SPOTLIGHT ON PERICARDIAL DISEASE
|
|
|
- Ezra Price
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Vet Times The website for the veterinary profession SPOTLIGHT ON PERICARDIAL DISEASE Author : DAN FORSTER Categories : Vets Date : February 16, 2009 DAN FORSTER discusses the spectrum of disorders under this clinical umbrella and emphasises the value of a full investigation in light of variable prognoses PERICARDIAL diseases comprise a small proportion of clinically important cardiovascular diseases in dogs and cats (estimated at one per cent). Although significantly less common than valvular, congenital or myocardial heart disease, pericardial disease is regarded as one of the most common causes of right-sided congestive heart failure in dogs. However, pericardial disease is rare in cats. Congenital or acquired Congenital pericardial disorders: - peritoneal-pericardial diaphragmatic hernia (PPDH); - pericardial defects; and - pericardial cysts. Acquired pericardial disorders: - pericardial neoplasia; 1 / 14
2 - constrictive pericarditis; and - pericardial effusion. Anatomy The heart and great vessels are enveloped in the pericardial sac, which is composed of two layers: a tough outer fibroserous membrane (parietal pericardium) and a delicate inner serous membrane (visceral pericardium). A pericardial cavity is formed between the two layers; normal cats and dogs have approximately 0.25ml/kg of pericardial fluid in this cavity. The blood supply is from the pericardial branches of the aorta, internal thoracic and musculophrenic arteries. Innervation is from the vagus nerve, left recurrent pharyngeal nerve, and oesophageal plexus. There is also a rich sympathetic nerve supply from stellate and first dorsal root ganglions. The phrenic nerve may also supply sensory fibres to the pericardium. Function The pericardium is very distensible when first filled and non-distensible when full. An increase in volume leads to hypertrophy and this serves to increase reserve volume and compliance. The true physiological role of the pericardium remains controversial, but various theories have been postulated. It is not essential for normal cardiovascular function and adverse effects are not associated with surgical removal. The pericardium helps protect the heart from adjacent infection and malignancy, and also functions to anchor the heart in position within the chest. The pericardium is continuous with the greater vessels at the heart base and the sternopericardiac ligament at the apex. Pericardial fluid may help reduce friction generated by the beating heart and may also help to prevent overdistention. Peritoneal-pericardial diaphragmatic hernia This uncommon congenital defect causes a persistent communication between the pericardial and peritoneal cavities, allowing abdominal contents to enter the pericardial sac. The liver and gall bladder are the most common organs to herniate. Associated abdominal wall hernias and sternebrae abnormalities may occur. Some studies suggest a predisposition among males and Weimaraners. Clinical signs are not always obvious from a young age. Patients may initially present with respiratory or gastrointestinal signs. An associated pericardial effusion is unusual, but this has 2 / 14
3 been reported; surgical correction carries a good prognosis. Pericardial neoplasia The most commonly reported cardiac tumours are haemangiosarcomas, originating in the right atrial wall or atrial appendage, and heart-base tumours (chemodectoma or aortic body tumour). Ectopic thyroid carcinomas and mesotheliomas are less common. Metastatic carcinoma to the heart may also occur. Tumours of the pericardium are not usually exfoliative, so echocardiography of the heart entirety is important to rule out neoplasia when pericardial effusion is present. Neoplasia is reportedly the most common cause of pericardial effusion in dogs. Lymphosarcoma, mesothelioma and metastatic carcinoma have been reported in cats. Haemangiosarcomas are particularly common in German shepherd dogs and may be associated with metastases (such as in the kidney, liver, spleen or lungs see Figure 1 ) as well as systemic illness and arrhythmias. Pericardial effusion Most diseases that affect the pericardium result in pericardial effusion. Effusions can be transudative, exudative (inflammatory), or sanguineous. Causes of pericardial transudation include right-sided congestive heart failure and hypoproteinaemia. Transudative pericardial effusions are usually subclinical. Infectious pericarditis is an uncommon cause of pericardial effusion in small animals and usually causes a fibrinous exudate. Various bacterial and fungal organisms have been associated with such infections for example, bacterial pericarditis may be associated with bite wounds or migrating foreign bodies, whereas coccidiomycosis is an important cause of effusions in endemic regions. In cats, feline infectious peritonitis and toxoplasmosis are potential causes of inflammatory effusions. Idiopathic (benign) pericardial effusion is regarded as the second most common cause of pericardial effusion in dogs. The effusion is usually sanguineous and must be differentiated from neoplastic effusion. The presence of blood in the effusion is more suggestive of atrial rupture, which can occur secondary to chronic mitral insufficiency. Large-breed dogs are most commonly affected, with both neoplastic and idiopathic effusions. The majority of pericardial effusions are sanguineous and port wine in colour. Acute or chronic 3 / 14
4 Pericardial effusion may develop relatively slowly or rapidly. As fluid collects, the filling ability (diastolic function) is impeded. The right side of the heart suffers more than the left. With rapid (acute) filling, right heart dysfunction also occurs rapidly. With gradual accumulation, the pericardium can stretch to accommodate a greater volume of fluid with less cardiac impairment. Cardiac tamponade is the term given for an impairment of ventricular filling as a consequence of increased intrapericardial pressure caused by the accumulation of fluid within the pericardial cavity. As pericardial fluid accumulates, more pressure is needed to push blood into the right and left ventricles during diastole to maintain cardiac output. As intrapericardial pressure continues to increase, cardiac output decreases and systemic venous pressure increases. Gradual rises in pressure often lead to signs of systemic congestion (such as ascites and pleural effusion), whereas acute increases in pressure may lead to the development of cardiac shock before signs of systemic congestion are evident. Diagnosis Clinical signs depend on the rate of rise of intrapericardial pressures. Typical signs are weakness, exercise intolerance and dyspnoea. Muffled heart sounds, jugular venous distension and weakened arterial pulses in combination are suggestive of pericardial effusion. Signs of rightsided heart failure (for example, ascites) may also be present. Echocardiography Echocardiography is the quickest and safest method of diagnosing the condition. The pericardial fluid will appear as an anechoic space between the epicardium and pericardium. The approximate volume of the effusion can also be appreciated, although the pressure within the pericardial sac is more important. The entirety of the heart should be checked to rule out neoplasia as a cause. The location of any masses is useful to help establish what type of tumour is present (see earlier). Electrocardiography Electrocardiography may also show some typical features of pericardial effusion. Features may include low-amplitude QRS complexes, sinus tachycardia, ventricular premature beats and possibly electrical alternans ( Figure 2 ). This is created by a beatto-beat variation in amplitude of QRS complexes as the heart swings within the fluid-filled sac. Radiology 4 / 14
5 Radiology is useful, but care should be taken in restraint and the use of sedation is not recommended or necessary. A large globose heart is typical, with well-defined borders of the cardiac silhouette ( Figure 3 ). Concurrent pleural effusion and metastases are possible. Distension of the caudal vena cava, ascites ( Figure 4 ) and hepatomegaly are more common features in chronic effusions. Further tests - Cytology. Studies indicate that cytology is of little value in distinguishing between idiopathic and neoplastic aetiologies. - Biochemistry. The ph of fluid may help: ph of less than seven has been linked to an inflam matory aetiology, while ph of more than seven suggests a nonneoplastic aetiology. - Bacterial culture. This is useful in infectious effusions. Treatment Pericardiocentesis This allows rapid control, especially if cardiac tamponade has developed. See the next section for the technique involved. Corticosteroids These have been suggested in some studies to help prevent recurrence in idiopathic cases. Pericardectomy This procedure involves surgical removal of the pericardial sac via thoracoscopy or thoracotomy. Percutaneous balloon pericardiotomy This may be a useful palliative treatment of recurrent pericardial effusion. Note that diuretics are contraindicated as they can further reduce the blood pressure and increase the risk of cardiocirculatory collapse. Pericardiocentesis technique Animals with pericardial effusion have poor venous driving pressure, so intravenous fluids are useful to aid venous return. Animals should have an ECG during the procedure so changes can be 5 / 14
6 monitored for example, if the myocardium is pierced. Some patients may allow the procedure to be performed conscious and light sedation may be necessary in others. The approach can be from the left or right there are arguments for and against both approaches and sternal or lateral recumbency can be used. A 14-gauge to 18-gauge needle or catheter is useful for the procedure. From the right side an area between the third to eighth ribs should be clipped from the sternum to above the costochondral junction. The puncture site should be based on thoracic radiographs (most commonly between the fourth and fifth intercostal spaces). The area can be injected with 1-2ml of local anaesthetic and five minutes should be allowed for the block to take effect. The catheter should be inserted at a right angle to the skin for 1.5 inches. The angle is then changed to a cranioventral angle towards the downside shoulder. The lung parenchyma is above this angle of entry so damage to lungs should not be an issue. Ultrasound guided centesis may be helpful with smaller effusions. When fluid is obtained it is typically port wine coloured ( Figure 5 ) and at low pressure. Brighter or higher-pressure fluid may indicate heart blood. Effusion fluid should not clot so PCV can be checked to ensure fluid obtained is not blood. When fluid is obtained, the needle can be removed and the three-way tap can be attached. Pericardiocentesis is not risk free; coronary artery laceration is possible and can result in sudden death. The ECG will help ascertain if myocardial contact has occurred. Ventricular arrhythmias may occur if the heart surface is touched, but these are likely to subside quickly if the needle is withdrawn slightly. Constrictive pericarditis This occurs when pericardial disease is characterised by fibrosis of the pericardium (usually only the parietal pericardium). Often there is no associated effusion. The fibrosis causes a restriction to the filling of the right ventricle (like pericardial effusion). This condition may be a result of recurrent effusions, foreign bodies, infection or neoplasia. Presenting signs are the same as for pericardial effusion, and mainly middle-aged, large-breed dogs are affected. On radiography there is absence of a globose heart and variable amounts of effusion. Caudal vena cava enlargement and mild to moderate cardiomegaly may occur. Even with echocardiography, detection of a thickened pericardium can be difficult. Definitive diagnosis is hard. Cardiac catheterisation will demonstrate elevation of pressures, and surgical demonstration of fibrosis at parietal pericardectomy will often be necessary to confirm the diagnosis. Response to surgery is usually excellent. 6 / 14
7 Conclusion The prognosis of pericardial disease depends on the initial condition. For example, the most commonly encountered pericardial conditions are neoplastic and idiopathic pericardial effusion. These carry poor and good prognoses respectively, so it is important to investigate the disease fully before treatment options are discussed with owners of afflicted patients. References Atkins C E et al (1993). Intrapericardial cysts in the dog, Journal of Veterinary Internal Medicine 7: Berg R J and Wingfield W (1984). Pericardial effusion in the dog: a review of 42 cases, Journal of the American Animal Hospital Association 20: Brownlie S E and Cobb M A (1992). Intrapericardial neoplasia in 14 dogs, Journal of Small Animal Practice 37: Edwards N J (1996). The diagnostic value of pericardial fluid ph determination, Journal of the American Hospital Association 32: Ettinger S J and Feldman A C (2000). Pericardial disorders. In: Textbook of Veterinary Internal Medicine: Diseases of the Dog and Cat (4th edn), W B Saunders: 1,132-1,150. Dunning D et al (1998). Analysis of prognostic indicators for dogs with pericardial effusion: 46 cases ( ), Journal of the American Veterinary Medical Association 212: 1276 Hopper D L and Ware W A (1999). Cardiac tumours in dogs: , Journal of Veterinary Internal Medicine 13: / 14
8 Figure 1. Lung metastases as well as those in the kidney, liver or spleen may be associated with pericardial neoplasia. 8 / 14
9 Figure 2. Electrical alternans may be seen in pericardial effusion as the heart swings within the pericardial sac. 9 / 14
10 Figure 3 (above). An enlarged, very rounded heart with distinct borders is typical of pericardial effusion, although echocardiography is preferable for definitive diagnosis. 10 / 14
11 11 / 14
12 12 / 14
13 Figure 4 (left). Ascites may be seen in right sided heart failure associated with pericardial effusions. 13 / 14
14 Powered by TCPDF ( Figure 5. Pericardial effusions are usually port wine coloured. 14 / 14
Pericardial effusion has two basic presentations acute collapse and
 PERICARDIAL EFFUSION Mark Rishniw, BVSc, MS, DACVIM Department of Clinical Sciences College of Veterinary Medicine Cornell University Ithaca, New York Pericardial effusion has two basic presentations acute
PERICARDIAL EFFUSION Mark Rishniw, BVSc, MS, DACVIM Department of Clinical Sciences College of Veterinary Medicine Cornell University Ithaca, New York Pericardial effusion has two basic presentations acute
Pericardial Effusion in Dogs
 S P E C I A L F O C U S 372 PEER-REVIEWED CE ARTICLE #3 Pericardial Effusion in Dogs Veterinary Technician June 2006 Amy Campbell, CVT, VTS (ECC) Veterinary Emergency and Specialty Center of New England
S P E C I A L F O C U S 372 PEER-REVIEWED CE ARTICLE #3 Pericardial Effusion in Dogs Veterinary Technician June 2006 Amy Campbell, CVT, VTS (ECC) Veterinary Emergency and Specialty Center of New England
efferent fibers from t.. Heart Surface anatomy and heart sounds -Dry lecture -Gray s 169,
 A patient is diagnosed with ischemia (i.e., lack of blood flow) in a left lobar pulmonary vein. The attending physician determines that the ischemia is due to a vasospastic episode. Constriction of this
A patient is diagnosed with ischemia (i.e., lack of blood flow) in a left lobar pulmonary vein. The attending physician determines that the ischemia is due to a vasospastic episode. Constriction of this
Right-Sided Congestive Heart Failure Basics
 Right-Sided Congestive Heart Failure Basics OVERVIEW Failure of the right side of the heart to pump blood at a sufficient rate to meet the needs of the body or to prevent blood from pooling within the
Right-Sided Congestive Heart Failure Basics OVERVIEW Failure of the right side of the heart to pump blood at a sufficient rate to meet the needs of the body or to prevent blood from pooling within the
Pericardial Effusion
 Pericardial Effusion How does the heart work? The heart is the organ responsible for pumping blood to and from all tissues of the body. The heart is divided into right and left sides. The job of the right
Pericardial Effusion How does the heart work? The heart is the organ responsible for pumping blood to and from all tissues of the body. The heart is divided into right and left sides. The job of the right
Canine Pericardial Effusion: Diagnosis,Treatment, and Prognosis *
 An In-Depth Look: CANINE PERICARDIAL EFFUSION CE Article #2 Canine Pericardial Effusion: Diagnosis,Treatment, and Prognosis * Scott P. Shaw, DVM, DACVECC John E. Rush, DVM, MS, DACVIM (Cardiology), DACVECC
An In-Depth Look: CANINE PERICARDIAL EFFUSION CE Article #2 Canine Pericardial Effusion: Diagnosis,Treatment, and Prognosis * Scott P. Shaw, DVM, DACVECC John E. Rush, DVM, MS, DACVIM (Cardiology), DACVECC
Cardiomyopathy and Less Common Canine Heart Disease
 Cardiomyopathy and Less Common Canine Heart Disease John E. Rush, DVM, MS, DACVIM (Cardiology), ACVECC Cummings School of Veterinary Medicine at Tufts University Dilated cardiomyopathy (DCM) is the second
Cardiomyopathy and Less Common Canine Heart Disease John E. Rush, DVM, MS, DACVIM (Cardiology), ACVECC Cummings School of Veterinary Medicine at Tufts University Dilated cardiomyopathy (DCM) is the second
PERICARDIAL DIAESE. Kaijun Cui Associated professor Sichuan University
 PERICARDIAL DIAESE Kaijun Cui Associated professor Sichuan University CLASSIFICATION acute pericarditis pericardial effusion cardiac tamponade constrictive pericarditis congenitally absent pericardium
PERICARDIAL DIAESE Kaijun Cui Associated professor Sichuan University CLASSIFICATION acute pericarditis pericardial effusion cardiac tamponade constrictive pericarditis congenitally absent pericardium
Calvin 9 year old NM DLH. Dr. Norman Ackerman Memorial Radiography Case Challenge
 September 2014 Dr. Norman Ackerman served the University of Florida, College of Veterinary Medicine with distinction as Professor of Radiology from 1979 to 1994. A concerned teacher of veterinary students
September 2014 Dr. Norman Ackerman served the University of Florida, College of Veterinary Medicine with distinction as Professor of Radiology from 1979 to 1994. A concerned teacher of veterinary students
Pulmonic Stenosis. How does the heart work?
 Pulmonic Stenosis How does the heart work? The heart is the organ responsible for pumping blood to and from all tissues of the body. The heart is divided into right and left sides. The job of the right
Pulmonic Stenosis How does the heart work? The heart is the organ responsible for pumping blood to and from all tissues of the body. The heart is divided into right and left sides. The job of the right
Heart Anatomy. 7/5/02 Stephen G Davenport 1
 Heart Anatomy Copyright 1999, Stephen G. Davenport, No part of this publication may be reproduced, stored in a retrieval system, or transmitted, in any form without prior written permission. 7/5/02 Stephen
Heart Anatomy Copyright 1999, Stephen G. Davenport, No part of this publication may be reproduced, stored in a retrieval system, or transmitted, in any form without prior written permission. 7/5/02 Stephen
The Heart. The Heart A muscular double pump. The Pulmonary and Systemic Circuits
 C H A P T E R 19 The Heart The Heart A muscular double pump circuit takes blood to and from the lungs Systemic circuit vessels transport blood to and from body tissues Atria receive blood from the pulmonary
C H A P T E R 19 The Heart The Heart A muscular double pump circuit takes blood to and from the lungs Systemic circuit vessels transport blood to and from body tissues Atria receive blood from the pulmonary
10. Thick deposits of lipids on the walls of blood vessels, called, can lead to serious circulatory issues. A. aneurysm B. atherosclerosis C.
 Heart Student: 1. carry blood away from the heart. A. Arteries B. Veins C. Capillaries 2. What is the leading cause of heart attack and stroke in North America? A. alcohol B. smoking C. arteriosclerosis
Heart Student: 1. carry blood away from the heart. A. Arteries B. Veins C. Capillaries 2. What is the leading cause of heart attack and stroke in North America? A. alcohol B. smoking C. arteriosclerosis
2. right heart = pulmonary pump takes blood to lungs to pick up oxygen and get rid of carbon dioxide
 A. location in thorax, in inferior mediastinum posterior to sternum medial to lungs superior to diaphragm anterior to vertebrae orientation - oblique apex points down and to the left 2/3 of mass on left
A. location in thorax, in inferior mediastinum posterior to sternum medial to lungs superior to diaphragm anterior to vertebrae orientation - oblique apex points down and to the left 2/3 of mass on left
Atrioventricular Valve Dysplasia
 Atrioventricular Valve Dysplasia How does the heart work? The heart is the organ responsible for pumping blood to and from all tissues of the body. The heart is divided into right and left sides. The job
Atrioventricular Valve Dysplasia How does the heart work? The heart is the organ responsible for pumping blood to and from all tissues of the body. The heart is divided into right and left sides. The job
The pericardial sac is composed of the outer fibrous pericardium
 Pericardiectomy for Constrictive or Recurrent Inflammatory Pericarditis Mauricio A. Villavicencio, MD, Joseph A. Dearani, MD, and Thoralf M. Sundt, III, MD Anatomy and Preoperative Considerations The pericardial
Pericardiectomy for Constrictive or Recurrent Inflammatory Pericarditis Mauricio A. Villavicencio, MD, Joseph A. Dearani, MD, and Thoralf M. Sundt, III, MD Anatomy and Preoperative Considerations The pericardial
The Heart. Size, Form, and Location of the Heart. 1. Blunt, rounded point; most inferior part of the heart.
 12 The Heart FOCUS: The heart is composed of cardiac muscle cells, which are elongated, branching cells that appear striated. Cardiac muscle cells behave as a single electrical unit, and the highly coordinated
12 The Heart FOCUS: The heart is composed of cardiac muscle cells, which are elongated, branching cells that appear striated. Cardiac muscle cells behave as a single electrical unit, and the highly coordinated
THE HEART. A. The Pericardium - a double sac of serous membrane surrounding the heart
 THE HEART I. Size and Location: A. Fist-size weighing less than a pound (250 to 350 grams). B. Located in the mediastinum between the 2 nd rib and the 5 th intercostal space. 1. Tipped to the left, resting
THE HEART I. Size and Location: A. Fist-size weighing less than a pound (250 to 350 grams). B. Located in the mediastinum between the 2 nd rib and the 5 th intercostal space. 1. Tipped to the left, resting
THE HEART OBJECTIVES: LOCATION OF THE HEART IN THE THORACIC CAVITY CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM
 BIOLOGY II CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM ACTIVITY #3 NAME DATE HOUR THE HEART OBJECTIVES: Describe the anatomy of the heart and identify and give the functions of all parts. (pp. 356 363) Trace the flow of blood
BIOLOGY II CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM ACTIVITY #3 NAME DATE HOUR THE HEART OBJECTIVES: Describe the anatomy of the heart and identify and give the functions of all parts. (pp. 356 363) Trace the flow of blood
Anatomy of the Heart. Figure 20 2c
 Anatomy of the Heart Figure 20 2c Pericardium & Myocardium Remember, the heart sits in it s own cavity, known as the mediastinum. The heart is surrounded by the Pericardium, a double lining of the pericardial
Anatomy of the Heart Figure 20 2c Pericardium & Myocardium Remember, the heart sits in it s own cavity, known as the mediastinum. The heart is surrounded by the Pericardium, a double lining of the pericardial
The Cardiovascular System Part I: Heart Outline of class lecture After studying part I of this chapter you should be able to:
 The Cardiovascular System Part I: Heart Outline of class lecture After studying part I of this chapter you should be able to: 1. Describe the functions of the heart 2. Describe the location of the heart,
The Cardiovascular System Part I: Heart Outline of class lecture After studying part I of this chapter you should be able to: 1. Describe the functions of the heart 2. Describe the location of the heart,
11/10/2014. Muscular pump Two atria Two ventricles. In mediastinum of thoracic cavity 2/3 of heart's mass lies left of midline of sternum
 It beats over 100,000 times a day to pump over 1,800 gallons of blood per day through over 60,000 miles of blood vessels. During the average lifetime, the heart pumps nearly 3 billion times, delivering
It beats over 100,000 times a day to pump over 1,800 gallons of blood per day through over 60,000 miles of blood vessels. During the average lifetime, the heart pumps nearly 3 billion times, delivering
Pericardial diseases
 Pericardial diseases Anatomy of the pericardium Consists of parietal and visceral membranes. The space between them(pericardial space is normally filled by a lymph like fluid. The fluid s normal quantity
Pericardial diseases Anatomy of the pericardium Consists of parietal and visceral membranes. The space between them(pericardial space is normally filled by a lymph like fluid. The fluid s normal quantity
Ch 19: Cardiovascular System - The Heart -
 Ch 19: Cardiovascular System - The Heart - Give a detailed description of the superficial and internal anatomy of the heart, including the pericardium, the myocardium, and the cardiac muscle. Trace the
Ch 19: Cardiovascular System - The Heart - Give a detailed description of the superficial and internal anatomy of the heart, including the pericardium, the myocardium, and the cardiac muscle. Trace the
Practical radiography in small animal practice III: cases with a heart murmur
 Practical radiography in small animal practice III: cases with a heart murmur Francisco Llabrés-Díaz, Davies Veterinary Specialists, Manor Farm Business Park, Higham Gobion, Hertfordshire SG5 3HR, England
Practical radiography in small animal practice III: cases with a heart murmur Francisco Llabrés-Díaz, Davies Veterinary Specialists, Manor Farm Business Park, Higham Gobion, Hertfordshire SG5 3HR, England
Cardiac tamponade and Pericardiocentesis Made Easy
 Cardiac tamponade and Pericardiocentesis Made Easy www.cardiconcept.com Etiology of pericardial diseases. Non Infectious cause Infectious cause European Heart Journal (2015) 36, 2921 2964 Recommendations
Cardiac tamponade and Pericardiocentesis Made Easy www.cardiconcept.com Etiology of pericardial diseases. Non Infectious cause Infectious cause European Heart Journal (2015) 36, 2921 2964 Recommendations
4. The two inferior chambers of the heart are known as the atria. the superior and inferior vena cava, which empty into the left atrium.
 Answer each statement true or false. If the statement is false, change the underlined word to make it true. 1. The heart is located approximately between the second and fifth ribs and posterior to the
Answer each statement true or false. If the statement is false, change the underlined word to make it true. 1. The heart is located approximately between the second and fifth ribs and posterior to the
The Cardiovascular System. Chapter 15. Cardiovascular System FYI. Cardiology Closed systemof the heart & blood vessels. Functions
 Chapter 15 Cardiovascular System FYI The heart pumps 7,000 liters (4000 gallons) of blood through the body each day The heart contracts 2.5 billion times in an avg. lifetime The heart & all blood vessels
Chapter 15 Cardiovascular System FYI The heart pumps 7,000 liters (4000 gallons) of blood through the body each day The heart contracts 2.5 billion times in an avg. lifetime The heart & all blood vessels
Unit 6: Circulatory System. 6.2 Heart
 Unit 6: Circulatory System 6.2 Heart Functions of Circulatory System 1. The heart is the pump necessary to circulate blood to all parts of the body 2. Arteries, veins and capillaries are the structures
Unit 6: Circulatory System 6.2 Heart Functions of Circulatory System 1. The heart is the pump necessary to circulate blood to all parts of the body 2. Arteries, veins and capillaries are the structures
The heart & Cardiovascular system
 The heart & Cardiovascular system The heart s continuous pulse create a base for our understanding of rhythms in everyday life. Bonnie Bainbridge Cohen The heart constantly beats throughout our lives never
The heart & Cardiovascular system The heart s continuous pulse create a base for our understanding of rhythms in everyday life. Bonnie Bainbridge Cohen The heart constantly beats throughout our lives never
Cardiovascular Anatomy Dr. Gary Mumaugh
 Cardiovascular Anatomy Dr. Gary Mumaugh Location of Heart Approximately the size of your fist Location o Superior surface of diaphragm o Left of the midline in mediastinum o Anterior to the vertebral column,
Cardiovascular Anatomy Dr. Gary Mumaugh Location of Heart Approximately the size of your fist Location o Superior surface of diaphragm o Left of the midline in mediastinum o Anterior to the vertebral column,
The Circulatory System. The Heart, Blood Vessels, Blood Types
 The Circulatory System The Heart, Blood Vessels, Blood Types The Closed Circulatory System Humans have a closed circulatory system, typical of all vertebrates, in which blood is confined to vessels and
The Circulatory System The Heart, Blood Vessels, Blood Types The Closed Circulatory System Humans have a closed circulatory system, typical of all vertebrates, in which blood is confined to vessels and
AP2 Lab 1 - Blood & Heart
 AP2 Lab 1 - Blood & Heart Project 1 - Formed Elements Identification & Recognition See fig. 17.10 and Table 17.2. Instructor may also provide other images. Note: See Fig. 17.11 All formed elements are
AP2 Lab 1 - Blood & Heart Project 1 - Formed Elements Identification & Recognition See fig. 17.10 and Table 17.2. Instructor may also provide other images. Note: See Fig. 17.11 All formed elements are
DIAGNOSING HEART FAILURE IN DOGS
 Vet Times The website for the veterinary profession https://www.vettimes.co.uk DIAGNOSING HEART FAILURE IN DOGS Author : Mike Martin Categories : Vets Date : November 7, 2011 Mike Martin offers advice
Vet Times The website for the veterinary profession https://www.vettimes.co.uk DIAGNOSING HEART FAILURE IN DOGS Author : Mike Martin Categories : Vets Date : November 7, 2011 Mike Martin offers advice
CV Anatomy Quiz. Dr Ella Kim Dr Pip Green
 CV Anatomy Quiz Dr Ella Kim Dr Pip Green Q1 The location of the heart is correctly described as A) lateral to the lungs. B) medial to the sternum. C) superior to the diaphragm. D) posterior to the spinal
CV Anatomy Quiz Dr Ella Kim Dr Pip Green Q1 The location of the heart is correctly described as A) lateral to the lungs. B) medial to the sternum. C) superior to the diaphragm. D) posterior to the spinal
Identify the lines used in anatomical surface descriptions of the thorax. median line mid-axillary line mid-clavicular line
 L 14 A B O R A T O R Y Thorax THORACIC WALL Identify the lines used in anatomical surface descriptions of the thorax. median line mid-axillary line mid-clavicular line Identify the surface landmarks of
L 14 A B O R A T O R Y Thorax THORACIC WALL Identify the lines used in anatomical surface descriptions of the thorax. median line mid-axillary line mid-clavicular line Identify the surface landmarks of
The HEART. What is it???? Pericardium. Heart Facts. This muscle never stops working It works when you are asleep
 This muscle never stops working It works when you are asleep The HEART It works when you eat It really works when you exercise. What is it???? Located between the lungs in the mid thoracic region Apex
This muscle never stops working It works when you are asleep The HEART It works when you eat It really works when you exercise. What is it???? Located between the lungs in the mid thoracic region Apex
Clinical Anatomy Series Cardiac Anatomy
 2012 Scottish Universities Medical Journal, Dundee Published online: Feb 2012 Vol 1 Issue 1: page 76-80 Kennedy J Clinical Anatomy Cardiac Anatomy Clinical Anatomy Series Cardiac Anatomy John Kennedy (5
2012 Scottish Universities Medical Journal, Dundee Published online: Feb 2012 Vol 1 Issue 1: page 76-80 Kennedy J Clinical Anatomy Cardiac Anatomy Clinical Anatomy Series Cardiac Anatomy John Kennedy (5
The Cardiovascular System
 The Cardiovascular System The Manila Times College of Subic Prepared by: Stevens B. Badar, RN, MANc THE HEART Anatomy of the Heart Location and Size approx. the size of a person s fist, hollow and cone-shaped,
The Cardiovascular System The Manila Times College of Subic Prepared by: Stevens B. Badar, RN, MANc THE HEART Anatomy of the Heart Location and Size approx. the size of a person s fist, hollow and cone-shaped,
THE PERICARDIUM: LOOKING OUTSIDE THE HEART
 THE PERICARDIUM: LOOKING OUTSIDE THE HEART DISCLOSURE Relevant relationships with commercial entities none Potential for conflicts of interest within this presentation none Steps taken to review and mitigate
THE PERICARDIUM: LOOKING OUTSIDE THE HEART DISCLOSURE Relevant relationships with commercial entities none Potential for conflicts of interest within this presentation none Steps taken to review and mitigate
Circulation. Circulation = is a process used for the transport of oxygen, carbon! dioxide, nutrients and wastes through-out the body
 Circulation Circulation = is a process used for the transport of oxygen, carbon! dioxide, nutrients and wastes through-out the body Heart = muscular organ about the size of your fist which pumps blood.
Circulation Circulation = is a process used for the transport of oxygen, carbon! dioxide, nutrients and wastes through-out the body Heart = muscular organ about the size of your fist which pumps blood.
Chapter 20 (1) The Heart
 Chapter 20 (1) The Heart Learning Objectives Describe the location and structure of the heart Describe the path of a drop of blood from the superior vena cava or inferior vena cava through the heart out
Chapter 20 (1) The Heart Learning Objectives Describe the location and structure of the heart Describe the path of a drop of blood from the superior vena cava or inferior vena cava through the heart out
Lecture 2: Clinical anatomy of thoracic cage and cavity II
 Lecture 2: Clinical anatomy of thoracic cage and cavity II Dr. Rehan Asad At the end of this session, the student should be able to: Identify and discuss clinical anatomy of mediastinum such as its deflection,
Lecture 2: Clinical anatomy of thoracic cage and cavity II Dr. Rehan Asad At the end of this session, the student should be able to: Identify and discuss clinical anatomy of mediastinum such as its deflection,
Pericardial Diseases 2015 Update
 Pericardial Diseases 2015 Update BRUCE W. USHER, MD PROFESSOR OF MEDICINE CARDIOLOGY DIVISION MEDICAL UNIVERSITY SOUTH CAROLINA CHARLESTON, SOUTH CAROLINA GUIDELINES: PERICARDIAL DISEASES Ø European Society
Pericardial Diseases 2015 Update BRUCE W. USHER, MD PROFESSOR OF MEDICINE CARDIOLOGY DIVISION MEDICAL UNIVERSITY SOUTH CAROLINA CHARLESTON, SOUTH CAROLINA GUIDELINES: PERICARDIAL DISEASES Ø European Society
Diagnosis of heart failure in dogs with mitral valve disease
 Vet Times The website for the veterinary profession https://www.vettimes.co.uk Diagnosis of heart failure in dogs with mitral valve disease Author : PHILLIP SPEER Categories : Vets Date : March 31, 2014
Vet Times The website for the veterinary profession https://www.vettimes.co.uk Diagnosis of heart failure in dogs with mitral valve disease Author : PHILLIP SPEER Categories : Vets Date : March 31, 2014
Bronchioles. Alveoli. Type I alveolar cells are very thin simple squamous epithelial cells and form most of the lining of an alveolus.
 276 Bronchioles Bronchioles continue on to form bronchi. The primary identifying feature is the loss of hyaline cartilage. The epithelium has become simple ciliated columnar, and there is a complete ring
276 Bronchioles Bronchioles continue on to form bronchi. The primary identifying feature is the loss of hyaline cartilage. The epithelium has become simple ciliated columnar, and there is a complete ring
Test Review Circulatory System Chapters
 Test Review Circulatory System Chapters 13-2010 1. The tissue that forms the tight fitting sac around the heart is the a. parietal pericardium c. myocardium b. visceral pericardium d. endocardium 2. Which
Test Review Circulatory System Chapters 13-2010 1. The tissue that forms the tight fitting sac around the heart is the a. parietal pericardium c. myocardium b. visceral pericardium d. endocardium 2. Which
Dana Alrafaiah. - Moayyad Al-Shafei. -Mohammad H. Al-Mohtaseb. 1 P a g e
 - 6 - Dana Alrafaiah - Moayyad Al-Shafei -Mohammad H. Al-Mohtaseb 1 P a g e Quick recap: Both lungs have an apex, base, mediastinal and costal surfaces, anterior and posterior borders. The right lung,
- 6 - Dana Alrafaiah - Moayyad Al-Shafei -Mohammad H. Al-Mohtaseb 1 P a g e Quick recap: Both lungs have an apex, base, mediastinal and costal surfaces, anterior and posterior borders. The right lung,
Restrictive Cardiomyopathy in Cats (a Type of Heart-Muscle Disease) Basics
 Restrictive Cardiomyopathy in Cats (a Type of Heart-Muscle Disease) Basics OVERVIEW The heart of the cat is composed of four chambers; the top two chambers are the left and right atria and the bottom two
Restrictive Cardiomyopathy in Cats (a Type of Heart-Muscle Disease) Basics OVERVIEW The heart of the cat is composed of four chambers; the top two chambers are the left and right atria and the bottom two
PLEURAE and PLEURAL RECESSES
 PLEURAE and PLEURAL RECESSES By Dr Farooq Aman Ullah Khan PMC 26 th April 2018 Introduction When sectioned transversely, it is apparent that the thoracic cavity is kidney shaped: a transversely ovoid space
PLEURAE and PLEURAL RECESSES By Dr Farooq Aman Ullah Khan PMC 26 th April 2018 Introduction When sectioned transversely, it is apparent that the thoracic cavity is kidney shaped: a transversely ovoid space
the Cardiovascular System I
 the Cardiovascular System I By: Dr. Nabil A Khouri MD, MsC, Ph.D MEDIASTINUM 1. Superior Mediastinum 2. inferior Mediastinum Anterior mediastinum. Middle mediastinum. Posterior mediastinum Anatomy of
the Cardiovascular System I By: Dr. Nabil A Khouri MD, MsC, Ph.D MEDIASTINUM 1. Superior Mediastinum 2. inferior Mediastinum Anterior mediastinum. Middle mediastinum. Posterior mediastinum Anatomy of
Mediastinum and pericardium
 Mediastinum and pericardium Prof. Abdulameer Al-Nuaimi E-mail: a.al-nuaimi@sheffield.ac.uk E. mail: abdulameerh@yahoo.com The mediastinum: is the central compartment of the thoracic cavity surrounded by
Mediastinum and pericardium Prof. Abdulameer Al-Nuaimi E-mail: a.al-nuaimi@sheffield.ac.uk E. mail: abdulameerh@yahoo.com The mediastinum: is the central compartment of the thoracic cavity surrounded by
Right lung. -fissures:
 -Right lung is shorter and wider because it is compressed by the right copula of the diaphragm by the live.. 2 fissure, 3 lobes.. hilum : 2 bronchi ( ep-arterial, hyp-arterial ), one artery mediastinal
-Right lung is shorter and wider because it is compressed by the right copula of the diaphragm by the live.. 2 fissure, 3 lobes.. hilum : 2 bronchi ( ep-arterial, hyp-arterial ), one artery mediastinal
Principles of Anatomy and Physiology
 Principles of Anatomy and Physiology 14 th Edition CHAPTER 20 The Cardiovascular System: The Heart Introduction The purpose of the chapter is to: 1. Learn about the components of the cardiovascular system
Principles of Anatomy and Physiology 14 th Edition CHAPTER 20 The Cardiovascular System: The Heart Introduction The purpose of the chapter is to: 1. Learn about the components of the cardiovascular system
10/23/2017. Muscular pump Two atria Two ventricles. In mediastinum of thoracic cavity 2/3 of heart's mass lies left of midline of sternum
 It beats over 100,000 times a day to pump over 1,800 gallons of blood per day through over 60,000 miles of blood vessels. During the average lifetime, the heart pumps nearly 3 billion times, delivering
It beats over 100,000 times a day to pump over 1,800 gallons of blood per day through over 60,000 miles of blood vessels. During the average lifetime, the heart pumps nearly 3 billion times, delivering
DESCRIPTION: This is the part of the trunk, which is located between the root of the neck and the superior border of the abdominal region.
 1 THE THORACIC REGION DESCRIPTION: This is the part of the trunk, which is located between the root of the neck and the superior border of the abdominal region. SHAPE : T It has the shape of a truncated
1 THE THORACIC REGION DESCRIPTION: This is the part of the trunk, which is located between the root of the neck and the superior border of the abdominal region. SHAPE : T It has the shape of a truncated
Cardiovascular System
 Cardiovascular System The Heart Cardiovascular System The Heart Overview What does the heart do? By timed muscular contractions creates pressure gradients blood moves then from high pressure to low pressure
Cardiovascular System The Heart Cardiovascular System The Heart Overview What does the heart do? By timed muscular contractions creates pressure gradients blood moves then from high pressure to low pressure
Clinical significance of cardiac murmurs: Get the sound and rhythm!
 Clinical significance of cardiac murmurs: Get the sound and rhythm! Prof. dr. Gunther van Loon, DVM, PhD, Ass Member ECVDI, Dip ECEIM Dept. of Large Animal Internal Medicine Ghent University, Belgium Murmurs
Clinical significance of cardiac murmurs: Get the sound and rhythm! Prof. dr. Gunther van Loon, DVM, PhD, Ass Member ECVDI, Dip ECEIM Dept. of Large Animal Internal Medicine Ghent University, Belgium Murmurs
Chapter 20: Cardiovascular System: The Heart
 Chapter 20: Cardiovascular System: The Heart I. Functions of the Heart A. List and describe the four functions of the heart: 1. 2. 3. 4. II. Size, Shape, and Location of the Heart A. Size and Shape 1.
Chapter 20: Cardiovascular System: The Heart I. Functions of the Heart A. List and describe the four functions of the heart: 1. 2. 3. 4. II. Size, Shape, and Location of the Heart A. Size and Shape 1.
Background & Indications Probe Selection
 Teresa S. Wu, MD, FACEP Director, EM Ultrasound Program & Fellowship Co-Director, Simulation Based Training Program & Fellowship Associate Program Director, EM Residency Program Maricopa Medical Center
Teresa S. Wu, MD, FACEP Director, EM Ultrasound Program & Fellowship Co-Director, Simulation Based Training Program & Fellowship Associate Program Director, EM Residency Program Maricopa Medical Center
Matters of the Heart: Comprehensive Cardiology SARAH BEANLANDS RN BSCN MSC
 Matters of the Heart: Comprehensive Cardiology SARAH BEANLANDS RN BSCN MSC Who am I? Class Outline Gross anatomy of the heart Trip around the heart Micro anatomy: cellular and tissue level Introduction
Matters of the Heart: Comprehensive Cardiology SARAH BEANLANDS RN BSCN MSC Who am I? Class Outline Gross anatomy of the heart Trip around the heart Micro anatomy: cellular and tissue level Introduction
Septal Defects. How does the heart work?
 Septal Defects How does the heart work? The heart is the organ responsible for pumping blood to and from all tissues of the body. The heart is divided into right and left sides. The job of the right side
Septal Defects How does the heart work? The heart is the organ responsible for pumping blood to and from all tissues of the body. The heart is divided into right and left sides. The job of the right side
Figure 10.1A Transparency Master 79
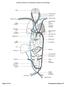 Brain Carotid arteries Jugular vein Right front leg Lungs (inflated) Cranial Right atrium To left front leg Left subclavian Bronchus capillaries Brachiocephalic vein Left atrium Dorsal aorta Right ventricle
Brain Carotid arteries Jugular vein Right front leg Lungs (inflated) Cranial Right atrium To left front leg Left subclavian Bronchus capillaries Brachiocephalic vein Left atrium Dorsal aorta Right ventricle
Human Anatomy, First Edition
 Human Anatomy, First Edition McKinley & O'Loughlin Chapter 22 : Heart 1 Functions of the Heart Center of the cardiovascular system, the heart. Connects to blood vessels that transport blood between the
Human Anatomy, First Edition McKinley & O'Loughlin Chapter 22 : Heart 1 Functions of the Heart Center of the cardiovascular system, the heart. Connects to blood vessels that transport blood between the
THE CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM. Part 1
 THE CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM Part 1 CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM Blood Heart Blood vessels What is the function of this system? What other systems does it affect? CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM Functions Transport gases,
THE CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM Part 1 CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM Blood Heart Blood vessels What is the function of this system? What other systems does it affect? CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM Functions Transport gases,
Πνευμονική υπέρταση και περικαρδιακή συλλογή. Τρόποι αντιμετώπισης
 Πνευμονική υπέρταση και περικαρδιακή συλλογή. Τρόποι αντιμετώπισης Γεώργιος Λάζαρος Καρδιολόγος, Διευθυντής ΕΣΥ Α Πανεπιστημιακή Καρδιολογική Κλινική Ιπποκράτειο Γ.Ν. Αθηνών Pericardial syndromes o Acute
Πνευμονική υπέρταση και περικαρδιακή συλλογή. Τρόποι αντιμετώπισης Γεώργιος Λάζαρος Καρδιολόγος, Διευθυντής ΕΣΥ Α Πανεπιστημιακή Καρδιολογική Κλινική Ιπποκράτειο Γ.Ν. Αθηνών Pericardial syndromes o Acute
Chapter 5: Other mediastinal structures. The Large Arteries. The Aorta. Ascending aorta
 Chapter 5: Other mediastinal structures The Large Arteries The Aorta The aorta is the main arterial trunk of the systemic circulation and in the healthy state its wall contain a large amount of yellow
Chapter 5: Other mediastinal structures The Large Arteries The Aorta The aorta is the main arterial trunk of the systemic circulation and in the healthy state its wall contain a large amount of yellow
Cardiovascular System
 Cardiovascular System Purpose Transport oxygen and nutrients Take waste products away from tissues & organs Things we learned Blood pressure: the force of blood pushing against the walls of blood vessels
Cardiovascular System Purpose Transport oxygen and nutrients Take waste products away from tissues & organs Things we learned Blood pressure: the force of blood pushing against the walls of blood vessels
Skin supplied by T1-4 (medial upper arm and neck) T5-9- epigastrium Visceral afferents from skin and heart are the same dorsal root ganglio
 Cardio 2 ECG... 3 Cardiac Remodelling... 11 Valvular Diseases... 13 Hypertension... 18 Aortic Coarctation... 24 Erythropoiesis... 27 Haemostasis... 30 Anaemia... 36 Atherosclerosis... 44 Angina... 48 Myocardial
Cardio 2 ECG... 3 Cardiac Remodelling... 11 Valvular Diseases... 13 Hypertension... 18 Aortic Coarctation... 24 Erythropoiesis... 27 Haemostasis... 30 Anaemia... 36 Atherosclerosis... 44 Angina... 48 Myocardial
Acute Pericardial Tamponade
 Acute Pericardial Tamponade Marx: Rosen's Emergency Medicine: Concepts and Clinical Practice, 5th ed. Epidemiology The reported incidence of acute pericardial tamponade is approximately 2% in patients
Acute Pericardial Tamponade Marx: Rosen's Emergency Medicine: Concepts and Clinical Practice, 5th ed. Epidemiology The reported incidence of acute pericardial tamponade is approximately 2% in patients
The Cardiovascular System
 11 PART A The Cardiovascular System PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Jerry L. Cook, Sam Houston University ESSENTIALS OF HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY EIGHTH EDITION ELAINE N. MARIEB The Cardiovascular
11 PART A The Cardiovascular System PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Jerry L. Cook, Sam Houston University ESSENTIALS OF HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY EIGHTH EDITION ELAINE N. MARIEB The Cardiovascular
An Uncommon Cardiac Etiology of Liver Cirrhosis, Recurrent Ascites, Atrial Fibrillation and Congestive Heart Failure
 Cronicon OPEN ACCESS EC CARDIOLOGY Case Report An Uncommon Cardiac Etiology of Liver Cirrhosis, Recurrent Ascites, Atrial Fibrillation and Congestive Heart Failure Montaser Y Ismail 1 *, Mohammed I Nassar
Cronicon OPEN ACCESS EC CARDIOLOGY Case Report An Uncommon Cardiac Etiology of Liver Cirrhosis, Recurrent Ascites, Atrial Fibrillation and Congestive Heart Failure Montaser Y Ismail 1 *, Mohammed I Nassar
LECTURE 5. Anatomy of the heart
 LECTURE 5. Anatomy of the heart Main components of the CVS: Heart Blood circulatory system arterial compartment haemomicrocirculatory (=microvascular) compartment venous compartment Lymphatic circulatory
LECTURE 5. Anatomy of the heart Main components of the CVS: Heart Blood circulatory system arterial compartment haemomicrocirculatory (=microvascular) compartment venous compartment Lymphatic circulatory
Label Diagram #1 (Pg. 664)
 Chapter 18 The Cardiovascular System 18.1 Heart Anatomy The Pulmonary and Systemic Circuits Oxygen rich vs. Oxygen Poor Heart is a transport system consisting of two side-by-side pumps Right side receives
Chapter 18 The Cardiovascular System 18.1 Heart Anatomy The Pulmonary and Systemic Circuits Oxygen rich vs. Oxygen Poor Heart is a transport system consisting of two side-by-side pumps Right side receives
The Cardiovascular System
 The Cardiovascular System https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=ohmmtqkgs50 Human Anatomy & Physiology P. Wilson 1 Introduction The functions of the cardiovascular system are: to bring oxygen & nutrients to
The Cardiovascular System https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=ohmmtqkgs50 Human Anatomy & Physiology P. Wilson 1 Introduction The functions of the cardiovascular system are: to bring oxygen & nutrients to
CMS Limitations Guide - Radiology Services
 CMS Limitations Guide - Radiology Services Starting October 1, 2015, CMS will update their existing medical necessity limitations on tests and procedures to correspond to ICD-10 codes. This limitations
CMS Limitations Guide - Radiology Services Starting October 1, 2015, CMS will update their existing medical necessity limitations on tests and procedures to correspond to ICD-10 codes. This limitations
The Cardiovascular System
 Essentials of Human Anatomy & Physiology Elaine N. Marieb Slides 11.1 11.19 Seventh Edition Chapter 11 The Cardiovascular System Functions of the Cardiovascular system Function of the heart: to pump blood
Essentials of Human Anatomy & Physiology Elaine N. Marieb Slides 11.1 11.19 Seventh Edition Chapter 11 The Cardiovascular System Functions of the Cardiovascular system Function of the heart: to pump blood
Clinico-diagnostic aspects of right sided heart failure in dogs
 2017; 6(6): 49-53 ISSN (E): 2277-7695 ISSN (P): 2349-8242 NAAS Rating 2017: 5.03 TPI 2017; 6(6): 49-53 2017 TPI www.thepharmajournal.com Received: 10-04-2017 Accepted: 11-05-2017 K Lakshmi Assistant Professor,
2017; 6(6): 49-53 ISSN (E): 2277-7695 ISSN (P): 2349-8242 NAAS Rating 2017: 5.03 TPI 2017; 6(6): 49-53 2017 TPI www.thepharmajournal.com Received: 10-04-2017 Accepted: 11-05-2017 K Lakshmi Assistant Professor,
Pericardial Diseases. Smonporn Boonyaratavej, MD. Division of Cardiology, Department of Medicine Chulalongkorn University
 Pericardial Diseases Smonporn Boonyaratavej, MD Division of Cardiology, Department of Medicine Chulalongkorn University Cardiac Center, King Chulalongkorn Memorial Hospital 21 AUGUST 2016 Pericardial
Pericardial Diseases Smonporn Boonyaratavej, MD Division of Cardiology, Department of Medicine Chulalongkorn University Cardiac Center, King Chulalongkorn Memorial Hospital 21 AUGUST 2016 Pericardial
Cardiovascular System
 Cardiovascular System I. Structure of the Heart A. Average adult heart is 14 cm long and 9 cm wide. B. Lies in the mediastinum. C. Enclosed in the pericardium. 1. Fibrous pericardium- Outer, tough connective
Cardiovascular System I. Structure of the Heart A. Average adult heart is 14 cm long and 9 cm wide. B. Lies in the mediastinum. C. Enclosed in the pericardium. 1. Fibrous pericardium- Outer, tough connective
Anatomy of thoracic wall
 Anatomy of thoracic wall Topographic Anatomy of the Thorax 1 Bones of Thoracic wall ribs 1-7"true" ribs -those which attach directly to the sternum true ribs actually attach to the sternum by means of
Anatomy of thoracic wall Topographic Anatomy of the Thorax 1 Bones of Thoracic wall ribs 1-7"true" ribs -those which attach directly to the sternum true ribs actually attach to the sternum by means of
The Heart and Heart Disease
 The Heart and Heart Disease Illustration of the heart by Leonardo DaVinci heart-surgeon.com/ history.html 2/14/2010 1 I. Location, Size and Position of the Heart A. Triangular organ located 1. of mass
The Heart and Heart Disease Illustration of the heart by Leonardo DaVinci heart-surgeon.com/ history.html 2/14/2010 1 I. Location, Size and Position of the Heart A. Triangular organ located 1. of mass
Heart Dissection. 5. Locate the tip of the heart or the apex. Only the left ventricle extends all the way to the apex.
 Heart Dissection Page 1 of 6 Background: The heart is a four-chambered, hollow organ composed primarily of cardiac muscle tissue. It is located in the center of the chest in between the lungs. It is the
Heart Dissection Page 1 of 6 Background: The heart is a four-chambered, hollow organ composed primarily of cardiac muscle tissue. It is located in the center of the chest in between the lungs. It is the
Ventricular Tachycardia Basics
 Ventricular Tachycardia Basics OVERVIEW Ventricular refers to the ventricles of the heart; tachycardia is the medical term for rapid heart rate The heart of the dog or cat is composed of four chambers;
Ventricular Tachycardia Basics OVERVIEW Ventricular refers to the ventricles of the heart; tachycardia is the medical term for rapid heart rate The heart of the dog or cat is composed of four chambers;
Approximately the size of your fist Location Superior surface of diaphragm Left of the midline in mediastinum Anterior to the vertebral column,
 Dr. Gary Mumaugh Approximately the size of your fist Location Superior surface of diaphragm Left of the midline in mediastinum Anterior to the vertebral column, posterior to the sternum Posteriorly the
Dr. Gary Mumaugh Approximately the size of your fist Location Superior surface of diaphragm Left of the midline in mediastinum Anterior to the vertebral column, posterior to the sternum Posteriorly the
The Heart & Pericardium Dr. Rakesh Kumar Verma Assistant Professor Department of Anatomy KGMU UP Lucknow
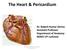 The Heart & Pericardium Dr. Rakesh Kumar Verma Assistant Professor Department of Anatomy KGMU UP Lucknow Fibrous skeleton Dense fibrous connective tissue forms a structural foundation around AV & arterial
The Heart & Pericardium Dr. Rakesh Kumar Verma Assistant Professor Department of Anatomy KGMU UP Lucknow Fibrous skeleton Dense fibrous connective tissue forms a structural foundation around AV & arterial
The Cardiovascular System (Heart)
 The Cardiovascular System The Cardiovascular System (Heart) A closed system of the heart and blood vessels The heart pumps blood Blood vessels allow blood to circulate to all parts of the body The function
The Cardiovascular System The Cardiovascular System (Heart) A closed system of the heart and blood vessels The heart pumps blood Blood vessels allow blood to circulate to all parts of the body The function
Large veins of the thorax Brachiocephalic veins
 Large veins of the thorax Brachiocephalic veins Right brachiocephalic vein: formed at the root of the neck by the union of the right subclavian & the right internal jugular veins. Left brachiocephalic
Large veins of the thorax Brachiocephalic veins Right brachiocephalic vein: formed at the root of the neck by the union of the right subclavian & the right internal jugular veins. Left brachiocephalic
Cardiovascular Nursing Practice: A Comprehensive Resource Manual and Study Guide for Clinical Nurses 2 nd Edition
 Cardiovascular Nursing Practice: A Comprehensive Resource Manual and Study Guide for Clinical Nurses 2 nd Edition Table of Contents Volume 1 Chapter 1: Cardiovascular Anatomy and Physiology Basic Cardiac
Cardiovascular Nursing Practice: A Comprehensive Resource Manual and Study Guide for Clinical Nurses 2 nd Edition Table of Contents Volume 1 Chapter 1: Cardiovascular Anatomy and Physiology Basic Cardiac
Cardiovascular System
 System examination The initial examination of the cardiovascular system should be done in-situ on opening the thoracic cavity, to evaluate abnormalities of size and position. The four major areas for gross
System examination The initial examination of the cardiovascular system should be done in-situ on opening the thoracic cavity, to evaluate abnormalities of size and position. The four major areas for gross
INTRODUCTORY REMARKS:
 INTRODUCTORY REMARKS: The circulatory system provides a way for the blood to be transported throughout the body. This provides nutrients to the cells and allows wastes to be removed. Open vs. Closed Circulatory
INTRODUCTORY REMARKS: The circulatory system provides a way for the blood to be transported throughout the body. This provides nutrients to the cells and allows wastes to be removed. Open vs. Closed Circulatory
Chapter 14. Circulatory System Images. VT-122 Anatomy & Physiology II
 Chapter 14 Circulatory System Images VT-122 Anatomy & Physiology II The mediastinum Dog heart Dog heart Cat heart Dog heart ultrasound Can see pericardium as distinct bright line Pericardial effusion Fluid
Chapter 14 Circulatory System Images VT-122 Anatomy & Physiology II The mediastinum Dog heart Dog heart Cat heart Dog heart ultrasound Can see pericardium as distinct bright line Pericardial effusion Fluid
Normal Pericardial Physiology
 Normal Pericardial Physiology Normal pericardium contains 20-30 ml of lymphoid fluid lubricating function that facilitates normal myocardial rotation and translation during each cardiac cycle in that the
Normal Pericardial Physiology Normal pericardium contains 20-30 ml of lymphoid fluid lubricating function that facilitates normal myocardial rotation and translation during each cardiac cycle in that the
Anatomy Lecture 8. In the previous lecture we talked about the lungs, and their surface anatomy:
 Anatomy Lecture 8 In the previous lecture we talked about the lungs, and their surface anatomy: 1-Apex:it lies 1 inch above the medial third of clavicle. 2-Anterior border: it starts from apex to the midpoint
Anatomy Lecture 8 In the previous lecture we talked about the lungs, and their surface anatomy: 1-Apex:it lies 1 inch above the medial third of clavicle. 2-Anterior border: it starts from apex to the midpoint
Pericardial effusion, Cardiac Tamponade, and echo guided pericardiocentesis
 KSC 2017 Echo5- Myocardial and Pericardial disease Pericardial effusion, Cardiac Tamponade, and echo guided pericardiocentesis Ji-Hyun Jung Division of Cardiology Sejong Hospital KSC 2017 The 61 th Annual
KSC 2017 Echo5- Myocardial and Pericardial disease Pericardial effusion, Cardiac Tamponade, and echo guided pericardiocentesis Ji-Hyun Jung Division of Cardiology Sejong Hospital KSC 2017 The 61 th Annual
Lecturer: Ms DS Pillay ROOM 2P24 25 February 2013
 Lecturer: Ms DS Pillay ROOM 2P24 25 February 2013 Thoracic Wall Consists of thoracic cage Muscle Fascia Thoracic Cavity 3 Compartments of the Thorax (Great Vessels) (Heart) Superior thoracic aperture
Lecturer: Ms DS Pillay ROOM 2P24 25 February 2013 Thoracic Wall Consists of thoracic cage Muscle Fascia Thoracic Cavity 3 Compartments of the Thorax (Great Vessels) (Heart) Superior thoracic aperture
Cardiovascular System
 Cardiovascular System angio BELLWORK Day One: Define using technology hemo/hema cardio Medical Therapeutics Standards 11) Outline the gross normal structure and function of all body systems and summarize
Cardiovascular System angio BELLWORK Day One: Define using technology hemo/hema cardio Medical Therapeutics Standards 11) Outline the gross normal structure and function of all body systems and summarize
UNDERSTANDING CHYLE IN CATS
 Vet Times The website for the veterinary profession https://www.vettimes.co.uk UNDERSTANDING CHYLE IN CATS Author : DAN FORSTER Categories : Vets Date : February 11, 2008 DAN FORSTER discusses diagnosis
Vet Times The website for the veterinary profession https://www.vettimes.co.uk UNDERSTANDING CHYLE IN CATS Author : DAN FORSTER Categories : Vets Date : February 11, 2008 DAN FORSTER discusses diagnosis
Index. Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type.
 Index Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A Acute coronary syndrome(s), anticoagulant therapy in, 706, 707 antiplatelet therapy in, 702 ß-blockers in, 703 cardiac biomarkers in,
Index Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A Acute coronary syndrome(s), anticoagulant therapy in, 706, 707 antiplatelet therapy in, 702 ß-blockers in, 703 cardiac biomarkers in,
VT Ablation in Structural Heart Disease Patient Information
 Melbourne Heart Rhythm VT Ablation in Structural Heart Disease Patient Information Ventricular Tachycardia in Structural Heart Disease (VT-SHD) Ventricular tachycardia (VT) is an abnormal rapid heart rhythm
Melbourne Heart Rhythm VT Ablation in Structural Heart Disease Patient Information Ventricular Tachycardia in Structural Heart Disease (VT-SHD) Ventricular tachycardia (VT) is an abnormal rapid heart rhythm
