Index ... Wolf, Direct Diagnosis in Radiology. Vascular Imaging (ISBN ), 2009 Georg Thieme Verlag KG
|
|
|
- Morgan Payne
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 A abdomen acute 142, 188 abscess vs. carotid body tumor 103 vs. jugular vein thrombosis 108 acral gangrene, ischemic 255 acute aortic syndrome adenopathy, vs. jugular vein thrombosis 108 adult coarctation 137 adventitia, cystic degeneration vs. peripheral arterial aneurysm 260 vs. thromboangiitis obliterans 283 amaurosis fugax 115 amyloid angiopathy cerebral vs. hypertensive hemorrhage 53 amyotrophic lateral sclerosis, vs. spinal dural AVM 85 anemia 216 aneurysm 3 aortic, see aortic aneurysm atherosclerotic, vs. infectious 164 crescent sign 158, 160, 165, 179, 183, 186, 211 dissecting, vs. abdominal aortic aneurysm 181 false vs. abdominal aortic aneurysm 181 after arterial puncture vs. arteriovenous fistula 250 fusiform vs. giant 67 giant vs. fusiform 70 infectious 71, inflammatory, vs. infectious 164 mycotic 71 72, vs. inflammatory, abdominal 185 vs. ruptured 188 peripheral arterial post-therapy imaging saccular vs. mycotic 72 thoracic 124 vs. thromboangiitis obliterans 283 venous, vs. peripheral arterial aneurysm 260 visceral arteries angina abdominal 203 pectoris 141 angioma 18 cavernous 9 vs. cerebral AVM 21 venous angiomatosis, cerebellar and retinal 33 angiopathy, cerebral amyloid aorta acute aortic syndrome aneurysm, see aortic aneurysm arch, see aortic arch bifurcation, obliteration 196 chronic occlusive disease coarctation diameter values 179 dissection vs. penetrating ulcer 147 vs. traumatic rupture 157 endoleaks after stenting hematoma, intramural 147, insufficiency 152 occlusion pseudocoarctation 137 rupture vs. aortic dissection 154 traumatic small, syndrome 193 ulcer, see aortic ulcer aortic aneurysm 147 abdominal inflammatory 181, ruptured vs. dissection 154 vs. intramural hematoma 150 mycotic, abdominal
2 vs. penetrating ulcer 147 thoracic ruptured vs. traumatic rupture 157 aortic arch duplication and aberrant left subclavian artery 131 with retroesophageal segment 128 right, and aberrant left subclavian artery 131 syndrome 138 aortic syndrome, acute aortic ulcer vs. aortic aneurysm 160 vs. dissection 154 vs. intramural hematoma 150 penetrating vs. intramural hematoma 150 vs. thoracic aortic aneurysm 168 aortocaval fistula 188 aortoenteric fistula 188 aphasia 115 apnea 128 appetite loss 104, 138 arachnoid cysts 32 arachnoid granulations, vs. major sinus thrombosis 74 arcuate ligament 204 arms, see extremities; upper extremity arterial puncture and arteriovenous fistula and false aneurysm arteria lusoria 131 arteries diameter values, legs 255 occlusion, embolic vasospasm, vs. embolic arterial occlusion 263 see also occlusive arterial disease; peripheral arterial occlusive disease; vascular arteriolosclerosis 54 arteriosclerotic encephalopathy 54 arteriovenous fistula, see fistula arteriovenous malformation (AVM) 8, 15 cerebral cranial, vs. saccular aneurysm 64 dural, vs. spinal dural 85 vs. hypertensive hemorrhage 53 pulmonary, and telangiectasia 175 spinal spinal dural vs. venous angioma 12 vs. von Hippel Lindau syndrome 34 arteritis giant cell vs. Takayasu 140 vs. intracranial atherosclerosis 57 Takayasu 106, arthralgia 138 ascites 220, 227 astrocytoma pilocytic 32 vs. von Hippel Lindau syndrome 34 vs. spinal AVM 82 ataxia 9 atherosclerosis 193 vs. giant cell arteritis 106 vs. internal carotid dissection 116 intracranial vs. intracranial vasculitis 38 vs. ischemic insult 60 plaques, vs. intramural hematoma of aorta 150 renal arteries 232 vs. Takayasu arteritis 140 vs. thromboangiitis obliterans 283 ulcerated plaques 147 vs. vertebral artery dissection 120 and visceral artery aneurysms 208 atherosclerotic aneurysm, vs. infectious aneurysm 164 autoimmune vasculitis, vs. thromboangiitis obliterans
3 B Baker cyst vs. deep venous thrombosis 276 vs. peripheral arterial aneurysm 260 balance, impaired 98 Binswanger disease 54 bladder disorders 81, 84 see also kidneys; renal bleeding, see hemorrhage blood pressure left right difference 122 upper lower extremity difference 141, 167 bowel ischemia 152 brachiocephalic vein occlusion 274 brain 1 80 brainstem ischemia 120 Budd Chiari syndrome Buerger disease 281 bulbar paralysis 54 buphthalmos 28 bypass, extracranial intracranial C cannabis 283 capillary telangiectasia 6 8 caput medusae 12, 217, 220 caroticocavernous fistula 25 carotid artery dissection 111, fistula with cavernous sinus stenosis, extracranial see also internal carotid artery carotid body, tumor cavernoma 9 cavernous angioma 9 vs. cerebral AVM 21 cavernous hemangioma, vs. spinal AVM 82 cavernous malformation 8, 9 11 vs. cerebral amyloid angiopathy 48 vs. hypertensive hemorrhage 53 vs. venous angioma 12 cavernous sinus fistula with carotid artery central venous stenosis, upper extremity cerebellar and retinal angiomatosis 33 cerebral amyloid angiopathy cerebral AVM vs. dural AVM 24 cerebral hemorrhage 20 cerebral infarct 35, 111, 115, 138 see also ischemic insult/stroke cerebral vein, thrombosis cervical lymph nodes, enlarged 107 chemosis 22 chest Child Turcotte Pugh classification 220, 221 cholesteatoma, vs. glomus tympanicum tumor 97 cholesterol granuloma 87 Churg Strauss syndrome 207 cirrhosis, liver 227 claudication 258, 281 extremities 104, 138 intermittent 193, 255 jaws 104 spinal, vs. occlusive venous, vs. occlusive clear-cell ependymoma, vs. hemangioblastoma 32 coagulation disorders 43, 49, 220, 229 vs. hypertensive hemorrhage 53 coarctation adult 137 aorta atypical, vs. aortic occlusive disease 195 infantile 137 cobweb tissue, in aortic dissection 151 cocaine misuse 35, 64, 283 compartment syndrome, vs. occlusive 286
4 compression central veins, vs. stenosis 274 portal vein, vs. thrombosis 224 compression syndrome 204 compression therapy, complications 265 conjunctival inflammation 25 connective tissue disorders congenital, vs. Takayasu arteritis 140 vs. thromboangiitis obliterans 283 corkscrew arteries 206, 281, 282 coronary artery, and aortic dissection 152 coronary syndrome, acute 142 cortical veins, thrombosed 53 cranial AVM, vs. saccular aneurysm 64 cranial nerve palsy 22 crescent sign, aneurysm 158, 160, 165, 179, 183, 186, 211 Curaçao criteria, telangiectasia 175 cyanosis 137, 173, 275 cyst, synovial, vs. peripheral aneurysm 260 D D-dimer test, positive 171, 275 DeBakey classification, aortic dissection 152 degenerative joint disease, vs. occlusive dementia 22, 46, 54 developmental venous anomaly 12 dialysis shunt, stenosis diplopia 9 dissection aorta 147, vs. traumatic rupture 157 vs. extracranial carotid stenosis 111 vs. false aneurysm 264 internal carotid artery vs. intracranial atherosclerosis 57 vs. moya-moya disease 42 vs. subclavian steal syndrome 124 thrombosed 147 vs. intramural hematoma of aorta 150 vertebral artery diuresis, cessation 246 dolichoectasia, vertebrobasilar 3 vs. fusiform aneurysm 70 dome sign 275 drug misuse, vs. hypertensive hemorrhage 53 duplication aortic arch , 131 inferior vena cava superior vena cava dural arteriovenous fistula 15 dural AVM vs. cerebral AVM 21 vs. spinal dural AVM 85 dural sinus, thrombosis 74 dysphagia 98, 101, 128, 131, 159 dysplasia, see fibromuscular dysplasia dyspnea 128, 159, 171, 173 E edema , 275 effort thrombosis, vs. central venous stenosis 274 Ehlers Danlos syndrome vs. fibromuscular dysplasia 239 vs. Takayasu arteritis 140 embolic arterial occlusion embolism vs. occlusive disease 256 pulmonary vs. acute aortic syndrome 142 vs. subclavian steal syndrome 124 empty triangle sign 73 encasement, vascular, vs. moya-moya disease 42 encephalopathy 35, 54 endoleaks, after aortic stent placement entrapment, vs. thromboangiitis obliterans
5 ependymoma clear-cell, vs. hemangioblastoma 32 vs. spinal AVM 82 epileptic seizures 28 epistaxis 137, 173, 175 epsilon sign 135 ergotamine 35, 263, 283 erythema 271, 281 exophthalmos, pulsatile 25 extracranial intracranial bypass extremities F facial nerve palsy 4, 94 schwannoma, vs. glomus tympanicum tumor 97 fatigue 104 femoral vein, thrombosis 276 fetal hydrocephalus 15 fever 104, 107, 138, 162, 183, 200, 205, 275 fibromuscular dysplasia vs. internal carotid dissection 116 vs. peripheral arterial occlusive and renal artery stenosis 232, 234 vs. vertebral artery dissection 120 fibrosis, retroperitoneal 183, 185 fistula aortocaval, vs. ruptured aneurysm 188 aortoenteric, vs. ruptured aneurysm 188 arteriovenous 269, 270 after arterial puncture after renal biopsy vs. deep venous thrombosis 276 dural 15, 22 vs. false aneurysm 264 caroticocavernous carotid artery and cavernous sinus flow artifacts, vs. tumor infiltration, renal vein 252 flow sounds, epigastric 203 Fontaine classification 255 fusiform aneurysm vs. giant aneurysm 67 G gait disturbances 31, 120 gastrointestinal bleeding/hemorrhage 188, , 220 giant aneurysm vs. fusiform aneurysm 70 giant cell arteritis glaucoma 28 glioma vs. capillary telangiectasia 8 vs. hemangioblastoma 32 low-grade, vs. cerebral AVM 21 vs. mycotic aneurysm 72 glomus jugulare tumor vs. aberrant internal carotid artery 87 vs. glomus tympanicum tumor 97 vs. high jugular bulb 90 vs. jugular bulb dehiscence 92 glomus tumor, vs. dural AVM 24 glomus tympanicum tumor vs. aberrant internal carotid artery 87 granuloma, cholesterol 87 granulomatosis, vs. mesenteric vasculitis 207 H Hach classification 278 Hampton hump 169 hand, ischemia 122 headache 20, 22, 31, 35, 65, 107, 115, 120, 173 chronic 9 temporal 104 thunderclap 63 head and neck region
6 hearing loss 86, 92, 94, 98 heart failure 173, 229, 248 vs. Budd Chiari syndrome 228 congestive, vs. portal hypertension 220 in newborns 15 vs. varicose veins 280 hemangioblastoma retinal 33 vs. von Hippel Lindau syndrome 34 hemangioma, cavernous, vs. spinal AVM 82 hematemesis 216 hematochezia 216 hematoma vs. deep venous thrombosis 276 intramural, aorta vs. aortic aneurysm 160 vs. aortic dissection 152 vs. penetrating aortic ulcer 147 hematuria 248 hemianopia 28 hemiplegia 28 hemoptysis 171 hemorrhage 81 acute, and cerebral amyloid angiopathy 46 cerebral 20 gastrointestinal 188, , 220 hypertensive intracerebral, spontaneous intraventricular 39 perimesencephalic, vs. saccular aneurysm 64 subarachnoid 39, 68, 71 vs. saccular aneurysm 64 warning 188 hemorrhagic tumor, vs. hypertension 53 Henoch Schönlein purpura, vs. vasculitis 207 hepatic venous occlusive disease 228 hepatocellular carcinoma, tumor thrombus 224 hepatomegaly 227, 229 hereditary hemorrhagic telangiectasia Hippel Lindau syndrome hoarseness 98, 101, 159 honeycomb sign 205 Horner syndrome 115, 120 Hunt and Huss classification 63 hydrocephalus, fetal 15 hypercoagulability 43, 221, 263 hypertension 138, 238, 248 arterial 243 crisis 152 hemorrhage portal recurrent 240 hypoglossal nerve, deficits 115 hypotension 186 hypovolemic shock 157, 167, 186 I ileus, paralytic 205 impotence 81, 84, 196 infantile coarctation 137 infarction, see cerebral infarct infectious aneurysm 71 inferior vena cava duplication thrombosis inflammatory bowel disease 200 internal carotid artery aberrant vs. glomus tympanicum tumor 97 dissection ectopic, vs. jugular bulb dehiscence 92 intracerebral hemorrhage, spontaneous intracranial pressure, elevated 51, 73 intracranial vasculitis intramedullary tumor, vs. spinal AVM 82 intramural hematoma, aorta 147, vs. aneurysm
7 vs. dissection 152 vs. penetrating ulcer 147 inverted three sign 135 ischemia 39 acute, bilateral 196 bowel 152 cerebral, see cerebral infarct complete 261 hand 122 lower extremities 152 mesenteric 205 acute chronic minor vessels see also transient ischemic attack ischemic insult/stroke 51, in children ischemic nephropathy 234 islet cell tumor, vs. visceral artery aneurysm 212 J jaundice 227 joint disease, degenerative, vs. occlusive jugular bulb dehiscence 87, high jugular fossa meningioma, vs. glomus jugulare tumor 99 schwannoma vs. glomus jugulare tumor 99 vs. high jugular bulb 90 vs. jugular bulb dehiscence 92 jugular vein, thrombosis K kidneys see also renal; tubular necrosis Klippel Trenaunay syndrome 30 knuckle sign 169 L left subclavian artery, aberrant legs, see lower extremity Leriche syndrome vs. chronic occlusive disease 195 leukoencephalopathy, periventricular 54 liver cirrhosis 227 failure 220, 227 see also hepatic, hepatolower extremity arterial diameter values 255 bilateral swelling 229 deep venous thrombosis ischemia 152 lumbago 81 lumbar radiculopathy, vs. occlusive lymphadenopathy vs. carotid body tumor 103 retroperitoneal, vs. IVC duplication 178 lymphedema, vs. varicose veins 280 M malabsorption syndrome 203 malformation, vascular 3 Marfan syndrome, vs. Takayasu arteritis 140 mediolysis, segmental arterial, vs. vasculitis 207 MELD score 220 melena 216 meningioma vs. giant aneurysm 67 jugular fossa, vs. glomus jugulare tumor 99 vs. mycotic aneurysm 72 meningism 63 mental retardation 28 mesenteric arteries, vasculitis
8 mesenteric ischemia acute chronic mesenteric veins, thrombosis metastasis vs. capillary telangiectasia 8 vs. carotid body tumor 103 vs. cerebral amyloid angiopathy 48 vs. glomus jugulare tumor 99 vs. hemangioblastoma 32 vs. von Hippel Lindau syndrome 34 microangiopathy 54 minor vessels, ischemia model for end-stage liver disease (MELD) 220 Mönckeberg arteriosclerosis, vs. occlusive disease 256 motor symptoms 54 moya-moya disease vs. intracranial atherosclerosis 57 multiple sclerosis, vs. minor vessel ischemia 55 murmur arteriovenous fistulas 266 dialysis shunt stenosis 271 myalgia 138, 205 mycotic aneurysm myelopathy, sensorimotor 84 myocardial infarction 104, 152 N nausea 22, 31, 51, 73, 120, 122, 221 neck region nephropathy, ischemic 234 nephrotic syndrome 229 neurological deficits 152 focal 9, 20, 22, 63 multifocal 35 neuropathy 281 neurovascular compression 4 5 nevus, facial 28 night sweats 138 O occlusion, acute vs. Budd Chiari syndrome 228 vs. peripheral arterial occlusive disease 256 vs. subclavian steal syndrome 124 occlusive arterial disease chronic, aorta embolic vs. intracranial vasculitis 38 see also peripheral arterial occlusive disease oligodendroglioma 11 ophthalmopathy, thyroid 27 optic atrophy 22 optic disk edema 22 orbital pseudotumor 27 Ormond disease 183 Osler Weber Rendu disease 172 otic artery, persistent (primitive) 3 P Pacchioni granulations, vs. major sinus thrombosis 74 Paget von Schrötter syndrome 274 pain abdominal 138, 180, 183, 203, 227 back 84, 141, 159, 167, 180, 183, 186, 229 chest 138, 141, 145, 149, 152, 167, 171 ear 73, 86 muscle 255 neck region 115, 120 radicular 81 see also headache pancreas, islet cell tumor 212 paraganglioma, vs. dural AVM 24 paralysis, bulbar 54 paralytic ileus 205 pelvis, deep venous thrombosis peripheral arterial occlusive disease 196, ,
9 phlegmasia cerulea dolens, vs. occlusion 263 pilocytic astrocytoma 32, 34 pleural effusion 274 pneumonia, vs. pulmonary embolism 171 polyangiitis, vs. mesenteric vasculitis 207 polyarteritis nodosa, vs. mesenteric vasculitis 206 polycythemia 31 popliteal artery aneurysm 258, 259 vs. thromboangiitis obliterans 283 entrapment, vs. occlusive disease 256 popliteal vein, thrombosis, vs. aneurysm 260 portal hypertension , 227 portal vein, thrombosis primitive trigeminal artery 1 3 proatlantal artery 3 pseudoaneurysm 264 vs. aortic aneurysm 160 pseudocoarctation, aorta 137 pseudotumor, orbital 27 pulmonary artery embolism 142, 229 loop, vs. aortic arch duplication 128 pulsation 186 pulse, weak or absent, left hand 122 pulseless disease 138 purpura, vs. mesenteric vasculitis 207 R radiculopathy, lumbar, vs. occlusive rectal disorders 81, 84 renal artery stenosis 152, after transplant , 246 vs. fibromuscular dysplasia 239 in-stent renal biopsy, and arteriovenous fistula renal carcinoma, metastasis vs. carotid body tumor 103 vs. glomus jugulare tumor 99 renal failure 137, 138 see also bladder; kidneys; tubular necrosis renal vein thrombosis, after transplant 245, tumor infiltration retardation, mental 28 retinal angiomatosis 33 retinal hemangioblastoma 33 rupture aortic vs. dissection 154 traumatic aortic aneurysm, thoracic contained, vs. aneurysm 185 visceral arteries 208 Rutherford classification 255 S saccular aneurysm vs. mycotic aneurysm 72 salt and pepper pattern 90, 92, 94, 97, 98, 99, 101, 102, 103 saphenous vein, lesser, insufficiency 279 sarcoidosis, vs. Takayasu arteritis 140 schwannoma facial nerve, vs. glomus tympanicum tumor 97 vs. giant aneurysm 67 jugular fossa vs. glomus jugulare tumor 99 vs. high jugular bulb 90 vs. jugular bulb dehiscence 92 vagus nerve, vs. carotid body tumor 103 sclerosis medial calcific 256 multiple, vs. ischemia of minor vessels
10 segmental arterial mediolysis, vs. mesenteric vasculitis 207 seizures 9, 12, 20, 173 in newborns 43 sensorimotor myelopathy 84 sepsis 107 shock, hypovolemic 157, 167, 186 shunt infection, vs. stenosis 271 shunt vein, stenosis sinusoidal obstruction syndrome 228 sinus thrombosis sling, vascular, vs. saccular aneurysm 64 small vessel disease 54 soft palate, paresis 98 Spetzler Martin classification, cerebral AVM 20 spinal canal spinal claudication, vs. occlusive splenic artery aneurysm tortuosity 212 splenomegaly 220 squamous cell carcinoma, vs. glomus tumor 97 Stanford classification 142, 148, 152, 153, 154 steal syndrome, subclavian stenosis central venous, upper extremity dialysis shunt extracranial, carotid artery stent placement aorta, and endoleaks and renal arterial stenosis stridor 128 string of pearls pattern acute mesenteric ischemia 200 fibromuscular dysplasia 116, 120, 234, 236, 237, 239, 257 mesenteric vasculitis 205, 206 string sign 115 stroke 46, 56 ischemic, in children see also ischemic insult/stroke; thrombosis Sturge Weber syndrome subarachnoid hemorrhage 64, 68, 71, 120 subclavian artery subclavian steal syndrome subclavian vein, stenosis 272, 273 superficial temporal artery, tenderness to palpation 104 superior mesenteric artery, aneurysm 211 superior pulmonary vein 125 superior vena cava, duplication sweating 63, 138 swelling extremities 229, 258 neck region 107 syncope 171 synovial cyst, vs. aneurysm 260 systemic lupus erythematosus, vs. vasculitis 207 T tachycardia 275 Takayasu arteritis vs. abdominal aortic aneurysm 185 vs. chronic occlusive disease of aorta 195 vs. giant cell arteritis 106 vs. mesenteric vasculitis 206 tamponade, pericardial 152 telangiectasia 6 8 hereditary hemorrhagic thoracic outlet syndrome, vs. stenosis 274 thoracic stent graft, and subclavian steal syndrome 124 thromboangiitis obliterans thrombophlebitis 27, 281 thrombosed dissection vs. intramural hematoma of aorta 150 vs. penetrating aortic ulcer
11 thrombosis deep venous, pelvis and lower extremity effort, vs. central venous stenosis 274 inferior vena cava vs. internal carotid dissection 116 jugular vein local, vs. embolic arterial occlusion 263 major sinus and cerebral vein mesenteric vein vs. ischemia 200 peripheral 258 popliteal vein, vs. aneurysm 260 portal vein venous, in pelvis and lower extremity thrombus, tumor vs. inferior vena cava thrombosis 229 vs. portal vein thrombosis 224 vs. tumor infiltration, renal vein 252 thunderclap headache 63 thyroid carcinoma, metastasis vs. carotid body tumor 103 vs. glomus jugulare tumor 99 thyroid ophthalmopathy 27 tinnitus, pulsatile 22, 86, 92, 94, 98, 115 tongue, paralysis 98 transient ischemic attack (TIA) 39, 54, 56, 68, 111, 115, 120 transplant dysfunction 243 renal artery stenosis , 246 renal vein thrombosis 245, swelling 246 trauma, multiple 157 trigeminal artery, persistent (primitive) 1 3 trigeminal neuralgia 4 tubular necrosis, acute 245, 246 tumor glomus jugulare vs. aberrant internal carotid artery 89 vs. high jugular bulb 90 vs. jugular bulb dehiscence 92 glomus tympanicum vs. aberrant internal carotid artery 89 hemorrhagic 53 infiltration into renal vein intramedullary, vs. spinal AVM 82 see also individual tumors/sites U ulcer, aorta vs. aneurysm 160 vs. dissection 153 vs. intramural hematoma 150 penetrating , 168, 181 upper extremity central venous stenosis claudication 138 edema urinary stasis 183 V vagus nerve, schwannoma, vs. carotid tumor 103 varices 220, 278 varicose veins vascular encasement, vs. moya-moya 42 vascular malformation 3 vascular sling, vs. saccular aneurysm 64 vasculitis autoimmune, vs. thromboangiitis obliterans 283 vs. fibromuscular dysplasia 239 intracranial vs. intracranial atherosclerosis 57 mesenteric arteries vs. subclavian steal syndrome
12 vasospasm arterial, vs. embolic arterial occlusion 263 vs. intracranial atherosclerosis 57 vs. intracranial vasculitis 38 vs. moya-moya disease 42 vegetative symptoms 63 vein of Galen malformation venous angioma venous anomaly, developmental 12 venous claudication, vs. occlusive venous stenosis, central, arm vertebral artery, dissection vertebrobasilar dolichoectasia 3 vs. fusiform aneurysm 70 vertigo 120, 122, 137 Virchow Robin spaces, prominent, vs. ischemia 55 visceral arteries, aneurysms vision, impaired 104, 122, 138 see also ophthalmopathy visual acuity, loss 25 vomiting 22, 31, 51, 63, 73, 200, 221 von Hippel Lindau syndrome W Wegener granulomatosis, vs. vasculitis 207 weight loss 104, 138, 183, 203, 205 Westermark sign 169 Wyburn Mason syndrome
CMS Limitations Guide - Radiology Services
 CMS Limitations Guide - Radiology Services Starting October 1, 2015, CMS will update their existing medical necessity limitations on tests and procedures to correspond to ICD-10 codes. This limitations
CMS Limitations Guide - Radiology Services Starting October 1, 2015, CMS will update their existing medical necessity limitations on tests and procedures to correspond to ICD-10 codes. This limitations
CMS Limitations Guide MRA Radiology Services
 CMS Limitations Guide MRA Radiology Services Starting July 1, 2008, CMS has placed numerous medical necessity limits on tests and procedures. This reference guide provides you with all of the latest changes.
CMS Limitations Guide MRA Radiology Services Starting July 1, 2008, CMS has placed numerous medical necessity limits on tests and procedures. This reference guide provides you with all of the latest changes.
NON-ATHEROSCLEROTIC PATHOLOGY OF THE CAROTID ARTERIES
 NON-ATHEROSCLEROTIC PATHOLOGY OF THE CAROTID ARTERIES Leslie M. Scoutt, MD, FACR Professor of Diagnostic Radiology & Surgery Vice Chair, Dept of Radiology & Biomedical Imaging Chief, Ultrasound Section
NON-ATHEROSCLEROTIC PATHOLOGY OF THE CAROTID ARTERIES Leslie M. Scoutt, MD, FACR Professor of Diagnostic Radiology & Surgery Vice Chair, Dept of Radiology & Biomedical Imaging Chief, Ultrasound Section
PERPHERAL ARTERY ANEURYSM. By Pooja Sharma and Susanna Sebastianpillai
 PERPHERAL ARTERY ANEURYSM By Pooja Sharma and Susanna Sebastianpillai Defintions True Aneurysm Involves all three layers of the vessel. Have two basic shapes; Fusiform = symmetric widening of the vessels
PERPHERAL ARTERY ANEURYSM By Pooja Sharma and Susanna Sebastianpillai Defintions True Aneurysm Involves all three layers of the vessel. Have two basic shapes; Fusiform = symmetric widening of the vessels
Medical Review Guidelines Magnetic Resonance Angiography
 Medical Review Guidelines Magnetic Resonance Angiography Medical Guideline Number: MRG2001-05 Effective Date: 2/13/01 Revised Date: 2/14/2006 OHCA Reference OAC 317:30-5-24. Radiology. (f) Magnetic Resonance
Medical Review Guidelines Magnetic Resonance Angiography Medical Guideline Number: MRG2001-05 Effective Date: 2/13/01 Revised Date: 2/14/2006 OHCA Reference OAC 317:30-5-24. Radiology. (f) Magnetic Resonance
Subclavian artery Stenting
 Subclavian artery Stenting Etiology Atherosclerosis Takayasu s arteritis Fibromuscular dysplasia Giant Cell Arteritis Radiation-induced Vascular Injury Thoracic Outlet Syndrome Neurofibromatosis Incidence
Subclavian artery Stenting Etiology Atherosclerosis Takayasu s arteritis Fibromuscular dysplasia Giant Cell Arteritis Radiation-induced Vascular Injury Thoracic Outlet Syndrome Neurofibromatosis Incidence
Contrast Guidelines for Common CT/CTA & MRI/MRA
 Contrast Guidelines for Common /A & /MRA Body Imaging Gastrointestinal CLINICAL GUIDELINES EXAM DESCRIPTION /A CPT CODES EXAM DESCRIPTION /MRA CPT CODES Abdominal mass Abdomen & Pelvis w 74177 Abdomen
Contrast Guidelines for Common /A & /MRA Body Imaging Gastrointestinal CLINICAL GUIDELINES EXAM DESCRIPTION /A CPT CODES EXAM DESCRIPTION /MRA CPT CODES Abdominal mass Abdomen & Pelvis w 74177 Abdomen
Clinician s Guide To Ordering NeuroImaging Studies
 Clinician s Guide To Ordering NeuroImaging Studies MRI CT South Jersey Radiology Associates The purpose of this general guide is to assist you in choosing the appropriate imaging test to best help your
Clinician s Guide To Ordering NeuroImaging Studies MRI CT South Jersey Radiology Associates The purpose of this general guide is to assist you in choosing the appropriate imaging test to best help your
AORTIC DISSECTION. DISSECTING ANEURYSMS OF THE AORTA or CLASSIFICATION
 DISSECTING ANEURYSMS OF THE AORTA or AORTIC DISSECTION CLASSIFICATION DeBakey classified aortic dissections into types I, II, and III :- Type I dissection the tear site originates in the ascending aorta,
DISSECTING ANEURYSMS OF THE AORTA or AORTIC DISSECTION CLASSIFICATION DeBakey classified aortic dissections into types I, II, and III :- Type I dissection the tear site originates in the ascending aorta,
WASHINGTON UNIVERSITY SCHOOL OF MEDICINE. Cranial Health History Form
 WASHINGTON UNIVERSITY SCHOOL OF MEDICINE Cranial Health History Form Welcome to the Neurosurgery Department at Washington University. To help us treat you, please fill this form out completely. Your Name:
WASHINGTON UNIVERSITY SCHOOL OF MEDICINE Cranial Health History Form Welcome to the Neurosurgery Department at Washington University. To help us treat you, please fill this form out completely. Your Name:
CMS Limitations Guide - Radiology Services
 CMS Limitations Guide - Radiology Services Starting October 1, 2015, CMS will update their existing medical necessity limitations on tests and procedures to correspond to ICD-10 codes. This limitations
CMS Limitations Guide - Radiology Services Starting October 1, 2015, CMS will update their existing medical necessity limitations on tests and procedures to correspond to ICD-10 codes. This limitations
Vasculitis local: systemic
 Vasculitis Inflammation of the vessel wall. Signs and symptoms: 1- local: according to the involved tissue 2- systemic:(fever, myalgia, arthralgias, and malaise) Pathogenesis 1- immune-mediated 2- infectious
Vasculitis Inflammation of the vessel wall. Signs and symptoms: 1- local: according to the involved tissue 2- systemic:(fever, myalgia, arthralgias, and malaise) Pathogenesis 1- immune-mediated 2- infectious
Overview of Stroke: Etiologies, Demographics, Syndromes, and Outcomes. Alex Abou-Chebl, MD, FSVIN Medical Director, Stroke Baptist Health Louisville
 Overview of Stroke: Etiologies, Demographics, Syndromes, and Outcomes Alex Abou-Chebl, MD, FSVIN Medical Director, Stroke Baptist Health Louisville Disclosure Statement of Financial Interest Within the
Overview of Stroke: Etiologies, Demographics, Syndromes, and Outcomes Alex Abou-Chebl, MD, FSVIN Medical Director, Stroke Baptist Health Louisville Disclosure Statement of Financial Interest Within the
Multislice CT. - fast scanning - submilimeter slices
 CT angiography Multislice CT - fast scanning - submilimeter slices CT angiography - Minimal invasivity - High resolution (similar to DSA, higher than MRI) - Cannot assess hemodynamics (contrary to DSA)
CT angiography Multislice CT - fast scanning - submilimeter slices CT angiography - Minimal invasivity - High resolution (similar to DSA, higher than MRI) - Cannot assess hemodynamics (contrary to DSA)
Varicose Veins Vascular Tumors
 Varicose Veins Vascular Tumors Varicose veins: Dilated tortuous increased intraluminal pressure incompetence of the venous valves. superficial veins of the upper and lower leg (m.c, high venous pressures,
Varicose Veins Vascular Tumors Varicose veins: Dilated tortuous increased intraluminal pressure incompetence of the venous valves. superficial veins of the upper and lower leg (m.c, high venous pressures,
Notifiable Medical Conditions
 Notifiable Medical Conditions A Acoustic neuroma Addison s disease Agoraphobia AIDS Alcohol problems Alzheimer s disease Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis - see Motor Neurone Disease Amputations Aneurysm Angina
Notifiable Medical Conditions A Acoustic neuroma Addison s disease Agoraphobia AIDS Alcohol problems Alzheimer s disease Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis - see Motor Neurone Disease Amputations Aneurysm Angina
Vascular Malformations of the Brain. William A. Cox, M.D. Forensic Pathologist/Neuropathologist. September 8, 2014
 Vascular Malformations of the Brain William A. Cox, M.D. Forensic Pathologist/Neuropathologist September 8, 2014 Vascular malformations of the brain are classified into four principal groups: arteriovenous
Vascular Malformations of the Brain William A. Cox, M.D. Forensic Pathologist/Neuropathologist September 8, 2014 Vascular malformations of the brain are classified into four principal groups: arteriovenous
Identifying Cerebrovascular Disorders. Wengui Yu, MD, PhD Department of Neurology, University of California, Irvine
 Identifying Cerebrovascular Disorders Wengui Yu, MD, PhD Department of Neurology, University of California, Irvine Objectives Review different types of cerebrovascular disorders. Briefly discuss etiology,
Identifying Cerebrovascular Disorders Wengui Yu, MD, PhD Department of Neurology, University of California, Irvine Objectives Review different types of cerebrovascular disorders. Briefly discuss etiology,
An aneurysm is a localized abnormal dilation of a blood vessel or the heart Types: 1-"true" aneurysm it involves all three layers of the arterial
 An aneurysm is a localized abnormal dilation of a blood vessel or the heart Types: 1-"true" aneurysm it involves all three layers of the arterial wall (intima, media, and adventitia) or the attenuated
An aneurysm is a localized abnormal dilation of a blood vessel or the heart Types: 1-"true" aneurysm it involves all three layers of the arterial wall (intima, media, and adventitia) or the attenuated
HEART AND SOUL STUDY OUTCOME EVENT - MORBIDITY REVIEW FORM
 REVIEW DATE REVIEWER'S ID HEART AND SOUL STUDY OUTCOME EVENT - MORBIDITY REVIEW FORM : DISCHARGE DATE: RECORDS FROM: Hospitalization ER Please check all that may apply: Myocardial Infarction Pages 2, 3,
REVIEW DATE REVIEWER'S ID HEART AND SOUL STUDY OUTCOME EVENT - MORBIDITY REVIEW FORM : DISCHARGE DATE: RECORDS FROM: Hospitalization ER Please check all that may apply: Myocardial Infarction Pages 2, 3,
/ / / / / / Hospital Abstraction: Stroke/TIA. Participant ID: Hospital Code: Multi-Ethnic Study of Atherosclerosis
 Multi-Ethnic Study of Atherosclerosis Participant ID: Hospital Code: Hospital Abstraction: Stroke/TIA History and Hospital Record 1. Was the participant hospitalized as an immediate consequence of this
Multi-Ethnic Study of Atherosclerosis Participant ID: Hospital Code: Hospital Abstraction: Stroke/TIA History and Hospital Record 1. Was the participant hospitalized as an immediate consequence of this
Nicolas Bianchi M.D. May 15th, 2012
 Nicolas Bianchi M.D. May 15th, 2012 New concepts in TIA Differential Diagnosis Stroke Syndromes To learn the new definitions and concepts on TIA as a condition of high risk for stroke. To recognize the
Nicolas Bianchi M.D. May 15th, 2012 New concepts in TIA Differential Diagnosis Stroke Syndromes To learn the new definitions and concepts on TIA as a condition of high risk for stroke. To recognize the
Vascular pathology. dr. Budiana Tanurahardja.,SpPA
 Vascular pathology dr. Budiana Tanurahardja.,SpPA DEPARTMENT of ANATOMIC PATHOLOGY FACULTY of MEDICINE UNIVERSITY of INDONESIA Center of Anatomic Pathology Studies Vascular Pathology Normal blood vessels.
Vascular pathology dr. Budiana Tanurahardja.,SpPA DEPARTMENT of ANATOMIC PATHOLOGY FACULTY of MEDICINE UNIVERSITY of INDONESIA Center of Anatomic Pathology Studies Vascular Pathology Normal blood vessels.
Case Presentation VASCULITIS. Case Presentation. Case Presentation. Vasculitis
 Case Presentation VASCULITIS The patient is a 24 year old woman who presented to the emergency room with left-sided weakness. She was confused and complained of a severe headache. She was noted to have
Case Presentation VASCULITIS The patient is a 24 year old woman who presented to the emergency room with left-sided weakness. She was confused and complained of a severe headache. She was noted to have
Vascular Disorders. Nervous System Disorders (Part B-1) Module 8 -Chapter 14. Cerebrovascular disease S/S 1/9/2013
 Nervous System Disorders (Part B-1) Module 8 -Chapter 14 Overview ACUTE NEUROLOGIC DISORDERS Vascular Disorders Infections/Inflammation/Toxins Metabolic, Endocrinologic, Nutritional, Toxic Neoplastic Traumatic
Nervous System Disorders (Part B-1) Module 8 -Chapter 14 Overview ACUTE NEUROLOGIC DISORDERS Vascular Disorders Infections/Inflammation/Toxins Metabolic, Endocrinologic, Nutritional, Toxic Neoplastic Traumatic
Vasculitis local: systemic
 Vasculitis Inflammation of the vessel wall. Signs and symptoms: 1- local: according to the involved tissue 2- systemic:(fever, myalgia, arthralgias, and malaise) Pathogenesis 1- immune-mediated inflammation
Vasculitis Inflammation of the vessel wall. Signs and symptoms: 1- local: according to the involved tissue 2- systemic:(fever, myalgia, arthralgias, and malaise) Pathogenesis 1- immune-mediated inflammation
VASCULITIS. Case Presentation. Case Presentation
 VASCULITIS Case Presentation The patient is a 24 year old woman who presented to the emergency room with left-sided weakness. She was confused and complained of a severe headache. She was noted to have
VASCULITIS Case Presentation The patient is a 24 year old woman who presented to the emergency room with left-sided weakness. She was confused and complained of a severe headache. She was noted to have
Non-Invasive Vascular Studies
 Non-Invasive Vascular Studies Policy Number: 2.01.509 Last Review: 7/2018 Origination: 7/2016 Next Review: 7/2019 Policy Blue Cross and Blue Shield of Kansas City (Blue KC) will provide coverage for Non-
Non-Invasive Vascular Studies Policy Number: 2.01.509 Last Review: 7/2018 Origination: 7/2016 Next Review: 7/2019 Policy Blue Cross and Blue Shield of Kansas City (Blue KC) will provide coverage for Non-
Aneurysms & a Brief Discussion on Embolism
 Aneurysms & a Brief Discussion on Embolism Aneurysms, overview = congenital or acquired dilations of blood vessels or the heart True aneurysms -involve all three layers of the artery (intima, media, and
Aneurysms & a Brief Discussion on Embolism Aneurysms, overview = congenital or acquired dilations of blood vessels or the heart True aneurysms -involve all three layers of the artery (intima, media, and
ST - segment Elevation Myocardial Infarction complicating an atypical Kawasaki disease
 ST - segment Elevation Myocardial Infarction complicating an atypical Kawasaki disease Raluca PRISECARU, Marc VINCENT, Steven VERCAUTEREN Brussels Heart Center, Brussels, Belgium Disclosure None Clinical
ST - segment Elevation Myocardial Infarction complicating an atypical Kawasaki disease Raluca PRISECARU, Marc VINCENT, Steven VERCAUTEREN Brussels Heart Center, Brussels, Belgium Disclosure None Clinical
Subject Index. Automated triggering 88 AVM 128, 129
 Subject Index A Abberrant right subclavian artery 150 Abdominal aorta 195-208 aneurysm (AAA) 198 aneurysm branching vessels 201 aortic dissection 203 dark-blood imaging 197 eccentric aneurysm 199 fusiform
Subject Index A Abberrant right subclavian artery 150 Abdominal aorta 195-208 aneurysm (AAA) 198 aneurysm branching vessels 201 aortic dissection 203 dark-blood imaging 197 eccentric aneurysm 199 fusiform
A Case of Carotid-Cavernous Fistula
 A Case of Carotid-Cavernous Fistula By : Mohamed Elkhawaga 2 nd Year Resident of Ophthalmology Alexandria University A 19 year old male patient came to our outpatient clinic, complaining of : -Severe conjunctival
A Case of Carotid-Cavernous Fistula By : Mohamed Elkhawaga 2 nd Year Resident of Ophthalmology Alexandria University A 19 year old male patient came to our outpatient clinic, complaining of : -Severe conjunctival
CT of Acute Thoracic Aortic Syndromes Stuart S. Sagel, M.D.
 CT of Acute Thoracic Aortic Syndromes Stuart S. Sagel, M.D. Thoracic Aortic Aneurysms Atherosclerotic Dissection Penetrating ulcer Mycotic Inflammatory (vasculitis) Traumatic Aortic Imaging Options Catheter
CT of Acute Thoracic Aortic Syndromes Stuart S. Sagel, M.D. Thoracic Aortic Aneurysms Atherosclerotic Dissection Penetrating ulcer Mycotic Inflammatory (vasculitis) Traumatic Aortic Imaging Options Catheter
CUMULATIVE ILLNESS RATING SCALE (CIRS)
 CUMULATIVE ILLNESS RATING SCALE (CIRS) The CIRS used in this protocol is designed to provide an assessment of recurrent or ongoing chronic comorbid conditions, classified by 14 organ systems. Using the
CUMULATIVE ILLNESS RATING SCALE (CIRS) The CIRS used in this protocol is designed to provide an assessment of recurrent or ongoing chronic comorbid conditions, classified by 14 organ systems. Using the
PTA 106 Unit 1 Lecture 3
 PTA 106 Unit 1 Lecture 3 The Basics Arteries: Carry blood away from the heart toward tissues. They typically have thicker vessels walls to handle increased pressure. Contain internal and external elastic
PTA 106 Unit 1 Lecture 3 The Basics Arteries: Carry blood away from the heart toward tissues. They typically have thicker vessels walls to handle increased pressure. Contain internal and external elastic
Head MRA/MRV studies of the head may be considered medically necessary for the following strongly suspected vascular diseases:
 Original Issue Date (Created): July 1, 2002 Most Recent Review Date (Revised): January 28, 2014 Effective Date: September 5, 2014 I. POLICY Head MRA/MRV studies of the head may be considered medically
Original Issue Date (Created): July 1, 2002 Most Recent Review Date (Revised): January 28, 2014 Effective Date: September 5, 2014 I. POLICY Head MRA/MRV studies of the head may be considered medically
CT Imaging of Blunt and Penetrating Vascular Trauma DENNIS FOLEY MEDICAL COLLEGE WISCONSIN
 CT Imaging of Blunt and Penetrating Vascular Trauma DENNIS FOLEY MEDICAL COLLEGE WISCONSIN THORACO ABDOMINAL TRAUMA 0 10 20 30 40 50 60 5 cc/sec 30 secs 1.25 mm/ 55 mm Z1.375 2.5 mm/ 55 mm Z 1.375 Grade
CT Imaging of Blunt and Penetrating Vascular Trauma DENNIS FOLEY MEDICAL COLLEGE WISCONSIN THORACO ABDOMINAL TRAUMA 0 10 20 30 40 50 60 5 cc/sec 30 secs 1.25 mm/ 55 mm Z1.375 2.5 mm/ 55 mm Z 1.375 Grade
Neuropathology lecture series. III. Neuropathology of Cerebrovascular Disease. Physiology of cerebral blood flow
 Neuropathology lecture series III. Neuropathology of Cerebrovascular Disease Physiology of cerebral blood flow Brain makes up only 2% of body weight Percentage of cardiac output: 15-20% Percentage of O
Neuropathology lecture series III. Neuropathology of Cerebrovascular Disease Physiology of cerebral blood flow Brain makes up only 2% of body weight Percentage of cardiac output: 15-20% Percentage of O
Physician s Vascular Interpretation Examination Content Outline
 Physician s Vascular Interpretation Examination Content Outline (Outline Summary) # Domain Subdomain Percentage 1 2 3 4 5 6 Cerebrovascular Abdominal Peripheral Arterial - Duplex Imaging Peripheral Arterial
Physician s Vascular Interpretation Examination Content Outline (Outline Summary) # Domain Subdomain Percentage 1 2 3 4 5 6 Cerebrovascular Abdominal Peripheral Arterial - Duplex Imaging Peripheral Arterial
Department of Radiology University of California San Diego. MR Angiography. Techniques & Applications. John R. Hesselink, M.D.
 Department of Radiology University of California San Diego MR Angiography Techniques & Applications John R. Hesselink, M.D. Vascular Imaging Arterial flow void Flow enhancement Gadolinium enhancement Vascular
Department of Radiology University of California San Diego MR Angiography Techniques & Applications John R. Hesselink, M.D. Vascular Imaging Arterial flow void Flow enhancement Gadolinium enhancement Vascular
Cerebrovascular Disease
 Neuropathology lecture series Cerebrovascular Disease Physiology of cerebral blood flow Brain makes up only 2% of body weight Percentage of cardiac output: 15-20% Percentage of O 2 consumption (resting):
Neuropathology lecture series Cerebrovascular Disease Physiology of cerebral blood flow Brain makes up only 2% of body weight Percentage of cardiac output: 15-20% Percentage of O 2 consumption (resting):
Marc Norman, Ph.D. - Do Not Use without Permission 1. Cerebrovascular Accidents. Marc Norman, Ph.D. Department of Psychiatry
 Cerebrovascular Accidents Marc Norman, Ph.D. Department of Psychiatry Neuropsychiatry and Behavioral Medicine Neuropsychology Clinical Training Seminar 1 5 http://www.nlm.nih.gov/medlineplus/ency/images/ency/fullsize/18009.jpg
Cerebrovascular Accidents Marc Norman, Ph.D. Department of Psychiatry Neuropsychiatry and Behavioral Medicine Neuropsychology Clinical Training Seminar 1 5 http://www.nlm.nih.gov/medlineplus/ency/images/ency/fullsize/18009.jpg
Aortic arch pathology. Cerebral ischemia following carotid artery stenosis.
 Important: -Subclavian Steal Syndrome -Cerebral ischemia Aortic arch pathology. Cerebral ischemia following carotid artery stenosis. Mina Aubeed & Alba Hernández Pinilla Aortic arch pathology Common arch
Important: -Subclavian Steal Syndrome -Cerebral ischemia Aortic arch pathology. Cerebral ischemia following carotid artery stenosis. Mina Aubeed & Alba Hernández Pinilla Aortic arch pathology Common arch
Dr Rodney Itaki Lecturer Anatomical Pathology Discipline. University of Papua New Guinea School of Medicine & Health Sciences Division of Pathology
 Vasculitis Dr Rodney Itaki Lecturer Anatomical Pathology Discipline University of Papua New Guinea School of Medicine & Health Sciences Division of Pathology Disease Spectrum Hypersensitivity vasculitis/microscopic
Vasculitis Dr Rodney Itaki Lecturer Anatomical Pathology Discipline University of Papua New Guinea School of Medicine & Health Sciences Division of Pathology Disease Spectrum Hypersensitivity vasculitis/microscopic
Patient #1 A Spouse $534,946.73
 Shock Loss Report MM & RX Combined PUNBR: 002 GRNBR: 248 Warning Amount: 100000 Over Amount: 200000 Incurred MM 1/1/2014 through 12/31/2016 PaidMM 1/1/2016 through 12/31/2016 Incurred RX 12/16/2015 through
Shock Loss Report MM & RX Combined PUNBR: 002 GRNBR: 248 Warning Amount: 100000 Over Amount: 200000 Incurred MM 1/1/2014 through 12/31/2016 PaidMM 1/1/2016 through 12/31/2016 Incurred RX 12/16/2015 through
2. Subarachnoid Hemorrhage
 Causes: 2. Subarachnoid Hemorrhage A. Saccular (berry) aneurysm - Is the most frequent cause of clinically significant subarachnoid hemorrhage is rupture of a saccular (berry) aneurysm. B. Vascular malformation
Causes: 2. Subarachnoid Hemorrhage A. Saccular (berry) aneurysm - Is the most frequent cause of clinically significant subarachnoid hemorrhage is rupture of a saccular (berry) aneurysm. B. Vascular malformation
Student Outline. Improving Transportation Safety: Commercial Driver Medical Examiner Training CHAPTER 1. General FMCSA Information
 Student Outline CHAPTER 1 General FMCSA Information FMCSA Mission Statement / Dedicated to Safety / NRCME Important Definitions Regulations Vs. Medical Guidelines Privacy and the Medical Examination 13
Student Outline CHAPTER 1 General FMCSA Information FMCSA Mission Statement / Dedicated to Safety / NRCME Important Definitions Regulations Vs. Medical Guidelines Privacy and the Medical Examination 13
THORACIC AORTIC DISSECTION
 The Essence of Aortic Dissection THORACIC AORTIC DISSECTION Aortic dissection can be classified as acute if it s onset has been less than 14 days or chronic if its onset has been more than 14 days. Mortality
The Essence of Aortic Dissection THORACIC AORTIC DISSECTION Aortic dissection can be classified as acute if it s onset has been less than 14 days or chronic if its onset has been more than 14 days. Mortality
Vascular Technology Examination Content Outline
 Vascular Technology Examination Content Outline (Outline Summary) # Domain Subdomain Percentage 1 Normal Anatomy, Perfusion, and Function Evaluate normal anatomy, perfusion, function 2 Pathology, Perfusion,
Vascular Technology Examination Content Outline (Outline Summary) # Domain Subdomain Percentage 1 Normal Anatomy, Perfusion, and Function Evaluate normal anatomy, perfusion, function 2 Pathology, Perfusion,
Stroke / CVA TIA Trauma Dizziness Headaches. Acoustic Neuroma Syrinx Visual Change Vascular Lesions (AVM) Elevated Prolactin Vertigo Bell s palsy
 Head Brain Alzheimer s Mental Status Change Confusion Dementia Memory Loss Dizziness Headaches MRI Brain w/o 70551 Tumor / Mass / Cancer Cranial Nerve Lesions HIV Infection Suspected MS Neurofibromatosis
Head Brain Alzheimer s Mental Status Change Confusion Dementia Memory Loss Dizziness Headaches MRI Brain w/o 70551 Tumor / Mass / Cancer Cranial Nerve Lesions HIV Infection Suspected MS Neurofibromatosis
Richard C. Staab Memorial Symposium. Vascular Primer for the Internist Sharolyn Cook DO OSU Dept of IM, Cardiology Division
 Richard C. Staab Memorial Symposium Vascular Primer for the Internist Sharolyn Cook DO OSU Dept of IM, Cardiology Division Goals of our 50 min Together Review the incidence and prevalence of vascular disease
Richard C. Staab Memorial Symposium Vascular Primer for the Internist Sharolyn Cook DO OSU Dept of IM, Cardiology Division Goals of our 50 min Together Review the incidence and prevalence of vascular disease
Contents. 1 Embryological and Anatomical Introduction... 1
 1 Embryological and Anatomical Introduction.... 1 1.1 Preliminary Remarks.................... 1 1.2 Leptomeninges....................... 21 1.3 Subpial Space........................ 22 1.3.1 Anatomy...........................
1 Embryological and Anatomical Introduction.... 1 1.1 Preliminary Remarks.................... 1 1.2 Leptomeninges....................... 21 1.3 Subpial Space........................ 22 1.3.1 Anatomy...........................
c) What is the name of RBC (erythrocyte) formation? Where do blood cells form?
 UNIT 6: CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM 1) List the three general functions of BLOOD. REVIEW QUESTIONS Blood 2) a) What are the three formed elements /cellular elements in blood? b) Describe the composition of the
UNIT 6: CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM 1) List the three general functions of BLOOD. REVIEW QUESTIONS Blood 2) a) What are the three formed elements /cellular elements in blood? b) Describe the composition of the
Cardiovascular Disease
 Cardiovascular Disease Certification Examination Blueprints Blueprint for the Full-Day, Multiple-Choice Questions Component of the Exam: Purpose of the exam The exam is designed to evaluate the knowledge,
Cardiovascular Disease Certification Examination Blueprints Blueprint for the Full-Day, Multiple-Choice Questions Component of the Exam: Purpose of the exam The exam is designed to evaluate the knowledge,
Initial symptom or syndrome: (1) FOCAL WEAKNESS OR NUMBNESS
 View the referenced DVD patient cases, especially if few hospital or clinic patients are encountered for any one symptom or syndrome. The DVD patient cases are referenced by initial symptom or syndrome
View the referenced DVD patient cases, especially if few hospital or clinic patients are encountered for any one symptom or syndrome. The DVD patient cases are referenced by initial symptom or syndrome
Visceral aneurysm. Diagnosis and Interventions M.NEDEVSKA
 Visceral aneurysm Diagnosis and Interventions M.NEDEVSKA History 1953 De Bakeyand Cooley Visceral aneurysm VAAs rare, reported incidence of 0.01 to 0.2% on routine autopsies. Clinically important Potentially
Visceral aneurysm Diagnosis and Interventions M.NEDEVSKA History 1953 De Bakeyand Cooley Visceral aneurysm VAAs rare, reported incidence of 0.01 to 0.2% on routine autopsies. Clinically important Potentially
vasculitis Patomorfologia vasculitis (arteritis) caused by infections vasculitis (arteritis) caused by infections
 Patomorfologia Lecture 12 prof hab. n. med. Andrzej Marszałek VASCULITIS infectious vasculitis non-infectious causes: Aspergillus Rickettsiae vasculitis (arteritis) caused by infections Mucormycosis syphylis
Patomorfologia Lecture 12 prof hab. n. med. Andrzej Marszałek VASCULITIS infectious vasculitis non-infectious causes: Aspergillus Rickettsiae vasculitis (arteritis) caused by infections Mucormycosis syphylis
Cerebral Vascular Diseases. Nabila Hamdi MD, PhD
 Cerebral Vascular Diseases Nabila Hamdi MD, PhD Outline I. Stroke statistics II. Cerebral circulation III. Clinical symptoms of stroke IV. Pathogenesis of cerebral infarcts (Stroke) 1. Ischemic - Thrombotic
Cerebral Vascular Diseases Nabila Hamdi MD, PhD Outline I. Stroke statistics II. Cerebral circulation III. Clinical symptoms of stroke IV. Pathogenesis of cerebral infarcts (Stroke) 1. Ischemic - Thrombotic
Imaging abdominal vascular emergencies. V.Stoynova
 Imaging abdominal vascular emergencies V.Stoynova Abdominal vessels V. Stoynova 2 Acute liver bleeding trauma anticoagulant therapy liver disease : HCC, adenoma, meta, FNH, Hemangioma Diagnosis :CT angiography
Imaging abdominal vascular emergencies V.Stoynova Abdominal vessels V. Stoynova 2 Acute liver bleeding trauma anticoagulant therapy liver disease : HCC, adenoma, meta, FNH, Hemangioma Diagnosis :CT angiography
Cryptogenic Enlargement Of Bilateral Superior Ophthalmic Veins
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Radiology Volume 18 Number 1 Cryptogenic Enlargement Of Bilateral Superior Ophthalmic Veins K Kragha Citation K Kragha. Cryptogenic Enlargement Of Bilateral Superior Ophthalmic
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Radiology Volume 18 Number 1 Cryptogenic Enlargement Of Bilateral Superior Ophthalmic Veins K Kragha Citation K Kragha. Cryptogenic Enlargement Of Bilateral Superior Ophthalmic
Atlas of the Vasculitic Syndromes
 CHAPTER e40 Atlas of the Vasculitic Syndromes Carol A. Langford Anthony S. Fauci Diagnosis of the vasculitic syndromes is usually based upon characteristic histologic or arteriographic findings in a patient
CHAPTER e40 Atlas of the Vasculitic Syndromes Carol A. Langford Anthony S. Fauci Diagnosis of the vasculitic syndromes is usually based upon characteristic histologic or arteriographic findings in a patient
Internal Carotid Artery Dissection
 May 2011 Internal Carotid Artery Dissection Carolyn April, HMS IV Agenda Presentation of a clinical case Discussion of the clinical features of ICA dissection Discussion of the imaging modalities used
May 2011 Internal Carotid Artery Dissection Carolyn April, HMS IV Agenda Presentation of a clinical case Discussion of the clinical features of ICA dissection Discussion of the imaging modalities used
Vascular Malformations of the Brain: A Review of Imaging Features and Risks
 Vascular Malformations of the Brain: A Review of Imaging Features and Risks Comprehensive Neuroradiology: Best Practices October 27-30, 2016 Sudhakar R. Satti, MD Associate Director Neurointerventional
Vascular Malformations of the Brain: A Review of Imaging Features and Risks Comprehensive Neuroradiology: Best Practices October 27-30, 2016 Sudhakar R. Satti, MD Associate Director Neurointerventional
DEPARTMENT OF HEALTH & HUMAN SERVICES Public Health Service
 M AY. 6. 2011 10:37 A M F D A - C D R H - O D E - P M O N O. 4147 P. 1 DEPARTMENT OF HEALTH & HUMAN SERVICES Public Health Service Food and Drug Administration 10903 New Hampshire Avenue Document Control
M AY. 6. 2011 10:37 A M F D A - C D R H - O D E - P M O N O. 4147 P. 1 DEPARTMENT OF HEALTH & HUMAN SERVICES Public Health Service Food and Drug Administration 10903 New Hampshire Avenue Document Control
Non-Traumatic Neuro Emergencies
 Department of Radiology University of California San Diego Non-Traumatic Neuro Emergencies John R. Hesselink, M.D. Nontraumatic Neuroemergencies 1. Acute focal neurological deficit 2. Worst headache of
Department of Radiology University of California San Diego Non-Traumatic Neuro Emergencies John R. Hesselink, M.D. Nontraumatic Neuroemergencies 1. Acute focal neurological deficit 2. Worst headache of
Learning Objectives for Rotations in Vascular Surgery Year 3 Basic Clerkship
 Learning Objectives for Rotations in Vascular Surgery Year 3 Basic Clerkship CLINICAL PROBLEMS IN VASCULAR SURGERY 1. ABDOMINAL AORTIC ANEURYSM A 70 year old man presents in the emergency department with
Learning Objectives for Rotations in Vascular Surgery Year 3 Basic Clerkship CLINICAL PROBLEMS IN VASCULAR SURGERY 1. ABDOMINAL AORTIC ANEURYSM A 70 year old man presents in the emergency department with
Vessels. Clinical correlations. Published on Second Faculty of Medicine, Charles University (
 Published on Second Faculty of Medicine, Charles University ( https://www.lf2.cuni.cz) LF2 > Vessels Vessels The test on the vessels and lymphatic system is in written format and follows the general rules
Published on Second Faculty of Medicine, Charles University ( https://www.lf2.cuni.cz) LF2 > Vessels Vessels The test on the vessels and lymphatic system is in written format and follows the general rules
The Peripheral Vascular System
 The Peripheral Vascular System Anatomy and Physiology Arteries Arteries contain 3 concentric layers of tissue: - the intima - the media - the adventitia The intima The endothelium of the intima has metabolic
The Peripheral Vascular System Anatomy and Physiology Arteries Arteries contain 3 concentric layers of tissue: - the intima - the media - the adventitia The intima The endothelium of the intima has metabolic
VASCULITIS AND VASCULOPATHY
 VASCULITIS AND VASCULOPATHY Mantosh S. Rattan @CincyKidsRad facebook.com/cincykidsrad Disclosure No relevant financial disclosures Outline Overview Referral pathways MR imaging Case examples Vasculitis
VASCULITIS AND VASCULOPATHY Mantosh S. Rattan @CincyKidsRad facebook.com/cincykidsrad Disclosure No relevant financial disclosures Outline Overview Referral pathways MR imaging Case examples Vasculitis
Copy Right- Hongqi ZHANG-Department of Anatomy-Fudan University. Systematic Anatomy. Angiology Part 4. Veins. Dr.Hongqi Zhang ( 张红旗 )
 Systematic Anatomy Angiology Part 4 Veins Dr.Hongqi Zhang ( 张红旗 ) Email: zhanghq58@126.com 1 General introduction of the veins Vessel which return the blood back to atrium No pulsation,veneous blood, metabolic
Systematic Anatomy Angiology Part 4 Veins Dr.Hongqi Zhang ( 张红旗 ) Email: zhanghq58@126.com 1 General introduction of the veins Vessel which return the blood back to atrium No pulsation,veneous blood, metabolic
A A U
 PVD Venous AUC Rating Sheet 2nd Round 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 Median I NI MADM Rating Agree Disagree Upper Extremity Venous Evaluation Table 1. Venous Duplex of the Upper Extremities for Patency
PVD Venous AUC Rating Sheet 2nd Round 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 Median I NI MADM Rating Agree Disagree Upper Extremity Venous Evaluation Table 1. Venous Duplex of the Upper Extremities for Patency
9/11/11. Temporal Arteritis. Background. Background. Richard E. Castillo, OD, DO NORTHEASTERN STATE UNIVERSITY Director, Ophthalmic Surgery Service
 Temporal Arteritis Richard E. Castillo, OD, DO NORTHEASTERN STATE UNIVERSITY Director, Ophthalmic Surgery Service 1 Background Giant Cell Arteritis Temporal Arteritis Cranial Arteritis Granulomatous Arteritis
Temporal Arteritis Richard E. Castillo, OD, DO NORTHEASTERN STATE UNIVERSITY Director, Ophthalmic Surgery Service 1 Background Giant Cell Arteritis Temporal Arteritis Cranial Arteritis Granulomatous Arteritis
Job Task Analysis for ARDMS Abdomen Data Collected: June 30, 2011
 Job Task Analysis for ARDMS Abdomen Data Collected: June 30, 2011 Reported: Analysis Summary for: Abdomen Examination Survey Dates 06/13/2011-06/26/2011 Invited Respondents 6,000 Surveys with Demographics
Job Task Analysis for ARDMS Abdomen Data Collected: June 30, 2011 Reported: Analysis Summary for: Abdomen Examination Survey Dates 06/13/2011-06/26/2011 Invited Respondents 6,000 Surveys with Demographics
List of Qualifying Conditions
 List of Qualifying Conditions Cancer Conditions 1) Adrenal cancer 2) Bladder cancer 3) Bone cancer all forms 4) Brain cancer 5) Breast cancer 6) Cervical cancer 7) Colon cancer 8) Colorectal cancer 9)
List of Qualifying Conditions Cancer Conditions 1) Adrenal cancer 2) Bladder cancer 3) Bone cancer all forms 4) Brain cancer 5) Breast cancer 6) Cervical cancer 7) Colon cancer 8) Colorectal cancer 9)
Contractor Information. LCD Information. Local Coverage Determination (LCD): Magnetic Resonance Angiography (L34424) Document Information
 Local Coverage Determination (LCD): Magnetic Resonance Angiography (L34424) Links in PDF documents are not guaranteed to work. To follow a web link, please use the MCD Website. Contractor Information Contractor
Local Coverage Determination (LCD): Magnetic Resonance Angiography (L34424) Links in PDF documents are not guaranteed to work. To follow a web link, please use the MCD Website. Contractor Information Contractor
PREAMBLE GENERAL DIAGNOSTIC RADIOLOGY
 PREAMBLE The General Diagnostic Radiology category is intended to cover the body of knowledge a practicing board certified Diagnostic Radiologist should know. Since the range of content relevant to the
PREAMBLE The General Diagnostic Radiology category is intended to cover the body of knowledge a practicing board certified Diagnostic Radiologist should know. Since the range of content relevant to the
10/19/12. Uncommon Causes of Stroke. José Biller, MD, FACP, FAAN, FAHA Disclosures. Dr. Biller has no disclosures to report
 10/19/12 Uncommon Causes of Stroke José Biller, MD, FACP, FAAN, FAHA Loyola University Chicago Stritch School of Medicine Chicago, IL José Biller, MD, FACP, FAAN, FAHA Disclosures Dr. Biller has no disclosures
10/19/12 Uncommon Causes of Stroke José Biller, MD, FACP, FAAN, FAHA Loyola University Chicago Stritch School of Medicine Chicago, IL José Biller, MD, FACP, FAAN, FAHA Disclosures Dr. Biller has no disclosures
Guidelines for Ultrasound Surveillance
 Guidelines for Ultrasound Surveillance Carotid & Lower Extremity by Ian Hamilton, Jr, MD, MBA, RPVI, FACS Corporate Medical Director BlueCross BlueShield of Tennessee guidelines for ultrasound surveillance
Guidelines for Ultrasound Surveillance Carotid & Lower Extremity by Ian Hamilton, Jr, MD, MBA, RPVI, FACS Corporate Medical Director BlueCross BlueShield of Tennessee guidelines for ultrasound surveillance
Overview of imaging modalities for cerebral aneurysms
 Overview of imaging modalities for cerebral aneurysms Soroush Zaghi BIDMC PCE: Radiology August 2008 (Images from BIDMC, PACS.) Our Patient: Presentation Our patient is a 57 y/o woman who reports blowing
Overview of imaging modalities for cerebral aneurysms Soroush Zaghi BIDMC PCE: Radiology August 2008 (Images from BIDMC, PACS.) Our Patient: Presentation Our patient is a 57 y/o woman who reports blowing
Supplementary Material Two List of clinical papers using ferumoxytol
 Supplementary Material Two List of clinical papers using ferumoxytol This table was created as supplementary material for the review titled Current and Potential Imaging Applications of Ferumoxytol for
Supplementary Material Two List of clinical papers using ferumoxytol This table was created as supplementary material for the review titled Current and Potential Imaging Applications of Ferumoxytol for
3 Circulatory Pathways
 40 Chapter 3 Circulatory Pathways Systemic Arteries -Arteries carry blood away from the heart to the various organs of the body. -The aorta is the longest artery in the body; it branches to give rise to
40 Chapter 3 Circulatory Pathways Systemic Arteries -Arteries carry blood away from the heart to the various organs of the body. -The aorta is the longest artery in the body; it branches to give rise to
What is the appropriate evaluation of cryptogenic stroke, and when is a hypercoagulability work-up needed? David E. Thaler, MD, PhD, FAHA
 What is the appropriate evaluation of cryptogenic stroke, and when is a hypercoagulability work-up needed? David E. Thaler, MD, PhD, FAHA Neurologist in Chief, Tufts Medical Center Professor and Chair
What is the appropriate evaluation of cryptogenic stroke, and when is a hypercoagulability work-up needed? David E. Thaler, MD, PhD, FAHA Neurologist in Chief, Tufts Medical Center Professor and Chair
Cardiothoracic and Cardiothoracic Surgery ICD-10-CM 2014: Reference Mapping Card
 2014: Reference Mapping Card 162.3 Malignant neoplasm upper lobe lung 162.5 Malignant neoplasm lower lobe lung 162.9 lung/bronchus 396.2 396.3 Mitral insufficiency, aortic stenosis Mitral aortic valve
2014: Reference Mapping Card 162.3 Malignant neoplasm upper lobe lung 162.5 Malignant neoplasm lower lobe lung 162.9 lung/bronchus 396.2 396.3 Mitral insufficiency, aortic stenosis Mitral aortic valve
CENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTEM TRAUMA and Subarachnoid Hemorrhage. By: Shifaa AlQa qa
 CENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTEM TRAUMA and Subarachnoid Hemorrhage By: Shifaa AlQa qa Subarachnoid Hemorrhage Causes: Rupture of a saccular (berry) aneurysm Vascular malformation Trauma Hematologic disturbances
CENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTEM TRAUMA and Subarachnoid Hemorrhage By: Shifaa AlQa qa Subarachnoid Hemorrhage Causes: Rupture of a saccular (berry) aneurysm Vascular malformation Trauma Hematologic disturbances
Blood Vessel Disorders
 Blood Vessel Disorders Objectives: Hyperlipidemia Arterioschlerosis Disorders associated with arteries Disorders associated with veins Hypertension and hypotension Part 1: Diseases Associated with Arterial
Blood Vessel Disorders Objectives: Hyperlipidemia Arterioschlerosis Disorders associated with arteries Disorders associated with veins Hypertension and hypotension Part 1: Diseases Associated with Arterial
SUPPLEMENTAL MATERIAL
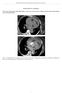 SUPPLEMENTL MTERIL Marie erna, Martin Kocher, Rohit Philip Thomas. cute aorta, overview of acute T findings and endovascular treatment options (doi: 10.5507/bp.2016.060) Fig. 1. : Non-enhanced T, hemopericardium
SUPPLEMENTL MTERIL Marie erna, Martin Kocher, Rohit Philip Thomas. cute aorta, overview of acute T findings and endovascular treatment options (doi: 10.5507/bp.2016.060) Fig. 1. : Non-enhanced T, hemopericardium
Introduction to Neuroimaging spine. John J. McCormick MD
 Introduction to Neuroimaging spine John J. McCormick MD Neuroanatomy Netter drawings Radiographic Anatomy Cervical Spine Cervical Spine Oblique View Cervical Spine Dens View Thoracic Spine Lumbar Spine
Introduction to Neuroimaging spine John J. McCormick MD Neuroanatomy Netter drawings Radiographic Anatomy Cervical Spine Cervical Spine Oblique View Cervical Spine Dens View Thoracic Spine Lumbar Spine
Cardiac Pathology & Rehabilitation
 Cardiac Pathology & Rehabilitation Which of the following best describes the physical activity performed in my leisure time? A. I perform vigorous physical activity 3X/week for 20 minutes each time B.
Cardiac Pathology & Rehabilitation Which of the following best describes the physical activity performed in my leisure time? A. I perform vigorous physical activity 3X/week for 20 minutes each time B.
Cerebrovascular Disease
 Neuropathology lecture series Cerebrovascular Disease Kurenai Tanji, M.D., Ph.D. December 11, 2007 Physiology of cerebral blood flow Brain makes up only 2% of body weight Percentage of cardiac output:
Neuropathology lecture series Cerebrovascular Disease Kurenai Tanji, M.D., Ph.D. December 11, 2007 Physiology of cerebral blood flow Brain makes up only 2% of body weight Percentage of cardiac output:
Abdominal Exam: The examination of the abdomen used by physicians to detect an abdominal aortic aneurysm.
 Glossary of Terms Abdominal Exam: The examination of the abdomen used by physicians to detect an abdominal aortic aneurysm. Angiogram: A diagnostic test requiring the insertion of a catheter into an artery
Glossary of Terms Abdominal Exam: The examination of the abdomen used by physicians to detect an abdominal aortic aneurysm. Angiogram: A diagnostic test requiring the insertion of a catheter into an artery
Visceral Vascular Ultrasound. Joel Thompson, MD, MPH Borg & Ide Imaging
 Visceral Vascular Ultrasound Joel Thompson, MD, MPH Borg & Ide Imaging Objectives: Review major abdominal vascular structures Identify normal peak systolic velocity (PSV) for major abdominal arteries.
Visceral Vascular Ultrasound Joel Thompson, MD, MPH Borg & Ide Imaging Objectives: Review major abdominal vascular structures Identify normal peak systolic velocity (PSV) for major abdominal arteries.
M555 Medical Neuroscience Blood Flow in CNS Meninges Blood Brain Barrier CSF
 M555 Medical Neuroscience Blood Flow in CNS Meninges Blood Brain Barrier CSF Arterial Blood Flow to CNS approximately % of what goes wrong within the skull that produces neurological deficits is vascular
M555 Medical Neuroscience Blood Flow in CNS Meninges Blood Brain Barrier CSF Arterial Blood Flow to CNS approximately % of what goes wrong within the skull that produces neurological deficits is vascular
Vasculitis. Edward Dwyer, M.D. Division of Rheumatology. Vasculitis
 Edward Dwyer, M.D. Division of Rheumatology VASCULITIS is a primary inflammatory disease process of the vasculature Determinants of the Clinical Manifestations of : Target organ involved Size of vessel
Edward Dwyer, M.D. Division of Rheumatology VASCULITIS is a primary inflammatory disease process of the vasculature Determinants of the Clinical Manifestations of : Target organ involved Size of vessel
Using 3-Digit ICD-9-CM Codes with the Elixhauser Comorbidity Index
 Congestive Heart Failure 398.91 Rheumatic heart failure (congestive) 398 Other rheumatic heart disease 402.01, 402.11, 402.91 402 Hypertensive heart disease 404.01, 404.03, 404.11, 404.13, 404.91, 404.93
Congestive Heart Failure 398.91 Rheumatic heart failure (congestive) 398 Other rheumatic heart disease 402.01, 402.11, 402.91 402 Hypertensive heart disease 404.01, 404.03, 404.11, 404.13, 404.91, 404.93
Urinary tract embolization
 Beograd, 14.10.2012 Urinary tract embolization asist. Peter Popovič, MD, MSc Head of abdominal radiology department, Institute of Radiology, UMC Ljubljana Embolization Who and when procedure: local/general
Beograd, 14.10.2012 Urinary tract embolization asist. Peter Popovič, MD, MSc Head of abdominal radiology department, Institute of Radiology, UMC Ljubljana Embolization Who and when procedure: local/general
PAEDIATRIC VASCULITIS
 PAEDIATRIC VASCULITIS Lawrence Owino Okong o, Mmed (UoN); Mphil. (UCT). Lecturer, Department of Paediatrics and Child Health, University of Nairobi. Paediatrician/ Rheumatologist. OUTLINE Introduction
PAEDIATRIC VASCULITIS Lawrence Owino Okong o, Mmed (UoN); Mphil. (UCT). Lecturer, Department of Paediatrics and Child Health, University of Nairobi. Paediatrician/ Rheumatologist. OUTLINE Introduction
Schedule of Benefits. for Professional Fees Vascular Procedures
 Schedule of Benefits for Professional Fees 2018 Vascular Procedures ANASTOMOSIS RULES 820 Arteriovenous anastomosis in arm 1453 Arteriovenous anastomosis, open by basilic vein transposition 1465 Splenorenal
Schedule of Benefits for Professional Fees 2018 Vascular Procedures ANASTOMOSIS RULES 820 Arteriovenous anastomosis in arm 1453 Arteriovenous anastomosis, open by basilic vein transposition 1465 Splenorenal
ADDITIONS. The following codes have been added.
 ADDITIONS The following codes have been added. 99446 Interprofessional telephone/internet assessment and management service provided by treating/requesting physician or other qualified health care professional;
ADDITIONS The following codes have been added. 99446 Interprofessional telephone/internet assessment and management service provided by treating/requesting physician or other qualified health care professional;
CTP perfusion CT CT perfusion for the evaluation of heavily calcified coronary lesions 70 coronary in-stent restenosis 72
 4 Contents 3 10 1 CT 14 1. CT 14 2. CT 16 3. CT 18 4. CT 3 21 MPR 23 MRI 24 1 27 2 3T 1.5T 29 30 40 44 pericardial recess 45 CT 47 48 CT 50 CTA 54 multivessel disease 58 chronic total coronary occlusion:
4 Contents 3 10 1 CT 14 1. CT 14 2. CT 16 3. CT 18 4. CT 3 21 MPR 23 MRI 24 1 27 2 3T 1.5T 29 30 40 44 pericardial recess 45 CT 47 48 CT 50 CTA 54 multivessel disease 58 chronic total coronary occlusion:
Vascular Malformations
 Vascular Malformations LTC Robert Shih Chief of Neuroradiology Walter Reed Medical Center Special thanks to LTC Alice Smith (retired) Disclosures: None. This presentation reflects the personal views of
Vascular Malformations LTC Robert Shih Chief of Neuroradiology Walter Reed Medical Center Special thanks to LTC Alice Smith (retired) Disclosures: None. This presentation reflects the personal views of
