Vol. 40, No. 6, December 1996 BIOCHEMISTRY and MOLECULAR BIOLOGY INTERNATIONAL Poges
|
|
|
- Duane Ross
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Vol. 40, No. 6, December 1996 BIOCHEMISTRY and MOLECULAR BIOLOGY INTERNATIONAL Poges MODULATION OF OUABAIN SENSITIVE SODIUM POTASSIUM PUMP OF ERYTHROCYTES FROM PATIENTS WITH CHRONIC RENAL FAILURE : ROLE OF ACUTE HEMODIALYSlS R. PRASAD*, R. MOND, S. JAIN 1, G. KAUR AND K.S. CHUGH 2 Departments of Biochemistry, Internal Medicine I and Nephrology 2, Postgraduate Institute of Medical Education and Research, Chandigarh , (INDIA) Received September 25, 1996 SUMMARY Significantly higher levels of plasma urea creatinine and potassium were observed in patients with renal failure compared to normal controls. The RBC sodium concentration was raised whereas the RBC potassium concentration was decreased in chronic renal failure. These alterations in the RBC Na f af~d K J concentrations were associated with decrease in ouabain sensitive sodium efflux rate and ouabain sensitive sodium efflux rate constant. However, there was no significant impact of acute hemodialysis on the intracellular electrolytes levels, ouabain sensitive sodium efflux rate and ouabain sensitive sodium efflux rate constant. These findings suggest an intrinsic alteration in the transport capacity of Na +-K + pump which could account for the rise in intracellular sodium and fall in intracellular potassium content in the RBCs of chronic renal failure patients. INTRODUCTION Challenges to sodium and potassium homeostasis are manifold and require mechanisms to cope with both surfeit and deficit of total body sodium and potassium. The concentration of sodium inside the cell and the transport of Na = and K + across the cell membranes are largely mediated by a specific transport system termed the Na+-K + pump (1-4). Several authors have reported an alteration in the RBC sodium content in patients with chronic renal failure and have provided evidence for a defect in the sodium transport of erythrocytes (5-7). *Corresponding Author /96/ /0 Capyright 1996 by Academic Pres.~ Au.~tralia. All rights af reproduction in any forra reserved.
2 BIOCHEMISTRYond MOLECULAR BIOLOGY INTERNATIONAL Earlier studies to delineate the mechanisms of increase in intracellular sodium have been limited to the measurement of pump mediated sodium efflux, the passive sodium leak and Na+-K + ATPase activity (8-10). The exact mechanism responsible for the alteration in sodium and potassium homeostasis in patients with chronic renal failure remain unclear. To detect the alterations, we studied the concentration of red cell sodium as a measure of ouabain sensitive efflux (EOS). EOS when expressed as a fraction of the original red cell sodium concentration, gives a measure of the ouabain sensitive sodium efflux rate constant (ERCSos), were measured by a non-radioactive technique as described by Cumberbatch and Morgan (11). This technique measures only the net ouabain-sensitive sodium transport. In addition the impact of hemodialysis was assessed on the sodium efflux rate and efflux rate constant in the RBC of patients with chronic renal failure. MATERIAL AND METHODS Cations contents and sodium transport were studied in the uremic RBCs obtained from the 15 male patients with chronic renal failure. The etiology of chronic renal failure was chronic glomerulonephritis; benign nephrosclerosi.~, diabetic nephropathy and chronic interstitial nephritis. The ellect ol ucute hemodialysis on cation content and sodium transport in RBCs of patients with chronic renal failure was also assessed. The age range of the patients included in this study was 32 to 58 years (mean ± SD ). all control subjects were normotensive with no significant medical problem. Fresh venous blood was drawn from the patients and controls in heparinized tubes, centrifuged at 3000 g. Plasma and buffy coat were removed by aspiration. RBCs were washed four times with a washing solution containing 152 mm choline chloride and 1 mm MgCI 2 buffered with 10 mm tris Hepes (ph 7.4) at 4 C in cold centrifuge. Measurement of intracellular and plasma cations Washed RBCs were completely lysed in double distilled water. After centrifugation, the sodium and potassium concentrations in the supernetant were measured by flame photometry. Plasma sodium and potassium levels were also measured by the same technique. 1088
3 BIOCHEMISTRYand MOLECULAR BIOLOGY INTERNATIONAL Measurement of plasma urea and creatinine Plasma urea and creatinine were measured on autoanalyser (Technicon- SAM-II). Measurement of ouabain sensitive efflux rate and efflux rate constants of sodium in RBCs The ouabain sensitive sodium efflux rate and efflux rate constant in tile RBCs were measured using a new, simple and non-radioactive technique described by Cumberbatch and Morgan (11). 20 pl of ouabain 10.2 mol I 1 in 80% ethanol was added to each aliquot contains 3.5 ml of heparinized venous blood from patients of chronic renal failure and the healthy controls to give a final concentration of approximately 10.4 tool I "1. The samples were shaken at 37 C for one hour. Two samples to which only 20pl of 80% ethanol had been added, were shaken at 37 C served as controls, the ouabain sensitive effluxes were than calculated from the increase in Na]RB C between O and 1 hr of incubation. Efflux rate [ESos ] [Na]RBC = = mmol/i cells/h Incubation time (h) Efflux rate constant (ERCSos ] ESos [Na]RBC = h-1 [Na]WRBc = Sodium content of washed rbc at zero hour Statistical Analysis Results were expressed as means+s.d. Statistical significance was determined using Student's unpaired t-test between the groups and Student's paired t-test within the groups. RESULTS Urea, creatinine and potassium were significantly higher in chronic renal failure patients in comparison to healthy control subjects (Table 1). The mean sodium concentration expressed as millimoles per litre of cell was significantly higher as compared to the mean value of healthy control (10_ 1.0 retool/i). Mean potassium content in the RbCs of chronic renal failure patients was significantly lower as compared to the controls (Table 2). 1089
4 BIOCHEMISTRYond MOLECULAR BIOLOGY INTERNATIONAL TABLE 1 : Plasma biochemical parameters in chronic renal failure and normal healthy subjects Parameter _.C hron_ i.c_re.ha_l_ fa_ i_lu r_e g_rou_p_... Control group Before hemodialysis After hemodialysis Urea 162.0± 17.O 100.0:1: (mg/dl) Creatinine 10.0 ± ± (mg/dl) Sodium ± (meq/i) Potassium ± (meq/i) The values are expressed as mean :I:S.D. in 15 subjects of the chronic renal failure and 10 normal controls p < 0.05 was considered as significant Ouabain sensitive sodium efflux rate and efflux rate constants are summarized in Table 2. There was significant reduction in ouabain sensitive sodium efflux rate in the RBCs of patients with chronic renal failure compared to the controls. A significant reduction was also observed in ouabain sensitive sodium efflux rate constant in the RBCs of chronic renal failure patients compared to the controls. The reduction in ouabain sensitive sodium efflux rate constant in RBCs of chronic renal failure patients was in proportion to the reduction of ouabain sensitive efflux rate in these patients. Whereas hemodialysis with low potassium solution in chronic renal failure patients fully corrected the hyperkalemia, there was no significant effect on intracellular RBCs sodium and potassium contents before and after acute hemodialysis. Further, we did not find any significant change in ouabain sensitive sodium efflux rate and rate constants in RBCs of chronic renal failure patients before and after dialysis. 1090
5 BIOOHEMISTRYond MOLECULAR BIOLOGY INTERNATIONAL DISCUSSION In the present study, an alteration was observed in the distribution of electrolytes (Na +, K +) between the plasma and intracellular fluid of RBCs in patients with chronic renal failure. This imbalance of electrolytes is primarily attributed to the defect in ouabain sensitive Na + K + pump which controls the homeostasis of sodium and potassium intracellularly. Increased level of sodium and decreased levels of potassium in the RBCs of chronic renal failure patients are associated with decrease in ouabain sensitive sodium efflux rate. It has been suggested that certain factors in the uremic plasma may lead to a decrease in the activity of Na-K pump. In an earlier study, [Na+-K +] ATPase activity of normal erythrocytes exposed to uremic plasma was 16% lower than that of normal erythrocytes exposed together. Krammer et al observed that Na efflux of normal erythrocytes was depressed by exposure to uremic plasma (9). it was TABLE 2: sodium, potassium, ouabain sensitive sodium efflux rate and ouabain sensitive sodium efflux rate constant in RBCs of chronic renal failure and control subjects Parameter _Chron ic_renaj_ f. a iju r_e _group... Before hemodialysis After Hemodialysis Control group RBC sodium 13.5_ (mmol/i cells) RBC potassium O+4.0 (mmol/i cells) Efflux rate 2.0_ _+O _+0.2 [ESSos ] nmol/i cells/h Efflux rate O. 17 _ constant ERCSos (h"1) The values are expressed as mean + SD in 15 subjects of the chronic renal failure and 10 normal controls P<0.05 was considered as significant. 1091
6 Vol. 40, NO. 6, 1996 BIOOHEMISTRYond MOLECULAR BIOLOGY INTERNATIONAL therefore suggested that accumulation of uremic toxins inhibits the cellular Na +- K 4 ATPase, resulting in abnormalities in the cellular cation content (12). A digoxin-like substance has been postulated to accumulate in the plasnla of uremic patients (1 3). Such a substance could bind tightly or irreversibly to the membrane of uremic erythrocytes and modulate the Na-K pump activity. However, the exact nature of the toxin present in uremic plasma has not yet been characterized. No significant change was observed either in the sodium and potassium levels or ouabain sensitive sodium efflux rate in the RBCs of chronic renal failure patients after acute hemodialysis. Although, hyperkalemia was fully corrected in patients on hemodialysis, the latter was not always associated with improvement in the Na-K pump activity. The persistence of the defect in Na-K pump on dialysis may reflect inadequate removal of putative uremic toxin responsible for this abnormality. This possibility is supported by the partial correction of plasma urea and creatinine on dialysis in uremic patients. On the other hand, reduction in the potassium content in the leukocytes (12) and muscle cells (14) in uremic patients can be normalized by hemodialysis. Serum potassium concentration in chronic renal failure is maintained within normal limits both by renal and extra renal adaptive mechanisms ( ). Despite a marked decrease in glomerular filtration rate, renal adaptation provides for a rapid increase in potassium excretion per surviving nephron to the extent that potassium excretion may exceed filtered load in patients with a major decrease in functional renal mass (17-19). However, the capacity of the surviving nephrons to excrete an additional acute potassium load is impaired (1 8). Therefore, the observed hyperkaiemia in chronic renal failure is suggestive to the presence of an increase excretory burden, possibly due to ingestion of potassium rich foods and medications, since it is corrected by hemodialysis with low potassium solutions. 1092
7 BIOCHEMISTRYond MOLECULAR BIOLOGY INTERNATIONAL In addition to the decrease in ouabain sensitive sodium efflux rate in tile RBCs of patients of chronic renal failure, a decrease n ouabain se~sitive sodiuni efflux rate constant was found in the RBCs of patients of chronic renal failure. It can be inferred that low turnover rate of Na-K pump which may lead to diminished sodium efflux and increase in the intracellular Na + concentration and decrease in the potassium concentration in the RBCs in chronic renal failure. The turnover of Na+-K + pump may also be influenced by intracellular sodium itself (20,21). Alternatively the increase intracellular RBC sodium could result from increase in sodium influx in chronic renal failure, but earlier studies have shown that there is no difference in the sodium influx in the uremic and normal erythrocytes (9). Acknowledgements This work was sponsored by Potash and Phosphate Institute of Canada and India Programme, Sector 19, Delhi-Gurgaon Road, Gurgaon. We also thank Dr. G. Dev, Director, Potash and Phosphate Institute of Canada for his invaluable interest and encouragement during the entire period of this study. REFERENCES 1. Glynn, I.M. (1962). Brit. Med. Bull. 24, Reddy, P.C. (1992). J. Neurol Transm. (Gen. sect.) 89, Cumberbatch, M. and Morgan, B. (1981). Clin. Sci. 60, Whittman, R. and wheeler, K.D. (1970). Annu. Rev. Physiol. 32, Cheng, J.T., Kahn, T. and Kaji, D.M. (1984). J. Clin. Invest. 745, Swaminathan, R., Clegg, G., Cumberbatch, M., Zarelan, Z. algol Mackenna, F. (1982). Clin. Sci. 62, Corry, D.B., Tuck, M.L., Brickman, A.S., Yanagawa, N. and Lee, D.B.N. (1986). Kid. Int. 29, Cole, C.H., Bafe, J.W. and Welt, L.G. (1968). Trans. Assoc. Am. Physicians 81,
8 BIOCHEMISTRYond MOLECULAR BIOLOGY INTERNATIONAL 9. Kramer, H.J., Gosopodinov, D. and Kruch, F. (1976). Nephron. 16, Edmonson, P.S., Hilton, P.J., Jones, N.F., Patrick, J. and Thomas, R.D. (1975). Clin. sci. Mol. Med. 49, Cumberbatch, M. and Morgan, B. (1978). Clin. Chim. acta 89, Patrick, J. and Jones, N.F. (1974). Clin. Sci. Mol. Med. 46, Graves, S.W., Brown, B. and Valdes, R. Jr. (1983). Ann. Intern. med. 99, Cole, C.H. (1973). Clin. Sci. Mol. Med. 45, Bank, N. and Aynedjian, H.S. (1973). J. Clin. Invest. 52, Mitch, W.E. and Wilcox, C.S. (1982). Am. J. Med. 72, Schultze, R.G. (1971). J. Clin. Invest. 50, Keith, N. (1943). Arch. Intern. reed. 71, Leaf, A. and Camara, A.A. (1949). J. Clin. Invest. 28, Sach J.R. (1970). J. Gen. Physiol. 56, Knight, A. and Welt, L.G. (1974). J. gen. Physiol. 63,
EFFECT OF ACUTE SALINE LOADING ON THE ERYTH ROCYTE SODIUM TRANSPORT IN CHILDREN
 Acta Medica et Biologica Vol. 36, No. 109-113, 1989 EFFECT OF ACUTE SALINE LOADING ON THE ERYTH ROCYTE SODIUM TRANSPORT IN CHILDREN M. UCHIYAMA I. SATOKATA T. AIKAWA K. SAKAI Department 0/ pediatrics,
Acta Medica et Biologica Vol. 36, No. 109-113, 1989 EFFECT OF ACUTE SALINE LOADING ON THE ERYTH ROCYTE SODIUM TRANSPORT IN CHILDREN M. UCHIYAMA I. SATOKATA T. AIKAWA K. SAKAI Department 0/ pediatrics,
LITHIUM ADMINISTRATION TO PATIENTS
 Br. J. Pharmac. (1976), 57, 323-327 AN IRREVERSIBLE EFFECT OF LITHIUM ADMINISTRATION TO PATIENTS C. LINGSCH & K. MARTIN Department of Pharmacology, University of Cambridge, Hills Road, Cambridge CB2 2QD
Br. J. Pharmac. (1976), 57, 323-327 AN IRREVERSIBLE EFFECT OF LITHIUM ADMINISTRATION TO PATIENTS C. LINGSCH & K. MARTIN Department of Pharmacology, University of Cambridge, Hills Road, Cambridge CB2 2QD
Mechanism of Alteration of Sodium Potassium Pump of Erythrocytes from Patients with Chronic Renal Failure
 Downloaded from http://www.jci.org on November 25, 217. https://doi.org/1.1172/jci1116 Mechanism of Alteration of Sodium Potassium Pump of Erythrocytes from Patients with Chronic Renal Failure Jen-Tse
Downloaded from http://www.jci.org on November 25, 217. https://doi.org/1.1172/jci1116 Mechanism of Alteration of Sodium Potassium Pump of Erythrocytes from Patients with Chronic Renal Failure Jen-Tse
COMPARISON OF SERUM ZINC AND SERUM POTASSIUM CONCENTRATION IN CHRONIC RENAL FAILURE PATIENTS
 COMPARISON OF SERUM ZINC AND SERUM POTASSIUM CONCENTRATION IN CHRONIC RENAL FAILURE PATIENTS *Punam Yadav Department of Chemistry, M. S. College, Saharanpur U.P. *Author for Correspondence ABSTRACT Abnormal
COMPARISON OF SERUM ZINC AND SERUM POTASSIUM CONCENTRATION IN CHRONIC RENAL FAILURE PATIENTS *Punam Yadav Department of Chemistry, M. S. College, Saharanpur U.P. *Author for Correspondence ABSTRACT Abnormal
Asian Journal of Phytomedicine and Clinical Research Journal home page:
 Research Article CODEN: AJPCFF ISSN: 2321 0915 Asian Journal of Phytomedicine and Clinical Research Journal home page: www.ajpcrjournal.com EFFECTIVENESS OF INTRADIALYTIC STRETCHING EXERCISE ON MUSCLE
Research Article CODEN: AJPCFF ISSN: 2321 0915 Asian Journal of Phytomedicine and Clinical Research Journal home page: www.ajpcrjournal.com EFFECTIVENESS OF INTRADIALYTIC STRETCHING EXERCISE ON MUSCLE
EXCRETION QUESTIONS. Use the following information to answer the next two questions.
 EXCRETION QUESTIONS Use the following information to answer the next two questions. 1. Filtration occurs at the area labeled A. V B. X C. Y D. Z 2. The antidiuretic hormone (vasopressin) acts on the area
EXCRETION QUESTIONS Use the following information to answer the next two questions. 1. Filtration occurs at the area labeled A. V B. X C. Y D. Z 2. The antidiuretic hormone (vasopressin) acts on the area
Potassium secretion. E k = -61 log ([k] inside / [k] outside).
![Potassium secretion. E k = -61 log ([k] inside / [k] outside). Potassium secretion. E k = -61 log ([k] inside / [k] outside).](/thumbs/80/80478709.jpg) 1 Potassium secretion In this sheet, we will continue talking about ultrafiltration in kidney but with different substance which is K+. Here are some informations that you should know about potassium;
1 Potassium secretion In this sheet, we will continue talking about ultrafiltration in kidney but with different substance which is K+. Here are some informations that you should know about potassium;
INHIBITS CHOLINE TRANSPORT IN HUMAN ERYTHROCYTES
 Br. J. clin. Pharmac. (1974), 1, 365-370 LITHIUM TREATMENT STRONGLY INHIBITS CHOLINE TRANSPORT IN HUMAN ERYTHROCYTES G. LEE, C. LINGSCH, P.T. LYLE & K. MARTIN Department of Pharmacology, University of
Br. J. clin. Pharmac. (1974), 1, 365-370 LITHIUM TREATMENT STRONGLY INHIBITS CHOLINE TRANSPORT IN HUMAN ERYTHROCYTES G. LEE, C. LINGSCH, P.T. LYLE & K. MARTIN Department of Pharmacology, University of
RENAL FUNCTION An Overview
 RENAL FUNCTION An Overview UNIVERSITY OF PNG SCHOOL OF MEDICINE AND HEALTH SCIENCES DIVISION OF BASIC MEDICAL SCIENCES DISCIPLINE OF BIOCHEMISTRY & MOLECULAR BIOLOGY PBL MBBS II SEMINAR VJ. Temple 1 Kidneys
RENAL FUNCTION An Overview UNIVERSITY OF PNG SCHOOL OF MEDICINE AND HEALTH SCIENCES DIVISION OF BASIC MEDICAL SCIENCES DISCIPLINE OF BIOCHEMISTRY & MOLECULAR BIOLOGY PBL MBBS II SEMINAR VJ. Temple 1 Kidneys
Introduction. 1. Introduction
 1. Introduction Chronic kidney disease (CKD) encompasses a spectrum of different pathophysiologic processes associated with abnormal kidney function, and a progressive decline in glomerular filtration
1. Introduction Chronic kidney disease (CKD) encompasses a spectrum of different pathophysiologic processes associated with abnormal kidney function, and a progressive decline in glomerular filtration
Stimulation of Active K + Transport by Anti-L Antibodies in Trypsin-Treated Low Potassium Sheep Erythrocytes
 LETTER TO THE EDITOR Stimulation of Active K + Transport by Anti-L Antibodies in Trypsin-Treated Low Potassium Sheep Erythrocytes Dear Sir: In this letter we attempt to resolve a discrepancy on the effect
LETTER TO THE EDITOR Stimulation of Active K + Transport by Anti-L Antibodies in Trypsin-Treated Low Potassium Sheep Erythrocytes Dear Sir: In this letter we attempt to resolve a discrepancy on the effect
WHY DO WE NEED AN EXCRETORY SYSTEM? Function: To eliminate waste To maintain water and salt balance To maintain blood pressure
 EXCRETORY SYSTEM WHY DO WE NEED AN EXCRETORY SYSTEM? Function: To eliminate waste To maintain water and salt balance To maintain blood pressure These wastes include: Carbon dioxide Mostly through breathing
EXCRETORY SYSTEM WHY DO WE NEED AN EXCRETORY SYSTEM? Function: To eliminate waste To maintain water and salt balance To maintain blood pressure These wastes include: Carbon dioxide Mostly through breathing
INCREASE IN ACCUMULATION OF L-DOPA (3,4-DIHYDROXY PHENYLALANINE) IN BRAIN SLICES BY ALCOHOL
 INCREASE IN ACCUMULATION OF L-DOPA (3,4-DIHYDROXY PHENYLALANINE) IN BRAIN SLICES BY ALCOHOL KENICHI KANIIKE* AND HIROSHI YOSHIDA Department of Pharmacology, Faculty of Medicine, Osaka University, Osaka
INCREASE IN ACCUMULATION OF L-DOPA (3,4-DIHYDROXY PHENYLALANINE) IN BRAIN SLICES BY ALCOHOL KENICHI KANIIKE* AND HIROSHI YOSHIDA Department of Pharmacology, Faculty of Medicine, Osaka University, Osaka
Sodium Movements in the Human Red Blood Cell
 Sodium Movements in the Human Red Blood Cell JOHN R. SACHS From the Department of Hematology, Walter Reed Army Institute of Research, Washington, D. C. 212, and the Department of Physiology, Yale University
Sodium Movements in the Human Red Blood Cell JOHN R. SACHS From the Department of Hematology, Walter Reed Army Institute of Research, Washington, D. C. 212, and the Department of Physiology, Yale University
RENAL FAILURE IN CHILDREN Dr. Mai Mohamed Elhassan Assistant Professor Jazan University
 RENAL FAILURE IN CHILDREN Dr. Mai Mohamed Elhassan Assistant Professor Jazan University OBJECTIVES By the end of this lecture each student should be able to: Define acute & chronic kidney disease(ckd)
RENAL FAILURE IN CHILDREN Dr. Mai Mohamed Elhassan Assistant Professor Jazan University OBJECTIVES By the end of this lecture each student should be able to: Define acute & chronic kidney disease(ckd)
THE EFFECTS OF CHOLESTEROL DEPLETION ON THE SODIUM PUMP IN HUMAN RED CELLS
 Experimental Physiology (1991), 76, 437-443 Printed in Great Britain THE EFFECTS OF CHOLESTEROL DEPLETION ON THE SODIUM PUMP IN HUMAN RED CELLS F. J. LUCIO*, B. M. HENDRYt AND J. C. ELLORY* * University
Experimental Physiology (1991), 76, 437-443 Printed in Great Britain THE EFFECTS OF CHOLESTEROL DEPLETION ON THE SODIUM PUMP IN HUMAN RED CELLS F. J. LUCIO*, B. M. HENDRYt AND J. C. ELLORY* * University
BCH 450 Biochemistry of Specialized Tissues
 BCH 450 Biochemistry of Specialized Tissues VII. Renal Structure, Function & Regulation Kidney Function 1. Regulate Extracellular fluid (ECF) (plasma and interstitial fluid) through formation of urine.
BCH 450 Biochemistry of Specialized Tissues VII. Renal Structure, Function & Regulation Kidney Function 1. Regulate Extracellular fluid (ECF) (plasma and interstitial fluid) through formation of urine.
and water over min using Lanoxin brand of or dialysis performed for the next 24 h. Bloods were
 Br. J. clin. Pharmac. (1980), 9, 593-597 0 LOADING DOSE OF DIGOXIN IN RENAL FAILURE M.H. GAULT, D.N. CHURCHILL & J. KALRA Faculty of Medicine, Memorial University and the Renal Unit, The General Hospital,
Br. J. clin. Pharmac. (1980), 9, 593-597 0 LOADING DOSE OF DIGOXIN IN RENAL FAILURE M.H. GAULT, D.N. CHURCHILL & J. KALRA Faculty of Medicine, Memorial University and the Renal Unit, The General Hospital,
Physio 12 -Summer 02 - Renal Physiology - Page 1
 Physiology 12 Kidney and Fluid regulation Guyton Ch 20, 21,22,23 Roles of the Kidney Regulation of body fluid osmolarity and electrolytes Regulation of acid-base balance (ph) Excretion of natural wastes
Physiology 12 Kidney and Fluid regulation Guyton Ch 20, 21,22,23 Roles of the Kidney Regulation of body fluid osmolarity and electrolytes Regulation of acid-base balance (ph) Excretion of natural wastes
Chronic Kidney Disease - An Overview
 REVIEW ARTICLE KERALA MEDICAL JOURNAL Chronic Kidney Disease - An Overview Rajesh R Nair Department of Nephrology, Amrita Institute of Medical Sciences, Kochi, Kerala* ABSTRACT Published on 28 th December
REVIEW ARTICLE KERALA MEDICAL JOURNAL Chronic Kidney Disease - An Overview Rajesh R Nair Department of Nephrology, Amrita Institute of Medical Sciences, Kochi, Kerala* ABSTRACT Published on 28 th December
The kidney. (Pseudo) Practical questions. The kidneys are all about keeping the body s homeostasis. for questions Ella
 The kidney (Pseudo) Practical questions for questions Ella (striemit@gmail.com) The kidneys are all about keeping the body s homeostasis Ingestion Product of metabolism H 2 O Ca ++ Cl - K + Na + H 2 O
The kidney (Pseudo) Practical questions for questions Ella (striemit@gmail.com) The kidneys are all about keeping the body s homeostasis Ingestion Product of metabolism H 2 O Ca ++ Cl - K + Na + H 2 O
The principal functions of the kidneys
 Renal physiology The principal functions of the kidneys Formation and excretion of urine Excretion of waste products, drugs, and toxins Regulation of body water and mineral content of the body Maintenance
Renal physiology The principal functions of the kidneys Formation and excretion of urine Excretion of waste products, drugs, and toxins Regulation of body water and mineral content of the body Maintenance
The Kidney & Its Role in Maintaining Homeostasis. A lesson on the importance of,, &
 The Kidney & Its Role in Maintaining Homeostasis A lesson on the importance of,, & How Does the Body Maintain Homeostasis? Every cell produces metabolic waste. Product of cellular respiration: CO 2 Another
The Kidney & Its Role in Maintaining Homeostasis A lesson on the importance of,, & How Does the Body Maintain Homeostasis? Every cell produces metabolic waste. Product of cellular respiration: CO 2 Another
Fluids and electrolytes
 Body Water Content Fluids and electrolytes Infants have low body fat, low bone mass, and are 73% or more water Total water content declines throughout life Healthy males are about 60% water; healthy females
Body Water Content Fluids and electrolytes Infants have low body fat, low bone mass, and are 73% or more water Total water content declines throughout life Healthy males are about 60% water; healthy females
Efflux of Red Cell Water into Buffered Hypertonic Solutions
 Efflux of Red Cell Water into Buffered Hypertonic Solutions EDWIN G. OLMSTEAD From the School of Medicine, University of North Dakota, Grand Forks ABSTRACT Buffered NaCI solutions hypertonic to rabbit
Efflux of Red Cell Water into Buffered Hypertonic Solutions EDWIN G. OLMSTEAD From the School of Medicine, University of North Dakota, Grand Forks ABSTRACT Buffered NaCI solutions hypertonic to rabbit
BIOL 2402 Fluid/Electrolyte Regulation
 Dr. Chris Doumen Collin County Community College BIOL 2402 Fluid/Electrolyte Regulation 1 Body Water Content On average, we are 50-60 % water For a 70 kg male = 40 liters water This water is divided into
Dr. Chris Doumen Collin County Community College BIOL 2402 Fluid/Electrolyte Regulation 1 Body Water Content On average, we are 50-60 % water For a 70 kg male = 40 liters water This water is divided into
Managing Acid Base and Electrolyte Disturbances with RRT
 Managing Acid Base and Electrolyte Disturbances with RRT John R Prowle MA MSc MD MRCP FFICM Consultant in Intensive Care & Renal Medicine RRT for Regulation of Acid-base and Electrolyte Acid base load
Managing Acid Base and Electrolyte Disturbances with RRT John R Prowle MA MSc MD MRCP FFICM Consultant in Intensive Care & Renal Medicine RRT for Regulation of Acid-base and Electrolyte Acid base load
Solid phase radioimmunoassay for /^-microglobulin; a sensitive index for renal allograft evaluation
 Solid phase radioimmunoassay for /^-microglobulin; a sensitive index for renal allograft evaluation Manjula S. Kumar, Ph.D. Department of Immunopathology William E. Braun, M.D. Department of Hypertension
Solid phase radioimmunoassay for /^-microglobulin; a sensitive index for renal allograft evaluation Manjula S. Kumar, Ph.D. Department of Immunopathology William E. Braun, M.D. Department of Hypertension
Chronic Kidney Disease. Dr Mohan B. Biyani A. Professor of Medicine University of Ottawa/Ottawa Hospital
 Chronic Kidney Disease Dr Mohan B. Biyani A. Professor of Medicine University of Ottawa/Ottawa Hospital Health Seminar Series Date 12 May 2013 Objectives Normal functioning of Kidneys. Risk factors to
Chronic Kidney Disease Dr Mohan B. Biyani A. Professor of Medicine University of Ottawa/Ottawa Hospital Health Seminar Series Date 12 May 2013 Objectives Normal functioning of Kidneys. Risk factors to
** Accordingly GFR can be estimated by using one urine sample and do creatinine testing.
 This sheet includes the lecture and last year s exam. When a patient goes to a clinic, we order 2 tests: 1) kidney function test: in which we measure UREA and CREATININE levels, and electrolytes (Na+,
This sheet includes the lecture and last year s exam. When a patient goes to a clinic, we order 2 tests: 1) kidney function test: in which we measure UREA and CREATININE levels, and electrolytes (Na+,
H 2 O, Electrolytes and Acid-Base Balance
 H 2 O, Electrolytes and Acid-Base Balance Body Fluids Intracellular Fluid Compartment All fluid inside the cells 40% of body weight Extracellular Fluid Compartment All fluid outside of cells 20% of body
H 2 O, Electrolytes and Acid-Base Balance Body Fluids Intracellular Fluid Compartment All fluid inside the cells 40% of body weight Extracellular Fluid Compartment All fluid outside of cells 20% of body
Definition : Stages : ( RIFLE vs. AKIN ) Causes and classification : Pre-renal Renal Post- renal Clinical manifestations and Complication Management
 AKI Definition : Stages : ( RIFLE vs. AKIN ) Causes and classification : Pre-renal Renal Post- renal Clinical manifestations and Complication Management and indications for RRT Etiology prerenal causes
AKI Definition : Stages : ( RIFLE vs. AKIN ) Causes and classification : Pre-renal Renal Post- renal Clinical manifestations and Complication Management and indications for RRT Etiology prerenal causes
Lecture-2 Review of the previous lecture:
 Lecture-2 Review of the previous lecture: -Kidney s function is to clean the blood by the removing of the waste plus adding some valuable substances -kidney failure will lead to death for many reasons,
Lecture-2 Review of the previous lecture: -Kidney s function is to clean the blood by the removing of the waste plus adding some valuable substances -kidney failure will lead to death for many reasons,
ONLINE HEMODIALYSIS TRAINING SESSION 1
 ONLINE HEMODIALYSIS TRAINING SESSION 1 This document is a supplement to the Online Training. Do not reproduce. Copyright Dialysis4Career. All Rights Reserved. The Renal System - A highly sophisticated
ONLINE HEMODIALYSIS TRAINING SESSION 1 This document is a supplement to the Online Training. Do not reproduce. Copyright Dialysis4Career. All Rights Reserved. The Renal System - A highly sophisticated
BPG 03: Continuous Renal Replacement Therapy (CRRT)
 BPG 03: Continuous Renal Replacement Therapy (CRRT) Statement of Best Practice Patient s requiring Continuous Renal Replacement Therapy (CRRT) will receive appropriate therapy to meet their individual
BPG 03: Continuous Renal Replacement Therapy (CRRT) Statement of Best Practice Patient s requiring Continuous Renal Replacement Therapy (CRRT) will receive appropriate therapy to meet their individual
Physiology questions review
 Physiology questions review 1- The consumption of O2 by the kidney: a- decrease as blood flow increases b- regulated by erythropoiten c- remains constant as blood flow increase d- direct reflects the level
Physiology questions review 1- The consumption of O2 by the kidney: a- decrease as blood flow increases b- regulated by erythropoiten c- remains constant as blood flow increase d- direct reflects the level
Acid and Base Balance
 Acid and Base Balance 1 2 The Body and ph Homeostasis of ph is tightly controlled Extracellular fluid = 7.4 Blood = 7.35 7.45 < 7.35: Acidosis (acidemia) > 7.45: Alkalosis (alkalemia) < 6.8 or > 8.0: death
Acid and Base Balance 1 2 The Body and ph Homeostasis of ph is tightly controlled Extracellular fluid = 7.4 Blood = 7.35 7.45 < 7.35: Acidosis (acidemia) > 7.45: Alkalosis (alkalemia) < 6.8 or > 8.0: death
Renal Disease and PK/PD. Anjay Rastogi MD PhD Division of Nephrology
 Renal Disease and PK/PD Anjay Rastogi MD PhD Division of Nephrology Drugs and Kidneys Kidney is one of the major organ of drug elimination from the human body Renal disease and dialysis alters the pharmacokinetics
Renal Disease and PK/PD Anjay Rastogi MD PhD Division of Nephrology Drugs and Kidneys Kidney is one of the major organ of drug elimination from the human body Renal disease and dialysis alters the pharmacokinetics
Collin College. BIOL Anatomy & Physiology. Urinary System. Summary of Glomerular Filtrate
 Collin College BIOL. 2402 Anatomy & Physiology Urinary System 1 Summary of Glomerular Filtrate Glomerular filtration produces fluid similar to plasma without proteins GFR ~ 125 ml per min If nothing else
Collin College BIOL. 2402 Anatomy & Physiology Urinary System 1 Summary of Glomerular Filtrate Glomerular filtration produces fluid similar to plasma without proteins GFR ~ 125 ml per min If nothing else
Ch 17 Physiology of the Kidneys
 Ch 17 Physiology of the Kidneys Review Anatomy on your own SLOs List and describe the 4 major functions of the kidneys. List and explain the 4 processes of the urinary system. Diagram the filtration barriers
Ch 17 Physiology of the Kidneys Review Anatomy on your own SLOs List and describe the 4 major functions of the kidneys. List and explain the 4 processes of the urinary system. Diagram the filtration barriers
Acute kidney injury definition, causes and pathophysiology. Financial Disclosure. Some History Trivia. Key Points. What is AKI
 Acute kidney injury definition, causes and pathophysiology Financial Disclosure Current support: Center for Sepsis and Critical Illness Award P50 GM-111152 from the National Institute of General Medical
Acute kidney injury definition, causes and pathophysiology Financial Disclosure Current support: Center for Sepsis and Critical Illness Award P50 GM-111152 from the National Institute of General Medical
Effects of Amiloride on the Transport of Sodium and Other Ions in the Alga Hydrodictyon reticulatum
 Gen. Physiol. Biophys. (1987). 6, 255-263 255 Effects of Amiloride on the Transport of Sodium and Other Ions in the Alga Hydrodictyon reticulatum R. RYBOVÁ, R. METLIČKA and K. JANÁČEK Academy of Sciences.
Gen. Physiol. Biophys. (1987). 6, 255-263 255 Effects of Amiloride on the Transport of Sodium and Other Ions in the Alga Hydrodictyon reticulatum R. RYBOVÁ, R. METLIČKA and K. JANÁČEK Academy of Sciences.
Potassium A NNA VINNIKOVA, M. D.
 Potassium A NNA VINNIOVA, M. D. DIVISION OF NEPHROLOGY Graphics by permission from The Fluid, Electrolyte and Acid-Base Companion, S. Faubel and J. Topf, http://www.pbfluids.com Do you want to hear a Sodium
Potassium A NNA VINNIOVA, M. D. DIVISION OF NEPHROLOGY Graphics by permission from The Fluid, Electrolyte and Acid-Base Companion, S. Faubel and J. Topf, http://www.pbfluids.com Do you want to hear a Sodium
Ch 19: The Kidneys. Functional unit of kidneys:?? Developed by John Gallagher, MS, DVM
 Ch 19: The Kidneys Homeostatic regulation of ECF volume and BP Osmolarity 290 mosm Ion balance Na+ and K+, etc. ph (acid-base balance Excretion of wastes & foreign substances Hormone production EPO Renin
Ch 19: The Kidneys Homeostatic regulation of ECF volume and BP Osmolarity 290 mosm Ion balance Na+ and K+, etc. ph (acid-base balance Excretion of wastes & foreign substances Hormone production EPO Renin
CONCERNING THE EFFECTS OF MAGNESIUM SULFATE ON RENAL FUNCTION, ELECTROLYTE EXCRETION, AND CLEARANCE OF MAGNESIUM
 CONCERNING THE EFFECTS OF MAGNESIUM SULFATE ON RENAL FUNCTION, ELECTROLYTE EXCRETION, AND CLEARANCE OF MAGNESIUM B. I. Heller,, J. F. Hammarsten, F. L. Stutzman J Clin Invest. 1953;32(9):858-861. https://doi.org/10.1172/jci102803.
CONCERNING THE EFFECTS OF MAGNESIUM SULFATE ON RENAL FUNCTION, ELECTROLYTE EXCRETION, AND CLEARANCE OF MAGNESIUM B. I. Heller,, J. F. Hammarsten, F. L. Stutzman J Clin Invest. 1953;32(9):858-861. https://doi.org/10.1172/jci102803.
Applicable To Employees of Gundersen Boscobel Area Hospital laboratory and Gundersen Palmer Lutheran Hospital and Clinic Laboratories.
 Subject Sodium Potassium Chloride ISE - C311 Index Number Lab-8828 Section Laboratory Subsection Regional/Affiliates Category Departmental Contact Betty Tilleraas Last Revised 4/12/2017 References Required
Subject Sodium Potassium Chloride ISE - C311 Index Number Lab-8828 Section Laboratory Subsection Regional/Affiliates Category Departmental Contact Betty Tilleraas Last Revised 4/12/2017 References Required
STUDY ON MICROALBUMINURIA AND OXIDATIVESTRESS IN DIABETICS. B. Suneel, R.R.Aparna, D.Balakrishna, B.Sowjanya and M.Audisesha Reddy.
 Volume: 2: Issue-4: Oct - Dec -2011 ISSN 0976-4550 STUDY ON MICROALBUMINURIA AND OXIDATIVESTRESS IN DIABETICS * B. Suneel, R.R.Aparna, D.Balakrishna, B.Sowjanya and M.Audisesha Reddy. * Department of Biochemistry,
Volume: 2: Issue-4: Oct - Dec -2011 ISSN 0976-4550 STUDY ON MICROALBUMINURIA AND OXIDATIVESTRESS IN DIABETICS * B. Suneel, R.R.Aparna, D.Balakrishna, B.Sowjanya and M.Audisesha Reddy. * Department of Biochemistry,
Ch 4 Cells & Their Environment
 Ch 4 Cells & Their Environment Biology Mrs. Stolipher MEMBRANE STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION Membranes organize the chemical activities of cells Membranes are selectively permeable They control the flow of substances
Ch 4 Cells & Their Environment Biology Mrs. Stolipher MEMBRANE STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION Membranes organize the chemical activities of cells Membranes are selectively permeable They control the flow of substances
Acute Kidney Injury. I. David Weiner, M.D. Division of Nephrology, Hypertension and Transplantation University of Florida and NF/SGVHS
 Acute Kidney Injury I. David Weiner, M.D. Division of Nephrology, Hypertension and Transplantation University of Florida and NF/SGVHS 374-6102 David.Weiner@medicine.ufl.edu www.renallectures.com Concentration
Acute Kidney Injury I. David Weiner, M.D. Division of Nephrology, Hypertension and Transplantation University of Florida and NF/SGVHS 374-6102 David.Weiner@medicine.ufl.edu www.renallectures.com Concentration
Excretory System Workbook
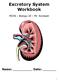 Excretory System Workbook MCHS Biology 20 Mr. Korotash Name: Date: 1 Study the diagram above. Name the structures and indicate their functions by completing the following table: Structure 1. Function 2.
Excretory System Workbook MCHS Biology 20 Mr. Korotash Name: Date: 1 Study the diagram above. Name the structures and indicate their functions by completing the following table: Structure 1. Function 2.
Emergency Medical Training Services Emergency Medical Technician Paramedic Program Outlines Outline Topic: Patho Instructor Notes Revised: 11/2013
 Emergency Medical Training Services Emergency Medical Technician Paramedic Program Outlines Outline Topic: Patho Instructor Notes Revised: 11/2013 Cells form 4 basic tissue groups: 1. Epithelial 2. Connective
Emergency Medical Training Services Emergency Medical Technician Paramedic Program Outlines Outline Topic: Patho Instructor Notes Revised: 11/2013 Cells form 4 basic tissue groups: 1. Epithelial 2. Connective
Altered Membrane Sodium Transport in Bartter's Syndrome
 Altered Membrane Sodium Transport in Bartter's Syndrome JERRY D. GARDNER, ARTEMIS P. SiMoPouLos, ALLEN LAPEY, and SHLOMO SHIBOLET From the Digestive and Hereditary Diseases Branch and the Metabolic Diseases
Altered Membrane Sodium Transport in Bartter's Syndrome JERRY D. GARDNER, ARTEMIS P. SiMoPouLos, ALLEN LAPEY, and SHLOMO SHIBOLET From the Digestive and Hereditary Diseases Branch and the Metabolic Diseases
RENAL TUBULAR ACIDOSIS An Overview
 RENAL TUBULAR ACIDOSIS An Overview UNIVERSITY OF PNG SCHOOL OF MEDICINE AND HEALTH SCIENCES DISCIPLINE OF BIOCHEMISTRY & MOLECULAR BIOLOGY CLINICAL BIOCHEMISTRY PBL MBBS IV VJ. Temple 1 What is Renal Tubular
RENAL TUBULAR ACIDOSIS An Overview UNIVERSITY OF PNG SCHOOL OF MEDICINE AND HEALTH SCIENCES DISCIPLINE OF BIOCHEMISTRY & MOLECULAR BIOLOGY CLINICAL BIOCHEMISTRY PBL MBBS IV VJ. Temple 1 What is Renal Tubular
CCRN Review - Renal. CCRN Review - Renal 10/16/2014. CCRN Review Renal. Sodium Critical Value < 120 meq/l > 160 meq/l
 CCRN Review Renal Leanna R. Miller, RN, MN, CCRN-CMC, PCCN-CSC, CEN, CNRN, CMSRN, NP Education Specialist LRM Consulting Nashville, TN Sodium 136-145 Critical Value < 120 meq/l > 160 meq/l Sodium Etiology
CCRN Review Renal Leanna R. Miller, RN, MN, CCRN-CMC, PCCN-CSC, CEN, CNRN, CMSRN, NP Education Specialist LRM Consulting Nashville, TN Sodium 136-145 Critical Value < 120 meq/l > 160 meq/l Sodium Etiology
Principles of Anatomy and Physiology
 Principles of Anatomy and Physiology 14 th Edition CHAPTER 27 Fluid, Electrolyte, and Acid Base Fluid Compartments and Fluid In adults, body fluids make up between 55% and 65% of total body mass. Body
Principles of Anatomy and Physiology 14 th Edition CHAPTER 27 Fluid, Electrolyte, and Acid Base Fluid Compartments and Fluid In adults, body fluids make up between 55% and 65% of total body mass. Body
HIHIM 409 7/26/2009. Kidney and Nephron. Fermamdo Vega, M.D. 1
 Function of the Kidneys Nephrology Fernando Vega, M.D. Seattle Healing Arts Center Remove Wastes Regulate Blood Pressure Regulate Blood Volume Regulates Electrolytes Converts Vitamin D to active form Produces
Function of the Kidneys Nephrology Fernando Vega, M.D. Seattle Healing Arts Center Remove Wastes Regulate Blood Pressure Regulate Blood Volume Regulates Electrolytes Converts Vitamin D to active form Produces
Understanding. Your Kidneys. Laurie Biel, RN,BSN, CNN The MGH Center For Renal Education March 28, 2016
 Understanding Your Kidneys Laurie Biel, RN,BSN, CNN The MGH Center For Renal Education March 28, 2016 Today s Discussion - The Role of your kidneys Common causes of kidney disease Treatment for kidney
Understanding Your Kidneys Laurie Biel, RN,BSN, CNN The MGH Center For Renal Education March 28, 2016 Today s Discussion - The Role of your kidneys Common causes of kidney disease Treatment for kidney
DIDS INHIBITION OF SARCOPLASMIC RETICULUM ANION EFFLUX AND CALCIUM TRANSPORT
 DIDS INHIBITION OF SARCOPLASMIC RETICULUM ANION EFFLUX AND CALCIUM TRANSPORT Kevin P. Campbell and David H. MacLennan Reprinted from ANNALS OF THE NEW YORK ACADEMY OF SCIENCES Volume 358 Pages 328-331
DIDS INHIBITION OF SARCOPLASMIC RETICULUM ANION EFFLUX AND CALCIUM TRANSPORT Kevin P. Campbell and David H. MacLennan Reprinted from ANNALS OF THE NEW YORK ACADEMY OF SCIENCES Volume 358 Pages 328-331
014 Chapter 14 Created: 9:25:14 PM CST
 014 Chapter 14 Created: 9:25:14 PM CST Student: 1. Functions of the kidneys include A. the regulation of body salt and water balance. B. hydrogen ion homeostasis. C. the regulation of blood glucose concentration.
014 Chapter 14 Created: 9:25:14 PM CST Student: 1. Functions of the kidneys include A. the regulation of body salt and water balance. B. hydrogen ion homeostasis. C. the regulation of blood glucose concentration.
BIOL 2402 Renal Function
 BIOL 2402 Renal Function Dr. Chris Doumen Collin County Community College 1 Renal Clearance and GFR Refers to the volume of blood plasma from which a component is completely removed in one minute by all
BIOL 2402 Renal Function Dr. Chris Doumen Collin County Community College 1 Renal Clearance and GFR Refers to the volume of blood plasma from which a component is completely removed in one minute by all
Potassium regulation. -Kidney is a major regulator for potassium Homeostasis.
 Potassium regulation. -Kidney is a major regulator for potassium Homeostasis. Normal potassium intake, distribution, and output from the body. Effects of severe hyperkalemia Partial depolarization of cell
Potassium regulation. -Kidney is a major regulator for potassium Homeostasis. Normal potassium intake, distribution, and output from the body. Effects of severe hyperkalemia Partial depolarization of cell
Water, Electrolytes, and Acid-Base Balance
 Chapter 27 Water, Electrolytes, and Acid-Base Balance 1 Body Fluids Intracellular fluid compartment All fluids inside cells of body About 40% of total body weight Extracellular fluid compartment All fluids
Chapter 27 Water, Electrolytes, and Acid-Base Balance 1 Body Fluids Intracellular fluid compartment All fluids inside cells of body About 40% of total body weight Extracellular fluid compartment All fluids
Body water content. Fluid compartments. Regulation of water output. Water balance and ECF osmolallty. Regulation of water intake
 Body water content Infants have low body fat, low bone mass, and are 73% or more water Total water content declines throughout life Healthy males are about 60% water; females 50% This difference reflects
Body water content Infants have low body fat, low bone mass, and are 73% or more water Total water content declines throughout life Healthy males are about 60% water; females 50% This difference reflects
Renal Physiology - Lectures
 Renal Physiology 2011 Lisa M. Harrison-Bernard, PhD lharris@lsuhsc.edu Renal Physiology - Lectures Physiology of Body Fluids 2. Structure & Function of the Kidneys 3. Renal Clearance & Glomerular Filtration
Renal Physiology 2011 Lisa M. Harrison-Bernard, PhD lharris@lsuhsc.edu Renal Physiology - Lectures Physiology of Body Fluids 2. Structure & Function of the Kidneys 3. Renal Clearance & Glomerular Filtration
Aspirin Resistance in Patients with Chronic Renal Failure (P 5325)
 Aspirin Resistance in Patients with Chronic Renal Failure (P 5325) Beste Ozben Sadic 1, Azra Tanrikulu 1, Mehmet Koc 2, Tomris Ozben 3, Oguz Caymaz 1 1 Marmara University, Faculty of Medicine, Department
Aspirin Resistance in Patients with Chronic Renal Failure (P 5325) Beste Ozben Sadic 1, Azra Tanrikulu 1, Mehmet Koc 2, Tomris Ozben 3, Oguz Caymaz 1 1 Marmara University, Faculty of Medicine, Department
entirely by glomerular filtration and was neither reabsorbed nor secreted
 6I2.46I.63 INORGANIC SULPHATE EXCRETION BY THE HUMAN KIDNEY. BY CUTHBERT L. COPE. (From the Biochemistry Department, Oxford, and the Radcliffe Infirmary, Oxford.) IN putting forward his modern theory of
6I2.46I.63 INORGANIC SULPHATE EXCRETION BY THE HUMAN KIDNEY. BY CUTHBERT L. COPE. (From the Biochemistry Department, Oxford, and the Radcliffe Infirmary, Oxford.) IN putting forward his modern theory of
Chapter 20 8/23/2016. Fluids and Electrolytes. Fluid (Water) Fluid (Water) (Cont.) Functions
 Chapter 20 Fluids and Electrolytes All items and derived items 2015, 2011, 2006 by Mosby, Inc., an imprint of Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved. Fluid (Water) Functions Provides an extracellular transportation
Chapter 20 Fluids and Electrolytes All items and derived items 2015, 2011, 2006 by Mosby, Inc., an imprint of Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved. Fluid (Water) Functions Provides an extracellular transportation
CSI (Clinical Scenario Investigation): Hyperkalemia
 CSI (Clinical Scenario Investigation): Hyperkalemia Alison Thomas, RN(EC), MN, CNeph(C) Ann Jones, RN(EC), MSN, CNeph(C) Joyce Hunter, RN, Vascular Access Co-ordinator Simcoe Muskoka Regional Kidney Care
CSI (Clinical Scenario Investigation): Hyperkalemia Alison Thomas, RN(EC), MN, CNeph(C) Ann Jones, RN(EC), MSN, CNeph(C) Joyce Hunter, RN, Vascular Access Co-ordinator Simcoe Muskoka Regional Kidney Care
OBJECTVES OF LEARNING
 OBJECTVES OF LEARNING ACUTE RENAL FAILURE AND RENAL REPLACEMENT THERAPY DR.TAI CHENG SHENG RECOGNITION OF DEFINITION OF ARF RECOGNITION OF CAUSE OF ARF RECOGNITION OF PATHOGENESIS OF ARF RECOGNITION OF
OBJECTVES OF LEARNING ACUTE RENAL FAILURE AND RENAL REPLACEMENT THERAPY DR.TAI CHENG SHENG RECOGNITION OF DEFINITION OF ARF RECOGNITION OF CAUSE OF ARF RECOGNITION OF PATHOGENESIS OF ARF RECOGNITION OF
Chapter 21. Diuretic Agents. Mosby items and derived items 2008, 2002 by Mosby, Inc., an affiliate of Elsevier Inc.
 Chapter 21 Diuretic Agents Renal Structure and Function Kidneys at level of umbilicus Each weighs 160 to 175 g and is 10 to 12 cm long Most blood flow per gram of weight in body 22% of cardiac output (CO)
Chapter 21 Diuretic Agents Renal Structure and Function Kidneys at level of umbilicus Each weighs 160 to 175 g and is 10 to 12 cm long Most blood flow per gram of weight in body 22% of cardiac output (CO)
Urinary. Smooth, collapsible, muscular sac stores urine. Figure Slide 15.21a
 Urinary Smooth, collapsible, muscular sac stores urine Figure 15.6 Slide 15.21a Urinary Bladder Wall Walls are and folded in an empty bladder Bladder can significantly without increasing internal pressure
Urinary Smooth, collapsible, muscular sac stores urine Figure 15.6 Slide 15.21a Urinary Bladder Wall Walls are and folded in an empty bladder Bladder can significantly without increasing internal pressure
Etiological evaluation of hearing loss in chronic renal failure
 Original article Etiological evaluation of hearing loss in chronic renal failure 1Dr. K.G.Somashekara, 2 Dr. B.V. Chandre Gowda, 3 Dr. Smitha.S.G, 4Dr. Amrita Suzanne Mathew 1Professor and Head, Department
Original article Etiological evaluation of hearing loss in chronic renal failure 1Dr. K.G.Somashekara, 2 Dr. B.V. Chandre Gowda, 3 Dr. Smitha.S.G, 4Dr. Amrita Suzanne Mathew 1Professor and Head, Department
Sodium Transport Parameters in Erythrocytes of Patients with Primary Aldosteronism
 Sodium Transport Parameters in Erythrocytes of Patients with Primary Aldosteronism JEAN B. SMITH, MARY B. WADE, NAOMI S. FINEBERG, AND MYRON H. WEINBERGER SUMMARY Primary aldosteronism is an uncommon cause
Sodium Transport Parameters in Erythrocytes of Patients with Primary Aldosteronism JEAN B. SMITH, MARY B. WADE, NAOMI S. FINEBERG, AND MYRON H. WEINBERGER SUMMARY Primary aldosteronism is an uncommon cause
Boston, Mass.) per L. and the bicarbonate 35 meq. per L. The bath was maintained at approximately ph 7.4 by equilibration
 CHANGES IN ACID-BASE BALANCE OF UREMIC PATIENTS DURING HEMODIALYSIS1 By JOHN M. WELLER,2 ROY C. SWAN,3 AND JOHN P. MERRILL 4 (From the Department of Medicine, Peter Bent Brigham Hospital and Harvard Medical
CHANGES IN ACID-BASE BALANCE OF UREMIC PATIENTS DURING HEMODIALYSIS1 By JOHN M. WELLER,2 ROY C. SWAN,3 AND JOHN P. MERRILL 4 (From the Department of Medicine, Peter Bent Brigham Hospital and Harvard Medical
CHAPTER 27 LECTURE OUTLINE
 CHAPTER 27 LECTURE OUTLINE I. INTRODUCTION A. Body fluid refers to body water and its dissolved substances. B. Regulatory mechanisms insure homeostasis of body fluids since their malfunction may seriously
CHAPTER 27 LECTURE OUTLINE I. INTRODUCTION A. Body fluid refers to body water and its dissolved substances. B. Regulatory mechanisms insure homeostasis of body fluids since their malfunction may seriously
Calcium and Magnesium Contents of Mammalian Erythrocyte Membranes1) (Received July 3, 1972)
 No. 1 171 Chem. Pharm. Bull. 21(1)171-475(1973) UDC 591.05: 546.3.05.08 Calcium and Magnesium Contents of Mammalian Erythrocyte Membranes1) TATSUZO FUJII, TAKASHI SATO, and TAKASHI HANZAWA Faculty of Pharmacy,
No. 1 171 Chem. Pharm. Bull. 21(1)171-475(1973) UDC 591.05: 546.3.05.08 Calcium and Magnesium Contents of Mammalian Erythrocyte Membranes1) TATSUZO FUJII, TAKASHI SATO, and TAKASHI HANZAWA Faculty of Pharmacy,
Biomarkers of renal diseases. By Dr. Gouse Mohiddin Shaik
 By Dr. Gouse Mohiddin Shaik Introduction Renal system performs several functions Excretory Waste products like urea, creatinine, drug, toxins clearance Regulatory Water, electrolyte and acid base balance
By Dr. Gouse Mohiddin Shaik Introduction Renal system performs several functions Excretory Waste products like urea, creatinine, drug, toxins clearance Regulatory Water, electrolyte and acid base balance
Renal Quiz - June 22, 21001
 Renal Quiz - June 22, 21001 1. The molecular weight of calcium is 40 and chloride is 36. How many milligrams of CaCl 2 is required to give 2 meq of calcium? a) 40 b) 72 c) 112 d) 224 2. The extracellular
Renal Quiz - June 22, 21001 1. The molecular weight of calcium is 40 and chloride is 36. How many milligrams of CaCl 2 is required to give 2 meq of calcium? a) 40 b) 72 c) 112 d) 224 2. The extracellular
Urinary System. consists of the kidneys, ureters, urinary bladder and urethra
 Urinary System 1 Urinary System consists of the kidneys, ureters, urinary bladder and urethra 2 Location of Kidneys The kidneys which are positioned retroperitoneally lie on either side of the vertebral
Urinary System 1 Urinary System consists of the kidneys, ureters, urinary bladder and urethra 2 Location of Kidneys The kidneys which are positioned retroperitoneally lie on either side of the vertebral
NIH Public Access Author Manuscript Kidney Int. Author manuscript; available in PMC 2013 November 01.
 NIH Public Access Author Manuscript Published in final edited form as: Kidney Int. 2013 May ; 83(5): 779 782. doi:10.1038/ki.2012.468. Need to quickly excrete K +? Turn off NCC Alicia A. McDonough 1 and
NIH Public Access Author Manuscript Published in final edited form as: Kidney Int. 2013 May ; 83(5): 779 782. doi:10.1038/ki.2012.468. Need to quickly excrete K +? Turn off NCC Alicia A. McDonough 1 and
THe Story of salty Sam
 THe Story of salty Sam Understanding fluids, urea and electrolyte balance; a quantitative approach. A self-directed learning activity. Part One. meet salty sam Salty Sam is a pretty average 70 kg bloke,
THe Story of salty Sam Understanding fluids, urea and electrolyte balance; a quantitative approach. A self-directed learning activity. Part One. meet salty sam Salty Sam is a pretty average 70 kg bloke,
TOMOFUSA USUI M.D.* information has been available on zinc status in. thyroid disease. The present study was undertaken
 Postgraduate Medical Journal (December 198) 56, 833-837 YOSHIKAZU NISHI M.D.* Zinc metabolism in thyroid disease TOMOFUSA USUI M.D.* RYOSO KAWATE M.D.t *Department of Pediatrics, and tdepartment of Internal
Postgraduate Medical Journal (December 198) 56, 833-837 YOSHIKAZU NISHI M.D.* Zinc metabolism in thyroid disease TOMOFUSA USUI M.D.* RYOSO KAWATE M.D.t *Department of Pediatrics, and tdepartment of Internal
Chapter 10: Urinary System & Excretion
 Chapter 10: Urinary System & Excretion Organs of Urinary System Kidneys (2) form urine Ureters (2) Carry urine from kidneys to bladder Bladder Stores urine Urethra Carries urine from bladder to outside
Chapter 10: Urinary System & Excretion Organs of Urinary System Kidneys (2) form urine Ureters (2) Carry urine from kidneys to bladder Bladder Stores urine Urethra Carries urine from bladder to outside
simultaneously excreted. They also brought forward some evidence to
 THE EXCRETION OF CHLORIDES AND BICARBON- ATES BY THE HUMAN KIDNEY. BY H. W. DAVIES, M.B., B.S., J. B. S. HALDANE, M.A. AND G. L. PESKETT, B.A. (From the Laboratory, Cherwell, Oxford.) AM BARD and PAPI
THE EXCRETION OF CHLORIDES AND BICARBON- ATES BY THE HUMAN KIDNEY. BY H. W. DAVIES, M.B., B.S., J. B. S. HALDANE, M.A. AND G. L. PESKETT, B.A. (From the Laboratory, Cherwell, Oxford.) AM BARD and PAPI
Functions of the Urinary System
 The Urinary System Functions of the Urinary System Elimination of waste products Nitrogenous wastes Toxins Drugs Regulate aspects of homeostasis Water balance Electrolytes Acid-base balance in the blood
The Urinary System Functions of the Urinary System Elimination of waste products Nitrogenous wastes Toxins Drugs Regulate aspects of homeostasis Water balance Electrolytes Acid-base balance in the blood
PHSI2006/2906: Integrated Physiology B
 PHSI2006/2906: Integrated Physiology B TOPIC 1: RESPIRATION 1. The Mechanics of Breathing...2 2. Work of Breathing....5 3. Pulmonary Gas Exchange.. 10 4. Transport of Oxygen...16 5. Control of Respiration...20
PHSI2006/2906: Integrated Physiology B TOPIC 1: RESPIRATION 1. The Mechanics of Breathing...2 2. Work of Breathing....5 3. Pulmonary Gas Exchange.. 10 4. Transport of Oxygen...16 5. Control of Respiration...20
network of thin-walled capillaries closely surrounded by a pear-shaped epithelial membrane called the Bowman s capsule
 Renal Terminology Renal-Root Words & Combining Forms calyx cortex glomerul/o medulla nephr/o pyel/o py/o ur/o ren/o cuplike division of the kidney outer layer of kidney glomerula inner or central portion
Renal Terminology Renal-Root Words & Combining Forms calyx cortex glomerul/o medulla nephr/o pyel/o py/o ur/o ren/o cuplike division of the kidney outer layer of kidney glomerula inner or central portion
Rini Purwanti Sekretaris PD IPDI Jatim
 Kidney Emergency Rini Purwanti Sekretaris PD IPDI Jatim overview The kidneys are a pair of small ( about the size of your fist-sized ), bean shaped organs that lie on either side of your spine, located
Kidney Emergency Rini Purwanti Sekretaris PD IPDI Jatim overview The kidneys are a pair of small ( about the size of your fist-sized ), bean shaped organs that lie on either side of your spine, located
Chapter 27: WATER, ELECTROLYTES, AND ACID-BASE BALANCE
 Chapter 27: WATER, ELECTROLYTES, AND ACID-BASE BALANCE I. RELATED TOPICS Integumentary system Cerebrospinal fluid Aqueous humor Digestive juices Feces Capillary dynamics Lymph circulation Edema Osmosis
Chapter 27: WATER, ELECTROLYTES, AND ACID-BASE BALANCE I. RELATED TOPICS Integumentary system Cerebrospinal fluid Aqueous humor Digestive juices Feces Capillary dynamics Lymph circulation Edema Osmosis
SIMILAR NATURE OF IONIC IMBALANCES IN CARDIOVASCULAR AND RENAL DISORDERS
 Original Article SIMILAR NATURE OF IONIC IMBALANCES IN CARDIOVASCULAR AND RENAL DISORDERS Shahid SM 1, Akram H 2, Jawed M 3 & Mahboob T 4 ABSTRACT Background: Several studies have reported improper ionic
Original Article SIMILAR NATURE OF IONIC IMBALANCES IN CARDIOVASCULAR AND RENAL DISORDERS Shahid SM 1, Akram H 2, Jawed M 3 & Mahboob T 4 ABSTRACT Background: Several studies have reported improper ionic
JMSCR Vol 06 Issue 03 Page March 2018
 www.jmscr.igmpublication.org Impact Factor (SJIF): 6.379 Index Copernicus Value: 71.58 ISSN (e)-2347-176x ISSN (p) 2455-0450 DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.18535/jmscr/v6i3.46 Effects of Hypothyroidism on
www.jmscr.igmpublication.org Impact Factor (SJIF): 6.379 Index Copernicus Value: 71.58 ISSN (e)-2347-176x ISSN (p) 2455-0450 DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.18535/jmscr/v6i3.46 Effects of Hypothyroidism on
(5), the presumed site of potassium secretion. RENAL EXCRETION OF POTASSIUM IN NORMAL AND SODIUM
 RENAL EXCRETION OF POTASSIUM IN NORMAL AND SODIUM DEPLETED DOGS' By HELEN M. ANDERSON AND JOHN H. LARAGH WITH THE TECHNICAL ASSISTANCE OF CLARA W. HALL, SALLY MOORE, AND JOSEPH HARTOG (From the Department
RENAL EXCRETION OF POTASSIUM IN NORMAL AND SODIUM DEPLETED DOGS' By HELEN M. ANDERSON AND JOHN H. LARAGH WITH THE TECHNICAL ASSISTANCE OF CLARA W. HALL, SALLY MOORE, AND JOSEPH HARTOG (From the Department
Elevated Serum Creatinine, a simplified approach
 Elevated Serum Creatinine, a simplified approach Primary Care Update Creighton University School of Medicine. April 27 th, 2018 Disclosure Slide I have no disclosures and have no conflicts with this presentation.
Elevated Serum Creatinine, a simplified approach Primary Care Update Creighton University School of Medicine. April 27 th, 2018 Disclosure Slide I have no disclosures and have no conflicts with this presentation.
12/7/10. Excretory System. The basic function of the excretory system is to regulate the volume and composition of body fluids by:
 Excretory System The basic function of the excretory system is to regulate the volume and composition of body fluids by: o o removing wastes returning needed substances to the body for reuse Body systems
Excretory System The basic function of the excretory system is to regulate the volume and composition of body fluids by: o o removing wastes returning needed substances to the body for reuse Body systems
Correction of hypervolaemic hypernatraemia by inducing negative Na + and K + balance in excess of negative water balance: a new quantitative approach
 Nephrol Dial Transplant (2008) 23: 2223 2227 doi: 10.1093/ndt/gfm932 Advance Access publication 18 February 2008 Original Article Correction of hypervolaemic hypernatraemia by inducing negative Na + and
Nephrol Dial Transplant (2008) 23: 2223 2227 doi: 10.1093/ndt/gfm932 Advance Access publication 18 February 2008 Original Article Correction of hypervolaemic hypernatraemia by inducing negative Na + and
Normal kidneys filter large amounts of organic
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE - NEPHROLOGY Effect Of Lanthanum Carbonate vs Calcium Acetate As A Phosphate Binder In Stage 3-4 CKD- Treat To Goal Study K.S. Sajeev Kumar (1), M K Mohandas (1), Ramdas Pisharody (1),
ORIGINAL ARTICLE - NEPHROLOGY Effect Of Lanthanum Carbonate vs Calcium Acetate As A Phosphate Binder In Stage 3-4 CKD- Treat To Goal Study K.S. Sajeev Kumar (1), M K Mohandas (1), Ramdas Pisharody (1),
THE CLINICAL BIOCHEMISTRY OF KIDNEY FUNCTIONS. Dr Boldizsár CZÉH
 THE CLINICAL BIOCHEMISTRY OF KIDNEY FUNCTIONS Dr Boldizsár CZÉH The kidneys are vital organs Functional unit: Nephron RENAL FUNCTIONS Electrolyte & Fluid Balances Acid-Base Balances Elimination of Metabolic
THE CLINICAL BIOCHEMISTRY OF KIDNEY FUNCTIONS Dr Boldizsár CZÉH The kidneys are vital organs Functional unit: Nephron RENAL FUNCTIONS Electrolyte & Fluid Balances Acid-Base Balances Elimination of Metabolic
Date... Name... Group... Urine sample (Tube No 2)
 Date... Name... Group... Instructions for the practical lesson on biochemistry Topic: Non-protein nitrogen compounds Task 1: Estimation of creatinine in serum and urine 1. Trichloroacetic acid 1.22 mol/l
Date... Name... Group... Instructions for the practical lesson on biochemistry Topic: Non-protein nitrogen compounds Task 1: Estimation of creatinine in serum and urine 1. Trichloroacetic acid 1.22 mol/l
