Trends in Incident and Recurrent Rates of First-Ever Ischemic Stroke in Taiwan between 2000 and 2011
|
|
|
- Gervase Boone
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Journal of Stroke 2016;18(1): Original Article Trends in Incident and Recurrent Rates of First-Ever Ischemic Stroke in Taiwan between 2000 and 2011 Meng Lee, a Yi-Ling Wu, a Bruce Ovbiagele b a Department of Neurology, Chang Gung University College of Medicine, Chang Gung Memorial Hospital, Chiayi branch, Taiwan b Department of Neurosciences, Medical University of South Carolina, Charleston, South Carolina, USA Background and Purpose The burden of stroke is comparatively greater in Asian countries than in the Western world. While there has been a documented recent decline in the incidence of stroke in several Western nations due to better risk factor management, much less is known about the nature and trajectory of stroke in Asia over the last decade. The objective of this study was to explore risk factors, medication use, incidence, and one-year recurrence of stroke in Taiwan. Methods We conducted a nationwide cohort study by reviewing all hospitalized patients ( 18 years) with a primary diagnosis of ischemic stroke between 2001 and 2011 from Taiwan National Health Insurance Research Database. Results A total of 291,381 first-ever ischemic stroke patients were enrolled between 2000 and The average age was about 70 years and approximately 58.6% of them were men. While prevalence of diabetes mellitus and hyperlipidemia, as well as use of statins, antiplatelet agents, and oral anticoagulant agents for atrial fibrillation significantly increased; incidence (142.3 vs per 100,000 in 2000 and 2011, respectively) and one-year recurrence (9.6% vs. 7.8% in 2000 and 2011, respectively) of stroke declined during this period of time. Conclusions Over the last decade in Taiwan, rates of primary ischemic stroke and one-year recurrent stroke decreased by 9% and 18% respectively. Correspondence: Meng Lee Department of Neurology, Chang Gung University College of Medicine, Chang Gung Memorial Hospital, Chiayi branch, 6 West Section, Chiapu Road, Puzi, Taiwan bluccc@adm.cgmh.org.tw Received: July 20, 2015 Revised: October 23, 2015 Accepted: October 25, 2015 The authors have no financial conflicts of interest. Keywords Ischemic stroke; Incidence; Recurrence; Cohort Introduction Compared with a nonfatal myocardial infarction, a nonfatal stroke causes a 1.5-fold greater loss of disability-adjusted lifeyear. 1 Nonetheless, over the past decade there has been a clear and impressive decline in the incidence of stroke in several Western nations. 2-5 The positive change in the occurrence of stroke in these countries has been attributed primarily to better screening and treatment of established risk factors for stroke, particularly hypertension. 6 The burden of stroke is greater in Asian countries than in the Western world, including a substantially higher incidence of stroke than myocardial infarction. 7-9 However, data on the extent to which several Asia countries have recently fared with regard to improvement in stroke outcomes are relatively sparse. One study suggested the incidence of stroke decreased from 1961 to 2000 in Japan 7 and an overview study revealed that recurrent stroke decreased in each decade from 1960 to Certainly more nationwide data on the evolving nature and trajectory of stroke in Asia are needed for research and planning purposes. The objective of this study was to explore risk factors, medication use, incidence, and one-year recurrence of stroke using the entire population in Taiwan by National Health Insurance Research Database (NHIRD). Copyright 2016 Korean Stroke Society This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Non-Commercial License ( which permits unrestricted non-commercial use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited pissn: eissn:
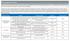
2 Vol. 18 / No. 1 / January 2016 Methods Study design and dataset We retrospectively assessed data collected 2000 through 2012, from Taiwan NHIRD. Taiwan has implemented a singlepayer, compulsory National Health Insurance program in 1995, which includes reimburses of outpatient visits, hospital admissions, prescriptions for 99% of Taiwanese population. All contracted institutions must file claims according to standard formats, which are subsequently transformed into NHIRD. Study population We identified all hospitalized patients ( 18 years) who were admitted with a primary diagnosis of ischemic stroke (International Classification of Diseases, Ninth Revision codes 433, 434, 436) for the first time between 2000 and A prior study validating the diagnosis of acute ischemic stroke in National Health Insurance claims data using the Taiwan Stroke Registry as a reference revealed a positive predictive value of 88.4% and sensitivity of 97.3%. 11 Another cross-sectional study showed that among confirmed cases of acute ischemic stroke in a hospital medical record, 94.5% were assigned ischemic stroke as the principal diagnosis in the NHIRD. 12 We only enrolled patients receiving brain computed tomography (CT) or magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) during hospitalization with the assumption that all patients with symptoms of acute stroke should receive brain imaging. This approach was intended to exclude stroke patients who were hospitalized for rehabilitation during chronic stage. Although brain imaging, especially CT, may not be able to reveal the cerebral infarction in patients with symptoms or signs of acute stroke, it can easily exclude intracranial hemorrhage. Thus NHIRD had a low probability of misclassifying hemorrhagic stroke into ischemic stroke if brain imaging was done. The first-ever ischemic stroke during study period was defined as the index stroke. Patients were excluded if they had history of any strokes between 1997 and Patients were classified into three groups according to a year of stroke occurrence, which are , , and This was a nationwide study that included all available and eligible patients. Main outcome measures The primary outcome of this study was incidence of ischemic stroke in Taiwan. The incidence rate was defined as numbers of first-ever stroke patients each year divided by midyear population per 100,000 population. The leading secondary outcome was the one-year stroke recurrent rate, defined as numbers of patients with first recurrent stroke (ischemic or hemorrhagic) within one year after index stroke divided by numbers of index stroke patients. The followed-up started from index stroke to stroke recurrence, or one year after index stroke, whichever came first. Statistical analysis Baseline characteristics were presented as medians (interquartile ranges) for continuous variables and percentages for categorical variables, as appropriate. All statistics analyses were performed with SAS statistical software, version 9.2 (SAS Institute Inc., Cary, USA). Results A total of 291,381 first-ever ischemic stroke patients were enrolled between 2000 and The average age was about 70 years and approximately 58.6% of them were men. The average length of hospital stay was about 7 days. More than half of patients had history of hypertension, which was from 59% to 63% and the frequency of hypertension in ischemic stroke was not much different in three time period. The frequencies of diabetes mellitus (from 29.6% to 34.0%) and hyperlipidemia (from 22.0% to 40.6%) increased steadily during study periods. Frequencies of atrial fibrillation (from 7.3% to 10.4%), chronic kidney disease (from 3.9% to 5.0%), and heart failure (from 7.3% to 9.3%) also increased during the study periods. The frequencies of brain CT use was decreased from 94.4% in to 79.6% in while brain MRI use was increased from 22.1% in to 55.4% in General characteristics are described in Table 1. During the study periods, 30-day in hospital mortality was from 1.7% to 1.9%. About 37% of first-ever ischemic stroke patients received calcium channel blockers for antihypertension therapy during admission throughout the study period. The use of angiotensin receptor blockers was increased from 6% to 18.1% during the study periods. Frequencies of angiotensin-converting-enzyme inhibitors (16%) and diuretics (13%) were much the same among three time sections. The use of statin in ischemic stroke patients was increased from 8.8% in , 21.9% in , and to 30.8% in Stroke patients received antiplatelet were 76.1% in , 85.3% in and 86.6% in , respectively. There was 30.0% in , 28.9% in , and 34.5% in , respectively, of ischemic stroke patients with atrial fibrillation received oral anticoagulant agents during the hospitalization. The incidence rate of ischemic stroke for people aged 18 years or older decreased gradually from 2000 (142.3 per
3 Lee, et al. Trend of Incident and Recurrent Stroke in Taiwan Table 1. Characteristic of hospitalized first-ever ischemic stroke patients from Taiwanese National Health Insurance Database ( ), N = 291,381 Year , N= 92,525 Year , N= 95,681 Year , N= 94,543 Age (median, interquartile range [IQR]) 70 (61-77) 69 (59-77) 69 (59-78) Sex Male (%) < Length of stay (day) (median, IQR) 7 (5-13) 7 (5-14) 7 (5-14) Computed tomography (CT) (%) < Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) (%) < Medical history (%) Hypertension < Diabetes < Hyperlipidemia < Ischemic Heart Disease < Atrial Fibrillation < Chronic Kidney Disease < Heart Failure < day in hospital mortality (%) < Medications Calcium channel blockers (CCBs) Angiotensin-converting-enzyme inhibitors (ACEIs) Angiotensin receptor blockers (ARBs) < Diuretics < Statins < Antiplatelet agents < Warfarin or novel oral anticoagulants (NOACs) for atrial fibrillation < P value Ischemic stroke incidence rate All Male Female One-year recurrent rate All Male Female Per 100,000 population P for trend< Percentage P for trend< Year Year Figure 1. Trend of stroke incidence rate. Source: Taiwan National Health Insurance Database and Ministry of Interior. 100,000 persons) to 2011 (129.5 per 100,000 persons) except there was an obvious drop in 2003 then increased in 2004 (Figure 1). One-year stroke recurrent rate decreased gradually which was 9.61% in 2000 and decreased to 7.27% in 2011 except there was an obvious drop in 2003 then increased in 2004 (Figure 2). Compare to women, men had a higher incident rate and recurrent rate of stroke. We suspected the Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome, 14 March 2003 through 5 July 2003 in Figure 2. Trend of one-year stroke recurrent rate. Taiwan, may cause decreasing rate of ischemic stroke hospitalization. To explore the possible explanation for the drop of stroke incidence in 2003, we compared the stroke incidence in March through July from 2002 to 2004 and found that stroke incidence was substantially decreased in May and June, 2003, as compared to May and June in 2002 and 2004 (Table 2)
4 Vol. 18 / No. 1 / January 2016 Table 2. Crude stroke incidence rate from March to July between 2002 and 2004 (per 100,000 population) Year Discussion Month March April May June July This study provided an overview of baseline characteristics, risk factors, medication use during hospitalization, incidence, and one-year recurrence of first-ever ischemic stroke using the entire population of Taiwan from 2000 to Several findings, strengths and limitations merit discussion. We used stroke hospitalization to represent incidence and recurrence of ischemic stroke with the assumption that all acute ischemic stroke patients should be hospitalized and the current health care system in Taiwan supports and encourages such a practice. However, a very small proportion of patients, likely those with minor stroke, may receive brain imaging at emergency departments or outpatient clinics but not be hospitalized due to various reasons, such as non-availability of beds or patients not wanting to wait. We found both incidence and recurrence of stroke dropped in May and June in 2003, which was during the fierce SARS epidemic in Taiwan. During that period of time, patients and medical doctors were less inclined to facilitate hospitalization unless the patient s condition was highly severe. Thus many patients with strokes of relatively minor severity may not have been counted in our analysis thereby potentially underestimating the real incidence and recurrence of ischemic stroke during that period of time. Two studies exploring the incidence of stroke were conducted in 1980s 13 and 1990s, 14 respectively, in certain communities in Taiwan. The annual incidence rate of stroke for people aged 36 years or older in a study, from 1986 to 1990, was 330 per 100,000 population. 13 The other population-based stroke survey from 1993 to1996 reported that the annual incidence rate of stroke for people aged 50 years or older was 527 per 100,000 population. 14 Since the current population was age 18 or older and we focused on incidence of ischemic stroke, as well as incidence of stroke was likely declining from 1986 to 2011, the annual incidence rate was lower in this study. The characteristics of the stroke risk factors in this study is generally consistent with a large stroke registry from 2006 to 2008 but the rates of statin (30% vs. 38%) and antiplatelet (87% vs. 94%) use during hospitalization were somewhat lower in this study. 15 While the current study included only firstever ischemic stroke, the prior study 15 also included 34% recurrent ischemic stroke patients, which may have led the treating medical doctors to adopt a more aggressive vascular risk reduction strategy. Also hospitals participating in a stroke registry are presumably highly motivated to improve care quality and may generally have more awareness of/interest in the use of evidence-based therapies for stroke risk reduction. We found mortality rate was lower in this study, as compared to the prior stroke registry study (1.9% vs. 4% 15 ) which is likely due to the fact that this study only enrolled first-ever ischemic stroke. It is informative to compare the trends in stroke incidence, recurrence, and management of stroke in Taiwan with data from other Asian countries, such as Korea. Among hospital admissions with stroke as the primary diagnostic code during 2001 to 2009, hospitalizations for ischemic stroke increased substantially in Korea. 16 This apparent rise in annual ischemic stroke incidence in Korea was likely due to an increase in the country s elderly population. 16 However, the median age of the current study in Taiwan did not change during the study period. Moreover, a comparison of survey data obtained in 2002 vs showed a significant improvement in hypertension awareness, treatment, and control in Taiwan, which may have contributed to its declining incidence of ischemic stroke. 17 Ischemic stroke incidence in the population aged years was 226 per 100,000 person-years (including first-ever and recurrent ischemic stroke) in Korea 146 per 100,000 persons in our population aged 18 years or older (first-ever ischemic stroke only); while the annual rate of recurrent ischemic stroke was about 5.0% in Japan during 2007 to 2009 vs. a 7.7% annual recurrent stroke (ischemic or hemorrhagic) rate noted in Taiwan. 18 In the Fukuoka ischemic stroke registry, mean age was 70 years, 76% had hypertension, 27% diabetes mellitus, 46% hyperlipidemia, and 26% atrial fibrillation. 19 Our study had similar frequencies of stroke risk factors except only 10% patients had atrial fibrillation in this study. Since diagnosis of atrial fibrillation in hospitalized ischemic stroke patients typically relies on a single baseline 12-lead electrocardiogram or history of atrial fibrillation, it is conceivable that the frequency of paroxysmal atrial fibrillation in admitted ischemic stroke patients in Taiwan might be underestimated. Among ischemic stroke patients with atrial fibrillation in this study, 34% vs. 10% in a Chinese ischemic stroke registry, 20 received oral anticoagulants during hospitalization. The underuse of oral anticoagulant therapy in eligible Asian stroke patients during hospitalization may in part be due to concerns about hemorrhagic transformation. Also, 31% patients received statin therapy in this study at discharge vs. 35% in Fukuoka stroke registry, which is highly comparable
5 Lee, et al. Trend of Incident and Recurrent Stroke in Taiwan As compared to a prior study based on the control arms of clinical trials for secondary stroke prevention, the current study had higher recurrent rate of stroke (8% vs. 5% 10 ). The difference may exist in the prior study excluded patients with atrial fibrillation or severe carotid stenosis 10 while this study included all first-ever ischemic stroke patients. Also, people participating in clinical trials may receive more rigorous risk factors control, which turns out to have lower recurrent stroke. Furthermore, the current study enrolled patients in the acute stage when the risk of recurrent stroke is high, whereas secondary stroke prevention trials, in general, enrolled patients after the acute stage. We found the one-year recurrent stroke was declining from 2000 to 2011, which may be explained by increasing use of statin (8.8% to 30.8%), antiplatelet agents (76.1% to 86.6%), and oral anticoagulant agents in atrial fibrillation (30.0% to 34.5%) during hospitalization among this period of time. In addition to the limitations mentioned above, NHIRD does not provide information on a few established stroke risk factors, e.g. smoking and blood pressure levels during followup period. Also, we did not explore medication use at outpatient clinics after discharge from the first-ever ischemic stroke. Thus we could not explore the impact of these factors on the incidence and recurrence of stroke. In conclusion, in accord with recent trends around the world, 2-5 we observed that the annual incidence and one-year recurrence rates of stroke declined over the last decade in Taiwan. However, it would seem that the magnitude of reduction for incident stroke seen in Western nations of approximately 20% was much greater than the more modest 9% decrease noted in Taiwan. We observed a rise in the use of statins, antiplatelet agents, and oral anticoagulant agents for atrial fibrillation in Taiwan during this period of time, which probably contributed to the declining rate of stroke, but there appears to more room for improvement in risk factor control if Taiwan hopes to gain at least the same level of decrease in incident stroke observed in Western countries. References 1. Granger BB, Swedberg K, Ekman I, Granger CB, Olofsson B, McMurray JJ, et al. Adherence to candesartan and placebo and outcomes in chronic heart failure in the CHARM programme: double-blind, randomised, controlled clinical trial. Lancet 2005; 366: Hall MJ, Levant S, DeFrances CJ. Hospitalization for stroke in US hospitals, NCHS Data Brief 2012: Rosengren A, Giang KW, Lappas G, Jern C, Torén K, Björck L. Twenty-four-year trends in the incidence of ischemic stroke in Sweden from 1987 to Stroke 2013;44: Wang Y, Rudd AG, Wolfe CD. Trends and survival between ethnic groups after stroke: the South London Stroke Register. Stroke 2013;44: Ovbiagele B. National sex-specific trends in hospital-based stroke rates. J Stroke Cerebrovasc Dis 2011;20: Gu Q, Burt VL, Dillon CF, Yoon S. Trends in antihypertensive medication use and blood pressure control among United States adults with hypertension: the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey, 2001 to Circulation 2012; 126: Shih CL, Chen CH, Sheu CF, Lang HC, Hsieh CL. Validating and improving the reliability of the EORTC qlq-c30 using a multidimensional Rasch model. Value Health 2013;16: Tsai CT, Lai LP, Hwang JJ, Chen WP, Chiang FT, Hsu KL, et al. Renin-angiotensin system component expression in the HL-1 atrial cell line and in a pig model of atrial fibrillation. J Hypertens 2008;26: Lee M, Wu YL, Saver JL, Lee HC, Lee JD, Chang KC, et al. Is clopidogrel better than aspirin following breakthrough strokes while on aspirin? A retrospective cohort study. BMJ Open 2014; 4:e Hong KS, Yegiaian S, Lee M, Lee J, Saver JL. Declining stroke and vascular event recurrence rates in secondary prevention trials over the past 50 years and consequences for current trial design. Circulation 2011;123: Hsieh CY, Chen CH, Li CY, Lai ML. Validating the diagnosis of acute ischemic stroke in a national health insurance claims database. J Formos Med Assoc 2015;114: Cheng CL, Kao YH, Lin SJ, Lee CH, Lai ML. Validation of the National Health Insurance Research Database with ischemic stroke cases in Taiwan. Pharmacoepidemiol Drug Saf 2011;20: Hu HH, Sheng WY, Chu FL, Lan CF, Chiang BN. Incidence of stroke in Taiwan. Stroke 1992;23: Fuh JL, Wang SJ, Liu HC, Shyu HY. Incidence of stroke on Kinmen, Taiwan. Neuroepidemiology 2000;19: Hsieh FI, Lien LM, Chen ST, Bai CH, Sun MC, Tseng HP, et al. Get With the Guidelines-Stroke performance indicators: surveillance of stroke care in the Taiwan Stroke Registry: Get With the Guidelines-Stroke in Taiwan. Circulation 2010;122: Hong KS, Bang OY, Kang DW, Yu KH, Bae HJ, Lee JS, et al. Stroke statistics in Korea: part I. Epidemiology and risk factors: a report from the Korean stroke society and clinical research center for stroke. J Stroke 2013;15: Su TC, Bai CH, Chang HY, You SL, Chien KL, Chen MF, et al. Evidence for improved control of hypertension in Taiwan:
6 Vol. 18 / No. 1 / January J Hypertens 2008;26: Suzuki N, Sato M, Houkin K, Terayama Y, Uchiyama S, Daida H, et al. One-year atherothrombotic vascular events rates in outpatients with recent non-cardioembolic ischemic stroke: the EVEREST (Effective Vascular Event REduction after STroke) registry. J Stroke Cerebrovasc Dis 2012;21: Ishitsuka K, Kamouchi M, Hata J, Fukuda K, Matsuo R, Kuroda J, et al. High blood pressure after acute ischemic stroke is associated with poor clinical outcomes: Fukuoka Stroke Registry. Hypertension 2014;63: Wang C, Yang Z, Wang C, Wang Y, Zhao X, Liu L, et al. Significant underuse of warfarin in patients with nonvalvular atrial fibrillation: results from the China national stroke registry. J Stroke Cerebrovasc Dis 2014;23: Makihara N, Kamouchi M, Hata J, Matsuo R, Ago T, Kuroda J, et al. Statins and the risks of stroke recurrence and death after ischemic stroke: the Fukuoka Stroke Registry. Atherosclerosis 2013;231:
Is clopidogrel better than aspirin following breakthrough strokes while on aspirin? A retrospective cohort study
 Research Is clopidogrel better than aspirin following breakthrough strokes while on aspirin? A retrospective cohort study Meng Lee, 1 Yi-Ling Wu, 1 Jeffrey L Saver, 2 Hsuei-Chen Lee, 3 Jiann-Der Lee, 1
Research Is clopidogrel better than aspirin following breakthrough strokes while on aspirin? A retrospective cohort study Meng Lee, 1 Yi-Ling Wu, 1 Jeffrey L Saver, 2 Hsuei-Chen Lee, 3 Jiann-Der Lee, 1
Do Not Cite. Draft for Work Group Review.
 Defect Free Acute Inpatient Ischemic Stroke Measure Bundle Measure Description Percentage of patients aged 18 years and older with a diagnosis of ischemic stroke OR transient ischemic attack who were admitted
Defect Free Acute Inpatient Ischemic Stroke Measure Bundle Measure Description Percentage of patients aged 18 years and older with a diagnosis of ischemic stroke OR transient ischemic attack who were admitted
Study period Total sample size (% women) 899 (37.7%) Warfarin Aspirin
 Table S2 Sex- specific differences in oral anticoagulant prescription for stroke prevention in AF Total sample size (% women) Anticoagulant(s) studied Gage (2000) 1 Missouri, USA Discharged during 597
Table S2 Sex- specific differences in oral anticoagulant prescription for stroke prevention in AF Total sample size (% women) Anticoagulant(s) studied Gage (2000) 1 Missouri, USA Discharged during 597
The Diabetes Epidemic in Korea
 Review Article Endocrinol Metab 2016;31:349-33 http://dx.doi.org/.3803/enm.2016.31.3.349 pissn 2093-96X eissn 2093-978 The Diabetes Epidemic in Korea Junghyun Noh Department of Internal Medicine, Inje
Review Article Endocrinol Metab 2016;31:349-33 http://dx.doi.org/.3803/enm.2016.31.3.349 pissn 2093-96X eissn 2093-978 The Diabetes Epidemic in Korea Junghyun Noh Department of Internal Medicine, Inje
Risk Factors for Ischemic Stroke: Electrocardiographic Findings
 Original Articles 232 Risk Factors for Ischemic Stroke: Electrocardiographic Findings Elley H.H. Chiu 1,2, Teng-Yeow Tan 1,3, Ku-Chou Chang 1,3, and Chia-Wei Liou 1,3 Abstract- Background: Standard 12-lead
Original Articles 232 Risk Factors for Ischemic Stroke: Electrocardiographic Findings Elley H.H. Chiu 1,2, Teng-Yeow Tan 1,3, Ku-Chou Chang 1,3, and Chia-Wei Liou 1,3 Abstract- Background: Standard 12-lead
The University of Mississippi School of Pharmacy
 LONG TERM PERSISTENCE WITH ACEI/ARB THERAPY AFTER ACUTE MYOCARDIAL INFARCTION: AN ANALYSIS OF THE 2006-2007 MEDICARE 5% NATIONAL SAMPLE DATA Lokhandwala T. MS, Yang Y. PhD, Thumula V. MS, Bentley J.P.
LONG TERM PERSISTENCE WITH ACEI/ARB THERAPY AFTER ACUTE MYOCARDIAL INFARCTION: AN ANALYSIS OF THE 2006-2007 MEDICARE 5% NATIONAL SAMPLE DATA Lokhandwala T. MS, Yang Y. PhD, Thumula V. MS, Bentley J.P.
Epidemiology and Prevention of Stroke
 Copyright Information Copyright protected material has been deleted from this presentation. References to the deleted material are provided for each slide. Epidemiology and Prevention of Stroke Larry B.
Copyright Information Copyright protected material has been deleted from this presentation. References to the deleted material are provided for each slide. Epidemiology and Prevention of Stroke Larry B.
Supplementary Online Content
 Supplementary Online Content Inohara T, Xian Y, Liang L, et al. Association of intracerebral hemorrhage among patients taking non vitamin K antagonist vs vitamin K antagonist oral anticoagulants with in-hospital
Supplementary Online Content Inohara T, Xian Y, Liang L, et al. Association of intracerebral hemorrhage among patients taking non vitamin K antagonist vs vitamin K antagonist oral anticoagulants with in-hospital
The Epidemiologic Transition of Diabetes Mellitus in Taiwan: Implications for Reversal of Female Preponderance from a National Cohort
 18 The Open Diabetes Journal, 29, 2, 18-23 Open Access The Epidemiologic Transition of Diabetes Mellitus in Taiwan: Implications for Reversal of Female Preponderance from a National Cohort Chin-Hsiao Tseng
18 The Open Diabetes Journal, 29, 2, 18-23 Open Access The Epidemiologic Transition of Diabetes Mellitus in Taiwan: Implications for Reversal of Female Preponderance from a National Cohort Chin-Hsiao Tseng
The randomized study of efficiency and safety of antithrombotic therapy in
 .. [ ] 18 150 160 mg/d 2 mg/d INR 2.0 3.0( 75 INR 1.6 2.5) 704 369 335 420 59.7% 63.3 9.9 19 2 24 2.7% 6.0% P =0.03 OR 0.44 95% CI 0.198 0.960 56% 62% 1.8% 4.6% P =0.04 OR 0.38 95% CI 0.147 0.977 52% 10.6%
.. [ ] 18 150 160 mg/d 2 mg/d INR 2.0 3.0( 75 INR 1.6 2.5) 704 369 335 420 59.7% 63.3 9.9 19 2 24 2.7% 6.0% P =0.03 OR 0.44 95% CI 0.198 0.960 56% 62% 1.8% 4.6% P =0.04 OR 0.38 95% CI 0.147 0.977 52% 10.6%
SUPPLEMENTAL MATERIAL
 SUPPLEMENTAL MATERIAL 1 Supplemental Table 1. ICD codes Diagnoses, surgical procedures, and pharmacotherapy used for defining the study population, comorbidity, and outcomes Study population Atrial fibrillation
SUPPLEMENTAL MATERIAL 1 Supplemental Table 1. ICD codes Diagnoses, surgical procedures, and pharmacotherapy used for defining the study population, comorbidity, and outcomes Study population Atrial fibrillation
Canadian Best Practice Recommendations for Stroke Care. (Updated 2008) Section # 3 Section # 3 Hyperacute Stroke Management
 Canadian Best Practice Recommendations for Stroke Care (Updated 2008) Section # 3 Section # 3 Hyperacute Stroke Management Reorganization of Recommendations 2008 2006 RECOMMENDATIONS: 2008 RECOMMENDATIONS:
Canadian Best Practice Recommendations for Stroke Care (Updated 2008) Section # 3 Section # 3 Hyperacute Stroke Management Reorganization of Recommendations 2008 2006 RECOMMENDATIONS: 2008 RECOMMENDATIONS:
NeuroPI Case Study: Anticoagulant Therapy
 Case: An 82-year-old man presents to the hospital following a transient episode of left visual field changes. His symptoms lasted 20 minutes and resolved spontaneously. He has a normal neurological examination
Case: An 82-year-old man presents to the hospital following a transient episode of left visual field changes. His symptoms lasted 20 minutes and resolved spontaneously. He has a normal neurological examination
CURRICULUM VITAE China Medical College, College of Medicine, Taichung, Taiwan, R.O.C.
 CURRICULUM VITAE NAME: Huang, Chung-Ming OFFICE ADDRESS: China Medical University Hospital, No. 2, Yuh-Der Road, Taichung, Taiwan, R.O.C., 北 路 2 EDUCATION: 1978-1985 China Medical College, College of Medicine,
CURRICULUM VITAE NAME: Huang, Chung-Ming OFFICE ADDRESS: China Medical University Hospital, No. 2, Yuh-Der Road, Taichung, Taiwan, R.O.C., 北 路 2 EDUCATION: 1978-1985 China Medical College, College of Medicine,
DECLARATION OF CONFLICT OF INTEREST
 DECLARATION OF CONFLICT OF INTEREST Warfarin and the risk of major bleeding events in patients with atrial fibrillation: a population-based study Laurent Azoulay PhD 1,2, Sophie Dell Aniello MSc 1, Teresa
DECLARATION OF CONFLICT OF INTEREST Warfarin and the risk of major bleeding events in patients with atrial fibrillation: a population-based study Laurent Azoulay PhD 1,2, Sophie Dell Aniello MSc 1, Teresa
Christy Pu Institutes Degree Department Period National Yang-Ming University (Taiwan)
 Christy Pu cypu@ym.edu.tw Degree Institutes Degree Department Period National Yang-Ming University (Taiwan) PhD Public Health 09/2005~06/2008 University of Oxford (UK) MSc Economics 08/2002~07/2003 University
Christy Pu cypu@ym.edu.tw Degree Institutes Degree Department Period National Yang-Ming University (Taiwan) PhD Public Health 09/2005~06/2008 University of Oxford (UK) MSc Economics 08/2002~07/2003 University
Alan Barber. Professor of Clinical Neurology University of Auckland
 Alan Barber Professor of Clinical Neurology University of Auckland Presented with L numbness & slurred speech 2 episodes; 10 mins & 2 hrs Hypertension Type II DM Examination pulse 80/min reg, BP 160/95
Alan Barber Professor of Clinical Neurology University of Auckland Presented with L numbness & slurred speech 2 episodes; 10 mins & 2 hrs Hypertension Type II DM Examination pulse 80/min reg, BP 160/95
03/30/2016 DISCLOSURES TO OPERATE OR NOT THAT IS THE QUESTION CAROTID INTERVENTION IS INDICATED FOR ASYMPTOMATIC CAROTID OCCLUSIVE DISEASE
 CAROTID INTERVENTION IS INDICATED FOR ASYMPTOMATIC CAROTID OCCLUSIVE DISEASE Elizabeth L. Detschelt, M.D. Allegheny Health Network Vascular and Endovascular Symposium April 2, 2016 DISCLOSURES I have no
CAROTID INTERVENTION IS INDICATED FOR ASYMPTOMATIC CAROTID OCCLUSIVE DISEASE Elizabeth L. Detschelt, M.D. Allegheny Health Network Vascular and Endovascular Symposium April 2, 2016 DISCLOSURES I have no
Chia-Lin Li, Ph.D. Professor Department of Health Care Management College of Management Chang Gung University
 Chia-Lin Li, Ph.D. Professor Department of Health Care Management College of Management Chang Gung University clli@mail.cgu.edu.tw Academic Background Ph.D. Institute of Public Health, National Yang-Ming
Chia-Lin Li, Ph.D. Professor Department of Health Care Management College of Management Chang Gung University clli@mail.cgu.edu.tw Academic Background Ph.D. Institute of Public Health, National Yang-Ming
Clinical Features and Subtypes of Ischemic Stroke Associated with Peripheral Arterial Disease
 Cronicon OPEN ACCESS EC NEUROLOGY Research Article Clinical Features and Subtypes of Ischemic Stroke Associated with Peripheral Arterial Disease Jin Ok Kim, Hyung-IL Kim, Jae Guk Kim, Hanna Choi, Sung-Yeon
Cronicon OPEN ACCESS EC NEUROLOGY Research Article Clinical Features and Subtypes of Ischemic Stroke Associated with Peripheral Arterial Disease Jin Ok Kim, Hyung-IL Kim, Jae Guk Kim, Hanna Choi, Sung-Yeon
RESUME Sep National Medical License, Taiwan Oct Board of Interal Medicine, Taiwan Aug Board of Cardiology, Internal Medicine, Taiwan
 RESUME Ye-Hsu Lu, M.D. Office Address: No.100, Ziyou 1st Rd., Sanmin Dist., Kaohsiung City 80708, Taiwan TEL: +886-7-3121101 ext. 7741 (Office), +886-918867017 (Cell) FAX: +886-7-3234845 E-mail: yehslu@gmail.com
RESUME Ye-Hsu Lu, M.D. Office Address: No.100, Ziyou 1st Rd., Sanmin Dist., Kaohsiung City 80708, Taiwan TEL: +886-7-3121101 ext. 7741 (Office), +886-918867017 (Cell) FAX: +886-7-3234845 E-mail: yehslu@gmail.com
The ESC Registry on Chronic Ischemic Coronary Disease
 EURObservational Research Programme The ESC Registry on Chronic Ischemic Coronary Disease Prof. Fausto J. Pinto, FESC, FACC, FASE, FSCAI Immediate Past-President, ESC University Hospital Sta Maria University
EURObservational Research Programme The ESC Registry on Chronic Ischemic Coronary Disease Prof. Fausto J. Pinto, FESC, FACC, FASE, FSCAI Immediate Past-President, ESC University Hospital Sta Maria University
Redgrave JN, Coutts SB, Schulz UG et al. Systematic review of associations between the presence of acute ischemic lesions on
 6. Imaging in TIA 6.1 What type of brain imaging should be used in suspected TIA? 6.2 Which patients with suspected TIA should be referred for urgent brain imaging? Evidence Tables IMAG1: After TIA/minor
6. Imaging in TIA 6.1 What type of brain imaging should be used in suspected TIA? 6.2 Which patients with suspected TIA should be referred for urgent brain imaging? Evidence Tables IMAG1: After TIA/minor
Retrospective Study on the Safety and Efficacy of Clopidogrel in the Treatment of Acute Cerebral Infarction
 International Journal of Neurologic Physical Therapy 2018; 4(1): 24-28 http://www.sciencepublishinggroup.com/j/ijnpt doi: 10.11648/j.ijnpt.20180401.14 ISSN: 2575-176X (Print); ISSN: 2575-1778 (Online)
International Journal of Neurologic Physical Therapy 2018; 4(1): 24-28 http://www.sciencepublishinggroup.com/j/ijnpt doi: 10.11648/j.ijnpt.20180401.14 ISSN: 2575-176X (Print); ISSN: 2575-1778 (Online)
Frequency of Cardiac Risk Factors in. Ischemic
 Frequency of Cardiac Risk Factors in Ischemic Stroke CORRESPONDING AUTHOR: MUSHTAQUE AHMED, MD EMAIL: BUGHIOAHMED@GMAIL.COM NEW YORK PRESBYTERIAN WEILL CORNELLL MEDICAL COLLEGE, NY ABSTRACT Stroke is the
Frequency of Cardiac Risk Factors in Ischemic Stroke CORRESPONDING AUTHOR: MUSHTAQUE AHMED, MD EMAIL: BUGHIOAHMED@GMAIL.COM NEW YORK PRESBYTERIAN WEILL CORNELLL MEDICAL COLLEGE, NY ABSTRACT Stroke is the
Condition Congestive heart failure I11.0; I13.0; I13.2; I42.0; I50 CO3C Left ventricular dysfunction I50.1; I50.9 E11 1; E11 9
 Comparative effectiveness and safety of non-vitamin K antagonists oral anticoagulants (OACs) and warfarin in daily clinical practice: A propensity weighted nationwide cohort study. Supplementary material
Comparative effectiveness and safety of non-vitamin K antagonists oral anticoagulants (OACs) and warfarin in daily clinical practice: A propensity weighted nationwide cohort study. Supplementary material
NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CLINICAL EXCELLENCE SCOPE
 NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CLINICAL EXCELLENCE 1 Guideline title SCOPE Myocardial infarction: secondary prevention in primary and secondary care for patients following a myocardial infarction 1.1
NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CLINICAL EXCELLENCE 1 Guideline title SCOPE Myocardial infarction: secondary prevention in primary and secondary care for patients following a myocardial infarction 1.1
Dr Julia Hopyan Stroke Neurologist Sunnybrook Health Sciences Centre
 Dr Julia Hopyan Stroke Neurologist Sunnybrook Health Sciences Centre Objectives To learn what s new in stroke care 2010-11 1) Acute stroke management Carotid artery stenting versus surgery for symptomatic
Dr Julia Hopyan Stroke Neurologist Sunnybrook Health Sciences Centre Objectives To learn what s new in stroke care 2010-11 1) Acute stroke management Carotid artery stenting versus surgery for symptomatic
Stroke Statistics in Korea: Part I. Epidemiology and Risk Factors: A Report from the Korean Stroke Society and Clinical Research Center for Stroke
 Journal of Stroke 213;15(1):2-2 Special Report Stroke Statistics in Korea: Part I. Epidemiology and Risk Factors: A Report from the Korean Stroke Society and Clinical Research Center for Stroke Keun-Sik
Journal of Stroke 213;15(1):2-2 Special Report Stroke Statistics in Korea: Part I. Epidemiology and Risk Factors: A Report from the Korean Stroke Society and Clinical Research Center for Stroke Keun-Sik
Supplementary Appendix
 Supplementary Appendix This appendix has been provided by the authors to give readers additional information about their work. Supplement to: Olesen JB, Lip GYH, Kamper A-L, et al. Stroke and bleeding
Supplementary Appendix This appendix has been provided by the authors to give readers additional information about their work. Supplement to: Olesen JB, Lip GYH, Kamper A-L, et al. Stroke and bleeding
National Horizon Scanning Centre. Irbesartan (Aprovel) for prevention of cardiovascular complications in patients with persistent atrial fibrillation
 Irbesartan (Aprovel) for prevention of cardiovascular complications in patients with persistent atrial fibrillation August 2008 This technology summary is based on information available at the time of
Irbesartan (Aprovel) for prevention of cardiovascular complications in patients with persistent atrial fibrillation August 2008 This technology summary is based on information available at the time of
Usefulness of a large automated health records database in pharmacoepidemiology
 Environ Health Prev Med (2011) 16:313 319 DOI 10.1007/s12199-010-0201-y REGULAR ARTICLE Usefulness of a large automated health records database in pharmacoepidemiology Hirokuni Hashikata Kouji H. Harada
Environ Health Prev Med (2011) 16:313 319 DOI 10.1007/s12199-010-0201-y REGULAR ARTICLE Usefulness of a large automated health records database in pharmacoepidemiology Hirokuni Hashikata Kouji H. Harada
List of Exhibits Adult Stroke
 List of Exhibits Adult Stroke List of Exhibits Adult Stroke i. Ontario Stroke Audit Hospital and Patient Characteristics Exhibit i. Hospital characteristics from the Ontario Stroke Audit, 200/ Exhibit
List of Exhibits Adult Stroke List of Exhibits Adult Stroke i. Ontario Stroke Audit Hospital and Patient Characteristics Exhibit i. Hospital characteristics from the Ontario Stroke Audit, 200/ Exhibit
Variability in Blood Pressure Medications Prescribed to Stroke Patients at Hospital Discharge
 Variability in Blood Pressure Medications Prescribed to Stroke Patients at Hospital Discharge A. Lantzy, MSN, RN, L. Simo, A. Carlson-Chalifoux, MS, RN, AGACNP-BC, CCRN, SCRN, P. Feit, MS, A. Sharrief,
Variability in Blood Pressure Medications Prescribed to Stroke Patients at Hospital Discharge A. Lantzy, MSN, RN, L. Simo, A. Carlson-Chalifoux, MS, RN, AGACNP-BC, CCRN, SCRN, P. Feit, MS, A. Sharrief,
Program Metrics. New Unique ID. Old Unique ID. Metric Set Metric Name Description. Old Metric Name
 Program Metrics The list below includes the metrics that will be calculated by the PINNACLE Registry for the outpatient office setting. These include metrics for, Atrial Fibrillation, Hypertension and.
Program Metrics The list below includes the metrics that will be calculated by the PINNACLE Registry for the outpatient office setting. These include metrics for, Atrial Fibrillation, Hypertension and.
Quality Payment Program: Cardiology Specialty Measure Set
 Quality Payment Program: Cardiology Specialty Set Title Number CMS Reporting Method(s) Heart Failure (HF): Angiotensin- Converting Enzyme (ACE) Inhibitor or Angiotensin Receptor Blocker (ARB) Therapy for
Quality Payment Program: Cardiology Specialty Set Title Number CMS Reporting Method(s) Heart Failure (HF): Angiotensin- Converting Enzyme (ACE) Inhibitor or Angiotensin Receptor Blocker (ARB) Therapy for
Characteristics of Hospitalized Patients with Atrial Fibrillation in Taiwan: A Nationwide Observation
 The American Journal of Medicine (2007) 120, 819.e1-819.e7 CLINICAL RESEARCH STUDY Characteristics of Hospitalized Patients with Atrial Fibrillation in Taiwan: A Nationwide Observation Cheng-Han Lee, MD,
The American Journal of Medicine (2007) 120, 819.e1-819.e7 CLINICAL RESEARCH STUDY Characteristics of Hospitalized Patients with Atrial Fibrillation in Taiwan: A Nationwide Observation Cheng-Han Lee, MD,
Branko N Huisa M.D. Assistant Professor of Neurology UNM Stroke Center
 Branko N Huisa M.D. Assistant Professor of Neurology UNM Stroke Center THE END! CHANGABLE Blood pressure Diabetes Mellitus Hyperlipidemia Atrial fibrillation Nicotine Drug abuse Life style NOT CHANGABLE
Branko N Huisa M.D. Assistant Professor of Neurology UNM Stroke Center THE END! CHANGABLE Blood pressure Diabetes Mellitus Hyperlipidemia Atrial fibrillation Nicotine Drug abuse Life style NOT CHANGABLE
ischemic stroke, transient ischemic attack, or peripheral artery embolism
 Appendix Table S1: ICD- 8/1 codes and ATC- codes Population Acute myocardial infarction Defined from primary inpatient diagnoses codes PCI Defined from procedure codes Non- valvular atrial fibrillation
Appendix Table S1: ICD- 8/1 codes and ATC- codes Population Acute myocardial infarction Defined from primary inpatient diagnoses codes PCI Defined from procedure codes Non- valvular atrial fibrillation
Malignant transformation of oral submucous fibrosis in Taiwan: A nationwide population-based retrospective cohort study
 Accepted: 9 March 2017 DOI: 10.1111/jop.12570 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Malignant transformation of oral submucous fibrosis in Taiwan: A nationwide population-based retrospective cohort study Po-Yu Yang 1,2 Yi-Tzu
Accepted: 9 March 2017 DOI: 10.1111/jop.12570 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Malignant transformation of oral submucous fibrosis in Taiwan: A nationwide population-based retrospective cohort study Po-Yu Yang 1,2 Yi-Tzu
2/7/
 Disclosure Intracranial Atherosclerosis an update None Mai N. Nguyen-Huynh, MD, MAS Assistant Professor of Neurology UCSF Neurovascular Service February 7, 2009 Case #1 60 y.o. Chinese-speaking speaking
Disclosure Intracranial Atherosclerosis an update None Mai N. Nguyen-Huynh, MD, MAS Assistant Professor of Neurology UCSF Neurovascular Service February 7, 2009 Case #1 60 y.o. Chinese-speaking speaking
Differences in Clinical Features in Patients with Acute Coronary Syndrome and Stroke: Japanese Multicenter Registry Results
 doi: 10.2169/internalmedicine.1020-18 Intern Med Advance Publication http://internmed.jp ORIGINAL ARTICLE Differences in Clinical Features in Patients with Acute Coronary Syndrome and Stroke: Japanese
doi: 10.2169/internalmedicine.1020-18 Intern Med Advance Publication http://internmed.jp ORIGINAL ARTICLE Differences in Clinical Features in Patients with Acute Coronary Syndrome and Stroke: Japanese
Results from RE-LY and RELY-ABLE
 Results from RE-LY and RELY-ABLE Assessment of the safety and efficacy of dabigatran etexilate (Pradaxa ) in longterm stroke prevention EXECUTIVE SUMMARY Dabigatran etexilate (Pradaxa ) has shown a consistent
Results from RE-LY and RELY-ABLE Assessment of the safety and efficacy of dabigatran etexilate (Pradaxa ) in longterm stroke prevention EXECUTIVE SUMMARY Dabigatran etexilate (Pradaxa ) has shown a consistent
The Epidemiology of Diabetes in Korea
 Review http://dx.doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2011.35.4.303 pissn 2233-6079 eissn 2233-6087 D I A B E T E S & M E T A B O L I S M J O U R N A L The Epidemiology of Diabetes in Korea Dae Jung Kim Department of Endocrinology
Review http://dx.doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2011.35.4.303 pissn 2233-6079 eissn 2233-6087 D I A B E T E S & M E T A B O L I S M J O U R N A L The Epidemiology of Diabetes in Korea Dae Jung Kim Department of Endocrinology
Quality Measures MIPS CV Specific
 Quality Measures MIPS CV Specific MEASURE NAME Atrial Fibrillation and Atrial Flutter: Chronic Anticoagulation Therapy CAHPS for MIPS Clinician/Group Survey Cardiac Rehabilitation Patient Referral from
Quality Measures MIPS CV Specific MEASURE NAME Atrial Fibrillation and Atrial Flutter: Chronic Anticoagulation Therapy CAHPS for MIPS Clinician/Group Survey Cardiac Rehabilitation Patient Referral from
Condition/Procedure Measure Compliance Criteria Reference Attribution Method
 Premium Specialty: Cardiology Credentialed Specialties include: Cardiac Diagnostic, Cardiology, Cardiovascular Disease, Clinical Cardiac Electrophysiology, and Interventional Cardiology This document is
Premium Specialty: Cardiology Credentialed Specialties include: Cardiac Diagnostic, Cardiology, Cardiovascular Disease, Clinical Cardiac Electrophysiology, and Interventional Cardiology This document is
Controversies in Anticoagulation : Optimizing Outcome in NOACs for GI Bleeding Risk
 Controversies in Anticoagulation : Optimizing Outcome in NOACs for GI Bleeding Risk Boyoung Joung, MD, PhD Professor, Division of Cardiology Director of Electrophysiology Laboratory Severance Cardiovascular
Controversies in Anticoagulation : Optimizing Outcome in NOACs for GI Bleeding Risk Boyoung Joung, MD, PhD Professor, Division of Cardiology Director of Electrophysiology Laboratory Severance Cardiovascular
Supplementary Online Content
 Supplementary Online Content Lin Y-S, Chen Y-L, Chen T-H, et al. Comparison of Clinical Outcomes Among Patients With Atrial Fibrillation or Atrial Flutter Stratified by CHA 2 DS 2 -VASc Score. JAMA Netw
Supplementary Online Content Lin Y-S, Chen Y-L, Chen T-H, et al. Comparison of Clinical Outcomes Among Patients With Atrial Fibrillation or Atrial Flutter Stratified by CHA 2 DS 2 -VASc Score. JAMA Netw
Trends and Variations in General Medical Services Indicators for Coronary Heart Disease: Analysis of QRESEARCH Data
 Trends and Variations in General Medical Services Indicators for Coronary Heart Disease: Analysis of QRESEARCH Data Authors: Professor Julia Hippisley-Cox Professor Mike Pringle Professor of Clinical Epidemiology
Trends and Variations in General Medical Services Indicators for Coronary Heart Disease: Analysis of QRESEARCH Data Authors: Professor Julia Hippisley-Cox Professor Mike Pringle Professor of Clinical Epidemiology
CONCISE GUIDE National Clinical Guidelines for Stroke 2nd Edition
 CONCISE GUIDE 2004 National for Stroke 2nd Edition This concise guide summarises the recommendations, graded according to the evidence, from the National 2nd edition. As critical aspects of care are not
CONCISE GUIDE 2004 National for Stroke 2nd Edition This concise guide summarises the recommendations, graded according to the evidence, from the National 2nd edition. As critical aspects of care are not
CLINICAL PROCESS IMPROVEMENT INITIATIVE (CPII) EFFICIENCY REPORT EXPLANATION January 4, 2016
 CLINICAL PROCESS IMPROVEMENT INITIATIVE (CPII) EFFICIENCY REPORT EXPLANATION January 4, 2016 WHAT IS AN EPISODE OF CARE? An episode of care is a grouping of a patient s health care claims for a unique
CLINICAL PROCESS IMPROVEMENT INITIATIVE (CPII) EFFICIENCY REPORT EXPLANATION January 4, 2016 WHAT IS AN EPISODE OF CARE? An episode of care is a grouping of a patient s health care claims for a unique
Table S10 Mortality Study
 Table S10 Mortality Study Framingham Heart Study, Benjamin (1998) 1 ELAT Study, Austria and Serbia Stollberger (2004) 2 Copenhagen City Heart study, Denmark Friberg (2004) 3 Patel (2004) 4 Invited residents
Table S10 Mortality Study Framingham Heart Study, Benjamin (1998) 1 ELAT Study, Austria and Serbia Stollberger (2004) 2 Copenhagen City Heart study, Denmark Friberg (2004) 3 Patel (2004) 4 Invited residents
Symptomatic Venous Thromboembolism after Total Hip/Knee Replacement: A Population-based Taiwan Study
 IMPROVING PATIENT SAFETY Preventing & Managing Venous Thromboembolism Session 8 Data Driving Strategies for VTE Prevention and Management 3/30/2012; 15.35-15.55 Symptomatic Venous Thromboembolism after
IMPROVING PATIENT SAFETY Preventing & Managing Venous Thromboembolism Session 8 Data Driving Strategies for VTE Prevention and Management 3/30/2012; 15.35-15.55 Symptomatic Venous Thromboembolism after
Long-Term Care Updates
 Long-Term Care Updates October/November 2015 By Daniel Kerner, PharmD A stroke occurs when blood flow to the brain is stopped or slowed, resulting in death or damage to brain cells. There are three main
Long-Term Care Updates October/November 2015 By Daniel Kerner, PharmD A stroke occurs when blood flow to the brain is stopped or slowed, resulting in death or damage to brain cells. There are three main
APPENDIX A NORTH AMERICAN SYMPTOMATIC CAROTID ENDARTERECTOMY TRIAL
 APPENDIX A Primary Findings From Selected Recent National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke-Sponsored Clinical Trials That Have shaped Modern Stroke Prevention Philip B. Gorelick 178 NORTH
APPENDIX A Primary Findings From Selected Recent National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke-Sponsored Clinical Trials That Have shaped Modern Stroke Prevention Philip B. Gorelick 178 NORTH
NOAC trials for AF: A review
 NOAC trials for AF: A review Chern-En Chiang, MD, PhD, FACC, FESC General Clinical Research Center Division of Cardiology Taipei Veterans General Hospital National Yang-Ming University Taipei, Taiwan Presenter
NOAC trials for AF: A review Chern-En Chiang, MD, PhD, FACC, FESC General Clinical Research Center Division of Cardiology Taipei Veterans General Hospital National Yang-Ming University Taipei, Taiwan Presenter
Supplementary Appendix
 Supplementary Appendix Increased Risk of Atrial Fibrillation and Thromboembolism in Patients with Severe Psoriasis: a Nationwide Population-based Study Tae-Min Rhee, MD 1, Ji Hyun Lee, MD 2, Eue-Keun Choi,
Supplementary Appendix Increased Risk of Atrial Fibrillation and Thromboembolism in Patients with Severe Psoriasis: a Nationwide Population-based Study Tae-Min Rhee, MD 1, Ji Hyun Lee, MD 2, Eue-Keun Choi,
Role of Clopidogrel in Acute Coronary Syndromes. Hossam Kandil,, MD. Professor of Cardiology Cairo University
 Role of Clopidogrel in Acute Coronary Syndromes Hossam Kandil,, MD Professor of Cardiology Cairo University ACS Treatment Strategies Reperfusion/Revascularization Therapy Thrombolysis PCI (with/ without
Role of Clopidogrel in Acute Coronary Syndromes Hossam Kandil,, MD Professor of Cardiology Cairo University ACS Treatment Strategies Reperfusion/Revascularization Therapy Thrombolysis PCI (with/ without
Quality Payment Program: Cardiology Specialty Measure Set
 Measure Title * Reportable via PINNACLE α Reportable via Diabetes Collaborative CQMC v1.0 Measure High Priority Measure Cross Cutting Measure Heart Failure (HF): Angiotensin- Converting Enzyme (ACE) Inhibitor
Measure Title * Reportable via PINNACLE α Reportable via Diabetes Collaborative CQMC v1.0 Measure High Priority Measure Cross Cutting Measure Heart Failure (HF): Angiotensin- Converting Enzyme (ACE) Inhibitor
Supplementary Information. Statins Improve Long Term Patency of Arteriovenous Fistula for
 Supplementary Information Statins Improve Long Term Patency of Arteriovenous Fistula for Hemodialysis Hao-Hsiang Chang MD, MSc 1,2, Yu-Kang Chang PhD 3, Chia-Wen Lu MD 1, Chi-Ting Huang 3, Chiang-Ting
Supplementary Information Statins Improve Long Term Patency of Arteriovenous Fistula for Hemodialysis Hao-Hsiang Chang MD, MSc 1,2, Yu-Kang Chang PhD 3, Chia-Wen Lu MD 1, Chi-Ting Huang 3, Chiang-Ting
Acute Medical Management. Bogachan Sahin, M.D., Ph.D. Department of Neurology
 Acute Medical Management Bogachan Sahin, M.D., Ph.D. Department of Neurology Outline Head-of-bed position Blood pressure management Antiplatelet therapy Anticoagulation Statin therapy Rehabilitation and
Acute Medical Management Bogachan Sahin, M.D., Ph.D. Department of Neurology Outline Head-of-bed position Blood pressure management Antiplatelet therapy Anticoagulation Statin therapy Rehabilitation and
Disclosures. An Update on TIA and Minor Stroke. The Agenda PROGNOSIS PATHOPHYSIOLOGY GUIDELINES AND PROVEN MANAGEMENT STRATEGIES AGGRESSIVE TREATMENT
 Disclosures An Update on TIA and Minor Stroke Dr. Johnston is principal investigator for the POINT trial, sponsored by the NIH but with drug and placebo contributed by Sanofi-Aventis. S. Claiborne Johnston,
Disclosures An Update on TIA and Minor Stroke Dr. Johnston is principal investigator for the POINT trial, sponsored by the NIH but with drug and placebo contributed by Sanofi-Aventis. S. Claiborne Johnston,
Epidemiologic characteristics of cervical cancer in Korean women
 Review Article J Gynecol Oncol Vol. 25, No. 1:70-74 pissn 2005-0380 eissn 2005-0399 Epidemiologic characteristics of cervical cancer in Korean women Hyun-Joo Seol, Kyung-Do Ki, Jong-Min Lee Department
Review Article J Gynecol Oncol Vol. 25, No. 1:70-74 pissn 2005-0380 eissn 2005-0399 Epidemiologic characteristics of cervical cancer in Korean women Hyun-Joo Seol, Kyung-Do Ki, Jong-Min Lee Department
Research Article Risk Factors for Chronic Subdural Hematoma after a Minor Head Injury in the Elderly: A Population-Based Study
 BioMed Research International, Article ID 218646, 6 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2014/218646 Research Article Risk Factors for Chronic Subdural Hematoma after a Minor Head Injury in the Elderly: A Population-Based
BioMed Research International, Article ID 218646, 6 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2014/218646 Research Article Risk Factors for Chronic Subdural Hematoma after a Minor Head Injury in the Elderly: A Population-Based
Hypertension is a common comorbidity associated with
 Metformin and Risk of Hypertension in Taiwanese Patients With Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Chin-Hsiao, MD, PhD Background- Whether metformin use may reduce hypertension risk has not been studied. This study
Metformin and Risk of Hypertension in Taiwanese Patients With Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Chin-Hsiao, MD, PhD Background- Whether metformin use may reduce hypertension risk has not been studied. This study
The Impact of Smoking on Acute Ischemic Stroke
 Smoking The Impact of Smoking on Acute Ischemic Stroke Wei-Chieh Weng, M.D. Department of Neurology, Chang-Gung Memorial Hospital, Kee-Lung, Taiwan Smoking related mortality Atherosclerotic vascular disease
Smoking The Impact of Smoking on Acute Ischemic Stroke Wei-Chieh Weng, M.D. Department of Neurology, Chang-Gung Memorial Hospital, Kee-Lung, Taiwan Smoking related mortality Atherosclerotic vascular disease
National Horizon Scanning Centre. Irbesartan (Aprovel) for heart failure with preserved systolic function. August 2008
 Irbesartan (Aprovel) for heart failure with preserved systolic function August 2008 This technology summary is based on information available at the time of research and a limited literature search. It
Irbesartan (Aprovel) for heart failure with preserved systolic function August 2008 This technology summary is based on information available at the time of research and a limited literature search. It
Updates in Stroke Management. Jessica A Starr, PharmD, FCCP, BCPS Associate Clinical Professor Auburn University Harrison School of Pharmacy
 Updates in Stroke Management Jessica A Starr, PharmD, FCCP, BCPS Associate Clinical Professor Auburn University Harrison School of Pharmacy Disclosure I have no actual or potential conflict of interest
Updates in Stroke Management Jessica A Starr, PharmD, FCCP, BCPS Associate Clinical Professor Auburn University Harrison School of Pharmacy Disclosure I have no actual or potential conflict of interest
Huangdao People's Hospital
 Table of contents 1. Background... 3 2. Integrated care pathway implementation... 6 (1) Workload indicators... 6 A. In eligible for care pathway... 6 B. Care pathway implementation... 7 (2) Outcome indicators...
Table of contents 1. Background... 3 2. Integrated care pathway implementation... 6 (1) Workload indicators... 6 A. In eligible for care pathway... 6 B. Care pathway implementation... 7 (2) Outcome indicators...
A nationwide population-based study. Pai-Feng Hsu M.D. Shao-Yuan Chuang PhD
 The Association of Clinical Symptomatic Hypoglycemia with Cardiovascular Events and Total Death in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus A nationwide population-based study Pai-Feng Hsu M.D. Shao-Yuan Chuang PhD Taipei
The Association of Clinical Symptomatic Hypoglycemia with Cardiovascular Events and Total Death in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus A nationwide population-based study Pai-Feng Hsu M.D. Shao-Yuan Chuang PhD Taipei
<INSERT COUNTRY/SITE NAME> All Stroke Events
 WHO STEPS STROKE INSTRUMENT For further guidance on All Stroke Events, see Section 5, page 5-15 All Stroke Events Patient Identification and Patient Characteristics (I 1) Stroke
WHO STEPS STROKE INSTRUMENT For further guidance on All Stroke Events, see Section 5, page 5-15 All Stroke Events Patient Identification and Patient Characteristics (I 1) Stroke
Liping Liu Dpet. of Neurology and Stroke Center Beijing Tiantan Hospital Capital Medical University
 Liping Liu Dpet. of Neurology and Stroke Center Beijing Tiantan Hospital Capital Medical University Disclosures Conflict of interest disclosures: No Disclosures Funding The CHANCE trial is funded by the
Liping Liu Dpet. of Neurology and Stroke Center Beijing Tiantan Hospital Capital Medical University Disclosures Conflict of interest disclosures: No Disclosures Funding The CHANCE trial is funded by the
Slide 1. Slide 2 Conflict of Interest Disclosure. Slide 3 Stroke Facts. The Treatment of Intracranial Stenosis. Disclosure
 Slide 1 The Treatment of Intracranial Stenosis Helmi Lutsep, MD Vice Chair and Dixon Term Professor, Department of Neurology, Oregon Health & Science University Chief of Neurology, VA Portland Health Care
Slide 1 The Treatment of Intracranial Stenosis Helmi Lutsep, MD Vice Chair and Dixon Term Professor, Department of Neurology, Oregon Health & Science University Chief of Neurology, VA Portland Health Care
>27 years of old, were enrolled. The success rates for apo B and LDL-C goal attainments were evaluated and compared by categorization and by sex.
 Original Article Goal attainments and their discrepancies for low density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C) and apolipoprotein B (apo B) in over 2,000 Chinese patients with known coronary artery disease
Original Article Goal attainments and their discrepancies for low density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C) and apolipoprotein B (apo B) in over 2,000 Chinese patients with known coronary artery disease
Therapy for Acute Stroke. Systems of Care for TIA
 Therapy for Acute Stroke and Systems of Care for TIA Gregory W. Albers, MD Coyote Foundation Professor of Neurology and Neurological Sciences Director, Stanford Stroke Center Stanford University Medical
Therapy for Acute Stroke and Systems of Care for TIA Gregory W. Albers, MD Coyote Foundation Professor of Neurology and Neurological Sciences Director, Stanford Stroke Center Stanford University Medical
Ischemic Stroke in Critically Ill Patients with Malignancy
 Ischemic Stroke in Critically Ill Patients with Malignancy Jeong-Am Ryu 1, Oh Young Bang 2, Daesang Lee 1, Jinkyeong Park 1, Jeong Hoon Yang 1, Gee Young Suh 1, Joongbum Cho 1, Chi Ryang Chung 1, Chi-Min
Ischemic Stroke in Critically Ill Patients with Malignancy Jeong-Am Ryu 1, Oh Young Bang 2, Daesang Lee 1, Jinkyeong Park 1, Jeong Hoon Yang 1, Gee Young Suh 1, Joongbum Cho 1, Chi Ryang Chung 1, Chi-Min
A study to find out relationship in between serum uric acid level and stroke
 International Journal of Advances in Medicine Tripathi VD et al. Int J Adv Med. 2017 Oct;4(5):1255-1259 http://www.ijmedicine.com pissn 2349-3925 eissn 2349-3933 Original Research Article DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18203/2349-3933.ijam20173661
International Journal of Advances in Medicine Tripathi VD et al. Int J Adv Med. 2017 Oct;4(5):1255-1259 http://www.ijmedicine.com pissn 2349-3925 eissn 2349-3933 Original Research Article DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18203/2349-3933.ijam20173661
The problem of uncontrolled hypertension
 (2002) 16, S3 S8 2002 Nature Publishing Group All rights reserved 0950-9240/02 $25.00 www.nature.com/jhh The problem of uncontrolled hypertension Department of Public Health and Clinical Medicine, Norrlands
(2002) 16, S3 S8 2002 Nature Publishing Group All rights reserved 0950-9240/02 $25.00 www.nature.com/jhh The problem of uncontrolled hypertension Department of Public Health and Clinical Medicine, Norrlands
Treatment of Right Colonic Diverticulitis: The Role of Nonoperative Treatment
 Original Article Journal of the Korean Society of DOI: 10.3393/jksc.2010.26.6.402 pissn 2093-7822 eissn 2093-7830 Treatment of Right Colonic Diverticulitis: The Role of Nonoperative Treatment Ma Ru Kim,
Original Article Journal of the Korean Society of DOI: 10.3393/jksc.2010.26.6.402 pissn 2093-7822 eissn 2093-7830 Treatment of Right Colonic Diverticulitis: The Role of Nonoperative Treatment Ma Ru Kim,
Clinical Updates in the Treatment of Hypertension JNC 7 vs. JNC 8. Lauren Thomas, PharmD PGY1 Pharmacy Practice Resident South Pointe Hospital
 Clinical Updates in the Treatment of Hypertension JNC 7 vs. JNC 8 Lauren Thomas, PharmD PGY1 Pharmacy Practice Resident South Pointe Hospital Objectives Review the Eighth Joint National Committee (JNC
Clinical Updates in the Treatment of Hypertension JNC 7 vs. JNC 8 Lauren Thomas, PharmD PGY1 Pharmacy Practice Resident South Pointe Hospital Objectives Review the Eighth Joint National Committee (JNC
Stroke secondary prevention. Gill Cluckie Stroke Nurse Consultant St. George s Hospital
 Stroke secondary prevention Gill Cluckie Stroke Nurse Consultant St. George s Hospital Stroke recurrence The risk of recurrent stroke is greatest after first stroke 2 3% of survivors of a first stroke
Stroke secondary prevention Gill Cluckie Stroke Nurse Consultant St. George s Hospital Stroke recurrence The risk of recurrent stroke is greatest after first stroke 2 3% of survivors of a first stroke
The effectiveness of telephone reminders and SMS messages on compliance with colorectal cancer screening: an open-label, randomized controlled trial
 Page1 of 5 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 The effectiveness of telephone reminders and SMS messages on compliance with colorectal cancer screening: an
Page1 of 5 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 The effectiveness of telephone reminders and SMS messages on compliance with colorectal cancer screening: an
SUPPLEMENTAL MATERIAL
 SUPPLEMENTAL MATERIAL Cognitive impairment evaluated with Vascular Cognitive Impairment Harmonization Standards in a multicenter prospective stroke cohort in Korea Supplemental Methods Participants From
SUPPLEMENTAL MATERIAL Cognitive impairment evaluated with Vascular Cognitive Impairment Harmonization Standards in a multicenter prospective stroke cohort in Korea Supplemental Methods Participants From
Intracranial Atherosclerosis in Asians
 Intracranial Atherosclerosis in Asians Anthony S. Kim, MD Assistant Clinical Professor of Neurology UCSF Neurovascular Service February 27, 2010 Disclosures Research Support National Institutes of Health
Intracranial Atherosclerosis in Asians Anthony S. Kim, MD Assistant Clinical Professor of Neurology UCSF Neurovascular Service February 27, 2010 Disclosures Research Support National Institutes of Health
Is there a mechanism of interaction between hypertension and dyslipidaemia?
 Is there a mechanism of interaction between hypertension and dyslipidaemia? Neil R Poulter International Centre for Circulatory Health NHLI, Imperial College London Daegu, Korea April 2005 Observational
Is there a mechanism of interaction between hypertension and dyslipidaemia? Neil R Poulter International Centre for Circulatory Health NHLI, Imperial College London Daegu, Korea April 2005 Observational
Risk of pneumonia among patients with splenectomy: a retrospective populationbased
 Risk of pneumonia among patients with splenectomy: a retrospective populationbased cohort study Shih-Wei Lai, a,b Cheng-Li Lin, a,c Kuan-Fu Liao d,e From the a College of Medicine, China Medical University,
Risk of pneumonia among patients with splenectomy: a retrospective populationbased cohort study Shih-Wei Lai, a,b Cheng-Li Lin, a,c Kuan-Fu Liao d,e From the a College of Medicine, China Medical University,
AF in Asian: which NOAC to choose for particular patient and at what dose? DEJIA HUANG West China Hospital of Sichuan University, Chengdu, China
 AF in Asian: which NOAC to choose for particular patient and at what dose? DEJIA HUANG West China Hospital of Sichuan University, Chengdu, China Case report 64-year-old Chinese man with history of hypertension,
AF in Asian: which NOAC to choose for particular patient and at what dose? DEJIA HUANG West China Hospital of Sichuan University, Chengdu, China Case report 64-year-old Chinese man with history of hypertension,
Supplementary webappendix
 Supplementary webappendix This webappendix formed part of the original submission and has been peer reviewed. We post it as supplied by the authors. Supplement to: Hart RG, Diener H-C, Coutts SB, et al,
Supplementary webappendix This webappendix formed part of the original submission and has been peer reviewed. We post it as supplied by the authors. Supplement to: Hart RG, Diener H-C, Coutts SB, et al,
Drug Utilization Study of Statin in Hemorrhagic Stroke
 Health Science International Conference (HSIC 2017) Drug Utilization Study of Statin in Hemorrhagic Stroke Nailis Syifa 1 *, Cici Dwi 1 and Didik Hasmono 2 1 Pharmacy department, University of Muhammadiyah
Health Science International Conference (HSIC 2017) Drug Utilization Study of Statin in Hemorrhagic Stroke Nailis Syifa 1 *, Cici Dwi 1 and Didik Hasmono 2 1 Pharmacy department, University of Muhammadiyah
New PINNACLE Measures The below measures for PINNACLE will be added as new measures to the outcomes reporting starting with Version 2.0.
 New PINNACLE Measures The below measures for PINNACLE will be added as new measures to the outcomes reporting starting with Version 2.0. Measure Steward Measure Name Measure Description Rationale for Adding
New PINNACLE Measures The below measures for PINNACLE will be added as new measures to the outcomes reporting starting with Version 2.0. Measure Steward Measure Name Measure Description Rationale for Adding
Finland and Sweden and UK GP-HOSP datasets
 Web appendix: Supplementary material Table 1 Specific diagnosis codes used to identify bladder cancer cases in each dataset Finland and Sweden and UK GP-HOSP datasets Netherlands hospital and cancer registry
Web appendix: Supplementary material Table 1 Specific diagnosis codes used to identify bladder cancer cases in each dataset Finland and Sweden and UK GP-HOSP datasets Netherlands hospital and cancer registry
Stroke is the third-leading cause of death and a major
 Long-Term Mortality and Recurrent Stroke Risk Among Chinese Stroke Patients With Predominant Intracranial Atherosclerosis Ka Sing Wong, MD; Huan Li, MD Background and Purpose The goal of this study was
Long-Term Mortality and Recurrent Stroke Risk Among Chinese Stroke Patients With Predominant Intracranial Atherosclerosis Ka Sing Wong, MD; Huan Li, MD Background and Purpose The goal of this study was
Unstable INR Has Implications for Healthcare Resource Use. Janssen Pharmaceuticals, Inc.
 Unstable INR Has Implications for Healthcare Resource Use Janssen Pharmaceuticals, Inc. Stable INR is essential for effective anticoagulation treatment Achieving a stable international normalized ratio
Unstable INR Has Implications for Healthcare Resource Use Janssen Pharmaceuticals, Inc. Stable INR is essential for effective anticoagulation treatment Achieving a stable international normalized ratio
L. Fauchier (1), S. Taillandier (1), I. Lagrenade (1), C. Pellegrin (1), L. Gorin (1), A. Bernard (1), B. Rauzy (1), D. Babuty (1), GYL.
 Prognosis in patients with atrial fibrillation and CHA 2 DS 2 VASc score=0 in a real world community based cohort study: Loire Valley Atrial Fibrillation project L. Fauchier (1), S. Taillandier (1), I.
Prognosis in patients with atrial fibrillation and CHA 2 DS 2 VASc score=0 in a real world community based cohort study: Loire Valley Atrial Fibrillation project L. Fauchier (1), S. Taillandier (1), I.
Blood Pressure Reduction Among Acute Stroke Patients A Randomized Controlled Clinical Trial
 Blood Pressure Reduction Among Acute Stroke Patients A Randomized Controlled Clinical Trial Jiang He, Yonghong Zhang, Tan Xu, Weijun Tong, Shaoyan Zhang, Chung-Shiuan Chen, Qi Zhao, Jing Chen for CATIS
Blood Pressure Reduction Among Acute Stroke Patients A Randomized Controlled Clinical Trial Jiang He, Yonghong Zhang, Tan Xu, Weijun Tong, Shaoyan Zhang, Chung-Shiuan Chen, Qi Zhao, Jing Chen for CATIS
Insomnia and the Risk of Atrial Fibrillation: A Population-Based Cohort Study
 Original Article Acta Cardiol Sin 2017;33:165 172 doi: 10.6515/ACS20160611B EP & Arrythmia Insomnia and the Risk of Atrial Fibrillation: A Population-Based Cohort Study Hsiu-Hao Lee, 1,2 Yueh-Chung Chen,
Original Article Acta Cardiol Sin 2017;33:165 172 doi: 10.6515/ACS20160611B EP & Arrythmia Insomnia and the Risk of Atrial Fibrillation: A Population-Based Cohort Study Hsiu-Hao Lee, 1,2 Yueh-Chung Chen,
CHADS 2 Score, Statin Therapy, and Risks of Atrial Fibrillation
 CLINICAL RESEARCH STUDY CHADS 2 Score, Statin Therapy, and Risks of Atrial Fibrillation Chen-Ying Hung, MD, a Ching-Heng Lin, PhD, b El-Wui Loh, PhD, c Chih-Tai Ting, MD, PhD, a,d Tsu-Juey Wu, MD, PhD
CLINICAL RESEARCH STUDY CHADS 2 Score, Statin Therapy, and Risks of Atrial Fibrillation Chen-Ying Hung, MD, a Ching-Heng Lin, PhD, b El-Wui Loh, PhD, c Chih-Tai Ting, MD, PhD, a,d Tsu-Juey Wu, MD, PhD
Non-commercial use only
 Italian Journal of Medicine 2016; volume 10:202-206 Embolic stroke of undetermined source: a retrospective analysis from an Italian Stroke Unit Marco Masina, 1 Annalena Cicognani, 1 Carla Lofiego, 2 Simona
Italian Journal of Medicine 2016; volume 10:202-206 Embolic stroke of undetermined source: a retrospective analysis from an Italian Stroke Unit Marco Masina, 1 Annalena Cicognani, 1 Carla Lofiego, 2 Simona
The Hypertension Clinic is a part of the Internal Medicine
 Original Article Hypertension Registry at the Bangkok Hospital Medical Center: The First 7 Months Experience OBJECTIVE: The Hypertension Registry at the Bangkok Hospital Medical Center was established
Original Article Hypertension Registry at the Bangkok Hospital Medical Center: The First 7 Months Experience OBJECTIVE: The Hypertension Registry at the Bangkok Hospital Medical Center was established
Role of Pharmacoepidemiology in Drug Evaluation
 Role of Pharmacoepidemiology in Drug Evaluation Martin Wong MD, MPH School of Public Health and Primary Care Faculty of Medicine Chinese University of Hog Kong Outline of Content Introduction: what is
Role of Pharmacoepidemiology in Drug Evaluation Martin Wong MD, MPH School of Public Health and Primary Care Faculty of Medicine Chinese University of Hog Kong Outline of Content Introduction: what is
