Alice J Yee, Thomas Fuerst, Loren Salamone, Marjolein Visser, Maurice Dockrell, Marta Van Loan, and Marialice Kern
|
|
|
- Jessie Preston
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Calibration and validation of an air-displacement plethysmography method for estimating percentage body fat in an elderly population: a comparison among compartmental models 1 3 Alice J Yee, Thomas Fuerst, Loren Salamone, Marjolein Visser, Maurice Dockrell, Marta Van Loan, and Marialice Kern ABSTRACT Background: The use of hydrostatic weighing (HW) to measure body composition in the elderly can be difficult and is based on the assumption of constancy of body compartments. Objective: We calibrated and validated a new air-displacement plethysmography (AP) method for measuring body composition in the elderly. Design: A 4-compartment equation for calculating percentage body fat (%BF) that used body density (D b ), total body water, and bone mineral content was used as the criterion for evaluating %BF estimated by the 2- and 3-compartment models. D b was measured by HW [D b(hw) ] and by use of the AP instrument [D b(ap) ] in 30 elderly men and 28 elderly women aged y. Results: D b(ap) was not significantly different from D b(hw). However, analysis of variance showed a significant two-way interaction between sex and compartment model (P < 0.02), indicating that the comparisons between the sexes were different across all compartment models. The %BF calculated for the women was significantly higher than that calculated for the men by both HW and AP and for all compartment models. Conclusion: Our data indicate that D b(ap) was not significantly different from D b(hw). Although differences were seen in %BF between the sexes, we observed no significant differences among the compartment models within each sex for this group of older individuals. Am J Clin Nutr 2001;74: KEY WORDS Body composition, elderly, men, women, hydrostatic weighing, air-displacement plethysmography, multicompartment models, body density, percentage body fat INTRODUCTION For an aging population, maintenance of skeletal muscle mass is important to retain the ability to perform daily activities (1). Body weight increases from the age of 20 to 50 y but declines after the age of 70 y (2, 3). Along with a gain in body weight, the fat-free body mass declines by 25 30% between the ages of 30 and 70 y (3, 4), while fat mass increases with age (5). Aside from the need to establish guidelines for percentage body fat (%BF) in the elderly, body-composition assessment methods that are quick, easy to use in elderly and other special populations, and provide results similar to those obtained with existing techniques need to be developed, calibrated, and validated. Hydrodensitometry or hydrostatic weighing (HW), also known as underwater weighing, has been the criterion for bodycomposition measurement since the 1940s (6). HW requires complicated or often custom-made equipment, greater test times than do other methods, and a high degree of subject participation. Unlike HW, the air-displacement plethysmography (AP) instrument we used to measure body composition in the current study places fewer demands on the subject. There remains, however, a need to validate and calibrate this AP method, especially for special populations such as the elderly. Studies by Dempster and Aikens (7) and McCrory et al (8) in which this AP method was used reported that it is a valid and reliable method for assessing the volume of inanimate objects and of men and women aged y. However, when examining elderly women, Bergsma- Kadijk et al (9) found that the estimation of %BF was 5% different between the 2-compartment (2C) and the 4-compartment (4C) model that used HW; they concluded that a 2C model was unacceptable compared with a 4C model in an elderly population. Studies in which this AP instrument was used in an elderly population are lacking, and validity issues arise with the use of a 2C equation for comparison, which does not account for changes in bone mineral content (BMC) or total body water (TBW). The assumptions of the 2C model [that the density of the fat mass and fat-free mass (FFM) is constant] may not be appropriate for an elderly population (9 12). Therefore, this study had 2 purposes: 1) to compare body density (D b ) measured by the new AP instrument [D b(ap) ] with D b measured by HW [D b(hw) ] in an elderly 1 From the Exercise Physiology Laboratory, the Department of Kinesiology, San Francisco State University; the Department of Radiology, University of California San Francisco; the Department of Epidemiology, the Graduate School of Public Health, University of Pittsburgh; the National Institute on Aging, the Epidemiology, Demography, and Biometry Program, Bethesda, MD; and the Western Human Nutrition Research Center, the US Department of Agriculture, University of California, Davis. 2 Supported by the NIH (grant AG 62106) and the Research Infrastructure in Minority Institutions Program of the National Center for Research Resources with funding from the Office of Research on Minority Health of the NIH (grant RR ). 3 Address reprint requests to M Kern, Department of Kinesiology, 1600 Holloway Avenue, San Francisco State University, San Francisco, CA mkern@sfsu.edu. Received February 15, Accepted for publication January 30, Am J Clin Nutr 2001;74: Printed in USA American Society for Clinical Nutrition 637
2 638 YEE ET AL population, and 2) to compare the 2C model with multicompartment models [3-compartment (3C) and 4C] of body-composition assessment in an elderly population. SUBJECTS AND METHODS Subjects Thirty men and 30 women aged y were recruited by the University of California, San Francisco, through advertisements placed in the university and local communities and by contact with senior citizen organizations in the area. Informed consent of the subjects was obtained before their participation in the study. The study was performed in accordance with the Committee for the Protection of Human Subjects at San Francisco State University. The subjects were required to be healthy y-old adults who could walk up a flight of stairs and submerge themselves completely underwater. Subjects were recruited to fill 3 categories of body mass index (BMI; in kg/m 2 ): 1) normal weight (BMI = 21 24), 2) overweight (BMI = 25 29), and 3) obese (BMI 30) (13). The final distribution of subjects across the BMI categories was 25%, 50%, and 25%, respectively. The study required 1 session per individual. At each session, height, weight, D b (measured by HW or the AP instrument), residual volume (RV), TBW, and BMC were measured. BMC and TBW were measured at the University of California, San Francisco. All other measurements were done at San Francisco State University. Dry measurements were performed first and HW last. Each session began in the morning and lasted 5 6 h and was done after the participants fasted overnight (14). Residual volume RV was measured by a helium rebreathing technique performed on a Collins SVR/PLUS (Braintree, MA) with a functional residual capacity test. With the mouthpiece in place, the subject was asked to breathe normally until the spirometer equilibrated. After equilibration, the subject performed a maximal inspiration followed by a forced maximal exhalation, which allowed inspiratory and expiratory reserve capacity to be measured, respectively. RV was calculated as the functional residual capacity minus the expiratory reserve capacity (15). For more consistent results, the subject performed this procedure 3 times with 5 min of rest between each test. Carbon dioxide absorbant and dessicant were checked and, if necessary, changed during the rest periods. The same examiner was used for all subjects. The average of the 3 tests was used as the calculation of RV. Hydrostatic weighing D b was measured while participants wore bathing suits and sat on a chair suspended in a fiberglass tank. The subjects were asked to submerge themselves underwater and perform a forced exhalation. Subjects repeated this task 10 times. Measurements were taken with an autopsy scale and were recorded to the nearest 0.01 kg. The average of the 3 highest weights was used for the calculation of D b. Body mass index Height was measured to the nearest 0.1 cm and weight was measured to the nearest 0.1 kg on a calibrated Detecto weight scale (Cardinal Scale Manufacturing Company, Webb City, MO). BMI was calculated in kg/m 2 (16). Air-displacement plethysmography The Bod Pod body-composition system (Life Measurement, Inc, Concord, CA) was also used to measure D b. Body weight, body volume, and thoracic lung volume were measured for each subject by using a dual-chambered plethysmograph, an electronic weigh scale, and BOD POD software, version 1.0 (Life Measurement, Inc) as described by McCrory et al (8). Bone mineral content BMC was measured by using a QDR-4500A bone densitometer (Hologic Inc, Waltham, MA) with a fan beam array. All scans were performed and analyzed with the instrument s proprietary software (version 8.21, Hologic Inc) at the University of California, San Francisco, by the same technician according to the standard operating procedures recommended by the manufacturer (17). Total body water Deuterium dilution was used to measure TBW. A baseline venipuncture plasma sample was taken at the beginning of testing. A measured amount of deionized water and deuterium (0.1 g 2 H 2 O/estimated kg TBW) was taken orally by each subject. A final venipuncture plasma sample was taken at the end of the study 4 h after dosing to ensure equilibration of the deuterium with the body water. Subjects were not allowed to have any food or beverages during the 4-h equilibration period. The samples were frozen and shipped to the University of Chicago for analysis of TBW (18). Percentage body fat equations D b measured by HW and by the AP instrument were compared in the 4C, 3C, and 2C equations. The 2C AP %BF and BMC results were automatically reported by the proprietary software of these devices, whereas the results for HW required additional calculations (19). The following %BF equations were used: Siri s 2C and 3C models (16, 17) and Selinger s 4C model (16). 2C HW = %BF from HW with use of Siri s equation = {[4.95/D b(hw) ] 4.50} 100 (1) 2C AP = %BF from AP with use of Siri s equation = {[4.95/D b(ap) ] 4.50} 100 (2) 3C BMCHW = %BF corrected for BMC and HW with use of Siri s mineral density formula = {[6.386/D b(hw) ] + [3.961 m] 6.090} 100 (3) 3C TBWHW = %BF corrected for TBW and HW with the use of Siri s TBW formula = {[2.118/D b(hw) ] [0.78 w] 1.354} 100 (4) 3C BMCAP = %BF corrected for BMC and AP with the use of Siri s mineral density formula = {[6.386/D b(ap) ] + [3.961 m] 6.090} 100 (5) 3C TBWAP = %BF corrected for TBW and AP with the use of Siri s TBW formula = {[2.118/D b(ap) ] [0.78 w] 1.354} 100 (6)
3 BODY COMPOSITION IN AN ELDERLY POPULATION 639 TABLE 1 Subject characteristics 1 All Men Women Variable (n = 58) (n = 30) (n = 28) Age (y) 73.1 ± ± ± 2.34 Height (cm) ± ± ± Weight (kg) 75.9 ± ± ± BMI (kg/m 2 ) 27.3 ± ± ± 5.09 TBW (L) 36.9 ± ± ± BMC (g) ± ± ± D b(hw) ± ± ± D b(ap) ± ± ± x ± SD. TBW, total body water; BMC, bone mineral content; D b(hw), body density measured by hydrostatic weighing; D b(ap), body density measured by air-displacement plethysmography. 2 Significantly different from men, P < C HW = %BF from HW with the use of Selinger s equation = {[2.747/D b(hw) ] [0.714 w] + [1.146 m] } 100 (7) 4C AP = %BF from AP with the use of Selinger s equation = {[2.747/D b(ap) ] [0.714 w] + [1.146 m] } 100 (8) where w is TBW as %BF and m is BMC as %BF. Statistics Pearson s correlation coefficient was used to determine the relation between D b(hw) and D b(ap). A three-way analysis of variance was used to determine significant differences in main effects and interactions. Analyses were adjusted for multiple pairwise comparisons by using Bonferroni s post hoc test. The values are reported as means ± SDs. Line plots were used for graphical purposes to denote linearity and homogeneity of the group. STATISCA version 5.0 (Stat Soft, Tulsa, OK) was used for statistical analyses. A probability level of <0.05 was used to determine statistical significance. RESULTS Two women were eliminated from the data set because of their inability to properly perform the forced exhalation underwater and the adequate number of submergences. As expected, D b was significantly different between the men and women (Table 1), but D b(hw) was not significantly different from D b(ap). As also shown in Table 1, age and BMI were not significantly different between the sexes; all other variables were significantly different between the men and women. The mean TBW for all subjects combined was 36.9 ± 7.92 L for TBW. The ratio of TBW to FFM (TBW/FFM) was 71.5%, slightly below the accepted standard of 73% (20). The average TBW for men was 43.0 ± 5.16 L and TBW/FFM was 70.4%. In women, TBW averaged ± 4.55 L and TBW/FFM was 76.1%. The BMC for men and women combined was ± g, giving a ratio of BMC to FFM (BMC/FFM) of 4.5%. The reference norm for BMC/FFM is 6.8% ± 0.9% (16). BMC was higher in the men than in the women ( ± compared with ± g), resulting in a lower BMC/FFM in the men (4.4% compared with 4.6% of the reference norm of 6.8% in men and women, respectively). No significant differences were observed in %BF for the main effects of sex, method, or compartment model. However, a significant interaction was observed for sex by compartment models. %BF was significantly higher for the women than the men in all compartment models (Table 2). Pearson s correlation coefficients (Table 3) were used to examine the association between %BF from HW and AP, as well to compare the 2C equations with the multicompartment equations. The correlation coefficient for D b(hw) compared with D b(ap) was r = 0.91 for both sexes combined, 0.74 for men, and 0.89 for women. Not surprisingly, the combination of the sexes yielded higher correlations because of the larger sample size and the heterogeneity of the group, which consequently created a greater range in the data (Figures 1 3 and Table 3). DISCUSSION In this group of elderly men and women, no significant differences were found between D b measured by either HW or the AP instrument. This agrees with the results of the study conducted by McCrory et al (8) in which the 2C AP model was as valid and reliable as the 2C HW model. No significant differences were found between the first and second trials when AP was compared with HW. Dempster and Aitkens (7) showed in their study, which used inanimate objects, excellent reliability with repeated measures. A between-day analysis that was done by using 1 cylinder and 20 trials yielded a %BF error of 0.1%. When 5 sequential measures were performed with the use of different volumes (25, 50, 75, 100, 125, and 150 ml), a linear plot was drawn with r 2 = This however, does not eliminate the possible effect of TBW and BMC on the calculation of %BF in the multicomponent models. Significant differences were found in the interaction of the compartment models (2C, 3C, and 4C equations) and sex (men and women). Within a sex group, the compartment models did not differ in the estimation of %BF; however, between the sexes the estimates of %BF for all compartment models were different: the women had higher %BF than the did the men. These findings differ from the results reported by Bergsma-Kadijk et al (9) in which the 2C and 3C compartment models were significantly TABLE 2 Percentage body fat as calculated with use of the different body-composition models 1 All Men Women 2 Models (n = 58) (n = 30) (n = 28) 4C HW 31.8 ± ± ± C AP 32.2 ± ± ± C BMCHW 26.8 ± ± ± C TBWHW 33.3 ± ± ± C BMCAP 27.8 ± ± ± C TBWAP 33.6 ± ± ± C HW 33.6 ± ± ± C AP 34.4 ± ± ± x ± SD. 4C, 4 compartment; 3C, 3 compartment; 2C, 2 compartment, HW, hydrostatic weighing; AP, air-displacement plethysmography; BMC, bone mineral content; TBW, total body water. 2 For all values, there was a significant sex by compartment model interaction, P < 0.05.
4 640 YEE ET AL TABLE 3 Pearson s correlation coefficients for the relations between methods used to calculate percentage body fat 1 2C HW 3C BMCHW 3C TBWHW 2C AP 3C BMCAP 3C TBWAP 4C AP 4C HW All 2C HW C BMCHW C TBWHW C AP C BMCAP C TBWAP C AP C HW Men 2C HW C BMCHW C TBWHW C AP C BMCAP C TBWAP C AP C HW Women 2C HW C BMCHW C TBWHW C AP C BMCAP C TBWAP C AP C HW C, 2 compartment; 3C, 3 compartment; 4C, 4 compartment; HW, hydrostatic weighing; BMC, bone mineral content; TBW, total body water; AP, airdisplacement plethysmography. 2 P < different from the 4C model when tested on elderly women. A review by Heymsfield et al (21) analyzed measured compared with calculated densities of the 4 compartments of the body: fat, water, protein, and minerals. They concluded that the 4C model accounted for >97% of the total body weight whether the densities were calculated or measured. By contrast, a 2C model was not able to yield such a high percentage because of the assumptions of a 2C model and a steady decline in total body calcium, potassium (minerals), and protein for both elderly men and women after the age of 25 y (21). As shown in Table 2, the older individuals had a greater %BF than the younger ones, which was compounded by the loss of FFM or sarcopenia in the older individuals (9, 13). The mean %BF in this population with the use of the 4C model was ± 6.31% for the men and 37.6 ± 8.11% for the women. The men had a %BF > 44% greater than that of the reference man, which is normally considered to be 15%BF. The women had a %BF >33% greater than that of the reference woman, which is normally 25%BF (13). These elevated amounts of %BF are similar to those previously reported in the literature (13). Declining BMC (21, 22) and fluctuations of TBW (23, 24) are not uncommon in the elderly (25). First, other studies showed that BMC was 6.8 ± 0.9% of FFM (16). This would yield a predicted BMC of 3410 ± 450 g given the FFM of this elderly population. In this study, the BMC was 2276 ± 547 g. This is 2.5 SDs below the reference value of 6.8% of FFM. The lower BMC in our study population may have been due to the calibration of the QDR-4500A bone densitometer or may represent the actual bone mineral status of this elderly population. Age-related bone loss likely led to a lower BMC in the elderly men and women studied here. Consequently, the fraction of total FFM that is represented by BMC will be lower than that seen in a younger population. The bone mineral calibration of the QDR-4500A bone densitometer has been compared with previous models (17). In general, close agreement (mean differences of <1 2%) was seen FIGURE 1. Scatter plot of the relation between percentage body fat measured by the 2-compartment (2C) models and that measured by the 4-compartment (4C) equation. HW, hydrostatic weighing; AP, air-displacement plethysmography instrument. 2C HW = x , R = The equations used to calculate percentage body fat are given in the text.
5 BODY COMPOSITION IN AN ELDERLY POPULATION 641 FIGURE 2. Scatter plot of the relation between percentage body fat measured by the 3-compartment (3C) models and that measured by the 4-compartment (4C) equation. BMC, bone mineral content; HW, hydrostatic weighing; TBW, total body water; AP, air-displacement plethysmography instrument. 3C BMCHW = x , R = 0.91; 3C TBWHW = x , R = 0.99; 3C BMCAP = x , R = 0.89; 3C TBWAP = x , R = The equations used to calculate percentage body fat are given in the text. when the bone mineral density results of the spine, femur, or forearm from the QDR-4500A bone densitometer were compared with those from earlier Hologic models. However, 2 studies showed that the total body BMC measured by the QDR- 4500A bone densitometer is 5 6% lower than that observed with the QDR-2000 (26) and QDR-1000 bone densitometers (27). Second, TBW varies with age and FFM (24). It is commonly believed that the older the individual the less body water he or she has because of higher body fat or reduced hydration (13). However, Schoeller and Jones (24) noted that with advancing age overall hydration remains constant and may become even slightly higher, suggesting that the hydration status of the elderly was not a factor that affected body composition. The human body, if normally hydrated, consists of 73% of FFM as water (24, 26). Consequently, if this elderly group were normally hydrated, the TBW should be 37 L; in fact, the average measured TBW for this sample was ± 7.92 L. Changes in hydration amounts with advancing age are currently unknown. Some researchers have reported dehydration among elderly individuals (13, 16), whereas others have not (24). Our results suggest that this group of elderly individuals was not dehydrated, which allows us to conclude that the 2C water estimations are valid. Addition of the BMC to the 3C model (Figure 2) resulted in no significant difference in the estimate of %BF compared with the 2C (Figure 1), 3C TBW, and 4C (Figure 3) models. Thus, the addition of TBW (Figure 2) did not result in a significant difference in the estimation of %BF in either the 3C or 4C models. Furthermore, the combination of BMC and TBW in the 4C model did not result in an estimate of %BF significantly different from that of any of the other models. In conclusion, HW has drawbacks when used in an elderly population. The tests are time consuming and the subjects must be in good physical condition to perform the procedure. The new AP instrument was faster, less physically challenging for the participants, and provided results that were not significantly different FIGURE 3. Scatter plot of the relation between percentage body fat measured by the 4-compartment (4C) model with hydrostatic weighing (HW) and that measured by the 4C model with the air-displacement plethysmography (AP) instrument. 4C AP = x , R = The equations used to calculate percentage body fat are given in the text. from those obtained with traditional HW. Finally, the use of multicompartment models did not provide estimates of %BF significantly different from those obtained by the 2C model in this particular group of older individuals. We thank Frank Verducci of San Francisco State University for his knowledge, expertise, and support of this project. REFERENCES 1. Marks BL, Rippe JM. The importance of fat free mass maintenance in weight loss programmes. Sports Med 1996;22: Borkan GA, Hults DE, Gerzof SG, Robbins AH, Silbert CK. Age changes in body composition revealed by computed tomography. J Gerontol 1983;38: Bemben MG, Massey BH, Bemben DA, Boileau RA, Misner JE. Age-related patterns in body composition for men aged yr. Med Sci Sports Exerc 1995;27: Grimsby G, Saltin B. Mini review: the aging muscle. Clin Physiol 1983;3: Poehlman ET, Toth MJ, Bunyard LB, et al. Physiological predictors of increasing total and central adiposity in aging men and women. Arch Intern Med 1995;155: Behnke AR, Wilmore JH. The specific gravity of healthy men. JAMA 1942;118: Dempster P, Aitkens S. A new air displacement method for the determination of human body composition. Med Sci Sports Exerc 1995;27: McCrory MA, Gomez TD, Bernauer EM, Mole PA. Evaluation of a new air displacement plethysmograph for measuring human body composition. Med Sci Sports Exerc 1995;27: Bergsma-Kadijk J, Baumeister B, Deurenberg P. Measurement of body fat in young and elderly women: comparison between a fourcompartment model and widely used reference methods. Br J Nutr 1996;75: Forslund AH, Johansson AG, Sjodin A, Bryding G, Ljunghall S, Hambraeus L. Evaluation of modified multicompartment models to calculate body composition in healthy males. Am J Clin Nutr 1996; 63: Pace N, Rathbun EN. Studies on body composition III. The body water and chemically combined nitrogen content in relation to fat content. J Biol Chem 1945;158:
6 642 YEE ET AL 12. Friedl KE, DeLuca JP, Marchitelli LJ, Vogel JA. Reliability of bodyfat estimations from a four-compartment model by using density, body water, and bone mineral measurement. Am J Clin Nutr 1992; 55: Spirduso WW. Physical development and decline. In: Physical dimensions of aging. Champaign, IL: Human Kinetics, 1995: Thomas TR, Crough LD, Araujo J. Dietary preparation and percentage fat measurement by hydrostatic weighing. Br J Sports Med 1988;22: Cherniak RM. Assessment of ventilatory function. In: Pulmonary function testing. Philadelphia: WB Saunders, 1992: Lohman TG. Advances in body composition assessment. Champaign, IL: Human Kinetics, Fuerst T, Gluer CC, Genant HK. Performance evaluation of a new bone densitometer: Hologic QDR J Bone Miner Res 1995; 10(suppl):S370 (abstr). 18. Schoeller DA, Hnilicka JM. Reliability of the doubly labeled water method for the measurement of total daily energy expenditure in free-living subjects. J Nutr 1996;126(suppl):S Heyward V. Advanced fitness assessment and exercise prescription. 2nd ed. Champaign, IL: Human Kinetics, Hewitt MJ, Going SB, Williams DP, Lohman TP. Hydration of the fat-free body mass in children and adults: implications for body composition assessment. Am J Physiol1 993;265:E Heymsfield SB, Wang J, Lichtman S, Kamen Y, Kehayias J, Pierson RN Jr. Body composition in elderly subjects: a critical appraisal of clinical methodology. Am J Clin Nutr 1989;50: Ooms ME, Lips P, Van Lingen A, Valkenburg HA. Determinants of bone mineral density and risk factors for osteoporosis in healthy elderly women. J Bone Miner Res 1993;8: Steen GB, Isaksson B, Svanberg A. Body composition at 70 and 75 years of age: a longitudinal population study. J Clin Exp Gerontol 1979;1: Schoeller DA, Jones PJH. Changes in total body water with age. Am J Clin Nutr 1989;50: Chumlea WC, Baumgartner RN. Status of anthropometry and body composition data in elderly subjects. Am J Clin Nutr 1989;50: Fuerst T, Genant HK. Evaluation of body composition and total body bone mass with the Hologic QDR Osteoporos Int 1996; 6(suppl):S202 (abstr). 27. Bouyoucef SE, Cullum ID, Ell PJ. Cross-calibration of a fan-beam X-ray densitometer with a pencil-beam system. Br J Radiol 1996; 69:
Chapter 17: Body Composition Status and Assessment
 Chapter 17: Body Composition Status and Assessment American College of Sports Medicine. (2010). ACSM's resource manual for guidelines for exercise testing and prescription (6th ed.). New York: Lippincott,
Chapter 17: Body Composition Status and Assessment American College of Sports Medicine. (2010). ACSM's resource manual for guidelines for exercise testing and prescription (6th ed.). New York: Lippincott,
Body composition in children and adults by air displacement plethysmography
 European Journal of Clinical Nutrition (1999) 53, 382±387 ß 1999 Stockton Press. All rights reserved 0954±3007/99 $12.00 http://www.stockton-press.co.uk/ejcn Body composition in children and adults by
European Journal of Clinical Nutrition (1999) 53, 382±387 ß 1999 Stockton Press. All rights reserved 0954±3007/99 $12.00 http://www.stockton-press.co.uk/ejcn Body composition in children and adults by
Body composition techniques and the four-compartment model in children
 J Appl Physiol 89: 613 620, 2000. Body composition techniques and the four-compartment model in children DAVID A. FIELDS AND MICHAEL I. GORAN Division of Physiology and Metabolism, Department of Nutrition
J Appl Physiol 89: 613 620, 2000. Body composition techniques and the four-compartment model in children DAVID A. FIELDS AND MICHAEL I. GORAN Division of Physiology and Metabolism, Department of Nutrition
As of the wrestling season, the National
 Evaluation of Air Displacement for Assessing Body Composition of Collegiate Wrestlers ALAN C. UTTER 1, FREDRIC L. GOSS 2, PAMELA D. SWAN 3, GREGORY S. HARRIS 1, ROBERT J. ROBERTSON 2, and GREGORY A. TRONE
Evaluation of Air Displacement for Assessing Body Composition of Collegiate Wrestlers ALAN C. UTTER 1, FREDRIC L. GOSS 2, PAMELA D. SWAN 3, GREGORY S. HARRIS 1, ROBERT J. ROBERTSON 2, and GREGORY A. TRONE
COMPARISON OF AIR DISPLACEMENT PLETHYSMOGRAPHY TO HYDROSTATIC WEIGHING FOR ESTIMATING TOTAL BODY DENSITY IN CHILDREN
 COMPARISON OF AIR DISPLACEMENT PLETHYSMOGRAPHY TO HYDROSTATIC WEIGHING FOR ESTIMATING TOTAL BODY DENSITY IN CHILDREN Geo Claros 1, Holly R Hull 1, and David A Fields 1,2 * 1 Department of Health and Exercise
COMPARISON OF AIR DISPLACEMENT PLETHYSMOGRAPHY TO HYDROSTATIC WEIGHING FOR ESTIMATING TOTAL BODY DENSITY IN CHILDREN Geo Claros 1, Holly R Hull 1, and David A Fields 1,2 * 1 Department of Health and Exercise
Applied Physiology, Nutrition, and Metabolism
 Applied Physiology, Nutrition, and Metabolism Predicted Versus Measured Thoracic Gas Volumes of Collegiate Athletes Made by the BOD POD Air Displacement Plethysmography System Journal: Applied Physiology,
Applied Physiology, Nutrition, and Metabolism Predicted Versus Measured Thoracic Gas Volumes of Collegiate Athletes Made by the BOD POD Air Displacement Plethysmography System Journal: Applied Physiology,
Air-displacement plethysmography for the measurement of body composition in children aged 6 48 months
 nature publishing group Clinical Investigation Articles Air-displacement plethysmography for the measurement of body composition in children aged 6 48 months Ryan P. Rosendale 1 and Cynthia J. Bartok 1
nature publishing group Clinical Investigation Articles Air-displacement plethysmography for the measurement of body composition in children aged 6 48 months Ryan P. Rosendale 1 and Cynthia J. Bartok 1
Note that metric units are used in the calculation of BMI. The following imperial-metric conversions are required:
 Body Composition Body Composition: Assessment and Interpretation Body composition has great practical and functional significance for many of us: scientists, clinicians and the general population. It can
Body Composition Body Composition: Assessment and Interpretation Body composition has great practical and functional significance for many of us: scientists, clinicians and the general population. It can
Documentation, Codebook, and Frequencies
 Documentation, Codebook, and Frequencies Dual-Energy X-ray Absorptiometry Femur Bone Measurements Examination Survey Years: 2005 to 2006 SAS Transport File: DXXFEM_D.XPT January 2009 NHANES 2005 2006 Data
Documentation, Codebook, and Frequencies Dual-Energy X-ray Absorptiometry Femur Bone Measurements Examination Survey Years: 2005 to 2006 SAS Transport File: DXXFEM_D.XPT January 2009 NHANES 2005 2006 Data
COMPARISON OF BODY COMPOSITION ASSESSMENT IN WOMEN USING SKINFOLD THICKNESS EQUATIONS, BIOELECTRICAL IMPEDANCE ANALYSIS AND UNDERWATER WEIGHING
 STUDIES IN PHYSICAL CULTURE AND TOURISM Vol. 17, No. 3, 2010 EFTEKHAR MOHAMMADI, SAEID SHAKERIAN Faculty of Physical Education & Sports Science, Shahid Chamran University, Iran COMPARISON OF BODY COMPOSITION
STUDIES IN PHYSICAL CULTURE AND TOURISM Vol. 17, No. 3, 2010 EFTEKHAR MOHAMMADI, SAEID SHAKERIAN Faculty of Physical Education & Sports Science, Shahid Chamran University, Iran COMPARISON OF BODY COMPOSITION
British Journal of Nutrition
 (2008), 99, 432 441 q The Authors 2007 doi: 10.1017/S0007114507815789 Usefulness of different techniques for measuring body composition changes during weight loss in overweight and obese women Cláudia
(2008), 99, 432 441 q The Authors 2007 doi: 10.1017/S0007114507815789 Usefulness of different techniques for measuring body composition changes during weight loss in overweight and obese women Cláudia
Luís B Sardinha, Timothy G Lohman, Pedro J Teixeira, Dartagnan P Guedes, and Scott B Going
 Comparison of air displacement plethysmography with dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry and 3 field methods for estimating body composition in middle-aged men 1,2 Luís B Sardinha, Timothy G Lohman, Pedro
Comparison of air displacement plethysmography with dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry and 3 field methods for estimating body composition in middle-aged men 1,2 Luís B Sardinha, Timothy G Lohman, Pedro
Body composition assessment in extreme obesity and after massive weight loss induced by gastric bypass surgery
 Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab 84: E1080 E1088, 003. First published February 5, 003; 10.115/ajpendo.005.00. Body composition assessment in extreme obesity and after massive weight loss induced by gastric
Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab 84: E1080 E1088, 003. First published February 5, 003; 10.115/ajpendo.005.00. Body composition assessment in extreme obesity and after massive weight loss induced by gastric
Bone Mineral and Body Composition Measurements: Cross-Calibration of Pencil-Beam and Fan-Beam Dual- Energy X-Ray Absorptiometers*
 JOURNAL OF BONE AND MINERAL RESEARCH Volume 13, Number 10, 1998 Blackwell Science, Inc. 1998 American Society for Bone and Mineral Research Bone Mineral and Body Composition Measurements: Cross-Calibration
JOURNAL OF BONE AND MINERAL RESEARCH Volume 13, Number 10, 1998 Blackwell Science, Inc. 1998 American Society for Bone and Mineral Research Bone Mineral and Body Composition Measurements: Cross-Calibration
Anthropometry and methods of body composition measurement for research and eld application in the elderly
 (2000) 54, Suppl 3, S26±S32 ß 2000 Macmillan Publishers Ltd All rights reserved 0954±3007/00 $15.00 www.nature.com/ejcn Anthropometry and methods of body composition measurement for research and eld application
(2000) 54, Suppl 3, S26±S32 ß 2000 Macmillan Publishers Ltd All rights reserved 0954±3007/00 $15.00 www.nature.com/ejcn Anthropometry and methods of body composition measurement for research and eld application
Roberto D Sainz and Alessandro Urlando
 Evaluation of a new pediatric air-displacement plethysmograph for body-composition assessment by means of chemical analysis of bovine tissue phantoms 1 3 Roberto D Sainz and Alessandro Urlando ABSTRACT
Evaluation of a new pediatric air-displacement plethysmograph for body-composition assessment by means of chemical analysis of bovine tissue phantoms 1 3 Roberto D Sainz and Alessandro Urlando ABSTRACT
DEXA Bone Mineral Density Tests and Body Composition Analysis Information for Health Professionals
 DEXA Bone Mineral Density Tests and Body Composition Analysis Information for Health Professionals PERFORMANCE DEXA is an advanced technology originally used to, and still capable of assessing bone health
DEXA Bone Mineral Density Tests and Body Composition Analysis Information for Health Professionals PERFORMANCE DEXA is an advanced technology originally used to, and still capable of assessing bone health
Measurement of total body water using 2 H dilution: impact of different calculations for determining body fat
 British Journal of Nutrition (2002), 88, 325 329 q The Authors 2002 DOI: 10.1079/BJN2002654 Measurement of total body water using 2 H dilution: impact of different calculations for determining body fat
British Journal of Nutrition (2002), 88, 325 329 q The Authors 2002 DOI: 10.1079/BJN2002654 Measurement of total body water using 2 H dilution: impact of different calculations for determining body fat
ESPEN Congress The Hague 2017
 ESPEN Congress The Hague 2017 Paediatric specificities of nutritional assessment Body composition measurement in children N. Mehta (US) 39 th ESPEN Congress The Hague, Netherlands Body Composition Measurement
ESPEN Congress The Hague 2017 Paediatric specificities of nutritional assessment Body composition measurement in children N. Mehta (US) 39 th ESPEN Congress The Hague, Netherlands Body Composition Measurement
Whole Body Dual X-Ray Absorptiometry to Determine Body Composition
 Page: 1 of 6 Last Review Status/Date: March 2015 Determine Body Composition Description Using low dose x-rays of two different energy levels, whole body dual x-ray absorptiometry (DXA) measures lean tissue
Page: 1 of 6 Last Review Status/Date: March 2015 Determine Body Composition Description Using low dose x-rays of two different energy levels, whole body dual x-ray absorptiometry (DXA) measures lean tissue
Body-composition assessment in infancy: air-displacement plethysmography compared with a reference 4-compartment model 1 4
 Body-composition assessment in infancy: air-displacement plethysmography compared with a reference 4-compartment model 1 4 Kenneth J Ellis, Manjiang Yao, Roman J Shypailo, Alessandro Urlando, William W
Body-composition assessment in infancy: air-displacement plethysmography compared with a reference 4-compartment model 1 4 Kenneth J Ellis, Manjiang Yao, Roman J Shypailo, Alessandro Urlando, William W
Multi-Compartment Model (MCM) and Body Composition Measurement Techniques
 White Paper Contents Multi Compartment Model (MCM) 1 Methods comparable to MCM 2 Methods NOT comparable to MCMC 3 References 6 Multi-Compartment Model (MCM) and Body Composition Measurement Techniques
White Paper Contents Multi Compartment Model (MCM) 1 Methods comparable to MCM 2 Methods NOT comparable to MCMC 3 References 6 Multi-Compartment Model (MCM) and Body Composition Measurement Techniques
special communication
 special communication Determining bone and total body mineral content from body density and bioelectrical response spectroscopy STEVEN F. SICONOLFI, 1 RANDAL J. GRETEBECK, 2 WILLIAM W. WONG, 3 SHERIL S.
special communication Determining bone and total body mineral content from body density and bioelectrical response spectroscopy STEVEN F. SICONOLFI, 1 RANDAL J. GRETEBECK, 2 WILLIAM W. WONG, 3 SHERIL S.
The Assessment of Body Composition in Health and Disease
 The Assessment of Body Composition in Health and Disease Giorgio Bedogni, Paolo Brambilla, Stefano Bellentani and Claudio Tiribelli CHAPTER 3 BODY AND NUTRITIONAL STATUS Nutritional status can be operationally
The Assessment of Body Composition in Health and Disease Giorgio Bedogni, Paolo Brambilla, Stefano Bellentani and Claudio Tiribelli CHAPTER 3 BODY AND NUTRITIONAL STATUS Nutritional status can be operationally
Interaction of clothing and body mass index affects validity of air-displacement plethysmography in adults
 Nutrition 24 (2008) 148 154 Applied nutritional investigation Interaction of clothing and body mass index affects validity of air-displacement plethysmography in adults Kimberly J. Shafer, Ph.D., R.D.,
Nutrition 24 (2008) 148 154 Applied nutritional investigation Interaction of clothing and body mass index affects validity of air-displacement plethysmography in adults Kimberly J. Shafer, Ph.D., R.D.,
Alterations in growth and body composition during puberty. I. Comparing multicompartment body composition models
 Alterations in growth and body composition during puberty. I. Comparing multicompartment body composition models JAMES N. ROEMMICH, 1 PAMELA A. CLARK, 1 ARTHUR WELTMAN, 2,3 AND ALAN D. ROGOL 1,4 1 Division
Alterations in growth and body composition during puberty. I. Comparing multicompartment body composition models JAMES N. ROEMMICH, 1 PAMELA A. CLARK, 1 ARTHUR WELTMAN, 2,3 AND ALAN D. ROGOL 1,4 1 Division
Can the LeanScreen App Accurately Assess Percent Body Fat and Waistto-Hip
 Can the LeanScreen App Accurately Assess Percent Body Fat and Waistto-Hip Ratio? EXCLUSIVE ACE SPONSORED RESEARCH BY RAY MARX, JOHN P. PORCARI, PH.D., SCOTT DOBERSTEIN, M.S., RICHARD MIKAT, PH.D., AND
Can the LeanScreen App Accurately Assess Percent Body Fat and Waistto-Hip Ratio? EXCLUSIVE ACE SPONSORED RESEARCH BY RAY MARX, JOHN P. PORCARI, PH.D., SCOTT DOBERSTEIN, M.S., RICHARD MIKAT, PH.D., AND
Simopoulos AP (ed): Nutrition and Fitness: Obesity, the Metabolic Syndrome, Cardiovascular Disease and Cancer. Basel, Karger, 2005, vol 94, pp 60 67
 WRN94060.qxd 4/11/05 4:57 PM Page 60 Simopoulos AP (ed): Nutrition and Fitness: Obesity, the Metabolic Syndrome, Cardiovascular Disease and Cancer. Basel, Karger, 2005, vol 94, pp 60 67 Physical Activity
WRN94060.qxd 4/11/05 4:57 PM Page 60 Simopoulos AP (ed): Nutrition and Fitness: Obesity, the Metabolic Syndrome, Cardiovascular Disease and Cancer. Basel, Karger, 2005, vol 94, pp 60 67 Physical Activity
Body Composition Analysis by Air Displacement Plethysmography in Normal Weight to Extremely Obese Adults
 Body Composition Analysis by Air Displacement Plethysmography in Normal Weight to Extremely Obese Adults Kazanna C. Hames 1,2, Steven J. Anthony 2, John C. Thornton 3, Dympna Gallagher 3 and Bret H. Goodpaster
Body Composition Analysis by Air Displacement Plethysmography in Normal Weight to Extremely Obese Adults Kazanna C. Hames 1,2, Steven J. Anthony 2, John C. Thornton 3, Dympna Gallagher 3 and Bret H. Goodpaster
Norland Densitometry A Tradition of Excellence
 Norland Densitometry A Tradition of Excellence Norland DXA Bone Density Measurement Osteoporosis is a disease marked by reduced bone strength leading to an increased risk of fractures. About 54 million
Norland Densitometry A Tradition of Excellence Norland DXA Bone Density Measurement Osteoporosis is a disease marked by reduced bone strength leading to an increased risk of fractures. About 54 million
Body composition measurement in severe obesity Sai Krupa Das
 Body composition measurement in severe obesity Sai Krupa Das Purpose of review Severe obesity is accompanied by large increases in fat mass and alterations in the composition of fat free mass, in particular
Body composition measurement in severe obesity Sai Krupa Das Purpose of review Severe obesity is accompanied by large increases in fat mass and alterations in the composition of fat free mass, in particular
Validity of non-invasive methods for body composition measurements in older adults
 Graduate Theses and Dissertations Graduate College 2012 Validity of non-invasive methods for body composition measurements in older adults Yulong Li Iowa State University Follow this and additional works
Graduate Theses and Dissertations Graduate College 2012 Validity of non-invasive methods for body composition measurements in older adults Yulong Li Iowa State University Follow this and additional works
Robert R Biaggi, Michael W Vollman, Mary A Nies, Craig E Brener, Paul J Flakoll, Deanna K Levenhagen, Ming Sun, Zafer Karabulut, and Kong Y Chen
 Comparison of air-displacement plethysmography with hydrostatic weighing and bioelectrical impedance analysis for the assessment of body composition in healthy adults 1 3 Robert R Biaggi, Michael W Vollman,
Comparison of air-displacement plethysmography with hydrostatic weighing and bioelectrical impedance analysis for the assessment of body composition in healthy adults 1 3 Robert R Biaggi, Michael W Vollman,
The Bone Wellness Centre - Specialists in DEXA Scanning 855 Broadview Avenue Suite # 305 Toronto, Ontario M4K 3Z1
 The Bone Wellness Centre - Specialists in DEXA Scanning 855 Broadview Avenue Suite # 305 Toronto, Ontario M4K 3Z1 Patient: Birth Date: 48.2 years Height / Weight: 150.0 cm 72.0 kg Sex / Ethnic: Female
The Bone Wellness Centre - Specialists in DEXA Scanning 855 Broadview Avenue Suite # 305 Toronto, Ontario M4K 3Z1 Patient: Birth Date: 48.2 years Height / Weight: 150.0 cm 72.0 kg Sex / Ethnic: Female
The Bone Wellness Centre - Specialists in DEXA Scanning 855 Broadview Avenue Suite # 305 Toronto, Ontario M4K 3Z1
 The Bone Wellness Centre - Specialists in DEXA Scanning 855 Broadview Avenue Suite # 305 Toronto, Ontario M4K 3Z1 Patient: Birth Date: 43.4 years Height / Weight: 170.0 cm 66.0 kg Sex / Ethnic: Female
The Bone Wellness Centre - Specialists in DEXA Scanning 855 Broadview Avenue Suite # 305 Toronto, Ontario M4K 3Z1 Patient: Birth Date: 43.4 years Height / Weight: 170.0 cm 66.0 kg Sex / Ethnic: Female
BONE DENSITY AS A SOURCE OF ERROR MEASURING. BODY COMPOSITION WITH THE BOD POD and idxa IN FEMALE RUNNERS THESIS. the Degree Master of Science in the
 BONE DENSITY AS A SOURCE OF ERROR MEASURING BODY COMPOSITION WITH THE BOD POD and idxa IN FEMALE RUNNERS THESIS Presented in Partial Fulfillment of the Requirements for the Degree Master of Science in
BONE DENSITY AS A SOURCE OF ERROR MEASURING BODY COMPOSITION WITH THE BOD POD and idxa IN FEMALE RUNNERS THESIS Presented in Partial Fulfillment of the Requirements for the Degree Master of Science in
Segmental Body Composition Assessment for Obese Japanese Adults by Single-Frequency Bioelectrical Impedance Analysis with 8-point Contact Electrodes
 Segmental Body Composition Assessment for Obese Japanese Adults by Single-Frequency Bioelectrical Impedance Analysis with 8-point Contact Electrodes Susumu Sato 1), Shinichi Demura 2), Tamotsu Kitabayashi
Segmental Body Composition Assessment for Obese Japanese Adults by Single-Frequency Bioelectrical Impedance Analysis with 8-point Contact Electrodes Susumu Sato 1), Shinichi Demura 2), Tamotsu Kitabayashi
Location of body fat and body size impacts DXA soft tissue measures: a simulation study
 (2008) 62, 553 559 & 2008 Nature Publishing Group All rights reserved 0954-3007/08 $30.00 www.nature.com/ejcn ORIGINAL ARTICLE Location of body fat and body size impacts DXA soft tissue measures: a simulation
(2008) 62, 553 559 & 2008 Nature Publishing Group All rights reserved 0954-3007/08 $30.00 www.nature.com/ejcn ORIGINAL ARTICLE Location of body fat and body size impacts DXA soft tissue measures: a simulation
Evaluation of body fat in fatter and leaner 10-y-old African American and white children: the Baton Rouge Children s Study 1 3
 Original Research Communications Evaluation of body fat in fatter and leaner 10-y-old African American and white children: the Baton Rouge Children s Study 1 3 George A Bray, James P DeLany, David W Harsha,
Original Research Communications Evaluation of body fat in fatter and leaner 10-y-old African American and white children: the Baton Rouge Children s Study 1 3 George A Bray, James P DeLany, David W Harsha,
The Bone Wellness Centre - Specialists in Dexa Scanning 855 Broadview Avenue Suite # 305 Toronto, Ontario M4K 3Z1
 Birth Date: 24.7 years Height / Weight: 8.0 cm 79.0 kg Sex / Ethnic: Male Patient ID: Total Body Tissue Quantitation Composition Reference: Total Tissue 40% 30% 20% 0% 20 30 40 50 60 70 80 90 00 Centile
Birth Date: 24.7 years Height / Weight: 8.0 cm 79.0 kg Sex / Ethnic: Male Patient ID: Total Body Tissue Quantitation Composition Reference: Total Tissue 40% 30% 20% 0% 20 30 40 50 60 70 80 90 00 Centile
Evaluating body fat in girls and female adolescents: advantages and disadvantages of dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry 1 4
 Evaluating body fat in girls and female adolescents: advantages and disadvantages of dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry 1 4 William W Wong, Albert C Hergenroeder, Janice E Stuff, Nancy F Butte, E O Brian
Evaluating body fat in girls and female adolescents: advantages and disadvantages of dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry 1 4 William W Wong, Albert C Hergenroeder, Janice E Stuff, Nancy F Butte, E O Brian
Twelve percent of children under 2 years1 and 10% of 2 5 year olds are obese
 Fields Insights From Body Composition Studies David Fields, PhD Twelve percent of children under 2 years1 and 10% of 2 5 year olds are obese (National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey; body mass
Fields Insights From Body Composition Studies David Fields, PhD Twelve percent of children under 2 years1 and 10% of 2 5 year olds are obese (National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey; body mass
The Bone Wellness Centre - Specialists in DEXA Scanning 855 Broadview Avenue Suite # 305 Toronto, Ontario M4K 3Z1
 Birth Date: 40.2 years Height / Weight: 158.0 cm 52.0 kg Sex / Ethnic: Female Patient ID: Total Body Tissue Quantitation Composition Reference: Total Tissue 50% 40% 30% 20% 20 30 40 50 60 70 80 90 100
Birth Date: 40.2 years Height / Weight: 158.0 cm 52.0 kg Sex / Ethnic: Female Patient ID: Total Body Tissue Quantitation Composition Reference: Total Tissue 50% 40% 30% 20% 20 30 40 50 60 70 80 90 100
Healthy percentage body fat ranges: an approach for developing guidelines based on body mass index 1 3
 Healthy percentage body fat ranges: an approach for developing guidelines based on body mass index 1 3 Dympna Gallagher, Steven B Heymsfield, Moonseong Heo, Susan A Jebb, Peter R Murgatroyd, and Yoichi
Healthy percentage body fat ranges: an approach for developing guidelines based on body mass index 1 3 Dympna Gallagher, Steven B Heymsfield, Moonseong Heo, Susan A Jebb, Peter R Murgatroyd, and Yoichi
Validation Study of Multi-Frequency Bioelectrical Impedance with Dual-Energy X-ray Absorptiometry Among Obese Patients
 OBES SURG (2014) 24:1476 1480 DOI 10.1007/s11695-014-1190-5 OTHER Validation Study of Multi-Frequency Bioelectrical Impedance with Dual-Energy X-ray Absorptiometry Among Obese Patients Silvia L. Faria
OBES SURG (2014) 24:1476 1480 DOI 10.1007/s11695-014-1190-5 OTHER Validation Study of Multi-Frequency Bioelectrical Impedance with Dual-Energy X-ray Absorptiometry Among Obese Patients Silvia L. Faria
Encompass. Eastern Kentucky University. Lee Doernte Eastern Kentucky University. January 2018
 Eastern Kentucky University Encompass Online Theses and Dissertations Student Scholarship January 2018 Use Of Dual Energy X-Ray Absorptiometry Measurements To Evaluate Total Body Volume When Compared To
Eastern Kentucky University Encompass Online Theses and Dissertations Student Scholarship January 2018 Use Of Dual Energy X-Ray Absorptiometry Measurements To Evaluate Total Body Volume When Compared To
The Bone Wellness Centre - Specialists in Dexa Total Body 855 Broadview Avenue Suite # 305 Toronto, Ontario M4K 3Z1
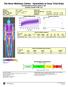 Patient: Obese, Sample Birth Date: 0/Jan/966 44.4 years Height / Weight: 72.0 cm 95.0 kg Sex / Ethnic: Male Patient ID: Referring Physician: DR. SMITH Measured: 07/Jun/200 7:0:52 PM (.40) Analyzed: 02/Apr/203
Patient: Obese, Sample Birth Date: 0/Jan/966 44.4 years Height / Weight: 72.0 cm 95.0 kg Sex / Ethnic: Male Patient ID: Referring Physician: DR. SMITH Measured: 07/Jun/200 7:0:52 PM (.40) Analyzed: 02/Apr/203
Body Composition. Lecture Overview. Measuring of Body Composition. Powers & Howely pp Methods of measuring body composition
 Body Composition Powers & Howely pp 344-356 Lecture Overview Methods of measuring body composition Two-component system Body fatness for health & fitness Obesity and weight control Diet, exercise, and
Body Composition Powers & Howely pp 344-356 Lecture Overview Methods of measuring body composition Two-component system Body fatness for health & fitness Obesity and weight control Diet, exercise, and
Longitudinal Study of Total Body Potassium in Healthy Men
 Original Research Longitudinal Study of Total Body Potassium in Healthy Men Angela Andreoli, MD, PhD, Stella L. Volpe, PhD, Sarah J. Ratcliffe, PhD, Nicola Di Daniele, MD, Antonio Imparato, PhD, Luigi
Original Research Longitudinal Study of Total Body Potassium in Healthy Men Angela Andreoli, MD, PhD, Stella L. Volpe, PhD, Sarah J. Ratcliffe, PhD, Nicola Di Daniele, MD, Antonio Imparato, PhD, Luigi
Duncan Macfarlane IHP, HKU Parts of this lecture were based on lecture notes provided by the Lindsay Carter Anthropometric Archive, AUT, NZ
 Body composition assessment issues in athletes 1 Duncan Macfarlane IHP, HKU Parts of this lecture were based on lecture notes provided by the Lindsay Carter Anthropometric Archive, AUT, NZ LEARNING OUTCOMES:
Body composition assessment issues in athletes 1 Duncan Macfarlane IHP, HKU Parts of this lecture were based on lecture notes provided by the Lindsay Carter Anthropometric Archive, AUT, NZ LEARNING OUTCOMES:
Management of Obesity in Postmenopausal Women
 Management of Obesity in Postmenopausal Women Yong Seong Kim, M.D. Division of Endocrinology and Metabolism Inha University College of Medicine & Hospital E mail : yongskim@inha.ac.kr Abstract Women have
Management of Obesity in Postmenopausal Women Yong Seong Kim, M.D. Division of Endocrinology and Metabolism Inha University College of Medicine & Hospital E mail : yongskim@inha.ac.kr Abstract Women have
The physical educator s role is evolving into that of a teacher who is well educated
 Assessment and Interpretation of Body Composition in Physical Education PAT VEHRS RON HAGER Should you use skinfolds, bio-electrical impedence, or BMI? The physical educator s role is evolving into that
Assessment and Interpretation of Body Composition in Physical Education PAT VEHRS RON HAGER Should you use skinfolds, bio-electrical impedence, or BMI? The physical educator s role is evolving into that
Original Article. Paul Deurenberg 1 PhD and Mabel Deurenberg-Yap 2 MD, PhD. Asia Pacific J Clin Nutr (2002) 11(1): 1 7
 Asia Pacific J Clin Nutr (2002) 11(1): 1 7 1 Original Article Validation of skinfold thickness and hand-held impedance measurements for estimation of body fat percentage among Singaporean Chinese, Malay
Asia Pacific J Clin Nutr (2002) 11(1): 1 7 1 Original Article Validation of skinfold thickness and hand-held impedance measurements for estimation of body fat percentage among Singaporean Chinese, Malay
Body composition assessment for development of an international growth standard for preadolescent and adolescent children
 Body composition assessment for development of an international growth standard for preadolescent and adolescent children Timothy G. Lohman and Scott B. Going Abstract General considerations in assessing
Body composition assessment for development of an international growth standard for preadolescent and adolescent children Timothy G. Lohman and Scott B. Going Abstract General considerations in assessing
The Bone Wellness Centre - Specialists in DEXA Scanning 855 Broadview Avenue Suite # 305 Toronto, Ontario M4K 3Z1
 The Bone Wellness Centre - Specialists in DEXA Scanning 855 Broadview Avenue Suite # 305 Toronto, Ontario M4K 3Z1 Patient: Birth Date: 29.5 years Height / Weight: 156.0 cm 57.0 kg Sex / Ethnic: Female
The Bone Wellness Centre - Specialists in DEXA Scanning 855 Broadview Avenue Suite # 305 Toronto, Ontario M4K 3Z1 Patient: Birth Date: 29.5 years Height / Weight: 156.0 cm 57.0 kg Sex / Ethnic: Female
VALIDITY AND RELIABILITY OF BODY COMPOSITION TECHNIQUES IN HEALTHY ADULTS
 VALIDITY AND RELIABILITY OF BODY COMPOSITION TECHNIQUES IN HEALTHY ADULTS A^> 3
VALIDITY AND RELIABILITY OF BODY COMPOSITION TECHNIQUES IN HEALTHY ADULTS A^> 3
bioelectrical impedance measurements. Aviation Space and Environmental Medicine, 59,
 MS ID: 9761874491197639 Authors: Macias et al Title: Body fat measurement by bioelectrical impedance versus air displacement plethysmography: a validation to design bioelectrical impedance equations in
MS ID: 9761874491197639 Authors: Macias et al Title: Body fat measurement by bioelectrical impedance versus air displacement plethysmography: a validation to design bioelectrical impedance equations in
A Pilot Study of Exercise Training to Reduce Trunk Fat in Adults With HIV Associated Fat Redistribution
 A Pilot Study of Exercise Training to Reduce Trunk Fat in Adults With HIV Associated Fat Redistribution Ronenn Roubenoff, Lauren Weiss, Ann McDermott, Tanya Heflin, Gregory J. Cloutier, Michael Wood and
A Pilot Study of Exercise Training to Reduce Trunk Fat in Adults With HIV Associated Fat Redistribution Ronenn Roubenoff, Lauren Weiss, Ann McDermott, Tanya Heflin, Gregory J. Cloutier, Michael Wood and
Total daily energy expenditure among middle-aged men and women: the OPEN Study 1 3
 Total daily energy expenditure among middle-aged men and women: the OPEN Study 1 3 Janet A Tooze, Dale A Schoeller, Amy F Subar, Victor Kipnis, Arthur Schatzkin, and Richard P Troiano ABSTRACT Background:
Total daily energy expenditure among middle-aged men and women: the OPEN Study 1 3 Janet A Tooze, Dale A Schoeller, Amy F Subar, Victor Kipnis, Arthur Schatzkin, and Richard P Troiano ABSTRACT Background:
Validity of Anthropometric Regression Equations for Predicting Changes in Body Fat of Obese Females
 AMERICAN JOURNAL OF HUMAN BIOLOGY 1:97-101 (1989) Validity of Anthropometric Regression Equations for Predicting Changes in Body Fat of Obese Females DOUGLAS L. BALLOR AND VICTOR L. KATCH Behnke Laboratory
AMERICAN JOURNAL OF HUMAN BIOLOGY 1:97-101 (1989) Validity of Anthropometric Regression Equations for Predicting Changes in Body Fat of Obese Females DOUGLAS L. BALLOR AND VICTOR L. KATCH Behnke Laboratory
VALIDITY OF VARIOUS BIOELECTICAL IMPEDANCE ANALYSIS (BIA) ANALYZERS IN ASSESSING BODY FATNESS AMONG HONG KONG UNIVERSITY STUDENTS
 VALIDITY OF VARIOUS BIOELECTICAL IMPEDANCE ANALYSIS (BIA) ANALYZERS IN ASSESSING BODY FATNESS AMONG HONG KONG UNIVERSITY STUDENTS BY CHAN YIU WA 03014339 AN HONOURS PROJECT SUBMITTED IN PARTIAL FULFILLMENT
VALIDITY OF VARIOUS BIOELECTICAL IMPEDANCE ANALYSIS (BIA) ANALYZERS IN ASSESSING BODY FATNESS AMONG HONG KONG UNIVERSITY STUDENTS BY CHAN YIU WA 03014339 AN HONOURS PROJECT SUBMITTED IN PARTIAL FULFILLMENT
Body composition assessment methods
 2018; 3(1): 484-488 ISSN: 2456-0057 IJPNPE 2018; 3(1): 484-488 2018 IJPNPE www.journalofsports.com Received: 15-11-2017 Accepted: 16-12-2017 Rohit Bhairvanath Adling Director of Physical Education, Dadapatil
2018; 3(1): 484-488 ISSN: 2456-0057 IJPNPE 2018; 3(1): 484-488 2018 IJPNPE www.journalofsports.com Received: 15-11-2017 Accepted: 16-12-2017 Rohit Bhairvanath Adling Director of Physical Education, Dadapatil
How Useful Is Body Mass Index for Comparison of Body Fatness across Age, Sex, and Ethnic Groups?
 American Journal of Epidemiology Copyright O 1996 by The Johns Hopkins University School of Hygiene and Public Health All rights reserved Vol. 143, No. 3 Printed In U.SA. How Useful Is Body Mass Index
American Journal of Epidemiology Copyright O 1996 by The Johns Hopkins University School of Hygiene and Public Health All rights reserved Vol. 143, No. 3 Printed In U.SA. How Useful Is Body Mass Index
Body composition analysis by dual energy X-ray absorptiometry in female diabetics differ between manufacturers
 European Journal of Clinical Nutrition (1997) 51, 449±454 ß 1997 Stockton Press. All rights reserved 0954±3007/97 $12.00 Body composition analysis by dual energy X-ray absorptiometry in female diabetics
European Journal of Clinical Nutrition (1997) 51, 449±454 ß 1997 Stockton Press. All rights reserved 0954±3007/97 $12.00 Body composition analysis by dual energy X-ray absorptiometry in female diabetics
Body Composition. Chapters 18 and 23
 Body Composition Chapters 18 and 23 Somatotype (Body Type) Soft roundness? endormorphy High muscle mass? mesomorphy Linearity and fragility? ectomorphy Body Composition Methods Height Weight Tables e.g.
Body Composition Chapters 18 and 23 Somatotype (Body Type) Soft roundness? endormorphy High muscle mass? mesomorphy Linearity and fragility? ectomorphy Body Composition Methods Height Weight Tables e.g.
The New England Journal of Medicine
 The New England Journal of Medicine Copyright, 2000, by the Massachusetts Medical Society VOLUME 342 F EBRUARY 17, 2000 NUMBER 7 THE EFFECT OF WEIGHT LOSS IN OVERWEIGHT, LACTATING WOMEN ON THE GROWTH OF
The New England Journal of Medicine Copyright, 2000, by the Massachusetts Medical Society VOLUME 342 F EBRUARY 17, 2000 NUMBER 7 THE EFFECT OF WEIGHT LOSS IN OVERWEIGHT, LACTATING WOMEN ON THE GROWTH OF
BODY COMPOSITION: AN ANALYSIS BETWEEN THE FOOTBALLER AND THANG-TA PRACTITIONER OF MANIPUR
 BODY COMPOSITION: AN ANALYSIS BETWEEN THE FOOTBALLER AND THANG-TA PRACTITIONER OF MANIPUR T. INAOBI SINGH 1, MAIBAM CHOURJIT SINGH 2, CHETAN MAIBAM 3 1 Department of Physical Education & Sports Science,
BODY COMPOSITION: AN ANALYSIS BETWEEN THE FOOTBALLER AND THANG-TA PRACTITIONER OF MANIPUR T. INAOBI SINGH 1, MAIBAM CHOURJIT SINGH 2, CHETAN MAIBAM 3 1 Department of Physical Education & Sports Science,
Comparison of Body Composition Assessment Techniques in Older Adults
 University of Tennessee, Knoxville Trace: Tennessee Research and Creative Exchange Masters Theses Graduate School 8-2005 Comparison of Body Composition Assessment Techniques in Older Adults Rebekah Ann
University of Tennessee, Knoxville Trace: Tennessee Research and Creative Exchange Masters Theses Graduate School 8-2005 Comparison of Body Composition Assessment Techniques in Older Adults Rebekah Ann
Weight Management: Finding a Healthy Balance. discuss the differences between overweight and obese and their implications for health;
 CHAPTER 11 Weight Management: Finding a Healthy Balance After completing this chapter you should be able to: discuss the differences between overweight and obese and their implications for health; explain
CHAPTER 11 Weight Management: Finding a Healthy Balance After completing this chapter you should be able to: discuss the differences between overweight and obese and their implications for health; explain
Body composition A tool for nutritional assessment
 Body composition A tool for nutritional assessment Ingvar Bosaeus Clinical Nutrition Unit Sahlgrenska University Hospital NSKE Oslo 2012-01-18 Outline What is body composition? What is nutritional assessment?
Body composition A tool for nutritional assessment Ingvar Bosaeus Clinical Nutrition Unit Sahlgrenska University Hospital NSKE Oslo 2012-01-18 Outline What is body composition? What is nutritional assessment?
The effect of a meal on measures of impedance and percent body fat estimated using contact-electrode bioelectrical impedance technology
 European Journal of Clinical Nutrition (2013) 67, 950 955 & 2013 Macmillan Publishers Limited All rights reserved 0954-3007/13 www.nature.com/ejcn ORIGINAL ARTICLE The effect of a meal on measures of impedance
European Journal of Clinical Nutrition (2013) 67, 950 955 & 2013 Macmillan Publishers Limited All rights reserved 0954-3007/13 www.nature.com/ejcn ORIGINAL ARTICLE The effect of a meal on measures of impedance
A Comparison of Hydrostatic Weighing and Air Displacement Plethysmography in Adults With Spinal Cord Injury
 2106 ORIGINAL ARTICLE A Comparison of Hydrostatic Weighing and Air Displacement Plethysmography in Adults With Spinal Cord Injury Jody L. Clasey, PhD, David R. Gater Jr, MD, PhD ABSTRACT. Clasey JL, Gater
2106 ORIGINAL ARTICLE A Comparison of Hydrostatic Weighing and Air Displacement Plethysmography in Adults With Spinal Cord Injury Jody L. Clasey, PhD, David R. Gater Jr, MD, PhD ABSTRACT. Clasey JL, Gater
Journal of Exercise Physiologyonline (JEPonline)
 Fluid Load and Body Composition 1 Journal of Exercise Physiologyonline (JEPonline) Volume 12 Number 2 April 2009 Managing Editor Tommy Boone, Ph.D Editor-in-Chief Jon K. Linderman, Ph.D. Review Board Todd
Fluid Load and Body Composition 1 Journal of Exercise Physiologyonline (JEPonline) Volume 12 Number 2 April 2009 Managing Editor Tommy Boone, Ph.D Editor-in-Chief Jon K. Linderman, Ph.D. Review Board Todd
Does standardized BMD still remove differences between Hologic and GE-Lunar state-of-the-art DXA systems?
 Osteoporos Int (2010) 21:1227 1236 DOI 10.1007/s00198-009-1062-3 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Does standardized BMD still remove differences between Hologic and GE-Lunar state-of-the-art DXA systems? B. Fan & Y. Lu
Osteoporos Int (2010) 21:1227 1236 DOI 10.1007/s00198-009-1062-3 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Does standardized BMD still remove differences between Hologic and GE-Lunar state-of-the-art DXA systems? B. Fan & Y. Lu
DIALYSIS OUTCOMES Quality Initiative
 Bipedal Bioelectrical Impedance Analysis Reproducibly Estimates Total Body Water in Hemodialysis Patients Robert F. Kushner, MD, and David M. Roxe, MD Formal kinetic modeling for hemodialysis patients
Bipedal Bioelectrical Impedance Analysis Reproducibly Estimates Total Body Water in Hemodialysis Patients Robert F. Kushner, MD, and David M. Roxe, MD Formal kinetic modeling for hemodialysis patients
Bedside methods versus dual energy X-ray absorptiometry for body composition measurement in COPD
 Eur Respir J ; 19: 66 631 DOI: 1.1183/931936..796 Printed in UK all rights reserved Copyright #ERS Journals Ltd European Respiratory Journal ISSN 93-1936 Bedside methods versus dual energy X-ray absorptiometry
Eur Respir J ; 19: 66 631 DOI: 1.1183/931936..796 Printed in UK all rights reserved Copyright #ERS Journals Ltd European Respiratory Journal ISSN 93-1936 Bedside methods versus dual energy X-ray absorptiometry
Title:Body adiposity index performance in estimating body fat in a sample of severely obese Brazilian patients
 Author's response to reviews Title:Body adiposity index performance in estimating body fat in a sample of severely obese Brazilian patients Authors: Giliane Belarmino (giliane85@hotmail.com) Lilian M Horie
Author's response to reviews Title:Body adiposity index performance in estimating body fat in a sample of severely obese Brazilian patients Authors: Giliane Belarmino (giliane85@hotmail.com) Lilian M Horie
EXTRACELLULAR WATER REFERENCE VALUES. Extracellular Water: Reference values for Adults
 CHAPTER 5 Extracellular Water: Reference values for Adults Analiza M. Silva, Jack Wang, Richard N. Pierson Jr., ZiMian Wang, David B. Allison Steven B. Heymsfield, Luis B. Sardinha, Stanley Heshka ABSTRACT
CHAPTER 5 Extracellular Water: Reference values for Adults Analiza M. Silva, Jack Wang, Richard N. Pierson Jr., ZiMian Wang, David B. Allison Steven B. Heymsfield, Luis B. Sardinha, Stanley Heshka ABSTRACT
Interpreting DEXA Scan and. the New Fracture Risk. Assessment. Algorithm
 Interpreting DEXA Scan and the New Fracture Risk Assessment Algorithm Prof. Samir Elbadawy *Osteoporosis affect 30%-40% of women in western countries and almost 15% of men after the age of 50 years. Osteoporosis
Interpreting DEXA Scan and the New Fracture Risk Assessment Algorithm Prof. Samir Elbadawy *Osteoporosis affect 30%-40% of women in western countries and almost 15% of men after the age of 50 years. Osteoporosis
Review Comparison of body composition methods: a literature analysis
 European Journal of Clinical Nutrition (1997) 51, 495±503 ß 1997 Stockton Press. All rights reserved 0954±3007/97 $12.00 Review Comparison of body composition methods: a literature analysis M Fogelholm
European Journal of Clinical Nutrition (1997) 51, 495±503 ß 1997 Stockton Press. All rights reserved 0954±3007/97 $12.00 Review Comparison of body composition methods: a literature analysis M Fogelholm
Assessment of body composition of Sri Lankan Australian children using ethnic specific equations
 J.Natn.Sci.Foundation Sri Lanka 2015 43 (2): 111-118 DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.4038/jnsfsr.v43i2.7938 RESEARCH ARTICLE Assessment of body composition of Sri Lankan Australian children using ethnic specific
J.Natn.Sci.Foundation Sri Lanka 2015 43 (2): 111-118 DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.4038/jnsfsr.v43i2.7938 RESEARCH ARTICLE Assessment of body composition of Sri Lankan Australian children using ethnic specific
The Ins and Outs of Body Composition Research
 The Ins and Outs of Body Composition Research Jordan R. Moon, PhD, CSCS*D, HFS NSCA State Director: Colorado Research Director: MusclePharm Sports Science Institute Faculty: United States Sports Academy
The Ins and Outs of Body Composition Research Jordan R. Moon, PhD, CSCS*D, HFS NSCA State Director: Colorado Research Director: MusclePharm Sports Science Institute Faculty: United States Sports Academy
Precision of measurement and body size in whole-body air-displacement plethysmography
 ]> PAPER (2001) 25, 1161±1167 ß 2001 Nature Publishing Group All rights reserved 0307±0565/01 $15.00 www.nature.com/ijo of measurement and body size in whole-body air-displacement plethysmography JCK Wells
]> PAPER (2001) 25, 1161±1167 ß 2001 Nature Publishing Group All rights reserved 0307±0565/01 $15.00 www.nature.com/ijo of measurement and body size in whole-body air-displacement plethysmography JCK Wells
In-vivo precision of the GE Lunar idxa for the measurement of visceral adipose tissue in
 1 2 In-vivo precision of the GE Lunar idxa for the measurement of visceral adipose tissue in adults: the influence of body mass index 3 4 Running title: Precision of the idxa for the measurement of visceral
1 2 In-vivo precision of the GE Lunar idxa for the measurement of visceral adipose tissue in adults: the influence of body mass index 3 4 Running title: Precision of the idxa for the measurement of visceral
Nutritional Methodology-Body Composition
 Nutritional Methodology-Body Composition An Evaluation of Dual-Energy X-Ray Absorptiometry and Underwater Weighing to Estimate Body Composition by Means of Carcass Analysis in Piglets 1 Per Elowsson,*
Nutritional Methodology-Body Composition An Evaluation of Dual-Energy X-Ray Absorptiometry and Underwater Weighing to Estimate Body Composition by Means of Carcass Analysis in Piglets 1 Per Elowsson,*
C H A P T E R 14 BODY WEIGHT, BODY COMPOSITION, AND SPORT
 C H A P T E R 14 BODY WEIGHT, BODY COMPOSITION, AND SPORT Learning Objectives Differentiate among body build, body size, and body composition. Find out what tissues of the body constitute fat-free mass.
C H A P T E R 14 BODY WEIGHT, BODY COMPOSITION, AND SPORT Learning Objectives Differentiate among body build, body size, and body composition. Find out what tissues of the body constitute fat-free mass.
Potassium per kilogram fat-free mass and total body potassium: predictions from sex, age, and anthropometry
 Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab 284: E416 E423, 2003. First published October 15, 2002; 10.1152/ajpendo.00199.2001. Potassium per kilogram fat-free mass and total body potassium: predictions from sex, age,
Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab 284: E416 E423, 2003. First published October 15, 2002; 10.1152/ajpendo.00199.2001. Potassium per kilogram fat-free mass and total body potassium: predictions from sex, age,
Cross-calibration of fat and lean measurements by dualenergy X-ray absorptiometry to pig carcass analysis in the pediatric body weight range13
 Cross-calibration of fat and lean measurements by dualenergy X-ray absorptiometry to pig carcass analysis in the pediatric body weight range13 Stephen J Pintauro, Tim R Nagy, Christa M Duthie, and Michael
Cross-calibration of fat and lean measurements by dualenergy X-ray absorptiometry to pig carcass analysis in the pediatric body weight range13 Stephen J Pintauro, Tim R Nagy, Christa M Duthie, and Michael
Dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry based body volume measurement for 4-compartment body composition 1 3
 Dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry based body volume measurement for 4-compartment body composition 1 3 Joseph P Wilson, Kathleen Mulligan, Bo Fan, Jennifer L Sherman, Elizabeth J Murphy, Viva W Tai, Cassidy
Dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry based body volume measurement for 4-compartment body composition 1 3 Joseph P Wilson, Kathleen Mulligan, Bo Fan, Jennifer L Sherman, Elizabeth J Murphy, Viva W Tai, Cassidy
NUMBER 1 OF 1 THIS QUERY FORM MUST BE RETURNED WITH ALL PROOFS FOR CORRECTIONS
 NUMBER 1 OF 1 AUTHOR QUERIES DATE 1/24/2008 JOB NAME JSC ARTICLE 200052 QUERIES FOR AUTHORS Malavolti et al THIS QUERY FORM MUST BE RETURNED WITH ALL PROOFS FOR CORRECTIONS AU1) Please provide at least
NUMBER 1 OF 1 AUTHOR QUERIES DATE 1/24/2008 JOB NAME JSC ARTICLE 200052 QUERIES FOR AUTHORS Malavolti et al THIS QUERY FORM MUST BE RETURNED WITH ALL PROOFS FOR CORRECTIONS AU1) Please provide at least
BUILDING A PERSONALISED DIET PLAN FOR YOUR CLIENT
 BUILDING A PERSONALISED DIET PLAN FOR YOUR CLIENT The first 3 steps for creating a sound nutritional plan Introduction 2 Here is what you will learn in this unit: The role of diet on fitness, athletic
BUILDING A PERSONALISED DIET PLAN FOR YOUR CLIENT The first 3 steps for creating a sound nutritional plan Introduction 2 Here is what you will learn in this unit: The role of diet on fitness, athletic
Is percentage body fat differentially related to body mass index in Hispanic Americans, African Americans, and European Americans?
 Is percentage body fat differentially related to body mass index in Hispanic Americans, African Americans, and European Americans? 1 3 José R Fernández, Moonseong Heo, Steven B Heymsfield, Richard N Pierson
Is percentage body fat differentially related to body mass index in Hispanic Americans, African Americans, and European Americans? 1 3 José R Fernández, Moonseong Heo, Steven B Heymsfield, Richard N Pierson
Sports Performance 15. Section 3.2: Body Composition
 Sports Performance 15 Section 3.2: Body Composition The relative percentage of muscle, fat, bone and other tissue in the body Our primary concern in this unit is body fatness and how it pertains to athletic
Sports Performance 15 Section 3.2: Body Composition The relative percentage of muscle, fat, bone and other tissue in the body Our primary concern in this unit is body fatness and how it pertains to athletic
Body Composition Methods: Comparisons and Interpretation
 Journal of Diabetes Science and Technology Volume 2, Issue 6, November 2008 Diabetes Technology Society OBESITY TECHNOLOGY Body Composition Methods: Comparisons and Interpretation Dana L., Ph.D., 1,2 Richard
Journal of Diabetes Science and Technology Volume 2, Issue 6, November 2008 Diabetes Technology Society OBESITY TECHNOLOGY Body Composition Methods: Comparisons and Interpretation Dana L., Ph.D., 1,2 Richard
Measurement of Total RBC Volume Relative to Lean Body Mass for Diagnosis of Polycythemia
 Hematopathology / TOTAL RBC VOLUME AND BODY FAT Measurement of Total RBC Volume Relative to Lean Body Mass for Diagnosis of Polycythemia Nathaniel I. Berlin, MD, 1 and S. Mitchell Lewis, MD 2 Key Words:
Hematopathology / TOTAL RBC VOLUME AND BODY FAT Measurement of Total RBC Volume Relative to Lean Body Mass for Diagnosis of Polycythemia Nathaniel I. Berlin, MD, 1 and S. Mitchell Lewis, MD 2 Key Words:
Measurement of Total RBC Volume Relative to Lean Body Mass for Diagnosis of Polycythemia
 Hematopathology / TOTAL RBC VOLUME AND BODY FAT Measurement of Total RBC Volume Relative to Lean Body Mass for Diagnosis of Polycythemia Nathaniel I. Berlin, MD, 1 and S. Mitchell Lewis, MD 2 Key Words:
Hematopathology / TOTAL RBC VOLUME AND BODY FAT Measurement of Total RBC Volume Relative to Lean Body Mass for Diagnosis of Polycythemia Nathaniel I. Berlin, MD, 1 and S. Mitchell Lewis, MD 2 Key Words:
Whole Body Dual X-Ray Absorptiometry (DXA) to Determine Body Composition
 Whole Body Dual X-Ray Absorptiometry (DXA) to Determine Body Composition Policy Number: 6.01.40 Last Review: 4/2018 Origination: 4/2005 Next Review: 4/2019 Policy Blue Cross and Blue Shield of Kansas City
Whole Body Dual X-Ray Absorptiometry (DXA) to Determine Body Composition Policy Number: 6.01.40 Last Review: 4/2018 Origination: 4/2005 Next Review: 4/2019 Policy Blue Cross and Blue Shield of Kansas City
Concordance of a Self Assessment Tool and Measurement of Bone Mineral Density in Identifying the Risk of Osteoporosis in Elderly Taiwanese Women
 TZU CHI MED J September 2008 Vol 20 No 3 available at http://ajws.elsevier.com/tcmj Tzu Chi Medical Journal Original Article Concordance of a Self Assessment Tool and Measurement of Bone Mineral Density
TZU CHI MED J September 2008 Vol 20 No 3 available at http://ajws.elsevier.com/tcmj Tzu Chi Medical Journal Original Article Concordance of a Self Assessment Tool and Measurement of Bone Mineral Density
Comparison Of Body Composition Techniques In Determining Body Fat Percentages In College Age Students
 Illinois State University ISU ReD: Research and edata Theses and Dissertations 3-18-2014 Comparison Of Body Composition Techniques In Determining Body Fat Percentages In College Age Students Jillian Louise
Illinois State University ISU ReD: Research and edata Theses and Dissertations 3-18-2014 Comparison Of Body Composition Techniques In Determining Body Fat Percentages In College Age Students Jillian Louise
BODY MASS INDEX AND BODY FAT CONTENT IN ELITE ATHLETES. Abstract. Introduction. Volume 3, No. 2, 2011, UDC :572.
 EXERCISE AND QUALITY OF LIFE Volume 3, No. 2, 2011, 43-48 UDC 796.034.6-051:572.087 Research article BODY MASS INDEX AND BODY FAT CONTENT IN ELITE ATHLETES Jelena Popadiã Gaãeša *, Otto Barak, Dea Karaba
EXERCISE AND QUALITY OF LIFE Volume 3, No. 2, 2011, 43-48 UDC 796.034.6-051:572.087 Research article BODY MASS INDEX AND BODY FAT CONTENT IN ELITE ATHLETES Jelena Popadiã Gaãeša *, Otto Barak, Dea Karaba
