Early Life Effects on Hypothalamic Circuitry. By: The Mystery Gang
|
|
|
- Christina Harrison
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Early Life Effects on Hypothalamic Circuitry By: The Mystery Gang
2
3 Hypothalamic Circuits Controlling Energy Balance ARH (Arcuate nucleus of the Hypothalamus) Subgroup of Neurons 1: coexpress Neuropeptide Y (NPY) and agouti-related peptide (AgRP) Subgroup of Neurons 2: expresses Proopiomelanocortin (POMC) derived peptides like alpha-melanocyte stimulating hormones PVH, DMH, and LHA Other areas implicated in the control of feeding Glucose Regulation and the Hypothalamus Reduction of hepatic gluconeogenesis
4 Copyright 2006 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Benjamin Cummings Hypothalamic Nuclei Figure 12.13b
5 Development of Hypothalamic Feeding Circuits Initiated by cell proliferation in the neuroepithelium of the third ventricle Generation of neuronal progenitors that produce postmitotic neurons Those neurons migrate to their location in all parts of the Hypothalamus
6
7 Development of Hypothalamic Feeding Circuits Human/Non-Human Primate Studies: Rodent Studies: Neuronal Birthdating Hypothalamic Neurogenesis Studies Development of HFC Early Production of in utero NPY in the DMH and Early Production of the LHA NPY immunoreactive NPY and obesity in fibers (21 weeks of animals gestation) TAKEAWAY: There are 2 major critical periods (midgestation and early postnatal life) when alterations can affect hypothalamic neurogenesis. This can have long term consequences to nutrition and metabolism
8 Leptin and Hypothalamic Development Important for the Formation of Hypothalamic Feeding Circuits Too little Leptin The formation of ARH circuits Axonal Formation in the ARH NPY/AgRP, and POMC Takeaway: Critical Periods exist! Too much Leptin/ The Leptin Surge Earlier leptin surges Altered hypothalamic responses The effects of a blunted postnatal surge Takeaway: leptin surges are important at the right times
9 Insulin and Hypothalamic Development Important for development of hypothalamic circuits that regulate energy homeostasis Hyperinsulinism Induced obesity, increased hypothalamic norepinephrine and the density of norepinephrine -containing fibers in the PVH Decreased brain NPY mrna and protein expression, altered neural morphology in the ARH in the fetus Morphological changes in the VMH Takeaway: hyperinsulinism during pregnancy could induce alterations in hypothalamic organization
10 Hyperinsulinism and Pregnancy Hypertrophic myocardiopathy: hypertrophy of the septum and ventricular walls that can in some cases obstruct blood flow. Rizzo G, Arduini D, Romanini C. Accelerated cardiac growth and abnormal cardiac flow in fetuses of diabetic mothers. Obstet Gynecol. 1992;80:
11
12 Embryonic Birthdate of Hypothalamic Leptin- Activated Neurons in Mice Terminology/ Recap E0- the day of conception P0- the day of birth BrdU: 5-Bromo-2-deoxyuridine A marker of dividing cells/proliferation synthetic nucleoside, gets incorporated into new DNA ARH- arcuate nucleus DMH- dorsomedial nucleus PVH- paraventricular nucleus LHA- lateral hypothalamic nucleus POMC - A precursor protein; a precursor to alpha MSH, an agonist for MC4R - Mutations in either POMC or MC4R leads to severe obesity - In CNS, concentrated mainly in ARH, an area with strong functional ties to appetite and food intake
13 Embryonic Birthdate of Hypothalamic LeptinActivated Neurons in Mice The Study - Used BrdU, as well as HuC/D (which is a marker for cell differentiation) to examine the birth of neurons that transmit leptin signaling - Pregnant dams (female parent of an animal) were injected with BrdU at P 10, 12, 14, 16 0r 18 to evaluate the birthdate of cells in key hypothalamic nuclei that are involved in energy balance regulation
14 Embryonic Birthdate of Hypothalamic Leptin- Activated Neurons in Mice Materials, Methods and Immunohistochemistry - - Bred wild type mice, were provided food and water ad libitum (as they saw fit, is often shortened to ad lib) 12-hour light and 12 hour dark cycle, temperature controlled environment Litter size 6-8 pups (after culling average litter size was 7 pups) Only male offspring were studied Pregnant mice were administered a single intraperitoneal injection of BrdU Later, once brains were removed and immersed in 20% sucrose in a 0.02 M potassium PBS (a buffer solution) solution at 4 C overnight, frozen coronal sections were cut and stored in antifreeze at -20 C until put to use Used double labeling of both BrdU and HuC/D to monitor the proliferation and differentiation of cells
15 Embryonic Birthdate of Hypothalamic Leptin- Activated Neurons in Mice Results: Birthdate of neurons in the ARH,VMH, DMH, PVH and of leptin-activated neurons in the hypothalamus - In the ARH, BrdU injection on E12 showed the highest numbers of BrdU-labeled cells and decreased by about 4-to-5 fold between E From double labeling (BrdU and HuC/D) found that peak of neurogenesis occurred at E12 - In VMH, similar results to ARH results - Double labeling experiments found that neurogenesis peak also occurred at E12 - In DMH,double labeling experiments found that majority of neurons in DMH were born between E12-E14 - In PVH, animals that were given BrdU injection on E12 showed highest numbers of BrdU labeled cells - Double labeling experiments showed that neurogenesis also peaked at E12 - In conclusion, double staining experiments showed that 30-50% of leptin sensitive neurons in adult hypothalamus were born during a particularly short developmental period- namely, E12. At most, only 10% were born during a later embryonic stage.
16 Embryonic Birthdate of Hypothalamic Leptin- Activated Neurons in Mice - Results: Birthdate of neurons in the ARH, PVH, DMH, and of leptin activated neurons in the hypothalamus
17 Discussion The majority of hypothalamic nuclei that control energy homeostasis were born between E12 and E14. - What does this timing of the proliferation of leptin activated neurons in the hypothalamus implicate? The paper found that cells in the hypothalamus were derived from precursors in the lower portion of the third ventricle. The paper also found that the development of the hypothalamus had two parts: A portion in-utero which determined the cell number in the hypothalamus, and an extra-utero portion which established neuronal connections Hypothalamic neurogenesis is not restricted to neonatal periods and can be enhanced by external cues (3665)
18 Discussion cont. Environmental changes can affect the development of the hypothalamus between E12 and E14 Maternal nutrition affects hypothalamic cellular proliferation - Maternal high-fat feeding increases cellular proliferation in rats...which yields higher numbers of neurons that contain orexigenic neuropeptides in the PVH and LHA (3665) - Maternal malnutrition reduces orexigenic neurons in the hypothalamus, as well as reducing NPY neurons in the ARH (3665)
19
20 Discussion cont. What is this paper trying to prove? This paper aims to show the significance of the time period of the production of leptin receptor neurons in the hypothalamus, and what external stimuli can affect the nature of the hypothalamus in this critical period. Maternal actions have a tremendous influence on the cognitive development of a fetus, especially in the hypothalamus.
21
22 Background Knowledge The brain may be particularly vulnerable to the effects of obesogenic diets during early life periods of rapid growth, maturation, and brain development
23 What can early life exposure to obesogenic diets do? How does it affect the future generations?
24 Factors Reviewed 1) Varying levels of HFD : 40%, 60%, 25%... %kcal derived from fat 2) Different ratios of fats : sugars : %kcal from sugar? Independent? With HFD? 3) Timing of Exposure: Perinatal period vs Juvenile/adolescent Period 4) Duration of Exposure: # of weeks exposed
25
26
27 Rodent Model Findings Maternal Consumption of HFD beginning before mating and ending before weaning : 1) Caused evident hippocampal-dependent spatial learning deficits in offspring at 4 weeks of age 2) Detrimental effects are more pronounced during early life 3) Progeny performed worse in the MWM during adulthood relative to offspring born from dams on standard chow 4) Animals that were switched to standard chow at weaning were equally impaired in learning the learning task compared to animals weaned on the HFD
28 Contrasting Results A) Under some conditions, prenatal and perinatal exposure to a HFD does not impair hippocampal dependent learning and memory. (No change between experiment and control) a) One study showed that HFD induced memory deficits may be overcome by switching the pups to standard chow at weaning B) Other reports indicate that pre-weaning HFD exposure confers cognitive deficits that persist into adulthood, even when the animals were fed a standard chow diet post weaning a) Progeny born from dams fed a HFD performed worse in the MWM How do we interpret these differing results?
29 Possible Explanation: % of fat and sugar in the diet A) MWM deficit study despite weaning on chow utilized HFD with 45% kcal from fat a) Page et al. utilized 45% HFD with a considerably higher proportion of kcal from sugar compared with HFD used by others b) Page et al. had 17% sugar in HFD B) Recovery of Function results utilized HFD with 60% kcal from fat a) White et al. study had 7% sugar in HFD It is possible that the combined impact of high sugar and fat in the diet is greater than the impact of fat alone.
30 What developmental processes does it interrupt? What do we know? What SHOULD we know?
31 Extension of HFD Diet Duration Goal: To study the impact of perinatal through childhood and/or early adulthood consumption of an obesogenic diet on learning and memory and function
32 Results A) Progeny of dams maintained on HFD(60-65% kcal from fat) who were fed the HFD for over 2 months post weaning exhibited impaired performance in MWM a) When HFD was fed throughout both pre- and post-natal development as well as post-weaning, the offspring had deficits in spatial learning capabilities (MWM) during adulthood (Lepinay et al. 2015) B) HFD(39%kcal from fat) diet when confined exclusively to either the prenatal or postnatal phase, HFD-feeding had no effect on spatial memory in MWM (Lepinay et al. 2015) Similar findings using Novel Context Mismatch task**
33 Juvenile and Adolescent Period
34 Methods Obesogenic Diets: High Fat Diet (HFD) - either 45% or 60% kcal from fat 11% High Fructose Corn Syrup (HFCS-55) 10% Sucrose solution Hippocampal Cognitive Tasks: Barnes Maze Morris Water Maze (MWM) Object-in-place Test Two-Stage Radial Maze Y Maze Novel Object Location Recognition Groton Maze Learning Task
35 Juvenile and Adolescent Period Animal Models: Obesogenic dietary factors negatively impact hippocampal function in juvenile/adolescents > adults HFD consumption impaired spatial memory retention and spatial reversal learning in juvenile/adolescents Impaired relational memory flexibility (two-stage radial arm maze) in rats exposed to HFD first 11 weeks post weaning, as opposed to those who began HFD at wk12 (Boitard et al) impaired in Novel Location Recognition task (hippocampal-dependent) in mice given HFD at wk5, compared to those given HFD at wk8 (Valladolid et al) Dietary sugars have particularly negative effects on hippocampus during juvenile/adolescent period (even in absence of elevated fat intake) Impaired hippocampal-dependent spatial learning and memory learning in juvenile rats fed 11% HFCS, compared to adult counterparts and control (H2O) conditions Intermittent sucrose access experiments: Study 1 (Kendig et al): Both adolescents and adults* reveal impaired Morris Water Maze performance Study 2 (Reichelt et al) : juvenile rats had impaired object-in-place task performance (episodic contextual memory)
36 Juvenile and Adolescent Period Dietary factors contribute more to memory impairments than do caloric intake or obesity Study 1 (Valladolid et al): Adolescent and adult mice fed HFD for 8 weeks or for 8 weeks followed by 5 weeks of food restriction Study 2 (Kaczmarczyk et al): short-term (1 week) HFD feeding of juvenile mice Adolescent mice: (-) Novel Object Recognition performance, even after 5 week food restriction Significant (-) spatial memory [Y maze] Noted before onset of weight gain or impaired glucose metabolism Study 3 (Hsu et al): 11% HFCS or control (H2O) given to adult and adolescent rats Adolescent rats: (-) spatial Barnes Maze performance Despite similar caloric intake and levels of body weight gain as control condition *Consideration for future studies: identify which specific dietary factors cause these early life obesogenic diet-induced cognitive defects
37 Juvenile and Adolescent Period Humans: Study 1 (Nyaradi et al): Western dietary pattern during early adolescence (14 y.o.) poor cognitive performance in late adolescence Study 2 (Baym et al): Cross-sectional study of 7-9 year olds Saturated fatty acid intake in children (-) performance in hippocampal-dependent relational and item memory tasks Independent of BMI
38 Neurobiological Mechanisms Inflammation/Cytokines: Obesity chronic low-grade inflammation levels of proinflammatory cytokines in brain (TNFα, IL-6) impaired hippocampal-dependent memory Maternal fat consumption and inflammation affects brain inflammation and behavior of offspring via IL-1β and IL-6 and microglial expression Hsu et al Study: IL-1β and IL-6 in adolescent rats fed 11% HFCS, not found in adults Reveals link between neuroinflammation and hippocampal function Boitard et al Study: Untreated animals: no change in TNFα and IL-1β Post LPS injection: significant in TNFα and IL-1β Reveals dietary manipulation affects neuroinflammatory signal pathways, which in turn affect hippocampal function
39 Neurobiological Mechanisms Neurotrophic Factors: Neurogenesis and Synaptic Plasticity Essential for hippocampal-dependent memory and learning Brain derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) maternal HFD consumption = hippocampal BDNF expression in offspring = (-) impact on neurogenesis and synaptic plasticity in hippocampal neurons Insulin and Insulin-like growth factor-1 (IGF-1) Promote neurogenesis and synaptogenesis in dentate gyrus (Kuang et al) Maternal consumption of high sucrose Impaired spatial learning with IGF-1 and downstream PI3K and pakt in hippocampus of offspring Leptin Facilitates synaptic plasticity via AMPA receptor trafficking at synapses Peripheral and intra-hippocampal leptin injections into db/db rodents with cognitive deficits enhanced hippocampal-dependent spatial learning and memory performance (Valladolid et al) HFD-fed juvenile rats resistance of PI3K/AKT pathway in OBRb-expressing neurons in hippocampus impaired hippocampal-dep. Cognitive function
40 Conclusions Perinatal: Perinatal and Juvenile exposure to a chow diet supplemented with saturated fat, cholesterol, and sugar produces elevations in expression of Cytokines TNF-Alpha and IL-6 Juvenile/Adolescent: Particularly vulnerable to effects of obesogenic diet on hippocampal function due to increased expression of pro-inflammatory cytokines and changes in the expression of neurotrophic factors Sugar displays more negative effects on memory than high fat intake Future Research: identify the specific dietary factors that cause these early life obesogenic diet-induced cognitive deficits Look into epigenetic mechanisms of how diet may alter genes and neurotrophic factors crucial for learning and memory function
41 SlidesCarnival icons are editable shapes. This means that you can: Resize them without losing quality. Change line color, width and style. Isn t that nice? :) Examples:
42 Now you can use any emoji as an icon! And of course it resizes without losing quality and you can change the color. How? Follow Google instructions and many more...
Metabolic Programming. Mary ET Boyle, Ph. D. Department of Cognitive Science UCSD
 Metabolic Programming Mary ET Boyle, Ph. D. Department of Cognitive Science UCSD nutritional stress/stimuli organogenesis of target tissues early period critical window consequence of stress/stimuli are
Metabolic Programming Mary ET Boyle, Ph. D. Department of Cognitive Science UCSD nutritional stress/stimuli organogenesis of target tissues early period critical window consequence of stress/stimuli are
Nutritional Programming of Hypothalamic Development: Critical Periods and Windows of Opportunity. Team FENAPS (Finesse)
 Nutritional Programming of Hypothalamic Development: Critical Periods and Windows of Opportunity Team FENAPS (Finesse) Overview Introduction Influence of Hypothalamus on Energy Control Critical Periods
Nutritional Programming of Hypothalamic Development: Critical Periods and Windows of Opportunity Team FENAPS (Finesse) Overview Introduction Influence of Hypothalamus on Energy Control Critical Periods
Mary ET Boyle, Ph. D. Department of Cognitive Science UCSD
 Mary ET Boyle, Ph. D. Department of Cognitive Science UCSD Is obesity a brain disorder? What is the evidence to support obesity is a brain disorder? Environmental, biological, and behavioral issues Over
Mary ET Boyle, Ph. D. Department of Cognitive Science UCSD Is obesity a brain disorder? What is the evidence to support obesity is a brain disorder? Environmental, biological, and behavioral issues Over
Insulin-Leptin Interactions
 Insulin-Leptin Interactions Ahmed S., Al-Azzam N., Cao B. Karshaleva B., Sriram S., Vu K. If you understand a system, you can predict it. Agenda - Energy homeostasis Overview of leptin and insulin Signaling
Insulin-Leptin Interactions Ahmed S., Al-Azzam N., Cao B. Karshaleva B., Sriram S., Vu K. If you understand a system, you can predict it. Agenda - Energy homeostasis Overview of leptin and insulin Signaling
PLENARY LECTURES. Australian Neuroscience Society Annual Meeting Melbourne 3-6 February 2013 Page 1
 PLENARY LECTURES Australian Neuroscience Society Annual Meeting Melbourne 3-6 February 2013 Page 1 Plenary Lectures S sunday PLE-SUN-01 ANS OVERSEAS LECTURE ELUCIDATING RECEPTOR TYROSINE KINASE-DEPENDENT
PLENARY LECTURES Australian Neuroscience Society Annual Meeting Melbourne 3-6 February 2013 Page 1 Plenary Lectures S sunday PLE-SUN-01 ANS OVERSEAS LECTURE ELUCIDATING RECEPTOR TYROSINE KINASE-DEPENDENT
Copyright 2017 The Guilford Press
 This is a chapter excerpt from Guilford Publications. Eating Disorders and Obesity: A Comprehensive Handbook, Third Edition. Edited by Kelly D. Brownell and B. Timothy Walsh. Copyright 2017. Purchase this
This is a chapter excerpt from Guilford Publications. Eating Disorders and Obesity: A Comprehensive Handbook, Third Edition. Edited by Kelly D. Brownell and B. Timothy Walsh. Copyright 2017. Purchase this
Environmental Justice and the Early- Life Origins of Health Disparities: Why Mom Matters
 Environmental Justice and the Early- Life Origins of Health Disparities: Why Mom Matters Tania Hassanzadeh Dominic Le Bailey Ryan Bass Connections: Brain and Society, Summer 2013 Mentors: Dr. Staci Bilbo,
Environmental Justice and the Early- Life Origins of Health Disparities: Why Mom Matters Tania Hassanzadeh Dominic Le Bailey Ryan Bass Connections: Brain and Society, Summer 2013 Mentors: Dr. Staci Bilbo,
Exercising Our Minds: Effects of Exercise on Brain Structure & Function
 Public Lecture Exercising Our Minds: Effects of Exercise on Brain Structure & Function Dr. Brian R. Christie Division of Medical Sciences, University of Victoria Cellular and Physiological Sciences, UBC
Public Lecture Exercising Our Minds: Effects of Exercise on Brain Structure & Function Dr. Brian R. Christie Division of Medical Sciences, University of Victoria Cellular and Physiological Sciences, UBC
CNS Control of Food Intake. Adena Zadourian & Andrea Shelton
 CNS Control of Food Intake Adena Zadourian & Andrea Shelton Controlling Food Intake Energy Homeostasis (Change in body adiposity + compensatory changes in food intake) Background Information/Review Insulin
CNS Control of Food Intake Adena Zadourian & Andrea Shelton Controlling Food Intake Energy Homeostasis (Change in body adiposity + compensatory changes in food intake) Background Information/Review Insulin
Leptin Intro/Signaling. ATeamP: Angelo, Anthony, Charlie, Gabby, Joseph
 Leptin Intro/Signaling ATeamP: Angelo, Anthony, Charlie, Gabby, Joseph Overview Intro to Leptin Definition & Sources Physiology Bound vs. Free Receptors Signaling JAK/STAT MAPK PI3K ACC Experimental findings
Leptin Intro/Signaling ATeamP: Angelo, Anthony, Charlie, Gabby, Joseph Overview Intro to Leptin Definition & Sources Physiology Bound vs. Free Receptors Signaling JAK/STAT MAPK PI3K ACC Experimental findings
Leptin, Nutrition, and the Programming of Hypothalamic Feeding Circuits
 Lucas A, Makrides M, Ziegler EE (eds): Importance of Growth for Health and Development. Nestlé Nutr Inst Workshop Ser Pediatr Program, vol 65, pp 25 39, Nestec Ltd., Vevey/S. Karger AG, Basel, 2010. Leptin,
Lucas A, Makrides M, Ziegler EE (eds): Importance of Growth for Health and Development. Nestlé Nutr Inst Workshop Ser Pediatr Program, vol 65, pp 25 39, Nestec Ltd., Vevey/S. Karger AG, Basel, 2010. Leptin,
Internal Regulation II Energy
 Internal Regulation II Energy Reading: BCP Chapter 16 lookfordiagnosis.com Homeostasis Biologically, what is necessary for life is a coordinated set of chemical reactions. These reactions take place in
Internal Regulation II Energy Reading: BCP Chapter 16 lookfordiagnosis.com Homeostasis Biologically, what is necessary for life is a coordinated set of chemical reactions. These reactions take place in
Early Life Origins of Obesity: Role of Hypothalamic Programming
 Journal of Pediatric Gastroenterology and Nutrition 48:S31 S38 # 2009 by European Society for Pediatric Gastroenterology, Hepatology, and Nutrition and North American Society for Pediatric Gastroenterology,
Journal of Pediatric Gastroenterology and Nutrition 48:S31 S38 # 2009 by European Society for Pediatric Gastroenterology, Hepatology, and Nutrition and North American Society for Pediatric Gastroenterology,
Neurophysiology of the Regulation of Food Intake and the Common Reward Pathways of Obesity and Addiction. Laura Gunter
 Neurophysiology of the Regulation of Food Intake and the Common Reward Pathways of Obesity and Addiction Laura Gunter The Brain as the Regulatory Center for Appetite The brain is the integration center
Neurophysiology of the Regulation of Food Intake and the Common Reward Pathways of Obesity and Addiction Laura Gunter The Brain as the Regulatory Center for Appetite The brain is the integration center
Ghrelin mediates stressinduced. behavior in mice. Chuang et al 2011 L3: Love, Lust, Labor
 Ghrelin mediates stressinduced food-reward behavior in mice Chuang et al 2011 L3: Love, Lust, Labor Agenda Introduction What is Ghrelin? Previous Models New model Methods Results Discussion Conclusion
Ghrelin mediates stressinduced food-reward behavior in mice Chuang et al 2011 L3: Love, Lust, Labor Agenda Introduction What is Ghrelin? Previous Models New model Methods Results Discussion Conclusion
Bi156 lecture 2, 1/6/12. Eating and weight regulation
 Bi156 lecture 2, 1/6/12 Eating and weight regulation Introduction: weight regulation in an affluent society In our society much effort and money is expended on regulation of weight. Failure to maintain
Bi156 lecture 2, 1/6/12 Eating and weight regulation Introduction: weight regulation in an affluent society In our society much effort and money is expended on regulation of weight. Failure to maintain
The Milk of Paradise?: New Research on Maternal Obesity, Breast Milk Quality, and Infant Metabolic Health
 The Milk of Paradise?: New Research on Maternal Obesity, Breast Milk Quality, and Infant Metabolic Health Ellen W. Demerath, PhD Associate Professor, Division of Epidemiology and Community Health School
The Milk of Paradise?: New Research on Maternal Obesity, Breast Milk Quality, and Infant Metabolic Health Ellen W. Demerath, PhD Associate Professor, Division of Epidemiology and Community Health School
Chapter 12. Ingestive Behavior
 Chapter 12 Ingestive Behavior Drinking a. fluid compartments b. osmometric thirst c. volumetric thirst Eating a. energy sources b. starting a meal c. stopping a meal d. eating disordersd Drinking a. fluid
Chapter 12 Ingestive Behavior Drinking a. fluid compartments b. osmometric thirst c. volumetric thirst Eating a. energy sources b. starting a meal c. stopping a meal d. eating disordersd Drinking a. fluid
Figure 1: The leptin/melanocortin pathway Neuronal populations propagate the signaling of various molecules (leptin, insulin, ghrelin) to control
 Leptin Deficiency Introduction The leptin/melanocortin pathway plays a key role in the hypothalamic control of food intake. It is activated following the systemic release of the adipokine leptin (LEP)
Leptin Deficiency Introduction The leptin/melanocortin pathway plays a key role in the hypothalamic control of food intake. It is activated following the systemic release of the adipokine leptin (LEP)
Why Obesity Is A Chronic Disease
 Why Obesity Is A Chronic Disease Arya M Sharma, MD, FRCP(C) Professor of Medicine Chair in Obesity Research & Management University of Alberta Edmonton, AB, Canada www.drsharma.ca Global Obesity Map 2014
Why Obesity Is A Chronic Disease Arya M Sharma, MD, FRCP(C) Professor of Medicine Chair in Obesity Research & Management University of Alberta Edmonton, AB, Canada www.drsharma.ca Global Obesity Map 2014
LESSON 3.3 WORKBOOK. How do we decide when and how much to eat?
 Appetite The psychological desire to eat, driven by feelings of pleasure from the brain. Hunger The biological or physiological need to eat, caused by a release of hormones from the digestive tract. LESSON
Appetite The psychological desire to eat, driven by feelings of pleasure from the brain. Hunger The biological or physiological need to eat, caused by a release of hormones from the digestive tract. LESSON
Ophthalmology, Radiation Oncology,
 Supporting Online Material Journal: Nature Neuroscience Article Title: Corresponding Author: All Authors: Affiliations: Tanycytes of the Hypothalamic Median Eminence Form a Diet- Responsive Neurogenic
Supporting Online Material Journal: Nature Neuroscience Article Title: Corresponding Author: All Authors: Affiliations: Tanycytes of the Hypothalamic Median Eminence Form a Diet- Responsive Neurogenic
Stressin with Ghrelin. Peptide Pods: Lara, Elijah, Karen, Brandon, Milena, Max & Lucile
 Stressin with Ghrelin Peptide Pods: Lara, Elijah, Karen, Brandon, Milena, Max & Lucile Agenda Ghrelin Essentials Review Associations of Ghrelin with eating, stress, metabolic factors, etc. High-fat diet
Stressin with Ghrelin Peptide Pods: Lara, Elijah, Karen, Brandon, Milena, Max & Lucile Agenda Ghrelin Essentials Review Associations of Ghrelin with eating, stress, metabolic factors, etc. High-fat diet
298 Biomed Environ Sci, 2015; 28(4):
 298 Biomed Environ Sci, 2015; 28(4): 298-302 Letter to the Editor Effects of Maternal Linseed Oil Supplementation on Metabolic Parameters in Cafeteria Diet-induced Obese Rats * BENAISSA Nawel 1, MERZOUK
298 Biomed Environ Sci, 2015; 28(4): 298-302 Letter to the Editor Effects of Maternal Linseed Oil Supplementation on Metabolic Parameters in Cafeteria Diet-induced Obese Rats * BENAISSA Nawel 1, MERZOUK
Assessing mouse behaviors: Modeling pediatric traumatic brain injury
 Assessing mouse behaviors: Modeling pediatric traumatic brain injury Bridgette Semple Ph.D. Postdoctoral Fellow, Noble Laboratory Department of Neurological Surgery, UCSF Pediatric Traumatic Brain Injury
Assessing mouse behaviors: Modeling pediatric traumatic brain injury Bridgette Semple Ph.D. Postdoctoral Fellow, Noble Laboratory Department of Neurological Surgery, UCSF Pediatric Traumatic Brain Injury
Ingestive Behavior: Feeding & Weight Regulation. Hypovolemic vs. Osmotic Thirst
 Ingestive Behavior: Feeding & Weight Regulation 1 Hypovolemic Thirst Receptors, CNS, Responses Salt Appetite Digestive components Glucose Homeostasis: Insulin & Glucagon Diabetes Mellitus 1 & 2 CNS Hypothalamic
Ingestive Behavior: Feeding & Weight Regulation 1 Hypovolemic Thirst Receptors, CNS, Responses Salt Appetite Digestive components Glucose Homeostasis: Insulin & Glucagon Diabetes Mellitus 1 & 2 CNS Hypothalamic
Gene expression of NPY and POMC in the arcuate nucleus of adult male rats subjected to early postnatal food restriction
 Effects on adult gene expression 6 Gene expression of NPY and POMC in the arcuate nucleus of adult male rats subjected to early postnatal food restriction Floor Remmers Pieter Voorn Hilde P. Lok Allert
Effects on adult gene expression 6 Gene expression of NPY and POMC in the arcuate nucleus of adult male rats subjected to early postnatal food restriction Floor Remmers Pieter Voorn Hilde P. Lok Allert
Environmental influences on brain and behaviour
 Environmental influences on brain and behaviour Abdul H. Mohammed Dept. of Neurotec Karolinska Institutet Stockholm, Sweden IBRO African Neuroscience School, Nairobi, 2005 Environmental interventions affecting
Environmental influences on brain and behaviour Abdul H. Mohammed Dept. of Neurotec Karolinska Institutet Stockholm, Sweden IBRO African Neuroscience School, Nairobi, 2005 Environmental interventions affecting
Disclosure. Michael K. Georgieff, MD Research Support: Mead Johnson Nutrition Brain Iron Deficiency
 Disclosure In accordance with the Accreditation Council for Continuing Medical Education Standards, parallel documents from other accrediting bodies, and Annenberg Center for Health Sciences policy, the
Disclosure In accordance with the Accreditation Council for Continuing Medical Education Standards, parallel documents from other accrediting bodies, and Annenberg Center for Health Sciences policy, the
Management of Obesity. Objectives. Background Impact and scope of Obesity. Control of Energy Homeostasis Methods of treatment Medications.
 Medical Management of Obesity Ben O Donnell, MD 1 Objectives Background Impact and scope of Obesity Control of Energy Homeostasis Methods of treatment Medications 2 O'Donnell 1 Impact of Obesity According
Medical Management of Obesity Ben O Donnell, MD 1 Objectives Background Impact and scope of Obesity Control of Energy Homeostasis Methods of treatment Medications 2 O'Donnell 1 Impact of Obesity According
Chapter 1. General introduction. Part of this chapter is adapted from Adan et.al., Br.J.Pharmacol. 2006;149:815
 Chapter 1 General introduction Part of this chapter is adapted from Adan et.al., Br.J.Pharmacol. 2006;149:815 Chapter 1 B. Tiesjema, 2007 GENERAL INTRODUCTION NEURAL CIRCUITS INVOLVED IN ENERGY BALANCE
Chapter 1 General introduction Part of this chapter is adapted from Adan et.al., Br.J.Pharmacol. 2006;149:815 Chapter 1 B. Tiesjema, 2007 GENERAL INTRODUCTION NEURAL CIRCUITS INVOLVED IN ENERGY BALANCE
The Epigenetics of Obesity: Individual, Social, and Environmental Influences. K. J. Claycombe, Ph.D.
 The Epigenetics of Obesity: Individual, Social, and Environmental Influences K. J. Claycombe, Ph.D. What can happen to our gene(s) that would cause obesity? Modification via Epigenetic alterations C
The Epigenetics of Obesity: Individual, Social, and Environmental Influences K. J. Claycombe, Ph.D. What can happen to our gene(s) that would cause obesity? Modification via Epigenetic alterations C
Gestational Diet Folic Acid Content and. Development and Function of Food Intake Regulation in Rats
 Gestational Diet Folic Acid Content and Development and Function of Food Intake Regulation in Rats by Neil Victor Yang A thesis submitted in conformity with the requirements for the degree of Master of
Gestational Diet Folic Acid Content and Development and Function of Food Intake Regulation in Rats by Neil Victor Yang A thesis submitted in conformity with the requirements for the degree of Master of
Neonatal ghrelin programs development of hypothalamic feeding circuits
 RESEAR CH AR TICLE Neonatal ghrelin programs development of hypothalamic feeding circuits Sophie M. Steculorum, 1,2 Gustav Collden, 2 Berengere Coupe, 1 Sophie Croizier, 1,2 Sarah Lockie, 3 Zane B. Andrews,
RESEAR CH AR TICLE Neonatal ghrelin programs development of hypothalamic feeding circuits Sophie M. Steculorum, 1,2 Gustav Collden, 2 Berengere Coupe, 1 Sophie Croizier, 1,2 Sarah Lockie, 3 Zane B. Andrews,
Obesity in aging: Hormonal contribution
 Obesity in aging: Hormonal contribution Hormonal issues in obesity and aging Hormonal role in regulation of energy balance Genetic component in hormonal regulation Life style contribution to hormonal changes
Obesity in aging: Hormonal contribution Hormonal issues in obesity and aging Hormonal role in regulation of energy balance Genetic component in hormonal regulation Life style contribution to hormonal changes
Developmental programming in maternal diabetes and obesity
 Developmental programming in maternal diabetes and obesity Frans André Van Assche Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology, University Hospital, K. U. Leuven, Herestraat 49, 3000 Leuven, Belgium Corresponding
Developmental programming in maternal diabetes and obesity Frans André Van Assche Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology, University Hospital, K. U. Leuven, Herestraat 49, 3000 Leuven, Belgium Corresponding
Leptin-Insulin Signaling in the Brain. BY TEAM CEPHALIC Aman Hamdard, Kevin Artiga, Megan Imreh, Ronald Baldonado, and Sharri Mo
 Leptin-Insulin Signaling in the Brain BY TEAM CEPHALIC Aman Hamdard, Kevin Artiga, Megan Imreh, Ronald Baldonado, and Sharri Mo Agenda Leptin in the Hypothalamus: Pathways and Roles Cross-talk between
Leptin-Insulin Signaling in the Brain BY TEAM CEPHALIC Aman Hamdard, Kevin Artiga, Megan Imreh, Ronald Baldonado, and Sharri Mo Agenda Leptin in the Hypothalamus: Pathways and Roles Cross-talk between
perk/erk STAT5B
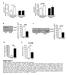 pakt/akt relative to saline (fold).5.5.5 control perk/erk relative to saline (fold).6.4..8.6.4. p=.6 control db/+ Hsp6 VDAC Hsp6/VDAC (relative to db/+) 8 6 4 db/+ C db/+ Hsp6 Hsp6/actin (relative to db/+)
pakt/akt relative to saline (fold).5.5.5 control perk/erk relative to saline (fold).6.4..8.6.4. p=.6 control db/+ Hsp6 VDAC Hsp6/VDAC (relative to db/+) 8 6 4 db/+ C db/+ Hsp6 Hsp6/actin (relative to db/+)
Epigenetic Pathways Linking Parental Effects to Offspring Development. Dr. Frances A. Champagne Department of Psychology, Columbia University
 Epigenetic Pathways Linking Parental Effects to Offspring Development Dr. Frances A. Champagne Department of Psychology, Columbia University Prenatal & Postnatal Experiences Individual differences in brain
Epigenetic Pathways Linking Parental Effects to Offspring Development Dr. Frances A. Champagne Department of Psychology, Columbia University Prenatal & Postnatal Experiences Individual differences in brain
Ingestive Behaviors 21. Introduction. Page 1. control and story lines. (a review of general endocrinology) Integration (or the basic reflex arc model)
 Ingestive Behaviors 21 (a review of general endocrinology) A neuroendocrine system: components, a reflex arc, the endocrine system, the AN, endocrine / nervous systems as afferents and efferents, the theoretical
Ingestive Behaviors 21 (a review of general endocrinology) A neuroendocrine system: components, a reflex arc, the endocrine system, the AN, endocrine / nervous systems as afferents and efferents, the theoretical
The hypothalamus has been the traditional focus of. Embryonic Birthdate of Hypothalamic Leptin- Activated Neurons in Mice
 ENERGY BALANCE-OBESITY Embryonic Birthdate of Hypothalamic Leptin- Activated Neurons in Mice Yuko Ishii and Sebastien G. Bouret The Saban Research Institute (Y.I., S.G.B.), Neuroscience Program, Children
ENERGY BALANCE-OBESITY Embryonic Birthdate of Hypothalamic Leptin- Activated Neurons in Mice Yuko Ishii and Sebastien G. Bouret The Saban Research Institute (Y.I., S.G.B.), Neuroscience Program, Children
EARLY BRAIN AND CHILDHOOD DEVELOPMENT
 EARLY BRAIN AND CHILDHOOD DEVELOPMENT WILLIAM M BELLAS, DO, FAAP SANFORD CHILDREN S HOSPITAL DIVISION OF NEONATAL-PERINATAL MEDICINE CLINICAL ASSOCIATE PROFESSOR OF PEDIATRICS UND SCHOOL OF MEDICINE &
EARLY BRAIN AND CHILDHOOD DEVELOPMENT WILLIAM M BELLAS, DO, FAAP SANFORD CHILDREN S HOSPITAL DIVISION OF NEONATAL-PERINATAL MEDICINE CLINICAL ASSOCIATE PROFESSOR OF PEDIATRICS UND SCHOOL OF MEDICINE &
HIGH FOLATE, BUT NOT HIGH MULTIVITAMIN GESTATIONAL DIETS, AFFECT THE SEROTONERGIC REGULATION OF FOOD INTAKE IN FEMALE WISTAR OFFSPRING
 HIGH FOLATE, BUT NOT HIGH MULTIVITAMIN GESTATIONAL DIETS, AFFECT THE SEROTONERGIC REGULATION OF FOOD INTAKE IN FEMALE WISTAR OFFSPRING by Abraham Poon A thesis submitted in conformity with the requirements
HIGH FOLATE, BUT NOT HIGH MULTIVITAMIN GESTATIONAL DIETS, AFFECT THE SEROTONERGIC REGULATION OF FOOD INTAKE IN FEMALE WISTAR OFFSPRING by Abraham Poon A thesis submitted in conformity with the requirements
The Role of the Immune System in Translating Early-Life Experience to Later-Life Brain and Behavior
 The Role of the Immune System in Translating Early-Life Experience to Later-Life Brain and Behavior STACI D. BILBO DEPARTMENT OF PSYCHOLOGY AND NEUROSCIENCE DUKE UNIVERSITY Thanks to! Dr. Mark Hutchinson
The Role of the Immune System in Translating Early-Life Experience to Later-Life Brain and Behavior STACI D. BILBO DEPARTMENT OF PSYCHOLOGY AND NEUROSCIENCE DUKE UNIVERSITY Thanks to! Dr. Mark Hutchinson
Effects of Stress and Food During Prenatal Development. Presented by The Peptide Pods
 Effects of Stress and Food During Prenatal Development Presented by The Peptide Pods Nutritional programing of hypothalamic development: critical periods and windows of opportunity By: SG Bouret Presented
Effects of Stress and Food During Prenatal Development Presented by The Peptide Pods Nutritional programing of hypothalamic development: critical periods and windows of opportunity By: SG Bouret Presented
JOURNAL OF PHYSIOLOGY AND PHARMACOLOGY 2009, 60, Suppl 3,
 JOURNAL OF PHYSIOLOGY AND PHARMACOLOGY 2009, 60, Suppl 3, 17-35 www.jpp.krakow.pl P. GUILLOTEAU 1, R. ZABIELSKI 2, H.M. HAMMON 3, C.C. METGES 3 ADVERSE EFFECTS OF NUTRITIONAL PROGRAMMING DURING PRENATAL
JOURNAL OF PHYSIOLOGY AND PHARMACOLOGY 2009, 60, Suppl 3, 17-35 www.jpp.krakow.pl P. GUILLOTEAU 1, R. ZABIELSKI 2, H.M. HAMMON 3, C.C. METGES 3 ADVERSE EFFECTS OF NUTRITIONAL PROGRAMMING DURING PRENATAL
University of Groningen. Dietary lipid quality, environment and the developing brain Schipper, Anniek Lidewij
 University of Groningen Dietary lipid quality, environment and the developing brain Schipper, Anniek Lidewij IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version (publisher's PDF) if you
University of Groningen Dietary lipid quality, environment and the developing brain Schipper, Anniek Lidewij IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version (publisher's PDF) if you
PART I. INTRODUCTION TO BRAIN DEVELOPMENT
 NEURAL DEVELOPMENT AND BRAIN PLASTICITY A PRÉCIS TO UNDERSTANDING THE EFFECTS OF EARLY ADVERSITY Charles A. Nelson III, Ph.D. Children s Hospital Boston/Harvard Medical School Harvard Center on the Developing
NEURAL DEVELOPMENT AND BRAIN PLASTICITY A PRÉCIS TO UNDERSTANDING THE EFFECTS OF EARLY ADVERSITY Charles A. Nelson III, Ph.D. Children s Hospital Boston/Harvard Medical School Harvard Center on the Developing
Ingestive Behaviors 33. Introduction. Page 1. control and story lines. (a review of general endocrinology) Integration (or the basic reflex arc model)
 Ingestive Behaviors 33 (a review of general endocrinology) A neuroendocrine system: components, a reflex arc, the endocrine system, the AN, endocrine / nervous systems as afferents and efferents, the theoretical
Ingestive Behaviors 33 (a review of general endocrinology) A neuroendocrine system: components, a reflex arc, the endocrine system, the AN, endocrine / nervous systems as afferents and efferents, the theoretical
Method of leptin dosing, strain, and group housing influence leptin sensitivity in high-fat-fed weanling mice
 Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol 284: R87 R100, 2003; 10.1152/ajpregu.00431.2002. Method of leptin dosing, strain, and group housing influence leptin sensitivity in high-fat-fed weanling mice HEATHER
Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol 284: R87 R100, 2003; 10.1152/ajpregu.00431.2002. Method of leptin dosing, strain, and group housing influence leptin sensitivity in high-fat-fed weanling mice HEATHER
JAI La Leche League Epigenetics and Breastfeeding: The Longterm Impact of Breastmilk on Health Disclosure Why am I interested in epigenetics?
 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 JAI La Leche League Epigenetics and Breastfeeding: The Longterm Impact of Breastmilk on Health By Laurel Wilson, IBCLC, CLE, CCCE, CLD Author of The Greatest Pregnancy
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 JAI La Leche League Epigenetics and Breastfeeding: The Longterm Impact of Breastmilk on Health By Laurel Wilson, IBCLC, CLE, CCCE, CLD Author of The Greatest Pregnancy
How to measure rodent behavior and perform a neurological screen.
 An Organ Systems Approach to Experimental Targeting of the Metabolic Syndrome How to measure rodent behavior and perform a neurological screen. Fiona Harrison, PhD Department of Medicine Vanderbilt University
An Organ Systems Approach to Experimental Targeting of the Metabolic Syndrome How to measure rodent behavior and perform a neurological screen. Fiona Harrison, PhD Department of Medicine Vanderbilt University
Development of the Nervous System. Leah Militello, class of 2018
 Development of the Nervous System Leah Militello, class of 2018 Learning Objectives 1. Describe the formation and fate of the neural tube and neural crest including timing and germ layer involved. 2. Describe
Development of the Nervous System Leah Militello, class of 2018 Learning Objectives 1. Describe the formation and fate of the neural tube and neural crest including timing and germ layer involved. 2. Describe
THE ROLE OF DIETARY FAT IN HYPOTHALAMIC INSULIN AND LEPTIN RESISTANCE AND THE PATHOGENESIS OF OBESITY. Kelly Ann Posey.
 THE ROLE OF DIETARY FAT IN HYPOTHALAMIC INSULIN AND LEPTIN RESISTANCE AND THE PATHOGENESIS OF OBESITY By Kelly Ann Posey Dissertation Submitted to the Faculty of the Graduate School of Vanderbilt University
THE ROLE OF DIETARY FAT IN HYPOTHALAMIC INSULIN AND LEPTIN RESISTANCE AND THE PATHOGENESIS OF OBESITY By Kelly Ann Posey Dissertation Submitted to the Faculty of the Graduate School of Vanderbilt University
Postnatal Development of Hypothalamic Leptin Receptors
 CHAPTER ELEVEN Postnatal Development of Hypothalamic Leptin Receptors Elizabeth C. Cottrell,*,1 Julian G. Mercer, and Susan E. Ozanne* Contents I. Introduction 202 II. The Leptin System 203 A. Sources
CHAPTER ELEVEN Postnatal Development of Hypothalamic Leptin Receptors Elizabeth C. Cottrell,*,1 Julian G. Mercer, and Susan E. Ozanne* Contents I. Introduction 202 II. The Leptin System 203 A. Sources
1 Neuroregulation of Appetite
 Chapter 1 / Neuroregulation of Appetite 3 1 Neuroregulation of Appetite Ofer Reizes, PhD, Stephen C. Benoit, PhD, and Deborah J. Clegg, PhD CONTENTS INTRODUCTION THE DUAL-CENTERS HYPOTHESIS CONTROL OF
Chapter 1 / Neuroregulation of Appetite 3 1 Neuroregulation of Appetite Ofer Reizes, PhD, Stephen C. Benoit, PhD, and Deborah J. Clegg, PhD CONTENTS INTRODUCTION THE DUAL-CENTERS HYPOTHESIS CONTROL OF
Hypothalamic Neural Projections Are Permanently Disrupted in Diet-Induced Obese Rats
 Short Article Hypothalamic Neural Projections Are Permanently Disrupted in Diet-Induced Obese Rats Sebastien G. Bouret, 1,2, * Judith N. Gorski, 3,4,5 Christa M. Patterson, 3,4 Stephen Chen, 1 Barry E.
Short Article Hypothalamic Neural Projections Are Permanently Disrupted in Diet-Induced Obese Rats Sebastien G. Bouret, 1,2, * Judith N. Gorski, 3,4,5 Christa M. Patterson, 3,4 Stephen Chen, 1 Barry E.
Motivation 1 of 6. during the prandial state when the blood is filled
 Motivation 1 of 6 I. INTRODUCTION A. Motivation: a condition (usually internal) that initiates, activates, or maintains goal-directed behavior. B. Archery analogy 1. undrawn bow has no potential energy
Motivation 1 of 6 I. INTRODUCTION A. Motivation: a condition (usually internal) that initiates, activates, or maintains goal-directed behavior. B. Archery analogy 1. undrawn bow has no potential energy
Digestion: Endocrinology of Appetite
 Digestion: Endocrinology of Dr. Ritamarie Loscalzo Medical Disclaimer: The information in this presentation is not intended to replace a one on one relationship with a qualified health care professional
Digestion: Endocrinology of Dr. Ritamarie Loscalzo Medical Disclaimer: The information in this presentation is not intended to replace a one on one relationship with a qualified health care professional
Stress & The Neuroprotective Factors of Exercise. Week 9: Thursday, November 29 Sonia Romo
 Stress & The Neuroprotective Factors of Exercise Week 9: Thursday, November 29 Sonia Romo Today s Agenda Old Brain in a New Society Stress and the Immune System Stress and CVD Stress and Metabolic Syndrome
Stress & The Neuroprotective Factors of Exercise Week 9: Thursday, November 29 Sonia Romo Today s Agenda Old Brain in a New Society Stress and the Immune System Stress and CVD Stress and Metabolic Syndrome
Insulin Sensitivity and the Onset of Hyperphagia in Fatty Rats
 University of Tennessee, Knoxville Trace: Tennessee Research and Creative Exchange Masters Theses Graduate School 12-2004 Insulin Sensitivity and the Onset of Hyperphagia in Fatty Rats Holiday Agnes Durham
University of Tennessee, Knoxville Trace: Tennessee Research and Creative Exchange Masters Theses Graduate School 12-2004 Insulin Sensitivity and the Onset of Hyperphagia in Fatty Rats Holiday Agnes Durham
Peripubertal, leptin-deficient ob/ob female mice were used in an investigation of
 ESSICK-BROOKSHIRE, ELIZABETH ANN, M.S. The Effects of Peripherally Administered 17-β Estradiol and BIBP3226, a NPY Y1 Receptor Antagonist, on Food Intake, Body Mass, Reproductive Development and Behavior
ESSICK-BROOKSHIRE, ELIZABETH ANN, M.S. The Effects of Peripherally Administered 17-β Estradiol and BIBP3226, a NPY Y1 Receptor Antagonist, on Food Intake, Body Mass, Reproductive Development and Behavior
! acts via the autonomic nervous system. ! maintaining body weight within tight limits. ! ventromedial (VMN) ! arcuate (ARC) ! neuropeptide Y (NPY)
 Brain Regulates energy homeostatis Glucose Sensing in the Brain Seminar 2012 Gareth Price! acts in response to circulating signals of nutrient states! acts via the autonomic nervous system Ensures a balance
Brain Regulates energy homeostatis Glucose Sensing in the Brain Seminar 2012 Gareth Price! acts in response to circulating signals of nutrient states! acts via the autonomic nervous system Ensures a balance
Temperature, Regulation, Thirst, and Hunger
 PSYB64 Lecture 6 Temperature, Regulation, Thirst, and Hunger 1. Homeostasis 2. Temperature 3. Thirst 4. Hunger 5. Obesity & Hunger Disorders HOMEOSTASIS Homeostasis: Physiological equilibrium Motivation:
PSYB64 Lecture 6 Temperature, Regulation, Thirst, and Hunger 1. Homeostasis 2. Temperature 3. Thirst 4. Hunger 5. Obesity & Hunger Disorders HOMEOSTASIS Homeostasis: Physiological equilibrium Motivation:
Amylinergic control of food intake in lean and obese rodents
 Zurich Open Repository and Archive University of Zurich Main Library Winterthurerstr. 190 CH-8057 Zurich www.zora.uzh.ch Year: 2011 Amylinergic control of food intake in lean and obese rodents Boyle, C
Zurich Open Repository and Archive University of Zurich Main Library Winterthurerstr. 190 CH-8057 Zurich www.zora.uzh.ch Year: 2011 Amylinergic control of food intake in lean and obese rodents Boyle, C
Prenatal alcohol exposure and metabolic disease in adulthood
 8 th International Research Conference on Adolescents and Adults with FASD Prenatal alcohol exposure and metabolic disease in adulthood Prof Karen Moritz Director Child Health Research Centre University
8 th International Research Conference on Adolescents and Adults with FASD Prenatal alcohol exposure and metabolic disease in adulthood Prof Karen Moritz Director Child Health Research Centre University
Tanycytes as gatekeepers of the Metabolic Brain
 Tanycytes as gatekeepers of the Metabolic Brain Vincent Prevot Inserm team Development and Plasticity of the Postnatal Brain Jean-Pierre Aubert Research Centre, U837, Lille France Metabolic signals and
Tanycytes as gatekeepers of the Metabolic Brain Vincent Prevot Inserm team Development and Plasticity of the Postnatal Brain Jean-Pierre Aubert Research Centre, U837, Lille France Metabolic signals and
BRAIN DEVELOPMENT STRUCTURES OF THE BRAIN DEVELOPMENTAL PROCESSES THE IMPORTANCE OF EXPERIENCE BRAIN DAMAGE AND RECOVERY
 BRAIN DEVELOPMENT STRUCTURES OF THE BRAIN DEVELOPMENTAL PROCESSES THE IMPORTANCE OF EXPERIENCE BRAIN DAMAGE AND RECOVERY Brain Development Virtually all human behavior is governed by the brain. Exceptions?
BRAIN DEVELOPMENT STRUCTURES OF THE BRAIN DEVELOPMENTAL PROCESSES THE IMPORTANCE OF EXPERIENCE BRAIN DAMAGE AND RECOVERY Brain Development Virtually all human behavior is governed by the brain. Exceptions?
PI3Ka inactivation in leptin receptor cells increases leptin sensitivity but disrupts growth and reproduction
 PI3Ka inactivation in leptin receptor cells increases leptin sensitivity but disrupts growth and reproduction David Garcia-Galiano,, Jennifer W. Hill, Carol F. Elias JCI Insight. 2017;2(23):e96728.. Research
PI3Ka inactivation in leptin receptor cells increases leptin sensitivity but disrupts growth and reproduction David Garcia-Galiano,, Jennifer W. Hill, Carol F. Elias JCI Insight. 2017;2(23):e96728.. Research
Like mother, like offspring Does maternal overweight predict health outcomes?
 Like mother, like offspring Does maternal overweight predict health outcomes? Patricia Iozzo, MD, PhD Institute of Clinical Physiology National Research Council (CNR), Pisa, Italy Brussels 16 October 2017
Like mother, like offspring Does maternal overweight predict health outcomes? Patricia Iozzo, MD, PhD Institute of Clinical Physiology National Research Council (CNR), Pisa, Italy Brussels 16 October 2017
March 30, ASN Comments and Additions to Select, Proposed Topics and Questions are in Red Below
 March 30, 2018 The American Society for Nutrition (ASN) appreciates the opportunity to comment on the proposed topics and supporting scientific questions that will be considered during the development
March 30, 2018 The American Society for Nutrition (ASN) appreciates the opportunity to comment on the proposed topics and supporting scientific questions that will be considered during the development
Review Article Current Thoughts on Maternal Nutrition and Fetal Programming of the Metabolic Syndrome
 Journal of Pregnancy Volume 2013, Article ID 368461, 13 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2013/368461 Review Article Current Thoughts on Maternal Nutrition and Fetal Programming of the Metabolic Syndrome
Journal of Pregnancy Volume 2013, Article ID 368461, 13 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2013/368461 Review Article Current Thoughts on Maternal Nutrition and Fetal Programming of the Metabolic Syndrome
Industrialized Food Components and Obesity Risk. Kylie Kavanagh, VMS MS MPH Department of Pathology
 Industrialized Food Components and Obesity Risk Kylie Kavanagh, VMS MS MPH Department of Pathology Overview Role of science in policy development Components versus calories Past lessons (trans fat) Present
Industrialized Food Components and Obesity Risk Kylie Kavanagh, VMS MS MPH Department of Pathology Overview Role of science in policy development Components versus calories Past lessons (trans fat) Present
Endocrine System. Regulating Blood Sugar. Thursday, December 14, 17
 Endocrine System Regulating Blood Sugar Stress results in nervous and hormonal responses. The adrenal glands are located above each kidney. Involved in stress response. Stress Upsets Homeostasis Stress
Endocrine System Regulating Blood Sugar Stress results in nervous and hormonal responses. The adrenal glands are located above each kidney. Involved in stress response. Stress Upsets Homeostasis Stress
Maximizing the Role of WIC Nutritionists in Prevention of DM2 among High Risk Clients ESTHER G. SCHUSTER, MS,RD,CDE
 Maximizing the Role of WIC Nutritionists in Prevention of DM2 among High Risk Clients ESTHER G. SCHUSTER, MS,RD,CDE Heavy Numbers Surgeon General report: 68% of adults in U. S. are overweight or obese
Maximizing the Role of WIC Nutritionists in Prevention of DM2 among High Risk Clients ESTHER G. SCHUSTER, MS,RD,CDE Heavy Numbers Surgeon General report: 68% of adults in U. S. are overweight or obese
Eligibility The NCSF online quizzes are open to any currently certified fitness professional, 18 years or older.
 Eligibility The NCSF online quizzes are open to any currently certified fitness professional, 18 years or older. Deadlines Course completion deadlines correspond with the NCSF Certified Professionals certification
Eligibility The NCSF online quizzes are open to any currently certified fitness professional, 18 years or older. Deadlines Course completion deadlines correspond with the NCSF Certified Professionals certification
Myokines, Exercise, Metabolism. ATeamP: Angelo, Anthony, Charlie, Gabby, Joseph
 Myokines, Exercise, Metabolism ATeamP: Angelo, Anthony, Charlie, Gabby, Joseph Overview: Why? Evolutionary perspective How? Myokines: what they are and what they do Exercise and physiology Energy restriction
Myokines, Exercise, Metabolism ATeamP: Angelo, Anthony, Charlie, Gabby, Joseph Overview: Why? Evolutionary perspective How? Myokines: what they are and what they do Exercise and physiology Energy restriction
THE ROLE OF INSULIN RECEPTOR SIGNALING IN THE BRAIN. COGS 163 By: Pranav Singh Alexandra Villar
 THE ROLE OF INSULIN RECEPTOR SIGNALING IN THE BRAIN COGS 163 By: Pranav Singh Alexandra Villar INTRODUCTION Insulin is a hormone produced in the pancreas by the islets of Langerhans that regulates the
THE ROLE OF INSULIN RECEPTOR SIGNALING IN THE BRAIN COGS 163 By: Pranav Singh Alexandra Villar INTRODUCTION Insulin is a hormone produced in the pancreas by the islets of Langerhans that regulates the
Zhu et al, page 1. Supplementary Figures
 Zhu et al, page 1 Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1: Visual behavior and avoidance behavioral response in EPM trials. (a) Measures of visual behavior that performed the light avoidance behavior
Zhu et al, page 1 Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1: Visual behavior and avoidance behavioral response in EPM trials. (a) Measures of visual behavior that performed the light avoidance behavior
FLASH CARDS. Kalat s Book Chapter 10 Alphabetical
 FLASH CARDS www.biologicalpsych.com Kalat s Book Chapter 10 Alphabetical AgRP AgRP Agouti-related peptide; synthesized in hypothalamus. Acts as an appetite stimulator. Also decreases metabolism. aldosterone
FLASH CARDS www.biologicalpsych.com Kalat s Book Chapter 10 Alphabetical AgRP AgRP Agouti-related peptide; synthesized in hypothalamus. Acts as an appetite stimulator. Also decreases metabolism. aldosterone
Is ghrelin a signal for the development of metabolic systems?
 Commentaries Is ghrelin a signal for the development of metabolic systems? Kevin L. Grove and Michael A. Cowley Division of Neuroscience, Oregon National Primate Research Center, Oregon Health & Science
Commentaries Is ghrelin a signal for the development of metabolic systems? Kevin L. Grove and Michael A. Cowley Division of Neuroscience, Oregon National Primate Research Center, Oregon Health & Science
Reminders. What s a Neuron? Animals at Birth. How are Neurons formed? Prenatal Neural Development. Week 28. Week 3 Week 4. Week 10.
 Reminders What s a Neuron? Exam 1 Thursday Multiple Choice and Short Answer Bring Scantron form and #2 pencil Includes Chapter 1- Chapter 3 BUT NOT 3.1 (We will cover this on the next test) You may use
Reminders What s a Neuron? Exam 1 Thursday Multiple Choice and Short Answer Bring Scantron form and #2 pencil Includes Chapter 1- Chapter 3 BUT NOT 3.1 (We will cover this on the next test) You may use
Mice lacking the syndecan-3 gene are resistant to diet-induced obesity
 Research article Mice lacking the syndecan-3 gene are resistant to diet-induced obesity April D. Strader, 1 Ofer Reizes, 2 Stephen C. Woods, 1 Stephen C. Benoit, 1 and Randy J. Seeley 1 1 Department of
Research article Mice lacking the syndecan-3 gene are resistant to diet-induced obesity April D. Strader, 1 Ofer Reizes, 2 Stephen C. Woods, 1 Stephen C. Benoit, 1 and Randy J. Seeley 1 1 Department of
Overall Energy metabolism: Integration and Regulation
 Overall Energy metabolism: Integration and Regulation We have discussed various fuels which are oxidized via different catabolic pathways to generate ATP, or reducing equivalents required to carry out
Overall Energy metabolism: Integration and Regulation We have discussed various fuels which are oxidized via different catabolic pathways to generate ATP, or reducing equivalents required to carry out
Hormonal Regulation of Food Intake
 Physiol Rev 85: 1131 1158, 2005; doi:10.1152/physrev.00015.2004. Hormonal Regulation of Food Intake SARAH STANLEY, KATIE WYNNE, BARBARA McGOWAN, AND STEPHEN BLOOM Endocrine Unit, Imperial College Faculty
Physiol Rev 85: 1131 1158, 2005; doi:10.1152/physrev.00015.2004. Hormonal Regulation of Food Intake SARAH STANLEY, KATIE WYNNE, BARBARA McGOWAN, AND STEPHEN BLOOM Endocrine Unit, Imperial College Faculty
Nutrition & Physical Activity Profile Worksheets
 Nutrition & Physical Activity Profile Worksheets In these worksheets you will consider nutrition-related and physical activity-related health indicators for your community. If you cannot find local-level
Nutrition & Physical Activity Profile Worksheets In these worksheets you will consider nutrition-related and physical activity-related health indicators for your community. If you cannot find local-level
a b c Physical appearance of mice Lean mass Adipocyte size d e f
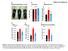 LFD HFD LFD HFD Area under curve (GTT) HFD-VSL#3 LFD HFD Area under curve (ITT) HFD-VSL#3 Liver TG content (% l) HFD-VSL#3 LFD HFD HFD-VSL#3 LFD HFD HFD-VSL#3 LFD HFD HFD + VSL#3 Lean mass (gm) Mean adipocyte
LFD HFD LFD HFD Area under curve (GTT) HFD-VSL#3 LFD HFD Area under curve (ITT) HFD-VSL#3 Liver TG content (% l) HFD-VSL#3 LFD HFD HFD-VSL#3 LFD HFD HFD-VSL#3 LFD HFD HFD + VSL#3 Lean mass (gm) Mean adipocyte
Supplemental data Supplemental Figure Legends Supplemental Figure 1. Supplemental Figure 2.
 Supplemental data Supplemental Figure Legends Supplemental Figure 1. Analysis of deletion of AMPK!2 in POMC and AgRP neurons in control and POMC!2KO and AgRP!2KO mice. (A) mmunofluorescence analysis for
Supplemental data Supplemental Figure Legends Supplemental Figure 1. Analysis of deletion of AMPK!2 in POMC and AgRP neurons in control and POMC!2KO and AgRP!2KO mice. (A) mmunofluorescence analysis for
Chapter 10 Lecture. Health: The Basics Tenth Edition. Reaching and Maintaining a Healthy Weight
 Chapter 10 Lecture Health: The Basics Tenth Edition Reaching and Maintaining a Healthy Weight OBJECTIVES Define overweight and obesity, describe the current epidemic of overweight/obesity in the United
Chapter 10 Lecture Health: The Basics Tenth Edition Reaching and Maintaining a Healthy Weight OBJECTIVES Define overweight and obesity, describe the current epidemic of overweight/obesity in the United
From Implantation to Neural Tube
 By 28 weeks after conception, brain has virtually all the neurons it will ever have. At birth, the brain weighs about.75lb (25% of adult weight) At 3 years of age, 80% of adult weight. At 5 years of age,
By 28 weeks after conception, brain has virtually all the neurons it will ever have. At birth, the brain weighs about.75lb (25% of adult weight) At 3 years of age, 80% of adult weight. At 5 years of age,
Prss56, a novel marker of adult neurogenesis in the mouse brain. - Supplemental Figures 1 to 5- Brain Structure and Function
 Prss56, a novel marker of adult neurogenesis in the mouse brain - Supplemental Figures 1 to 5- Brain Structure and Function Alexandre Jourdon 1,2, Aurélie Gresset 1, Nathalie Spassky 1, Patrick Charnay
Prss56, a novel marker of adult neurogenesis in the mouse brain - Supplemental Figures 1 to 5- Brain Structure and Function Alexandre Jourdon 1,2, Aurélie Gresset 1, Nathalie Spassky 1, Patrick Charnay
Effects of perinatal exposure to BPA on obesity and metabolic disease later in life
 Effects of perinatal exposure to BPA on obesity and metabolic disease later in life Beverly S. Rubin, PhD, Tufts University School of Medicine, Boston MA 02111 Institute of Medicine Roundtable: The Interplay
Effects of perinatal exposure to BPA on obesity and metabolic disease later in life Beverly S. Rubin, PhD, Tufts University School of Medicine, Boston MA 02111 Institute of Medicine Roundtable: The Interplay
NNZ-2566 in Rett Syndrome and Autism Spectrum Disorders Role and Update
 NNZ-2566 in Rett Syndrome and Autism Spectrum Disorders Role and Update 1 Overview The natural growth factor IGF-1 is broken down in the body to IGF-1[1-3] NNZ-2566 is an analogue of IGF-1[1-3] developed
NNZ-2566 in Rett Syndrome and Autism Spectrum Disorders Role and Update 1 Overview The natural growth factor IGF-1 is broken down in the body to IGF-1[1-3] NNZ-2566 is an analogue of IGF-1[1-3] developed
Epigenetic processes are fundamental to development because they permit a
 Early Life Nutrition and Epigenetic Markers Mark Hanson, PhD Epigenetic processes are fundamental to development because they permit a range of phenotypes to be formed from a genotype. Across many phyla
Early Life Nutrition and Epigenetic Markers Mark Hanson, PhD Epigenetic processes are fundamental to development because they permit a range of phenotypes to be formed from a genotype. Across many phyla
Hypothalamic TLR2 triggers sickness behavior via a microglia-neuronal axis
 Hypothalamic TLR triggers sickness behavior via a microglia-neuronal axis Sungho Jin, *, Jae Geun Kim,, *, Jeong Woo Park, Marco Koch,, Tamas L. Horvath and Byung Ju Lee Department of Biological Sciences,
Hypothalamic TLR triggers sickness behavior via a microglia-neuronal axis Sungho Jin, *, Jae Geun Kim,, *, Jeong Woo Park, Marco Koch,, Tamas L. Horvath and Byung Ju Lee Department of Biological Sciences,
-Impuls- Übergewicht und Adipositas bei Kindern: Entwicklung, Folgen & Präventionsstrategien
 -Impuls- Übergewicht und Adipositas bei Kindern: Entwicklung, Folgen & Präventionsstrategien Prof. Dr. med Dr. (h.c.) Arya M Sharma, Chair in Obesity Research & Management University of Alberta Edmonton,
-Impuls- Übergewicht und Adipositas bei Kindern: Entwicklung, Folgen & Präventionsstrategien Prof. Dr. med Dr. (h.c.) Arya M Sharma, Chair in Obesity Research & Management University of Alberta Edmonton,
Empower Preventive Medicine. Timothy J. McCormick, DO, MPH 4221 Baymeadows Suite 6 Jacksonville, FL
 Empower Preventive Medicine Timothy J. McCormick, DO, MPH 4221 Baymeadows Suite 6 Jacksonville, FL 32217 904-367-4005 Drtim@emprevmed.com Obesity Medicine Old paradigm: Obesity was a matter of willpower,
Empower Preventive Medicine Timothy J. McCormick, DO, MPH 4221 Baymeadows Suite 6 Jacksonville, FL 32217 904-367-4005 Drtim@emprevmed.com Obesity Medicine Old paradigm: Obesity was a matter of willpower,
Introduction. Leptin secretion after a high-fat meal in normal-weight rats: strong predictor of long-term body fat accrual on a high-fat diet
 Leptin secretion after a high-fat meal in normal-weight rats: strong predictor of long-term body fat accrual on a high-fat diet - Diet - Activity - Genetics etc. Introduction Obesity - Cardiovascular disease
Leptin secretion after a high-fat meal in normal-weight rats: strong predictor of long-term body fat accrual on a high-fat diet - Diet - Activity - Genetics etc. Introduction Obesity - Cardiovascular disease
An important function of the central nervous
 Perspectives in Diabetes Insulin Signaling in the Central Nervous System A Critical Role in Metabolic Homeostasis and Disease From C. elegans to Humans Daniel Porte, Jr., 1,2,3 Denis G. Baskin, 3 and Michael
Perspectives in Diabetes Insulin Signaling in the Central Nervous System A Critical Role in Metabolic Homeostasis and Disease From C. elegans to Humans Daniel Porte, Jr., 1,2,3 Denis G. Baskin, 3 and Michael
