Upper Gastrointestinal Mucosal Changes in Patients with Congestive Heart Failure
|
|
|
- Muriel Poole
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Med. J. Cairo Univ., Vol. 81, No. 1, December: , Upper Gastrointestinal Mucosal Changes in Patients with Congestive Heart Failure ZAIN E.A. SAYED, M.D. 1 ; MOHAMMAD ABDEL-GHANY, M.D. 2 ; LOBNA ABDEL-WAHID, M.D. 1 ELHAM A. HASSAN, M.D. 3 and KHALED M. ATTALLAH, M.D. 4 The Departments of Internal Medicine 1, Cardiology 2, Tropical Medicine 3, Assiut University and Tropical Medicine & Gastroenterology 4, National Liver Institute, Menoufia University, Egypt Abstract Introduction: Congestive heart failure increases systemic venous pressure which is transmitted to the inferior vena cava and the hepatic veins, this may induce gastro-intestinal changes. This research aimed to study gastro-intestinal tract changes in patients with congestive heart failure. Aims and Methods: 120 patients with congestive heart failure (CHF) presenting with gastro-intestinal symptoms underwent upper endoscopy. All patients underwent echocardiography to determine the ejection fraction and the degree of tricuspid regurgitation and pulmonary hypertension. Abdominal ultrasound was done to measure the diameters of the hepatic veins, the inferior vena cava, and the portal vein for which pulsatility index was assessed. Results: Gastric mucosal changes were present in 106 (88.4%), duodenal mucosal changes in 71 (59.2%), and esophageal mucosal changes in 3 (2.5%) patients. Gastric mucosal changes were the following: Mosaic-like pattern (n=92,76.7%), punctate spots (n=73,60%), thickened folds (n=20,16.7%), watermelon stomach (n=8,6.7%), and telangiectasia (n=35, 29.2%). Duodenal mucosal changes were the following: Mosaic-like pattern (n=58,48.4%), thickened folds (n=17,14.2%), and telangiectasia (n=7,5.9%). Gastrointestinal symptoms were significantly associated with gastropathy and duodenopathy (p<0.001). There was a positive correlation between the degree of gastro-intestinal symptoms and gastropathy and duodenopathy (Gamma=0.6, p=0.03 and 0.5, p=0.04 respectively). Patients with gastropathy and duodenopathy had higher mean inferior vena cava (IVC) and hepatic vein diameters than those without gastropathy and duodenopathy. Low EF was associated with increased portal vein, IVC and hepatic vein diameters, (p=0.02, 0.008, 0.002) respectively. Moreover it was associated with gastro-intestinal symptoms, gastropathy and duodenopathy (p<0.001). There was a positive correlation between the ejection fraction and severity of gastrointestinal symptoms (r=0.6, p<0.001). Tricuspid regurgitation was associated with gastro-intestinal symptoms, stomach gastropathy, diameter of hepatic vein and IVC ( p=0.007, 0.019, <0.001, <0.001). Mean pulsatility index in patients in the present study was 0.7 ±0.53 and there was positive corre- Correspondence to: Dr. Zain E.A. Sayed, The Department of Internal Medicine, Assiut University lation between pulsatility index and Pulmonary Artery Systolic Pressure (PASP) (r=0.61, p=0.02). Patients with low ejection fraction have a higher pulsatility index than patients with higher ejection fraction (0.7 ±0.67, 0.6±0.18, p=0.26). Conclusion: CHF is associated with gastro -intestinal changes which are significantly associated with the severity of congestive heart failure. Key Words: Congestive heart failure Duodenopathy Gastropathy Pulsatility index. Introduction CONGESTIVE changes in the gastric mucosa were first described by McCormack et al., in patients with portal hypertension (portal hypertensive or congestive gastropathy) [1]. Similar congestive mucosal changes also have been described in the duodenum, jejunum and colon [2]. Chronic heart failure (CHF) is a multi-organ disease with increasing evidence for the involvement of the gastrointestinal (GI) system in this syndrome. In CHF, the increased systemic venous congestion is readily transmitted to the inferior vena cava (IVC) and the hepatic veins (HV) and hepatic sinusoids [3]. Increased sinusoidal pressure, leads to an increase in the resistance to blood flow in the portal vein (PV) and hereby to congestion in its draining territories this leads to congestion of GIT mucosa with several structural changes [4]. The aim of this study to define gastro-intestinal tract changes in patients with CHF, assessed with upper endoscopy and abdominal ultrasound. Patients and Methods This was a cross-sectional prospective study of patients with CHF that were selected from Assiut University Hospitals based Gastroenterology and Cardiology departments during a period from March 2012 to March The study was ap- 1009
2 1010 Upper Gastrointestinal Mucosal Changes in Patients proved by the regional Ethical Committee of AUH and informed consent was obtained from all the participants before enrollment. Study population: Adult 120 patients with CHF and having gastrointestinal (GI) symptoms (e.g. abdominal pain, heartburn, nausea, vomiting, severe anorexia or weight loss) assessed by the Patient Assessment of Gastrointestinal Disorders-Symptom Severity Index (PAGI-SYM) (reference) were included in the study [5]. Heart failure defined as patients with symptoms typical of heart failure: (Breathlessness at rest or on exercise, fatigue, tiredness, ankle swelling), signs typical of heart failure: (Tachycardia, tachypnoea, orthopnoea, paroxysmal nocturnal dyspnea, pulmonary rales, pleural effusion, raised jugular venous pressure, peripheral oedema, hepatomegaly) and objective evidence of a structural or functional abnormality of the heart at rest (cardiomegaly, third heart sound, cardiac murmurs, abnormality on the echocardiogram) [6]. Patients with haemodynamic instability, positive hepatitis markers (HBsAg, HCVAb), chronic liver disease of non cardiac origin, H. pylori infection and those received mediations affecting GIT mucosa e.g. NSAIDs were excluded from this study. All patients were subjected to the following: Full clinical history and examination. Transthoracic echocardiography was done to diagnose any structural heart disease, assess LV dimensions and function, assess degree of tricuspid regurgitation (TR) and PASP. Trans-abdominal ultrasonography to assess the following: - Maximum width (in mm) of the distal part of the main trunk of the left, the middle, and the right HVs, just proximal to their entry into the IVC (during shallow inspiration after at least 5 minutes of rest). - Maximum transverse diameter of the IVC just above its confluence with the HVs (with breathing held in expiration). - Maximum width of the PV at the porta-hepatis. - Assessment of liver and spleen status and the presence of vascular collaterals. - Portal vein Pulsatility index (PI) calculated as follows: (Peak maximum velocity) - (Peak minimum velocity) / (Peak maximum velocity) using ultrasonic Doppler. Upper Endoscopy: Endoscopic changes were classified by using a modification of the grading system for portal hypertensive gastropathy [7] : Grade 0, normalappearing mucosa; grade 1 (mild), mosaic like pattern and/or fine punctate speckling of the mucosa; grade 2 (moderate), blunted and thickened folds and/or telangiectasia; and grade 3 (severe), cherry red spots and/or diffusely or linearly hyperaemic mucosa. Statistical analysis: Statistical analysis was performed using Statistical Package for the Social Sciences (SPSS-version 17). Continuous data were expressed as Means ±Standard deviation (SD) and compared using Student t-test. Categorical variables were expressed as percentage and compared using chi-square ( χ 2 ) test. Correlations were assessed by the Spearman rank correlation coefficient among continuous variables and Gamma statistics for ordinal variables. p-values of less than 0.05 were considered significant. Results Characteristics of the study population: The baseline demographic and clinical characteristics of 120 studied patients with CHF are summarized in table 1 where the mean age of the patients was 33.4±8.8 years and males constituted 61.7%. The majority of cardiac patients presented with severe GIT symptoms (41.7%). Rheumatic heart disease was the commonest cause for these cardiac patients (44.2%) and 38.3% of them had severe degree of tricuspid regurge. Table (1): Demographic and clinical characteristics of the study patients. Patients (n=120) No (%) Male 74 (61.7) Age 33.4±8.8 Git symptoms * : Mild 21 (17.5) Moderate 49 (40.8) Severe 50 (41.7) Causes of heart failure: Dilated cardiomyopathy 13 (10.9) Ischemic cardiomyopathy 49 (40.8) Peripartum cardiomyopathy 5 (4.2) Rheumatic heart disease 53 (44.2) Degree of tricuspid regurge: No regurge 6 (5) Mild 40 (33.3) Moderate 28 (23.3) Severe 46 (38.3) * Assessed by the patient assessment of gastrointestinal disorders-symptom severity index (PAGI-SYM).
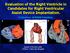
3 Zain E.A. Sayed, et al Endoscopic findings: The endoscopic findings were listed in Table (2) and Fig. (1). Gastric mucosal changes (gastropathy) were present in 106 (88.4%) patients, where, mosaic like pattern lesions were the commonest endoscopic changes. In addition, duodenal mucosal changes (duodenopathy) were found in 71 (59.2%) patients, and esophageal mucosal changes in 3 (2.5%) patients that were the least endoscopic changes. Some patients had more than one endoscopic lesion. Table (2): Endoscopic findings in the study patients. Endoscopic lesions * No. (%) Esophageal changes: Linear veins in distal third 3 (2.5) Varices 0 Gastric changes: Mosaic-like pattern 92 (76.7) Thickened folds 20 (16.7) Punctuate spots 73 (60) Watermelon stomach 8 (6.7) Telangiectasia Duodenal changes: 35 (29.2) Mosaic-like pattern 58 (48.4) Thickened folds 17 (14.2) Telangiectasia 7 (5.9) * The patient may have one or more endoscopic lesion(s). Patients with moderate and severe upper-gi symptoms had significantly more gastropathy and doudenopathy than those with mild symptoms (p<0.001 for both). In addition, there was a positive correlation between the degree of severity of upper- GI symptoms and severity of gastropathy and doudenopathy (Gamma=0.6, p=0.03 and 0.5, p=0.04 respectively). Ultrasonographic (dopplar) and Echocardiographic findings: The mean PI in patients in our patients was 0.7±0.53. There was positive correlation between PI and PASP (r=0.61, p=0.02). Patients with low EF have a higher PI than patient higher EF but without statistical significance (0.7 ±0.67 vs. 0.6±0.18, p=0.26). Comparison between GIT symptoms, endoscopic lesions and ultrasonographic and echocardiographic findings: Cardiac patients with moderate and severe upper-gi symptoms had higher mean inferior vena cava and hepatic vein diameters than those with mild symptoms indicating that hepatic vein and IVC diameters were significantly associated with the severity of upper-gi symptoms (p<0.001 for both). Despite portal vein diameter was not significantly altered it showed a tendency toward increased values with severity of upper-gi symptoms in patients with CHF Table (3). Additionally, cardiac patients with gastropathy and duodenopathy had higher mean inferior vena cava and hepatic vein diameters than those without gastropathy and duodenopathy. Tables (4,5). Regarding echocardiographic changes, low EF was associated with increasing severity of upper- GI symptoms and the presence of gastropathy and duodenopathy (p<0.001 for all). Moreover, it was associated with larger portal vein, IVC and hepatic vein diameters, (p=0.02, 0.008, 0.002) respectively. On the other hand, Tricuspid regurgitation was associated with upper-gi symptoms, stomach changes, and increased hepatic vein and IVC diameters (p=0.007, 0.019, <0.001, <0.001 respectively). Table (3): Relation between GIT symptoms and ultrasonographic findings. Patients with mild symptoms (n=21) Patients with moderate and severe symptoms (n=99) IVC diameter 13.4± ±4.9 <0.001 Hepatic vein diameter 8.3± ± 1.7 <0.001 Portal vein 9.3± ± Table (4): Ultrasonographic findings in patients with and without gastropathy. Patients with Patients without gastropathy gastropathy p (n=106) (n=14) IVC diameter 19.2± ± 1.3 <0.001 Hepatic vein diameter 9.8± ± Table (5): Ultrasonographic findings in patients with and without doudenopathy. Patients with Patients without doudenopathy doudenopathy p (n=71 ) (n=49) IVC diameter 20.4± ±4.3 <0.001 Hepatic vein diameter 10.2± ± 1.5 <0.001 p
4 1012 Upper Gastrointestinal Mucosal Changes in Patients Fig. (1-A): Esophageal linear veins. Fig. (1-B): Gastric mosaic like pattern. Fig. (1-C): Thickened gastric folds. Fig. (1-D): Gastric telangiectasia. Fig. (1-E): Watermelon stomach. Fig. (1-F): Duodenal mosaic-like pattern. Fig. (1-G): Duodenal thickened folds. Fig. (1-H): Duodenal telangiectasia. Fig. (1): Endoscopic view showing different aspects of congestive mucosopathy.
5 Zain E.A. Sayed, et al Discussion The present study assessed the frequency of upper gastrointestinal mucosal changes in patients with CHF, where gastropathy were the most common finding followed by duodenopathy. With agreement with Raja et al., [8] we found no patient had esophageal varices; only 3 patients (2.5%) have dilated veins that do not meet the criteria of esophageal varices Previous studies showed that low frequency of esophageal varies in patients with CHF ranged from 1.2% to 6.7% [9-11]. The absence of cardiac cirrhosis may explain the lack of esophageal varices in the present study patients since high porto-systemic pressure gradient is required for the formation of esophageal varices that is not present in cardiac cirrhosis [8]. Gastric mucosal changes observed in the present study were a mosaic-like pattern, thickened mucosal folds, watermelon stomach, punctate spots and telangiectasia. These results were compatible with previous studies that demonstrated several abnormalities of gastric mucosa in mosaic pattern including antral vascular ectasia, mucosal thickening and areas of telangiectasias [8,12]. These changes were similar to portal hypertensive gastropathy [13,14]. In this study, the duodenal findings were mild changes (mosaic-like pattern) that were the most common findings, followed by moderate changes (thickened mucosal folds, telangiectasia) and none had severe changes. Duodenopathy was less frequent than gastropathy. This might be clarified by the compact mucosal layer of the stomach with interruption of the area gastricae appearance with congestion as mosaic like. Similar changes are infrequent in the duodenum because of the supporting tissue in the lamina propria and the absence of the area gastricae. These results were consistent with Raja et al., [8] who found the common duodenal changes were mild but less frequent than gastropathy. In our study, these changes congestive mucosopathy in patients with CHF were similar to those caused by portal hypertension. However, a portosystemic venous pressure gradient exists in CHF, is much lower than that which occurs with cirrhosis. In congestive heart failure, the increase in systemic venous pressure is transmitted to the portal circulation via the hepatic venous bed and thus mucosal congestion is to be expected [4,15]. Patients with CHF have an increased splanchnic fluid volume, an important factor in maintaining splanchnic venous hypertension [6]. In addition, the low cardiac output state and arterial hypoxemia that occur in CHF might contribute to splanchnic hypoperfusion leading to GI mucosal changes [16]. We found that patients with moderate and severe upper-gi symptoms had significantly higher frequency of gastropathy and doudenopathy. Increasing severity of upper-gi symptoms was associated with increasing gastropathy and doudenopathy severity and increasing diameter of hepatic veins and IVC. However, severity of symptoms was not associated with portal vein diameter in our study. One possible explanation for this observation is that medication received by patients to treat CHF e.g. nitrites may control portal pressure. In this study, these cardiac patients had higher portal vein pulsatility index (PI) that was positively correlated with PASP. These results agreed with Shih et al., [17] who reported that patients with high right atrial pressure representing right sided cardiac congestion had a high PI. Furthermore; the waveform changes of portal blood flow correlate well with right heart function. So, with the agreement with Hu and colleagues [18], the measurement of portal vein PI change is a simple and noninvasive method to identify right heart failure and is helpful for the diagnosis of stagnant or hepatofugal portal blood flow. Regarding cardiac changes, degree of severity of tricuspid regurgitation was associated with gastrointestinal symptoms, stomach changes, and increased diameter of hepatic vein and IVC diameters. This can be explained by that with increasing severity of tricuspid regurgitation, the right ventricular systolic pressure is more efficiently transmitted to the systemic veins and the portal circulation; possibly, this leads to more congestive changes [19]. In addition, low EF was associated with larger IVC, hepatic vein and portal vein diameters manifested as systemic and splanchnic congestion thus, a more severe effect on the mucosa and consequently increasing severity of GIT symptoms, gastropathy and duodenopathy. In Conclusion: Congestive mucosopathy gastropathy and duodenopathy is common in patients with CHF. Severity of this finding is related to severity of hepatic congestion caused by tricuspid regurgitation and or right ventricular dysfunction that is the predominant mechanism. The measurement of
6 1014 Upper Gastrointestinal Mucosal Changes in Patients portal vein PI is an indirect non-invasive method of right ventricular dysfunction. Conflicts of interest: The authors declare that they had no conflicts of interest concerning this article. References 1- McCORMACK T.T., SIMS J., EYRE-BROOK I., KENNEDY H., GOEPEL J., JOHNSON A.G., et al.: Gastric lesions in portal hypertension: Inflammatory gastritis or congestive gastropathy? Gut., 26: , KRACK A., SHARMA R., FIGULLA H.R. and ANKER S.D.: The importance of the gastrointestinal system in the pathogenesis of heart failure. Eur. Heart J., 26 (22): , HESS O.M. and CARROLL J.D.: Clinical assessment of heart failure. In: Libby P., Bonow R.O., Mann D.L., Zipes D.P., Braunwald E. (eds). Braunwald's heart disease: A textbook of cardiovascular medicine. 8th ed. Philadelphia: Saunders Elsevier, p , GIALLOURAKIS C.C., ROSENBERG P.M. and FRIED- MAN L.S.: The liver in heart failure. Clin. Liver Dis., 6: , viii-ix, REVICKI D.A., RENTZ A.M., TACK J., STANGHELL- INI V., TALLEY N.J., KAHRILAS P., DE LA LOGE C., TRUDEAU E. and DUBOIS D.: Responsiveness and interpretation of a symptom severity index specific to upper gastrointestinal disorders. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. Sep., 2 (9): , KENNETH D., MCMURRAY, ALAIN C.S., et al.: ESC Guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of acute and chronic heart failure. Eur. Heart J., 29: , TAOR R.E., FOX B., WARE J. and JOHNSON A.G.: Gastritis: Gastroscopic and microscopic. Endoscopy, 7: , RAJA K., KOCHHAR R., SETHY P.K., DUTTA U., BALI H.K. and VARMA J.S.: An endoscopic study of upper-gi mucosal changes in patients with congestive heart failure. Gastrointest. Endosc., 60 (6): , GARRET N. and GALL E.A.: Esophageal varices without Hepatic Cirrhosis. Arch. Path., 55: , LUDINGTON L.G.: A study of 158 cases of esophageal varices. Surg. Gynec. Obstet., 106: , PALMER E.D. and BRICK I.B.: Esophageal varices: Causes other than cirrhosis and portal vein block. J. Am. Geriat. Soc., 3: 681-6, SANDEK A., ANKER S.D. and VON HAEHLING S.: The gut and intestinal bacteria in chronic heart failure. Curr. Drug. Metab., 10 (1): 22-8, SARIN S.K., SREENIVAS D.V., LAHORI D. and SA- RAYA A.: Factors influencing development of portal hypertensive gastropathy in patients with portal hypertension. Gastroenterology, 102: 994-9, PIQUE J.M.: Portal hypertensive gastropathy. Baillieres Clin. Gastroenterol., 11: , BARAKAT M.: Portal vein pulsatility and spectral width changes in patients with portal hypertension: Relation to the severity of liver disease. The British Journal of Radiology, 75: , PEITZMAN A.: Principles of circulatory support and the treatment of hemorrhagic shock. In: Snyder J.V., Pinsky M.R., eds. Oxygen Transport in the Clinically Ill. Chicago: Year Book Medical Puublisers Inc., , SHIH C.Y., YANG S.S., HU J.T., LIN C.L., LAI Y.C. and CHANG C.W.: Portal vein pulsatility index is a more important indicator than congestion index in the clinical evaluation of right heart function. World J. Gastroenterol., February 7, 12 (5): , HU J.T., YANG S.S., LAI Y.C., SHIH C.Y. and CHANG C.W.: Percentage of peak-to-peak pulsatility of portal blood flow can predict right-sided congestive heart failure. World J. Gastroenterol., 9: , HALLEY C. and GRIFFIN B.P.: Valular heart disease. In: Stoller J.K., Michota F.A., Mandell B.F. The Cleveland Clinic Intensive Review of Internal Medicine. 5 th ed. Philadelphia: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, p , 2009.
CORRELATION OF PORTAL VEIN PULSATILITY PATTERN AND SEVERITY OF LIVER DISEASE IN PATIENTS WITH CIRRHOSIS AND PORTAL HYPERTENSION
 CORRELATION OF PORTAL VEIN PULSATILITY PATTERN AND SEVERITY OF LIVER DISEASE IN PATIENTS WITH CIRRHOSIS AND PORTAL HYPERTENSION Anish Subedee, Benu Lohani, Shashi Sharma Abstract: Objective: To correlate
CORRELATION OF PORTAL VEIN PULSATILITY PATTERN AND SEVERITY OF LIVER DISEASE IN PATIENTS WITH CIRRHOSIS AND PORTAL HYPERTENSION Anish Subedee, Benu Lohani, Shashi Sharma Abstract: Objective: To correlate
Congestive Heart Failure Patient Profile. Patient Identity - Mr. Douglas - 72 year old man - No drugs, smokes, moderate social alcohol consumption
 Congestive Heart Failure Patient Profile Patient Identity - Mr. Douglas - 72 year old man - No drugs, smokes, moderate social alcohol consumption Chief Complaint - SOB - When asked: Increasing difficulty
Congestive Heart Failure Patient Profile Patient Identity - Mr. Douglas - 72 year old man - No drugs, smokes, moderate social alcohol consumption Chief Complaint - SOB - When asked: Increasing difficulty
Looking Outside the Box: Incidental Extracardiac Finding in Echo
 Looking Outside the Box: Incidental Extracardiac Finding in Echo Dr. Aijaz Shah Head of Division, Adult Echocardiography Laboratory Prince Sultan Cardiac Centre Riyadh Case 1 17 year old boy presented
Looking Outside the Box: Incidental Extracardiac Finding in Echo Dr. Aijaz Shah Head of Division, Adult Echocardiography Laboratory Prince Sultan Cardiac Centre Riyadh Case 1 17 year old boy presented
Charles Spencer MD, FRCP Consultant Cardiologist Mid Staffs NHSFT
 Charles Spencer MD, FRCP Consultant Cardiologist Mid Staffs NHSFT Key Messages Heart Failure is Common Heart failure is complex Heart Failure is a major issue for the NHS Heart Failure has a worse prognosis
Charles Spencer MD, FRCP Consultant Cardiologist Mid Staffs NHSFT Key Messages Heart Failure is Common Heart failure is complex Heart Failure is a major issue for the NHS Heart Failure has a worse prognosis
Tranjugular Intrahepatic Portosystemic Shunt
 Tranjugular Intrahepatic Portosystemic Shunt Christopher Selhorst July 25, 2005 BIDMC Radiology Overview Portal Hypertension Indications, Contraindications The Procedure Case Review Complications Outcomes
Tranjugular Intrahepatic Portosystemic Shunt Christopher Selhorst July 25, 2005 BIDMC Radiology Overview Portal Hypertension Indications, Contraindications The Procedure Case Review Complications Outcomes
Point-of-Care Ultrasound Closer look at the Inferior Vena Cavae &
 Point-of-Care Ultrasound Closer look at the Inferior Vena Cavae & Brief Introduction to Gross Systolic Function Omar S. Darwish, MS, DO Certified in Point-of-Care Ultrasound Hospitalist University of California,
Point-of-Care Ultrasound Closer look at the Inferior Vena Cavae & Brief Introduction to Gross Systolic Function Omar S. Darwish, MS, DO Certified in Point-of-Care Ultrasound Hospitalist University of California,
Endoscopic Management of Vascular Lesions of the GI tract
 Endoscopic Management of Vascular Lesions of the GI tract Lake Louise, June 2014 Sergio Zepeda Gómez MD Assistant Professor Division of Gastroenterology University of Alberta, Edmonton Best Practice &
Endoscopic Management of Vascular Lesions of the GI tract Lake Louise, June 2014 Sergio Zepeda Gómez MD Assistant Professor Division of Gastroenterology University of Alberta, Edmonton Best Practice &
Right Heart Hemodynamics: Echo-Cath Discrepancies
 Department of cardiac, thoracic and vascular sciences University of Padua, School of Medicine Padua, Italy Right Heart Hemodynamics: Echo-Cath Discrepancies Luigi P. Badano, MD, PhD, FESC, FACC **Dr. Badano
Department of cardiac, thoracic and vascular sciences University of Padua, School of Medicine Padua, Italy Right Heart Hemodynamics: Echo-Cath Discrepancies Luigi P. Badano, MD, PhD, FESC, FACC **Dr. Badano
Echo Doppler Assessment of Right and Left Ventricular Hemodynamics.
 Echo Doppler Assessment of Right and Left Ventricular Hemodynamics. Itzhak Kronzon, MD, FASE, FACC, FESC, FAHA, FACP, FCCP Northwell, Lenox Hill Hospital, New York Professor of Cardiology Hofstra University
Echo Doppler Assessment of Right and Left Ventricular Hemodynamics. Itzhak Kronzon, MD, FASE, FACC, FESC, FAHA, FACP, FCCP Northwell, Lenox Hill Hospital, New York Professor of Cardiology Hofstra University
Identification of congestive heart failure via respiratory variation of inferior vena cava diameter,
 American Journal of Emergency Medicine (2009) 27, 71 75 www.elsevier.com/locate/ajem Brief Report Identification of congestive heart failure via respiratory variation of inferior vena cava diameter, David
American Journal of Emergency Medicine (2009) 27, 71 75 www.elsevier.com/locate/ajem Brief Report Identification of congestive heart failure via respiratory variation of inferior vena cava diameter, David
The Doppler Examination. Katie Twomley, MD Wake Forest Baptist Health - Lexington
 The Doppler Examination Katie Twomley, MD Wake Forest Baptist Health - Lexington OUTLINE Principles/Physics Use in valvular assessment Aortic stenosis (continuity equation) Aortic regurgitation (pressure
The Doppler Examination Katie Twomley, MD Wake Forest Baptist Health - Lexington OUTLINE Principles/Physics Use in valvular assessment Aortic stenosis (continuity equation) Aortic regurgitation (pressure
Pericardial Disease: Case Examples. Echo Fiesta 2017
 Pericardial Disease: Case Examples Echo Fiesta 2017 2014 2014 MFMER MFMER 3346252-1 slide-1 Objectives Have a systematic approach to evaluation of constriction 2014 MFMER 3346252-2 CASE 1 2013 MFMER 3248567-3
Pericardial Disease: Case Examples Echo Fiesta 2017 2014 2014 MFMER MFMER 3346252-1 slide-1 Objectives Have a systematic approach to evaluation of constriction 2014 MFMER 3346252-2 CASE 1 2013 MFMER 3248567-3
The right heart: the Cinderella of heart failure
 The right heart: the Cinderella of heart failure Piotr Ponikowski, MD, PhD, FESC Medical University, Centre for Heart Disease Clinical Military Hospital Wroclaw, Poland none Disclosure Look into the Heart
The right heart: the Cinderella of heart failure Piotr Ponikowski, MD, PhD, FESC Medical University, Centre for Heart Disease Clinical Military Hospital Wroclaw, Poland none Disclosure Look into the Heart
Hemodynamic Assessment. Assessment of Systolic Function Doppler Hemodynamics
 Hemodynamic Assessment Matt M. Umland, RDCS, FASE Aurora Medical Group Milwaukee, WI Assessment of Systolic Function Doppler Hemodynamics Stroke Volume Cardiac Output Cardiac Index Tei Index/Index of myocardial
Hemodynamic Assessment Matt M. Umland, RDCS, FASE Aurora Medical Group Milwaukee, WI Assessment of Systolic Function Doppler Hemodynamics Stroke Volume Cardiac Output Cardiac Index Tei Index/Index of myocardial
Comprehensive Hemodynamics By Doppler Echocardiography. The Echocardiographic Swan-Ganz Catheter.
 Comprehensive Hemodynamics By Doppler Echocardiography. The Echocardiographic Swan-Ganz Catheter. Itzhak Kronzon, MD, FASE, FACC, FESC, FAHA, FACP, FCCP North Shore HS, LIJ/Lenox Hill Hospital, New York
Comprehensive Hemodynamics By Doppler Echocardiography. The Echocardiographic Swan-Ganz Catheter. Itzhak Kronzon, MD, FASE, FACC, FESC, FAHA, FACP, FCCP North Shore HS, LIJ/Lenox Hill Hospital, New York
Echocardiography: Guidelines for Valve Quantification
 Echocardiography: Guidelines for Echocardiography: Guidelines for Chamber Quantification British Society of Echocardiography Education Committee Richard Steeds (Chair), Gill Wharton (Lead Author), Jane
Echocardiography: Guidelines for Echocardiography: Guidelines for Chamber Quantification British Society of Echocardiography Education Committee Richard Steeds (Chair), Gill Wharton (Lead Author), Jane
Non-Invasive Bed-Side Assessment of Pulmonary Vascular Resistance in Critically Ill Pediatric Patients with Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome
 Aim of the Work This study aimed to evaluate the degree of pulmonary hypertension as well as alterations in the pulmonary vascular resistance in critically ill children with ARDS using bed- side echocardiography.
Aim of the Work This study aimed to evaluate the degree of pulmonary hypertension as well as alterations in the pulmonary vascular resistance in critically ill children with ARDS using bed- side echocardiography.
PIAF study: Placental insufficiency and aortic isthmus flow Jean-Claude Fouron, MD
 Dear colleagues, I would like to thank you very sincerely for agreeing to participate in our multicentre study on the clinical significance of recording fetal aortic isthmus flow during placental circulatory
Dear colleagues, I would like to thank you very sincerely for agreeing to participate in our multicentre study on the clinical significance of recording fetal aortic isthmus flow during placental circulatory
Background: Bedside ultrasound is emerging as a useful tool in the assessment of
 Abstract: Background: Bedside ultrasound is emerging as a useful tool in the assessment of intravascular volume status by examining measurements of the inferior vena cava (IVC). Many previous studies do
Abstract: Background: Bedside ultrasound is emerging as a useful tool in the assessment of intravascular volume status by examining measurements of the inferior vena cava (IVC). Many previous studies do
Diagnosis & Management of Heart Failure. Abena A. Osei-Wusu, M.D. Medical Fiesta
 Diagnosis & Management of Heart Failure Abena A. Osei-Wusu, M.D. Medical Fiesta Learning Objectives: 1) Become familiar with pathogenesis of congestive heart failure. 2) Discuss clinical manifestations
Diagnosis & Management of Heart Failure Abena A. Osei-Wusu, M.D. Medical Fiesta Learning Objectives: 1) Become familiar with pathogenesis of congestive heart failure. 2) Discuss clinical manifestations
Prof. Dr. Iman Riad Mohamed Abdel Aal
 The Use of New Ultrasound Indices to Evaluate Volume Status and Fluid Responsiveness in Septic Shock Patients Thesis Submitted for partial fulfillment of MD degree in Anesthesiology, Surgical Intensive
The Use of New Ultrasound Indices to Evaluate Volume Status and Fluid Responsiveness in Septic Shock Patients Thesis Submitted for partial fulfillment of MD degree in Anesthesiology, Surgical Intensive
DOPPLER HEMODYNAMICS (1) QUANTIFICATION OF PRESSURE GRADIENTS and INTRACARDIAC PRESSURES
 THORAXCENTRE DOPPLER HEMODYNAMICS (1) QUANTIFICATION OF PRESSURE GRADIENTS and INTRACARDIAC PRESSURES J. Roelandt DOPPLER HEMODYNAMICS Intracardiac pressures and pressure gradients Volumetric measurement
THORAXCENTRE DOPPLER HEMODYNAMICS (1) QUANTIFICATION OF PRESSURE GRADIENTS and INTRACARDIAC PRESSURES J. Roelandt DOPPLER HEMODYNAMICS Intracardiac pressures and pressure gradients Volumetric measurement
Echocardiography. Guidelines for Valve and Chamber Quantification. In partnership with
 Echocardiography Guidelines for Valve and Chamber Quantification In partnership with Explanatory note & references These guidelines have been developed by the Education Committee of the British Society
Echocardiography Guidelines for Valve and Chamber Quantification In partnership with Explanatory note & references These guidelines have been developed by the Education Committee of the British Society
Certificate in Clinician Performed Ultrasound (CCPU) Syllabus. Rapid Cardiac Echo (RCE)
 Certificate in Clinician Performed Ultrasound (CCPU) Syllabus Rapid Cardiac Echo (RCE) Purpose: Rapid Cardiac Echocardiography (RCE) This unit is designed to cover the theoretical and practical curriculum
Certificate in Clinician Performed Ultrasound (CCPU) Syllabus Rapid Cardiac Echo (RCE) Purpose: Rapid Cardiac Echocardiography (RCE) This unit is designed to cover the theoretical and practical curriculum
Evaluation of Clinical, Biochemical and Ultrasound Parameters in Diagnosis of Oesophageal Varices
 Med. J. Cairo Univ., Vol. 78, No. 2, June: 105-109, 2010 www.medicaljournalofcairouniversity.com Evaluation of Clinical, Biochemical and Ultrasound Parameters in Diagnosis of Oesophageal Varices FAWZY
Med. J. Cairo Univ., Vol. 78, No. 2, June: 105-109, 2010 www.medicaljournalofcairouniversity.com Evaluation of Clinical, Biochemical and Ultrasound Parameters in Diagnosis of Oesophageal Varices FAWZY
PART II ECHOCARDIOGRAPHY LABORATORY OPERATIONS ADULT TRANSTHORACIC ECHOCARDIOGRAPHY TESTING
 PART II ECHOCARDIOGRAPHY LABORATORY OPERATIONS ADULT TRANSTHORACIC ECHOCARDIOGRAPHY TESTING STANDARD - Primary Instrumentation 1.1 Cardiac Ultrasound Systems SECTION 1 Instrumentation Ultrasound instruments
PART II ECHOCARDIOGRAPHY LABORATORY OPERATIONS ADULT TRANSTHORACIC ECHOCARDIOGRAPHY TESTING STANDARD - Primary Instrumentation 1.1 Cardiac Ultrasound Systems SECTION 1 Instrumentation Ultrasound instruments
Value of echocardiography in chronic dyspnea
 Value of echocardiography in chronic dyspnea Jahrestagung Schweizerische Gesellschaft für /Schweizerische Gesellschaft für Pneumologie B. Kaufmann 16.06.2016 Chronic dyspnea Shortness of breath lasting
Value of echocardiography in chronic dyspnea Jahrestagung Schweizerische Gesellschaft für /Schweizerische Gesellschaft für Pneumologie B. Kaufmann 16.06.2016 Chronic dyspnea Shortness of breath lasting
COMPREHENSIVE EVALUATION OF FETAL HEART R. GOWDAMARAJAN MD
 COMPREHENSIVE EVALUATION OF FETAL HEART R. GOWDAMARAJAN MD Disclosure No Relevant Financial Relationships with Commercial Interests Fetal Echo: How to do it? Timing of Study -optimally between 22-24 weeks
COMPREHENSIVE EVALUATION OF FETAL HEART R. GOWDAMARAJAN MD Disclosure No Relevant Financial Relationships with Commercial Interests Fetal Echo: How to do it? Timing of Study -optimally between 22-24 weeks
Adel Hasanin Ahmed 1
 Adel Hasanin Ahmed 1 PERICARDIAL DISEASE The pericardial effusion ends anteriorly to the descending aorta and is best visualised in the PLAX. PSAX is actually very useful sometimes for looking at posterior
Adel Hasanin Ahmed 1 PERICARDIAL DISEASE The pericardial effusion ends anteriorly to the descending aorta and is best visualised in the PLAX. PSAX is actually very useful sometimes for looking at posterior
Sandipan Ghose, Md. Azizul Hoque, Md. Khalilur Rahman, Mohd. Harun-or-Rashid
 Sandipan Ghose, Md. Azizul Hoque, Md. Khalilur Rahman, Mohd. Harun-or-Rashid Liver cirrhosis may be defined as a diffuse process characterized by fibrosis and conversion of normal liver architecture into
Sandipan Ghose, Md. Azizul Hoque, Md. Khalilur Rahman, Mohd. Harun-or-Rashid Liver cirrhosis may be defined as a diffuse process characterized by fibrosis and conversion of normal liver architecture into
Evaluation of Left Ventricular Diastolic Dysfunction by Doppler and 2D Speckle-tracking Imaging in Patients with Primary Pulmonary Hypertension
 ESC Congress 2011.No 85975 Evaluation of Left Ventricular Diastolic Dysfunction by Doppler and 2D Speckle-tracking Imaging in Patients with Primary Pulmonary Hypertension Second Department of Internal
ESC Congress 2011.No 85975 Evaluation of Left Ventricular Diastolic Dysfunction by Doppler and 2D Speckle-tracking Imaging in Patients with Primary Pulmonary Hypertension Second Department of Internal
Diastolic Heart Function: Applying the New Guidelines Case Studies
 Diastolic Heart Function: Applying the New Guidelines Case Studies Mitral Regurgitation The New ASE William Guidelines: A. Zoghbi Role MD, of FASE, 2D/3D MACCand CMR Professor and Chairman, Department
Diastolic Heart Function: Applying the New Guidelines Case Studies Mitral Regurgitation The New ASE William Guidelines: A. Zoghbi Role MD, of FASE, 2D/3D MACCand CMR Professor and Chairman, Department
What effects will proximal or distal disease have on an waveform?
 Spectral Doppler Interpretation Director Director of of Ultrasound Ultrasound Education Education & & Quality Quality Assurance Assurance Baylor Baylor College College of of Medicine Medicine Division
Spectral Doppler Interpretation Director Director of of Ultrasound Ultrasound Education Education & & Quality Quality Assurance Assurance Baylor Baylor College College of of Medicine Medicine Division
gastritis or congestive gastropathy?
 Gut, 1985, 26, 1226-1232 Gastric lesions in portal hypertension: inflammatory gastritis or congestive gastropathy? T T McCORMACK, J SIMS, I EYRE-BROOK, H KENNEDY, J GOEPEL, A G JOHNSON, AND D R TRIGER
Gut, 1985, 26, 1226-1232 Gastric lesions in portal hypertension: inflammatory gastritis or congestive gastropathy? T T McCORMACK, J SIMS, I EYRE-BROOK, H KENNEDY, J GOEPEL, A G JOHNSON, AND D R TRIGER
INVESTIGATIONS OF GASTROINTESTINAL DISEAS
 INVESTIGATIONS OF GASTROINTESTINAL DISEAS Lecture 1 and 2 دز اسماعيل داود فرع الطب كلية طب الموصل Radiological tests of structure (imaging) Plain X-ray: May shows soft tissue outlines like liver, spleen,
INVESTIGATIONS OF GASTROINTESTINAL DISEAS Lecture 1 and 2 دز اسماعيل داود فرع الطب كلية طب الموصل Radiological tests of structure (imaging) Plain X-ray: May shows soft tissue outlines like liver, spleen,
Cardiac Radiology In-Training Test Questions for Diagnostic Radiology Residents
 Cardiac Radiology In-Training Test Questions for Diagnostic Radiology Residents March, 2013 Sponsored by: Commission on Education Committee on Residency Training in Diagnostic Radiology 2013 by American
Cardiac Radiology In-Training Test Questions for Diagnostic Radiology Residents March, 2013 Sponsored by: Commission on Education Committee on Residency Training in Diagnostic Radiology 2013 by American
Doppler Ultrasonography of the Liver: What Every General Radiologist Should Know
 Doppler Ultrasonography of the Liver: What Every General Radiologist Should Know Poster No.: C-1658 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Authors: Keywords: DOI: Educational Exhibit T. González de la Huebra Labrador,
Doppler Ultrasonography of the Liver: What Every General Radiologist Should Know Poster No.: C-1658 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Authors: Keywords: DOI: Educational Exhibit T. González de la Huebra Labrador,
British Society of Echocardiography
 British Society of Echocardiography Affiliated to the British Cardiac Society A Minimum Dataset for a Standard Adult Transthoracic Echocardiogram From the British Society of Echocardiography Education
British Society of Echocardiography Affiliated to the British Cardiac Society A Minimum Dataset for a Standard Adult Transthoracic Echocardiogram From the British Society of Echocardiography Education
Echocardiography as a diagnostic and management tool in medical emergencies
 Echocardiography as a diagnostic and management tool in medical emergencies Frank van der Heusen MD Department of Anesthesia and perioperative Care UCSF Medical Center Objective of this presentation Indications
Echocardiography as a diagnostic and management tool in medical emergencies Frank van der Heusen MD Department of Anesthesia and perioperative Care UCSF Medical Center Objective of this presentation Indications
P = 4V 2. IVC Dimensions 10/20/2014. Comprehensive Hemodynamic Evaluation by Doppler Echocardiography. The Simplified Bernoulli Equation
 Comprehensive Hemodynamic Evaluation by Doppler Echocardiography Itzhak Kronzon, MD North Shore LIJ/ Lenox Hill Hospital New York, NY Disclosure: Philips Healthcare St. Jude Medical The Simplified Bernoulli
Comprehensive Hemodynamic Evaluation by Doppler Echocardiography Itzhak Kronzon, MD North Shore LIJ/ Lenox Hill Hospital New York, NY Disclosure: Philips Healthcare St. Jude Medical The Simplified Bernoulli
Capsule Endoscopy: Is it Really Helpful in the Diagnosis of Small Bowel Diseases? Kashif Malik, Muhammad Joher Amin, Syed Waqar Hassan Shah
 Original Article Capsule Endoscopy: Is it Really Helpful in the Diagnosis of Small Bowel Diseases? Kashif Malik, Muhammad Joher Amin, Syed Waqar Hassan Shah ABSTRACT Objective: To determine the diagnostic
Original Article Capsule Endoscopy: Is it Really Helpful in the Diagnosis of Small Bowel Diseases? Kashif Malik, Muhammad Joher Amin, Syed Waqar Hassan Shah ABSTRACT Objective: To determine the diagnostic
58 year old male complaining of 3-week history of increasing epigastric pain
 Peptic Ulcer Disease 58 year old male complaining of 3-week history of increasing epigastric pain Has had dyspepsia in the past for which he took Tums, but this is much worse and only partially relieved
Peptic Ulcer Disease 58 year old male complaining of 3-week history of increasing epigastric pain Has had dyspepsia in the past for which he took Tums, but this is much worse and only partially relieved
Echocardiographic changes after aortic valve replacement: Does the failure rate of mitral valve change? Original Article
 Echocardiographic changes after aortic valve replacement: Does the failure rate of mitral valve change? Abstract Arezoo Khosravi (1), Hadi Sheykhloo (2), Reza Karbasi-Afshar (1), Amin Saburi (3) Original
Echocardiographic changes after aortic valve replacement: Does the failure rate of mitral valve change? Abstract Arezoo Khosravi (1), Hadi Sheykhloo (2), Reza Karbasi-Afshar (1), Amin Saburi (3) Original
SHORT REPORT. N. E. Manghat, 1 * A. J. Broadley, 2 M. A. Puckett, 1 J. Isaacs 1 and I. Currie 3
 EJVES Extra 6, 10 14 (2003) doi: 10.1016/S1533-3167(03)00061-X, available online at http://www.sciencedirect.com on SHORT REPORT High Output Cardiac Failure Caused by Popliteal Pseudoaneurysm and Arteriovenous
EJVES Extra 6, 10 14 (2003) doi: 10.1016/S1533-3167(03)00061-X, available online at http://www.sciencedirect.com on SHORT REPORT High Output Cardiac Failure Caused by Popliteal Pseudoaneurysm and Arteriovenous
HISTORY. Question: What category of heart disease is suggested by the fact that a murmur was heard at birth?
 HISTORY 23-year-old man. CHIEF COMPLAINT: Decreasing exercise tolerance of several years duration. PRESENT ILLNESS: The patient is the product of an uncomplicated term pregnancy. A heart murmur was discovered
HISTORY 23-year-old man. CHIEF COMPLAINT: Decreasing exercise tolerance of several years duration. PRESENT ILLNESS: The patient is the product of an uncomplicated term pregnancy. A heart murmur was discovered
Physiology #14. Heart Failure & Circulatory Shock. Mohammad Ja far Tuesday 5/4/2016. Turquoise Team. Page 0 of 13
 45 Physiology #14 Heart Failure & Circulatory Shock Mohammad Ja far Tuesday 5/4/2016 Turquoise Team Page 0 of 13 Heart Failure: It s a condition in which the heart can t perform its function properly;
45 Physiology #14 Heart Failure & Circulatory Shock Mohammad Ja far Tuesday 5/4/2016 Turquoise Team Page 0 of 13 Heart Failure: It s a condition in which the heart can t perform its function properly;
Μαρία Μπόνου Διευθύντρια ΕΣΥ, ΓΝΑ Λαϊκό
 Μαρία Μπόνου Διευθύντρια ΕΣΥ, ΓΝΑ Λαϊκό Diastolic HF DD: Diastolic Dysfunction DHF: Diastolic HF HFpEF: HF with preserved EF DD Pathophysiologic condition: impaired relaxation, LV compliance, LV filling
Μαρία Μπόνου Διευθύντρια ΕΣΥ, ΓΝΑ Λαϊκό Diastolic HF DD: Diastolic Dysfunction DHF: Diastolic HF HFpEF: HF with preserved EF DD Pathophysiologic condition: impaired relaxation, LV compliance, LV filling
Questions on Chamber Quantitation
 Questions on Chamber Quantitation @RobertoMLang Which of the following statements is true? 1. The aortic annulus should be measured in midsystole. 2. The aortic annulus should be measured in enddiastole.
Questions on Chamber Quantitation @RobertoMLang Which of the following statements is true? 1. The aortic annulus should be measured in midsystole. 2. The aortic annulus should be measured in enddiastole.
Echocardiographic Cardiovascular Risk Stratification: Beyond Ejection Fraction
 Echocardiographic Cardiovascular Risk Stratification: Beyond Ejection Fraction October 4, 2014 James S. Lee, M.D., F.A.C.C. Associates in Cardiology, P.A. Silver Spring, M.D. Disclosures Financial none
Echocardiographic Cardiovascular Risk Stratification: Beyond Ejection Fraction October 4, 2014 James S. Lee, M.D., F.A.C.C. Associates in Cardiology, P.A. Silver Spring, M.D. Disclosures Financial none
Hemodynamic Monitoring
 Perform Procedure And Interpret Results Hemodynamic Monitoring Tracheal Tube Cuff Pressure Dean R. Hess PhD RRT FAARC Hemodynamic Monitoring Cardiac Rate and Rhythm Arterial Blood Pressure Central Venous
Perform Procedure And Interpret Results Hemodynamic Monitoring Tracheal Tube Cuff Pressure Dean R. Hess PhD RRT FAARC Hemodynamic Monitoring Cardiac Rate and Rhythm Arterial Blood Pressure Central Venous
Original Article. Gastrointestinal bleeding in acute pancreatitis: etiology, clinical features, risk factors and outcome
 Tropical Gastroenterology 2015;36(1):31 35 Original Article Gastrointestinal bleeding in acute pancreatitis: etiology, clinical features, risk factors and outcome Surinder S Rana 1, Vishal Sharma 1, Deepak
Tropical Gastroenterology 2015;36(1):31 35 Original Article Gastrointestinal bleeding in acute pancreatitis: etiology, clinical features, risk factors and outcome Surinder S Rana 1, Vishal Sharma 1, Deepak
ECHO HAWAII. My home. Pulmonary Hypertension and Pulmonary Embolism: Role of Echo U.S.A. Japan. Hawaii Island 1/9/2018
 Pulmonary Hypertension and Pulmonary Embolism: Role of Echo ECHO HAWAII January 15 19, 2018 Kenya Kusunose, MD, PhD, FASE Tokushima University Hospital Japan My home Japan U.S.A Hawaii Island 1 Economy
Pulmonary Hypertension and Pulmonary Embolism: Role of Echo ECHO HAWAII January 15 19, 2018 Kenya Kusunose, MD, PhD, FASE Tokushima University Hospital Japan My home Japan U.S.A Hawaii Island 1 Economy
Susan P. D Anna MSN, APRN BC February 14, 2019
 Is there Equal Opportunity in Heart Failure?? Susan P. D Anna MSN, APRN BC February 14, 2019 Disclosures: I have no financial disclosures. I am not an expert on this topic, but see a lot of women with
Is there Equal Opportunity in Heart Failure?? Susan P. D Anna MSN, APRN BC February 14, 2019 Disclosures: I have no financial disclosures. I am not an expert on this topic, but see a lot of women with
Heart Failure. Cardiac Anatomy. Functions of the Heart. Cardiac Cycle/Hemodynamics. Determinants of Cardiac Output. Cardiac Output
 Cardiac Anatomy Heart Failure Professor Qing ZHANG Department of Cardiology, West China Hospital www.blaufuss.org Cardiac Cycle/Hemodynamics Functions of the Heart Essential functions of the heart to cover
Cardiac Anatomy Heart Failure Professor Qing ZHANG Department of Cardiology, West China Hospital www.blaufuss.org Cardiac Cycle/Hemodynamics Functions of the Heart Essential functions of the heart to cover
Outline. Echocardiographic Assessment of Pericardial Effusion/Tamponade: The Essentials
 Echocardiographic Assessment of Pericardial Effusion/Tamponade: The Essentials John R Schairer DO FACC Henry Ford Heart and Vascular Institute No Disclosures Outline Normal Anatomy and Physiology Pathophysiology
Echocardiographic Assessment of Pericardial Effusion/Tamponade: The Essentials John R Schairer DO FACC Henry Ford Heart and Vascular Institute No Disclosures Outline Normal Anatomy and Physiology Pathophysiology
An Uncommon Cardiac Etiology of Liver Cirrhosis, Recurrent Ascites, Atrial Fibrillation and Congestive Heart Failure
 Cronicon OPEN ACCESS EC CARDIOLOGY Case Report An Uncommon Cardiac Etiology of Liver Cirrhosis, Recurrent Ascites, Atrial Fibrillation and Congestive Heart Failure Montaser Y Ismail 1 *, Mohammed I Nassar
Cronicon OPEN ACCESS EC CARDIOLOGY Case Report An Uncommon Cardiac Etiology of Liver Cirrhosis, Recurrent Ascites, Atrial Fibrillation and Congestive Heart Failure Montaser Y Ismail 1 *, Mohammed I Nassar
The Causes of Heart Failure
 The Causes of Heart Failure Andy Birchall HFSN Right heart failure LVSD - HFREF Valve regurgitation or stenosis Dropsy CCF congestive cardiac failure Cor pulmonale Pulmonary hypertension HFPEF LVF Definitions
The Causes of Heart Failure Andy Birchall HFSN Right heart failure LVSD - HFREF Valve regurgitation or stenosis Dropsy CCF congestive cardiac failure Cor pulmonale Pulmonary hypertension HFPEF LVF Definitions
Adult Echocardiography Examination Content Outline
 Adult Echocardiography Examination Content Outline (Outline Summary) # Domain Subdomain Percentage 1 2 3 4 5 Anatomy and Physiology Pathology Clinical Care and Safety Measurement Techniques, Maneuvers,
Adult Echocardiography Examination Content Outline (Outline Summary) # Domain Subdomain Percentage 1 2 3 4 5 Anatomy and Physiology Pathology Clinical Care and Safety Measurement Techniques, Maneuvers,
Study of H. Pylori Infection in Patients with Portal Hypertensive Gastropathy
 218 Original article Study of H. Pylori Infection in Patients with Portal Hypertensive Gastropathy Hosam Ibrahim 1, Nancy Y Asaad 2, Hosam Eldin M. Seleem 1 and Israa MA Nouh 1 Tropical Medicine 1 and
218 Original article Study of H. Pylori Infection in Patients with Portal Hypertensive Gastropathy Hosam Ibrahim 1, Nancy Y Asaad 2, Hosam Eldin M. Seleem 1 and Israa MA Nouh 1 Tropical Medicine 1 and
Echo in Pulmonary HTN
 Echo in Pulmonary HTN Steven A. Goldstein MD FACC FASE Professor of Medicine Georgetown University Medical Center MedStar Heart Institute Washington Hospital Center Monday, October 10, 2017 Pulmonary Artery
Echo in Pulmonary HTN Steven A. Goldstein MD FACC FASE Professor of Medicine Georgetown University Medical Center MedStar Heart Institute Washington Hospital Center Monday, October 10, 2017 Pulmonary Artery
Pediatric Echocardiography Examination Content Outline
 Pediatric Echocardiography Examination Content Outline (Outline Summary) # Domain Subdomain Percentage 1 Anatomy and Physiology Normal Anatomy and Physiology 10% 2 Abnormal Pathology and Pathophysiology
Pediatric Echocardiography Examination Content Outline (Outline Summary) # Domain Subdomain Percentage 1 Anatomy and Physiology Normal Anatomy and Physiology 10% 2 Abnormal Pathology and Pathophysiology
What is the mechanism of the audible carotid bruit? How does one calculate the velocity of blood flow?
 CASE 8 A 65-year-old man with a history of hypertension and coronary artery disease presents to the emergency center with complaints of left-sided facial numbness and weakness. His blood pressure is normal,
CASE 8 A 65-year-old man with a history of hypertension and coronary artery disease presents to the emergency center with complaints of left-sided facial numbness and weakness. His blood pressure is normal,
Quantitation of right ventricular dimensions and function
 SCCS Basics of cardiac assessment Quantitation of right ventricular dimensions and function Tomasz Kukulski, MD PhD Dept of Cardiology, Congenital Heart Disease and Electrotherapy Silesian Medical University
SCCS Basics of cardiac assessment Quantitation of right ventricular dimensions and function Tomasz Kukulski, MD PhD Dept of Cardiology, Congenital Heart Disease and Electrotherapy Silesian Medical University
Gastroenterology. Certification Examination Blueprint. Purpose of the exam
 Gastroenterology Certification Examination Blueprint Purpose of the exam The exam is designed to evaluate the knowledge, diagnostic reasoning, and clinical judgment skills expected of the certified gastroenterologist
Gastroenterology Certification Examination Blueprint Purpose of the exam The exam is designed to evaluate the knowledge, diagnostic reasoning, and clinical judgment skills expected of the certified gastroenterologist
Spontaneous portosystemic venous shunts in liver cirrhosis: Anatomy, pathophysiology, hemodynamic changes and imaging findings
 Spontaneous portosystemic venous shunts in liver cirrhosis: Anatomy, pathophysiology, hemodynamic changes and imaging findings Poster No.: C-3193 Congress: ECR 2010 Type: Educational Exhibit Topic: Vascular
Spontaneous portosystemic venous shunts in liver cirrhosis: Anatomy, pathophysiology, hemodynamic changes and imaging findings Poster No.: C-3193 Congress: ECR 2010 Type: Educational Exhibit Topic: Vascular
THE RIGHT VENTRICLE IN PULMONARY HYPERTENSION R. DRAGU
 THE RIGHT VENTRICLE IN PULMONARY HYPERTENSION R. DRAGU Cardiology Dept. Rambam Health Care Campus Rappaport Faculty of Medicine Technion, Israel Why the Right Ventricle? Pulmonary hypertension (PH) Right
THE RIGHT VENTRICLE IN PULMONARY HYPERTENSION R. DRAGU Cardiology Dept. Rambam Health Care Campus Rappaport Faculty of Medicine Technion, Israel Why the Right Ventricle? Pulmonary hypertension (PH) Right
Paediatric Cardiology. Acyanotic CHD. Prof F F Takawira
 Paediatric Cardiology Acyanotic CHD Prof F F Takawira Aetiology Chromosomal Down syndrome, T13, T18 Genetic syndromes (gene defects) Velo-Cardio-facial (22 del) Genetic syndromes (undefined aetiology)
Paediatric Cardiology Acyanotic CHD Prof F F Takawira Aetiology Chromosomal Down syndrome, T13, T18 Genetic syndromes (gene defects) Velo-Cardio-facial (22 del) Genetic syndromes (undefined aetiology)
CARDIAC PROBLEMS IN PREGNANCY
 CARDIAC PROBLEMS IN PREGNANCY LAS VEGAS, NEVADA, USA 27 February 1 March 2016 SUCCESSFUL TREATMENT WITH RECOMBINANT TISSUE PLASMINOGEN ACTIVATOR OF MASSIVE PULMONARY EMBOLISM IN THE 16 TH WEEK OF PREGNANCY
CARDIAC PROBLEMS IN PREGNANCY LAS VEGAS, NEVADA, USA 27 February 1 March 2016 SUCCESSFUL TREATMENT WITH RECOMBINANT TISSUE PLASMINOGEN ACTIVATOR OF MASSIVE PULMONARY EMBOLISM IN THE 16 TH WEEK OF PREGNANCY
The role of bedside ultrasound in the diagnosis of pericardial effusion and cardiac tamponade
 Symposium The role of bedside ultrasound in the diagnosis of pericardial effusion and cardiac tamponade Adam Goodman, Phillips Perera, Thomas Mailhot, Diku Mandavia Department of Emergency Medicine, Los
Symposium The role of bedside ultrasound in the diagnosis of pericardial effusion and cardiac tamponade Adam Goodman, Phillips Perera, Thomas Mailhot, Diku Mandavia Department of Emergency Medicine, Los
Evaluation of the Right Ventricle in Candidates for Right Ventricular Assist Device Implantation.
 Evaluation of the Right Ventricle in Candidates for Right Ventricular Assist Device Implantation. Evaluation of RVAD Function. Ioannis A Paraskevaidis Attikon University Hospital Historical Perspective
Evaluation of the Right Ventricle in Candidates for Right Ventricular Assist Device Implantation. Evaluation of RVAD Function. Ioannis A Paraskevaidis Attikon University Hospital Historical Perspective
Is it HF secondary to rheumatic heart disease???
 Is it HF secondary to rheumatic heart disease??? Is mitral regurg. Is complication of CHF??? Cardiomyopathy Definition The term cardiomyopathy is purely descriptive, meaning disease of the heart muscle
Is it HF secondary to rheumatic heart disease??? Is mitral regurg. Is complication of CHF??? Cardiomyopathy Definition The term cardiomyopathy is purely descriptive, meaning disease of the heart muscle
ΚΑΡΔΙΟΛΟΓΟΣ EUROPEAN ACCREDITATION IN TRANSTHORACIC AND TRANSESOPHAGEAL ECHOCARDIOGRAPHY
 1 ΚΑΡΔΙΟΛΟΓΟΣ EUROPEAN ACCREDITATION IN TRANSTHORACIC AND TRANSESOPHAGEAL ECHOCARDIOGRAPHY 2 Constrictive pericarditis (CP) is characterized by impaired ventricular filling due to a stiffened or noncompliant
1 ΚΑΡΔΙΟΛΟΓΟΣ EUROPEAN ACCREDITATION IN TRANSTHORACIC AND TRANSESOPHAGEAL ECHOCARDIOGRAPHY 2 Constrictive pericarditis (CP) is characterized by impaired ventricular filling due to a stiffened or noncompliant
Presenter: Steven Brust, HCS-D, HCS-H Product Manager, Home Health Coding Center
 Presenter: Steven Brust, HCS-D, HCS-H Product Manager, Home Health Coding Center Pinpoint & properly assign the appropriate heart failure codes Left- vs. Right-sided Left ventricular failure (LVF) may
Presenter: Steven Brust, HCS-D, HCS-H Product Manager, Home Health Coding Center Pinpoint & properly assign the appropriate heart failure codes Left- vs. Right-sided Left ventricular failure (LVF) may
Left Ventricular Diastolic Dysfunction in South Indian Essential Hypertensive Patient
 Left Ventricular Diastolic Dysfunction in South Indian Essential Hypertensive Patient Dr. Peersab.M. Pinjar 1, Dr Praveenkumar Devarbahvi 1 and Dr Vasudeva Murthy.C.R 2, Dr.S.S.Bhat 1, Dr.Jayaraj S G 1
Left Ventricular Diastolic Dysfunction in South Indian Essential Hypertensive Patient Dr. Peersab.M. Pinjar 1, Dr Praveenkumar Devarbahvi 1 and Dr Vasudeva Murthy.C.R 2, Dr.S.S.Bhat 1, Dr.Jayaraj S G 1
Index. Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type.
 Index Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A Acute coronary syndrome(s), anticoagulant therapy in, 706, 707 antiplatelet therapy in, 702 ß-blockers in, 703 cardiac biomarkers in,
Index Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A Acute coronary syndrome(s), anticoagulant therapy in, 706, 707 antiplatelet therapy in, 702 ß-blockers in, 703 cardiac biomarkers in,
Visceral Vascular Ultrasound. Joel Thompson, MD, MPH Borg & Ide Imaging
 Visceral Vascular Ultrasound Joel Thompson, MD, MPH Borg & Ide Imaging Objectives: Review major abdominal vascular structures Identify normal peak systolic velocity (PSV) for major abdominal arteries.
Visceral Vascular Ultrasound Joel Thompson, MD, MPH Borg & Ide Imaging Objectives: Review major abdominal vascular structures Identify normal peak systolic velocity (PSV) for major abdominal arteries.
Estimation of Right Atrial Pressure from the Inspiratory Collapse of the Inferior Vena cava in Pediatric Patients
 Original Article Iran J Pediatr Jun 2010; Vol 20 (No 2), Pp:206-210 Estimation of Right Atrial Pressure from the Inspiratory Collapse of the Inferior Vena cava in Pediatric Patients Hamid Amoozgar*, MD;
Original Article Iran J Pediatr Jun 2010; Vol 20 (No 2), Pp:206-210 Estimation of Right Atrial Pressure from the Inspiratory Collapse of the Inferior Vena cava in Pediatric Patients Hamid Amoozgar*, MD;
Assessment and Diagnosis of Heart Failure
 Assessment and Diagnosis of Heart Failure Heart failure (HF) is a complex clinical syndrome resulting from any structural or functional impairment of ventricular filling or ejection of blood and is characterized
Assessment and Diagnosis of Heart Failure Heart failure (HF) is a complex clinical syndrome resulting from any structural or functional impairment of ventricular filling or ejection of blood and is characterized
Left ventricular diastolic function and filling pressure in patients with dilated cardiomyopathy
 Left ventricular diastolic function and filling pressure in patients with dilated cardiomyopathy Bogdan A. Popescu University of Medicine and Pharmacy Bucharest, Romania My conflicts of interest: I have
Left ventricular diastolic function and filling pressure in patients with dilated cardiomyopathy Bogdan A. Popescu University of Medicine and Pharmacy Bucharest, Romania My conflicts of interest: I have
Pericardial Diseases. Smonporn Boonyaratavej, MD. Division of Cardiology, Department of Medicine Chulalongkorn University
 Pericardial Diseases Smonporn Boonyaratavej, MD Division of Cardiology, Department of Medicine Chulalongkorn University Cardiac Center, King Chulalongkorn Memorial Hospital 21 AUGUST 2016 Pericardial
Pericardial Diseases Smonporn Boonyaratavej, MD Division of Cardiology, Department of Medicine Chulalongkorn University Cardiac Center, King Chulalongkorn Memorial Hospital 21 AUGUST 2016 Pericardial
Acute impairment of basal left ventricular rotation but not twist and untwist are involved in the pathogenesis of acute hypertensive pulmonary oedema
 Acute impairment of basal left ventricular rotation but not twist and untwist are involved in the pathogenesis of acute hypertensive pulmonary oedema A.D. Margulescu 1,2, R.C. Sisu 1,2, M. Florescu 2,
Acute impairment of basal left ventricular rotation but not twist and untwist are involved in the pathogenesis of acute hypertensive pulmonary oedema A.D. Margulescu 1,2, R.C. Sisu 1,2, M. Florescu 2,
A study of Brain Natriuretic Peptide levels in acute cardiac failure
 Original Research Article A study of Brain Natriuretic Peptide levels in acute cardiac failure Bhavik Prajapati 1*, Anirudh Kulkarni 2 1 Assistant Professor, Department of Medicine, SMS Multispecialty
Original Research Article A study of Brain Natriuretic Peptide levels in acute cardiac failure Bhavik Prajapati 1*, Anirudh Kulkarni 2 1 Assistant Professor, Department of Medicine, SMS Multispecialty
Virtual Mentor American Medical Association Journal of Ethics December 2008, Volume 10, Number 12:
 Virtual Mentor American Medical Association Journal of Ethics December 2008, Volume 10, Number 12: 805-809. CLINICAL PEARL Indications for Use of TIPS in Treating Portal Hypertension Elizabeth C. Verna,
Virtual Mentor American Medical Association Journal of Ethics December 2008, Volume 10, Number 12: 805-809. CLINICAL PEARL Indications for Use of TIPS in Treating Portal Hypertension Elizabeth C. Verna,
CASE DISCUSSION. Dr JAYASREE VEERABOINA 2nd yr PG MS OBG
 CASE DISCUSSION Dr JAYASREE VEERABOINA 2nd yr PG MS OBG Normal Cardiovascular changes in Pregnancy CARDIAC OUTPUT 5 th wk -- starts 12 wks -- 30-35% 30-32 wks -- 40% During labour -- 50% After delivery
CASE DISCUSSION Dr JAYASREE VEERABOINA 2nd yr PG MS OBG Normal Cardiovascular changes in Pregnancy CARDIAC OUTPUT 5 th wk -- starts 12 wks -- 30-35% 30-32 wks -- 40% During labour -- 50% After delivery
Doppler Basic & Hemodynamic Calculations
 Doppler Basic & Hemodynamic Calculations August 19, 2017 Smonporn Boonyaratavej MD Division of Cardiology, Department of Medicine Chulalongkorn University Cardiac Center, King Chulalongkorn Memorial Hospital
Doppler Basic & Hemodynamic Calculations August 19, 2017 Smonporn Boonyaratavej MD Division of Cardiology, Department of Medicine Chulalongkorn University Cardiac Center, King Chulalongkorn Memorial Hospital
Cor pulmonale. Dr hamid reza javadi
 1 Cor pulmonale Dr hamid reza javadi 2 Definition Cor pulmonale ;pulmonary heart disease; is defined as dilation and hypertrophy of the right ventricle (RV) in response to diseases of the pulmonary vasculature
1 Cor pulmonale Dr hamid reza javadi 2 Definition Cor pulmonale ;pulmonary heart disease; is defined as dilation and hypertrophy of the right ventricle (RV) in response to diseases of the pulmonary vasculature
Protocol Identifier Subject Identifier Visit Description. [Y] Yes [N] No. [Y] Yes [N] N. If Yes, admission date and time: Day Month Year
![Protocol Identifier Subject Identifier Visit Description. [Y] Yes [N] No. [Y] Yes [N] N. If Yes, admission date and time: Day Month Year Protocol Identifier Subject Identifier Visit Description. [Y] Yes [N] No. [Y] Yes [N] N. If Yes, admission date and time: Day Month Year](/thumbs/76/74263761.jpg) PAST MEDICAL HISTORY Has the subject had a prior episode of heart failure? o Does the subject have a prior history of exposure to cardiotoxins, such as anthracyclines? URGENT HEART FAILURE VISIT Did heart
PAST MEDICAL HISTORY Has the subject had a prior episode of heart failure? o Does the subject have a prior history of exposure to cardiotoxins, such as anthracyclines? URGENT HEART FAILURE VISIT Did heart
The Whipple Operation Illustrations
 The Whipple Operation Illustrations Fig. 1. Illustration of the sixstep pancreaticoduodenectomy (Whipple operation) as described in a number of recent text books by Dr. Evans. The operation is divided
The Whipple Operation Illustrations Fig. 1. Illustration of the sixstep pancreaticoduodenectomy (Whipple operation) as described in a number of recent text books by Dr. Evans. The operation is divided
Congestive Heart Failure or Heart Failure
 Congestive Heart Failure or Heart Failure Dr Hitesh Patel Ascot Cardiology Group Heart Failure Workshop April, 2014 Question One What is the difference between congestive heart failure and heart failure?
Congestive Heart Failure or Heart Failure Dr Hitesh Patel Ascot Cardiology Group Heart Failure Workshop April, 2014 Question One What is the difference between congestive heart failure and heart failure?
Copyright 2011, 2007 by Mosby, Inc., an affiliate of Elsevier Inc. Normal Cardiac Anatomy
 Mosby,, an affiliate of Elsevier Normal Cardiac Anatomy Impaired cardiac pumping Results in vasoconstriction & fluid retention Characterized by ventricular dysfunction, reduced exercise tolerance, diminished
Mosby,, an affiliate of Elsevier Normal Cardiac Anatomy Impaired cardiac pumping Results in vasoconstriction & fluid retention Characterized by ventricular dysfunction, reduced exercise tolerance, diminished
What effects will proximal or distal disease have on a waveform?
 Spectral Doppler Interpretation Director of Ultrasound Education & Quality Assurance Baylor College of Medicine Division of Maternal-Fetal Medicine Maternal Fetal Center Imaging Manager Texas Children
Spectral Doppler Interpretation Director of Ultrasound Education & Quality Assurance Baylor College of Medicine Division of Maternal-Fetal Medicine Maternal Fetal Center Imaging Manager Texas Children
Exercise ECG (TMT) is a commonly used investigation in the
 Journal of the association of physicians of india july 2013 VOL. 61 65 Case Reports The Common, Less Common and Uncommon Examples of Exercise ECG MJ Jacob *, Puneet Kumar +, Mudalsha Ravina +, Amrita Tiwari
Journal of the association of physicians of india july 2013 VOL. 61 65 Case Reports The Common, Less Common and Uncommon Examples of Exercise ECG MJ Jacob *, Puneet Kumar +, Mudalsha Ravina +, Amrita Tiwari
Definition: HPS is a disease process with a triad of: 1- Liver disease. 2- Widespread intrapulmonary vasodilatation. 3- Gas exchange abnormality prese
 Hepatopulmonary syndrome (HPS) By Alaa Haseeb, MS.c Definition: HPS is a disease process with a triad of: 1- Liver disease. 2- Widespread intrapulmonary vasodilatation. 3- Gas exchange abnormality presenting
Hepatopulmonary syndrome (HPS) By Alaa Haseeb, MS.c Definition: HPS is a disease process with a triad of: 1- Liver disease. 2- Widespread intrapulmonary vasodilatation. 3- Gas exchange abnormality presenting
Appendix 9: Endoscopic Ultrasound in Gastroenterology
 Appendix 9: Endoscopic Ultrasound in Gastroenterology This curriculum is intended for clinicians who perform endoscopic ultrasonography (EUS) in gastroenterology. It includes standards for theoretical
Appendix 9: Endoscopic Ultrasound in Gastroenterology This curriculum is intended for clinicians who perform endoscopic ultrasonography (EUS) in gastroenterology. It includes standards for theoretical
Impedance Cardiography (ICG) Application of ICG in Intensive Care and Emergency
 Impedance Cardiography (ICG) Application of ICG in Intensive Care and Emergency Aim of haemodynamic monitoring in ICU and ED Detection and therapy of insufficient organ perfusion Answers to common cardiovascular
Impedance Cardiography (ICG) Application of ICG in Intensive Care and Emergency Aim of haemodynamic monitoring in ICU and ED Detection and therapy of insufficient organ perfusion Answers to common cardiovascular
Diastolic Heart Failure. Edwin Tulloch-Reid MBBS FACC Consultant Cardiologist Heart Institute of the Caribbean December 2012
 Diastolic Heart Failure Edwin Tulloch-Reid MBBS FACC Consultant Cardiologist Heart Institute of the Caribbean December 2012 Disclosures Have spoken for Merck, Sharpe and Dohme Sat on a physician advisory
Diastolic Heart Failure Edwin Tulloch-Reid MBBS FACC Consultant Cardiologist Heart Institute of the Caribbean December 2012 Disclosures Have spoken for Merck, Sharpe and Dohme Sat on a physician advisory
Diversion of the inferior vena cava following repair of atrial septal defect causing hypoxemia
 Marshall University Marshall Digital Scholar Internal Medicine Faculty Research Spring 5-2004 Diversion of the inferior vena cava following repair of atrial septal defect causing hypoxemia Ellen A. Thompson
Marshall University Marshall Digital Scholar Internal Medicine Faculty Research Spring 5-2004 Diversion of the inferior vena cava following repair of atrial septal defect causing hypoxemia Ellen A. Thompson
Abdominal Doppler Mastering the next level of vascular anatomy in the belly. Cindy A. Owen, RDMS, RVT
 Abdominal Doppler Mastering the next level of vascular anatomy in the belly Cindy A. Owen, RDMS, RVT Introduction Abdominal Doppler is a tough exam Success is dependent on: Patient body habitus Patient
Abdominal Doppler Mastering the next level of vascular anatomy in the belly Cindy A. Owen, RDMS, RVT Introduction Abdominal Doppler is a tough exam Success is dependent on: Patient body habitus Patient
Department of General Medicine, Kilpauk Medical College and Hospital, Chennai, Tamil Nadu, India * Corresponding author
 Original Research Article Study on clinical assessment of volume status and correlation to the respiratory variation in inferior vena cava diameter by echocardiography, a non-invasive method of measuring
Original Research Article Study on clinical assessment of volume status and correlation to the respiratory variation in inferior vena cava diameter by echocardiography, a non-invasive method of measuring
