Biomédica ISSN: Instituto Nacional de Salud Colombia
|
|
|
- Grant Oliver
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Biomédica ISSN: Instituto Nacional de Salud Colombia Travi, Bruno L.; Tabares, Carlos Javier; Cadena, Horacio Leishmania ( Viannia) braziliensis infection in two Colombian dogs: a note on infectivity for sand flies and response to treatment Biomédica, vol. 26, núm. 1, octubre, 2006, pp Instituto Nacional de Salud Bogotá, Colombia Available in: How to cite Complete issue More information about this article Journal's homepage in redalyc.org Scientific Information System Network of Scientific Journals from Latin America, the Caribbean, Spain and Portugal Non-profit academic project, developed under the open access initiative
2 Biomédica 2006;26(Supl.1): CUTANEOUS LEISHMANIASIS IN COLOMBIAN DOGS COMUNICACIÓN BREVE Leishmania (Viannia) braziliensis infection in two Colombian dogs: a note on infectivity for sand flies and response to treatment Bruno L. Travi, Carlos Javier Tabares, Horacio Cadena Centro Internacional de Entrenamiento e Investigaciones Médicas, Cali, Colombia. Introduction. Although canine cutaneous leishmaniasis has been reported in several foci of South America, no published information from Colombia is available. Objective. We report on two cases found in the Pacific coast region of this country, which presented as a single scrotal ulcer in one dog, and two ulcers on the external surface of the ear in a second dog. Materials and methods. Parasites were isolated by culture in Senekjie s culture medium and identified using monoclonal antibodies. The capacity of these dogs to transmit the parasites to sand fly vectors (Lutzomyia trapidoi, Lutzomyia gomezi, Lutzomyia longipalpis, Lutzomyia youngi) was tested by allowing the flies to feed on the lesion borders. Results. Both isolates were identified as Leishmania (Viannia) braziliensis. No infections were detected upon dissection of engorged flies. A single peri-and sub-lesional injection of 1-2 ml of pentavalent antimony in the dog with ear lesions resulted in clinical cure 6 weeks post-treatment. Conclusions. These observations suggest that although dogs are susceptible to L. braziliensis, their reservoir competence could be low. However, if further studies indicate that canines are capable reservoir hosts of L. Viannia spp., the local treatment of lesions could become a feasible approach to diminish the risk of human infection in the peridomestic setting, without sacrificing infected dogs. Keywords: Leishmania braziliensis, dog diseases, cutaneous leishmaniasis, Leishmania reservoir, therapy Infección por Leishmania (Viannia) braziliensis en dos perros colombianos: una nota sobre infectividad para flebótomos y respuesta al tratamiento. Introducción. A pesar de que la leishmaniasis cutánea canina ha sido reportada en varios focos de Sudamérica, no existe información publicada de Colombia. Objetivo. Se reportan dos casos hallados en la región de la costa Pacífica de este país, que se presentaron como una úlcera escrotal única en un perro y como dos úlceras en la cara externa de la oreja en un segundo individuo. Materiales y métodos. Los parásitos fueron aislados por cultivo en medio de Senekjie e identificados empleando anticuerpos monoclonales. La capacidad de los perros para transmitir parásitos a los flebótomos vectores (Lutzomyia trapidoi, Lutzomyia gomezi, Lutzomyia longipalpis, Lutzomyia youngi) se ensayó permitiendo que los insectos se alimentaran sobre el borde de las lesiones. Resultados. Ambos aislamientos se identificaron como Leishmania (Viannia) braziliensis. No se detectaron infecciones durante la disección de los flebótomos alimentados. Una sola inyección peri- y sub-lesional de 1-2 ml de antimonio pentavalente en el perro con las lesiones auriculares resultó en la curación clínica a las 6 semanas post-tratamiento. Conclusiones. Estas observaciones sugieren que aunque los perros son susceptibles a L. braziliensis, su competencia como reservorio podría ser baja. Sin embargo, si estudios posteriores demuestran que los caninos tienen capacidad de reservorio para especies de L. Viannia, el tratamiento local de las lesiones podría ser una estrategia factible para disminuir el riesgo de infección humana en el peridomicilio, sin necesidad de sacrificar a los perros infectados. 249
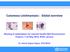
3 TRAVI B.L., TABARES C.J., CADENA H. Biomédica 2006;26(Supl.1): Palabras clave: Leishmania braziliensis, leishmaniasis cutánea, enfermedades de los perros, terapia The natural infection of dogs with Leishmania (Viannia) spp. in rural and periurban areas of South American countries such as Argentina, Brazil, Perú and Venezuela has been reported by several authors (1-8). However in Colombia, where three species of Leishmania (Viannia) are endemic (9), no published information on canine cutaneous leishmaniasis is available. There is no doubt that dogs play an essential role in the peridomestic transmission of visceral leishmaniasis (10), yet only risk factor analyses and isolation of Leishmania from lesions have suggested that they could play a role in American cutaneous leishmaniasis (1,7,11), and consequently confirmatory studies are still pending. We report on two cases of canine leishmaniasis in adult male, mongrel dogs residing in different endemic areas of cutaneous leishmaniasis in the Colombian Pacific coast. Materials and methods The first individual suspicious of having cutaneous leishmaniasis, an adult male, was found during a dog screening for American cutaneous leishmaniasis (n=52 dogs) in the municipality of Tumaco, Nariño (1 48 N, 78 46W), an area endemic for cutaneous leishmaniasis. The animal, which was the only individual with lesions, had a chronic scrotal ulcer of unknown evolution time. The second dog, also an adult male, resided in Bajo Calima, municipality of Buenaventura (4 2' N, 77 4 W), a small rural town distant 30 km from the Pacific coast in the department of Valle del Cauca. It was brought to CIDEIM for diagnosis, presenting a large ulcer and a satellite lesion on the external face of the ear, of less than 6 months of evolution (figure 1a). Dermal scrapings stained with 2% Giemsa and aspirate-cultures (n=4) seeded in Senekjie s culture medium of samples obtained from the lesion borders were used as diagnostic Corresponding: Bruno L. Travi, CIDEIM, Apartado Aéreo 5390, Cali, Colombia. Telephone: (572) ; fax: (572) travib@cideim.org.co Recibido: 11/04/05; aceptado: 23/06/05 methods (12). To test the capacity of these dogs to transmit Leishmania to sand flies, the animals were subjected to xenodiagnosis. For this purpose, Lutzomyia trapidoi and Lutzomyia gomezi, which are the prevalent sand fly species in this region (13), were collected in the field, and groups of female flies were caged in 500 ml plastic containers furnished with fine mesh. The dogs were anesthetized with xylacine (2 mg/ kg; Rompun, Bayer) and the lesion borders exposed for 30' to the bites of sand flies. Between 30 and 40 flies took a blood meal on each dog. The individual with the ear lesions also was exposed to colonized Lutzomyia longipalpis (n=20 engorged), the common Leishmania infantum (= L. chagasi) vector in the Americas, which is widely used as experimental vector for several Leishmania species including Leishmania (Viannia) spp. (14). Also, wild-caught Lutzomyia youngi (n=10 engorged), a natural vector of cutaneous leishmaniasis in South America, was used in the latter individual (15,16). Engorged flies were maintained on a sugar water diet, and dissected 6-7 days postfeeding, when parasites regularly multiply and migrate to the anterior midgut and stomodeal valve (17). Results Although no amastigotes were detected in either dog by microscopic examination of dermal scrapings, promastigotes readily grew in Senekjie s culture medium after one week of incubation at 25 C. Both isolates were identified as Leishmania braziliensis using a panel of monoclonal antibodies that discriminates between different species of the subgenus Viannia (18). No gut infections with Leishmania promastigotes were detected in any of the sand flies fed on either dog upon individual dissection of the flies. Only the dog with ear lesions was available for treatment, and based on previous reports of successful local therapy we decided to apply a similar approach. Between 1 and 2 ml of meglumine antimoniate (Glucantime ) were injected subcutaneously at different sites around and under the lesions. Although only one injection 250
4 Biomédica 2006;26(Supl.1): CUTANEOUS LEISHMANIASIS IN COLOMBIAN DOGS Figure 1. Cutaneous leishmaniasis due to Leishmania (Viannia) braziliensis in a mongrel dog. A primary ulcer and small satellite lesion (arrow) on the external surface of the ear were present at the time of diagnosis (left). Clinical cure was achieved in approximately 6 weeks after a single peri-lesional injection of pentavalent antimony was applied (right). was applied, the ulcers began to heal 15 days after treatment and clinical resolution was achieved in approximately 6 weeks, with hair regrowth and only a small, flat scar (figure 1b). Aspirates from the scar obtained at this time point were negative by culture; no clinical follow-up of this individual was possible beyond this period. Discussion The results suggest that despite the fact that canines are susceptible to L. braziliensis, developing cutaneous lesions, their reservoir status in American cutaneous leishmaniasis should be evaluated in greater detail if control measures targeted at this species are to be applied. Vexenat et al. (19) were capable of infecting a low proportion of Lutzomyia whitmani ( %) by feeding them on the lesions of 3/9 dogs naturally infected with L. braziliensis. It is conceivable that our negative results were due to the low number of amastigotes present in the lesions, as suggested by the absence of parasites in the dermal scrapings. On the other hand, it is feasible that the number of sand flies fed on the dogs (<50) per xenodiagnosis was insufficient to detect truly infective individuals. More recent work in our laboratory involving patients with cutaneous leishmaniasis suggested that xenodiagnoses carried out with less than 50 engorged flies have low sensitivity, even in patients showing large numbers of amastigotes in the lesions (CIDEIM, unpublished). Therefore, negative xenodiagnoses obtained upon dissection of fewer than 50 sand flies should be interpreted with caution. Nevertheless, the observations made on these two dogs contrasted with xenodiagnoses performed on dogs infected with L. infantum in which parasites are readily transmitted to sand flies, including non-natural vector species (20-22). In our case, the low reservoir competence was emphasized by the negative results obtained with Lutzomyia trapidoi, L. gomezi, and L. youngi, which are proven vectors of cutaneous leishmaniasis (13,15), and have shown to acquire Leishmania at high rates (37-44%) after feeding on laboratory animals experimentally infected with L. Viannia (23; CIDEIM unpublished). It is interesting to note that in the Pacific coast region of Colombia Leishmania (Viannia) panamensis accounts for the majority (>90%) of human cases (24), but the only two dogs that we have found with skin ulcers were infected with L. braziliensis. Although this may be a fortuitous observation, further field and experimental studies are necessary to assess dog susceptibility to 251
5 TRAVI B.L., TABARES C.J., CADENA H. Biomédica 2006;26(Supl.1): Leishmania (Viannia) spp. and establish the reservoir role in Colombian foci of American cutaneous leishmaniasis. Studies in Brazil have shown that the majority of lesions were localized on the ears (63.6% of all lesions detected), and this may have epidemiological implications because in other Leishmania species (L. infantum) we determined that transmission to sand flies was more efficient at this site than in other body areas (21,25). Systemic and local therapy for canine cutaneous leishmaniasis using pentavalent antimonials have resulted in cure rates ranging from 80.9 to 86.6%, however in the intramuscular treatment clinical resolution was followed by recurrence in a high percentage of animals (>40%) (5,25). Clinical cure, even in the absence of parasite clearance, could be beneficial to reduce potential reservoir competence. Therefore, if canines prove to be efficient sources of Leishmania for the natural vectors, treatment of skin ulcers with local injections of pentavalent antimonials could become a reasonable approach to diminish the risk of human infection in the peridomestic setting without sacrificing infected dogs. Conflict of interests The authors of the present article declare that there are no conflicts of interest that may have influenced the results of this work. Financing This study was partially supported by TMRC grant n I-P50 AI , and CIDEIM. References 1. Padilla AM, Marco JD, Diosque P, Segura MA, Mora MC, Fernández MM et al. Canine infection and the possible role of dogs in the transmission of American tegumentary leishmaniosis in Salta, Argentina. Vet Parasitol 2002;110: Sherlock IA, Maia H, Dias-Lima AG. Preliminary results of a project about the ecology of Phlebotomus vectors of cutaneous leishmaniasis in the State of Bahia. Rev Soc Bras Med Trop 1996;29: Nunes MP, Jackson JM, Carvalho RW, Furtado NJ, Coutinho SG. Serological survey for canine cutaneous and visceral leishmaniasis in areas at risk for transmission in Rio de Janeiro where prophylactic measures had been adopted. Mem Inst Oswaldo Cruz 1991;86: Aguilar CM, Rangel EF, García L, Fernández E, Momen H, Grimaldi Filho G, et al. Zoonotic cutaneous leishmaniasis due to Leishmania (Viannia) braziliensis associated with domestic animals in Venezuela and Brazil. Mem Inst Oswaldo Cruz 1990;84: Barbosa Santos EG, Marzochi MC, Conceicao NF, Brito CM, Pacheco RS. Epidemiological survey on canine population with the use of immunoleish skin test in endemic areas of human American cutaneous leishmaniasis in the State of Rio de Janeiro, Brazil. Rev Inst Med Trop Sao Paulo 1998;40: Reithinger R, Espinoza JC, Davies CR. The transmission dynamics of canine American cutaneous leishmaniasis in Huanuco, Peru. Am J Trop Med Hyg 2003; 69: Reithinger R, Canales Espinoza J, Llanos-Cuentas A, Davies CR. Domestic dog ownership: a risk factor for human infection with Leishmania (Viannia) species. Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg 2003;97: Serra CMB, Leal CA, Figueiredo F, Schubach TM, Duarte R, Uchôa CMA et al. Canine tegumentary leishmaniasis in Morada das Águias (Serra da Tiririca), Maricá, Rio de Janeiro, Brazil. Cad Saúde Pública 2003;19: Saravia NG, Holguín AF, McMahon-Pratt D, D Alessandro A. Mucocutaneous leishmaniasis in Colombia: Leishmania braziliensis subspecies diversity. Am J Trop Med Hyg 1985;34: Tesh RB. Control of zoonotic visceral leishmaniasis: is it time to change strategies? Am J Trop Med Hyg 1995;52: Reithinger R, Davies CR. Is the domestic dog (Canis familiaris) a reservoir host of American cutaneous leishmaniasis? A critical review of the current evidence. Am J Trop Med Hyg 1999;61: Escobar MA, Martínez F, Scout Smith D, Palma GI. American cutaneous leishmaniasis (tegumentary): a diagnostic challenge. Trop Doc 1992;22(Suppl.1): Travi BL, Montoya J, Solarte Y, Lozano L, Jaramillo C. Leishmaniasis in Colombia. I. Studies on the phlebotomine fauna associated with endemic foci in the Pacific Coast region. Am J Trop Med Hyg 1988;39: Da Silva AL, Williams P, Melo MN, Mayrink W. Susceptibility of laboratory-reared female Lutzomyia longipalpis (Lutz & Neiva, 1912) to infection by different species and strains of Leishmania Ross, Mem Inst Oswaldo Cruz 1990;85: Feliciangeli MD. Vectors of leishmaniases in Venezuela. Parassitologia 1991;33(Suppl): Rojas E, Scorza JV. Xenodiagnóstico con Lutzomyia youngi en casos venezolanos de leishmaniasis cutánea por Leishmania braziliensis. Mem Inst Oswaldo Cruz 1989;84:
6 Biomédica 2006;26(Supl.1): CUTANEOUS LEISHMANIASIS IN COLOMBIAN DOGS 17. Walters LL. Leishmania differentiation in natural and unnatural sand fly hosts. J Eukaryot Microbiol 1993;40: McMahon-Pratt D, Bennett E, David JR. Monoclonal antibodies that distinguish subspecies of Leishmania braziliensis. J Immunol 1982;129: Vexenat JA, Barretto AC, Rosa A de C. Experimental infection of Lutzomyia whitmani in dogs infected with Leishmania braziliensis braziliensis. Mem Inst Oswaldo Cruz 1986;81: Molina R, Amela C, Nieto J, San Andrés M, González F, Castillo JA, et al. Infectivity of dogs naturally infected with Leishmania infantum to colonized Phlebotomus perniciosus. Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg 1994;88: Travi BL, Tabares CJ, Cadena H, Ferro C, Osorio Y. Canine visceral leishmaniasis in Colombia: relationship between clinical and parasitological status, and infectivity to sand flies. Am J Trop Med Hyg 2001;64: Travi BL, Ferro C, Cadena H, Montoya-Lerma J, Adler GH. Canine visceral leishmaniasis: dog infectivity to sand flies from non-endemic areas. Res Vet Sci 2002;72: Jaramillo C, Travi BL, Montoya J. Vector competence of some Neotropical sandflies for the Leishmania (Viannia) braziliensis complex. Med Vet Entomol 1994;8: Weigle KA, Saravia NG, de Davalos M, Moreno LH, D Alessandro A. Leishmania braziliensis from the Pacific coast region of Colombia: foci of transmission, clinical spectrum and isoenzyme phenotypes. Am J Trop Med Hyg 1986;35: Pirmez C, Coutinho SG, Marzochi MC, Nunes MP, Grimaldi G Jr. Canine american cutaneous leishmaniasis: a clinical and immunological study in dogs naturally infected with Leishmania braziliensis braziliensis in an endemic area of Rio de Janeiro, Brazil. Am J Trop Med Hyg 1988;38:
Downloaded from:
 Campbell-Lendrum, D; Dujardin, JP; Martinez, E; Feliciangeli, MD; Perez, JE; de Silans, L; Desjeux, P (2001) Domestic and peridomestic transmission of American cutaneous leishmaniasis: Changing epidemiological
Campbell-Lendrum, D; Dujardin, JP; Martinez, E; Feliciangeli, MD; Perez, JE; de Silans, L; Desjeux, P (2001) Domestic and peridomestic transmission of American cutaneous leishmaniasis: Changing epidemiological
Evidence for Leishmania (Viannia) Parasites in the Skin and Blood of Patients Before and After Treatment
 MAJOR ARTICLE Evidence for Leishmania (Viannia) Parasites in the Skin and Blood of Patients Before and After Treatment Carolina Vergel, Ricardo Palacios, a Horacio Cadena, Claudia Jimena Posso, Liliana
MAJOR ARTICLE Evidence for Leishmania (Viannia) Parasites in the Skin and Blood of Patients Before and After Treatment Carolina Vergel, Ricardo Palacios, a Horacio Cadena, Claudia Jimena Posso, Liliana
Susceptibility of Spiny Rats (Proechimys semispinosus) to Leishmania (Viannia) panamensis and Leishmania (Leishmania) chagasi
 Mem Inst Oswaldo Cruz, Rio de Janeiro, Vol. 97(6): 887-892, September 2002 887 Susceptibility of Spiny Rats (Proechimys semispinosus) to Leishmania (Viannia) panamensis and Leishmania (Leishmania) chagasi
Mem Inst Oswaldo Cruz, Rio de Janeiro, Vol. 97(6): 887-892, September 2002 887 Susceptibility of Spiny Rats (Proechimys semispinosus) to Leishmania (Viannia) panamensis and Leishmania (Leishmania) chagasi
data indicating a 31% efficacy in northwest Colombia. 6
 Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg., 64(3, 4), 2001, pp. 187 193 Copyright 2001 by The American Society of Tropical Medicine and Hygiene TREATMENT FAILURE IN CHILDREN IN A RANDOMIZED CLINICAL TRIAL WITH 10 AND 20 DAYS
Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg., 64(3, 4), 2001, pp. 187 193 Copyright 2001 by The American Society of Tropical Medicine and Hygiene TREATMENT FAILURE IN CHILDREN IN A RANDOMIZED CLINICAL TRIAL WITH 10 AND 20 DAYS
Biomédica ISSN: Instituto Nacional de Salud Colombia
 Biomédica ISSN: 0120-4157 biomedica@ins.gov.co Instituto Nacional de Salud Colombia Adler, Gregory H.; Becerra, María Teresa; Travi, Bruno L. Feeding success of Lutzomyia evans(diptera: Psychodidae) experimentally
Biomédica ISSN: 0120-4157 biomedica@ins.gov.co Instituto Nacional de Salud Colombia Adler, Gregory H.; Becerra, María Teresa; Travi, Bruno L. Feeding success of Lutzomyia evans(diptera: Psychodidae) experimentally
Neglected Diseases (NDs) Landscape in Brazil and South America
 Frontiers in Science on Neglected Diseases 13 th November 2014 Neglected Diseases (NDs) Landscape in Brazil and South America Jeffrey Shaw São Paulo University Biomedical Sciences Institute jeffreyj@usp.br
Frontiers in Science on Neglected Diseases 13 th November 2014 Neglected Diseases (NDs) Landscape in Brazil and South America Jeffrey Shaw São Paulo University Biomedical Sciences Institute jeffreyj@usp.br
Lesion aspirate culture for the diagnosis and isolation of Leishmania spp. from patients with cutaneous leishmaniasis
 62 Mem Inst Oswaldo Cruz, Rio de Janeiro, Vol. 104(1): 62-66, February 2009 Lesion aspirate culture for the diagnosis and isolation of Leishmania spp. from patients with cutaneous leishmaniasis Zélia Maria
62 Mem Inst Oswaldo Cruz, Rio de Janeiro, Vol. 104(1): 62-66, February 2009 Lesion aspirate culture for the diagnosis and isolation of Leishmania spp. from patients with cutaneous leishmaniasis Zélia Maria
Etiologic Agent of an Epidemic of Cutaneous Leishmaniasis in Tolima, Colombia
 Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg., 78(2), 2008, pp. 276 282 Copyright 2008 by The American Society of Tropical Medicine and Hygiene Etiologic Agent of an Epidemic of Cutaneous Leishmaniasis in Tolima, Colombia Isabel
Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg., 78(2), 2008, pp. 276 282 Copyright 2008 by The American Society of Tropical Medicine and Hygiene Etiologic Agent of an Epidemic of Cutaneous Leishmaniasis in Tolima, Colombia Isabel
Lutzomyia migonei is a permissive vector competent for Leishmania infantum
 Guimarães et al. Parasites & Vectors (2016) 9:159 DOI 10.1186/s13071-016-1444-2 RESEARCH Lutzomyia migonei is a permissive vector competent for Leishmania infantum Open Access Vanessa Cristina Fitipaldi
Guimarães et al. Parasites & Vectors (2016) 9:159 DOI 10.1186/s13071-016-1444-2 RESEARCH Lutzomyia migonei is a permissive vector competent for Leishmania infantum Open Access Vanessa Cristina Fitipaldi
Laboratory diagnosis of Blood and tissue flagellates
 Laboratory diagnosis of Blood and tissue flagellates (Leishmania and trypanosma) Sarah Alharbi Clinical Laboratory department Collage of Applied Medical Sciences King Saud University Leishmania and trypanosma:
Laboratory diagnosis of Blood and tissue flagellates (Leishmania and trypanosma) Sarah Alharbi Clinical Laboratory department Collage of Applied Medical Sciences King Saud University Leishmania and trypanosma:
Seasonality of Lutzomyia fairtigi (Diptera: Psychodidae: Phlebotominae), a species endemic to Eastern Colombia
 Mem Inst Oswaldo Cruz, Rio de Janeiro, Vol. 103(5): 477-482, August 2008 477 Seasonality of Lutzomyia fairtigi (Diptera: Psychodidae: Phlebotominae), a species endemic to Eastern Colombia Jorge Alberto
Mem Inst Oswaldo Cruz, Rio de Janeiro, Vol. 103(5): 477-482, August 2008 477 Seasonality of Lutzomyia fairtigi (Diptera: Psychodidae: Phlebotominae), a species endemic to Eastern Colombia Jorge Alberto
Biomédica ISSN: Instituto Nacional de Salud Colombia
 Biomédica ISSN: 0120-4157 biomedica@ins.gov.co Instituto Nacional de Salud Colombia Rojas, Carlos A.; Weigle, Kristen A.; Tovar, Rafael; Morales, Alba L.; Alexander, Bruce A multifaceted intervention to
Biomédica ISSN: 0120-4157 biomedica@ins.gov.co Instituto Nacional de Salud Colombia Rojas, Carlos A.; Weigle, Kristen A.; Tovar, Rafael; Morales, Alba L.; Alexander, Bruce A multifaceted intervention to
Recommendations for Coping with Leishmaniasis: A Review of Control Strategies. Centro de Convenções de Reboças Red Room 17: 00h
 Recommendations for Coping with Leishmaniasis: A Review of Control Strategies Centro de Convenções de Reboças 08.04.2014 Red Room 17: 00h Leishmaniasis - a Global Problem Visceral 2012 300 000 cases 20,000
Recommendations for Coping with Leishmaniasis: A Review of Control Strategies Centro de Convenções de Reboças 08.04.2014 Red Room 17: 00h Leishmaniasis - a Global Problem Visceral 2012 300 000 cases 20,000
The Most Common Parasitic Infections In Yemen. Medical Parasitology
 The Most Common Parasitic Infections In Yemen Medical Parasitology ﻓﺎﯾز اﻟﺧوﻻﻧﻲ / د 2 : is a vector-borne disease that transmitted by sandflies and caused by obligate intracellular protozoa of the genus
The Most Common Parasitic Infections In Yemen Medical Parasitology ﻓﺎﯾز اﻟﺧوﻻﻧﻲ / د 2 : is a vector-borne disease that transmitted by sandflies and caused by obligate intracellular protozoa of the genus
Case Report Development of Cutaneous Leishmaniasis after Leishmania Skin Test
 Case Reports in Medicine Volume 2011, Article ID 631079, 4 pages doi:10.1155/2011/631079 Case Report Development of Cutaneous Leishmaniasis after Leishmania Skin Test Paulo R. Machado, 1, 2 Augusto M.
Case Reports in Medicine Volume 2011, Article ID 631079, 4 pages doi:10.1155/2011/631079 Case Report Development of Cutaneous Leishmaniasis after Leishmania Skin Test Paulo R. Machado, 1, 2 Augusto M.
Development of Mathematical models predicting the density of vectors: Case of sandflies vectors of leishmaniasis
 Development of Mathematical models predicting the density of vectors: Case of sandflies vectors of leishmaniasis HABIBA MEJHED Département Génie Informatique, Ecole Nationale des sciences appliquées Université
Development of Mathematical models predicting the density of vectors: Case of sandflies vectors of leishmaniasis HABIBA MEJHED Département Génie Informatique, Ecole Nationale des sciences appliquées Université
Proceedings of the World Small Animal Veterinary Association Sydney, Australia 2007
 Proceedings of the World Small Animal Veterinary Association Sydney, Australia 2007 Hosted by: Australian Small Animal Veterinary Association (ASAVA) Australian Small Animal Veterinary Association (ASAVA)
Proceedings of the World Small Animal Veterinary Association Sydney, Australia 2007 Hosted by: Australian Small Animal Veterinary Association (ASAVA) Australian Small Animal Veterinary Association (ASAVA)
HAEMOFLAGELLATES. Dr. Anuluck Junkum Department of Parasitology Faculty of Medicine
 HAEMOFLAGELLATES Dr. Anuluck Junkum Department of Parasitology Faculty of Medicine Objective Can describe the morphology, life cycle, pathology, diagnosis and prevention of Leishmania spp. and Trypanosoma
HAEMOFLAGELLATES Dr. Anuluck Junkum Department of Parasitology Faculty of Medicine Objective Can describe the morphology, life cycle, pathology, diagnosis and prevention of Leishmania spp. and Trypanosoma
CONTROLE DAS LEISHMANIOSES O QUE FALTA FAZER? Centro de Convenções de Reboças Red Room 17: 00h
 CONTROLE DAS LEISHMANIOSES O QUE FALTA FAZER? Centro de Convenções de Reboças 08.04.2014 Red Room 17: 00h Leishmaniasis - a Global Problem Visceral 2012 300 000 cases 20,000 deaths (6.7%) 310 million at
CONTROLE DAS LEISHMANIOSES O QUE FALTA FAZER? Centro de Convenções de Reboças 08.04.2014 Red Room 17: 00h Leishmaniasis - a Global Problem Visceral 2012 300 000 cases 20,000 deaths (6.7%) 310 million at
Intralesional meglumine antimoniate for the treatment of localised cutaneous leishmaniasis: a retrospective review of a Brazilian referral centre
 512 Mem Inst Oswaldo Cruz, Rio de Janeiro, Vol. 111(8): 512-516, August 2016 Intralesional meglumine antimoniate for the treatment of localised cutaneous leishmaniasis: a retrospective review of a Brazilian
512 Mem Inst Oswaldo Cruz, Rio de Janeiro, Vol. 111(8): 512-516, August 2016 Intralesional meglumine antimoniate for the treatment of localised cutaneous leishmaniasis: a retrospective review of a Brazilian
Use of PCR RFLP to identify Leishmania species in naturally-infected dogs
 Veterinary Parasitology 140 (2006) 231 238 www.elsevier.com/locate/vetpar Use of PCR RFLP to identify Leishmania species in naturally-infected dogs Hélida Monteiro de Andrade a, *, Alexandre Barbosa Reis
Veterinary Parasitology 140 (2006) 231 238 www.elsevier.com/locate/vetpar Use of PCR RFLP to identify Leishmania species in naturally-infected dogs Hélida Monteiro de Andrade a, *, Alexandre Barbosa Reis
Serological tests fail to discriminate dogs with visceral leishmaniasis that transmit Leishmania infantum to the vector Lutzomyia longipalpis
 Rev Soc Bras Med Trop 50(4):483-488, July-August, 2017 doi: 10.1590/0037-8682-0014-2017 Major Article Serological tests fail to discriminate dogs with visceral leishmaniasis that transmit Leishmania infantum
Rev Soc Bras Med Trop 50(4):483-488, July-August, 2017 doi: 10.1590/0037-8682-0014-2017 Major Article Serological tests fail to discriminate dogs with visceral leishmaniasis that transmit Leishmania infantum
Welcome to the Jungle! Dr Aileen Oon, 2017 Microbiology Registrar
 Welcome to the Jungle! Dr Aileen Oon, 2017 Microbiology Registrar AA 55M presented with sores on left olecranon and umbilical area Umbilical sores present for 3 weeks Left olecranon lesions for 1 week
Welcome to the Jungle! Dr Aileen Oon, 2017 Microbiology Registrar AA 55M presented with sores on left olecranon and umbilical area Umbilical sores present for 3 weeks Left olecranon lesions for 1 week
BIO Parasitology Spring 2009
 BIO 475 - Parasitology Spring 2009 Stephen M. Shuster Northern Arizona University http://www4.nau.edu/isopod Lecture 5 Discovery of the Disease In 1924 the Kala-Azar Commission noted that the distribution
BIO 475 - Parasitology Spring 2009 Stephen M. Shuster Northern Arizona University http://www4.nau.edu/isopod Lecture 5 Discovery of the Disease In 1924 the Kala-Azar Commission noted that the distribution
Prevalence of Cutaneous Leishmaniasis among HIV and Non-HIV Patients attending some Selected Hospitals in Jos Plateau State
 International Journal of Current Microbiology and Applied Sciences ISSN: 2319-7706 Volume 7 Number 06 (2018) Journal homepage: http://www.ijcmas.com Original Research Article https://doi.org/10.20546/ijcmas.2018.706.307
International Journal of Current Microbiology and Applied Sciences ISSN: 2319-7706 Volume 7 Number 06 (2018) Journal homepage: http://www.ijcmas.com Original Research Article https://doi.org/10.20546/ijcmas.2018.706.307
Survey of Wild Mammal Hosts of Cutaneous Leishmaniasis Parasites in Panamá and Costa Rica
 Survey of Wild Mammal Hosts of Cutaneous Leishmaniasis Parasites in Panamá and Costa Rica Kadir González, Instituto Conmemorativo Gorgas de Estudios de la Salud Jose E Calzada, Instituto Conmemorativo
Survey of Wild Mammal Hosts of Cutaneous Leishmaniasis Parasites in Panamá and Costa Rica Kadir González, Instituto Conmemorativo Gorgas de Estudios de la Salud Jose E Calzada, Instituto Conmemorativo
Cutaneous Leishmaniasis : Global overview
 Cutaneous Leishmaniasis : Global overview Meeting of stakeholders for selected Health R&D Demostration Projects, 7-10 May 2014, WHO, Geneva Dr. Daniel Argaw Dagne, NTD/WHO CSR - DDC AFRO Leishmaniasis
Cutaneous Leishmaniasis : Global overview Meeting of stakeholders for selected Health R&D Demostration Projects, 7-10 May 2014, WHO, Geneva Dr. Daniel Argaw Dagne, NTD/WHO CSR - DDC AFRO Leishmaniasis
SUMMARY. Cutaneous leishmaniasis with only skin involvement: single to multiple skin ulcers, satellite lesions and nodular lymphangitis.
 SUMMARY Leishmaniasis is a disease affecting predominantly people in the developing countries; 350 million people worldwide are at risk and yearly more than 2 million new cases occur. Leishmaniasis is
SUMMARY Leishmaniasis is a disease affecting predominantly people in the developing countries; 350 million people worldwide are at risk and yearly more than 2 million new cases occur. Leishmaniasis is
Animal models for infectious diseases caused by parasites: Leishmaniasis
 Drug Discovery Today: Disease Models Vol. 1, No. 1 2004 DRUG DISCOVERY TODAY DISEASE MODELS Editors-in-Chief Jan Tornell AstraZeneca, Sweden Denis Noble University of Oxford, UK Infectious diseases Animal
Drug Discovery Today: Disease Models Vol. 1, No. 1 2004 DRUG DISCOVERY TODAY DISEASE MODELS Editors-in-Chief Jan Tornell AstraZeneca, Sweden Denis Noble University of Oxford, UK Infectious diseases Animal
Leishmania panamensis transmission in the domestic environment: the results of a prospective epidemiological survey in Santander, Colombia
 Biomédica 2006;26(Supl.1):131-44 LEISHMANIA PANAMENSIS EPIDEMIOLOGY ARTÍCULO ORIGINAL Leishmania panamensis transmission in the domestic environment: the results of a prospective epidemiological survey
Biomédica 2006;26(Supl.1):131-44 LEISHMANIA PANAMENSIS EPIDEMIOLOGY ARTÍCULO ORIGINAL Leishmania panamensis transmission in the domestic environment: the results of a prospective epidemiological survey
Detection of Leishmania in Unaffected Mucosal Tissues of Patients with Cutaneous Leishmaniasis Caused by Leishmania (Viannia) Species
 MAJOR ARTICLE Detection of Leishmania in Unaffected Mucosal Tissues of Patients with Cutaneous Leishmaniasis Caused by Leishmania (Viannia) Species Roger Adrian Figueroa, Leyder Elena Lozano, Ibeth Cristina
MAJOR ARTICLE Detection of Leishmania in Unaffected Mucosal Tissues of Patients with Cutaneous Leishmaniasis Caused by Leishmania (Viannia) Species Roger Adrian Figueroa, Leyder Elena Lozano, Ibeth Cristina
Biomédica Journal of the Instituto Nacional de Salud Volume 34, 2014
 Biomédica Journal of the Volume 34, 2014 EDITORIAL BOARD Luis Alberto Gómez Carlos Arturo Hernández Rubén Santiago Nicholls Emeritus Researcher Pan American Health Organization Brasilia, Brazil Enrique
Biomédica Journal of the Volume 34, 2014 EDITORIAL BOARD Luis Alberto Gómez Carlos Arturo Hernández Rubén Santiago Nicholls Emeritus Researcher Pan American Health Organization Brasilia, Brazil Enrique
Treatment of Cutaneous Leishmaniasis with Allopurinol and Stibogluconate
 165 Treatment of Cutaneous Leishmaniasis with Allopurinol and S. Martinez, M. Gonzalez, and M. E. Vernaza From the Department of Internal Medicine, University of Cauca, Popayan, and the University Hospital
165 Treatment of Cutaneous Leishmaniasis with Allopurinol and S. Martinez, M. Gonzalez, and M. E. Vernaza From the Department of Internal Medicine, University of Cauca, Popayan, and the University Hospital
Analysis of Enhancing Effect of Sand Fly Saliva on Leishmania Infection in Mice
 INFCTION AND IMMUNITY, May 1991, p. 1592-1598 19-9567/91/51592-7$2./ Copyright X) 1991, American Society for Microbiology Vol. 59, No. 5 Analysis of nhancing ffect of Sand Fly Saliva on Leishmania Infection
INFCTION AND IMMUNITY, May 1991, p. 1592-1598 19-9567/91/51592-7$2./ Copyright X) 1991, American Society for Microbiology Vol. 59, No. 5 Analysis of nhancing ffect of Sand Fly Saliva on Leishmania Infection
Leishmaniasis. CDR R.L. Gutierrez Oct 2014
 Leishmaniasis CDR R.L. Gutierrez Oct 2014 Overview Protozoan parasite(s) of tissue and WBCs Many species / Many Syndromes (Cutaneous / Visceral) Pathogen: Location - Old World vs. New World Host: Immune
Leishmaniasis CDR R.L. Gutierrez Oct 2014 Overview Protozoan parasite(s) of tissue and WBCs Many species / Many Syndromes (Cutaneous / Visceral) Pathogen: Location - Old World vs. New World Host: Immune
Clinical Picture of Cutaneous Leishmaniases Due to Leishmania (Leishmania) mexicana in the Yucatan Peninsula, Mexico
 Mem Inst Oswaldo Cruz, Rio de Janeiro, Vol. 96(2): 163-167, February 2001 Clinical Picture of Cutaneous Leishmaniases Due to Leishmania (Leishmania) mexicana in the Yucatan Peninsula, Mexico Fernando J
Mem Inst Oswaldo Cruz, Rio de Janeiro, Vol. 96(2): 163-167, February 2001 Clinical Picture of Cutaneous Leishmaniases Due to Leishmania (Leishmania) mexicana in the Yucatan Peninsula, Mexico Fernando J
Leishmaniasis: A forgotten disease among neglected people
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Health Volume 11 Number 2 Leishmaniasis: A forgotten disease among neglected people Y Homsi, G Makdisi Citation Y Homsi, G Makdisi. Leishmaniasis: A forgotten disease
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Health Volume 11 Number 2 Leishmaniasis: A forgotten disease among neglected people Y Homsi, G Makdisi Citation Y Homsi, G Makdisi. Leishmaniasis: A forgotten disease
Leishmaniasis, Kala Azar(The Black Fever)
 Leishmaniasis, Kala Azar(The Black Fever) By Lawrence Hall Etiologic agent Protist obligate intracellular parasite, Transmission Vectors Phylum: Euglenozoa (genus Leishmania) Over 21 species that infect
Leishmaniasis, Kala Azar(The Black Fever) By Lawrence Hall Etiologic agent Protist obligate intracellular parasite, Transmission Vectors Phylum: Euglenozoa (genus Leishmania) Over 21 species that infect
Animal Models of Leishmaniasis Relevant to Vaccine Development. David Sacks Laboratory of Parasitic Diseases NIAID, NIH
 Animal Models of Leishmaniasis Relevant to Vaccine Development David Sacks Laboratory of Parasitic Diseases NIAID, NIH Leishmaniasis: A spectrum of diseases associated with a diversity of parasite species,
Animal Models of Leishmaniasis Relevant to Vaccine Development David Sacks Laboratory of Parasitic Diseases NIAID, NIH Leishmaniasis: A spectrum of diseases associated with a diversity of parasite species,
Leishmaniasis. MAJ Kris Paolino September 2014
 Leishmaniasis MAJ Kris Paolino September 2014 Thanks to COL (Ret) Kent Kester MAJ Leyi Lin http://www.niaid.nih.gov/topics/leishmaniasis History Sir William Boog Leishman (1865-1926) Matriculated at the
Leishmaniasis MAJ Kris Paolino September 2014 Thanks to COL (Ret) Kent Kester MAJ Leyi Lin http://www.niaid.nih.gov/topics/leishmaniasis History Sir William Boog Leishman (1865-1926) Matriculated at the
Ana Maria Marassá [1], Eunice Aparecida Bianchi Galati [2], Denise Pimentel Bergamaschi [3] and Cleide Aschenbrenner Consales [4] INTRODUCTION METHODS
![Ana Maria Marassá [1], Eunice Aparecida Bianchi Galati [2], Denise Pimentel Bergamaschi [3] and Cleide Aschenbrenner Consales [4] INTRODUCTION METHODS Ana Maria Marassá [1], Eunice Aparecida Bianchi Galati [2], Denise Pimentel Bergamaschi [3] and Cleide Aschenbrenner Consales [4] INTRODUCTION METHODS](/thumbs/74/70176367.jpg) Revista da Sociedade Brasileira de Medicina Tropical 46(5):547-554, Sep-Oct, 2013 http://dx.doi.org/10.1590/0037-8682-0168-2013 Major Case Report Article Blood feeding patterns of Nyssomyia intermedia
Revista da Sociedade Brasileira de Medicina Tropical 46(5):547-554, Sep-Oct, 2013 http://dx.doi.org/10.1590/0037-8682-0168-2013 Major Case Report Article Blood feeding patterns of Nyssomyia intermedia
Natural infection of Didelphis aurita (Mammalia: Marsupialia) with Leishmania infantum in Brazil
 Carreira et al. Parasites & Vectors 2012, 5:111 RESEARCH Open Access Natural infection of Didelphis aurita (Mammalia: Marsupialia) with Leishmania infantum in Brazil João Carlos Araujo Carreira 1, Alba
Carreira et al. Parasites & Vectors 2012, 5:111 RESEARCH Open Access Natural infection of Didelphis aurita (Mammalia: Marsupialia) with Leishmania infantum in Brazil João Carlos Araujo Carreira 1, Alba
New insights on leishmaniasis in immunosuppressive conditions
 New insights on leishmaniasis in immunosuppressive conditions Javier Moreno Immunoparasitology Unit WHO Collaborative Center for Leishmaniasis Centro Nacional de Microbiología INSTITUTO DE SALUD CARLOS
New insights on leishmaniasis in immunosuppressive conditions Javier Moreno Immunoparasitology Unit WHO Collaborative Center for Leishmaniasis Centro Nacional de Microbiología INSTITUTO DE SALUD CARLOS
Canine leishmaniosis new concepts and insights on an expanding zoonosis: part two
 Review Canine leishmaniosis new concepts and insights on an expanding zoonosis: part two Guadalupe Miró 1*, Luis Cardoso 2*, Maria Grazia Pennisi 3*, Gaetano Oliva 4* and Gad Baneth 5* 1 Departmento de
Review Canine leishmaniosis new concepts and insights on an expanding zoonosis: part two Guadalupe Miró 1*, Luis Cardoso 2*, Maria Grazia Pennisi 3*, Gaetano Oliva 4* and Gad Baneth 5* 1 Departmento de
FAMILIAL AGGREGATION OF MUCOSAL LEISHMANIASIS IN NORTHEAST BRAZIL
 Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg., 73(1), 2005, pp. 69 73 Copyright 2005 by The American Society of Tropical Medicine and Hygiene FAMILIAL AGGREGATION OF MUCOSAL LEISHMANIASIS IN NORTHEAST BRAZIL LÉA CASTELLUCCI,*
Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg., 73(1), 2005, pp. 69 73 Copyright 2005 by The American Society of Tropical Medicine and Hygiene FAMILIAL AGGREGATION OF MUCOSAL LEISHMANIASIS IN NORTHEAST BRAZIL LÉA CASTELLUCCI,*
The epidemiology and control of leishmaniasis in Andean countries. Epidemiologia e controle da leishmaniose nos países andinos
 REVISÃO REVIEW 925 The epidemiology and control of leishmaniasis in Andean countries Epidemiologia e controle da leishmaniose nos países andinos Clive Richard Davies 1 Richard Reithinger 1 Diarmid Campbell-Lendrum
REVISÃO REVIEW 925 The epidemiology and control of leishmaniasis in Andean countries Epidemiologia e controle da leishmaniose nos países andinos Clive Richard Davies 1 Richard Reithinger 1 Diarmid Campbell-Lendrum
Intralesional Infiltration with Meglumine Antimoniate for the Treatment of Leishmaniasis Recidiva Cutis in Ecuador
 In order to provide our readers with timely access to new content, papers accepted by the American Journal of Tropical Medicine and Hygiene are posted online ahead of print publication. Papers that have
In order to provide our readers with timely access to new content, papers accepted by the American Journal of Tropical Medicine and Hygiene are posted online ahead of print publication. Papers that have
Series Editors Samuel J. Black, University of Massachusetts, Amherst, MA, US.A. J. Richard Seed, University of North Carolina, Chapel Hill, NC, US.A.
 LEISHMANIA World Class Parasites VOLUME 4 Volumes in the World Class Parasites book series are written for researchers, students and scholars who enjoy reading about excellent research on problems of global
LEISHMANIA World Class Parasites VOLUME 4 Volumes in the World Class Parasites book series are written for researchers, students and scholars who enjoy reading about excellent research on problems of global
Leishmania and Human Immunodeficiency Virus Coinfection: the First 10 Years
 CLINICAL MICROBIOLOGY REVIEWS, Apr. 1997, p. 298 319 Vol. 10, No. 2 0893-8512/97/$04.00 0 Copyright 1997, American Society for Microbiology Leishmania and Human Immunodeficiency Virus Coinfection: the
CLINICAL MICROBIOLOGY REVIEWS, Apr. 1997, p. 298 319 Vol. 10, No. 2 0893-8512/97/$04.00 0 Copyright 1997, American Society for Microbiology Leishmania and Human Immunodeficiency Virus Coinfection: the
Subclinical Form of the American Visceral Leishmaniasis
 Mem Inst Oswaldo Cruz, Rio de Janeiro, Vol. 99(8): 889-893, December 2004 889 Subclinical Form of the American Visceral Leishmaniasis Mônica Elinor Alves Gama/ +, Jackson Maurício Lopes Costa*, Cláudia
Mem Inst Oswaldo Cruz, Rio de Janeiro, Vol. 99(8): 889-893, December 2004 889 Subclinical Form of the American Visceral Leishmaniasis Mônica Elinor Alves Gama/ +, Jackson Maurício Lopes Costa*, Cláudia
Acta Dermatovenerol Croat 2008;16(2):60-64 CLINICAL ARTICLE
 2008;16(2):60-64 CLINICAL ARTICLE Clinical Efficacy of Intramuscular Meglumine Antimoniate Alone and in Combination with Intralesional Meglumine Antimoniate in the Treatment of Old World Cutaneous Leishmaniasis
2008;16(2):60-64 CLINICAL ARTICLE Clinical Efficacy of Intramuscular Meglumine Antimoniate Alone and in Combination with Intralesional Meglumine Antimoniate in the Treatment of Old World Cutaneous Leishmaniasis
Challenges for Latin America s. Information on Drug Consumption
 Challenges for Latin America s Information on Drug Consumption Fatima Marinho, MD, MPH, PHD Coordinator of Information and Health Analysis - PAHO International Day against Drug Abuse & Illicit Trafficking
Challenges for Latin America s Information on Drug Consumption Fatima Marinho, MD, MPH, PHD Coordinator of Information and Health Analysis - PAHO International Day against Drug Abuse & Illicit Trafficking
Variables associated with the post-treatment healing of lesions in patients with American cutaneous leishmaniasis in Paraná State, Brazil
 Brazilian Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences vol. 45, n. 4, oct./dec., 2009 Article Variables associated with the post-treatment healing of lesions in patients with American cutaneous leishmaniasis in
Brazilian Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences vol. 45, n. 4, oct./dec., 2009 Article Variables associated with the post-treatment healing of lesions in patients with American cutaneous leishmaniasis in
Leishmania (Viannia) naiffi: rare enough to be neglected?
 Mem Inst Oswaldo Cruz, Rio de Janeiro, Vol. 0(): 9-800, September 05 9 Leishmania (Viannia) naiffi: rare enough to be neglected? Giselle Aparecida Fagundes-Silva, Gustavo Adolfo Sierra Romero, Elisa Cupolillo
Mem Inst Oswaldo Cruz, Rio de Janeiro, Vol. 0(): 9-800, September 05 9 Leishmania (Viannia) naiffi: rare enough to be neglected? Giselle Aparecida Fagundes-Silva, Gustavo Adolfo Sierra Romero, Elisa Cupolillo
Kinetoplastids Handout
 Kinetoplastids Handout 1 Kinetoplastids widespread group of flagellated protozoa parasitize virtually all animal groups as well as plants and insects 3 distinct kinetoplastid species cause human disease
Kinetoplastids Handout 1 Kinetoplastids widespread group of flagellated protozoa parasitize virtually all animal groups as well as plants and insects 3 distinct kinetoplastid species cause human disease
International Journal of Integrative Biology A journal for biology beyond borders ISSN
 Research International Journal of Integrative Biology A journal for biology beyond borders ISSN 0973-8363 Infectivity of Leishmania infantum treated with amphotericin B plus Phlebotomus salivary gland
Research International Journal of Integrative Biology A journal for biology beyond borders ISSN 0973-8363 Infectivity of Leishmania infantum treated with amphotericin B plus Phlebotomus salivary gland
The Harvard community has made this article openly available. Please share how this access benefits you. Your story matters.
 Maxadilan-simile expression in Nyssomyia neivai, a sandfly vector in an endemic region of Brazil, and its immunogenicity in patients with American tegumentary leishmaniasis The Harvard community has made
Maxadilan-simile expression in Nyssomyia neivai, a sandfly vector in an endemic region of Brazil, and its immunogenicity in patients with American tegumentary leishmaniasis The Harvard community has made
Leishmaniasis in the WhO european region
 Leishmaniasis in the WhO european region This information leaflet contains six sections and is intended for a generic and public health audience: 1.Leishmaniasis is present in europe. What are the risks
Leishmaniasis in the WhO european region This information leaflet contains six sections and is intended for a generic and public health audience: 1.Leishmaniasis is present in europe. What are the risks
Proven and putative vectors of American cutaneous leishmaniasis in Brazil: aspects of their biology and vectorial competence
 Mem Inst Oswaldo Cruz, Rio de Janeiro, Vol. 104(7): 937-954, November 2009 937 Proven and putative vectors of American cutaneous leishmaniasis in Brazil: aspects of their biology and vectorial competence
Mem Inst Oswaldo Cruz, Rio de Janeiro, Vol. 104(7): 937-954, November 2009 937 Proven and putative vectors of American cutaneous leishmaniasis in Brazil: aspects of their biology and vectorial competence
Evaluation of Change in Canine Diagnosis Protocol Adopted by the Visceral Leishmaniasis Control Program in Brazil and a New Proposal for Diagnosis
 Evaluation of Change in Canine Diagnosis Protocol Adopted by the Visceral Leishmaniasis Control Program in Brazil and a New Proposal for Diagnosis Wendel Coura-Vital 1,2,7, Henrique Gama Ker 1,3, Bruno
Evaluation of Change in Canine Diagnosis Protocol Adopted by the Visceral Leishmaniasis Control Program in Brazil and a New Proposal for Diagnosis Wendel Coura-Vital 1,2,7, Henrique Gama Ker 1,3, Bruno
Case Report Occupationally Acquired American Cutaneous Leishmaniasis
 Case Reports in Dermatological Medicine Volume 2012, Article ID 279517, 4 pages doi:10.1155/2012/279517 Case Report Occupationally Acquired American Cutaneous Leishmaniasis Maria Edileuza Felinto de Brito,
Case Reports in Dermatological Medicine Volume 2012, Article ID 279517, 4 pages doi:10.1155/2012/279517 Case Report Occupationally Acquired American Cutaneous Leishmaniasis Maria Edileuza Felinto de Brito,
Persistence of Leishmania Parasites in Scars after Clinical Cure of American Cutaneous Leishmaniasis: Is There a Sterile Cure?
 MAJOR ARTICLE Persistence of Leishmania Parasites in Scars after Clinical Cure of American Cutaneous Leishmaniasis: Is There a Sterile Cure? Mitzi G. Mendonça, 1,a Maria E. F de Brito, 2 Eduardo H. G.
MAJOR ARTICLE Persistence of Leishmania Parasites in Scars after Clinical Cure of American Cutaneous Leishmaniasis: Is There a Sterile Cure? Mitzi G. Mendonça, 1,a Maria E. F de Brito, 2 Eduardo H. G.
World Health Organization Department of Communicable Disease Surveillance and Response
 WHO Report on Global Surveillance of Epidemic-prone Infectious Diseases World Health Organization Department of Communicable Disease Surveillance and Response This document has been downloaded from the
WHO Report on Global Surveillance of Epidemic-prone Infectious Diseases World Health Organization Department of Communicable Disease Surveillance and Response This document has been downloaded from the
NIH Public Access Author Manuscript Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg. Author manuscript; available in PMC 2013 June 01.
 NIH Public Access Author Manuscript Published in final edited form as: Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg. 2012 June ; 106(6): 376 381. doi:10.1016/j.trstmh.2012.03.007. A proposed new clinical staging system for
NIH Public Access Author Manuscript Published in final edited form as: Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg. 2012 June ; 106(6): 376 381. doi:10.1016/j.trstmh.2012.03.007. A proposed new clinical staging system for
Montenegro s skin reactions and antibodies against different Leishmania species in dogs from a visceral leishmaniosis endemic area
 Veterinary Parasitology 139 (2006) 21 28 www.elsevier.com/locate/vetpar Montenegro s skin reactions and antibodies against different Leishmania species in dogs from a visceral leishmaniosis endemic area
Veterinary Parasitology 139 (2006) 21 28 www.elsevier.com/locate/vetpar Montenegro s skin reactions and antibodies against different Leishmania species in dogs from a visceral leishmaniosis endemic area
Antibodies against Lutzomyia longipalpis saliva in the fox Cerdocyon thous and the sylvatic cycle of Leishmania chagasi
 Transactions of the Royal Society of Tropical Medicine and Hygiene (2007) 101, 127 133 available at www.sciencedirect.com journal homepage: www.elsevierhealth.com/journals/trst Antibodies against Lutzomyia
Transactions of the Royal Society of Tropical Medicine and Hygiene (2007) 101, 127 133 available at www.sciencedirect.com journal homepage: www.elsevierhealth.com/journals/trst Antibodies against Lutzomyia
Blood Smears Only 6 October Sample Preparation and Quality Control 15B-K
 NEW YORK STATE Parasitology Proficiency Testing Program Blood Smears Only 6 October 5 The purpose of the New York State Proficiency Testing Program in the category of Parasitology - Blood Smears Only is
NEW YORK STATE Parasitology Proficiency Testing Program Blood Smears Only 6 October 5 The purpose of the New York State Proficiency Testing Program in the category of Parasitology - Blood Smears Only is
Visceral leishmaniasis: an endemic disease with global impact
 Visceral leishmaniasis: an endemic disease with global impact Professor Olivier Lortholary, MD, PhD Department of Infectious and Tropical diseases Hôpital Necker-Enfants Malades Université Paris Descartes
Visceral leishmaniasis: an endemic disease with global impact Professor Olivier Lortholary, MD, PhD Department of Infectious and Tropical diseases Hôpital Necker-Enfants Malades Université Paris Descartes
Epidemiological Study of Cutaneous Leishmaniasis in Tuz
 International Journal of Current Microbiology and Applied Sciences ISSN: 2319-7706 Volume 6 Number 1 (2017) pp. 477-483 Journal homepage: http://www.ijcmas.com Original Research Article http://dx.doi.org/10.20546/ijcmas.2017.601.056
International Journal of Current Microbiology and Applied Sciences ISSN: 2319-7706 Volume 6 Number 1 (2017) pp. 477-483 Journal homepage: http://www.ijcmas.com Original Research Article http://dx.doi.org/10.20546/ijcmas.2017.601.056
Antigen-triggered interferon-γ and interleukin-10 pattern in cured mucosal leishmaniasis patients is shaped during the active phase of disease
 bs_bs_banner Clinical and Experimental Immunology ORIGINAL ARTICLE doi:1.1111/cei.12364 Antigen-triggered interferon-γ and interleukin-1 pattern in cured mucosal leishmaniasis patients is shaped during
bs_bs_banner Clinical and Experimental Immunology ORIGINAL ARTICLE doi:1.1111/cei.12364 Antigen-triggered interferon-γ and interleukin-1 pattern in cured mucosal leishmaniasis patients is shaped during
Sodium Stibogluconate treatment for cutaneous leishmaniasis: A clinical study of 43 cases from the north of Jordan
 Sodium Stibogluconate treatment for cutaneous leishmaniasis: A clinical study of 43 cases from the north of Jordan Mamoun Mohammad Al-Athamneh Hiathem Qasem Abu Al-haija Ra ed Smadi Ayman S. Qaqaa Heba
Sodium Stibogluconate treatment for cutaneous leishmaniasis: A clinical study of 43 cases from the north of Jordan Mamoun Mohammad Al-Athamneh Hiathem Qasem Abu Al-haija Ra ed Smadi Ayman S. Qaqaa Heba
Control of leishmaniasis
 SIXTIETH WORLD HEALTH ASSEMBLY A60/10 Provisional agenda item 12.3 22 March 2007 Control of leishmaniasis Report by the Secretariat BACKGROUND 1. Leishmaniasis is endemic in 88 countries in the world and
SIXTIETH WORLD HEALTH ASSEMBLY A60/10 Provisional agenda item 12.3 22 March 2007 Control of leishmaniasis Report by the Secretariat BACKGROUND 1. Leishmaniasis is endemic in 88 countries in the world and
Miltefosine for New World Cutaneous Leishmaniasis
 MAJOR ARTICLE for New World Cutaneous sis J. Soto, 1 B. A. Arana, 4 J. Toledo, 1 N. Rizzo, 4 J. C. Vega, 2 A. Diaz, 4 M. Luz, 1 P. Gutierrez, 1 M. Arboleda, 3 J. D. Berman, 6,a K. Junge, 5 J. Engel, 5
MAJOR ARTICLE for New World Cutaneous sis J. Soto, 1 B. A. Arana, 4 J. Toledo, 1 N. Rizzo, 4 J. C. Vega, 2 A. Diaz, 4 M. Luz, 1 P. Gutierrez, 1 M. Arboleda, 3 J. D. Berman, 6,a K. Junge, 5 J. Engel, 5
Masson Paris 198S. Ann. Parasitol. Hum. Comp., , n 2, pp
 Masson Paris 198S. Ann. Parasitol. Hum. Comp., 1988 63, n 2, pp. 134-145. OBSERVATIONS ON THE DEVELOPMENT OF LEISHMANIA (L.) CHAGASI CUNHA AND CHAGAS IN THE MIDGUT OF THE SANDFLY VECTOR LUTZOMYIA LONGIPALPIS
Masson Paris 198S. Ann. Parasitol. Hum. Comp., 1988 63, n 2, pp. 134-145. OBSERVATIONS ON THE DEVELOPMENT OF LEISHMANIA (L.) CHAGASI CUNHA AND CHAGAS IN THE MIDGUT OF THE SANDFLY VECTOR LUTZOMYIA LONGIPALPIS
New Insights into Diagnosing Leishmaniasis
 New Insights into Diagnosing Leishmaniasis Eric Zini Snow meeting, 13 March 2009 Climate Variability and Visceral Leishmaniasis in Europe WHO/TDR, Jan. 2008 Late Eighties Maroli et al., Trop Med Int Health
New Insights into Diagnosing Leishmaniasis Eric Zini Snow meeting, 13 March 2009 Climate Variability and Visceral Leishmaniasis in Europe WHO/TDR, Jan. 2008 Late Eighties Maroli et al., Trop Med Int Health
~Trichinella Spiralis:
 Musculoskeletal System **Today we are going to talk about the parasites that affect the musculoskeletal system ~Trichinella Spiralis: It s a small nematode that measures to about 2-3mm in length. In general
Musculoskeletal System **Today we are going to talk about the parasites that affect the musculoskeletal system ~Trichinella Spiralis: It s a small nematode that measures to about 2-3mm in length. In general
Criteria of Chagas Disease Cure
 Mem Inst Oswaldo Cruz, Rio de Janeiro, Vol. 94, Suppl. I: 331-335, 1999 331 Criteria of Chagas Disease Cure J Romeu Cançado Cadeira de Terapêutica Clínica, Universidade Federal de Minas Gerais, Caixa Postal
Mem Inst Oswaldo Cruz, Rio de Janeiro, Vol. 94, Suppl. I: 331-335, 1999 331 Criteria of Chagas Disease Cure J Romeu Cançado Cadeira de Terapêutica Clínica, Universidade Federal de Minas Gerais, Caixa Postal
Leishmania (Viannia) braziliensis in dogs in Brazil: epidemiology, co-infection, and clinical aspects
 in Brazil: epidemiology, co-infection, and clinical aspects F.S. Carvalho 1, A.A. Wenceslau 2, G.R. Albuquerque 2, A.D. Munhoz 2, E. Gross 2, P.L.S. Carneiro 3, H.C. Oliveira 4, J.M. Rocha 4, I.A. Santos
in Brazil: epidemiology, co-infection, and clinical aspects F.S. Carvalho 1, A.A. Wenceslau 2, G.R. Albuquerque 2, A.D. Munhoz 2, E. Gross 2, P.L.S. Carneiro 3, H.C. Oliveira 4, J.M. Rocha 4, I.A. Santos
Eliza Yoshie do Rosário, Odair Genaro, João C França-Silva, Roberto T da Costa, Wilson Mayrink, Alexandre Barbosa Reis*, Mariângela Carneiro/ +
 Mem Inst Oswaldo Cruz, Rio de Janeiro, Vol. 100(2): 197-203, April 2005 197 Evaluation of enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay using crude Leishmania and recombinant antigens as a diagnostic marker for canine
Mem Inst Oswaldo Cruz, Rio de Janeiro, Vol. 100(2): 197-203, April 2005 197 Evaluation of enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay using crude Leishmania and recombinant antigens as a diagnostic marker for canine
Therapeutic Options for Visceral Leishmaniasis
 Drugs (2013) 73:1863 1888 DOI 10.1007/s40265-013-0133-0 REVIEW ARTICLE Therapeutic Options for Visceral Leishmaniasis Begoña Monge-Maillo Rogelio López-Vélez Published online: 30 October 2013 Ó The Author(s)
Drugs (2013) 73:1863 1888 DOI 10.1007/s40265-013-0133-0 REVIEW ARTICLE Therapeutic Options for Visceral Leishmaniasis Begoña Monge-Maillo Rogelio López-Vélez Published online: 30 October 2013 Ó The Author(s)
Revista de Salud Pública ISSN: Universidad Nacional de Colombia Colombia
 Revista de Salud Pública ISSN: 0124-0064 revistasp_fmbog@unal.edu.co Universidad Nacional de Colombia Colombia Aponte-González, Johanna; Rincón, Carlos; Eslava-Schmalbach, Javier The impact of under-recording
Revista de Salud Pública ISSN: 0124-0064 revistasp_fmbog@unal.edu.co Universidad Nacional de Colombia Colombia Aponte-González, Johanna; Rincón, Carlos; Eslava-Schmalbach, Javier The impact of under-recording
Studying the Dynamics of Visceral Leishmaniasis Epidemic in India - A System Dynamic Approach for Policy Development
 Studying the Dynamics of Visceral Leishmaniasis Epidemic in India - A System Dynamic Approach for Policy Development Hiba Ahmed Supervised by: Pål Davidsen Submitted in Partial Fulfillment Of the Requirement
Studying the Dynamics of Visceral Leishmaniasis Epidemic in India - A System Dynamic Approach for Policy Development Hiba Ahmed Supervised by: Pål Davidsen Submitted in Partial Fulfillment Of the Requirement
Laurenti, Marcia D.; Chaves, Luis F
 NAOSITE: Nagasaki University's Ac Title Author(s) Citation Cutaneous Leishmaniasis in dogs: is reservoir role? Calzada, José E.; Saldaña, Azael; G Vanessa; Santamaría, Ana María; Rod Laurenti, Marcia D.;
NAOSITE: Nagasaki University's Ac Title Author(s) Citation Cutaneous Leishmaniasis in dogs: is reservoir role? Calzada, José E.; Saldaña, Azael; G Vanessa; Santamaría, Ana María; Rod Laurenti, Marcia D.;
Tropical medicine rounds
 Oxford, IJD International 0011-9059 Blackwell 41 UK Science, Journal Ltd 2002 of Dermatology Tropical medicine rounds Cutaneous André Báfica, Leishmaniasis Fabiano Oliveira, Luiz A. R. Freitas, Eliane
Oxford, IJD International 0011-9059 Blackwell 41 UK Science, Journal Ltd 2002 of Dermatology Tropical medicine rounds Cutaneous André Báfica, Leishmaniasis Fabiano Oliveira, Luiz A. R. Freitas, Eliane
ORIGINAL GENDER DIFFERENCES IN MOTIVATIONS TO PRACTICE PHYSICAL ACTIVITY AND SPORT IN OLD AGE
 Martín, M.; Moscoso, D. y Pedrajas, N. (2013). Diferencias de género en las motivaciones para practicar actividades físico-deportivas en la vejez / Gender differences in motivations to practice physical
Martín, M.; Moscoso, D. y Pedrajas, N. (2013). Diferencias de género en las motivaciones para practicar actividades físico-deportivas en la vejez / Gender differences in motivations to practice physical
Regional Update EW 30 Influenza (August 9, h GMT; 12 h EST)
 Regional Update EW 30 Influenza (August 9, 2011-17 h GMT; 12 h EST) PAHO interactive influenza data: HUhttp://ais.paho.org/phip/viz/ed_flu.aspU Influenza Regional Reports: HUhttp://new.paho.org/hq/index.php?option=com_content&task=view&id=3352&Itemid=2469&to=2246U
Regional Update EW 30 Influenza (August 9, 2011-17 h GMT; 12 h EST) PAHO interactive influenza data: HUhttp://ais.paho.org/phip/viz/ed_flu.aspU Influenza Regional Reports: HUhttp://new.paho.org/hq/index.php?option=com_content&task=view&id=3352&Itemid=2469&to=2246U
Charles University Faculty of Science Department Parasitology. INTERACTION PHLEBOTOMUS LEISHMANIA Ph.D. Thesis MARTINA HAJMOVÁ
 Charles University Faculty of Science Department Parasitology INTERACTION PHLEBOTOMUS LEISHMANIA Ph.D. Thesis MARTINA HAJMOVÁ 2006 Thesis advisor: prof. RNDr. Petr Volf, CSc. Curriculum vitae: Martina
Charles University Faculty of Science Department Parasitology INTERACTION PHLEBOTOMUS LEISHMANIA Ph.D. Thesis MARTINA HAJMOVÁ 2006 Thesis advisor: prof. RNDr. Petr Volf, CSc. Curriculum vitae: Martina
Blocked stomodeal valve of the insect vector: similar mechanism of transmission in two trypanosomatid models
 International Journal for Parasitology 34 (2004) 1221 1227 www.parasitology-online.com Blocked stomodeal valve of the insect vector: similar mechanism of transmission in two trypanosomatid models P. Volf
International Journal for Parasitology 34 (2004) 1221 1227 www.parasitology-online.com Blocked stomodeal valve of the insect vector: similar mechanism of transmission in two trypanosomatid models P. Volf
MINUTES ON BIOCODEX TRAIN THE TRAINERS PARIS FRANCE JULY
 Artículo de interés TH MINUTES ON BIOCODEX TRAIN THE TRAINERS PARIS FRANCE JULY 10 2015 RESUMEN HENRY C OHEN, M.D. 1 2 3, CARLOS VELASCO, M.D., YVAN VANDENPLAS, M.D., 4 5 WILFRIDO CORONEL, M.D., JORGE
Artículo de interés TH MINUTES ON BIOCODEX TRAIN THE TRAINERS PARIS FRANCE JULY 10 2015 RESUMEN HENRY C OHEN, M.D. 1 2 3, CARLOS VELASCO, M.D., YVAN VANDENPLAS, M.D., 4 5 WILFRIDO CORONEL, M.D., JORGE
Departamento de Parasitologia, Instituto de Ciências Biológicas 3
 Mem Inst Oswaldo Cruz, Rio de Janeiro, Vol. 105(8): 10331039, December 2010 1033 The molecular detection of different Leishmania species within sand flies from a cutaneous and visceral leishmaniasis sympatric
Mem Inst Oswaldo Cruz, Rio de Janeiro, Vol. 105(8): 10331039, December 2010 1033 The molecular detection of different Leishmania species within sand flies from a cutaneous and visceral leishmaniasis sympatric
Comparative Microsatellite Typing of New World Leishmania infantum Reveals Low Heterogeneity among Populations and Its Recent Old World Origin
 Comparative Microsatellite Typing of New World Leishmania infantum Reveals Low Heterogeneity among Populations and Its Recent Old World Origin Katrin Kuhls 1 *, Mohammad Zahangir Alam 1 a, Elisa Cupolillo
Comparative Microsatellite Typing of New World Leishmania infantum Reveals Low Heterogeneity among Populations and Its Recent Old World Origin Katrin Kuhls 1 *, Mohammad Zahangir Alam 1 a, Elisa Cupolillo
Vector Hazard Report: Malaria, Leishmaniasis and Dengue Risk in Honduras
 Vector Hazard Report: Malaria, Leishmaniasis and Dengue Risk in Honduras Information gathered from products of The Walter Reed Biosystematics Unit (WRBU) Systematic Catalog of Culicidae VectorMap All material
Vector Hazard Report: Malaria, Leishmaniasis and Dengue Risk in Honduras Information gathered from products of The Walter Reed Biosystematics Unit (WRBU) Systematic Catalog of Culicidae VectorMap All material
Irma Fatima Agrela/ +, Maria Dora Feliciangeli
 Mem Inst Oswaldo Cruz, Rio de Janeiro, Vol. 110(5): 611-617, August 2015 611 Effect of Leishmania spp infection on the survival, life expectancy, fecundity and fertility of Lutzomyia longipalpis s.l. and
Mem Inst Oswaldo Cruz, Rio de Janeiro, Vol. 110(5): 611-617, August 2015 611 Effect of Leishmania spp infection on the survival, life expectancy, fecundity and fertility of Lutzomyia longipalpis s.l. and
Mixed infection of Leishmania infantum and Leishmania braziliensis in rodents from endemic urban area of the New World
 Ferreira et al. BMC Veterinary Research (2015) 11:71 DOI 10.1186/s12917-015-0392-y RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Mixed infection of Leishmania infantum and Leishmania braziliensis in rodents from endemic
Ferreira et al. BMC Veterinary Research (2015) 11:71 DOI 10.1186/s12917-015-0392-y RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Mixed infection of Leishmania infantum and Leishmania braziliensis in rodents from endemic
Morphological forms of hemoflagellates
 Parasitology Lecture: 1 Hemoflagellates (blood and tissue flagellates) *Classification: - Sub-kingdom: Protozoa -Phylum: Sarcomastigophora -Sub-phylum: Mastigiphora -Class: Zoomastigophora د. رائد *Flagellates
Parasitology Lecture: 1 Hemoflagellates (blood and tissue flagellates) *Classification: - Sub-kingdom: Protozoa -Phylum: Sarcomastigophora -Sub-phylum: Mastigiphora -Class: Zoomastigophora د. رائد *Flagellates
Experimental infection of Leishmania (L.) chagasi in a cell line derived from Lutzomyia longipalpis (Diptera:Psychodidae)
 Mem Inst Oswaldo Cruz, Rio de Janeiro, Vol. 100(6): 519-525, October 2005 519 Experimental infection of Leishmania (L.) chagasi in a cell line derived from Lutzomyia longipalpis (Diptera:Psychodidae) Felio
Mem Inst Oswaldo Cruz, Rio de Janeiro, Vol. 100(6): 519-525, October 2005 519 Experimental infection of Leishmania (L.) chagasi in a cell line derived from Lutzomyia longipalpis (Diptera:Psychodidae) Felio
Iranian J Parasitol: Vol. 8, No.3, July -Sep 2013, pp Iranian J Parasitol. Open access Journal at ijpa.tums.ac.ir
 Iranian J Parasitol: Vol. 8, No.3, July -Sep 2013, pp.396-401 Iranian J Parasitol Tehran University of Medical Sciences Publication http:// tums.ac.ir Open access Journal at http:// ijpa.tums.ac.ir Iranian
Iranian J Parasitol: Vol. 8, No.3, July -Sep 2013, pp.396-401 Iranian J Parasitol Tehran University of Medical Sciences Publication http:// tums.ac.ir Open access Journal at http:// ijpa.tums.ac.ir Iranian
Major Article. CD8+ T cells in situ in different clinical forms of human cutaneous leishmaniasis
 Major Article Revista da Sociedade Brasileira de Medicina Tropical 46(6):728-734, Nov-Dec, 213 http://dx.doi.org/1.159/37-8682-174-213 CD8+ T cells in situ in different clinical forms of human cutaneous
Major Article Revista da Sociedade Brasileira de Medicina Tropical 46(6):728-734, Nov-Dec, 213 http://dx.doi.org/1.159/37-8682-174-213 CD8+ T cells in situ in different clinical forms of human cutaneous
Archives of Veterinary Science ISSN X CHARACTERIZATION OF CANINE LEISHMANIASIS BY PCR-RFLP IN CUIABA, MATO GROSSO, BRAZIL
 Archives of Veterinary Science ISSN 1517-784X v.17, n.2, p.68-72, 2012 www.ser.ufpr.br/veterinary CHARACTERIZATION OF CANINE LEISHMANIASIS BY PCR-RFLP IN CUIABA, MATO GROSSO, BRAZIL Arleana do Bom Parto
Archives of Veterinary Science ISSN 1517-784X v.17, n.2, p.68-72, 2012 www.ser.ufpr.br/veterinary CHARACTERIZATION OF CANINE LEISHMANIASIS BY PCR-RFLP IN CUIABA, MATO GROSSO, BRAZIL Arleana do Bom Parto
T-cell responses associated with resistance to Leishmania infection in individuals from endemic areas for Leishmania (Viannia) braziliensis
 Mem Inst Oswaldo Cruz, Rio de Janeiro, Vol. 102(5): 625-630, August 2007 625 T-cell responses associated with resistance to Leishmania infection in individuals from endemic areas for Leishmania (Viannia)
Mem Inst Oswaldo Cruz, Rio de Janeiro, Vol. 102(5): 625-630, August 2007 625 T-cell responses associated with resistance to Leishmania infection in individuals from endemic areas for Leishmania (Viannia)
