Cardiac Arrest Survivors and Implantable Defibrillator Recipients:
|
|
|
- Edgar Burns
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 South East Wales Cardiac Network Arrhythmia Pathway Cardiac Arrest Survivors and Implantable Defibrillator Recipients: Background: Implementation of the Recommendations contained in Standard 5 of the Cardiac Disease National Service Framework for Wales This document has been produced at the request of the Cardiac Networks Coordinating Group on behalf of the South East Wales Cardiac Network (SEWCN) and the Mid and South West Wales Cardiac Network (MSWWCN). Authorship: This document is co-authored by Dr Rob Bleasdale (Consultant Cardiologist, Royal Glamorgan Hospital), Dr Phillip Campbell (Consultant Cardiologist, Royal Gwent Hospital), Dr Eiry Edmunds (Consultant Cardiologist, West Wales General Hospital), Andrea Gasson (Nurse Practitioner, Royal Glamorgan Hospital), Dr Jonathon Goodfellow, Consultant cardiologist, Princess of Wales Hospital), Mandie Welch (BHF Arrhythmia Specialist Nurse) Cardiac Arrest Survivors: Cardiac arrest remains a common cause of death, killing in the region of 250 people a day in the UK. Less than 5% of these victims survive if the event occurs out of hospital. The chain of care delivered by the Ambulance service through to the A&E department to the Heart Rhythm Specialist/ Electrophysiologist is key to the quality of treatment offered to the individual patient. All cardiac arrest survivors successfully resuscitated at the scene of their collapse should undergo a full clinical assessment and a 12 lead ECG should be recorded. Once transferred to the A&E department this information remains key to the management of the patient. All paperwork and paper copies of rhythm strips should be carefully handed over to the attending medical staff. The attending medical staff are responsible for ensuring that this information is transferred to the hospital records. This process should be backed up by an electronic download of the automated external defibrillator (AED) on the return of the ambulance/ paramedic crew to their base. This should be printed off and attached to a further copy of the patient s relevant Ambulance Trust yellow sheet. This entire document should be sent to the local Heart Rhythm Specialist/ Electrophysiologist. If the history, ECG and biochemistry confirm the diagnosis of a myocardial infarction resulting in new Q waves on the ECG then usual post myocardial infarction guidance should be followed. If however there is evidence of reversible ischaemia then in-patient revascularisation is recommended in consultation with local Heart Rhythm Specialist/ Electrophysiologist. If the cause of the cardiac arrest remains uncertain from the in hospital clinical assessment then the patient should be reviewed by local Heart Rhythm Specialist/ Electrophysiologist on that index admission. Finally even if there is strong evidence of a transient and reversible cause for the cardiac arrest, suggested by a normal ECG, a structurally normal heart demonstrated with an inpatient transthoracic echocardiogram and the absence of a family history of premature sudden cardiac death below the age of forty years, the patient should still be seen by the local Heart Rhythm Specialist/ Electrophysiologist on that index admission. South East Wales Cardiac Network Page 1 of 9 Arrhythmia Pathway Cardiac Arrest and ICDs Final Version
2 This guidance therefore culminates in all patients admitted having survived a cardiac arrest being assessed by the local Heart Rhythm Specialist/ Electrophysiologist on that index admission with exception of patients that experience a cardiac arrest during a Q wave myocardial infarction. See Appendix 1 Implantable Cardioverter Defibrillator (ICD) Recipients Presenting to the District General Hospital: The indications for ICD implantation are expanding and more and more devices are being implanted. This results in an escalating probability that these patients will present to all clinical areas of clinical care in the district general hospital (DGH). Whilst cardiologists and many physicians have had experience with patients who have these complex devices in situ many clinicians, including surgeons, may not have. ICD Patients Attending Accident and Emergency after Multiple Shock Therapies: Implantable cardiac defibrillators are sophisticated and reliable devices, however the most common complication of device therapy is inappropriate shock delivery. When patients with a discharging ICD are admitted to A&E it is often difficult for the non-specialist to determine whether or not therapy is appropriate. A correctly functioning device may be mistaken for a malfunctioning device and vice-versa. Therapy may be correctly delivered according to device programming, but be inappropriate to the presenting situation. An additional problem for such patients is that medical staff unfamiliar with ICDs frequently have unwarranted concerns about themselves receiving shocks from the ICD. Fear of coming into contact with the patient could adversely effect management. The Network has looked to provide guidance to the non-specialist about the management of ICD patients presenting with a discharging device. These guidelines are intended to supply the knowledge required to safely manage such patients when shock therapy is either appropriate or inappropriate without the need for specialist knowledge of device function or programming. A simple decision tree is provided, dividing patients in to those with, or without cardiac arrest. Action points are provided throughout the decision tree with extra information available for those points marked with an exclamation mark. The guidelines are available on the map of medicine where a mouse click will direct the user to the relevant extra information. Details of where to seek expert help is also provided. There a potential to deviate away from appendix 2 to bring list guidance in line with the map of medicine guidance on this topic which was also authored by Dr Campbell. See Appendix One Map of Medicine Implantable Cardioverter Defibrillator Guidance ICD Patients undergoing elective Surgery: See Appendix 3 ICD Patients Undergoing Emergency: This guidance has been compiled to help in Surgery Introduction: emergency decision making when a patient with an ICD requires urgent or emergency surgery. Where possible the protocol for Elective Surgery should be followed and the ICD checked and reprogrammed prior to surgery. South East Wales Cardiac Network Page 2 of 9 Arrhythmia Pathway Cardiac Arrest and ICDs Final Version
3 General Patient Considerations: ICDs are implanted to treat Ventricular Tachycardia (VT) therefore if a patient has an ICD in situ they are, by definition, at risk of serious cardiac arrhythmias and may have severe underlying structural heart disease eg severe left ventricular impairment or hypertrophic cardiomyopathy (HCM). In addition ICDs can also act as pacemakers in the event of bradycardia. Where possible a SENIOR ANAESTHETIST should be responsible for the patient and advice should be sought from the on-site CARDIOLOGIST or local implant centre. Diathermy: ICDs receive electrical information from the heart and are capable of interpreting the electrical signal. If the electrical signal received is fast the ICD may interpret this as VT or VF and deliver a therapy. This may be in the form of fast burst pacing (anti-tachy-pacing) or shock delivery. Diathermy used during surgery may give rise to electrical interference which could be detected by the ICD and misinterpreted as an electrical signal originating from the ventricle. This could give rise to inhibition of the pacemaker function, speeding up of pacing rate or triggering of the antitachycardia function. It may be necessary to inhibit the ICD (see Inhibition of ICD). If a device s battery is depleted electrical interference can cause a device to stop working completely. The use of diathermy may also induce energy in the leads causing tissue heating. For the above reasons manufacturers of ICDs and pacemakers recommend: AVOIDANCE of diathermy If diathermy is unavoidable BIPOLAR diathermy should be used Limit its use to short bursts Ensure the return electrode is positioned so that the current is far away from the ICD and leads Ensure the cables are well away from the implant site Consider external/transvenous pacing if patient is pacing dependent and pacemaker function is significantly affected by diathermy Inhibition of the ICD: If the ICD needs to be inhibited from delivering a shock a clinical magnet can be placed over the device and held in place with Micropore tape. This usually (but not always) inhibits shock delivery. If this is done The patient should have continuous cardiac monitoring during the time the ICD is inhibited Resuscitation equipment should be available at all times The ICD must be checked post-operatively to ensure correct functioning Essential Equipment:: If the patient requires pacemaker function then cardiac monitoring may misinterpret a pacing spike as evidence of cardiac activation. Rarely the pacemaker output may fail to capture the ventricle. If the defibrillator function is disabled then alternative defibrillation may be required in the event of a cardiac arrhythmia. Therefore the following must be available Continuous cardiac monitoring Alternative method of detecting a patient s pulse eg arterial line(ideally) or pulse oximeter (as minimum) South East Wales Cardiac Network Page 3 of 9 Arrhythmia Pathway Cardiac Arrest and ICDs Final Version
4 Availability of cardiopulmonary resuscitation equipment including external defibrillator and temporary external/transvenous pacing Following emergency/urgent surgery it is good practice to ensure the device is functioning normally before discharge and this should be considered as a routine in all patients with complex devices in situ. ICD Patients and the End of Life Pathways: Many patients with ICDs in situ are able to enjoy a prolonged life expectancy with a reasonable quality of life. However in patients who have progressive cardiac failure and other co-morbid conditions, the shocks from the device or even the thought of the device shocking can cause physical suffering and severe anxiety. When terminal illnesses such as end stage heart failure or cancer are diagnosed, patients may find the additional stress of anticipation an ICD shock an unnecessary burden, particularly as the outcome will have no impact on the underlying condition. The incidence of arrhythmias may increase with the development of electrolyte imbalance, hypoxia and pain, potentially leading to an increase in shock therapy. Multiple discharges are not conducive to the peaceful and dignified death. For these patients the option of deactivating the device can be a sound medical, ethical and legal decision for them. Indications for Deactivation: Patient preference in advanced disease Imminent death (activation inappropriate in the dying phase) Withdrawal of anti-arrhythmic medications While an active DNR ( Do Not Resuscitate order is in force) Discussion for ICD Deactivation: The discussion regarding deactivation should be an open discussion between patient, next of kin and supervising cardiologist, nurse specialist and/ or cardio physiologist and should take place whilst the patient is able to be involved in the decision making process. In situations where the patient is a non-cardiac specialist environment such as medical, surgical wards, hospices or at home the decision still remains the patient s and the health care professional responsible for their care should be encouraged to initiate this discussion. Many experts believe these issues should be discussed prior to implantation in order that the patient has time to consider these issues autonomously should the situation arise in the future. The patient and next of kin are to be made aware that by deactivating the ICD the device will no longer provided therapies in the event of life threatening arrhythmias. The actual turning off of the device is not a painful procedure and will only take a matter of seconds to complete. It is important to try and avoid last minute decisions, not only to avoid unnecessary distress but also to avoid these decisions being deferred to the out of hours services. In these or other urgent/emergency situations where immediate action is necessary, a magnet can be placed over the device. The magnet causes the device to become deactivated only whilst the magnet is in place. Once the magnet is removed the device becomes active again. The will not stop the device functioning as a pacemenker. South East Wales Cardiac Network Page 4 of 9 Arrhythmia Pathway Cardiac Arrest and ICDs Final Version
5 Ethical/Legal issues: To ensure that legal and ethical issued are considered, the patient must be fully informed of their options. Good clinical practice emphasises the importance of shared decision-making between health professionals and patient and, if appropriate, their families throughout the course of the patient s illness. Patients are legally and ethically able to refuse/withdraw from medical interventions which sustain life. Deactivation of ICDs needs to be addressed in the same way as withdrawing/withholding of others treatments which prolong life (BMA 2007). An ICD deactivation would not itself cause death or introduce a new pathological problem. When a patient does not have capacity to make his/her decisions, health professionals caring for them have a moral and legal duty to act in the patients best interests. An assessment of best interests includes balancing the risks and benefits associated with any given treatment. In most cases an ICD will confer greater benefit than harm. However, in some situations, the possibility that recurrent ICD activation might prevent a comfortable death could be judged to outweigh any benefit of prolonging life for a brief period of time. Any such decision process should be multidisciplinary and comply with the Mental Capacity Act Apart from ethical and legal considerations, cultural and religious differences may influence a patient s decision to deactivate. This factor must be taken into account by care providers and the patient s beliefs should be given precedence over their own. References. All Wales Care Pathway for the Last Days of Life Arrhythmia Alliance (2007). Implantable Cardioverter Defibrillators (ICDs) in dying patients. Available on line: - arrythnmiaalliance.org.uk. British Heart Foundation.( 2007) Implantable Cardioverter Defibrillators in patients who are reaching end of life. Available at: - British Medical Association. (2007).Withholding and withdrawing Life-prolonging Medical Treatment: Guidance for Decision making. London:Blackwell Publishing. British Medical Association (2005) The Mental Capacity Act 2005:- Guidance for Health Professionals. London.Available at: National Institute of Clinical Excellence.(2006). Implantable Cardioverter for Arrhythmias: Review of technology appraisal 11.` National Service Framework Tackling CHD and Arrhythmias in Wales (Draft Document 2007). Standard 5. South East Wales Cardiac Network Page 5 of 9 Arrhythmia Pathway Cardiac Arrest and ICDs Final Version
6 Appendix 1: South East Wales Cardiac Network Page 6 of 9 Arrhythmia Pathway Cardiac Arrest and ICDs Final Version
7 Appendix 2: South East Wales Cardiac Network Page 7 of 9 Arrhythmia Pathway Cardiac Arrest and ICDs Final Version
8 Appendix 3: IMPLANTABLE CARDIOVERTER DEFIBRILLATOR AND ELECTIVE SURGERY AS SOON AS A DATE FOR SURGERY IS KNOWN CONTACT YOUR LOCAL CARDIAC PHYSIOLOGY DEPARTMENT WHO WILL LIAISE WITH THE IMPLANTING CENTRE TO MAKE THE NECESSARY ARRANGEMENTS FOR DEVICE REPROGRAMMING AS REQUIRED FOR THE PROCEDURE ON THE PROCEDURE DAY, PLEASE CONTACT YOUR LOCAL CARDIAC PHYSIOLOGY DEPARTMENT WHO WILL CONFIRM WITH YOU WHO WILL BE AVAILABLE TO DE-ACTIVATE THE DEVICE This could be your local Cardiac Physiologist if facilities and expertise are available, or a Cardiac Physiologist from the Implanting Centre or in certain circumstances a Company Technical Support Representative may be called THE ICD NEEDS TO BE REPROGRAMMED TO MONITOR ONLY OR DISABLED WITH A MAGNET CARDIAC MONITORING SHOULD BE MAINTAINED THROUGHOUT PROCEDURE UNTIL ICD REACTIVATED EXTERNAL DEFIBRILLATOR SHOULD BE MADE AVAILABLE THROUGHOUT PROCEDURE DIATHERMY SHOULD BE AVIODED, WHEN UNAVOIDABLE THEN BIPOLAR SHOULD BE USED. IF MONOPOLAR IS USED THEN PLACE RETURN PAD WHERE THE CURRENT PASSES AS FAR AWAY FROM THE ICD LEADS AS POSSIBLE FOLLOWING SURGERY IT IS ESSENTIAL THAT THE DEVICE IS RE-ACTIVATED South East Wales Cardiac Network Page 8 of 9 Arrhythmia Pathway Cardiac Arrest and ICDs Final Version
9 Appendix 4: PROTOCOL FOR THE MANAGEMENT OF PATIENTS WITH IMPLANTABLE CARDIOVERTER DEFIBRILLATORS (ICD) REQUIRING URGENT/EMERGENCY SURGERY General: If there is sufficient time then the steps advised in the Elective Surgical Procedures protocol should be followed. The use of surgical diathermy/electrocautery is contraindicated in patients who have ICDs. It is however recognised that its use may at times be unavoidable. A senior anaesthetist should be responsible for the patient. Advice should be sought from the on-site cardiologist or local cardiac centre. Essential equipment: Cardio-pulmonary resuscitation equipment, external defibrillator with external pacing capabilities (and someone trained in its use). Continuous ECG monitoring. Diathermy: If diathermy use us unavoidable then bipolar is preferable to monopolar. Ensure the cables are kept away from the ICD implant site and an effective method of detecting that a true pulse is present is used ie pulse oximetry (as a minimum) and arterial line (ideally). Deactivation of ICD: In an emergency, if needed, the ICD may be deactivated by the placement of a clinical magnet over the implant site. The magnet can be secured with Micropore tape. During deactivation it is vital that the patient has continuous cardiac monitoring and any subsequent arrhythmias (VT/VF) are treated using the external defibrillator equipment. If the ICD has been deactivated then the magnet should be removed as soon as possible at the end of the procedure. ICD check following surgery: If the ICD has been deactivated using a magnet the ICD function must be checked postoperatively. Until that time the patient should be kept monitored and any arrhythmias treated appropriately. BACKGROUND: In broad terms, patients receive an implantable defibrillator because 1: they have survived a life-threatening ventricular arrhythmia and are at risk of having further life-threatening arrhythmias. 2: they have severe cardiac disease (usually with severe LV impairment) and are deemed to be at high risk of life-threatening ventricular arrhythmias. The ICD is designed to detect rapid heart rates and to respond appropriately. It does this be either trying to pace terminate a ventricular tachycardia or by delivering an electrical impulse directly to the endocardium. In addition to defibrillation ICDs may also provide a bradycardia pacing function eg there may be an accompanying complete heart block. The use of surgical diathermy/electrocautery can lead to electrical interference which may be detected and misinterpreted by the ICD. The electrical signal may be interpreted as a ventricular arrhythmia leading to inappropriate shock delivery or the signal may be interpreted as a normal cardiac impulse resulting in inappropriate inhibition of bradycardia pacing. The electrical energy may also cause tissue heating at the lead tips through high frequency current delivery. South East Wales Cardiac Network Page 9 of 9 Arrhythmia Pathway Cardiac Arrest and ICDs Final Version
Cardiac Arrest Survivors and Implantable Defibrillator Recipients:
 South East Wales Cardiac Network Arrhythmia Pathway Cardiac Arrest Survivors and Implantable : Background: Implementation of the Recommendations contained in Standard 5 of the Cardiac National Service
South East Wales Cardiac Network Arrhythmia Pathway Cardiac Arrest Survivors and Implantable : Background: Implementation of the Recommendations contained in Standard 5 of the Cardiac National Service
NORTH OF ENGLAND CARDIOVASCULAR NETWORK (NECVN)
 NORTH OF ENGLAND CARDIOVASCULAR NETWORK (NECVN) Operational policy for optimal management of: Cardiac pacemakers, Implantable cardioverter defibrillators (ICD), Cardiac resynchronisation devices, (CRT-D,
NORTH OF ENGLAND CARDIOVASCULAR NETWORK (NECVN) Operational policy for optimal management of: Cardiac pacemakers, Implantable cardioverter defibrillators (ICD), Cardiac resynchronisation devices, (CRT-D,
Peri-operative management of pacemakers and implantable cardiac defibrillators
 Guideline Title: Peri-operative management of patients fitted with Permanent Pacemakers (PPMs) and Implantable Cardioverter Defibrillators (ICDs). Author(s): Jessica Osman (Chief Pacing Physiologist),
Guideline Title: Peri-operative management of patients fitted with Permanent Pacemakers (PPMs) and Implantable Cardioverter Defibrillators (ICDs). Author(s): Jessica Osman (Chief Pacing Physiologist),
Flowchart for ICD patients undergoing Surgery or procedures involving diathermy/magnetic fields
 Flowchart for ICD patients undergoing Surgery or procedures involving diathermy/magnetic fields Identify patient with an ICD at POAC. Notify Cardiac Physiologist that patient is due to have surgery and
Flowchart for ICD patients undergoing Surgery or procedures involving diathermy/magnetic fields Identify patient with an ICD at POAC. Notify Cardiac Physiologist that patient is due to have surgery and
Deactivating the shock function of an implantable cardioverter defibrillator (ICD) towards the end of life
 Deactivating the shock function of an implantable cardioverter defibrillator (ICD) towards the end of life A guide for patients and carers This leaflet is for people who have an implantable cardiac defibrillator
Deactivating the shock function of an implantable cardioverter defibrillator (ICD) towards the end of life A guide for patients and carers This leaflet is for people who have an implantable cardiac defibrillator
Title Deactivation of Implantable Cardioverter Defibrillators (ICD) towards the end of life Guidelines
 Document Control Title Deactivation of Implantable Cardioverter Defibrillators (ICD) towards the end of life Guidelines Author Lead Nurse for Cardiac Support Services Northern Arrhythmia Care Coordinator
Document Control Title Deactivation of Implantable Cardioverter Defibrillators (ICD) towards the end of life Guidelines Author Lead Nurse for Cardiac Support Services Northern Arrhythmia Care Coordinator
BRITISH HEART RHYTHM SOCIETY GUIDELINES FOR THE MANAGEMENT OF PATIENTS WITH CARDIAC IMPLANTABLE ELECTRONIC DEVICES (CIEDs) AROUND THE TIME OF SURGERY
 BRITISH HEART RHYTHM SOCIETY GUIDELINES FOR THE MANAGEMENT OF PATIENTS WITH CARDIAC IMPLANTABLE ELECTRONIC DEVICES (CIEDs) AROUND THE TIME OF SURGERY Honey Thomas, Andy Turley and Chris Plummer on behalf
BRITISH HEART RHYTHM SOCIETY GUIDELINES FOR THE MANAGEMENT OF PATIENTS WITH CARDIAC IMPLANTABLE ELECTRONIC DEVICES (CIEDs) AROUND THE TIME OF SURGERY Honey Thomas, Andy Turley and Chris Plummer on behalf
Procedure for the Reprogramming of Pacemakers (PPMs) Prior to Elective and Emergency Surgery
 Procedure for the Reprogramming of Pacemakers (PPMs) Prior to Elective and Emergency Surgery Version 1 2012 Aimee Nelson/ Natalie topping Version 2 October 2017 Natalie Archer Dr D. J. McEneaney Dr D.J.
Procedure for the Reprogramming of Pacemakers (PPMs) Prior to Elective and Emergency Surgery Version 1 2012 Aimee Nelson/ Natalie topping Version 2 October 2017 Natalie Archer Dr D. J. McEneaney Dr D.J.
Date of Meeting: Ratified Date: 11/03/2010
 Document Type: GUIDELINE Unique Identifier: CORP/GUID/086 Title: Implantable Cardioverter Defibrillator (ICD) Scope: Lancashire and Cumbria Cardiac and Stroke Network Lancashire and Cumbria wide Author/Originator
Document Type: GUIDELINE Unique Identifier: CORP/GUID/086 Title: Implantable Cardioverter Defibrillator (ICD) Scope: Lancashire and Cumbria Cardiac and Stroke Network Lancashire and Cumbria wide Author/Originator
British Society for Dermatological Surgery (BSDS) & British Heart Rhythm Society (BHRS) Guidance on Implanted Devices & Dermatological Surgery
 British Society for Dermatological Surgery (BSDS) & British Heart Rhythm Society (BHRS) Guidance on Implanted Devices & Dermatological Surgery Contents Page 1. Introduction 2. Summary & PPM 3. ICD & ILR
British Society for Dermatological Surgery (BSDS) & British Heart Rhythm Society (BHRS) Guidance on Implanted Devices & Dermatological Surgery Contents Page 1. Introduction 2. Summary & PPM 3. ICD & ILR
Subcutaneous implantable cardioverter defibrillator insertion for preventing sudden cardiac death
 NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CARE EXCELLENCE Interventional procedure consultation document Subcutaneous implantable cardioverter defibrillator insertion for preventing sudden cardiac death A subcutaneous
NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CARE EXCELLENCE Interventional procedure consultation document Subcutaneous implantable cardioverter defibrillator insertion for preventing sudden cardiac death A subcutaneous
Specialised Services Policy Position PP151
 Specialised Services Policy Position PP151 Complex Devices: Implantable Cardioverter Defibrillators and Cardiac Resynchronisation Therapy for arrhythmias and heart failure January 2019 Version 1.0 Document
Specialised Services Policy Position PP151 Complex Devices: Implantable Cardioverter Defibrillators and Cardiac Resynchronisation Therapy for arrhythmias and heart failure January 2019 Version 1.0 Document
Emergency Department Management of Patients with Implantable Cardioverter Defibrillators
 IAEM Clinical Guideline Emergency Department Management of Patients with Implantable Cardioverter Defibrillators Version 1 June 2014 DISCLAIMER IAEM recognises that patients, their situations, Emergency
IAEM Clinical Guideline Emergency Department Management of Patients with Implantable Cardioverter Defibrillators Version 1 June 2014 DISCLAIMER IAEM recognises that patients, their situations, Emergency
PERIOPERATIVE MANAGEMENT: CARDIAC PACEMAKERS AND DEFIBRILLATORS
 PERIOPERATIVE MANAGEMENT: CARDIAC PACEMAKERS AND DEFIBRILLATORS DR SUSAN CORCORAN CARDIOLOGIST ONCE UPON A TIME.. Single chamber pacemakers Programmed at 70/min VVI 70 UNIPOLAR SYSTEMS A Unipolar Pacing
PERIOPERATIVE MANAGEMENT: CARDIAC PACEMAKERS AND DEFIBRILLATORS DR SUSAN CORCORAN CARDIOLOGIST ONCE UPON A TIME.. Single chamber pacemakers Programmed at 70/min VVI 70 UNIPOLAR SYSTEMS A Unipolar Pacing
Cardiac Pacing. Learning outcomes. Introduction. The cardiac impulse - its formation and its failure CHAPTER. To understand:
 Cardiac Pacing CHAPTER 10 Learning outcomes To understand: The indications for cardiac pacing in the peri-arrest setting How to perform percussion pacing How to apply non-invasive, transcutaneous electrical
Cardiac Pacing CHAPTER 10 Learning outcomes To understand: The indications for cardiac pacing in the peri-arrest setting How to perform percussion pacing How to apply non-invasive, transcutaneous electrical
NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CLINICAL EXCELLENCE
 NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CLINICAL EXCELLENCE Implantable cardioverter defibrillators for the treatment of arrhythmias and cardiac resynchronisation therapy for the treatment of heart failure (review
NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CLINICAL EXCELLENCE Implantable cardioverter defibrillators for the treatment of arrhythmias and cardiac resynchronisation therapy for the treatment of heart failure (review
Deactivating implantable cardiac defibrillators in end of life care. Dr Laurence O Toole Consultant Cardiologist STH NHS FT 20 th November 2014
 Deactivating implantable cardiac defibrillators in end of life care Dr Laurence O Toole Consultant Cardiologist STH NHS FT 20 th November 2014 Implantable Cardiac Defibrillators (ICDs) ICDs have 3 main
Deactivating implantable cardiac defibrillators in end of life care Dr Laurence O Toole Consultant Cardiologist STH NHS FT 20 th November 2014 Implantable Cardiac Defibrillators (ICDs) ICDs have 3 main
Implantable Cardioverter Defibrillator
 12:13:18 CTPALS067 V2_CTPALS01 25/04/2017 11:19 Page 1 Implantable Cardioverter Defibrillator A device to help correct abnormal heart rhythms This leaflet has been written to provide information about
12:13:18 CTPALS067 V2_CTPALS01 25/04/2017 11:19 Page 1 Implantable Cardioverter Defibrillator A device to help correct abnormal heart rhythms This leaflet has been written to provide information about
DEFIBRILLATORS. Prof. Yasser Mostafa Kadah
 DEFIBRILLATORS Prof. Yasser Mostafa Kadah Basics Defibrillation is definitive treatment for life-threatening cardiac arrhythmias such as ventricular fibrillation Defibrillation consists of delivering therapeutic
DEFIBRILLATORS Prof. Yasser Mostafa Kadah Basics Defibrillation is definitive treatment for life-threatening cardiac arrhythmias such as ventricular fibrillation Defibrillation consists of delivering therapeutic
Different indications for pacemaker implantation are the following:
 Patient Resources: ICD/Pacemaker Overview ICD/Pacemaker Overview What is a pacemaker? A pacemaker is a device that uses low energy electrical pulses to prompt the heart to beat whenever a pause in the
Patient Resources: ICD/Pacemaker Overview ICD/Pacemaker Overview What is a pacemaker? A pacemaker is a device that uses low energy electrical pulses to prompt the heart to beat whenever a pause in the
Title and contents page 1 Who should read this document 2 Scope of the Guideline 2 Background 2 What is new in this version 2
 Temporary Transvenous Pacing Guideline Classification: Clinical Guideline Lead Author: Dr Peter Woolfson Additional author(s): Dr Alan Fitchet Sister Joanne Hughes, Matron Julie Winstanley Authors Division:
Temporary Transvenous Pacing Guideline Classification: Clinical Guideline Lead Author: Dr Peter Woolfson Additional author(s): Dr Alan Fitchet Sister Joanne Hughes, Matron Julie Winstanley Authors Division:
NHS. Implantable cardioverter defibrillators (ICDs) for arrhythmias. National Institute for Health and Clinical Excellence. Issue date: January 2006
 NHS National Institute for Health and Clinical Excellence Issue date: January 2006 Implantable cardioverter defibrillators (ICDs) for arrhythmias Understanding NICE guidance information for people with
NHS National Institute for Health and Clinical Excellence Issue date: January 2006 Implantable cardioverter defibrillators (ICDs) for arrhythmias Understanding NICE guidance information for people with
Pediatric pacemakers & ICDs:
 Pediatric pacemakers & ICDs: perioperative management Manchula Navaratnam Clinical Assistant Professor LPCH, Stanford SPA 2016 Conflict of interest: none Objectives Indications in pediatrics Components
Pediatric pacemakers & ICDs: perioperative management Manchula Navaratnam Clinical Assistant Professor LPCH, Stanford SPA 2016 Conflict of interest: none Objectives Indications in pediatrics Components
Arrhythmia Care in the DGH What Still Needs to be Done? Dr. Sundeep Puri Consultant Cardiologist
 Arrhythmia Care in the DGH What Still Needs to be Done? Dr. Sundeep Puri Consultant Cardiologist LOTS!!! This presentation confines itself to the situation in the North West. The views expressed are my
Arrhythmia Care in the DGH What Still Needs to be Done? Dr. Sundeep Puri Consultant Cardiologist LOTS!!! This presentation confines itself to the situation in the North West. The views expressed are my
Quality Standards for the Implantation of Cardiac Rhythm Management Devices. Pan- London Arrhythmia Project Group. Version 3 (18 th July 2011)
 Quality Standards for the Implantation of Cardiac Rhythm Management Devices Pan- London Arrhythmia Project Group Version 3 (18 th July 2011) 1 Standards for Implantation of Permanent Pacemakers (including
Quality Standards for the Implantation of Cardiac Rhythm Management Devices Pan- London Arrhythmia Project Group Version 3 (18 th July 2011) 1 Standards for Implantation of Permanent Pacemakers (including
Permanent Pacemaker Implantation Post Cardiac Surgery: A Cautionary Tale
 Permanent Pacemaker Implantation Post Cardiac Surgery: A Cautionary Tale Jason Collinson & Stuart Tan Essex Cardiothoracic Centre, Basildon and Thurrock University Hospital. Contact: jason.collinson@nhs.net
Permanent Pacemaker Implantation Post Cardiac Surgery: A Cautionary Tale Jason Collinson & Stuart Tan Essex Cardiothoracic Centre, Basildon and Thurrock University Hospital. Contact: jason.collinson@nhs.net
Tachycardia Devices Indications and Basic Trouble Shooting
 Tachycardia Devices Indications and Basic Trouble Shooting Peter A. Brady, MD., FRCP Cardiology Review Course London, March 6 th, 2014 2011 MFMER 3134946-1 Tachycardia Devices ICD Indications Primary and
Tachycardia Devices Indications and Basic Trouble Shooting Peter A. Brady, MD., FRCP Cardiology Review Course London, March 6 th, 2014 2011 MFMER 3134946-1 Tachycardia Devices ICD Indications Primary and
Implantation of an Implantable Cardioverter Defibrillator (ICD)
 PLEASE PRINT WHOLE FORM DOUBLE SIDED ON YELLOW PAPER Patient Information to be retained by patient affix patient label What is an Implantable? Your doctor has recommended that you have an Implantable.
PLEASE PRINT WHOLE FORM DOUBLE SIDED ON YELLOW PAPER Patient Information to be retained by patient affix patient label What is an Implantable? Your doctor has recommended that you have an Implantable.
Use of Automated External Defibrillators (AED s) Frequently Asked Questions
 Use of Automated External Defibrillators (AED s) Frequently Asked Questions With thanks to Sheffield City Council, HR Service 1 Use of Defibrillators Frequently Asked Questions What is a defibrillator?
Use of Automated External Defibrillators (AED s) Frequently Asked Questions With thanks to Sheffield City Council, HR Service 1 Use of Defibrillators Frequently Asked Questions What is a defibrillator?
Automated external defibrillators
 MEDICAL DEVICES Automated external defibrillators Our advice www.hpra.ie Automated external defibrillators MEDICAL DEVICES Automated external defibrillators An automated external defibrillator (AED) is
MEDICAL DEVICES Automated external defibrillators Our advice www.hpra.ie Automated external defibrillators MEDICAL DEVICES Automated external defibrillators An automated external defibrillator (AED) is
Management of RT patients with implanted cardiac devices: From recommendation to implementation
 Management of RT patients with implanted cardiac devices: From recommendation to implementation Coen Hurkmans Clinical Physicist Catharina Hospital Eindhoven The Netherlands 1/22 Outline CIED relocation.
Management of RT patients with implanted cardiac devices: From recommendation to implementation Coen Hurkmans Clinical Physicist Catharina Hospital Eindhoven The Netherlands 1/22 Outline CIED relocation.
OBJECTIVE. 1. Define defibrillation. 2. Describe Need and history of defibrillation. 3. Describe the principle and mechanism of defibrillation.
 Defibrillators OBJECTIVE 1. Define defibrillation. 2. Describe Need and history of defibrillation. 3. Describe the principle and mechanism of defibrillation. 4. Types and classes of defibrillator 5. Describe
Defibrillators OBJECTIVE 1. Define defibrillation. 2. Describe Need and history of defibrillation. 3. Describe the principle and mechanism of defibrillation. 4. Types and classes of defibrillator 5. Describe
Policy Register No: Status: Public. Contributes to Care Quality Commission Outcome 4
 Operational Policy for Transfer of ST Elevation MI (STEMI) patients to Essex Cardiothoracic Centre (ECTC) for Primary Percutaneous Coronary Intervention Policy Register No: 09122 Status: Public Developed
Operational Policy for Transfer of ST Elevation MI (STEMI) patients to Essex Cardiothoracic Centre (ECTC) for Primary Percutaneous Coronary Intervention Policy Register No: 09122 Status: Public Developed
M Series with Rectilinear Biphasic Waveform Defibrillator Option Indications for Use
 DEFIBRILLATOR OPTION General Information Introduction M Series products are available with an advanced electrical design that provides a unique rectilinear biphasic waveform for defibrillation and cardioversion.
DEFIBRILLATOR OPTION General Information Introduction M Series products are available with an advanced electrical design that provides a unique rectilinear biphasic waveform for defibrillation and cardioversion.
Implantation of a Cardiac Resynchronisation Therapy-Defibrillator (CRT-D)
 PLEASE PRINT WHOLE FORM DOUBLE SIDED ON YELLOW PAPER Patient Information to be retained by patient Implantation of a Cardiac Resynchronisation Therapy-Defibrillator (CRT-D) affix patient label What is
PLEASE PRINT WHOLE FORM DOUBLE SIDED ON YELLOW PAPER Patient Information to be retained by patient Implantation of a Cardiac Resynchronisation Therapy-Defibrillator (CRT-D) affix patient label What is
Restraint and the Mental Capacity Act 2005 in operational policing Mental Health & Policing Briefing Sheet 4
 2010 Restraint and the Mental Capacity Act 2005 in operational policing Mental Health & Policing Briefing Sheet 4 This guidance was written to help police officers and partners working in health and social
2010 Restraint and the Mental Capacity Act 2005 in operational policing Mental Health & Policing Briefing Sheet 4 This guidance was written to help police officers and partners working in health and social
New scientific documents from EHRA Management of patients with defibrillator shocks
 New scientific documents from EHRA Management of patients with defibrillator shocks Frieder Braunschweig MD PhD FESC Karolinska University Hospital Stockholm, Sweden Evolution of ICD therapy Worldwide
New scientific documents from EHRA Management of patients with defibrillator shocks Frieder Braunschweig MD PhD FESC Karolinska University Hospital Stockholm, Sweden Evolution of ICD therapy Worldwide
Figure 2. Normal ECG tracing. Table 1.
 Figure 2. Normal ECG tracing that navigates through the left ventricle. Following these bundle branches the impulse finally passes to the terminal points called Purkinje fibers. These Purkinje fibers are
Figure 2. Normal ECG tracing that navigates through the left ventricle. Following these bundle branches the impulse finally passes to the terminal points called Purkinje fibers. These Purkinje fibers are
09/05/2018. True/False: All pacemakers have defibrillation capabilities.
 Paul G. Tarasi M.D. Staff Anesthesiologist Allegheny Health Network Adjunct Clinical Assistant Professor of Anesthesiology Temple University School of Medicine Describe different types of implanted cardiac
Paul G. Tarasi M.D. Staff Anesthesiologist Allegheny Health Network Adjunct Clinical Assistant Professor of Anesthesiology Temple University School of Medicine Describe different types of implanted cardiac
Cardiac Resynchronisation Therapy Defibrillator (CRT-D)
 Patient information Cardiac Resynchronisation Therapy Defibrillator (CRT-D) i Important information for all patients requiring resynchronisation therapy. Golden Jubilee National Hospital Agamemnon Street
Patient information Cardiac Resynchronisation Therapy Defibrillator (CRT-D) i Important information for all patients requiring resynchronisation therapy. Golden Jubilee National Hospital Agamemnon Street
Direct Current Cardioversion (DCCV)
 PLEASE PRINT WHOLE FORM DOUBLE SIDED ON YELLOW PAPER Patient Information to be retained by patient affix patient label What is a This is a procedure carried out under a brief anaesthetic, which uses a
PLEASE PRINT WHOLE FORM DOUBLE SIDED ON YELLOW PAPER Patient Information to be retained by patient affix patient label What is a This is a procedure carried out under a brief anaesthetic, which uses a
Need to Know: Implantable Devices. Carolyn Brown RN, MN, CCRN Education Coordinator Emory Healthcare Atlanta, Georgia
 Need to Know: Implantable Devices Carolyn Brown RN, MN, CCRN Education Coordinator Emory Healthcare Atlanta, Georgia Disclosure Statement I have no relationships to disclose. Objectives Discuss the most
Need to Know: Implantable Devices Carolyn Brown RN, MN, CCRN Education Coordinator Emory Healthcare Atlanta, Georgia Disclosure Statement I have no relationships to disclose. Objectives Discuss the most
MEDICAL DEVICES. our advice on. automated external. defibrillators
 MEDICAL DEVICES our advice on automated external defibrillators An Automated External Defibrillator (AED) is a medical device that analyses a person s heart rhythm and, when needed, delivers a shock to
MEDICAL DEVICES our advice on automated external defibrillators An Automated External Defibrillator (AED) is a medical device that analyses a person s heart rhythm and, when needed, delivers a shock to
Tech Corner. ATP in the Fast VT zone
 Tech Corner ATP in the Fast VT zone NOTE: PLEASE NOTE THAT THE FOLLOWING INFORMATION IS A GENERAL DESCRIPTION OF THE FUNCTION. DETAILS AND PARTICULAR CASES ARE NOT DESCRIBED IN THE ARTICLE. FOR ADDITIONAL
Tech Corner ATP in the Fast VT zone NOTE: PLEASE NOTE THAT THE FOLLOWING INFORMATION IS A GENERAL DESCRIPTION OF THE FUNCTION. DETAILS AND PARTICULAR CASES ARE NOT DESCRIBED IN THE ARTICLE. FOR ADDITIONAL
L: Cardiovascular. Saskatchewan Association of Licensed Practical Nurses, Competency Profile for LPNs, 3rd Ed. 107
 L: Cardiovascular Saskatchewan Association of Licensed Practical Nurses, Competency Profile for LPNs, 3rd Ed. 107 Major Competency Area: L Cardiovascular Competency: L-1 Cardiovascular Nursing Date: January
L: Cardiovascular Saskatchewan Association of Licensed Practical Nurses, Competency Profile for LPNs, 3rd Ed. 107 Major Competency Area: L Cardiovascular Competency: L-1 Cardiovascular Nursing Date: January
Model 5392 EPG Temporary Pacer
 Model 5392 EPG Temporary Pacer Compatible Components Reference Card 5392 Surgical Cables 5487 Disposable, short 5487L Disposable, long 5832S Reusable, small clip 5833S 5833SL Disposable, small clip, short
Model 5392 EPG Temporary Pacer Compatible Components Reference Card 5392 Surgical Cables 5487 Disposable, short 5487L Disposable, long 5832S Reusable, small clip 5833S 5833SL Disposable, small clip, short
The protection you need - without touching your heart
 The S ICD System The protection you need - without touching your heart listen to your heart Patient information You have options An implantable defibrillator, commonly known as an ICD, is a device designed
The S ICD System The protection you need - without touching your heart listen to your heart Patient information You have options An implantable defibrillator, commonly known as an ICD, is a device designed
Cardiac Electrical Therapies. By Omar AL-Rawajfah, PhD, RN
 Cardiac Electrical Therapies By Omar AL-Rawajfah, PhD, RN Outlines What are cardiac electrical therapies Ablation Defibrillation Cardioversion What are the nursing considerations for each type of therapy
Cardiac Electrical Therapies By Omar AL-Rawajfah, PhD, RN Outlines What are cardiac electrical therapies Ablation Defibrillation Cardioversion What are the nursing considerations for each type of therapy
Supplemental Material
 Supplemental Material 1 Table S1. Codes for Patient Selection Cohort Codes Primary PM CPT: 33206 or 33207 or 33208 (without 33225) ICD-9 proc: 37.81, 37.82, 37.83 Primary ICD Replacement PM Replacement
Supplemental Material 1 Table S1. Codes for Patient Selection Cohort Codes Primary PM CPT: 33206 or 33207 or 33208 (without 33225) ICD-9 proc: 37.81, 37.82, 37.83 Primary ICD Replacement PM Replacement
Transcutaneous Pacing on Zoll Defibrillator Version 4 Related Documents SOP-Zoll defibrillator ; Phillips MRX SOP Dr Randal McRoberts
 Emergency Medical Retrieval Service (EMRS) www.emrs.scot.nhs.uk Standard Operating Procedure Public Distribution Title Transcutaneous Pacing on Zoll Defibrillator Version 4 Related Documents SOP-Zoll defibrillator
Emergency Medical Retrieval Service (EMRS) www.emrs.scot.nhs.uk Standard Operating Procedure Public Distribution Title Transcutaneous Pacing on Zoll Defibrillator Version 4 Related Documents SOP-Zoll defibrillator
MONITORING PATIENTS WITH A TEMPORARY EXTERNAL EPICARDIAL PACEMAKER PURPOSE POLICY STATEMENTS SITE APPLICABILITY PRACTICE LEVEL/COMPETENCIES
 PURPOSE Guidelines for caring for and monitoring patients with a temporary external epicardial pacemaker. Epicardial pacemaker monitoring is performed on a continuous basis by a nurse to evaluate the effectiveness
PURPOSE Guidelines for caring for and monitoring patients with a temporary external epicardial pacemaker. Epicardial pacemaker monitoring is performed on a continuous basis by a nurse to evaluate the effectiveness
EnTrust D154VRC Single Chamber ICD 35J delivered 8 seconds BOL, 11.8 seconds ERI 10.7 years**** 35cc, 68g Programmable Active Can
 EnTrust D154ATG Dual Chamber ICD 35J delivered 8 seconds BOL, 11 seconds ERI 7.7 years** 35cc***, 68g Programmable Active Can EnTrust D154VRC Single Chamber ICD 35J delivered 8 seconds BOL, 11.8 seconds
EnTrust D154ATG Dual Chamber ICD 35J delivered 8 seconds BOL, 11 seconds ERI 7.7 years** 35cc***, 68g Programmable Active Can EnTrust D154VRC Single Chamber ICD 35J delivered 8 seconds BOL, 11.8 seconds
THE FOLLOWING QUESTIONS RELATE TO THE RESUSCITATION COUNCIL (UK) RESUSCITATION GUIDELINES 2005
 THE FOLLOWING QUESTIONS RELATE TO THE RESUSCITATION COUNCIL (UK) RESUSCITATION GUIDELINES 2005 1. The guidelines suggest that in out-of-hospital cardiac arrests, attended but unwitnessed by health care
THE FOLLOWING QUESTIONS RELATE TO THE RESUSCITATION COUNCIL (UK) RESUSCITATION GUIDELINES 2005 1. The guidelines suggest that in out-of-hospital cardiac arrests, attended but unwitnessed by health care
Newer pacemakers also can monitor your blood temperature, breathing, and other factors and adjust your heart rate to changes in your activity.
 Pacemakers & Defibrillators A pacemaker system consists of a battery, a computerized generator and wires with sensors called electrodes on one end. The battery powers the generator, and both are surrounded
Pacemakers & Defibrillators A pacemaker system consists of a battery, a computerized generator and wires with sensors called electrodes on one end. The battery powers the generator, and both are surrounded
STANDARD OPERATING PROCEDURE (SOP)
 STANDARD OPERATING PROCEDURE (SOP) MRI Scanning for Patients with Cardiac Implantable Electronic Devices (Pacemakers and Implantable Cardiac Defibrillators) Effective date 05/04/2018 Version number V1.0
STANDARD OPERATING PROCEDURE (SOP) MRI Scanning for Patients with Cardiac Implantable Electronic Devices (Pacemakers and Implantable Cardiac Defibrillators) Effective date 05/04/2018 Version number V1.0
SPORTS AND EXERCISE ADVICE IN PATIENTS WITH ICD AND PPM
 SPORTS AND EXERCISE ADVICE IN PATIENTS WITH ICD AND PPM Rio De Janeiro 2016 Sport and Exercise Cardiology Symposium SBC/SOCERJ ACC Sharlene M. Day, MD Associate Professor, Cardiovascular Medicine Director,
SPORTS AND EXERCISE ADVICE IN PATIENTS WITH ICD AND PPM Rio De Janeiro 2016 Sport and Exercise Cardiology Symposium SBC/SOCERJ ACC Sharlene M. Day, MD Associate Professor, Cardiovascular Medicine Director,
NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR CLINICAL EXCELLENCE SCOPE. Clinical guideline for the management of atrial fibrillation
 NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR CLINICAL EXCELLENCE 1 Guideline title SCOPE Clinical guideline for the management of atrial fibrillation 1.1 Short title Atrial fibrillation 2 Background a) The National Institute
NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR CLINICAL EXCELLENCE 1 Guideline title SCOPE Clinical guideline for the management of atrial fibrillation 1.1 Short title Atrial fibrillation 2 Background a) The National Institute
Implantable Cardioverter-Defibril. Defibrillators. Ratko Magjarević
 Implantable Cardioverter-Defibril Defibrillators Ratko Magjarević University of Zagreb Faculty of Electrical Engineering and Computing Croatia ratko.magjarevic@fer.hr Ventricular Fibrillation Ventricular
Implantable Cardioverter-Defibril Defibrillators Ratko Magjarević University of Zagreb Faculty of Electrical Engineering and Computing Croatia ratko.magjarevic@fer.hr Ventricular Fibrillation Ventricular
Manual Defibrillators, Automatic External Defibrillators, Cardioversion, and External Pacing. D. J. McMahon cewood rev
 Manual Defibrillators, Automatic External Defibrillators, Cardioversion, and External Pacing D. J. McMahon 141001 cewood rev 2017-10-04 Key Points Defibrillators: - know the definition & electrical value
Manual Defibrillators, Automatic External Defibrillators, Cardioversion, and External Pacing D. J. McMahon 141001 cewood rev 2017-10-04 Key Points Defibrillators: - know the definition & electrical value
Left Ventricular Assist Devices LVAD. North Country EMS Program Agency 3/21/12
 Left Ventricular Assist Devices LVAD North Country EMS Program Agency 3/21/12 Objectives Describe indications for and functions of ventricular assist devices (LVAD) Differentiate assessment findings of
Left Ventricular Assist Devices LVAD North Country EMS Program Agency 3/21/12 Objectives Describe indications for and functions of ventricular assist devices (LVAD) Differentiate assessment findings of
Lesson 4-3: Cardiac Emergencies. CARDIAC EMERGENCIES Angina, AMI, CHF and AED
 Lesson 4-3: Cardiac Emergencies CARDIAC EMERGENCIES Angina, AMI, CHF and AED THREE FAMILIAR CARDIAC CONDITIONS Angina Pectoris Acute Myocardial Infarction Congestive Heart Failure ANGINA PECTORIS Chest
Lesson 4-3: Cardiac Emergencies CARDIAC EMERGENCIES Angina, AMI, CHF and AED THREE FAMILIAR CARDIAC CONDITIONS Angina Pectoris Acute Myocardial Infarction Congestive Heart Failure ANGINA PECTORIS Chest
856 Unintentional Deactivation of ICDs Mayo Clin Proc, August 2002, Vol 77 Figure 1. Case 3. Printout from Guidant programmer (Guidant Corp, St Paul,
 Mayo Clin Proc, August 2002, Vol 77 Unintentional Deactivation of ICDs 855 Case Report Unintentional Deactivation of Implantable Cardioverter-Defibrillators in Health Care Settings MARY JANE RASMUSSEN,
Mayo Clin Proc, August 2002, Vol 77 Unintentional Deactivation of ICDs 855 Case Report Unintentional Deactivation of Implantable Cardioverter-Defibrillators in Health Care Settings MARY JANE RASMUSSEN,
Dos and Don t in Cardiac Arrhythmia. Case 1 -ECG. Case 1. Management. Emergency Admissions. Reduction of TE risk -CHADS 2 score. Hospital Admissions
 Emergency Admissions Dos and Don t in Cardiac Arrhythmia Tom Wong, MD, FESC Consultant Cardiologist, Honorary Senior Lecturer Royal Brompton & Harefield Hospitals National Heart and Lung Institute, Imperial
Emergency Admissions Dos and Don t in Cardiac Arrhythmia Tom Wong, MD, FESC Consultant Cardiologist, Honorary Senior Lecturer Royal Brompton & Harefield Hospitals National Heart and Lung Institute, Imperial
ICD: Basics, Programming and Trouble-shooting
 ICD: Basics, Programming and Trouble-shooting Amir AbdelWahab, MD Electrophysiology and Pacing Service Cardiology Department Cairo University Feb 2013 Evolution of ICD Technology ICD Evolution Indications
ICD: Basics, Programming and Trouble-shooting Amir AbdelWahab, MD Electrophysiology and Pacing Service Cardiology Department Cairo University Feb 2013 Evolution of ICD Technology ICD Evolution Indications
Three Lives Saved: UWA s Experience With Defibrillators. Eddie Stoelwinder
 Three Lives Saved: UWA s Experience With Defibrillators Eddie Stoelwinder BACKGROUND Sudden Cardiac Arrest (SCA) Death occurs instantly or shortly after the onset of symptoms The most common cause of
Three Lives Saved: UWA s Experience With Defibrillators Eddie Stoelwinder BACKGROUND Sudden Cardiac Arrest (SCA) Death occurs instantly or shortly after the onset of symptoms The most common cause of
Puzzling Pacemakers Cheryl Herrmann, APN, CCRN, CCNS-CSC-CMC
 Puzzling Pacemakers Cheryl Herrmann, APN, CCRN, CCNS-CSC-CMC Pacemaker: An electric device implanted in the body to regulate the heart beat. Delivers electrical stimuli over leads with electrodes in contact
Puzzling Pacemakers Cheryl Herrmann, APN, CCRN, CCNS-CSC-CMC Pacemaker: An electric device implanted in the body to regulate the heart beat. Delivers electrical stimuli over leads with electrodes in contact
Inappropriate electrical shocks: Tackling the beast
 ESC Paris 2011 Inappropriate electrical shocks: Tackling the beast Gerhard Hindricks University of Leipzig Heart Center Dept. of Electrophysiology ESC Paris 2011 Inappropriate electrical shocks: Tackling
ESC Paris 2011 Inappropriate electrical shocks: Tackling the beast Gerhard Hindricks University of Leipzig Heart Center Dept. of Electrophysiology ESC Paris 2011 Inappropriate electrical shocks: Tackling
UNDERSTANDING ELECTROPHYSIOLOGY STUDIES
 UNDERSTANDING ELECTROPHYSIOLOGY STUDIES Testing and Treating Your Heart s Electrical System A Problem with Your Heart Rhythm The speed and pattern of a heartbeat is called the heart rhythm. The rhythm
UNDERSTANDING ELECTROPHYSIOLOGY STUDIES Testing and Treating Your Heart s Electrical System A Problem with Your Heart Rhythm The speed and pattern of a heartbeat is called the heart rhythm. The rhythm
MEDICAL POLICY Cardioverter Defibrillators
 POLICY........ PG-0224 EFFECTIVE......06/01/09 LAST REVIEW... 01/27/17 MEDICAL POLICY Cardioverter Defibrillators GUIDELINES This policy does not certify benefits or authorization of benefits, which is
POLICY........ PG-0224 EFFECTIVE......06/01/09 LAST REVIEW... 01/27/17 MEDICAL POLICY Cardioverter Defibrillators GUIDELINES This policy does not certify benefits or authorization of benefits, which is
Cardiac implantable electronic devices (CIEDs) in children include pacemakers and implantable cardioverter defibrillators (ICDs).
 Management of Children with Cardiac Devices Guideline originally developed by Leann Miles, APRN; Lindsey Pumphrey, RN; Srikant Das, MD, and the ANGELS Team. Last reviewed by Lindsey Pumphrey, RN, Srikant
Management of Children with Cardiac Devices Guideline originally developed by Leann Miles, APRN; Lindsey Pumphrey, RN; Srikant Das, MD, and the ANGELS Team. Last reviewed by Lindsey Pumphrey, RN, Srikant
2009 CPT Codes for Cardiac Device Monitoring
 2009 CPT Codes for Cardiac Device Monitoring December 2008 Notices Current Procedural Terminology (CPT ) is copyright 2008 American Medical Association. All Rights reserved. No fee schedules, basic units,
2009 CPT Codes for Cardiac Device Monitoring December 2008 Notices Current Procedural Terminology (CPT ) is copyright 2008 American Medical Association. All Rights reserved. No fee schedules, basic units,
Review of Pacemakers and ICD Therapy: Overview and Patient Management
 Review of Pacemakers and ICD Therapy: Overview and Patient Management Pacing Systems Charles J. Love, MD FACC FAHA FHRS CCDS Professor of Medicine Director, Cardiac Rhythm Device Services OSU Division
Review of Pacemakers and ICD Therapy: Overview and Patient Management Pacing Systems Charles J. Love, MD FACC FAHA FHRS CCDS Professor of Medicine Director, Cardiac Rhythm Device Services OSU Division
NEIL CISPER TECHNICAL FIELD ENGINEER ICD/CRTD BASICS
 NEIL CISPER TECHNICAL FIELD ENGINEER ICD/CRTD BASICS OBJECTIVES Discuss history of ICDs Review the indications for ICD and CRT therapy Describe basic lead and device technology Discuss different therapies
NEIL CISPER TECHNICAL FIELD ENGINEER ICD/CRTD BASICS OBJECTIVES Discuss history of ICDs Review the indications for ICD and CRT therapy Describe basic lead and device technology Discuss different therapies
Non-Invasive Ablation of Ventricular Tachycardia
 Non-Invasive Ablation of Ventricular Tachycardia Dr Shaemala Anpalakhan Newcastle upon Tyne Hospitals NHS Foundation Trust Freeman Road, Newcastle Upon Tyne, NE7 7DN Contact: shaemala@doctors.org.uk Introduction
Non-Invasive Ablation of Ventricular Tachycardia Dr Shaemala Anpalakhan Newcastle upon Tyne Hospitals NHS Foundation Trust Freeman Road, Newcastle Upon Tyne, NE7 7DN Contact: shaemala@doctors.org.uk Introduction
Objectives 2/15/2016. Learn the function of an implanted cardioverter defibrillator (ICD)
 M. Thomas Beets MD, FAAFP, HMDC Texas New Mexico Hospice Organization/Texas Academy of Palliative Medicine February 27, 2016 Objectives Learn the function of an implanted cardioverter defibrillator (ICD)
M. Thomas Beets MD, FAAFP, HMDC Texas New Mexico Hospice Organization/Texas Academy of Palliative Medicine February 27, 2016 Objectives Learn the function of an implanted cardioverter defibrillator (ICD)
Destructive Device Removal - Sparks and Deletion of Therapy History From an Implantable Cardioverter Defibrillator. Case Reports
 Case Reports Destructive Device Removal - Sparks and Deletion of Therapy History From an Implantable Cardioverter Defibrillator Takashi Kurita, 1 MD, Shigeyuki Ueda, 2 MD, Hideo Okamura, 2 MD, Takashi
Case Reports Destructive Device Removal - Sparks and Deletion of Therapy History From an Implantable Cardioverter Defibrillator Takashi Kurita, 1 MD, Shigeyuki Ueda, 2 MD, Hideo Okamura, 2 MD, Takashi
NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CARE EXCELLENCE
 NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CARE EXCELLENCE Medical technology guidance FINAL SCOPE ENDURALIFE-powered CRT-D devices for the treatment of heart failure 1 Technology 1.1 Description of the technology
NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CARE EXCELLENCE Medical technology guidance FINAL SCOPE ENDURALIFE-powered CRT-D devices for the treatment of heart failure 1 Technology 1.1 Description of the technology
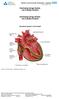
THE HEART THE CIRCULATORY SYSTEM
 THE HEART THE CIRCULATORY SYSTEM There are three primary closed cycles: 1) Cardiac circulation pathway of blood within the heart 2) Pulmonary circulation blood from the heart to lungs and back 3) Systemic
THE HEART THE CIRCULATORY SYSTEM There are three primary closed cycles: 1) Cardiac circulation pathway of blood within the heart 2) Pulmonary circulation blood from the heart to lungs and back 3) Systemic
ADVANCED LIFE SUPPORT
 ANSWERS IN ITALICS WITH REFERENCES 1. The guidelines suggest that in out-of-hospital cardiac arrests, attended but unwitnessed by health care professionals equipped with a manual defibrillator, the providers
ANSWERS IN ITALICS WITH REFERENCES 1. The guidelines suggest that in out-of-hospital cardiac arrests, attended but unwitnessed by health care professionals equipped with a manual defibrillator, the providers
Electrophysiology Studies and Catheter Ablation. Electrophysiology Studies and Catheter Ablation
 Electrophysiology Studies Cardiac Conduction System. Mdmedicine.wordpress.com Patient Information Leaflet for: Electrophysiology Studies Available via Trust Docs Version: 6 Trust Docs ID: 10 Page 1 of
Electrophysiology Studies Cardiac Conduction System. Mdmedicine.wordpress.com Patient Information Leaflet for: Electrophysiology Studies Available via Trust Docs Version: 6 Trust Docs ID: 10 Page 1 of
Diploma in Electrocardiography
 The Society for Cardiological Science and Technology Diploma in Electrocardiography The Society makes this award to candidates who can demonstrate the ability to accurately record a resting 12-lead electrocardiogram
The Society for Cardiological Science and Technology Diploma in Electrocardiography The Society makes this award to candidates who can demonstrate the ability to accurately record a resting 12-lead electrocardiogram
DOWNLOAD OR READ : VALIDITY OF CARDIAC IMPLANTABLE ELECTRONIC DEVICES IN ASSESSING DAILY PHYSICAL ACTIVITY PDF EBOOK EPUB MOBI
 DOWNLOAD OR READ : VALIDITY OF CARDIAC IMPLANTABLE ELECTRONIC DEVICES IN ASSESSING DAILY PHYSICAL ACTIVITY PDF EBOOK EPUB MOBI Page 1 Page 2 validity of cardiac implantable electronic devices in assessing
DOWNLOAD OR READ : VALIDITY OF CARDIAC IMPLANTABLE ELECTRONIC DEVICES IN ASSESSING DAILY PHYSICAL ACTIVITY PDF EBOOK EPUB MOBI Page 1 Page 2 validity of cardiac implantable electronic devices in assessing
Synopsis of Management on Ventricular arrhythmias. M. Soni MD Interventional Cardiologist
 Synopsis of Management on Ventricular arrhythmias M. Soni MD Interventional Cardiologist No financial disclosure Premature Ventricular Contraction (PVC) Ventricular Bigeminy Ventricular Trigeminy Multifocal
Synopsis of Management on Ventricular arrhythmias M. Soni MD Interventional Cardiologist No financial disclosure Premature Ventricular Contraction (PVC) Ventricular Bigeminy Ventricular Trigeminy Multifocal
Specialist Palliative Care Referral for Patients
 Specialist Palliative Care Referral for Patients This guideline covers referrals for patients with progressive terminal illness, whether due to cancer or other disease. For many patients in the late stages
Specialist Palliative Care Referral for Patients This guideline covers referrals for patients with progressive terminal illness, whether due to cancer or other disease. For many patients in the late stages
Troubleshooting ICD. NASPE Training Lancashire & South Cumbria Cardiac Network
 Troubleshooting ICD NASPE Training Lancashire & South Cumbria Cardiac Network Bradycardia Pacing by ICD Isolated ICD discharge Multiple discharges Appropriate Inappropriate No ICD Therapy or delay in ICD
Troubleshooting ICD NASPE Training Lancashire & South Cumbria Cardiac Network Bradycardia Pacing by ICD Isolated ICD discharge Multiple discharges Appropriate Inappropriate No ICD Therapy or delay in ICD
C1: Medical Standards for Safety Critical Workers with Cardiovascular Disorders
 C1: Medical Standards for Safety Critical Workers with Cardiovascular Disorders GENERAL ISSUES REGARDING MEDICAL FITNESS-FOR-DUTY 1. These medical standards apply to Union Pacific Railroad (UPRR) employees
C1: Medical Standards for Safety Critical Workers with Cardiovascular Disorders GENERAL ISSUES REGARDING MEDICAL FITNESS-FOR-DUTY 1. These medical standards apply to Union Pacific Railroad (UPRR) employees
NICE Action Plan 6/13 Transient loss of consciousness ('blackouts') management in adults and young people NICE CG 109 December 2013
 NICE Action Plan 6/13 Transient loss of consciousness ('blackouts') management in adults and young people NICE CG 109 December 2013 Title: Prepared by: Presented by: Main aim: Recommendations: Previous
NICE Action Plan 6/13 Transient loss of consciousness ('blackouts') management in adults and young people NICE CG 109 December 2013 Title: Prepared by: Presented by: Main aim: Recommendations: Previous
Date of Meeting: Ratified Date: 03/06/2009
 Document Type: PROTOCOL Title: Management And Transfer Of Patients With Acute Scope: Cardiac Network-wide Author/Originator and Title: Dr Ranjit More & members of the Cardiac Network Clinical Advisory
Document Type: PROTOCOL Title: Management And Transfer Of Patients With Acute Scope: Cardiac Network-wide Author/Originator and Title: Dr Ranjit More & members of the Cardiac Network Clinical Advisory
Understanding our advice ~ December The use of troponin testing in acute coronary syndromes
 Understanding our advice ~ December 2003 The use of troponin testing in acute coronary syndromes The use of troponin testing in acute coronary syndromes Purpose of this document NHS Quality Improvement
Understanding our advice ~ December 2003 The use of troponin testing in acute coronary syndromes The use of troponin testing in acute coronary syndromes Purpose of this document NHS Quality Improvement
Cardiovascular Nursing Practice: A Comprehensive Resource Manual and Study Guide for Clinical Nurses 2 nd Edition
 Cardiovascular Nursing Practice: A Comprehensive Resource Manual and Study Guide for Clinical Nurses 2 nd Edition Table of Contents Volume 1 Chapter 1: Cardiovascular Anatomy and Physiology Basic Cardiac
Cardiovascular Nursing Practice: A Comprehensive Resource Manual and Study Guide for Clinical Nurses 2 nd Edition Table of Contents Volume 1 Chapter 1: Cardiovascular Anatomy and Physiology Basic Cardiac
LifeVest. Sven Reek, Aarau. Conflict of interest: none
 LifeVest Sven Reek, Aarau Conflict of interest: none WCD (LifeVest, ZOLL, Pittsburg,PA) Technical aspects Wearable garment with 4 dry ECG electrodes (detection) 3 defibrillation pads External defibrillator
LifeVest Sven Reek, Aarau Conflict of interest: none WCD (LifeVest, ZOLL, Pittsburg,PA) Technical aspects Wearable garment with 4 dry ECG electrodes (detection) 3 defibrillation pads External defibrillator
Procedure for exceptional magnetic resonance scanning in patients with standard (non-mr-conditional) pacemakers
 Procedure for exceptional magnetic resonance scanning in patients Category: Summary: Standard Operating Procedure This procedure outlines the process for assessing the safety and suitability of, and for
Procedure for exceptional magnetic resonance scanning in patients Category: Summary: Standard Operating Procedure This procedure outlines the process for assessing the safety and suitability of, and for
ICD THERAPIES: are they harmful or just high risk markers?
 ICD THERAPIES: are they harmful or just high risk markers? Konstantinos P. Letsas, MD, PhD, FESC LAB OF CARDIAC ELECTROPHYSIOLOGY EVANGELISMOS GENERAL HOSPITAL ATHENS ICD therapies are common In a meta-analysis
ICD THERAPIES: are they harmful or just high risk markers? Konstantinos P. Letsas, MD, PhD, FESC LAB OF CARDIAC ELECTROPHYSIOLOGY EVANGELISMOS GENERAL HOSPITAL ATHENS ICD therapies are common In a meta-analysis
EMT. Chapter 14 Review
 EMT Chapter 14 Review Review 1. All of the following are common signs and symptoms of cardiac ischemia, EXCEPT: A. headache. B. chest pressure. C. shortness of breath. D. anxiety or restlessness. Review
EMT Chapter 14 Review Review 1. All of the following are common signs and symptoms of cardiac ischemia, EXCEPT: A. headache. B. chest pressure. C. shortness of breath. D. anxiety or restlessness. Review
About atrial fibrillation (AFib) Atrial Fibrillation (AFib) What is AFib? What s the danger? Who gets AFib?
 Understanding AFib Atrial Fibrillation (AFib) About AFib 3 How Your Heart Works 4 Types of AFib 5 Symptoms 5 Risk Factors 5 How is AFib Diagnosed? 6 Treatment 6 What to Ask Your Doctor 7 A normal heartbeat
Understanding AFib Atrial Fibrillation (AFib) About AFib 3 How Your Heart Works 4 Types of AFib 5 Symptoms 5 Risk Factors 5 How is AFib Diagnosed? 6 Treatment 6 What to Ask Your Doctor 7 A normal heartbeat
The ARREST Trial: Amiodarone for Resuscitation After Out-of-Hospital Cardiac Arrest Due to Ventricular Fibrillation
 The ARREST Trial: Amiodarone for Resuscitation After Out-of-Hospital Cardiac Arrest Due to Ventricular Fibrillation Introduction The ARREST (Amiodarone in out-of-hospital Resuscitation of REfractory Sustained
The ARREST Trial: Amiodarone for Resuscitation After Out-of-Hospital Cardiac Arrest Due to Ventricular Fibrillation Introduction The ARREST (Amiodarone in out-of-hospital Resuscitation of REfractory Sustained
Manual Defibrillators, Automatic External Defibrillators, Cardioversion, and External Pacing
 Manual Defibrillators, Automatic External Defibrillators, Cardioversion, and External Pacing Key Points Defibrillators: - know the definition & electrical value of a joule - monophasic vs biphasic types:
Manual Defibrillators, Automatic External Defibrillators, Cardioversion, and External Pacing Key Points Defibrillators: - know the definition & electrical value of a joule - monophasic vs biphasic types:
Implantable Cardioverter Defibrillator (ICD) and Cardiac Resynchronisation Therapy Defibrillator (CRT-D)
 How can I help reduce healthcare associated infections? Infection control is important to the well-being of our patients and for that reason we have infection control procedures in place. Keeping your
How can I help reduce healthcare associated infections? Infection control is important to the well-being of our patients and for that reason we have infection control procedures in place. Keeping your
Cardiovascular Technology Profession Statement
 Cardiovascular Technology Profession Statement Prepared by The Malaysian Society of Cardiovascular Technologist (MSCVT) Content:- 1) Background 2) Description of Profession 3) Scope of Duties 4) References
Cardiovascular Technology Profession Statement Prepared by The Malaysian Society of Cardiovascular Technologist (MSCVT) Content:- 1) Background 2) Description of Profession 3) Scope of Duties 4) References
The Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy (HCM) Center
 The Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy (HCM) Center Comprehensive HCM management from a team you can trust An internationally recognized Center of Excellence in the diagnosis and treatment of HCM The most advanced
The Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy (HCM) Center Comprehensive HCM management from a team you can trust An internationally recognized Center of Excellence in the diagnosis and treatment of HCM The most advanced
