Patterns of Chinese medicine use in prescriptions for treating Alzheimer s disease in Taiwan
|
|
|
- Preston Booth
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 DOI /s Chinese Medicine RESEARCH Patterns of Chinese medicine use in prescriptions for treating Alzheimer s disease in Taiwan Shun Ku Lin 1, Sui Hing Yan 2, Jung Nien Lai 3,4* and Tung Hu Tsai 5 Open Access Abstract Background: Certain Chinese medicine (CM) herbs and acupuncture may protect against Alzheimer s disease (AD). However, there is a lack of research regarding the use of CM in patients with AD. The aim of this study was to investigate CM usage patterns in patients with AD, and identify the Chinese herbal formulae most commonly used for AD. Methods: This retrospective, nationwide, population-based cohort study was conducted using a randomly sampled cohort of one million patients, selected from the National Health Insurance Research Database between 1997 and 2008 in Taiwan. CM use and the top ten most frequently prescribed formulae for treating AD were assessed, including average formulae dose and frequency of prescriptions. Demographic characteristics, including sex, age and insurance level were examined, together with geographic location. Existing medical conditions with the behavioral and psychological symptoms of dementia, and medications associated with CM were also examined. Factors associated with CM use were analyzed by multiple logistic regressions. Results: The cohort included 1137 newly diagnosed AD patients, who were given conventional treatment for AD between 1997 and Among them, 78.2 % also used CM treatments, including Chinese herbal remedies, acupuncture and massage manipulation. Female patients (aor 1.57 with 95 % CI ) and those living in urban areas (aor 3.00 with 95 % CI in the middle of Taiwan) were more likely to use CM. After adjusting for demographic factors, AD patients suffering from the behavioral and psychological symptoms of dementia were more likely to seek CM treatment than those with no symptoms (aor 2.26 with 95 % CI in patients suffering more than three symptoms). Bu-Zhong-Yi-Qi-Tang and Ji-Sheng-Shen-Qi-Wan were the two formulae most frequently prescribed by CM practitioners for treating AD. Conclusion: Most people with AD who consumed herbal products used supplement qi, nourish the blood, and quiet the heart spirit therapy as complementary medicines to relieve AD-related symptoms, in addition to using standard anti-ad treatments. Background Alzheimer s disease (AD) is a neurodegenerative disease characterized by substantial memory impairment, aphasia, apraxia, agnosia and function disturbance [1]. AD is the most common cause of dementia in older people and accounts for % of reported dementia cases in the World [2]. Although psychosocial and pharmacologic *Correspondence: jnlaitpee@gmail.com 3 The Graduate Institute of Integrated Medicine, China Medical University, Taichung, Taiwan Full list of author information is available at the end of the article interventions can be effective for alleviating AD-related symptoms [3], there is currently no curative treatment for AD. It has been reported that some Chinese herbs may protect brain cells against AD [4, 5]. However, clinical evidence regarding the efficacy of Chinese medicine (CM) for treating AD is limited. This study therefore aims to investigate the extent to which CM is used by patients suffering from AD, and to identify the most common Chinese herbal formulae used by AD patients to treat their symptoms Lin et al. This article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License ( creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/), which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons license, and indicate if changes were made. The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver ( zero/1.0/) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated.
2 Page 2 of 9 Methods This study was approved by the Taipei City Hospital Institutional Review Board under study number TCH- IRB E (Additional file 1) and National Health Research Institutes under study number NHIRD (Additional file 2). The research and associated reporting have been conducted in accordance with conventional ethical principles to protect the identities of the patients involved. Data resources This retrospective, nationwide, population-based cohort study was conducted using a randomly sampled cohort of one million patients, selected from the National Health Insurance Research Database (NHIRD) between 1997 and 2008 in Taiwan. The National Health Insurance (NHI) system covers over 97 % of the population of Taiwan and provides full reimbursement to its members for treatments based on CM, including Chinese herbal products, acupuncture, moxibustion and traumatology manipulative therapies. The NHI also holds all of the medical records for CM treatments prescribed by licensed CM practitioners [6]. One million patient records were randomly selected from those of the 23 million Taiwanese people currently insured under the NHI system. No significant differences were observed in the demographic distribution between the random sample and the original NHIRD. The medical records used in this study were collected for the dates between the 1st of January, 1996 and the 31st of December, The NHIRD database contained complete data pertaining to clinical visits, and hospitalization records, including visit date, hospital, physician specialist, major diagnoses and the dosage and frequency of any medicines prescribed. The Bureau of National Health Insurance requires physicians to record major diagnoses according to the format described in the International Classification of Diseases, Ninth Revision, Clinical Modification (ICD-9-CM). Study sample Figure 1 shows a flowchart describing of the sample selection process. First, all patients without dementia (ICD-9 codes: 290.0, 290.1, 290.2, 290.3, 290.4, 294.1, and 331) were excluded (n = 965,572). Second, we excluded patients with a dementia diagnosis not made by a qualified neurologist or psychologist (n = 13,403), along with patients that did not receive anti-ad treatment (n = 19,822). Doctors in Taiwan are requested by the Bureau of National Health Insurance to only prescribe anti-ad drugs to patients that fulfill the criteria outlined by the National Institute of Neurological and Communicative Disorders and Stroke (NINCDS), the Alzheimer s One million random sample of NHIRD N=1,000,000 Patients with demen a, N = 34,428 Demen a pa ents diagnosedbya neurologist or psychologist doctor, N= 21,025 Pa ents approvad for Alzheimer's medica on by NHI, N=1,203 New cases of Alzheimer's disease, N=1,137 CM use n = 889(78.2%) Exclusion of pa ents without demen a diagnosis, N=965,572 Exclusion of pa ents which are not diagnosis by a neurologist or psychologist doctors, N=13,403 Exclusion of pa ents not taking an -Alzheimer's medica on, N=19,822 Exclusion of cases of Alzheimer's disease diagnosed before the end of 1996 and with missing informa on concerning age, N=66 CM non-use n = 248(21.8%) Fig. 1 Flow chart detailing the recruitment of subjects from random sample of one million patients from the NHIRD between 1997 and 2008 Disease and Related Disorders Association (ADRDA) or the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders (DSM IV-TR). Finally, cases of AD diagnosed before the end of 1996 were excluded from the current study, as well as those without complete NHI reimbursement data (n = 66) to ensure that all of the patients represented newly diagnosed cases of AD. Upon completion of this exclusion process, we had a study cohort consisting of 1137 patients. Study variables Several demographic factors were selected from previous studies [7]. The patients were categorized into six different age groups: <45, 45 54, 55 64, 65 74, and 85 years of age. The geographic locations of the patients were sorted into seven different regions with similar regional environments: Taipei City and Kaohsiung City, the Northern, Central, Eastern and Southern regions of Taiwan, and the outlying islands. The amount of money to which each patient was insured was divided into four levels: 0, 1 19,999, 20,000 39,999 and >40,000 new Taiwanese dollars. The 0 insured level included unemployed and retired patients, for whom the insurance costs were covered by the government or other family members.
3 Page 3 of 9 The NHIRD database was searched for diagnosis and treatment records relating to the behavioral and psychological symptoms of dementia (BPSD), including delirium (ICD9 codes: , and ), delusions (ICD9 codes: , and ), depression (ICD9 codes: , and ), sleep disturbances (ICD9 codes: and 307.4), hallucination (ICD9 codes: 7801, 2913 and 2928) and behavioral disturbances (ICD9 codes: and ). The reimbursement database contains all of the important details relating to the prescription of conventional medicines for treating AD. The types of prescription drugs used to treat AD were categorized as follows: donepezil, rivastigmine, galantamine, memantine, deprenyl, antipsychotic, antimanic, anxiolytic and antidepressant. The comorbidities of the patients were categorized using the icd-9-cm codes. Notably, the results of previous studies have shown that some comorbidities, including diabetes mellitus (icd9 codes: 249 and 250), hypertension (icd9 codes: ), hyperlipidemia (icd9 codes: 272), chronic kidney disease (icd9 codes: 585, 586 and 588), cerebral vascular accident (icd9 codes: ) and atherosclerosis (icd9 codes: 440), can affect the prognosis and treatment of patients diagnosed with AD. Chinese medicine treatment Chinese herbal products (CHPs) composed of one or more herbs (i.e., herbal formulae), which are covered by the NHI system, are more widely adopted by Taiwanese patients than any other form of CM. [8] Information pertaining to CHPs was obtained from the Department of Chinese Medicine and Pharmacy (DCMP), Ministry of Health and Welfare, Taiwan, including the name and ingredients of their herbal formula, as well as their pharmaceutical effects, DCMP manufacturing code and manufacturer. CHPs with the same good manufacturing practices and DCMP standards were sorted into the same group [9]. The acupuncture therapy including acupoint and frequency and massage manipulation and treatment position were also record by the NHI system. Statistical analysis The factors associated with the CM treatments used in the current study were analyzed using multiple logistic regression with a significance level of α = An odds ratio was used to quantify the relationships between the different conditions and CM use. All of the odds ratios were adjusted based on the demographic factors described above. Version 9.3 of the SAS statistical analysis software (version 9.4; SAS Institute Inc., Cary, NC, USA) was used for data management and analysis. Results The NHIRD of outpatient claims contained information pertaining to the claims of 1137 patients with AD from 1997 to Among them, 889 (78.2 %) AD patients used CM outpatient services. The mean age of non-cm users was slightly higher than that of CM users. Table 1 shows details concerning the demographic and medication distributions of the CM and non-cm users. After adjusting for demographic factors, the results clearly showed that AD patients suffering from one or more BPSD (one symptom: OR = 0.90, 95 % CI ; two symptoms: OR = 1.94, 95 % CI ; three or more symptoms: OR = 2.26, 95 % CI ) were more likely to seek CM treatment than those with no BPSD. Female patients and those living in urban areas were more likely to seek CM treatment than male patients and those living in rural areas. No discernible difference was observed in CM use between AD patients suffering from one or more comorbidities (one: OR = 1.1, 95 % CI ; two: OR = 0.91, 95 % CI ; and three or more types: OR = 1.76, 95 % CI ) and those with no comorbidity. Analyses of the major disease categories for all CM visits are summarized in Table 2. These results show that 18,138 (73.3 %) visits were treated with prescribed CHPs, whereas the remaining visits were treated with acupuncture and traumatology manipulative therapies. AD patients tended to use CHPs rather than acupuncture. Symptoms, signs and ill-defined conditions was cited as the most common reason for using CM (20.2 %, 5011 visits), followed sequentially by diseases of the musculoskeletal system and connective tissue (20.0 %, 4962 visits), diseases of the respiratory system (14.3 %, 3542 visits) and diseases of the digestive system (12.2 %, 3024 visits). Of the AD patients evaluated in the current study, 9.3 % sought CMs with the aim of treating their mental disorders, diseases of the nervous system and sense organs. Table 3 shows the details of the CHPs most frequently prescribed by CM practitioners for treating mental disorders and diseases of the nervous system. The results show that Bu-Zhong-Yi-Qi-Tang was the most frequently prescribed CHP, followed by Ji-Sheng-Shen-Qi-Wan, Ma- Zi-Ren-Wan and Tian-Wang-Bu-Xin-Dan. The potential effects of the herbs contained in the 10 most common formulae are shown in Table 4. It is noteworthy that several herbs, including Ginseng Radix (Ren-Shen) and Angelicae Sinensis Radix Integra (Dang-Gui), appeared repeatedly in formulae reported to be effective against AD. Table 5 shows that 77.1 % of the AD patients consumed Bu-Zhong-Yi-Qi-Tang during the period covered by the current study. After adjusting for demographic factors, the results revealed that female AD patients
4 Page 4 of 9 Table 1 Demographic and medication characteristics and results of multiple logistic regression for CM use among patients with Alzheimer s disease Characteristics CM a users CM a non-users aor b (95 % CI c ) No. of cases 889 (78.2 %) 248 (21.8 %) Age at diagnosis (incidence rate) <45 (0.001 %) 7 (0.8 %) 2 (0.8 %) 0.78 ( ) (0.036 %) 27 (3 %) 2 (0.8 %) 3.64 ( ) (0.246 %) 115 (12.9 %) 27 (10.9 %) (1.185 %) 309 (34.8 %) 92 (37.1 %) 0.74 ( ) (7.105 %) 381 (42.9 %) 107 (43.1 %) 0.83 ( ) 85 ( %) 50 (5.6 %) 18 (7.3 %) 0.61 ( ) Mean years Sex Female (0.13 %) 530 (59.6 %) 121(48.8 %) 1.57 ( ) Male (0.10 %) 359 (40.4 %) 127 (51.2 %) 1 Insured region Taipei city 137 (15.4 %) 61 (24.6 %) 1 Kaohsiung city 71 (8 %) 14 (5.6 %) 2.38 ( ) Northern Taiwan 200 (22.5 %) 58 (23.4 %) 1.65 ( ) Middle Taiwan 209 (23.5 %) 32 (12.9 %) 3.00 ( ) Southern Taiwan 240 (27 %) 78 (31.5 %) 1.39 ( ) Eastern Taiwan 21 (2.4 %) 4 (1.6 %) 2.48 ( ) Outlying island 11 (1.2 %) 1 (0.4 %) 4.98 ( ) Insured amount (NT$ d ) (39.7 %) 94 (37.9 %) 0.99 ( ) 1 19, (54.7 %) 140 (56.5 %) 1 20,000 39, (3.6 %) 8 (3.2 %) 0.90 ( ) 400, (2 %) 6 (2.4 %) 0.77 ( ) Numbers of anti-alzheimer s or BPSD drugs 1 28 (3.1 %) 8 (3.2 %) (16.3 %) 51 (20.6 %) 0.81 ( ) (35.8 %) 87 (35.1 %) 1.04 ( ) (44.8 %) 102 (41.1 %) 1.12 ( ) Numbers of dementia BPSD e (11.5 %) 46 (18.5 %) (13.7 %) 61 (24.6 %) 0.90 ( ) Delirium 4 3 Delusions 13 7 Depression Behavioral disturbance 4 2 Sleep disturbances Hallucination (28.1 %) 58 (23.4 %) 1.94 ( ) Delirium + delusions 8 7 Delirium + depression 2 1 Delirium + behavioral Delirium + sleep 12 6 Table 1 continued Characteristics CM a users CM a non-users aor b (95 % CI c ) Delirium + hallucination Delusions depres sion Delusions + behav ioral Delusions + sleep Delusions + hallucination Depression behav ioral Depression + sleep 21 8 Depression + hallucination 0 1 Behavioral + sleep 6 0 Behavioral + hallucination Sleep + hallucination (46.7 %) 83 (33.5 %) 2.26 ( ) Numbers of comorbidity 0 25 (2.81 %) 10 (4.03 %) (8.32 %) 27 (10.89 %) 1.1 ( ) (16.7 %) 65 (26.21 %) 0.91 ( ) (72.2 %) 146 (58.87 %) 1.76 ( ) a CM refers to Chinese medicine b aor refers to adjust odds ratio c CI refers to confidence interval d NT$ refers to new Taiwan dollars, of which 1 US $ = 30 NT$ e BPSD refers to behavioral and psychological symptoms of dementia (OR = 1.23, 95 % CI ) were more likely to consume Bu-Zhong-Yi-Qi-Tang than male patients. Discussion To the best of our knowledge, this study was the first reported one using a random national-level sample to document the usage characteristics of traditional Chinese medicines in AD patients. The incidence of AD was less than 0.3 % in people aged years, with the incidence increasing with increasing age. In people aged 85 years or older, the incidence was found to be 17.9 %, which is low compared with results of previous surveys [10, 11]. Notably, all of the patients described in the current study were newly diagnosed with AD by board-certified neurologists or psychiatrists and selected from a random sample of one million patients. Furthermore, these patients were selected from the insured general population of Taiwan and the rate of insured people was consistently above
5 Page 5 of 9 Table 2 Frequency distribution of Chinese medicine visits by major disease categories (according to 9th ICD codes) in Alzheimer s patients from 1997 to 2008 in Taiwan Major disease category ICD-9-CM code range Number of visits (%) Chinese herbal remedies Acupuncture, or manipulative therapies Total of CM Infectious and parasitic diseases (0.2) 5 (0.02) 47 (0.2) Neoplasms (0.5) 0 (0) 119 (0.5) Endocrine, nutritional, blood and metabolic (3.2) 25 (0.1) 824 (3.3) diseases, and immunity disorders Mental disorders, diseases of the nervous system (7.7) 389 (1.6) 2290 (9.3) and sense organs Diseases of the circulatory system (4.1) 162 (0.7) 1168 (4.7) Diseases of the respiratory system (13.9) 93 (0.4) 3542 (14.3) Diseases of the digestive system (11.9) 70 (0.3) 3024 (12.2) Diseases of the genitourinary system (3.2) 40 (0.2) 829 (3.3) Diseases of the skin and subcutaneous tissue (1.3) 9 (0.04) 336 (1.4) Diseases of the musculoskeletal system and connective (8.1) 2946 (11.9) 4962 (20.0) tissue Symptoms, signs, and ill-defined conditions (15.7) 1134 (4.6) 5011 (20.2) Injury and poisoning (0.3) 852 (3.4) 929 (3.8) Supplementary classification V01 V82, E800 0 (0) 4 (0.02) 4 (0.02) E999 Others a 322 (1.3) 848 (3.4) 1170 (4.7) Total 18,138 (73.3) 6613 (26.7) 24,751 (100.0) a Other includes ICD-9-CM code range and missing/error data 97 % since The possibility of selection or recall bias could therefore be excluded. More than 78 % of the AD patients in the cohort were used some form of CM during the 12 years covered by the current study. High accessibility and full coverage for CM through the NHI scheme in Taiwan could lead to an increase in CM use. Furthermore, several Chinese herbs may be effective as alternative therapies for treating AD and related disorders [12]. The current findings also show that women and those living in urban areas are more likely to use CM than men and patients living rural areas. Similar trends were reported previously [13]. BPSD relating to AD such as delusions, paranoia, hallucinations and anxiety could lead to an increase in caregiver burden and accelerate the progression of AD [14]. AD patients suffering from one or more BPSD were more likely to use traditional CM than those with no BPSD. In addition, using anti-ad or BPSD drugs did not lead to a reduction in CM use. AD patients consumed herbal therapies with the aim of relieving their AD-related symptoms, rather than using these treatments as alternatives to standard anti-ad treatments (i.e., herbal therapies were consumed as complementary medicines). The category symptoms, signs and ill-defined conditions was the most frequently cited diagnosis in the disease category for CM visits to classify the diagnosis pattern of CM. This phenomenon has also been observed in several other patient populations [15]. In addition, 9.3 % of patients with AD in the mental disorders, diseases of the nervous system and sense organs disease category had specifically sought out CM to treat their condition. CM treatments were generally used as adjuvant therapies to relieve AD-related symptoms rather than being used as replacements for conventional anti- AD treatment. The category diseases of the digestive system was cited as one of the most common reasons for using CHPs (11.9 %, 2954 visits), with Ma-Zi-Ren-Wan being used to treat constipation [16]. Constipation is a common problem among geriatric patients, especially those with AD, in whom it is generally exacerbated by a lack of exercise or the side effects of anti-ad drugs [17]. Severe constipation in AD patients can lead to confusion and symptoms of irritability or aggression because of the pain and discomfort associated with this condition [18]. Moreover, emodin, which is the major chemical constituent of Ma-Zi-Ren-Wan, protects the cortical neurons from β-amyloid-induced toxicity, representing a possible mechanism for treating AD [19]. In this study, Bu-Zhong-Yi-Qi-Tang was determined to be the most
6 Page 6 of 9 Table 3 Ten most commonly used herbal formulae prescribed by CM practitioners for treating mental disorders, diseases of the nervous system and sense organs (total prescriptions: 1901) Herbal formulae English name Average formulae dose (g/ day) Ren-Shen CHF dose (g/day) Ren-Shen herbs (g/day) Dang-Qui CHF dose (g/day) Dang-Qui herbs (g/day) Frequency of prescriptions (%) Bu-Zhong-Yi-Qi- Tang Ji-Sheng-Shen- Qi-Wan Center-supplementing Qi-boosting decoction Life saver kidney Qi Pill (33.1) (28.3) Ma-Zi-Ren-Wan Cannabis fruit pill (26.9) Tian-Wang-Bu- Xin-Dan Celestial emperor heart-supplementing elixir (25) Gan-Mai-Da- Zao-Tang Sheng-Mai-San Tian-Ma-Gou- Teng-Yin Liu-Wei-Di- Huang-Wan Qi-Bao-Mei-Ran- Dan Tao-Hong-Si-Wu- Tang Licorice, wheat, and jujube decoction Pulse-engendering powder Gastrodia and uncaria beverage Six-ingredient rehmannia pill Seven-jewel beard-blackening elixir Peach Kernel and Carthamus four agents decoction (22.1) (20.8) (20) (17.7) (14.9) (13.6) commonly prescribed formula, especially for female AD patients. Bu-Zhong-Yi-Qi-Tang led to elevated levels of dopamine and noradrenaline in the cortical tissues of mice, as well as improved attention, learning function and memory [20, 21]. Bu-Zhong-Yi-Qi-Tang was also used to treat elderly patients with weakness and fatigue [22]. Some frequently prescribed formulae have been reported to exhibit potentially positive effects on AD. For example, Sheng-Mai-San was reported to improve memory and decrease neuronal apoptosis in the hippocampus [23]. Furthermore, Ji-Sheng-Shen-Qi-Wan and Liu-Wei-Di-Huang-Wan, which both belong to the Di-Huang-Wan group of formulae and share similar herbal components, were reported to increase cognitive function after 2 months of treatment [24]. Some formulae were reported to show neuroprotective activity. For example, Tian-Ma-Gou-Teng-Yin led to a reduction in necrosis and apoptosis in neuronal cells through a variety of pharmacological effects, including anti-inflammatory, antioxidative and antiapoptotic activities [25]. Tao-Hong-Si-Wu-Tang exhibited neuroprotective effects against focal cerebral ischemia. Moreover, Gan-Mai-Da-Zao-Tang exhibited sedative and anti-anxiety effects in an animal model [26]. All of the aforementioned formulae, which are standard formulae recommended by the DCMP, Ministry of Health and Welfare, Taiwan, must be modified by qualified CM practitioners in accordance with the principle of syndrome pattern identification as the basis for determining treatment. Table 4 lists all of the herbs contained in the top ten most frequently prescribed formulae. Ginseng Radix (Ren-Shen), which is the major constituent herb in three of the top ten formulae, has been reported to show multiple effects against AD-related factors such as decreasing β-amyloid formation [27], increasing choline acetyltransferase [28] and forming a competitive interaction with the N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor [29]. Ginseng Radix has also been reported to increase
7 Page 7 of 9 Table 4 Potential effects of the herbs contained in the ten most common formulae prescribed by CM practitioners for treating Alzheimer s disease Herbal formulae Constituents a, b, c, d Bu-Zhong-Yi-Qi-Tang Astragali Ji-Sheng-Shen-Qi-Wan a, c Ma-Zi-Ren-Wan a, c Radix Cruda (Huang-qi),Ginseng Radix (Ren-shen) a, b, c, d, Glycyrrhizae Radix cum Liquido Fricta (Zhi-gan-cao), Atractylodis MacrocephalaeRhizoma (Bai-zhu), Angelicae Sinensis Radix Integra (Dang-gui) a, c, d, CitriReticulatae Pericarpium (Chenpi), Cimicifugae Rhizoma (Sheng-ma), Bupleuri Radix (Chai-hu), Zingiberis Rhizoma Recens (Sheng-jiang), Jujubae Fructus (Da-zao) Rehmanniae Radix (Di-huang), Poria cum (Fu-ling) a, c, Corni Fructus (Shan-zhu-yu), Dioscoreae Rhizoma (Shan-yao), Moutan Cortex (Mu-dan-pi), Alismatis Rhizoma (Ze-xie), Aconiti Radix Lateralis (Fu-zi), Cinnamomi Cortex (Rrou-gui), Achyranthis Bidentatae Radix (Huai-niu-xi), Plantaginis Semen (Che-qian-zi) Cannabis Fructus (Ma-zi-ren), Rhei Radix et Rhizoma (Da-huang) c, Paeoniae Radix Alba (Bai-shao) a, Aurantii Fructus Immaturus (Zhi-shi), Magnoliae Officinalis Cortex (Hou-po), Armeniacae Semen (Xing-ren) a, b, c, d Tian-Wang-Bu-Xin-Dan Rehmanniae Radix (Di-huang), Ginseng Radix (Ren-shen) a, b, c, d, Polygalae Radix (Yuan-zhi) c, Scrophulariae Radix(Xuan-shen), Platycladi Semen (Bai-zi-ren), Platycodonis Radix (Jie-geng), Asparagi Radix (Tian-men-dong), Salviae Miltiorrhizae Radix (Dan-shen) c, Ziziphi Spinosi Semen (Suan-zao-ren), Ophiopogonis Radix (Mai-men-dong), Poria cum PiniRadice (Fu-shen) a, c, Angelicae Sinensis Radix Integra (Dang-gui) a, c, d, Schisandrae Fructus (Wu-wei-zi) Gan-Mai-Da-Zao-Tang Glycyrrhizae Radix Cruda (Zhi-gan-cao),Jujubae Fructus (Da-zao), Tritici Semen (Xiao-mai) a, b, c, d Sheng-Mai-San Ginseng Radix (Ren-shen) a, b, c, d,ophiopogonis Radix (Mai-men-dong), Schisandrae Fructus (Wu-wei-zi) Tian-Ma-Gou-Teng-Yin a, c Gastrodiae Rhizoma (Tian-ma) c, Uncariae Ramulus cum Uncis (Gou-teng) a, Haliotidis Concha (Shi-jue-ming), Gardeniae Fructus(Shan-zhi-zi), Scutellariae Radix (Huang-qin), Eucommiae Cortex (Du-zhong), Loranthiseu Visci Ramus (Sang-ji-sheng), LeonuriHerba (Yi-mu-cao), PolygoniMultiflori Caulis (Ye-jiao-teng), Achyranthis Bidentatae Radix (Huai-niu-xi), Poria cum Pini Radice (Fu-shen) a, c Liu-Wei-Di-Huang-Wan c Rehmanniae Radix (Di-huang), Poria cum (Fu-ling) c, CorniFructus (Shan-zhu-yu), DioscoreaeRhizoma (Shan-yao), Moutan Cortex (Mu-dan-pi), AlismatisRhizoma (Ze-xie) Qi-Bao-Mei-Ran-Dan a, c, d a, c, PolygoniMultiflori Radix (He-shou-wu), AchyranthisBidentatae Radix (Huai-niu-xi), AngelicaeSinensis Radix Integra (Dang-gui) d, Poria cum (Fu-ling), Cuscutae Semen (Tu-si-zi), LyciiFructus (Gou-qi-zi), PsoraleaeFructus (Po-gu-zhi) a, c, d Tao-Hong-Si-Wu-Tang Persicae Semen (Yao-ren), Carthamustinctorius Flos (Hong-hua), Angelicae Sinensis Radix Integra (Dang-gui) a, c, d, Chuanxiong Rhizoma (Chuan-xiong), Paeoniae Radix Alba (Bai-shao) a, Rehmanniae Radix (Di-huang) a Formula containing a single herb that might promote the neurotransmitter acetylcholine b Formula containing a single herb that might inhibit the N-methyl-D-aspartate (NMDA) receptor c Formula containing a single herb that might reduce the β-amyloid d Formulae containing a single herb that might decrease the Tau protein cognitive function [30]. Angelicae Sinensis Radix Integra (Dang-Gui) is the key component of Bu-Zhong-Yi-Qi- Tang, Tian-Wang-Bu-Xin-Dan and Tao-Hong-Si-Wu- Tang. An ethanolic extract of Dang-Gui enhanced cholinergic function [31], inhibited acetylcholinesterase [32], reduced β-amyloid associated neurotoxicity and decreased Tau protein hyperphosphorylation in a dosedependent manner [33]. There were several limitations associated with the current study. First, health foods containing herbs, folk medicines and prescriptions from CM practitioners without a license from the Taiwanese authorities were not included in this study. Therefore CHP use may have therefore been underestimated. However, high healthcare insurance coverage and low prices of government-approved CM led to a reduction in herbal folk medicine use. Second, it is not possible to draw any conclusions regarding the relationship between cognitive function and CM use because of a general lack of detailed clinical data. This study focused primarily on a patient population with AD, the AD diagnosis was rigorously censored by the Bureau of National Health Insurance. Third, this study was conducted retrospectively and did not include a randomized placebo group. Lastly, the CM formulae were modified according to the principle of syndrome differentiation. Conclusions Most people with AD who consumed herbal products used supplement qi, nourish the blood, and quiet the heart spirit therapy as complementary medicines to
8 Page 8 of 9 Table 5 Demographic characteristics of Bu Zhong Yi Qi Tang use among patients with Alzheimer s disease Characteristics Bu Zhong Yi Qi Tang users (%) CM a users not using Bu Zhong Yi Qi Tang (%) aor b (95 % CI c ) No. of cases 685 (77.1) 204 (22.9) Age at diagnosis <45 5 (0.7) 2 (1) 0.69 ( ) (3.1) 2 (1) 3.17 ( ) (12.8) 22 (10.8) (32.1) 70 (34.3) 0.72 ( ) (44.1) 92 (45.1) 0.92 ( ) (6.5) 16 (7.8) 0.64 ( ) Sex Female 377 (55.0) 99 (48.5) 1.23 ( ) Male 308 (45.0) 104 (51.0) 1 Numbers of anti Alzheimer s or BPSD drugs 1 26 (3.8) 11 (5.4) (19.4) 55 (27.0) 0.82 ( ) (37.8) 75 (36.8) 1.32 ( ) (39.0) 63 (40.9) 1.04 ( ) Numbers of dementia BPSD d 0 84 (12.3) 42 (20.6) (16.8) 63 (30.9) 0.72 ( ) (30.1) 52 (25.5) 2.11 ( ) (40.9) 63 (30.9) 2.75 ( ) Numbers of comorbidity 0 22 (3.2) 12 (5.9) (13.1) 35 (17.2) 1.21 ( ) (17.4) 57 (27.9) 1.02 ( ) (66.3) 99 (48.5) 2.24 ( ) a CM refers to traditional Chinese medicine b aor refers to adjust odds ratio c CI refers to confidence interval d BPSD refers to behavioral and psychological symptoms of dementia relieve AD-related symptoms, in addition to using standard anti-ad treatments. Additional files Additional file 1. The approval Letter from Taipei City Hospital Institutional Review Board. Additional file 2. The approval Letter from National Institutes of Health. Abbreviations AD: Alzheimer s disease; CM: Chinese medicine; CHPs: Chinese herbal products; BPSD: behavioral and psychological symptoms of dementia; NHIRD: National Health Insurance Research Database; NHI: National Health Insurance; ICD-9-CM: international classification of diseases, ninth revision, clinical modification; NINCDS-ADRDA: National Institute of Neurological and Communicative Disorders and Stroke-Alzheimer s Disease and Related Disorders Association; DSM IV: diagnostic and statistical manual of mental disorders; DCMP: Department of Chinese medicine and pharmacy; GMP: good manufacturing practice; MMSE: mini-mental state examination. Authors contributions SKL, SHY, and JNL designed the study. SKL and JNL acquired the data. SKL analyzed the data. SKL, SHY, and THT wrote the manuscript. SKL, SHY, and THT revised the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript. Author details 1 Department of Chinese Medicine, Taipei City Hospital, Ren-Ai Branch, Taipei, Taiwan. 2 Department of Neurology, Taipei City Hospital, Ren-Ai Branch, Taipei, Taiwan. 3 The Graduate Institute of Integrated Medicine, China Medical University, Taichung, Taiwan. 4 School of Chinese Medicine, China Medical University, Taichung, Taiwan. 5 Institute of Traditional Medicine, School of Medicine, National Yang-Ming University, Taipei, Taiwan. Acknowledgements This research was conducted at the Institute of Traditional Medicine at the School of Medicine, National Yang-Ming University, Taiwan. The authors would like to express sincere gratitude for the partial support provided for this project in the form of grants from the Department of Health, Taipei City Government 102XDAA00111), the Department of Chinese Medicine and Pharmacy (CCMP-102-CMB-7), and the National Science Council, Taiwan (NSC B MY2). We would like to thank language editor Mrs. Judy Wu for professional assistance.
9 Page 9 of 9 Competing interests The sponsors of the study did not participate in the study design, data analysis, data interpretation, or writing of the report. All data was collected from the National Health Research Database. All authors had financial support from the Department of Health, Taipei City Government (Taiwan), the Department of Chinese Medicine and Pharmacy, and the National Science Council (Taiwan) for the submitted work; no financial relationships with any organizations that might have an interest in the submitted work in the previous 5 years; and no other relationships or activities that could appear to have influenced the submitted work. Received: 22 July 2014 Accepted: 23 March 2016 References 1. Ballard C, Gauthier S, Corbett A, Brayne C, Aarsland D, Jones E. Alzheimer s disease. Lancet. 2011;377: Markowitsch HJ, Staniloiu A. Amnesic disorders. Lancet. 2012;380: McShane R, Areosa Sastre A, Minakaran N. Memantine for dementia. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2006;(2):CD Yan H, Li L, Tang XC. Treating senile dementia with traditional Chinese medicine. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2006;3: Stange R, Amhof R, Moebus S. Complementary and alternative medicine: attitudes and patterns of use by German physicians in a national survey. J Altern Complement Med. 2008;14: Hsieh SC, Lai JN, Lee CF, Hu FC, Tseng WL, Wang JD. The prescribing of Chinese herbal products in Taiwan: a cross-sectional analysis of the national health insurance reimbursement database. Pharmacoepidemiol Drug Saf. 2008;17: Chang LC, Huang N, Chou YJ, Lee CH, Kao FY, Huang YT. Utilization patterns of Chinese medicine and Western medicine under the National Health Insurance Program in Taiwan, a population-based study from 1997 to BMC Health Serv Res. 2008;8: Lin SK, Tsai YT, Lai JN, Wu CT. Demographic and medication characteristics of traditional Chinese medicine users among dementia patients in Taiwan: a nationwide database study. J Ethnopharmacol. 2015;161: Chen FP, Chen TJ, Kung YY, Chen YC, Chou LF, Chen FJ, Hwang SJ. Use frequency of traditional Chinese medicine in Taiwan. BMC Health Serv Res. 2007;23: Liu CK, Lai CL, Tai CT, Lin RT, Yen YY, Howng SL. Incidence and subtypes of dementia in southern Taiwan: impact of socio-demographic factors. Neurology. 1998;50: Zhang MI, Katzman R, Yu E, Liu W, Xiao SF, Yan H. A preliminary analysis of incidence of dementia in Shanghai, China. Psychiatry Clin Neurosci. 1998;52: Dos Santos-Neto LL, de Vilhena Toledo MA, Medeiros-Souza P, de Souza GA. The use of herbal medicine in Alzheimer s disease a systematic review. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2006;3: Huang CH, Tsai YT, Lai JN, Hsu FL. Prescription pattern of Chinese herbal products for diabetes mellitus in Taiwan: a population-based study. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2013;2013: Schulz R, O Brien AT, Bookwala J, Fleissner K. Psychiatric and physical morbidity effects of dementia caregiving: prevalence, correlates, and causes. Gerontologist. 1995;35: Lai JN, Wu CT, Wang JD. Prescription pattern of Chinese herbal products for breast cancer in Taiwan: a population-based study. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2012;2012: Jong MS, Hwang SJ, Chen YC, Chen TJ, Chen FJ, Chen FP. Prescriptions of Chinese herbal medicine for constipation under the national health insurance in Taiwan. J Chin Med Assoc. 2010;73: Henley DB, Sundell KL, Sethuraman G, Siemers ER. Alzheimer s disease neuroimaging initiative: safety profile of Alzheimer s disease populations in Alzheimer s disease neuroimaging initiative and other 18-month studies. Alzheimers Dement. 2012;8: Allan L, McKeith I, Ballard C, Kenny RA. The prevalence of autonomic symptoms in dementia and their association with physical activity, activities of daily living and quality of life. Dement Geriatr Cogn Disord. 2006;22: Liu T, Jin H, Sun QR, Xu JH, Hu HT. Neuroprotective effects of emodin in rat cortical neurons against beta-amyloid-induced neurotoxicity. Brain Res. 2010;1347: Shih HC, Chang KH, Chen FL, Chen CM, Chen SC, Lin YT, Shibuya A. Antiaging effects of the traditional Chinese medicine Bu-zhong-yi-qi-tang in mice. Am J Chin Med. 2000;28: Kimura M, Sasada T, Kanai M, Kawai Y, Yoshida Y, Hayashi E, Iwata S, Takabayashi A. Preventive effect of a traditional herbal medicine, Hochu-ekkito, on immunosuppression induced by surgical stress. Surg Today. 2000;38: Toshiaki K, Nobuhiko S, Eiichi T, Shinya S, Yutaka S, Hiroshi O, Hideki O, Katsutoshi T. Assessment of effects of traditional herbal medicines on elderly patients with weakness using a self-controlled trial. Geriatr Gerontol Int. 2004;4: Wu Y, Wen YL, Du L. Effect of Shengmaisan on learning and memory abilities and hippocampal nitric oxide synthase expression and neuronal apoptosis in rats with vascular dementia. Nan Fang Yi Ke Da Xue Xue Bao. 2010;30: Iwasaki K, Kobayashi S, Chimura Y, Taguchi M, Inoue K, Cho S, Akiba T, Arai H, Cyong JC, Sasaki H. A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled clinical trial of the Chinese herbal medicine ba wei di huang wan in the treatment of dementia. J Am Geriatr Soc. 2004;52: Chik SC, Or TC, Luo D, Yang CL, Lau AS. Pharmacological effects of active compounds on neurodegenerative disease with gastrodia and uncariadecoction, a commonly used poststroke decoction. Sci World J. 2013;14: Chen HC, Hsieh MT, Lai E. Studies on the suanzaorentang in the treatment of anxiety. Psychopharmacology. 1985;85: Song XY, Hu JF, Chu SF, Zhang Z, Xu S, Yuan YH, Han N, Liu Y, Niu F, He X, Chen NH. Ginsenoside Rg1 attenuates okadaic acid induced spatial memory impairment by the GSK3β/tau signaling pathway and the Aβ formation prevention in rats. Eur J Pharmacol. 2004;710: Shi S, Shi R, Hashizume K. American ginseng improves neurocognitive function in senescence-accelerated mice: possible role of the upregulated insulin and choline acetyltransferase gene expression. Geriatr Gerontol Int. 2012;12: Kim S, Kim T, Ahn K, Park WK, Nah SY, Rhim H. Ginsenoside Rg3 antagonizes NMDA receptors through a glycine modulatory site in rat cultured hippocampal neurons. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2004;323: Heo JH, Lee ST, Chu K, Oh MJ, Park HJ, Shim JY, Kim M. An open-label trial of Korean red ginseng as an adjuvant treatment for cognitive impairment in patients with Alzheimer s disease. Eur J Neurol. 2008;15: Cheng LL, Chen XN, Wang Y, Yu L, Kuang X, Wang LL, Yang W, Du JR. Z-ligustilide isolated from radix Angelicae sinensis ameliorates the memory impairment induced by scopolamine in mice. Fitoterapia. 2011;82: Park SJ, Jung JM, Lee HE, Lee YW, Kim DH, Kim JM, Hong JG, Lee CH, Jung IH, Cho YB, Jang DS, Ryu JH. The memory ameliorating effects of INM-176, an ethanolic extract of Angelica gigas, against scopolamine- or Aβ(1-42) - induced cognitive dysfunction in mice. J Ethnopharmacol. 2012;143: Zhang ZI, Zhao R, Qi J, Wen S, Tang Y, Wang D. Inhibition of glycogen synthase kinase-3β by Angelica sinensis extract decreases β-amyloid-induced neurotoxicity and tau phosphorylation in cultured cortical neurons. J Neurosci Res. 2011;89:
EMPEROR'S COLLEGE MTOM COURSE SYLLABUS HERB FORMULAE II
 COURSE DESCRIPTION The second of three courses in the Herb Formulae series. Categories covered in Formulae II include the Tonify Qi and Blood, Regulate Qi, Invigorate the Blood, Stop Bleeding, Stabilize
COURSE DESCRIPTION The second of three courses in the Herb Formulae series. Categories covered in Formulae II include the Tonify Qi and Blood, Regulate Qi, Invigorate the Blood, Stop Bleeding, Stabilize
Root & Branch Bulk Formula List
 An asterisk * indicates the inclusion of 1 or more granule versions of an herb because of limited availability on the American herbal market. These products are usually animal in nature like E Jiao, Shui
An asterisk * indicates the inclusion of 1 or more granule versions of an herb because of limited availability on the American herbal market. These products are usually animal in nature like E Jiao, Shui
In Western medicine, there are three stages to a miscarriage or spontaneous
 7 Prevention of Miscarriage In Western medicine, there are three stages to a miscarriage or spontaneous abortion: 1) threatened miscarriage, 2) incomplete miscarriage, and 3) complete miscarriage. The
7 Prevention of Miscarriage In Western medicine, there are three stages to a miscarriage or spontaneous abortion: 1) threatened miscarriage, 2) incomplete miscarriage, and 3) complete miscarriage. The
INTRODUCTION TO HERBAL MEDICINE
 COURSE DESCRIPTION This course provides students with an overview of the ideas and concepts they will encounter in their study of Chinese Herbology throughout the Masters program, as well as the basic
COURSE DESCRIPTION This course provides students with an overview of the ideas and concepts they will encounter in their study of Chinese Herbology throughout the Masters program, as well as the basic
Research Article Prescription Patterns of Chinese Herbal Products for Osteoporosis in Taiwan: A Population-Based Study
 Evidence-Based Complementary and Alternative Medicine Volume 2012, Article ID 752837, 6 pages doi:10.1155/2012/752837 Research Article Prescription Patterns of Chinese Herbal Products for Osteoporosis
Evidence-Based Complementary and Alternative Medicine Volume 2012, Article ID 752837, 6 pages doi:10.1155/2012/752837 Research Article Prescription Patterns of Chinese Herbal Products for Osteoporosis
EMPEROR'S COLLEGE MTOM COURSE SYLLABUS HERB FORMULAE I
 COURSE DESCRIPTION The first of three courses in the Herb Formulae series. These courses can be taken in any order. The Herb Formulae series analyzes the functions, ingredients, and properties of approximately
COURSE DESCRIPTION The first of three courses in the Herb Formulae series. These courses can be taken in any order. The Herb Formulae series analyzes the functions, ingredients, and properties of approximately
Single Herbs III / Quiz I
 Single Herbs III / Quiz I 1. What herb is good to generate fluids? A. Ren Shen C. Xi Yang Shen B. Tai Zi Shen D. All the Shens 2. What herb is best for Qi collapse? A. Huang Qi C. Dang Shen B. Ren Shen
Single Herbs III / Quiz I 1. What herb is good to generate fluids? A. Ren Shen C. Xi Yang Shen B. Tai Zi Shen D. All the Shens 2. What herb is best for Qi collapse? A. Huang Qi C. Dang Shen B. Ren Shen
Our ongoing interest in spirit
 Soothing the Troubled Spirit with Blue Poppy Originals Formulas with Honora Lee Wolfe Our ongoing interest in spirit Western practitioners of Chinese medicine have always had more interest in diseases
Soothing the Troubled Spirit with Blue Poppy Originals Formulas with Honora Lee Wolfe Our ongoing interest in spirit Western practitioners of Chinese medicine have always had more interest in diseases
Liu Jing and Liu Jing Diagnosis System in Classical TCM Discussions of Six Divisions or Six Confirmations Diagnosis System in Classical TCM Texts
 Liu Jing and Liu Jing Diagnosis System in Classical TCM Discussions of Six Divisions or Six Confirmations Diagnosis System in Classical TCM Texts Liu Jing Bian Zheng system had developed about 1800 years
Liu Jing and Liu Jing Diagnosis System in Classical TCM Discussions of Six Divisions or Six Confirmations Diagnosis System in Classical TCM Texts Liu Jing Bian Zheng system had developed about 1800 years
The Herbalist s Corner
 Acupuncture Today, July 2008 The Herbalist s Corner Jake Paul Fratkin, OMD. L.Ac. MANAGING A PATIENT WITH MULTIPLE COMPLAINTS A situation common to American herbalist/acupuncturists is the arrival of a
Acupuncture Today, July 2008 The Herbalist s Corner Jake Paul Fratkin, OMD. L.Ac. MANAGING A PATIENT WITH MULTIPLE COMPLAINTS A situation common to American herbalist/acupuncturists is the arrival of a
3 Clouded Vision (Mu Hun)
 The Treatment of Disease in TCM Vol. 2: Diseases of the Eyes, Ears, Nose & Throat Author: Sionneau, Philippe & Lü, Gang www.bluepoppy.com www.sionneau.com 3 Clouded Vision (Mu Hun) This refers to dimness
The Treatment of Disease in TCM Vol. 2: Diseases of the Eyes, Ears, Nose & Throat Author: Sionneau, Philippe & Lü, Gang www.bluepoppy.com www.sionneau.com 3 Clouded Vision (Mu Hun) This refers to dimness
Research Article The Traditional Chinese Medicine Prescription Pattern of Endometriosis Patients in Taiwan: A Population-Based Study
 Hindawi Publishing Corporation Evidence-Based Complementary and Alternative Medicine Volume 2012, Article ID 591391, 9 pages doi:10.1155/2012/591391 Research Article The Traditional Chinese Medicine Prescription
Hindawi Publishing Corporation Evidence-Based Complementary and Alternative Medicine Volume 2012, Article ID 591391, 9 pages doi:10.1155/2012/591391 Research Article The Traditional Chinese Medicine Prescription
Acupuncture and Herbs Eliminate Meniere s Disease
 Acupuncture and Herbs Eliminate Meniere s Disease Published by HealthCMi on June 2018 Acupuncture has been proven clinically effective for the treatment of Meniere s disease, a disorder characterized by
Acupuncture and Herbs Eliminate Meniere s Disease Published by HealthCMi on June 2018 Acupuncture has been proven clinically effective for the treatment of Meniere s disease, a disorder characterized by
Principles of Differentiation and Prescription for Vitiligo in Traditional Chinese Medicine Based on a Literature Investigation
 Received: May 13, 2015 Accepted after revision: October 19, 2015 Published online: December 3, 2015 2015 The Author(s) Published by S. Karger AG, Basel 2296 7362/15/0024 0149$39.50/0 This article is licensed
Received: May 13, 2015 Accepted after revision: October 19, 2015 Published online: December 3, 2015 2015 The Author(s) Published by S. Karger AG, Basel 2296 7362/15/0024 0149$39.50/0 This article is licensed
TWO CASES OF HYPERTHYROIDISM
 The Herbalist s Corner Jake Paul Fratkin, OMD, L.Ac. Acupuncture Today, January, 2008 TWO CASES OF HYPERTHYROIDISM Hyperthyroidism is not often seen in the clinic, but Chinese herbal medicine can be very
The Herbalist s Corner Jake Paul Fratkin, OMD, L.Ac. Acupuncture Today, January, 2008 TWO CASES OF HYPERTHYROIDISM Hyperthyroidism is not often seen in the clinic, but Chinese herbal medicine can be very
Acupuncture Heals Erectile Dysfunction Finding
 Acupuncture Heals Erectile Dysfunction Finding Published by HealthCMI on 02 May 2018. erectile dysfunction. Acupuncture and herbs are effective for the treatment of erectile dysfunction. In research conducted
Acupuncture Heals Erectile Dysfunction Finding Published by HealthCMI on 02 May 2018. erectile dysfunction. Acupuncture and herbs are effective for the treatment of erectile dysfunction. In research conducted
Course: Formulas 1 Date: December 2, 2009 Class #: 10. Function in Formula. Disperse stagnation
 Course: Formulas 1 Date: December 2, 2009 Class #: 10 Xi Jiao Di Huang Tang : o Clear Heat toxins o o Disperse stagnation : o Heat in the blood Xi jiao Sheng di Shao yao Mu dan pi Clear Heart heat Nourish
Course: Formulas 1 Date: December 2, 2009 Class #: 10 Xi Jiao Di Huang Tang : o Clear Heat toxins o o Disperse stagnation : o Heat in the blood Xi jiao Sheng di Shao yao Mu dan pi Clear Heart heat Nourish
Genome-wide association study of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma in Chinese subjects identifies susceptibility loci at PLCE1 and C20orf54
 CORRECTION NOTICE Nat. Genet. 42, 759 763 (2010); published online 22 August 2010; corrected online 27 August 2014 Genome-wide association study of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma in Chinese subjects
CORRECTION NOTICE Nat. Genet. 42, 759 763 (2010); published online 22 August 2010; corrected online 27 August 2014 Genome-wide association study of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma in Chinese subjects
4-1 Dyspnea (Chuan, 喘 )
 4-1 Dyspnea (Chuan, 喘 ) Concept Breathing with difficulty (open wide mouth, raise shoulders) Etiology and pathogenesis Climatic factors Phlegm fluid Emotion Chronic diseases Exertion Over sex Diagnosis
4-1 Dyspnea (Chuan, 喘 ) Concept Breathing with difficulty (open wide mouth, raise shoulders) Etiology and pathogenesis Climatic factors Phlegm fluid Emotion Chronic diseases Exertion Over sex Diagnosis
In the October, 2009 issue of ACUPUNCTURE TODAY, I wrote on how to use pulse
 The Herbalist s Corner Acupuncture Today, April, 2010 TREATING COMPLEX MULTI-LAYERED CASES Part 2: Treatment Jake Paul Fratkin, OMD, L.Ac. In the October, 2009 issue of ACUPUNCTURE TODAY, I wrote on how
The Herbalist s Corner Acupuncture Today, April, 2010 TREATING COMPLEX MULTI-LAYERED CASES Part 2: Treatment Jake Paul Fratkin, OMD, L.Ac. In the October, 2009 issue of ACUPUNCTURE TODAY, I wrote on how
Professor Huang Huang
 Clinical Application of Jing Fang (Classical Formulas) A seminar with Professor Huang Huang Nanjing University of Chinese Medicine February 2014 Sydney Melbourne Proudly brought to you by CHINA BOOKS EDUCATION
Clinical Application of Jing Fang (Classical Formulas) A seminar with Professor Huang Huang Nanjing University of Chinese Medicine February 2014 Sydney Melbourne Proudly brought to you by CHINA BOOKS EDUCATION
FOUNDATIONS, ACUPUNCTURE, CHINESE HERBAL MEDICINE, BIO-MEDICINE. Stage Four Review
 ICAOM LEARNING PROFICIENCY EXAMINATION FOUNDATIONS, ACUPUNCTURE, CHINESE HERBAL MEDICINE, BIO-MEDICINE Review and know the following: Stage Four Review 1. Familiar with the disease or symptom of the following
ICAOM LEARNING PROFICIENCY EXAMINATION FOUNDATIONS, ACUPUNCTURE, CHINESE HERBAL MEDICINE, BIO-MEDICINE Review and know the following: Stage Four Review 1. Familiar with the disease or symptom of the following
1 Eczema (Shi Zhen, 湿疹 ) Eczema/ 湿疹 pic
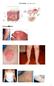 1 Eczema (Shi Zhen, 湿疹 ) Eczema/ 湿疹 pic 1 [Introduction] dermal inflammation: polymorphous serious itching symmetrical chronic / recurrence effusing tendency delayed allergic reaction int factors ext factors
1 Eczema (Shi Zhen, 湿疹 ) Eczema/ 湿疹 pic 1 [Introduction] dermal inflammation: polymorphous serious itching symmetrical chronic / recurrence effusing tendency delayed allergic reaction int factors ext factors
Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, June 2010, Vol. 30, No. 2
 132 Experts Experience LIU De-xi s Experience in the TCM Differential Treatment of Liver for Male Climacteric Syndrome WU Pei-tian Sanya Municipal Hospital of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Sanya, Hainan
132 Experts Experience LIU De-xi s Experience in the TCM Differential Treatment of Liver for Male Climacteric Syndrome WU Pei-tian Sanya Municipal Hospital of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Sanya, Hainan
Thirty-two Cases of Vascular Headache Treated by Acupuncture Combined with Chinese Herbal Decoction
 Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, December 2009, Vol. 29, No. 4 253 Thirty-two Cases of Vascular Headache Treated by Acupuncture Combined with Chinese Herbal Decoction HE Qing-yong 1, LIANG Jun
Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, December 2009, Vol. 29, No. 4 253 Thirty-two Cases of Vascular Headache Treated by Acupuncture Combined with Chinese Herbal Decoction HE Qing-yong 1, LIANG Jun
Single Herbs III / Quiz II
 Single Herbs III / Quiz II 1. What herb can nourish St Yin and brightens the eyes? A. Mai Dong C. Sha Shen B. Shi Hu D. Tian Dong 2. What herb can be used for an exterior invasion with Yin Xu? A. Sha Shen
Single Herbs III / Quiz II 1. What herb can nourish St Yin and brightens the eyes? A. Mai Dong C. Sha Shen B. Shi Hu D. Tian Dong 2. What herb can be used for an exterior invasion with Yin Xu? A. Sha Shen
C 22. Calming LV, tranquilizing internal wind (13) LV yang. Shi Jue Ming ** Properties: Salty, mild cold LV. Actions: Suppress LV yang, clear eye heat
 C 22. Calming LV, tranquilizing internal wind (13) LV yang Shi Jue Ming ** Zhen Zhu Mu * (Long Gu -)*** Mu Li *** Dai Zhe Shi ** Bai Ji Li/Ci Ji Li Wind/spasm Gou Teng ** Tian Ma *** Di Long ** Quan Xie
C 22. Calming LV, tranquilizing internal wind (13) LV yang Shi Jue Ming ** Zhen Zhu Mu * (Long Gu -)*** Mu Li *** Dai Zhe Shi ** Bai Ji Li/Ci Ji Li Wind/spasm Gou Teng ** Tian Ma *** Di Long ** Quan Xie
Appendix 2. Detailed information about herbal prescriptions used in the included trials
 Appendix 2. Detailed information about herbal prescriptions used in the included trials First author (Year) Herbal Medicinal Preparation Name Chen Tongqiao (2013) 22 huoxue Guo Biyan (2004) 23 Qingdu Granule
Appendix 2. Detailed information about herbal prescriptions used in the included trials First author (Year) Herbal Medicinal Preparation Name Chen Tongqiao (2013) 22 huoxue Guo Biyan (2004) 23 Qingdu Granule
Used for exterior conditions such as common colds, fevers, and flu s. Many of these formulas induce sweating. This category can be subdivided into
 Section 1 Used for exterior conditions such as common colds, fevers, and flu s. Many of these formulas induce sweating. This category can be subdivided into formulas the release cold or heat. Traditionally
Section 1 Used for exterior conditions such as common colds, fevers, and flu s. Many of these formulas induce sweating. This category can be subdivided into formulas the release cold or heat. Traditionally
Blood deficiency. Yuxing Liu. Academy of Oriental Medicine at Austin
 Blood deficiency Yuxing Liu Academy of Oriental Medicine at Austin Key Symptoms Pale: tongue, nails, complexion, eyelids Dizziness; Floaters, blurred vision Poor concentration, memory Palpitations; Insomnia,
Blood deficiency Yuxing Liu Academy of Oriental Medicine at Austin Key Symptoms Pale: tongue, nails, complexion, eyelids Dizziness; Floaters, blurred vision Poor concentration, memory Palpitations; Insomnia,
Acupuncture Today, July, 2010.
 The Herbalist Corner Acupuncture Today, July, 2010. BROADENING STRATEGIES IN THE TREATMENT OF INSOMNIA Jake Paul Fratkin, OMD, L.Ac. Successful treatment of insomnia can be an elusive goal, especially
The Herbalist Corner Acupuncture Today, July, 2010. BROADENING STRATEGIES IN THE TREATMENT OF INSOMNIA Jake Paul Fratkin, OMD, L.Ac. Successful treatment of insomnia can be an elusive goal, especially
Acupuncture And Herbs Proven Effective For PID Treatment
 Acupuncture And Herbs Proven Effective For PID Treatment Published by HealthCMi on 29 May 2018 Researchers find acupuncture combined with herbal medicine effective for the treatment of chronic pelvic inflammatory
Acupuncture And Herbs Proven Effective For PID Treatment Published by HealthCMi on 29 May 2018 Researchers find acupuncture combined with herbal medicine effective for the treatment of chronic pelvic inflammatory
copyright 2017 by AJTCVM All Rights Reserved Herbal Formula Spotlight
 copyright 2017 by AJTCVM All Rights Reserved Herbal Formula Spotlight Tao Hong Si Wu Tang (Four-Substance Decoction with Safflower and Peach Pit) Tao Hong Si Wu Tang (Four-Substance Decoction with Safflower
copyright 2017 by AJTCVM All Rights Reserved Herbal Formula Spotlight Tao Hong Si Wu Tang (Four-Substance Decoction with Safflower and Peach Pit) Tao Hong Si Wu Tang (Four-Substance Decoction with Safflower
Single Herbs II / Quiz II
 1. What herb is good to treat cholesterol? A. Shan Zha C. Shen Qu B. Mai Ya D. Gu Ya 2. What herb can inhibit lactation? A. Shan Zha C. Shen Qu B. Mai Ya D. Lai Fu Zi 3. What herb can dissolve stones?
1. What herb is good to treat cholesterol? A. Shan Zha C. Shen Qu B. Mai Ya D. Gu Ya 2. What herb can inhibit lactation? A. Shan Zha C. Shen Qu B. Mai Ya D. Lai Fu Zi 3. What herb can dissolve stones?
Frequently asked questions regarding concentrated herbs
 Frequently asked questions regarding concentrated herbs How many raw herbs are needed to make the concentrates? There are several possibilities to answer that question. The simplest answer is that 250
Frequently asked questions regarding concentrated herbs How many raw herbs are needed to make the concentrates? There are several possibilities to answer that question. The simplest answer is that 250
An Increased Risk of Reversible Dementia May Occur After Zolpidem Derivative Use in the Elderly Population
 An Increased Risk of Reversible Dementia May Occur After Zolpidem Derivative Use in the Elderly Population A Population-Based Case-Control Study Hsin-I Shih, Che-Chen Lin, Yi-Fang Tu, Chia-Ming Chang,
An Increased Risk of Reversible Dementia May Occur After Zolpidem Derivative Use in the Elderly Population A Population-Based Case-Control Study Hsin-I Shih, Che-Chen Lin, Yi-Fang Tu, Chia-Ming Chang,
Bi Syndrome: Painful. Formula: Wū Tóu Tāng (Aconite Decoction) Ingredients: zhì chuān wū, má huáng, sháo yào, huáng qí, gān căo, fēng mì
 Bi Syndrome: Painful Formula: Wū Tóu Tāng (Aconite Decoction) Ingredients: zhì chuān wū, má huáng, sháo yào, huáng qí, gān căo, fēng mì Cara O. Frank, L.OM, 2017 1 Bi Syndrome Fixed Formula: Yì Yĭ Rén
Bi Syndrome: Painful Formula: Wū Tóu Tāng (Aconite Decoction) Ingredients: zhì chuān wū, má huáng, sháo yào, huáng qí, gān căo, fēng mì Cara O. Frank, L.OM, 2017 1 Bi Syndrome Fixed Formula: Yì Yĭ Rén
Section 4 補陰劑. Liù Wèi Dì Huáng Wán (Six-Ingredient Pill with Rehmannia) 六味地黃丸六味地黃丸. Yin-Tonifying Formulas. Chinese Herbal Formulas and Applications
 Section 4 Chinese Herbal Formulas and Applications 補陰劑 Yin-Tonifying Formulas 六味地黃丸六味地黃丸 Pinyin Name: Liu Wei Di Huang Literal Name: Six-Ingredient Pill with Rehmannia Alternate Names: Liu Wei Ti Huang,
Section 4 Chinese Herbal Formulas and Applications 補陰劑 Yin-Tonifying Formulas 六味地黃丸六味地黃丸 Pinyin Name: Liu Wei Di Huang Literal Name: Six-Ingredient Pill with Rehmannia Alternate Names: Liu Wei Ti Huang,
Chien-Tung Wu 1,2, Jeng-Nan Tzeng 3, Jung-Nien Lai 2,4*, Shun-Hua Tsan 5 and Jung-Der Wang 6,7
 Lai et al. Chinese Medicine 2012, 7:22 RESEARCH Open Access Prescription profile of Chinese herbal products containing coumestrol, genestein, and/or daidzein among female users: an analysis of national
Lai et al. Chinese Medicine 2012, 7:22 RESEARCH Open Access Prescription profile of Chinese herbal products containing coumestrol, genestein, and/or daidzein among female users: an analysis of national
Huang Qi (Radix Astragali)
 Chinese Medical Herbology and Pharmacology Pinyin Name: Huang Qi Alternate Chinese Names: Jin Huang Qi, Jian Qi, Kou Qi Original Source: Shen Nong Ben Cao Jing (Divine Husbandman s Classic of the Materia
Chinese Medical Herbology and Pharmacology Pinyin Name: Huang Qi Alternate Chinese Names: Jin Huang Qi, Jian Qi, Kou Qi Original Source: Shen Nong Ben Cao Jing (Divine Husbandman s Classic of the Materia
Research Article Utilization Pattern of Traditional Chinese Medicine among Fracture Patients: A Taiwan Hospital-Based Cross-Sectional Study
 Evidence-Based Complementary and Alternative Medicine, Article ID 1706517, 9 pages https://doi.org/10.1155/2018/1706517 Research Article Utilization Pattern of Traditional Chinese Medicine among Fracture
Evidence-Based Complementary and Alternative Medicine, Article ID 1706517, 9 pages https://doi.org/10.1155/2018/1706517 Research Article Utilization Pattern of Traditional Chinese Medicine among Fracture
Comprehensive rehabilitation with integrative medicine for subacute stroke: A.
 Comprehensive rehabilitation with integrative medicine for subacute stroke: A multicenter randomized controlled trial Jianqiao Fang Ph.D. M.D. *1,2 fangjianqiao7532@163.com Lifang Chen Ph.D. M.D. 1 clfang@163.com
Comprehensive rehabilitation with integrative medicine for subacute stroke: A multicenter randomized controlled trial Jianqiao Fang Ph.D. M.D. *1,2 fangjianqiao7532@163.com Lifang Chen Ph.D. M.D. 1 clfang@163.com
Efficacious Formulas for the Treatment of Gout
 Efficacious Formulas for the Treatment of Gout by Simon A. Becker, Dipl. Ac & C.H. Introduction In Chinese Medicine, gout belongs to the disease category of wind damp impediment (feng shi bi). It results
Efficacious Formulas for the Treatment of Gout by Simon A. Becker, Dipl. Ac & C.H. Introduction In Chinese Medicine, gout belongs to the disease category of wind damp impediment (feng shi bi). It results
Dementia in Taiwan area
 Translational Neuroscience and Clinics ISSN print edition: 2096-0441 ISSN electronic edition: 2096-0670 CN print edition: 10-1319/R CN electronic edition: 11-6030/R DOI Vol. 2, No. 1, March 2016, pp 38
Translational Neuroscience and Clinics ISSN print edition: 2096-0441 ISSN electronic edition: 2096-0670 CN print edition: 10-1319/R CN electronic edition: 11-6030/R DOI Vol. 2, No. 1, March 2016, pp 38
Section Two. Chapter 1 Herbs for relieving superficial syndrome (Biao Zheng) 解表藥 (23) A. Pungent & warm 辛溫解表 (13)
 Section Two Chapter 1 Herbs for relieving superficial syndrome (Biao Zheng) 解表藥 (23) A. Pungent & warm 辛溫解表 (13) Pungent, warm, SD of wind cold: no sweating, aversion to cold/fever, pain, sp/tense pulse
Section Two Chapter 1 Herbs for relieving superficial syndrome (Biao Zheng) 解表藥 (23) A. Pungent & warm 辛溫解表 (13) Pungent, warm, SD of wind cold: no sweating, aversion to cold/fever, pain, sp/tense pulse
The Diabetes Epidemic in Korea
 Review Article Endocrinol Metab 2016;31:349-33 http://dx.doi.org/.3803/enm.2016.31.3.349 pissn 2093-96X eissn 2093-978 The Diabetes Epidemic in Korea Junghyun Noh Department of Internal Medicine, Inje
Review Article Endocrinol Metab 2016;31:349-33 http://dx.doi.org/.3803/enm.2016.31.3.349 pissn 2093-96X eissn 2093-978 The Diabetes Epidemic in Korea Junghyun Noh Department of Internal Medicine, Inje
Journal of Chinese Medicine. Vol.20, No.1, Vol.20, No.3,
 163 Journal of Chinese Medicine Vol.20, No.1,2 1-96 Vol.20, No.3,4 97-162 ~ - 145 45-135 21 117 79-19 137-135 ~ - 137 65 87-65 - 145-65 - 153-79 - 153-87 47-137 - 65-87 - 47-145 - 145-47 - 19 164 153 HT7
163 Journal of Chinese Medicine Vol.20, No.1,2 1-96 Vol.20, No.3,4 97-162 ~ - 145 45-135 21 117 79-19 137-135 ~ - 137 65 87-65 - 145-65 - 153-79 - 153-87 47-137 - 65-87 - 47-145 - 145-47 - 19 164 153 HT7
ANALYSIS OF EMERGENCY DEPARTMENT UTILIZATION BY ELDERLY PATIENTS UNDER NATIONAL HEALTH INSURANCE
 ANALYSIS OF EMERGENCY DEPARTMENT UTILIZATION BY ELDERLY PATIENTS UNDER NATIONAL HEALTH INSURANCE Jin-An Huang, Rhay-Hung Weng, 1 Wen-Chen Tsai, 2 Wei-Hsiung Hu, and Dar-Yu Yang Department of Emergency
ANALYSIS OF EMERGENCY DEPARTMENT UTILIZATION BY ELDERLY PATIENTS UNDER NATIONAL HEALTH INSURANCE Jin-An Huang, Rhay-Hung Weng, 1 Wen-Chen Tsai, 2 Wei-Hsiung Hu, and Dar-Yu Yang Department of Emergency
Version Practitioner Guide
 Version 1.0 2017 Practitioner Guide KAMWO MERIDIAN HERBS The oldest herbal dispensary & supplier of professional, natural health products on the East Coast. With thousands of options for your practice
Version 1.0 2017 Practitioner Guide KAMWO MERIDIAN HERBS The oldest herbal dispensary & supplier of professional, natural health products on the East Coast. With thousands of options for your practice
Emergency Nursing By BAI REN XING ZHU BIAN
 Emergency Nursing By BAI REN XING ZHU BIAN If searching for a ebook Emergency Nursing by BAI REN XING ZHU BIAN in pdf format, then you have come on to faithful site. We presented the utter option of this
Emergency Nursing By BAI REN XING ZHU BIAN If searching for a ebook Emergency Nursing by BAI REN XING ZHU BIAN in pdf format, then you have come on to faithful site. We presented the utter option of this
The Chinese Herbology Abbreviated Content Outline (Effective as of February 1, 2014)
 The Chinese Herbology Abbreviated Content Outline (Effective as of February 1, 2014) Note to Candidate: This document serves as a guide to assist in examination preparation for candidates who have met
The Chinese Herbology Abbreviated Content Outline (Effective as of February 1, 2014) Note to Candidate: This document serves as a guide to assist in examination preparation for candidates who have met
The Chinese Herbology Expanded Content Outline (Effective as of February 1, 2014)
 The Chinese Herbology Expanded Content Outline (Effective as of February 1, 2014) Note to Candidate: This document serves as a guide to assist in examination preparation for candidates who have met NCCAOM
The Chinese Herbology Expanded Content Outline (Effective as of February 1, 2014) Note to Candidate: This document serves as a guide to assist in examination preparation for candidates who have met NCCAOM
Beginning to Read Mandarin Chinese
 Beginning to Read Mandarin Chinese Pronunciation tips for the Chinese Romanized alphabet (hanyu pin yin) Simple Vowels a e i u o like the a in father or ah ha! like the e in the (the Arican English schwa
Beginning to Read Mandarin Chinese Pronunciation tips for the Chinese Romanized alphabet (hanyu pin yin) Simple Vowels a e i u o like the a in father or ah ha! like the e in the (the Arican English schwa
In this chapter, I present the general treatment principles used in Chinese andrology
 Book 1 Chapter 7 General Treatment Principles in Chinese Andrology In this chapter, I present the general treatment principles used in Chinese andrology and correlate them with common Chinese medicinal
Book 1 Chapter 7 General Treatment Principles in Chinese Andrology In this chapter, I present the general treatment principles used in Chinese andrology and correlate them with common Chinese medicinal
Chinese Herbal Patent
 Chinese Herbal Patent Yuxing Liu Ph. D Academy of Oriental Medicine at Austin What is Herbal Patent Introduction Advantages of Herbal patent Effective: Convenient: Cheaper: Characters of Herbal Patent
Chinese Herbal Patent Yuxing Liu Ph. D Academy of Oriental Medicine at Austin What is Herbal Patent Introduction Advantages of Herbal patent Effective: Convenient: Cheaper: Characters of Herbal Patent
NCCAOM Reinst atement Examination Conte nt Outline f or the Diplomate of Chinese Herbology Certification
 2018 NCCAOM Reinst atement Examination Conte nt Outline f or the Diplomate of Chinese Herbology Certification 2018 NCCAOM N CCAOM 2025 M Street NW, Suite 800 Washington D.C., 20036 (202) 381-1140 - Direct
2018 NCCAOM Reinst atement Examination Conte nt Outline f or the Diplomate of Chinese Herbology Certification 2018 NCCAOM N CCAOM 2025 M Street NW, Suite 800 Washington D.C., 20036 (202) 381-1140 - Direct
Chinese herb formulae for treatment of erectile dysfunction: a systematic review of randomised controlled clinical trials
 REVIEW ARTICLE Chinese herb formulae for treatment of erectile dysfunction: a systematic review of randomised controlled clinical trials G. Xiong 1,B.Li 2,K.Wang 1 &H.Li 1 1 Department of Urology, West
REVIEW ARTICLE Chinese herb formulae for treatment of erectile dysfunction: a systematic review of randomised controlled clinical trials G. Xiong 1,B.Li 2,K.Wang 1 &H.Li 1 1 Department of Urology, West
Dang Gui Si Ni Tang Tangkuei Decoction for Frigid Extremities
 Dang Gui Si Ni Tang Tangkuei Decoction for Frigid Extremities D F E G ctions: Warms the channels, disperses cold, nourishes the xue, and unblocks the xue vessels. hief Deputy (a) Dang Gui (b) Gui Zhi (c)
Dang Gui Si Ni Tang Tangkuei Decoction for Frigid Extremities D F E G ctions: Warms the channels, disperses cold, nourishes the xue, and unblocks the xue vessels. hief Deputy (a) Dang Gui (b) Gui Zhi (c)
Functions and applications of Long Yan Rou and Suan Zao Ren By Alexandre Djukanovic
 Functions and applications of Long Yan Rou and Suan Zao Ren By Alexandre Djukanovic 龍眼肉 lóng yăn ròu, "dragon eye flesh 酸棗仁 suān zăo rén, "sour date seed" 1. Summary In this paper the functions and uses
Functions and applications of Long Yan Rou and Suan Zao Ren By Alexandre Djukanovic 龍眼肉 lóng yăn ròu, "dragon eye flesh 酸棗仁 suān zăo rén, "sour date seed" 1. Summary In this paper the functions and uses
CMHB221 Chinese Herbal Formulae
 CMHB221 Chinese Herbal Formulae Session Three Tonifying Chinese herbal formulae: Qi: o o o o o English name; Pin yin name and Chinese name Composition; dosage and administration Functions and indications
CMHB221 Chinese Herbal Formulae Session Three Tonifying Chinese herbal formulae: Qi: o o o o o English name; Pin yin name and Chinese name Composition; dosage and administration Functions and indications
Treatment and management of Lumbago with Du Huo Ji Sheng Tang and Yan Hu Zhi Tong Wan A Case Study
 Treatment and management of Lumbago with Du Huo Ji Sheng Tang and Yan Hu Zhi Tong Wan A Case Study Alina Garofil and Ming Cheng Middlesex Universality Please send all correspondences to Dr Ming Cheng,
Treatment and management of Lumbago with Du Huo Ji Sheng Tang and Yan Hu Zhi Tong Wan A Case Study Alina Garofil and Ming Cheng Middlesex Universality Please send all correspondences to Dr Ming Cheng,
Safety and health training model It is expected that better recognition of hazards can reduce risks to workers. Course depth and suitable teaching met
 Y.J. Hong, Y.H. Lin, H.H. Pai, et al DEVELOPING A SAFETY AND HEALTH TRAINING MODEL FOR PETROCHEMICAL WORKERS Yu-Jue Hong, Ya-Hsuan Lin, Hsiu-Hua Pai, 1 Yung-Chang Lai, 2 and I-Nong Lee 3 Institute of Public
Y.J. Hong, Y.H. Lin, H.H. Pai, et al DEVELOPING A SAFETY AND HEALTH TRAINING MODEL FOR PETROCHEMICAL WORKERS Yu-Jue Hong, Ya-Hsuan Lin, Hsiu-Hua Pai, 1 Yung-Chang Lai, 2 and I-Nong Lee 3 Institute of Public
The final definitive version in Complementary Therapies in Medicine is available online at:
 WestminsterResearch http://www.westminster.ac.uk/westminsterresearch Chinese herbal medicine for treating menopausal symptoms in London women: developing a good practice protocol via the factor analysis
WestminsterResearch http://www.westminster.ac.uk/westminsterresearch Chinese herbal medicine for treating menopausal symptoms in London women: developing a good practice protocol via the factor analysis
CMHB221 Chinese Herbal Formulae
 CMHB221 Chinese Herbal Formulae Session Four Tonifying Chinese herbal formulae: Xue; Qi and Xue: o o o o o English name; Pin yin name and Chinese name Composition; dosage and administration Functions and
CMHB221 Chinese Herbal Formulae Session Four Tonifying Chinese herbal formulae: Xue; Qi and Xue: o o o o o English name; Pin yin name and Chinese name Composition; dosage and administration Functions and
Section 3. Blood-Tonifying Herbs. Dang Gui (Radicis Angelicae Sinensis) Chapter 17 Section 3 Blood-Tonifying Herbs
 Section 3 Blood-Tonifying Herbs Pinyin Name: Dang Gui Literal Name: state of return, ought to return Alternate Chinese Names: Xi Gui, Gan Gui, Quan Dang Gui, Qin Dang Gui, Yun Dang Gui, Chuan Dang Gui
Section 3 Blood-Tonifying Herbs Pinyin Name: Dang Gui Literal Name: state of return, ought to return Alternate Chinese Names: Xi Gui, Gan Gui, Quan Dang Gui, Qin Dang Gui, Yun Dang Gui, Chuan Dang Gui
Clinical Observations
 98 Clinical Observations Clinical Observations on 100 Cases of Ulcerative Colitis Treated with the Method of Clearing Away Heat, Expelling Dampness, Promoting Blood Circulation and Healing Ulcer YE Bai,
98 Clinical Observations Clinical Observations on 100 Cases of Ulcerative Colitis Treated with the Method of Clearing Away Heat, Expelling Dampness, Promoting Blood Circulation and Healing Ulcer YE Bai,
Understanding of Senile Dementia by Children and Adolescents: Why Grandma Can t Remember Me?
 138 Understanding of Senile Dementia by Children and Adolescents: Why Grandma Can t Remember Me? Jong-Ling Fuh 1, Shuu-Jiun Wang 1, and Kai-Di Juang 2 Abstract- Background: The present study sought to
138 Understanding of Senile Dementia by Children and Adolescents: Why Grandma Can t Remember Me? Jong-Ling Fuh 1, Shuu-Jiun Wang 1, and Kai-Di Juang 2 Abstract- Background: The present study sought to
The updated incidences and mortalities of major cancers in China, 2011
 DOI 10.1186/s40880-015-0042-6 REVIEW Open Access The updated incidences and mortalities of major cancers in China, 2011 Wanqing Chen *, Rongshou Zheng, Hongmei Zeng and Siwei Zhang Abstract Introduction:
DOI 10.1186/s40880-015-0042-6 REVIEW Open Access The updated incidences and mortalities of major cancers in China, 2011 Wanqing Chen *, Rongshou Zheng, Hongmei Zeng and Siwei Zhang Abstract Introduction:
Case Study for Degenerative Arthritis of the Knee
 1. Case Study for Degenerative Arthritis of the Knee 2. Two Cases of Thoracic Diseases with Effective Clinical Results 3. Dr. Pu-Tao Chang on Health Preservation Ginseng (Ren Shen) 4. Pharmacodynamics
1. Case Study for Degenerative Arthritis of the Knee 2. Two Cases of Thoracic Diseases with Effective Clinical Results 3. Dr. Pu-Tao Chang on Health Preservation Ginseng (Ren Shen) 4. Pharmacodynamics
Effects of Chai Hu (Radix Burpleuri) Containing Formulation on Plasma β-endorphin, Epinephrine and Dopamine in Patients
 The American Journal of Chinese Medicine, Vol. 33, No. 5, 737 745 2005 World Scientific Publishing Company Institute for Advanced Research in Asian Science and Medicine Effects of Chai Hu (Radix Burpleuri)
The American Journal of Chinese Medicine, Vol. 33, No. 5, 737 745 2005 World Scientific Publishing Company Institute for Advanced Research in Asian Science and Medicine Effects of Chai Hu (Radix Burpleuri)
Research Article Prescription Pattern of Chinese Herbal Products for Diabetes Mellitus in Taiwan: A Population-Based Study
 Evidence-Based Complementary and Alternative Medicine Volume 2013, Article ID 201329, 10 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2013/201329 Research Article Prescription Pattern of Chinese Herbal Products for
Evidence-Based Complementary and Alternative Medicine Volume 2013, Article ID 201329, 10 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2013/201329 Research Article Prescription Pattern of Chinese Herbal Products for
Canqiu Yu 1, Jinwei Chen 2, Li Huang 3*
 A STUDY ON THE ANTITUMOUR EFFECT OF TOTAL FLAVONOIDS FROM PTERIS MULTIFIDA POIR IN H22 TUMOUR-BEARING MICE 459 Canqiu Yu 1, Jinwei Chen 2, Li Huang 3* 1 Department of General Surgery, The Second Xiangya
A STUDY ON THE ANTITUMOUR EFFECT OF TOTAL FLAVONOIDS FROM PTERIS MULTIFIDA POIR IN H22 TUMOUR-BEARING MICE 459 Canqiu Yu 1, Jinwei Chen 2, Li Huang 3* 1 Department of General Surgery, The Second Xiangya
MEN'S SEXUAL AND PROSTATE PROBLEMS IN CHINESE MEDICINE
 MEN'S SEXUAL AND PROSTATE PROBLEMS IN CHINESE MEDICINE While Chinese medicine has a rich tradition in the diagnosis and treatment of gynaecological problems, fewer ancient or modern texts are dedicated
MEN'S SEXUAL AND PROSTATE PROBLEMS IN CHINESE MEDICINE While Chinese medicine has a rich tradition in the diagnosis and treatment of gynaecological problems, fewer ancient or modern texts are dedicated
Appropriate Quality regarde as
 A systematic review of antibiotic prescription associated with upper respiratory tract infections in China (Jing Li, MS 1 ) Supplemental Digital Content-Table 1. Quality assessment of included studies
A systematic review of antibiotic prescription associated with upper respiratory tract infections in China (Jing Li, MS 1 ) Supplemental Digital Content-Table 1. Quality assessment of included studies
Christy Pu Institutes Degree Department Period National Yang-Ming University (Taiwan)
 Christy Pu cypu@ym.edu.tw Degree Institutes Degree Department Period National Yang-Ming University (Taiwan) PhD Public Health 09/2005~06/2008 University of Oxford (UK) MSc Economics 08/2002~07/2003 University
Christy Pu cypu@ym.edu.tw Degree Institutes Degree Department Period National Yang-Ming University (Taiwan) PhD Public Health 09/2005~06/2008 University of Oxford (UK) MSc Economics 08/2002~07/2003 University
Incidence and Risk of Alcohol Use Disorders by Age, Gender and Poverty Status: A Population-Based-10 Year Follow-Up Study
 Incidence and Risk of Alcohol Use Disorders by Age, Gender and Poverty Status: A Population-Based-10 Year Chun-Te Lee 1,2, Chiu-Yueh Hsiao 3, Yi-Chyan Chen 4,5, Oswald Ndi Nfor 6, Jing-Yang Huang 6, Lee
Incidence and Risk of Alcohol Use Disorders by Age, Gender and Poverty Status: A Population-Based-10 Year Chun-Te Lee 1,2, Chiu-Yueh Hsiao 3, Yi-Chyan Chen 4,5, Oswald Ndi Nfor 6, Jing-Yang Huang 6, Lee
Oriental Herbology II HERBS THAT CALM SPIRIT. Lana Farson, M.S., L.Ac. Symptoms of uncalm spirit. CALM SPIRIT HERBS 2 types
 riental Herbology II HERBS THAT CALM SPIRIT Lana Farson, M.S., L.Ac. 1 Symptoms of uncalm spirit 2 CALM SPIRIT HERBS 2 types 1.Sedative Herbs that calm spirit (Excess Type cases) 2.Nourishing herbs that
riental Herbology II HERBS THAT CALM SPIRIT Lana Farson, M.S., L.Ac. 1 Symptoms of uncalm spirit 2 CALM SPIRIT HERBS 2 types 1.Sedative Herbs that calm spirit (Excess Type cases) 2.Nourishing herbs that
Acupuncture Outmatches Drug For IBS
 Acupuncture Outmatches Drug For IBS Published by HealthCMi on December 2017 Acupuncture and Chinese herbal medicine are found effective for the alleviation of IBS (irritable bowel syndrome). Two independent
Acupuncture Outmatches Drug For IBS Published by HealthCMi on December 2017 Acupuncture and Chinese herbal medicine are found effective for the alleviation of IBS (irritable bowel syndrome). Two independent
24 h. P > h. R doi /j. issn
 38 4 2015 4 Vol. 38 No. 4 Apr. 2015 Journal of Beijing University of Traditional Chinese Medicine 271 2 ~ 3 * 1 2 2 2 2 2 1# 1 201203 2 2 ~ 3 55 2 18 37 24 2 0 8 16 24 24 h 2 P > 0. 05 P < 0. 05 P < 0.
38 4 2015 4 Vol. 38 No. 4 Apr. 2015 Journal of Beijing University of Traditional Chinese Medicine 271 2 ~ 3 * 1 2 2 2 2 2 1# 1 201203 2 2 ~ 3 55 2 18 37 24 2 0 8 16 24 24 h 2 P > 0. 05 P < 0. 05 P < 0.
Clear Heat and Cool Blood Herbs
 Course: Chinese Herbology 1 Date: October 28, 2008 Class #: 6 Clear Heat/Cool Blood Herbs Clear Heat and Cool Blood Herbs Introduction Used for Ying and Xue stages, the 2 deepest of the four levels of
Course: Chinese Herbology 1 Date: October 28, 2008 Class #: 6 Clear Heat/Cool Blood Herbs Clear Heat and Cool Blood Herbs Introduction Used for Ying and Xue stages, the 2 deepest of the four levels of
The progressing research of traditional Chinese medicine treatment of. insomnia. Liu Jing1 a
 4th International Conference on Education, Management and Computing Technology (ICEMCT 2017) The progressing research of traditional Chinese medicine treatment of insomnia Liu Jing1 a 1 Shandong University
4th International Conference on Education, Management and Computing Technology (ICEMCT 2017) The progressing research of traditional Chinese medicine treatment of insomnia Liu Jing1 a 1 Shandong University
An Overview of Traditional Chinese Herbal Formulae and a Proposal of a New Code System for Expressing the Formula Titles
 Advance Access Publication 4 August 2004 ecam 2004;1(2)125 132 doi:10.1093/ecam/neh019 Review An Overview of Traditional Chinese Herbal Formulae and a Proposal of a New Code System for Expressing the Formula
Advance Access Publication 4 August 2004 ecam 2004;1(2)125 132 doi:10.1093/ecam/neh019 Review An Overview of Traditional Chinese Herbal Formulae and a Proposal of a New Code System for Expressing the Formula
Summary of Chapter 44 of the Líng Shū
 Summary of Chapter 44 of the Líng Shū Shùn Qì Yī Rì Fēn Wéi Sì Shí The Human Healthy Energy in the Day and Night Corresponds with the Energies of the Four Seasons Paragraph 1 The initiation of the various
Summary of Chapter 44 of the Líng Shū Shùn Qì Yī Rì Fēn Wéi Sì Shí The Human Healthy Energy in the Day and Night Corresponds with the Energies of the Four Seasons Paragraph 1 The initiation of the various
The Foundations of Oriental Medicine Abbreviated Content Outline
 The Foundations of Oriental Medicine Abbreviated Content Outline (Effective as of February 1, 2014) Note to Candidate: This document serves as a guide to assist in examination preparation for candidates
The Foundations of Oriental Medicine Abbreviated Content Outline (Effective as of February 1, 2014) Note to Candidate: This document serves as a guide to assist in examination preparation for candidates
Pin-Yi Lin, 1 Yueh-Ting Tsai, 1 Jung-Nien Lai, 1,2 Chia-Hao Yeh, 3 and Ruei-Chi Fang Introduction
 Hindawi Publishing Corporation Evidence-Based Complementary and Alternative Medicine Volume 2014, Article ID 460386, 11 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2014/460386 Research Article Bian Zheng Lun Zhi as
Hindawi Publishing Corporation Evidence-Based Complementary and Alternative Medicine Volume 2014, Article ID 460386, 11 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2014/460386 Research Article Bian Zheng Lun Zhi as
Literature-based analysis on relationship of symptoms, drugs and therapies in treatment of intestinal diseases
 Online Submissions: http://www.journaltcm.com J Tradit Chin Med 0 February ; (): 6- info@journaltcm.com ISSN 05-9 0 JTCM. All rights reserved. LITERATURE STUDY TOPIC Literature-based analysis on relationship
Online Submissions: http://www.journaltcm.com J Tradit Chin Med 0 February ; (): 6- info@journaltcm.com ISSN 05-9 0 JTCM. All rights reserved. LITERATURE STUDY TOPIC Literature-based analysis on relationship
An Gong Niu Huang Wan Calm the Palace Pill with Cattle Gallstone
 An Gong Niu Huang Wan Calm the Palace Pill with Cattle Gallstone Niu Huang Huang Lian Huang Qin Zhi Zi Xiong Huang Honey Gold Leaf coating Zhen Zhu Chief Assistant Envoy Niu Huang Huang Lian Huang Qin
An Gong Niu Huang Wan Calm the Palace Pill with Cattle Gallstone Niu Huang Huang Lian Huang Qin Zhi Zi Xiong Huang Honey Gold Leaf coating Zhen Zhu Chief Assistant Envoy Niu Huang Huang Lian Huang Qin
CURRICULUM VITAE China Medical College, College of Medicine, Taichung, Taiwan, R.O.C.
 CURRICULUM VITAE NAME: Huang, Chung-Ming OFFICE ADDRESS: China Medical University Hospital, No. 2, Yuh-Der Road, Taichung, Taiwan, R.O.C., 北 路 2 EDUCATION: 1978-1985 China Medical College, College of Medicine,
CURRICULUM VITAE NAME: Huang, Chung-Ming OFFICE ADDRESS: China Medical University Hospital, No. 2, Yuh-Der Road, Taichung, Taiwan, R.O.C., 北 路 2 EDUCATION: 1978-1985 China Medical College, College of Medicine,
HERB PHARMACOPOEIA IV
 COURSE DESCRIPTION The fourth course in the Herb Pharmacopeia series. Herb Pharmacopeia IV covers herbs in the Qi Tonics, Blood Tonics, Yang Tonics, Yin Tonics, Stop Diarrhea, Astringe Essence, and External
COURSE DESCRIPTION The fourth course in the Herb Pharmacopeia series. Herb Pharmacopeia IV covers herbs in the Qi Tonics, Blood Tonics, Yang Tonics, Yin Tonics, Stop Diarrhea, Astringe Essence, and External
Classic formula quantity comparison between FCG Granules and standard 5:1 ratio granules
 Classic formula quantity comparison between FCG Granules and standard 5:1 ratio granules Raw Name herb (g) Zhi bai di huang wan Equiv. factor FCG (g) Shu di huang 24 5 4.8 Shan zhu yu 12 5 2.4 Mu dan pi
Classic formula quantity comparison between FCG Granules and standard 5:1 ratio granules Raw Name herb (g) Zhi bai di huang wan Equiv. factor FCG (g) Shu di huang 24 5 4.8 Shan zhu yu 12 5 2.4 Mu dan pi
Fu Zi (Radix Aconiti Lateralis Praeparata)
 Pinyin Name: Fu Zi Literal Name: appendage Original Source: Shen Nong Ben Cao Jing (Divine Husbandman s Classic of the Materia Medica) in the second century English Name: aconite, prepared daughter root
Pinyin Name: Fu Zi Literal Name: appendage Original Source: Shen Nong Ben Cao Jing (Divine Husbandman s Classic of the Materia Medica) in the second century English Name: aconite, prepared daughter root
BLOOD STASIS 1. AETIOLOGY
 BLOOD STASIS Blood stasis is a common and damaging pathogenic factor that is at the root of many serious diseases. A characteristic of Blood stasis is that it can only occur after a prolonged period of
BLOOD STASIS Blood stasis is a common and damaging pathogenic factor that is at the root of many serious diseases. A characteristic of Blood stasis is that it can only occur after a prolonged period of
CMU Faculty Profile Yu-Chen Lee
 Yu-Chen Lee Dean, Acupuncture department of China Medicine University Hospital Assistant Professor, Graduate Institution of Acupuncture Sciences, China Medicine University Ph.D., China Medicine University
Yu-Chen Lee Dean, Acupuncture department of China Medicine University Hospital Assistant Professor, Graduate Institution of Acupuncture Sciences, China Medicine University Ph.D., China Medicine University
Middlesex University Research Repository
 Middlesex University Research Repository An open access repository of Middlesex University research http://eprints.mdx.ac.uk Garofil, Alina and Cheng, Ming Zhao (2014) Treatment and management of lumbago
Middlesex University Research Repository An open access repository of Middlesex University research http://eprints.mdx.ac.uk Garofil, Alina and Cheng, Ming Zhao (2014) Treatment and management of lumbago
ANTA PROFESSIONAL SEMINAR. Achieving healthy MOTHERHOOD with Chinese Herbal Medicine
 ANTA PROFESSIONAL SEMINAR Achieving healthy MOTHERHOOD with Chinese Herbal Medicine FERTILITY FERTILITY Normal fertility depends upon the following factors: The integrity of the female and male reproductive
ANTA PROFESSIONAL SEMINAR Achieving healthy MOTHERHOOD with Chinese Herbal Medicine FERTILITY FERTILITY Normal fertility depends upon the following factors: The integrity of the female and male reproductive
Western medical The herb is indicated in the treatment of pneumonia, mouth ulcer, hoarse voice, esophagitis, etc.
 Bei Sha Shen Introduction Radix glehniae is the dried root of Glehnia littoralis Fr. Schmidt ex Miq. (Fam. Umbelliferae). The drug is collected in summer and autumn, removed from rootlet, washed clean,
Bei Sha Shen Introduction Radix glehniae is the dried root of Glehnia littoralis Fr. Schmidt ex Miq. (Fam. Umbelliferae). The drug is collected in summer and autumn, removed from rootlet, washed clean,
Clinical Observations on 46 Cases of Globus Hystericus Treated with Modified Banxia Houpu Decoction
 Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, June 2010, Vol. 30, No. 2 103 Clinical Observations on 46 Cases of Globus Hystericus Treated with Modified Banxia Houpu Decoction BO Ping 1, CHEN Qi-ming 2, ZHU
Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, June 2010, Vol. 30, No. 2 103 Clinical Observations on 46 Cases of Globus Hystericus Treated with Modified Banxia Houpu Decoction BO Ping 1, CHEN Qi-ming 2, ZHU
Acupuncture for the syndrome of prolapsed lumbar Intervertebral disc --Case studies and clinical experiences
 Acupuncture for the syndrome of prolapsed lumbar Intervertebral disc --Case studies and clinical experiences By Dr. Yin Hongchun Email: h.yin1@btopenworld.com Tel: 02086722088 Main point of diagnosis (1)
Acupuncture for the syndrome of prolapsed lumbar Intervertebral disc --Case studies and clinical experiences By Dr. Yin Hongchun Email: h.yin1@btopenworld.com Tel: 02086722088 Main point of diagnosis (1)
SUMMARY REPORT OF ACUPUNCTURE SESSION
 SUMMARY REPORT OF ACUPUNCTURE SESSION 1 Presenter: Jaung-Geng Lin 2 Introduction to acupuncture session In this session, we had 26 posters and 12 posters were selected for presentation and discussion.
SUMMARY REPORT OF ACUPUNCTURE SESSION 1 Presenter: Jaung-Geng Lin 2 Introduction to acupuncture session In this session, we had 26 posters and 12 posters were selected for presentation and discussion.
Cognitive Abilities Screening Instrument, Chinese Version 2.0 (CASI C-2.0): Administration and Clinical Application
 Continuing Medical Education 180 Cognitive Abilities Screening Instrument, Chinese Version 2.0 (CASI C-2.0): Administration and Clinical Application Ker-Neng Lin 1,2, Pei-Ning Wang 1,3, Hsiu-Chih Liu 1,3,
Continuing Medical Education 180 Cognitive Abilities Screening Instrument, Chinese Version 2.0 (CASI C-2.0): Administration and Clinical Application Ker-Neng Lin 1,2, Pei-Ning Wang 1,3, Hsiu-Chih Liu 1,3,
