History of Vascular Modelling. William Harvey discovery of the circulation 1628
|
|
|
- Lauren Stevens
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 History of Vascular Modelling William Harvey discovery of the circulation 1628
2 William Harvey ( ) Since all things, both argument and ocular demonstration, show that the blood passes through the lungs and heart by the force of the ventricles, and is sent for distribution to all parts of the body, where it makes its way into the veins and porosites of the flesh, and then flows by the veins from the circumference on every side to the centre, from the lesser to the greater veins, and is by them finally discharged into the vena cava and right auricle of the heart, and this in such a quantity or in such a flux and reflux thither by the arteries, hither by the veins, as cannot possibly be supplied by the ingesta, and is much greater than can be required for mere purposes of nutrition; it is absolutely necessary to conclude that the blood in the animal body is impelled in a circle, and is in a state of ceaseless motion. (1628)
3 History of Vascular Modelling Stephen Hales Vegetable staticks 1733 blood pressure measurements flow resistance occurs mainly in the microcirculation effects of elasticity of the arteries
4 History of Vascular Modelling Development of fluid dynamics Euler Daniel Bernoulli (Professor of Anatomy) Poiseuille (Physician)
5 History of Vascular Modelling Thomas Young Developed the theory of wave propagation in elastic tubes ` the enquiry, in what manner, and in what degree, the circulation of the blood depends on the muscular and elastic powers of the heart and of the arteries, supposing the nature of those powers be known, must become simply a question belonging to the most refined departments of the theory of hydraulics. 1809
6 History of Vascular Modelling Flow profile and the link with atherosclerosis Wormersley 1955 velocity profile and viscosity Caro, Fitz-Gerald & Schroter 1971 correlation between low wall shear stress and fatty streaks Fry 1973 transport of lipoproteins through the arterial wall
7 Modelling pulse propagation in the systemic & pulmonary circulation Nicholas Hill, Mathematics & Statistics, University of Glasgow Gareth Vaughan, Mathematics & Statistics, University of Glasgow Mette Olufsen, Mathematics, North Carolina State University, U.S.A. Martin Johnson, Scottish Pulmonary Vascular Unit, Western Infirmary, Glasgow Christopher Sainsbury, BHF Glasgow Cardiovascular Research Centre, University of Glasgow Xi an, 6 April, 2011 Acknowledgements: Professor Charles Peskin, Courant Institute, New York University & EPSRC.
8 The Cardiovascular System: Systemic circulation: Systemic arteries Systemic veins Pulmonary circulation: Pulmonary arteries Pulmonary veins Left and right heart: Atrium Ventricle
9 Pulmonary Circulation Right Ventricle Pulmonary Artery Capillary Blood Vessels Pulmonary Veins Left Atrium Pulmonary capillary blood volume 150 ml Blood-Gas exchange area 70 m 2 Average capillary radius 4 µm
10 Systemic arteries: Consist of Large arteries (cm) Small arteries (mm) Arterioles (100 µm) Capillaries (50 µm) Pressure drop across resistance arteries Pulmonary vasculature: Consists of Pulmonary arteries (mm) Pulmonary Capillaries (4 µm) Pressurised venous system
11 Systemic Artery Model 1-D cross-sectional average Large systemic arteries tapered vessels Structured tree vascular beds Olufsen, M.S. et al., Numerical Simulation and Experimental Validation of Blood Flow in Arteries with Structured-Tree Outflow Conditions, Annals of Biomedical Engineering, 28, , 2000.
12 Mathematical Model 1D fluid dynamics model for wave-propagation in the large arteries nonlinear, moving walls, flat velocity profile with a boundary layer, solved numerically. Smaller arteries modelled as a structured tree using linearised equations that allow mathematical analysis. Use fast recursive algorithms. New algorithm to calculate pressure and flow within structured tree.
13 The large arteries
14 Flow Equations for Large Arteries
15 Equations for Flow in the Structured Tree
16 Impedance Relation
17 Recursion for the Impedance
18 Flow measurements using MRI
19 Pulmonary Arterial System Data
20 The Pulmonary Arterial Tree The asymmetric structured tree model. For any vessel r = & i j αβ r = αr and r = βr daughter1 parent daughter2 parent r 0 Cast of the pulmonary arteries and branch classification schemes.
21 Structured Tree
22 Parameters determining parent/daughter radius ratios Area ratio is is given by d1 2 r 2 r 2 d1 d2 pa η = ( r + ) Radius exponent ξ r ξ r ξ r ξ pa d1 d2 pa d2 pa Radius ratio is γ = α / β / = 1.16 &1.08 = +, ξ = 2.7 α = r / r and β = r / r
23 Results for systemic arteries: simulated versus measured flow rates
24 1. Pressure Results systemic arteries 200 Pressure (mmhg) time (sec) 0.5 Pressure pulse for successive generations in the femoral artery vascular bed
25 Femoral Artery Vascular Bed Pressure pulse for successive generations. Note propagation of the pressure wave. Pressure decreases and becomes steadier in the smaller vessels. Pressures depend on length to radius ratios and area ratios, but do not depend strongly on the number of generations.
26 Intravascular pressure as a function of vessel diameter (Levy 2001)
27 Mean pressure v. vessel radius Shows extremes & mean for branches in the femoral structured tree. Mean pressure > 50 log 10 (r).
28 2. Pulmonary arteries & veins
29 The Large Pulmonary Arteries
30 A model for pulmonary circulation Sketch of main vessels with 4 vascular beds Need to link arteries and veins
31
32
33 Measurements of large pulmonary arteries
34 Inflow data - pulmonary artery Have good quality flow measurements in the large vessels
35 Pulmonary Vein Return Flow
36 Small pulmonary arterioles and venules Assume arterial and venous trees are topologically similar so that trees of vascular beds can be linked together. Material and geometrical properties are different. Obtain a matching condition to link the large arteries with the large veins by calculating an overall admittance for the whole bed of small vessels.
37 Governing equations
38
39
40
41 Matching conditions for the large arteries and veins which leads to convolution integrals in real space
42 Pulmonary disease
43
44
45
46
47
48 Effects of rarefaction
49 Note earlier arrival of pressure peak
50
51 3. Normal v. Increased Rarefaction in the Microcirculation - Pressure Ascending aorta Right radial artery Pressure waveforms: averages of 7 waveforms from 7 healthy individuals. Normal microcirculation solid circle. Increased rarefaction open circle. η = ( r + r ) / r = 1.16 & d1 d2 pa
52 Parameters determining parent/daughter radius ratios d1 d2 pa η = ( r + r ) / r = 1.16 &1.08 r ξ r ξ r ξ pa d1 d2 = +, ξ = 2.7 α = r / r and β = r / r d1 pa d2 pa γ = α / β = r / r d1 d2
53 Normal vs Increased Rarefaction in the Microcirculation - Flow Flow waveform at right radial artery: averages of 7 healthy individuals. Normal microcirculation solid circle. Increased rarefaction open circle. η = ( r + r ) / r = 1.16 & d1 d2 pa
54 Conclusions First numerical simulations of periodic pulsatile flow in the full pulmonary circulation. First calculations of pressure drop in small arteries. Comparisions between clinical data and model results. Evidence of changes in large vessel waveforms associated with changes in physiology of vascular beds, similar to those seen clinically.
55 The Real System Many challenges: flexible, complex, individual, able to sustain a great range of flow rates and regimes.
CHAPTER 4 Basic Physiological Principles
 4-1 CHAPTER 4 Basic Physiological Principles Now that we have a working anatomical knowledge of the heart and circulatory system, we will next develop a functional and quantitative knowledge of the cardiovascular
4-1 CHAPTER 4 Basic Physiological Principles Now that we have a working anatomical knowledge of the heart and circulatory system, we will next develop a functional and quantitative knowledge of the cardiovascular
Cardiovascular Physiology
 Cardiovascular Physiology Lecture 1 objectives Explain the basic anatomy of the heart and its arrangement into 4 chambers. Appreciate that blood flows in series through the systemic and pulmonary circulations.
Cardiovascular Physiology Lecture 1 objectives Explain the basic anatomy of the heart and its arrangement into 4 chambers. Appreciate that blood flows in series through the systemic and pulmonary circulations.
Confirmation, Falsification, and Fallibility
 Confirmation, Falsification, and Fallibility Phil 12: Logic and Decision Making Winter 2010 UC San Diego 1/15/2010 1 1 Review Key feature of scientific reasoning: confirming or falsifying hypotheses based
Confirmation, Falsification, and Fallibility Phil 12: Logic and Decision Making Winter 2010 UC San Diego 1/15/2010 1 1 Review Key feature of scientific reasoning: confirming or falsifying hypotheses based
CVS Hemodynamics. Change in blood pressure:
 CVS Hemodynamics -The distribution of blood inside the circulation: The major part of blood volume is found in the venous system 60% (2/3), that s why veins are called the capacitance vessels. -Arteries
CVS Hemodynamics -The distribution of blood inside the circulation: The major part of blood volume is found in the venous system 60% (2/3), that s why veins are called the capacitance vessels. -Arteries
Collin County Community College
 Collin County Community College BIOL. 2402 Anatomy & Physiology WEEK 6 Blood Vessels 1 Anatomy of Blood Vessels Walls of blood vessels contain 3 distinct layers : Tunica intima innermost layer includes
Collin County Community College BIOL. 2402 Anatomy & Physiology WEEK 6 Blood Vessels 1 Anatomy of Blood Vessels Walls of blood vessels contain 3 distinct layers : Tunica intima innermost layer includes
Blood flows away from the heart in arteries, to the capillaries and back to the heart in the veins
 Cardiovascular System Summary Notes The cardiovascular system includes: The heart, a muscular pump The blood, a fluid connective tissue The blood vessels, arteries, veins and capillaries Blood flows away
Cardiovascular System Summary Notes The cardiovascular system includes: The heart, a muscular pump The blood, a fluid connective tissue The blood vessels, arteries, veins and capillaries Blood flows away
CVS Hemodynamics. Faisal I. Mohammed, MD,PhD.
 CVS Hemodynamics Faisal I. Mohammed, MD,PhD. Objectives point out the physical characteristics of the circulation: distribution of blood volume total cross sectional area velocity blood pressure List the
CVS Hemodynamics Faisal I. Mohammed, MD,PhD. Objectives point out the physical characteristics of the circulation: distribution of blood volume total cross sectional area velocity blood pressure List the
Any of these questions could be asked as open question or lab question, thus study them well
 Any of these questions could be asked as open question or lab question, thus study them well describe the factors which regulate cardiac output describe the sympathetic and parasympathetic control of heart
Any of these questions could be asked as open question or lab question, thus study them well describe the factors which regulate cardiac output describe the sympathetic and parasympathetic control of heart
What is the mechanism of the audible carotid bruit? How does one calculate the velocity of blood flow?
 CASE 8 A 65-year-old man with a history of hypertension and coronary artery disease presents to the emergency center with complaints of left-sided facial numbness and weakness. His blood pressure is normal,
CASE 8 A 65-year-old man with a history of hypertension and coronary artery disease presents to the emergency center with complaints of left-sided facial numbness and weakness. His blood pressure is normal,
Structure. Arteries. 21_01d 4/18/12. The Cardiovascular System: Blood Vessels and Hemodynamics. Dr Badri Paudel GMC
 Goal of the Cardiovascular System: deliver blood to all parts of the body The Cardiovascular System: Blood Vessels and Hemodynamics Dr Badri Paudel GMC Does so by using different types of tubing, attached
Goal of the Cardiovascular System: deliver blood to all parts of the body The Cardiovascular System: Blood Vessels and Hemodynamics Dr Badri Paudel GMC Does so by using different types of tubing, attached
Contents 1 Computational Haemodynamics An Introduction 2 The Human Cardiovascular System
 Contents 1 Computational Haemodynamics An Introduction... 1 1.1 What is Computational Haemodynamics (CHD)... 1 1.2 Advantages of CHD... 3 1.3 Applications in the Cardiovascular System... 4 1.3.1 CHD as
Contents 1 Computational Haemodynamics An Introduction... 1 1.1 What is Computational Haemodynamics (CHD)... 1 1.2 Advantages of CHD... 3 1.3 Applications in the Cardiovascular System... 4 1.3.1 CHD as
Blood Flow, Blood Pressure, Cardiac Output. Blood Vessels
 Blood Flow, Blood Pressure, Cardiac Output Blood Vessels Blood Vessels Made of smooth muscle, elastic and fibrous connective tissue Cells are not electrically coupled Blood Vessels Arteries arterioles
Blood Flow, Blood Pressure, Cardiac Output Blood Vessels Blood Vessels Made of smooth muscle, elastic and fibrous connective tissue Cells are not electrically coupled Blood Vessels Arteries arterioles
Physics of the Cardiovascular System
 Dentistry College Medical Physics Physics of the Cardiovascular System The cells of the body act like individual engines. In order for them to function they must have: - 1. Fuel from our food to supply
Dentistry College Medical Physics Physics of the Cardiovascular System The cells of the body act like individual engines. In order for them to function they must have: - 1. Fuel from our food to supply
Cardiovascular system
 Cardiovascular system L-4 Blood pressure & special circulation Dr Than Kyaw 27 February 2012 Blood Pressure (BP) Pressure generation and flow Blood is under pressure within its closed system. Pressure
Cardiovascular system L-4 Blood pressure & special circulation Dr Than Kyaw 27 February 2012 Blood Pressure (BP) Pressure generation and flow Blood is under pressure within its closed system. Pressure
Physiology - 8 Hemodynamics - 1 M.jafar 24/3/2016 Turquoise Team
 21 Physiology - 8 Hemodynamics - 1 M.jafar 24/3/2016 Turquoise Team Hemodynamics Today we will take about hemodynamics which is the study of the movement of blood and of the forces concerned. Now how the
21 Physiology - 8 Hemodynamics - 1 M.jafar 24/3/2016 Turquoise Team Hemodynamics Today we will take about hemodynamics which is the study of the movement of blood and of the forces concerned. Now how the
2.01 Remember the structures of the circulatory system
 2.01 Remember the structures of the circulatory system Essential questions What are the structures of blood? What are the structures of the circulatory system? circulatory system 2 Structures of the circulatory
2.01 Remember the structures of the circulatory system Essential questions What are the structures of blood? What are the structures of the circulatory system? circulatory system 2 Structures of the circulatory
A study of computational modeling of abdominal aortic aneurysm
 A study of computational modeling of abdominal aortic aneurysm S.M. Kim (a), M.P Lee (b), H.C Kang (c), J.H Lee (d), J.H Jeong (e), S.G Roh (f) (a) Department of Medical Bio Engineering, College of Biosystem,
A study of computational modeling of abdominal aortic aneurysm S.M. Kim (a), M.P Lee (b), H.C Kang (c), J.H Lee (d), J.H Jeong (e), S.G Roh (f) (a) Department of Medical Bio Engineering, College of Biosystem,
Stochastic Simulation of Human Pulmonary Blood Flow and Transit Time Frequency Distribution Based on Anatomic and Elasticity Data
 Copyright 212 Tech Science Press MCB, vol.9, no.4, pp.269-284, 212 Stochastic Simulation of Human Pulmonary Blood Flow and Transit Time Frequency Distribution Based on Anatomic and Elasticity Data Wei
Copyright 212 Tech Science Press MCB, vol.9, no.4, pp.269-284, 212 Stochastic Simulation of Human Pulmonary Blood Flow and Transit Time Frequency Distribution Based on Anatomic and Elasticity Data Wei
Non-Newtonian pulsatile blood flow in a modeled artery with a stenosis and an aneurysm
 Non-Newtonian pulsatile blood flow in a modeled artery with a stenosis and an aneurysm I. Husain, C. Langdon and J. Schwark Department of Mathematics Luther College University of Regina Regina, Saskatchewan
Non-Newtonian pulsatile blood flow in a modeled artery with a stenosis and an aneurysm I. Husain, C. Langdon and J. Schwark Department of Mathematics Luther College University of Regina Regina, Saskatchewan
IB TOPIC 6.2 THE BLOOD SYSTEM
 IB TOPIC 6.2 THE BLOOD SYSTEM TERMS TO KNOW circulation ventricle artery vein THE BLOOD SYSTEM 6.2.U1 - Arteries convey blood at high pressure from the ventricles to the tissues of the body Circulation
IB TOPIC 6.2 THE BLOOD SYSTEM TERMS TO KNOW circulation ventricle artery vein THE BLOOD SYSTEM 6.2.U1 - Arteries convey blood at high pressure from the ventricles to the tissues of the body Circulation
1 (a) Fig PhysicsAndMathsTutor.com
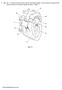 1 (a) Fig. 1.1 shows the human heart and the main blood vessels. The functions of the parts of the heart and some of the blood vessels are given in Table 1.1. A K B J H C D G E F Fig. 1.1 Complete Table
1 (a) Fig. 1.1 shows the human heart and the main blood vessels. The functions of the parts of the heart and some of the blood vessels are given in Table 1.1. A K B J H C D G E F Fig. 1.1 Complete Table
Major Function of the Cardiovascular System. Transportation. Structures of the Cardiovascular System. Heart - muscular pump
 Structures of the Cardiovascular System Heart - muscular pump Blood vessels - network of tubes Blood - liquid transport vehicle brachiocephalic trunk superior vena cava right pulmonary arteries right pulmonary
Structures of the Cardiovascular System Heart - muscular pump Blood vessels - network of tubes Blood - liquid transport vehicle brachiocephalic trunk superior vena cava right pulmonary arteries right pulmonary
Lab Activity 25. Blood Vessels & Circulation. Portland Community College BI 232
 Lab Activity 25 Blood Vessels & Circulation Portland Community College BI 232 Artery and Vein Histology Walls have 3 layers: Tunica intima Tunica media Tunica externa 2 Tunica Intima Is the innermost layer
Lab Activity 25 Blood Vessels & Circulation Portland Community College BI 232 Artery and Vein Histology Walls have 3 layers: Tunica intima Tunica media Tunica externa 2 Tunica Intima Is the innermost layer
CIRCULATORY SYSTEM BLOOD VESSELS
 Name: Block: CIRCULATORY SYSTEM Multicellular organisms (above the level of roundworms) rely on a circulatory system to bring nutrients to, and take wastes away from, cells. In higher organisms such as
Name: Block: CIRCULATORY SYSTEM Multicellular organisms (above the level of roundworms) rely on a circulatory system to bring nutrients to, and take wastes away from, cells. In higher organisms such as
VASCULAR SYSTEM: THE HEMODYNAMICS Lecture 1. Dr. Ana-Maria Zagrean
 VASCULAR SYSTEM: THE HEMODYNAMICS Lecture 1 Dr. Ana-Maria Zagrean Hemodynamics -is the study of the physical laws of blood circulation -studies the properties of both the content = blood and the container
VASCULAR SYSTEM: THE HEMODYNAMICS Lecture 1 Dr. Ana-Maria Zagrean Hemodynamics -is the study of the physical laws of blood circulation -studies the properties of both the content = blood and the container
Modeling the Vascular System and Its Capillary Networks
 CHAPTER 1 Modeling the Vascular System and Its Capillary Networks THOMAS H. DAWSON United States Naval Academy, Annapolis, Maryland Abstract. Modeling of the vascular system and its capillary networks
CHAPTER 1 Modeling the Vascular System and Its Capillary Networks THOMAS H. DAWSON United States Naval Academy, Annapolis, Maryland Abstract. Modeling of the vascular system and its capillary networks
BIOL 219 Spring Chapters 14&15 Cardiovascular System
 1 BIOL 219 Spring 2013 Chapters 14&15 Cardiovascular System Outline: Components of the CV system Heart anatomy Layers of the heart wall Pericardium Heart chambers, valves, blood vessels, septum Atrioventricular
1 BIOL 219 Spring 2013 Chapters 14&15 Cardiovascular System Outline: Components of the CV system Heart anatomy Layers of the heart wall Pericardium Heart chambers, valves, blood vessels, septum Atrioventricular
(2) (1) (3) (4) BLOOD PATHWAY ASSESSMENT RUBRIC
 BLOODPATHWAYASSESSMENT(4) BLOOD%PATHWAY%ASSESSMENT%(3)% BLOODPATHWAYASSESSMENT(3) (4) (3) (2) (1) Using a completely blank diagram of the heart, all valves, chambers, great vessels, and direction of blood
BLOODPATHWAYASSESSMENT(4) BLOOD%PATHWAY%ASSESSMENT%(3)% BLOODPATHWAYASSESSMENT(3) (4) (3) (2) (1) Using a completely blank diagram of the heart, all valves, chambers, great vessels, and direction of blood
Chapter 9. Body Fluid Compartments. Body Fluid Compartments. Blood Volume. Blood Volume. Viscosity. Circulatory Adaptations to Exercise Part 4
 Body Fluid Compartments Chapter 9 Circulatory Adaptations to Exercise Part 4 Total body fluids (40 L) Intracellular fluid (ICF) 25 L Fluid of each cell (75 trillion) Constituents inside cell vary Extracellular
Body Fluid Compartments Chapter 9 Circulatory Adaptations to Exercise Part 4 Total body fluids (40 L) Intracellular fluid (ICF) 25 L Fluid of each cell (75 trillion) Constituents inside cell vary Extracellular
Biology. A Guide to the Natural World. Chapter 30 Lecture Outline Transport and Exchange 1: Blood and Breath. Fifth Edition.
 Biology A Guide to the Natural World Chapter 30 Lecture Outline Transport and Exchange 1: Blood and Breath Fifth Edition David Krogh 30.1 The Cardiovascular System The Cardiovascular System The human cardiovascular
Biology A Guide to the Natural World Chapter 30 Lecture Outline Transport and Exchange 1: Blood and Breath Fifth Edition David Krogh 30.1 The Cardiovascular System The Cardiovascular System The human cardiovascular
The Circulatory System (p )
 The Circulatory System (p. 268-281) How Does Gravity Affect Blood Circulation? As with all land animals, the giraffe and the corn snake are constantly subject to the force of gravity The circulatory system
The Circulatory System (p. 268-281) How Does Gravity Affect Blood Circulation? As with all land animals, the giraffe and the corn snake are constantly subject to the force of gravity The circulatory system
Vascular System Part One
 Vascular System Part One Objectives Trace the route taken by blood as it leaves, and then returns to the heart. Describe the structure of the walls of arteries and veins. Discuss the structure and function
Vascular System Part One Objectives Trace the route taken by blood as it leaves, and then returns to the heart. Describe the structure of the walls of arteries and veins. Discuss the structure and function
CIRCULATION. Cardiovascular & lymphatic systems Functions. Transport Defense / immunity Homeostasis
 CIRCULATION CIRCULATION Cardiovascular & lymphatic systems Functions Transport Defense / immunity Homeostasis 2 Types of Circulatory Systems Open circulatory system Contains vascular elements Mixing of
CIRCULATION CIRCULATION Cardiovascular & lymphatic systems Functions Transport Defense / immunity Homeostasis 2 Types of Circulatory Systems Open circulatory system Contains vascular elements Mixing of
Chapter 14. The Cardiovascular System
 Chapter 14 The Cardiovascular System Introduction Cardiovascular system - heart, blood and blood vessels Cardiac muscle makes up bulk of heart provides force to pump blood Function - transports blood 2
Chapter 14 The Cardiovascular System Introduction Cardiovascular system - heart, blood and blood vessels Cardiac muscle makes up bulk of heart provides force to pump blood Function - transports blood 2
CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM
 CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM Overview Heart and Vessels 2 Major Divisions Pulmonary Circuit Systemic Circuit Closed and Continuous Loop Location Aorta Superior vena cava Right lung Pulmonary trunk Base of heart
CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM Overview Heart and Vessels 2 Major Divisions Pulmonary Circuit Systemic Circuit Closed and Continuous Loop Location Aorta Superior vena cava Right lung Pulmonary trunk Base of heart
A patient-specific lumped-parameter model of coronary circulation
 A patient-specific lumped-parameter model of coronary circulation Zheng Duanmu 1*, Min Yin 1, Xueling Fan 1*, Xilan Yang 2, and Xiaoyu Luo 3 1 State Key Laboratory for Strength and Vibration of Mechanical
A patient-specific lumped-parameter model of coronary circulation Zheng Duanmu 1*, Min Yin 1, Xueling Fan 1*, Xilan Yang 2, and Xiaoyu Luo 3 1 State Key Laboratory for Strength and Vibration of Mechanical
2402 : Anatomy/Physiology
 Dr. Chris Doumen Lecture 1 2402 : Anatomy/Physiology Hemo Dynamics and Blood Vessels I nt r oduc t i on TextBook Readings Pages 721 through 734. Make use of the figures in your textbook ; a picture is
Dr. Chris Doumen Lecture 1 2402 : Anatomy/Physiology Hemo Dynamics and Blood Vessels I nt r oduc t i on TextBook Readings Pages 721 through 734. Make use of the figures in your textbook ; a picture is
ISSN: ISO 9001:2008 Certified International Journal of Engineering and Innovative Technology (IJEIT) Volume 4, Issue 1, July 2014
 Mathematical Modelling and Simulation of Human Systemic Arterial System Ketan B. Naik, Dr. P H. Bhathawala Department of Applied Sciences and Humanities, Parul Institute of Engineering and Technology,
Mathematical Modelling and Simulation of Human Systemic Arterial System Ketan B. Naik, Dr. P H. Bhathawala Department of Applied Sciences and Humanities, Parul Institute of Engineering and Technology,
Which method is better to measure arterial stiffness; augmentation index, pulse wave velocity, carotid distensibility? 전북의대내과 김원호
 Which method is better to measure arterial stiffness; augmentation index, pulse wave velocity, carotid distensibility? 전북의대내과 김원호 Arterial stiffness Arterial stiffness is inversely related to arterial
Which method is better to measure arterial stiffness; augmentation index, pulse wave velocity, carotid distensibility? 전북의대내과 김원호 Arterial stiffness Arterial stiffness is inversely related to arterial
Lecture 13: The Cardiovascular System ref: Cardiovascular Physiology, D. Mohrman and L. Heller, 4th ed. McGraw-Hill (1997)
 Lecture 13: The Cardiovascular System ref: Cardiovascular Physiology, D. Mohrman and L. Heller, 4th ed. McGraw-Hill (1997) Blood Heart Blood Vessels Arteries - capillaries - Veins Ventilation-Perfusion
Lecture 13: The Cardiovascular System ref: Cardiovascular Physiology, D. Mohrman and L. Heller, 4th ed. McGraw-Hill (1997) Blood Heart Blood Vessels Arteries - capillaries - Veins Ventilation-Perfusion
The Cardiovascular. Parts and Functions
 The Cardiovascular Parts and Functions Parts The cardiovascular system consists of 3 major parts that work together. 1- Heart 2- Lungs 3- Blood Vessels Blood Vessels There are blood vessels that carry
The Cardiovascular Parts and Functions Parts The cardiovascular system consists of 3 major parts that work together. 1- Heart 2- Lungs 3- Blood Vessels Blood Vessels There are blood vessels that carry
Scrub In: Red blood cells are called: Which component of blood is necessary for the initiation of the blood clotting process:
 Scrub In: Red blood cells are called: a. erythrocytes b. leukocytes c. melanocytes d. thrombocytes Which component of blood is necessary for the initiation of the blood clotting process: a. erythrocytes
Scrub In: Red blood cells are called: a. erythrocytes b. leukocytes c. melanocytes d. thrombocytes Which component of blood is necessary for the initiation of the blood clotting process: a. erythrocytes
IB TOPIC 6.2 THE BLOOD SYSTEM
 IB TOPIC 6.2 THE BLOOD SYSTEM THE BLOOD SYSTEM TERMS TO KNOW circulation ventricle artery vein 6.2.U1 - Arteries convey blood at high pressure from the ventricles to the tissues of the body Circulation
IB TOPIC 6.2 THE BLOOD SYSTEM THE BLOOD SYSTEM TERMS TO KNOW circulation ventricle artery vein 6.2.U1 - Arteries convey blood at high pressure from the ventricles to the tissues of the body Circulation
CIRCULATION Blood and Blood Vessels
 CIRCULATION Blood and Blood Vessels Blood Vessels The 5 Main Types 1. Arteries 2. Arterioles 3. Capillaries 4. Venules 5. Veins http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=pgi80ue-amo Arteries: 1) Arteries Function
CIRCULATION Blood and Blood Vessels Blood Vessels The 5 Main Types 1. Arteries 2. Arterioles 3. Capillaries 4. Venules 5. Veins http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=pgi80ue-amo Arteries: 1) Arteries Function
The Heart & Circulation (I)
 The Heart & Circulation (I) (Ch. 1. Modeling and Simulation in Medicine and the Life Sciences) 1.1 Plan of the Circulation - Function of the heart? - Figure 1.1: The left heart receives blood that is rich
The Heart & Circulation (I) (Ch. 1. Modeling and Simulation in Medicine and the Life Sciences) 1.1 Plan of the Circulation - Function of the heart? - Figure 1.1: The left heart receives blood that is rich
C3, 4, 5, 6, & 7 Worksheet. C3 Describe the inter-relationships of the structures of the heart
 Name: Date: C3, 4, 5, 6, & 7 Worksheet C3 Describe the inter-relationships of the structures of the heart 1. Label and give the functions of the following: a. left and right atrium: b. left and right ventricle:
Name: Date: C3, 4, 5, 6, & 7 Worksheet C3 Describe the inter-relationships of the structures of the heart 1. Label and give the functions of the following: a. left and right atrium: b. left and right ventricle:
Health Science 20 Circulatory System Notes
 Health Science 20 Circulatory System Notes Functions of the Circulatory System The circulatory system functions mainly as the body s transport system. It transports: o Oxygen o Nutrients o Cell waste o
Health Science 20 Circulatory System Notes Functions of the Circulatory System The circulatory system functions mainly as the body s transport system. It transports: o Oxygen o Nutrients o Cell waste o
Blood Vessels and Our Pulse
 Blood Vessels and Our Pulse Blood Vessels in Your Body All the blood vessels in your body joined together in a straight line would reach from St. John s, Newfoundland, to Victoria, British Columbia, and
Blood Vessels and Our Pulse Blood Vessels in Your Body All the blood vessels in your body joined together in a straight line would reach from St. John s, Newfoundland, to Victoria, British Columbia, and
Cardiovascular System Blood Vessels
 Cardiovascular System Blood Vessels Structure of Blood Vessels The three layers (tunics) Tunica intima composed of simple squamous epithelium Tunica media sheets of smooth muscle Contraction vasoconstriction
Cardiovascular System Blood Vessels Structure of Blood Vessels The three layers (tunics) Tunica intima composed of simple squamous epithelium Tunica media sheets of smooth muscle Contraction vasoconstriction
Chapter 2 The Human Cardiovascular System
 Chapter 2 The Human Cardiovascular System 2.1 Introduction Before delving into the computational methods of CHD, this chapter provides a preliminary understanding of the circulatory system from a physiological
Chapter 2 The Human Cardiovascular System 2.1 Introduction Before delving into the computational methods of CHD, this chapter provides a preliminary understanding of the circulatory system from a physiological
Practical Histology. Cardiovascular System. Dr Narmeen S. Ahmad
 Practical Histology Cardiovascular System Dr Narmeen S. Ahmad The Cardiovascular System A closed system of the heart and blood vessels Functions of cardiovascular system: Transport nutrients, hormones
Practical Histology Cardiovascular System Dr Narmeen S. Ahmad The Cardiovascular System A closed system of the heart and blood vessels Functions of cardiovascular system: Transport nutrients, hormones
Special Lecture 10/28/2012
 Special Lecture 10/28/2012 HYPERTENSION Dr. HN Mayrovitz Special Lecture 10/28/2012 Arterial Blood Pressure (ABP) - Definitions ABP Review Indirect Oscillographic Method Resistance (R), Compliance (C)
Special Lecture 10/28/2012 HYPERTENSION Dr. HN Mayrovitz Special Lecture 10/28/2012 Arterial Blood Pressure (ABP) - Definitions ABP Review Indirect Oscillographic Method Resistance (R), Compliance (C)
Bellwork Define: hemostasis anticoagulation hemophilia (Then write the underline portion of the two state standards in your notes).
 Bellwork Define: hemostasis anticoagulation hemophilia (Then write the underline portion of the two state standards in your notes). A&P Standards 31) Identify the liquid and cellular components of blood
Bellwork Define: hemostasis anticoagulation hemophilia (Then write the underline portion of the two state standards in your notes). A&P Standards 31) Identify the liquid and cellular components of blood
What was the range of the resting heart rates in males after the exercise programme?
 Q1.Scientists investigated the effect of a 6-week exercise programme on the resting heart rate of males and females. The scientists recruited a large group of male volunteers and a large group of female
Q1.Scientists investigated the effect of a 6-week exercise programme on the resting heart rate of males and females. The scientists recruited a large group of male volunteers and a large group of female
The Cardiovascular System
 Essentials of Human Anatomy & Physiology Elaine N. Marieb Seventh Edition Chapter 11 The Cardiovascular System Slides 11.1 11.19 Lecture Slides in PowerPoint by Jerry L. Cook The Cardiovascular System
Essentials of Human Anatomy & Physiology Elaine N. Marieb Seventh Edition Chapter 11 The Cardiovascular System Slides 11.1 11.19 Lecture Slides in PowerPoint by Jerry L. Cook The Cardiovascular System
Cardiovascular Anatomy Dr. Gary Mumaugh
 Cardiovascular Anatomy Dr. Gary Mumaugh Location of Heart Approximately the size of your fist Location o Superior surface of diaphragm o Left of the midline in mediastinum o Anterior to the vertebral column,
Cardiovascular Anatomy Dr. Gary Mumaugh Location of Heart Approximately the size of your fist Location o Superior surface of diaphragm o Left of the midline in mediastinum o Anterior to the vertebral column,
The elastance model implemented in a left ventricle finite element model. Pim van Ooij TU Eindhoven BMTE Juni 2006
 The elastance model implemented in a left ventricle finite element model Pim van Ooij TU Eindhoven BMTE 06.29 Juni 2006 1 Summary Since heart diseases are the second largest cause of death in the western
The elastance model implemented in a left ventricle finite element model Pim van Ooij TU Eindhoven BMTE 06.29 Juni 2006 1 Summary Since heart diseases are the second largest cause of death in the western
Steady State Computer Model of Human Vascular for Analyzing Effects of Stenosis
 Steady State Computer Model of Human Vascular for Analyzing Effects of Stenosis University of Illinois at Chicago Professor Andreas Linninger Michael Naskrent December 2, 2013 Table of Contents Abstract...
Steady State Computer Model of Human Vascular for Analyzing Effects of Stenosis University of Illinois at Chicago Professor Andreas Linninger Michael Naskrent December 2, 2013 Table of Contents Abstract...
THE COMPLETE GUIDE TO VASCULAR ULTRASOUND
 THE COMPLETE GUIDE TO VASCULAR ULTRASOUND PETER H. ARGER, M.D., F.A.I.U.M., F.A.C.R. Professor Emeritus Department of Radiology University of Pennsylvania Medical Center Hospital of the University of Pennsylvania
THE COMPLETE GUIDE TO VASCULAR ULTRASOUND PETER H. ARGER, M.D., F.A.I.U.M., F.A.C.R. Professor Emeritus Department of Radiology University of Pennsylvania Medical Center Hospital of the University of Pennsylvania
Level 2 Anatomy and Physiology Bite size revision. Respiratory System. The order of the passage of oxygen into the body (inhalation/inspiration) is: -
 Respiratory System Function of the respiratory system The lungs are located in the chest cavity and their function is to intake oxygen and remove carbon dioxide from the body. Structure of the respiratory
Respiratory System Function of the respiratory system The lungs are located in the chest cavity and their function is to intake oxygen and remove carbon dioxide from the body. Structure of the respiratory
MESA DAY CONTEST RULES
 FOR CENTER DIRECTOR S USE ONLY ANSWERS MODEL SCIENCE THE HEART High School All Grades Students MUST be prepared to answer each question with a complete sentence or sentences. 1. What is the size of the
FOR CENTER DIRECTOR S USE ONLY ANSWERS MODEL SCIENCE THE HEART High School All Grades Students MUST be prepared to answer each question with a complete sentence or sentences. 1. What is the size of the
Simulation of Aorta Artery Aneurysms Using Active Electronic Circuit
 American Journal of Applied Sciences 4 (4): 03-0, 007 ISSN 546-939 007 Science Publications Simulation of Aorta Artery Aneurysms Using Active Electronic Circuit Kamran Hassani, Mahdi Navidbakhsh and 3
American Journal of Applied Sciences 4 (4): 03-0, 007 ISSN 546-939 007 Science Publications Simulation of Aorta Artery Aneurysms Using Active Electronic Circuit Kamran Hassani, Mahdi Navidbakhsh and 3
Numerical Simulation of Blood Flow in the System of Human Coronary Arteries with and without Bypass Graft
 Numerical Simulation of Blood Flow in the System of Human Coronary Arteries with and without Bypass Graft BURASKORN NUNTADILOK 1, BENCHAWAN WIWATANAPATAPHEE 1 MEECHOKE CHUEDOUNG 1, THANONGCHAI SIRIAPISITH
Numerical Simulation of Blood Flow in the System of Human Coronary Arteries with and without Bypass Graft BURASKORN NUNTADILOK 1, BENCHAWAN WIWATANAPATAPHEE 1 MEECHOKE CHUEDOUNG 1, THANONGCHAI SIRIAPISITH
Cardiovascular System. Supplementary Information
 Cardiovascular System Supplementary Information THE CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM - 1 - THE CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM FUNCTION Transport system carrying nutrient, gases, hormones and waste products to and from the
Cardiovascular System Supplementary Information THE CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM - 1 - THE CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM FUNCTION Transport system carrying nutrient, gases, hormones and waste products to and from the
BSc School C Level 2a Module 6 Cardiovascular Mechanics. Notes for Cardiovascular Fluid Mechanics
 BSc School C Level 2a Module 6 Cardiovascular Mechanics Page 1 of 18 BSc School C Level 2a Module 6 Cardiovascular Mechanics Notes for Cardiovascular Fluid Mechanics K.H. Parker Department of Bioengineering
BSc School C Level 2a Module 6 Cardiovascular Mechanics Page 1 of 18 BSc School C Level 2a Module 6 Cardiovascular Mechanics Notes for Cardiovascular Fluid Mechanics K.H. Parker Department of Bioengineering
Blood Vessels. Types of Blood Vessels Arteries carry blood away from the heart Capillaries smallest blood vessels. Veins carry blood toward the heart
 C H A P T E R Blood Vessels 20 Types of Blood Vessels Arteries carry blood away from the heart Capillaries smallest blood vessels The site of exchange of molecules between blood and tissue fluid Veins
C H A P T E R Blood Vessels 20 Types of Blood Vessels Arteries carry blood away from the heart Capillaries smallest blood vessels The site of exchange of molecules between blood and tissue fluid Veins
Computational Models of Functional Hyperaemia in the Cerebro-vasculature
 18 th World IMACS / MODSIM Congress, Cairns, Australia 13-17 July 9 http://mssanz.org.au/modsim9 Computational Models of Functional Hyperaemia in the Cerebro-vasculature T. David 1, S. Alzaidi 1, H. Farr
18 th World IMACS / MODSIM Congress, Cairns, Australia 13-17 July 9 http://mssanz.org.au/modsim9 Computational Models of Functional Hyperaemia in the Cerebro-vasculature T. David 1, S. Alzaidi 1, H. Farr
The cardiovascular system
 The cardiovascular system Components of the Cardiovascular system Heart Vessels: Arteries Capillaries Veins Functions of CVS: Transportation system where blood is the transporting vehicle Carries oxygen,
The cardiovascular system Components of the Cardiovascular system Heart Vessels: Arteries Capillaries Veins Functions of CVS: Transportation system where blood is the transporting vehicle Carries oxygen,
Properties and modelling of the venous blood flow. 1111, Budapest, Műegyetem rkp. 3. D ép. 3. em Tel: Fax:
 Properties and modelling of the venous blood flow 1111, Budapest, Műegyetem rkp. 3. D ép. 3. em Tel: 463 16 80 Fax: 463 30 91 www.hds.bme.hu Overview of the lectures Introduction Properties of the venous
Properties and modelling of the venous blood flow 1111, Budapest, Műegyetem rkp. 3. D ép. 3. em Tel: 463 16 80 Fax: 463 30 91 www.hds.bme.hu Overview of the lectures Introduction Properties of the venous
Chapter 20 (1) The Heart
 Chapter 20 (1) The Heart Learning Objectives Describe the location and structure of the heart Describe the path of a drop of blood from the superior vena cava or inferior vena cava through the heart out
Chapter 20 (1) The Heart Learning Objectives Describe the location and structure of the heart Describe the path of a drop of blood from the superior vena cava or inferior vena cava through the heart out
Cardiovascular System
 Cardiovascular System I. Structure of the Heart A. Average adult heart is 14 cm long and 9 cm wide. B. Lies in the mediastinum. C. Enclosed in the pericardium. 1. Fibrous pericardium- Outer, tough connective
Cardiovascular System I. Structure of the Heart A. Average adult heart is 14 cm long and 9 cm wide. B. Lies in the mediastinum. C. Enclosed in the pericardium. 1. Fibrous pericardium- Outer, tough connective
The Cardiovascular System
 The Cardiovascular System The Cardiovascular System A closed system of the heart and blood vessels The heart pumps blood Blood vessels allow blood to circulate to all parts of the body The function of
The Cardiovascular System The Cardiovascular System A closed system of the heart and blood vessels The heart pumps blood Blood vessels allow blood to circulate to all parts of the body The function of
Branching Blood Vessels
 Jonathan Borne Union Springs Academy Union Springs, NY Summer 2000 Research Host: Mary D. S. Frame, Ph.D. University of Rochester School of Medicine and Dentistry Page 1 of 8 Suggestions for Teachers Purpose:
Jonathan Borne Union Springs Academy Union Springs, NY Summer 2000 Research Host: Mary D. S. Frame, Ph.D. University of Rochester School of Medicine and Dentistry Page 1 of 8 Suggestions for Teachers Purpose:
CPM Specifications Document Aortofemoral Normal:
 CPM Specifications Document Aortofemoral Normal: OSMSC 0003_0000 0006_0000 May 24, 2013 Version 1 Open Source Medical Software Corporation 2013 Open Source Medical Software Corporation. All Rights Reserved.
CPM Specifications Document Aortofemoral Normal: OSMSC 0003_0000 0006_0000 May 24, 2013 Version 1 Open Source Medical Software Corporation 2013 Open Source Medical Software Corporation. All Rights Reserved.
Lecture 8. Heart and Circulatory System. Lecture 8
 Lecture 8 Heart and Circulatory System Lecture 8 1. Introduction 2. Blood 3. Blood Vessels & Blood Pressure 4. The Heart 5. Cardiovascular (Circulatory) System 2 1 Circulatory System Function 1. Transport
Lecture 8 Heart and Circulatory System Lecture 8 1. Introduction 2. Blood 3. Blood Vessels & Blood Pressure 4. The Heart 5. Cardiovascular (Circulatory) System 2 1 Circulatory System Function 1. Transport
QUIZ 1. Tuesday, March 2, 2004
 Harvard-MIT Division of Health Sciences and Technology HST.542J: Quantitative Physiology: Organ Transport Systems Instructors: Roger Mark and Jose Venegas MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY Departments
Harvard-MIT Division of Health Sciences and Technology HST.542J: Quantitative Physiology: Organ Transport Systems Instructors: Roger Mark and Jose Venegas MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY Departments
Anatomy & Physiology of Cardiovascular System. Chapter 18 & 19
 Anatomy & Physiology of Cardiovascular System Chapter 18 & 19 Objectives..cont 1. Discuss the physiological stages of cardiac muscle contraction. 2. Trace a typical ECG and label each wave or complex 3.
Anatomy & Physiology of Cardiovascular System Chapter 18 & 19 Objectives..cont 1. Discuss the physiological stages of cardiac muscle contraction. 2. Trace a typical ECG and label each wave or complex 3.
A. Incorrect! The left ventricle receives oxygenated blood from the lungs via the left atrium.
 Anatomy and Physiology - Problem Drill 16: The Cardiovascular System No. 1 of 10 Instruction: (1) Read the problem statement and answer choices carefully (2) Work the problems on paper as needed (3) Pick
Anatomy and Physiology - Problem Drill 16: The Cardiovascular System No. 1 of 10 Instruction: (1) Read the problem statement and answer choices carefully (2) Work the problems on paper as needed (3) Pick
THE CIRCULATORY SYSTEM
 Biology 30S THE CIRCULATORY SYSTEM Name: This module adapted from bblearn.merlin.mb.ca 1 Introduction to Circulation The first organ to form, and the last organ to die. The heart is the pump of life. The
Biology 30S THE CIRCULATORY SYSTEM Name: This module adapted from bblearn.merlin.mb.ca 1 Introduction to Circulation The first organ to form, and the last organ to die. The heart is the pump of life. The
Lectures on Medical Biophysics Department of Biophysics, Medical Faculty, Masaryk University in Brno. Biophysics of cardiovascular system
 Lectures on Medical Biophysics Department of Biophysics, Medical Faculty, Masaryk University in Brno Biophysics of cardiovascular system 1 Lecture outline Mechanical properties of blood vessels Reynolds
Lectures on Medical Biophysics Department of Biophysics, Medical Faculty, Masaryk University in Brno Biophysics of cardiovascular system 1 Lecture outline Mechanical properties of blood vessels Reynolds
Ch 9 Transport of substances in humans
 Ch 9 Transport of substances in humans Think about (Ch 9, p.2) 1. Blood transports various substances and distributes heat around the body. It also plays a role in body defence. 2. Blood is a liquid tissue
Ch 9 Transport of substances in humans Think about (Ch 9, p.2) 1. Blood transports various substances and distributes heat around the body. It also plays a role in body defence. 2. Blood is a liquid tissue
The ancient Babylonians, Egyptians, Indians and Chinese believed the heart was the centre of thinking and emotions
 The Concept of Mind The ancient Babylonians, Egyptians, Indians and Chinese believed the heart was the centre of thinking and emotions Hippocrates 460 BC 370 BC - Thoughts, ideas, and feelings come from
The Concept of Mind The ancient Babylonians, Egyptians, Indians and Chinese believed the heart was the centre of thinking and emotions Hippocrates 460 BC 370 BC - Thoughts, ideas, and feelings come from
37 1 The Circulatory System
 H T H E E A R T 37 1 The Circulatory System The circulatory system and respiratory system work together to supply cells with the nutrients and oxygen they need to stay alive. a) The respiratory system:
H T H E E A R T 37 1 The Circulatory System The circulatory system and respiratory system work together to supply cells with the nutrients and oxygen they need to stay alive. a) The respiratory system:
Figure ) The specific chamber of the heart that is indicated by letter A is called the. Diff: 1 Page Ref: 364
 Essentials of Anatomy and Physiology, 9e (Marieb) Chapter 11 The Cardiovascular System Short Answer Figure 11.1 Using Figure 11.1, identify the following: 1) The Purkinje fibers are indicated by label.
Essentials of Anatomy and Physiology, 9e (Marieb) Chapter 11 The Cardiovascular System Short Answer Figure 11.1 Using Figure 11.1, identify the following: 1) The Purkinje fibers are indicated by label.
The Cardiovascular System: Vessels and Routes. Pulmonary Circulation H E A R T. Systemic Circulation
 The Cardiovascular System: Vessels and Routes 1. Overview of Blood Circulation A. Pulmonary Circulation Lung Arterioles Pulmonary Artery Capillaries Pulmonary Circulation Venules Pulmonary Veins H E A
The Cardiovascular System: Vessels and Routes 1. Overview of Blood Circulation A. Pulmonary Circulation Lung Arterioles Pulmonary Artery Capillaries Pulmonary Circulation Venules Pulmonary Veins H E A
Cardiovascular System
 Cardiovascular System Purpose Transport oxygen and nutrients Take waste products away from tissues & organs Things we learned Blood pressure: the force of blood pushing against the walls of blood vessels
Cardiovascular System Purpose Transport oxygen and nutrients Take waste products away from tissues & organs Things we learned Blood pressure: the force of blood pushing against the walls of blood vessels
Simulations of pulsatile blood flow in tapered S-shaped inplane and out-of-plane coronary arteries
 Simulations of pulsatile blood flow in tapered S-shaped inplane and out-of-plane coronary arteries Author Johnston, Barbara, Johnston, Peter Published 2009 Conference Title 18th IMACS World Congress MODSIM09
Simulations of pulsatile blood flow in tapered S-shaped inplane and out-of-plane coronary arteries Author Johnston, Barbara, Johnston, Peter Published 2009 Conference Title 18th IMACS World Congress MODSIM09
Rela=onship Between Proximal Pressure and Flow
 Parameters of Vascular Function Model 1: Relationships between Pressure and Flow in a Single Vessel The following data were collected by perfusing individual arterioles and measuring the relationship between
Parameters of Vascular Function Model 1: Relationships between Pressure and Flow in a Single Vessel The following data were collected by perfusing individual arterioles and measuring the relationship between
2. capillaries - allow exchange of materials between blood and tissue fluid
 Chapter 19 - Vascular System A. categories and general functions: 1. arteries - carry blood away from heart 2. capillaries - allow exchange of materials between blood and tissue fluid 3. veins - return
Chapter 19 - Vascular System A. categories and general functions: 1. arteries - carry blood away from heart 2. capillaries - allow exchange of materials between blood and tissue fluid 3. veins - return
Mr. Epithelium s Anatomy and Physiology Test SSSS
 Mr. Epithelium s Anatomy and Physiology Test SSSS You have 50 minutes to complete this test packet. One 8.5 x 11 cheat sheet is allowed, along with 1 non-programmable calculator dedicated to computation.
Mr. Epithelium s Anatomy and Physiology Test SSSS You have 50 minutes to complete this test packet. One 8.5 x 11 cheat sheet is allowed, along with 1 non-programmable calculator dedicated to computation.
PHYSIOLOGICAL PULSATILE WAVEFORM THROUGH AXISYMMETRIC STENOSED ARTERIES: NUMERICAL SIMULATION
 PHYSIOLOGICAL PULSATILE WAVEFORM THROUGH AXISYMMETRIC STENOSED ARTERIES: NUMERICAL SIMULATION Jayme Pinto Ortiz University of São Paulo - Avenida Prof. Luciano Gualberto, travessa3 nº 380 - CEP - 05508-900
PHYSIOLOGICAL PULSATILE WAVEFORM THROUGH AXISYMMETRIC STENOSED ARTERIES: NUMERICAL SIMULATION Jayme Pinto Ortiz University of São Paulo - Avenida Prof. Luciano Gualberto, travessa3 nº 380 - CEP - 05508-900
2. What makes up the most of your blood? least of your blood? 1. Look like red discs, have a pale center, no nucleus, similar in size
 I Can Statements I can identify the major components of blood and where they are formed. Identify the four components of blood in the diagram below. 1. Label each section of the pie chart with the correct
I Can Statements I can identify the major components of blood and where they are formed. Identify the four components of blood in the diagram below. 1. Label each section of the pie chart with the correct
Georgios C. Bompotis Cardiologist, Director of Cardiological Department, Papageorgiou Hospital,
 Georgios C. Bompotis Cardiologist, Director of Cardiological Department, Papageorgiou Hospital, Disclosure Statement of Financial Interest I, Georgios Bompotis DO NOT have a financial interest/arrangement
Georgios C. Bompotis Cardiologist, Director of Cardiological Department, Papageorgiou Hospital, Disclosure Statement of Financial Interest I, Georgios Bompotis DO NOT have a financial interest/arrangement
Heart and Lung Dissection
 Heart and Lung Dissection Name(s) Before you begin any work or dissection of your specimen, please try to identify the following. You will need to illustrate what you see, so make sure to note size, texture
Heart and Lung Dissection Name(s) Before you begin any work or dissection of your specimen, please try to identify the following. You will need to illustrate what you see, so make sure to note size, texture
NROSCI/BIOSC 1070 and MSNBIO Cardiovascular 1&2. August 28 & 30, 2017
 NROSCI/BIOSC 1070 and MSNBIO 2070 Cardiovascular 1-2 August 28 & 30, 2017 We, as multicellular organisms, cannot depend on diffusion alone to bring critical substances to our cells and to eliminate wastes.
NROSCI/BIOSC 1070 and MSNBIO 2070 Cardiovascular 1-2 August 28 & 30, 2017 We, as multicellular organisms, cannot depend on diffusion alone to bring critical substances to our cells and to eliminate wastes.
AN ATOMY OF THE CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM
 Student Name CHAPTER 18 AN ATOMY OF THE CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM T he heart is actually two pumps one moves blood to the lungs, the other pushes it out into the body. These two functions seem rather elementary
Student Name CHAPTER 18 AN ATOMY OF THE CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM T he heart is actually two pumps one moves blood to the lungs, the other pushes it out into the body. These two functions seem rather elementary
The Cardiac Cycle Clive M. Baumgarten, Ph.D.
 The Cardiac Cycle Clive M. Baumgarten, Ph.D. OBJECTIVES: 1. Describe periods comprising cardiac cycle and events within each period 2. Describe the temporal relationships between pressure, blood flow,
The Cardiac Cycle Clive M. Baumgarten, Ph.D. OBJECTIVES: 1. Describe periods comprising cardiac cycle and events within each period 2. Describe the temporal relationships between pressure, blood flow,
Chapter 05 Cardiovascular System
 Chapter 05 Cardiovascular System 1 Cardiovascular System: Heart and Blood Vessels 2 Points to ponder What are the functions of the cardiovascular system? What is the anatomy of the heart? Of blood vessels,
Chapter 05 Cardiovascular System 1 Cardiovascular System: Heart and Blood Vessels 2 Points to ponder What are the functions of the cardiovascular system? What is the anatomy of the heart? Of blood vessels,
Circulation.notebook March 07, Maintaining Dynamic Equilibrium. Oct 11 3:27 PM. Circulatory System p
 Unit 3 Maintaining Dynamic Equilibrium Circulatory system The heart Blood Blood Pressure Circulatory Disorders Oct 11 3:27 PM Circulatory System p.304 307 If an organism is small and flat it can transport
Unit 3 Maintaining Dynamic Equilibrium Circulatory system The heart Blood Blood Pressure Circulatory Disorders Oct 11 3:27 PM Circulatory System p.304 307 If an organism is small and flat it can transport
