Clinical and laboratory findings in a series of cases of infective endocarditis
|
|
|
- Winfred Little
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 /03/79-05/423 Jornal de Pediatria Copyright 2003 by Sociedade Brasileira de Pediatria Jornal de Pediatria - Vol. 79, Nº5, ORIGINAL ARTICLE Clinical and laboratory findings in a series of cases of infective endocarditis Carla A.Z. Pereira, 1 Scheila C.G.P. Rocio, 1 Maria-Fátima R. Ceolin, 2 Ana-Paula N.B. Lima, 2 Felippe Borlot, 3 Roberto S.T. Pereira, 4 Sandra F. Moreira-Silva 5 Abstract Objective: To describe clinical and laboratory data of infective endocarditis (IE) in 28 children from Vitória, state of Espírito Santo, Brazil. Methods: We reviewed the medical records of 28 children aged 18 years and under admitted to the Infectious Diseases Unit of Nossa Senhora da Glória Children s Hospital with a diagnosis of IE from January 1993 to December The diagnosis of IE was based on the criteria established by the Duke Endocarditis Service (Duke University, Durham, North Carolina, USA): positive blood cultures and echocardiogram (primary criteria); and fever, history of heart disease, recent heart murmur, and vascular and immunological phenomena (secondary criteria). A specific protocol was filled out by interns and medical students and revised by physicians from the hospital medical team to obtain the following data: age, sex, clinical and laboratory findings, and results of transthoracic echocardiography. In all cases, three blood samples were collected under aseptic conditions and inoculated in aerobic and anaerobic environments. The samples were then incubated at 37º C and tested with the Vitec System automatized system (Biolab). Results: Among 28 patients, 16 were boys. Age was between 3 and 180 months (mean 70.6±59.2 months). Most children (68%) came from the metropolitan area of Vitória, and half presented a history of cardiopathy. The most frequent clinical findings which led to suspicion of IE were: prolonged fever in all cases, new or changing regurgitant murmur (67.9%), dyspnea (57.1%), hepatomegaly (57.1%), vascular phenomena (32.2%), splenomegaly (28.6%), and Osler s nodes (7.1%). Blood cultures were positive in 16 patients (57.1%), and community-acquired S. aureus was the most frequently isolated pathogen (56.6%). Despite the treatment, fever persisted for 2.5 to 30 days (median = 18.0 days). Mean leukocyte count at admission was 11,657±7,085mm 3. Transthoracic echocardiography showed endocardial lesion in all patients, evidencing vegetations in the tricuspid valve (25%), mitral valve (25%), and intraventricular communication border (28%). Thirteen (46.4%) children presented concomitant sepsis and three (10.7%) developed hospital-acquired infection. There was one death (3.6%). Conclusions: IE in our country is frequent among children younger than 2 years with congenital cardiopathy. Community-acquired S. aureus was the most frequently isolated microorganism in children with no previous cardiac lesion. J Pediatr (Rio J) 2003;79(5):423-8: Overweight, obesity, prevalence. 1. Resident physician, Hospital Infantil Nossa Senhora da Glória, Vitória, ES. 2. MD, Infectious Diseases Service, Hospital Infantil Nossa Senhora da Glória, Vitória, ES. 3. Medical student, Escola Superior de Ciências da Santa Casa de Misericórdia, Vitória, ES. 4. MD, Chief, Pediatric Heart Disease Service, Hospital Infantil Nossa Senhora da Glória, Vitória, ES. 5. Master s Degree. Coordinator, Medical Residence Program in Pediatric Infectious Diseases, Hospital Infantil Nossa Senhora da Glória, Vitória, ES. Manuscript received Oct , accepted for publication Jul
2 424 Jornal de Pediatria - Vol. 79, Nº5, 2003 Infective endocarditis in children Pereira CAZ et alii Introduction Infective endocarditis is defined as an inflammatory process of the endocardium of a valve or chamber, on a septal defect, or the chordae tendineae, as a result of an infection by bacteria, virus, fungus or mycobacteria and rickettsias, which in the majority of cases occurs in people with pre-existing abnormalities of the cardiovascular system. 1,2 It is responsible for around 0.2 to 0.5% of all pediatric hospital admissions and is a significant cause of mortality (20-64%) among children and adolescents despite advances in treatment and prophylaxis with antimicrobial agents. A number of different factors affect prognosis, clinical parameters, the type of microorganism involved and the presence of a prosthetic heart valve. 2-4 In the absence of a previous cardiac lesion the disease is considered rare in children. 5,6 In adults it is common among intravenous drug users and people more than fifty years old. 4 In children a growing increase in the number of cases have been reported, principally in newborns and young infants, with a concomitant change in the bacterial profile. The prevalence of Staphylococcus aureus and other bacteria which were previously less often identified with Infective endocarditis. 4,6 In these patients, endocarditis is acute and generally associated with congenital cardiac defects. Cases of classic subacute endocarditis, caused by Streptococcus viridans have reduced due to the reduction in the prevalence of rheumatic fever and its cardiac sequelae. In addition to the reduction in the number of rheumatic fever cases, improvements to the care of high risk newborns, an increase in invasive procedures and early surgical interventions in congenital cardiopathies have contributed to an increase in the number of patients in this age group exposed to the risk of Infective endocarditis. 2,4 Although the disease is uncommon, it is serious and is considered a significant cause of morbidity and mortality in children and therapeutic success depends upon early and precise diagnosis. Despite authors having described a number of different diagnosis criteria based on clinical and pathological parameters, the criteria currently most accepted are the Duke criteria which include echocardiographic examination parameters 7,8 (Table 1). The value of this examination has been questioned, but its validity has been confirmed if a bidimensional color Doppler echocardiogram is used and the cardiologist has experience in interpreting the results. With the publication of new Infective endocarditis diagnosis criteria by the Endocarditis Service at Duke University, it is now considered that the two main criteria for certain diagnosis of Infective endocarditis are multiple positive blood cultures for typical germs and echocardiogram evidence of myocardial lesions and/or vegetation growth on heart valves, intramyocardial abscesses, or recent partial decomposition of a prosthetic valve. 7,8 Table 1 - Duke criteria for the diagnosis of infective endocarditis 4,7 Major criteria Positive blood culture for IE Typical microorganism for IE from two isolated blood cultures: Streptococcus viridans, Streptococcus bovis, HACEK group or Staphylococcus aureus and Enterococcus sp acquired in the community without primary focus Persistent positive blood cultures Evidence of endocardiac lesion, positive echocardiogram for IE New regurgitant murmur Minor criteria Predisposition: previous heart lesion Fever higher than 38 ºC Vascular phenomena (eg.: Janeway s lesions) Immunologic phenomena (eg.: Osler s nodes) Suggestive microbiologic findings: positive blood culture, without major criteria Echocardiogram: consistent with IE, without major criteria HACEKgroup = Haemophilus sp; Actinobacillus actinomycetem comitans; Cardiobacterium hominis; Eikenella corrodens; Kingella kingae. The use of echocardiography in adults has confirmed its utility, especially the transesophageal echocardiogram, since this offers greatly amplified image observation fields. In children, the transesophageal echocardiography examination has limited uses for which reason the transthoracic echocardiogram examination is routinely used. 2,9,10 As Infective endocarditis in children is a heterogeneous entity, its management also requires careful criteria based on laboratory and clinical evidence in addition to the echocardiographic criteria. 11,12 As studies of transthoracic echocardiogram in Infective endocarditis of children have reported variable results in terms of diagnostic sensitivity, we propose to describe a series of 28 cases of Infective endocarditis treated at the Nossa Senhora da Glória Children s Hospital, in Vitória-ES, with emphasis on clinical and laboratory findings and transthoracic echocardiogram examinations, in order to verify the characteristics of the disease in our locale. Patients and Methods All children, under eighteen, diagnosed with Infective endocarditis, and interned at the Infectious Diseases Service at the Nossa Senhora da Glória Children s Hospital, Vitória - Espírito Santo, during the period between January 1993
3 Infective endocarditis in children Pereira CAZ et alii and December 2001 were included. The criteria for a diagnosis of Infective endocarditis were those published by the Duke Endocarditis Service (Duke University, Durham, North Carolina - USA), 7 in which one of the main diagnosis parameters is the demonstration of echocardiographic evidence of a myocardial lesion and/or vegetation on heart valves, intramyocardial abscesses or recent partial decomposition of a prosthetic valve. The Nossa Senhora da Glória Children s Hospital is a public hospital, part of the Espirito Santo state network where its Pediatric Infectious Diseases and Cardiology Services are centers of excellence, also caring for patients from the south of the state of Bahia and the east of the state of Minas Gerais. Using a specialized pro forma, filled out by the resident doctors and academics at the Infectious Diseases Service, and revised by the team doctors, sex, clinical and laboratory findings and the results from transthoracic echocardiography were recorded for each of the 28 children who fulfilled the clinical and laboratory criteria for a diagnosis of Infective endocarditis. All of the laboratory examinations were performed at the routine hospital laboratory. In all cases blood cultures were carried by collecting blood (three samples) under aseptic conditions and were inoculated in aerobic and anaerobic media, incubated at a temperature of 37 ºC and tested with an automated system - Vitec System (Biolab). The study was submitted to and approved by the Committee for Ethics and research at the Nossa Senhora da Glória Children s Hospital. Jornal de Pediatria - Vol. 79, Nº5, (28.6%) and small, painful intradermal nodes on the pads of the fingers (Osler nodes, 7.1%). Blood cultures were positive in 16 (57.1%) of the 28 cases. Community acquired Staphylococcus aureus was the most frequently isolated germ (9/ %). There was a statistically significant difference in the frequency of the different types of germ isolated from children older or younger than 24 months: Staphylococcus aureus was found in the eight cases which involved children older than 24 months, without previous cardiac lesions, and in only one of the cases involving children younger than 24 months. The other seven children with positive blood culture results were all younger than 24 months old and the microorganisms isolated from them were: Streptococcus viridans in two cases (12.5%), Enterobacter sp in four cases (25.5%) and Candida tropicalis in one case (6.2%). There was persistent fever, despite antimicrobial treatment, lasting between 2.5 and 30 days, with a median of 18.0 days. On admission leukogram had a wide variety of values for total number of leukocytes (average value of 11,657+7,085 mm 3 ), but with obvious predominance of young neutrophils in all cases if the average values were compared on admission and discharge (p < 0.000) (Table 3). Transthoracic echocardiogram showed endocardiac vegetation in all cases, especially in the tricuspid (25.0%) and mitral (25.0%) valves and at the limits of intraventricular communication (28.6%) (Figure 1). Thirteen (46.4%) children presented concomitant sepsis and three (10.7%) developed nosocomial infections. There was one death (3.6% of cases). Statistical analysis Statistical analysis was performed using the SPSS- CDC Inc for Windows software program (Statistical Package for the Social Sciences of Centers Diseases Control - USA. Release ). Averages were compared using the paired t test or with the Wilcoxon test. Proportions were compared with the Yates corrected Chi-square test, or with Fisher s exact test. Results Data on age, sex, clinical and bacteriological characteristics and the principal echocardiogram findings are shown in Table 2. The previous cardiopathies observed were 12 congenital cardiopathies (85.7%) and two rheumatic cardiopathies (14.3%). The most clinical findings which most often led to a suspicion of Infective endocarditis, and so resulted in the echocardiogram, were: prolonged fever (100%), heart murmur (67.9%), dyspnea (57.1%), hepatomegaly (57.1%), vascular phenomena (32.2%), including small erythematous lesions or painless hemorrhaging on the palms of the hands or soles of the feet (Janeway lesions), splenomegaly Discussion A number of Pediatric Cardiology Units have reported the observation that cases of endocarditis infectious are increasing, primarily among children under two years old, mainly due to the increase in survival rates among children who have had surgery for cardiopathies resulting from the improved care afforded by intensive care units. 4,6 Taking into account the fact that in pediatrics Infective endocarditis is a heterogeneous entity, we must look at all possible criteria, from laboratory findings, echocardiographic and all criteria already described as defining clinical criteria of the disease, 5,7,11 summing up all possible effort in an attempt to achieve a definite diagnosis with urgency, permitting early and adequate treatment, thus reducing the mortality of children with endocarditis. Recent publications demonstrate a significant change in pediatric Infective endocarditis, alterations in prevalence, age distribution and the microorganisms involved as causative agents. 3,4,6 Our results, similar to results reported in literature, demonstrate a changing Infective endocarditis epidemiological profile in our locale too. Fifty percent of cases occurred in newborns and infants, and Staphylococcus aureus was frequently isolated from positive blood cultures. Although blood cultures were only positive in 57.1% of
4 426 Jornal de Pediatria - Vol. 79, Nº5, 2003 Infective endocarditis in children Pereira CAZ et alii Table 2 - Main demographic, clinical, echocardiographic and laboratorial data of 28 cases of infective endocarditis, at HINSG, from 1993 to 2001 Case Age Sex Previous heart Sepsis Murmur Petechiae Hepatomegaly Microorganism Vegetations Evolution (months) disease 1 6 F + C. Cong. + + Entero IVC border discharge 2 41 F + + Staphilo RV end. discharge F + + Staphilo Mitral discharge 4 5 F + C. Cong. + Strepto IVC border discharge 5 6 F + + Entero LV end. discharge 6 5 M + C. Cong. + + Staphilo IVC border discharge F Staphilo Tricuspid discharge M Staphilo Lung discharge F Negative Mitral discharge M + C. Cong Entero IVC border discharge 11 3 M + Entero Tricuspid discharge 12 8 M + C. Cong C.tropic. IVC border discharge M + Negative Mitral discharge M + C. Cong. + Negative Lung discharge M Strepto Mitral discharge M + + Negative Tricúspide discharge M + C. Reum. + + Negative Mitral discharge M Staphilo Mitral discharge M + Staphilo Tricuspid discharge M + C. Cong. + + Staphilo Tricuspid discharge F + + Staphilo RV end. discharge M + Negative Tricuspid discharge F + C. Cong. + Negative IVC border discharge F + C. Reum. + + Negative Mitral discharge M + C. Cong. + Negative IVC border discharge F + C. Cong Negative Tricuspid discharge 27 3 F + C. Cong. + + Negative Lung death M + C. Cong. + Negative IVC border discharge End = endocardium, + present, absent % END = endocardium, IVC = intraventricular communication. Figure Mitral LV End. Tricuspid Limit of IVC Pulmonary RV End. < 24 months > 24 months Location of the lesions observed on the echocardiogram in 28 cases of infective endocarditis cases, the results reinforce the idea of the elevated prevalence of S. aureus as the etiologic agent in acute Infective endocarditis in our environment. In contrast we do not have an adequate explanation for the low frequency of positive blood in this series of cases, bearing in mind that blood samples were collected in a an apparently adequate manner. It is possible that previous antibiotic use is the main factor as many patients arrive at the Children s Hospital having been transferred from other Health Units. The role of transthoracic echocardiograms as a means of diagnosis for children with a clinical suspicion of Infective endocarditis remains controversial and is the cause of disagreement between a number of authors. 5,7,8,11 Some authors consider the method to be of too low a sensitivity to be a method for diagnosing EI in patients with few of the clinical criteria of the disease, 9,12 however others believe
5 Infective endocarditis in children Pereira CAZ et alii Jornal de Pediatria - Vol. 79, Nº5, Table 3 - Comparison of hemoglobin, leukocytes and neutrophils values in rods of 28 cases of infective endocarditis on admission and discharge, HINSG, Statistics Hemoglobin Leukocytes No. of rods Admission Discharge Admission Discharge Admission Discharge Mean ,657 8, Median ,550 9, Standard deviation ,085 2, Range Minimum value , Maximum value ,000 15, p 0.861* 0.192* * paired test Wilcoxon s test (variable without normal distribution). that the use of echocardiography in the evaluation of children with a clinical suspicion of endocarditis has ample applications, primarily because in pediatrics, the transthoracic echo offers an excellent field. 4,11 In the present study characteristic alterations to the results from this examination were one of the inclusion criteria. Nevertheless it is important to remember that cases in which the transthoracic echocardiogram was negative and which did not meet the criteria for a diagnosis of Infective endocarditis could still have had lesions from Infective endocarditis, without obvious evidence, and were treated as sepsis and excluded from the Infective endocarditis group. The microbiology of Infective endocarditis in children has changed considerably as is reported by a number of authors, with a decrease in the number of cases due to infections by Streptococcus viridans and the appearance of new etiological agents which were uncommon in past decades. An important factor in this change is the increased survival rate of children with congenital cardiopathies, and another is the increased incidence of staphylococcal infections. 6,11,12 We too observed this fact and our results demonstrate that Infective endocarditis was frequent among children less than two years old and those with congenital cardiopathies. They also demonstrate that community acquired Staphylococcus aureus was frequently isolated as an infecting microorganism in children with no previous cardiac lesions. Acknowledgements Thanks to Dr. Alba Lília de Almeida Leite, pediatrician at the Infectious Diseases Service at the Nossa Senhora da Glória Children s Hospital, for help with monitoring cases and to Dr. Fausto Edmundo Lima Pereira, Professor and Doctor at the Infectious Diseases Center at the Universidade Federal do Espírito Santo, for help in the final revision of the text and for continuous support for research and scientific production. Thanks also to the staff at the Medical Records Storage Service at HINSG, for their dedication. References 1. Estlow MM. Prevention of infective endocarditis in the pediatric congenital heart population. J Pediatr Nurs 1998;24: Karchmer AW. Endocardite infecciosa. In: Braunwald E, editor. Tratado de Medicina Cardiovascular. 5th ed. São Paulo: Roca; p Mansur AJ, Grinberg M, Cardoso RHA, da Luz PL, Bellotti G, Pileggi F. Determinants of prognosis in 300 episodes of infective endocarditis. Thorac Cardiovasc Surg 1996;44: Foronda A, Foronda G, Camargo LFA. Endocardite Infecciosa. In: Ebaid M, editor. Cardiologia em Pediatria. 1st ed. São Paulo: Roca; p Sable CA, Rome JJ, Martin GR, Patel KM, Karr SS. Indications for echocardiography in the diagnosis of infective endocarditis in children. Am J Cardiol 1995;75: Ashkenazi S, Levy O, Blieden L. Trends of childhood infective endocarditis in Israel with emphasis on children under 2 years of age. Pediatr Cardiol 1997;18: Durack DT, Lukes AS, Bright DK. New criteria for diagnosis of infective endocarditis: utilization of specific echocardiographic findings. Duke Endocarditis Service. Am J Med 1994;96: Bayer AS, Bolger AF, Taubert KA, Wilson W, Steckelberg J, Karchmer AW, et al. Diagnosis and management of infective endocarditis and its complications. Circulation 1998;98: Aly AM, Simpson PM, Humes RA. The role of transthoracic echocardiography in the diagnosis of infective endocarditis in children. Arch Pediatr Adolesc Med 1999;153:950-4.
6 428 Jornal de Pediatria - Vol. 79, Nº5, Barreto J, Waderlinder J, Reitich J. Hallarzgos ecocardiográficos y de laboratorio en pacientes pediátricos con endocarditis infecciosa. Bol Hosp Ninos J M de los Rios 1998;34: Li JS, Milazzo-Jr AS. Bacterial endocarditis in infants and children. Clin Infect Dis 2000;30: Heper G, Yorukoglu Y. Clinical, bacteriologic and echocardiographic evaluation of infective endocarditis in Ankara, Turkey. Angiology 2002;53: Infective endocarditis in children Pereira CAZ et alii Corresponding author: Sandra F. Moreira-Silva Rua Natalina Daher Carneiro, 55/302 - Jardim da Penha CEP Vitória, ES, Brazil Tel.: +55 (27) Fax: +55 (27) / sanfag@zaz.com.br
Michael Stander, Pharm.D.
 Michael Stander, Pharm.D. Endocarditis: Goals Epidemiology Presentation of acute and subacute. Diagnosis: What is Dukes Criteria and how do we approach the diagnosis of endocarditis? Treatment: Understand
Michael Stander, Pharm.D. Endocarditis: Goals Epidemiology Presentation of acute and subacute. Diagnosis: What is Dukes Criteria and how do we approach the diagnosis of endocarditis? Treatment: Understand
Heart on Fire: Infective Endocarditis. Objectives. Disclosure 8/27/2018. Mary McGreal DNP, RN, ANP-c, CCRN
 Heart on Fire: Infective Endocarditis Mary McGreal DNP, RN, ANP-c, CCRN Objectives Discuss the incidence of infective endocarditis? Discuss the pathogenesis of infective endocarditis? Discuss clinical
Heart on Fire: Infective Endocarditis Mary McGreal DNP, RN, ANP-c, CCRN Objectives Discuss the incidence of infective endocarditis? Discuss the pathogenesis of infective endocarditis? Discuss clinical
INFECTIOUS endocarditis (IE) is a
 ORIGINAL INVESTIGATION Diagnosis of Infective Endocarditis Sensitivity of the Duke vs von Reyn Criteria Maija Heiro, MD; Jukka Nikoskelainen, MD, PhD; Jaakko J. Hartiala, MD, PhD; Markku K. Saraste, MD;
ORIGINAL INVESTIGATION Diagnosis of Infective Endocarditis Sensitivity of the Duke vs von Reyn Criteria Maija Heiro, MD; Jukka Nikoskelainen, MD, PhD; Jaakko J. Hartiala, MD, PhD; Markku K. Saraste, MD;
April 16, 09:00-09:15 중앙대학교 윤신원
 April 16, 09:00-09:15 중앙대학교 윤신원 When to perform Echocardiography in IE? Vegetations?(pathologic Whatever the level hallmark) of suspicion Intracardiac abscess? Confirm or R/O at the Earliest opportunity.
April 16, 09:00-09:15 중앙대학교 윤신원 When to perform Echocardiography in IE? Vegetations?(pathologic Whatever the level hallmark) of suspicion Intracardiac abscess? Confirm or R/O at the Earliest opportunity.
Infective Endocarditis
 Infective Endocarditis Definition Historical perspective Classification Epidemiological Features Etiology Pathogenesis Clinical presentation Diagnosis Treatment options Prevention Infective endocarditis
Infective Endocarditis Definition Historical perspective Classification Epidemiological Features Etiology Pathogenesis Clinical presentation Diagnosis Treatment options Prevention Infective endocarditis
Challenging clinical situation
 Challenging clinical situation A young patient with prosthetic aortic valve endocarditis Gilbert Habib La Timone Hospital Marseille - France October 25 th 2014 Case report History of the disease Clinical
Challenging clinical situation A young patient with prosthetic aortic valve endocarditis Gilbert Habib La Timone Hospital Marseille - France October 25 th 2014 Case report History of the disease Clinical
Infective endocarditis (IE) By Assis. Prof. Nader Alaridah MD, PhD
 Infective endocarditis (IE) By Assis. Prof. Nader Alaridah MD, PhD Infective endocarditis (IE) is an inflammation of the endocardium.. inner of the heart muscle & the epithelial lining of heart valves.
Infective endocarditis (IE) By Assis. Prof. Nader Alaridah MD, PhD Infective endocarditis (IE) is an inflammation of the endocardium.. inner of the heart muscle & the epithelial lining of heart valves.
Daniel C. DeSimone, MD Assistant Professor of Medicine
 Daniel C. DeSimone, MD Assistant Professor of Medicine Faculty photo will be placed here Desimone.Daniel@mayo.edu 2015 MFMER 3543652-1 Infective Endocarditis Mayo School of Continuous Professional Development
Daniel C. DeSimone, MD Assistant Professor of Medicine Faculty photo will be placed here Desimone.Daniel@mayo.edu 2015 MFMER 3543652-1 Infective Endocarditis Mayo School of Continuous Professional Development
Bacterial Endocarditis
 Objectives Bacterial Endocarditis John C. Rotschafer, Pharm. D. Professor College of Pharmacy University of Minnesota Identify which valves are commonly involved with endocarditis Identify common pathogens
Objectives Bacterial Endocarditis John C. Rotschafer, Pharm. D. Professor College of Pharmacy University of Minnesota Identify which valves are commonly involved with endocarditis Identify common pathogens
Endocarditis, including Prophylaxis
 Endocarditis, including Prophylaxis ACOI Board Review 2018 gerald.blackburn@beaumont.org (No Disclosures) Infective Endocarditis Persistant bacteremia (blood cultures drawn >12 hrs apart) w/ organisms
Endocarditis, including Prophylaxis ACOI Board Review 2018 gerald.blackburn@beaumont.org (No Disclosures) Infective Endocarditis Persistant bacteremia (blood cultures drawn >12 hrs apart) w/ organisms
Infective Endocarditis
 Infective Endocarditis Infective Endocarditis Historical Perspective.. A concretion larger than a pigeon s egg; contained in the left auricle. Burns, 1809 Osler s Gulstonian lectures provided the 1 st
Infective Endocarditis Infective Endocarditis Historical Perspective.. A concretion larger than a pigeon s egg; contained in the left auricle. Burns, 1809 Osler s Gulstonian lectures provided the 1 st
NATIONAL HEART FOUNDATION HOSPITAL & RESEARCH INSTITUTE
 Welcome INFECTIVE ENDOCARDITIS: WHERE WE ARE AT 2005? DR MD HABIBUR RAHMAN FCPS(Medicine) NATIONAL HEART FOUNDATION HOSPITAL & RESEARCH INSTITUTE DEFINITION OF INFECTIVE ENDOCARDITIS Infective endocarditis
Welcome INFECTIVE ENDOCARDITIS: WHERE WE ARE AT 2005? DR MD HABIBUR RAHMAN FCPS(Medicine) NATIONAL HEART FOUNDATION HOSPITAL & RESEARCH INSTITUTE DEFINITION OF INFECTIVE ENDOCARDITIS Infective endocarditis
Infective Endocarditis
 Frank Lowy Infective Endocarditis 1. Introduction Infective endocarditis (IE) is an infection of the heart valves. A large number of different bacteria are capable of causing this disease. Depending on
Frank Lowy Infective Endocarditis 1. Introduction Infective endocarditis (IE) is an infection of the heart valves. A large number of different bacteria are capable of causing this disease. Depending on
VEGETATION NEGATIVE INFECTIVE ENDOCARDITIS A VIEW POINT... Mumbai Dec 2005 Annual scientific sessions
 VEGETATION NEGATIVE INFECTIVE ENDOCARDITIS A VIEW POINT... Mumbai Dec 2005 Annual scientific sessions S.Venkatesan,G.Gnanavelu,G.Karthikeyan,V.Jaganathan,R.Alagesan M.Annamalai,S.Shanmugasundaram, S.Geetha,A.Balaguru.G.Anuradha
VEGETATION NEGATIVE INFECTIVE ENDOCARDITIS A VIEW POINT... Mumbai Dec 2005 Annual scientific sessions S.Venkatesan,G.Gnanavelu,G.Karthikeyan,V.Jaganathan,R.Alagesan M.Annamalai,S.Shanmugasundaram, S.Geetha,A.Balaguru.G.Anuradha
Dr Babak Tamizi far MD. Assistant Professor Of Internal Medicine Al-Zahra Hospital Isfahan University Of Medical Sciences
 Dr Babak Tamizi far MD. Assistant Professor Of Internal Medicine Al-Zahra Hospital Isfahan University Of Medical Sciences ١ ٢ ٣ A 57-year-old man presents with new-onset fever, shortness of breath, lower
Dr Babak Tamizi far MD. Assistant Professor Of Internal Medicine Al-Zahra Hospital Isfahan University Of Medical Sciences ١ ٢ ٣ A 57-year-old man presents with new-onset fever, shortness of breath, lower
An assessment of the current diagnostic criteria for infective endocarditis
 REVIEW An assessment of the current diagnostic criteria for infective endocarditis Albert W Chan MD FRCPC, Heather J Ross MD FRCPC AW Chan, HJ Ross. An assessment of the current diagnostic criteria for
REVIEW An assessment of the current diagnostic criteria for infective endocarditis Albert W Chan MD FRCPC, Heather J Ross MD FRCPC AW Chan, HJ Ross. An assessment of the current diagnostic criteria for
Update on the prevention, diagnosis and management of Infective Endocarditis (IE)
 Update on the prevention, diagnosis and management of Infective Endocarditis (IE) Dr.Ahmed Yahya Mohammed Alarhabi MD, MsC,FcUSM,FACC,MAHA Consultant Interventional Cardiologist Head of Cardiac Center
Update on the prevention, diagnosis and management of Infective Endocarditis (IE) Dr.Ahmed Yahya Mohammed Alarhabi MD, MsC,FcUSM,FACC,MAHA Consultant Interventional Cardiologist Head of Cardiac Center
Pr AMEL OMEZZINE LETAIEF CHU FarhatHached Sousse
 Pr AMEL OMEZZINE LETAIEF CHU FarhatHached Sousse cours de collège infectiologie Sousse le27/02/2013 ENDOCARDITIS There is a change in epidemiology Clinical features of IE remains classical Diagnosis of
Pr AMEL OMEZZINE LETAIEF CHU FarhatHached Sousse cours de collège infectiologie Sousse le27/02/2013 ENDOCARDITIS There is a change in epidemiology Clinical features of IE remains classical Diagnosis of
Infective Endocarditis Empirical therapy Antibiotic Guidelines. Contents
 Infective Endocarditis Empirical therapy Antibiotic Guidelines Classification: Clinical Guideline Lead Author: Antibiotic Steering Group Additional author(s): as above Authors Division: Division of Clinical
Infective Endocarditis Empirical therapy Antibiotic Guidelines Classification: Clinical Guideline Lead Author: Antibiotic Steering Group Additional author(s): as above Authors Division: Division of Clinical
A Predictable Outcome of a Preventable Disease. Sanjay Kamboj, MD; Shaminder Gupta, MD; Glenn P. Kelley, MD; Fred Helmcke, MD; and Fred A.
 Clinical Case of the Month A Predictable Outcome of a Preventable Disease Sanjay Kamboj, MD; Shaminder Gupta, MD; Glenn P. Kelley, MD; Fred Helmcke, MD; and Fred A. Lopez, MD Infective endocarditis is
Clinical Case of the Month A Predictable Outcome of a Preventable Disease Sanjay Kamboj, MD; Shaminder Gupta, MD; Glenn P. Kelley, MD; Fred Helmcke, MD; and Fred A. Lopez, MD Infective endocarditis is
A Study of Infective Endocarditis in Malta
 Science Journal of Clinical Medicine 2017; 6(6): 98-104 http://www.sciencepublishinggroup.com/j/sjcm doi: 10.11648/j.sjcm.20170606.11 ISSN: 2327-2724 (Print); ISSN: 2327-2732 (Online) A Study of Infective
Science Journal of Clinical Medicine 2017; 6(6): 98-104 http://www.sciencepublishinggroup.com/j/sjcm doi: 10.11648/j.sjcm.20170606.11 ISSN: 2327-2724 (Print); ISSN: 2327-2732 (Online) A Study of Infective
Microbiological diagnosis of infective endocarditis; what is new?
 Microbiological diagnosis of infective endocarditis; what is new? Dr Amani El Kholy, MD Professor of Clinical Pathology (Microbiology), Faculty of Medicine, Cairo University ESC 2017 1 Objectives Lab Diagnostic
Microbiological diagnosis of infective endocarditis; what is new? Dr Amani El Kholy, MD Professor of Clinical Pathology (Microbiology), Faculty of Medicine, Cairo University ESC 2017 1 Objectives Lab Diagnostic
Infective Endocarditis for Primary Care Physicians
 Infective Endocarditis for Primary Care Physicians David N Gilbert, MD Disclosures Consultant to: Merck Pfizer Medicine Company Cempra 1 Introduction There are roughly 30,000 new cases of IE in the US
Infective Endocarditis for Primary Care Physicians David N Gilbert, MD Disclosures Consultant to: Merck Pfizer Medicine Company Cempra 1 Introduction There are roughly 30,000 new cases of IE in the US
Sepsis and Infective Endocarditis
 Sepsis and Infective Endocarditis Michal Holub Department of Infectious Diseases First Faculty of Medicine Charles University in Prague and University Military Hospital Bacteremia and Sepsis bacteremia
Sepsis and Infective Endocarditis Michal Holub Department of Infectious Diseases First Faculty of Medicine Charles University in Prague and University Military Hospital Bacteremia and Sepsis bacteremia
Infective endocarditis
 Infective endocarditis This is caused by microbial infection of a heart valve (native or prosthetic), the lining of a cardiac chamber or blood vessel, or a congenital anomaly (e.g. septal defect). The
Infective endocarditis This is caused by microbial infection of a heart valve (native or prosthetic), the lining of a cardiac chamber or blood vessel, or a congenital anomaly (e.g. septal defect). The
Diagnostic strategy. Dr Pilar Tornos Hospital Vall d Hebron Barcelona
 Diagnostic strategy Dr Pilar Tornos Hospital Vall d Hebron Barcelona Faculty disclosure Pilar Tornos I disclose the following financial relationships: Paid speaker for Recordati, Edwards. Diagnosis of
Diagnostic strategy Dr Pilar Tornos Hospital Vall d Hebron Barcelona Faculty disclosure Pilar Tornos I disclose the following financial relationships: Paid speaker for Recordati, Edwards. Diagnosis of
VALVULAR HEART DISEASE
 VALVULAR HEART DISEASE Stenosis: failure of a valve to open completely, obstructing forward flow. - almost always due to a chronic process (e.g., calcification or valve scarring). Insufficiency : failure
VALVULAR HEART DISEASE Stenosis: failure of a valve to open completely, obstructing forward flow. - almost always due to a chronic process (e.g., calcification or valve scarring). Insufficiency : failure
Echocardiography after stroke - where to look
 Echocardiography after stroke - where to look Vuyisile T. Nkomo, MD,MPH, FACC, FASE Joint Cardiac Imaging Society of South Africa/Mayo Clinic Echocardiography Workshop 2017 2016 MFMER slide-1 Disclosures
Echocardiography after stroke - where to look Vuyisile T. Nkomo, MD,MPH, FACC, FASE Joint Cardiac Imaging Society of South Africa/Mayo Clinic Echocardiography Workshop 2017 2016 MFMER slide-1 Disclosures
results in stenosis or insufficiency (regurgitation or incompetence), or both.
 results in stenosis or insufficiency (regurgitation or incompetence), or both. The outcome of valvular disease depends on : 1-the valve involved 2-the degree of impairment 3-the cause of its development
results in stenosis or insufficiency (regurgitation or incompetence), or both. The outcome of valvular disease depends on : 1-the valve involved 2-the degree of impairment 3-the cause of its development
Double Outlet Right Ventricle with Anterior and Left-Sided Aorta and Subpulmonary Ventricular Septal Defect
 Case Report Double Outlet Right Ventricle with Anterior and Left-Sided rta and Subpulmonary Ventricular Septal Defect Luciana Braz Peixoto, Samira Morhy Borges Leal, Carlos Eduardo Suaide Silva, Sandra
Case Report Double Outlet Right Ventricle with Anterior and Left-Sided rta and Subpulmonary Ventricular Septal Defect Luciana Braz Peixoto, Samira Morhy Borges Leal, Carlos Eduardo Suaide Silva, Sandra
Diagnosis and management of bacterial endocarditis in 2003 Blaithnead Murtagh, MD, O.H. Frazier, MD, and George V. Letsou, MD
 Diagnosis and management of bacterial endocarditis in 2003 Blaithnead Murtagh, MD, O.H. Frazier, MD, and George V. Letsou, MD The diagnosis of infective endocarditis has been notoriously difficult. Over
Diagnosis and management of bacterial endocarditis in 2003 Blaithnead Murtagh, MD, O.H. Frazier, MD, and George V. Letsou, MD The diagnosis of infective endocarditis has been notoriously difficult. Over
A study of clinical and etiological profile of infective endocarditis and its correlation with echocardiography in patients of rheumatic heart disease
 International Journal of Advances in Medicine Sarkar A et al. Int J Adv Med. 2017 Oct;4(5):1323-1327 http://www.ijmedicine.com pissn 2349-3925 eissn 2349-3933 Original Research Article DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18203/2349-3933.ijam20174177
International Journal of Advances in Medicine Sarkar A et al. Int J Adv Med. 2017 Oct;4(5):1323-1327 http://www.ijmedicine.com pissn 2349-3925 eissn 2349-3933 Original Research Article DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18203/2349-3933.ijam20174177
INFECTIVE ENDOCARDITIS IN CHILDREN
 INFECTIVE ENDOCARDITIS IN CHILDREN Rohayati Taib RIPAS Hospital, Bundar Seri Begawan, Brunei Darussalam Infective Endocarditis (IE) is a microbial infection of the endocardium. It encompasses both bacterial
INFECTIVE ENDOCARDITIS IN CHILDREN Rohayati Taib RIPAS Hospital, Bundar Seri Begawan, Brunei Darussalam Infective Endocarditis (IE) is a microbial infection of the endocardium. It encompasses both bacterial
Infective Endocarditis
 Chapter 32 Infective Endocarditis Lisa B. Hightow and Meera Kelley The term infective endocarditis (IE) refers to infection of the endocardial surface of the heart and implies a physical presence of microganisms
Chapter 32 Infective Endocarditis Lisa B. Hightow and Meera Kelley The term infective endocarditis (IE) refers to infection of the endocardial surface of the heart and implies a physical presence of microganisms
Joshua Budhu M.S, Dorian Wood B.S, Marvin Crawford M.D, Khuram Ashraf M.D, Frederick Doamekpor M.D, Olufunke Akinbobuyi M.D
 Accepted Manuscript Aerococcus Viridans Infectious Endocarditis Complicated by Splenic Infarction Joshua Budhu M.S, Dorian Wood B.S, Marvin Crawford M.D, Khuram Ashraf M.D, Frederick Doamekpor M.D, Olufunke
Accepted Manuscript Aerococcus Viridans Infectious Endocarditis Complicated by Splenic Infarction Joshua Budhu M.S, Dorian Wood B.S, Marvin Crawford M.D, Khuram Ashraf M.D, Frederick Doamekpor M.D, Olufunke
INFECTIVE ENDOCARDITIS AMONGST INTRAVENOUS DRUG ABUSERS SEEN AT THE UNIVERSITY HOSPITAL, KUALA LUMPUR
 Med. J. Malaysia Vol. 42 No. 4 December 1987 INFECTIVE ENDOCARDITIS AMONGST INTRAVENOUS DRUG ABUSERS SEEN AT THE UNIVERSITY HOSPITAL, KUALA LUMPUR R. JAYAMALAR MBBS, MRCP. "N. PARASAKTHI MBBS, MSc. "S.D.
Med. J. Malaysia Vol. 42 No. 4 December 1987 INFECTIVE ENDOCARDITIS AMONGST INTRAVENOUS DRUG ABUSERS SEEN AT THE UNIVERSITY HOSPITAL, KUALA LUMPUR R. JAYAMALAR MBBS, MRCP. "N. PARASAKTHI MBBS, MSc. "S.D.
PRINCIPLES OF ENDOCARDITIS
 015 // Endocarditis CONTENTS 140 Principles of Endocarditis 141 Native Valve Endocarditis 143 Complications of Native Valve Endocarditis 145 Right Heart Endocarditis 145 Prosthetic Valve Endocarditis 146
015 // Endocarditis CONTENTS 140 Principles of Endocarditis 141 Native Valve Endocarditis 143 Complications of Native Valve Endocarditis 145 Right Heart Endocarditis 145 Prosthetic Valve Endocarditis 146
WRITTEN BY: Thaer Al-qatish & Sarah Awaisheh
 WRITTEN BY: Thaer Al-qatish & Sarah Awaisheh Not all informations in the slides are included in this sheet so please study the slides. 3 kinds of Intracardiac infections: -endocarditis(inflammation of
WRITTEN BY: Thaer Al-qatish & Sarah Awaisheh Not all informations in the slides are included in this sheet so please study the slides. 3 kinds of Intracardiac infections: -endocarditis(inflammation of
Dysfunction of transcatheter mitral valve prosthesis. Early valve degeneration or thrombosis - that is the question.
 Dysfunction of transcatheter mitral valve prosthesis. Early valve degeneration or thrombosis - that is the question. Böhm A., Hricak V., Tomasovic B., Bena M., Postulka J. The National Institute of, Department
Dysfunction of transcatheter mitral valve prosthesis. Early valve degeneration or thrombosis - that is the question. Böhm A., Hricak V., Tomasovic B., Bena M., Postulka J. The National Institute of, Department
ARTICLE. The Role of Transthoracic Echocardiography in the Diagnosis of Infective Endocarditis in Children
 ARTICLE The Role of Transthoracic Echocardiography in the Diagnosis of Infective Endocarditis in Children Ashraf M. Aly, MD, PhD; Pippa M. Simpson, PhD; Richard A. Humes, MD Background: Infective endocarditis
ARTICLE The Role of Transthoracic Echocardiography in the Diagnosis of Infective Endocarditis in Children Ashraf M. Aly, MD, PhD; Pippa M. Simpson, PhD; Richard A. Humes, MD Background: Infective endocarditis
Infective Endocarditis:
 CME Workshop Infective Endocarditis: Prophylaxis, Diagnosis and Management Presented at a CME program, University of Manitoba, Winnipeg, Manitoba, December 2001. By Davinder S. Jassal, MD; and John M.
CME Workshop Infective Endocarditis: Prophylaxis, Diagnosis and Management Presented at a CME program, University of Manitoba, Winnipeg, Manitoba, December 2001. By Davinder S. Jassal, MD; and John M.
Overview. Clinical Scenario. Endocarditis: Treatment & Prevention. Prophylaxis The Concept. Jeremy D. Young, MD, MPH. Division of Infectious Diseases
 Endocarditis: Treatment & Prevention Jeremy D. Young, MD, MPH Division of Infectious Diseases Clinical Scenario Patient with MVP scheduled to have wisdom teeth extracted. Has systolic murmur with mid-systolic
Endocarditis: Treatment & Prevention Jeremy D. Young, MD, MPH Division of Infectious Diseases Clinical Scenario Patient with MVP scheduled to have wisdom teeth extracted. Has systolic murmur with mid-systolic
Case Report. Infective Endocarditis with Fistulized Mitral Aortic Pseudoaneurysm for Left Ventricle. Introduction. Case Report.
 Infective Endocarditis with Fistulized Mitral Aortic Pseudoaneurysm for Left Ventricle Noemi Rocio Andrade Alban 1, Marcos Merula de Almeida 1, Washington Luiz Batista da Costa 1, Mário Luiz Ribeiro 1,2,
Infective Endocarditis with Fistulized Mitral Aortic Pseudoaneurysm for Left Ventricle Noemi Rocio Andrade Alban 1, Marcos Merula de Almeida 1, Washington Luiz Batista da Costa 1, Mário Luiz Ribeiro 1,2,
Getting the Point of Injection Safety
 Getting the Point of Injection Safety Barbara Montana, MD, MPH, FACP Medical Director Communicable Disease Service Outbreak of Enterococcus faecalis endocarditis associated with an oral surgery practice
Getting the Point of Injection Safety Barbara Montana, MD, MPH, FACP Medical Director Communicable Disease Service Outbreak of Enterococcus faecalis endocarditis associated with an oral surgery practice
Prognostic factors in infective endocarditis
 Boston University OpenBU Theses & Dissertations http://open.bu.edu Boston University Theses & Dissertations 2016 Prognostic factors in infective endocarditis Grzybinski, Sarah https://hdl.handle.net/2144/19176
Boston University OpenBU Theses & Dissertations http://open.bu.edu Boston University Theses & Dissertations 2016 Prognostic factors in infective endocarditis Grzybinski, Sarah https://hdl.handle.net/2144/19176
Suggested Reading: Pages Donald P. Levine, M.D. Professor of Medicine Page 1 of 8
 Professor of Medicine Page 1 of 8 ENDOCARDITIS I. General A. infectivie endocarditis (IE) 1. definition: infection of the endocardial surface of the heart; implies the physical presence of microorganisms
Professor of Medicine Page 1 of 8 ENDOCARDITIS I. General A. infectivie endocarditis (IE) 1. definition: infection of the endocardial surface of the heart; implies the physical presence of microorganisms
New guidelines for the antibiotic treatment of streptococcal, enterococcal and staphylococcal endocarditis. D. C. Shanson
 Journal of Antimicrobial Chemotherapy (1998) 42, 292 296 New guidelines for the antibiotic treatment of streptococcal, enterococcal and staphylococcal endocarditis JAC D. C. Shanson Microbiology Department,
Journal of Antimicrobial Chemotherapy (1998) 42, 292 296 New guidelines for the antibiotic treatment of streptococcal, enterococcal and staphylococcal endocarditis JAC D. C. Shanson Microbiology Department,
Apport des recommandations européennes
 Apport des recommandations européennes Gilbert Habib Cardiology Department- La Timone Marseille - France Bordeaux le 28 Juin 2011 Infective Endocarditis: a changing disease new high-risk subgroups IVDA
Apport des recommandations européennes Gilbert Habib Cardiology Department- La Timone Marseille - France Bordeaux le 28 Juin 2011 Infective Endocarditis: a changing disease new high-risk subgroups IVDA
Infective Endocarditis عبد المهيمن أحمد
 Infective Endocarditis إعداد : عبد المهيمن أحمد أحمد علي Infective endocarditis Inflammation of the heart valve or endocardium of the heart. The agents are usually bacterial, but other organisms can also
Infective Endocarditis إعداد : عبد المهيمن أحمد أحمد علي Infective endocarditis Inflammation of the heart valve or endocardium of the heart. The agents are usually bacterial, but other organisms can also
Supplementary appendix
 Supplementary appendix This appendix formed part of the original submission and has been peer reviewed. We post it as supplied by the authors. Supplement to: Dayer MJ, Jones S, Prendergast B, et al. Incidence
Supplementary appendix This appendix formed part of the original submission and has been peer reviewed. We post it as supplied by the authors. Supplement to: Dayer MJ, Jones S, Prendergast B, et al. Incidence
The changing landscape of infective endocarditis (IE)in congenital heart disease (CHD)
 The changing landscape of infective endocarditis (IE)in congenital heart disease (CHD) Rekwan Sittiwangkul,MD Department of Pediatrics. Chiang Mai University Hospital, 24 th March 2018 Infective endocarditis
The changing landscape of infective endocarditis (IE)in congenital heart disease (CHD) Rekwan Sittiwangkul,MD Department of Pediatrics. Chiang Mai University Hospital, 24 th March 2018 Infective endocarditis
The changing epidemiology and clinical features of infective endocarditis: A retrospective study of 196 episodes in a teaching hospital in China
 Zhu et al. BMC Cardiovascular Disorders (2017) 17:113 DOI 10.1186/s12872-017-0548-8 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access The changing epidemiology and clinical features of infective endocarditis: A retrospective
Zhu et al. BMC Cardiovascular Disorders (2017) 17:113 DOI 10.1186/s12872-017-0548-8 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access The changing epidemiology and clinical features of infective endocarditis: A retrospective
MULTIVALVULAR INFECTIVE ENDOCARDITIS CLINICAL FEATURES, ECHOCARDIOGRAPHIC DATA AND OUTCOMES
 Article Original MULTIVALVULAR INFECTIVE ENDOCARDITIS CLINICAL FEATURES, ECHOCARDIOGRAPHIC DATA AND OUTCOMES L. ABID, B. JERBI, I. TRABELSI, A. ZNAZEN*, S. KRICHÈNE, D. ABID, M. AKROUT, S. MALLEK, F. TRIKI,
Article Original MULTIVALVULAR INFECTIVE ENDOCARDITIS CLINICAL FEATURES, ECHOCARDIOGRAPHIC DATA AND OUTCOMES L. ABID, B. JERBI, I. TRABELSI, A. ZNAZEN*, S. KRICHÈNE, D. ABID, M. AKROUT, S. MALLEK, F. TRIKI,
Experience in heart transplant as salvage treatment for infective endocarditis
 Experience in heart transplant as salvage treatment for infective endocarditis Prof. Pierre Tattevin Infectious Diseases & ICU, Rennes Univ. Hosp INSERM U 835, Hôpital Pontchaillou, Rennes, France AEPEI:
Experience in heart transplant as salvage treatment for infective endocarditis Prof. Pierre Tattevin Infectious Diseases & ICU, Rennes Univ. Hosp INSERM U 835, Hôpital Pontchaillou, Rennes, France AEPEI:
Infective Endocarditis
 Definition Infective Endocarditis Pattaya Riengchan M.D. MAR 16, 2017 Infection of endocardial surface of the heart and implies the physical presence microorganisms in the lesion Heart valves are most
Definition Infective Endocarditis Pattaya Riengchan M.D. MAR 16, 2017 Infection of endocardial surface of the heart and implies the physical presence microorganisms in the lesion Heart valves are most
Outcomes After Surgical Treatment of Native and Prosthetic Valve Infective Endocarditis
 Outcomes After Surgical Treatment of Native and Prosthetic Valve Infective Endocarditis Mahesh B. Manne, MD, MPH, Nabin K. Shrestha, MD, Bruce W. Lytle, MD, Edward R. Nowicki, MD, MS, Eugene Blackstone,
Outcomes After Surgical Treatment of Native and Prosthetic Valve Infective Endocarditis Mahesh B. Manne, MD, MPH, Nabin K. Shrestha, MD, Bruce W. Lytle, MD, Edward R. Nowicki, MD, MS, Eugene Blackstone,
ACCME/Disclosures 4/13/2016 IDPB
 ACCME/Disclosures The USCAP requires that anyone in a position to influence or control the content of CME disclose any relevant financial relationship WITH COMMERCIAL INTERESTS which they or their spouse/partner
ACCME/Disclosures The USCAP requires that anyone in a position to influence or control the content of CME disclose any relevant financial relationship WITH COMMERCIAL INTERESTS which they or their spouse/partner
Hearts afire: Infective endocarditis
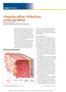 Hearts afire: Infective endocarditis By Kim McCarron, MS, CRNP Clinical Associate Professor Towson University Towson, Md. Editorial Advisory Board Member Nursing made Incredibly Easy! Picturing endocarditis
Hearts afire: Infective endocarditis By Kim McCarron, MS, CRNP Clinical Associate Professor Towson University Towson, Md. Editorial Advisory Board Member Nursing made Incredibly Easy! Picturing endocarditis
Nosocomial Infection in a Pediatric Intensive Care Unit in a Developing Country
 BJID 2003; 7 (December) 375 Nosocomial Infection in a Pediatric Intensive Care Unit in a Developing Country Marcelo L. Abramczyk 1,2, Werther B. Carvalho 1,2, Eduardo S. Carvalho 2 and Eduardo A. S. Medeiros
BJID 2003; 7 (December) 375 Nosocomial Infection in a Pediatric Intensive Care Unit in a Developing Country Marcelo L. Abramczyk 1,2, Werther B. Carvalho 1,2, Eduardo S. Carvalho 2 and Eduardo A. S. Medeiros
Infective endocarditis (IE) is an
 Jason Andrade, MD, Ellamae Stadnick, MD, Aneez Mohamed, MD Infective endocarditis prophylaxis: An update for clinical practice Antibiotic therapy to prevent endocarditis is now considered un - necessary
Jason Andrade, MD, Ellamae Stadnick, MD, Aneez Mohamed, MD Infective endocarditis prophylaxis: An update for clinical practice Antibiotic therapy to prevent endocarditis is now considered un - necessary
Clinical Profile & Outcome of Infective Endocarditis patients admitted in tertiary care center in eastern part of Nepal
 10 Original Article Clinical Profile & Outcome of Infective Endocarditis patients admitted in tertiary care center in eastern part of Nepal Sherpa K, Shah P, Khati Y, Jha SK, Sharma SK, Karki P Department
10 Original Article Clinical Profile & Outcome of Infective Endocarditis patients admitted in tertiary care center in eastern part of Nepal Sherpa K, Shah P, Khati Y, Jha SK, Sharma SK, Karki P Department
The Diagnostic Challenge of Infective Endocarditis: Cutaneous Vasculitis Leading to the Diagnosis of Infective Endocarditis
 MEDICAL PRACTICE The Diagnostic Challenge of Infective Endocarditis: Cutaneous Vasculitis Leading to the Diagnosis of Infective Endocarditis Tracey Conti, MD, and Beth Barnet, MD Background: Signs and
MEDICAL PRACTICE The Diagnostic Challenge of Infective Endocarditis: Cutaneous Vasculitis Leading to the Diagnosis of Infective Endocarditis Tracey Conti, MD, and Beth Barnet, MD Background: Signs and
FEATURE. Infective Endocarditis: Diagnosis and Treatment. Tony Main (Meds 2011) Faculty Reviewer: Dr. Linrui Guo
 FEATURE Infective Endocarditis: Diagnosis and Treatment Tony Main (Meds 2011) Faculty Reviewer: Dr. Linrui Guo Introduction When one thinks of infectious disease, endocarditis infection of the heart- does
FEATURE Infective Endocarditis: Diagnosis and Treatment Tony Main (Meds 2011) Faculty Reviewer: Dr. Linrui Guo Introduction When one thinks of infectious disease, endocarditis infection of the heart- does
E chocardiography is a valuable tool in the diagnostic
 1020 CARDIOVASCULAR MEDICINE Repeated echocardiographic examinations of patients with suspected infective endocarditis M L C Vieira, M Grinberg, P M A Pomerantzeff, J L Andrade, A J Mansur... See end of
1020 CARDIOVASCULAR MEDICINE Repeated echocardiographic examinations of patients with suspected infective endocarditis M L C Vieira, M Grinberg, P M A Pomerantzeff, J L Andrade, A J Mansur... See end of
Infective Endocarditis in Elderly Patients
 AGING AND INFECTIOUS DISEASES Thomas T. Yoshikawa, Section Editor INVITED ARTICLE Infective Endocarditis in Elderly Patients Vinod K. Dhawan Charles R. Drew University of Medicine and Science, Martin Luther
AGING AND INFECTIOUS DISEASES Thomas T. Yoshikawa, Section Editor INVITED ARTICLE Infective Endocarditis in Elderly Patients Vinod K. Dhawan Charles R. Drew University of Medicine and Science, Martin Luther
AHA Scientific Statement
 AHA Scientific Statement Infective Endocarditis in Adults: Diagnosis, Antimicrobial Therapy, and Management of Complications A Scientific Statement for Healthcare Professionals From the American Heart
AHA Scientific Statement Infective Endocarditis in Adults: Diagnosis, Antimicrobial Therapy, and Management of Complications A Scientific Statement for Healthcare Professionals From the American Heart
INFECTIVE ENDOCARDITIS is a constantlyevolvingdisease.
 Clinical Features of Staphylococcus aureus Endocarditis A 10-Year Experience in Denmark ORIGINAL INVESTIGATION Bent L. Røder, MD; Dorte A. Wandall, MD; Niels Frimodt-Møller, MD, DMSc; Frank Espersen, MD,
Clinical Features of Staphylococcus aureus Endocarditis A 10-Year Experience in Denmark ORIGINAL INVESTIGATION Bent L. Røder, MD; Dorte A. Wandall, MD; Niels Frimodt-Møller, MD, DMSc; Frank Espersen, MD,
General management of infective endocarditis
 General management of infective endocarditis Team approach in infective endocarditis Gilbert Habib La Timone Hospital Marseille - France Eurovalves Barcelona 2017 The echolab «Heart Team" Infective Endocarditis
General management of infective endocarditis Team approach in infective endocarditis Gilbert Habib La Timone Hospital Marseille - France Eurovalves Barcelona 2017 The echolab «Heart Team" Infective Endocarditis
We are IntechOpen, the first native scientific publisher of Open Access books. International authors and editors. Our authors are among the TOP 1%
 We are IntechOpen, the first native scientific publisher of Open Access books 3,350 108,000 1.7 M Open access books available International authors and editors Downloads Our authors are among the 151 Countries
We are IntechOpen, the first native scientific publisher of Open Access books 3,350 108,000 1.7 M Open access books available International authors and editors Downloads Our authors are among the 151 Countries
Supplementary Appendix
 Supplementary Appendix This appendix has been provided by the authors to give readers additional information about their work. Supplement to: Kang D-H, Kim Y-J, Kim S-H, et al. Early surgery versus conventional
Supplementary Appendix This appendix has been provided by the authors to give readers additional information about their work. Supplement to: Kang D-H, Kim Y-J, Kim S-H, et al. Early surgery versus conventional
Disclosures. Native Valve Endocarditis and its Complications. Outline. Outline. Basics. Basics 3/23/2017
 Native Valve Endocarditis and its Complications SCVP and Binford Dammin Society of Infectious Disease Pathologists Shared Companion Meeting USCAP 2017 Annual Meeting Disclosures Relevant financial relationships
Native Valve Endocarditis and its Complications SCVP and Binford Dammin Society of Infectious Disease Pathologists Shared Companion Meeting USCAP 2017 Annual Meeting Disclosures Relevant financial relationships
Echocardiography in Endocarditis
 Echocardiography in Endocarditis Bicol Hospital, Legazpi City, Philippines July 2016 Gregg S. Pressman MD, FACC, FASE Einstein Medical Center Philadelphia, USA Demographics of IE Incidence is 1.4 12.7/100,000
Echocardiography in Endocarditis Bicol Hospital, Legazpi City, Philippines July 2016 Gregg S. Pressman MD, FACC, FASE Einstein Medical Center Philadelphia, USA Demographics of IE Incidence is 1.4 12.7/100,000
LVHN Cardiac Diagnostic Testing PCP/PCP Office Testing Cheat Sheet. September 2017
 LVHN Cardiac Diagnostic Testing PCP/PCP Office Testing Cheat Sheet September 2017 1. ECHOCARDIOGRAM A (transthoracic) echocardiogram (2D Echo) is a 2-dimensional graphic of the heart s movement, valves
LVHN Cardiac Diagnostic Testing PCP/PCP Office Testing Cheat Sheet September 2017 1. ECHOCARDIOGRAM A (transthoracic) echocardiogram (2D Echo) is a 2-dimensional graphic of the heart s movement, valves
Infections Amenable to OPAT. (Nabin Shrestha + Ajay Mathur)
 3 Infections Amenable to OPAT (Nabin Shrestha + Ajay Mathur) Decisions regarding outpatient treatment of infections vary with the institution, the prescribing physician, the individual patient s condition
3 Infections Amenable to OPAT (Nabin Shrestha + Ajay Mathur) Decisions regarding outpatient treatment of infections vary with the institution, the prescribing physician, the individual patient s condition
Right-Sided Bacterial Endocarditis
 New Concepts in the Treatment of the Uncontrollable Infection Agustin Arbulu, M.D., Ali Kafi, M.D., Norman W. Thorns, M.D., and Robert F. Wilson, M.D. ABSTRACT Our experience with 25 patients with right-sided
New Concepts in the Treatment of the Uncontrollable Infection Agustin Arbulu, M.D., Ali Kafi, M.D., Norman W. Thorns, M.D., and Robert F. Wilson, M.D. ABSTRACT Our experience with 25 patients with right-sided
The New England Journal of Medicine. Review Articles
 Review Articles Medical Progress INFECTIVE ENDOCARDITIS IN ADULTS ELEFTHERIOS MYLONAKIS, M.D., AND STEPHEN B. CALDERWOOD, M.D. INFECTIVE endocarditis, a microbial infection of the endocardial surface of
Review Articles Medical Progress INFECTIVE ENDOCARDITIS IN ADULTS ELEFTHERIOS MYLONAKIS, M.D., AND STEPHEN B. CALDERWOOD, M.D. INFECTIVE endocarditis, a microbial infection of the endocardial surface of
Cardiovascular Images
 Cardiovascular Images Pulmonary Embolism Diagnosed From Right Heart Changes Seen After Exercise Stress Echocardiography Brian C. Case, MD; Micheas Zemedkun, MD; Amarin Sangkharat, MD; Allen J. Taylor,
Cardiovascular Images Pulmonary Embolism Diagnosed From Right Heart Changes Seen After Exercise Stress Echocardiography Brian C. Case, MD; Micheas Zemedkun, MD; Amarin Sangkharat, MD; Allen J. Taylor,
, David Stultz, MD.
 http://www.dilbert.com Infective Endocarditis David Stultz, MD Cardiology Fellow, PGY 4 December 8, 2004 Handouts available in PDF format at www.drstultz.com Topics to be covered Epidemiology Microbiology
http://www.dilbert.com Infective Endocarditis David Stultz, MD Cardiology Fellow, PGY 4 December 8, 2004 Handouts available in PDF format at www.drstultz.com Topics to be covered Epidemiology Microbiology
Clinical Characteristics and In-Hospital Prognosis of Infective Endocarditis in Two Eastern Counties of Taiwan
 Original Article Acta Cardiol Sin 2014;30:151 156 Infective Endocarditis Clinical Characteristics and In-Hospital Prognosis of Infective Endocarditis in Two Eastern Counties of Taiwan Jen-Che Hsieh, 1,4
Original Article Acta Cardiol Sin 2014;30:151 156 Infective Endocarditis Clinical Characteristics and In-Hospital Prognosis of Infective Endocarditis in Two Eastern Counties of Taiwan Jen-Che Hsieh, 1,4
Management of infective endocarditis in children
 Management of infective endocarditis in children Ashutosh Marwah, MD* Savitri Shrivastava, MD DM FAMS FACC* INTRODUCTION Infective endocarditis (IE) continues to remain a serious disease despite advances
Management of infective endocarditis in children Ashutosh Marwah, MD* Savitri Shrivastava, MD DM FAMS FACC* INTRODUCTION Infective endocarditis (IE) continues to remain a serious disease despite advances
, David Stultz, MD.
 http://www.dilbert.com Infective Endocarditis David Stultz, MD Cardiology Fellow, PGY 6 August 31, 2005 Topics to be covered Epidemiology Microbiology Clinical presentation Physical Exam Findings Diagnostic
http://www.dilbert.com Infective Endocarditis David Stultz, MD Cardiology Fellow, PGY 6 August 31, 2005 Topics to be covered Epidemiology Microbiology Clinical presentation Physical Exam Findings Diagnostic
The microbial diagnosis of infective endocarditis (IE)
 The microbial diagnosis of infective endocarditis (IE) Pierrette Melin Medical Microbiology pm-chulg sbimc 10.05.2007 1 Introduction for diagnosis Review of microbiological investigation of IE and perspectives
The microbial diagnosis of infective endocarditis (IE) Pierrette Melin Medical Microbiology pm-chulg sbimc 10.05.2007 1 Introduction for diagnosis Review of microbiological investigation of IE and perspectives
Echocardiographic Diagnosis of Rheumatic Heart Disease
 Echocardiographic Diagnosis of Rheumatic Heart Disease Nigel Wilson Paediatric Cardiologist Paediatric and Congenital Cardiac Services Auckland City and Starship Hospitals Auckland, New Zealand Auckland
Echocardiographic Diagnosis of Rheumatic Heart Disease Nigel Wilson Paediatric Cardiologist Paediatric and Congenital Cardiac Services Auckland City and Starship Hospitals Auckland, New Zealand Auckland
THE INCREASING IMPORTANCE OF HEALTH CARE-ASSOCIATED INFECTIVE ENDOCARDITIS
 THE INCREASING IMPORTANCE OF HEALTH CARE-ASSOCIATED INFECTIVE ENDOCARDITIS Javier López Díaz Instituto de Ciencias del Corazón (ICICOR) Hospital Clínico de Valladolid, Spain No conflict of interest Page
THE INCREASING IMPORTANCE OF HEALTH CARE-ASSOCIATED INFECTIVE ENDOCARDITIS Javier López Díaz Instituto de Ciencias del Corazón (ICICOR) Hospital Clínico de Valladolid, Spain No conflict of interest Page
Cardiac Diagnostic Testing Reference Guide January 2018
 STAT Cardiac Testing is available for inpatients only. ECHOCARDIOGRAM Cardiac Diagnostic Testing A (transthoracic) echocardiogram (2D Echo) is a 2-dimensional graphic of the heart's movement, valves and
STAT Cardiac Testing is available for inpatients only. ECHOCARDIOGRAM Cardiac Diagnostic Testing A (transthoracic) echocardiogram (2D Echo) is a 2-dimensional graphic of the heart's movement, valves and
Endocardite infectieuse
 Endocardite infectieuse 1. Raccourcir le traitement: jusqu où? 2. Proposer un traitement ambulatoire: à partir de quand? Endocardite infectieuse A B 90 P = 0.014 20 P = 0.0005 % infective endocarditis
Endocardite infectieuse 1. Raccourcir le traitement: jusqu où? 2. Proposer un traitement ambulatoire: à partir de quand? Endocardite infectieuse A B 90 P = 0.014 20 P = 0.0005 % infective endocarditis
Epidemiology and Prevention
 Epidemiology and Prevention Neurological Complications of Infective Endocarditis Risk Factors, Outcome, and Impact of Cardiac Surgery: A Multicenter Observational Study Emilio García-Cabrera, MSc; Nuria
Epidemiology and Prevention Neurological Complications of Infective Endocarditis Risk Factors, Outcome, and Impact of Cardiac Surgery: A Multicenter Observational Study Emilio García-Cabrera, MSc; Nuria
Rotation: Echocardiography: Transthoracic Echocardiography (TTE)
 Rotation: Echocardiography: Transthoracic Echocardiography (TTE) Rotation Format and Responsibilities: Fellows rotate in the echocardiography laboratory in each clinical year. Rotations during the first
Rotation: Echocardiography: Transthoracic Echocardiography (TTE) Rotation Format and Responsibilities: Fellows rotate in the echocardiography laboratory in each clinical year. Rotations during the first
Surgical Indications of Infective Endocarditis in Children
 2016 Annual Spring Scientific Conference of the KSC April 15-16, 2016 Surgical Indications of Infective Endocarditis in Children Cheul Lee, MD Pediatric and Congenital Cardiac Surgery Seoul St. Mary s
2016 Annual Spring Scientific Conference of the KSC April 15-16, 2016 Surgical Indications of Infective Endocarditis in Children Cheul Lee, MD Pediatric and Congenital Cardiac Surgery Seoul St. Mary s
Modifiers of the clinical course of infective endocarditis
 Modifiers of the clinical course of infective endocarditis Ulrika Snygg-Martin M.D., Ph.D. Infectious Diseases Clinic Sahlgrenska University Hospital Gothenburg, Sweden Infective endocarditis : modifiers
Modifiers of the clinical course of infective endocarditis Ulrika Snygg-Martin M.D., Ph.D. Infectious Diseases Clinic Sahlgrenska University Hospital Gothenburg, Sweden Infective endocarditis : modifiers
IN THE PREANTIBIOTIC ERA, NATIVE
 ORIGINAL CONTRIBUTION Complicated Left-Sided Native Valve Endocarditis in Adults Risk Classification for Mortality Rodrigo Hasbun, MD Holenarasipur R. Vikram, MD Lydia A. Barakat, MD Joan Buenconsejo,
ORIGINAL CONTRIBUTION Complicated Left-Sided Native Valve Endocarditis in Adults Risk Classification for Mortality Rodrigo Hasbun, MD Holenarasipur R. Vikram, MD Lydia A. Barakat, MD Joan Buenconsejo,
Outcome of Infective Endocarditis: Improved Results Over 18 Years ( )
 ORIGINAL RESEARCH Outcome of Infective Endocarditis: Improved Results Over 18 Years (1990 2007) Pachirat O 1, Limwattananon S 2, Tantisirin C 3 and Tatsanavivat P 1 1 Cardiovascular Unit, Srinagarind Hospital,
ORIGINAL RESEARCH Outcome of Infective Endocarditis: Improved Results Over 18 Years (1990 2007) Pachirat O 1, Limwattananon S 2, Tantisirin C 3 and Tatsanavivat P 1 1 Cardiovascular Unit, Srinagarind Hospital,
Endocarditis: Medical vs. Surgical Treatment. Nabin K. Shrestha, MD, MPH Infectious Diseases
 Endocarditis: Medical vs. Surgical Treatment Nabin K. Shrestha, MD, MPH Infectious Diseases Conflicts of interest Nothing to disclose 2 Complications of infective endocarditis Local complications Heart
Endocarditis: Medical vs. Surgical Treatment Nabin K. Shrestha, MD, MPH Infectious Diseases Conflicts of interest Nothing to disclose 2 Complications of infective endocarditis Local complications Heart
Consensus Statement on Infective Endocarditis / Abridged Version
 CONSENSUS Consensus Statement on Infective Endocarditis / Abridged Version Argentine Society of Cardiology General Directors Secretary (Area of Regulations and Consensuses) Dr. Gustavo Giunta MTSAC 1.
CONSENSUS Consensus Statement on Infective Endocarditis / Abridged Version Argentine Society of Cardiology General Directors Secretary (Area of Regulations and Consensuses) Dr. Gustavo Giunta MTSAC 1.
Infective endocarditis
 Infective endocarditis Today's lecture is about infective endocarditis, the Dr started the lecture by asking what are the most common causative agents of infective endocarditis? 1-Group A streptococci
Infective endocarditis Today's lecture is about infective endocarditis, the Dr started the lecture by asking what are the most common causative agents of infective endocarditis? 1-Group A streptococci
DICE Session. The endocarditis team. Bernard Iung Bichat Hospital, Paris Diderot University Paris, France
 DICE Session. The endocarditis team Bernard Iung Bichat Hospital, Paris Diderot University Paris, France Faculty disclosure First name - last name I disclose the following financial relationships: Consultant
DICE Session. The endocarditis team Bernard Iung Bichat Hospital, Paris Diderot University Paris, France Faculty disclosure First name - last name I disclose the following financial relationships: Consultant
Infective Endocarditis in King Faisal Specialist Hospital: A Review of 35 Consecutive Adult Patients
 Infective Endocarditis in King Faisal Specialist Hospital: A Review of 35 Consecutive Adult Patients Murtada A. Halim, MRCP* M. Oussama Jeroudi, MD Edward N. Mercer, MD, FRCP(C), FACC M. Eid Fawzy, MRCP,
Infective Endocarditis in King Faisal Specialist Hospital: A Review of 35 Consecutive Adult Patients Murtada A. Halim, MRCP* M. Oussama Jeroudi, MD Edward N. Mercer, MD, FRCP(C), FACC M. Eid Fawzy, MRCP,
Research Presentation June 23, Nimish Muni Resident Internal Medicine
 Research Presentation June 23, 2009 Nimish Muni Resident Internal Medicine Research Question In adult patients with repaired Tetralogy of Fallot, how does Echocardiography compare to MRI in evaluating
Research Presentation June 23, 2009 Nimish Muni Resident Internal Medicine Research Question In adult patients with repaired Tetralogy of Fallot, how does Echocardiography compare to MRI in evaluating
Épidémiologie des endocardites infectieuses à Staphylococcus aureus (Epidemiology of S. aureus endocarditis)
 Épidémiologie des endocardites infectieuses à Staphylococcus aureus (Epidemiology of S. aureus endocarditis) Lyon, 30 Novembre 2018 Univ.-Prof. Dr. med. Achim J. Kaasch Institut für Medizinische Mikrobiologie
Épidémiologie des endocardites infectieuses à Staphylococcus aureus (Epidemiology of S. aureus endocarditis) Lyon, 30 Novembre 2018 Univ.-Prof. Dr. med. Achim J. Kaasch Institut für Medizinische Mikrobiologie
BASIC KNOWLEDGE ABOUT INFECTIVE ENDOCARDITIS FOR CLINICIAN
 BASIC KNOWLEDGE ABOUT INFECTIVE ENDOCARDITIS FOR CLINICIAN When should I suspect infective endocarditis? Antibiotic regimen Patient care after completion of treatment Prophylactic Regimens Prosthetic Valve
BASIC KNOWLEDGE ABOUT INFECTIVE ENDOCARDITIS FOR CLINICIAN When should I suspect infective endocarditis? Antibiotic regimen Patient care after completion of treatment Prophylactic Regimens Prosthetic Valve
