MANAGEMENT AND PREVENTION OF REFEEDING SYNDROME IN INPATIENTS: A PRACTICAL APPROACH
|
|
|
- Blake Barnett
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 MANAGEMENT AND PREVENTION OF REFEEDING SYNDROME IN INPATIENTS: A PRACTICAL APPROACH Prof. Zeno Stanga, MD Nutritional Medicine Department of Diabetes, Endocrinology, Nutritional Medicine and Metabolism - University Hospital of Bern - Switzerland
2 Submitted to Nutrition
3 Definition of the refeeding syndrome ( RFS ) POTENTIALLY LIFE-THREATENING METABOLIC CONDITION ASSOCIATED WITH low-serum electrolyte and vitamin concentrations fluid imbalance sodium-retention disturbance of organ function resulting from over-rapid or unbalanced refeeding of a severe malnourished catabolic patient NICE. Clin. Guid / Crook MA. Nutrition 2014 / Stanga Z et al. Eur J Clin Nutr 2008
4 Diagnosis during nutritional therapy SHIFT IN ELECTROLYTES WITHIN 72 HOURS AFTER START OF NUTRITIONAL THERAPY Decrease of PO 4 from baseline >30% or below <0.6 mmol/l Any two other electrolyte shifts below normal range Mg <0.75 mmol/l, PO 4 <0.80 mmol/l, K <3.5 mmol/l YES ASSOCIATED WITH CLINICAL SYMPTOMS? NO IMMINENT RFS YES MANIFEST RFS
5 Diagnosis during nutritional therapy SHIFT IN ELECTROLYTES WITHIN 72 HOURS AFTER START OF NUTRITIONAL THERAPY Decrease of PO 4 from baseline >30% or below <0.6 mmol/l Any two other electrolyte shifts below normal range Mg <0.75 mmol/l, PO 4 <0.80 mmol/l, K <3.5 mmol/l YES ASSOCIATED WITH CLINICAL SYMPTOMS? NO IMMINENT RFS YES MANIFEST RFS
6
7 Reference Initial energy/day Proteins Fluids/day Vitamins (before/during) Solomon et al. JPEN 1990 Dewar et al. Clinical Nutrition 2001 Crook et al. Nutrition 2001 / 2010 Nutrition 2014 Kraft et al. Nutr Clin Pract 2005 NICE Guidelines 2006 Stanga et al. Eur J Clin Nutr 2008 Nutrition 2014 / kcal/kg g 20 kcal/kg 10 kcal/kg high risk: 5 kcal/kg 50-60% CHO, 15-25% fat 20-30% g ml/kg, 0 fluid balance 7.5 kcal/kg _ <1 L/d 10 kcal/kg high risk: 5 kcal/kg kcal/kg high risk: 5 kcal/kg 50-60% CHO, 30-40% fat _ 15-20% 0 fluid balance ml/kg, 0 fluid balance Stroud et al. Gut kcal/kg Royal College of Psychiatrists 2005 MARSIPAN (RCP) 2014 Mehanna et al. BMJ 2008 ESPEN Blue Book 2012 thiamine IV or PO for 2 d thiamine 300 mg IV, than 100 mg daily during refeeding. In addition Vit B12, Vit B6 and folate thiamine mg IV or 100 mg PO for 5-7 d & multivitamin mg thiamine PO for 10 d & multivitamin for 10 days mg thiamine IV or PO for 3 d & multivitamin for 10 days thiamine and B vitamins IV for 3 days kcal/kg _ kcal/kg high risk: 5-10 kcal/kg 10 kcal/kg high risk: 5 kcal/kg kcal/kg high risk: 5 kcal/kg 50-60% CHO, 30-40% fat _ max ml/kg thiamine PO 4x/d for 7-10 days _ 15-20% carefully fluid repletion ml/kg, 0 fluid balance mg thiamine PO for 10 d & multivitamin for 10 days mg thiamine IV or PO for 3 d & multivitamin for 10 days
8 Reference Initial energy/day Proteins Fluids/day Vitamins (before/during) Solomon et al. JPEN 1990 Dewar et al. Clinical Nutrition 2001 Crook et al. Nutrition 2001 / 2010 Nutrition 2014 Kraft et al. Nutr Clin Pract 2005 NICE Guidelines 2006 Stanga et al. Eur J Clin Nutr 2008 Nutrition 2014 / kcal/kg g 20 kcal/kg 10 kcal/kg high risk: 5 kcal/kg 50-60% CHO, 15-25% fat 20-30% g ml/kg, 0 fluid balance 7.5 kcal/kg _ <1 L/d 10 kcal/kg high risk: 5 kcal/kg kcal/kg high risk: 5 kcal/kg 50-60% CHO, 30-40% fat _ 15-20% 0 fluid balance ml/kg, 0 fluid balance Stroud et al. Gut kcal/kg Royal College of Psychiatrists 2005 MARSIPAN (RCP) 2014 Mehanna et al. BMJ 2008 ESPEN Blue Book 2012 thiamine IV or PO for 2 d Thiamine 300 mg IV, than 100 mg daily during refeeding. In addition Vit B12, Vit B6 and folate thiamine mg IV or 100 mg PO for 5-7 d & multivitamin mg thiamine PO for 10 d & multivitamin for 10 days mg thiamine IV or PO for 3 d & multivitamin for 10 days thiamine and B vitamins IV for 3 days kcal/kg _ kcal/kg high risk: 5-10 kcal/kg 10 kcal/kg high risk: 5 kcal/kg kcal/kg high risk: 5 kcal/kg 50-60% CHO, 30-40% fat _ max ml/kg thiamine PO 4x/d for 7-10 days _ 15-20% carefully fluid repletion ml/kg, 0 fluid balance mg thiamine PO for 10 d & multivitamin for 10 days mg thiamine IV or PO for 3 d & multivitamin for 10 days
9 Screening for nutritional risk & screening for the risk Assess hydration status & check electrolytes (K, Mg, PO 4, Na, Ca) Stratification of the risk according to risk factors NO RISK LOW RISK HIGH RISK VERY HIGH RISK
10 Criteria for determination of patients at risk MAJOR RISK FACTORS (A) BMI < 16 kg/m2 Unintentional weight loss > 15% in the preceding 3-6 months Very little or no nutritional intake for > 10 days Low levels of serum Mg, PO 4 or K prior to feed MINOR RISK FACTORS (B) BMI < 18.5 kg/m2 Unintentional weight loss > 10% in the preceding 3-6 months Very little or no nutritional intake for > 5 days History of alcool or drug abuse NICE: National Institute for Health and Clinical Excellence. 2006
11 Criteria for determination of patients at risk MAJOR RISK FACTORS (A) BMI < 16 kg/m2 Unintentional weight loss > 15% in the preceding 3-6 months Very little or no nutritional intake for > 10 days Low levels of serum Mg, PO 4 or K prior to feed MINOR RISK FACTORS (B) BMI < 18.5 kg/m2 Unintentional weight loss > 10% in the preceding 3-6 months Very little or no nutritional intake for > 5 days History of alcool or drug abuse RISK BY PATIENT S CATEGORY Hunger strike, eating disorders, chronic severe dieting After bariatric surgery, short bowel syndrome Oncology patients and fraily elderly (chronic debilitating disease) NICE: National Institute for Health and Clinical Excellence. 2006
12 Criteria for determination of patients at risk MAJOR RISK FACTORS (A) BMI < 16 kg/m2 Unintentional weight loss > 15% in the preceding 3-6 months Very little or no nutritional intake for > 10 days Low levels of serum Mg, PO 4 or K prior to feed MINOR RISK FACTORS (B) BMI < 18.5 kg/m2 Unintentional weight loss > 10% in the preceding 3-6 months Very little or no nutritional intake for > 5 days History of alcool or drug abuse RISK BY PATIENT S CATEGORY Hunger strike, eating disorders, chronic severe dieting After bariatric surgery, short bowel syndrome Oncology patients and fraily elderly (chronic debilitating disease) NICE: National Institute for Health and Clinical Excellence. 2006
13 Screening for nutritional risk & screening for the risk Assess hydration status & check electrolytes (K, Mg, PO 4, Na, Ca) Stratification of the risk according to risk factors NO RISK LOW RISK HIGH RISK VERY HIGH RISK Correct the existing deficit of dehydration and replace previous or ongoing abnormal fluid losses Nutritional support and fluids maintenance according to the standard of care Preventive measures: electrolytes repletion, thiamine substitution (at least 30 min. before refeeding) NICE. Clin. Guid / Crook MA. Nutrition 2014 / Stanga Z et al. Eur J Clin Nutr 2008
14 Predictors Prospective cohort study 243 patients starting EE oder PE 133 at risk Predictors (sensitivity 67%, specificity 80%) Poor intake for >10 days Weight loss of >15% Low plasma magnesium (< 0.7 mmol/l; p = 0.021) STARVATION is the most reliable predictor Rio A et al. BMJ Open 2013
15 Preventive measures CORRECT ELECTROLYTES LEVELS AND EVALUATE EMPIRICAL SUPPLEMENTATION BEFORE FEEDING IS INITIATED Supplement electrolytes prophylactically (unless pre-feeding plasma levels are high) in very high risk patients. Amounts depend on patient size and plasma concentrations, but usual daily requirements (man of 70 kg) are: K Mg PO mmol/kg/d mmol/kg/d mmol/kg/d GIVE mg THIAMINE I.V. OR ORALLY BEFORE FEEDING NICE. Clin. Guid / Crook MA. Nutrition 2014 / Stanga Z et al. Eur J Clin Nutr 2008
16 Screening for nutritional risk & screening for the risk Assess hydration status & check electrolytes (K, Mg, PO 4, Na, Ca) Stratification of the risk according to risk factors NO RISK LOW RISK HIGH RISK VERY HIGH RISK Correct the existing deficit of dehydration and replace previous or ongoing abnormal fluid losses Nutritional support and fluids maintenance according to the standard of care Preventive measures: electrolytes repletion, thiamine substitution (at least 30 min. before refeeding) Nutritional support Fluids maintenance Give micronutrients Nutritional support Fluids maintenance Give micronutrients Nutritional support Fluids maintenance Give micronutrients NICE. Clin. Guid / Crook MA. Nutrition 2014 / Stanga Z et al. Eur J Clin Nutr 2008
17 Nutritional & fluid management LOW RISK DAYS NUTRITIONAL SUPPORT by all routes kcal/kg/d 4 30 kcal/kg/d 5 full requirements * * I suggest to use individually clinical judgement in decision how slow / fast nutrition support should proceed to full target in the refeeding period FLUID AND SODIUM BALANCE Fluids to maintain zero balance, approx ml/kg/d No restriction in salt intake
18 Nutritional & fluid management LOW RISK DAYS NUTRITIONAL SUPPORT by all routes kcal/kg/d 4 30 kcal/kg/d 5 full requirements * * I suggest to use individually clinical judgement in decision how slow / fast nutrition support should proceed to full target in the refeeding period FLUID AND SODIUM BALANCE Fluids to maintain zero balance, approx ml/kg/d No restriction in salt intake
19 Screening for nutritional risk & screening for the risk Assess hydration status & check electrolytes (K, Mg, PO 4, Na, Ca) Stratification of the risk according to risk factors NO RISK LOW RISK HIGH RISK VERY HIGH RISK Correct the existing deficit of dehydration and replace previous or ongoing abnormal fluid losses Nutritional support and fluids maintenance according to the standard of care Preventive measures: electrolytes repletion, thiamine substitution (at least 30 min. before refeeding) Nutritional support Fluids maintenance Give micronutrients Nutritional support Fluids maintenance Give micronutrients Nutritional support Fluids maintenance Give micronutrients NICE. Clin. Guid / Crook MA. Nutrition 2014 / Stanga Z et al. Eur J Clin Nutr 2008
20 Nutritional & fluid management HIGH RISK DAYS NUTRITIONAL SUPPORT by all routes kcal/kg/d kcal/kg/d 6 30 kcal/kg/d 7 full requirements * * I suggest to use individually clinical judgement in decision how slow / fast nutrition support should proceed to full target in the refeeding period FLUID AND SODIUM BALANCE Fluids to maintain zero balance, D ml/kg/d, > D ml/kg/d Salt: restrict Na to <1 mmol/kg/d D1-7
21 Distribution of infused solutions 40 % 15 % 5 % Intracellular volume (ICV) Extracellular volume (ECV) Interstitial fluid Intravascular fluid 5% Glucose 0.9% NaCl Colloids LOBO DN et al. 2013, ISBN
22 Distribution of infused solutions 40 % 15 % 5 % Intracellular volume (ICV) Extracellular volume (ECV) Interstitial fluid Intravascular fluid 5% Glucose 0.9% NaCl Colloids LOBO DN et al. 2013, ISBN
23 Cristalloid solutions for fluid maintenance INFUSION ( 1000 ml ) Na (mmol) Cl (mmol) K (mmol) Glucose (g) 0g NaCl Lactate (mmol) Glocose 5% g NaCl 3g NaCl 1.8g NaCl Glucosaline 1: Glucosaline 2: Glucosaline 4: g NaCl Saline 0.9% g NaCl Ringer s lactate g NaCl Hartmann s LOBO DN et al. 2013, ISBN
24 Nutritional & fluid management HIGH RISK DAYS NUTRITIONAL SUPPORT by all routes kcal/kg/d kcal/kg/d 6 30 kcal/kg/d 7 full requirements * * I suggest to use individually clinical judgement in decision how slow / fast nutrition support should proceed to full target in the refeeding period FLUID AND SODIUM BALANCE Fluids to maintain zero balance, D ml/kg/d, > D ml/kg/d Salt: restrict Na to <1 mmol/kg/d D1-7
25 Screening for nutritional risk & screening for the risk Assess hydration status & check electrolytes (K, Mg, PO 4, Na, Ca) Stratification of the risk according to risk factors NO RISK LOW RISK HIGH RISK VERY HIGH RISK Correct the existing deficit of dehydration and replace previous or ongoing abnormal fluid losses Nutritional support and fluids maintenance according to the standard of care Preventive measures: electrolytes repletion, thiamine substitution (at least 30 min. before refeeding) Nutritional support Fluids maintenance Give micronutrients Nutritional support Fluids maintenance Give micronutrients Nutritional support Fluids maintenance Give micronutrients NICE. Clin. Guid / Crook MA. Nutrition 2014 / Stanga Z et al. Eur J Clin Nutr 2008
26 Nutritional & fluid management VERY HIGH RISK DAYS NUTRITIONAL SUPPORT by all routes kcal/kg/d kcal/kg/d kcal/kg/d 10 full requirements * * I suggest to use individually clinical judgement in decision how slow / fast nutrition support should proceed to full target in the refeeding period FLUID AND SODIUM BALANCE Fluids to maintain zero balance, D ml/kg/d, D ml/kg/d, > D ml/kg/d Salt: restrict Na to <1 mmol/kg/d D1-10
27 Nutritional & fluid management VERY HIGH RISK DAYS NUTRITIONAL SUPPORT by all routes kcal/kg/d kcal/kg/d kcal/kg/d 10 full requirements * * I suggest to use individually clinical judgement in decision how slow / fast nutrition support should proceed to full target in the refeeding period FLUID AND SODIUM BALANCE Fluids to maintain zero balance, D ml/kg/d, D ml/kg/d, > D ml/kg/d Salt: restrict Na to <1 mmol/kg/d D1-10
28 Screening for nutritional risk & screening for the risk Assess hydration status & check electrolytes (K, Mg, PO 4, Na, Ca) Stratification of the risk according to risk factors NO RISK LOW RISK HIGH RISK VERY HIGH RISK Correct the existing deficit of dehydration and replace previous or ongoing abnormal fluid losses Nutritional support and fluids maintenance according to the standard of care Preventive measures: electrolytes repletion, thiamine substitution (at least 30 min. before refeeding) Nutritional support Fluids maintenace Give micronutrients Nutritional support Fluids maintenance Give micronutrients Nutritional support Fluids maintenace Give micronutrients Clinical and laboratory monitoring, management of complications NICE. Clin. Guid / Crook MA. Nutrition 2014 / Stanga Z et al. Eur J Clin Nutr 2008
29 Monitoring Body weight (or fluid balance) Vital signs blood pressure, pulse rate, respiratory rate, oxygen sat. Clinical examination hydration state, oedema, cardiopulmonary state Lab serum-parameters PO 4, K, Mg, Na, Ca, glucose, urea, creatinine DAY 1-3 monitor daily DAY 4-6 monitor every 2 nd day DAY 7-10 monitor 1-2x weekly Crook MA. Nutrition 2009 / Stanga Z et al. Eur J Clin Nutr 2008
30 Monitoring Body weight (or fluid balance) Vital signs blood pressure, pulse rate, respiratory rate, oxygen sat. Clinical examination hydration state, oedema, cardiopulmonary state Lab serum-parameters PO 4, K, Mg, Na, Ca, glucose, urea, creatinine DAY 1-3 monitor daily DAY 4-6 monitor every 2 nd day DAY 7-10 monitor 1-2x weekly Crook MA. Nutrition 2009 / Stanga Z et al. Eur J Clin Nutr 2008
31 Electrolyte deficiency and replacement POTASSIUM REPLETION S-POTASSIUM Mild deficit mmol/l Moderate deficit mmol/l Severe deficit < 2.5 mmol/l RECOMMENDATION FOR REPLETION oral replacement with 20 mmol (as KCl or other formularies) OR i.v. replacement with 20 mmol KCl over 4-8 h check K levels the next day i.v. replacement with mmol KCl over 4-8 h check K levels after 8 hours if not normal levels, give further 20 mmol KCL i.v. replacement with 40 mmol KCl over 4-8 h check K levels after 8 hours if not normal levels, give further 40 mmol KCL Gennari FJ. NEJM 1998 / Boateng AA et al. Nutrition 2010 / ESPEN Blue Book 2011 Marinella MA et al. Int J Clin Pract 2008 / Stanga Z et al. Eur J Clin Nutr 2008
32 Electrolyte deficiency and replacement MAGNESIUM REPLETION S-MAGNESIUM Mild to moderate deficit mmol/l RECOMMENDATION FOR REPLETION oral replacement with mmol Mg-chlorid or Mg-citrat or Mg-L-aspartat oral Mg should be given in divided doses to minimise diarrhoea (absorption process is saturated at about 5-10 mmol Mg) Severe deficit < 0.5 mmol/l i.v. replacement with mmol MgSO 4 (4-6 g) over 4-8 h reassess every 8-12 h Brannan GB et al. J Clin Invest 1976 / Boateng AA et al. Nutrition 2010 / ESPEN Blue Book 2011 Weisinger JR et al. Lancet 1998 / Stanga Z et al. Eur J Clin Nutr 2008
33 Department of Diabetes, Endocrinology, Nutritional Medicine and Metabolism, University Hospital, Bern, Switzerland Zeno Stanga PENSA 2017 Manila Electrolyte deficiency and replacement MAGNESIUM REPLETION S-MAGNESIUM RECOMMENDATION FOR REPLETION Mild to moderate deficit mmol/l oral replacement with mmol Mg-chlorid or Mg-citrat or Mg-L-aspartat oral Mg should be given in divided doses to minimise diarrhoea (absorption process is saturated at about 5-10 mmol Mg) Severe deficit < 0.5 mmol/l i.v. replacement with mmol MgSO4 (4-6 g) over 4-8 h reassess every 8-12 h Brannan GB et al. J Clin Invest 1976 / Boateng AA et al. Nutrition 2010 / ESPEN Blue Book 2011 Weisinger JR et al. Lancet 1998 / Stanga Z et al. Eur J Clin Nutr 2008
34 Electrolyte deficiency and replacement PHOSPHATE REPLETION S-PHOSPHATE Mild deficit mmol/l Moderate deficit mmol/l Severe deficit < 0.32 mmol/l RECOMMENDATION FOR REPLETION oral replacement with 0.3 mmol/kg/d PO 4 (divided doses to minimise diarrhoea) OR i.v. replacement with 0.3 mmol/kg/d PO 4 (as K 3 PO 4 or Na 3 PO 4 ) over 8-12 h check PO 4 levels next day i.v. replacement with 0.6 mmol/kg/d PO 4 (as K 3 PO 4 or Na 3 PO 4 ) over 8-12 h check PO 4 levels after 8-12h and repeat infusion if necessary (max. of 50 mmol PO 4 in 24 h). same replacement therapy as above (moderate deficit) Thatte L et al. Am J Med 1995 / Crook MA. Nutrition 2009 / Stanga Z et al. Eur J Clin Nutr 2008
35 Energy ( kcal ) S-PO 4 ( mmol/l ) Department of Diabetes, Endocrinology, Nutritional Medicine and Metabolism, University Hospital, Bern, Switzerland Zeno Stanga PENSA 2017 Manila (13 ICUs) Enrollment: 72h after start feeding (EE/PE) & PO 4, 1:1 rand., stratification by PO 4 > 0.32 vs 0.32 mmol/l and BMI < 18 vs 18 kg/m 2 n = 170 Standard care n = 169 Hypocaloric management Energy intake / d ( mean) Lowest daily s-phosphates PO 4 -substitution i.v. ( mmol ) Days Days Doig GS et al. Lancet Respir Med 2015
36 Survival ( % ) Department of Diabetes, Endocrinology, Nutritional Medicine and Metabolism, University Hospital, Bern, Switzerland Zeno Stanga PENSA 2017 Manila Overall survival time 91% p = % Survival time ( days ) Doig GS et al. Lancet Respir Med 2015
37 Pending questions To date only low quality evidence exists... Too cautious energy step up? so far conflicting statements possible start feeding higher energy / CHO in hospital? Build-up of full food intake within 3-4 days? reduction of the catabolic phase Do we have to give electrolytes in a prophylactic way? prevention is better than cure Reliable predictors? How important is the clinical examination?
38 The big challenge
39 Take home message
40 UNIVERSITY HOSPITAL OF BERN - SWITZERLAND
Prevention of Electrolyte Disorders Refeeding Syndrome พญ.น นทพร เต มพรเล ศ
 Prevention of Electrolyte Disorders Refeeding Syndrome พญ.น นทพร เต มพรเล ศ Outline Refeeding Syndrome What is refeeding syndrome? What Electrolytes and minerals are involved? Who is at risk? How to manage
Prevention of Electrolyte Disorders Refeeding Syndrome พญ.น นทพร เต มพรเล ศ Outline Refeeding Syndrome What is refeeding syndrome? What Electrolytes and minerals are involved? Who is at risk? How to manage
Refeeding syndrome a practical approach
 Refeeding syndrome a practical approach PENG pre-bapen Conference Teaching Day Birmingham Monday 20 th November 2017 Rhys White Acting Clinical and Operational Lead Dietitian Guys and St Thomas NHS Foundation
Refeeding syndrome a practical approach PENG pre-bapen Conference Teaching Day Birmingham Monday 20 th November 2017 Rhys White Acting Clinical and Operational Lead Dietitian Guys and St Thomas NHS Foundation
Dutch consensus statement on Refeeding syndrome
 Dutch consensus statement on Refeeding syndrome Introduction Disease related malnutrition is a common problem in health care. The refeeding syndrome is defined as the severe and potentially fatal shifts
Dutch consensus statement on Refeeding syndrome Introduction Disease related malnutrition is a common problem in health care. The refeeding syndrome is defined as the severe and potentially fatal shifts
GUIDANCE NOTES. DIETETIC RISK ASSESSMENT FOR REFEEDING RECOMMENDED MEAL PLANS When commencing re-feeding: NICE (2006)
 When commencing re-feeding: NICE (2006) NICE (2006) Clinical Guideline 32 Nutrition support in adults: oral nutrition support, enteral tube feeding and parenteral nutrition (The following is based on www.nice.org.uk/cg032
When commencing re-feeding: NICE (2006) NICE (2006) Clinical Guideline 32 Nutrition support in adults: oral nutrition support, enteral tube feeding and parenteral nutrition (The following is based on www.nice.org.uk/cg032
Acute management of severe malnutrition. Dr Simon Gabe St Mark s Hospital, London
 Acute management of severe malnutrition Dr Simon Gabe St Mark s Hospital, London Malnutrition definition A state resulting from lack of uptake or intake of nutrition leading to altered body composition
Acute management of severe malnutrition Dr Simon Gabe St Mark s Hospital, London Malnutrition definition A state resulting from lack of uptake or intake of nutrition leading to altered body composition
THE PATHOPHYSIOLOGY OF THE REFEEDING SYNDROME
 THE PATHOPHYSIOLOGY OF THE REFEEDING SYNDROME Zeno Stanga, MD Division of Endocrinology, Diabetes and Clinical Nutrition Division of General Internal Medicine Minnesota Experiment Aim To guide the Allied
THE PATHOPHYSIOLOGY OF THE REFEEDING SYNDROME Zeno Stanga, MD Division of Endocrinology, Diabetes and Clinical Nutrition Division of General Internal Medicine Minnesota Experiment Aim To guide the Allied
Financial Interest Disclosure (over the past 24 months)
 : Across the Spectrum of Primary care Jan Greenwood, R.D. Nutrition Support Consultant The Basic Five Programs The opinions expressed in this presentation are that of the presenter and do not necessarily
: Across the Spectrum of Primary care Jan Greenwood, R.D. Nutrition Support Consultant The Basic Five Programs The opinions expressed in this presentation are that of the presenter and do not necessarily
Formulary and Prescribing Guidelines
 Formulary and Prescribing Guidelines SECTION 15: TREATMENT OF EATING DISORDERS 15.1 Introduction Please review the Trust document Guidelines for the assessment and treatment of eating disorders in the
Formulary and Prescribing Guidelines SECTION 15: TREATMENT OF EATING DISORDERS 15.1 Introduction Please review the Trust document Guidelines for the assessment and treatment of eating disorders in the
Over-feeding and over- hydration in elderly medical patients Lessons from the Liverpool Care Pathway. Correspondence to: Abstract Keywords
 Over-feeding and over-hydration in elderly medical patients Lessons from the Liverpool Care Pathway. Eleni Tsiompanou; Caroline Lucas; Lulu Kreeger; Mike Stroud Correspondence to: Dr Eleni Tsiompanou,
Over-feeding and over-hydration in elderly medical patients Lessons from the Liverpool Care Pathway. Eleni Tsiompanou; Caroline Lucas; Lulu Kreeger; Mike Stroud Correspondence to: Dr Eleni Tsiompanou,
Adaptation and re-feeding Hypokalemia Bone complications
 Adaptation and re-feeding Hypokalemia Bone complications René Klinkby Støving Odense University Hospital Denmark 10% 20% 30% 40% BMI 18.5 BMI 16.5 BMI 14.5 BMI 12.5 Willmore DW, The Metabolic Management
Adaptation and re-feeding Hypokalemia Bone complications René Klinkby Støving Odense University Hospital Denmark 10% 20% 30% 40% BMI 18.5 BMI 16.5 BMI 14.5 BMI 12.5 Willmore DW, The Metabolic Management
Refeeding Syndrom: Ein Update. Prof. Philipp Schuetz, Leitender Arzt Medizinische Uniklinik, Kantonsspital Aarau GESKES Kurs Aarau, April 14 th 2016
 Refeeding Syndrom: Ein Update Prof. Philipp Schuetz, Leitender Arzt Medizinische Uniklinik, Kantonsspital Aarau GESKES Kurs Aarau, April 14 th 2016 Email: Schuetzph@gmail.com Historical perspective First
Refeeding Syndrom: Ein Update Prof. Philipp Schuetz, Leitender Arzt Medizinische Uniklinik, Kantonsspital Aarau GESKES Kurs Aarau, April 14 th 2016 Email: Schuetzph@gmail.com Historical perspective First
Refeeding Low Weight Adolescents with AN
 RCPsych ED 2013 Refeeding Low Weight Adolescents with AN Graeme O Connor RD PhD Research Student -UCL Specialist paediatric Dietitian Great Ormond Street Hospital Foundation Trust Pathophysiology of starvation
RCPsych ED 2013 Refeeding Low Weight Adolescents with AN Graeme O Connor RD PhD Research Student -UCL Specialist paediatric Dietitian Great Ormond Street Hospital Foundation Trust Pathophysiology of starvation
Brief summary of the NICE guidelines December 2013
 Brief summary of the NICE guidelines December 2013 Intravenous fluid therapy in adults in hospital the relevance to Emergency Department Care Applicable to patients 16 years and older receiving i.v. fluids
Brief summary of the NICE guidelines December 2013 Intravenous fluid therapy in adults in hospital the relevance to Emergency Department Care Applicable to patients 16 years and older receiving i.v. fluids
Phosphoremia (mmol/l) Calcemia (mmol/l) Postnatal age (days) Postnatal age (days) Urinary Calcium (mg/kg/d) Phosphoremia (mmol/l)
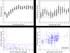 3,0 3,2 Calcemia (mmol/l) 2,8 2,6 2,4 2,2 2,0 1,8 Phosphoremia (mmol/l) 3,0 2,8 2,6 2,4 2,2 2,0 1,8 1,6 1,4 1,2 1,6 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 Postnatal age (days) 1,0 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11
3,0 3,2 Calcemia (mmol/l) 2,8 2,6 2,4 2,2 2,0 1,8 Phosphoremia (mmol/l) 3,0 2,8 2,6 2,4 2,2 2,0 1,8 1,6 1,4 1,2 1,6 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 Postnatal age (days) 1,0 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11
TOTAL PARENTERAL NUTRITION
 TOTAL PARENTERAL NUTRITION Indication See algorithm. Timing Start TPN as indicated on algorithm 1. There is no need to build up TPN volume. The volume of TPN (including lipids) should equate to the total
TOTAL PARENTERAL NUTRITION Indication See algorithm. Timing Start TPN as indicated on algorithm 1. There is no need to build up TPN volume. The volume of TPN (including lipids) should equate to the total
Nutrition in Pancreatic Cancer. Edmond Sung Consultant Gastroenterologist Lead Clinician for Clinical Nutrition and Endoscopy
 Nutrition in Pancreatic Cancer Edmond Sung Consultant Gastroenterologist Lead Clinician for Clinical Nutrition and Endoscopy Overview The pancreas and nutrition Nutrition screening - can we do this well?
Nutrition in Pancreatic Cancer Edmond Sung Consultant Gastroenterologist Lead Clinician for Clinical Nutrition and Endoscopy Overview The pancreas and nutrition Nutrition screening - can we do this well?
Case Study: Nutritional management of a patient at high risk of developing refeeding syndrome
 Case Study: Nutritional management of a patient at high risk of developing refeeding syndrome Dolman RC, PhD, Senior Lecturer; Conradie C, MSc, Lecturer Lombard MJ, PhD, Senior Lecturer; Nienaber A, MSc,
Case Study: Nutritional management of a patient at high risk of developing refeeding syndrome Dolman RC, PhD, Senior Lecturer; Conradie C, MSc, Lecturer Lombard MJ, PhD, Senior Lecturer; Nienaber A, MSc,
ESPEN Congress Geneva 2014 NUTRITION AT EXTREMES: THE UNLIKELY BENEFITS OF STARVATION
 ESPEN Congress Geneva 2014 NUTRITION AT EXTREMES: THE UNLIKELY BENEFITS OF STARVATION Management of the severely malnourished: the case of anorexia nervosa C. De la Cuerda (ES) Management of the severely
ESPEN Congress Geneva 2014 NUTRITION AT EXTREMES: THE UNLIKELY BENEFITS OF STARVATION Management of the severely malnourished: the case of anorexia nervosa C. De la Cuerda (ES) Management of the severely
Sample. Affix patient label within this box.
 Instructions for completing orders Complete pages 1-3 for General Inpatient Orders. All pathway compatible orders (indicated by ) within the General Inpatient Orders will be followed automatically. Optional
Instructions for completing orders Complete pages 1-3 for General Inpatient Orders. All pathway compatible orders (indicated by ) within the General Inpatient Orders will be followed automatically. Optional
Pediatric Dehydration and Oral Rehydration. May 16/17
 Pediatric Dehydration and Oral Rehydration May 16/17 Volume Depletion (hypovolemia): refers to any condition in which the effective circulating volume is reduced. It can be produced by salt and water loss
Pediatric Dehydration and Oral Rehydration May 16/17 Volume Depletion (hypovolemia): refers to any condition in which the effective circulating volume is reduced. It can be produced by salt and water loss
Long term monitoring. Dr Alison Culkin Research Dietitian St Mark s Hospital
 Long term monitoring Dr Alison Culkin Research Dietitian St Mark s Hospital Patient 23 year old lady 1/4/14 Colectomy for UC 3-7/4/14 Ischaemic bowel 4 laparotomies Jejunostomy at 35 cm 23/5/14 Weight
Long term monitoring Dr Alison Culkin Research Dietitian St Mark s Hospital Patient 23 year old lady 1/4/14 Colectomy for UC 3-7/4/14 Ischaemic bowel 4 laparotomies Jejunostomy at 35 cm 23/5/14 Weight
Salty Solutions or Salty Problems? Outline. Outline 29/04/2013
 Salty Solutions or Salty Problems? 18 th October 2012 Richard Seigne Anaesthetist 1 - Non fluid 40% T o t a l b o d y f l u i d 60% NaCl NaCl Intra-cellular fluid 2/3 KCl Interstitial fluid 3/4 of ECF
Salty Solutions or Salty Problems? 18 th October 2012 Richard Seigne Anaesthetist 1 - Non fluid 40% T o t a l b o d y f l u i d 60% NaCl NaCl Intra-cellular fluid 2/3 KCl Interstitial fluid 3/4 of ECF
Inflammatory Bowel Disease
 + Inflammatory Bowel Disease Christina Kalafsky, Dietetic Intern University of Maryland College Park Children s National Medical Center Case Study January 31, 2014 + Outline n Inflammatory Bowel Disease
+ Inflammatory Bowel Disease Christina Kalafsky, Dietetic Intern University of Maryland College Park Children s National Medical Center Case Study January 31, 2014 + Outline n Inflammatory Bowel Disease
September 2014 V0.17. Paediatric Daily Fluid Prescription & Balance Chart
 September 14 V0.17 Aims and outcomes of session. Aim: To provide guidance on correctly completing the paediatric daily fluid prescription & balance chart. Outcomes: Demonstrate the ability to: calculate
September 14 V0.17 Aims and outcomes of session. Aim: To provide guidance on correctly completing the paediatric daily fluid prescription & balance chart. Outcomes: Demonstrate the ability to: calculate
The top 5 things all doctors should know about nutrition. Dr Peter Mooney Consultant Gastroenterologist Leeds Teaching Hospitals NHS Trust
 The top 5 things all doctors should know about nutrition Dr Peter Mooney Consultant Gastroenterologist Leeds Teaching Hospitals NHS Trust ONE NUTRITION IS EVERYONE S PROBLEM 2018 2006 2013 2010 Mortality
The top 5 things all doctors should know about nutrition Dr Peter Mooney Consultant Gastroenterologist Leeds Teaching Hospitals NHS Trust ONE NUTRITION IS EVERYONE S PROBLEM 2018 2006 2013 2010 Mortality
CLINICAL GUIDELINE FOR INTRAVENOUS FLUID THERAPY FOR ADULTS IN HOSPITAL 1. Aim/Purpose of this Guideline
 CLINICAL GUIDELINE FOR INTRAVENOUS FLUID THERAPY FOR ADULTS IN HOSPITAL 1. Aim/Purpose of this Guideline 1.1. This guideline contains recommendations about general principles for managing intravenous (IV)
CLINICAL GUIDELINE FOR INTRAVENOUS FLUID THERAPY FOR ADULTS IN HOSPITAL 1. Aim/Purpose of this Guideline 1.1. This guideline contains recommendations about general principles for managing intravenous (IV)
Acid Base Balance. Professor Dr. Raid M. H. Al-Salih. Clinical Chemistry Professor Dr. Raid M. H. Al-Salih
 Acid Base Balance 1 HYDROGEN ION CONCENTRATION and CONCEPT OF ph Blood hydrogen ion concentration (abbreviated [H + ]) is maintained within tight limits in health, with the normal concentration being between
Acid Base Balance 1 HYDROGEN ION CONCENTRATION and CONCEPT OF ph Blood hydrogen ion concentration (abbreviated [H + ]) is maintained within tight limits in health, with the normal concentration being between
PAEDIATRIC FLUIDS RCH DEHYDRATION
 PAEDIATRIC FLUIDS RCH DEHYDRATION AIMS Understand normal fluids electrolyte requirements/ maintenance Understand how to assess DEHYDRATION in children Understand the difference between DEHYDRATION and
PAEDIATRIC FLUIDS RCH DEHYDRATION AIMS Understand normal fluids electrolyte requirements/ maintenance Understand how to assess DEHYDRATION in children Understand the difference between DEHYDRATION and
Pediatric Intensive Care Unit (PICU) Pediatric Diabetic Ketoacidosis (DKA) Admission Order Set
 Discontinue all previous orders Weight: kg DKA admit order set is for initial management Ongoing management required based on frequent reassessment of TFI, fluid balance and lab results. Admit to PICU
Discontinue all previous orders Weight: kg DKA admit order set is for initial management Ongoing management required based on frequent reassessment of TFI, fluid balance and lab results. Admit to PICU
Care of the Critically Unwell Patient. fluids
 Care of the Critically Unwell Patient fluids Are we made of water? YES! Humans are like cucumbers Water content at least half of body weight in healty adults (60%) blood volume 7% bw males 6% bw females
Care of the Critically Unwell Patient fluids Are we made of water? YES! Humans are like cucumbers Water content at least half of body weight in healty adults (60%) blood volume 7% bw males 6% bw females
Intensive Care Nutrition. Dr Alan Race BSc(Hons) PhD FRCA
 Intensive Care Nutrition Dr Alan Race BSc(Hons) PhD FRCA Objectives 1. What examiners say 2. Definition 3. Assessment 4. Requirements 5. Types of delivery 6. CALORIES Trial 7. Timing 8. Immunomodulation
Intensive Care Nutrition Dr Alan Race BSc(Hons) PhD FRCA Objectives 1. What examiners say 2. Definition 3. Assessment 4. Requirements 5. Types of delivery 6. CALORIES Trial 7. Timing 8. Immunomodulation
NUTRITION. Elizabeth Viner Smith & Catherine Jones Foundations of Critical Care Nursing September 2017
 NUTRITION Elizabeth Viner Smith & Catherine Jones Foundations of Critical Care Nursing September 2017 Step One Competency 1.19 Factors contributing to nutritional impairment in critical illness. Nutritional
NUTRITION Elizabeth Viner Smith & Catherine Jones Foundations of Critical Care Nursing September 2017 Step One Competency 1.19 Factors contributing to nutritional impairment in critical illness. Nutritional
Fluids and electrolytes: the basics
 Fluids and electrolytes: the basics This document is based on the handout from the Surgery for Finals course. The notes provided here summarise key aspects, focusing on areas that are popular in clinical
Fluids and electrolytes: the basics This document is based on the handout from the Surgery for Finals course. The notes provided here summarise key aspects, focusing on areas that are popular in clinical
Nutritional management of eating disorders. Louise Watson Clinical Dietitian South Island Eating Disorders Service
 Nutritional management of eating disorders Louise Watson Clinical Dietitian South Island Eating Disorders Service Contents Refeeding syndrome Target weight range Measuring height and weight Refeeding syndrome
Nutritional management of eating disorders Louise Watson Clinical Dietitian South Island Eating Disorders Service Contents Refeeding syndrome Target weight range Measuring height and weight Refeeding syndrome
Does the patient need an enteral feed out of hours?
 Out of hours Enteral tube feeding (Nasogastric) Starter Regimen for an Adult Inpatient With Renal Failure (Including management of re-feeding syndrome) Guidance for Practice 1. Introduction 1.1 This clinical
Out of hours Enteral tube feeding (Nasogastric) Starter Regimen for an Adult Inpatient With Renal Failure (Including management of re-feeding syndrome) Guidance for Practice 1. Introduction 1.1 This clinical
Refeeding Syndrome Guideline
 Refeeding Syndrome Guideline Author: Responsible Lead Executive Director: Endorsing Body: Governance or Assurance Committee Pamela Miller Biochemistry Implementation Date: January 2017 Version Number:
Refeeding Syndrome Guideline Author: Responsible Lead Executive Director: Endorsing Body: Governance or Assurance Committee Pamela Miller Biochemistry Implementation Date: January 2017 Version Number:
EU RISK MANAGEMENT PLAN (EU RMP) Nutriflex Omega peri emulsion for infusion , version 1.1
 EU RISK MANAGEMENT PLAN (EU RMP) Nutriflex Omega peri emulsion for infusion 13.7.2015, version 1.1 III.1. Elements for a Public Summary III.1.1. Overview of disease epidemiology Patients may need parenteral
EU RISK MANAGEMENT PLAN (EU RMP) Nutriflex Omega peri emulsion for infusion 13.7.2015, version 1.1 III.1. Elements for a Public Summary III.1.1. Overview of disease epidemiology Patients may need parenteral
Amino Acids and Sorbitol injection with/without Electrolytes NIRMIN *
 For the use of a registered medical practitioner or a Hospital or a Laboratory only Amino Acids and Sorbitol injection with/without Electrolytes NIRMIN * DESCRIPTION: NIRMIN * is a clear, colourless injection
For the use of a registered medical practitioner or a Hospital or a Laboratory only Amino Acids and Sorbitol injection with/without Electrolytes NIRMIN * DESCRIPTION: NIRMIN * is a clear, colourless injection
KENT STATE UNIVERSITY HEALTH CARE OF CHILDREN Nursing Pediatrics Case Studies: Child Dehydration
 Courtney Wiener 9/9/10 KENT STATE UNIVERSITY HEALTH CARE OF CHILDREN Nursing 30020 - Pediatrics Case Studies: Child Dehydration Introduction: Dehydration can be life threatening to a child since a majority
Courtney Wiener 9/9/10 KENT STATE UNIVERSITY HEALTH CARE OF CHILDREN Nursing 30020 - Pediatrics Case Studies: Child Dehydration Introduction: Dehydration can be life threatening to a child since a majority
6-7 JULY 2015, BIRMINGHAM CONGRESS
 6-7 JULY 2015, BIRMINGHAM CONGRESS Keywords: /Malnutrition/ Enteral feeding/critical illness This article has been double-blind peer reviewed Patients who are critically ill are at greater risk of malnutrition
6-7 JULY 2015, BIRMINGHAM CONGRESS Keywords: /Malnutrition/ Enteral feeding/critical illness This article has been double-blind peer reviewed Patients who are critically ill are at greater risk of malnutrition
Basic Fluid and Electrolytes
 Basic Fluid and Electrolytes Chapter 22 Basic Fluid and Electrolytes Introduction Infants and young children have a greater need for water and are more vulnerable to alterations in fluid and electrolyte
Basic Fluid and Electrolytes Chapter 22 Basic Fluid and Electrolytes Introduction Infants and young children have a greater need for water and are more vulnerable to alterations in fluid and electrolyte
Ensuring Safe Management of Parenteral Nutrition During Drug Shortages: Strategies and Protocols for Enabling Clinician Success
 Ensuring Safe Management of Parenteral Nutrition During Drug Shortages: Strategies and Protocols for Enabling Clinician Success Mandy Corrigan, MPH, RD, CNSC Nutrition Support Clinician mandycorrigan1@gmail.com
Ensuring Safe Management of Parenteral Nutrition During Drug Shortages: Strategies and Protocols for Enabling Clinician Success Mandy Corrigan, MPH, RD, CNSC Nutrition Support Clinician mandycorrigan1@gmail.com
Refeeding syndrome: An overlooked condition?
 Focused Review Refeeding syndrome: An overlooked condition? Yuttiwat Vorakunthada MD, Passisd Laoveeravat MD, Wasawat Vutthikraivit MD, Weerapong Lilitwat MD, FAAP, Ariwan Rakvit MD, FACG Abstract Refeeding
Focused Review Refeeding syndrome: An overlooked condition? Yuttiwat Vorakunthada MD, Passisd Laoveeravat MD, Wasawat Vutthikraivit MD, Weerapong Lilitwat MD, FAAP, Ariwan Rakvit MD, FACG Abstract Refeeding
Small Bowel Obstruction after operation in a severely malnourished man. By: Ms Bounmark Phoumesy
 Small Bowel Obstruction after operation in a severely malnourished man By: Ms Bounmark Phoumesy Normal length of GI tract Normal length(achieved by age 9) Small bowel 600cm (Men: 630 cm; Women: 592 cm)
Small Bowel Obstruction after operation in a severely malnourished man By: Ms Bounmark Phoumesy Normal length of GI tract Normal length(achieved by age 9) Small bowel 600cm (Men: 630 cm; Women: 592 cm)
ISOVALERIC ACIDAEMIA -ACUTE DECOMPENSATION (standard version)
 Contact Details Name: Hospital Telephone: This protocol has 5 pages ISOVALERIC ACIDAEMIA -ACUTE DECOMPENSATION (standard version) Please read carefully. Meticulous treatment is very important as there
Contact Details Name: Hospital Telephone: This protocol has 5 pages ISOVALERIC ACIDAEMIA -ACUTE DECOMPENSATION (standard version) Please read carefully. Meticulous treatment is very important as there
A Guide to Prescribing Adult Oral Nutritional Supplements in West Kent CCG
 A Guide to Prescribing Adult Oral Nutritional Supplements in West Kent CCG Aim This guideline has been designed to support primary care prescribers initiating nutrition support for adults in West Kent.
A Guide to Prescribing Adult Oral Nutritional Supplements in West Kent CCG Aim This guideline has been designed to support primary care prescribers initiating nutrition support for adults in West Kent.
ESPEN Congress The Hague 2017
 ESPEN Congress The Hague 2017 Using the gut in acute care patients Permissive underfeeding in practice J.-C. Preiser (BE) PERMISSIVE UNDERFEEDING IN PRACTICE ESPEN congress Jean-Charles Preiser, M.D.,
ESPEN Congress The Hague 2017 Using the gut in acute care patients Permissive underfeeding in practice J.-C. Preiser (BE) PERMISSIVE UNDERFEEDING IN PRACTICE ESPEN congress Jean-Charles Preiser, M.D.,
IV Fluids Do you know what you are doing?
 IV Fluids Do you know what you are doing? Probably not Dr Mike Stroud Gastroenterologist and Senior Lecturer in Medicine & Nutrition Southampton University Hospitals Foundation Trust CG 174 December 2013
IV Fluids Do you know what you are doing? Probably not Dr Mike Stroud Gastroenterologist and Senior Lecturer in Medicine & Nutrition Southampton University Hospitals Foundation Trust CG 174 December 2013
INTRAVENOUS FLUID THERAPY. Tom Heaps Consultant Acute Physician
 INTRAVENOUS FLUID THERAPY Tom Heaps Consultant Acute Physician LEARNING OBJECTIVES 1. Crystalloids vs colloids 2. Balanced vs non-balanced solutions 3. Composition of various IV fluids 4. What is normal
INTRAVENOUS FLUID THERAPY Tom Heaps Consultant Acute Physician LEARNING OBJECTIVES 1. Crystalloids vs colloids 2. Balanced vs non-balanced solutions 3. Composition of various IV fluids 4. What is normal
Chapter 16 Nutrition, Fluids and Electrolytes, and Acid-Base Balance Nutrition Nutrients Water o Functions Promotes metabolic processes Transporter
 Chapter 16 Nutrition, Fluids and Electrolytes, and Acid-Base Balance Nutrition Nutrients Water o Functions Promotes metabolic processes Transporter for nutrients and wastes Lubricant Insulator and shock
Chapter 16 Nutrition, Fluids and Electrolytes, and Acid-Base Balance Nutrition Nutrients Water o Functions Promotes metabolic processes Transporter for nutrients and wastes Lubricant Insulator and shock
Workshop: MARSIPAN: Management of Really Sick
 Workshop: MARSIPAN: Management of Really Sick Patients with Anorexia Nervosa URSULA PHILPOT LEEDS BECKETT UNIVERSITY 1 MARSIPAN MARSIPAN Junior Checklist MDT gp experts evidence and consensus http://www.rcpsych.ac.uk/usefulresources/publications/
Workshop: MARSIPAN: Management of Really Sick Patients with Anorexia Nervosa URSULA PHILPOT LEEDS BECKETT UNIVERSITY 1 MARSIPAN MARSIPAN Junior Checklist MDT gp experts evidence and consensus http://www.rcpsych.ac.uk/usefulresources/publications/
Parenteral Nutrition in IBD: Any indication?
 Parenteral Nutrition in IBD: Any indication? Name: Institution: Marianna Arvanitakis Erasme University Hospital, Brussels, Belgium Clinical case 42 year old male Crohn s disease since he was 16 years old
Parenteral Nutrition in IBD: Any indication? Name: Institution: Marianna Arvanitakis Erasme University Hospital, Brussels, Belgium Clinical case 42 year old male Crohn s disease since he was 16 years old
NHS Grampian Staff Guideline for the Management of Acute Hypokalaemia in Adults
 NHS Grampian Staff Guideline for the Management of Acute Hypokalaemia in Adults Co-ordinators: Medicines Information Pharmacist Consultation Group: See relevant page in guidance Approver: Medicine Guidelines
NHS Grampian Staff Guideline for the Management of Acute Hypokalaemia in Adults Co-ordinators: Medicines Information Pharmacist Consultation Group: See relevant page in guidance Approver: Medicine Guidelines
Diabetic Ketoacidosis
 Diabetic Ketoacidosis Definition: Diabetic Ketoacidosis is one of the most serious acute complications of diabetes. It s more common in young patients with type 1 diabetes mellitus. It s usually characterized
Diabetic Ketoacidosis Definition: Diabetic Ketoacidosis is one of the most serious acute complications of diabetes. It s more common in young patients with type 1 diabetes mellitus. It s usually characterized
ESPEN Congress Copenhagen 2016
 ESPEN Congress Copenhagen 2016 THE DIVERSITY OF OBESITY MALNUTRITION IN THE OBESE R. Barazzoni (IT) Malnutrition in the obese patient Rocco Barazzoni Dept of Medical, Surgical and Health Sciences University
ESPEN Congress Copenhagen 2016 THE DIVERSITY OF OBESITY MALNUTRITION IN THE OBESE R. Barazzoni (IT) Malnutrition in the obese patient Rocco Barazzoni Dept of Medical, Surgical and Health Sciences University
IV Fluids. I.V. Fluid Osmolarity Composition 0.9% NaCL (Normal Saline Solution, NSS) Uses/Clinical Considerations
 IV Fluids When administering IV fluids, the type and amount of fluid may influence patient outcomes. Make sure to understand the differences between fluid products and their effects. Crystalloids Crystalloid
IV Fluids When administering IV fluids, the type and amount of fluid may influence patient outcomes. Make sure to understand the differences between fluid products and their effects. Crystalloids Crystalloid
Dietetic Outcomes in Home Parenteral Nutrition
 Dietetic Outcomes in Home Parenteral Nutrition Dr Alison Culkin Research Dietitian Intestinal Failure & Home Parenteral Nutrition St Mark s Hospital PENG Meeting November 2011 The Dietetic Outcomes Model
Dietetic Outcomes in Home Parenteral Nutrition Dr Alison Culkin Research Dietitian Intestinal Failure & Home Parenteral Nutrition St Mark s Hospital PENG Meeting November 2011 The Dietetic Outcomes Model
Electrolytes Solution
 Electrolytes Solution Substances that are not dissociated in solution are called nonelectrolytes, and those with varying degrees of dissociation are called electrolytes. Urea and dextrose are examples
Electrolytes Solution Substances that are not dissociated in solution are called nonelectrolytes, and those with varying degrees of dissociation are called electrolytes. Urea and dextrose are examples
IS THERE A PLACE IN THE ICU FOR PERMISSIVE UNDERFEEDING AND WHERE? ENGELA FRANCIS RD(SA)
 IS THERE A PLACE IN THE ICU FOR PERMISSIVE UNDERFEEDING AND WHERE? ENGELA FRANCIS RD(SA) DEFINITION: PERMISSIVE UNDERFEEDING No clear definition in literature Permissive underfeeding definition prior to
IS THERE A PLACE IN THE ICU FOR PERMISSIVE UNDERFEEDING AND WHERE? ENGELA FRANCIS RD(SA) DEFINITION: PERMISSIVE UNDERFEEDING No clear definition in literature Permissive underfeeding definition prior to
Dehydration (severe)
 Dehydration (severe) ETAT Module 5 Adapted from Emergency Triage Assessment and Treatment (ETAT): Manual for Participants, World Health Organization, 2005 Learning Objectives Learn causes of severe dehydration
Dehydration (severe) ETAT Module 5 Adapted from Emergency Triage Assessment and Treatment (ETAT): Manual for Participants, World Health Organization, 2005 Learning Objectives Learn causes of severe dehydration
Paediatric Best Practice Guidelines. Eating Disorders
 Paediatric Best Practice Guidelines Eating Disorders Background Relatively common 0.5-0.7% adolescent females have anorexia nervosa, 5-10% of eating disorders occur in males. Anorexia nervosa associated
Paediatric Best Practice Guidelines Eating Disorders Background Relatively common 0.5-0.7% adolescent females have anorexia nervosa, 5-10% of eating disorders occur in males. Anorexia nervosa associated
How to use electrolytes correctly. Dr David Marlin
 How to use electrolytes correctly Dr David Marlin Why are many people scared of feeding electrolytes to horses? What is an electrolyte? Common name = Chemical name = Chemical formula = Salt Sodium Chloride
How to use electrolytes correctly Dr David Marlin Why are many people scared of feeding electrolytes to horses? What is an electrolyte? Common name = Chemical name = Chemical formula = Salt Sodium Chloride
THE AUTHOR OF THIS WHAT S NEW IN NUTRITION? OBJECTIVES & OUTLINE EVIDENCE-BASED MEDICINE: PARENTERAL NUTRITION (PN)
 WHAT S NEW IN NUTRITION? Alisha Mutch, Pharm.D., BCPS THE AUTHOR OF THIS PRESENTATION HAS NOTHING TO DISCLOSE. OBJECTIVES & OUTLINE MALNUTRITION OBJECTIVES Indicate when parenteral nutrition (PN) is warranted
WHAT S NEW IN NUTRITION? Alisha Mutch, Pharm.D., BCPS THE AUTHOR OF THIS PRESENTATION HAS NOTHING TO DISCLOSE. OBJECTIVES & OUTLINE MALNUTRITION OBJECTIVES Indicate when parenteral nutrition (PN) is warranted
Feeding the septic patient How and when? Masterclass ICU nurses
 Feeding the septic patient How and when? Masterclass ICU nurses Case Male, 60 - No PMH - L 1.74 m and W 85 kg Pneumococcal pneumonia Stable hemodynamics - No AKI MV in prone position (PEEP 16 - FiO2 60%)
Feeding the septic patient How and when? Masterclass ICU nurses Case Male, 60 - No PMH - L 1.74 m and W 85 kg Pneumococcal pneumonia Stable hemodynamics - No AKI MV in prone position (PEEP 16 - FiO2 60%)
Parenteral Nutrition in Oncology
 Parenteral Nutrition in Oncology Presenter: Pam Wagner, RD, CNSC Learning Objectives List indications for initiating PN in oncology patients Describe considerations when determining an appropriate candidate
Parenteral Nutrition in Oncology Presenter: Pam Wagner, RD, CNSC Learning Objectives List indications for initiating PN in oncology patients Describe considerations when determining an appropriate candidate
INTRAVENOUS FLUIDS PRINCIPLES
 INTRAVENOUS FLUIDS PRINCIPLES Postnatal physiological weight loss is approximately 5-10% Postnatal diuresis is delayed in Respiratory Distress Syndrome (RDS) Preterm babies have limited capacity to excrete
INTRAVENOUS FLUIDS PRINCIPLES Postnatal physiological weight loss is approximately 5-10% Postnatal diuresis is delayed in Respiratory Distress Syndrome (RDS) Preterm babies have limited capacity to excrete
Fluid therapy in children
 Fluid therapy in children TJ Neuhaus and G Reusz Lucerne and Budapest ESPN 2012 Kraków Parenteral maintenance in children Daily requirements - Holliday and Segar, 1957 Fluid Patient weight: 25 kg 1-10
Fluid therapy in children TJ Neuhaus and G Reusz Lucerne and Budapest ESPN 2012 Kraków Parenteral maintenance in children Daily requirements - Holliday and Segar, 1957 Fluid Patient weight: 25 kg 1-10
The History & Practice of IV Fluid Therapy have we advanced in 185 years?
 The History & Practice of IV Fluid Therapy have we advanced in 185 years? Liam Plant Clinical Professor of Renal Medicine University College Cork Consultant Renal Physician Cork University Hospital National
The History & Practice of IV Fluid Therapy have we advanced in 185 years? Liam Plant Clinical Professor of Renal Medicine University College Cork Consultant Renal Physician Cork University Hospital National
Electrolyte Disorders in ICU. Debashis Dhar
 Electrolyte Disorders in ICU Debashis Dhar INTRODUCTION Monovalent ions most important Na,K main cations and Cl &HCO - 3 main anions Mg,Ca & Phosphate are major divalent ions Normal Physiology Body tries
Electrolyte Disorders in ICU Debashis Dhar INTRODUCTION Monovalent ions most important Na,K main cations and Cl &HCO - 3 main anions Mg,Ca & Phosphate are major divalent ions Normal Physiology Body tries
Module 8: Practice Problems
 Module 8: Practice Problems 1. Convert a blood plasma level range of 5 to 20 µg/ml of tobramycin (Z = 467.52) to µmol/l. 5 µg/ml = 10.7 µmol/l 20 µg/ml = 42.8 µmol/l 2. A preparation contains in each milliliter,
Module 8: Practice Problems 1. Convert a blood plasma level range of 5 to 20 µg/ml of tobramycin (Z = 467.52) to µmol/l. 5 µg/ml = 10.7 µmol/l 20 µg/ml = 42.8 µmol/l 2. A preparation contains in each milliliter,
WATER, SODIUM AND POTASSIUM
 WATER, SODIUM AND POTASSIUM Attila Miseta Tamás Kőszegi Department of Laboratory Medicine, 2016 1 Average daily water intake and output of a normal adult 2 Approximate contributions to plasma osmolality
WATER, SODIUM AND POTASSIUM Attila Miseta Tamás Kőszegi Department of Laboratory Medicine, 2016 1 Average daily water intake and output of a normal adult 2 Approximate contributions to plasma osmolality
Index No: MMG11/1. Version: 1. Date ratified: 12 th November 2013
 Index No: Intravenous fluid prescription in children For previously well children aged one month to 16 years (excluding renal, cardiac, diabetic ketoacidosis and acute burns patients) Version: 1 Date ratified:
Index No: Intravenous fluid prescription in children For previously well children aged one month to 16 years (excluding renal, cardiac, diabetic ketoacidosis and acute burns patients) Version: 1 Date ratified:
Managing Acid Base and Electrolyte Disturbances with RRT
 Managing Acid Base and Electrolyte Disturbances with RRT John R Prowle MA MSc MD MRCP FFICM Consultant in Intensive Care & Renal Medicine RRT for Regulation of Acid-base and Electrolyte Acid base load
Managing Acid Base and Electrolyte Disturbances with RRT John R Prowle MA MSc MD MRCP FFICM Consultant in Intensive Care & Renal Medicine RRT for Regulation of Acid-base and Electrolyte Acid base load
Drug Shortages with Parenteral Nutrition
 Drug Shortages with Parenteral Nutrition Carol J Rollins, MS, RD, PharmD, BCNSP Coordinator, Nutrition Support Team The University of Arizona Medical Center www.nutritioncare.org Conflict of Interest None
Drug Shortages with Parenteral Nutrition Carol J Rollins, MS, RD, PharmD, BCNSP Coordinator, Nutrition Support Team The University of Arizona Medical Center www.nutritioncare.org Conflict of Interest None
DKA Adult ICU Powerplan
 DKA Adult ICU Powerplan Key Points for ED to ICU DKA power plan In addition to NS fluids and maintenance the regular insulin drip will either already be infusing from ED or needs to be initiated. Regular
DKA Adult ICU Powerplan Key Points for ED to ICU DKA power plan In addition to NS fluids and maintenance the regular insulin drip will either already be infusing from ED or needs to be initiated. Regular
Chapter 27: WATER, ELECTROLYTES, AND ACID-BASE BALANCE
 Chapter 27: WATER, ELECTROLYTES, AND ACID-BASE BALANCE I. RELATED TOPICS Integumentary system Cerebrospinal fluid Aqueous humor Digestive juices Feces Capillary dynamics Lymph circulation Edema Osmosis
Chapter 27: WATER, ELECTROLYTES, AND ACID-BASE BALANCE I. RELATED TOPICS Integumentary system Cerebrospinal fluid Aqueous humor Digestive juices Feces Capillary dynamics Lymph circulation Edema Osmosis
Biochemical parameters
 Biochemical parameters Urea The liver produces urea if amino acids break down. Urea production is bigger after a protein rich meal and when endogenous catabolism is increased (infections, internal bleedings,
Biochemical parameters Urea The liver produces urea if amino acids break down. Urea production is bigger after a protein rich meal and when endogenous catabolism is increased (infections, internal bleedings,
Nutrition. ICU Fellowship Training Radboudumc
 Nutrition ICU Fellowship Training Radboudumc Critical Care MCQ s Nasogastric (NG) and nasojejunal (NJ) feeding tubes: A. Enteral nutrition is associated with a reduced risk of bacterial and toxin translocation.
Nutrition ICU Fellowship Training Radboudumc Critical Care MCQ s Nasogastric (NG) and nasojejunal (NJ) feeding tubes: A. Enteral nutrition is associated with a reduced risk of bacterial and toxin translocation.
Using Balanced Fluids in Paediatrics: Implementing NICE Guidance without breaking the bank
 Using Balanced Fluids in Paediatrics: Implementing NICE Guidance without breaking the bank Adam Sutherland Senior Clinical Pharmacist, RMCH Clinical Lecturer, University of Manchester NIHR MClinRes Trainee,
Using Balanced Fluids in Paediatrics: Implementing NICE Guidance without breaking the bank Adam Sutherland Senior Clinical Pharmacist, RMCH Clinical Lecturer, University of Manchester NIHR MClinRes Trainee,
L.Mageswary Dietitian Hospital Selayang
 L.Mageswary Dietitian Hospital Selayang 14 15 AUG ASMIC 2015 Learning Objectives 1. To understand the importance of nutrition support in ICU 2. To know the right time to feed 3. To understand the indications
L.Mageswary Dietitian Hospital Selayang 14 15 AUG ASMIC 2015 Learning Objectives 1. To understand the importance of nutrition support in ICU 2. To know the right time to feed 3. To understand the indications
Guidelines for managing adults at risk of refeeding syndrome.
 Guidelines for managing adults at risk of refeeding syndrome. Version: V3.0 Ratified by: Out of Hospital Division Governance Meeting Clinical Nutrition Group Date ratified: 12 th January 2018 Name of author
Guidelines for managing adults at risk of refeeding syndrome. Version: V3.0 Ratified by: Out of Hospital Division Governance Meeting Clinical Nutrition Group Date ratified: 12 th January 2018 Name of author
PATIENTS PRESENTING WITH SUSPECTED OR CONFIRMED ANOREXIA NERVOSA
 Guideline for Treating Patients with Anorexia Nervosa when Admitted as a Medical Emergency Trust Reference E2/2012 PATIENTS PRESENTING WITH SUSPECTED OR CONFIRMED ANOREXIA NERVOSA AN CONFIRMED Inform Gastro
Guideline for Treating Patients with Anorexia Nervosa when Admitted as a Medical Emergency Trust Reference E2/2012 PATIENTS PRESENTING WITH SUSPECTED OR CONFIRMED ANOREXIA NERVOSA AN CONFIRMED Inform Gastro
Results Report. Welcome to Your ABT Report!
 Results Report Athlete Name: SHEPPARD, JOSEPH Date of Blood Draw: Feb 10, 2018 Panel: ABT Bronze Panel ABT Expert: Dr. Rock Welcome to Your ABT Report! Thank you for trusting AthleteBloodTest.com to be
Results Report Athlete Name: SHEPPARD, JOSEPH Date of Blood Draw: Feb 10, 2018 Panel: ABT Bronze Panel ABT Expert: Dr. Rock Welcome to Your ABT Report! Thank you for trusting AthleteBloodTest.com to be
Package leaflet: Information for the patient
 Package leaflet: Information for the patient KLORUR NATRIUMI Solution for injection 1000 mg / 10 ml (10 %) Solution for injection 85 mg / 10 ml (0.85 %) Solution for infusion 0.9% (Sodium chloride) Read
Package leaflet: Information for the patient KLORUR NATRIUMI Solution for injection 1000 mg / 10 ml (10 %) Solution for injection 85 mg / 10 ml (0.85 %) Solution for infusion 0.9% (Sodium chloride) Read
ICU NUTRITION UPDATE : ESPEN GUIDELINES Mirey Karavetian Assistant Professor Zayed University
 ICU NUTRITION UPDATE : ESPEN GUIDELINES 2018 Mirey Karavetian Assistant Professor Zayed University http://www.espen.org/files/espen- Guidelines/ESPEN_Guideline_on_clinical_nutrition_in_-ICU.pdf Medical
ICU NUTRITION UPDATE : ESPEN GUIDELINES 2018 Mirey Karavetian Assistant Professor Zayed University http://www.espen.org/files/espen- Guidelines/ESPEN_Guideline_on_clinical_nutrition_in_-ICU.pdf Medical
Emergency Department Chest Pain, Suspected Cardiac Adult Order Set
 Form Title Form Number Chest Pain, Suspected Cardiac Adult Order Set 20746 2018, Alberta Health Services, CKCM This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0
Form Title Form Number Chest Pain, Suspected Cardiac Adult Order Set 20746 2018, Alberta Health Services, CKCM This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0
Metabolic Control in Critical Care: Nutrition Therapy
 LOGO Metabolic Control in Critical Care: Nutrition Therapy ผศ.นพ.พรพจน เปรมโยธ น สาขาโภชนาการคล น ก ภาคว ชาอาย รศาสตร คณะแพทยศาสตร ศ ร ราชพยาบาล 2016 SCCM/ASPEN Guidelines Nutrition Therapy in the ICU
LOGO Metabolic Control in Critical Care: Nutrition Therapy ผศ.นพ.พรพจน เปรมโยธ น สาขาโภชนาการคล น ก ภาคว ชาอาย รศาสตร คณะแพทยศาสตร ศ ร ราชพยาบาล 2016 SCCM/ASPEN Guidelines Nutrition Therapy in the ICU
Introduction to Clinical Nutrition
 M-III Introduction to Clinical Nutrition Donald F. Kirby, MD Chief, Section of Nutrition Division of Gastroenterology 1 Things We Take for Granted Air to Breathe Death Taxes Another Admission Our Next
M-III Introduction to Clinical Nutrition Donald F. Kirby, MD Chief, Section of Nutrition Division of Gastroenterology 1 Things We Take for Granted Air to Breathe Death Taxes Another Admission Our Next
Title The Prescription of Adult Inpatient Parenteral Nutrition (PN) Guideline. Author s job title Consultant Gastroenterologist Directorate Medicine
 Document Control Title The Prescription of Adult Inpatient Parenteral Nutrition (PN) Guideline Author Author s job title Consultant Gastroenterologist Directorate Medicine Department Medicine Version Date
Document Control Title The Prescription of Adult Inpatient Parenteral Nutrition (PN) Guideline Author Author s job title Consultant Gastroenterologist Directorate Medicine Department Medicine Version Date
Principles of Fluid Balance
 Principles of Fluid Balance I. The Cellular Environment: Fluids and Electrolytes A. Water 1. Total body water (TBW) = 60% of total body weight 2. Fluid Compartments in the Body a. Intracellular Compartment
Principles of Fluid Balance I. The Cellular Environment: Fluids and Electrolytes A. Water 1. Total body water (TBW) = 60% of total body weight 2. Fluid Compartments in the Body a. Intracellular Compartment
By; Ashraf El Houfi MD MS (pulmonology) MRCP (UK) FRCP (London) EDIC Consultant ICU Dubai Hospital
 By; Ashraf El Houfi MD MS (pulmonology) MRCP (UK) FRCP (London) EDIC Consultant ICU Dubai Hospital Introduction The significance of nutrition in hospital setting (especially the ICU) cannot be overstated.
By; Ashraf El Houfi MD MS (pulmonology) MRCP (UK) FRCP (London) EDIC Consultant ICU Dubai Hospital Introduction The significance of nutrition in hospital setting (especially the ICU) cannot be overstated.
NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CLINICAL EXCELLENCE
 NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CLINICAL EXCELLENCE Centre for Clinical Practice SCOPE Clinical guideline title: Intravenous fluid therapy in adults in hospital Quality standard title: Intravenous fluid
NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CLINICAL EXCELLENCE Centre for Clinical Practice SCOPE Clinical guideline title: Intravenous fluid therapy in adults in hospital Quality standard title: Intravenous fluid
Physician Orders PEDIATRIC: LEB Eating Disorder Admit Plan
 Initiate Orders Phase Care Sets/Protocols/PowerPlans Initiate Powerplan Phase Phase: LEB Eating Disorder Admit Phase, When to Initiate: When patient arrives to unit LEB Eating Disorder Admit Phase Admission/Transfer/Discharge
Initiate Orders Phase Care Sets/Protocols/PowerPlans Initiate Powerplan Phase Phase: LEB Eating Disorder Admit Phase, When to Initiate: When patient arrives to unit LEB Eating Disorder Admit Phase Admission/Transfer/Discharge
Bleomycin, Etoposide and CISplatin (BEP) Therapy
 Bleomycin, Etoposide and CISplatin (BEP) Therapy INDICATIONS FOR USE: INDICATION ICD10 Regimen Code Adjuvant treatment of high risk (vascular invasion C62 00300a carcinoma) stage 1 nonseminoma germ cell
Bleomycin, Etoposide and CISplatin (BEP) Therapy INDICATIONS FOR USE: INDICATION ICD10 Regimen Code Adjuvant treatment of high risk (vascular invasion C62 00300a carcinoma) stage 1 nonseminoma germ cell
SUMMARY OF PRODUCT CHARACTERISTICS
 SUMMARY OF PRODUCT CHARACTERISTICS 1. NAME OF THE VETERINARY MEDICINAL PRODUCT Aqupharm 3 Solution for Infusion 2. QUALITATIVE AND QUANTITATIVE COMPOSITION Active ingredients Sodium Chloride Glucose Anhydrous
SUMMARY OF PRODUCT CHARACTERISTICS 1. NAME OF THE VETERINARY MEDICINAL PRODUCT Aqupharm 3 Solution for Infusion 2. QUALITATIVE AND QUANTITATIVE COMPOSITION Active ingredients Sodium Chloride Glucose Anhydrous
keyword: diuretics Drug monitoring Monitoring diuretics in primary care 2 March 2009 best tests
 www.bpac.org.nz keyword: diuretics Drug monitoring Monitoring diuretics in primary care 2 March 2009 best tests Why do we monitor patients taking diuretics and what do we monitor? Monitoring a person on
www.bpac.org.nz keyword: diuretics Drug monitoring Monitoring diuretics in primary care 2 March 2009 best tests Why do we monitor patients taking diuretics and what do we monitor? Monitoring a person on
A R T H U R R. H. V A N Z A N T E N, MD PHD I N T E R N I S T - I N T E N S I V I S T H O S P I T A L MEDICAL DIRECTOR G E L D E R S E V A L L E I
 FEEDING THE OBESE CRITICALLY ILL PATIENT A R T H U R R. H. V A N Z A N T E N, MD PHD I N T E R N I S T - I N T E N S I V I S T H O S P I T A L MEDICAL DIRECTOR G E L D E R S E V A L L E I HOSPITAL, EDE,
FEEDING THE OBESE CRITICALLY ILL PATIENT A R T H U R R. H. V A N Z A N T E N, MD PHD I N T E R N I S T - I N T E N S I V I S T H O S P I T A L MEDICAL DIRECTOR G E L D E R S E V A L L E I HOSPITAL, EDE,
Ernährungstherapie des Kritisch Kranken Enteral Parenteral Ganz egal?
 Ernährungstherapie des Kritisch Kranken Enteral Parenteral Ganz egal? PD Dr. med. Claudia Heidegger Service des Soins Intensifs Genf/Schweiz Dresden 11. Juni 2016 Nutrition News Nutrition controversy in
Ernährungstherapie des Kritisch Kranken Enteral Parenteral Ganz egal? PD Dr. med. Claudia Heidegger Service des Soins Intensifs Genf/Schweiz Dresden 11. Juni 2016 Nutrition News Nutrition controversy in
Nutrition care plan for surgical patients. Objectives
 Slide 1 Nutrition care plan for surgical patients Surgical Nutrition Training Module Level 1 Philippine Society of General Surgeons Committee on Surgical Training In this session we will discuss the most
Slide 1 Nutrition care plan for surgical patients Surgical Nutrition Training Module Level 1 Philippine Society of General Surgeons Committee on Surgical Training In this session we will discuss the most
Acute Stroke with Alteplase Administration Order Set
 Review Due Date: 2017 October PATIENT CARE DERS Weight: Adverse Reactions or Intolerances Drug No Yes (list) Food No Yes (list) _ Latex No Yes Admission Admit to Neurology service: Dr. Critical Care Diagnosis:
Review Due Date: 2017 October PATIENT CARE DERS Weight: Adverse Reactions or Intolerances Drug No Yes (list) Food No Yes (list) _ Latex No Yes Admission Admit to Neurology service: Dr. Critical Care Diagnosis:
