GCE BIOLOGY - BY2. Mark Scheme - January (b) (i) birds; 1. (ii) Borneo {1.61/ 1.62/1.6}; 1
|
|
|
- Mitchell Lane
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 GCE BIOLOGY - BY Mark Scheme - January 03 (a) A species is a group of organisms that {can interbreed/ reproduce}; (under natural conditions) produce fertile offspring; (b) (i) birds; (ii) Borneo {.6/.6/.6}; (iii) (Least at poles to) {greatest/ increasing} at equator; (c) (i) X at second split from left or anywhere along that line; (ii) Same genus( but different species)/ tells us the genus; (d) (i) homologous; (ii) analogous; total [9]
2 (a) Thin small diffusion distance; Accept small diffusion distance/ pathway Large surface area- (large contact with air) for diffusion/ gas exchange/ OWTTE; Moist- allow gases to dissolve/ gases go into solution (to cross membrane); Not diffuse into Permeable-to allow gases to pass through (the respiratory surface); NOT blood supply 3 max (b) (i) Through {(general) body surface/skin}; NOT gills (ii) Fast flowing; maintains {concentration/ diffusion} gradient/absorbs more oxygen at surface/ OWTTE; (iii) They dry out/ unable to remain moist/ lose water; They clump together (because of surface tension.)/ collapse/ lie on top of each other; (c) Blood flows (across gill) in opposite direction to water; NOT different direction {Concentration/ diffusion} gradient is maintained across whole surface/ {concentration/ diffusion} gradient is maintained constantly/ blood always meets water with a higher oxygen concentration/ equilibrium is never reached ; NOT concentration gradient maintained for longer/ maintains a high concentration gradient A greater concentration of oxygen in the blood is achieved/ allows more oxygen to diffuse in/ higher % saturated blood/ allows more {diffusion/ exchange} of gases/ more take up of oxygen/ ORA; NOT makes it more efficient alone 3 total []
3 3 (a) A Cortex/ parenchyma B Endodermis; C Xylem; D Phloem. marks for all 4, mark for or 3 (b) (i) Xylem Both correct for mark (ii) Phloem; NOT letters only (c) (i) {Translocation/ movement/ transport/ carry NOT flow} of {products of photosynthesis/ sucrose/organic compounds/ sugars/ amino acids}/ description of source to sink/ translocation; (NOT nutrients/ other named sugar/ named ions) (ii) Carry out {metabolism/respiration} /to supply (sieve cells) with {energy/atp}/ contain mitochondria for {ATP/ active transport}; NOT contain organelles that the sieve cells do not have/ not loading sieve cell (d) (i) Apoplast; via cell walls; NOT plasmodesmata Symplast; via {cytoplasm/ plasmodesmata}; [ mark for name, mark for correct route, for each] (ii) Makes the water pass through {symplast/living part of cell/ cytoplasm}/ prevents it going through {apoplast/ cell walls}; NOT impermeable alone/ makes water take another route 3 Total [0] 3
4 4 (a) (i) A- incomplete metamorphosis B-complete metamorphosis BOTH; (ii) X- {nymph/ larva/ instar} Y- pupa (accept chrysalis/ cocoon/ pupal stage) BOTH; (b) (Exoskeleton is) {rigid/ hard/ non- living/ does not grow/ owtte}; 3 They shed (the exoskeleton)/ ecdysis/ moult; Then grow (a new one)/ allows growth/ vulnerable whilst hardening ; (c) Fluid filled cavity (surrounded by a membrane); {Protective/ hard/ leathery} {shell/ outer covering/ coat}; (embryo within) yolk sac/ food store/ yolk for nutrition/ own internal nutrient supply; [any ] (d) (the young are retained) for a {considerable/ longer} time in the mother s womb or uterus; (The embryo is) nourished there from {the mother s blood supply /the placenta}/ {unlimited nutrients/ OWTTE}; Protection qualified; The young are {born in a relatively advanced state of development/ well developed/ more advanced growth in womb}; [Any 3] NOT parental care/ ref to number of offspring 3 4 Total [0] 4
5 5 (a) (i) (Oxygen) dissociation (curve); (ii) similar shaped curve drawn to left of given curve; (must start/ end at same points) NOT above 00% (iii) {Foetal haemoglobin/ it} has {higher greater} affinity for oxygen (than adult)/ picks up oxygen easier/ more readily forms oxyhaemoglobin/ reaches saturation at lower partial pressures; NOT more quickly (this ensures) oxygen moves from mother( s blood) to foetus (in the placenta); (b) (i) Move to right; (ii) Bohr; (iii) (Muscles/ cells give off) more carbon dioxide/ higher partial pressure of carbon dioxide; carbon dioxide dissolves to make carbonic acid/lowering ph; which reduces affinity of Haemoglobin for oxygen/reference to Hydrogen displacing Oxygen from Haemoglobin/ oxygen dissociates more readily; (more) oxygen is released added demand when muscles need it (for aerobic respiration)/ OWTTE; 4 5 Total [0] 5
6 6 (a) Parasites are organisms that (live on or in another organism called the host and) {obtain nourishment / feed on it}; at the expense of /causing harm to the host; NOT negative effect unqualified (b) (i) Hooks+ suckers both; (ii) Any Attach the worm (to the wall of the gut)/ for attachment; the worm does not get moved along/ resisting peristalsis; passed out with undigested food remains/ prevents it being egested; (c) (It lives surrounded by) food that has been digested/ broken down by the {host/ human s digestive system/ OWTTE}; (It is very long ) gives a large surface area (to absorb digested food); (It is flat/ thin ) short distance for diffusion; NOT thin membrane 3 (d) Any It lays large numbers of {eggs/ larva/ embryos/ offspring}; eggs can resist adverse conditions/ OWTTE; correct reference to hermaphroditism; Not asexual reproduction 6 Total [0] 6
7 7 (a) A In buccal cavity/ mouth; B teeth (and tongue) {mechanically/ physically} break down food /to provide large surface area; C (Saliva added from) salivary glands; D (saliva) contains mucus to lubricate; E Amylase substrate is starch, product is maltose/ disaccharides; F Stomach adapted for protein digestion/ protein digestion {starts/ begins} in stomach/ proteins are partially digested in the stomach; G Produces hydrochloric acid/ low ph in stomach; H Peptidase/Pepsin s substrate is {protein/ polypeptides}, products are {polypeptides/peptides}; reject ref to other enzymes I Small intestine (is adapted to) completes (protein /carbohydrate) digestion/ Description of {disaccharide/ polpeptide} digestion in small intestine; J Named enzyme produced by small intestine; K Two named enzymes produced by pancreas; L correct reference to endo- exo- peptidases; M Absorption takes place in the ileum/small intestine; N Villi / microvilli increase surface area; O Glucose/ monosaccharides/ products are absorbed by diffusion and active transport; 7
8 7 (b) A Heart (muscle) is myogenic; B It can contract without any nerve stimulation; C The stimulus to contract originates in the sinoatrial node (SAN); D Which controls the rate of beating / acts as pacemaker; E It is situated in the wall of right atrium/auricle. (on diagram); F Electrical impulse from the SAN causes the two atria/auricles to contract; G Thin layer of connective tissue prevents the stimulus spreading to the ventricles; H At the bottom of the wall separating the two atria /auricles is the atriventricular node AVN. (on diagram); I This delays the impulse ( about 0. sec) before passing it to the ventricles; J The impulse is sent to the apex /tip of the ventricles; K Along bundle branches / Bundle of His; L And is conveyed upwards along Purkinje/ Purkyne fibres; M Causing (a wave of) ventricular contraction starting from the lowermost part of the ventricles; N The SAN may be stimulated by various factors to change its pacing; 0 One example hormones (adrenalin), exercise, body temperature, etc. (allow ref. autonomic nervous system; 7 Total [0] 8
UNIT 2 BIODIVERSITY AND PHYSIOLOGY OF BODY SYSTEMS MARK SCHEME GENERAL INSTRUCTIONS
 GCE AS and A LEVEL BIOLOGY Specimen Assessment Materials 148 UNIT 2 BIODIVERSITY AND PHYSIOLOGY OF BODY SYSTEMS MARK SCHEME GENERAL INSTRUCTIONS Recording of marks Examiners must mark in red ink. One tick
GCE AS and A LEVEL BIOLOGY Specimen Assessment Materials 148 UNIT 2 BIODIVERSITY AND PHYSIOLOGY OF BODY SYSTEMS MARK SCHEME GENERAL INSTRUCTIONS Recording of marks Examiners must mark in red ink. One tick
Digestion & The Alimentary Canal
 For more awesome GSE and level resources, visit us at www.savemyexams.co.uk/ igestion & The limentary anal Question Paper Level Subject Exam oard Topic Sub Topic ooklet O Level iology ambridge International
For more awesome GSE and level resources, visit us at www.savemyexams.co.uk/ igestion & The limentary anal Question Paper Level Subject Exam oard Topic Sub Topic ooklet O Level iology ambridge International
My Question Paper. Copyright WJEC CBAC Ltd. All rights reserved Page 1 of 22
 My Question Paper Copyright WJEC CBAC Ltd. All rights reserved Page 1 of 22 1. The diagrams below show sections through the duodenum and ileum at the same magnification (a) Name the structure labelled
My Question Paper Copyright WJEC CBAC Ltd. All rights reserved Page 1 of 22 1. The diagrams below show sections through the duodenum and ileum at the same magnification (a) Name the structure labelled
CIE Biology A-level Topic 8: Transport in mammals
 CIE Biology A-level Topic 8: Transport in mammals Notes Circulatory systems can either be open, for instance in insects, or closed, like in fish and mammals where the blood is confined to blood vessels
CIE Biology A-level Topic 8: Transport in mammals Notes Circulatory systems can either be open, for instance in insects, or closed, like in fish and mammals where the blood is confined to blood vessels
Website: Page 1. Page 113»Exercise» Question 1:
 Page 113»Exercise» Question 1: The kidneys in human beings are a part of the system for (a) nutrition. (b) respiration. (c) excretion. (d) transportation. (c) In human beings, the kidneys are a part of
Page 113»Exercise» Question 1: The kidneys in human beings are a part of the system for (a) nutrition. (b) respiration. (c) excretion. (d) transportation. (c) In human beings, the kidneys are a part of
PART A: MULTIPLE CHOICE (100 questions 65% of exam mark)
 1 PART A: MULTIPLE CHOICE (100 questions 65% of exam mark) I: Wellness and Homeostasis 1. Determine the false statement about homeostasis. A) Homeostasis refers to the body s attempt to adjust to a fluctuating
1 PART A: MULTIPLE CHOICE (100 questions 65% of exam mark) I: Wellness and Homeostasis 1. Determine the false statement about homeostasis. A) Homeostasis refers to the body s attempt to adjust to a fluctuating
BYA6 Physiology and the Environment
 version 1.1 GCE 2005 January Series abc Mark Scheme Biology Specification A BYA6 Physiology and the Environment Mark schemes are prepared by the Principal Examiner and considered, together with the relevant
version 1.1 GCE 2005 January Series abc Mark Scheme Biology Specification A BYA6 Physiology and the Environment Mark schemes are prepared by the Principal Examiner and considered, together with the relevant
Contact us:
 Class X Chapter 6 Life Processes Science Question 1: Why is diffusion insufficient to meet the oxygen requirements of multi-cellular organisms like humans? Multicellular organisms such as humans possess
Class X Chapter 6 Life Processes Science Question 1: Why is diffusion insufficient to meet the oxygen requirements of multi-cellular organisms like humans? Multicellular organisms such as humans possess
Flatworms. Phylum Platyhelminthes
 Flatworms Phylum Platyhelminthes Characteristics of Flatworms Flatworms are acoelomates, which means they have no coelom. A coelom is a fluid-filled body cavity The digestive cavity is the only body cavity
Flatworms Phylum Platyhelminthes Characteristics of Flatworms Flatworms are acoelomates, which means they have no coelom. A coelom is a fluid-filled body cavity The digestive cavity is the only body cavity
Exampro GCSE Biology. B2.1 Cells. Name: Class: Foundation tier. Author: Date: Time: 81. Marks: 81. Comments: Page 1 of 27
 Exampro GCSE Biology B2. Cells Foundation tier Name: Class: Author: Date: Time: 8 Marks: 8 Comments: Page of 27 Q. Diabetes is a disease in which the concentration of glucose in a person s blood may rise
Exampro GCSE Biology B2. Cells Foundation tier Name: Class: Author: Date: Time: 8 Marks: 8 Comments: Page of 27 Q. Diabetes is a disease in which the concentration of glucose in a person s blood may rise
Section 5.1 The heart and heart disease
 Section 5.1 The heart and heart disease Mammals are too large to rely on diffusion. They need a circulatory system to move substances around the body. Blood moves down pressure gradients, from high to
Section 5.1 The heart and heart disease Mammals are too large to rely on diffusion. They need a circulatory system to move substances around the body. Blood moves down pressure gradients, from high to
Physiology Quiz (30 Points)
 Physiology Quiz (30 Points) Name: 1. What prevents antibiotics from being effective against viruses? A. Viruses have a high rate of mutation. B. Viruses have no RNA. C. Viruses have no metabolism. D. Viruses
Physiology Quiz (30 Points) Name: 1. What prevents antibiotics from being effective against viruses? A. Viruses have a high rate of mutation. B. Viruses have no RNA. C. Viruses have no metabolism. D. Viruses
B4 NUTRITION 4.3 Animal Nutrition
 B4 NUTRITION 4.3 Animal Nutrition 1. State the term balanced diet & describe how balanced diet is related to age, sex & activity of an individual. Balanced diet: A diet that contains all the main nutrients
B4 NUTRITION 4.3 Animal Nutrition 1. State the term balanced diet & describe how balanced diet is related to age, sex & activity of an individual. Balanced diet: A diet that contains all the main nutrients
PART B: WRITTEN RESPONSE. Use the following diagram to answer question 1. X Y
 PART B: WRITTEN RESPONSE Value: 50 marks Suggested Time: 75 minutes Use the following diagram to answer question 1. X Y 1. Name structures X and Y and explain how each functions in protein synthesis. (4
PART B: WRITTEN RESPONSE Value: 50 marks Suggested Time: 75 minutes Use the following diagram to answer question 1. X Y 1. Name structures X and Y and explain how each functions in protein synthesis. (4
Station One: Nutrition
 Station One: Nutrition Name that thing! 1. Chemical substances, found in foods, which are used in the human body. 2. Nutrient in human diet where foods are the only possible source of the nutrient. 3.
Station One: Nutrition Name that thing! 1. Chemical substances, found in foods, which are used in the human body. 2. Nutrient in human diet where foods are the only possible source of the nutrient. 3.
All organisms must obtain and process essential nutrients (food) *** Exception: Venus Fly Traps undergo photosynthesis but needs source of nitrogen
 All organisms must obtain and process essential nutrients (food) AUTOTROPHS self feeder makes their own food eg. Plants do not require a digestive tract *** Exception: Venus Fly Traps undergo photosynthesis
All organisms must obtain and process essential nutrients (food) AUTOTROPHS self feeder makes their own food eg. Plants do not require a digestive tract *** Exception: Venus Fly Traps undergo photosynthesis
Ch 7 Nutrition in humans
 Ch 7 Nutrition in humans Think about (Ch 7, p.2) 1. The stomach churns food into smaller pieces physically. The stomach wall secretes proteases to chemically digest proteins. It also releases hydrochloric
Ch 7 Nutrition in humans Think about (Ch 7, p.2) 1. The stomach churns food into smaller pieces physically. The stomach wall secretes proteases to chemically digest proteins. It also releases hydrochloric
Question Expected Answers Marks Additional Guidance two marks for correct answer 1 (a) a single value between 67 and 80 ; ; max 2
 Question Expected Answers Marks Additional Guidance two marks for correct answer 1 (a) a single value between 67 and 80 ; ; max 2 If answer incorrect, allow one mark for appropriate working i.e. 60 divided
Question Expected Answers Marks Additional Guidance two marks for correct answer 1 (a) a single value between 67 and 80 ; ; max 2 If answer incorrect, allow one mark for appropriate working i.e. 60 divided
Bell Work. b. is wrong because combining two glucose molecules requires energy, it does not release energy
 Bell Work How is energy made available to the cell to move large starch molecules across the cell membrane through the process of endocytosis? a. removing a phosphate from ATP b. combining two glucose
Bell Work How is energy made available to the cell to move large starch molecules across the cell membrane through the process of endocytosis? a. removing a phosphate from ATP b. combining two glucose
Animal Survival. Standard Grade Biology
 Animal Survival Standard Grade Biology Give 5 reasons why the body needs food. The Need for Food The 3 main types of food are carbohydrate, fat and protein. State the chemical elements present in each.
Animal Survival Standard Grade Biology Give 5 reasons why the body needs food. The Need for Food The 3 main types of food are carbohydrate, fat and protein. State the chemical elements present in each.
Many people suffer from stomach ulcers caused by a species of bacteria called Helicobacter pylori.
 The diagram below shows the human digestive system. (a) (b) Label the stomach and pancreas on the diagram. Many people suffer from stomach ulcers caused by a species of bacteria called Helicobacter pylori.
The diagram below shows the human digestive system. (a) (b) Label the stomach and pancreas on the diagram. Many people suffer from stomach ulcers caused by a species of bacteria called Helicobacter pylori.
Biology 12 August 2003 Provincial Examination
 Biology 12 August 2003 Provincial Examination ANSWER KEY / SCORING GUIDE CURRICULUM: Organizers 1. Cell Biology 2. Cell Processes and Applications 3. Human Biology Sub-Organizers A, B, C, D E, F, G, H
Biology 12 August 2003 Provincial Examination ANSWER KEY / SCORING GUIDE CURRICULUM: Organizers 1. Cell Biology 2. Cell Processes and Applications 3. Human Biology Sub-Organizers A, B, C, D E, F, G, H
Organisation. AQA Biology topic 2
 Organisation AQA Biology topic 2 2.1 Principles of Organisation Cells, tissues, organs and systems Basically, all living things are made up of cells A group of CELLS makes up a TISSUE A group of TISSUES
Organisation AQA Biology topic 2 2.1 Principles of Organisation Cells, tissues, organs and systems Basically, all living things are made up of cells A group of CELLS makes up a TISSUE A group of TISSUES
2. Complete this table to give the function of the following organelles:
 1. Label these diagrams of cells: 2. Complete this table to give the function of the following organelles: Organelle Cell Membrane Cell Wall Chloroplast Mitochondria Vacuole 3. State 2 differences between
1. Label these diagrams of cells: 2. Complete this table to give the function of the following organelles: Organelle Cell Membrane Cell Wall Chloroplast Mitochondria Vacuole 3. State 2 differences between
B2.1 Cells and simple cell transport. B2.2 Tissues, organs and organ systems
 B2.1.1 Cells and simple cell transport B2.1 Cells and simple cell transport Know that most human and animal cells have the following parts: a nucleus, which controls the activities of the cell; cytoplasm,
B2.1.1 Cells and simple cell transport B2.1 Cells and simple cell transport Know that most human and animal cells have the following parts: a nucleus, which controls the activities of the cell; cytoplasm,
Biochemistry Name: Practice Questions
 Name: Practice Questions 1. Carbohydrate molecules A and B come in contact with the cell membrane of the same cell. Molecule A passes through the membrane readily, but molecule B does not. It is most likely
Name: Practice Questions 1. Carbohydrate molecules A and B come in contact with the cell membrane of the same cell. Molecule A passes through the membrane readily, but molecule B does not. It is most likely
The diagram below shows the parts of the body that digest and absorb food.
 The diagram below shows the parts of the body that digest and absorb food. It also shows some details about the structure of the stomach. (a) Complete the table to show whether each structure is an organ,
The diagram below shows the parts of the body that digest and absorb food. It also shows some details about the structure of the stomach. (a) Complete the table to show whether each structure is an organ,
Angel International School - Manipay
 c Grade 10 Angel International School - Manipay 1 st Term Examination November 2016 Biology Duration: 3Hours Index No:- Choose the correct answer and underline it. (1) When a red stain is added to a culture
c Grade 10 Angel International School - Manipay 1 st Term Examination November 2016 Biology Duration: 3Hours Index No:- Choose the correct answer and underline it. (1) When a red stain is added to a culture
Ms. Golub & Ms. Sahar Date: Unit 2- Test #1
 Name Ms. Golub & Ms. Sahar Date: Unit 2- Test #1 1. The interaction between guard cells and a leaf opening would not be involved in A) diffusion of carbon dioxide B) maintaining homeostasis C) heterotrophic
Name Ms. Golub & Ms. Sahar Date: Unit 2- Test #1 1. The interaction between guard cells and a leaf opening would not be involved in A) diffusion of carbon dioxide B) maintaining homeostasis C) heterotrophic
Question Expected Answers Marks Additional Guidance 1 (a) C ; E ; A ; B ; 4. PhysicsAndMathsTutor.com
 Question Expected Answers Marks Additional Guidance 1 (a) C ; E ; A ; B ; 4 Question Expected Answers Marks Additional Guidance (b) (i) P wave combined with larger peak before QRS complex ; Note: - look
Question Expected Answers Marks Additional Guidance 1 (a) C ; E ; A ; B ; 4 Question Expected Answers Marks Additional Guidance (b) (i) P wave combined with larger peak before QRS complex ; Note: - look
HUMAN NUTRITION 08 MAY 2013
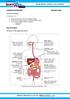 HUMAN NUTRITION 08 MAY 2013 Lesson Description In this lesson, we: Study the structure of the human digestive system Look at the processes used in the human digestive system Look at the two different types
HUMAN NUTRITION 08 MAY 2013 Lesson Description In this lesson, we: Study the structure of the human digestive system Look at the processes used in the human digestive system Look at the two different types
CIE Biology GCSE 7: Human nutrition
 CIE Biology GCSE 7: Human nutrition Notes Humans need many different nutrients to survive. To receive these nutrients in the correct quantities, a balanced diet must be eaten. A balanced diet includes
CIE Biology GCSE 7: Human nutrition Notes Humans need many different nutrients to survive. To receive these nutrients in the correct quantities, a balanced diet must be eaten. A balanced diet includes
BIOLOGY - BY2. No. Answer Mark. (ii) 1 egg 1 mark for both (not: zygote) 7 adult/imago 2-6 nymphs (allow: instar) 2
 BIOLOGY - BY. (a) (i) Incomplete metamorphosis (ii) egg mark for both (not: zygote) 7 adult/imago -6 nymphs (allow: instar) (b) (i) Complete metamorphosis (ii) A Egg B Larva (allow: maggot) C Pupa (allow:
BIOLOGY - BY. (a) (i) Incomplete metamorphosis (ii) egg mark for both (not: zygote) 7 adult/imago -6 nymphs (allow: instar) (b) (i) Complete metamorphosis (ii) A Egg B Larva (allow: maggot) C Pupa (allow:
Angel International School - Manipay 3r d Term Examination July, 2015 Biology
 Grade 07 Angel International School - Manipay 3r d Term Examination July, 2015 Biology Duration: 2 Hours Part I Choose the correct answer and underline it. 1. Which of the following does not manufacture
Grade 07 Angel International School - Manipay 3r d Term Examination July, 2015 Biology Duration: 2 Hours Part I Choose the correct answer and underline it. 1. Which of the following does not manufacture
Carbohydrates. Mark Scheme. Save My Exams! The Home of Revision. Exam Board 3.1 Biological Molecules Carbohydrates. Page 1.
 Carbohydrates Mark Scheme Level Subject Exam Board Module Topic Booklet A Level Biology AQA 3.1 Biological Molecules 3.1. Carbohydrates Mark Scheme Time Allowed: 59 minutes Score: /4 Percentage: /100 Grade
Carbohydrates Mark Scheme Level Subject Exam Board Module Topic Booklet A Level Biology AQA 3.1 Biological Molecules 3.1. Carbohydrates Mark Scheme Time Allowed: 59 minutes Score: /4 Percentage: /100 Grade
Plants and animals are examples of multicellular organisms. They contain millions of cells in their body.
 Revision 1 Q1. Which of the following statements is true? A. A cell is the basic unit for animals only. B. A multicellular organism has more than one cell in its body. C. Plant cells and animal cells only
Revision 1 Q1. Which of the following statements is true? A. A cell is the basic unit for animals only. B. A multicellular organism has more than one cell in its body. C. Plant cells and animal cells only
Chapter 2: Human Body Systems Work Independently and Together
 Chapter 2: Human Body Systems Work Independently and Together 2.1 Body Systems Body systems Are made up of parts that work together as a whole Are connected to one or more other Will not function well
Chapter 2: Human Body Systems Work Independently and Together 2.1 Body Systems Body systems Are made up of parts that work together as a whole Are connected to one or more other Will not function well
Human Organ Systems. Circulatory, Respiratory, Digestive
 Human Organ Systems Circulatory, Respiratory, Digestive The Circulatory System The circulatory system picks up and transports nutrients and oxygen to all the cells in the body, and carries wastes to the
Human Organ Systems Circulatory, Respiratory, Digestive The Circulatory System The circulatory system picks up and transports nutrients and oxygen to all the cells in the body, and carries wastes to the
The process by which nutrient molecules pass through the wall of your digestive system into your blood. ABSORPTION AS RELATED TO DIGESTION
 ABSORPTION AS RELATED TO DIGESTION The process by which nutrient molecules pass through the wall of your digestive system into your blood. 3 FUNCTIONS OF DIGESTION Breaks down food into molecules the body
ABSORPTION AS RELATED TO DIGESTION The process by which nutrient molecules pass through the wall of your digestive system into your blood. 3 FUNCTIONS OF DIGESTION Breaks down food into molecules the body
Transport Systems in Plants and Animals
 Transport Systems in Plants and Animals Mark Scheme Level Subject Exam Board Unit Topic Difficulty Level Booklet GCSE Biology AQA B3 Transport Systems in Plants and Animals Bronze Level Mark Scheme Time
Transport Systems in Plants and Animals Mark Scheme Level Subject Exam Board Unit Topic Difficulty Level Booklet GCSE Biology AQA B3 Transport Systems in Plants and Animals Bronze Level Mark Scheme Time
Title: Dec 12 8:42 AM (1 of 37) Chapter 11: Digestion and Excretion
 Title: Dec 12 8:42 AM (1 of 37) Chapter 11: Digestion and Excretion Introduction to Digestion Read pages 352 358 Make summary notes on this section Creat a Concept Map on the Essential Nutrients, including:
Title: Dec 12 8:42 AM (1 of 37) Chapter 11: Digestion and Excretion Introduction to Digestion Read pages 352 358 Make summary notes on this section Creat a Concept Map on the Essential Nutrients, including:
231/2 BIOLOGY (2017) PAPER 2(Theory)
 231/2 BIOLOGY (2017) PAPER 2(Theory) 1 MARKING SCHEME 1. (a) Albinism; sickle cell anaemia; Haemophilia; colour blindness; b) (i) Inversion Occurs when chromatids break at two places; and when rejoining
231/2 BIOLOGY (2017) PAPER 2(Theory) 1 MARKING SCHEME 1. (a) Albinism; sickle cell anaemia; Haemophilia; colour blindness; b) (i) Inversion Occurs when chromatids break at two places; and when rejoining
Name Date Class. 2. Is the following sentence true or false? Food is required for the body to. maintain homeostasis, keeping a steady internal state.
 CHAPTER 11 FOOD AND DIGESTION SECTION 11 1 Food and Energy (pages 370-380) This section tells about the six nutrients needed by the body. It also describes the Food Guide Pyramid and how to read labels
CHAPTER 11 FOOD AND DIGESTION SECTION 11 1 Food and Energy (pages 370-380) This section tells about the six nutrients needed by the body. It also describes the Food Guide Pyramid and how to read labels
What is the evidence from the diagram that haemoglobin has a quaternary structure? (1)
 Q1. The diagram shows a molecule of haemoglobin. (a) What is the evidence from the diagram that haemoglobin has a quaternary structure? (1) (i) A gene codes for the α-polypeptide chain. There are 43 bases
Q1. The diagram shows a molecule of haemoglobin. (a) What is the evidence from the diagram that haemoglobin has a quaternary structure? (1) (i) A gene codes for the α-polypeptide chain. There are 43 bases
Kingdom Phylum Class Genus. Annelid(s)/ annelida Vertebrate/ vertebrata/ chordate/ chordata; Insect/ insecta;
 1. (a) BIOLOGY BY2 Kingdom Phylum Class Genus Planta(e)/ plant(s); 4 Annelid(s)/ annelida Vertebrate/ vertebrata/ chordate/ chordata; Insect/ insecta; (b) (i) A = Fungi; 2 B = Protoctist(a)/ protoctists/
1. (a) BIOLOGY BY2 Kingdom Phylum Class Genus Planta(e)/ plant(s); 4 Annelid(s)/ annelida Vertebrate/ vertebrata/ chordate/ chordata; Insect/ insecta; (b) (i) A = Fungi; 2 B = Protoctist(a)/ protoctists/
***Non-living things may show one or more of these Characteristics, but NEVER ALL of them
 -Living things are highly ORGANIZED -Living things are made up of one or more CELLS -Living things use ENERGY -Living things GROW and develop -Living things RESPOND to changes in the environment -Living
-Living things are highly ORGANIZED -Living things are made up of one or more CELLS -Living things use ENERGY -Living things GROW and develop -Living things RESPOND to changes in the environment -Living
Reproduction Worksheet
 Name: Date: Reproduction Worksheet Directions: Base your answers to questions 1-4 on the diagram below and your knowledge of biology. 1. Identify the structure in which sperm is produced. What is the name
Name: Date: Reproduction Worksheet Directions: Base your answers to questions 1-4 on the diagram below and your knowledge of biology. 1. Identify the structure in which sperm is produced. What is the name
30.1 Organization of the Human Body
 30.1 Organization of the Human Body Lesson Objectives Describe how the human body is organized. Explain homeostasis. Lesson Summary Organization of the Body The levels of organization in a multicellular
30.1 Organization of the Human Body Lesson Objectives Describe how the human body is organized. Explain homeostasis. Lesson Summary Organization of the Body The levels of organization in a multicellular
MARK SCHEME for the October/November 2014 series 5090 BIOLOGY. 5090/22 Paper 2 (Theory), maximum raw mark 80
 www.onlineexamhelp.com CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS Cambridge Ordinary Level MARK SCHEME for the October/November 2014 series 5090 BIOLOGY 5090/22 Paper 2 (Theory), maximum raw mark 80 This mark
www.onlineexamhelp.com CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS Cambridge Ordinary Level MARK SCHEME for the October/November 2014 series 5090 BIOLOGY 5090/22 Paper 2 (Theory), maximum raw mark 80 This mark
GCE AS/A level 1072/01 BIOLOGY BY2
 Surname Centre Number Candidate Number Other Names 2 GCE AS/A level 1072/01 BIOLOGY BY2 S15-1072-01 P.M. MONDAY, 1 June 2015 1 hour 30 minutes For s use Question Maximum Mark Mark Awarded 1. 5 2. 10 3.
Surname Centre Number Candidate Number Other Names 2 GCE AS/A level 1072/01 BIOLOGY BY2 S15-1072-01 P.M. MONDAY, 1 June 2015 1 hour 30 minutes For s use Question Maximum Mark Mark Awarded 1. 5 2. 10 3.
d) Cardiovascular System Higher Human Biology
 d) Cardiovascular System Higher Human Biology What can your remember about the heart and blood vessels? What is the Cardiovascular System? The cardiovascular system, also known as the circulatory system,
d) Cardiovascular System Higher Human Biology What can your remember about the heart and blood vessels? What is the Cardiovascular System? The cardiovascular system, also known as the circulatory system,
WORD BANK liver mouth teeth anus
 )ur Digestive System ibel the parts pf your digestive system. Name pancreas stomach esophagus salivary glands WORD BANK liver mouth teeth anus gall bladder large intestine small intestine Topic 3.1 Digestive
)ur Digestive System ibel the parts pf your digestive system. Name pancreas stomach esophagus salivary glands WORD BANK liver mouth teeth anus gall bladder large intestine small intestine Topic 3.1 Digestive
Warm Up Where in a flower would you find xylem and phloem? 2. Where in a flower would you find palisade cells?
 Body Systems Warm Up 4-4-16 1. Where in a flower would you find xylem and phloem? 2. Where in a flower would you find palisade cells? 3. Where in a flower would you find root hair cells? 4. What organelle
Body Systems Warm Up 4-4-16 1. Where in a flower would you find xylem and phloem? 2. Where in a flower would you find palisade cells? 3. Where in a flower would you find root hair cells? 4. What organelle
The human digestive system
 Cells A tissue Organs Organ systems Principles of organisation The basic building blocks of all living organisms. A group of cells with similar structure and function. Groups of tissues performing specific
Cells A tissue Organs Organ systems Principles of organisation The basic building blocks of all living organisms. A group of cells with similar structure and function. Groups of tissues performing specific
CONTEXT POINT 2: Plants and animals transport dissolved nutrients and gases in a fluid medium.
 CONTEXT POINT 2: Plants and animals transport dissolved nutrients and gases in a fluid medium. Identify the form(s) in which each of the following is carried in mammalian blood: Carbon dioxide 70% as hydrogen
CONTEXT POINT 2: Plants and animals transport dissolved nutrients and gases in a fluid medium. Identify the form(s) in which each of the following is carried in mammalian blood: Carbon dioxide 70% as hydrogen
Stem cells. Stem cells can be found in embryos, in adult animals and in the meristems in plants.
 Stem cells A stem cell is an undifferentiated cell of an organism which can produce more cells of the same type. Certain other cells can arise from stem cells when they differentiate. Stem cells can be
Stem cells A stem cell is an undifferentiated cell of an organism which can produce more cells of the same type. Certain other cells can arise from stem cells when they differentiate. Stem cells can be
Human Body Systems. Long narrow tube mixes enzymes with food Small nutrient molecules diffuse into blood
 Human Body Systems Living Environment AIS Mr. DuRoss Digestive System : Break down large food molecules into smaller parts that the body can use Mouth Esophagus Stomach Small intestine Large intestine
Human Body Systems Living Environment AIS Mr. DuRoss Digestive System : Break down large food molecules into smaller parts that the body can use Mouth Esophagus Stomach Small intestine Large intestine
Chapter 15 Food and Digestion
 Chapter 15 Food and Digestion Activity: Use Qualitative Observations (5 senses) to describe: What happens when you see candy? How does it smell? How do you chomp it into smaller pieces or swallow candy
Chapter 15 Food and Digestion Activity: Use Qualitative Observations (5 senses) to describe: What happens when you see candy? How does it smell? How do you chomp it into smaller pieces or swallow candy
Unit 4: Summary. Similarities and Differences Between Living Things
 Unit 4: Summary Similarities and Differences Between Living Things Review cell theory All living things made of cells Cells perform life functions Cells come from pre existing cells What are life functions?
Unit 4: Summary Similarities and Differences Between Living Things Review cell theory All living things made of cells Cells perform life functions Cells come from pre existing cells What are life functions?
The Digestive System CP Biology
 The Digestive System CP Biology Objectives Explain how food provides energy. Identify the 6 forms of nutrients your body needs and describe their use in the body. Identify the organs of the digestive system;
The Digestive System CP Biology Objectives Explain how food provides energy. Identify the 6 forms of nutrients your body needs and describe their use in the body. Identify the organs of the digestive system;
Mammalian Transport and The Heart
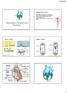 Cardiovascular System AS-G, Chapters 8-9 Blood flows through the body in a closed system (circuit) driven by the pumping power of the heart Closed vs open: does the system have vessels contained the entire
Cardiovascular System AS-G, Chapters 8-9 Blood flows through the body in a closed system (circuit) driven by the pumping power of the heart Closed vs open: does the system have vessels contained the entire
Enamel Dentine Pulp cavity nerves & blood vessels Gums & Bone Crown & root. Tooth type and job. Why do humans have more than one type of tooth?
 Tooth type and job Enamel Dentine Pulp cavity nerves & blood vessels Gums & Bone Crown & root Be able to sketch & label this Tooth type and job Why do humans have more than one type of tooth? Omnivores
Tooth type and job Enamel Dentine Pulp cavity nerves & blood vessels Gums & Bone Crown & root Be able to sketch & label this Tooth type and job Why do humans have more than one type of tooth? Omnivores
7.4 Digestion. Highlight the definition of mechanical digestion.
 7.4 Digestion Digestion is the breakdown of large, insoluble food molecules into small, water-soluble food molecules so that they can be absorbed into the bloodstream. The large food molecules are starch,
7.4 Digestion Digestion is the breakdown of large, insoluble food molecules into small, water-soluble food molecules so that they can be absorbed into the bloodstream. The large food molecules are starch,
Circulation. Sinoatrial (SA) Node. Atrioventricular (AV) Node. Cardiac Conduction System. Cardiac Conduction System. Linked to the nervous system
 Circulation Cardiac Conduction System AHS A H S Your body resembles a large roadmap. There are routes or arteries that take you downtown to the heart of the city and veins that take you to the outskirts
Circulation Cardiac Conduction System AHS A H S Your body resembles a large roadmap. There are routes or arteries that take you downtown to the heart of the city and veins that take you to the outskirts
Questions on Digestion
 Name: Questions on Digestion Directions: The following questions are taken from previous IB Final Papers on Topic 6.1 (Digestion). Answer all questions. This will serve as a study guide for the next quiz.
Name: Questions on Digestion Directions: The following questions are taken from previous IB Final Papers on Topic 6.1 (Digestion). Answer all questions. This will serve as a study guide for the next quiz.
Biology 20: Digestive System Did you get it? Questions and Answers
 Biology 20: Digestive System Did you get it? Questions and Answers Mouth 1. What is the purpose of chewing? a. break food into smaller pieces so there is a greater SA for chemicals to work on. 2. Salivary
Biology 20: Digestive System Did you get it? Questions and Answers Mouth 1. What is the purpose of chewing? a. break food into smaller pieces so there is a greater SA for chemicals to work on. 2. Salivary
Objective 4- Digestion
 Objective 4- Digestion 1. Describe why cells require nutrients Supply energy for metabolism (cell activities), matter for synthesis of new materials, cell reproduction, secretion and to regulate cell processes
Objective 4- Digestion 1. Describe why cells require nutrients Supply energy for metabolism (cell activities), matter for synthesis of new materials, cell reproduction, secretion and to regulate cell processes
Mid Term Review. 1. step 1, only 3. both step 1 and step 2 2. step 2, only 4. neither step 1 nor step 2
 Name Mid Term Review 1. Diagrams, tables, and graphs are used by scientists mainly to 1. design a research plan for an experiment 3. organize data 2. test a hypothesis 4. predict the independent variable
Name Mid Term Review 1. Diagrams, tables, and graphs are used by scientists mainly to 1. design a research plan for an experiment 3. organize data 2. test a hypothesis 4. predict the independent variable
Nutrients and Digestion
 Nutrients and Digestion Nutrition what is needed to be taken in to keep the body healthy Essential Nutrients Carbohydrates Fats Proteins Minerals Vitamins Water Carbohydrates Types of sugars combined in
Nutrients and Digestion Nutrition what is needed to be taken in to keep the body healthy Essential Nutrients Carbohydrates Fats Proteins Minerals Vitamins Water Carbohydrates Types of sugars combined in
>>> FOCUS. Context. Digestion. The human digestive system
 Context All living organisms need nutrients, which provide materials and energy for survival. These nutrients need to be broken down before they can be used by cells. Plants make their own food using energy
Context All living organisms need nutrients, which provide materials and energy for survival. These nutrients need to be broken down before they can be used by cells. Plants make their own food using energy
6) An animal with the cross section shown above has a: a) Gastrovascular cavity b) Pseudocoelom c) Coelom
 1) A 12 foot tall human: a) Would need a disproportionally larger and stronger skeleton than a 6 foot tall human b) Would need a disproportionally smaller and weaker skeleton than a 2 foot tall human c)
1) A 12 foot tall human: a) Would need a disproportionally larger and stronger skeleton than a 6 foot tall human b) Would need a disproportionally smaller and weaker skeleton than a 2 foot tall human c)
Questions on Transport
 Name: Questions on Transport Directions: The following questions are taken from previous IB Final Papers on Topic 6.2 (The Transport System). Answer all questions. This will serve as a study guide for
Name: Questions on Transport Directions: The following questions are taken from previous IB Final Papers on Topic 6.2 (The Transport System). Answer all questions. This will serve as a study guide for
Martin Uckermann Unofficial Mark Scheme. F211, AS Biology. May 2013 OCR
 Martin Uckermann Unofficial Mark Scheme F211, AS Biology May 2013 OCR This mark scheme only deduce how the paper could be marked according to previous ones Question I. a.) i.) [2 marks] A nucleus B chloroplast
Martin Uckermann Unofficial Mark Scheme F211, AS Biology May 2013 OCR This mark scheme only deduce how the paper could be marked according to previous ones Question I. a.) i.) [2 marks] A nucleus B chloroplast
The Digestive System
 Digestive System 1 Name The Digestive System Purpose: To describe how food moves through the digestive system. To identify the parts of the digestive system. Background Information: Food provides us with
Digestive System 1 Name The Digestive System Purpose: To describe how food moves through the digestive system. To identify the parts of the digestive system. Background Information: Food provides us with
Chapter 9: Digestion Review Assignment
 _ Date: Mark: /45 Chapter 9: Digestion Review Assignment 45 Multiple Choice = 45 Marks Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Which of the following roles do
_ Date: Mark: /45 Chapter 9: Digestion Review Assignment 45 Multiple Choice = 45 Marks Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Which of the following roles do
Ingestion Digestion- Absorption- Elimination
 DIGESTIVE SYSTEM 1 FUNCTIONS Organization GI tract==mouth anus Accessory organs Salivary glands, liver, pancreas, gallbladder Major Functions: Ingestion-mouth, teeth, tongue Digestion- chemical and mechanical
DIGESTIVE SYSTEM 1 FUNCTIONS Organization GI tract==mouth anus Accessory organs Salivary glands, liver, pancreas, gallbladder Major Functions: Ingestion-mouth, teeth, tongue Digestion- chemical and mechanical
What is Digestion? The break down of food into molecules that are small enough to be absorbed and used by the body
 Digestive System What is Digestion? The break down of food into molecules that are small enough to be absorbed and used by the body What is Digestion? This involves: Ingestion and propulsion of food along
Digestive System What is Digestion? The break down of food into molecules that are small enough to be absorbed and used by the body What is Digestion? This involves: Ingestion and propulsion of food along
Downloaded from
 BAL BHARATI PUBLIC SCHOOL, PITAMPURA, DELHI-110034 CLASS 10 NOTES TERM 1 Topic: Life processes Q1. Define the following terms: 1) nutrition 2) photosynthesis 3) peristalsis 4) excretion 5) osmoregulation
BAL BHARATI PUBLIC SCHOOL, PITAMPURA, DELHI-110034 CLASS 10 NOTES TERM 1 Topic: Life processes Q1. Define the following terms: 1) nutrition 2) photosynthesis 3) peristalsis 4) excretion 5) osmoregulation
Assessment Schedule 2017 Biology: Demonstrate understanding of biological ideas relating to a mammal(s) as a consumer(s) (90929)
 NCEA Level 1 Biology (90929) 2017 page 1 of 6 Assessment Schedule 2017 Biology: Demonstrate understanding of biological ideas relating to a mammal(s) as a consumer(s) (90929) Evidence Statement QUESTION
NCEA Level 1 Biology (90929) 2017 page 1 of 6 Assessment Schedule 2017 Biology: Demonstrate understanding of biological ideas relating to a mammal(s) as a consumer(s) (90929) Evidence Statement QUESTION
MARK SCHEME for the October/November 2009 question paper for the guidance of teachers 0610 BIOLOGY. 0610/02 Paper 2 (Core Theory), maximum raw mark 80
 UNIVERSITY OF CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS International General Certificate of Secondary Education MARK SCHEME for the October/November 2009 question paper for the guidance of teachers 0610 BIOLOGY
UNIVERSITY OF CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS International General Certificate of Secondary Education MARK SCHEME for the October/November 2009 question paper for the guidance of teachers 0610 BIOLOGY
3.0 Healthy human function depends on a variety of interacting and reacting systems
 3.0 Healthy human function depends on a variety of interacting and reacting systems Vocabulary: Mechanical digestion: physical break down of food into very small pieces. Chemical digestion: breakdown of
3.0 Healthy human function depends on a variety of interacting and reacting systems Vocabulary: Mechanical digestion: physical break down of food into very small pieces. Chemical digestion: breakdown of
1) Four main feeding mechanisms of animals a) Suspension feeders i) (1) Humpback whales b) Substrate feeders i)
 1 AP Biology March 2008 Digestion Chapter 41 Homeostatic mechanisms manage an animal s energy budget. 1) Four main feeding mechanisms of animals Suspension feeders (1) Humpback whales Substrate feeders
1 AP Biology March 2008 Digestion Chapter 41 Homeostatic mechanisms manage an animal s energy budget. 1) Four main feeding mechanisms of animals Suspension feeders (1) Humpback whales Substrate feeders
Use words from the box to complete Figure 1 by putting the parts of the body in order of size from smallest to largest.
 1 The human body is organised to carry out many different functions. (a) Use words from the box to complete Figure 1 by putting the parts of the body in order of size from smallest to largest. The smallest
1 The human body is organised to carry out many different functions. (a) Use words from the box to complete Figure 1 by putting the parts of the body in order of size from smallest to largest. The smallest
Proteins their functions and uses revision 4
 Proteins their functions and uses revision 4 48 minutes 48 marks Page of 4 Q. The diagram shows the digestive system. (a) Complete the following sentences about digestive enzymes. (i) Amylase works in
Proteins their functions and uses revision 4 48 minutes 48 marks Page of 4 Q. The diagram shows the digestive system. (a) Complete the following sentences about digestive enzymes. (i) Amylase works in
Nutrition. Why do humans need food? How do some animals get their food? ROUGHAGE NUTRIENTS. Animals make energy available using:
 Nutrition the activities by which organisms Why do humans need food? Animals make energy available using: obtain and process material needed for energy, growth, repair, and to maintain homeostasis humans
Nutrition the activities by which organisms Why do humans need food? Animals make energy available using: obtain and process material needed for energy, growth, repair, and to maintain homeostasis humans
The Digestive System
 The Digestive System Key words Pharynx oesophagus stomach intestine epiglottis gall bladder Pancreas peristalsis liver enzyme rectum sphincter Pyloric duodenum jejunum ileum bile lipase Amylase trypsin
The Digestive System Key words Pharynx oesophagus stomach intestine epiglottis gall bladder Pancreas peristalsis liver enzyme rectum sphincter Pyloric duodenum jejunum ileum bile lipase Amylase trypsin
Interactions Among Animal Systems. Biology 10(A)
 Interactions Among Animal Systems Biology 10(A) Interactions Among Animal Systems Learning Objectives Identify major organ systems in animals Describe the interactions that occur among systems to carry
Interactions Among Animal Systems Biology 10(A) Interactions Among Animal Systems Learning Objectives Identify major organ systems in animals Describe the interactions that occur among systems to carry
The Human Digestive Tract
 The Human Digestive Tract The Mouth salivary glands (parotid, sublingual, submaxillary) - produces saliva --->lubricate food ---> dissolves food particles ---> allows us to taste food --->contains amylase
The Human Digestive Tract The Mouth salivary glands (parotid, sublingual, submaxillary) - produces saliva --->lubricate food ---> dissolves food particles ---> allows us to taste food --->contains amylase
There are enzymes in biological washing powders. Biological washing powder has to be used at temperatures below 45 C.
 There are enzymes in biological washing powders. Biological washing powder has to be used at temperatures below 45 C. The enzymes in biological washing powders do not work on the stains on clothes at temperatures
There are enzymes in biological washing powders. Biological washing powder has to be used at temperatures below 45 C. The enzymes in biological washing powders do not work on the stains on clothes at temperatures
Paper Reference. Thursday 8 January 2009 Morning Time: 1 hour
 Centre No. Candidate No. Paper Reference(s) 6102/01 Edexcel GCE Biology Advanced Subsidiary Unit Test 2B Thursday 8 January 2009 Morning Time: 1 hour Materials required for examination Ruler Paper Reference
Centre No. Candidate No. Paper Reference(s) 6102/01 Edexcel GCE Biology Advanced Subsidiary Unit Test 2B Thursday 8 January 2009 Morning Time: 1 hour Materials required for examination Ruler Paper Reference
Chapter 6---Life Processes
 Chapter 6---Life Processes 1. In Photosynthetic process, atmospheric carbon di oxide is to carbohydrates a) oxidised b) Reduced c) Neutralised d) Burnt 2. When water enters the guard cells the stomata
Chapter 6---Life Processes 1. In Photosynthetic process, atmospheric carbon di oxide is to carbohydrates a) oxidised b) Reduced c) Neutralised d) Burnt 2. When water enters the guard cells the stomata
Page 2. Q1.Substances can move into and out of cells. (a) (i) How does oxygen move into and out of cells? Draw a ring around one answer.
 Q1.Substances can move into and out of cells. (a) (i) How does oxygen move into and out of cells? Draw a ring around one answer. diffusion digestion photosynthesis (ii) Diagram 1 shows the percentage concentration
Q1.Substances can move into and out of cells. (a) (i) How does oxygen move into and out of cells? Draw a ring around one answer. diffusion digestion photosynthesis (ii) Diagram 1 shows the percentage concentration
Cardiovascular System Notes
 Cardiovascular System Notes Cardiovascular System a transportation system that carries needed substances to cells and waste products away from cells. Functions Transports nutrients to cells Transports
Cardiovascular System Notes Cardiovascular System a transportation system that carries needed substances to cells and waste products away from cells. Functions Transports nutrients to cells Transports
HUMAN BODY SYSTEMS EXAM (S7L2)
 HUMAN BODY SYSTEMS EXAM (S7L2) Multiple Choice Directions: Select the best answer for each of the following questions. 1. Teeth are part of the skeletal system, but they are also part of the digestive
HUMAN BODY SYSTEMS EXAM (S7L2) Multiple Choice Directions: Select the best answer for each of the following questions. 1. Teeth are part of the skeletal system, but they are also part of the digestive
DIGESTION SBI 3C: NOVEMBER 2010
 DIGESTION SBI 3C: NOVEMBER 2010 DIAGRAM OF DIGESTIVE SYSTEM: Mouth Esophagus Liver Gallbladder Large Intestine Appendix Stomach Pancreas Small Intestine Rectum Anus STAGES OF DIGESTION: 1. INGESTION Taking
DIGESTION SBI 3C: NOVEMBER 2010 DIAGRAM OF DIGESTIVE SYSTEM: Mouth Esophagus Liver Gallbladder Large Intestine Appendix Stomach Pancreas Small Intestine Rectum Anus STAGES OF DIGESTION: 1. INGESTION Taking
Human Digestion. Junior Science
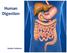 Human Digestion Junior Science True or False The word stomach comes from the Greek meaning Throat. Butterflies in the stomach have nothing to do with the stomach. It is possible to live without your stomach.
Human Digestion Junior Science True or False The word stomach comes from the Greek meaning Throat. Butterflies in the stomach have nothing to do with the stomach. It is possible to live without your stomach.
Why is diffusion insufficient to meet the oxygen requirements of multi-cellular organisms like
 Page 95»Question» Question 1: Why is diffusion insufficient to meet the oxygen requirements of multi-cellular organisms like humans? Multicellular organisms such as humans possess complex body designs.
Page 95»Question» Question 1: Why is diffusion insufficient to meet the oxygen requirements of multi-cellular organisms like humans? Multicellular organisms such as humans possess complex body designs.
Topic 6: Human Physiology
 Topic 6: Human Physiology 6.1 Digestion and Absorption D.1 Human Nutrition D.2 Digestion Essential Understandings: The structure of the digestive system allows it to move, digest, and absorb food. A balanced
Topic 6: Human Physiology 6.1 Digestion and Absorption D.1 Human Nutrition D.2 Digestion Essential Understandings: The structure of the digestive system allows it to move, digest, and absorb food. A balanced
