Hydrocolloid Consultant Rutgers Adjunct Professor
|
|
|
- Annabella King
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 CARBYDRATES Basic Theory Alan H. King, Ph.D. Hydrocolloid Consultant Rutgers Adjunct Professor Rutgers ffice: Rm #321A, (848) Home ffice: (908) ;
2 utline Introduction CH Structure Reactions of CHs Function of Simple CHs in Foods
3 Introduction Definition/Nomenclature CH Classification CH Metabolism Carbohydrates in Foods CHs = Aliphatic polyhydroxy compounds which carry a carbonyl group.
4 Carbohydrate = Carbon Hydrate i.e., C(H 2 ) or C n (H 2 ) n, or C 6 (H 2 ) 6 = C 6 H 12 6 C 2 +H 2 Sugar + 2
5 Simple Sugar Nomenclature -SE = free sugar, esp. aldose sugar -URNIC = -C (carboxyl) group at 1 o carbon -SIDE = substitution at anomeric carbon = glycoside -AN = polymer. E.g., glucan = glucose polymer Introduction to Food Science ISMERS = compounds with same chemical composition but different structures. (general term) STEREISMERS = isomers differing only in spacial arrangement of groups (e.g., - groups) ENANTIMERS = mirror image isomers (e.g., D- vs L- sugars) ANMERS = isomers differing only in position of anomeric carbon groups EPIMERS = Stereoisomers differing only in position of last asymmetric carbon groups
6 CH Classification I Monosaccharides ligosaccharides Polysaccharides
7 CH Classification II Monosaccharides pen chain Cyclic forms Planar, Haworth projection 3-dimensional 5 and 6 carbon most common
8 Glucose & -D-glucopyranose H C CH 2 H C C H H C H C CH 2 Fischer Projection (straight chain) Haworth Projection
9 -D-glucopyranose
10 CH Classification III Introduction to Food Science Monosaccharides pen chain Cyclic forms Planar, Haworth projection 3-dimensional 5 and 6 carbon most common
11 CH Classification IV ligosaccharides (2 20 monos) Disaccharides Sucrose Maltose Lactose Higher ligosaccharides
12 CH Classification V Polysaccharides > 20 monosaccharide units Homo- and heteroglycans Linear Branched
13 Linear vs Branched Polymers linear Mannose backbone RE branched RE RE = reducing end Substituted Galactose side groups
14 CH Metabolism I Contributions to diet Major source of calories 4 Kcal/g Texture, sweetness Simple vs complex CHs
15 CH Metabolism II Enzyme activity Main means of digestion n specific sugars
16
17 CH Metabolism III Dietary fiber Indigestible polysaccharides Function of Sweetness Positives Negatives
18
19 Carbohydrates in Foods Naturally present 3/4 of dry weight Sucrose Fruit Cereals Animal products Added CHs Introduction to Food Science
20 Free Sugars in Fruit (% Fresh vs (Dry) Basis) Introduction to Food Science Fruit D-Glucose D-Fructose Sucrose % H 2 Apple 1.17 (7.5) 6.04 (38.7) 3.8 (24.2) 84.4 Grape 6.86 (37.3) 7.84 (42.6) 2.2 (12.2) 81.6 Peach 0.91 (8.3) 1.18 (10.8) 6.9 (63.5) 89.1 Pear 0.95 (5.7) 6.77 (40.3) 1.6 (9.6) 83.2 Cherry 6.49 (33.1) 7.38 (37.7) 0.22 (1.1) 80.4 Strawberry 2.09 (20.7) 2.4 (23.8) 1.03 (10.2) 89.9
21 Free Sugars in Vegetables (% Fresh vs (Dry) Basis Basis) Vegetable D-Glucose D-Fructose Sucrose % H 2 Beet 0.18 (1.4) 0.16 (1.3) 6.1 (48.1) 87.3 Carrot 0.85 (7.2) 0.85 (7.2) 4.2 (35.9) 88.2 nion 2.07 (19) 1.1 (10) 0.9 (8.2) 89.1 Spinach 0.09 (1) 0.04 (0.4) 0.06 (0.6) 90.7 Sweet corn 0.34 (1.2) 0.3 (1.1) 3.0 (11.1) 72.7 Tomato 1.1 (17.2) 1.3 (20.6) 0.01 (0.2) 93.5
22 Sugars in Common Foods Food Sugar present(%) Soft Drinks 9 Cracker 12 Ice cream 18 Ready-to-eat cereals (dry) 1-50 range juice 10 Catsup 29 Cake (dry mix) 36 Jello (dry) 83
23 Carbohydrate Structure I Monosaccharides Glycosides ligosaccharides Polysaccharides
24 Carbohydrate Structure II Monosaccharides Important ones D-glyceraldehyde source
25 = CH = CH 2 D-Glycerose D-Triose Aldoses D-Tetroses = D-Erythrose D-Pentoses D-Threose D-Ribose D-Arabinose D-Xylose D-Lyxose D-Hexoses D-Allose D-Altrose D-Glucose D-Mannose D-Gulose D-Idose D-Galactose D-Talose
26 Carbohydrate Structure III Monosaccharides Important ones D-glyceraldehyde source Straight chain does not explain all Rxs Ring formation Mutarotation Haworth projection
27 H 1 C RING FRMATIN 2 4 C C C 3 5 C 6 CH CH
28 Glucose Anomers: Hemiacetals Reducing sugars Mutarotate C C C C C CH Ring opens here - Mutarotation 6 CH 2 Ring here for furanose -D-Glucose (m.p. 146 o, [ ] = +112 o ) -D-Glucose (m.p. 150 o, [ ] = +19 o ) or
29 HAWRTH PRJECTIN D- L- 4 6 CH { L-) D-) { D-) L-) D-GLUCSE D-Glucopyranose)
30 Carbohydrate Structure IV Glycosides Alcohol + acid - H 2 Physiological function Base stable, acid labile Rx with other sugars
31 Glycosides CH 2 CH 2 aglycon + R H + R + H 2 D-glucose alkyl D-glucopyranoside
32 Carbohydrate Structure V ligosaccharides Disaccharides Homogeneous Heterogeneous
33 H CH 2 CH 2 D glucopyranosyl-(1 4)- D glucopyranose Maltose H CH 2 CH 2 H D glucopyranosyl-(1 6)- D glucopyranose Isomaltose Disaccharides of Glucose H CH 2 CH 2 H D glucopyranosyl-(1 4)- D glucopyranose Cellobiose CH 2 H CH 2 D glucopyranosyl-(1 6)- D glucopyranose Gentiobiose CH 2 H 2 HC H D glucopyranosyl-(1 1)- L glucopyranoside Trehalose
34 Heterogeneous Disaccharides CH 2 CH 2 H hemiacetal -Lactose -D-galactopyranosyl (1-4)- -D-glucopyranose CH 2 1 H 1 CH H 4 CH Sucrose -D-glucopyranosyl-(1-2)- -D-fructofuranoside
35 Carbohydrate Structure VI ligosaccharides Disaccharides Homogeneous Heterogeneous Reducing vs Non-reducing Higher ligosaccharides
36 Heterogeneous Disaccharides CH 2 CH 2 H hemiacetal -Lactose -D-galactopyranosyl (1-4)- -D-glucopyranose CH 2 1 H 1 CH H 4 CH Sucrose -D-glucopyranosyl-(1-2)- -D-fructofuranoside
37 Carbohydrate Structure VII Polysaccharides General Starch (I) Source Composition Amylose Amylopectin Structure
38 Starch Granules I Introduction to Food Science Tapioca Granules Wheat Granules Potato Granules
39 Starch Granules II Rice Granules Corn Granules
40 Carbohydrate Structure VIII Polysaccharides General Starch (I) Source Composition Amylose (linear) Amylopectin (branched)
41 Amylose Introduction to Food Science Amylose The Helical Structure Amylose Fractions Showing the Helical Structure
42 1,6 Linkage Amylopectin 1,4 Linkage ^^^ Amylopectin Amylopectin Branching
43 Starch Source Amylose % Amylopectin % Corn Tapioca Waxy maize Nil 99+
44 Carbohydrate Structure IX Polysaccharides Starch (II) Granules Gelatinization Rx with Iodine
45 Structrue of molecules in layer of a starch granule. Thickened areas represent micelles produced by association of chains
46 Carbohydrate Structure X Polysaccharides Starch (II) Granules Gelatinization Rx with Iodine
47 Starch Granules III Introduction to Food Science Micrograph of Potato Starch Granules Micrograph of Potato Starch Granules (polarized light shows Maltese Cross) A B
48 Brabender Swelling Profiles at 6% Solids
49 Starch Rx w/ I 2 Clathrates Model of an iodine-filled amylose helix (Rundle, Foster, and Baldwin, 1944)
50 Polysaccharides Starch (III) Modification Why? Crosslinking Stabilization Retrogradation Freeze/Thaw stability Introduction to Food Science Carbohydrate Structure XI
51
52 Starch granule structure Introduction to Food Science X = Cross-linking; H = Hydrogen bonding Gel phase Micelles Cross-linking to supplement hydrogen bonding in a starch granule Stabilization> > (Complements of NATINAL STARCH) ^ = Blocking action =Stabilizing agent
53 Reactions of Carbohydrates I Hydrolysis Acyclic CH Reactions CH Dehydration/Thermal degradation Browning Reactions - nonenzymatic
54 Reactions of Carbohydrates II Hydrolysis Mechanism Products of hydrolysis Corn Syrups Compositions DE (dextrose equivalents)
55 Reactions of Carbohydrates III Hydrolysis Starch (Amylose), considered as a condensation polymer of glucose
56 Typical, Commercial HFCS Products Components Normal 55% Fructose 90% Fructose Glucose Fructose ligosaccharides Relative sweetness
57 Reactions of Carbohydrates IV Acyclic CH Reactions Ring size transitions Mutarotation Enolization - Lobry de Bruyn- Alberda van Ekenstein Rx
58 Glucose Equilibrium Cpds -D-glucofuranose 0.003% -D-glucopyranose D-glucose (aldehydo-dglucose) -D-glucofuranose -D-glucopyranose Interconversion of D-glucose isomers in aqueous solution
59 Reactions of Carbohydrates VI D-glucose enediol D-glucose, D-mannose D-fructose Lobry de Bruyn-Alberda van Ekenstein reaction of D-glucose.
60 Reactions of Carbohydrates VII CH Dehydration/Thermal degradation Browning Reactions - non-enzymatic Caramelization Enolization Dehydration Polymerization
61 hydroxyacetylfuran enediol 3-deoxyosone 3,4-dideoxyosone hydroxymethylfurfural (HMF) Formation of hydroxymethylfurfural by dehydration of a hexose enediol
62 Reactions of Carbohydrates VIII Browning Reactions - non-enzymatic Caramelization Maillard reaction Amino groups Reducing sugar Water Positive vs negative effects Controlling the Rx
63
64 Function of Simple CHs in Foods I Reactions with other Ingredients Water Flavors Sweeteners Alcohols Bulking Agents
65 = 6 Glu = 7 Glu = 8 Glu Host Molecule Guest Molecule Schardinger dextrin Bacillus macerans amylase
66 Sugar Alcohols; Sweetness Sugar alcohol Relative sweetness Xylitol 90 Sorbitol 63 Galactitol 58 Maltitol 68 Lactitol 35 Sugar alcohols in tap water at 25 o C Sucrose = 100
67 Function of Simple CHs in Foods II Bulking Agents Maltodextrins Polydextrose
68 Dietary Fiber NEW DIETARY FIBER DEFINITIN - Dietary fiber is the edible parts of plants or analogous carbohydrates that are resistant to digestion and absorption in the human small intestine with complete or partial fermentation in the large intestine. Dietary fiber includes polysaccharides, oligosaccharides, lignin, and associated plant substances. Dietary fibers promote beneficial physiological effects including laxation, and/or blood cholesterol attenuation, and/or blood glucose attenuation.
69 Polydextrose Composition % Polymer Glucose Sorbitol Levoglucosan Water Sulphated ash
Module-04: Food carbohydrates: Monosaccharides and Oligosaccharides
 Paper No. 01 Paper Title: Food Chemistry Module-04: Food carbohydrates: Monosaccharides and Oligosaccharides Monosaccharides The simplest form of carbohydrates is the monosaccharide. Monosaccharides are
Paper No. 01 Paper Title: Food Chemistry Module-04: Food carbohydrates: Monosaccharides and Oligosaccharides Monosaccharides The simplest form of carbohydrates is the monosaccharide. Monosaccharides are
Fundamentals of Organic Chemistry. CHAPTER 6: Carbohydrates
 Fundamentals of Organic Chemistry CHEM 109 For Students of Health Colleges Credit hrs.: (2+1) King Saud University College of Science, Chemistry Department CHEM 109 CHAPTER 6: Carbohydrates Carbohydrates
Fundamentals of Organic Chemistry CHEM 109 For Students of Health Colleges Credit hrs.: (2+1) King Saud University College of Science, Chemistry Department CHEM 109 CHAPTER 6: Carbohydrates Carbohydrates
24.1 Introduction to Carbohydrates
 24.1 Introduction to Carbohydrates Carbohydrates (sugars) are abundant in nature: They are high energy biomolecules. They provide structural rigidity for organisms (plants, crustaceans, etc.). The polymer
24.1 Introduction to Carbohydrates Carbohydrates (sugars) are abundant in nature: They are high energy biomolecules. They provide structural rigidity for organisms (plants, crustaceans, etc.). The polymer
CLASS 11th. Biomolecules
 CLASS 11th 01. Carbohydrates These are the compound of carbon, hydrogen and oxygen having hydrogen and oxygen in the same ratio as that of water, i.e. 2 : 1. They are among the most widely distributed
CLASS 11th 01. Carbohydrates These are the compound of carbon, hydrogen and oxygen having hydrogen and oxygen in the same ratio as that of water, i.e. 2 : 1. They are among the most widely distributed
Chemistry 110. Bettelheim, Brown, Campbell & Farrell. Ninth Edition. Introduction to General, Organic and Biochemistry Chapter 20 Carbohydrates
 hemistry 110 Bettelheim, Brown, ampbell & Farrell Ninth Edition Introduction to General, rganic and Biochemistry hapter 20 arbohydrates Polyhydroxy Aldehydes & Ketones arbohydrates A A arbohydrate is a
hemistry 110 Bettelheim, Brown, ampbell & Farrell Ninth Edition Introduction to General, rganic and Biochemistry hapter 20 arbohydrates Polyhydroxy Aldehydes & Ketones arbohydrates A A arbohydrate is a
I (CH 2 O) n or H - C - OH I
 V. ARBYDRATE arbohydrates (glycans) have the following basic composition: I ( ) n or - - I Many carbohydrates are soluble in water. The usual chemical test for the simpler carbohydrates is heating with
V. ARBYDRATE arbohydrates (glycans) have the following basic composition: I ( ) n or - - I Many carbohydrates are soluble in water. The usual chemical test for the simpler carbohydrates is heating with
CHAPTER 27 CARBOHYDRATES SOLUTIONS TO REVIEW QUESTIONS
 27 09/17/2013 11:12:35 Page 397 APTER 27 ARBYDRATES SLUTINS T REVIEW QUESTINS 1. In general, the carbohydrate carbon oxidation state determines the carbon s metabolic energy content. The more oxidized
27 09/17/2013 11:12:35 Page 397 APTER 27 ARBYDRATES SLUTINS T REVIEW QUESTINS 1. In general, the carbohydrate carbon oxidation state determines the carbon s metabolic energy content. The more oxidized
Carbohydrates. Chapter 12
 Carbohydrates Chapter 12 Educational Goals 1. Given a Fischer projection of a monosaccharide, classify it as either aldoses or ketoses. 2. Given a Fischer projection of a monosaccharide, classify it by
Carbohydrates Chapter 12 Educational Goals 1. Given a Fischer projection of a monosaccharide, classify it as either aldoses or ketoses. 2. Given a Fischer projection of a monosaccharide, classify it by
Number of Carbohydrate Units
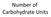 Number of Carbohydrate Units Monosaccharides = single unit Disaccharides = two units Oligiosaccharide = 3 10 units Polysaccharide = 11+ units Bonus: Can you name the most common Mono (4), Di(3), and Poly(4)
Number of Carbohydrate Units Monosaccharides = single unit Disaccharides = two units Oligiosaccharide = 3 10 units Polysaccharide = 11+ units Bonus: Can you name the most common Mono (4), Di(3), and Poly(4)
Chapter-8 Saccharide Chemistry
 Chapter-8 Saccharide Chemistry Page 217-228 Carbohydrates (Saccharides) are most abundant biological molecule, riginally produced through C 2 fixation during photosynthesis I (C 2 ) n or - C - I where
Chapter-8 Saccharide Chemistry Page 217-228 Carbohydrates (Saccharides) are most abundant biological molecule, riginally produced through C 2 fixation during photosynthesis I (C 2 ) n or - C - I where
!"#$%&'()*+(!,-./012-,345(
 (!"#$%&'()*+(!,-./012-,345( (!"#"$%&'()$*%#+,'(-(.+/&/*+,%&(01"2+34$5( 6%#+,"(!/$75#38+(92+41( CAPTER 20: Learning Objectives:! >
(!"#$%&'()*+(!,-./012-,345( (!"#"$%&'()$*%#+,'(-(.+/&/*+,%&(01"2+34$5( 6%#+,"(!/$75#38+(92+41( CAPTER 20: Learning Objectives:! >
Carbohydrate Chemistry 2016 Family & Consumer Sciences Conference Karin Allen, PhD
 Carbohydrate Chemistry 2016 Family & Consumer Sciences Conference Karin Allen, PhD Overview Carbohydrate chemistry General characteristics Sugar chemistry Starch chemistry 10 minute break Iodine test for
Carbohydrate Chemistry 2016 Family & Consumer Sciences Conference Karin Allen, PhD Overview Carbohydrate chemistry General characteristics Sugar chemistry Starch chemistry 10 minute break Iodine test for
Carbohydrates CHAPTER SUMMARY
 14 2 cellulose 2 2 arbohydrates 2 amylose APTER SUMMARY 14.1 hemical Nature of arbohydrates - Polyhydroxy Aldehydes and Ketones arbohydrates are a class of organic biopolymers which consist of polyhydroxy
14 2 cellulose 2 2 arbohydrates 2 amylose APTER SUMMARY 14.1 hemical Nature of arbohydrates - Polyhydroxy Aldehydes and Ketones arbohydrates are a class of organic biopolymers which consist of polyhydroxy
Classification of Carbohydrates. monosaccharide disaccharide oligosaccharide polysaccharide
 Carbohydrates Classification of Carbohydrates monosaccharide disaccharide oligosaccharide polysaccharide Monosaccharide is not cleaved to a simpler carbohydrate on hydrolysis glucose, for example, is a
Carbohydrates Classification of Carbohydrates monosaccharide disaccharide oligosaccharide polysaccharide Monosaccharide is not cleaved to a simpler carbohydrate on hydrolysis glucose, for example, is a
Carbohydrates - Chemical Structure
 Carbohydrates - Chemical Structure Carbohydrates consist of the elements carbon (C), hydrogen (H) and oxygen (O) with a ratio of hydrogen twice that of carbon and oxygen. Carbohydrates include sugars,
Carbohydrates - Chemical Structure Carbohydrates consist of the elements carbon (C), hydrogen (H) and oxygen (O) with a ratio of hydrogen twice that of carbon and oxygen. Carbohydrates include sugars,
Chapter 1. Chemistry of Life - Advanced TABLE 1.2: title
 Condensation and Hydrolysis Condensation reactions are the chemical processes by which large organic compounds are synthesized from their monomeric units. Hydrolysis reactions are the reverse process.
Condensation and Hydrolysis Condensation reactions are the chemical processes by which large organic compounds are synthesized from their monomeric units. Hydrolysis reactions are the reverse process.
BIOMOLECULES & SPECTROSCOPY TABLE OF CONTENTS S.NO. TOPIC PAGE NO. i) Carbohydrates B3. ii) Proteins & Nucleic Acids.
 BIOMOLECULES & SPECTROSCOPY TABLE OF CONTENTS S.NO. TOPIC PAGE NO. 1. Biomolecules i) Carbohydrates B3 ii) Proteins & Nucleic Acids iii) Steroids iv) Terpenes & Cartenoids B27 B61 B65 2. Spectroscopy v)
BIOMOLECULES & SPECTROSCOPY TABLE OF CONTENTS S.NO. TOPIC PAGE NO. 1. Biomolecules i) Carbohydrates B3 ii) Proteins & Nucleic Acids iii) Steroids iv) Terpenes & Cartenoids B27 B61 B65 2. Spectroscopy v)
Chemistry B11 Chapters 13 Esters, amides and carbohydrates
 Chapters 13 Esters, amides and carbohydrates Esters: esters are derived from carboxylic acids (the hydrogen atom in the carboxyl group of carboxylic acid is replaced by an alkyl group). The functional
Chapters 13 Esters, amides and carbohydrates Esters: esters are derived from carboxylic acids (the hydrogen atom in the carboxyl group of carboxylic acid is replaced by an alkyl group). The functional
CARBOHYDRATES (SUGARS)
 ARBYDRATES (SUGARS) ARBYDRATES: 1. Most Abundant Molecules on Earth: (100 MILLIN METRI TNS f 2 And 2 0 onverted To ellulose and ther Plant Products/Year) 2. FUNTINS: Diet, Energy, Structural, Signalling
ARBYDRATES (SUGARS) ARBYDRATES: 1. Most Abundant Molecules on Earth: (100 MILLIN METRI TNS f 2 And 2 0 onverted To ellulose and ther Plant Products/Year) 2. FUNTINS: Diet, Energy, Structural, Signalling
Anomeric carbon Erythritol is achiral because of a mirror plane in the molecule and therefore, the product is optically inactive.
 APTER 22 Practice Exercises 22.1 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 D-Ribulose L-Ribulose D-Xyulose L-Xyulose (one pair of enantiomers) (a second pair of enantiomers) 22.3 2 Anomeric carbon Glycosidic bond 3 () Methyl -D-mannopyranoside
APTER 22 Practice Exercises 22.1 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 D-Ribulose L-Ribulose D-Xyulose L-Xyulose (one pair of enantiomers) (a second pair of enantiomers) 22.3 2 Anomeric carbon Glycosidic bond 3 () Methyl -D-mannopyranoside
BCH 4053 Spring 2001 Chapter 7 Lecture Notes
 BC 4053 Spring 2001 Chapter 7 Lecture Notes 1 Chapter 7 Carbohydrates 2 Carbohydrates: Nomenclature ydrates of carbon General formula (C 2 ) n (simple sugars) or C x ( 2 0) y Monosaccharides (simple sugars)
BC 4053 Spring 2001 Chapter 7 Lecture Notes 1 Chapter 7 Carbohydrates 2 Carbohydrates: Nomenclature ydrates of carbon General formula (C 2 ) n (simple sugars) or C x ( 2 0) y Monosaccharides (simple sugars)
2/25/2015. Chapter 6. Carbohydrates. Outline. 6.1 Classes of Carbohydrates. 6.1 Classes of Carbohydrates. 6.1 Classes of Carbohydrates
 Lecture Presentation Chapter 6 Carbohydrates Julie Klare Fortis College Smyrna, GA Outline 6.7 Carbohydrates and Blood The simplest carbohydrates are monosaccharides (mono is Greek for one, sakkhari is
Lecture Presentation Chapter 6 Carbohydrates Julie Klare Fortis College Smyrna, GA Outline 6.7 Carbohydrates and Blood The simplest carbohydrates are monosaccharides (mono is Greek for one, sakkhari is
What are Carbohydrates? Aldoses and Ketoses
 What are Carbohydrates? Polyhydroxylated aldehydes and ketones Commonly called sugars General formula of common sugars!glucose: C 6 ( 2 ) 6!Glyceraldehyde: C 3 ( 2 ) 3 Talking points: C 2 ACS Division
What are Carbohydrates? Polyhydroxylated aldehydes and ketones Commonly called sugars General formula of common sugars!glucose: C 6 ( 2 ) 6!Glyceraldehyde: C 3 ( 2 ) 3 Talking points: C 2 ACS Division
Chapter 20 Carbohydrates Chapter 20
 Chapter 20 Carbohydrates Chapter 20 1 Carbohydrates Carbohydrate: A polyhydroxyaldehyde or polyhydroxyketone, or a substance that gives these compounds on hydrolysis. Monosaccharide: A carbohydrate that
Chapter 20 Carbohydrates Chapter 20 1 Carbohydrates Carbohydrate: A polyhydroxyaldehyde or polyhydroxyketone, or a substance that gives these compounds on hydrolysis. Monosaccharide: A carbohydrate that
Ch13. Sugars. What biology does with monosaccharides disaccharides and polysaccharides. version 1.0
 Ch13 Sugars What biology does with monosaccharides disaccharides and polysaccharides. version 1.0 Nick DeMello, PhD. 2007-2015 Ch13 Sugars Haworth Structures Saccharides can form rings. That creates a
Ch13 Sugars What biology does with monosaccharides disaccharides and polysaccharides. version 1.0 Nick DeMello, PhD. 2007-2015 Ch13 Sugars Haworth Structures Saccharides can form rings. That creates a
Glycosides. Carbohydrates
 Carbohydrates A carbohydrate is a large biological molecule consisting of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen atoms, usually with a hydrogen:oxygen atom ratio of 2:1. Glycosides Acetal derivatives formed when
Carbohydrates A carbohydrate is a large biological molecule consisting of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen atoms, usually with a hydrogen:oxygen atom ratio of 2:1. Glycosides Acetal derivatives formed when
Carbohydrates 26 SUCROSE
 26 arbohydrates SURSE 26.3 IRALITY F MNSAARIDES 2 (R)-glyceraldehyde 25 [α] D = + 13.5 o 2 Fischer projection carbonyl group at top carbonyl near top 2 2 2 2 Fischer projection D-galactose 2 2 Fischer
26 arbohydrates SURSE 26.3 IRALITY F MNSAARIDES 2 (R)-glyceraldehyde 25 [α] D = + 13.5 o 2 Fischer projection carbonyl group at top carbonyl near top 2 2 2 2 Fischer projection D-galactose 2 2 Fischer
For more info visit
 Carbohydrates Classification of carbohydrates: Monosaccharides: Polyhydroxy aldehydes or polyhydroxy ketones which cannot be decomposed by hydrolysis to give simpler carbohydrates.examples: Glucose, Fructose,
Carbohydrates Classification of carbohydrates: Monosaccharides: Polyhydroxy aldehydes or polyhydroxy ketones which cannot be decomposed by hydrolysis to give simpler carbohydrates.examples: Glucose, Fructose,
Chapter 23: Carbohydrates hydrates of carbon: general formula C n (H 2 O) n. Polymers: large molecules made up of repeating smaller units (monomer)
 Chapter : Carbohydrates hydrates of carbon: general formula C n ( ) n Plants: photosynthesis hν C + C + Polymers: large molecules made up of repeating smaller units (monomer) Biopolymers: Monomer units:
Chapter : Carbohydrates hydrates of carbon: general formula C n ( ) n Plants: photosynthesis hν C + C + Polymers: large molecules made up of repeating smaller units (monomer) Biopolymers: Monomer units:
Carbohydrates hydrates of carbon: general formula C n (H 2 O) n. Polymers: large molecules made up of repeating smaller units (monomer)
 Carbohydrates hydrates of carbon: general formula C n ( ) n Plants: photosynthesis hν 6 C + 6 C 6 6 + 6 Polymers: large molecules made up of repeating smaller units (monomer) Biopolymers: carbohydrates
Carbohydrates hydrates of carbon: general formula C n ( ) n Plants: photosynthesis hν 6 C + 6 C 6 6 + 6 Polymers: large molecules made up of repeating smaller units (monomer) Biopolymers: carbohydrates
2.2: Sugars and Polysaccharides François Baneyx Department of Chemical Engineering, University of Washington
 2.2: Sugars and Polysaccharides François Baneyx Department of hemical Engineering, University of Washington baneyx@u.washington.edu arbohydrates or saccharides are abundant compounds that play regulatory
2.2: Sugars and Polysaccharides François Baneyx Department of hemical Engineering, University of Washington baneyx@u.washington.edu arbohydrates or saccharides are abundant compounds that play regulatory
Carbohydrates 1. Steven E. Massey, Ph.D. Assistant Professor Bioinformatics Department of Biology University of Puerto Rico Río Piedras
 Carbohydrates 1 Steven E. Massey, Ph.D. Assistant Professor Bioinformatics Department of Biology University of Puerto Rico Río Piedras Office & Lab: NCN#343B Tel: 787-764-0000 ext. 7798 E-mail: stevenemassey@gmail.com
Carbohydrates 1 Steven E. Massey, Ph.D. Assistant Professor Bioinformatics Department of Biology University of Puerto Rico Río Piedras Office & Lab: NCN#343B Tel: 787-764-0000 ext. 7798 E-mail: stevenemassey@gmail.com
Carbohydrates. Organic compounds which comprise of only C, H and O. C x (H 2 O) y
 Carbohydrates Organic compounds which comprise of only C, H and O C x (H 2 O) y Carbohydrates Monosaccharides Simple sugar Soluble in water Precursors in synthesis triose sugars of other (C3) molecules
Carbohydrates Organic compounds which comprise of only C, H and O C x (H 2 O) y Carbohydrates Monosaccharides Simple sugar Soluble in water Precursors in synthesis triose sugars of other (C3) molecules
CHAPTER 23. Carbohydrates
 CAPTER 23 Carbohydrates 1 Introduction Carbohydrates are naturally occurring compounds of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen. Carbohydrates have the empirical formula C 2. Carbohydrates have the general formula
CAPTER 23 Carbohydrates 1 Introduction Carbohydrates are naturally occurring compounds of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen. Carbohydrates have the empirical formula C 2. Carbohydrates have the general formula
A Getting-It-On Review and Self-Test. . Carbohydrates are
 A Getting-It-n Review and Self-Test arbohydrates arbohydrates, one of the three principal classes of foods, contain only three elements: (1), (2), and (3). The name carbohydrate is derived from the French
A Getting-It-n Review and Self-Test arbohydrates arbohydrates, one of the three principal classes of foods, contain only three elements: (1), (2), and (3). The name carbohydrate is derived from the French
Carbohydrates. Green plants turn H 2 O, CO 2, and sunlight into carbohydrates.
 Chapter 27 Carbohydrates Green plants turn 2 O, CO 2, and sunlight into carbohydrates. Introduction to General, Organic, and Biochemistry, 10e John Wiley & Sons, Inc Morris ein, Scott Pattison, and Susan
Chapter 27 Carbohydrates Green plants turn 2 O, CO 2, and sunlight into carbohydrates. Introduction to General, Organic, and Biochemistry, 10e John Wiley & Sons, Inc Morris ein, Scott Pattison, and Susan
Dr. Entedhar Carbohydrates Carbohydrates are carbon compounds that have aldehyde (C-H=0) or ketone (C=O) moiety and comprises polyhyroxyl alcohol
 Dr. Entedhar Carbohydrates Carbohydrates are carbon compounds that have aldehyde (C-H=0) or ketone (C=O) moiety and comprises polyhyroxyl alcohol (polyhydroxyaldehyde or polyhyroxyketone); their polymers,which
Dr. Entedhar Carbohydrates Carbohydrates are carbon compounds that have aldehyde (C-H=0) or ketone (C=O) moiety and comprises polyhyroxyl alcohol (polyhydroxyaldehyde or polyhyroxyketone); their polymers,which
Lecture 2 Carbohydrates
 Lecture 2 Carbohydrates Sources of CHOs Wholegrains major dietary intake Vegetables, legumes ad fruit contain dietary fibre Milk products provide lactose essential for infants Glycogen is a storage carbohydrate,
Lecture 2 Carbohydrates Sources of CHOs Wholegrains major dietary intake Vegetables, legumes ad fruit contain dietary fibre Milk products provide lactose essential for infants Glycogen is a storage carbohydrate,
Chem 263 Nov 22, Carbohydrates (also known as sugars or saccharides) See Handout
 hem 263 Nov 22, 2016 arbohydrates (also known as sugars or saccharides) See andout Approximately 0.02% of the sun s energy is used on this planet for photosynthesis in which organisms convert carbon dioxide
hem 263 Nov 22, 2016 arbohydrates (also known as sugars or saccharides) See andout Approximately 0.02% of the sun s energy is used on this planet for photosynthesis in which organisms convert carbon dioxide
I. Carbohydrates Overview A. Carbohydrates are a class of biomolecules which have a variety of functions. 1. energy
 Chapter 22 Carbohydrates Chem 306 Roper I. Carbohydrates Overview A. Carbohydrates are a class of biomolecules which have a variety of functions. 1. energy 2. energy storage 3. structure 4. other functions!
Chapter 22 Carbohydrates Chem 306 Roper I. Carbohydrates Overview A. Carbohydrates are a class of biomolecules which have a variety of functions. 1. energy 2. energy storage 3. structure 4. other functions!
Chapter 18. Carbohydrates with an Introduction to Biochemistry. Carbohydrates with an Introduction to Biochemistry page 1
 Chapter 18 Carbohydrates with an Introduction to Biochemistry Carbohydrates with an Introduction to Biochemistry page 1 Introduction to Proteins, Carbohydrates, Lipids, and Bioenergetics Metabolism and
Chapter 18 Carbohydrates with an Introduction to Biochemistry Carbohydrates with an Introduction to Biochemistry page 1 Introduction to Proteins, Carbohydrates, Lipids, and Bioenergetics Metabolism and
Chapter 27 Carbohydrates
 Chapter 27 Carbohydrates Green plants turn 2 O, CO 2, and sunlight into carbohydrates. Introduction to General, Organic, and Biochemistry, 10e John Wiley & Sons, Inc Morris ein, Scott Pattison, and Susan
Chapter 27 Carbohydrates Green plants turn 2 O, CO 2, and sunlight into carbohydrates. Introduction to General, Organic, and Biochemistry, 10e John Wiley & Sons, Inc Morris ein, Scott Pattison, and Susan
Chapter 22 Carbohydrates
 Chapter 22 Carbohydrates Introduction Classification of Carbohydrates Carbohydrates have the general formula C x (H 2 O) y Carbohydrates are defined as polyhydroxy aldehydes or ketones or substances that
Chapter 22 Carbohydrates Introduction Classification of Carbohydrates Carbohydrates have the general formula C x (H 2 O) y Carbohydrates are defined as polyhydroxy aldehydes or ketones or substances that
Carbohydrates. Monosaccharides
 Carbohydrates Carbohydrates (also called saccharides) are molecular compounds made from just three elements: carbon, hydrogen and oxygen. Monosaccharides (e.g. glucose) and disaccharides (e.g. sucrose)
Carbohydrates Carbohydrates (also called saccharides) are molecular compounds made from just three elements: carbon, hydrogen and oxygen. Monosaccharides (e.g. glucose) and disaccharides (e.g. sucrose)
Carbohydrate Chemistry
 Carbohydrate Chemistry The term carbohydrate is derived from the Cn(2O)n general chemical formula Carbohydrates are polyhydroxy aldehydes or ketones, or substances that yield such compounds on hydrolysis
Carbohydrate Chemistry The term carbohydrate is derived from the Cn(2O)n general chemical formula Carbohydrates are polyhydroxy aldehydes or ketones, or substances that yield such compounds on hydrolysis
Chapter 23 Carbohydrates and Nucleic Acids. Carbohydrates
 Chapter 23 Carbohydrates and Nucleic Acids Carbohydrates Synthesized by plants using sunlight to convert CO 2 and H 2 O to glucose and O 2. Polymers include starch and cellulose. Starch is storage unit
Chapter 23 Carbohydrates and Nucleic Acids Carbohydrates Synthesized by plants using sunlight to convert CO 2 and H 2 O to glucose and O 2. Polymers include starch and cellulose. Starch is storage unit
Lecture Notes Chem 51C S. King. Chapter 28 Carbohydrates. Starch, Glycogen and cellulose are all polymers of glucose.
 Lecture otes hem 51 S. King hapter 28 arbohydrates arbohydrates are the most abundant class of organic compounds in the plant world. They are synthesized by nearly all plants and animals, which use them
Lecture otes hem 51 S. King hapter 28 arbohydrates arbohydrates are the most abundant class of organic compounds in the plant world. They are synthesized by nearly all plants and animals, which use them
Chapter 16: Carbohydrates
 Vocabulary Aldose: a sugar that contains an aldehyde group as part of its structure Amylopectin: a form of starch; a branched chain polymer of glucose Amylose: a form of starch; a linear polymer of glucose
Vocabulary Aldose: a sugar that contains an aldehyde group as part of its structure Amylopectin: a form of starch; a branched chain polymer of glucose Amylose: a form of starch; a linear polymer of glucose
Structural Polysaccharides
 Carbohydrates & ATP Carbohydrates include both sugars and polymers of sugars. The simplest carbohydrates are the monosaccharides, or simple sugars; these are the monomers from which more complex carbohydrates
Carbohydrates & ATP Carbohydrates include both sugars and polymers of sugars. The simplest carbohydrates are the monosaccharides, or simple sugars; these are the monomers from which more complex carbohydrates
Chapter 7 Overview. Carbohydrates
 Chapter 7 Overview n Carbohydrates main ingredient for energy production Most abundant biomolecule in nature Direct link between solar energy & chemical energy Glucose our main energy source Carbohydrates
Chapter 7 Overview n Carbohydrates main ingredient for energy production Most abundant biomolecule in nature Direct link between solar energy & chemical energy Glucose our main energy source Carbohydrates
Organic Chemistry III
 rganic Chemistry III (Yuki Goto, Bioorganic Chemistry Lab.) rganic chemistry of biomolecules rganic chemistry of radicals 6/6 (Wed) 6/13 (Wed) 6/20 (Wed) 6/27 (Wed) 7/4 (Wed) Examples of biomolecules?
rganic Chemistry III (Yuki Goto, Bioorganic Chemistry Lab.) rganic chemistry of biomolecules rganic chemistry of radicals 6/6 (Wed) 6/13 (Wed) 6/20 (Wed) 6/27 (Wed) 7/4 (Wed) Examples of biomolecules?
Carbohydrates A General Introduction. Graduate course in Carbohydrate Chemistry
 Carbohydrates A General Introduction Sugar Sucrose, Saccharose, Cane sugar, Beet sugar, Table sugar β-d-fructofuranosyl-(2 1)-α-D-glucopyranoside β-d-fruf-(2 1)-α-D-Glcp Sugar oney (fructose + glucose)
Carbohydrates A General Introduction Sugar Sucrose, Saccharose, Cane sugar, Beet sugar, Table sugar β-d-fructofuranosyl-(2 1)-α-D-glucopyranoside β-d-fruf-(2 1)-α-D-Glcp Sugar oney (fructose + glucose)
Chemistry 1050 Exam 3 Study Guide
 Chapter 12 Chemistry 1050 Exam 3 Study Guide 12.1 a) Identify alkenes, alkynes and aromatics as unsaturated hydrocarbons. Determine the number of hydrogen atoms needed to complete an alkene structure.
Chapter 12 Chemistry 1050 Exam 3 Study Guide 12.1 a) Identify alkenes, alkynes and aromatics as unsaturated hydrocarbons. Determine the number of hydrogen atoms needed to complete an alkene structure.
CLASS 12th. Biomolecules
 CLASS 12th Biomolecules 01. Introduction Biomolecules may be defined as complex lifeless chemical substances which form the basis of life. i.e. they not only build up living system (creatures) but are
CLASS 12th Biomolecules 01. Introduction Biomolecules may be defined as complex lifeless chemical substances which form the basis of life. i.e. they not only build up living system (creatures) but are
MahaAbuAjamieh. BahaaNajjar. MamoonAhram
 7 MahaAbuAjamieh BahaaNajjar MamoonAhram Carbohydrates (saccharides) can be classified into these main categories: 1. Monosaccharides, they are simplesugars (the simplest units), such as glucose, galactose
7 MahaAbuAjamieh BahaaNajjar MamoonAhram Carbohydrates (saccharides) can be classified into these main categories: 1. Monosaccharides, they are simplesugars (the simplest units), such as glucose, galactose
B.sc. III Chemistry Paper b. Submited by :- Dr. Sangeeta Mehtani Associate Professor Deptt. Of Chemistry PGGCG, sec11 Chd
 B.sc. III Chemistry Paper b Submited by :- Dr. Sangeeta Mehtani Associate Professor Deptt. Of Chemistry PGGCG, sec11 Chd CARBOYDRATES Carbohydrates polyhydroxyaldehydes or polyhydroxyketones of formula
B.sc. III Chemistry Paper b Submited by :- Dr. Sangeeta Mehtani Associate Professor Deptt. Of Chemistry PGGCG, sec11 Chd CARBOYDRATES Carbohydrates polyhydroxyaldehydes or polyhydroxyketones of formula
Chapter 24: Carbohydrates
 Chapter 24: Carbohydrates [Sections: 24.1 24.10] 1. Carbohydrates definition naturally occuring compounds derived from carbon, oxygen and hydrogen the net molecular formula comes from each carbon having
Chapter 24: Carbohydrates [Sections: 24.1 24.10] 1. Carbohydrates definition naturally occuring compounds derived from carbon, oxygen and hydrogen the net molecular formula comes from each carbon having
Biochemistry: Macromolecules
 1 Biology: Macromolecules 2 Carbohydrates Carbohydrate organic compound containing carbon, hydrogen, & oxygen in a 1:2:1 ratio Meaning: hydrated carbon ratio of h:0 is 2:1 (same as in water) Source: plants
1 Biology: Macromolecules 2 Carbohydrates Carbohydrate organic compound containing carbon, hydrogen, & oxygen in a 1:2:1 ratio Meaning: hydrated carbon ratio of h:0 is 2:1 (same as in water) Source: plants
Welcome to Class 7. Class 7: Outline and Objectives. Introductory Biochemistry
 Welcome to Class 7 Introductory Biochemistry Class 7: Outline and Objectives l Monosaccharides l Aldoses, ketoses; hemiacetals; epimers l Pyranoses, furanoses l Mutarotation, anomers l Disaccharides and
Welcome to Class 7 Introductory Biochemistry Class 7: Outline and Objectives l Monosaccharides l Aldoses, ketoses; hemiacetals; epimers l Pyranoses, furanoses l Mutarotation, anomers l Disaccharides and
ANSC 689 PHYSIOLOGICAL CHEMISTRY OF LIVESTOCK SPECIES Carbohydrate Chemistry
 I. General structures A. D-Aldoses ANSC 689 PHYSIOLOGICAL CHEMISTRY OF LIVESTOCK SPECIES 1. All monosaccharides are aldehydes or ketones with multiple hydroxyl groups (i.e., alcohol groups). 2. Smallest
I. General structures A. D-Aldoses ANSC 689 PHYSIOLOGICAL CHEMISTRY OF LIVESTOCK SPECIES 1. All monosaccharides are aldehydes or ketones with multiple hydroxyl groups (i.e., alcohol groups). 2. Smallest
ANSC 619 PHYSIOLOGICAL CHEMISTRY OF LIVESTOCK SPECIES
 I. General structures ANSC 619 PHYSIOLOGICAL CHEMISTRY OF LIVESTOCK SPECIES A. D-Aldoses 1. All monosaccharides are aldehydes or ketones with multiple hydroxyl groups (i.e., alcohol groups). 2. Smallest
I. General structures ANSC 619 PHYSIOLOGICAL CHEMISTRY OF LIVESTOCK SPECIES A. D-Aldoses 1. All monosaccharides are aldehydes or ketones with multiple hydroxyl groups (i.e., alcohol groups). 2. Smallest
IntroducKon to Carbohydrates
 Carbohidratos IntroducKon to Carbohydrates Carbohydrates (sugars) are abundant in nature: They are high energy biomolecules. They provide structural rigidity for organisms (plants, crustaceans, etc.).
Carbohidratos IntroducKon to Carbohydrates Carbohydrates (sugars) are abundant in nature: They are high energy biomolecules. They provide structural rigidity for organisms (plants, crustaceans, etc.).
Questions- Carbohydrates. A. The following structure is D-sorbose. (Questions 1 7) CH 2 OH C = O H C OH HO C H H C OH
 Questions- Carbohydrates A. The following structure is D-sorbose. (Questions 1 7) CH 2 C = O H C HO C H H C CH 2 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Which characteristic is different when comparing the open-chain forms of
Questions- Carbohydrates A. The following structure is D-sorbose. (Questions 1 7) CH 2 C = O H C HO C H H C CH 2 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Which characteristic is different when comparing the open-chain forms of
2. Structural e.g. bacterial cell walls, cellulose. 3. Information e.g. signals on proteins and membranes.
 hapter 8 - arbohydrates ydrates of arbon: m ( 2 ) n Saccharides: Latin: Saccharum = Sugar 1. Energy transport and storage. 2. Structural e.g. bacterial cell walls, cellulose. 3. Information e.g. signals
hapter 8 - arbohydrates ydrates of arbon: m ( 2 ) n Saccharides: Latin: Saccharum = Sugar 1. Energy transport and storage. 2. Structural e.g. bacterial cell walls, cellulose. 3. Information e.g. signals
CARBOHYDRATES (H 2. Empirical formula: C x. O) y
 CARBYDRATES 1 CARBYDRATES Empirical formula: C x ( 2 ) y 2 CARBYDRATES- WERE? In solid parts of: plants, up to 80% animals, do not exceed 2% In plants: main storage material (starch) building material
CARBYDRATES 1 CARBYDRATES Empirical formula: C x ( 2 ) y 2 CARBYDRATES- WERE? In solid parts of: plants, up to 80% animals, do not exceed 2% In plants: main storage material (starch) building material
Definition of a Carbohydrate
 * Atoms held together by covalent bonds Definition of a Carbohydrate * Organic macromolecules * Consist of C, H, & O atoms * Usually in a 1:2:1 ratio of C:H : O Functions Performed by Carbohydrates Used
* Atoms held together by covalent bonds Definition of a Carbohydrate * Organic macromolecules * Consist of C, H, & O atoms * Usually in a 1:2:1 ratio of C:H : O Functions Performed by Carbohydrates Used
Chemistry 1120 Exam 2 Study Guide
 Chemistry 1120 Exam 2 Study Guide Chapter 6 6.1 Know amines are derivatives of ammonia, which is not an amine. Classify amines as primary, secondary or tertiary. Master Tutor Section 6.1 Review Section
Chemistry 1120 Exam 2 Study Guide Chapter 6 6.1 Know amines are derivatives of ammonia, which is not an amine. Classify amines as primary, secondary or tertiary. Master Tutor Section 6.1 Review Section
Name LastName Student ID
 Name LastName Student ID 1) (12 points) Imidazopyridine derivatives such as 1-deaza-9H-purines (like 1) and 3- deaza-9h-purines (like 2) represent privileged structures in medicinal chemistry and they
Name LastName Student ID 1) (12 points) Imidazopyridine derivatives such as 1-deaza-9H-purines (like 1) and 3- deaza-9h-purines (like 2) represent privileged structures in medicinal chemistry and they
Topic 4 - #2 Carbohydrates Topic 2
 Topic 4 - #2 Carbohydrates Topic 2 Biologically Important Monosaccharide Derivatives There are a large number of monosaccharide derivatives. A variety of chemical and enzymatic reactions produce these
Topic 4 - #2 Carbohydrates Topic 2 Biologically Important Monosaccharide Derivatives There are a large number of monosaccharide derivatives. A variety of chemical and enzymatic reactions produce these
Dr. Nafith Abu Tarboush. Rana N. Talj
 2 Dr. Nafith Abu Tarboush June 19 th 2013 Rana N. Talj Review: Fischer suggested a projection in which the horizontal bonds are projecting towards the viewer and the vertical ones project away from the
2 Dr. Nafith Abu Tarboush June 19 th 2013 Rana N. Talj Review: Fischer suggested a projection in which the horizontal bonds are projecting towards the viewer and the vertical ones project away from the
Dr. Mahendra P. Bhatt (BMLT, MS-Ph.D., Post-doctorate) Associate Professor Clinical Biochemistry
 Dr. Mahendra P. Bhatt (BMLT, MS-Ph.D., Post-doctorate) Associate Professor Clinical Biochemistry mahendramlt@gmail.com Students will be able to describe: Biochemical organization of the cell Transport
Dr. Mahendra P. Bhatt (BMLT, MS-Ph.D., Post-doctorate) Associate Professor Clinical Biochemistry mahendramlt@gmail.com Students will be able to describe: Biochemical organization of the cell Transport
Long time ago, people who sacrifice their sleep, family, food, laughter, and other joys of life were called SAINTS. But now, they are called STUDENTS!
 Long time ago, people who sacrifice their sleep, family, food, laughter, and other joys of life were called SAINTS. But now, they are called STUDENTS! Monosaccharaides Q. Can hydrolysis occur at anytime
Long time ago, people who sacrifice their sleep, family, food, laughter, and other joys of life were called SAINTS. But now, they are called STUDENTS! Monosaccharaides Q. Can hydrolysis occur at anytime
Chemistry 107 Exam 3 Study Guide
 Chapter 7 Chemistry 107 Exam 3 Study Guide 7.1 Recognize the aldehyde, ketone and hydroxyl (-OH) functional groups found in carbohydrates. Differentiate between mono-, di-, and polysaccharides. Master
Chapter 7 Chemistry 107 Exam 3 Study Guide 7.1 Recognize the aldehyde, ketone and hydroxyl (-OH) functional groups found in carbohydrates. Differentiate between mono-, di-, and polysaccharides. Master
Chapter 7 Carbohydrates
 Chapter 7 Carbohydrates Definition of Carbohydrates carbohydrate: hydrate of carbon ; C n ( 2 ) m Examples: glucose (C 6 12 6 or C 6 ( 2 ) 6 ), sucrose (C 12 22 11 or C 12 ( 2 ) 11 ) saccharide: simple
Chapter 7 Carbohydrates Definition of Carbohydrates carbohydrate: hydrate of carbon ; C n ( 2 ) m Examples: glucose (C 6 12 6 or C 6 ( 2 ) 6 ), sucrose (C 12 22 11 or C 12 ( 2 ) 11 ) saccharide: simple
among the most important organic compounds in the living organisms;
 CARBOHYDRATES Elena Rivneac PhD, Associate Professor Department of Biochemistry and Clinical Biochemistry State University of Medicine and Pharmacy "Nicolae Testemitanu" CARBOHYDRATESare among the most
CARBOHYDRATES Elena Rivneac PhD, Associate Professor Department of Biochemistry and Clinical Biochemistry State University of Medicine and Pharmacy "Nicolae Testemitanu" CARBOHYDRATESare among the most
Carbohydrates. 1. Using the terms provided below, complete the concept map showing the characteristics of organic compounds.
 Name: Class: Date: Grade 10 Science Related Reading/Biology Carbohydrates Biology Gr10 1. Using the terms provided below, complete the concept map showing the characteristics of organic compounds. maltose
Name: Class: Date: Grade 10 Science Related Reading/Biology Carbohydrates Biology Gr10 1. Using the terms provided below, complete the concept map showing the characteristics of organic compounds. maltose
This place covers: Reducing the size of material from which sugars are to be extracted; Presses and knives therefor,
 CPC - C13B - 2017.08 C13B PRODUCTION OF SUCROSE; APPARATUS SPECIALLY ADAPTED THEREFOR (chemically synthesised sugars or sugar derivatives C07H; fermentation or enzyme-using processes for preparing compounds
CPC - C13B - 2017.08 C13B PRODUCTION OF SUCROSE; APPARATUS SPECIALLY ADAPTED THEREFOR (chemically synthesised sugars or sugar derivatives C07H; fermentation or enzyme-using processes for preparing compounds
The D-Aldoses: (CH 2 O) x : X = 3 to 6. Kiliani-Fisher Synthesis (CH 2 O) 3. D-glyceraldehyde. 1) HCN 2) DibalH or (CH 2 O) 4 H HO.
 The D-Aldoses: (C 2 ) : X = 3 to 6 (C 2 ) 3 Kiliani-Fisher Synthesis D-glyceraldehyde 1) C 2) Dibal 2, Pd/BaS 4 3) 3 + (C 2 ) 4 D-erythrose D-threose 1) C 2) Dibal 2, Pd/BaS 4 3) 3 + (C 2 ) 5 D-Ribose
The D-Aldoses: (C 2 ) : X = 3 to 6 (C 2 ) 3 Kiliani-Fisher Synthesis D-glyceraldehyde 1) C 2) Dibal 2, Pd/BaS 4 3) 3 + (C 2 ) 4 D-erythrose D-threose 1) C 2) Dibal 2, Pd/BaS 4 3) 3 + (C 2 ) 5 D-Ribose
IntroducKon to Carbohydrates
 Carbohidratos IntroducKon to Carbohydrates Carbohydrates (sugars) are abundant in nature: They are high energy biomolecules. They provide structural rigidity for organisms (plants, crustaceans, etc.).
Carbohidratos IntroducKon to Carbohydrates Carbohydrates (sugars) are abundant in nature: They are high energy biomolecules. They provide structural rigidity for organisms (plants, crustaceans, etc.).
Dr. Basima Sadiq Ahmed PhD. Clinical biochemist
 Dr. Basima Sadiq Ahmed PhD. Clinical biochemist MEDICAL AND BIOLOGICAL IMPORTANCE 1. major source of energy for man. e.g, glucose is used in the human body for energy production. 2. serve as reserve food
Dr. Basima Sadiq Ahmed PhD. Clinical biochemist MEDICAL AND BIOLOGICAL IMPORTANCE 1. major source of energy for man. e.g, glucose is used in the human body for energy production. 2. serve as reserve food
BIOCHEMISTRY UNIT 2 Part 4 ACTIVITY #4 (Chapter 5) CARBOHYDRATES
 AP BIOLOGY BIOCHEMISTRY UNIT 2 Part 4 ACTIVITY #4 (Chapter 5) NAME DATE PERIOD CARBOHYDRATES GENERAL CHARACTERISTICS: Polymers of simple sugars Classified according to number of simple sugars Sugars 3
AP BIOLOGY BIOCHEMISTRY UNIT 2 Part 4 ACTIVITY #4 (Chapter 5) NAME DATE PERIOD CARBOHYDRATES GENERAL CHARACTERISTICS: Polymers of simple sugars Classified according to number of simple sugars Sugars 3
Biomolecules are organic molecules produced by living organisms which consists mainly of the following elements:
 Biomolecules are organic molecules produced by living organisms which consists mainly of the following elements: These elements are non-metals which combine in various ways to form biomolecules through
Biomolecules are organic molecules produced by living organisms which consists mainly of the following elements: These elements are non-metals which combine in various ways to form biomolecules through
IB Biology BIOCHEMISTRY. Biological Macromolecules SBI3U7. Topic 3. Thursday, October 4, 2012
 + IB Biology SBI3U7 BIOCHEMISTRY Topic 3 Biological Macromolecules Essential Questions: 1.What are the 4 main types of biological macromolecules and what is their function within cells? 2.How does the
+ IB Biology SBI3U7 BIOCHEMISTRY Topic 3 Biological Macromolecules Essential Questions: 1.What are the 4 main types of biological macromolecules and what is their function within cells? 2.How does the
15. BIOMOLECULES. B ΔG < 0, feasible S. Adinosin
 15. BIMLECULES Synopsis: Biochemistry : The branch of science that deals with the study of the chemical composition and structure of living organisms and also various changes taking place within them.
15. BIMLECULES Synopsis: Biochemistry : The branch of science that deals with the study of the chemical composition and structure of living organisms and also various changes taking place within them.
Basic Biochemistry. Classes of Biomolecules
 Basic Biochemistry ABE 580 Classes of Biomolecules Carbohydrates Lipids Amino Acids Nucleic Acids Other 1 Carbohydrates Sugars Composed of C, H, O (C n H 2n O n ) Biological Uses Energy source/storage
Basic Biochemistry ABE 580 Classes of Biomolecules Carbohydrates Lipids Amino Acids Nucleic Acids Other 1 Carbohydrates Sugars Composed of C, H, O (C n H 2n O n ) Biological Uses Energy source/storage
Carbohydrates I. Scheme 1. Carbohydrates are classified into two main classes, sugars and polysaccharides.
 Carbohydrates I 11.1 Introduction Carbohydrates are polyhydroxy aldehydes or ketones. They are primarily produced by plants and form a very large group of naturally occurring organic substances. Some common
Carbohydrates I 11.1 Introduction Carbohydrates are polyhydroxy aldehydes or ketones. They are primarily produced by plants and form a very large group of naturally occurring organic substances. Some common
Sheet #8 Dr. Nafeth Abu-Tarboush
 1 arbohydrates There are two topic goals in our study of carbohydrates: Monosaccharides: to recognize their structure, properties, & their stereochemistry. The nature of di-, oligo- & polysaccharides.
1 arbohydrates There are two topic goals in our study of carbohydrates: Monosaccharides: to recognize their structure, properties, & their stereochemistry. The nature of di-, oligo- & polysaccharides.
Carbohydrates. Dr. Mamoun Ahram Summer,
 Carbohydrates Dr. Mamoun Ahram Summer, 2017-2018 Resource This lecture Campbell and Farrell s Biochemistry, Chapter 16 What are they? Carbohydrates are polyhydroxy aldehydes or ketones Saccharide is another
Carbohydrates Dr. Mamoun Ahram Summer, 2017-2018 Resource This lecture Campbell and Farrell s Biochemistry, Chapter 16 What are they? Carbohydrates are polyhydroxy aldehydes or ketones Saccharide is another
Maillard browning reaction: a non-enzymatic browning. Advantages of Maillard browning
 Maillard browning reaction: a non-enzymatic browning Under some conditions, reducing sugars produce brown colors that are desirable and important in some foods. Other brown colors obtained upon heating
Maillard browning reaction: a non-enzymatic browning Under some conditions, reducing sugars produce brown colors that are desirable and important in some foods. Other brown colors obtained upon heating
Carbohydrates. Learning Objective
 , one of the four major classes of biomolecules, are aldehyde or ketone compounds with multiple hydroxyl groups. They function as energy stores, metabolic intermediates and important fuels for the body.
, one of the four major classes of biomolecules, are aldehyde or ketone compounds with multiple hydroxyl groups. They function as energy stores, metabolic intermediates and important fuels for the body.
BCH 445 Biochemistry of nutrition Dr. Mohamed Saad Daoud
 BCH 445 Biochemistry of nutrition Dr. Mohamed Saad Daoud 1 Carbohydrates Carbohydrates: Compounds composed of carbon, oxygen, and hydrogen arranged as monosaccharides or multiples of monosaccharides. Most,
BCH 445 Biochemistry of nutrition Dr. Mohamed Saad Daoud 1 Carbohydrates Carbohydrates: Compounds composed of carbon, oxygen, and hydrogen arranged as monosaccharides or multiples of monosaccharides. Most,
Carbohydrates are a large group of organic compounds occurring in and including,, and. They contain hydrogen and oxygen in the same ratio as (2:1).
 Carbohydrates are a large group of organic compounds occurring in and and including,, and. They contain hydrogen and oxygen in the same ratio as (2:1). Why we study carbohydrates 1) carbohydrates are the
Carbohydrates are a large group of organic compounds occurring in and and including,, and. They contain hydrogen and oxygen in the same ratio as (2:1). Why we study carbohydrates 1) carbohydrates are the
Carbohydrates. b. What do you notice about the orientation of the OH and H groups in glucose? Are they in the axial or equatorial position?
 1. The 3D structure of glucose and galactose are shown. Carbohydrates D-glucose D-galactose a. Is the axial or equatorial position more stable in the chair conformation? b. What do you notice about the
1. The 3D structure of glucose and galactose are shown. Carbohydrates D-glucose D-galactose a. Is the axial or equatorial position more stable in the chair conformation? b. What do you notice about the
Carbohydrates. What are they? What do cells do with carbs? Where do carbs come from? O) n. Formula = (CH 2
 Carbohydrates What are they? Formula = (C 2 O) n where n > 3 Also called sugar Major biomolecule in body What do cells do with carbs? Oxidize them for energy Store them to oxidize later for energy Use
Carbohydrates What are they? Formula = (C 2 O) n where n > 3 Also called sugar Major biomolecule in body What do cells do with carbs? Oxidize them for energy Store them to oxidize later for energy Use
HW #9: 21.36, 21.52, 21.54, 21.56, 21.62, 21.68, 21.70, 21.76, 21.82, 21.88, 21.94, Carbohydrates
 Chemistry 131 Lectures 16 & 17: Carbohydrates Chapter 21 in McMurry, Ballantine, et. al. 7 th edition 05/24/18, 05/25/18 W #9: 21.36, 21.52, 21.54, 21.56, 21.62, 21.68, 21.70, 21.76, 21.82, 21.88, 21.94,
Chemistry 131 Lectures 16 & 17: Carbohydrates Chapter 21 in McMurry, Ballantine, et. al. 7 th edition 05/24/18, 05/25/18 W #9: 21.36, 21.52, 21.54, 21.56, 21.62, 21.68, 21.70, 21.76, 21.82, 21.88, 21.94,
Waseem Abu Obeida. Salsabeel Fleifal. Mamoon Ahram
 8 Waseem Abu Obeida Salsabeel Fleifal Mamoon Ahram Anomers Anomers cyclic monosaccharides or glycosides that are epimers, they differ from each other in the configuration of C-1 if they are aldoses or
8 Waseem Abu Obeida Salsabeel Fleifal Mamoon Ahram Anomers Anomers cyclic monosaccharides or glycosides that are epimers, they differ from each other in the configuration of C-1 if they are aldoses or
Chemistry 106 Lecture Notes Examination 5 Materials. *Hydrated Carbons.
 hemistry 106 Lecture Notes Examination 5 Materials hapter 23: arbohydrates & Nucleic Acids arbohydrates Definition: *ompounds made of,, &. Example: *ydrated arbons. Glucose: 6 12 6 an be written as 6(
hemistry 106 Lecture Notes Examination 5 Materials hapter 23: arbohydrates & Nucleic Acids arbohydrates Definition: *ompounds made of,, &. Example: *ydrated arbons. Glucose: 6 12 6 an be written as 6(
Carbohydrates suga. AP Biology
 Carbohydrates suga Carbohydrates energyo molecules C 2 O O O O O *4 Cal/gram Carbohydrates Carbohydrates are composed of C,, O carbo - hydr - ate C 2 O (C 12 2 O) x C 6 12 O 6 Function: energy energy storage
Carbohydrates suga Carbohydrates energyo molecules C 2 O O O O O *4 Cal/gram Carbohydrates Carbohydrates are composed of C,, O carbo - hydr - ate C 2 O (C 12 2 O) x C 6 12 O 6 Function: energy energy storage
Polymers: large molecules made up of repeating smaller units (monomer) peptides and proteins (Chapter 25) nucleic acids (Chapter 26)
 Chapter 23: Carbohydrates hydrates of carbon: general formula C n (H 2 O) n Plants: photosynthesis 6 CO 2 + 6 H 2 O hν C 6 H 12 O 6 + 6 O 2 Polymers: large molecules made up of repeating smaller units
Chapter 23: Carbohydrates hydrates of carbon: general formula C n (H 2 O) n Plants: photosynthesis 6 CO 2 + 6 H 2 O hν C 6 H 12 O 6 + 6 O 2 Polymers: large molecules made up of repeating smaller units
Chapter 11 Lecture Notes: Carbohydrates
 Educational Goals Chapter 11 Lecture Notes: Carbohydrates 1. Given a Fischer projection of a monosaccharide, classify it as either aldoses or ketoses. 2. Given a Fischer projection of a monosaccharide,
Educational Goals Chapter 11 Lecture Notes: Carbohydrates 1. Given a Fischer projection of a monosaccharide, classify it as either aldoses or ketoses. 2. Given a Fischer projection of a monosaccharide,
