. The menaquinones, collectively known as vitamin K 2
|
|
|
- Abel Howard
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Part Fat Soluble Vitamins Risk Assessment Vitamin K General Information Chemistry Vitamin K is not a single compound but a group of homologous fat-soluble compounds derived from -methyl-1,4-naphthoquinone. Phylloquinone (-methyl-3-phytyl-1,4-naphthoquinone) is designated as vitamin K 1. The menaquinones, collectively known as vitamin K, are a large series of compounds containing an unsaturated side chain with differing numbers of isoprenyl units at the 3 position in the methyl-1,4-naphthoquinone nucleus. Depending on the number of isoprenyl units the individual compounds are designated as menaquinone-n-(mk-n). Several synthetic water-soluble compounds containing the -methyl-1,4-naphthoquinone structure also exist. These include menadione (vitamin K 3 ) and menadiol (vitamin K 4 ) (see table). Table: Summary of the nomenclature of the various forms of vitamin K Name Synonyms/chemical name Source Phylloquinone -methyl-3-phytyl-1,4-naphthoquinone Plants phytomenadione phytoandione phytylmenadione Vitamin K Menaquinone Menatetranone Gram +ve bacteria Menaquinone K4 Vitamin MK-4 Vitamin K 3 Menadione -methyl-1,4-naphthoquinone Synthetic Vitamin K 4 Menadiol Menaquinol Synthetic -methyl-1,4-naphthoquinol -methyl-1,4-naphthohydroquinone reduced menadione Natural occurrence is synthesised by plants. The vitamin K series is synthesised by various Gram-positive bacteria present in the jejunum and ileum. Occurrence in food, food supplements and medicines Dietary vitamin K is largely obtained from green leafy vegetables and vegetable oils, with lesser amounts present in dairy products, meat and eggs. Vitamin K is also present as K 1 and K in multi-vitamin food supplements and as K 1 and K 4 in licensed medicines. Vitamins K 1 and K 4 are used in the treatment or prophylaxis of haemorrhage as a result of low blood level of prothrombin or Factor VII, malabsorption or use of coumarin anticoagulants. UK food supplements may contain up to mg vitamin K (either as K 1 or K ) for general consumption and 0.0 mg in supplements intended for women from pre-conception to nursing. 154
2 Expert Group on Vitamins and Minerals 003 Other sources of exposure Vitamin K (as the K series) is also provided by the bacterial flora in the intestine, and this contributes significantly towards the daily requirement of the vitamin. Recommended amounts Although vitamin K is known to be essential, recommendations on adequate nutritional intakes have not been precisely established, because of the unquantified contribution made by the intestinal bacteria. COMA considered that an intake of mg/kg bw/day was probably adequate with regard to the coagulation function of vitamin K and noted that synthetic preparations of K 3 were best avoided for nutritional purposes, due to their link with haemolysis and liver damage in the newborn (COMA, 1991). The Infant Formula and Follow-on Formula regulations (1995) recommend a minimum vitamin K intake of mg/100 kcal. Analysis of tissue levels and vitamin K status Functional tests of blood clotting were initially used to assess vitamin K status. However, a radioimmunoassay which measures the ratio of prothrombin to partially carboxylated prothrombin in plasma (the latter is formed during vitamin K deficiency) is now available. Measurement of the carboxylation of serum osteocalcin, and plasma vitamin K 1 are also used to determine vitamin K status. However, the measurement of plasma vitamin K 1 is of limited value because it reflects recent dietary intake. Brief overview of non-nutritional effects Vitamin K (in particular, the water-soluble form) has been reported to potentiate the analgesic effect of opiates and salicylates, and induce radiosensitisation. Function Vitamin K catalyses the carboxylation of a number of protein factors involved in blood clotting including prothrombin, forming the calcium binding sites on glutamyl side chains in the protein. Once carboxylated, the glutamates are referred to as gamma-carboxyglutamic acid (GLA). GLA-containing proteins are also found in the bone. For example, bone GLA protein (or osteocalcin) is thought to be involved in the limitation of bone growth, and matrix GLA protein may be involved in mobilisation and deposition of bone calcium. Kidney GLA proteins may be involved in reabsorption of calcium by the kidney tubules and solubilisation of calcium salts in urine. GLA-containing proteins have also been found in the placenta, pancreas, spleen and lungs, but the majority of these have not yet been characterised. Vitamin K-dependent proteins are also thought to have roles in cell signalling and brain lipid metabolism. 155
3 Part Fat Soluble Vitamins Deficiency Vitamin K is widely available from the diet and is also provided by gut bacteria. Thus, deficiency is generally secondary to conditions such as malabsorption or impaired gut synthesis. Hospitalised patients can be at risk of vitamin K deficiency following the use of antibiotics or gastrointestinal surgery. Newborn babies have low levels of vitamin K, which may result in haemorrhagic disease of the newborn. Interactions It has been shown experimentally that excessive vitamin E exposure results in increased prothrombin times which are normalised by vitamin K. The effects of vitamin K 1 are also antagonised by excessive oral intakes of vitamin A. interacts with coumarin anticoagulants. The effect of -methyl-1,4-napthoquinone (vitamin K 3 ) is antagonised by actinomycin D. The carcinogenic activity of benzo(a)pyrene has been shown to be increased by vitamin K 1, as a result of induction of cytochrome P450 1A1 (CYP1A1). In contrast, vitamin K 3 decreased CYP1A1 activity. Absorption and bioavailability Vitamin K is readily absorbed, but there are conflicting reports on whether this is higher from supplements or from a food matrix. The bioavailability of vitamin K 1 is the same from raw and cooked broccoli and is unaffected by the fat content of the meal. Absorption of vitamin K 1 takes place in the proximal small intestine by a saturable, energy dependent process. Absorption of bacterial menaquinones (K ) occurs in the terminal ileum by passive diffusion. Absorption of vitamin K is enhanced by bile salts and pancreatic juice. Overall, 40-70% of vitamin K may be absorbed in the jejunum, but absorption is lower elsewhere in the digestive system. Vitamin K 3 is believed to be absorbed by passive diffusion in the distal intestine and colon. Distribution and metabolism Vitamin K is transported via the lymph in chylomicrons and concentrated in the liver prior to wide distribution. The body pool of vitamin K is low. The metabolism of vitamins K 1 and K involves the formation of an epoxide and a quinone, which can then be reduced by NAD(P)H reductases. The reduced form is involved in carboxylation reactions. The carboxylic acid derivatives of vitamin K 1 are conjugated with glucuronic acid. In rats, vitamin K 1 can be converted to K in the tissues. Vitamin K 3 is thought to be metabolised by conjugation with sulphate, phosphate and glucuronide. Excretion Approximately 30-40% of vitamin K is excreted, via the bile, in the faeces as partially degraded, conjugated water-soluble metabolites. Smaller quantities (approximately 15%) are excreted in the urine as water-soluble metabolites. 156
4 Expert Group on Vitamins and Minerals 003 Toxicity Human data There are relatively few reports of human toxicity following ingestion. High doses of water-soluble vitamin K 3 (menadione) may result in oxidative damage, red cell fragility and the formation of methaemoglobin. High doses of vitamin K 3 given to premature infants to treat intracranial and pulmonary haemorrhage have been reported to have caused hyperbilirubinaemia and overloading of the immature liver, resulting in kernicterus and brain toxicity. Fewer cases have been reported recently as a safer level has been established. Local hypersensitivity reactions to dermal injections of vitamin K (mostly of the K 1 form) have been reported. They are thought to be delayed-type hypersensitivity reactions. Animal data Acute doses of vitamin K 1 (phylloquinone) up to 5,000 mg/kg bw caused no fatalities in rats, mice or chicks. In contrast, oral vitamin K 3 (menadione) administration to rats, chicks and mice resulted in anaemia and death. Parenteral administration of high doses of K 3 to dogs caused methaemoglobinaemia, urobilinuria and urobilinogenuria, and fatal liver damage. No data on reproductive toxicity have been identified. Carcinogenicity and genotoxicity No data on carcinogenicity have been identified. was negative in the Ames bacterial mutagenicity test, but there are conflicting reports of its ability to cause sister chromatid exchange in human and animal leukocytes. Mechanisms of toxicity Menadione causes oxidative damage and lipid peroxidation. Dose response characterisation No data have been identified. 157
5 Part Fat Soluble Vitamins Vulnerable groups Individuals with glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase deficiency are more susceptible to the development of methaemoglobinaemia, and this would include oxidative damage caused by menadione (vitamin K 3 ). Infants are vulnerable to vitamin K 3 toxicity. An initial suggestion that intramuscular administration of vitamin K was associated with childhood cancer has not been supported in further studies. Genetic variations No data have been identified. Studies of particular importance in the risk assessment (For full review see or the enclosed CD). Human data Israels et al., 1987 Sister chromatid exchange (SCE) was measured in human leukocytes taken from adult and placental blood. In the presence of 1 M vitamin K 1, the mean number of SCEs per metaphase increased significantly from in placental blood to and from to in adult blood. Co-incubation with vitamin K 1 did not affect the number of SCEs caused by benzpyrene or mitomycin C. Cornelissen et al., 1991 The numbers of SCEs were measured in the peripheral blood lymphocytes of six newborn babies 4 hrs after intra-muscular injection with 1 mg vitamin K 1 (as the drug Konakion) and in six control neonates. The mean number of SCEs per metaphase was in the vitamin K 1 group compared to in the controls. The mean number of chromosome aberrations per 100 mitoses was in the vitamin K group compared to in the controls. Plasma vitamin K 1 concentration ranged from to.55 M. The authors concluded that there was no evidence that vitamin K 1 treatment caused genotoxicity. However, it is possible that taking the sample 4 hours after treatment may have been too early to detect SCEs. Craciun et al., 1998 Eight elite female athletes were given 10 mg/day vitamin K 1 for one month and markers of bone health were assessed before and after treatment. Four of the eight athletes had been amenorrhoeic for more than 1 year whilst the others had been taking oral contraceptives. The athletes dietary vitamin K intake was stated to be in excess of the mg/kg bw/day RDA value. At baseline, the amenorrhoeic group was biochemically vitamin K deficient as assessed by the calcium binding activity of circulating osteocalcin. In all subjects, supplementation was associated with an increase in the calcium binding capacity of osteocalcin, indicating correction of a deficiency. In the amenorrhoeic group 158
6 Expert Group on Vitamins and Minerals 003 supplementation was associated with a 15-0 % increase in bone formation markers and a 0-5% decrease in bone resorption markers. No adverse effects were noted at 10 mg/day. Booth et al., 1999 In a trial in a metabolic unit using a 3 x 15 day crossover design, both younger and older male and female subjects were fed a mixed diet containing 0.10 mg vitamin K 1 per day. During two of the 15-day residency periods, the diet was supplemented with either broccoli (0.377 mg total K 1 per day) or K 1 fortified oil (0.417 mg total K 1 per day). No adverse effects were noted at mg total K 1 per day. Animal data Molitor and Robinson, 1940 Toxicity studies were conducted in mice, chicks and rats. in single oral doses up to 5,000 mg/kg bw, produced no fatalities in mice, whereas vitamin K 3 was highly toxic. Intraperitoneal studies showed that doses of 00 mg/kg bw of vitamin K 3 caused 100% mortality in mice but intraperitoneal doses of vitamin K 1 as high as 5,000 mg/kg bw failed to cause death. In sub-chronic studies in rats, daily feeding over a 30 day period of 500 mg/kg bw of vitamin K 3 was fatal and smaller doses resulted in pronounced anaemia. Daily doses as high as 000 mg/kg bw vitamin K 1 produced no ill effects. Israels et al., 1987 Five foetal sheep were given a 1 mg dose of vitamin K 1 into the femoral vein via a catheter. The mean number of SCEs per metaphase increased from at 15 minutes pre-injection to at 4 hours post-injection. Before treatment the level of vitamin K 1 was not detectable, but increased to 0.3 M after treatment. The increase in SCE was low but was stated to be statistically significant. No positive controls were used and it is difficult to assess the biological importance of the result. The in vitro dose response curve for SCE induction was investigated in both foetal and adult sheep leukocytes incubated with vitamin K 1. The doses tested ranged from 0.1 nm to 1 M. At 0.1 nm the number of SCEs in the adult cells (from the dam) were not significantly different from the solvent control. However, the number of SCEs in the foetal cells was significantly increased compared to the controls. The increase in SCEs in the adult cells became significant at 10 nm. The actual numbers of SCEs at different dose levels were not given but the figure indicates that SCEs in adults increased from approximately 6 to 9 per metaphase and in the foetus from 4.3 to 7.5 per metaphase. Edenharder et al., 1999 Vitamins K 1, K 3,K 4 and 1,4 naphthoquinone caused a concentration-related reduction in the mutagenicity of six heterocyclic amines in the Ames Salmonella assay. The mechanism for the anti-mutagenic effect was related to reduced activities of 7-ethoxyresorufin-O-deethylase (EROD) and 7-methoxyresorufin-Odemethylase (MROD), markers for cytochrome P450 1A1 and 1A activity. In further enzyme kinetic experiments, vitamins K 3 and K 4 behaved as competitive inhibitors of -amino-3-methyl-imidazo[4,5-f] quinoline induced mutagenesis. The mechanism of the anti-mutagenic effect of vitamin K 1 was not investigated. 159
7 Part Fat Soluble Vitamins Exposure assessment Total Exposure/intake: Food Mean: mg/day (based on National Food Survey 000, DEFRA, 001). Data for 97.5th percentile not available. Supplements up to 0.0 mg/day (Annex 4; OTC, 001) Estimated maximum intake: = 0.7 mg/day No potential high intake groups have been identified. Risk assessment The data are sparse but the different forms of vitamin K are associated with different adverse effects. There are relatively few reports of human toxicity for vitamin K 1 (phylloquinone) and it is stated to be well tolerated in animal studies. Although there are some reports of genotoxicity in vitro and in vivo, no effect was found in cells taken from babies given prophylactic intramuscular vitamin K 1. The significance of the positive genotoxicity findings is uncertain. High doses of vitamin K 3 (menadione) may result in oxidative damage, red cell fragility and the formation of methaemoglobin. Hyperbilirubinaemia, resulting in kernicterus and toxicity to the neonatal brain occurred in premature infants given high doses of vitamin K 3. Local hypersensitivity reactions to injections have been reported. In animal studies, vitamin K 3 administration has resulted in anaemia, haemoglobinaemia, urobilinuria and urobilinogenuria. High doses have also been reported to cause liver damage. Vitamin K 3 has demonstrated some mutagenic activity in the Ames test, possibly as a result of the structure of the side chain. Few data are available relating to vitamins K and K 4. ESTABLISHMENT OF GUIDANCE LEVEL There are insufficient data from studies in humans or animals to establish a Safe Upper Level for vitamin K. There are clear differences in the toxicity of different forms of vitamin K. (phylloquinone) the form occurring naturally in food is not associated with adverse effects at high doses in animal studies. Acute doses up to 5,000 mg/kg bw did not cause fatalities in rats, mice or chicks. Human supplementation studies in small numbers of subjects suggest that, although having biological activity, doses of up to 10 mg/day for 1 month are not associated with adverse effects. Applying an uncertainty factor of 10 for inter-individual variation because of the very limited human database, indicates that for guidance purposes, a daily supplementary intake of 1 mg/day would be 160
8 Expert Group on Vitamins and Minerals 003 unlikely to result in adverse effects. This is equivalent to mg/kg bw in a 60 kg adult. There are insufficient data available to provide guidance on total intakes. The water soluble forms of vitamin K, particularly K 3 (menadione) are more active and can be toxic at high doses in both humans and animals. Use of menadione in food supplements is therefore undesirable. References Booth, S. L., O Brien-Morse, M.E., Dallal, G.E., Davidson, K.W. and Gundberg, C.M. (1999). Response of vitamin K status to different intakes and sources of phylloquinone-rich foods: comparison of younger and older adults. American Journal of Clinical Nutrition 70, COMA (1991). Dietary Reference Values for Food Energy and Nutrients for the United Kingdom. Report of the Panel on Dietary Reference Values, Committee on Medical Aspects of Food and Nutrition Policy. HMSO, London. Cornelissen, M., Smeets, D., Merkx, G. De Abreu. R, Kollee, L and Monnens, M. (1991). Analysis of chromosome aberrations and sister chromatid exchange in peripheral blood lymphocytes of newborns after vitamin K prophylaxis at birth. Pediatric Research 30, Craciun, A. M., Wolff, J, Knapen M.H.J., Brouns, F. and Vermeer, C. (1998). Improved bone metabolism in female elite athletes after vitamin K supplementation. International Journal of Sports Medicine 19, Edenharder, R, Worf-Wandelburg A, Decker, M. and Platt, KL. (1999). Antimutagenic effects and possible mechanisms of action of vitamins and regulated compounds against genotoxic heterocyclic amines from cooked food. Mutation Research 444, Israels, L. G., Friesen, E., Jansen, A.H. and Israels, E.D. (1987) increases sister chromatid exchange in vitro in human leukocytes and in vivo in fetal sheep cells: A possible role for vitamin K deficiency in the fetus. Pediatric Research, Molitor, H. and Robinson, H.J. (1940) Oral and parenteral toxicity of vitamin K 1, phthicol and -methyl-1,4- naphthoquinone. Proceedings of the Society for Experimental Biology and Medicine 43,
Vitamin K. Amina Ziyad Elaf Sohaib
 Vitamin K Amina Ziyad Elaf Sohaib What is Vitamin K? Fat soluble compound Necessary for the synthesis of several proteins required for blood clotting 1) Vit K 1 (Phylloquinone) - natural form - found in
Vitamin K Amina Ziyad Elaf Sohaib What is Vitamin K? Fat soluble compound Necessary for the synthesis of several proteins required for blood clotting 1) Vit K 1 (Phylloquinone) - natural form - found in
Sultan Qaboos University. College of Agricultural & Marine Sciences. Vitamin K. Lecture Summary
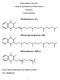 Sultan Qaboos University College of Agricultural & Marine Sciences Vitamin K Lecture Summary Name: Mohsin Mohammed Taqi Mohsin Al-Saleh ID #: M020944-99 0 Introduction: Vitamin K is a group of structurally
Sultan Qaboos University College of Agricultural & Marine Sciences Vitamin K Lecture Summary Name: Mohsin Mohammed Taqi Mohsin Al-Saleh ID #: M020944-99 0 Introduction: Vitamin K is a group of structurally
Biochemistry of Vitamin K
 Lecture 4 Biochemistry of Vitamin K The Objectives Types and chemistry of vitamin K Sources and daily requirements Functions Synthesis of γ-carboxyglutamate in: Prothrombin and blood clotting factors Osteocalcin
Lecture 4 Biochemistry of Vitamin K The Objectives Types and chemistry of vitamin K Sources and daily requirements Functions Synthesis of γ-carboxyglutamate in: Prothrombin and blood clotting factors Osteocalcin
D. Vitamin K -- Group of naphthoquinones having antihemorrhagic activity.
 D. Vitamin K -- Group of naphthoquinones having antihemorrhagic activity. 1. Structures VITAMIN K1; Phytonadione; 2-Methyl-3-phytyl-1,4-naphthoquinone VITAMIN K2; Menaquinone-6 and 7; N=6,7 n 2. Function
D. Vitamin K -- Group of naphthoquinones having antihemorrhagic activity. 1. Structures VITAMIN K1; Phytonadione; 2-Methyl-3-phytyl-1,4-naphthoquinone VITAMIN K2; Menaquinone-6 and 7; N=6,7 n 2. Function
Vitamin K in Cystic Fibrosis
 Vitamin K in Cystic Fibrosis Martin J. Shearer PhD, MRCPath Consultant Clinical Scientist Honorary Senior Lecturer Centre for Haemostasis and Thrombosis, Guy s and St. Thomas Foundation Trust London, UK
Vitamin K in Cystic Fibrosis Martin J. Shearer PhD, MRCPath Consultant Clinical Scientist Honorary Senior Lecturer Centre for Haemostasis and Thrombosis, Guy s and St. Thomas Foundation Trust London, UK
Vitamins. Nafith Abu Tarboush, DDS, MSc, PhD
 Vitamins Nafith Abu Tarboush, DDS, MSc, PhD natarboush@ju.edu.jo www.facebook.com/natarboush Vitamins Organic compounds required by an organism in tiny amounts as a vital nutrient Cannot be synthesized
Vitamins Nafith Abu Tarboush, DDS, MSc, PhD natarboush@ju.edu.jo www.facebook.com/natarboush Vitamins Organic compounds required by an organism in tiny amounts as a vital nutrient Cannot be synthesized
NEW MK-7 SELECT INTRODUCTION
 NEW MK-7 SELECT INTRODUCTION As we have all known for several years now, the presence of optimal amounts of vitamin D is essential for maintaining optimal bone health and bone calcification, as noted by
NEW MK-7 SELECT INTRODUCTION As we have all known for several years now, the presence of optimal amounts of vitamin D is essential for maintaining optimal bone health and bone calcification, as noted by
Konakion MM. Phytomenadione Composition. Properties and effects. Pharmacokinetics
 פורמט עלון זה נקבע ע"י משרד הבריאות ותוכנו נבדק ואושר על ידו בנובמבר 2015 Konakion MM Phytomenadione Composition Active ingredient: phytomenadione (synthetic vitamin K 1 ). Ampoules MM 10 mg/ml in a bile
פורמט עלון זה נקבע ע"י משרד הבריאות ותוכנו נבדק ואושר על ידו בנובמבר 2015 Konakion MM Phytomenadione Composition Active ingredient: phytomenadione (synthetic vitamin K 1 ). Ampoules MM 10 mg/ml in a bile
Classes of Nutrients A Diet
 Ch. 7 Notes Section 1: What is Nutrition? is the science or study of food and the ways the body uses food. are substances in food that provide energy or help form body tissues and are necessary for life
Ch. 7 Notes Section 1: What is Nutrition? is the science or study of food and the ways the body uses food. are substances in food that provide energy or help form body tissues and are necessary for life
Nutrition and Energy 1
 Nutrition and Energy 1 Food Energy The ingestion of food serves two primary functions: 1. it provides a source of energy 2. it provides raw materials the animal is unable to manufacture for itself. 2 Basal
Nutrition and Energy 1 Food Energy The ingestion of food serves two primary functions: 1. it provides a source of energy 2. it provides raw materials the animal is unable to manufacture for itself. 2 Basal
Lecture Notes 2: Protiens
 Lecture Notes 2: Protiens BY/ARSHED ABD ALI SHIHAD Proteins and Amino Acids What Are Proteins? Large molecules Made up of chains of amino acids Are found in every cell in the body Are involved in most
Lecture Notes 2: Protiens BY/ARSHED ABD ALI SHIHAD Proteins and Amino Acids What Are Proteins? Large molecules Made up of chains of amino acids Are found in every cell in the body Are involved in most
Objectives: by reading this topic; the student would be able to:
 Objectives: by reading this topic; the student would be able to: 1. Describe the structure, dietary sources, and metabolism of fat soluble vitamins. 2. Identify the biochemical role of fat soluble vitamins.
Objectives: by reading this topic; the student would be able to: 1. Describe the structure, dietary sources, and metabolism of fat soluble vitamins. 2. Identify the biochemical role of fat soluble vitamins.
number Done by Corrected by Doctor Nafeth
 number 38 Done by Omar Odeh Corrected by Doctor Nafeth 1 Micronutrients: Vitamins Chapter 28 lipp. In the end of this course, we will talk about fat soluble vitamins. We took water soluble vitamins last
number 38 Done by Omar Odeh Corrected by Doctor Nafeth 1 Micronutrients: Vitamins Chapter 28 lipp. In the end of this course, we will talk about fat soluble vitamins. We took water soluble vitamins last
5.17 PENTHIOPYRAD (253)
 Penthiopyrad 189 5.17 PENTHIOPYRAD (253) TOXICOLOGY Penthiopyrad is the International Organization for Standardization (ISO) approved name for N-[2- (1,3-dimethylbutyl)-3-thienyl]-1-methyl-3-(trifluoromethyl)-1H-pyrazole-4-carboxamide
Penthiopyrad 189 5.17 PENTHIOPYRAD (253) TOXICOLOGY Penthiopyrad is the International Organization for Standardization (ISO) approved name for N-[2- (1,3-dimethylbutyl)-3-thienyl]-1-methyl-3-(trifluoromethyl)-1H-pyrazole-4-carboxamide
COMMITTEE FOR MEDICINAL PRODUCTS FOR VETERINARY USE
 European Medicines Agency Veterinary Medicines and Inspections EMEA/CVMP/77290/05-FINAL March 2005 COMMITTEE FOR MEDICINAL PRODUCTS FOR VETERINARY USE FLUAZURON SUMMARY REPORT 1. Fluazuron is an insect
European Medicines Agency Veterinary Medicines and Inspections EMEA/CVMP/77290/05-FINAL March 2005 COMMITTEE FOR MEDICINAL PRODUCTS FOR VETERINARY USE FLUAZURON SUMMARY REPORT 1. Fluazuron is an insect
Dithianon DITHIANON (180)
 Dithianon 201 5.11 DITHIANON (180) TOXICOLOGY Dithianon (C 14 H 4 N 2 O 2 S 2 ) is the International Organization for Standardization (ISO) approved name for 5,10-dihydro-5,10-dioxonaphtho[2,3-b]-1,4-dithiine-2,3-dicarbonitrile
Dithianon 201 5.11 DITHIANON (180) TOXICOLOGY Dithianon (C 14 H 4 N 2 O 2 S 2 ) is the International Organization for Standardization (ISO) approved name for 5,10-dihydro-5,10-dioxonaphtho[2,3-b]-1,4-dithiine-2,3-dicarbonitrile
LABORATORY REPORT SAMPLE. Summary of Deficient Test Results. Vitamin B12 Pantothenate Biotin Spectrox Immunidex
 LABORATORY REPORT Account Number: Name: Jon Doe Gender: Male DOB: 12/28/1984 Requisition Number: Summary of Deficient Test Results Testing determined the following functional deficiencies: Oleic Acid Borderline
LABORATORY REPORT Account Number: Name: Jon Doe Gender: Male DOB: 12/28/1984 Requisition Number: Summary of Deficient Test Results Testing determined the following functional deficiencies: Oleic Acid Borderline
VITAMINS-FAT SOLUBLE [LIPPINCOTT S ] Deeba S. Jairajpuri
![VITAMINS-FAT SOLUBLE [LIPPINCOTT S ] Deeba S. Jairajpuri VITAMINS-FAT SOLUBLE [LIPPINCOTT S ] Deeba S. Jairajpuri](/thumbs/88/115610056.jpg) VITAMINS-FAT SOLUBLE [LIPPINCOTT S 381-394] Deeba S. Jairajpuri VITAMIN A othe term retinoids includes both natural and synthetic forms of vitamin A essential for vision, reproduction, growth and maintenance
VITAMINS-FAT SOLUBLE [LIPPINCOTT S 381-394] Deeba S. Jairajpuri VITAMIN A othe term retinoids includes both natural and synthetic forms of vitamin A essential for vision, reproduction, growth and maintenance
SOME ASPECTS OF INFANT FEEDING. Quak Seng Hock
 SOME ASPECTS OF INFANT FEEDING Quak Seng Hock Contents Introduction Importance of proper nutrition in the infant Breastfeeding Nutritional requirements of infants Introducing solid food Vitamin requirements
SOME ASPECTS OF INFANT FEEDING Quak Seng Hock Contents Introduction Importance of proper nutrition in the infant Breastfeeding Nutritional requirements of infants Introducing solid food Vitamin requirements
Personal Practice. Vitamin K During Infancy: Current Status and Recommendations
 Personal Practice Vitamin K During Infancy: Current Status and Recommendations Meharban Singh Vitamin K is usually the first vitamin given at birth. Dietary deficiency of vitamin K in healthy subjects
Personal Practice Vitamin K During Infancy: Current Status and Recommendations Meharban Singh Vitamin K is usually the first vitamin given at birth. Dietary deficiency of vitamin K in healthy subjects
COMMITTEE FOR VETERINARY MEDICINAL PRODUCTS
 The European Agency for the Evaluation of Medicinal Products Veterinary Medicines and Inspections EMEA/MRL/451/98-FINAL June 1998 COMMITTEE FOR VETERINARY MEDICINAL PRODUCTS BACITRACIN SUMMARY REPORT (1)
The European Agency for the Evaluation of Medicinal Products Veterinary Medicines and Inspections EMEA/MRL/451/98-FINAL June 1998 COMMITTEE FOR VETERINARY MEDICINAL PRODUCTS BACITRACIN SUMMARY REPORT (1)
PACKAGE LEAFLET: Information for the patient VITAMINE E Sugar coated tablets 10 mg (Alpha tocopherol acetate)
 PACKAGE LEAFLET: Information for the patient VITAMINE E Sugar coated tablets 10 mg (Alpha tocopherol acetate) Read all of this leaflet carefully before you start taking this medicine. - Keep this leaflet.
PACKAGE LEAFLET: Information for the patient VITAMINE E Sugar coated tablets 10 mg (Alpha tocopherol acetate) Read all of this leaflet carefully before you start taking this medicine. - Keep this leaflet.
Vitamin K. Emily Rohan Sarah Steinmetz
 Vitamin K Emily Rohan Sarah Steinmetz How much do we need? Adequate Intake (AI) Life Stage Group Adequate Intake Level 0-6 months 2.0 ug/day 7-12 months 2.5 ug/day 1-3 years 30 ug/day 4-8 years 55 ug/day
Vitamin K Emily Rohan Sarah Steinmetz How much do we need? Adequate Intake (AI) Life Stage Group Adequate Intake Level 0-6 months 2.0 ug/day 7-12 months 2.5 ug/day 1-3 years 30 ug/day 4-8 years 55 ug/day
OPINION OF THE SCIENTIFIC COMMITTEE ON FOOD ON THE TOLERABLE UPPER INTAKE LEVEL OF VITAMIN K
 FOREWORD OPINION OF THE SCIENTIFIC COMMITTEE ON FOOD ON THE TOLERABLE UPPER INTAKE LEVEL OF VITAMIN K (EXPRESSED ON 4 APRIL 2003) This opinion is one in the series of opinions of the Scientific Committee
FOREWORD OPINION OF THE SCIENTIFIC COMMITTEE ON FOOD ON THE TOLERABLE UPPER INTAKE LEVEL OF VITAMIN K (EXPRESSED ON 4 APRIL 2003) This opinion is one in the series of opinions of the Scientific Committee
OVERVIEW OF DIETARY PROTEINS AND NITROGEN BALANCE
 OVERVIEW OF DIETARY PROTEINS AND NITROGEN BALANCE Proteins and Amino Acids What Are Proteins? Large molecules Made up of chains of amino acids Are found in every cell in the body Are involved in most of
OVERVIEW OF DIETARY PROTEINS AND NITROGEN BALANCE Proteins and Amino Acids What Are Proteins? Large molecules Made up of chains of amino acids Are found in every cell in the body Are involved in most of
COMMITTEE FOR VETERINARY MEDICINAL PRODUCTS
 The European Agency for the Evaluation of Medicinal Products Veterinary Medicines and Inspections EMEA/MRL/016/95-FINAL COMMITTEE FOR VETERINARY MEDICINAL PRODUCTS COLISTIN SUMMARY REPORT (1) 1. Colistin
The European Agency for the Evaluation of Medicinal Products Veterinary Medicines and Inspections EMEA/MRL/016/95-FINAL COMMITTEE FOR VETERINARY MEDICINAL PRODUCTS COLISTIN SUMMARY REPORT (1) 1. Colistin
What is Dietary Fibre?
 Fibre What is Dietary Fibre? Non digestible part of plant foods Consists of one or more of edible CHO polymers and synthetic CHO polymers Types of Dietary Fiber There are many different types of fiber,
Fibre What is Dietary Fibre? Non digestible part of plant foods Consists of one or more of edible CHO polymers and synthetic CHO polymers Types of Dietary Fiber There are many different types of fiber,
COMMITTEE FOR MEDICINAL PRODUCTS FOR VETERINARY USE
 European Medicines Agency Veterinary Medicines and Inspections EMEA/MRL/904/04-FINAL June 2004 COMMITTEE FOR MEDICINAL PRODUCTS FOR VETERINARY USE ALTRENOGEST SUMMARY REPORT (3) 1. Altrenogest (or allyltrenbolone)
European Medicines Agency Veterinary Medicines and Inspections EMEA/MRL/904/04-FINAL June 2004 COMMITTEE FOR MEDICINAL PRODUCTS FOR VETERINARY USE ALTRENOGEST SUMMARY REPORT (3) 1. Altrenogest (or allyltrenbolone)
AquaMEPHYTON (PHYTONADIONE) Aqueous Colloidal Solution of Vitamin K 1
 9073025 INJECTION AquaMEPHYTON (PHYTONADIONE) Aqueous Colloidal Solution of Vitamin K 1 WARNING - INTRAVENOUS AND INTRAMUSCULAR USE Severe reactions, including fatalities, have occurred during and immediately
9073025 INJECTION AquaMEPHYTON (PHYTONADIONE) Aqueous Colloidal Solution of Vitamin K 1 WARNING - INTRAVENOUS AND INTRAMUSCULAR USE Severe reactions, including fatalities, have occurred during and immediately
Module Two: Detoxification Systems
 Module Two: Detoxification Systems Liana Shanti, CN www.healthmasteryinstitute.com Module 1 Who should detox and why What we are detoxing from Module 2 Now we look at the systems in the body that are responsible
Module Two: Detoxification Systems Liana Shanti, CN www.healthmasteryinstitute.com Module 1 Who should detox and why What we are detoxing from Module 2 Now we look at the systems in the body that are responsible
1. Which nutrient is so vital to health that you wouldn't live more than a few days without it? A) vitamins B) water C) minerals D) protein
 Nutrition & You, 4e (Blake) Chapter 1 What Is Nutrition? Legend: For sentences / statements that DO NOT HAVE answer choices, Answer A if TRUE Answer B IF False 1. Which nutrient is so vital to health that
Nutrition & You, 4e (Blake) Chapter 1 What Is Nutrition? Legend: For sentences / statements that DO NOT HAVE answer choices, Answer A if TRUE Answer B IF False 1. Which nutrient is so vital to health that
COMMITTEE FOR VETERINARY MEDICINAL PRODUCTS
 The European Agency for the Evaluation of Medicinal Products Veterinary Medicines Evaluation Unit EMEA/MRL/114/96-FINAL June 1996 COMMITTEE FOR VETERINARY MEDICINAL PRODUCTS EPRINOMECTIN SUMMARY REPORT
The European Agency for the Evaluation of Medicinal Products Veterinary Medicines Evaluation Unit EMEA/MRL/114/96-FINAL June 1996 COMMITTEE FOR VETERINARY MEDICINAL PRODUCTS EPRINOMECTIN SUMMARY REPORT
COMMITTEE FOR VETERINARY MEDICINAL PRODUCTS
 The European Agency for the Evaluation of Medicinal Products Veterinary Medicines Evaluation Unit EMEA/MRL/488/98-FINAL July 1998 COMMITTEE FOR VETERINARY MEDICINAL PRODUCTS DIETHYLENE GLYCOL MONOETHYL
The European Agency for the Evaluation of Medicinal Products Veterinary Medicines Evaluation Unit EMEA/MRL/488/98-FINAL July 1998 COMMITTEE FOR VETERINARY MEDICINAL PRODUCTS DIETHYLENE GLYCOL MONOETHYL
Vitamin K (Phylloquinone)
 Vitamin K (Phylloquinone) What is Vitamin K? Vitamin K is a fat-soluble vitamin which plays a key role in blood coagulation. Its name comes from the German name, Koagulationsvitamin. There are three forms,
Vitamin K (Phylloquinone) What is Vitamin K? Vitamin K is a fat-soluble vitamin which plays a key role in blood coagulation. Its name comes from the German name, Koagulationsvitamin. There are three forms,
Vitamin K & Antioxidants. NUT1602 E-Tutor 2018
 Vitamin K & Antioxidants NUT1602 E-Tutor 2018 Vitamin K O Can be obtained from non-food source O Bacteria in the GI tract O Acts primarily in blood clotting O Prothrombin O Metabolism of bone proteins
Vitamin K & Antioxidants NUT1602 E-Tutor 2018 Vitamin K O Can be obtained from non-food source O Bacteria in the GI tract O Acts primarily in blood clotting O Prothrombin O Metabolism of bone proteins
Biacid: A EU approved natural growth promoter for Broilers
 Biacid is a blend of calcium salts of organic acids and essential oils. Through the optimal combination of calcium salts of organic acids and essential oils, it enhances broiler microflora within the gut
Biacid is a blend of calcium salts of organic acids and essential oils. Through the optimal combination of calcium salts of organic acids and essential oils, it enhances broiler microflora within the gut
Six Nutrients. Nutrients: substances in food that your body needs to stay healthy. Carbohydrates Protein Fat Minerals Vitamins Water
 Nutrients Six Nutrients Nutrients: substances in food that your body needs to stay healthy Carbohydrates Protein Fat Minerals Vitamins Water Water Function: most essential nutrient Helps digest and absorb
Nutrients Six Nutrients Nutrients: substances in food that your body needs to stay healthy Carbohydrates Protein Fat Minerals Vitamins Water Water Function: most essential nutrient Helps digest and absorb
CIE Biology GCSE 7: Human nutrition
 CIE Biology GCSE 7: Human nutrition Notes Humans need many different nutrients to survive. To receive these nutrients in the correct quantities, a balanced diet must be eaten. A balanced diet includes
CIE Biology GCSE 7: Human nutrition Notes Humans need many different nutrients to survive. To receive these nutrients in the correct quantities, a balanced diet must be eaten. A balanced diet includes
Opinion of the Scientific Committee on Food on the Tolerable Upper Intake Level of Vitamin K
 EUROPEAN COMMISSION HEALTH & CONSUMER PROTECTION DIRECTORATE-GENERAL Directorate C - Scientific Opinions C2 - Management of scientific committees; scientific co-operation and networks Scientific Committee
EUROPEAN COMMISSION HEALTH & CONSUMER PROTECTION DIRECTORATE-GENERAL Directorate C - Scientific Opinions C2 - Management of scientific committees; scientific co-operation and networks Scientific Committee
Compounds with vitamin K activity all have a common. Vitamin K in Parenteral Nutrition. Metabolic Function
 GASTROENTEROLOGY 2009;137:S105 S118 Vitamin K in Parenteral Nutrition MARTIN J. SHEARER Centre for Haemostasis and Thrombosis, St Thomas Hospital, London, United Kingdom Vitamin K (as phylloquinone and
GASTROENTEROLOGY 2009;137:S105 S118 Vitamin K in Parenteral Nutrition MARTIN J. SHEARER Centre for Haemostasis and Thrombosis, St Thomas Hospital, London, United Kingdom Vitamin K (as phylloquinone and
Vitamin K2: Are You Consuming Enough? March 22, 2017 by Chris Kresser Abridged by Dr. Michael Schwarz
 Vitamin K2: Are You Consuming Enough? March 22, 2017 by Chris Kresser Abridged by Dr. Michael Schwarz Did you know that vitamin K1 and vitamin K2 are different types of vitamin K? Before 2006, the USDA
Vitamin K2: Are You Consuming Enough? March 22, 2017 by Chris Kresser Abridged by Dr. Michael Schwarz Did you know that vitamin K1 and vitamin K2 are different types of vitamin K? Before 2006, the USDA
Cell Organization, Nutrition, Digestion, and Excretion
 Cell Organization, Nutrition, Digestion, and Excretion Cell Organization: 1. Put these terms in order from least complex to most complex: Tissue, cell, organ, organelle, organism, organ system 1. Organelle
Cell Organization, Nutrition, Digestion, and Excretion Cell Organization: 1. Put these terms in order from least complex to most complex: Tissue, cell, organ, organelle, organism, organ system 1. Organelle
Vitamin K. Emily Rohan Sarah Steinmetz
 Vitamin K Emily Rohan Sarah Steinmetz How much do we need? Adequate Intake (AI) Institute of Medicine. Dietary reference intakes for vitamin A, vitamin K, arsenic, boron, chromium, copper, iodine, iron,
Vitamin K Emily Rohan Sarah Steinmetz How much do we need? Adequate Intake (AI) Institute of Medicine. Dietary reference intakes for vitamin A, vitamin K, arsenic, boron, chromium, copper, iodine, iron,
Short Bowel Syndrome: Medical management
 Short Bowel Syndrome: Medical management La Sindrome dell'intestino Corto in età pediatrica Brescia 18 marzo 2011 Jon A.Vanderhoof, M.D. Division of Pediatric GI Harvard Medical School Children s Hospital,
Short Bowel Syndrome: Medical management La Sindrome dell'intestino Corto in età pediatrica Brescia 18 marzo 2011 Jon A.Vanderhoof, M.D. Division of Pediatric GI Harvard Medical School Children s Hospital,
EU RISK MANAGEMENT PLAN (EU RMP) Nutriflex Omega peri emulsion for infusion , version 1.1
 EU RISK MANAGEMENT PLAN (EU RMP) Nutriflex Omega peri emulsion for infusion 13.7.2015, version 1.1 III.1. Elements for a Public Summary III.1.1. Overview of disease epidemiology Patients may need parenteral
EU RISK MANAGEMENT PLAN (EU RMP) Nutriflex Omega peri emulsion for infusion 13.7.2015, version 1.1 III.1. Elements for a Public Summary III.1.1. Overview of disease epidemiology Patients may need parenteral
COMMITTEE FOR VETERINARY MEDICINAL PRODUCTS
 The European Agency for the Evaluation of Medicinal Products Veterinary Medicines Evaluation Unit EMEA/MRL/0128/96-FINAL July 1996 COMMITTEE FOR VETERINARY MEDICINAL PRODUCTS CEFAPIRIN SUMMARY REPORT (1)
The European Agency for the Evaluation of Medicinal Products Veterinary Medicines Evaluation Unit EMEA/MRL/0128/96-FINAL July 1996 COMMITTEE FOR VETERINARY MEDICINAL PRODUCTS CEFAPIRIN SUMMARY REPORT (1)
COMMITTEE FOR VETERINARY MEDICINAL PRODUCTS
 The European Agency for the Evaluation of Medicinal Products Veterinary Medicines Evaluation Unit EMEA/MRL/527/98-FINAL January 1999 COMMITTEE FOR VETERINARY MEDICINAL PRODUCTS AZAMETHIPHOS SUMMARY REPORT
The European Agency for the Evaluation of Medicinal Products Veterinary Medicines Evaluation Unit EMEA/MRL/527/98-FINAL January 1999 COMMITTEE FOR VETERINARY MEDICINAL PRODUCTS AZAMETHIPHOS SUMMARY REPORT
30.1 Organization of the Human Body
 30.1 Organization of the Human Body Organization of the Body The levels of organization in the body include cells, tissues, organs, and organ systems. At each level of organization, these parts of the
30.1 Organization of the Human Body Organization of the Body The levels of organization in the body include cells, tissues, organs, and organ systems. At each level of organization, these parts of the
VITAMIN B6 History B
 VITAMIN B 6 History Gyorgy demonstrated a characteristic type of dermatitis in rats produced by a factor different from known vitamins 1937 : He showed that the factor was present in yeast & liver and
VITAMIN B 6 History Gyorgy demonstrated a characteristic type of dermatitis in rats produced by a factor different from known vitamins 1937 : He showed that the factor was present in yeast & liver and
COMMITTEE FOR VETERINARY MEDICINAL PRODUCTS
 The European Agency for the Evaluation of Medicinal Products Veterinary Medicines and Information Technology Unit EMEA/MRL/050/95-FINAL February 1996 COMMITTEE FOR VETERINARY MEDICINAL PRODUCTS AMINOSIDINE
The European Agency for the Evaluation of Medicinal Products Veterinary Medicines and Information Technology Unit EMEA/MRL/050/95-FINAL February 1996 COMMITTEE FOR VETERINARY MEDICINAL PRODUCTS AMINOSIDINE
Digestion and Absorption
 Digestion and Absorption Digestion and Absorption Digestion is a process essential for the conversion of food into a small and simple form. Mechanical digestion by mastication and swallowing Chemical digestion
Digestion and Absorption Digestion and Absorption Digestion is a process essential for the conversion of food into a small and simple form. Mechanical digestion by mastication and swallowing Chemical digestion
Contemporary Nutrition
 Contemporary Nutrition Chapter 6 Proteins Overview of Protein Body is made up of thousands of substances that are made of proteins Each protein has own unique structure and function More than 300 different
Contemporary Nutrition Chapter 6 Proteins Overview of Protein Body is made up of thousands of substances that are made of proteins Each protein has own unique structure and function More than 300 different
VITAMIN K 1 INJECTION Phytonadione Injectable Emulsion, USP Aqueous Dispersion of Vitamin K 1
 VITAMIN K 1 INJECTION Phytonadione Injectable Emulsion, USP Aqueous Dispersion of Vitamin K 1 Ampul Rx only Protect from light. Keep ampuls in tray until time of use. WARNING INTRAVENOUS AND INTRAMUSCULAR
VITAMIN K 1 INJECTION Phytonadione Injectable Emulsion, USP Aqueous Dispersion of Vitamin K 1 Ampul Rx only Protect from light. Keep ampuls in tray until time of use. WARNING INTRAVENOUS AND INTRAMUSCULAR
Summary of Product Characteristics
 NAME OF THE MEDICINAL PRODUCT Summary of Product Characteristics Konakion MM Paediatric Ampoules 2 mg/ 0.2 ml oral solution or solution for injection. 2 QUALITATIVE AND QUANTITATIVE COMPOSITION Each ampoule
NAME OF THE MEDICINAL PRODUCT Summary of Product Characteristics Konakion MM Paediatric Ampoules 2 mg/ 0.2 ml oral solution or solution for injection. 2 QUALITATIVE AND QUANTITATIVE COMPOSITION Each ampoule
Vitamins. Vitamins (continued) Lipid-Soluble Vitamins (A, D, E, K) Vitamins Serve Important Roles in Function of Body
 Vitamins Drugs for Nutritional Disorders Organic substances are needed in small amounts Promote growth Maintain health Vitamins Human cells cannot produce vitamins Exception: vitamin D Vitamins or provitamins
Vitamins Drugs for Nutritional Disorders Organic substances are needed in small amounts Promote growth Maintain health Vitamins Human cells cannot produce vitamins Exception: vitamin D Vitamins or provitamins
Nutrients. Chapter 25 Nutrition, Metabolism, Temperature Regulation
 Chapter 25 Nutrition, Metabolism, Temperature Regulation 25-1 Nutrients Chemicals used by body to produce energy, provide building blocks or function in other chemical reactions Classes Carbohydrates,
Chapter 25 Nutrition, Metabolism, Temperature Regulation 25-1 Nutrients Chemicals used by body to produce energy, provide building blocks or function in other chemical reactions Classes Carbohydrates,
COMMITTEE FOR VETERINARY MEDICINAL PRODUCTS
 The European Agency for the Evaluation of Medicinal Products Veterinary Medicines Evaluation Unit EMEA/MRL/526/98-FINAL January 1999 COMMITTEE FOR VETERINARY MEDICINAL PRODUCTS APRAMYCIN SUMMARY REPORT
The European Agency for the Evaluation of Medicinal Products Veterinary Medicines Evaluation Unit EMEA/MRL/526/98-FINAL January 1999 COMMITTEE FOR VETERINARY MEDICINAL PRODUCTS APRAMYCIN SUMMARY REPORT
SCHOOL OF HEALTH SCIENCES DIVISION OF DIETETICS, NUTRITION AND BIOLOGICAL SCIENCES, PHYSIOTHERAPY, PODIATRY, RADIOGRAPHY LEVEL 2 / DIET 1
 SCHOOL OF HEALTH SCIENCES DIVISION OF DIETETICS, NUTRITION AND BIOLOGICAL SCIENCES, PHYSIOTHERAPY, PODIATRY, RADIOGRAPHY LEVEL 2 / DIET 1 D2143/ Nutrition DATE: 28/04/2014 WRITING TIME: 120 minutes TIME:
SCHOOL OF HEALTH SCIENCES DIVISION OF DIETETICS, NUTRITION AND BIOLOGICAL SCIENCES, PHYSIOTHERAPY, PODIATRY, RADIOGRAPHY LEVEL 2 / DIET 1 D2143/ Nutrition DATE: 28/04/2014 WRITING TIME: 120 minutes TIME:
MCT AND THE ROLES NUTRITION
 MCT AND THE ROLES NUTRITION Nguyen Hoang Nhut Hoa Department of Nutrition Children's Hospital 2 OBJECTIVES Structure Absorption and metabolic Effects of MCT in the treatment of certain diseases Demand
MCT AND THE ROLES NUTRITION Nguyen Hoang Nhut Hoa Department of Nutrition Children's Hospital 2 OBJECTIVES Structure Absorption and metabolic Effects of MCT in the treatment of certain diseases Demand
Metabolism Paracetamol is metabolised in the liver and excreted in the urine mainly as glucuronide and sulphate conjugates.
 FEBRAMOL Composition Febramol 150 Suppositories Each suppository contains Paracetamol 150 mg. Suppositories, Tablets & Syrup Febramol 300 Suppositories Each suppository contains Paracetamol 300 mg. Each
FEBRAMOL Composition Febramol 150 Suppositories Each suppository contains Paracetamol 150 mg. Suppositories, Tablets & Syrup Febramol 300 Suppositories Each suppository contains Paracetamol 300 mg. Each
Summary of Product Characteristics
 1 NAME OF THE MEDICINAL PRODUCT Tipol 75mg Suppositories Summary of Product Characteristics 2 QUALITATIVE AND QUANTITATIVE COMPOSITION Each suppository contains 75mg of paracetamol For a full list of excipients,
1 NAME OF THE MEDICINAL PRODUCT Tipol 75mg Suppositories Summary of Product Characteristics 2 QUALITATIVE AND QUANTITATIVE COMPOSITION Each suppository contains 75mg of paracetamol For a full list of excipients,
COMMITTEE FOR VETERINARY MEDICINAL PRODUCTS
 The European Agency for the Evaluation of Medicinal Products Veterinary Medicines and Inspections EMEA/MRL/815/02-FINAL January 2002 COMMITTEE FOR VETERINARY MEDICINAL PRODUCTS COLISTIN SUMMARY REPORT
The European Agency for the Evaluation of Medicinal Products Veterinary Medicines and Inspections EMEA/MRL/815/02-FINAL January 2002 COMMITTEE FOR VETERINARY MEDICINAL PRODUCTS COLISTIN SUMMARY REPORT
PDF created with pdffactory trial version
 General Nutrition Concepts Importance of Nutrition Health Appearance Behavior Mood Role of Nutrients in Diet Growth and development Provide energy Regulate metabolism 2 Calories in Food Carbohydrates Protein
General Nutrition Concepts Importance of Nutrition Health Appearance Behavior Mood Role of Nutrients in Diet Growth and development Provide energy Regulate metabolism 2 Calories in Food Carbohydrates Protein
EXSC- STANDARD 14. Nutrients
 SPORTS NUTRITION EXSC- STANDARD 14 Nutrients Standard 14 Gather relevant information from multiple authoritative print and digital sources related to the importance of a balanced diet in the achievement
SPORTS NUTRITION EXSC- STANDARD 14 Nutrients Standard 14 Gather relevant information from multiple authoritative print and digital sources related to the importance of a balanced diet in the achievement
Zahraa Muneer. Enas Ajarma. Saleem
 2 Zahraa Muneer Enas Ajarma Saleem Blood parameters: 1. RBCs count 2. Haematocrit 3. Haemoglobin content In new-born babies all three parameters of blood are higher than in normal adults. This happens
2 Zahraa Muneer Enas Ajarma Saleem Blood parameters: 1. RBCs count 2. Haematocrit 3. Haemoglobin content In new-born babies all three parameters of blood are higher than in normal adults. This happens
Chapter 15 Food and Digestion
 Chapter 15 Food and Digestion 15.1A Food and Energy Functions of Nutrients 1. 2. 3. 4. Calories = amt. of energy in food RDA depends on age, gender, size and activity level Types of Nutrients (includes
Chapter 15 Food and Digestion 15.1A Food and Energy Functions of Nutrients 1. 2. 3. 4. Calories = amt. of energy in food RDA depends on age, gender, size and activity level Types of Nutrients (includes
220 SUBJECT INDEX. D Diarrhea and sodium balance, 74 weanling, 161,179,208,212; see also Infection
 Subject Index Acid balance, see ph Allergy, food, see also Immunity and beikost, 143-144 and breast milk, 91,143 and formula, 89-90 Antidiuretic hormone, 66 67 Antigens, see also Immunity determinants,
Subject Index Acid balance, see ph Allergy, food, see also Immunity and beikost, 143-144 and breast milk, 91,143 and formula, 89-90 Antidiuretic hormone, 66 67 Antigens, see also Immunity determinants,
Chapter 15 Food and Digestion
 Chapter 15 Food and Digestion Activity: Use Qualitative Observations (5 senses) to describe: What happens when you see candy? How does it smell? How do you chomp it into smaller pieces or swallow candy
Chapter 15 Food and Digestion Activity: Use Qualitative Observations (5 senses) to describe: What happens when you see candy? How does it smell? How do you chomp it into smaller pieces or swallow candy
Initial Assessment. Coriander Seed Oil
 Initial Assessment Coriander Seed Oil Name of Applicant: Nestec Ltd. Contact person(s): Nigel Baldwin, Intertek Cantox Novel Food Classification: 2.1. Introduction An application for the authorisation
Initial Assessment Coriander Seed Oil Name of Applicant: Nestec Ltd. Contact person(s): Nigel Baldwin, Intertek Cantox Novel Food Classification: 2.1. Introduction An application for the authorisation
Folic Acid and vitamin B12
 Folic Acid and vitamin B12 ILOs: by the end of this lecture, you will be able to: 1. Understand that vitamins are crucial nutrients that are important to health. 2. Know that folic acid and vitamin B12
Folic Acid and vitamin B12 ILOs: by the end of this lecture, you will be able to: 1. Understand that vitamins are crucial nutrients that are important to health. 2. Know that folic acid and vitamin B12
DURATION: 3 HOURS TOTAL MARKS: 165. External Examiner: Ms C Biggs Internal Examiner: Dr K Pillay
 DURATION: 3 HOURS TOTAL MARKS: 165 External Examiner: Ms C Biggs Internal Examiner: Dr K Pillay NOTE: THIS EXAM PAPER CONSISTS OF SIX (6) PAGES PLUS A MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONNAIRE (MCQ) ANSWER BOOKLET
DURATION: 3 HOURS TOTAL MARKS: 165 External Examiner: Ms C Biggs Internal Examiner: Dr K Pillay NOTE: THIS EXAM PAPER CONSISTS OF SIX (6) PAGES PLUS A MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONNAIRE (MCQ) ANSWER BOOKLET
The Scientific Committee for Animal Nutrition is requested to give an opinion on the following questions:
 Report of the Scientific Committee for Animal Nutrition on the use of Avoparcin in feedingstuffs for dairy cattle (Opinion expressed on 29 September 1994) (Opinion reconfirmed on 24 March 1995) TERMS OF
Report of the Scientific Committee for Animal Nutrition on the use of Avoparcin in feedingstuffs for dairy cattle (Opinion expressed on 29 September 1994) (Opinion reconfirmed on 24 March 1995) TERMS OF
Chapter 1 & 2 All of the following are macronutrients except Carbohydrates Lipids Protein * Vitamins
 Chapter 1 & 2 All of the following are macronutrients except Carbohydrates Lipids Protein * Vitamins Gram per gram blank provides the most k calories Alcohol Carbohydrates * Lipids Proteins Which of the
Chapter 1 & 2 All of the following are macronutrients except Carbohydrates Lipids Protein * Vitamins Gram per gram blank provides the most k calories Alcohol Carbohydrates * Lipids Proteins Which of the
COMMITTEE FOR VETERINARY MEDICINAL PRODUCTS
 The European Agency for the Evaluation of Medicinal Products Veterinary Medicines and Information Technology EMEA/MRL/754/00-FINAL July 2000 COMMITTEE FOR VETERINARY MEDICINAL PRODUCTS CEFACETRILE SUMMARY
The European Agency for the Evaluation of Medicinal Products Veterinary Medicines and Information Technology EMEA/MRL/754/00-FINAL July 2000 COMMITTEE FOR VETERINARY MEDICINAL PRODUCTS CEFACETRILE SUMMARY
Nutrition Notes website.notebook October 19, Nutrition
 Nutrition Nutrition Notes website.notebook October 19, 2016 Food is any substance that is ingested ("eaten") and helps sustain life. Food categories: Meats and Alternative Dairy Products Fruits and Vegetables
Nutrition Nutrition Notes website.notebook October 19, 2016 Food is any substance that is ingested ("eaten") and helps sustain life. Food categories: Meats and Alternative Dairy Products Fruits and Vegetables
1 Risk Assessment Vitamin C
 Part Water Soluble Vitamins Risk Assessment Vitamin C General information Chemistry Vitamin C is a six-carbon compound structurally related to glucose, consisting of two inter-convertible compounds: L-ascorbic
Part Water Soluble Vitamins Risk Assessment Vitamin C General information Chemistry Vitamin C is a six-carbon compound structurally related to glucose, consisting of two inter-convertible compounds: L-ascorbic
The digestive system consists of an alimentary canal and several accessory organs. The Digestive System
 The digestive system consists of an alimentary canal and several accessory organs. The Digestive System The Digestive System The digestive system mechanically and chemically breaks down food. Mechanical
The digestive system consists of an alimentary canal and several accessory organs. The Digestive System The Digestive System The digestive system mechanically and chemically breaks down food. Mechanical
INTESTINAL MICROBIOTA EXAMPLES OF INDIVIDUAL ANALYSES
 EXAMPLES OF INDIVIDUAL ANALYSES INTESTINAL MICROBIOTA Microbiota in the animal or human intestine has evolved together with the host. Consequently, the gastrointestinal tract could be considered a metacommunity,
EXAMPLES OF INDIVIDUAL ANALYSES INTESTINAL MICROBIOTA Microbiota in the animal or human intestine has evolved together with the host. Consequently, the gastrointestinal tract could be considered a metacommunity,
Early Years Foundation Stage
 Early Years Foundation Stage Food and Nutrition Policy Introduction all settings Food and nutrition is an integral part of the ethos of all GEMS settings. We believe that it is important for children to
Early Years Foundation Stage Food and Nutrition Policy Introduction all settings Food and nutrition is an integral part of the ethos of all GEMS settings. We believe that it is important for children to
Cycloxydim CYCLOXYDIM (179)
 Cycloxydim 125 5.9 CYCLOXYDIM (179) TOXICOLOGY Cycloxydim is the ISO approved name for (5RS)-2-[(EZ)-1-(ethoxyimino)butyl]-3-hydroxy-5-[(3RS)- thian-3-yl]cyclohex-2-en-1-one (IUPAC). The CAS chemical name
Cycloxydim 125 5.9 CYCLOXYDIM (179) TOXICOLOGY Cycloxydim is the ISO approved name for (5RS)-2-[(EZ)-1-(ethoxyimino)butyl]-3-hydroxy-5-[(3RS)- thian-3-yl]cyclohex-2-en-1-one (IUPAC). The CAS chemical name
A breakthrough in the treatment of OSTEOPOROSIS
 Vit. K2 A breakthrough in the treatment of OSTEOPOROSIS OSTEOPOROSIS is a systemic disease of the skeleton apparatus implying compromised bone mineral density and microarchitecture which increases fracture
Vit. K2 A breakthrough in the treatment of OSTEOPOROSIS OSTEOPOROSIS is a systemic disease of the skeleton apparatus implying compromised bone mineral density and microarchitecture which increases fracture
COMMITTEE FOR VETERINARY MEDICINAL PRODUCTS
 The European Agency for the Evaluation of Medicinal Products Veterinary Medicines and Information Technology EMEA/MRL/499/98-FINAL September 1998 COMMITTEE FOR VETERINARY MEDICINAL PRODUCTS CEFACETRILE
The European Agency for the Evaluation of Medicinal Products Veterinary Medicines and Information Technology EMEA/MRL/499/98-FINAL September 1998 COMMITTEE FOR VETERINARY MEDICINAL PRODUCTS CEFACETRILE
Safety Assessment of Yestimun Beta-Glucans
 Safety Assessment of Yestimun Beta-Glucans Name of Applicant: Leiber GmbH, Bramsche, Germany Contact person(s): Marion Hartong Novel Food Classification: Article 1.2(d) Introduction An application for
Safety Assessment of Yestimun Beta-Glucans Name of Applicant: Leiber GmbH, Bramsche, Germany Contact person(s): Marion Hartong Novel Food Classification: Article 1.2(d) Introduction An application for
COMMITTEE FOR VETERINARY MEDICINAL PRODUCTS
 The European Agency for the Evaluation of Medicinal Products Veterinary Medicines and Inspections EMEA/MRL/175/96-FINAL December 1999 COMMITTEE FOR VETERINARY MEDICINAL PRODUCTS ALTRENOGEST SUMMARY REPORT
The European Agency for the Evaluation of Medicinal Products Veterinary Medicines and Inspections EMEA/MRL/175/96-FINAL December 1999 COMMITTEE FOR VETERINARY MEDICINAL PRODUCTS ALTRENOGEST SUMMARY REPORT
Fat Soluble Vitamins. Vitamin A
 Fat Soluble Vitamins Vitamin A The biochemical basis on which vitamin A requirements were established The EAR was set based on data pertaining to the assurance of adequate stores of vitamin A (Table 19).
Fat Soluble Vitamins Vitamin A The biochemical basis on which vitamin A requirements were established The EAR was set based on data pertaining to the assurance of adequate stores of vitamin A (Table 19).
Nutrition for Health. Nutrients. Before You Read
 CHAPTER 10 LESSON 2 Nutrition for Health Nutrients BIG Idea Each nutrient in your diet plays a unique and essential role in keeping you healthy. Before You Read Sometimes figuring out what to eat can be
CHAPTER 10 LESSON 2 Nutrition for Health Nutrients BIG Idea Each nutrient in your diet plays a unique and essential role in keeping you healthy. Before You Read Sometimes figuring out what to eat can be
Nutrition Guide: Osteoporosis. Ways to support your bone healtt through a balanced diet.
 Nutrition Guide: Osteoporosis Ways to support your bone healtt through a balanced diet. Osteoporosis A disease affecting your bones Osteoporosis is known as the condition which affects bone health, and
Nutrition Guide: Osteoporosis Ways to support your bone healtt through a balanced diet. Osteoporosis A disease affecting your bones Osteoporosis is known as the condition which affects bone health, and
DIGESTION SBI 3C: NOVEMBER 2010
 DIGESTION SBI 3C: NOVEMBER 2010 DIAGRAM OF DIGESTIVE SYSTEM: Mouth Esophagus Liver Gallbladder Large Intestine Appendix Stomach Pancreas Small Intestine Rectum Anus STAGES OF DIGESTION: 1. INGESTION Taking
DIGESTION SBI 3C: NOVEMBER 2010 DIAGRAM OF DIGESTIVE SYSTEM: Mouth Esophagus Liver Gallbladder Large Intestine Appendix Stomach Pancreas Small Intestine Rectum Anus STAGES OF DIGESTION: 1. INGESTION Taking
Nutrition and Allergy
 Nutrition and Allergy Who Cares? William Reisacher, MD FACS FAAOA Assistant Professor Weill Cornell Medical College We should and why? Oxidant Load Chronic illnesses such as allergies have tremendous energy
Nutrition and Allergy Who Cares? William Reisacher, MD FACS FAAOA Assistant Professor Weill Cornell Medical College We should and why? Oxidant Load Chronic illnesses such as allergies have tremendous energy
NUTRITIONAL CARE IN ANEMIA
 االله الرحمن الرحيم بسم NUTRITIONAL CARE IN ANEMIA Nutrition Departement Faculty of Medicine University of North Sumatera Definition Deficit of circulating RBC associated with diminished oxygen-carrying
االله الرحمن الرحيم بسم NUTRITIONAL CARE IN ANEMIA Nutrition Departement Faculty of Medicine University of North Sumatera Definition Deficit of circulating RBC associated with diminished oxygen-carrying
Package Insert. Elkar
 Package Insert Elkar Product Summary 1. Name of the medicinal product Elkar 500 mg tablets 2. Qualitative and quantitative composition Each tablet contains levocarnitine 500 mg. 3. Pharmaceutical form
Package Insert Elkar Product Summary 1. Name of the medicinal product Elkar 500 mg tablets 2. Qualitative and quantitative composition Each tablet contains levocarnitine 500 mg. 3. Pharmaceutical form
Chapter 41: Animal Nutrition
 Metabolic Rate Animals are heterotrophs that require food for: 1) Fuel 2) Carbon Skeletons 3) Essential Nutrients Bioenergetics: Flow of energy through an organism Sets upper / lower limits Metabolic Rate:
Metabolic Rate Animals are heterotrophs that require food for: 1) Fuel 2) Carbon Skeletons 3) Essential Nutrients Bioenergetics: Flow of energy through an organism Sets upper / lower limits Metabolic Rate:
NUTRITION IN CHILDHOOD
 NUTRITION IN CHILDHOOD Nutrient requirement Children growing & developing need more nutritious food May be at risk for malnutrition if : - poor appetite for a long period - eat a limited number of food
NUTRITION IN CHILDHOOD Nutrient requirement Children growing & developing need more nutritious food May be at risk for malnutrition if : - poor appetite for a long period - eat a limited number of food
Regulation of Enzyme Activity
 Regulation of Enzyme Activity Enzyme activity must be regulated so that the proper levels of products are produced at all times and places This control occurs in several ways: - biosynthesis at the genetic
Regulation of Enzyme Activity Enzyme activity must be regulated so that the proper levels of products are produced at all times and places This control occurs in several ways: - biosynthesis at the genetic
Chapter 1. What You Eat and Why
 Chapter 1 What You Eat and Why What is nutrition? Nutrition is the science of food, the nutrients and the substances therein, their action, interaction, and balance in relation to health and disease,
Chapter 1 What You Eat and Why What is nutrition? Nutrition is the science of food, the nutrients and the substances therein, their action, interaction, and balance in relation to health and disease,
Boron. Boron is found (in the form of borates) in the oceans, rocks, coal, shale and some soils. Boron accumulates in plants.
 Part Trace Elements Risk Assessment Boron General information Chemistry Boron is a non-metallic element, which is found abundantly in nature, though only in compounds and in combination with sodium and
Part Trace Elements Risk Assessment Boron General information Chemistry Boron is a non-metallic element, which is found abundantly in nature, though only in compounds and in combination with sodium and
Feed Supplements and Veterinary Products
 Sel E Pro Water Soluble Powder Containing Vitamin E, Selenium & Biotin Vitamin E is a fat soluble intracellular antioxidant, involved in stabilising unsaturated fatty acids. The main antioxidant property
Sel E Pro Water Soluble Powder Containing Vitamin E, Selenium & Biotin Vitamin E is a fat soluble intracellular antioxidant, involved in stabilising unsaturated fatty acids. The main antioxidant property
What Are Proteins? Lecture 9: Proteins. Proteins: large complex molecules composed of amino acids. Nutrition 150 Shallin Busch, Ph.D.
 What Are Proteins? Lecture 9: Proteins Nutrition 150 Shallin Busch, Ph.D. Proteins: large complex molecules composed of amino acids. Contain carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen Primary source of nitrogen
What Are Proteins? Lecture 9: Proteins Nutrition 150 Shallin Busch, Ph.D. Proteins: large complex molecules composed of amino acids. Contain carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen Primary source of nitrogen
Prof. Marina Heinonen University of Helsinki Member of the NDA Panel and EFSA s WG on Novel Foods
 Guidance on Novel Foods Composition, production process and specification Prof. Marina Heinonen University of Helsinki Member of the NDA Panel and EFSA s WG on Novel Foods Info-Session 06 March 2017 Parma
Guidance on Novel Foods Composition, production process and specification Prof. Marina Heinonen University of Helsinki Member of the NDA Panel and EFSA s WG on Novel Foods Info-Session 06 March 2017 Parma
