Refeeding Syndrom: Ein Update. Prof. Philipp Schuetz, Leitender Arzt Medizinische Uniklinik, Kantonsspital Aarau GESKES Kurs Aarau, April 14 th 2016
|
|
|
- Russell Quinn
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Refeeding Syndrom: Ein Update Prof. Philipp Schuetz, Leitender Arzt Medizinische Uniklinik, Kantonsspital Aarau GESKES Kurs Aarau, April 14 th Historical perspective First observed in survivors of the Conzentration Camps 1
2 Is there a Definition of the refeeding syndrome? Life-threatening condition characterised by low-serum electrolyte and vitamin concentrations fluid imbalance sodium-retention disturbance of organ function resulting from over-rapid or unbalanced refeeding of a malnourished catabolic patient NICE. Clin. Guidelines 2006 / Stanga Z. Eur J Clin Nutr 2008 Prevalence of refeeding syndrome 10% pat. with gastrointestinal fistulae Fan et al. Nutrition % elderly patients (age 65 y) Kagansky et al. J Intern Med % cancer patients Gonzalez et al. Nutr Hosp % malnourished patients Hernandez-Aranda et al. Rev Gastroenterol Mex % pat. affected by anorexia nervosa (n = 69, mean BMI 15 kg/m²) Ornstein. J Adolesc Health
3 % Patients Prevalence of refeeding syndrome 10% pat. with gastrointestinal fistulae Fan et al. Nutrition % elderly patients (age 65 y) Kagansky et al. J Intern Med % cancer patients Gonzalez et al. Nutr Hosp % malnourished patients Hernandez-Aranda et al. Rev Gastroenterol Mex % pat. affected by anorexia nervosa (n = 69, mean BMI 15 kg/m²) Ornstein. J Adolesc Health 2003 HYPOPHOSPHATAEMIA (nadir) 55% 98% Days after start refeeding Pathophysiologic aspects of the RFS Starvation or malnutrition catabolic state insulin glucagon Boateng AA et al. Nutrition
4 Pathophysiologic aspects of the RFS Starvation or malnutrition catabolic state insulin glucagon Gluconeogenesis, proteolysis loss of weight depletion of vitamin & mineral stores Boateng AA et al. Nutrition 2010 Pathophysiologic aspects of the RFS Starvation or malnutrition catabolic state Gluconeogenesis, proteolysis REFEEDING Glucose insulin glucagon loss of weight depletion of vitamin & mineral stores lipogenesis steatohepatitis thiamine Wernicke enc., met. acidosis hyperosmotic state neutrophil function Boateng AA et al. Nutrition
5 Pathophysiologic aspects of the RFS Starvation or malnutrition catabolic state Gluconeogenesis, proteolysis REFEEDING Glucose insulin glucagon loss of weight depletion of vitamin & mineral stores lipogenesis steatohepatitis thiamine Wernicke enc., met. acidosis hyperosmotic state neutrophil function Insulin Na ECV heart failure edema Boateng AA et al. Nutrition 2010 Pathophysiologic aspects of the RFS Starvation or malnutrition catabolic state Gluconeogenesis, proteolysis REFEEDING Glucose insulin glucagon loss of weight depletion of vitamin & mineral stores lipogenesis steatohepatitis thiamine Wernicke enc., met. acidosis hyperosmotic state neutrophil function Insulin Na ECV heart failure edema Transcellular shifts of Glucose, PO 4, K, Mg Mg, K, PO 4 spasms tetany arrhythmias Boateng AA et al. Nutrition
6 Pathophysiologic aspects of the RFS PO 4 ATP RBC ATP, 2.3-DPG hemolysis anemia O 2 -delivery ischemia, hyperventilation central nervous, gastrontestinal system system respiratory alkalosis weakness tremor ataxia paralysis delirium, coma loss of appetite constipation Boateng AA et al. Nutrition 2010 Pathophysiologic aspects of the RFS PO 4 ATP RBC ATP, 2.3-DPG muscle weakness myalgia dyspnea rhabdomyolysis acute tubular necrosis hemolysis anemia O 2 -delivery ischemia, hyperventilation central nervous, gastrontestinal system system weakness tremor ataxia paralysis delirium, coma loss of appetite constipation respiratory alkalosis Boateng AA et al. Nutrition
7 Pathophysiologic aspects of the RFS PO 4 ATP RBC ATP, 2.3-DPG muscle weakness myalgia dyspnea rhabdomyolysis acute tubular necrosis anemia hemolysis O 2 -delivery ischemia, hyperventilation central nervous, gastrontestinal system system weakness tremor ataxia paralysis delirium, coma anorexia constipation respiratory alkalosis Boateng AA et al. Nutrition 2010 Criteria for determination of patients at risk of RFS ONE OF THE FOLLOWING BMI < 16 kg/m2 Unintentional weight loss > 15% in the preceding 3-6 months Very little or no nutritional intake for > 10 days Low levels of serum magnesium, phosphate or potassium prior to feed TWO OF THE FOLLOWING BMI < 18.5 kg/m2 Unintentional weight loss > 10% in the preceding 3-6 months Very little or no nutritional intake for > 5 days History of alcool or drug abuse NICE. Clinical Guidelines 2006 / Stanga Z et al. EJCN
8 Criteria for determination of patients at risk of RFS ONE OF THE FOLLOWING BMI < 16 kg/m2 Unintentional weight loss > 15% in the preceding 3-6 months Very little or no nutritional intake for > 10 days Low levels of serum magnesium, phosphate or potassium prior to feed TWO OF THE FOLLOWING BMI < 18.5 kg/m2 Unintentional weight loss > 10% in the preceding 3-6 months Very little or no nutritional intake for > 5 days History of alcool or drug abuse FURTHER PATIENTS AT RISK Hungerstrike, anorexia nervosa After bariatric surgery, short bowel syndrome Oncology patients and fraily elderly NICE. Clinical Guidelines 2006 / Stanga Z et al. EJCN 2007 Criteria for confirmation RFS Severly low electrolytes PO 4 < 0.32 mmol/l K < 2.5 mmol/l Mg < 0.5 mmol/l Fluid overload Peripheral oedema or acute circulatory fluid overload REFEEDING SYNDROME Disturbance to organ function respiratory failure, cardiac failure or pulmonary oedema Rio A et al. BMJ Open 2013 / Crook MA et al. Nutrition
9 General recommendations for management of RFS NICE. Clinical Guidelines 2006 / Stanga Z et al. EJCN 2007 General recommendations for management of RFS NICE. Clinical Guidelines 2006 / Stanga Z et al. EJCN
10 General recommendations for management of RFS NICE. Clinical Guidelines 2006 / Stanga Z et al. EJCN 2007 General recommendations for management of RFS NICE. Clinical Guidelines 2006 / Stanga Z et al. EJCN
11 General recommendations for management of RFS NICE. Clinical Guidelines 2006 / Stanga Z et al. EJCN 2007 General recommendations for management of RFS MEASURES DAYS 1-3 Energy Electrolytes Fluid Micronutrients Biochemistry Clinical exam kcal/kg/d (50-60% carbohydrates, 30-40% fat and 15-20% protein) Prophylactic supplementation Phosphate mmol/kg/d Potassium mmol/kg/d Magnesium mmol/kg/d ml/kg/d, sodium restriction <1 mmol/kg/d mg thiamine IV or PO before feeding is initiated, afterward daily Vitamines 200% DRI Trace elements 100% DRI PO 4, K, Mg, Glucose, Ca, Na daily BP, P, O-sat., hydration state, cardiopulmonary, weight NICE. Clinical Guidelines 2006 / Stanga Z et al. EJCN
12 General recommendations for management of RFS MEASURES DAYS 4-6 and DAYS 7-10 Energy Electrolytes Fluid Micronutrients Biochemistry Clinical exam kcal/kg/d, from day 7: kcal/kg/d (50-60% carbohydrates, 30-40% fat and 15-20% protein) Suppl. according to plasma concentrations Phosphate <0.6 mmol/l mmol over 12 h Potassium <3.5 mmol/l mmol over 12 h Magnesium <0.5 mmol/l 2-4 g MgSO 4 over 12 h ml/kg/d, from day 7: 30 ml/kg/d Vitamines 200% DRI, Trace elements 100% DRI PO 4, K, Mg, 2x/wk, afterward 1x/wk hydration state, cardiopulmonary, weight NICE. Clinical Guidelines 2006 / Stanga Z et al. EJCN 2007 Reference Energy Protein Electrolytes Fluids Micronutrients Solomon & Kirby JPEN 1990 Dewar & Horvath A Guide to Clinical Nutrition 2001 Crook et al. Nutrition 2001 Kraft et al. Nutr Clin Pract 2005 NICE Guidelines 2006 Stanga et al. Eur J Clin Nutr kcal/kg g _ 20 kcal/kg _ Replenish as required _ Thiamine IV or PO for 2 d 20 kcal/kg g Replenish as required _ Thiamine IV or PO for 2 d 25% of requirements 10 kcal/kg, high risk: 5 kcal/kg 10 kcal/kg 50-60% KH 30-40% fat mmol PO 4 pro 1000 kcal Replenish as required KCl: 2-4 mmol/kg Mg: mmol/kg PO 4 : mmol/kg 10-20% KCl: 1-3 mmol/kg Mg: mmol/kg PO 4 : mmol/kg Na: <1 mmol/kg <1l/d Thiamine mg IV or 100 mg PO 5-7 d & multivitamin 0 fluid balance 20-30ml/kg /d, 0 fluid balance mg Thiamine PO for 10 d & multivitamin mg Thiamine IV or PO for 3 d & multivitamin 12
13 Reference Energy Protein Electrolytes Fluids Micronutrients Solomon & Kirby JPEN 1990 Dewar & Horvath A Guide to Clinical Nutrition 2001 Crook et al. Nutrition 2001 Kraft et al. Nutr Clin Pract 2005 NICE Guidelines 2006 Stanga et al. Eur J Clin Nutr kcal/kg g _ 20 kcal/kg _ Replenish as required _ Thiamine IV or PO for 2 d 20 kcal/kg g Replenish as required _ Thiamine IV or PO for 2 d 25% of requirements 10 kcal/kg, high risk: 5 kcal/kg 10 kcal/kg 50-60% KH 30-40% fat mmol PO 4 pro 1000 kcal Replenish as required KCl: 2-4 mmol/kg Mg: mmol/kg PO 4 : mmol/kg 10-20% KCl: 1-3 mmol/kg Mg: mmol/kg PO 4 : mmol/kg Na: <1 mmol/kg <1l/d Thiamine mg IV or 100 mg PO 5-7 d & multivitamin 0 fluid balance 20-30ml/kg /d, 0 fluid balance mg Thiamine PO for 10 d & multivitamin mg Thiamine IV or PO for 3 d & multivitamin but what is the evidence? 13
14 Systematic review on RFS (2015, Natalie Friedli) Research Questions: I. What are definitions used for refeeding syndrome? II. How high is the incidence of refeeding syndrome? III. When did refeeding syndrome occur? IV. Does refeeding syndrome correlate with adverse outcome? V. What are risk factors for refeeding syndrome? VI. What are therapeutic strategies to prevent refeeding syndrome? Systematic review on RFS (2015, Natalie Friedli) 14
15 Definitions for RFS Author Y N= Def. RFS M arik, P. E., et al drop of PO4 by > 0.16mmol/l to below 0.65mmol/l Gaudiani L., et al Hypophosphatemia Gaudiani L., et al Hypophosphatemia <2.7mg/dl (0.87mmol/l) Heimburger, D.C., et Hypophosphatemia and clinical symptoms al. Nagata, J.M., et al Phosphorus < 3mg/dl Coskun, R., et al PO4 2.4 mg/l (0.77 mmol/l) Zeki, S., Clukin A., et PO4 < 0.6mmol/l al. Kagansky, N. et al PO4 <0.77mmol/l M arvin, V., et al PO4 drop of 0.15mmol/l to <0.80mmol/l from baseline in the first 7d of PN in patients with a period of > 48h without food. Terlevich, A., et al PO4 of < 0.50 mmol/l Lubart, E., et al PO4<1.6mg/dl (0.51mmol/l) Gonzalez Avila, G., et PO4<2.5 mg/dl (=0.8mmol/l) al. Goyale, A., et al a PO4 drop of >30%during the Refeeding hypophosphatemia = first 36h of PN administration. Whitelaw, M., et al severe electrolyte and fluid shifts in response to refeeding Luque, S., et al severe hydroelectro-lytic and metabolic disturbances Leclerc, A., et al Shift in fluid and electrolytes Garber A.K., et al Shifts in electrolytes Vignaud, M., et al all adverse events occuring during nutritional rehabilitation Hernandez-Aranda, J.C., et al any drop of electrolyte values under the reference range. M anning, S., et al Changes in fluid and electrolyte balance Grasso, S., et al electorlyte disorders Flesher, M.E., et al Electrolyte depletion associated with complications in early enteral feeding Gentile, M.G., et al ) Salt / water retention. 2) HP 3) Depletion of other electrolytes like K and M g and vitamins as B1, B6, etc. 4) Depletion of the thiamine co-factor of glycolysis. (M arinella, et. al / Solomon et al.) Hofer, M., et al Rio A, Whelan K, Goff L, et al K <2.5, PO4 <0.32, M g <0.5 mmol/l 2. Peripheral oedema or acute circulatory fluid overload 3. Disturbance to organ function including espiratory failure, cardiac failure and pulmonary oedema. Saito, S., T. Kobayashi, and S. Kato cardiovascular, repsiratory, neurological or psychological changes with Hypophosphatemia Elnenaei, M.O., et al Clinical features Chen Li-Ju, Chen Huan-Lin, et al Electrolyte shift and clinical symptoms Eichelberger, M., et al imbalances of electrolyte and fluid homeostasis, and organ dysfunction Faintuch, J., et al Relevant Electrolyte disturbances and clinical symptoms Herranz A., et al severe HP, hypok, hypom g, associated edema, and impaired carbohydrate metabolism Fan, C.G., et al symptoms and signs of electrolyte disturbances. - Hypophosphatämie - Elektrolytverschiebungen - Klinische Symptome Incidence rates for RFS Author Y N= Pat. Kollektiv Def. RFS Inzidenz 1. K <2.5, PO4 <0.32, M g <0.5 mmol/l 2. Peripheral oedema or acute circulatory fluid overload 3. Disturbance to organ function including Hofer, M patients under refeeding 0% AN espiratory failure, cardiac failure and pulmonary oedema. 1) Salt / water retention. 2) HP 3) Depletion of other electrolytes like K and M g and vitamins as B1, B6, etc. 4) Depletion of the thiamine co-factor Gentile, M.G Very severe AN in-patients 0% of glycolysis. Adolescents with AN between 12-18yrs, hospitalized fort he first Leclerc, A Shift in fluid and electrolytes 0% time for nutritional rehabilitation Elnenaei, M.O patients referred for commencement of PN Clinical features 0% Faintuch, J hungerstrikers who refuesed food for 43 days Relevant Electrolyte disturbances and clinical symptoms 0% Herranz A In patients receiving PN severe HP, hypok, hypom g, associated edema, and impaired carbohydrate metabolism after the start of NS with PN. 0% Luque, S adult patients with malnutrition receiving PN severe hydroelectro-lytic and metabolic disturbances 0% M anning, S alcoholics hospitalised for withdrawal Changes in fluid and electrolyte balance 0% Heimburger, D.C HIV infected patients Hypophosphatemia and clinical symptoms 0.70% 1. K <2.5, PO4 <0.32, M g <0.5 mmol/l 2. Peripheral oedema or acute circulatory fluid overload 3. Disturbance to organ function including Rio A, Whelan K, Goff Adults started on artificial nutrition support 2% L espiratory failure, cardiac failure and pulmonary oedema. Eichelberger, M Patients on a hungerstrike imbalances of electrolyte and fluid homeostasis, and organ dysfunction 3% Fan, C.G Patients with gastrointestinal fistula symptoms and signs of electrolyte disturbances 9.40% Vignaud, M Patients with AN all adverse events occuring during nutritional rehabilitation 10% Zeki, S., Clukin A Patients receiving PN or EN, not ICU PO4 < 0.6mmol/l 15% Chen Li-Ju, Chen Huan-Lin high risk for RFS according to NICE Electrolyte shift and clinical symptoms 20% people at guidelines. Gonzalez Avila, G Cancer patients receiving EN or PN PO4<2.5 mg/dl (=0.8mmol/l) 24.50% Lubart, E Frail elderly patients with feeding problems >72h PO4<1.6mg/dl (0.51mmol/l) 25% M arik, P. E ICU patients starved for at least 48h drop of PO4 by > 0.16mmol/l to below 0.65mmol/l 34% M arvin, V Adults on PN PO4 drop of 0.15mmol/l to <0.80mmol/l from baseline in the first 7d 34% Gaudiani L Adults with AN Hypophosphatemia 37% Gaudiani L AN patients hospitalized for refeeding Hypophosphatemia <2.7mg/dl (0.87mmol/l) 45% Saito, S Eating disorders patients hospitalized on a psychiatric ward cardiovascular, repsiratory, neurological or psychological changes with HP during RF 45% Coskun, R patients admitted to ICU and receiving either EN or PN PO4 2.4 mg/l (0.77 mmol/l) 52.14% Goyale, A patients referred for PN PO4 drop of >30%during the first 36h of PN administration. 62% Hernandez-Aranda, J.C with EN/PN screened. All with mild and severe malnutrition were included, they received PN or EN support for >7d any drop of electrolyte values under the reference range. 48% Flesher, M.E M alnourished patients on enteral feeding protocol Electrolyte depletion associated with complications in early enteral feeding 80% % falls klinische Symptome nötig % falls Hypophosphatämie Diagnosekriterium - Bis 80% nicht näher definierte Elektrolytverschiebung 15
16 Time course of appearance of RFS Author Y Title N= Def. RFS Occurence of RFS Gaudiani L., et al Severe Anorexia Nervosa: Outcomes from a M edical Stabilization Unit 25 Hypophosphatemia <2.7mg/dl (0.87mmol/l) 3.4 days Raj, K.S., et al Hypomagnesemia in adolescents with eating disorders hospitalized for medical instability 541 metabolic and clinical changes 4.9 +/- 5.5 days Fan, C.G., et al Refeeding Syndrome in Patients With Gastrointestinal Fistula 15 symptoms and signs of electrolyte disturbances. within 24h Gonzalez Avila, G., et al The incidence of the RFS in cancer patients who receive artificial nutritional treatment 106 PO4<2.5 mg/dl (=0.8mmol/l) Within 72h Hernandez-Aranda, J.C., et al M alnutrition and total parenteral nutrition: a cohort study to determine the incidence of refeeding syndrome 50 any drop of electrolyte values under the reference range. 55%at the third day Kagansky, N. et al Hypophosphatemia in old patients is associated with the RFS and reduced survival 651 HP <0.77mmol/l detected on 10.9+/- 21.5days of hospitalisastion Lubart, E., et al M ortality after Nastogastric Tube Feeding initiation in Long-Term Care Elderly with Oropharyngeal Dysphagia - The Contribution of RFS 40 PO4<1.6mg/dl (0.51mmol/l) 2nd and 3rd day M arik, P. E., et al Refeeding hypophosphatemia in Critically Ill Patients in an ICU 62 drop of PO4 by > 0.16mmol/l to below 0.65mmol/l 1.9 +/- 1.1 days M arvin, V., et al Incidence of hypophosphataemia in patients on PN 250 PO4 drop of 0.15mmol/l to <0.80mmol/l from baseline in the first 7d 3 days - Wenige Daten - Im Bereich der ersten 72h - Einzelne auch erst nach >10d. Correlation with adverse outcome? Author Year n= Population Mortality rate Other adverse outcome Vignaud, M., et al Patients with AN admitted to ICU 71% Hernandez-Aranda, J.C., et al Patiens receiving PN/EN and mild or severe malnutrition 29%(p=0.059). Longer LOS Lubart, E., et al Frail elderly patients with feeding problems >72h RFS as the cause of death in 6% Heimburger, D.C., et al HIV infected patients lower survival probability at 12 weeks Kagansky, N. et al Patients having HP compared with patients not having HP threefold increased mortality rates, but not an independent predictor for mortality Longer LOS Rio A, Whelan K, Goff L, et al Adults started on artificial nutrition support 0% Eichelberger, M., et al Patients on a hungerstrike 0% Goyale, A., et al Patients referred for PN when EN was contraindicated No correlation between death and RH Zeki, S., Clukin A., et al Patients receiving PN or EN, not ICU Death within 7 days and RH were not associated Coskun, R., et al Patients admitted to ICU and receiving either PN or EN ICU LOS longer M arik, P. E., et al ICU patients starved for at least 48h Longer LOS - Erhöhte Mortalität in einigen Studien - Keine Korrelation in anderen - Stark abhängig vom Patientenkollektiv - Schlechte Datenlage 16
17 Risk factors for RFS? Risk factor Numbers of studies using this Risk factor NICE 6 Poor caloric intake 6 Weight loss 3 Malnourished patients 3 Nasogastric feeding 3 No risk factors 3 Age >60yrs 2 Low prealbumin levels 2 Nutrition support introduced at full strength 2 Alcohol abuse 1 High NRS 1 Hypoalbuminaemia 1 Low serum magnesium level at baseline 1 IGF-1 <63.7ug/l 1 Cancer patients 1 Patients with GI-fistula 1 NICE criteria for identifying patients at high risk of refeeding problems (level D recommendations*) - Either the patient has one or more of the following: - BMI <16kg/m2 - Unintentional weight loss >15% in the past 3-6m - Little or no nutritional intake for >10 d - Low levels of K, PO4, or Mg before feeding. - Or the patient has two or more of the following: - BMI < Unintentional weight loss >10% in the past 3 6 m - Little or no nutritional intake for >5 d - History of alcohol misuse or drugs, including insulin, chemotherapy, antacids, or diuretics - NICE Empfehlungen scheinen zutreffend zu sein, ggf. müssen sie ergänzt werden. Therapeutic strategies for RFS Normokalorisch vs hypokalorische Ernährung Prophylaktische Elektrolytsubstitution und Gabe von Thiamin vs. keine Substitution - Pro und Kontra ausgeglichen! 17
18 NEW Randomized Trial in RFS (ICU) 13 hospital ICUs in Australia (11 sites) and New Zealand (two sites). 339 adult critically ill patients who developed refeeding syndrome within 72 h of commencing nutritional support in the ICU were enrolled Definition: serum phosphate concentration decreased to below 0.65 mmol 18
19 19
20 Nutritional reguirements / goals Schuetz P, Stanga Z, Keller U, Kondrup J, et al, Consensus guidelines for treatment of malnourished medical in patients (submitted) FelderS, Schuetz P, Schweiz Med Forum 2014;14(24):
21 Nutritional reguirements / goals 21
22 Hypokalaemia Hypomagnesaemia Hypophosphataemia Thiamine deficiency Salt & water retention Starvation or malnutrition Gluconeogenesis, glycogenolysis & protein catabolism K + Mg 2+ PO 4 2- REFEEDING SYNDROME Depletion of mineral and vitamin stores glucose uptake utilization of thiamine Glucose major energy source protein synthesis Na + retention ECV Insulin secretion Stanga Z. Eur J Clin Nutr 2008 Pending questions To date only low quality evidence exists... Too cautious energy step up? so far conflicting statements possible start feeding with 20 kcal/kg/d in hospital? Buildup of full food intake within 3-4 days? reduction of the catabolic phase Do we have to give electrolytes in a prophylactic way? prevention is better than cure Reliable predictors? How important is the clinical examination? 22
MANAGEMENT AND PREVENTION OF REFEEDING SYNDROME IN INPATIENTS: A PRACTICAL APPROACH
 MANAGEMENT AND PREVENTION OF REFEEDING SYNDROME IN INPATIENTS: A PRACTICAL APPROACH Prof. Zeno Stanga, MD Nutritional Medicine Department of Diabetes, Endocrinology, Nutritional Medicine and Metabolism
MANAGEMENT AND PREVENTION OF REFEEDING SYNDROME IN INPATIENTS: A PRACTICAL APPROACH Prof. Zeno Stanga, MD Nutritional Medicine Department of Diabetes, Endocrinology, Nutritional Medicine and Metabolism
Refeeding syndrome a practical approach
 Refeeding syndrome a practical approach PENG pre-bapen Conference Teaching Day Birmingham Monday 20 th November 2017 Rhys White Acting Clinical and Operational Lead Dietitian Guys and St Thomas NHS Foundation
Refeeding syndrome a practical approach PENG pre-bapen Conference Teaching Day Birmingham Monday 20 th November 2017 Rhys White Acting Clinical and Operational Lead Dietitian Guys and St Thomas NHS Foundation
THE PATHOPHYSIOLOGY OF THE REFEEDING SYNDROME
 THE PATHOPHYSIOLOGY OF THE REFEEDING SYNDROME Zeno Stanga, MD Division of Endocrinology, Diabetes and Clinical Nutrition Division of General Internal Medicine Minnesota Experiment Aim To guide the Allied
THE PATHOPHYSIOLOGY OF THE REFEEDING SYNDROME Zeno Stanga, MD Division of Endocrinology, Diabetes and Clinical Nutrition Division of General Internal Medicine Minnesota Experiment Aim To guide the Allied
Prevention of Electrolyte Disorders Refeeding Syndrome พญ.น นทพร เต มพรเล ศ
 Prevention of Electrolyte Disorders Refeeding Syndrome พญ.น นทพร เต มพรเล ศ Outline Refeeding Syndrome What is refeeding syndrome? What Electrolytes and minerals are involved? Who is at risk? How to manage
Prevention of Electrolyte Disorders Refeeding Syndrome พญ.น นทพร เต มพรเล ศ Outline Refeeding Syndrome What is refeeding syndrome? What Electrolytes and minerals are involved? Who is at risk? How to manage
Acute management of severe malnutrition. Dr Simon Gabe St Mark s Hospital, London
 Acute management of severe malnutrition Dr Simon Gabe St Mark s Hospital, London Malnutrition definition A state resulting from lack of uptake or intake of nutrition leading to altered body composition
Acute management of severe malnutrition Dr Simon Gabe St Mark s Hospital, London Malnutrition definition A state resulting from lack of uptake or intake of nutrition leading to altered body composition
Dutch consensus statement on Refeeding syndrome
 Dutch consensus statement on Refeeding syndrome Introduction Disease related malnutrition is a common problem in health care. The refeeding syndrome is defined as the severe and potentially fatal shifts
Dutch consensus statement on Refeeding syndrome Introduction Disease related malnutrition is a common problem in health care. The refeeding syndrome is defined as the severe and potentially fatal shifts
ESPEN Congress Geneva 2014 NUTRITION AT EXTREMES: THE UNLIKELY BENEFITS OF STARVATION
 ESPEN Congress Geneva 2014 NUTRITION AT EXTREMES: THE UNLIKELY BENEFITS OF STARVATION Management of the severely malnourished: the case of anorexia nervosa C. De la Cuerda (ES) Management of the severely
ESPEN Congress Geneva 2014 NUTRITION AT EXTREMES: THE UNLIKELY BENEFITS OF STARVATION Management of the severely malnourished: the case of anorexia nervosa C. De la Cuerda (ES) Management of the severely
Refeeding syndrome: An overlooked condition?
 Focused Review Refeeding syndrome: An overlooked condition? Yuttiwat Vorakunthada MD, Passisd Laoveeravat MD, Wasawat Vutthikraivit MD, Weerapong Lilitwat MD, FAAP, Ariwan Rakvit MD, FACG Abstract Refeeding
Focused Review Refeeding syndrome: An overlooked condition? Yuttiwat Vorakunthada MD, Passisd Laoveeravat MD, Wasawat Vutthikraivit MD, Weerapong Lilitwat MD, FAAP, Ariwan Rakvit MD, FACG Abstract Refeeding
Financial Interest Disclosure (over the past 24 months)
 : Across the Spectrum of Primary care Jan Greenwood, R.D. Nutrition Support Consultant The Basic Five Programs The opinions expressed in this presentation are that of the presenter and do not necessarily
: Across the Spectrum of Primary care Jan Greenwood, R.D. Nutrition Support Consultant The Basic Five Programs The opinions expressed in this presentation are that of the presenter and do not necessarily
Refeeding Low Weight Adolescents with AN
 RCPsych ED 2013 Refeeding Low Weight Adolescents with AN Graeme O Connor RD PhD Research Student -UCL Specialist paediatric Dietitian Great Ormond Street Hospital Foundation Trust Pathophysiology of starvation
RCPsych ED 2013 Refeeding Low Weight Adolescents with AN Graeme O Connor RD PhD Research Student -UCL Specialist paediatric Dietitian Great Ormond Street Hospital Foundation Trust Pathophysiology of starvation
Adaptation and re-feeding Hypokalemia Bone complications
 Adaptation and re-feeding Hypokalemia Bone complications René Klinkby Støving Odense University Hospital Denmark 10% 20% 30% 40% BMI 18.5 BMI 16.5 BMI 14.5 BMI 12.5 Willmore DW, The Metabolic Management
Adaptation and re-feeding Hypokalemia Bone complications René Klinkby Støving Odense University Hospital Denmark 10% 20% 30% 40% BMI 18.5 BMI 16.5 BMI 14.5 BMI 12.5 Willmore DW, The Metabolic Management
Case Study: Nutritional management of a patient at high risk of developing refeeding syndrome
 Case Study: Nutritional management of a patient at high risk of developing refeeding syndrome Dolman RC, PhD, Senior Lecturer; Conradie C, MSc, Lecturer Lombard MJ, PhD, Senior Lecturer; Nienaber A, MSc,
Case Study: Nutritional management of a patient at high risk of developing refeeding syndrome Dolman RC, PhD, Senior Lecturer; Conradie C, MSc, Lecturer Lombard MJ, PhD, Senior Lecturer; Nienaber A, MSc,
Formulary and Prescribing Guidelines
 Formulary and Prescribing Guidelines SECTION 15: TREATMENT OF EATING DISORDERS 15.1 Introduction Please review the Trust document Guidelines for the assessment and treatment of eating disorders in the
Formulary and Prescribing Guidelines SECTION 15: TREATMENT OF EATING DISORDERS 15.1 Introduction Please review the Trust document Guidelines for the assessment and treatment of eating disorders in the
Class 3: Refeeding Syndrome. Liz Hudson MPH, RD
 Class 3: Refeeding Syndrome Liz Hudson MPH, RD Case Study #1 NUTRITION ASSESSMENT: Consult PATIENT MEDICAL/HEALTH HISTORY: 49 y/o male with significant history of HTN, DM, and stage V CKD currently on
Class 3: Refeeding Syndrome Liz Hudson MPH, RD Case Study #1 NUTRITION ASSESSMENT: Consult PATIENT MEDICAL/HEALTH HISTORY: 49 y/o male with significant history of HTN, DM, and stage V CKD currently on
GUIDANCE NOTES. DIETETIC RISK ASSESSMENT FOR REFEEDING RECOMMENDED MEAL PLANS When commencing re-feeding: NICE (2006)
 When commencing re-feeding: NICE (2006) NICE (2006) Clinical Guideline 32 Nutrition support in adults: oral nutrition support, enteral tube feeding and parenteral nutrition (The following is based on www.nice.org.uk/cg032
When commencing re-feeding: NICE (2006) NICE (2006) Clinical Guideline 32 Nutrition support in adults: oral nutrition support, enteral tube feeding and parenteral nutrition (The following is based on www.nice.org.uk/cg032
6-7 JULY 2015, BIRMINGHAM CONGRESS
 6-7 JULY 2015, BIRMINGHAM CONGRESS Keywords: /Malnutrition/ Enteral feeding/critical illness This article has been double-blind peer reviewed Patients who are critically ill are at greater risk of malnutrition
6-7 JULY 2015, BIRMINGHAM CONGRESS Keywords: /Malnutrition/ Enteral feeding/critical illness This article has been double-blind peer reviewed Patients who are critically ill are at greater risk of malnutrition
Refeeding Syndrome Guideline
 Refeeding Syndrome Guideline Author: Responsible Lead Executive Director: Endorsing Body: Governance or Assurance Committee Pamela Miller Biochemistry Implementation Date: January 2017 Version Number:
Refeeding Syndrome Guideline Author: Responsible Lead Executive Director: Endorsing Body: Governance or Assurance Committee Pamela Miller Biochemistry Implementation Date: January 2017 Version Number:
List of Topics and Modules (2012)
 List of Topics and Modules (202) Code Title Credits for Live course Topic 0 Introduction to Clinical Nutrition EDU T0 M 0. Introduction to clinical nutrition support Topic Metabolism of Metabolism of Macronutrients,
List of Topics and Modules (202) Code Title Credits for Live course Topic 0 Introduction to Clinical Nutrition EDU T0 M 0. Introduction to clinical nutrition support Topic Metabolism of Metabolism of Macronutrients,
Refeeding Syndrome: An Important Complication Following Obesity Surgery
 Received: July 27, 2015 Accepted: October 28, 2015 Published online: January 9, 2016 2016 The Author(s) Published by S. Karger GmbH, Freiburg 1662 4033/15/0091 0012$39.50/0 This article is licensed under
Received: July 27, 2015 Accepted: October 28, 2015 Published online: January 9, 2016 2016 The Author(s) Published by S. Karger GmbH, Freiburg 1662 4033/15/0091 0012$39.50/0 This article is licensed under
ESPEN LLL Programme in Clinical Nutrition and Metabolism. List of Topics and Modules 2014
 ESPEN LLL Programme in Clinical Nutrition and Metabolism List of Topics and Modules 204 Code Title Credits for Live course Credits for on-line course Credits for Grading Quiz Topic 0 Introduction in Nutrition
ESPEN LLL Programme in Clinical Nutrition and Metabolism List of Topics and Modules 204 Code Title Credits for Live course Credits for on-line course Credits for Grading Quiz Topic 0 Introduction in Nutrition
Intensive Care Nutrition. Dr Alan Race BSc(Hons) PhD FRCA
 Intensive Care Nutrition Dr Alan Race BSc(Hons) PhD FRCA Objectives 1. What examiners say 2. Definition 3. Assessment 4. Requirements 5. Types of delivery 6. CALORIES Trial 7. Timing 8. Immunomodulation
Intensive Care Nutrition Dr Alan Race BSc(Hons) PhD FRCA Objectives 1. What examiners say 2. Definition 3. Assessment 4. Requirements 5. Types of delivery 6. CALORIES Trial 7. Timing 8. Immunomodulation
Refeeding syndrome as treatment complication of anorexia nervosa
 Psychiatr. Pol. ONLINE FIRST Nr 110: 1 11 Published ahead of print 30 September 2018 www.psychiatriapolska.pl ISSN 0033-2674 (PRINT), ISSN 2391-5854 (ONLINE) DOI: https://doi.org/10.12740/pp/onlinefirst/90275
Psychiatr. Pol. ONLINE FIRST Nr 110: 1 11 Published ahead of print 30 September 2018 www.psychiatriapolska.pl ISSN 0033-2674 (PRINT), ISSN 2391-5854 (ONLINE) DOI: https://doi.org/10.12740/pp/onlinefirst/90275
Does the patient need an enteral feed out of hours?
 Out of hours Enteral tube feeding (Nasogastric) Starter Regimen for an Adult Inpatient With Renal Failure (Including management of re-feeding syndrome) Guidance for Practice 1. Introduction 1.1 This clinical
Out of hours Enteral tube feeding (Nasogastric) Starter Regimen for an Adult Inpatient With Renal Failure (Including management of re-feeding syndrome) Guidance for Practice 1. Introduction 1.1 This clinical
, 吳文傑. Refeeding syndrome (RFS) is a well described but often forgotten condition,
 中文題目 : 再餵食症候群 - 病例報告 英文題目 : Refeeding syndrome in a patient with suspected MEN-I syndrome: a case report 作者 : 楊光祖 1, 沈曉津 2, 廖麗瑛 3 3*, 吳文傑 1 服務單位 : 臺北市立聯合醫院仁愛院區內科部臺北市立聯合醫院仁愛院區教學 2 研究部臺北市立聯合醫院仁愛院區消化內科 Introduction
中文題目 : 再餵食症候群 - 病例報告 英文題目 : Refeeding syndrome in a patient with suspected MEN-I syndrome: a case report 作者 : 楊光祖 1, 沈曉津 2, 廖麗瑛 3 3*, 吳文傑 1 服務單位 : 臺北市立聯合醫院仁愛院區內科部臺北市立聯合醫院仁愛院區教學 2 研究部臺北市立聯合醫院仁愛院區消化內科 Introduction
Predicting refeeding hypophosphataemia: insulin growth factor 1 (IGF-1) as a diagnostic biochemical marker for clinical practice
 Original Article Annals of Clinical Biochemistry 2015, Vol. 52(1) 82 87! The Author(s) 2014 Reprints and permissions: sagepub.co.uk/journalspermissions.nav DOI: 10.1177/0004563214523739 acb.sagepub.com
Original Article Annals of Clinical Biochemistry 2015, Vol. 52(1) 82 87! The Author(s) 2014 Reprints and permissions: sagepub.co.uk/journalspermissions.nav DOI: 10.1177/0004563214523739 acb.sagepub.com
Alterations in Fluids and Electrolytes During Refeeding Syndrome. Objectives. Refeeding Syndrome (RS) 4/26/2013. Barbara Magnuson, PharmD, BCNSP
 Alterations in Fluids and Electrolytes During Refeeding Syndrome Barbara Magnuson, PharmD, BCNSP Objectives Define refeeding syndrome including its signs and symptoms Identify fluid and electrolyte disturbances
Alterations in Fluids and Electrolytes During Refeeding Syndrome Barbara Magnuson, PharmD, BCNSP Objectives Define refeeding syndrome including its signs and symptoms Identify fluid and electrolyte disturbances
Nutritional management of eating disorders. Louise Watson Clinical Dietitian South Island Eating Disorders Service
 Nutritional management of eating disorders Louise Watson Clinical Dietitian South Island Eating Disorders Service Contents Refeeding syndrome Target weight range Measuring height and weight Refeeding syndrome
Nutritional management of eating disorders Louise Watson Clinical Dietitian South Island Eating Disorders Service Contents Refeeding syndrome Target weight range Measuring height and weight Refeeding syndrome
5/18/2017. Specific Electrolytes. Sodium. Sodium. Sodium. Sodium. Sodium
 Specific Electrolytes Hyponatremia Hypervolemic Replacing water (not electrolytes) after perspiration Freshwater near-drowning Syndrome of Inappropriate ADH Secretion (SIADH) Hypovolemic GI disease (decreased
Specific Electrolytes Hyponatremia Hypervolemic Replacing water (not electrolytes) after perspiration Freshwater near-drowning Syndrome of Inappropriate ADH Secretion (SIADH) Hypovolemic GI disease (decreased
Parenteral Nutrition in Oncology
 Parenteral Nutrition in Oncology Presenter: Pam Wagner, RD, CNSC Learning Objectives List indications for initiating PN in oncology patients Describe considerations when determining an appropriate candidate
Parenteral Nutrition in Oncology Presenter: Pam Wagner, RD, CNSC Learning Objectives List indications for initiating PN in oncology patients Describe considerations when determining an appropriate candidate
NUTRITION. Elizabeth Viner Smith & Catherine Jones Foundations of Critical Care Nursing September 2017
 NUTRITION Elizabeth Viner Smith & Catherine Jones Foundations of Critical Care Nursing September 2017 Step One Competency 1.19 Factors contributing to nutritional impairment in critical illness. Nutritional
NUTRITION Elizabeth Viner Smith & Catherine Jones Foundations of Critical Care Nursing September 2017 Step One Competency 1.19 Factors contributing to nutritional impairment in critical illness. Nutritional
Nutrition in Pancreatic Cancer. Edmond Sung Consultant Gastroenterologist Lead Clinician for Clinical Nutrition and Endoscopy
 Nutrition in Pancreatic Cancer Edmond Sung Consultant Gastroenterologist Lead Clinician for Clinical Nutrition and Endoscopy Overview The pancreas and nutrition Nutrition screening - can we do this well?
Nutrition in Pancreatic Cancer Edmond Sung Consultant Gastroenterologist Lead Clinician for Clinical Nutrition and Endoscopy Overview The pancreas and nutrition Nutrition screening - can we do this well?
SERUM PHOSPHORUS TESTING
 MEDICAL POLICY For use with the UnitedHealthcare Laboratory Benefit Management Program, administered by BeaconLBS SERUM PHOSPHORUS TESTING Policy Number: CMP - 035 Effective Date: January 21, 2017 Table
MEDICAL POLICY For use with the UnitedHealthcare Laboratory Benefit Management Program, administered by BeaconLBS SERUM PHOSPHORUS TESTING Policy Number: CMP - 035 Effective Date: January 21, 2017 Table
IS THERE A PLACE IN THE ICU FOR PERMISSIVE UNDERFEEDING AND WHERE? ENGELA FRANCIS RD(SA)
 IS THERE A PLACE IN THE ICU FOR PERMISSIVE UNDERFEEDING AND WHERE? ENGELA FRANCIS RD(SA) DEFINITION: PERMISSIVE UNDERFEEDING No clear definition in literature Permissive underfeeding definition prior to
IS THERE A PLACE IN THE ICU FOR PERMISSIVE UNDERFEEDING AND WHERE? ENGELA FRANCIS RD(SA) DEFINITION: PERMISSIVE UNDERFEEDING No clear definition in literature Permissive underfeeding definition prior to
Refeeding hypophosphataemia in a Malaysian intensive care unit: incidence, risk factors and outcomes
 Original Article Brunei Int Med J. 2015; 11 (2): 65-73 Refeeding hypophosphataemia in a Malaysian intensive care unit: incidence, risk factors and outcomes Azrina MD RALIB, Che Ainun Nasihah ISMAIL, Muhammad
Original Article Brunei Int Med J. 2015; 11 (2): 65-73 Refeeding hypophosphataemia in a Malaysian intensive care unit: incidence, risk factors and outcomes Azrina MD RALIB, Che Ainun Nasihah ISMAIL, Muhammad
Chapter 16 Nutrition, Fluids and Electrolytes, and Acid-Base Balance Nutrition Nutrients Water o Functions Promotes metabolic processes Transporter
 Chapter 16 Nutrition, Fluids and Electrolytes, and Acid-Base Balance Nutrition Nutrients Water o Functions Promotes metabolic processes Transporter for nutrients and wastes Lubricant Insulator and shock
Chapter 16 Nutrition, Fluids and Electrolytes, and Acid-Base Balance Nutrition Nutrients Water o Functions Promotes metabolic processes Transporter for nutrients and wastes Lubricant Insulator and shock
Hypophosphatemia is an uncommon condition
 HYPOPHOSPHATEMIA AND REFEEDING SYNDROME Nathan Lippo, DVM Resident, Emergency and Critical Care Medicine Christopher G. Byers, DVM, DACVECC Director, Intensive Care Internal Medicine Critical Care Department
HYPOPHOSPHATEMIA AND REFEEDING SYNDROME Nathan Lippo, DVM Resident, Emergency and Critical Care Medicine Christopher G. Byers, DVM, DACVECC Director, Intensive Care Internal Medicine Critical Care Department
Index. Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type.
 Index Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A Acetate, in pediatric surgical patients, 525 526 Acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS), immune-modulating nutrition in, 584 585 Aerobic
Index Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A Acetate, in pediatric surgical patients, 525 526 Acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS), immune-modulating nutrition in, 584 585 Aerobic
CCRN Review - Renal. CCRN Review - Renal 10/16/2014. CCRN Review Renal. Sodium Critical Value < 120 meq/l > 160 meq/l
 CCRN Review Renal Leanna R. Miller, RN, MN, CCRN-CMC, PCCN-CSC, CEN, CNRN, CMSRN, NP Education Specialist LRM Consulting Nashville, TN Sodium 136-145 Critical Value < 120 meq/l > 160 meq/l Sodium Etiology
CCRN Review Renal Leanna R. Miller, RN, MN, CCRN-CMC, PCCN-CSC, CEN, CNRN, CMSRN, NP Education Specialist LRM Consulting Nashville, TN Sodium 136-145 Critical Value < 120 meq/l > 160 meq/l Sodium Etiology
Nutrition and Medicine, 2006 Tufts University School of Medicine Nutrition and Acute Illness: Learning Objectives
 Nutrition and Medicine, 2006 Tufts University School of Medicine Nutrition and Acute Illness: Learning Objectives Margo N. Woods, D.Sc. 1. Define protein-calorie, or protein-energy malnutrition (PEM) and
Nutrition and Medicine, 2006 Tufts University School of Medicine Nutrition and Acute Illness: Learning Objectives Margo N. Woods, D.Sc. 1. Define protein-calorie, or protein-energy malnutrition (PEM) and
Investigations for Disorders of Calcium, Phosphate and Magnesium Homeostasis
 Investigations for Disorders of Calcium, Phosphate and Magnesium Homeostasis Tutorial for Specialist Portfolio Biomedical Scientists 03/02/2014 Dr Petros Kampanis Clinical Scientist 1. Calcium Most abundant
Investigations for Disorders of Calcium, Phosphate and Magnesium Homeostasis Tutorial for Specialist Portfolio Biomedical Scientists 03/02/2014 Dr Petros Kampanis Clinical Scientist 1. Calcium Most abundant
SECTION 15: TREATMENT OF EATING DISORDERS. Formulary and Prescribing Guidelines
 SECTION 15: TREATMENT OF EATING DISORDERS Formulary and Prescribing Guidelines 15.1 Introduction Please review the Trust document Guidelines for the assessment and treatment of eating disorders in the
SECTION 15: TREATMENT OF EATING DISORDERS Formulary and Prescribing Guidelines 15.1 Introduction Please review the Trust document Guidelines for the assessment and treatment of eating disorders in the
ESPEN Congress The Hague 2017
 ESPEN Congress The Hague 2017 Using the gut in acute care patients Permissive underfeeding in practice J.-C. Preiser (BE) PERMISSIVE UNDERFEEDING IN PRACTICE ESPEN congress Jean-Charles Preiser, M.D.,
ESPEN Congress The Hague 2017 Using the gut in acute care patients Permissive underfeeding in practice J.-C. Preiser (BE) PERMISSIVE UNDERFEEDING IN PRACTICE ESPEN congress Jean-Charles Preiser, M.D.,
EU RISK MANAGEMENT PLAN (EU RMP) Nutriflex Omega peri emulsion for infusion , version 1.1
 EU RISK MANAGEMENT PLAN (EU RMP) Nutriflex Omega peri emulsion for infusion 13.7.2015, version 1.1 III.1. Elements for a Public Summary III.1.1. Overview of disease epidemiology Patients may need parenteral
EU RISK MANAGEMENT PLAN (EU RMP) Nutriflex Omega peri emulsion for infusion 13.7.2015, version 1.1 III.1. Elements for a Public Summary III.1.1. Overview of disease epidemiology Patients may need parenteral
ICU NUTRITION UPDATE : ESPEN GUIDELINES Mirey Karavetian Assistant Professor Zayed University
 ICU NUTRITION UPDATE : ESPEN GUIDELINES 2018 Mirey Karavetian Assistant Professor Zayed University http://www.espen.org/files/espen- Guidelines/ESPEN_Guideline_on_clinical_nutrition_in_-ICU.pdf Medical
ICU NUTRITION UPDATE : ESPEN GUIDELINES 2018 Mirey Karavetian Assistant Professor Zayed University http://www.espen.org/files/espen- Guidelines/ESPEN_Guideline_on_clinical_nutrition_in_-ICU.pdf Medical
Acid Base Balance. Professor Dr. Raid M. H. Al-Salih. Clinical Chemistry Professor Dr. Raid M. H. Al-Salih
 Acid Base Balance 1 HYDROGEN ION CONCENTRATION and CONCEPT OF ph Blood hydrogen ion concentration (abbreviated [H + ]) is maintained within tight limits in health, with the normal concentration being between
Acid Base Balance 1 HYDROGEN ION CONCENTRATION and CONCEPT OF ph Blood hydrogen ion concentration (abbreviated [H + ]) is maintained within tight limits in health, with the normal concentration being between
Electrolyte Imbalance and Resuscitation. Dr. Mehmet Okumuş Sütçü Imam University Faculty of Medicine Department of Emergency Medicine
 Electrolyte Imbalance and Resuscitation Dr. Mehmet Okumuş Sütçü Imam University Faculty of Medicine Department of Emergency Medicine Presentation plan Definition of the electrolyte disturbances Conditions
Electrolyte Imbalance and Resuscitation Dr. Mehmet Okumuş Sütçü Imam University Faculty of Medicine Department of Emergency Medicine Presentation plan Definition of the electrolyte disturbances Conditions
Over-feeding and over- hydration in elderly medical patients Lessons from the Liverpool Care Pathway. Correspondence to: Abstract Keywords
 Over-feeding and over-hydration in elderly medical patients Lessons from the Liverpool Care Pathway. Eleni Tsiompanou; Caroline Lucas; Lulu Kreeger; Mike Stroud Correspondence to: Dr Eleni Tsiompanou,
Over-feeding and over-hydration in elderly medical patients Lessons from the Liverpool Care Pathway. Eleni Tsiompanou; Caroline Lucas; Lulu Kreeger; Mike Stroud Correspondence to: Dr Eleni Tsiompanou,
NHS Grampian Staff Guideline for the Management of Acute Hypokalaemia in Adults
 NHS Grampian Staff Guideline for the Management of Acute Hypokalaemia in Adults Co-ordinators: Medicines Information Pharmacist Consultation Group: See relevant page in guidance Approver: Medicine Guidelines
NHS Grampian Staff Guideline for the Management of Acute Hypokalaemia in Adults Co-ordinators: Medicines Information Pharmacist Consultation Group: See relevant page in guidance Approver: Medicine Guidelines
Refeeding Syndrome in Oncology: Report of Four Cases
 Elmer ress Case Report World J Oncol. 2017;8(1):25-29 Refeeding Syndrome in Oncology: Report of Four Cases Martin Windpessl a, b, Beate Mayrbaeurl a, Christian Baldinger a, Gernot Tiefenthaller a, Friedrich
Elmer ress Case Report World J Oncol. 2017;8(1):25-29 Refeeding Syndrome in Oncology: Report of Four Cases Martin Windpessl a, b, Beate Mayrbaeurl a, Christian Baldinger a, Gernot Tiefenthaller a, Friedrich
NHS Grampian Staff Guideline For The Management Of Acute Hypophosphataemia In Adults
 NHS Grampian Staff Guideline For The Management Of Acute Hypophosphataemia In Adults Co-ordinators: Medicine Information Pharmacist Consultation Group: See Page 5 Approver: Medicine Guidelines and Policies
NHS Grampian Staff Guideline For The Management Of Acute Hypophosphataemia In Adults Co-ordinators: Medicine Information Pharmacist Consultation Group: See Page 5 Approver: Medicine Guidelines and Policies
Calcium (Ca 2+ ) mg/dl
 Quick Guide to Laboratory Values Use this handy cheat-sheet to help you monitor laboratory values related to fluid and electrolyte status. Remember, normal values may vary according to techniques used
Quick Guide to Laboratory Values Use this handy cheat-sheet to help you monitor laboratory values related to fluid and electrolyte status. Remember, normal values may vary according to techniques used
Nutrition during and after HSCT: The physicians view WHAT IS THE EVIDENCE?
 Nutrition during and after HSCT: The physicians view WHAT IS THE EVIDENCE? Annic Baumgartner, Philipp Schuetz, Medizinische Uniklinik, Kantonsspital Aarau Swiss Blood Stem Cell Transplantation (SBST),
Nutrition during and after HSCT: The physicians view WHAT IS THE EVIDENCE? Annic Baumgartner, Philipp Schuetz, Medizinische Uniklinik, Kantonsspital Aarau Swiss Blood Stem Cell Transplantation (SBST),
Malnutrition Topic 6
 Malnutrition Topic 6 Module 6.3 Refeeding Syndrome and Methods for Safe Nutritional Intervention Kinga Szczepanek General and Oncology Surgery Unit, Stanley Dudrick s Memorial Hospital, 15 Tyniecka Str.,
Malnutrition Topic 6 Module 6.3 Refeeding Syndrome and Methods for Safe Nutritional Intervention Kinga Szczepanek General and Oncology Surgery Unit, Stanley Dudrick s Memorial Hospital, 15 Tyniecka Str.,
Entry Level Clinical Nutrition. Dr. Jeff Moss. Dr. Jeff Moss
 Entry Level Clinical Nutrition Part XII Micronutrient imbalances: Water soluble vitamins Jeffrey Moss, DDS, CNS, DACBN jeffmoss@mossnutrition.com 413-530-08580858 (cell) 1 Quality of life issues are the
Entry Level Clinical Nutrition Part XII Micronutrient imbalances: Water soluble vitamins Jeffrey Moss, DDS, CNS, DACBN jeffmoss@mossnutrition.com 413-530-08580858 (cell) 1 Quality of life issues are the
HISTORY OF THE KETOGENIC DIET
 Laura Roche RD Horizon Health Authority May 29, 2018 AGENDA History of the Ketogenic Diet Diet Pathophysiology Side Effects Pros and Cons How and Why the Diet works Ketogenic Diet for Type 2 Diabetes Ketogenic
Laura Roche RD Horizon Health Authority May 29, 2018 AGENDA History of the Ketogenic Diet Diet Pathophysiology Side Effects Pros and Cons How and Why the Diet works Ketogenic Diet for Type 2 Diabetes Ketogenic
Paediatric Best Practice Guidelines. Eating Disorders
 Paediatric Best Practice Guidelines Eating Disorders Background Relatively common 0.5-0.7% adolescent females have anorexia nervosa, 5-10% of eating disorders occur in males. Anorexia nervosa associated
Paediatric Best Practice Guidelines Eating Disorders Background Relatively common 0.5-0.7% adolescent females have anorexia nervosa, 5-10% of eating disorders occur in males. Anorexia nervosa associated
A Guide to Prescribing Adult Oral Nutritional Supplements in West Kent CCG
 A Guide to Prescribing Adult Oral Nutritional Supplements in West Kent CCG Aim This guideline has been designed to support primary care prescribers initiating nutrition support for adults in West Kent.
A Guide to Prescribing Adult Oral Nutritional Supplements in West Kent CCG Aim This guideline has been designed to support primary care prescribers initiating nutrition support for adults in West Kent.
By; Ashraf El Houfi MD MS (pulmonology) MRCP (UK) FRCP (London) EDIC Consultant ICU Dubai Hospital
 By; Ashraf El Houfi MD MS (pulmonology) MRCP (UK) FRCP (London) EDIC Consultant ICU Dubai Hospital Introduction The significance of nutrition in hospital setting (especially the ICU) cannot be overstated.
By; Ashraf El Houfi MD MS (pulmonology) MRCP (UK) FRCP (London) EDIC Consultant ICU Dubai Hospital Introduction The significance of nutrition in hospital setting (especially the ICU) cannot be overstated.
Parenteral Nutrition in IBD: Any indication?
 Parenteral Nutrition in IBD: Any indication? Name: Institution: Marianna Arvanitakis Erasme University Hospital, Brussels, Belgium Clinical case 42 year old male Crohn s disease since he was 16 years old
Parenteral Nutrition in IBD: Any indication? Name: Institution: Marianna Arvanitakis Erasme University Hospital, Brussels, Belgium Clinical case 42 year old male Crohn s disease since he was 16 years old
NUTRITIONAL OPTIMIZATION IN PRE LIVER TRANSPLANT PATIENTS
 NUTRITIONAL OPTIMIZATION IN PRE LIVER TRANSPLANT PATIENTS ACHIEVING NUTRITIONAL ADEQUACY Dr N MURUGAN Consultant Hepatologist Apollo Hospitals Chennai NUTRITION IN LIVER FAILURE extent of problem and consequences
NUTRITIONAL OPTIMIZATION IN PRE LIVER TRANSPLANT PATIENTS ACHIEVING NUTRITIONAL ADEQUACY Dr N MURUGAN Consultant Hepatologist Apollo Hospitals Chennai NUTRITION IN LIVER FAILURE extent of problem and consequences
ESPEN Congress Florence 2008
 ESPEN Congress Florence 2008 PN Guidelines presentation PN Guidelines in pancreas diseases L. Gianotti (Italy) ESPEN Guidelines on Parenteral Nutrition: Pancreas L.Gianotti, R.Meier, D.N.Lobo, C.Bassi,
ESPEN Congress Florence 2008 PN Guidelines presentation PN Guidelines in pancreas diseases L. Gianotti (Italy) ESPEN Guidelines on Parenteral Nutrition: Pancreas L.Gianotti, R.Meier, D.N.Lobo, C.Bassi,
Neoplastic Disease KNH 406
 Neoplastic Disease KNH 406 Cancer Carcinogenesis - Etiology Genes may be affected by antioxidants, soy, protein, fat, kcal, alcohol Nutritional genomics study of genetic variations that cause different
Neoplastic Disease KNH 406 Cancer Carcinogenesis - Etiology Genes may be affected by antioxidants, soy, protein, fat, kcal, alcohol Nutritional genomics study of genetic variations that cause different
Title The Prescription of Adult Inpatient Parenteral Nutrition (PN) Guideline. Author s job title Consultant Gastroenterologist Directorate Medicine
 Document Control Title The Prescription of Adult Inpatient Parenteral Nutrition (PN) Guideline Author Author s job title Consultant Gastroenterologist Directorate Medicine Department Medicine Version Date
Document Control Title The Prescription of Adult Inpatient Parenteral Nutrition (PN) Guideline Author Author s job title Consultant Gastroenterologist Directorate Medicine Department Medicine Version Date
Stellenwert der prä- und postoperativen Sicht des Chirurgen
 Interdisziplinäre Chirurgie Stellenwert der prä- und postoperativen Ernährung Sicht des Chirurgen Kantonsspital Luzern 24.11.2005 Prof. L. Krähenbühl Chirurgische Klinik Hôpital Cantonal Fribourg Problems
Interdisziplinäre Chirurgie Stellenwert der prä- und postoperativen Ernährung Sicht des Chirurgen Kantonsspital Luzern 24.11.2005 Prof. L. Krähenbühl Chirurgische Klinik Hôpital Cantonal Fribourg Problems
Online-Only Supplement: Early parenteral nutrition in critically ill patients with. short term relative contraindications to early enteral nutrition:
 Online-Only Supplement: Early parenteral nutrition in critically ill patients with short term relative contraindications to early enteral nutrition: A randomized controlled trial. Gordon S. Doig PhD, Fiona
Online-Only Supplement: Early parenteral nutrition in critically ill patients with short term relative contraindications to early enteral nutrition: A randomized controlled trial. Gordon S. Doig PhD, Fiona
Nutrition in Liver Disease An overview of the EASL Clinical Practice Guidelines
 Nutrition in Liver Disease An overview of the EASL Clinical Practice Guidelines Marike Bauermeister Registered Dietitian Wits Donald Gordon Medical Centre Malnutrition Malnutrition is a complication in
Nutrition in Liver Disease An overview of the EASL Clinical Practice Guidelines Marike Bauermeister Registered Dietitian Wits Donald Gordon Medical Centre Malnutrition Malnutrition is a complication in
WHEN To Initiate Parenteral Nutrition A Frequent Question With New Answers
 WHEN To Initiate Parenteral Nutrition A Frequent Question With New Answers Ainsley Malone, MS, RD, LD, CNSC, FAND, FASPEN Dubai International Nutrition Conference 2018 Disclosures No commercial relationship
WHEN To Initiate Parenteral Nutrition A Frequent Question With New Answers Ainsley Malone, MS, RD, LD, CNSC, FAND, FASPEN Dubai International Nutrition Conference 2018 Disclosures No commercial relationship
Intradialytic Parenteral Nutrition in Hemodialysis Patients. Hamdy Amin, Pharm.D., MBA, BCNSP Riyadh, Saudi Arabia
 Intradialytic Parenteral Nutrition in Hemodialysis Patients Hamdy Amin, Pharm.D., MBA, BCNSP Riyadh, Saudi Arabia Disclosure Information Intradialytic Parenteral Nutrition in Hemodialysis Patients Hamdy
Intradialytic Parenteral Nutrition in Hemodialysis Patients Hamdy Amin, Pharm.D., MBA, BCNSP Riyadh, Saudi Arabia Disclosure Information Intradialytic Parenteral Nutrition in Hemodialysis Patients Hamdy
ESPEN Congress Gothenburg Combined parenteral and enteral nutrition. Crohn s disease. Željko Krznarić
 ESPEN Congress Gothenburg 2011 Combined parenteral and enteral nutrition Crohn s disease Željko Krznarić ŽELJKO KRZNARIĆ, FEBGH U N I V E R S I T Y OF Z A G R E B C R O A T I A EDUCATIONAL SESSION COMBINED
ESPEN Congress Gothenburg 2011 Combined parenteral and enteral nutrition Crohn s disease Željko Krznarić ŽELJKO KRZNARIĆ, FEBGH U N I V E R S I T Y OF Z A G R E B C R O A T I A EDUCATIONAL SESSION COMBINED
Basic Fluid and Electrolytes
 Basic Fluid and Electrolytes Chapter 22 Basic Fluid and Electrolytes Introduction Infants and young children have a greater need for water and are more vulnerable to alterations in fluid and electrolyte
Basic Fluid and Electrolytes Chapter 22 Basic Fluid and Electrolytes Introduction Infants and young children have a greater need for water and are more vulnerable to alterations in fluid and electrolyte
WATER, SODIUM AND POTASSIUM
 WATER, SODIUM AND POTASSIUM Attila Miseta Tamás Kőszegi Department of Laboratory Medicine, 2016 1 Average daily water intake and output of a normal adult 2 Approximate contributions to plasma osmolality
WATER, SODIUM AND POTASSIUM Attila Miseta Tamás Kőszegi Department of Laboratory Medicine, 2016 1 Average daily water intake and output of a normal adult 2 Approximate contributions to plasma osmolality
Systematic review of transition phase feeding of children with severe acute malnutrition as inpatients
 Systematic review of transition phase feeding of children with severe acute malnutrition as inpatients Mark Manary 1 Indi Trehan 2 Ariana Weisz 3 February 2012 1 Helene B. Roberson Professor of Pediatrics,
Systematic review of transition phase feeding of children with severe acute malnutrition as inpatients Mark Manary 1 Indi Trehan 2 Ariana Weisz 3 February 2012 1 Helene B. Roberson Professor of Pediatrics,
The legally binding text is the original French version TRANSPARENCY COMMITTEE OPINION. 19 October 2011
 The legally binding text is the original French version TRANSPARENCY COMMITTEE OPINION 19 October 2011 PEDIAVEN AP-HP G15, solution for infusion 1000 ml of solution in two chamber bag, B/4 (CIP code: 419
The legally binding text is the original French version TRANSPARENCY COMMITTEE OPINION 19 October 2011 PEDIAVEN AP-HP G15, solution for infusion 1000 ml of solution in two chamber bag, B/4 (CIP code: 419
Who Needs Parenteral Nutrition? Is Parenteral Nutrition An Appropriate Intervention?
 Who Needs Parenteral Nutrition? 1 Is Parenteral Nutrition An Appropriate Intervention? Key questions to ask with initial consultation Can the gastrointestinal (GI) tract be utilized? Can the GI tract be
Who Needs Parenteral Nutrition? 1 Is Parenteral Nutrition An Appropriate Intervention? Key questions to ask with initial consultation Can the gastrointestinal (GI) tract be utilized? Can the GI tract be
Nutritional support on the Acute Medical Unit. Acute Medicine Conference 2017
 Nutritional support on the Acute Medical Unit Acute Medicine Conference 2017 Declaration of interests Travel grants to attend scientific/educational meetings: Shire Boston Scientific Almirall Organisational
Nutritional support on the Acute Medical Unit Acute Medicine Conference 2017 Declaration of interests Travel grants to attend scientific/educational meetings: Shire Boston Scientific Almirall Organisational
TOTAL PARENTERAL NUTRITION
 TOTAL PARENTERAL NUTRITION Indication See algorithm. Timing Start TPN as indicated on algorithm 1. There is no need to build up TPN volume. The volume of TPN (including lipids) should equate to the total
TOTAL PARENTERAL NUTRITION Indication See algorithm. Timing Start TPN as indicated on algorithm 1. There is no need to build up TPN volume. The volume of TPN (including lipids) should equate to the total
Diet what helps? Lindsey Allan Macmillan Oncology Dietitian Royal Surrey County Hospital, Guildford
 Diet what helps? Lindsey Allan Macmillan Oncology Dietitian Royal Surrey County Hospital, Guildford Diet and cancer Diet and cancer Nutrition research Lack of funding RCTs Low quality Small sample sizes
Diet what helps? Lindsey Allan Macmillan Oncology Dietitian Royal Surrey County Hospital, Guildford Diet and cancer Diet and cancer Nutrition research Lack of funding RCTs Low quality Small sample sizes
ISPUB.COM. Electrolyte Replacement: A Review. B Phillips INTRODUCTION ELECTROLYTES I. CALCIUM
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Internal Medicine Volume 5 Number 1 Electrolyte Replacement: A Review B Phillips Citation B Phillips. Electrolyte Replacement: A Review. The Internet Journal of Internal
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Internal Medicine Volume 5 Number 1 Electrolyte Replacement: A Review B Phillips Citation B Phillips. Electrolyte Replacement: A Review. The Internet Journal of Internal
Nutritional Demands of Disease and Trauma
 al Demands of Disease and Trauma Lecture 89 Medical School al Requirements Based on needs to support optimal physiological function Are changed by disease or injury metabolism is altered to prevent further
al Demands of Disease and Trauma Lecture 89 Medical School al Requirements Based on needs to support optimal physiological function Are changed by disease or injury metabolism is altered to prevent further
Guidelines for managing adults at risk of refeeding syndrome.
 Guidelines for managing adults at risk of refeeding syndrome. Version: V3.0 Ratified by: Out of Hospital Division Governance Meeting Clinical Nutrition Group Date ratified: 12 th January 2018 Name of author
Guidelines for managing adults at risk of refeeding syndrome. Version: V3.0 Ratified by: Out of Hospital Division Governance Meeting Clinical Nutrition Group Date ratified: 12 th January 2018 Name of author
Accepted Article. Celiac crisis in adults: a case report and review of the literature focusing in the prevention of refeeding syndrome
 Accepted Article Celiac crisis in adults: a case report and review of the literature focusing in the prevention of refeeding syndrome Marcela de Almeida Menezes, Vírginia Cabral, Sônia Letícia Silva Lorena
Accepted Article Celiac crisis in adults: a case report and review of the literature focusing in the prevention of refeeding syndrome Marcela de Almeida Menezes, Vírginia Cabral, Sônia Letícia Silva Lorena
Nutritional intervention in hospitalised paediatric patients. Dr Y.K.Amdekar
 Nutritional intervention in hospitalised paediatric patients Dr Y.K.Amdekar Back to basics Suboptimal nutrient intake is always dangerous in health and more so in disease to feed or not to feed is it a
Nutritional intervention in hospitalised paediatric patients Dr Y.K.Amdekar Back to basics Suboptimal nutrient intake is always dangerous in health and more so in disease to feed or not to feed is it a
DISCLOSURE. Learning Objectives. Controversies in Parenteral Nutrition
 Controversies in Parenteral Nutrition Christopher Duggan, MD, MPH Center for Nutrition Center for Advanced Intestinal Rehabilitation (CAIR) Division of Gastroenterology, Hepatology and Nutrition Boston
Controversies in Parenteral Nutrition Christopher Duggan, MD, MPH Center for Nutrition Center for Advanced Intestinal Rehabilitation (CAIR) Division of Gastroenterology, Hepatology and Nutrition Boston
I have no financial disclosures
 Athina Sikavitsas DO Children's Emergency Services University of Michigan Discuss DKA Presentation Assessment Treatment I have no financial disclosures 1 6 Y/O male presents with vomiting and abdominal
Athina Sikavitsas DO Children's Emergency Services University of Michigan Discuss DKA Presentation Assessment Treatment I have no financial disclosures 1 6 Y/O male presents with vomiting and abdominal
Phosphoremia (mmol/l) Calcemia (mmol/l) Postnatal age (days) Postnatal age (days) Urinary Calcium (mg/kg/d) Phosphoremia (mmol/l)
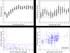 3,0 3,2 Calcemia (mmol/l) 2,8 2,6 2,4 2,2 2,0 1,8 Phosphoremia (mmol/l) 3,0 2,8 2,6 2,4 2,2 2,0 1,8 1,6 1,4 1,2 1,6 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 Postnatal age (days) 1,0 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11
3,0 3,2 Calcemia (mmol/l) 2,8 2,6 2,4 2,2 2,0 1,8 Phosphoremia (mmol/l) 3,0 2,8 2,6 2,4 2,2 2,0 1,8 1,6 1,4 1,2 1,6 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 Postnatal age (days) 1,0 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11
[No conflicts of interest]
![[No conflicts of interest] [No conflicts of interest]](/thumbs/86/94144068.jpg) [No conflicts of interest] Patients and staff at: Available evidence pre-calories Three meta-analyses: Gramlich L et al. Does enteral nutrition compared to parenteral nutrition result in better outcomes
[No conflicts of interest] Patients and staff at: Available evidence pre-calories Three meta-analyses: Gramlich L et al. Does enteral nutrition compared to parenteral nutrition result in better outcomes
Amino Acids and Sorbitol injection with/without Electrolytes NIRMIN *
 For the use of a registered medical practitioner or a Hospital or a Laboratory only Amino Acids and Sorbitol injection with/without Electrolytes NIRMIN * DESCRIPTION: NIRMIN * is a clear, colourless injection
For the use of a registered medical practitioner or a Hospital or a Laboratory only Amino Acids and Sorbitol injection with/without Electrolytes NIRMIN * DESCRIPTION: NIRMIN * is a clear, colourless injection
Nutritional Demands of Disease and Trauma
 Nutritional Demands of Disease and Trauma Lecture 89 2000 Northwestern University Medical School Nutritional Requirements Based on needs to support optimal physiological function Are changed by disease
Nutritional Demands of Disease and Trauma Lecture 89 2000 Northwestern University Medical School Nutritional Requirements Based on needs to support optimal physiological function Are changed by disease
Metabolic Control in Critical Care: Nutrition Therapy
 LOGO Metabolic Control in Critical Care: Nutrition Therapy ผศ.นพ.พรพจน เปรมโยธ น สาขาโภชนาการคล น ก ภาคว ชาอาย รศาสตร คณะแพทยศาสตร ศ ร ราชพยาบาล 2016 SCCM/ASPEN Guidelines Nutrition Therapy in the ICU
LOGO Metabolic Control in Critical Care: Nutrition Therapy ผศ.นพ.พรพจน เปรมโยธ น สาขาโภชนาการคล น ก ภาคว ชาอาย รศาสตร คณะแพทยศาสตร ศ ร ราชพยาบาล 2016 SCCM/ASPEN Guidelines Nutrition Therapy in the ICU
Case Report Thiamine Deficiency in Self-Induced Refeeding Syndrome, an Undetected and Potentially Lethal Condition
 Case Reports in Medicine, Article ID 605707, 6 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2014/605707 Case Report Thiamine Deficiency in Self-Induced Refeeding Syndrome, an Undetected and Potentially Lethal Condition
Case Reports in Medicine, Article ID 605707, 6 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2014/605707 Case Report Thiamine Deficiency in Self-Induced Refeeding Syndrome, an Undetected and Potentially Lethal Condition
Inflammatory Bowel Disease
 + Inflammatory Bowel Disease Christina Kalafsky, Dietetic Intern University of Maryland College Park Children s National Medical Center Case Study January 31, 2014 + Outline n Inflammatory Bowel Disease
+ Inflammatory Bowel Disease Christina Kalafsky, Dietetic Intern University of Maryland College Park Children s National Medical Center Case Study January 31, 2014 + Outline n Inflammatory Bowel Disease
Small Bowel Obstruction after operation in a severely malnourished man. By: Ms Bounmark Phoumesy
 Small Bowel Obstruction after operation in a severely malnourished man By: Ms Bounmark Phoumesy Normal length of GI tract Normal length(achieved by age 9) Small bowel 600cm (Men: 630 cm; Women: 592 cm)
Small Bowel Obstruction after operation in a severely malnourished man By: Ms Bounmark Phoumesy Normal length of GI tract Normal length(achieved by age 9) Small bowel 600cm (Men: 630 cm; Women: 592 cm)
Major Case Study: Enteral and Parenteral Nutrition Due 2/13/15 60 points. Ht: 5 11 Current wt: 156 # UBW: 167 # Serum albumin: 3.
 NUT 116BL Winter 2015 Name: yimeng Ma Section: Major Case Study: Enteral and Parenteral Nutrition Due 2/13/15 60 points Mr. R, a 35 yo drug user, is hospitalized after a motor vehicle accident (MVA). He
NUT 116BL Winter 2015 Name: yimeng Ma Section: Major Case Study: Enteral and Parenteral Nutrition Due 2/13/15 60 points Mr. R, a 35 yo drug user, is hospitalized after a motor vehicle accident (MVA). He
Long term monitoring. Dr Alison Culkin Research Dietitian St Mark s Hospital
 Long term monitoring Dr Alison Culkin Research Dietitian St Mark s Hospital Patient 23 year old lady 1/4/14 Colectomy for UC 3-7/4/14 Ischaemic bowel 4 laparotomies Jejunostomy at 35 cm 23/5/14 Weight
Long term monitoring Dr Alison Culkin Research Dietitian St Mark s Hospital Patient 23 year old lady 1/4/14 Colectomy for UC 3-7/4/14 Ischaemic bowel 4 laparotomies Jejunostomy at 35 cm 23/5/14 Weight
- Risk Management Plan - Nutriflex Omega plus-special-eu
 Date: 2015-07-24 Page: 108 of 201 VI.2. Elements for a Public Summary VI.2.1. Overview of disease epidemiology Patients may need parenteral nutrition (PN) for any variety of diseases or conditions that
Date: 2015-07-24 Page: 108 of 201 VI.2. Elements for a Public Summary VI.2.1. Overview of disease epidemiology Patients may need parenteral nutrition (PN) for any variety of diseases or conditions that
Clinical Nutrition in the 21st Century Malnutrition, sarcopenia and cachexia
 Clinical Nutrition in the 21st Century Malnutrition, sarcopenia and cachexia Stéphane M. Schneider, MD, PhD, FEBGH Professor of Nutrition and ESPEN ECPC Chair In proto-indo-european, Latin and Greek Under
Clinical Nutrition in the 21st Century Malnutrition, sarcopenia and cachexia Stéphane M. Schneider, MD, PhD, FEBGH Professor of Nutrition and ESPEN ECPC Chair In proto-indo-european, Latin and Greek Under
Metabolomics in nutrition research: biomarkers predicting mortality in children with severe acute malnutrition
 Metabolomics in nutrition research: biomarkers predicting mortality in children with severe acute malnutrition Michael Freemark Department of Pediatrics, Duke University Medical Center, the Duke Molecular
Metabolomics in nutrition research: biomarkers predicting mortality in children with severe acute malnutrition Michael Freemark Department of Pediatrics, Duke University Medical Center, the Duke Molecular
Feeding the critically ill child
 Feeding the critically ill child Khaw Sia (1913 1984) Lee Jan Hau, MBBS, MRCPCH, MCI Children s Intensive Care Unit September 2018 1 2 3 No disclosures Outline Is there a need to optimize enteral nutrition?
Feeding the critically ill child Khaw Sia (1913 1984) Lee Jan Hau, MBBS, MRCPCH, MCI Children s Intensive Care Unit September 2018 1 2 3 No disclosures Outline Is there a need to optimize enteral nutrition?
The Role of Parenteral Nutrition. in PEDIATRIC INTENSIVE CARE UNIT. Dzulfikar DLH. Pediatric Emergency and Intensive Care Unit
 The Role of Parenteral Nutrition in PEDIATRIC INTENSIVE CARE UNIT Dzulfikar DLH Pediatric Emergency and Intensive Care Unit Department of Child Health, Faculty of Medicine Universitas Padjajaran, Hasan
The Role of Parenteral Nutrition in PEDIATRIC INTENSIVE CARE UNIT Dzulfikar DLH Pediatric Emergency and Intensive Care Unit Department of Child Health, Faculty of Medicine Universitas Padjajaran, Hasan
Instrumental determination of electrolytes in urine. Amal Alamri
 Instrumental determination of electrolytes in urine Amal Alamri What is the Electrolytes? Electrolytes are positively and negatively chargedions, Found in Within body's cells extracellular fluids, including
Instrumental determination of electrolytes in urine Amal Alamri What is the Electrolytes? Electrolytes are positively and negatively chargedions, Found in Within body's cells extracellular fluids, including
