Relative contribution of calpain and cathepsins to protein degradation in muscle of sea bass (Dicentrarchus labrax L.)
|
|
|
- Julius Bell
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Please note that this is an author-produced PDF of an article accepted for publication following peer review. The definitive publisher-authenticated version is available on the publisher Web site Food Chemistry Vol. 88, Issue 3, December 2004, Pages Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved. Archimer, archive institutionnelle de l Ifremer Relative contribution of calpain and cathepsins to protein degradation in muscle of sea bass (Dicentrarchus labrax L.) Christine Delbarre-Ladrat*,1, Véronique Verrez-Bagnis 1, Joëlle Noël 1 and Joël Fleurence 1,2 1 IFREMER, DRV-VP, BP21105, Nantes Cedex 3, FRANCE 2 Present address: UFR Sciences et Techniques, ISOMER, BP 92208, Nantes Cedex 3, FRANCE *: Corresponding author : Tel.: ; fax: ; cladrat@ifremer.fr Abstract: The effects of a milli(m)-calpain isolated from the white muscle of sea bass (Dicentrarchus labrax L) and commercial cathepsins B, D and L, used in combination on the myofibrillar and sarcoplasmic proteins were examined. Protein digestion was first performed by the endogenous m-calpain, during 2 h before the addition of a mixture of cathepsins B, D and L and a further incubation up to 22 h. Calpain degraded a 27 kda sarcoplasmic component as well as myosin heavy chain, α-actinin, desmin and a 32 kda component from the myofibrillar fraction. A 97 kda component and the assumed creatine kinase aldolase doublet were degraded during the incubation of sarcoplasmic proteins with the cathepsin mixture while, among the myofibrillar proteins, myosin, actin, tropomyosin, and the 22 kda component were digested by the same enzymatic preparation. Myofibril-bound α-actinin and tropomyosin were released into the soluble fraction by m-calpain and the cathepsins mixture. Some smaller fragments were also produced. This appears to be the result of the cumulative action of each protease, as already investigated in our previous studies, except for the degradation of the sarcoplasmic 97 kda component. It was only degraded if the cathepsins were mixed; this indicates that the three cathepsins functioned synergistically on muscle proteins. No difference in the proteolytic effect of cathepsins was observed, whether calpain was acting first or not. This work showed that calpain did not modify any muscle protein prior to later hydrolysis by the catheptic proteinases. Keywords: Neutral calcium-dependent protease; Cathepsins; Proteolysis; Fish muscle; Postmortem aging 1
2 Introduction Despite awareness that proteolysis plays a critical role in post mortem aging of muscle resulting in tenderization, a clear understanding of the mechanisms responsible remains elusive. In contrast to mammalian muscles for which tenderness is beneficial to meat quality, tenderization of fish muscle results in its deterioration. The initial steps in this process include endogenous hydrolytic reactions brought about by enzymes. The role of cathepsins and calpains in the post mortem proteolysis of fish muscle has received limited attention compared to the extent of studies on these enzymes in mammalian tissue. Calpains (neutral calcium-dependent proteases) and cathepsins (lysosomal proteases) are the two major degradative pathways usually described as involved in the post mortem aging process. Two ubiquitous forms of calpains exist within the cells: micro(µ)-calpain, and milli(m)-calpain. Fish muscle calpains have received only little attention compared to mammalian counterparts (Geesink, Morton, Kent & Bickerstaffe, 2000 ; Toyohara & Makinodan, 1989 ; Jiang, Wang & Chen, 1991). It has been shown that, in sea bass muscle, they are differently expressed depending on the season of the year (Ladrat, Chaplet, Verrez- Bagnis, Noël & Fleurence, 2000). On the other hand, cathepsins B, D, L and H are the major cathepsins within the fish lysosomes (Aoki, Yamashita & Ueno, 2000) ; some of them have been studied for their enzymatic features (Lee, Chen & Jiang, 1993 ; Jiang, Lee & Chen, 1994 ; Goldman-Levkovitz, Rimon & Rimon, 1995 ; Heu, Kim, Cho, Godber & Pyeun, 1997) and for their ability to degrade muscle proteins (Jiang, Wang & Chen, 1992 ; Aoki & Ueno, 1997 ; Aranishi, Ogata, Hara, Osatomi & Ishihara, 1998). It would be expected that the respective action of each protease is possibly affected by the other proteases. In particular, endoproteases could degrade proteic substrates to be further proteolysed by other proteases. Moreover, calpains have been believed to initiate the proteolytic degradation of myofibrils by causing a little hydrolysis on proteins making them more susceptible to other proteases (Goll, Thompson, Taylor & Christiansen, 1992 ; Lamare, Taylor, Farout, Briand & Briand, 2002 ; Papa, Alvarez, Verrez-Bagnis, Fleurence & Benyamin, 1996). Our objective in the current study, therefore, was to improve our understanding of the mechanisms involved in post mortem deterioration of fish muscle and to acquire an insight into the concept of the synergistic effect of calpains and cathepsins. In our previous studies, the involvement of calpain and cathepsins in the proteolysis of sea bass white muscle during refrigerated storage was investigated using enzymes one by one (Verrez-Bagnis, Ladrat, Noelle & Fleurence, 2002 ; Ladrat, Verrez-Bagnis, Noël & Fleurence, 2003). In this work, these enzymes are used in combination. Material and methods Fish Live sea bass (Dicentrarchus labrax L.) were purchased from a local sea farm in Vendée (France) and killed by beheading. In a cold room, viscera and skin were removed and white muscle was recovered. Protein preparations for enzymatic digestions Sarcoplasmic proteins were extracted by homogenising the sea bass muscle frozen at death at 80 C in 4 volumes (w/v) of water containing 1 mm EDTA. The supernatant recovered after two centrifugations at g, 4 C for 15 minutes was used as the sarcoplasmic preparation. The protein content (9.3 mg/ml) was determined by Bradford assay (Bradford, 1976) using Bio-Rad reagent (Bio-Rad, Ivry-sur-Seine, France), and bovine serum albumin as the standard. 2
3 Myofibrils were isolated from fresh sea bass muscle according to the procedure of Wang (Wang, 1982), suspended in 50% (v/v) glycerol and stored at 20 C until use. Protein content was estimated at 12.5 mg/ml by Bradford assay. When needed, 800 µl of this preparation were taken and centrifuged three times at 4000 rpm for 15 minutes at ambient temperature. Each time, the pellet was washed in 1 ml water. The final pellet was used directly for myofibrillar protein digestion. Proteases preparation Cathepsin L from Paramecium tetraucelia was purchased from CALBIOCHEM (Merck Eurolab, Fontenay-sous-bois, France). Cathepsin B (Ref C6286) and cathepsin D (Ref C3138), both from bovine spleen, were from SIGMA (Saint-Quentin-Fallavier, France). No fish cathepsins were commercially available, but most data on the catalytic activity and molecular properties of cathepsins are consistent regardless of the source (Gildberg, 1988 ; Yamashita & Konagaya, 1990a ; Yamashita & Konagaya, 1990b). Milli-calpain was purified from sea bass muscle as previously described (Ladrat, Verrez-Bagnis, Noel & Fleurence, 2002). Proteolytic digestions Digestions were performed at 25 C during two hours with m-calpain and then a mixture of the three above cathepsins was added. Highly purified m-calpain (18.6 µg/ml enzyme) was added to sarcoplasmic or myofibrillar proteins to a final ratio of 1/500 (w/w) in the presence of 5 mm CaCl 2 and 5 mm β-mercaptoethanol in 50 mm Tris buffer ph 7. After two hours of incubation, 1 volume of 50 mm citrate phosphate buffer ph 5.5 was added in order to decrease the ph to 5.5 and the cathepsins mixture containing 35 µg cathepsin D (final 19 µg/ml), 10 µg cathepsin B (final 5.4 µg/ml) and 2 µg cathepsin L (final 1.1 µg/ml) in 50 mm citrate phosphate buffer was added. Incubations lasted up to 22 h. Aliquots were sampled at 0-30 min and 1.5 hour (corresponding to the action of calpain) and at 2 h-3 h-5 h and 22 h total incubation duration (corresponding to the digestion by the mixture of cathepsins). Three different treatments were performed in this combined experiment with calpain and cathepsins: the first one (treatment A) with both calpain and cathepsins mixture as indicated above, the second one (treatment B) with calpain and addition of 50 mm citrate phosphate buffer ph 5.5 instead of cathepsins, and the last one (treatment C) with 50 mm Tris buffer ph 7 instead of calpain with addition of the mixture of the cathepsins. A negative control (D) was carried out without any enzyme but with the appropriate buffer instead. Each digestion was done and analysed twice. Aliquots from the sarcoplasmic protein digestions were removed at specific intervals, mixed with 4x concentrated SDS-containing tracking dye and immediately heated for 3 min at 100 C. To follow the breakdown of myofibrillar proteins, a sampled aliquot was centrifuged at 4000 rpm, at room temperature for 15 min in the presence of inhibitors to stop the reaction (0.01 mm E64, 0.01 mm pepstatin A) and insoluble material precipitated. The pellet was dissolved in the same volume as initial aliquot of 40 mm Tris buffer containing 8 M urea and 4x SDS-containing tracking dye was added before boiling for 3 min. The remaining supernatant containing proteins released from myofibrils was added to 4x concentrated SDScontaining tracking dye and boiled. SDS-PAGE SDS-PAGE was carried out in a Mini-protean dual slab cell (Bio-Rad) according to the method of Laemmli (Laemmli, 1970) using 4-20 % polyacrylamide gradient gels. 5 µl of sample from the digestion of sarcoplasmic proteins, 5 µl of sample prepared from the pellet of digested myofibrillar proteins and 10 µl from the corresponding supernatant were loaded. 3
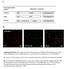
4 Molecular weight markers were from Bio-Rad (Broad Precision recombinant standards) or from SIGMA (SDS-6H and SDS-7 mixture: Myosin 205 kda, ß-galactosidase 116 kda, phosphorylase b 97.4 kda, bovine albumin 66 kda, egg albumin 45 kda, glyceraldehyde-3- phosphate dehydrogenase 36 kda, carbonic anhydrase 29 kda, trypsinogen 24 kda, trypsin inhibitor 20.1 kda, α-lactalbumin 14.2 kda). Average molecular weights were estimated from several analysed gels. After migration, gels were subsequently stained with Coomassie Brilliant Blue R250 or blotted overnight onto a membrane. Western blots of structural proteins Electrophoresis gels were blotted overnight at 15 C onto a 0.45 µm nitrocellulose membrane (Bio-Rad) at 30 V using a Mini-Transblot Cell (Bio-Rad) with transfer buffer containing 150 mm glycine, 20 mm Tris, 20 % methanol and 0.01 % SDS. Membranes were saturated with 8 % skimmed milk prepared in 0.9 % NaCl, washed with phosphate buffered saline (PBS) (137 mm NaCl, 2.7 mm KCl in 10 mm phosphate buffer ph 7.4) containing 0.05 % v/v Tween 20 and further incubated for 2 hours at room temperature with primary rabbit antibodies in 0.9 % NaCl. After being washed in PBS with 0.05 % v/v Tween 20, blots were incubated with secondary goat anti-rabbit IgG alcaline phosphatase conjugate diluted with 0.9 % NaCl containing 5 % bovine serum albumin. Enzymatic detection was carried out using nitroblue tetrazolium / 5-bromo-4-chloro-3-indolyl phosphate (NBT/BCIP) as the substrate resulting in brown red-coloured bands on the membrane. Polyclonal anti-α-actinin produced in the laboratory (1/300 dilution) was used as primary antibody on sarcoplasmic and myofibrillar proteins digestions while polyclonal anti-desmin (SIGMA, Ref D8281, 1/200 dilution) and polyclonal anti-tropomyosin (SIGMA, Ref T3651, 1/200 dilution) were used as primary antibodies for the in vitro proteolysis of myofibrillar proteins only. Image analysis The Coomassie Blue stained gels as well as the immunoblots were photographed with a CCD camera system (Image Master VDS-CL, Amersham Biosciences) and analysed with 1D-Elite software (Amersham Biosciences). Results Sarcoplasmic proteins combined digestion In this experiment in which both types of proteases were used in combination, the only modification on sarcoplasmic proteins caused by calpain was observed for the 27 kda band which was fragmented into a band of very close molecular weight as previously described (Figure 1A) (Verrez-Bagnis et al., 2002). But cathepsins were able to degrade the 97 kda protein and the creatine kinase-aldolase assumed doublet (41-39 doublet) as it was identified by comparisons of fish proteins pattern in a previous article (Ladrat et al., 2003). In this area, the real protein affected is not clear because of the existence of huge bands. A fragment around 34 kda was increasing. Two fragments (25 and 20.5 kda) were produced during the incubation with cathepsins. A 21.5 kda component was degraded. A 20.5 kda band was appearing in each experiment performed even when no enzyme was added giving evidence for an unidentified and uncontrolled occurring mechanism (Figure 1D). Comparing results from Figure 1C and 1A possibly indicated the synergistic effect of calpain and cathepsins. Treatment without the calpain but with the mixture of cathepsins (Figure 1C) showed that the 97 kda component, the creatine kinase-aldolase doublet and the 21.5 kda proteins were degraded while the 34 kda and 24 kda band were also increasing. Treatment B together with negative control on Figure 1 indicated that the cathepsins are really responsible for these changes in protein patterns. 4
5 α-actinin present in the soluble fraction of muscular proteins was affected neither by calpain nor by cathepsins (Figure 2) confirming the already observed stability in relation to each cathepsin action (Ladrat et al., 2003). Myofibrillar protein digestion During in vitro proteolysis of myofibrillar proteins by calpain followed by cathepsins (Figure 3), partial degradation of myosin heavy chain (MHC) was observed all over the incubation. Two fragments (140 and 78 kda) were generated by the action of calpain and subsequently degraded during the incubation with the mixed cathepsins. Calpain left actin intact before its degradation by cathepsins. Tropomyosin (34 kda) was degraded only after the addition of the cathepsins. Calpain caused the loss of the 32 kda component (assumed to be troponin T). Cathepsins cleaved the 22 kda band. Three other fragments appeared during the incubation with cathepsins: 68, 33 and 30 kda. At the end of the incubation, all the proteins were completely hydrolysed and only a smear was visible on the lane. The comparison of the different treatment groups and control (Figure 3) showed that the above mentioned changes are due to calpain and/or to cathepsins as indicated and not to an unidentified and uncontrolled factor as it was the case for the sarcoplasmic proteins. Moreover, no difference was observed in the changes induced by cathepsins between the experiments in which calpain was acting first (treatment A, Figure 3A) or not (treatment C, Figure 3C), thus suggesting m- calpain did not modify myofibrillar proteins in a manner that rendered them more susceptible to the action of cathepsins. As we can see in Figure 4II, α-actinin was degraded into a set of fragments by calpain (90 kda, 80, 71, and 37 kda). They were all degraded subsequently by the cathepsins but these latter proteases produced also a 99 kda and a 104 kda fragment from the remaining undegraded α-actinin subunit. Tropomyosin remained unchanged upon action of calpain as we can see on immunoblots on pellets (Figure 4III). It was afterwards degraded into a 32 kda fragment by cathepsins (Figure 4III). Control showed only a slight decrease in the probed band intensity without any degradation (data not shown). Desmin was rapidly and highly degraded by calpain (Figure 4IV) with degradation fragments visible as early as the beginning of incubation. No desmin was visible in the second sampling. This result confirmed the previous observation of Verrez-Bagnis et al. (2002). Some proteins were released from myofibrils into the supernatant before being completely degraded during treatment A ; in particular, two fragments of 62 and 54 kda were released into the soluble fraction (Figure 5I) by cathepsins. No visible difference in the action of the cathepsins was observed between treatments involving first action of calpain and the treatment without calpain (data not shown). Intact α-actinin and some of its breakdown fragments were released in the soluble fraction (Figure 5II). Calpain and cathepsins were able to liberate tropomyosin from myofibrils into the soluble fraction but only cathepsins could degrade it (Figure 5III). The observed action of the mixture of the all three cathepsins at ph 5.5 appears to be the result of the cumulative action of each cathepsin studied in a previous work (Ladrat et al., 2003) except for the 97 kda sarcoplasmic component which was broken down only by the mixture of the three cathepsins all together. Conclusion Our previous results showed that MHC, α-actinin, desmin, actin, troponin T, tropomyosin and other non identified protein bands can be degraded by cathepsins D, B, or L (Ladrat et al., 2003). This work showed that when these three cathepsins are mixed, each of the above proteins is also degraded. In addition, a 97 kda component was degraded by the mixture but not by each cathepsin taken apart from the others. In this case, the three cathepsins act in 5
6 synergy. When the cathepsin B, D and L mixture acted after the action of calpain, no difference was observed with the tratment without calpain suggesting calpain did not modify proteins and did not make them more susceptible to the further degradation by cathepsins as it was hypothesized by (Goll et al., 1992 ; Lamare et al., 2002 ; Papa et al., 1996). A combined incubation in which the myofibrils were first hydrolyzed by m-calpain then later subjected to a lysosomal extract has already been studied by Whipple and Koohmaraie (Whipple & Koohmaraie, 1991). It also led the authors to the conclusion that m-calpain did not alter any myofibrillar protein to be later hydrolyzed by the acidic proteinases. In vitro degradation of muscle proteins by isolated or purified proteases is far more extensive than the degradation occurring with normal postmortem storage. Attempts in vitro to reproduce events in vivo can never be absolute because of reaction conditions (temperature, ph, enzyme:substrate ratio). In particular, an accurate enzyme:substrate ratio selection close to the physiological ratio is complicated by the presence of naturally occurring inhibitors. Nevertheless, our analysis substantiates the idea that calpain and cathepsins do not function synergistically in post mortem muscles but does not rule out the action of calpain in the early phases of post mortem aging followed by the cathepsins action. 6
7 Reference list Aoki, T., & Ueno, R. (1997). Involvement of cathepsins B and L in the post-mortem autolysis of mackerel muscle. Food Research International, 30(8), Aoki, T., Yamashita, T., & Ueno, R. (2000). Distribution of cathepsins in red and white muscles among fish species. Fisheries Science, 66(4), Aranishi, F., Ogata, H., Hara, K., Osatomi, K., & Ishihara, T. (1998). Susceptibility of opioid peptides and myofibrillar proteins to carp cathepsin L. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 46(2), Bradford, M. M. (1976). A rapid and sensitive method for the quantification of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Analytical Biochemistry, 72, Geesink, G., Morton, J., Kent, M., & Bickerstaffe, R. (2000). Partial purification and characterization of Chinook salmon (Oncorhynchus tshawytscha) calpains and an evaluation of their role in postmortem proteolysis. Journal of Food Science, 65(8), Gildberg, A. (1988). Aspartic proteinases in fishes and aquatic invertebrates. Comparative Biochemistry and Physiology, 91B(3), Goldman-Levkovitz, S., Rimon, A., & Rimon, S. (1995). Purification, properties and specificity of cathepsin D from Cyprinus carpio. Comparative Biochemistry and Physiology, 112B(1), Goll, D. E., Thompson, V. F., Taylor, R. G., & Christiansen, J. A. (1992). Role of the calpain system in muscle growth. Biochimie, 74, Heu, M. S., Kim, H. R., Cho, D. M., Godber, J. S., & Pyeun, J. H. (1997). Purification and characterization of cathepsin L-like enzyme from the muscle of anchovy Engraulis japonica. Comparative Biochemistry and Physiology, 118B(3), Jiang, S.-T., Lee, J.-J., & Chen, H.-C. (1994). Purification and characterization of cathepsin B from ordinary muscle of mackerel (Scomber australasicus). Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 42, Jiang, S.-T., Wang, J.-H., & Chen, C.-S. (1991). Purification and some properties of calpain II from Tilapia muscle (Tilapia nilotica x Tilapia aurea). Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 39, Jiang, S.-T., Wang, Y.-T., & Chen, C.-S. (1992). Lysosomal enzyme effects on the postmortem changes in tilapia (Tilapia nilotica x T. aurea) muscle myofibrils. Journal of Food Science, 57(2), Ladrat, C., Chaplet, M., Verrez-Bagnis, V., Noël, J., & Fleurence, J. (2000). Neutral calciumactivated proteases from European sea bass (Dicentrarchus labrax L.) muscle: polymorphism and biochemistry studies. Comparative Biochemistry and Physiology, 125B, Ladrat, C., Verrez-Bagnis, V., Noel, J., & Fleurence, J. (2002). Milli-calpain from sea bass 7
8 (Dicentrarchus Labrax) white muscle: purification, characterization of its activity and activation in vitro. Marine Biotechnology, 4(1), Ladrat, C., Verrez-Bagnis, V., Noël, J., & Fleurence, J. (2003). In vitro proteolysis of myofibrillar and sarcoplasmic proteins of white muscle of sea bass (Dicentrarchus labrax L.): effects of cathepsins B, D and L. Food Chemistry, 81, Laemmli, U. K. (1970). Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature, 227, Lamare, M., Taylor, R. G., Farout, L., Briand, Y., & Briand, M. (2002). Changes in proteasome activity during postmortem aging of bovine muscle. Meat Science, 61, Lee, J.-J., Chen, H.-C., & Jiang, S.-T. (1993). Purification and characterization of proteinases identified as cathepsins L and L-like (58 kda) proteinase from mackerel (Scomber australasicus). Bioscience, Biotechnology and Biochemistry, 57(9), Papa, I., Alvarez, C., Verrez-Bagnis, V., Fleurence, J., & Benyamin, Y. (1996). Post mortem release of fish white muscle α-actinin as a marker of disorganisation. Journal of Science and Food Agriculture, 72(1), Toyohara, H., & Makinodan, Y. (1989). Comparison of calpain I and calpain II from carp muscle. Comparative Biochemistry and Physiology, 92B(3), Verrez-Bagnis, V., Ladrat, C., Noelle, J., & Fleurence, J. (2002). In vitro proteolysis of european sea bass (Dicentrarchus labrax) myofibrillar and sarcoplasmic proteins by an endogenous m-calpain. Journal of the Science and Food Agriculture, 82, Wang, K. (1982). Purification of titin and nebulin. Methods in Enzymology, 85, Whipple, G., & Koohmaraie, M. (1991). Degradation of myofibrillar enzymes and m-calpain, and the effects of zinc chloride. Journal of Animal Science, 69, Yamashita, M., & Konagaya, S. (1990a). Purification and characterization of cathepsin B from the white muscle of chum salmon, Oncorhynchus keta. Comparative Biochemistry and Physiology, 96B(4), Yamashita, M., & Konagaya, S. (1990b). Purification and characterization of cathepsin L from the white muscle of chum salmon, Oncorhynchus keta. Comparative Biochemistry and Physiology, 96B(2),
9 Figure 1: SDS-PAGE followed proteolysis of sarcoplasmic proteins by m-calpain for 2 h (lanes 2 to 4) followed by cathepsins mixture (lanes 5 to 8). A: combined experiment with m- calpain and cathepsins, B: treatment without cathepsins, C: treatment without m-calpain, D: control without any enzyme. Lanes 1 and 9: SDS-6H and SDS-7 molecular weight markers. Lane 2: initial reaction mixture at time 0 after the addition of the calpain, lane 3: reaction mixture after 30 min incubation, lane 4: 1.5 h incubation, cathepsins were added and sample was withdrawn at 2 h of total incubation (lane 5), lane 6: 3 h total incubation, lane 7: 5 h, lane 8: 20 h. Treatment A Treatment B doublet Treatment C Negative control
10 Figure 2: α-actinin on Western blots of sarcoplasmic proteins digested during the combined experiment in the presence of m-calpain and cathepsin mixture. Lane 1: initial reaction mixture at time 0 after the addition of the calpain, lane 2: reaction mixture after 30 min incubation, lane 3: 1.5 h incubation, cathepsins were added and sample was withdrawn at 2 h of total incubation (lane 4), lane 5: 3 h total incubation, lane 6: 5 h, lane 7: 20 h, lane 8: initial sarcoplasmic extract Figure 3: SDS-PAGE analysis of pellet from proteolysis of myofibrillar proteins by m-calpain for 2 h (lanes 2 to 4) followed by cathepsins mixture (lanes 5 to 8). A: combined experiment with m-calpain and cathepsins, B: treatment without cathepsins, C: treatment without m- calpain, D: control without any enzyme. Lanes 1 and 9: SDS-6H and SDS-7 molecular weight markers. Lane 2: initial reaction mixture at time 0 after the addition of the calpain, lane 3: reaction mixture after 30 min incubation, lane 4: 1.5 h incubation, cathepsins were added and sample was withdrawn at 2 h of total incubation (lane 5), lane 6: 3 h total incubation, lane 7: 5 h, lane 8: 20 h. Treatment A Treatment B MHC Actin Treatment C Negative control
11 Figure 4: SDS-PAGE and immunoblots of pellet during myofibrillar protein digestion in the combined experiment i.e. treatment A in the presence of m-calpain (lanes 2 to 4 at 0, 30 min and 1.5 h incubation) followed by cathepsins mixture (lanes 5 to 8 at 2, 3, 5 and 20 h incubation). I: SDS-PAGE stained with Coomassie Blue (identical to Figure 3A). II: α-actinin immunoblot. III: tropomyosin immunoblot. IV: desmin immunoblot. Lanes 1 and 9: SDS 6H and SDS-7 markers (see legend to figure 1) for SDS-PAGE or Broad Precision standards for immunoblots. Lane 10: initial myofibrillar extract. MHC Actin I II III IV 11
12 Figure 5: SDS-PAGE and immunoblots of supernatant during myofibrillar protein digestion in the combined experiment i.e. treatment A in the presence of m-calpain (lanes 2 to 4 at 0, 30 min and 1.5 h incubation) followed by cathepsins mixture (lanes 5 to 8 at 2, 3, 5 and 20 h incubation). I: SDS-PAGE stained with Coomassie Blue. II: α-actinin immunoblot. III: tropomyosin immunoblot. Lanes 1 and 9: SDS 6H and SDS-7 markers for SDS-PAGE and Broad Precision standards for blots.. I α-actinin II tropomyosin III 12
In vitro proteolysis of myofibrillar and sarcoplasmic proteins of white muscle of sea bass (Dicentrarchus labrax L.): effects of cathepsins B, D and L
 Please note that this is an author-produced PDF of an article accepted for publication following peer review. The definitive publisher-authenticated version is available on the publisher Web site Food
Please note that this is an author-produced PDF of an article accepted for publication following peer review. The definitive publisher-authenticated version is available on the publisher Web site Food
SUPPLEMENTARY MATERIAL
 SUPPLEMENTARY MATERIAL Purification and biochemical properties of SDS-stable low molecular weight alkaline serine protease from Citrullus Colocynthis Muhammad Bashir Khan, 1,3 Hidayatullah khan, 2 Muhammad
SUPPLEMENTARY MATERIAL Purification and biochemical properties of SDS-stable low molecular weight alkaline serine protease from Citrullus Colocynthis Muhammad Bashir Khan, 1,3 Hidayatullah khan, 2 Muhammad
Calpain and cathepsin activities in post mortem fish and meat muscles
 Please note that this is an author-produced PDF of an article accepted for publication following peer review. The definitive publisher-authenticated version is available on the publisher Web site Food
Please note that this is an author-produced PDF of an article accepted for publication following peer review. The definitive publisher-authenticated version is available on the publisher Web site Food
Calcium-Induced Fragmentation of Skeletal Muscle Nebulin Filaments'
 J. Biochem. 112, 775-779 (1992) Calcium-Induced Fragmentation of Skeletal Muscle Nebulin Filaments' Ryuichi Tatsumi and Koui Takahashi Meat Science Laboratory, Department of Animal Science, Faculty of
J. Biochem. 112, 775-779 (1992) Calcium-Induced Fragmentation of Skeletal Muscle Nebulin Filaments' Ryuichi Tatsumi and Koui Takahashi Meat Science Laboratory, Department of Animal Science, Faculty of
Protocol for Gene Transfection & Western Blotting
 The schedule and the manual of basic techniques for cell culture Advanced Protocol for Gene Transfection & Western Blotting Schedule Day 1 26/07/2008 Transfection Day 3 28/07/2008 Cell lysis Immunoprecipitation
The schedule and the manual of basic techniques for cell culture Advanced Protocol for Gene Transfection & Western Blotting Schedule Day 1 26/07/2008 Transfection Day 3 28/07/2008 Cell lysis Immunoprecipitation
Proteins and proteolytic activity changes during refrigerated storage in sea bass (Dicentrarchus labrax L.) muscle after high-pressure treatment
 Please note that this is an author-produced PDF of an article accepted for publication following peer review. The definitive publisher-authenticated version is available on the publisher Web site European
Please note that this is an author-produced PDF of an article accepted for publication following peer review. The definitive publisher-authenticated version is available on the publisher Web site European
Elisabeth Huff Lonergan, PhD Steven M. Lonergan, PhD Mark J. Anderson, PhD
 Elisabeth Huff Lonergan, PhD Steven M. Lonergan, PhD Mark J. Anderson, PhD The complexity of tenderness. Differences in tenderness due to postmortem aging is difficult to predict and manage Structure is
Elisabeth Huff Lonergan, PhD Steven M. Lonergan, PhD Mark J. Anderson, PhD The complexity of tenderness. Differences in tenderness due to postmortem aging is difficult to predict and manage Structure is
The Schedule and the Manual of Basic Techniques for Cell Culture
 The Schedule and the Manual of Basic Techniques for Cell Culture 1 Materials Calcium Phosphate Transfection Kit: Invitrogen Cat.No.K2780-01 Falcon tube (Cat No.35-2054:12 x 75 mm, 5 ml tube) Cell: 293
The Schedule and the Manual of Basic Techniques for Cell Culture 1 Materials Calcium Phosphate Transfection Kit: Invitrogen Cat.No.K2780-01 Falcon tube (Cat No.35-2054:12 x 75 mm, 5 ml tube) Cell: 293
Protein MultiColor Stable, Low Range
 Product Name: DynaMarker Protein MultiColor Stable, Low Range Code No: DM670L Lot No: ******* Size: 200 μl x 3 (DM670 x 3) (120 mini-gel lanes) Storage: 4 C Stability: 12 months at 4 C Storage Buffer:
Product Name: DynaMarker Protein MultiColor Stable, Low Range Code No: DM670L Lot No: ******* Size: 200 μl x 3 (DM670 x 3) (120 mini-gel lanes) Storage: 4 C Stability: 12 months at 4 C Storage Buffer:
N-Glycosidase F Deglycosylation Kit
 For life science research only. Not for use in diagnostic procedures. FOR IN VITRO USE ONLY. N-Glycosidase F Deglycosylation Kit Kit for the deglycosylation of asparagine-linked glycan chains on glycoproteins.
For life science research only. Not for use in diagnostic procedures. FOR IN VITRO USE ONLY. N-Glycosidase F Deglycosylation Kit Kit for the deglycosylation of asparagine-linked glycan chains on glycoproteins.
RayBio KinaseSTAR TM Akt Activity Assay Kit
 Activity Assay Kit User Manual Version 1.0 March 13, 2015 RayBio KinaseSTAR TM Akt Activity Kit Protocol (Cat#: 68AT-Akt-S40) RayBiotech, Inc. We Provide You With Excellent Support And Service Tel:(Toll
Activity Assay Kit User Manual Version 1.0 March 13, 2015 RayBio KinaseSTAR TM Akt Activity Kit Protocol (Cat#: 68AT-Akt-S40) RayBiotech, Inc. We Provide You With Excellent Support And Service Tel:(Toll
Supplementary material: Materials and suppliers
 Supplementary material: Materials and suppliers Electrophoresis consumables including tris-glycine, acrylamide, SDS buffer and Coomassie Brilliant Blue G-2 dye (CBB) were purchased from Ameresco (Solon,
Supplementary material: Materials and suppliers Electrophoresis consumables including tris-glycine, acrylamide, SDS buffer and Coomassie Brilliant Blue G-2 dye (CBB) were purchased from Ameresco (Solon,
Chromatin IP (Isw2) Fix soln: 11% formaldehyde, 0.1 M NaCl, 1 mm EDTA, 50 mm Hepes-KOH ph 7.6. Freshly prepared. Do not store in glass bottles.
 Chromatin IP (Isw2) 7/01 Toshi last update: 06/15 Reagents Fix soln: 11% formaldehyde, 0.1 M NaCl, 1 mm EDTA, 50 mm Hepes-KOH ph 7.6. Freshly prepared. Do not store in glass bottles. 2.5 M glycine. TBS:
Chromatin IP (Isw2) 7/01 Toshi last update: 06/15 Reagents Fix soln: 11% formaldehyde, 0.1 M NaCl, 1 mm EDTA, 50 mm Hepes-KOH ph 7.6. Freshly prepared. Do not store in glass bottles. 2.5 M glycine. TBS:
Isolation and Molecular Characterization of Local Goat Milk Casein for Nutraceutical Value
 Isolation and Molecular Characterization of Local Goat Milk Casein for Nutraceutical Value Mohd Akmal Azhar 1,*, and Norshafiqa Salim 2 1 Faculty of Engineering Technology, UMP Gambang, Lebuhraya Tun Razak,
Isolation and Molecular Characterization of Local Goat Milk Casein for Nutraceutical Value Mohd Akmal Azhar 1,*, and Norshafiqa Salim 2 1 Faculty of Engineering Technology, UMP Gambang, Lebuhraya Tun Razak,
Postmortem Proteolysis of Breast and Leg Muscles from Taiwan Colored Chickens and Silkie Bantams
 739 Postmortem Proteolysis of Breast and Leg Muscles from Taiwan Colored Chickens and Silkie Bantams Shih-Fen Tsai, Chia-Ying Lin, Jin-Jenn Lu and Rong-Ghi R. Chou* Department of Animal Science, National
739 Postmortem Proteolysis of Breast and Leg Muscles from Taiwan Colored Chickens and Silkie Bantams Shih-Fen Tsai, Chia-Ying Lin, Jin-Jenn Lu and Rong-Ghi R. Chou* Department of Animal Science, National
SUPPLEMENTARY MATERIAL
 SUPPLEMENTARY MATERIAL Table S1. Primers and fluorescent probes used for qrt-pcr analysis of relative expression levels of PPP family phosphatases. gene name forward primer, 5-3 probe, 5-3 reverse primer,
SUPPLEMENTARY MATERIAL Table S1. Primers and fluorescent probes used for qrt-pcr analysis of relative expression levels of PPP family phosphatases. gene name forward primer, 5-3 probe, 5-3 reverse primer,
Journal of Coastal Development ISSN: CHEMICAL ANALYSIS DURING THE PROCESSING OF DRIED SALTED ANCHOVY
 CHEMICAL ANALYSIS DURING THE PROCESSING OF DRIED SALTED ANCHOVY Eko Nurcahya Dewi *) Faculty of Fisheries and Marine Sciences University of Diponegoro, Jl. Hayam Wuruk 4A Semarang, Indonesia Received:
CHEMICAL ANALYSIS DURING THE PROCESSING OF DRIED SALTED ANCHOVY Eko Nurcahya Dewi *) Faculty of Fisheries and Marine Sciences University of Diponegoro, Jl. Hayam Wuruk 4A Semarang, Indonesia Received:
Plasma Membrane Protein Extraction Kit
 ab65400 Plasma Membrane Protein Extraction Kit Instructions for Use For the rapid and sensitive extraction and purification of Plasma Membrane proteins from cultured cells and tissue samples. This product
ab65400 Plasma Membrane Protein Extraction Kit Instructions for Use For the rapid and sensitive extraction and purification of Plasma Membrane proteins from cultured cells and tissue samples. This product
Protocol for protein SDS PAGE and Transfer
 Protocol for protein SDS PAGE and Transfer According to Laemmli, (1970) Alaa El -Din Hamid Sayed, Alaa_h254@yahoo.com Serum Selection of a protein source cell cultures (bacteria, yeast, mammalian, etc.)
Protocol for protein SDS PAGE and Transfer According to Laemmli, (1970) Alaa El -Din Hamid Sayed, Alaa_h254@yahoo.com Serum Selection of a protein source cell cultures (bacteria, yeast, mammalian, etc.)
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION DOI: 10.1038/NNANO.2012.80 Protein-Inorganic Hybrid Nanoflowers Jun Ge, Jiandu Lei, and Richard N. Zare Supporting Online Material Materials Proteins including albumin from bovine
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION DOI: 10.1038/NNANO.2012.80 Protein-Inorganic Hybrid Nanoflowers Jun Ge, Jiandu Lei, and Richard N. Zare Supporting Online Material Materials Proteins including albumin from bovine
PNGase F Instruction Manual
 PNGase F Instruction Manual Catalog Number 170-6883 Bio-Rad Laboratories, 2000 Alfred Nobel Dr., Hercules, CA 94547 4006094 Rev A Table of Contents Section 1 Introduction...1 Section 2 Kit Components and
PNGase F Instruction Manual Catalog Number 170-6883 Bio-Rad Laboratories, 2000 Alfred Nobel Dr., Hercules, CA 94547 4006094 Rev A Table of Contents Section 1 Introduction...1 Section 2 Kit Components and
Broad Spectrum Protease Inhibitor Cocktail
 Broad Spectrum Protease Inhibitor Cocktail Catalog number: AR1182 Boster s Broad Spectrum Protease Inhibitor Cocktail is a complex of various protease inhibitors, which has been tested for inhibiting proteases
Broad Spectrum Protease Inhibitor Cocktail Catalog number: AR1182 Boster s Broad Spectrum Protease Inhibitor Cocktail is a complex of various protease inhibitors, which has been tested for inhibiting proteases
ab E3 Ligase Auto- Ubiquitilylation Assay Kit
 ab139469 E3 Ligase Auto- Ubiquitilylation Assay Kit Instructions for Use For testing ubiquitin E3 ligase activity through assessment of their ability to undergo auto-ubiquitinylation This product is for
ab139469 E3 Ligase Auto- Ubiquitilylation Assay Kit Instructions for Use For testing ubiquitin E3 ligase activity through assessment of their ability to undergo auto-ubiquitinylation This product is for
Identification of Three Major Components in Fish Sarcoplasmic Proteins
 Nippon Suisan Gakkaishi 54(6), 999-1004 (1988) Identification of Three Major Components in Fish Sarcoplasmic Proteins Takayuki Nakagawa,*1 Shugo Watabe,*2 and Kanehisa Hashimoto*2 (Received November 6,
Nippon Suisan Gakkaishi 54(6), 999-1004 (1988) Identification of Three Major Components in Fish Sarcoplasmic Proteins Takayuki Nakagawa,*1 Shugo Watabe,*2 and Kanehisa Hashimoto*2 (Received November 6,
Mode of IMP and Pyrophosphate Enhancement of Myosin and Actin Extraction from Porcine Meat
 Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem., 77 (6), 1214 1218, 2013 Mode of IMP and Pyrophosphate Enhancement of Myosin and Actin Extraction from Porcine Meat Yukinobu NAKAMURA, 1;y Koshiro MIGITA, 2 Akihiro OKITANI,
Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem., 77 (6), 1214 1218, 2013 Mode of IMP and Pyrophosphate Enhancement of Myosin and Actin Extraction from Porcine Meat Yukinobu NAKAMURA, 1;y Koshiro MIGITA, 2 Akihiro OKITANI,
Collagenase Assay Kit
 Collagenase Assay Kit Catalog # 31 and 32 For Research Use Only - Not Human or Therapeutic Use INTRODUCTION Collagenases are members of the matrix metalloproteinase (MMP) family and degrade collagen types
Collagenase Assay Kit Catalog # 31 and 32 For Research Use Only - Not Human or Therapeutic Use INTRODUCTION Collagenases are members of the matrix metalloproteinase (MMP) family and degrade collagen types
CHAPTER 9 PARTIAL PURIFICATION AND CHARACTERIZATION OF CYSTEINE PROTEINASE INHIBITOR FROM CHICKEN PLASMA. 9.1 Abstract. 9.
 154 CHAPTER 9 PARTIAL PURIFICATION AND CHARACTERIZATION OF CYSTEINE PROTEINASE INHIBITOR FROM CHICKEN PLASMA 9.1 Abstract A high-molecular-weight cysteine proteinase inhibitor (CPI) was purified from chicken
154 CHAPTER 9 PARTIAL PURIFICATION AND CHARACTERIZATION OF CYSTEINE PROTEINASE INHIBITOR FROM CHICKEN PLASMA 9.1 Abstract A high-molecular-weight cysteine proteinase inhibitor (CPI) was purified from chicken
Cell Lysis Buffer. Catalog number: AR0103
 Cell Lysis Buffer Catalog number: AR0103 Boster s Cell Lysis Buffer is a ready-to-use Western blot related reagent solution used for efficient extraction of total soluble protein in nondenatured state
Cell Lysis Buffer Catalog number: AR0103 Boster s Cell Lysis Buffer is a ready-to-use Western blot related reagent solution used for efficient extraction of total soluble protein in nondenatured state
For the rapid, sensitive and accurate quantification of Ras in various samples
 ab128504 Ras Assay Kit Instructions for Use For the rapid, sensitive and accurate quantification of Ras in various samples This product is for research use only and is not intended for diagnostic use.
ab128504 Ras Assay Kit Instructions for Use For the rapid, sensitive and accurate quantification of Ras in various samples This product is for research use only and is not intended for diagnostic use.
Minute TM Plasma Membrane Protein Isolation and Cell Fractionation Kit User Manual (v5)
 Minute TM Plasma Membrane Protein Isolation and Cell Fractionation Kit Catalog number: SM-005 Description Minute TM plasma membrane (PM) protein isolation kit is a novel and patented native PM protein
Minute TM Plasma Membrane Protein Isolation and Cell Fractionation Kit Catalog number: SM-005 Description Minute TM plasma membrane (PM) protein isolation kit is a novel and patented native PM protein
Mitochondrial Trifunctional Protein (TFP) Protein Quantity Microplate Assay Kit
 PROTOCOL Mitochondrial Trifunctional Protein (TFP) Protein Quantity Microplate Assay Kit DESCRIPTION Mitochondrial Trifunctional Protein (TFP) Protein Quantity Microplate Assay Kit Sufficient materials
PROTOCOL Mitochondrial Trifunctional Protein (TFP) Protein Quantity Microplate Assay Kit DESCRIPTION Mitochondrial Trifunctional Protein (TFP) Protein Quantity Microplate Assay Kit Sufficient materials
Mammalian Membrane Protein Extraction Kit
 Mammalian Membrane Protein Extraction Kit Catalog number: AR0155 Boster s Mammalian Membrane Protein Extraction Kit is a simple, rapid and reproducible method to prepare cellular protein fractions highly
Mammalian Membrane Protein Extraction Kit Catalog number: AR0155 Boster s Mammalian Membrane Protein Extraction Kit is a simple, rapid and reproducible method to prepare cellular protein fractions highly
SUPPLEMENTAL INFORMATION
 SUPPLEMENTAL INFORMATION EXPERIMENTAL PROCEDURES Tryptic digestion protection experiments - PCSK9 with Ab-3D5 (1:1 molar ratio) in 50 mm Tris, ph 8.0, 150 mm NaCl was incubated overnight at 4 o C. The
SUPPLEMENTAL INFORMATION EXPERIMENTAL PROCEDURES Tryptic digestion protection experiments - PCSK9 with Ab-3D5 (1:1 molar ratio) in 50 mm Tris, ph 8.0, 150 mm NaCl was incubated overnight at 4 o C. The
Western Immunoblotting Preparation of Samples:
 Western Immunoblotting Preparation of Samples: Total Protein Extraction from Culture Cells: Take off the medium Wash culture with 1 x PBS 1 ml hot Cell-lysis Solution into T75 flask Scrap out the cells
Western Immunoblotting Preparation of Samples: Total Protein Extraction from Culture Cells: Take off the medium Wash culture with 1 x PBS 1 ml hot Cell-lysis Solution into T75 flask Scrap out the cells
Western Blot Analysis of Rat Pituitar Recognized by Human Antipituitary. y Antigens A. antibodies
 Endocrine Journal 1995, 42(1), 115-119 NOTE Western Blot Analysis of Rat Pituitar Recognized by Human Antipituitary y Antigens A ntibodies SHIGEKI YABE, MASAMI MURAKAMI*, KAYOKO MARUYAMA, HIDEKO MIWA,
Endocrine Journal 1995, 42(1), 115-119 NOTE Western Blot Analysis of Rat Pituitar Recognized by Human Antipituitary y Antigens A ntibodies SHIGEKI YABE, MASAMI MURAKAMI*, KAYOKO MARUYAMA, HIDEKO MIWA,
HCC1937 is the HCC1937-pcDNA3 cell line, which was derived from a breast cancer with a mutation
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Materials and Methods Human cell lines and culture conditions HCC1937 is the HCC1937-pcDNA3 cell line, which was derived from a breast cancer with a mutation in exon 20 of BRCA1
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Materials and Methods Human cell lines and culture conditions HCC1937 is the HCC1937-pcDNA3 cell line, which was derived from a breast cancer with a mutation in exon 20 of BRCA1
HiPer Western Blotting Teaching Kit
 HiPer Western Blotting Teaching Kit Product Code: HTI009 Number of experiments that can be performed: 5/20 Duration of Experiment: ~ 2 days Day 1: 6-8 hours (SDS- PAGE and Electroblotting) Day 2: 3 hours
HiPer Western Blotting Teaching Kit Product Code: HTI009 Number of experiments that can be performed: 5/20 Duration of Experiment: ~ 2 days Day 1: 6-8 hours (SDS- PAGE and Electroblotting) Day 2: 3 hours
Williams Lab Recipes ANTIBIOTICS
 Williams Lab Recipes ANTIBIOTICS 1000x Ampicillin (sodium salt) 100mg/ml recipe 1. Measure out 1 g of Ampicillin tri hydrate 2. Add Milli-Q H2O to 10 ml 3. Add ~.1 g of NaOH pellets (half pellet or more
Williams Lab Recipes ANTIBIOTICS 1000x Ampicillin (sodium salt) 100mg/ml recipe 1. Measure out 1 g of Ampicillin tri hydrate 2. Add Milli-Q H2O to 10 ml 3. Add ~.1 g of NaOH pellets (half pellet or more
Improve Protein Analysis with the New, Mass Spectrometry- Compatible ProteasMAX Surfactant
 Improve Protein Analysis with the New, Mass Spectrometry- Compatible Surfactant ABSTRACT Incomplete solubilization and digestion and poor peptide recovery are frequent limitations in protein sample preparation
Improve Protein Analysis with the New, Mass Spectrometry- Compatible Surfactant ABSTRACT Incomplete solubilization and digestion and poor peptide recovery are frequent limitations in protein sample preparation
Work-flow: protein sample preparation Precipitation methods Removal of interfering substances Specific examples:
 Dr. Sanjeeva Srivastava IIT Bombay Work-flow: protein sample preparation Precipitation methods Removal of interfering substances Specific examples: Sample preparation for serum proteome analysis Sample
Dr. Sanjeeva Srivastava IIT Bombay Work-flow: protein sample preparation Precipitation methods Removal of interfering substances Specific examples: Sample preparation for serum proteome analysis Sample
CHAPTER 7: REAGENTS AND SOLUTIONS
 7.1. ANALYSIS OF MODULATION OF SOD ENZYME Acetic acid (cat. no. 11007, Glaxo Qualigen, India): Bovine Serum Albumin stock solution (BSA, 1mg/ml): 1 mg of standard bovine serum albumin (cat. no. A2153,
7.1. ANALYSIS OF MODULATION OF SOD ENZYME Acetic acid (cat. no. 11007, Glaxo Qualigen, India): Bovine Serum Albumin stock solution (BSA, 1mg/ml): 1 mg of standard bovine serum albumin (cat. no. A2153,
2,6,9-Triazabicyclo[3.3.1]nonanes as overlooked. amino-modification products by acrolein
![2,6,9-Triazabicyclo[3.3.1]nonanes as overlooked. amino-modification products by acrolein 2,6,9-Triazabicyclo[3.3.1]nonanes as overlooked. amino-modification products by acrolein](/thumbs/86/94743397.jpg) Supplementary Information 2,6,9-Triazabicyclo[3.3.1]nonanes as overlooked amino-modification products by acrolein Ayumi Tsutsui and Katsunori Tanaka* Biofunctional Synthetic Chemistry Laboratory, RIKEN
Supplementary Information 2,6,9-Triazabicyclo[3.3.1]nonanes as overlooked amino-modification products by acrolein Ayumi Tsutsui and Katsunori Tanaka* Biofunctional Synthetic Chemistry Laboratory, RIKEN
Dental Research Institute, Faculty of Dentistry, University of Toronto, Toronto, Canada *For correspondence:
 Zymogram Assay for the Detection of Peptidoglycan Hydrolases in Streptococcus mutans Delphine Dufour and Céline M. Lévesque * Dental Research Institute, Faculty of Dentistry, University of Toronto, Toronto,
Zymogram Assay for the Detection of Peptidoglycan Hydrolases in Streptococcus mutans Delphine Dufour and Céline M. Lévesque * Dental Research Institute, Faculty of Dentistry, University of Toronto, Toronto,
Proteases in germinating finger millet (Eleusine coracana) seeds
 Biosci., Vol. 5, Number 3, September 1983, pp. 219 224. Printed in India. Proteases in germinating finger millet (Eleusine coracana) seeds Introduction U. VIDYAVATHI, B. SHIVARAJ and T. N. PATTABIRAMAN
Biosci., Vol. 5, Number 3, September 1983, pp. 219 224. Printed in India. Proteases in germinating finger millet (Eleusine coracana) seeds Introduction U. VIDYAVATHI, B. SHIVARAJ and T. N. PATTABIRAMAN
Protocol for Western Blo
 Protocol for Western Blo ng SDS-PAGE separa on 1. Make appropriate percentage of separa on gel according to the MW of target proteins. Related recommenda ons and rou ne recipes of separa on/stacking gels
Protocol for Western Blo ng SDS-PAGE separa on 1. Make appropriate percentage of separa on gel according to the MW of target proteins. Related recommenda ons and rou ne recipes of separa on/stacking gels
TFEB-mediated increase in peripheral lysosomes regulates. Store Operated Calcium Entry
 TFEB-mediated increase in peripheral lysosomes regulates Store Operated Calcium Entry Luigi Sbano, Massimo Bonora, Saverio Marchi, Federica Baldassari, Diego L. Medina, Andrea Ballabio, Carlotta Giorgi
TFEB-mediated increase in peripheral lysosomes regulates Store Operated Calcium Entry Luigi Sbano, Massimo Bonora, Saverio Marchi, Federica Baldassari, Diego L. Medina, Andrea Ballabio, Carlotta Giorgi
The following protocol describes the isolation of nuclei from tissue. Item. Catalog No Manufacturer
 SOP: Nuclei isolation from tissue and DNaseI treatment Date modified: 090923 Modified by: P. Sabo. (UW) The following protocol describes the isolation of nuclei from tissue. Ordering Information Item.
SOP: Nuclei isolation from tissue and DNaseI treatment Date modified: 090923 Modified by: P. Sabo. (UW) The following protocol describes the isolation of nuclei from tissue. Ordering Information Item.
TRACP & ALP double-stain Kit
 Table of Content I. Description... 2 II. Introduction... 2 III. Principles... 2 IV. Kit components... 3 V. Storage... 3 VI. Preparation of reagents... 3 VII. Methods... 4-7 Cell fixation... 4 Activity
Table of Content I. Description... 2 II. Introduction... 2 III. Principles... 2 IV. Kit components... 3 V. Storage... 3 VI. Preparation of reagents... 3 VII. Methods... 4-7 Cell fixation... 4 Activity
Mouse Cathepsin B ELISA Kit
 GenWay Biotech, Inc. 6777 Nancy Ridge Drive San Diego, CA 92121 Phone: 858.458.0866 Fax: 858.458.0833 Email: techline@genwaybio.com http://www.genwaybio.com Mouse Cathepsin B ELISA Kit Catalog No. GWB-ZZD154
GenWay Biotech, Inc. 6777 Nancy Ridge Drive San Diego, CA 92121 Phone: 858.458.0866 Fax: 858.458.0833 Email: techline@genwaybio.com http://www.genwaybio.com Mouse Cathepsin B ELISA Kit Catalog No. GWB-ZZD154
MYOFIBRILLAR STRUCTURAL CHANGES CAUSED BY MARINATION WITH CALCIUM PHOSPHATE OR CALCIUM CHLORIDE AND SODIUM PYROPHOSPHATE
 Cattlemen s Day 2002 MYOFIBRILLAR STRUCTURAL CHANGES CAUSED BY MARINATION WITH CALCIUM PHOSPHATE OR CALCIUM CHLORIDE AND SODIUM PYROPHOSPHATE T. E. Lawrence, A. T. Waylan, and C. L. Kastner Summary Ultrastructural
Cattlemen s Day 2002 MYOFIBRILLAR STRUCTURAL CHANGES CAUSED BY MARINATION WITH CALCIUM PHOSPHATE OR CALCIUM CHLORIDE AND SODIUM PYROPHOSPHATE T. E. Lawrence, A. T. Waylan, and C. L. Kastner Summary Ultrastructural
APPENDIX Heparin 2 mg heparin was dissolved in 0.9 % NaCl (10 ml). 200 µl of heparin was added to each 1 ml of blood to prevent coagulation.
 APPENDIX 1 Preparation of reagents 1.1. Preparation of dosing solution Nonylphenol 15 mg of Nonylphenol was dissolved in olive oil (10 ml) and used as stock solution. The stock solution was serially diluted
APPENDIX 1 Preparation of reagents 1.1. Preparation of dosing solution Nonylphenol 15 mg of Nonylphenol was dissolved in olive oil (10 ml) and used as stock solution. The stock solution was serially diluted
Islet viability assay and Glucose Stimulated Insulin Secretion assay RT-PCR and Western Blot
 Islet viability assay and Glucose Stimulated Insulin Secretion assay Islet cell viability was determined by colorimetric (3-(4,5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5- diphenyltetrazolium bromide assay using CellTiter
Islet viability assay and Glucose Stimulated Insulin Secretion assay Islet cell viability was determined by colorimetric (3-(4,5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5- diphenyltetrazolium bromide assay using CellTiter
MW.SDS.70L and MW-SDS.200 Kits
 ~'A'.'.A'k'~ ~ ~ ':if';"7'~~'!11;~\ C HEM IC A I CQ P.O. ~X 14508,$T,LQV1S,MQ;, ~17,;U$A SDS MOLECULAR WEIGHT MARKERS IN A DISCONTINUOUS BUFFER July 1988 Technical Bulletin No. MWS-877L ORDER DIRECT: USA/Canada
~'A'.'.A'k'~ ~ ~ ':if';"7'~~'!11;~\ C HEM IC A I CQ P.O. ~X 14508,$T,LQV1S,MQ;, ~17,;U$A SDS MOLECULAR WEIGHT MARKERS IN A DISCONTINUOUS BUFFER July 1988 Technical Bulletin No. MWS-877L ORDER DIRECT: USA/Canada
Mammalian Tissue Protein Extraction Reagent
 Mammalian Tissue Protein Extraction Reagent Catalog number: AR0101 Boster s Mammalian Tissue Protein Extraction Reagent is a ready-to-use Western blot related reagent solution used for efficient extraction
Mammalian Tissue Protein Extraction Reagent Catalog number: AR0101 Boster s Mammalian Tissue Protein Extraction Reagent is a ready-to-use Western blot related reagent solution used for efficient extraction
TECHNICAL BULLETIN. R 2 GlcNAcβ1 4GlcNAcβ1 Asn
 GlycoProfile II Enzymatic In-Solution N-Deglycosylation Kit Product Code PP0201 Storage Temperature 2 8 C TECHNICAL BULLETIN Product Description Glycosylation is one of the most common posttranslational
GlycoProfile II Enzymatic In-Solution N-Deglycosylation Kit Product Code PP0201 Storage Temperature 2 8 C TECHNICAL BULLETIN Product Description Glycosylation is one of the most common posttranslational
Purification and characterization of a cathepsin inhibitor from catfish (Pangasius sp.) of Indonesian water
 International Food Research Journal 20(2): 941-946 (2013) Journal homepage: http://www.ifrj.upm.edu.my Purification and characterization of a cathepsin from catfish (Pangasius sp.) of Indonesian water
International Food Research Journal 20(2): 941-946 (2013) Journal homepage: http://www.ifrj.upm.edu.my Purification and characterization of a cathepsin from catfish (Pangasius sp.) of Indonesian water
Purification of carp (Cyprinus carpio) kidney cathepsin C
 Purification of carp (Cyprinus carpio) kidney cathepsin C (Pemurnian enzim cathepsin C dari ginjal ikan mas Cyprinus carpio) Pangkey H. dan Lantu S. ABSTRACT Pemurnian enzim cathepsin C diperoleh melalui
Purification of carp (Cyprinus carpio) kidney cathepsin C (Pemurnian enzim cathepsin C dari ginjal ikan mas Cyprinus carpio) Pangkey H. dan Lantu S. ABSTRACT Pemurnian enzim cathepsin C diperoleh melalui
FOCUS SubCell. For the Enrichment of Subcellular Fractions. (Cat. # ) think proteins! think G-Biosciences
 169PR 01 G-Biosciences 1-800-628-7730 1-314-991-6034 technical@gbiosciences.com A Geno Technology, Inc. (USA) brand name FOCUS SubCell For the Enrichment of Subcellular Fractions (Cat. # 786 260) think
169PR 01 G-Biosciences 1-800-628-7730 1-314-991-6034 technical@gbiosciences.com A Geno Technology, Inc. (USA) brand name FOCUS SubCell For the Enrichment of Subcellular Fractions (Cat. # 786 260) think
ab Membrane Fractionation Kit Instructions for Use For the rapid and simple separation of membrane, cytosolic and nuclear cellular fractions.
 ab139409 Membrane Fractionation Kit Instructions for Use For the rapid and simple separation of membrane, cytosolic and nuclear cellular fractions. This product is for research use only and is not intended
ab139409 Membrane Fractionation Kit Instructions for Use For the rapid and simple separation of membrane, cytosolic and nuclear cellular fractions. This product is for research use only and is not intended
Recombinant Trypsin, Animal Origin Free
 Recombinant Trypsin, Animal Origin Free PRODUCT INFORMATION: BioGenomics r-trypsin powder is ready to use, animal origin free optimized for cell culture applications. It is derived by r-dna technology.
Recombinant Trypsin, Animal Origin Free PRODUCT INFORMATION: BioGenomics r-trypsin powder is ready to use, animal origin free optimized for cell culture applications. It is derived by r-dna technology.
Aperto Cell Lysis and Protein Solubilization Users Manual
 Aperto Cell Lysis and Protein Solubilization Users Manual Revision 2 THIS MANUAL APPLIES TO THE FOLLOWING PRODUCTS: 3A8600 Aperto, 5X Cell Lysis Buffer. 20mL 3A8610 Aperto, 5X Cell Lysis Buffer. 100mL
Aperto Cell Lysis and Protein Solubilization Users Manual Revision 2 THIS MANUAL APPLIES TO THE FOLLOWING PRODUCTS: 3A8600 Aperto, 5X Cell Lysis Buffer. 20mL 3A8610 Aperto, 5X Cell Lysis Buffer. 100mL
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure S1. Binding of full-length OGT and deletion mutants to PIP strips (Echelon Biosciences). Supplementary Figure S2. Binding of the OGT (919-1036) fragments with
Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure S1. Binding of full-length OGT and deletion mutants to PIP strips (Echelon Biosciences). Supplementary Figure S2. Binding of the OGT (919-1036) fragments with
Expression constructs
 Gene expressed in bebe3 ZmBEa Expression constructs 35S ZmBEa Pnos:Hygromycin r 35S Pnos:Hygromycin r 35S ctp YFP Pnos:Hygromycin r B -1 Chl YFP- Merge Supplemental Figure S1: Constructs Used for the Expression
Gene expressed in bebe3 ZmBEa Expression constructs 35S ZmBEa Pnos:Hygromycin r 35S Pnos:Hygromycin r 35S ctp YFP Pnos:Hygromycin r B -1 Chl YFP- Merge Supplemental Figure S1: Constructs Used for the Expression
Collagenase Assay Kit
 Collagenase Assay Kit Catalog # 31 and 32 For Research Use Only - Not Human or Therapeutic Use INTRODUCTION The collagenases are members of the matrix metalloproteinase (MMP) family and degrade collagen
Collagenase Assay Kit Catalog # 31 and 32 For Research Use Only - Not Human or Therapeutic Use INTRODUCTION The collagenases are members of the matrix metalloproteinase (MMP) family and degrade collagen
Antoine Bouchoux, Pierre-Emerson Cayemitte, Julien Jardin, Geneviève Gésan-Guiziou, and Bernard Cabane
 Biophysical Journal, Volume 96 Supplementary Material Casein Micelle Dispersions under Osmotic Stress Antoine Bouchoux, Pierre-Emerson Cayemitte, Julien Jardin, Geneviève Gésan-Guiziou, and Bernard Cabane
Biophysical Journal, Volume 96 Supplementary Material Casein Micelle Dispersions under Osmotic Stress Antoine Bouchoux, Pierre-Emerson Cayemitte, Julien Jardin, Geneviève Gésan-Guiziou, and Bernard Cabane
Supplementary data Supplementary Figure 1 Supplementary Figure 2
 Supplementary data Supplementary Figure 1 SPHK1 sirna increases RANKL-induced osteoclastogenesis in RAW264.7 cell culture. (A) RAW264.7 cells were transfected with oligocassettes containing SPHK1 sirna
Supplementary data Supplementary Figure 1 SPHK1 sirna increases RANKL-induced osteoclastogenesis in RAW264.7 cell culture. (A) RAW264.7 cells were transfected with oligocassettes containing SPHK1 sirna
Step 4. Step 4. Choose MW markers. Choose MW markers. Gel Electrophoresis of Proteins
 Gel Electrophoresis of Proteins Choose MW markers 16 Step 4 Gel Electrophoresis of Proteins A Practical Approach, Third Edition An overview of basic techniques to benefit any life scientist using electrophoretic
Gel Electrophoresis of Proteins Choose MW markers 16 Step 4 Gel Electrophoresis of Proteins A Practical Approach, Third Edition An overview of basic techniques to benefit any life scientist using electrophoretic
Trypsin Mass Spectrometry Grade
 058PR-03 G-Biosciences 1-800-628-7730 1-314-991-6034 technical@gbiosciences.com A Geno Technology, Inc. (USA) brand name Trypsin Mass Spectrometry Grade A Chemically Modified, TPCK treated, Affinity Purified
058PR-03 G-Biosciences 1-800-628-7730 1-314-991-6034 technical@gbiosciences.com A Geno Technology, Inc. (USA) brand name Trypsin Mass Spectrometry Grade A Chemically Modified, TPCK treated, Affinity Purified
The rabbit femoral artery was prepared and each arterial ring was permeabilized
 Online Supplement Nakmura et al. cgmp-dependent relaxation of smooth muscle Materials and Methods Measurement of tension The rabbit femoral artery was prepared and each arterial ring was permeabilized
Online Supplement Nakmura et al. cgmp-dependent relaxation of smooth muscle Materials and Methods Measurement of tension The rabbit femoral artery was prepared and each arterial ring was permeabilized
Title. Author(s)Thavaroj, Wichulada; Sakamoto, Mari; Konno, Yoshiko; CitationFisheries science, 82(5): Issue Date Doc URL.
 Title Preceding actin denaturation accelerates myosin dena Author(s)Thavaroj, Wichulada; Sakamoto, Mari; Konno, Yoshiko; CitationFisheries science, 82(5): 843-850 Issue Date 2016-09 Doc URL http://hdl.handle.net/2115/67081
Title Preceding actin denaturation accelerates myosin dena Author(s)Thavaroj, Wichulada; Sakamoto, Mari; Konno, Yoshiko; CitationFisheries science, 82(5): 843-850 Issue Date 2016-09 Doc URL http://hdl.handle.net/2115/67081
Plant tissue extraction kit. For extraction of soluble protein and other biomolecules and metabolites from plant tissues.
 ab206999 Plant tissue extraction kit Instructions for use: For extraction of soluble protein and other biomolecules and metabolites from plant tissues. This product is for research use only and is not
ab206999 Plant tissue extraction kit Instructions for use: For extraction of soluble protein and other biomolecules and metabolites from plant tissues. This product is for research use only and is not
Item Catalog Number Manufacturer 1,4-Dithioerythritol (1 g) D9680 Sigma-Aldrich
 SOP: Nuclei isolation from fresh mouse tissues and DNaseI treatment Date modified: 01/12/2011 Modified by: E. Giste/ T. Canfield (UW) The following protocol describes the isolation of nuclei and subsequent
SOP: Nuclei isolation from fresh mouse tissues and DNaseI treatment Date modified: 01/12/2011 Modified by: E. Giste/ T. Canfield (UW) The following protocol describes the isolation of nuclei and subsequent
PRODUCT INFORMATION & MANUAL
 PRODUCT INFORMATION & MANUAL 0.4 micron for Overall Exosome Isolation (Cell Media) NBP2-49826 For research use only. Not for diagnostic or therapeutic procedures. www.novusbio.com - P: 303.730.1950 - P:
PRODUCT INFORMATION & MANUAL 0.4 micron for Overall Exosome Isolation (Cell Media) NBP2-49826 For research use only. Not for diagnostic or therapeutic procedures. www.novusbio.com - P: 303.730.1950 - P:
HIV-1 Virus-like Particle Budding Assay Nathan H Vande Burgt, Luis J Cocka * and Paul Bates
 HIV-1 Virus-like Particle Budding Assay Nathan H Vande Burgt, Luis J Cocka * and Paul Bates Department of Microbiology, Perelman School of Medicine at the University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia, USA
HIV-1 Virus-like Particle Budding Assay Nathan H Vande Burgt, Luis J Cocka * and Paul Bates Department of Microbiology, Perelman School of Medicine at the University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia, USA
Protocol for purification of recombinant protein from 300 ml yeast culture
 Protocol for purification of recombinant protein from 300 ml yeast culture Equipment and reagents needed: Zirconia beads (0.5 mm diameter from BSP, Germany) Paint Shaker (at 4 C) Tube rotator for 15 ml
Protocol for purification of recombinant protein from 300 ml yeast culture Equipment and reagents needed: Zirconia beads (0.5 mm diameter from BSP, Germany) Paint Shaker (at 4 C) Tube rotator for 15 ml
Trident Membrane Protein Extraction Kit
 Cat. No. Size Shelf life GTX16373 5/ 20 tests 12 months at the appropriate storage temperatures (see below) Contents Component Storage Amount for 5 tests Amount for 20 tests Buffer A -20 o C 2.5 ml 10
Cat. No. Size Shelf life GTX16373 5/ 20 tests 12 months at the appropriate storage temperatures (see below) Contents Component Storage Amount for 5 tests Amount for 20 tests Buffer A -20 o C 2.5 ml 10
Anti-Lamin B1/LMNB1 Picoband Antibody
 Anti-Lamin B1/LMNB1 Picoband Antibody Catalog Number:PB9611 About LMNB1 Lamin-B1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the LMNB1 gene. The nuclear lamina consists of a two-dimensional matrix of proteins
Anti-Lamin B1/LMNB1 Picoband Antibody Catalog Number:PB9611 About LMNB1 Lamin-B1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the LMNB1 gene. The nuclear lamina consists of a two-dimensional matrix of proteins
Nature Methods: doi: /nmeth Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementary Figure 1 Subtiligase-catalyzed ligations with ubiquitin thioesters and 10-mer biotinylated peptides. (a) General scheme for ligations between ubiquitin thioesters and 10-mer, biotinylated
Supplementary Figure 1 Subtiligase-catalyzed ligations with ubiquitin thioesters and 10-mer biotinylated peptides. (a) General scheme for ligations between ubiquitin thioesters and 10-mer, biotinylated
SCS MOLECULAR WEIGHT MARKERS 2,500-17,000 Caltons
 LECTROPHORES/S Revised November 1992 SCS MOLECULAR WEIGHT MARKERS 2,500-17,000 Caltons I NTRODUCTION Electrophoresis in polyacrylamide gels in the presence of sodium dodecyl sulfate (SDS), an anionic detergent,
LECTROPHORES/S Revised November 1992 SCS MOLECULAR WEIGHT MARKERS 2,500-17,000 Caltons I NTRODUCTION Electrophoresis in polyacrylamide gels in the presence of sodium dodecyl sulfate (SDS), an anionic detergent,
UV Tracer TM Maleimide NHS ester
 UV Tracer TM Maleimide HS ester Product o.: 1020 Product ame: UV-Tracer TM Maleimide-HS ester Chemical Structure: Chemical Composition: C 41 H 67 5 18 Molecular Weight: 1014.08 Appearance: Storage: Yellow
UV Tracer TM Maleimide HS ester Product o.: 1020 Product ame: UV-Tracer TM Maleimide-HS ester Chemical Structure: Chemical Composition: C 41 H 67 5 18 Molecular Weight: 1014.08 Appearance: Storage: Yellow
Supplementary Information
 Supplementary Information Supplementary Figure 1. CD4 + T cell activation and lack of apoptosis after crosslinking with anti-cd3 + anti-cd28 + anti-cd160. (a) Flow cytometry of anti-cd160 (5D.10A11) binding
Supplementary Information Supplementary Figure 1. CD4 + T cell activation and lack of apoptosis after crosslinking with anti-cd3 + anti-cd28 + anti-cd160. (a) Flow cytometry of anti-cd160 (5D.10A11) binding
PhosFree TM Phosphate Assay Biochem Kit
 PhosFree TM Phosphate Assay Biochem Kit (Cat. # BK050) ORDERING INFORMATION To order by phone: (303) - 322-2254 To order by Fax: (303) - 322-2257 To order by e-mail: cservice@cytoskeleton.com Technical
PhosFree TM Phosphate Assay Biochem Kit (Cat. # BK050) ORDERING INFORMATION To order by phone: (303) - 322-2254 To order by Fax: (303) - 322-2257 To order by e-mail: cservice@cytoskeleton.com Technical
A Microfluidic ExoSearch Chip for Multiplexed Exosome Detection Towards Bloodbased Ovarian Cancer Diagnosis
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Lab on a Chip. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2015 Supplementary Information A Microfluidic ExoSearch Chip for Multiplexed Exosome Detection
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Lab on a Chip. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2015 Supplementary Information A Microfluidic ExoSearch Chip for Multiplexed Exosome Detection
1. Materials and Methods 1.1 Animals experiments process The experiments were approved by the Institution Animal Ethics Committee of Jilin University
 1. Materials and Methods 1.1 Animals experiments process The experiments were approved by the Institution Animal Ethics Committee of Jilin University (Reference NO. 2015-003). 96 Kunming (KM) mice (8 weeks;
1. Materials and Methods 1.1 Animals experiments process The experiments were approved by the Institution Animal Ethics Committee of Jilin University (Reference NO. 2015-003). 96 Kunming (KM) mice (8 weeks;
SYNOPSIS STUDIES ON THE PREPARATION AND CHARACTERISATION OF PROTEIN HYDROLYSATES FROM GROUNDNUT AND SOYBEAN ISOLATES
 1 SYNOPSIS STUDIES ON THE PREPARATION AND CHARACTERISATION OF PROTEIN HYDROLYSATES FROM GROUNDNUT AND SOYBEAN ISOLATES Proteins are important in food processing and food product development, as they are
1 SYNOPSIS STUDIES ON THE PREPARATION AND CHARACTERISATION OF PROTEIN HYDROLYSATES FROM GROUNDNUT AND SOYBEAN ISOLATES Proteins are important in food processing and food product development, as they are
STUDIES ON MUSTARD-STIMULATED PROTEASES AND INHIBITORS IN HUMAN EPIDERMAL KERATINOCYTES (HEK): DEVELOPMENT OF ANTIVESICANT DRUGS
 STUDIES ON MUSTARD-STIMULATED PROTEASES AND INHIBITORS IN HUMAN EPIDERMAL KERATINOCYTES (HEK): DEVELOPMENT OF ANTIVESICANT DRUGS Xiannu Jin 1, Radharaman Ray 2, Guang Xu 1 and Prabhati Ray 1 1 Department
STUDIES ON MUSTARD-STIMULATED PROTEASES AND INHIBITORS IN HUMAN EPIDERMAL KERATINOCYTES (HEK): DEVELOPMENT OF ANTIVESICANT DRUGS Xiannu Jin 1, Radharaman Ray 2, Guang Xu 1 and Prabhati Ray 1 1 Department
Luminescent platforms for monitoring changes in the solubility of amylin and huntingtin in living cells
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Molecular BioSystems. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2016 Contents Supporting Information Luminescent platforms for monitoring changes in the
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Molecular BioSystems. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2016 Contents Supporting Information Luminescent platforms for monitoring changes in the
Kit for assay of thioredoxin
 FkTRX-02-V2 Kit for assay of thioredoxin The thioredoxin system is the major protein disulfide reductase in cells and comprises thioredoxin, thioredoxin reductase and NADPH (1). Thioredoxin systems are
FkTRX-02-V2 Kit for assay of thioredoxin The thioredoxin system is the major protein disulfide reductase in cells and comprises thioredoxin, thioredoxin reductase and NADPH (1). Thioredoxin systems are
Protease Assay. (Cat. # ) think proteins! think G-Biosciences
 389PR 01 G-Biosciences 1-800-628-7730 1-314-991-6034 technical@gbiosciences.com A Geno Technology, Inc. (USA) brand name Protease Assay (Cat. # 786 028) think proteins! think G-Biosciences www.gbiosciences.com
389PR 01 G-Biosciences 1-800-628-7730 1-314-991-6034 technical@gbiosciences.com A Geno Technology, Inc. (USA) brand name Protease Assay (Cat. # 786 028) think proteins! think G-Biosciences www.gbiosciences.com
SensoLyte pnpp Alkaline Phosphatase Assay Kit *Colorimetric*
 SensoLyte pnpp Alkaline Phosphatase Assay Kit *Colorimetric* Catalog # 72146 Kit Size 500 Assays (96-well plate) Optimized Performance: This kit is optimized to detect alkaline phosphatase activity Enhanced
SensoLyte pnpp Alkaline Phosphatase Assay Kit *Colorimetric* Catalog # 72146 Kit Size 500 Assays (96-well plate) Optimized Performance: This kit is optimized to detect alkaline phosphatase activity Enhanced
INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF ENGINEERING SCIENCES & RESEARCH TECHNOLOGY
 [Ravish, 2(2): Feb., 2013] ISSN: 2277-9655 IJESRT INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF ENGINEERING SCIENCES & RESEARCH TECHNOLOGY Isolation And Characterization Of Proteolytic Bacteria And Its Protease Himani Ravish
[Ravish, 2(2): Feb., 2013] ISSN: 2277-9655 IJESRT INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF ENGINEERING SCIENCES & RESEARCH TECHNOLOGY Isolation And Characterization Of Proteolytic Bacteria And Its Protease Himani Ravish
Protein Cleavage Due to Pro-oxidative Activity in Some Spices
 Protein Cleavage Due to Pro-oxidative Activity in Some Spices Sittiwat Lertsiri Department of Biotechnology Faculty of Science, Mahidol University Phayathai, Bangkok 10400 Thailand Kanchana Dumri Department
Protein Cleavage Due to Pro-oxidative Activity in Some Spices Sittiwat Lertsiri Department of Biotechnology Faculty of Science, Mahidol University Phayathai, Bangkok 10400 Thailand Kanchana Dumri Department
Title. Author(s)Takahashi, Koui; Ji, JR. CitationMeat Science, 73(3): Issue Date Doc URL. Rights. Type.
 Title Changes in concentration of sarcoplasmic free calciu Author(s)Takahashi, Koui; Ji, JR CitationMeat Science, 73(3): 395-403 Issue Date 2006-07-01 Doc URL http://hdl.handle.net/2115/14511 Rights Copyright
Title Changes in concentration of sarcoplasmic free calciu Author(s)Takahashi, Koui; Ji, JR CitationMeat Science, 73(3): 395-403 Issue Date 2006-07-01 Doc URL http://hdl.handle.net/2115/14511 Rights Copyright
PRODUCT: RNAzol BD for Blood May 2014 Catalog No: RB 192 Storage: Store at room temperature
 PRODUCT: RNAzol BD for Blood May 2014 Catalog No: RB 192 Storage: Store at room temperature PRODUCT DESCRIPTION. RNAzol BD is a reagent for isolation of total RNA from whole blood, plasma or serum of human
PRODUCT: RNAzol BD for Blood May 2014 Catalog No: RB 192 Storage: Store at room temperature PRODUCT DESCRIPTION. RNAzol BD is a reagent for isolation of total RNA from whole blood, plasma or serum of human
E.Z.N.A. SQ Blood DNA Kit II. Table of Contents
 E.Z.N.A. SQ Blood DNA Kit II Table of Contents Introduction and Overview...2 Kit Contents/Storage and Stability...3 Blood Storage and DNA Yield...4 Preparing Reagents...5 100-500 μl Whole Blood Protocol...6
E.Z.N.A. SQ Blood DNA Kit II Table of Contents Introduction and Overview...2 Kit Contents/Storage and Stability...3 Blood Storage and DNA Yield...4 Preparing Reagents...5 100-500 μl Whole Blood Protocol...6
ENZYMES QUESTIONSHEET 1
 QUESTIONSHEET 1 The apparatus illustrated below can be used to investigate the activity of the enzyme catalase, which is found in liver. The liver tissue has been ground up and mixed with a buffer solution.
QUESTIONSHEET 1 The apparatus illustrated below can be used to investigate the activity of the enzyme catalase, which is found in liver. The liver tissue has been ground up and mixed with a buffer solution.
ab Human Citrate Synthase (CS) Activity Assay Kit
 ab119692 Human Citrate Synthase (CS) Activity Assay Kit Instructions for Use For the measurement of mitochondrial citrate synthase (CS) activity in Human samples This product is for research use only and
ab119692 Human Citrate Synthase (CS) Activity Assay Kit Instructions for Use For the measurement of mitochondrial citrate synthase (CS) activity in Human samples This product is for research use only and
Substrate Specificity and Salt Inhibition of Five Proteinases Isolated from the Pyloric Caeca and Stomach of Sardine
 Agric. Biol. Chem., 46 (6), 1565~1569, 1982 1565 Substrate Specificity and Salt Inhibition of Five Proteinases Isolated from the Pyloric Caeca and Stomach of Sardine Minoru Noda, Thanh Vo Van, Isao Kusakabe
Agric. Biol. Chem., 46 (6), 1565~1569, 1982 1565 Substrate Specificity and Salt Inhibition of Five Proteinases Isolated from the Pyloric Caeca and Stomach of Sardine Minoru Noda, Thanh Vo Van, Isao Kusakabe
