31-2. The Earthworm. . Relate the structure of systems. . Demonstrate dissection technique. . Identifythe major advancesof
|
|
|
- Austen Lee
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Name Class Date INVESTIGATION 31-2 The Earthworm Introduction The earthworm is a segmented worm. It exhibits more complex structures than any of the more primitive animals that you have studied thus far. Some of the special structures of the earthworm are a segmented body, a coelom (tube-within-a-tube body plan), a complex nervous system, excretory organs, and a circulatory system. In this investigation you will first examine the external anatomy of the earthworm and then carefully dissect it to observe its internal anatomy. Materials Earthworm, preserved Dissecting scissors Procedure Dissecting needle Dissecting pan Part A: The External Featuresof the Earthworm Dissecting pins 1. Make a rough sketch of your earthworm. Label the following parts: anterior end, posterior end, dorsal surface, ventral surface, clitellum. Note: The anterior is closer to the clitellum. The dorsal surface is darker than the ventral surface. ~ Purpose To identifythe maininternal and externalstructuresof the earthworm Objectives. Observe the major systems of the earthworm.. Demonstrate dissection technique.. Relate the structure of systems to their function.. Identifythe major advancesof the earthwormoverthe lower animals...", - :-, u :-I I 1M --.;-- ---Mr;nn n~rlinr ;n.h;o...nr~ 161
2 "1/:? UD',-. h_"_'_~'-~.._~u _C --_u_'u --"""--'-.~'- -- L 2. Pick up your earthworm and examine it. Find the prostomium, a small projection anterior to the first segment. The prostomium is not a segment. Directly behind and ventral to the prostomium is the mouth. Count the segments from the mouth backward to the clitellum. How many segments are there before the clitellum? 3. Run your finger very lightly along the ventral surface of the earthworm. The bristlelike structures you feel are called setae, which are slightly curved with pointed ends. There are four pair of setae on each segment. Each pair has a set of muscles to allow movement. What is the function of the setae? / 4. Locate segments 14 and 15. Using a hand lens, locate the oviducts on the ventral surface of segment 14 and the sperm ducts on the ventral surface of segment 15. What is the name for an animal which has both sexes in one individual? Anterior Clitellum Posterior 5. Label the diagram of the ventral surface of the earthworm with the following structures: prostomium, mouth, setae, sperm duct, oviducts, clitellum. Part 8: The Internal Organs of the Earthworm 1. CAUTION: Implements used for dissecting are sharp. Take care not to cut yourself. Begin your dissection just posterior to the clitellum, cutting toward the anterior end. Always point the tip of the scissors up, making sure you do not cut into any internal structures. If a structure gets nicked during cutting, it becomes very difficult, sometimes impossible, to see how it actually looks. When working with small, delicate structures, carefully use a probe to move them. 2. Place the earthworm in a dissecting pan with the dorsal side up and the anterior end away from you. Use your diagram of the external structures of the earthworm to make sure you have the earthworm oriented correctly. Begin cutting posterior to the clitellum and continue anteriorly along the mid-dorsal line as far as the prostomium. 3. Use the probe to carefully open up the earthworm by separating the edges of the cut. 4. Inside the earthworm you will observe that the outer segments become inner compartments, which are separated by very delicate partitions called septa. Carefully separate the septa from the wall with a probe. Notice that the body wall is separate from the intestines. The cavity between the body wall and the intestines is called the coelom. This cavity separates the outer and inner layers of the earthworm. 5. After cutting through the septa of several segments, begin to pin down the body wall. This allows other structures to be seen more easily. Slant the pins outward to keep them out of your way. Continue to cut the septa gradually until you reach the prostomium. / /
3 LID I -_+_.:_1 _n"".:_h+n",,".1m "ntinn ~""n~';"" n~,l:n' ;n thi. \Mnr~ 16 Name Class Date 6. After the earthworm is completely open, begin your observations of the internal structures, system by system. Carefully locate and observe each structure. After you have found the structure, label it on the diagram below. Segments Internal organs '
4 ... a. Digestive System The digestive system begins with the mouth or buccal cavity (segments 1 and 2) and is followed by the pharynx, on which many strands of muscle fibers may be observed. The esophagus is a thin-walled tube which continues posteriorly from the pharynx to segment 13 or 14. The crop and the gizzard are in segments 14 through 20. The walls of the gizzard are muscular for grinding food. The walls of the crop are thin. The rest of the digestive system is composed of the intestine which continues from segment 20 to the anus, the most posterior part. b. Circulatory System The large dorsal blood vessel carries blood from the posterior end of the earthworm to the anterior end. Five aortic arches connect the dorsal and ventral blood vessels. These arches are sometimes called "hearts" because they help pump blood. The "hearts" may be difficult to see as they are located behind the esophagus. The earthworm has a circulatory system superior to that of the lower animals that you have studied. Explain why this is necessary. c. Respiratory and Excretory Systems Since the skin is the organ of respiration in the earthworm there are no other organs to locate for this system. Explain how respiration takes place through the skin. What happens to the earthworm if its skin dries out? What happens to the earthworm, flooded? after a big rain, when the soil is
5 Name Class Date The excretory system's nephridia are the coiled tubes that can be observed on the sides of each segment. What is the function of the nephridia? d. Nervous System In segment 3 locate two small, white structures. These are the cerebral ganglia or the' 'brain." Nerves extend anteriorly from them. From each ganglion a nerve cord goes ventrally around the pharynx where it meets another nerve cord and continues to the posterior of the earthworm. Each segment has a lateral branch of the nerve cord, but they are often difficult to see. e. Reproductive System The three pairs of white masses in segments 9 through 13, next to the esophagus, are the seminal vesicles. They store the sperm produced by the testes. The seminal receptacles are much smaller than the seminal vesicles and lie on the ventral wall in segments 9 and 10. They are composed of four spherical bodies which receive the sperm from another worm at the time of mating. The ovaries and testes are ventral to the seminal vesicles making them difficult to observe. Analysesand Conclusions 1. What is the genus and species name for the earthworm you are dissecting? 2. Describe earthworm reproduction using all the structures you have located in the reproductive system. u_"u,-.c,- 1. 1~"
6 3. What are the three major developmental advancements of the earthworm? Going Further Even though earthworms do not have eyes and ears they are capable of responding to light and sound. Design an experiment that will show how they respond to either of these stimuli. Write up the procedure, do the experiment, record observations, and state conclusions according to what you have learned through your observations. Remember to have a control for all the other variables except the one being tested.
Biology Earthworm Dissection
 Biology 521 - Earthworm Dissection Kingdom Phylum Class Order Genus Species Animalia Annelida Oligochaeta Haplotaxida Lumbricus L. terrestris PRELAB: The earthworm is an excellent organism to study as
Biology 521 - Earthworm Dissection Kingdom Phylum Class Order Genus Species Animalia Annelida Oligochaeta Haplotaxida Lumbricus L. terrestris PRELAB: The earthworm is an excellent organism to study as
BIO Lab 18: Dissection of the Earthworm
 The Earthworm Harken to me, you that know what is just, my people who have My law in their heart: Fear not the reproach of men and be not afraid of their blasphemies. For the worm shall eat them up as
The Earthworm Harken to me, you that know what is just, my people who have My law in their heart: Fear not the reproach of men and be not afraid of their blasphemies. For the worm shall eat them up as
KIDSPIRATION by Riedell
 WORM DISSECTION KIDSPIRATION by Riedell CLASSIFICATION Kingdom: Phylum: ANIMALIA Annelida little rings Class: OLIGOCHAETA few bristles SETA (plural: setae) BRISTLES on VENTRAL surface http://www.pgjr.alpine.k12.ut.us/science/whitaker/animal_kingdom/earthworm/earthworm.html
WORM DISSECTION KIDSPIRATION by Riedell CLASSIFICATION Kingdom: Phylum: ANIMALIA Annelida little rings Class: OLIGOCHAETA few bristles SETA (plural: setae) BRISTLES on VENTRAL surface http://www.pgjr.alpine.k12.ut.us/science/whitaker/animal_kingdom/earthworm/earthworm.html
Zoology Exercise #10: Phylum Nematoda Lab Guide
 Zoology Exercise #10: Phylum Nematoda Lab Guide All animals with bilateral symmetry, except the acoelomates, have a body cavity. They are either true coelomates (where peritoneum covers both the inner
Zoology Exercise #10: Phylum Nematoda Lab Guide All animals with bilateral symmetry, except the acoelomates, have a body cavity. They are either true coelomates (where peritoneum covers both the inner
The Anatomy of the Earthworm
 Carolina Biological Supply Company presents The Anatomy of the Earthworm 2700 York Road Box 187 Burlington, North Carolina 27215 Gladstone, Oregon 97027 Abstract. This program facilitates a study of the
Carolina Biological Supply Company presents The Anatomy of the Earthworm 2700 York Road Box 187 Burlington, North Carolina 27215 Gladstone, Oregon 97027 Abstract. This program facilitates a study of the
Internal Morphology. 1.Cut the legs and wings (if present) off your specimen. 5.Use forceps to pull skeleton apart, exposing internal systems.
 Internal Morphology Insect Dissections Often the best approach to understanding internal morphology is by way of a dissection. For this reason, the entire chapter should be treated as a laboratory activity.
Internal Morphology Insect Dissections Often the best approach to understanding internal morphology is by way of a dissection. For this reason, the entire chapter should be treated as a laboratory activity.
LABORATORY EXERCISE 4 PHYLUM PLATYHELMINTHES
 GENUS PLANARIA Planaria sp. Lab 4, pg 1 LABORATORY EXERCISE 4 PHYLUM PLATYHELMINTHES With a soft brush, place a live Planaria in a small dish with a few millimeters of pond water. BEHAVIOR. Examine the
GENUS PLANARIA Planaria sp. Lab 4, pg 1 LABORATORY EXERCISE 4 PHYLUM PLATYHELMINTHES With a soft brush, place a live Planaria in a small dish with a few millimeters of pond water. BEHAVIOR. Examine the
Frog Dissection-Skin Vista Murrieta High School-- Biomedical Science. Mr. Diaz
 Frog Dissection-Skin Vista Murrieta High School-- Biomedical Science Mr. Diaz Background: Please read entire lab As members of the class Amphibia, frogs may live some of their adult lives on land, but
Frog Dissection-Skin Vista Murrieta High School-- Biomedical Science Mr. Diaz Background: Please read entire lab As members of the class Amphibia, frogs may live some of their adult lives on land, but
Crayfish Dissection. Objectives: Describe the appearance of various organs found in a crayfish. Name the organs that make up systems of the crayfish.
 Crayfish Dissection Objectives: Describe the appearance of various organs found in a crayfish. Name the organs that make up systems of the crayfish. Background: Like all crustaceans, a crayfish has a fairly
Crayfish Dissection Objectives: Describe the appearance of various organs found in a crayfish. Name the organs that make up systems of the crayfish. Background: Like all crustaceans, a crayfish has a fairly
In this lab, you will observe the external structures of a crayfish and dissect it to study its internal structures and systems.
 Crayfish Dissection Objectives: Describe the appearance of various organs found in a crayfish. Name the organs that make up systems of the crayfish. Materials: safety goggles, gloves, magnifying glass,
Crayfish Dissection Objectives: Describe the appearance of various organs found in a crayfish. Name the organs that make up systems of the crayfish. Materials: safety goggles, gloves, magnifying glass,
Name Date Per. HANDOUT Frog Dissection Lab
 Name Date Per UNIT 6 HANDOUT Frog Dissection Lab Purpose: To observe the anatomy of an amphibian To discover characteristics of complex vertebrates To compare anatomy of the frog to that of other organisms
Name Date Per UNIT 6 HANDOUT Frog Dissection Lab Purpose: To observe the anatomy of an amphibian To discover characteristics of complex vertebrates To compare anatomy of the frog to that of other organisms
Frog Dissection. Name: Block:
 Name: Block: Frog Dissection Background: As members of the class Amphibia, frogs may live some of their adult lives on land, but they must return to water to reproduce. Eggs are laid and fertilized in
Name: Block: Frog Dissection Background: As members of the class Amphibia, frogs may live some of their adult lives on land, but they must return to water to reproduce. Eggs are laid and fertilized in
7 weeks: 28 mm 8 weeks: 40 mm 15 weeks: 220 mm 17 weeks: 300 mm
 Fetal Pig Dissection Background Pigs are placental mammals and show the distinguishing characteristics of that group. In studying the anatomy of the fetal, or unborn, pig, you will see that its various
Fetal Pig Dissection Background Pigs are placental mammals and show the distinguishing characteristics of that group. In studying the anatomy of the fetal, or unborn, pig, you will see that its various
Crayfish Observation and Dissection
 Name Period Date Crayfish Observation and Dissection Purpose: In this lab, you will observe the external structures of a crayfish and dissect it to study its internal structures and systems. Materials:
Name Period Date Crayfish Observation and Dissection Purpose: In this lab, you will observe the external structures of a crayfish and dissect it to study its internal structures and systems. Materials:
Name Date: Block: Honors Marine Biology Mr. Conlan - Squid Dissection Lab Objective: Can you identify a squid s structures and their functions?
 Name Date: Block: Honors Marine Biology Mr. Conlan - Squid Dissection Lab Objective: Can you identify a squid s structures and their functions? Helpful Hints Everyone must wear safety goggles during the
Name Date: Block: Honors Marine Biology Mr. Conlan - Squid Dissection Lab Objective: Can you identify a squid s structures and their functions? Helpful Hints Everyone must wear safety goggles during the
Phylum Platyhelminthes
 Phylum Platyhelminthes Class? Dugesia (planaria, non-parasitic flatworm) Class? Liver fluke Class? Tapeworm Phylum Platyhelminthes Class Turbellaria Dugesia (planaria, non-parasitic flatworm) Class Trematoda
Phylum Platyhelminthes Class? Dugesia (planaria, non-parasitic flatworm) Class? Liver fluke Class? Tapeworm Phylum Platyhelminthes Class Turbellaria Dugesia (planaria, non-parasitic flatworm) Class Trematoda
Observing the Structure of a Squid
 Name Class Date Chapter 27 Worms and Mollusks Observing the Structure of a Squid Introduction You are probably familiar with clams, snails, slugs, squids, and octupuses, and you probably have noticed how
Name Class Date Chapter 27 Worms and Mollusks Observing the Structure of a Squid Introduction You are probably familiar with clams, snails, slugs, squids, and octupuses, and you probably have noticed how
FROG DISSECTION GUIDE
 FROG DISSECTION GUIDE I. Introduction Frogs belong to the class amphibian. Although many differences exist between humans and frogs, the basic body plans are similar. Humans and frogs both belong to the
FROG DISSECTION GUIDE I. Introduction Frogs belong to the class amphibian. Although many differences exist between humans and frogs, the basic body plans are similar. Humans and frogs both belong to the
Student Guide to the Frog Dissection
 Student Guide to the Frog Dissection Dissection Instructions 1. Place the frog in the dissecting pan ventral side up. 2. Use scissors to life the abdominal muscles away from the body cavity. Cut along
Student Guide to the Frog Dissection Dissection Instructions 1. Place the frog in the dissecting pan ventral side up. 2. Use scissors to life the abdominal muscles away from the body cavity. Cut along
2. What is the difference between a compound eye and your eye?
 INTRODUCTION: If numbers alone are used as a measure of success, the jointedlegged animals are the most successful animals. Their body segmentation suggests that they evolved from segmented worms. The
INTRODUCTION: If numbers alone are used as a measure of success, the jointedlegged animals are the most successful animals. Their body segmentation suggests that they evolved from segmented worms. The
Heart Dissection. 5. Locate the tip of the heart or the apex. Only the left ventricle extends all the way to the apex.
 Heart Dissection Page 1 of 6 Background: The heart is a four-chambered, hollow organ composed primarily of cardiac muscle tissue. It is located in the center of the chest in between the lungs. It is the
Heart Dissection Page 1 of 6 Background: The heart is a four-chambered, hollow organ composed primarily of cardiac muscle tissue. It is located in the center of the chest in between the lungs. It is the
Worksheet for Morgan/Carter Laboratory #19 Animals II Nematoda, Arthropoda, Echinodermata and Chordata
 Worksheet for Morgan/Carter Laboratory #19 Animals II Nematoda, Arthropoda, Echinodermata and Chordata BE SURE TO CAREFULLY READ THE INTRODUCTION PRIOR TO ANSWERING THE QUESTIONS!!! You will need to refer
Worksheet for Morgan/Carter Laboratory #19 Animals II Nematoda, Arthropoda, Echinodermata and Chordata BE SURE TO CAREFULLY READ THE INTRODUCTION PRIOR TO ANSWERING THE QUESTIONS!!! You will need to refer
Contribution of Animals. Many provide food for us and other animals. Clothing and shoes are sometimes made from animal products
 1 2 Contribution of Animals Many provide food for us and other animals Clothing and shoes are sometimes made from animal products Research shows that holding or petting a cat or dog slows the heartbeat
1 2 Contribution of Animals Many provide food for us and other animals Clothing and shoes are sometimes made from animal products Research shows that holding or petting a cat or dog slows the heartbeat
This booklet belongs to: Spring Page 1 of 10
 This booklet belongs to: Spring 2013 Page 1 of 10 Frog Dissection Background Amphibians are studied in science for a variety of reasons. Amphibians are unique in many ways because their anatomy allows
This booklet belongs to: Spring 2013 Page 1 of 10 Frog Dissection Background Amphibians are studied in science for a variety of reasons. Amphibians are unique in many ways because their anatomy allows
Mammalian Dissection: Fetal Pig Integrated Science 4 Honors
 Mammalian Dissection: Fetal Pig Integrated Science 4 Honors Name Per. Introduction Organisms are classified based on similarities and differences to: 1) make sense of the millions of organisms on record,
Mammalian Dissection: Fetal Pig Integrated Science 4 Honors Name Per. Introduction Organisms are classified based on similarities and differences to: 1) make sense of the millions of organisms on record,
3 Invertebrate Structure
 3 Invertebrate Structure INTRODUCTION TO DISSECTIONS This is the first of two labs of dissections. The vast majority of the next lab practical will come from these labs. This part of the lab manual contains
3 Invertebrate Structure INTRODUCTION TO DISSECTIONS This is the first of two labs of dissections. The vast majority of the next lab practical will come from these labs. This part of the lab manual contains
SESSION 2: THE MOUTH AND PHARYNX
 SESSION 2: THE MOUTH AND PHARYNX 9 In the pig s digestive tract, food flows in only one direction from mouth to anus.this allows for greatly specialized sections that can act independently of each other.
SESSION 2: THE MOUTH AND PHARYNX 9 In the pig s digestive tract, food flows in only one direction from mouth to anus.this allows for greatly specialized sections that can act independently of each other.
Mammalian Dissection: Fetal Pig 11/06
 Mammalian Dissection: Fetal Pig 11/06 Integrated Science 4 Name Per. Introduction Organisms are classified based on similarities and differences to: 1) make sense of the millions of organisms on record,
Mammalian Dissection: Fetal Pig 11/06 Integrated Science 4 Name Per. Introduction Organisms are classified based on similarities and differences to: 1) make sense of the millions of organisms on record,
Grasshopper Dissection
 Grasshopper Dissection 1 Background: GRASSHOPPERS are found almost everywhere. They will eat practically any wild or cultivated plant. In some areas of the United States special contraptions called hopperdozers
Grasshopper Dissection 1 Background: GRASSHOPPERS are found almost everywhere. They will eat practically any wild or cultivated plant. In some areas of the United States special contraptions called hopperdozers
Name: Fetal Pig Dissection Internal Anatomy
 In this lab exercise you will open the thoracic cavities and abdominal pelvic of a fetal pig and identify its major organs. Remember you are dissecting not butchering. The goal is for you to identify all
In this lab exercise you will open the thoracic cavities and abdominal pelvic of a fetal pig and identify its major organs. Remember you are dissecting not butchering. The goal is for you to identify all
Digestive System. The group of organs which performs the function of digestion constitute digestive system.
 Digestive System Definition:- The active biological process by which food materials impermeable to the cell membrane is converted into permeable to the cell membrane is called digestion. The group of organs
Digestive System Definition:- The active biological process by which food materials impermeable to the cell membrane is converted into permeable to the cell membrane is called digestion. The group of organs
Internal Insect Anatomy
 EEB 286 - Lab 4 (Internal insect anatomy) 1 Internal Insect Anatomy During today's lab we will look at the internal anatomy of Gromphadorhina portentosa, a tropical, Madagascan cockroach. Dissection of
EEB 286 - Lab 4 (Internal insect anatomy) 1 Internal Insect Anatomy During today's lab we will look at the internal anatomy of Gromphadorhina portentosa, a tropical, Madagascan cockroach. Dissection of
PHYLUM NEMATODA. Introduction. Ascaris lubricoides. External anatomy - preserved specimen. Internal anatomy - preserved specimen
 PHYLUM NEMATODA Introduction Commonly called round worms the phylum includes both free living and parasitic forms. Distinctive features include: a nearly perfect cylindrical body, radial or biradial arrangement
PHYLUM NEMATODA Introduction Commonly called round worms the phylum includes both free living and parasitic forms. Distinctive features include: a nearly perfect cylindrical body, radial or biradial arrangement
This booklet belongs to: Spring Page 1 of 10
 This booklet belongs to: Spring 2017 Page 1 of 10 Frog Dissection Background Amphibians are studied in science for a variety of reasons. Amphibians are unique in many ways because their anatomy allows
This booklet belongs to: Spring 2017 Page 1 of 10 Frog Dissection Background Amphibians are studied in science for a variety of reasons. Amphibians are unique in many ways because their anatomy allows
Introduction in human anatomy
 Introduction in human anatomy Overview of Anatomy Anatomy is the study of the body structure and the relationships of the various parts of the body Gross or macroscopic (visible structures) Microscopic
Introduction in human anatomy Overview of Anatomy Anatomy is the study of the body structure and the relationships of the various parts of the body Gross or macroscopic (visible structures) Microscopic
Biol 111 Comparative & Human Anatomy Lab 5: Digestive, Respiratory, and Urogenital Systems of the Shark Spring 2014
 Biol 111 Comparative & Human Anatomy Lab 5: Digestive, Respiratory, and Urogenital Systems of the Shark Spring 2014 Philip J. Bergmann Lab Objectives 1. To learn the component parts of the shark digestive,
Biol 111 Comparative & Human Anatomy Lab 5: Digestive, Respiratory, and Urogenital Systems of the Shark Spring 2014 Philip J. Bergmann Lab Objectives 1. To learn the component parts of the shark digestive,
STRUCTURAL ORGANSTAION
 STRUCTURAL ORGANSTAION IN ANIMALS ANIMAL TISSUES :- Are Classified in to four types 1.Epithelal Tissues 2.Connective Tissues 3.Muscular Tissues 4.Neural Tissues Vikasana - CET 2012 1.Epithelial Tissues
STRUCTURAL ORGANSTAION IN ANIMALS ANIMAL TISSUES :- Are Classified in to four types 1.Epithelal Tissues 2.Connective Tissues 3.Muscular Tissues 4.Neural Tissues Vikasana - CET 2012 1.Epithelial Tissues
Fetal Pig Dissection Materials Introduction A. Preparing the Fetal Pig Anterior Posterior Dorsal Ventral length gender mammary papillae
 Fetal Pig Dissection Materials Preserved Fetal Pig Cotton String Dissection tray Dissection pins Disposable Gloves Paper towels Dissection scissors Label pins Lab apron Re-sealable bag Dissection probe
Fetal Pig Dissection Materials Preserved Fetal Pig Cotton String Dissection tray Dissection pins Disposable Gloves Paper towels Dissection scissors Label pins Lab apron Re-sealable bag Dissection probe
Fetal Pig Dissection Day 2 Circulatory and Respiratory Systems
 Name: Date: Period: Fetal Pig Dissection Day 2 Circulatory and Respiratory Systems Dissection Roles (choose a different role from Day 1): Recorder reads directions out loud to group and records answers
Name: Date: Period: Fetal Pig Dissection Day 2 Circulatory and Respiratory Systems Dissection Roles (choose a different role from Day 1): Recorder reads directions out loud to group and records answers
Grasshopper Dissection
 Grasshopper Dissection Introduction: Insects are arthropods with jointed appendages, segmented bodies, and an exoskeleton composed of chitin. Insects are in the class Insecta, & are the largest and most
Grasshopper Dissection Introduction: Insects are arthropods with jointed appendages, segmented bodies, and an exoskeleton composed of chitin. Insects are in the class Insecta, & are the largest and most
Flatworms. Phylum Platyhelminthes
 Flatworms Phylum Platyhelminthes Characteristics of Flatworms Flatworms are acoelomates, which means they have no coelom. A coelom is a fluid-filled body cavity The digestive cavity is the only body cavity
Flatworms Phylum Platyhelminthes Characteristics of Flatworms Flatworms are acoelomates, which means they have no coelom. A coelom is a fluid-filled body cavity The digestive cavity is the only body cavity
Frog Dissection SNC2P Grade 10 Science Applied Biology Tissues, Organs and Systems of Living Things
 Frog Dissection SNC2P Grade 10 Science Applied Biology Tissues, Organs and Systems of Living Things Purpose To identify and examine the external and internal structures of the frog and compare them with
Frog Dissection SNC2P Grade 10 Science Applied Biology Tissues, Organs and Systems of Living Things Purpose To identify and examine the external and internal structures of the frog and compare them with
Key Anatomical Directions
 Dissection Anatomical Direction Before beginning a dissection, it is important to have an understanding of some of the basic directional terminology associated with the dissection of specimens. Some of
Dissection Anatomical Direction Before beginning a dissection, it is important to have an understanding of some of the basic directional terminology associated with the dissection of specimens. Some of
LAB 12-1 HEART DISSECTION GROSS ANATOMY OF THE HEART
 LAB 12-1 HEART DISSECTION GROSS ANATOMY OF THE HEART Because mammals are warm-blooded and generally very active animals, they require high metabolic rates. One major requirement of a high metabolism is
LAB 12-1 HEART DISSECTION GROSS ANATOMY OF THE HEART Because mammals are warm-blooded and generally very active animals, they require high metabolic rates. One major requirement of a high metabolism is
Dissection Lab Manuals: Required Content
 Dissection Lab Manuals: Required Content 1. Introduction a. Basic terminology (directions) b. External features of the cat c. Adaptations to predatory niche d. How to skin a cat e. How to make the incisions
Dissection Lab Manuals: Required Content 1. Introduction a. Basic terminology (directions) b. External features of the cat c. Adaptations to predatory niche d. How to skin a cat e. How to make the incisions
Fetal Pig Dissection Packet (2019)
 Name Period [Each person will turn in his/her own packet] [ Final Score out of 166 points: ] You may use the Virtual Fetal Pig Dissection website from Whitman College as a visual reference for all stages
Name Period [Each person will turn in his/her own packet] [ Final Score out of 166 points: ] You may use the Virtual Fetal Pig Dissection website from Whitman College as a visual reference for all stages
DISSECTION 8: URINARY AND REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEMS
 8546d_c01_1-42 6/25/02 4:32 PM Page 38 mac48 Mac 48: 420_kec: 38 Cat Dissection DISSECTION 8: URINARY AND REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEMS Typically, the urinary and reproductive systems are studied together, because
8546d_c01_1-42 6/25/02 4:32 PM Page 38 mac48 Mac 48: 420_kec: 38 Cat Dissection DISSECTION 8: URINARY AND REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEMS Typically, the urinary and reproductive systems are studied together, because
CJ Shuster A&P2 Lab Addenum Beef Heart Dissection 1. Heart Dissection. (taken from Johnson, Weipz and Savage Lab Book)
 CJ Shuster A&P2 Lab Addenum Beef Heart Dissection 1 Heart Dissection. (taken from Johnson, Weipz and Savage Lab Book) Introduction When you have finished examining the model, you are ready to begin your
CJ Shuster A&P2 Lab Addenum Beef Heart Dissection 1 Heart Dissection. (taken from Johnson, Weipz and Savage Lab Book) Introduction When you have finished examining the model, you are ready to begin your
BIOLOGY 30S: Fetal Pig Dissection Worksheet
 BIOLOGY 30S: Fetal Pig Dissection Worksheet Name: Part A: External Anatomy & Oral Cavity 1. How long (metric) is your fetal pig? 2. What is the age of your fetal pig? 3. What sense organs are located on
BIOLOGY 30S: Fetal Pig Dissection Worksheet Name: Part A: External Anatomy & Oral Cavity 1. How long (metric) is your fetal pig? 2. What is the age of your fetal pig? 3. What sense organs are located on
Homework Packet. The branch of biological science that studies and describes how body parts. The study of the shape and structure of body parts
 Anatomy & Physiology Chap. 1: The Human Body Name Block: P/W Homework Packet ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY DISTINCTIONS 1. Match the term on the right to the appropriate description on the left. Enter the correct
Anatomy & Physiology Chap. 1: The Human Body Name Block: P/W Homework Packet ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY DISTINCTIONS 1. Match the term on the right to the appropriate description on the left. Enter the correct
Name Partner(s) Name. Name your rat. Rat Dissection Lab
 Name Partner(s) Name Name your rat Rat Dissection Lab!!CAUTION!! You must follow all safety instructions as outlined in this lab manual and by your teacher. There are several sharp objects being used during
Name Partner(s) Name Name your rat Rat Dissection Lab!!CAUTION!! You must follow all safety instructions as outlined in this lab manual and by your teacher. There are several sharp objects being used during
Class XI Chapter 7 Structural Organisation in Animals Biology
 Question 1: in one word or one line. (i) Give the common name of Periplaneta americana. (ii) How many spermathecae are found in earthworm? (iii) What is the position of ovaries in the cockroach? (iv) How
Question 1: in one word or one line. (i) Give the common name of Periplaneta americana. (ii) How many spermathecae are found in earthworm? (iii) What is the position of ovaries in the cockroach? (iv) How
Class XI Chapter 7 Structural Organisation in Animals Biology
 Question 1: in one word or one line. (i) Give the common name of Periplaneta americana. (ii) How many spermathecae are found in earthworm? (iii) What is the position of ovaries in the cockroach? (iv) How
Question 1: in one word or one line. (i) Give the common name of Periplaneta americana. (ii) How many spermathecae are found in earthworm? (iii) What is the position of ovaries in the cockroach? (iv) How
Read Chapters 21 & 22, McKinley et al
 ACTIVITY 9: BLOOD AND HEART OBJECTIVES: 1) How to get ready: Read Chapters 21 & 22, McKinley et al., Human Anatomy, 5e. All text references are for this textbook. Read dissection instructions BEFORE YOU
ACTIVITY 9: BLOOD AND HEART OBJECTIVES: 1) How to get ready: Read Chapters 21 & 22, McKinley et al., Human Anatomy, 5e. All text references are for this textbook. Read dissection instructions BEFORE YOU
Unit Nine - The Respiratory System
 Unit Nine - The Respiratory System I. Introduction A. Definition: the respiratory system consists of the nose, nasal cavity, (throat), (voice box), (windpipe), bronchi and lungs (which contain the alveoli).
Unit Nine - The Respiratory System I. Introduction A. Definition: the respiratory system consists of the nose, nasal cavity, (throat), (voice box), (windpipe), bronchi and lungs (which contain the alveoli).
Fetal Pig Dissection Packet
 Fetal Pig Dissection Packet Name Period * Each person will turn in his/her own packet You may use the Virtual Fetal Pig Dissection website from Whitman College as a visual reference for all stages of dissection.
Fetal Pig Dissection Packet Name Period * Each person will turn in his/her own packet You may use the Virtual Fetal Pig Dissection website from Whitman College as a visual reference for all stages of dissection.
Chapter Guided Notes
 Chapter 34-35 Guided Notes 34.1 Phylum Platyhelminthes Flatworms Invertebrates w/ soft, symmetry 3 tissue layers organized into organs & systems Exhibit Planaria Freshwater -shaped anterior and a posterior
Chapter 34-35 Guided Notes 34.1 Phylum Platyhelminthes Flatworms Invertebrates w/ soft, symmetry 3 tissue layers organized into organs & systems Exhibit Planaria Freshwater -shaped anterior and a posterior
Bio 322 Human Anatomy Objectives for the laboratory exercise Respiratory System
 Bio 322 Human Anatomy Objectives for the laboratory exercise Respiratory System Required reading before beginning this lab: Saladin, KS: Human Anatomy 5 th ed (2017) Chapter 23 For this lab you will use
Bio 322 Human Anatomy Objectives for the laboratory exercise Respiratory System Required reading before beginning this lab: Saladin, KS: Human Anatomy 5 th ed (2017) Chapter 23 For this lab you will use
16/12/2012. The Flatworms. Characteristics
 Learning Outcome G3 Learning Outcome G3 Analyze the increasing complexity of the Phylum Platyhelminthes, the Phylum Nematoda and the Phylum Annelida Phylum Platyhelminthes, Nematoda and Annelida Student
Learning Outcome G3 Learning Outcome G3 Analyze the increasing complexity of the Phylum Platyhelminthes, the Phylum Nematoda and the Phylum Annelida Phylum Platyhelminthes, Nematoda and Annelida Student
Chapter 1- An Orientation to the Human Body
 Chapter 1- An Orientation to the Human Body Overview of Anatomy and Physiology: -Anatomy- of body parts and their relationships to one another. -Gross or Macroscopic= large and easily observable -Microscopic=
Chapter 1- An Orientation to the Human Body Overview of Anatomy and Physiology: -Anatomy- of body parts and their relationships to one another. -Gross or Macroscopic= large and easily observable -Microscopic=
Fetal Pig Dissection:
 Fetal Pig Dissection: REMEMBER: Dissection involves disassembling and observing something to determine its internal structure and develop an understanding of the relationship of those structures to function.
Fetal Pig Dissection: REMEMBER: Dissection involves disassembling and observing something to determine its internal structure and develop an understanding of the relationship of those structures to function.
Fetal Pig Dissection: External Anatomy
 Name Fetal Pig Dissection: External Anatomy External Anatomy 1. Determine the sex of your pig by looking for the urogenital opening. On females, this opening is located near the anus. On males, the opening
Name Fetal Pig Dissection: External Anatomy External Anatomy 1. Determine the sex of your pig by looking for the urogenital opening. On females, this opening is located near the anus. On males, the opening
Human Body. The student knows that the human body is made of systems with structure and functions that are related.
 Human Body The student knows that the human body is made of systems with structure and functions that are related. Cells Cells are the smallest living structures. All living things are made up of one or
Human Body The student knows that the human body is made of systems with structure and functions that are related. Cells Cells are the smallest living structures. All living things are made up of one or
Dissection: The Fetal Pig
 Lab Exercise Dissection: The Fetal Pig Objectives - To learn some of anatomical structures of the fetal pig. - To be able to make contrasts and comparisons of structures between different animal phyla
Lab Exercise Dissection: The Fetal Pig Objectives - To learn some of anatomical structures of the fetal pig. - To be able to make contrasts and comparisons of structures between different animal phyla
1. Distinguish between simple epithelium and compound epithelium.
 Structural organization in animals One mark 1. Which connective tissue helps in the attachment of muscle to bone? Tendons. 2. What is function of fibres in connective tissue? Fibres provide strength, elasticity
Structural organization in animals One mark 1. Which connective tissue helps in the attachment of muscle to bone? Tendons. 2. What is function of fibres in connective tissue? Fibres provide strength, elasticity
Pop Quiz 2. Give the dominant body form for each. List 2 causes of coral reef damage. What is the function of a colloblast? Scyphozoa anthozoa
 Pop Quiz 2 Give the dominant body form for each Scyphozoa anthozoa List 2 causes of coral reef damage. What is the function of a colloblast? Phylum Platyhelminthes Flatworms - the Simplest Bilateral Animals
Pop Quiz 2 Give the dominant body form for each Scyphozoa anthozoa List 2 causes of coral reef damage. What is the function of a colloblast? Phylum Platyhelminthes Flatworms - the Simplest Bilateral Animals
Anatomy the study of the structure of body parts and their relationships to one another (static)
 Anatomy the study of the structure of body parts and their relationships to one another (static) Word anatomy comes from the Greek words that mean to cut apart Physiology the study of the function of the
Anatomy the study of the structure of body parts and their relationships to one another (static) Word anatomy comes from the Greek words that mean to cut apart Physiology the study of the function of the
Laboratory Investigation 24A Chapter 24A: Human Skin
 Name Class Date Station # Laboratory Investigation 24A Chapter 24A: Human Skin Human Anatomy & Physiology: Integumentary System You may refer to pages 415-421 in your textbook for a general discussion
Name Class Date Station # Laboratory Investigation 24A Chapter 24A: Human Skin Human Anatomy & Physiology: Integumentary System You may refer to pages 415-421 in your textbook for a general discussion
Zoology. Lab Guide. Exercise 16A Class Asteroidea Sea Stars
 Zoology Exercise #16: Echinoderms Lab Guide STARFISH ONLY!!! Echinoderms contain the sea stars, brittle stars, sea urchins, sand dollars, and sea cucumbers. The name echinoderm is derived from this group
Zoology Exercise #16: Echinoderms Lab Guide STARFISH ONLY!!! Echinoderms contain the sea stars, brittle stars, sea urchins, sand dollars, and sea cucumbers. The name echinoderm is derived from this group
LAB: Sheep or Pig Heart Dissection
 Biology 12 Name: Circulatory System Per: Date: Observation: External Anatomy LAB: Sheep or Pig Heart Dissection 1. Line a dissecting tray with paper towel for easy clean up as the heart is fatty and will
Biology 12 Name: Circulatory System Per: Date: Observation: External Anatomy LAB: Sheep or Pig Heart Dissection 1. Line a dissecting tray with paper towel for easy clean up as the heart is fatty and will
Purpose: To observe the different structures of a male and female Ascaris lumbricoides.
 Biology 1 Name: Pre-lab Discussion: There are over 15,000 species in the Phylum Nematoda. They are round, unsegmented worms. Members of this phylum are free-living or parasitic. The parasitic species can
Biology 1 Name: Pre-lab Discussion: There are over 15,000 species in the Phylum Nematoda. They are round, unsegmented worms. Members of this phylum are free-living or parasitic. The parasitic species can
The Human Body: An Orientation
 The Human Body: An Orientation Body standing upright Anatomical Position feet slightly apart palms facing forward thumbs point away from body Directional Terms Superior and inferior toward and away from
The Human Body: An Orientation Body standing upright Anatomical Position feet slightly apart palms facing forward thumbs point away from body Directional Terms Superior and inferior toward and away from
Human Body Systems. Human Body Project Notes
 Human Body Systems Human Body Project Notes Human Body Organ Systems for the Project Big Idea: Organ systems are composed of organs that are made of more than one type of tissue. Tissues are made of one
Human Body Systems Human Body Project Notes Human Body Organ Systems for the Project Big Idea: Organ systems are composed of organs that are made of more than one type of tissue. Tissues are made of one
"^mz-cypo cricxj. dissection, we will examine the 3-dimensional structure of the mammalian brain and consider the functions of some of its parts.
 "^mz-cypo cricxj Sidogy083 ^ ^ furore fx^t-^tb ' BRAIN DISSECTION PURPOSE The brain, more than any other organ, is what determines the capabilities of an organism. It affects all aspects of the body from
"^mz-cypo cricxj Sidogy083 ^ ^ furore fx^t-^tb ' BRAIN DISSECTION PURPOSE The brain, more than any other organ, is what determines the capabilities of an organism. It affects all aspects of the body from
Biol 111 Comparative & Human Anatomy Lab 8: Circulatory System of the Shark Spring 2014
 Biol 111 Comparative & Human Anatomy Lab 8: Circulatory System of the Shark Spring 2014 Philip J. Bergmann Lab Objectives 1. To learn how the divisions of the circulatory system relate to one another.
Biol 111 Comparative & Human Anatomy Lab 8: Circulatory System of the Shark Spring 2014 Philip J. Bergmann Lab Objectives 1. To learn how the divisions of the circulatory system relate to one another.
Introduction. Study detail of structure - - Gross Anatomy. Study all structures in one part of body Study of internal structures as relate to skin
 Introduction What is Anatomy and Physiology? Anatomy study of the shape and structure of body parts and their relationships to one another Physiology study of how the body functions individually and cooperatively
Introduction What is Anatomy and Physiology? Anatomy study of the shape and structure of body parts and their relationships to one another Physiology study of how the body functions individually and cooperatively
Overview of Anatomy & Physiology
 Overview of Anatomy & Physiology Anatomy the study of the structure of body parts and their relationships to one another Gross or macroscopic Microscopic Developmental Physiology the study of the function
Overview of Anatomy & Physiology Anatomy the study of the structure of body parts and their relationships to one another Gross or macroscopic Microscopic Developmental Physiology the study of the function
 Name: Date: Period: The Dissection 1. Place your specimen dorsal side down. Make your incisions following the diagram below. Make sure to make shallow cuts with the scissors. DO NOT CUT TOO DEEP! You will
Name: Date: Period: The Dissection 1. Place your specimen dorsal side down. Make your incisions following the diagram below. Make sure to make shallow cuts with the scissors. DO NOT CUT TOO DEEP! You will
Microscopic Anatomy Cytology study of the cell Histology study of tissues
 Introduction to Anatomy and Physiology Dr. Gary Mumaugh Overview of Anatomy and Physiology Anatomy the study of the structure of body parts and their relationships to one another o Gross or macroscopic
Introduction to Anatomy and Physiology Dr. Gary Mumaugh Overview of Anatomy and Physiology Anatomy the study of the structure of body parts and their relationships to one another o Gross or macroscopic
Essentials of Anatomy and Physiology, 9e (Marieb) Chapter 1 The Human Body: An Orientation. Short Answer. Figure 1.1
 Essentials of Anatomy and Physiology, 9e (Marieb) Chapter 1 The Human Body: An Orientation Short Answer Figure 1.1 Using Figure 1.1, identify the following: 1) Label A points to the cavity. 2) Label B
Essentials of Anatomy and Physiology, 9e (Marieb) Chapter 1 The Human Body: An Orientation Short Answer Figure 1.1 Using Figure 1.1, identify the following: 1) Label A points to the cavity. 2) Label B
The Repr duct ve System. Function: producing offspring
 The Repr duct ve System Function: producing offspring Anatomy of male reproductive system Location: The reproductive organs are classified as external and internal genitalia. The external genitalia are
The Repr duct ve System Function: producing offspring Anatomy of male reproductive system Location: The reproductive organs are classified as external and internal genitalia. The external genitalia are
Animal Organs. SNC2P Biology
 Animal Organs SNC2P Biology The Hierarchy of Structure Level 5 Organism (many different organ systems working together Level 4 System (one or more organs that work together to perform a body function)
Animal Organs SNC2P Biology The Hierarchy of Structure Level 5 Organism (many different organ systems working together Level 4 System (one or more organs that work together to perform a body function)
Anatomy & Physiology Autopsy of a Banana Planes / Anatomical Directions
 Anatomy & Physiology Autopsy of a Banana Planes / Anatomical Directions Purpose: During this lab you will demonstrate your knowledge of directional terms by performing an autopsy on a banana. It is important
Anatomy & Physiology Autopsy of a Banana Planes / Anatomical Directions Purpose: During this lab you will demonstrate your knowledge of directional terms by performing an autopsy on a banana. It is important
Nervous system (blue) Insect Internal Systems and Physiology. Decentralized nervous system. Synapse gap 8/22/2012
 Nervous system (blue) Insect Internal Systems and Physiology Decentralized nervous system Brain (left) several lobes Ventral nerve cord Ganglia in many segments masses of nerve cells Synapse gap Synapse
Nervous system (blue) Insect Internal Systems and Physiology Decentralized nervous system Brain (left) several lobes Ventral nerve cord Ganglia in many segments masses of nerve cells Synapse gap Synapse
Our Sense Organs Ears
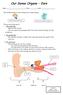 Our Sense Organs Ears Name: Class: Date: Ears enable people to hear things and to keep balance. This boy can hear with his ear. This boy s ears help him to balance. The ear has three parts: 1. The Outer
Our Sense Organs Ears Name: Class: Date: Ears enable people to hear things and to keep balance. This boy can hear with his ear. This boy s ears help him to balance. The ear has three parts: 1. The Outer
Carolina Biological Supply Company. Rats! Inquiry-Based Dissection with Carolina s Perfect Solution Specimens
 Carolina Biological Supply Company Rats! Inquiry-Based Dissection with Carolina s Perfect Solution Specimens Objectives Introduce basic mammalian anatomy using the rat Perform a rat dissection focusing
Carolina Biological Supply Company Rats! Inquiry-Based Dissection with Carolina s Perfect Solution Specimens Objectives Introduce basic mammalian anatomy using the rat Perform a rat dissection focusing
Epithelial Tissues. Types of Epithelial Tissues: Lining of Kidney
 Epithelial Tissues Covers the entire body surface and most of the body s inner cavities Outer epidermis (skin) protects from injury and drying out Inner epidermal tissue (on internal surfaces) often serves
Epithelial Tissues Covers the entire body surface and most of the body s inner cavities Outer epidermis (skin) protects from injury and drying out Inner epidermal tissue (on internal surfaces) often serves
#5 Cardiovascular II Blood Vessels
 #5 Cardiovascular II Blood Vessels Objectives: Identify a list of human arteries and veins using a virtual human dissection and a human model Dissect and identify a list of arteries and veins in the cat
#5 Cardiovascular II Blood Vessels Objectives: Identify a list of human arteries and veins using a virtual human dissection and a human model Dissect and identify a list of arteries and veins in the cat
Morphological characters of the pheretimoid earthworms in North America north of Mexico
 Morphological characters of the pheretimoid earthworms in North America north of Mexico This document is modified from the following paper: Chang, C.-H., Snyder, B., Szlavecz K. (2016) Asian pheretimoid
Morphological characters of the pheretimoid earthworms in North America north of Mexico This document is modified from the following paper: Chang, C.-H., Snyder, B., Szlavecz K. (2016) Asian pheretimoid
Step 1: Salivary Structures
 (Slide1) Step 1: Salivary Structures Remove the skin, fat and connective fascia to view the salivary glands and ducts. The submaxillary salivary gland is just behind the masseter muscle and pretty easy
(Slide1) Step 1: Salivary Structures Remove the skin, fat and connective fascia to view the salivary glands and ducts. The submaxillary salivary gland is just behind the masseter muscle and pretty easy
Name: Class: Date: Question #1. Question #2. What is the role of the heart in the circulatory system? It forms a network of blood vessels.
 9/30/2017 ody Systems Test Name: lass: ate: Question #1 What is the role of the heart in the circulatory system? It forms a network of blood vessels. It transports oxygen to all body cells. It helps the
9/30/2017 ody Systems Test Name: lass: ate: Question #1 What is the role of the heart in the circulatory system? It forms a network of blood vessels. It transports oxygen to all body cells. It helps the
Anatomy of the Heart
 Biology 212: Anatomy and Physiology II Anatomy of the Heart References: Saladin, KS: Anatomy and Physiology, The Unity of Form and Function 8 th (2018). Required reading before beginning this lab: Chapter
Biology 212: Anatomy and Physiology II Anatomy of the Heart References: Saladin, KS: Anatomy and Physiology, The Unity of Form and Function 8 th (2018). Required reading before beginning this lab: Chapter
CHAPTER 3 BASIC ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY
 CHAPTER 3 BASIC ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY SURFACE ANATOMY Surface anatomy is the identification of landmarks on the surface of the skin which allows us to compare our knowledge of our own surface anatomy
CHAPTER 3 BASIC ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY SURFACE ANATOMY Surface anatomy is the identification of landmarks on the surface of the skin which allows us to compare our knowledge of our own surface anatomy
29-2 Form and Function in Invertebrates Slide 1 of 52
 29-2 Form and Function in 1 of 52 How do different invertebrate phyla carry out life functions? 2 of 52 Feeding and Digestion Feeding and Digestion The simplest animals break down food primarily through
29-2 Form and Function in 1 of 52 How do different invertebrate phyla carry out life functions? 2 of 52 Feeding and Digestion Feeding and Digestion The simplest animals break down food primarily through
Human Anatomy Biology 351
 nnnnn 1 Human Anatomy Biology 351 Exam #2 Please place your name on the back of the last page of this exam. You must answer all questions on this exam. Because statistics demonstrate that, on average,
nnnnn 1 Human Anatomy Biology 351 Exam #2 Please place your name on the back of the last page of this exam. You must answer all questions on this exam. Because statistics demonstrate that, on average,
Sheep Brain Dissection
 Sheep Brain Dissection Mammalian brains have many features in common. Human brains may not be available, so sheep brains often are dissected as an aid to understanding the mammalian brain since he general
Sheep Brain Dissection Mammalian brains have many features in common. Human brains may not be available, so sheep brains often are dissected as an aid to understanding the mammalian brain since he general
CHAPTER 1 THE HUMAN BODY
 HPTER 1 THE HUMN OY TRUE/FLSE 1. midsagittal plane vertically divides the body through the midline into two equal left and right portions or halves. NS: T NOT: midsagittal plane vertically divides the
HPTER 1 THE HUMN OY TRUE/FLSE 1. midsagittal plane vertically divides the body through the midline into two equal left and right portions or halves. NS: T NOT: midsagittal plane vertically divides the
In this exercise, we will see what the body structure looks like and where the different organs are located within the body structure.
 AN ORGAN ISN T JUST A PIANO Teacher Notes The human body may be the most complex and versatile object in the world. Dozens of systems coordinate to perform the myriad operations that we require of it at
AN ORGAN ISN T JUST A PIANO Teacher Notes The human body may be the most complex and versatile object in the world. Dozens of systems coordinate to perform the myriad operations that we require of it at
Bodies and Systems. What is your body made of?
 What is your body made of? You might say that you are made of organs like skin and a heart. You might say that you are made of tissue, cells, or even atoms. All these answers are correct. Multicellular
What is your body made of? You might say that you are made of organs like skin and a heart. You might say that you are made of tissue, cells, or even atoms. All these answers are correct. Multicellular
