unusual case of CNS calcification encountered on an academic VA rheumatology service Summarize bilateral striatopallidodentate
Patrick R Wood, MD Fellow, Rheumatology University of Colorado Discuss an unusual case of CNS calcification encountered on an academic VA rheumatology service Summarize bilateral striatopallidodentate
Hemolytic uremic syndrome: Investigations and management
 Hemolytic uremic syndrome: Investigations and management SAWAI Toshihiro M.D., Ph.D. Department of Pediatrics, Shiga University of Medical Science Otsu, JAPAN AGENDA TMA; Thrombotic micro angiopathy STEC-HUS;
Hemolytic uremic syndrome: Investigations and management SAWAI Toshihiro M.D., Ph.D. Department of Pediatrics, Shiga University of Medical Science Otsu, JAPAN AGENDA TMA; Thrombotic micro angiopathy STEC-HUS;
