Class XI Chapter 7 Structural Organisation in Animals Biology
|
|
|
- Jean Holt
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Question 1: in one word or one line. (i) Give the common name of Periplaneta americana. (ii) How many spermathecae are found in earthworm? (iii) What is the position of ovaries in the cockroach? (iv) How many segments are present in the abdomen of cockroach? (v) Where do you find malphigian tubules? (i) The common name of Periplaneta americana is the American cockroach. (ii) Four pairs of spermathecae are present in earthworms. They are located between sixth and the ninth segments. They help in receiving and storing the spermatozoa during copulation. (iii) In a cockroach, the pair of ovaries is located between 12 th and 13 th abdominal segments. (iv) In both sexes, the abdomen of a cockroach consists of ten segments. (v) Malphigian tubules are main excretory organs of cockroaches. They form a part of the alimentary canal. Question 2: the following: (i) What is the function of nephridia? (ii) How many types of nephridia are found in earthworm based on their location? (i) Nephridia are segmentally arranged excretory organs present in earthworms. (ii) On the basis of their location, three types of nephridia are found in earthworms. They are: (a) Septal nephridia: These are present on both sides of the inter-segmental septa behind the 15 th segment. They open into the intestines. (b) Integumentary nephridia: These lie attached to the body wall from the third segment to the last segment, which opens on the body surface. Page 1 of 11
2 (c) Pharyngeal nephridia: These are present as three paired tufts in fourth, fifth, and sixth segments. Question 3: Draw a labelled diagram of the reproductive organs of an earthworm. Question 4: Draw a labelled diagram of alimentary canal of a cockroach. Page 2 of 11
3 Question 5: Distinguish between the following (a) Prostomium and peristomium (b) Septal nephridium and pharyngeal nephridium (a) Prostomium Peristomium Prostomium is a small fleshy lobe, which overhangs the mouth of an earthworm. It helps the organism push into the soil and is sensory in function. The first body segment in the earthworm is called the peristomium. It surrounds the mouth opening. (b) Septal nephridium Pharyngeal nephridium Page 3 of 11
4 They are present on both sides of intersegmental septa behind the 15 th segment. They open into the intestines. They are present as three paired tufts in the fourth, fifth, and sixth segments. Question 6: What are the cellular components of blood? Components of blood include erythrocytes (RBCs), leucocytes (WBCs), and thrombocytes (platelets). These components form 45% of blood. They are suspended in the remaining fluid portion, called plasma. Mammalian erythrocytes are biconcave, coloured cells devoid of a nucleus. They help in transporting respiratory gases. Leucocytes or white blood cells are nucleated cells. They can be divided into two types, granulocytes (neutrophils, eosinophils, and basophils) and agranulocytes (lymphocytes and monocytes). They help fight against various disease-causing germs entering the body. Thrombocytes are cell fragments produced from megarkaryocytes of the bone. They play a major role during blood coagulation. Question 7: What are the following and where do you find them in animal body (a) Chondriocytes (b) Axons (c) Ciliated epithelium Chondriocytes: They are cells of cartilages, and are present in small cavities within the matrix secreted by them. Axons: Page 4 of 11
5 They are long, slender projections of neurons that help in carrying nerve impulses from the neuron body. Axons aggregate in bundles which make up the nerves. Ciliated epithelium: It consists of simple columnar or cuboidal epithelium with cilia on their free surfaces. It is present on the inner surface of the oviducts and bronchioles. It helps in the movement of eggs or mucus in specific directions. Question 8: Describe various types of epithelial tissues with the help of labelled diagrams. Epithelial tissue lines the surface of a body and forms a protective covering. Epithelium cells are packed tightly together with little intercellular matrix. Epithelial tissue in the body is of two types. (a) Simple epithelium: It consists of a single layer of cells where cells are in direct contact with the basement membrane. It is further sub-divided into the following types: (i) Simple squamous epithelium: It consists of a single layer of flat cells with irregular boundaries. It is found in the walls of the blood vessels and in the lining of alveoli. (ii) Simple cuboidal epithelium: It consists of a single layer of cube-like cells. It is present in regions where secretion and absorption of substances takes place such as the proximal convoluted tubule region of the nephron. (iii) Simple columnar epithelium: It consists of a single layer of tall, slender cells with their nuclei present at the base of the cells. They may bear micro-villi on the free surfaces. Columnar epithelium forms the lining of the stomach and intestines, and is involved in the function of secretion and absorption. (iv) Ciliated epithelium: It consists of columnar or cuboidal cells with cilia on their free surfaces. They are present in bronchioles and oviducts from where they direct mucus and eggs in specific directions. Page 5 of 11
6 (v) Glandular epithelium:it consists of columnar or cuboidal cells involved in the secretion of substances. Glands are of two types, unicellular glands (goblet cells of the alimentary canal) and multicellular glands (salivary glands). They can be classified as exocrine (ductless glands) and endocrine glands (duct glands) by the method through which they release enzymes. (b) Compound epithelium: It consists of many layers of cells. It is involved mainly in the function of providing protection and has a limited role in secretion and absorption. Examples of compound epithelium include the dry surface of the skin or moist inner lining of the buccal cavity, pharynx, pancreatic ducts, and the inner lining of ducts of salivary glands. Question 9: Distinguish between (a) Simple epithelium and compound epithelium. (b) Cardiac muscle and striated muscle Page 6 of 11
7 (c) Dense regular and dense irregular connective tissues (d) Adipose and blood tissue (e) Simple gland and compound gland (a) Simple epithelium Compound epithelium 1. It is composed of only one layer of cells. 2. It is mainly involved in the function of absorption and secretion. 3. It is present in the lining of the stomach, intestine. 1. It is composed of many layers of cells. 2. It is mainly involved in the function of protection and has a limited role in absorption and secretion. 3. It is present in the lining of the pharynx and buccal cavity. (b) Cardiac muscles Striated muscles 1. They are involuntary in function. 2. They are multi-nucleate and branched. 3. They are found only in the heart. 1. They are voluntary in function. 2. They are multi-nucleate and unbranched. 3. They are found only in triceps, biceps, and limbs. (c) Dense regular connective tissues Dense irregular connective tissues Page 7 of 11
8 1. In dense regular connective tissues, collagen fibres are present in rows between parallel boundless fibres. 2. They are present in tendons and ligaments. 1. In dense irregular connective tissues, fibres are arranged irregularly. 2. They are present in the skin. (d) Adipose tissue Blood tissue 1. It is composed of collagen fibres, elastin fibres, fibroblasts, macrophages, and adipociytes. 2. It helps in the synthesis, storage, and metabolism of fats. 3. It is present beneath the skin. 1. It is composed of RBCs, WBCs, platelets, and plasma. 2. It helps in the transportation of food, wastes, gases, and hormones. 3. It is present in the blood vessels. (e) Simple glands Compound glands 1. They contain isolated glandular cells. 2. They are unicellular. 3. Examples include goblet cells of the alimentary canal. 1. They contain a cluster of secretory cells. 2. They are multicellular. 3. Examples include salivary glands. Question 10: Mark the odd one in each series: (a) Areolar tissue; blood; neuron; tendon Page 8 of 11
9 (b) RBC; WBC; platelets; cartilage (c) Exocrine; endocrine; salivary gland; ligament (d) Maxilla; mandible; labrum; athorax; coxa (a) Areolar tissue, blood, and tendons are examples of connective tissues. Neuron is an example of neural tissue. (b) RBCs, WBCs, and platelets are the three most important components of blood. Cartilage is therefore, the odd one out. (c) Exocrine, endocrine, and salivary glands are examples of simple glandular epithelium. Ligament is a connective tissue. (d) Maxilla, mandible, and labrum are mouthparts of a cockroach. Antennae, on the other hand, are present in the head region of cockroaches. (e) Protonema forms the developmental stage in the life cycle of a moss. Mesothorax, metathorax, and coxa are parts or segments present in the legs of a cockroach. Question 11: Match the terms in column I with those in column II: Column I Column II (a) Compound epithelium (b) Compound eye (c) Septal nephridia (d) Open circulatory system (e) Typhlosole (f) Osteocytes (g) Genitalia (i) Alimentry canal (ii) Cockroach (iii) Skin (iv) Mosaic vision (v) Earthworm (vi) Phallomere (vii) Bone Column I Column II Page 9 of 11
10 (a) Compound epithelium (b) Compound eye (c) Septal nephridia (d) Open circulatory system (e) Typhlosole (f) Osteocytes (g) Genitalia (iii) Skin (iv) Mosaic vision (v) Earthworm (ii) Cockroach (i) Alimentary canal (vii) Bone (vi) Phallomere Question 12: Mention briefly about the circulatory system of earthworm Earthworms (Pheretima) have closed blood vascular systems, which consists of the heart, blood vessels, and capillaries. The heart pumps blood for circulating it in one direction. Blood is supplied by smaller blood cells to the gut nerve cord and the body wall. Blood glands are present in the 4 th, 5 th, and 6 th segments, which produce blood cells and haemoglobin dissolved in blood plasma. Blood cells in earthworms are phagocytic in nature. Question 13: Draw a neat diagram of digestive system of frog. Page 10 of 11
11 Question 14: Mention the function of the following (a) Ureters in frog (b) Malpighian tubules (c) Body wall in earthworm (a) Ureters in frogs: A ureter acts as a urinogenital duct, which carries sperms along with urine in male frogs. (b) Malphigian tubules: Malphigian tubules are excretory organs in cockroaches. (c) Body wall in earthworms: In earthworms, the body wall consists of muscle layers. It helps in movement and burrowing. Page 11 of 11
Class XI Chapter 7 Structural Organisation in Animals Biology
 Question 1: in one word or one line. (i) Give the common name of Periplaneta americana. (ii) How many spermathecae are found in earthworm? (iii) What is the position of ovaries in the cockroach? (iv) How
Question 1: in one word or one line. (i) Give the common name of Periplaneta americana. (ii) How many spermathecae are found in earthworm? (iii) What is the position of ovaries in the cockroach? (iv) How
3. Draw a labelled diagram of the reproductive organs of an earthworm.
 1. Answer in one word or one line. (i) Give the common name of Periplanata americana. (ii) How many spermathecae are found in earthworm? (iii) What is the position of ovaries in cockroach? (iv) How many
1. Answer in one word or one line. (i) Give the common name of Periplanata americana. (ii) How many spermathecae are found in earthworm? (iii) What is the position of ovaries in cockroach? (iv) How many
Outline. Bio 105: Tissues Laboratory. Organization of the Human Body. Tissue - Epithelium. Tissues 3/2/ Copyright 2009 Pearson Education, Inc
 Outline Bio 105: Tissues Laboratory Laboratory 5 Reading: Chapter 4 I. Cell to cell contact II. Body Cavities III. Membranes IV. Homeostasis V. Integumentary System I. Includes skin, hair and nails 1 2
Outline Bio 105: Tissues Laboratory Laboratory 5 Reading: Chapter 4 I. Cell to cell contact II. Body Cavities III. Membranes IV. Homeostasis V. Integumentary System I. Includes skin, hair and nails 1 2
1. Distinguish between simple epithelium and compound epithelium.
 Structural organization in animals One mark 1. Which connective tissue helps in the attachment of muscle to bone? Tendons. 2. What is function of fibres in connective tissue? Fibres provide strength, elasticity
Structural organization in animals One mark 1. Which connective tissue helps in the attachment of muscle to bone? Tendons. 2. What is function of fibres in connective tissue? Fibres provide strength, elasticity
STRUCTURAL ORGANSTAION
 STRUCTURAL ORGANSTAION IN ANIMALS ANIMAL TISSUES :- Are Classified in to four types 1.Epithelal Tissues 2.Connective Tissues 3.Muscular Tissues 4.Neural Tissues Vikasana - CET 2012 1.Epithelial Tissues
STRUCTURAL ORGANSTAION IN ANIMALS ANIMAL TISSUES :- Are Classified in to four types 1.Epithelal Tissues 2.Connective Tissues 3.Muscular Tissues 4.Neural Tissues Vikasana - CET 2012 1.Epithelial Tissues
Hole s Human Anatomy and Physiology
 Hole s Human Anatomy and Physiology 1 Chapter 5 Tissues Four major tissue types 1. Epithelial 2. Connective 3. Muscle 4. Nervous 2 Epithelial Tissues General characteristics - cover organs and the body
Hole s Human Anatomy and Physiology 1 Chapter 5 Tissues Four major tissue types 1. Epithelial 2. Connective 3. Muscle 4. Nervous 2 Epithelial Tissues General characteristics - cover organs and the body
Unit II: Tissues and Integumentary System
 Unit II: Tissues and Integumentary System 2.1 - Tissues Chapter 4 Written Response #1 1. What is a tissue? 2. What are four major types of tissues? Tissue Definition: a group or mass of similar cells working
Unit II: Tissues and Integumentary System 2.1 - Tissues Chapter 4 Written Response #1 1. What is a tissue? 2. What are four major types of tissues? Tissue Definition: a group or mass of similar cells working
Tissues Chapter 5...Tissue - a group or mass of similar cells working together to perform certain common functions
 Tissues Chapter 5...Tissue - a group or mass of similar cells working together to perform certain common functions There are 4 major types of tissue Epithelial Connective Muscle Nervous 1. Epithelial Tissue
Tissues Chapter 5...Tissue - a group or mass of similar cells working together to perform certain common functions There are 4 major types of tissue Epithelial Connective Muscle Nervous 1. Epithelial Tissue
Chapter 5. Tissues. 4 Types of Body Tissues. Tissues
 Chapter 5 Tissues Tissues Tissues - groups of cells that are similar in structure & function RBC, WBC, & platelets are a group of cells working together to form BLOOD tissue Histology Pathohistology study
Chapter 5 Tissues Tissues Tissues - groups of cells that are similar in structure & function RBC, WBC, & platelets are a group of cells working together to form BLOOD tissue Histology Pathohistology study
Lab 1 ANIMAL TISSUES
 Lab 1 ANIMAL TISSUES Levels of Organization Animals are multicellular heterotrophs whose cells lack cell walls. Most animals exhibit a hierarchical level of organization: Cells are organized into tissues
Lab 1 ANIMAL TISSUES Levels of Organization Animals are multicellular heterotrophs whose cells lack cell walls. Most animals exhibit a hierarchical level of organization: Cells are organized into tissues
Lesson 9A Tissues in Animals
 Lesson 9A Tissues in Animals Levels of Organization in the Human Body Similar types of cells Different types of tissues Different organs Many organ systems cell tissue organ organ system organism Levels
Lesson 9A Tissues in Animals Levels of Organization in the Human Body Similar types of cells Different types of tissues Different organs Many organ systems cell tissue organ organ system organism Levels
Epithelial Tissues. Types of Epithelial Tissues: Lining of Kidney
 Epithelial Tissues Covers the entire body surface and most of the body s inner cavities Outer epidermis (skin) protects from injury and drying out Inner epidermal tissue (on internal surfaces) often serves
Epithelial Tissues Covers the entire body surface and most of the body s inner cavities Outer epidermis (skin) protects from injury and drying out Inner epidermal tissue (on internal surfaces) often serves
Cell and Tissue Types. Epithelial, Connective, Muscle, Nerve
 Cell and Tissue Types Epithelial, Connective, Muscle, Nerve Objectives Explain the major stages of the cell cycle and cellular division (mitosis). Describe specific events occurring in each of the phases
Cell and Tissue Types Epithelial, Connective, Muscle, Nerve Objectives Explain the major stages of the cell cycle and cellular division (mitosis). Describe specific events occurring in each of the phases
Anatomy &- Physiology Histology Worksheet
 Anatomy &- Physiology Histology Worksheet 1. The four primary tissue types found in the human body are a) squamous, cuboidal, columnar, glandular b) adipose, elastic, reticular, cartilage c) skeletal,
Anatomy &- Physiology Histology Worksheet 1. The four primary tissue types found in the human body are a) squamous, cuboidal, columnar, glandular b) adipose, elastic, reticular, cartilage c) skeletal,
Study of different tissues Abnormal cells and tissues can be compared to normal tissues to identify disease, such as cancer Being able to know and
 CHAPTER 4 Study of different tissues Abnormal cells and tissues can be compared to normal tissues to identify disease, such as cancer Being able to know and recognize normal tissues under the microscope
CHAPTER 4 Study of different tissues Abnormal cells and tissues can be compared to normal tissues to identify disease, such as cancer Being able to know and recognize normal tissues under the microscope
Body Tissues. Cells are specialized for particular functions Tissues - groups of cells with similar structure. and function Four primary tissue types:
 Chapter 3 Tissues Body Tissues Cells are specialized for particular functions Tissues - groups of cells with similar structure and function Four primary tissue types: Epithelium Connective tissue Nervous
Chapter 3 Tissues Body Tissues Cells are specialized for particular functions Tissues - groups of cells with similar structure and function Four primary tissue types: Epithelium Connective tissue Nervous
Anatomy & Homeostasis. Unit 5
 Anatomy & Homeostasis Unit 5 Main Ideas discuss with a buddy 2 What is Homeostasis? How is homeostasis different in single-celled organisms vs. multicellular organisms? What unique challenges to maintaining
Anatomy & Homeostasis Unit 5 Main Ideas discuss with a buddy 2 What is Homeostasis? How is homeostasis different in single-celled organisms vs. multicellular organisms? What unique challenges to maintaining
Human anatomy Unit III. Tissue
 Human anatomy Unit III Tissue Definition of Tissues Biological tissue is a collection of interconnected cells that perform a similar function within an organism. In other words, it is a group of cells
Human anatomy Unit III Tissue Definition of Tissues Biological tissue is a collection of interconnected cells that perform a similar function within an organism. In other words, it is a group of cells
Lab Animal Tissue. LEARNING OBJECTIVES: To understand the relationship between the structure and function of different animal tissues
 Name: Bio A.P. PURPOSE: HYPOTHESIS: NONE Lab Animal Tissue BACKGROUND: In animals, groups of closely related cells specialized to perform the same function are called tissues. There are four general classes
Name: Bio A.P. PURPOSE: HYPOTHESIS: NONE Lab Animal Tissue BACKGROUND: In animals, groups of closely related cells specialized to perform the same function are called tissues. There are four general classes
Histology. Study of body tissues
 Histology Study of body tissues 2 Introduction to Body Tissues 1. Composed of specialized cells of similar structure and perform a common function 2. Four major types (4 Cs) a. Epithelial - Cover b. Connective
Histology Study of body tissues 2 Introduction to Body Tissues 1. Composed of specialized cells of similar structure and perform a common function 2. Four major types (4 Cs) a. Epithelial - Cover b. Connective
B. Classification of epithelium: by number of cell layers present and by shape of the superficial cell layers.
 I. Introduction - tissue: group of cells that are closely associated, similar in structure and function, and perform a common or related function. - four primary tissues: epithelial tissue, connective
I. Introduction - tissue: group of cells that are closely associated, similar in structure and function, and perform a common or related function. - four primary tissues: epithelial tissue, connective
Epithelial Tissue lining, covering, glandular tissue > Function protect, absorption, filtration, secretion, excretion
 Chapter 4: TISSUES IX. Tissues Intro Epithelial Tissue lining, covering, glandular tissue > Function protect, absorption, filtration, secretion, excretion Connective Tissue most widespread tissue type
Chapter 4: TISSUES IX. Tissues Intro Epithelial Tissue lining, covering, glandular tissue > Function protect, absorption, filtration, secretion, excretion Connective Tissue most widespread tissue type
Histology. There are four basic tissue types in the body are :-
 Histology Lab.I There are four basic tissue types in the body are :- 1- Epithelial tissues (Epithelium) 2- Connective tissues 3- Muscular tissues 4- Nervous tissues 1-Epithelial tissues epithelial tissues
Histology Lab.I There are four basic tissue types in the body are :- 1- Epithelial tissues (Epithelium) 2- Connective tissues 3- Muscular tissues 4- Nervous tissues 1-Epithelial tissues epithelial tissues
Epithelial Tissue. Simple Cuboidal Function: secretion and absorption. Simple Squamous
 Epithelial Tissue General Functions: Lines and covers organs Absorbs / secretes substances Gas exchange Protection Special Characteristics: - have an apical surface on top - have a basement membrane below
Epithelial Tissue General Functions: Lines and covers organs Absorbs / secretes substances Gas exchange Protection Special Characteristics: - have an apical surface on top - have a basement membrane below
HISTOLOGY. Simple squamal lungs
 HISTOLOGY Lab Objectives: Students should be able to... 1. Visually identify each class of tissue and examples within each class 2. Indicate the location (in the human body and/or organ) and function of
HISTOLOGY Lab Objectives: Students should be able to... 1. Visually identify each class of tissue and examples within each class 2. Indicate the location (in the human body and/or organ) and function of
Chapter 05. Review. Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display.
 Chapter 05 Review 5.1: Introduction Similar cells with a common function are called tissues. The study of tissues is called histology. There are four (4) primary or major tissue types: 1. Epithelial Tissue
Chapter 05 Review 5.1: Introduction Similar cells with a common function are called tissues. The study of tissues is called histology. There are four (4) primary or major tissue types: 1. Epithelial Tissue
NOTES: CH 40 Introduction to Human Anatomy & Physiology
 NOTES: CH 40 Introduction to Human Anatomy & Physiology THE HUMAN BODY Anatomy Physiology (= structures) (= functions or processes) Characteristics of LIFE: 1) Made up of 1 or more CELLS. 2) Obtain and
NOTES: CH 40 Introduction to Human Anatomy & Physiology THE HUMAN BODY Anatomy Physiology (= structures) (= functions or processes) Characteristics of LIFE: 1) Made up of 1 or more CELLS. 2) Obtain and
Tissues. How do cells form tissues?
 Tissues How do cells form tissues? Using cell junctions Tissues Epithelial tissue Connective tissue Muscle tissue Nervous tissue Epithelial Tissue Closely packed cells in continuous sheets connected by
Tissues How do cells form tissues? Using cell junctions Tissues Epithelial tissue Connective tissue Muscle tissue Nervous tissue Epithelial Tissue Closely packed cells in continuous sheets connected by
Anatomy and Physiology 1 Chapter 4 Outline Tissues and Membranes
 Anatomy and Physiology 1 Chapter 4 Outline Tissues and Membranes 1 Tissue group of cells with similar structure and function o 4 major groups epithelial, connective, muscle, nerve Epithelial tissue (Fig
Anatomy and Physiology 1 Chapter 4 Outline Tissues and Membranes 1 Tissue group of cells with similar structure and function o 4 major groups epithelial, connective, muscle, nerve Epithelial tissue (Fig
Basic Histology. By Mrs. Bailey
 Basic Histology By Mrs. Bailey Primary Tissues 1. Epithelial Tissue 2. Connective Tissue 3. Muscle Tissue 4. Nervous Tissue Very cellular Supported by underlying connective tissue Epithelial & connective
Basic Histology By Mrs. Bailey Primary Tissues 1. Epithelial Tissue 2. Connective Tissue 3. Muscle Tissue 4. Nervous Tissue Very cellular Supported by underlying connective tissue Epithelial & connective
Unit I Problem 9 Histology: Basic Tissues of The Body
 Unit I Problem 9 Histology: Basic Tissues of The Body - What is the difference between cytology and histology? Cytology: it is the study of the structure and functions of cells and their contents. Histology:
Unit I Problem 9 Histology: Basic Tissues of The Body - What is the difference between cytology and histology? Cytology: it is the study of the structure and functions of cells and their contents. Histology:
Tissues. groups of cells similar in structure and function 4 types. epithelium connective muscle nervous
 Tissues groups of cells similar in structure and function 4 types epithelium connective muscle nervous Epithelial Tissue lining covering glandular Functions protection absorption filtration secretion Epithelium
Tissues groups of cells similar in structure and function 4 types epithelium connective muscle nervous Epithelial Tissue lining covering glandular Functions protection absorption filtration secretion Epithelium
Tissue: The Living Fabric: Part A
 PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Janice Meeking, Mount Royal College C H A P T E R 4 Tissue: The Living Fabric: Part A Tissues Groups of cells similar in structure and function Types of tissues Epithelial
PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Janice Meeking, Mount Royal College C H A P T E R 4 Tissue: The Living Fabric: Part A Tissues Groups of cells similar in structure and function Types of tissues Epithelial
The Tissue Level of Organization
 Tissue The Tissue Level of Organization Chapter 3 Definition an aggregation of cells in which each cooperates with all others in the performance of a given function Examples of general functions Movement
Tissue The Tissue Level of Organization Chapter 3 Definition an aggregation of cells in which each cooperates with all others in the performance of a given function Examples of general functions Movement
Body Tissues Pearson Education, Inc.
 Body Tissues Tissues Groups of cells with similar structure and function Four primary types: Epithelial tissue (epithelium).1 Connective tissue.2 Muscle tissue.3 Nervous tissue.4 Epithelial Tissues Locations:
Body Tissues Tissues Groups of cells with similar structure and function Four primary types: Epithelial tissue (epithelium).1 Connective tissue.2 Muscle tissue.3 Nervous tissue.4 Epithelial Tissues Locations:
Histology. Marcello Malpighi ( ) is regarded as Father of Histology.
 Histology The branch of biology which deals about tissue is called Histology. Marcello Malpighi (1628 1694) is regarded as Father of Histology. Tissue:- Group of identical or, unidentical cells which associate
Histology The branch of biology which deals about tissue is called Histology. Marcello Malpighi (1628 1694) is regarded as Father of Histology. Tissue:- Group of identical or, unidentical cells which associate
They cells can not function death.
 Jenna Hellack Jan 2001 Tissues What do you think happens when the cells use up their food and oxygen before there is time to replenish it? They cells can not function death. Blood Cell Cancer cell Plant
Jenna Hellack Jan 2001 Tissues What do you think happens when the cells use up their food and oxygen before there is time to replenish it? They cells can not function death. Blood Cell Cancer cell Plant
Tissues organs system organism. pg151
 Histology is the study of tissues A TISSUE is a group of cells, usually of one kind, & their intercellular substance (e.g. intercellular matrix in animal) which are linked together & perform a particular
Histology is the study of tissues A TISSUE is a group of cells, usually of one kind, & their intercellular substance (e.g. intercellular matrix in animal) which are linked together & perform a particular
Study of Tissues Dr. A. Ebneshahidi
 Study of Tissues Dr. A. Ebneshahidi Tissues Tissues are composed of cells similar in structure and specialized to perform a specific function for the body. The human body is made of four general types
Study of Tissues Dr. A. Ebneshahidi Tissues Tissues are composed of cells similar in structure and specialized to perform a specific function for the body. The human body is made of four general types
TISSUES. Dr. Gary Mumaugh
 TISSUES Dr. Gary Mumaugh Tissues Tissues - Groups of cells similar in structure and function and perform a common function Histology The study of tissues The four types of tissues Epithelial Connective
TISSUES Dr. Gary Mumaugh Tissues Tissues - Groups of cells similar in structure and function and perform a common function Histology The study of tissues The four types of tissues Epithelial Connective
What is histology? HISTOLOGY
 Introduction to Histology What is histology? HISTOLOGY histo = tissue ogy = study So HISTOLOGY = the study of tissues! What is a TISSUE? Tissues are groups of cells with specialized structural and functional
Introduction to Histology What is histology? HISTOLOGY histo = tissue ogy = study So HISTOLOGY = the study of tissues! What is a TISSUE? Tissues are groups of cells with specialized structural and functional
Air sacs of lungs and the lining of the heart, blood vessels, and lymphatic vessels
 Cells Location Function Simple squamous epithelium Air sacs of lungs and the lining of the heart, blood vessels, and lymphatic vessels Allows materials to pass through by diffusion and filtration, and
Cells Location Function Simple squamous epithelium Air sacs of lungs and the lining of the heart, blood vessels, and lymphatic vessels Allows materials to pass through by diffusion and filtration, and
Dr. Abeer.c.Yousif. Histology -2 nd stage. What is histology?
 What is histology? Histology is the science of microscopic anatomy of cells and tissues, in Greek language Histo= tissue and logos = study and it's tightly bounded to molecular biology, physiology, immunology
What is histology? Histology is the science of microscopic anatomy of cells and tissues, in Greek language Histo= tissue and logos = study and it's tightly bounded to molecular biology, physiology, immunology
Chapter 1: Cells and Tissues
 Chapter 1: Cells and Tissues Cells and Tissues Carry out all chemical activities needed to sustain life Cells are the building blocks of all living things Tissues are groups of cells that are similar in
Chapter 1: Cells and Tissues Cells and Tissues Carry out all chemical activities needed to sustain life Cells are the building blocks of all living things Tissues are groups of cells that are similar in
Tissues are: group of similar or identical cells that share a common function. used to build organs
 Tissues: Four classes Epithelium Connective Muscle Nervous Tissues are: group of similar or identical cells that share a common function. used to build organs Overview: Epithelial o Line body cavities
Tissues: Four classes Epithelium Connective Muscle Nervous Tissues are: group of similar or identical cells that share a common function. used to build organs Overview: Epithelial o Line body cavities
Chapter 4 Histology: The study of body tissues
 Chapter 4 Histology: The study of body tissues https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=zwxm2a0tfxm Body Tissues Cells are specialized for particular functions Tissues = groups of cells with similar structure and
Chapter 4 Histology: The study of body tissues https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=zwxm2a0tfxm Body Tissues Cells are specialized for particular functions Tissues = groups of cells with similar structure and
Basic Tissue Types and Functions
 Tissues Histology Basic Tissue Types and Functions 1) Epithelial tissue covering 2) Connective tissue support 3) Muscle tissue movement 4) Nervous tissue control Epithelial Tissue 1) Covers a body surface
Tissues Histology Basic Tissue Types and Functions 1) Epithelial tissue covering 2) Connective tissue support 3) Muscle tissue movement 4) Nervous tissue control Epithelial Tissue 1) Covers a body surface
Tissues. Group of cells that are similar in structure and function. 4 primary types. Epithelium (covering) Connective (support) Nervous(control)
 Tissues Tissues Group of cells that are similar in structure and function 4 primary types Epithelium (covering) Connective (support) Nervous(control) Epithelial tissue (epithelium) Lining, covering, and
Tissues Tissues Group of cells that are similar in structure and function 4 primary types Epithelium (covering) Connective (support) Nervous(control) Epithelial tissue (epithelium) Lining, covering, and
Tissues. Cells work together in functionally related groups called tissues Types of tissues: 1. Epithelial lining and covering. 2. Connective support
 Histology Tissues Cells work together in functionally related groups called tissues Types of tissues: 1. Epithelial lining and covering 2. Connective support 3. Muscle movement 4. Nervous control Epithelial
Histology Tissues Cells work together in functionally related groups called tissues Types of tissues: 1. Epithelial lining and covering 2. Connective support 3. Muscle movement 4. Nervous control Epithelial
Classification of Tissues
 6 R e v i e w S h e e t Exercise Classification of Tissues NAME LAB TIME/DATE Tissue Structure and Function General Review 1. Define tissue. A group of cells similar to one another in structure that perform
6 R e v i e w S h e e t Exercise Classification of Tissues NAME LAB TIME/DATE Tissue Structure and Function General Review 1. Define tissue. A group of cells similar to one another in structure that perform
Tissue Outline (chapter 4) Tissues group of cells that perform structural and roles. List the 4 types:
 Tissue Outline (chapter 4) Tissues group of cells that perform structural and roles. List the 4 types: 1. 2. 3. 4. I. Epithelial Tissue covers all the surfaces, inside & out. Are the major tissues of,
Tissue Outline (chapter 4) Tissues group of cells that perform structural and roles. List the 4 types: 1. 2. 3. 4. I. Epithelial Tissue covers all the surfaces, inside & out. Are the major tissues of,
Epithelial Lecture Test Questions
 Epithelial Lecture Test Questions 1. Which of the following free surfaces lack(s) epithelia: a. lung alveoli (air sacs) b. hard palate c. joint cavities d. abdominal cavity e. salivary gland ducts 2. Which
Epithelial Lecture Test Questions 1. Which of the following free surfaces lack(s) epithelia: a. lung alveoli (air sacs) b. hard palate c. joint cavities d. abdominal cavity e. salivary gland ducts 2. Which
Tissues are groups of cells with a common structure (form) and function (job).
 Dr Narmeen S. Ahmad Tissues are groups of cells with a common structure (form) and function (job). There are (4) types of tissue: 1. Epithelial 2. Connective 3. Muscle 4. Nervous Epithelial cells Epithelium
Dr Narmeen S. Ahmad Tissues are groups of cells with a common structure (form) and function (job). There are (4) types of tissue: 1. Epithelial 2. Connective 3. Muscle 4. Nervous Epithelial cells Epithelium
Histology= the study of tissues
 Unit 3-Histology Histology= the study of tissues A tissue is a group of cells that have a similar shape and function. Different types of tissues can be found in different organs. In humans, there are four
Unit 3-Histology Histology= the study of tissues A tissue is a group of cells that have a similar shape and function. Different types of tissues can be found in different organs. In humans, there are four
Epithelium. Four primary tissue types:
 Epithelium Four primary tissue types: Epithelial (covering) Connective (support) Nervous (control) Muscular (movement) Smooth muscle Cardiac muscle Skeletal muscle 1 Epithelial Tissue Features Epithelial
Epithelium Four primary tissue types: Epithelial (covering) Connective (support) Nervous (control) Muscular (movement) Smooth muscle Cardiac muscle Skeletal muscle 1 Epithelial Tissue Features Epithelial
Anatomy and Physiology Tissue Review
 Anatomy and Physiology Tissue Review OVERVIEW Histology practicals can be rough, especially when access to slides is limited to the lab period. This resource provides an opportunity to learn or review
Anatomy and Physiology Tissue Review OVERVIEW Histology practicals can be rough, especially when access to slides is limited to the lab period. This resource provides an opportunity to learn or review
Tissues. Definition. A group of similar cells and their intercellular substances specialized to perform a specific function.
 Chapter 4 - Tissues Tissues Definition A group of similar cells and their intercellular substances specialized to perform a specific function. Tissues Epithelial covers exposed surfaces, lines internal
Chapter 4 - Tissues Tissues Definition A group of similar cells and their intercellular substances specialized to perform a specific function. Tissues Epithelial covers exposed surfaces, lines internal
Lecture Overview. Chapter 4 Epithelial Tissues Lecture 9. Introduction to Tissues. Epithelial Tissues. Glandular Epithelium
 Visual Anatomy & Physiology First Edition Martini & Ober Chapter 4 Lecture 9 Lecture Overview Introduction to Tissues Location General characteristics Functions Classification Glandular Epithelium 2 Where
Visual Anatomy & Physiology First Edition Martini & Ober Chapter 4 Lecture 9 Lecture Overview Introduction to Tissues Location General characteristics Functions Classification Glandular Epithelium 2 Where
Tissues. tissue = many cells w/ same structure and function. cell shape aids its function tissue shape aids its function
 Tissues tissue = many cells w/ same structure and function cell shape aids its function tissue shape aids its function Histology = study of tissues 4 types of tissues Epithelial coverings contact openings
Tissues tissue = many cells w/ same structure and function cell shape aids its function tissue shape aids its function Histology = study of tissues 4 types of tissues Epithelial coverings contact openings
TISSUE. A group of cells that perform a similar function within an organism. Epithelium Connective Muscle Nervous CREDITS
 TISSUE A group of cells that perform a similar function within an organism. Epithelium Connective Muscle Nervous CREDITS Epithelium Connective Muscle Nervous Epithelium Composed of a layer of cells. Lines
TISSUE A group of cells that perform a similar function within an organism. Epithelium Connective Muscle Nervous CREDITS Epithelium Connective Muscle Nervous Epithelium Composed of a layer of cells. Lines
Tissues. tissue = many cells w/ same structure and function. cell shape aids function tissue shape aids function. Histology = study of tissues
 Tissues tissue = many cells w/ same structure and function cell shape aids function tissue shape aids function Histology = study of tissues 4 types of tissues Epithelial coverings contact openings Connective
Tissues tissue = many cells w/ same structure and function cell shape aids function tissue shape aids function Histology = study of tissues 4 types of tissues Epithelial coverings contact openings Connective
Tissue = groups of cells that are similar in structure and function
 Tissue = groups of cells that are similar in structure and function Types Epithelial - covering Connective - support Muscle - movement Nervous - control Membranes line body cavities and hold organs together
Tissue = groups of cells that are similar in structure and function Types Epithelial - covering Connective - support Muscle - movement Nervous - control Membranes line body cavities and hold organs together
Tissues 10/21/2016. Epithelial Tissue
 Tissues This is a generalized cell diagram. It shows the anatomy of a cell, but most cells do not actually look like this. Cells can have a wide variety of shapes and sizes, depending on their function.
Tissues This is a generalized cell diagram. It shows the anatomy of a cell, but most cells do not actually look like this. Cells can have a wide variety of shapes and sizes, depending on their function.
Histology Notes -Part 1: Epithelial Tissues
 Introduction Group of cells w/ similar structure & function = TISSUE Four Basic Tissue Types 1. Epithelial-covers 2. Connective-supports 3. Muscular*-produces movement (will discuss in the muscular system
Introduction Group of cells w/ similar structure & function = TISSUE Four Basic Tissue Types 1. Epithelial-covers 2. Connective-supports 3. Muscular*-produces movement (will discuss in the muscular system
Tissues and Membranes
 I. In the Beginning a. Egg + sperm! Tissues and Membranes b. 1 cell divides to make 2, 2 divide to make 4, 4 divide to make 8, and then? c. d. e. Totipotent: f. Pluripotent: II. III. Tissues a. Tissues
I. In the Beginning a. Egg + sperm! Tissues and Membranes b. 1 cell divides to make 2, 2 divide to make 4, 4 divide to make 8, and then? c. d. e. Totipotent: f. Pluripotent: II. III. Tissues a. Tissues
Epithelia of Coverings and Linings. Tissues. Tissue
 Tissue Tissues Chapter 3 Definition an aggregation of cells in which each cooperates with all others in the performance of a given function Examples of general functions Movement Protection Support Production
Tissue Tissues Chapter 3 Definition an aggregation of cells in which each cooperates with all others in the performance of a given function Examples of general functions Movement Protection Support Production
Chapter 20 UNIFYING CONCEPTS OF ANIMAL STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION
 Chapter 20 UNIFYING CONCEPTS OF ANIMAL STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION I. Life is based on many structural levels Levels of animal structure: Atoms and molecules Cells Tissues Organs Organ systems Organism: May
Chapter 20 UNIFYING CONCEPTS OF ANIMAL STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION I. Life is based on many structural levels Levels of animal structure: Atoms and molecules Cells Tissues Organs Organ systems Organism: May
A. cells that perform related functions and are similar in structure. B. extracellular material - made by cells and secreted into interstitial space
 I. tissue components A. cells that perform related functions and are similar in structure B. extracellular material - made by cells and secreted into interstitial space II. tissue types A. epithelium (e.)
I. tissue components A. cells that perform related functions and are similar in structure B. extracellular material - made by cells and secreted into interstitial space II. tissue types A. epithelium (e.)
Tissues Review 4 type
 Tissues Review 4 type Tissues Definition: a group of closely associated cells that perform related functions and are similar in structure Between cells: nonliving extracellular material Four basic types
Tissues Review 4 type Tissues Definition: a group of closely associated cells that perform related functions and are similar in structure Between cells: nonliving extracellular material Four basic types
BIOLOGY. Chapter 33 Animal Body: Histology Portion Pearson Education, Inc.
 BIOLOGY Chapter 33 Animal Body: Histology Portion Tissues: groups of cells with common function Tissue Category Epithelial (covers & lines) Simple squamous Simple cuboidal Simple columnar Tissues to know:
BIOLOGY Chapter 33 Animal Body: Histology Portion Tissues: groups of cells with common function Tissue Category Epithelial (covers & lines) Simple squamous Simple cuboidal Simple columnar Tissues to know:
Tissues, Glands, and Membranes. Chapter Five Mrs. Hornacek
 Tissues, Glands, and Membranes Chapter Five Mrs. Hornacek Objectives 1. Name the four main groups of tissues and give the location and general characteristics of each. 2. Differentiate between voluntary
Tissues, Glands, and Membranes Chapter Five Mrs. Hornacek Objectives 1. Name the four main groups of tissues and give the location and general characteristics of each. 2. Differentiate between voluntary
Practical Histology. Lab 3: Connective tissue
 Practical Histology Lab 3: Connective tissue Connective tissues Connective tissue provides structural support for the body by binding cells and tissues together to form organs. It also provides metabolic
Practical Histology Lab 3: Connective tissue Connective tissues Connective tissue provides structural support for the body by binding cells and tissues together to form organs. It also provides metabolic
Lecture Overview. Marieb s Human Anatomy and Physiology. Chapter 4 Tissues: The Living Fabric Epithelial Tissues Lecture 9. Introduction to Tissues
 Marieb s Human Anatomy and Physiology Marieb Hoehn Chapter 4 Tissues: The Living Fabric Epithelial Tissues Lecture 9 Lecture Overview Introduction to Tissues Epithelial Tissues Location General characteristics
Marieb s Human Anatomy and Physiology Marieb Hoehn Chapter 4 Tissues: The Living Fabric Epithelial Tissues Lecture 9 Lecture Overview Introduction to Tissues Epithelial Tissues Location General characteristics
THE TISSUE LEVEL OF ORGANIZATION PART I: EPITHELIAL TISSUE
 THE TISSUE LEVEL OF ORGANIZATION PART I: EPITHELIAL TISSUE 4 Main Tissue Types Epithelium Covers surfaces, lines cavities, forms glands Connective Tissue Support and protects body Muscular Tissue Movement
THE TISSUE LEVEL OF ORGANIZATION PART I: EPITHELIAL TISSUE 4 Main Tissue Types Epithelium Covers surfaces, lines cavities, forms glands Connective Tissue Support and protects body Muscular Tissue Movement
Name: Test Date: Chapter 4- Tissues. Use the choices to identify the major tissue types found below:
 Name: Test Date: Chapter 4- Tissues Use the choices to identify the major tissue types found below: A. Connective B. Epithelium C. Muscle D. Nervous 1. B Lines body cavities and covers the body s external
Name: Test Date: Chapter 4- Tissues Use the choices to identify the major tissue types found below: A. Connective B. Epithelium C. Muscle D. Nervous 1. B Lines body cavities and covers the body s external
UNIT 4 T I S S U E S
 UNIT 4 T I S S U E S WHAT IS A TISSUE Group of cells that work together to do a function Cells are similar Extracellular fluid around them is similar Histology EPITHELIAL TISSUE Also called epithelium
UNIT 4 T I S S U E S WHAT IS A TISSUE Group of cells that work together to do a function Cells are similar Extracellular fluid around them is similar Histology EPITHELIAL TISSUE Also called epithelium
TISSUE, INFLAMMATION AND REPAIR
 TISSUE, INFLAMMATION AND REPAIR TISSUE DEFINITION A group of cells with similar function/s and structure/morphology and similar extracellular substance HISTOLOGY The study of normal tissue HISTOPATHOLOGY
TISSUE, INFLAMMATION AND REPAIR TISSUE DEFINITION A group of cells with similar function/s and structure/morphology and similar extracellular substance HISTOLOGY The study of normal tissue HISTOPATHOLOGY
Classification of Tissues
 M06_MARI0000_00_SE_CH06.qxd 3/28/11 4:37 PM Page 35 NAME LAB TIME/DATE R E V I E W S H E E T EXERCISE 6 Classification of Tissues Tissue Structure and Function General Review 1. Define tissue. A group
M06_MARI0000_00_SE_CH06.qxd 3/28/11 4:37 PM Page 35 NAME LAB TIME/DATE R E V I E W S H E E T EXERCISE 6 Classification of Tissues Tissue Structure and Function General Review 1. Define tissue. A group
Tissue: The Living Fabric
 PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Vince Austin Human Anatomy & Physiology FIFTH EDITION Elaine N. Marieb Chapter 4 Tissue: The Living Fabric Part A Tissues Groups of cells similar in structure and
PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Vince Austin Human Anatomy & Physiology FIFTH EDITION Elaine N. Marieb Chapter 4 Tissue: The Living Fabric Part A Tissues Groups of cells similar in structure and
Introduction to Types of Body Tissue Putting it All Together. Packet #12
 Introduction to Types of Body Tissue Putting it All Together Packet #12 Introduction Body Tissues Tissues Groups of cells with similar structure and function Four primary types Epithelial tissue (epithelium)
Introduction to Types of Body Tissue Putting it All Together Packet #12 Introduction Body Tissues Tissues Groups of cells with similar structure and function Four primary types Epithelial tissue (epithelium)
Biology 325 Fall 2003
 Name: MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) Which of the following is not one of the primary tissue types? A) germinative tissue B) muscle
Name: MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) Which of the following is not one of the primary tissue types? A) germinative tissue B) muscle
Epithelial Tissue. Functions include: 1. Protection 4. Absorption 2. Secretion 5. Filtration 3. Sensory reception
 Tissues There are 4 primary tissue types in the human body: 1. Epithelial (covering/lining) 2. Connective (support) 3. Muscle (movement) 4. Nervous (control) Epithelium Epithelial Tissue Covers the surface
Tissues There are 4 primary tissue types in the human body: 1. Epithelial (covering/lining) 2. Connective (support) 3. Muscle (movement) 4. Nervous (control) Epithelium Epithelial Tissue Covers the surface
d SIMPLE EPITHELIA Top view Side view
 Chapter Two I UPLANd I 23 Cells, Tissues, and Integument me lea SIMPLE EPITHELIA There are four types of tissues in humans and these make up all of the organs and binding material in the body. Epithelial
Chapter Two I UPLANd I 23 Cells, Tissues, and Integument me lea SIMPLE EPITHELIA There are four types of tissues in humans and these make up all of the organs and binding material in the body. Epithelial
Histology= the study of tissues
 Histology 2014 Histology= the study of tissues A tissue is a group of cells that have a similar shape and function. Different types of tissues can be found in different organs. In humans, there are four
Histology 2014 Histology= the study of tissues A tissue is a group of cells that have a similar shape and function. Different types of tissues can be found in different organs. In humans, there are four
Dr Narmeen S. Ahmad. Lab 1
 Dr Narmeen S. Ahmad Lab 1 1 Tissues are groups of cells with a common structure (form) and function (job). There are (4) types of tissue: 1. Epithelial 2. Connective 3. Muscle 4. Nervous 2 Epithelial cells
Dr Narmeen S. Ahmad Lab 1 1 Tissues are groups of cells with a common structure (form) and function (job). There are (4) types of tissue: 1. Epithelial 2. Connective 3. Muscle 4. Nervous 2 Epithelial cells
Histology. The study of tissues.
 Histology The study of tissues. Body Tissues Cells are specialized for particular functions Tissues Groups of cells with similar structure and function Four primary types Epithelium Connective tissue Nervous
Histology The study of tissues. Body Tissues Cells are specialized for particular functions Tissues Groups of cells with similar structure and function Four primary types Epithelium Connective tissue Nervous
BIOH111. o Cell Biology Module o Tissue Module o Integumentary system o Skeletal system o Muscle system o Nervous system o Endocrine system
 BIOH111 o Cell Biology Module o Tissue Module o Integumentary system o Skeletal system o Muscle system o Nervous system o Endocrine system Endeavour College of Natural Health endeavour.edu.au 1 Textbook
BIOH111 o Cell Biology Module o Tissue Module o Integumentary system o Skeletal system o Muscle system o Nervous system o Endocrine system Endeavour College of Natural Health endeavour.edu.au 1 Textbook
يراهظلا( يئلاطلا جيسنلا
 Epithelium النسيج الطالئي )الظهاري( Features of Epithelium Epithelium occurs in the body as a sheet of cells that covers a body surface, lines a cavity, or forms a gland. Coverings, linings, glands. Derived
Epithelium النسيج الطالئي )الظهاري( Features of Epithelium Epithelium occurs in the body as a sheet of cells that covers a body surface, lines a cavity, or forms a gland. Coverings, linings, glands. Derived
Histology 101! !! Name:! Block: Identify and describe the functions of major tissue types including their subclasses and varieties!
 Histology 101 Identify and describe the functions of major tissue types including their subclasses and varieties Name: Block: "1 Introduction to Tissues Histology Notes Tissue (living fabric) : groups
Histology 101 Identify and describe the functions of major tissue types including their subclasses and varieties Name: Block: "1 Introduction to Tissues Histology Notes Tissue (living fabric) : groups
A Single Neuron from the Brain
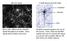 Nervous Tissue A Single Neuron from the Brain Dendrites Cell Body Axon Nerve cells, called neurons, transmit signals throughout our bodies. These signals tell our bodies what to do. Dendrites transmit
Nervous Tissue A Single Neuron from the Brain Dendrites Cell Body Axon Nerve cells, called neurons, transmit signals throughout our bodies. These signals tell our bodies what to do. Dendrites transmit
Connexons: hollow connective tubes
 Chapter 3 1. tight junctions: like a zipper, these junctions hold the cells tightly together making them impermeable to the extracellular fluid that surrounds them. 2. desmosomes: like buttons, these
Chapter 3 1. tight junctions: like a zipper, these junctions hold the cells tightly together making them impermeable to the extracellular fluid that surrounds them. 2. desmosomes: like buttons, these
ACTIVITY 2: HISTOLOGY AND INTEGUMENT
 ACTIVITY 2: HISTOLOGY AND INTEGUMENT Objectives: 1) How to get ready: Read Chapter 4 and 5, McKinley et al., Human Anatomy, 4e. All text references are for this textbook. 2) Identify each tissue (26 tissues)
ACTIVITY 2: HISTOLOGY AND INTEGUMENT Objectives: 1) How to get ready: Read Chapter 4 and 5, McKinley et al., Human Anatomy, 4e. All text references are for this textbook. 2) Identify each tissue (26 tissues)
Use for reference if needed:
 A- 2.5 Describe how structure and function are related in terms of cell and tissue types. I can recognize different types of body tissue. I can explain how different tissue structures affect their functions.
A- 2.5 Describe how structure and function are related in terms of cell and tissue types. I can recognize different types of body tissue. I can explain how different tissue structures affect their functions.
Epithelium Characteristics cont. 2. Apical Surface
 Epithelium Characteristics cont. 2. Apical Surface always has one exposed (apical) surface Some surfaces are smooth & slick, others may have: microvilli fingerlike extensions of the plasma membrane; increase
Epithelium Characteristics cont. 2. Apical Surface always has one exposed (apical) surface Some surfaces are smooth & slick, others may have: microvilli fingerlike extensions of the plasma membrane; increase
Cells are the basic unit of life
 Ch. 4 Tissues Cells are the basic unit of life Organism Organ System Organs Tissues Cells Living thing A group of organ systems working together Group of organs working together Each system has a specific
Ch. 4 Tissues Cells are the basic unit of life Organism Organ System Organs Tissues Cells Living thing A group of organ systems working together Group of organs working together Each system has a specific
A adipose cells. B capillary. C epithelium
 EPITHELIA Objective The objective of this class is to observe how different epithelia vary in terms of cell shape, size and number of cell layers enabling them to be well adapted for functions in different
EPITHELIA Objective The objective of this class is to observe how different epithelia vary in terms of cell shape, size and number of cell layers enabling them to be well adapted for functions in different
Section B: Epithelial Tissue 1. Where are epithelial tissues found within the body? 2. What are the functions of the epithelial tissues?
 Tissue worksheet Name Section A: Intro to Histology Cells are the smallest units of life. In complex organisms, cells group together with one another based on similar structure and function to form tissues.
Tissue worksheet Name Section A: Intro to Histology Cells are the smallest units of life. In complex organisms, cells group together with one another based on similar structure and function to form tissues.
What is a tissue? Points to ponder. Tissues Connective Tissue. 1. Connective tissue 2/23/2019. Organization and Regulation of Body Systems
 Organization and Regulation of Body Systems Chapter 04 Lecture Outline See separate PowerPoint slides for all figures and tables preinserted into PowerPoint without notes. Copyright 2016 McGraw-Hill Education.
Organization and Regulation of Body Systems Chapter 04 Lecture Outline See separate PowerPoint slides for all figures and tables preinserted into PowerPoint without notes. Copyright 2016 McGraw-Hill Education.
Epithelial Tissue. SAC Request. Epithelial Tissue 27/06/12. Linings and? BIOL241
 Epithelial Tissue Linings and? BIOL241 SAC Request From Audrey Rose Cabinet Coordinator Student Administrative Council SAC is looking for dedicated students to apply for the Student Cabinet, Fee Board,
Epithelial Tissue Linings and? BIOL241 SAC Request From Audrey Rose Cabinet Coordinator Student Administrative Council SAC is looking for dedicated students to apply for the Student Cabinet, Fee Board,
Tissues (Histology) Ch. 3 Human Anatomy lecture
 I. Histology the study of tissues A. 4 basic tissue types epithelial connective muscle nervous Tissues (Histology) Ch. 3 Human Anatomy lecture B. Usually found in combinations to form organs. C. As you
I. Histology the study of tissues A. 4 basic tissue types epithelial connective muscle nervous Tissues (Histology) Ch. 3 Human Anatomy lecture B. Usually found in combinations to form organs. C. As you
