The Challenge of Durability in Hip Replacement
|
|
|
- Aubrey Melton
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 The Challenge of Durability in Hip Replacement Gregory A. Tocks, D.O. Orthopedic Associates of Lancaster Ltd. INTRODUCTION Hip replacement is a very common operation, and the number of long-term postoperative survivors is growing continuously. According to the CDC, in 2010 there were 310,800 total hip replacements in the United States, 1 and by 2030 an annual total of 572,000 is projected. 2 In 2017, 739 total hip replacements were performed at Lancaster General Hospital. Since long-term survivors are at risk of needing a revision procedure, the durability of their prostheses, particularly at the bearing surfaces, is a major concern. Because of the stresses at the hip joint, the ideal component should minimize wear, maintain Fig. 1 Illustration of pink ceramic femoral head, white polyethylene liner, and metal acetabular cup. The femoral stem prosthesis is not shown. (From Depuy Pinnacle Polyethylene technique guide. 3 ). Fig. 2 A: Acetabular cup with cobalt-chromium femoral head and highly crossed-linked polyethylene liner; B: Acetabular cup with ceramic femoral head and highly crossed-linked polyethylene liner; C: Acetabular cup with ceramic femoral head and ceramic liner. stability, and preserve longevity. This article provides an outline of the common prosthetic bearing surfaces for total hip replacement, their comparative wear characteristics, advantages, and disadvantages. The techniques of hip surgery are not the focus of this article, but for the interested reader, the common surgical approaches and methods of hip arthroplasty are illustrated on the websites of one of the prosthesis manufacturers. 3 PROBLEM OF WEAR IN POLYETHYLENE ACETABULAR LINERS Currently, total hip arthroplasties consist of a femoral stem prosthesis, a modular femoral head, a modular acetabular liner, and an implanted acetabular cup (Figs. 1, 2). The acetabular liner is a polyethylene implant that is generally impacted into the acetabular cup. During the life of a total hip arthroplasty, wear primarily affects the polyethylene acetabular liner. The Consequences of Wear The wearing process in polyethylene liners produces small particles of polyethylene debris. The immune system responds by releasing macrophages and associated cytokines (e.g. TNF-α), which activate osteoclasts that produce osteolysis around the hip joint (Fig. 3, next page). The loss of bone causes micromotion of the hip implants, and further potentiates osteolysis. As a result of the osteolysis and wear, patients are at increased risk of several consequences, including periprosthetic fractures from simple falls or minor trauma, aseptic loosening of the prosthesis, or dislocation of the prosthesis. Conventional Polyethylene and Highly Crossed-Linked Polyethylene The polyethylene component has gone through two generations, termed conventional polyethylene, (CP) and highly crossed-linked polyethylene (XPE). The Journal of Lancaster General Hospital Fall 2018 Vol. 13 No. 3 81
2 In CP, radiation is used to form the hydrocarbon bonds, and the irradiation produces free radicals. If oxygen binds at the site of free radical formation, the resulting oxidation degrades the material s properties. CP is irradiated with doses of kgy,* and XPE is irradiated with doses of kgy. The higher dose increases the cross-linking potential between free radicals, but radiation doses greater than 100 kgy compromise the mechanical properties of the material. Another step in the process to reduce free radicals and oxidation is thermal stabilization, or heating. In the production of polyethylenes, various commercial companies use different types of radiation, radiation doses, and methods of stabilization, machining, and terminal sterilization. Wear is termed linear wear (femoral head penetration into the liner), and volumetric wear (amount of material lost). Linear wear is assessed in clinical studies, and volumetric wear in laboratory studies. Osteolysis has a higher propensity to occur with linear wear greater than 0.10 mm/yr and volumetric wear greater than 80 mm 3 /yr. 4 Laboratory simulator studies done prior to commercial release demonstrated less wear for XPE compared with CP Those in-vitro wear studies also demonstrated that with XPE, the degree of wear that occurs is not related to the size of the prosthetic femoral head selected, nor to the initial thickness of the polyethylene liner. (The importance of this characteristic will become clear in a discussion below.) XPE was introduced into clinical practice in 1999 with the expectation that lower wear rates invitro would translate to lower wear rates in vivo. Two randomized clinical studies followed patients for five years after total hip arthroplasties with XPE or CP. 12 Both studies concluded that, compared with CP, XPE had significantly fewer penetrations of the liner by the femoral head. The wear rate for XPE decreased by more 95% compared with the wear rates for CP, and tended to plateau after one year. Another study found that five years after total hip arthroplasty there was significantly less osteolysis on CT scan with XPE compared with CP (28% versus 80%). 13 Multiple other studies have since confirmed a reduction in wear rates for XPE compared with CP, which has translated into less osteolysis and aseptic loosening in total hip arthroplasties with XPE. Fig. 3. CT scan coronal (left slide) and axial (right slide) images showing significant osteolysis behind the previously implanted acetabular cup. FEMORAL HEAD AND ACETABULAR LINER BEARINGS Cobalt-Chromium & Crossed Linked Polyethylene (XPE) The most common femoral head composition used in total hip arthroplasty is made of a cobaltchromium (CoCr) metal alloy. As a result, the most widely used combinations in the U.S. are metal-onpolyethylene bearings (Fig.3), and most studies that compared CP to XPE wear used CoCr femoral heads. In 2013, the Swedish registry detected a trend toward fewer cup/liner revisions with the use of XPE, compared with an increase in the previous years when CP was used. 14 In 2014, the Australian arthroplasty registry also noted that, as time progressed, there was a lower revision rate with XPE compared with CP. 15 In high risk patients, larger femoral heads are used sometimes to decrease the risk of impingement of the femoral head or neck of the femoral prosthesis on the edge of the acetabulum or polyethylene liner. These contacts may produce a lever arm that causes a dislocation. To accommodate the larger femoral head, a thinner polyethylene liner would be needed, but as noted earlier, multiple studies have demonstrated that for XPE, thickness of the polyethylene liner does not affect the wear rate. A thinner XPE cup might also raise concern about fracture, but this also has not been an issue except in those acetabular cups placed more vertically, anteverted, or with a rim thickness at the locking mechanism < 4 mm. Since most non-cemented femoral prostheses are constructed of titanium, there has been concern recently about the bearing coupling between the * Gy = Gray, the International Unit of absorbed ionizing radiation. It is derived from the applied energy (in Joules) and the mass of the affected matter (in Kg). kgy = thousands of units. 82 The Journal of Lancaster General Hospital Fall 2018 Vol. 13 No. 3
3 CoCr femoral head and the titanium femoral prosthesis. This mixed metal construct may increase the risk of fretting** and corrosion at the modular junction, a process termed trunnionosis (Fig. 4). (The trunnion is the tapered portion of the femoral stem prosthesis where the femoral head is impacted during implantation.) With CoCr femoral heads, there have been reports of corrosion at the trunnion, metal wear at the trunnion, and adverse local tissue reactions from the metal debris. As a result, it has been proposed that ceramic femoral heads be used to avoid these reactions. However, registries have not reflected a statistically significant difference in revision rates between ceramic or CoCr femoral heads with XPE liners. Also, ceramic femoral heads typically are significantly more expensive than CoCr femoral heads and may not be cost effective. Studies have also revealed that XPE liners are more tolerant of acetabular component malposition. Together with the low wear characteristics of XPE, the cheaper cost of CoCr femoral heads, and the ability of metal-on-xpe bearings to withstand minor malposition, CoCr-XPE bearings should be the predominant couple in current total hip arthroplasties. Ceramic Bearings Ceramic bearings were first used in clinical practice in the 1970s. The ceramic components are fabricated from pure alumina, zirconia, and alumina matrix composite powder. In total joint replacement, ceramic constructs are available for both the femoral head and the acetabular liner. Ceramic constructs have stronger mechanical properties and lower wear rates. 16,17 Their hard structures and smoothly polished surfaces provide higher resistance to wear, and minimize frictional forces because of their hydrophilic properties. 18 Not only do ceramic-on-ceramic constructs have the lowest wear rate amongst all bearings, but they also cause less soft tissue reactions when compared to metal-on-polyethylene and metal-on-metal bearings. 19 Fig. 4 Example of trunnionosis of a cobalt chromium femoral head and the tapered portion of the femoral prosthesis. Because a ceramic component is not a metal alloy, there is less trunnionosis with the combination of a ceramic femoral head and a titanium femoral prosthesis, and less chance for metal debris and damage to the titanium trunnion. Also, the lack of metal debris makes ceramic femoral heads beneficial in patients with metal hypersensitivity. In-vivo studies have demonstrated excellent wear rates over a 10-year period for both ceramic-on-polyethylene, , and ceramic-on-ceramic bearings, with no statistically significant difference in osteolysis, wear rates, or implant failure Nonetheless, first-generation ceramic components had higher rates of component fracture than XPE liners with CoCr femoral heads. Fracture is catastrophic because it results in multiple fragments that may lead to third body wear and damage of the femoral prosthesis. Fortunately, the newest generation of mixed oxide ceramic materials has greatly reduced the risk of fracture to roughly 0.003% and 0.03% for Delta ceramic heads and liners, respectively. 30 The various factors that influence the risk of ceramic femoral head fractures include the cleanliness of the trunnion prior to head impaction, the amount of force used to impact the head on the trunnion, and the size and length of the femoral head. (Smaller heads and shorter necks have a higher risk of fracture.) Ceramic-on-ceramic hip constructs are also associated with increased squeaking. The Australian National Joint Registry noted a 4.2% rate of squeaking with this construct. 31 Squeaking can occur with every step, or with deep flexion, and is likely caused by malposition of the acetabular component with excessive inclination and anteversion. Squeaking may also occur with the loss of the fluid film lubricating the joint. Component malposition is also a factor, as it may result in increased loading against the edge of the cup. Care must be taken to avoid this complication because it may produce embarrassment and anxiety for the patient, and litigation against the surgeon. There is no clear evidence that squeaking increases ** Fretting: A special wear process that occurs at the contact area between two materials under load that are subjected to relative motion by vibration or some other force. The Journal of Lancaster General Hospital Fall 2018 Vol. 13 No. 3 83
4 Fig. 5 Acetabular cup with highly crossed-linked polyethylene liner and ceramicized femoral head. Fig. 6. Metal-on-metal hip prosthesis with femoral stem, cobalt chromium femoral head, metal liner, and metal acetabular cup. the wear rate of the implant, though there are suggestions that it may. In addition, ceramic heads have traditionally been significantly more expensive than CoCr, and their cost effectiveness is debatable. Ceramicized Femoral Heads Zirconium is a hard metal with properties like titanium. It is not found naturally as a metal, but can be refined, through a complex process, from zirconium silicate (ZrSiO4). However, Zirconium oxide (ZrO2) is not a metal but a ceramic. It was first used clinically in total hip arthroplasties in approximately 2003 as a zirconium oxide, ceramic, outer surface of approximately 5 μm on a zirconium metal femoral head (Fig. 5). This ceramic outer surface has similar mechanical properties to a fully ceramic bearing, including a smooth surface, increased scratch resistance, and increased hardness when compared to CoCr. In vitro studies confirm that ceramicized zirconium femoral heads share the improved resistance to wear of fully ceramic heads with polyethylene, especially with XPE. 32 The Australian Joint Registry reported a low revision rate of 3.3% at 11 years with this bearing couple. 33 However, in-vivo studies vary when comparing XPE with CoCr or ceramicized heads. Some studies show statistically significant differences in wear rate, and others demonstrate no difference Because of its zirconium alloy core, this composite will not fracture like fully ceramic heads. However, the oxide surface may be damaged if it contacts other metal surfaces, such as the rim of the acetabular metal shell during joint reductions and dislocations. Ceramicized femoral heads also have a higher resistance to fretting and corrosion of the trunnion compared to CoCr, so they may be a suitable option if there is concern about trunnionosis. Like ceramic heads, ceramicized heads are also a viable option in patients with metal hypersensitivity since they avoid metal debris and trunnionosis at the bearing junction. Like the all-ceramic heads, however, ceramicized heads are significantly more expensive than CoCr femoral heads. Also, only one company currently manufactures this product, and it should therefore only be used with this company s compatible femoral prosthesis. In sum, ceramicized heads are a good option because of their improved wear characteristics and good in-vivo results, but their increased cost, and production by only one manufacturer, limits their widespread use. METAL-ON-METAL FEMORAL HEAD AND LINER As discussed throughout this article, a primary concern in total hip replacements is the wear rates of bearing materials. A metal-on-metal (MoM) bearing includes a CoCr metal head and a metal acetabular liner. (Fig. 6) Traditional stemmed MoM hip replacements (and later resurfacings) were first introduced in the 1990s because they offered lower wear rates. For younger patients who need total hip replacement for osteoarthritis, longevity of the implant is a particularly important characteristic. It is estimated that since 1996, more than 1 million MoM implants have been inserted worldwide. MoM bearings can result from traditional hip replacement with a stemmed femoral prosthesis (Fig. 7B), or resurfacing of the femoral head with a metal cap (Fig. 7A), in which case more bone is preserved. The benefits of MoM bearings compared with metal-on-polyethylene include not only lower volumetric wear rates, but also greater stability of the implant; because metal inserts are thinner than polyethylene liners, larger femoral head sizes can be used. However, the use of MoM bearings in stemmed hip replacements is not recommended in the U.S. because there are reports in the literature of poor outcomes. When MoM bearings are inserted in patients who are more than 55 years old, have larger femoral heads, or have acetabular cups placed in excessive inclination, they have a higher risk of 84 The Journal of Lancaster General Hospital Fall 2018 Vol. 13 No. 3
5 Fig. 7. Radiographs of metal-on-metal prosthesis. A: Hip resurfacing prosthesis, B: Stemmed metal-on-metal total hip replacement. Fig. 8. A: MARS MRI axial image with pseudotumor (arrow) anterior to the femur and metal-on-metal prosthesis; B: Intraoperative image of previous metal-on-metal prosthesis causing extensive metallosis and soft tissue destruction. revision than polyethylene and ceramic bearings Soft tissue reactions from the metal ions of the MoM bearings are the key issues in failure of the implants and associated complications. The metal ions cause adverse local tissue reactions (ALTRs), osteolysis, enlarged bursae, effusions, creation of pseudotumors, destruction of the abductor muscles, and necrosis. (Fig. 8) A lymphocyte dominated immunologic response occurs in the tissue, known as aseptic lymphocyte-dominant vasculitis-associated lesions (ALVAL). Unfortunately, it is not possible to predict which patients will have these reactions to metal ions. Some patients have symptoms, others have none, but it is generally recommended that even asymptomatic patients should be evaluated yearly with radiographs to assess osteolysis and blood levels of cobalt and chromium ions. Metal ion levels > 7 ppb (parts per billion) are considered elevated, and should instigate advanced imaging. Metal artifact reduction sequence (MARS) MRI helps assess for presence of pseudotumors and integrity of the abductor and gluteal muscles. Optimum treatment of asymptomatic patients is debated. Treatment of symptomatic patients is multifactorial but commonly involves a revision total hip replacement. Placement of metal-on-polyethylene or ceramic-on-polyethylene bearing constructs are generally recommended for stable acetabular and femoral prostheses. Many companies have recalled their MoM stemmed hip replacements because of these unfavorable outcomes. Therefore, hip resurfacing is the only recommended MoM bearing, and should be reserved for younger patients with preserved femoral head bone stock. However, this operation is not typically performed by most orthopedic surgeons. CONCLUSION Substantial progress has been made in the bearing components of total hip replacements in the past 30 years. Newer highly crossed-link polyethylene liners have significantly decreased wear rates when compared with conventional polyethylene. Cobalt chromium femoral heads and highly crossed linked polyethylene liners are the dominant bearing couple used in the United States, due to excellent follow-up studies. Ceramic and ceramicized femoral heads have lower wear rates, but they are more costly. They may be viable options in younger patients, and those with metal hypersensitivities. Stemmed metal-on-metal hip replacements have largely been removed from the U.S. market due to post-operative complications, and the need for revision surgery. The ultimate goal will be to create a bearing couple with minimal complications and increased durability. Gregory A. Tocks, D.O. Orthopedic Associates of Lancaster Ltd. 170 North Pointe Blvd. Lancaster, PA (717) gtocks@fixbones.com The Journal of Lancaster General Hospital Fall 2018 Vol. 13 No. 3 85
6 References 1. Wolford M, Palso K, Bercovitz A: Hospitalization for total hip replacement among inpatients aged 45 and over: United States, Centers for Disease Control and Prevention nchs/data/databriefs/db186.htm 2. Kurtz S, Ong K, Lau E, et al: Projections of primary and revision hip and knee arthroplasty in the United States from 2005 to J Bone Joint Surg Am 2007;89(4): Depuy Pinnacle Polethylene technique guide: net/o16/llnwmb8/us%20mobile/synthes%20north%20 America/Product%20Support%20Materials/Technique%20 Guides/DSUSJRC (2)%20Pinnacle%20ST.pdf 4. Hammerberg EM, Wan Z, Dastane M, et al: Wear and range of motion of different femoral head sizes. J Arthroplasty 2010;25(6): Estok DM II, Burrough BR, Muratoglu OK, et al: Comparison of hip simulator wear of 2 different highly crossed-linked ultra high molecular weight polyethylene acetabular components using both 32- and 38-mm femoral heads. J Arthroplasty 2007;22(4): Muratoglu OK, Rubash HE, Bragdon CR, et al: Simulated normal gait wear testing of a highly crossed-linked polyethylene tibial insert. J Arthroplasty 2007;22(3): Laurent MP, Johnson TS, Crowninshielf RD, et al: Characterization of a highly crossed-linked ultrahigh molecular-weight polyethylene in clinical use in total hip arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty 2008;23(5): Ito H, Maloney CM, Crowninshield RD, et al. In vivo femoral head damage and its effect on polyethylene wear. J Arthroplasty 2010; 25(2): Shen FW, Lu Z, McKellop HA: Wear versus thickness and other features of 5 MRAD crosslinked UHMWPE acetabular liners. Clin Orthop Relat Res 2011; 469(2): McKellop H, Shen FW, DiMaio W, et al. Wear of gamma-crosslinked polyethylene acetabular cups against roughened femoral balls. Clin Orthop Relat Res 1999; 3369: McKellop HA, Shen FW, Lu B, et al. Effect of sterilization method and other modifications of the wear resistance of acetabular cups made of ultra-high molecular weight polyethylene: A hip simulator study. J Bone Joint Surg Am 2007;89 (10): Digas G, Karrholm J, Thanner J, et al. 5-year experience of highly crossed-linked polyethylene in cemented and uncemented sockets: Two randomized studies using radiostereometric analysis. Acta Orthop 2007;78(6): Leung SB, Egawa H, Stepniewski A, et al. Incidence and volume of pelvic osteolysis at early follow-up with highly crossed-linked and noncross-linked polyethylene. J Arthroplasty 2007;22(6, Suppl 2): Swedish Hip Arthroplasty Register: Annual Report registercentrum.blob.core.windows.net/shpr/r/annual-report HJnnK8Tie.pdf 15. Australian Orthopaedic Association: National joint replacement registry annual report Accessed on 6/25/ Campbell P, Shen FW, McKellop H: Biologic and tribologic considerations of alternative bearing surfaces. Clin Orthop Relat Res 2004;418: Macdonald N, Bankes M: Ceramic on ceramic hip prostheses: A review of past and modern materials. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg 2014;134(9): Di Puccio F, Mattei L: Biotribology of artificial hip joints. World J Orthop 2015;6 (1): Esposito C, Maclean F, Campbell P, et al. Periprosthetic tissues from third generation alumina-on-alumina total hip arthroplasties. J Arthroplasty 2013;28(5): So K, Goto K, Kuroda Y, et al. Minimum 10-year wear analysis of highly cross-linked polyethylene in cementless total hip arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty 2015; 30(12): Epinette JA, Manley MT: No differences found in bearing related hip survivorship at years follow-up between patients with ceramic on highly cross- linked polyethylene bearings compared to patients with ceramic on ceramic bearings. J Arthroplasty 2014;29(7): Kim YH, Park JW, Kulkarni SS, et al. A randomised prospective evaluation of ceramic-on-ceramic and ceramic-on-highly cross-linked polyethylene bearings in the same patients with primary cementless total hip arthroplasty. Int Orthop 2013;37(11): Nakashima Y, Sato T, Yamamoto T, et al. Results at a minimum of 10 years of follow- up for AMS and PerFix HA-coated cementless total hip arthroplasty: Impact of cross-linked polyethylene on implant longevity. J Orthop Sci 2013;18(6): Fukui K, Kaneuji A, Sugimori T, et al. Wear comparison between conventional and highly cross-linked polyethylene against a zirconia head: A concise follow-up, at an average 10 years, of a previous report. J Arthroplasty 2013; 28(9): Chana R, Facek M, Tilley S, et al. Ceramic-on-ceramic bearings in young patients: Outcomes and activity levels at minimum ten-year follow-up. Bone Joint J 2013;95-B(12): Synder M, Drobniewski M, Sibinski M: Long-term results of cementless hip arthroplasty with ceramic-on-ceramic articulation. Int Orthop 2012;36(11): Streit MR, Schröder K, Körber M, et al. High survival in young patients using a second generation uncemented total hip replacement. Int Orthop 2012;36(6): Solarino G, Piazzolla A, Notarnicola A, et al.long-term results of 32-mm alumina- on-alumina THA for avascular necrosis of the femoral head. J Orthop Traumatol 2012;13(1): Sugano N, Takao M, Sakai T, et al. Eleven- to 14-year follow-up results of cementless total hip arthroplasty using a third-generation alumina ceramic-on-ceramic bearing. J Arthroplasty 2012;27(5): Massin P, Lopes R, Masson B, et al. French Hip & Knee Society (SFHG): Does Biolox Delta ceramic reduce the rate of component fractures in total hip replacement? Orthop Traumatol Surg Res 2014;100(6 suppl):s317-s Own Dh, Russell NC, Smith PN, et al, An estimation of the incidence of squeaking and revision surgery for squeaking in ceramicon-ceramic total hip replacement: A meta-analysis and report from the Australian Orthopaedic Association National Joint Registry. Bone Joint J 2014;96-B(2): Good V, Ries M, Barrack RL, et al. Reduced wear with oxidized zirconium femoral heads. J Bone Joint Surg Am 2003;85-A(suppl 4): Australian Orthopaedic Association: National joint registry annual report Accessed 6/27/ Morison ZA, Patil S, Khan HA, et al. A randomized controlled trial comparing Oxinium and cobalt-chrome on standard and cross-linked polyethylene. J Arthroplasty 2014;29(9suppl): Jassim SS, Patel S, Wardle N: Five-year comparison of wear using oxidized zirconium and cobalt-chrome femoral heads in total hip arthroplasty: A multicenter randomized controlled trial. Bone Joint J 2015;97-B(7): Karidakis GK, Karachalios T: Oxidized zirconium head on crosslinked polyethylene liner in total hip arthroplasty: A 7- to 12-year in vivo comparative wear study. Clin Orthop Relat Res 2015;473(12): Australian Orthopaedic Association: National joint registry annual report National Joint Registry for England and Wales: Seventh Annual Report NJR%207th%20Annual%20Report% pdf 86 The Journal of Lancaster General Hospital Fall 2018 Vol. 13 No. 3
Bone Bangalore
 Dr Suresh Annamalai MBBS, MRCS(Edn), FRCS( Tr & Orth)(Edn), FEBOT(European Board), Young Hip and Knee Fellowship(Harrogate, UK) Consultant Arthroplasty and Arthroscopic Surgeon Manipal Hospital, Whitefield,
Dr Suresh Annamalai MBBS, MRCS(Edn), FRCS( Tr & Orth)(Edn), FEBOT(European Board), Young Hip and Knee Fellowship(Harrogate, UK) Consultant Arthroplasty and Arthroscopic Surgeon Manipal Hospital, Whitefield,
Case report: Pain L THR [ post THR 2 years; with history of trivial fall] Your Diagnosis?
![Case report: Pain L THR [ post THR 2 years; with history of trivial fall] Your Diagnosis? Case report: Pain L THR [ post THR 2 years; with history of trivial fall] Your Diagnosis?](/thumbs/78/78456133.jpg) Case report: Pain L THR [ post THR 2 years; with history of trivial fall] Your Diagnosis? Diagnosis: Ceramic head fracture In the 1970 s, Boutin implemented ceramic in modern total hip arthroplasty (THA).
Case report: Pain L THR [ post THR 2 years; with history of trivial fall] Your Diagnosis? Diagnosis: Ceramic head fracture In the 1970 s, Boutin implemented ceramic in modern total hip arthroplasty (THA).
Session 3: Controversies for Bearing Surfaces in THR
 : Controversies for Bearing Surfaces in THR Learning Objectives Upon completion of this activity, participants should be able to: 1. Understand the indications and known methods for the use of each of
: Controversies for Bearing Surfaces in THR Learning Objectives Upon completion of this activity, participants should be able to: 1. Understand the indications and known methods for the use of each of
Understanding Hip Implant Options
 Understanding Hip Implant Options Cup (Socket) Bearing (Liner) Head Stem (Femur) Modern Hip Implants (Ball) Metal Femoral Head on Marathon Cross-linked Polyethylene Liner Proven materials Polyethylene
Understanding Hip Implant Options Cup (Socket) Bearing (Liner) Head Stem (Femur) Modern Hip Implants (Ball) Metal Femoral Head on Marathon Cross-linked Polyethylene Liner Proven materials Polyethylene
CASE 56 Hip Pain. ? Diagnosis
 CSE 56 Hip Pain PIN IN THE HIP: 1. 50-year-old female who had undergone total hip arthroplasty [Metal on metal] of the right hip 3.4 years earlier. Shee had a tingling sensation in the trochanteric region
CSE 56 Hip Pain PIN IN THE HIP: 1. 50-year-old female who had undergone total hip arthroplasty [Metal on metal] of the right hip 3.4 years earlier. Shee had a tingling sensation in the trochanteric region
Zimmer TM. Continuum Acetabular System. Bringing together proven technologies.
 Zimmer TM Continuum Acetabular System Bringing together proven technologies. The power to meet individual patient needs. Zimmer Continuum Acetabular System provides highly flexible solutions for orthopaedic
Zimmer TM Continuum Acetabular System Bringing together proven technologies. The power to meet individual patient needs. Zimmer Continuum Acetabular System provides highly flexible solutions for orthopaedic
ARTICLE IN PRESS. Surface Oxidized Zirconium Total Hip Arthroplasty Head Damage Due to Closed Reduction. Effects on Polyethylene Wear
 The Journal of Arthroplasty Vol. 00 No. 0 2008 Surface Oxidized Zirconium Total Hip Arthroplasty Head Damage Due to Closed Reduction Effects on Polyethylene Wear William L. Jaffe, MD,* Eric J. Strauss,
The Journal of Arthroplasty Vol. 00 No. 0 2008 Surface Oxidized Zirconium Total Hip Arthroplasty Head Damage Due to Closed Reduction Effects on Polyethylene Wear William L. Jaffe, MD,* Eric J. Strauss,
Enhancing stability and increasing range of motion. Metasul LDH Large Diameter Head
 Enhancing stability and increasing range of motion Metasul LDH Large Diameter Head The Metasul large diameter head technology is the result of in-depth research, development and clinical experience that
Enhancing stability and increasing range of motion Metasul LDH Large Diameter Head The Metasul large diameter head technology is the result of in-depth research, development and clinical experience that
DePuy Orthopaedics, Inc. 700 Orthopaedic Drive Warsaw, IN USA Tel: +1 (800) Fax: +1 (574)
 References 1. Sanchez-Sotelo J, Haidukewych GJ, Boberg CJ. Hospital Cost of Dislocation After Primary Total Hip Arthroplasty. J Bone Joint Surg. 2006;88A:290-294. 2. Brodner W, Grübl A, Jankovsky R, Meisinger
References 1. Sanchez-Sotelo J, Haidukewych GJ, Boberg CJ. Hospital Cost of Dislocation After Primary Total Hip Arthroplasty. J Bone Joint Surg. 2006;88A:290-294. 2. Brodner W, Grübl A, Jankovsky R, Meisinger
Metal-on-metal articulations generate approximately to particles PSEUDOTUMORS FACTORS PATHOGENESIS
 PSEUDOTUMORS Vasu Pai ARMD Adverse reaction to metal debris. Langton identified that there is no clear consensus in the literature defining the boundaries of the terms metallosis, aseptic lymphocyte-dominated
PSEUDOTUMORS Vasu Pai ARMD Adverse reaction to metal debris. Langton identified that there is no clear consensus in the literature defining the boundaries of the terms metallosis, aseptic lymphocyte-dominated
FIXATION FIRST WEAR REDUCTION OXIDATIVE STABILITY MECHANICAL INTEGRITY PROVEN TECHNOLOGY
 FIXATION FIRST WEAR REDUCTION OXIDATIVE STABILITY MECHANICAL INTEGRITY PROVEN TECHNOLOGY Fixation First FIXATION FIRST 1958 Charnley Hip Over 1,000,000 implanted 1 96.2 percent survivorship at 32 years
FIXATION FIRST WEAR REDUCTION OXIDATIVE STABILITY MECHANICAL INTEGRITY PROVEN TECHNOLOGY Fixation First FIXATION FIRST 1958 Charnley Hip Over 1,000,000 implanted 1 96.2 percent survivorship at 32 years
Ceramic Femoral Heads and Acetabular Cup Liners
 Important Information: Please read prior to use in a clinical setting. The Surgeon should be familiar with the operative technique. Caution: Federal (U.S.A) law restricts this device to sale by or on the
Important Information: Please read prior to use in a clinical setting. The Surgeon should be familiar with the operative technique. Caution: Federal (U.S.A) law restricts this device to sale by or on the
National Joint Replacement Registry. Lay Summary 2015 Annual Report Hip and Knee Replacement
 National Joint Replacement Registry Lay Summary 2015 Annual Report Hip and Knee Replacement SUPPLEMENTARY REPORT 2015 TABLE OF CONTENTS Introduction... 1 A brief history of the Registry origins... 1 The
National Joint Replacement Registry Lay Summary 2015 Annual Report Hip and Knee Replacement SUPPLEMENTARY REPORT 2015 TABLE OF CONTENTS Introduction... 1 A brief history of the Registry origins... 1 The
Adverse Local Tissue Reaction in Total Hip Replacement
 Adverse Local Tissue Reaction in Total Hip Replacement Authors 1 David C Evans, 2 Ross A Miller, 3 Stephen J Incavo 1 MD Candidate, Baylor College of Medicine Class of 2018 2 Houston Methodist Hospital,
Adverse Local Tissue Reaction in Total Hip Replacement Authors 1 David C Evans, 2 Ross A Miller, 3 Stephen J Incavo 1 MD Candidate, Baylor College of Medicine Class of 2018 2 Houston Methodist Hospital,
Wear Properties of UHMWPE in CHARITE Artificial Inter-vertebral Disc
 Mechanics of Contact and Lubrication, MTM G230 Department of Mechanical & Industrial Enineering Northeastern University Spring 2006 Wear Properties of UHMWPE in CHARITE Artificial Inter-vertebral Disc
Mechanics of Contact and Lubrication, MTM G230 Department of Mechanical & Industrial Enineering Northeastern University Spring 2006 Wear Properties of UHMWPE in CHARITE Artificial Inter-vertebral Disc
CeramTec Medical Products. BIOLOX DUO Ceramic Bipolar System. Bone-sparing joint reconstruction with a maximum range of motion
 CeramTec Medical Products BIOLOX DUO Ceramic Bipolar System Bone-sparing joint reconstruction with a maximum range of motion 2 BIOLOX DUO Ceramic Bipolar System Less is more BIOLOX DUO is an alternative
CeramTec Medical Products BIOLOX DUO Ceramic Bipolar System Bone-sparing joint reconstruction with a maximum range of motion 2 BIOLOX DUO Ceramic Bipolar System Less is more BIOLOX DUO is an alternative
Product Information. *smith&nephew POLARCUP Dual Mobility System
 APPLYING SCIENCE TO MOBILITY Combined with VERILAST Technology for unmatched performance Product Information *smith&nephew POLARCUP Dual Mobility System APPLYING SCIENCE TO MOBILITY Combined with VERILAST
APPLYING SCIENCE TO MOBILITY Combined with VERILAST Technology for unmatched performance Product Information *smith&nephew POLARCUP Dual Mobility System APPLYING SCIENCE TO MOBILITY Combined with VERILAST
CERAMIC-ON-METAL. References: Cat No: version 2
 CERAMIC-ON-METAL References: 1. Beaule, P. E., et al. Jumbo femoral head for the treatment of recurrent dislocation following total hip replacement. J.Bone Joint Surg (2002). 84-A: 256-63. 2. Jolles, B.
CERAMIC-ON-METAL References: 1. Beaule, P. E., et al. Jumbo femoral head for the treatment of recurrent dislocation following total hip replacement. J.Bone Joint Surg (2002). 84-A: 256-63. 2. Jolles, B.
Medical Products Division. BIOLOX DUO Ceramic Bipolar System. Bone-sparing joint reconstruction with a maximum range of motion
 Medical Products Division BIOLOX DUO Ceramic Bipolar System Bone-sparing joint reconstruction with a maximum range of motion 2 BIOLOX DUO Keramisches Bipolarsystem BIOLOX DUO Ceramic Bipolar System Less
Medical Products Division BIOLOX DUO Ceramic Bipolar System Bone-sparing joint reconstruction with a maximum range of motion 2 BIOLOX DUO Keramisches Bipolarsystem BIOLOX DUO Ceramic Bipolar System Less
What Are Hip and Knee Replacement Implants Made Of?
 What Are Hip and Knee Replacement Implants Made Of? Hip and knee replacement surgery involve replacing the worn-out bone and cartilage lining your hip or knee joint with new implants that are composed
What Are Hip and Knee Replacement Implants Made Of? Hip and knee replacement surgery involve replacing the worn-out bone and cartilage lining your hip or knee joint with new implants that are composed
MARATHON Cross-Linked Polyethylene
 MARATHON Cross-Linked Polyethylene Fixation First... 1 Wear Reduction... 2 Oxidative Stability... 3 Mechanical Integrity... 4 Proven Technology...5-6 References... 7 Fixation First FIXATION FIRST Prodigy
MARATHON Cross-Linked Polyethylene Fixation First... 1 Wear Reduction... 2 Oxidative Stability... 3 Mechanical Integrity... 4 Proven Technology...5-6 References... 7 Fixation First FIXATION FIRST Prodigy
Enhanced Stability Constrained Liners. Design Rationale Surgical Technique
 Enhanced Stability Constrained Liners Design Rationale Surgical Technique The Pinnacle Acetabular Cup System was designed to maximize the number of options available to the surgeon, and provide those options
Enhanced Stability Constrained Liners Design Rationale Surgical Technique The Pinnacle Acetabular Cup System was designed to maximize the number of options available to the surgeon, and provide those options
G7 ACETABULAR SYSTEM. beautifully. efficient.
 G7 ACETABULAR SYSTEM beautifully efficient. HERITAGE MEETS MODERN DESIGN SIMPLICITY, EFFICIENCY AND PERFORMANCE The G7 System is a multi-bearing acetabular platform delivering simplicity, efficiency and
G7 ACETABULAR SYSTEM beautifully efficient. HERITAGE MEETS MODERN DESIGN SIMPLICITY, EFFICIENCY AND PERFORMANCE The G7 System is a multi-bearing acetabular platform delivering simplicity, efficiency and
Featuring. Technology. Product Rationale
 Featuring Technology Product Rationale 2 Optimum implant geometry Extending proven TRI-LOCK heritage The original TRI-LOCK Stem was introduced in 1981. This implant was the first proximally coated tapered-wedge
Featuring Technology Product Rationale 2 Optimum implant geometry Extending proven TRI-LOCK heritage The original TRI-LOCK Stem was introduced in 1981. This implant was the first proximally coated tapered-wedge
Optimum implant geometry
 Design Rationale Optimum implant geometry Extending proven Tri-Lock heritage The original Tri-Lock was introduced in 1981. This implant was the first proximally coated tapered-wedge hip stem available
Design Rationale Optimum implant geometry Extending proven Tri-Lock heritage The original Tri-Lock was introduced in 1981. This implant was the first proximally coated tapered-wedge hip stem available
The information contained in this document is intended for healthcare professionals only.
 The information contained in this document is intended for healthcare professionals only. Trident Hemispherical Acetabular Shell Trident PSL HA Acetabular Shell Featuring: The Trident Acetabular System
The information contained in this document is intended for healthcare professionals only. Trident Hemispherical Acetabular Shell Trident PSL HA Acetabular Shell Featuring: The Trident Acetabular System
Trusted technology. Trusted performance. Supporting healthcare professionals
 Trusted technology. Trusted performance. Supporting healthcare professionals Trusted technology. Trusted performance. The POLAR3 Total Hip Solution, powered by Smith & Nephew s proprietary VERILAST Technology,
Trusted technology. Trusted performance. Supporting healthcare professionals Trusted technology. Trusted performance. The POLAR3 Total Hip Solution, powered by Smith & Nephew s proprietary VERILAST Technology,
BIOLOX delta Option Ceramic Femoral Head System. Product Features and Instructions for Use
 BIOLOX delta Option Ceramic Femoral Head System Product Features and Instructions for Use Product Features BIOLOX delta ceramic heads are composed of 75% aluminum oxide and approximately 25% zirconia.
BIOLOX delta Option Ceramic Femoral Head System Product Features and Instructions for Use Product Features BIOLOX delta ceramic heads are composed of 75% aluminum oxide and approximately 25% zirconia.
BIOLOX delta Option Ceramic Femoral Head System
 BIOLOX delta Option Ceramic Femoral Head System Product Features and Instructions for Use Knees Hips Extremities Cement and Accessories PMI Technology Product Features BIOLOX delta ceramic heads are composed
BIOLOX delta Option Ceramic Femoral Head System Product Features and Instructions for Use Knees Hips Extremities Cement and Accessories PMI Technology Product Features BIOLOX delta ceramic heads are composed
Zimmer Longevity Highly Cross-linked Polyethylene. Clinical Value Dossier - APAC
 Zimmer Longevity Highly Cross-linked Polyethylene Clinical Value Dossier - APAC Table of Contents 1 Executive Summary...................................................... 1 2 Burden of Illness........................................................
Zimmer Longevity Highly Cross-linked Polyethylene Clinical Value Dossier - APAC Table of Contents 1 Executive Summary...................................................... 1 2 Burden of Illness........................................................
Stability without compromise. Epsilon Durasul Constrained Insert
 Stability without compromise Epsilon Durasul Constrained Insert History of Dislocation and Constrained Acetabular Inserts The Need for a Better Solution The Problem Dislocation is the second most common
Stability without compromise Epsilon Durasul Constrained Insert History of Dislocation and Constrained Acetabular Inserts The Need for a Better Solution The Problem Dislocation is the second most common
Optimum implant geometry
 Design Rationale Optimum implant geometry Extending the proven Tri-Lock heritage The original Tri-Lock was introduced in 1981. This implant was the first proximally coated tapered-wedge hip stem available
Design Rationale Optimum implant geometry Extending the proven Tri-Lock heritage The original Tri-Lock was introduced in 1981. This implant was the first proximally coated tapered-wedge hip stem available
Impingement in THA. Georgi I. Wassilew. Orthopaedic Department, Centrum für Muskuloskeletale Chirurgie Univ.-Prof. Dr. med. C.
 Georgi I. Wassilew Orthopaedic Department, Centrum für Muskuloskeletale Chirurgie Univ.-Prof. Dr. med. C. Perka Charité - Universitätsmedizin Berlin Orthoload club, Berlin Reasons for revision in THA Reason
Georgi I. Wassilew Orthopaedic Department, Centrum für Muskuloskeletale Chirurgie Univ.-Prof. Dr. med. C. Perka Charité - Universitätsmedizin Berlin Orthoload club, Berlin Reasons for revision in THA Reason
BIOTRIBOLOGICAL AND MECHANICAL ANALYSIS OF TOTAL HIP ARTHROPLASTIY FAILURE: How to break the code
 BIOTRIBOLOGICAL AND MECHANICAL ANALYSIS OF TOTAL HIP ARTHROPLASTIY FAILURE: How to break the code Patrick Chaboche, MD patrick.chaboche@wanadoo.fr Former Head of Department of Orthopaedic Surgery. Centre
BIOTRIBOLOGICAL AND MECHANICAL ANALYSIS OF TOTAL HIP ARTHROPLASTIY FAILURE: How to break the code Patrick Chaboche, MD patrick.chaboche@wanadoo.fr Former Head of Department of Orthopaedic Surgery. Centre
The information contained in this document is intended for healthcare professionals only.
 The information contained in this document is intended for healthcare professionals only. Trident Poly Acetabular System Trident PSL HA Acetabular Shell with X3 Poly insert Trident Hemispherical Acetabular
The information contained in this document is intended for healthcare professionals only. Trident Poly Acetabular System Trident PSL HA Acetabular Shell with X3 Poly insert Trident Hemispherical Acetabular
Total Hip Arthroplasty Using Metal Head on a Highly Cross-linked Polyethylene Liner
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Hip Pelvis 27(4): 216-222, 2015 http://dx.doi.org/10.5371/hp.2015.27.4.216 Print ISSN 2287-3260 Online ISSN 2287-3279 Total Hip Arthroplasty Using Metal Head on a Highly Cross-linked Polyethylene
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Hip Pelvis 27(4): 216-222, 2015 http://dx.doi.org/10.5371/hp.2015.27.4.216 Print ISSN 2287-3260 Online ISSN 2287-3279 Total Hip Arthroplasty Using Metal Head on a Highly Cross-linked Polyethylene
Exeter. Designed for Anatomic Restoration. Clinical Evidence Education
 Exeter Designed for Anatomic Restoration Clinical Evidence Education Anatomic Restoration Exeter re-creating biomechanics In hip replacement, the smallest adjustment can make a big difference. Stryker
Exeter Designed for Anatomic Restoration Clinical Evidence Education Anatomic Restoration Exeter re-creating biomechanics In hip replacement, the smallest adjustment can make a big difference. Stryker
1.1 Ceramic on Ceramic Bearings Used with Proximal Modular Stems in THA K. J. Keggi, J. M. Keggi, R. E. Kennon and T. McTighe
 1.1 Ceramic on Ceramic Bearings Used with Proximal Modular Stems in THA K. J. Keggi, J. M. Keggi, R. E. Kennon and T. McTighe Abstract Introduction: Osteolysis generated by wear debris remains a problem
1.1 Ceramic on Ceramic Bearings Used with Proximal Modular Stems in THA K. J. Keggi, J. M. Keggi, R. E. Kennon and T. McTighe Abstract Introduction: Osteolysis generated by wear debris remains a problem
Surface Roughness of Femoral Head Prostheses After Dislocation
 An Original Study Surface Roughness of Femoral Head Prostheses After Dislocation Kenny T. Mai, MD, Christopher Verioti, DO, Darryl D Lima, MD, PhD, Clifford W. Colwell, Jr., MD, and Kace A. Ezzet, MD Abstract
An Original Study Surface Roughness of Femoral Head Prostheses After Dislocation Kenny T. Mai, MD, Christopher Verioti, DO, Darryl D Lima, MD, PhD, Clifford W. Colwell, Jr., MD, and Kace A. Ezzet, MD Abstract
Peachy Mae T. Piana, MD
 Peachy Mae T. Piana, MD OUTLINE History of Total Hip Arthroplasty MoM Prosthesis Production of Metal Particles Defining Terminology: Metallosis, ARMD, ALTR, ALVAL, pseudotumor, periprosthetic reactive
Peachy Mae T. Piana, MD OUTLINE History of Total Hip Arthroplasty MoM Prosthesis Production of Metal Particles Defining Terminology: Metallosis, ARMD, ALTR, ALVAL, pseudotumor, periprosthetic reactive
TriboFit Hip System. Issue 3 - August 2013 English
 Important Information: Please read prior to use in a clinical setting. The surgeon should be familiar with the operative technique and all the information in this insert. Description: The TriboFit Hip
Important Information: Please read prior to use in a clinical setting. The surgeon should be familiar with the operative technique and all the information in this insert. Description: The TriboFit Hip
Dual Mobility System Surgical technique
 Trinity Dual Mobility System Surgical technique 2 Contents Operative summary 4 Overview 5 Operative technique 6 1. Acetabular reaming 6 Reamer guide 6 2. Acetabular shell trial 7 3. Acetabular shell implantation
Trinity Dual Mobility System Surgical technique 2 Contents Operative summary 4 Overview 5 Operative technique 6 1. Acetabular reaming 6 Reamer guide 6 2. Acetabular shell trial 7 3. Acetabular shell implantation
The power of simplicity
 The power of simplicity The power of simplicity Consider the facts, and take a look at the future: Revision TKA procedures are projected to double between now and 2015. 1 Restoration of a normal joint
The power of simplicity The power of simplicity Consider the facts, and take a look at the future: Revision TKA procedures are projected to double between now and 2015. 1 Restoration of a normal joint
Document No Rev. B Pg. 1 of 5 Approvals / Date Title: INSTRUCTIONS FOR USE DJO SURGICAL MODULAR REVISION HIP SYSTEM AND ACETABULAR CAGE
 Document No. 0400-0205 Rev. B Pg. 1 of 5 Approvals / Date Title: INSTRUCTIONS FOR USE DJO SURGICAL MODULAR REVISION HIP SYSTEM AND ACETABULAR CAGE Revision ECO Date ECO Summary of Changes Deann Rector
Document No. 0400-0205 Rev. B Pg. 1 of 5 Approvals / Date Title: INSTRUCTIONS FOR USE DJO SURGICAL MODULAR REVISION HIP SYSTEM AND ACETABULAR CAGE Revision ECO Date ECO Summary of Changes Deann Rector
Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, Graduate School of Medical Sciences, Kyushu University, Maidashi, Higashi-ku, Fukuoka , Japan
 Wear Resistant Performance of Highly Cross-Linked and Annealed Ultra-High Molecular Weight Polyethylene against Ceramic Heads in Total Hip Arthroplasty Taishi Sato, Yasuharu Nakashima, Mio Akiyama, Takuaki
Wear Resistant Performance of Highly Cross-Linked and Annealed Ultra-High Molecular Weight Polyethylene against Ceramic Heads in Total Hip Arthroplasty Taishi Sato, Yasuharu Nakashima, Mio Akiyama, Takuaki
DIRECT ANTERIOR APPROACH
 DIRECT ANTERIOR APPROACH JOINT REPLACEMENT PROGRAM 2301 25TH STREET SOUTH FARGO ND 58103 CENTER FOR MINIMAL INVASIVE JOINT SURGERY (p) 701-241-9300 (tf) 866-887-9300 www.jointpain.md FARGO FERGUS FALLS
DIRECT ANTERIOR APPROACH JOINT REPLACEMENT PROGRAM 2301 25TH STREET SOUTH FARGO ND 58103 CENTER FOR MINIMAL INVASIVE JOINT SURGERY (p) 701-241-9300 (tf) 866-887-9300 www.jointpain.md FARGO FERGUS FALLS
CAUTION: Ceramic liners are not approved for use in the United States.
 Total Hip Prostheses, Self-Centering Hip Prostheses and Hemi-Hip Prostheses IMPORTANT: This essential product information sheet does not include all of the information necessary for selection and use of
Total Hip Prostheses, Self-Centering Hip Prostheses and Hemi-Hip Prostheses IMPORTANT: This essential product information sheet does not include all of the information necessary for selection and use of
SURGICAL TECHNIQUE CEMENTED & PRESS-FIT UNIFIED INSTRUMENTATION INTRAOPERATIVE FLEXIBILITY PROVEN BIOMECHANICS
 SURGICAL TECHNIQUE CEMENTED & PRESS-FIT UNIFIED INSTRUMENTATION INTRAOPERATIVE FLEXIBILITY PROVEN BIOMECHANICS INTRODUCTION The Summit Tapered Hip System s comprehensive set of implants and instruments
SURGICAL TECHNIQUE CEMENTED & PRESS-FIT UNIFIED INSTRUMENTATION INTRAOPERATIVE FLEXIBILITY PROVEN BIOMECHANICS INTRODUCTION The Summit Tapered Hip System s comprehensive set of implants and instruments
Optimum implant geometry
 Surgical Technique Optimum implant geometry Extending proven Tri-Lock heritage The original Tri-Lock was introduced in 1981. This implant was the first proximally coated tapered-wedge hip stem available
Surgical Technique Optimum implant geometry Extending proven Tri-Lock heritage The original Tri-Lock was introduced in 1981. This implant was the first proximally coated tapered-wedge hip stem available
PINNACLE Acetabular Cup System
 PINNACLE Acetabular Cup System Clinical Summary A Prospective, Randomized Study of Cross-Linked and Non-Cross-Linked Polyethylene for Total Hip Arthroplasty at 10-Year Follow-Up Engh CA Jr., Hopper RH
PINNACLE Acetabular Cup System Clinical Summary A Prospective, Randomized Study of Cross-Linked and Non-Cross-Linked Polyethylene for Total Hip Arthroplasty at 10-Year Follow-Up Engh CA Jr., Hopper RH
UHMWPE LONGEVITY: INFLUENCES OF THE ORTHOPAEDIC TRIAD
 UHMWPE LONGEVITY: INFLUENCES OF THE ORTHOPAEDIC TRIAD AMERICAN ACADEMY OF ORTHOPAEDIC SURGEONS 66th Annual Meeting February 4-9, 1999 Anaheim, California COMMITTEE ON BIOMEDICAL ENGINEERING COMMITTEE ON
UHMWPE LONGEVITY: INFLUENCES OF THE ORTHOPAEDIC TRIAD AMERICAN ACADEMY OF ORTHOPAEDIC SURGEONS 66th Annual Meeting February 4-9, 1999 Anaheim, California COMMITTEE ON BIOMEDICAL ENGINEERING COMMITTEE ON
Hip Resurfacing vs. Standard Total Hip Replacement
 1 Hip Resurfacing vs. Standard Total Hip Replacement (My bias is obviously as a hip resurfacing proponent) Written June 6, 2011 HIP RESURFACING: PROS CONS 1. Less bone removal on the femur. 1. Femoral
1 Hip Resurfacing vs. Standard Total Hip Replacement (My bias is obviously as a hip resurfacing proponent) Written June 6, 2011 HIP RESURFACING: PROS CONS 1. Less bone removal on the femur. 1. Femoral
Acetabular Cup System. Clinical Summary
 Acetabular Cup System Clinical Summary A Prospective, Randomized Study of Cross-Linked and Non-Cross-Linked Polyethylene for Total Hip Arthroplasty at 10-Year Follow-Up Engh CA Jr., Hopper RH Jr., Huynh
Acetabular Cup System Clinical Summary A Prospective, Randomized Study of Cross-Linked and Non-Cross-Linked Polyethylene for Total Hip Arthroplasty at 10-Year Follow-Up Engh CA Jr., Hopper RH Jr., Huynh
ESC. Enhanced Stability Liners. Design Rationale & Surgical Technique
 ESC Enhanced Stability Liners Design Rationale & Surgical Technique Choice Without Compromise DePuy Synthes PINNACLE Hip Solutions are designed with a wide range of acetabular cup options, biological and
ESC Enhanced Stability Liners Design Rationale & Surgical Technique Choice Without Compromise DePuy Synthes PINNACLE Hip Solutions are designed with a wide range of acetabular cup options, biological and
Wear Analysis of Second-generation Highly Cross-Linked Polyethylene in Primary Total Hip Arthroplasty
 Wear Analysis of Second-generation Highly Cross-Linked Polyethylene in Primary Total Hip Arthroplasty Christopher Samujh, MD; Samrath Bhimani, MS; Langan Smith, BS; Arthur L. Malkani, MD abstract A major
Wear Analysis of Second-generation Highly Cross-Linked Polyethylene in Primary Total Hip Arthroplasty Christopher Samujh, MD; Samrath Bhimani, MS; Langan Smith, BS; Arthur L. Malkani, MD abstract A major
Dual Mobility System Evaluation surgical technique
 Trinity Dual Mobility System Evaluation surgical technique Contents Operative summary 4 Overview 5 Operative technique 6 1. Acetabular reaming 6 Reamer guide 6 2. Acetabular shell trial 6 3. Acetabular
Trinity Dual Mobility System Evaluation surgical technique Contents Operative summary 4 Overview 5 Operative technique 6 1. Acetabular reaming 6 Reamer guide 6 2. Acetabular shell trial 6 3. Acetabular
Furlong H-A.C. THR System
 Important Information Please read prior to use in a clinical setting. The Surgeon should be familiar with the operative technique. Caution Federal (U.S.A) law restricts this device to sale by or on the
Important Information Please read prior to use in a clinical setting. The Surgeon should be familiar with the operative technique. Caution Federal (U.S.A) law restricts this device to sale by or on the
Ceramic Bearings Should Be Routinely Used in THA. Disclosures 5/4/2015
 5/4/2015 Ceramic Bearings Should Be Routinely Used in THA Gwo-Chin Lee, MD Assistant Professor University of Pennsylvania Philadelphia, PA USA University of Pennsylvania Department of Orthopaedic Surgery
5/4/2015 Ceramic Bearings Should Be Routinely Used in THA Gwo-Chin Lee, MD Assistant Professor University of Pennsylvania Philadelphia, PA USA University of Pennsylvania Department of Orthopaedic Surgery
8.3 Tips and Tricks: Fracture of a Ceramic Insert
 Tips and Tricks 311 8.3 Tips and Tricks: Fracture of a Ceramic Insert with modern Ceramic Total Hip Replacement B.-W. Min, K.-S. Song, C.-H. Kang, K.-J. Lee, K.-C. Bae, C.-H. Cho and Y.-Y. Won Abstract
Tips and Tricks 311 8.3 Tips and Tricks: Fracture of a Ceramic Insert with modern Ceramic Total Hip Replacement B.-W. Min, K.-S. Song, C.-H. Kang, K.-J. Lee, K.-C. Bae, C.-H. Cho and Y.-Y. Won Abstract
StelKast Acetabular. Surgical Protocol and Product Specifications. Including ProForm, Provident, Provident Apical Threaded Hole & Systems
 StelKast Acetabular Surgical Protocol and Product Specifications Including ProForm, Provident, Provident Apical Threaded Hole & Systems StelKast Acetabular Surgical Protocol Introduction StelKast offers
StelKast Acetabular Surgical Protocol and Product Specifications Including ProForm, Provident, Provident Apical Threaded Hole & Systems StelKast Acetabular Surgical Protocol Introduction StelKast offers
ADDRESSING CLINICAL ISSUES OF CEMENTLESS HIP ARTHROPLASTY
 E C H E L O N P R I M A R Y H I P S Y S T E M P R O D U C T R A T I O N A L E ADDRESSING CLINICAL ISSUES OF CEMENTLESS HIP ARTHROPLASTY Echelon Primary Total Hip System HIGH OFFSET STANDARD OFFSET Cementless
E C H E L O N P R I M A R Y H I P S Y S T E M P R O D U C T R A T I O N A L E ADDRESSING CLINICAL ISSUES OF CEMENTLESS HIP ARTHROPLASTY Echelon Primary Total Hip System HIGH OFFSET STANDARD OFFSET Cementless
Wear and Osteolysis of Highly Crosslinked Polyethylene at 10 to 14 Years: The Effect of Femoral Head Size
 Clin Orthop Relat Res (2016) 474:365 371 DOI 10.1007/s11999-015-4319-5 Clinical Orthopaedics and Related Research A Publication of The Association of Bone and Joint Surgeons SYMPOSIUM: 2015 HIP SOCIETY
Clin Orthop Relat Res (2016) 474:365 371 DOI 10.1007/s11999-015-4319-5 Clinical Orthopaedics and Related Research A Publication of The Association of Bone and Joint Surgeons SYMPOSIUM: 2015 HIP SOCIETY
Total Hip Replacement. Find out why the Anterior Approach may be right for you.
 Total Hip Replacement Find out why the Anterior Approach may be right for you. UNDERSTANDING TOTAL HIP REPLACEMENT This brochure offers a brief overview of the Direct Anterior Approach to total hip arthroplasty.
Total Hip Replacement Find out why the Anterior Approach may be right for you. UNDERSTANDING TOTAL HIP REPLACEMENT This brochure offers a brief overview of the Direct Anterior Approach to total hip arthroplasty.
CONSENSUS ORTHOPEDICS INC.
 CONSENSUS ORTHOPEDICS INC. CONSENSUS HIP SYSTEMS Instructions for Use (IFU) IMPORTANT INFORMATION FOR SURGEON: PLEASE READ PRIOR TO IMPLANTING THIS DEVICE IN A CLINICAL SETTING. THE SURGEON SHOULD BE FAMILIAR
CONSENSUS ORTHOPEDICS INC. CONSENSUS HIP SYSTEMS Instructions for Use (IFU) IMPORTANT INFORMATION FOR SURGEON: PLEASE READ PRIOR TO IMPLANTING THIS DEVICE IN A CLINICAL SETTING. THE SURGEON SHOULD BE FAMILIAR
What is the Best Bearing Type? 1/11/2011
 What is the Best Bearing Type? 1/11/2011 A comparison of modern bearing types. Thomas P. Gross, M.D. As a patient there are four reasons you should consider a metal-on-metal bearing total hip replacement
What is the Best Bearing Type? 1/11/2011 A comparison of modern bearing types. Thomas P. Gross, M.D. As a patient there are four reasons you should consider a metal-on-metal bearing total hip replacement
RM Philosophy Innovation based on clinical evidence.
 RM Philosophy Innovation based on clinical evidence RM Philosophy Innovation based on clinical evidence Design 1973 RM Classic Cup First uncoated RM Classic Cup out of Polyacetal was inserted by E. Morscher
RM Philosophy Innovation based on clinical evidence RM Philosophy Innovation based on clinical evidence Design 1973 RM Classic Cup First uncoated RM Classic Cup out of Polyacetal was inserted by E. Morscher
Poor mid-term results of total hip arthroplasty with use of a Hylamer liner
 Acta Orthop. Belg., 2008, 74, 337-342 ORIGINAL STUDY Poor mid-term results of total hip arthroplasty with use of a Hylamer liner Adrian SKWARA, Simone STRACKE, Carsten O. TIBESKU, Susanne FUCHS-WINKELMANN
Acta Orthop. Belg., 2008, 74, 337-342 ORIGINAL STUDY Poor mid-term results of total hip arthroplasty with use of a Hylamer liner Adrian SKWARA, Simone STRACKE, Carsten O. TIBESKU, Susanne FUCHS-WINKELMANN
Active Articulation E1
 Active Articulation E1 Dual Mobility Hip System Design Rationale Knees Hips Extremities Cement and Accessories PMI Trauma Technology Active Articulation E1 Dual Mobility Hip System Dual Mobility: Not a
Active Articulation E1 Dual Mobility Hip System Design Rationale Knees Hips Extremities Cement and Accessories PMI Trauma Technology Active Articulation E1 Dual Mobility Hip System Dual Mobility: Not a
D E S I G N R A T I O N A L E
 D E S I G N R A T I O N A L E FREEDOM TO CHOOSE 1 PROVEN MODULAR SOLUTIONS The Pinnacle Acetabular Cup System is uniquely designed with a range of acetabular cup options, biological and mechanical fixation
D E S I G N R A T I O N A L E FREEDOM TO CHOOSE 1 PROVEN MODULAR SOLUTIONS The Pinnacle Acetabular Cup System is uniquely designed with a range of acetabular cup options, biological and mechanical fixation
Scandinavian Journal of Surgery 103: 54 59, 2013
 345SJS103110.1177/1457496913495345Hip resurfacing arthroplasty vs. large headed metal-on-metal total hip arthroplastym. Junnila, et al. ORIGINAL ARTICLE Scandinavian Journal of Surgery 103: 54 59, 2013
345SJS103110.1177/1457496913495345Hip resurfacing arthroplasty vs. large headed metal-on-metal total hip arthroplastym. Junnila, et al. ORIGINAL ARTICLE Scandinavian Journal of Surgery 103: 54 59, 2013
Designed for life. Implant technology with unmatched wear performance
 Designed for life Implant technology with unmatched wear performance Designed for life Wear performance combined with a multitude of options so you can find the right combination to restore the joints
Designed for life Implant technology with unmatched wear performance Designed for life Wear performance combined with a multitude of options so you can find the right combination to restore the joints
CLINICAL PAPER / ORTHOPEDIC
 HIP LEG LENGTH AND OFFSET Kelley T.C. and Swank M.L. (2009) Using CAS leads to more accurate positioning within the safe zone (inclination between 30 and 50, anteversion between 5 and 25 ) CAS improves
HIP LEG LENGTH AND OFFSET Kelley T.C. and Swank M.L. (2009) Using CAS leads to more accurate positioning within the safe zone (inclination between 30 and 50, anteversion between 5 and 25 ) CAS improves
GENESIS II/ LEGION Total Knee System
 GENESIS II/ LEGION Total Knee System The GENESIS II/LEGION knee with the VERILAST technology The knee tested to simulate 30 years of wear performance DISCLAIMER: Always speak to your doctor about the options
GENESIS II/ LEGION Total Knee System The GENESIS II/LEGION knee with the VERILAST technology The knee tested to simulate 30 years of wear performance DISCLAIMER: Always speak to your doctor about the options
FDA Safety Communication: Metal-on- Metal Hip Implants
 FDA Safety Communication: Metal-on- Metal Hip Implants Date Issued: Jan. 17, 2013 Audience: Orthopaedic surgeons Health care providers responsible for the ongoing care of patients with metal-onmetal hip
FDA Safety Communication: Metal-on- Metal Hip Implants Date Issued: Jan. 17, 2013 Audience: Orthopaedic surgeons Health care providers responsible for the ongoing care of patients with metal-onmetal hip
The Leader in Orthopaedic Innovation
 The Leader in Orthopaedic Innovation Wright is a leading international manufacturer and distributor of superior, easy to use, and innovative orthopaedic implants and instrumentation. For over 50 years,
The Leader in Orthopaedic Innovation Wright is a leading international manufacturer and distributor of superior, easy to use, and innovative orthopaedic implants and instrumentation. For over 50 years,
Progeny Hip Stem. Surgical Protocol and Product Specifications
 Progeny Hip Stem Surgical Protocol and Product Specifications Progeny Hip Stem Introduction With emphasis on maximum stability and ease of use, the StelKast ProgenyTM Hip System provides the surgeon with
Progeny Hip Stem Surgical Protocol and Product Specifications Progeny Hip Stem Introduction With emphasis on maximum stability and ease of use, the StelKast ProgenyTM Hip System provides the surgeon with
ACETABULAR CUP SURGICAL TECHNIQUE
 ACETABULAR CUP SURGICAL TECHNIQUE ACETABULAR CUP DEVICE INDICATIONS FOR USE The ICONACY I-Hip total hip replacement is indicated for the following conditions: 1. A severely painful and/or disabled hip
ACETABULAR CUP SURGICAL TECHNIQUE ACETABULAR CUP DEVICE INDICATIONS FOR USE The ICONACY I-Hip total hip replacement is indicated for the following conditions: 1. A severely painful and/or disabled hip
Peggers Super Summaries: THR and Revision Concepts
 Total Hip replacement: ARTICUALTIONS Ceramic on polyethylene Ceramic on ceramic for young Metal on metal (resurfacing) Metal (cobalt chrome) on polyethylene WEAR Wear debris similar to bacteria o < 10
Total Hip replacement: ARTICUALTIONS Ceramic on polyethylene Ceramic on ceramic for young Metal on metal (resurfacing) Metal (cobalt chrome) on polyethylene WEAR Wear debris similar to bacteria o < 10
SSSR HIP PROSTHESIS MODELS AND MATERIALS SURGICAL TECHNIQUES APPROACHES. Patrick Zingg Department of Orthopaedics University of Zurich, Balgrist
 HIP PROSTHESIS MODELS AND MATERIALS SURGICAL TECHNIQUES APPROACHES Patrick Zingg Department of Orthopaedics University of Zurich, Balgrist Zürich, Switzerland www.balgrist.ch IMPLANT TO BONE INTERFACE
HIP PROSTHESIS MODELS AND MATERIALS SURGICAL TECHNIQUES APPROACHES Patrick Zingg Department of Orthopaedics University of Zurich, Balgrist Zürich, Switzerland www.balgrist.ch IMPLANT TO BONE INTERFACE
Principles of acetabular fixation in primary and revision hip arthroplasty Piotr Wojciechowski, Damian Kusz, Anna WAGNER
 Principles of acetabular fixation in primary and revision hip arthroplasty Piotr Wojciechowski, Damian Kusz, Anna WAGNER Department of Orthopedics and Traumatology Medical University of Silesia Head of
Principles of acetabular fixation in primary and revision hip arthroplasty Piotr Wojciechowski, Damian Kusz, Anna WAGNER Department of Orthopedics and Traumatology Medical University of Silesia Head of
Case Report Recurrent Catastrophic Ceramic Femoral Head Failure in Total Hip Arthroplasty
 Case Reports in Orthopedics, Article ID 837954, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2014/837954 Case Report Recurrent Catastrophic Ceramic Femoral Head Failure in Total Hip Arthroplasty S. M. M. Tai, 1 L.
Case Reports in Orthopedics, Article ID 837954, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2014/837954 Case Report Recurrent Catastrophic Ceramic Femoral Head Failure in Total Hip Arthroplasty S. M. M. Tai, 1 L.
Cement Polished Tapered Stems of 12/14 Taper. 96 mm 98 mm 104 mm 110 mm 116 mm 122 mm 128 mm. Ceramic Femoral Head. Outer Diameter
 Design Philosophy Cementless Stems of 12/14 Taper Stem Length Neck shaft Angle STEM-N3 STEM-N4 STEM-N5 STEM-N6 STEM-N7 STEM-N8 STEM-N9 123 mm 125 mm 130 mm 135 mm 140 mm 145 mm 150 mm 132 Cement Polished
Design Philosophy Cementless Stems of 12/14 Taper Stem Length Neck shaft Angle STEM-N3 STEM-N4 STEM-N5 STEM-N6 STEM-N7 STEM-N8 STEM-N9 123 mm 125 mm 130 mm 135 mm 140 mm 145 mm 150 mm 132 Cement Polished
PyroCarbon Implants Durability + Biocompatibility
 PyroCarbon Implants Durability + Biocompatibility What is PyroCarbon? PyroCarbon is a specific form of carbon that has been tailored for durability and biocompatibility. PyroCarbon exhibits favorable wear
PyroCarbon Implants Durability + Biocompatibility What is PyroCarbon? PyroCarbon is a specific form of carbon that has been tailored for durability and biocompatibility. PyroCarbon exhibits favorable wear
Tri-Lock Bone Preservation Stem
 Tri-Lock Bone Preservation Stem Clinical Results of the Tri-lock BPS Femoral Stem at One Year Follow-Up William L. Healy, M.D. Lahey Clinic Medical Center Burlington, Massachusetts Introduction Cementless
Tri-Lock Bone Preservation Stem Clinical Results of the Tri-lock BPS Femoral Stem at One Year Follow-Up William L. Healy, M.D. Lahey Clinic Medical Center Burlington, Massachusetts Introduction Cementless
Pseudo tumor a cystic or solid mass (MRI or ultrasound) 1% of MOM pts develop pseudo tumors by 5 years 17 pts, all female, Pandit et al (JBJS, 2008)
 Pseudo tumor a cystic or solid mass (MRI or ultrasound) 1% of MOM pts develop pseudo tumors by 5 years 17 pts, all female, Pandit et al (JBJS, 2008) 8% at 5yrs FU indicated by preliminary study from same
Pseudo tumor a cystic or solid mass (MRI or ultrasound) 1% of MOM pts develop pseudo tumors by 5 years 17 pts, all female, Pandit et al (JBJS, 2008) 8% at 5yrs FU indicated by preliminary study from same
Duraloc CONSTRAINED LINER
 SURGICAL TECHNIQUE Duraloc CONSTRAINED LINER A COMPREHENSIVE ACETABULAR REVISION SYSTEM DURALOC CONSTRAINED LINER Introduction Dislocation is the most common postoperative complication in total hip reconstruction.
SURGICAL TECHNIQUE Duraloc CONSTRAINED LINER A COMPREHENSIVE ACETABULAR REVISION SYSTEM DURALOC CONSTRAINED LINER Introduction Dislocation is the most common postoperative complication in total hip reconstruction.
Cementless Acetabular Fixation With and Without Screws
 Cementless Acetabular Fixation With and Without Screws Analysis of Stability and Migration The Journal of Arthroplasty Vol. 25 No. 2 2010 Richard Iorio, MD,* Brian Puskas, MD,y William L. Healy, MD,* John
Cementless Acetabular Fixation With and Without Screws Analysis of Stability and Migration The Journal of Arthroplasty Vol. 25 No. 2 2010 Richard Iorio, MD,* Brian Puskas, MD,y William L. Healy, MD,* John
I want that next-generation knee
 I want that next-generation knee High flex Potentially longer-lasting More normal feeling Gender-optimized Less-invasive procedure Advanced design technology The last ten years have yielded an explosion
I want that next-generation knee High flex Potentially longer-lasting More normal feeling Gender-optimized Less-invasive procedure Advanced design technology The last ten years have yielded an explosion
Reaching new heights. Comprehensive. Efficient. Simple.
 Reaching new heights Comprehensive. Efficient. Simple. Various acetabular cup choices Compatible with the different head and liner options including VERILAST Technology Reach for proven OR efficient Instrumentation
Reaching new heights Comprehensive. Efficient. Simple. Various acetabular cup choices Compatible with the different head and liner options including VERILAST Technology Reach for proven OR efficient Instrumentation
Metal-on-Metal Bearings in Cementless Primary Total Hip Arthroplasty
 The Journal of Arthroplasty Vol. 19 No. 8 Suppl. 3 2004 Metal-on-Metal Bearings in Cementless Primary Total Hip Arthroplasty Christian P. Delaunay, MD Abstract: One hundred cementless titanium primary
The Journal of Arthroplasty Vol. 19 No. 8 Suppl. 3 2004 Metal-on-Metal Bearings in Cementless Primary Total Hip Arthroplasty Christian P. Delaunay, MD Abstract: One hundred cementless titanium primary
Case Report Anterior Subluxation after Total Hip Replacement Confirmed by Radiographs: Report of Two Cases
 SAGE-Hindawi Access to Research Advances in Orthopedics Volume 2011, Article ID 519254, 4 pages doi:10.4061/2011/519254 Case Report Anterior Subluxation after Total Hip Replacement Confirmed by Radiographs:
SAGE-Hindawi Access to Research Advances in Orthopedics Volume 2011, Article ID 519254, 4 pages doi:10.4061/2011/519254 Case Report Anterior Subluxation after Total Hip Replacement Confirmed by Radiographs:
LEGION Total Knee System. Exceptional Durability
 LEGION Total Knee System Exceptional Durability How many knee systems have been lab-tested to 30 years of simulated wear? Just one: LEGION Primary Knee System with VERILAST Technology The LEGION Primary
LEGION Total Knee System Exceptional Durability How many knee systems have been lab-tested to 30 years of simulated wear? Just one: LEGION Primary Knee System with VERILAST Technology The LEGION Primary
Robotic-Arm Assisted Surgery
 Mako TM Robotic-Arm Assisted Surgery for Total Hip Replacement A Patient s Guide Causes of Your Hip Pain Your joints are involved in almost every activity you do. Movements such as walking, bending and
Mako TM Robotic-Arm Assisted Surgery for Total Hip Replacement A Patient s Guide Causes of Your Hip Pain Your joints are involved in almost every activity you do. Movements such as walking, bending and
)501( COPYRIGHT 2018 BY THE ARCHIVES OF BONE AND JOINT SURGERY
 )501( COPYRIGHT 2018 BY THE ARCHIVES OF BONE AND JOINT SURGERY RESEARCH ARTICLE Total Hip Replacement Revision in a Single Brand Small Cementless Stem Our Experience after the Findings of the National
)501( COPYRIGHT 2018 BY THE ARCHIVES OF BONE AND JOINT SURGERY RESEARCH ARTICLE Total Hip Replacement Revision in a Single Brand Small Cementless Stem Our Experience after the Findings of the National
Move Ahead with Confidence. Hip Replacement Solutions from DePuy Orthopaedics
 Move Ahead with Confidence Hip Replacement Solutions from DePuy Orthopaedics The Healthy Hip Joint Pelvis Acetabulum (hip socket) Head of femur Neck of femur Femur (thigh bone) Head of femur in the acetabulum
Move Ahead with Confidence Hip Replacement Solutions from DePuy Orthopaedics The Healthy Hip Joint Pelvis Acetabulum (hip socket) Head of femur Neck of femur Femur (thigh bone) Head of femur in the acetabulum
- October 2013 English
 TOTAL HIP JOINT REPLACEMENT FOR CEMENTED APPLICATIONS FOR THE ATTENTION OF THE OPERATING SURGEON Total hip replacement provides the surgeon with a means of restoring mobility and reducing pain with the
TOTAL HIP JOINT REPLACEMENT FOR CEMENTED APPLICATIONS FOR THE ATTENTION OF THE OPERATING SURGEON Total hip replacement provides the surgeon with a means of restoring mobility and reducing pain with the
Design Rationale. ECHELON Primary Hip System
 Design Rationale ECHELON Primary Hip System ECHELON Primary Total Hip System Addressing clinical issues of cementless hip arthroplasty Cementless total hip arthroplasty has provided a proven method of
Design Rationale ECHELON Primary Hip System ECHELON Primary Total Hip System Addressing clinical issues of cementless hip arthroplasty Cementless total hip arthroplasty has provided a proven method of
Plain Film CT. Principal Modality (2): Case Report # [] Date accepted: 15 March 2014
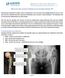
![Plain Film CT. Principal Modality (2): Case Report # [] Date accepted: 15 March 2014 Plain Film CT. Principal Modality (2): Case Report # [] Date accepted: 15 March 2014](/thumbs/89/100531147.jpg) Radiological Category: Musculoskeletal Principal Modality (1): Principal Modality (2): Plain Film CT Case Report # [] Submitted by: Dr. Jason E. Lally, M.D. Faculty reviewer: Dr. Naga Ramesh Chinapuvvula,
Radiological Category: Musculoskeletal Principal Modality (1): Principal Modality (2): Plain Film CT Case Report # [] Submitted by: Dr. Jason E. Lally, M.D. Faculty reviewer: Dr. Naga Ramesh Chinapuvvula,
Instrumentation Options
 Instrumentation Options With the introduction of Microplasty and Premier Instrumentation platforms and advancements such as our patented Slidex Technology, the Vanguard Complete Knee System is the surgeon
Instrumentation Options With the introduction of Microplasty and Premier Instrumentation platforms and advancements such as our patented Slidex Technology, the Vanguard Complete Knee System is the surgeon
