a - CM EARTICLE Clinics in diagnostic imaging (139) !Medical Education Singapore Med J 2012; 53(4) CASE PRESENTATION
|
|
|
- Harold Blair
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 !Medical Education Singapore Med J 2012; 53(4) 283 CM EARTICLE Clinics in diagnostic imaging (139) Wei Yang Liml, MBBS, FRCR, Nor Azam Mahmud2, MD, MMed, Wilfred CG Peh3, FRCP, FRCR a Fig. 1 Sagittal fat -suppressed PD -W MR image of the right knee taken in the plane of the posterior cruciate ligament. Fig. 2 Coronal fat -suppressed PD -W MR image taken at the level of the intercondylar notch. CASE PRESENTATION A 58 -year-old Indian man sustained a road traffic accident a few years ago. He presented with sudden onset of pain and swelling on the medial aspect of his right knee. He was unable to weight -bear on his knee and walk. On physical examination, the patient had a right knee effusion, with range of knee movement of degrees. There was tenderness of his medial joint line. Radiograph of the right knee was unremarkable. What do the magnetic resonance (MR) images of his right knee (Figs. 1 & 2) show? What is the diagnosis? 1 -Department of Diagnostic Radiology, Tan Tock Seng Hospital, Singapore 2Department of Diagnostic Radiology, University Science Malaysia, Malaysia, 3Department of Diagnostic Radiology, Khoo Teck Puat Hospital, Singapore Correspondence: Dr Wei Yang Lim, Registrar, Department of Diagnostic Radiology, Tan Tock Seng Hospital, 11 Jalan Tan Tock Seng, Singapore drlimweiyang@yahoo.com
2 !Medical Education IMAGE INTERPRETATION MR images of the right knee show a displaced bucket -handle tear of the medial meniscus. The torn fragment (arrows) was displaced into the intercondylar notch (Figs. 1& 2) and was seen as a curvilinear mass anterior to the posterior cruciate ligament (PCL), which gives the double PCL sign on the sagittal image (Fig. 1). Additional complex tears were noted in the posterior horn of the medial meniscus. The medial collateral ligament was slightly thickened with hyperintense signal, in keeping with a Grade 2 medial collateral ligament strain. Moderate joint effusion was also present. The lateral meniscus and the anterior and posterior cruciate ligaments were normal. DIAGNOSIS Displaced medial meniscus bucket -handle tear. CLINICAL COURSE Two weeks after the MR imaging, the patient underwent surgery. During the operation, a chronic bucket -handle tear of the medial meniscus was seen. This was considered to be non -repairable. Otherwise, the lateral meniscus, anterior cruciate and posterior cruciate ligaments were intact. Debridement of the medial meniscus was performed. The patient subsequently underwent a course of physiotherapy. On follow-up in the orthopaedic clinic, he could extend his knee fully. DISCUSSION The menisci are semi -lunar (C -shaped) fibrocartilage structures comprising predominantly type 1 collagen arranged primarily in a circumferential fashion, which gives the menisci the tensile strength.(1) Each meniscus has a concave superior surface and a flat inferior surface. These properties allow the menisci to serve a multitude of functions, such as distribution of stresses over the articular cartilage, shock absorption, stabilisation of the knee in flexion and extension, joint lubrication and secondary stabilisation of the knee after anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) injury.(1,2) The meniscus consists of a central avascular zone and a peripheral vascularised area, also known as the red zone!' 3) Its vascularity is important in the repair and healing of the meniscus. Each meniscus is divided arbitrarily into an anterior horn, body and a posterior horn. The anterior and posterior horns of both menisci attach to the anterior and posterior tibial plateau, respectively, at their root attachments. Closely -related ligaments include the anterior intermeniscal ligaments, meniscofemoral ligaments of Humphrey or Wrisberg and popliteomeniscal fascicles:1,2) On MR imaging, the menisci, being highly organised collagen structures, are homogeneously hypointense on all sequences.0,2) Normal anterior and posterior horns of the menisci have a triangular appearance on the sagittal MR images and should not measure morethan 6 mm in height.(4) The medial meniscus is typically larger than the lateral meniscus and has a wider posterior horn (1> The standard validated traditional MR pulse sequence is the proton density (PD) -weighted spin -echo sequence, with a long repetition time and short echo time.(2,5) Fast spin -echo PD - weighted sequences reduce the imaging time but may have a slightly lower sensitivity in detecting meniscal tears compared to conventional spin -echo sequences.(5) Fat suppression can also be performed to increase the dynamic range of the signal in the menisci, making tears more conspicuous, and to distinguish fatfrom fluid on fast spin -echo sequences.(5) Current imaging techniques employ an extremity coil, with slice thickness of 3-4 mm, inter - slice gap of mm, a field -of-view < 16 cm and matrix size of at least 256 x 192() Meniscal tears can be caused by either increased force on a normal meniscus, usually resulting in longitudinal or radial tears, or normal forces on a degenerative meniscus, usually producing horizontal tears in the posterior half ofthe men iscus.(1)the diagnostic criteria of meniscal tears on MR imaging consist of an abnormal signal within the meniscus that extends to the meniscal articular surface and abnormal meniscal morphology. Meniscal tears can be described as vertical, horizontal or complex:1) Meniscal lesions are usually best evaluated on both sagittal and coronal images.(6) The bucket -handle tear is a variant of the vertical tear, and consists of a vertical or oblique tear involving the posterior horn of the meniscus that extends longitudinally through the body and anterior horn. The inner meniscal fragment is often displaced into the intercondylar notch, which resembles a handle, whilethe larger peripheral portion resembles a bucket. Bucket -handle tears are more commonly seen in the medial meniscus.0) The tears usually involve younger patients and are associated with a higher incidence of concomitantacl tears.(8)several MR imaging signs of a displaced bucket -handle tear have been described, including the double PCL sign, displaced fragment in intercondylar notch sign, absent bow tie sign, anterior flipped meniscus sign and coronal truncation sign.(9) The overall sensitivity of MR imaging for the detection of meniscal bucket -handle tears is 64% 94%.0,10) The double PCL sign (Figs. 3a & b) describes the displaced bucket -handle fragment as a linear hypointense band, which is usually parallel to the anterior inferior aspect of the PCL, in the same plane in the midline sagittal MR image. This sign has been reported only in medial meniscus bucket -handle tears and is associated with decreased size of the posterior horn and body of the medial meniscus." Wright et al proposed that the sign is not seen in lateral meniscus bucket -handle tears because the more laterally -located ACL acts as a barrier to the meniscal fragments.(4) The double PCL sign has a low sensitivity of 27%-44% and a high specificity of 98% 10 0%.(1,9,12,e) The displaced fragment in the notch sign occurs when a meniscal fragment is seen in the intercondylar notch but not in the same plane as the PCL." This sign is encountered more often in the lateral bucket -handle tears and has a sensitivity of 60%-98% and a specificity of 73%-82%.(1) Rarely, when both medial and lateral bucket -handle tears are present with displacement of the fragments into the intercondylar notch, the displaced fragments, the ACL and PCL result in the appearance of four structures within the intercondylar notch on coronal MR images, hence the name, Singapore Med J 2012; 53(4) 284
3 1 '!Medical Education b 1. Fig. 3 a) Double-PCL sign in a 27 -year -old man with a displaced bucket -handle tear of the medial meniscus. Midline sagittal fat -suppressed PD -W MR image shows the double PCL sign. The displaced meniscal fragment (arrowheads) is located anterior and inferior to the 'real' PCL (arrows). (b) Coronal fat -suppressed PD -W MR image shows the torn fragment (arrowhead) located in the intercondylar notch adjacent to the PCL (arrows). The torn bucket -handle fragment remains attached to the remnant posterior horn of the medial meniscus. 4a ri Fig. 4 Absent bow -tie sign in a 20 -year -old man with a displaced bucket -handle tear of the medial meniscus. (a) Peripheral sagittal fat -suppressed PD -W MR image shows the absent bow -tie sign. The remnant posterior horn (arrows) of the medial meniscus is deficient in size and has an abnormal, flattened shape. (b) Midline sagittal fat -suppressed PD -W MR image taken at the level of the intercondylar notch shows a displaced bucket -handle fragment (arrowheads) located anterior to the PCL (arrows). (c) Coronal fat -suppressed PD -W MR image taken at the level of the intercondylar notch shows the displaced bucket -handle fragment (arrowhead). Note that the posterior horn of the remnant medial meniscus is deformed and smaller in size (small arrows) compared to the contralateral meniscus (large arrow). Subchondral bone marrow oedema is seen in the medial femoral condyle in Figs. 4a & c. 'quadruple cruciate sign'.(14) The body of the meniscus is continuous with the anterior and posterior horns on peripheral sagittal MR images, giving rise to a normal bow -tie configuration. The bow - tie sign is considered to be normal when two sagittal images demonstrate the normal bow -tie configuration, and absent when there is only one or none of the body segments detected.(9) The remaining anterior and posterior horns are often hypoplastic or truncated, with or without increased signal intensity.(8,9) The absent bow -tie sign (Figs. 4a & b) has a sensitivity of 58%-98%, although the specificity is 62%-100% (1,9,15) The anterior flipped meniscus sign (Figs. 5a & b) describes a bucket -handle tear where there is displacement of the meniscal fragment into the anterior compartment, with the displaced fragment vertically juxtaposed to the ipsilateral anterior horn." This results in an abnormally large anterior horn with a height > 6 mm and a meniscus -shaped hypointense area located just anterior to the normal -shaped anterior horn.(4) The normal anterior horn and the displaced fragment are often indistinguishable." This sign is more commonly seen in medial meniscus bucket - handle tears,o) with a specificity of 87%, which rises to 96% when utilised in conjunction with the absent bow -tie sign.(1.9 Occasionally, a variation may occur where the displaced meniscal fragment and ipsilateral anterior horn are not vertically juxtaposed but located next to each other in the same horizontal plane, giving rise to the appearance of two anterior horns, and hence, the 'double anterior horn sign'. The horn that is located more anteriorly represents the normal anterior horn, while the more posterior horn represents the displaced bucket -handle fragment." The coronal truncation sign (Figs. 6a -c) describes an amputated or deformed meniscus with a deficient meniscal body on coronal Singapore Med J 2012; 53(4) 285
4 !Medical Education 5a 5b 14. o -5i V o 1.6 ti 6 Cl p Fig. 5 Anterior flipped meniscus sign in 27 -year -old man with a displaced bucket -handle tear involving the body of the lateral meniscus. (a) Sagittal fat -suppressed PD -W MR image shows the anterior flipped meniscus sign. The displaced fragment (arrowheads) is located adjacent to the normal anterior horn of the lateral meniscus (arrows). This resembles an abnormally large meniscus with abnormal hyperintense linear signal. (b) Axial fat -suppressed PD -W MR image shows a large curvilinear displaced fragment (arrowhead) located adjacent to the normal anterior horn of the lateral meniscus (arrows). f6b op 6c fl I A r - _ - Fig. 6 Coronal truncation sign in a 30 -year -old man with a displaced bucket -handle tear affecting the medial meniscus. (a -c) Coronal fat - suppressed PD -W MR images of the medial meniscus were taken at intervals from (a) anterior to (c) posterior. On the (a) anterior and (c) posterior coronal images, the remnant anterior and posterior horns of the medial mensicus are seen as hypointense bands. (b) On the midcoronal image, the inner fragment of the medial meniscus (arrowhead) is displaced towards the intercondylar notch (arrowhead). The coronal truncation sign (arrows) of the small deformed remnant of the medial meniscus body is noted. As the components of the torn meniscus are continuous, the meniscus forms complete ring when viewed on the anterior to posterior coronal images. MR images:15) This sign is not useful when utilised alone, and has a sensitivity of 65% and specificity of 71% in detecting bucket - handle tears.(15) When the coronal truncation sign is present in combination with the absent bow -tie and displaced fragment signs, the specificity of detected tears is increased to 94%. Utilising a combination of the different MR imaging signs of bucket -handle tears has been shown to increase specificity.(15) Potential mimics of the double PCL sign include anatomical structures in the intercondylar region, which include intermeniscal ligaments, as well as meniscofemoral ligaments of Humphrey and Wrisberg. Careful examination of the given structure on sequential images can help avoid these pitfalls.(2,13) Abnormal structures such as loose bodies, osteophytes and fracture fragments in the intercondylar region can also be potential mimics:13) False positives in an absent bow -tie sign can occur in children or small adults and degenerative menisci. Postsurgical changes such as partial meniscectomy can also present with an absent bow -tie sign; however, this pitfall can be easily avoided by obtaining a proper history.(5,15) A radial tear can present with an absent bow -tie sign, and this can be differentiated from a bucket -handle tear by careful examination and the absence of a displaced fragment.(15) The surgical treatment options of bucket -handle meniscal tears include partial and complete meniscectomy and meniscal repair. The choice of treatment depends on the location and size of the tear. Meniscal repair aims to restore normal biomechanical function, while partial meniscectomy removes unstable tissues while preserving as much meniscus as possible, especially the outer vascular red zone.(1) Clinical success rates of meniscal repair Singapore Med J 2012; 53(4) 286
5 igamentsign,!medical Education have been shown to be poorer in patients with bucket -handle tears compared to those with simple tears.00 Shelbourne and Carr found no difference in the outcomes of patients with bucket -handle tears and ACL tears who have undergone either meniscal repair or partial meniscectomy.(17) CONCLUSION MR imaging is accurate in diagnosing bucket -handle tears of the meniscus, with detection of the displaced fragment in the intercondylar notch and the absent bow -tie signs being the most sensitive signs, and double PCL sign being the most specific for a medial meniscus bucket -handle tear. Specificity is increased when a combination of the different MR imaging signs is present. It is important to understand the meniscal anatomy and the potential mimics of bucket -handle tears in order to ensure an accurate diagnosis. ABSTRACT A 58 -year-old man presented with knee pain and swelling, following a previous injury. A displaced bucket -handle tear of the medial meniscus was diagnosed on magnetic resonance (MR) imaging and subsequently confirmed by arthroscopy. MR imaging is accurate in diagnosing bucket -handle tears. The different MR imaging signs of bucket -handle tears include the double posterior cruciate I displaced fragment in intercondylar notch sign, absent bow -tie sign, anterior flipped meniscus sign and coronal truncation sign. Specificity is increased when a combination of the different imaging signs is present. Understanding the meniscal anatomy and potential mimics of the bucket -handle tear is important in order to ensure an accurate diagnosis and appropriate management. Keywords: bucket -handle tears, displaced meniscal tears, knee injury, meniscal tear, meniscus Singapore Med J 2012; 53(4): REFERENCES 1. Fox MG. MR imaging of the meniscus: review, current trends, and clinical implications. Radio! Clin North Am 2007; 45: Tsou IYY, Peh WCG. Clinics in diagnostic imaging (63). Flipped bucket - handle tear of the lateral meniscus posterior horn. Singapore Med J 2001; 42: Hauger 0, Frack LR, Boutin RD, et al. Characterization of the "red zone" of knee meniscus: MR imaging and histologic correlation. Radiology 2000; 217: Wright DH, De Smet AA, Norris M. Bucket -handle tears of the medial and lateral menisci of the knee: value of MR imaging in detecting displaced fragments. Am J Roentgenol 1995; 165: Helms CA. The meniscus: recent advances in MR imaging of the knee. Am J Roentgenol 2002; 179: Magee T, Williams D. Detection of meniscal tears and marrow lesions using corona! MRI. Am J Roentgenol 2004; 183: Singson RD, Feldman F, Staron R, Kiernan H. MR imaging of displaced bucket handle tear of the medial meniscus. Am J Roentgenol 1991; 15 6: Stoller DW. The knee. In: Magnetic Resonance Imaging in Orthopaedics and Sports Medicine. 3rd ed. Philadelphia: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, 2007: Helms CA, Laorr A, Cannon WD Jr. The absent bow tie sign in bucket - handle tears of the menisci in the knee. Am J Roentgenol 1998; 170: Aydingoz U, Firat AK, Atay OA, Doral MN. MR imaging of meniscal bucket -handle tears: a review of signs and their relation to arthroscopic classification. Eur Radio! 2003; 13: Ruff C, WeingardtJP, Russ PD, Kilcoyne RF. MR imaging patterns of displaced meniscus injuries of the knee. Am J Roentgenol 1998; 170: Weiss KL, Morehouse HT, Levy IM. Sagittal MR images of the knee: a low - signal band parallel to the posterior cruciate ligament caused by a displaced bucket -handle tear. Am J Roentgenol 1991; 156: Venkatanarasimha N, Kamath A, Mukherjee K, Kamath S. Potential pitfalls of a double PCL sign. Skeletal Radio! 2009; 38: Bugnone AN, Ramnath RR, Davis SB, et al. The quadruple cruciate sign of simultaneous bicompartmental medial and lateral bucket -handle meniscal tears. Skeletal Radio! 2005; 34: Dorsay TA, Helms CA. Bucket -handle meniscal tears of the knee: sensitivity and specificity of MRI signs. Skeletal Radio! 2003; 32: Krych AJ, Pitts RT, Dajani KA, et al. Surgical repair of meniscal tears with concomitant anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction in patients 18 years and younger. Am J Sports Med 2010; 38: Shelbourne KD, Carr DR. Meniscal repair compared with meniscectomy for bucket -handle medial meniscal tears in anterior cruciate ligament - reconstructed knees. Am J Sports Med 2003; 31: Singapore Med J 2012; 53(4) 287
6 !Medical Education SINGAPORE MEDICAL COUNCIL CATEGORY 3B CME PROGRAMME (Code SMJ ) Question 1. Regarding normal meniscal anatomy: (a) The menisci comprise predominantly type 1 collagen. (b) The meniscus has a central vascularised area and peripheral avascular zone. (c) The menisci typically show homogeneous hyperintense signal on all sequences. (d) The medial meniscus is typically larger than the lateral meniscus. True False Question 2. With regard to meniscal tears: (a) Abnormal signal within the meniscus without extension to the articular surface is a diagnostic criterion for a meniscal tear. (b) Axial MR images are best for evaluation of meniscal lesions. (c) Bucket -handle tears are more commonly seen in the medial meniscus. (d) Bucket -handle tears are associated with a higher incidence of concomitant anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) tears Question 3. Regarding MR imaging features in bucket -handle tears: (a) The overall sensitivity of MR imaging for the detection of meniscal bucket -handle tears is 10 /0-30 /0. (b) The double posterior cruciate ligament (PCL) sign has been reported only in lateral meniscus bucket - handle tears. (c) The presence of both medial and lateral bucket -handle tears with displacement of the fragments into the intercondylar notch can result in a quadrate cruciate sign. (d) An abnormally small anterior horn is seen in the anterior flipped meniscus sign. Question 4. Regarding pitfalls in the diagnosis of bucket -handle tears: (a) Intermeniscal ligaments and meniscofemoral ligaments of Humphrey are potential mimics of a double PCL sign. (b) Patients with degenerative menisci can result in a false positive absent bow -tie sign. (c) Loose bodies in the intercondylar region can be a potential mimic. (d) The absence of a displaced fragment is useful to differentiate a radial tear from a bucket -handle tear in an absent bow -tie sign. Question 5. Regarding surgical treatment options of bucket -handle tears: (a) Partial and complete meniscectomy are surgical options. (b) The location and the size of the tear do not affect the choice of treatment. (c) Partial meniscectomy aims to preserve as much meniscus as possible from the outer vascular zone. (d) Meniscal repair in simple tears have a poorer clinical success rate compared to bucket -handle tears. Doctor's particulars: Name in full MCR number Specialty: address SUBMISSION INSTRUCTIONS: (1) Log on at the SMJ website: and select the appropriate set of questions. (2) Select your answers and provide your name, address and MCR number. Click on "Submit answers" to submit. RESULTS: (1) Answers will be published in the SMJ June 2012 issue. (2) The MC R numbers of successful candidates will be posted online at by 21 May (3) All online submissions will receive an automatic acknowledgment. (4) Passing mark is 60%. No mark will be deducted for incorrect answers. (5) The SMJ editorial office will submit the list of successful candidates to the Singapore Medical Council. (6) One CME point is awarded for successful candidates. Deadline for submission: (April 2012 SMJ 3B CME programme): 12 noon, 14 May Singapore Med J 2012; 53(4) 288
Post-injury painful and locked knee
 H R J Post-injury painful and locked knee, p. 54-59 Clinical Case - Test Yourself Musculoskeletal Imaging Post-injury painful and locked knee Ioannis I. Daskalakis 1, 2, Apostolos H. Karantanas 1, 2 1
H R J Post-injury painful and locked knee, p. 54-59 Clinical Case - Test Yourself Musculoskeletal Imaging Post-injury painful and locked knee Ioannis I. Daskalakis 1, 2, Apostolos H. Karantanas 1, 2 1
MRI of Bucket-Handle Te a rs of the Meniscus of the Knee 1
 MRI of ucket-handle Te a rs of the Meniscus of the Knee 1 Joon Yong Park, M.D., Young-uk Lee M.D., Eun-Chul Chung M.D., Hae-Won Park M.D., E u n - Kyung Youn M.D., Shin Ho Kook, M.D., Young Rae Lee, M.D.
MRI of ucket-handle Te a rs of the Meniscus of the Knee 1 Joon Yong Park, M.D., Young-uk Lee M.D., Eun-Chul Chung M.D., Hae-Won Park M.D., E u n - Kyung Youn M.D., Shin Ho Kook, M.D., Young Rae Lee, M.D.
Clinics in diagnostic imaging (177)
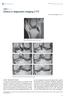 Singapore Med J 2017; 58(5): 241-245 doi: 10.11622/smedj.2017038 CMEArticle Clinics in diagnostic imaging (177) Poh Lye Paul See, MBBS, FRCR Fig. 1 Sagittal proton density (PD)-weighted fast spin-echo
Singapore Med J 2017; 58(5): 241-245 doi: 10.11622/smedj.2017038 CMEArticle Clinics in diagnostic imaging (177) Poh Lye Paul See, MBBS, FRCR Fig. 1 Sagittal proton density (PD)-weighted fast spin-echo
Meniscal tears on 3T MR: Patterns, pearls and pitfalls
 Meniscal tears on 3T MR: Patterns, pearls and pitfalls Poster No.: C-2221 Congress: ECR 2010 Type: Educational Exhibit Topic: Musculoskeletal Authors: J. C. Kandathil; Singapore/SG Keywords: Knee injuries,
Meniscal tears on 3T MR: Patterns, pearls and pitfalls Poster No.: C-2221 Congress: ECR 2010 Type: Educational Exhibit Topic: Musculoskeletal Authors: J. C. Kandathil; Singapore/SG Keywords: Knee injuries,
MENISCAL INJURY. Meniscus. Anterior Roots. Medial Meniscus. Lateral Meniscus. Posterior Roots. MRI and Arthroscopic Findings
 Meniscus Anterior Roots MENISCAL INJURY MRI and Arthroscopic Findings Medial Meniscus AH PH PH AH Lateral Meniscus Rawiwan Pattaweerakul Naresuan University Hospital Posterior Roots Meniscus Normal Meniscus
Meniscus Anterior Roots MENISCAL INJURY MRI and Arthroscopic Findings Medial Meniscus AH PH PH AH Lateral Meniscus Rawiwan Pattaweerakul Naresuan University Hospital Posterior Roots Meniscus Normal Meniscus
MRI of the Knee: Part 2 - menisci. Mark Anderson, M.D. University of Virginia Health System
 MRI of the Knee: Part 2 - menisci Mark Anderson, M.D. University of Virginia Health System Learning Objectives At the end of the presentation, each participant should be able to: describe the normal anatomy
MRI of the Knee: Part 2 - menisci Mark Anderson, M.D. University of Virginia Health System Learning Objectives At the end of the presentation, each participant should be able to: describe the normal anatomy
Meniscal Tears with Fragments Displaced: What you need to know.
 Meniscal Tears with Fragments Displaced: What you need to know. Poster No.: C-1339 Congress: ECR 2015 Type: Authors: Keywords: DOI: Educational Exhibit M. V. Ferrufino, A. Stroe, E. Cordoba, A. Dehesa,
Meniscal Tears with Fragments Displaced: What you need to know. Poster No.: C-1339 Congress: ECR 2015 Type: Authors: Keywords: DOI: Educational Exhibit M. V. Ferrufino, A. Stroe, E. Cordoba, A. Dehesa,
Role of magnetic resonance imaging in the evaluation of traumatic knee joint injuries
 Original Research Article Role of magnetic resonance imaging in the evaluation of traumatic knee joint injuries Dudhe Mahesh 1*, Rathi Varsha 2 1 Resident, 2 Professor, Department of Radio-Diagnosis, Grant
Original Research Article Role of magnetic resonance imaging in the evaluation of traumatic knee joint injuries Dudhe Mahesh 1*, Rathi Varsha 2 1 Resident, 2 Professor, Department of Radio-Diagnosis, Grant
MRI KNEE WHAT TO SEE. Dr. SHEKHAR SRIVASTAV. Sr.Consultant KNEE & SHOULDER ARTHROSCOPY
 MRI KNEE WHAT TO SEE Dr. SHEKHAR SRIVASTAV Sr.Consultant KNEE & SHOULDER ARTHROSCOPY MRI KNEE - WHAT TO SEE MRI is the most accurate and frequently used diagnostic tool for evaluation of internal derangement
MRI KNEE WHAT TO SEE Dr. SHEKHAR SRIVASTAV Sr.Consultant KNEE & SHOULDER ARTHROSCOPY MRI KNEE - WHAT TO SEE MRI is the most accurate and frequently used diagnostic tool for evaluation of internal derangement
Knee: Meniscus Back to Basics
 Knee: Meniscus Back to Basics Kyung Jin Suh kyungjin.suh@gmail.com Doctor Radiology, Daegu, KOREA Medial Lateral 7.7 10.2 11.6 9.6 10.6 mm Posterior > Anterior horn 10.6 mm Posterior = Anterior horn Medial
Knee: Meniscus Back to Basics Kyung Jin Suh kyungjin.suh@gmail.com Doctor Radiology, Daegu, KOREA Medial Lateral 7.7 10.2 11.6 9.6 10.6 mm Posterior > Anterior horn 10.6 mm Posterior = Anterior horn Medial
The Meniscus. History. Anatomy. Anatomy. Blood Supply. Attachments
 History The Meniscus W. Randall Schultz, MD, MS Austin, TX January 23, 2016 Meniscus originally thought to represent vestigial tissue 1883 first reported meniscal repair (Annandale) Total menisectomy treatment
History The Meniscus W. Randall Schultz, MD, MS Austin, TX January 23, 2016 Meniscus originally thought to represent vestigial tissue 1883 first reported meniscal repair (Annandale) Total menisectomy treatment
JMSCR Vol 05 Issue 01 Page January
 www.jmscr.igmpublication.org Impact Factor 5.244 Index Copernicus Value: 83.27 ISSN (e)-2347-176x ISSN (p) 2455-0450 DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.18535/jmscr/v5i1.28 Diagnostic Accuracy of Magnetic Resonance
www.jmscr.igmpublication.org Impact Factor 5.244 Index Copernicus Value: 83.27 ISSN (e)-2347-176x ISSN (p) 2455-0450 DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.18535/jmscr/v5i1.28 Diagnostic Accuracy of Magnetic Resonance
What is the most effective MRI specific findings for lateral meniscus posterior root tear in ACL injuries
 What is the most effective MRI specific findings for lateral meniscus posterior root tear in ACL injuries Kazuki Asai 1), Junsuke Nakase 1), Kengo Shimozaki 1), Kazu Toyooka 1), Hiroyuki Tsuchiya 1) 1)
What is the most effective MRI specific findings for lateral meniscus posterior root tear in ACL injuries Kazuki Asai 1), Junsuke Nakase 1), Kengo Shimozaki 1), Kazu Toyooka 1), Hiroyuki Tsuchiya 1) 1)
Do Not Fall on Your Knees - Recognizing Common and Uncommon Pitfalls that May Simulate Meniscal Tears
 Do Not Fall on Your Knees - Recognizing Common and Uncommon Pitfalls that May Simulate Meniscal Tears Poster No.: C-1146 Congress: ECR 2016 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: P. Musa Aguiar, J. Goncalves,
Do Not Fall on Your Knees - Recognizing Common and Uncommon Pitfalls that May Simulate Meniscal Tears Poster No.: C-1146 Congress: ECR 2016 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: P. Musa Aguiar, J. Goncalves,
Epidemiology. Meniscal Injury & Repair. Meniscus Anatomy. Meniscus Anatomy
 Epidemiology 60-70/100,000 per year Meniscal Injury & Repair Arthroscopic Mensiscectomy One of the most common orthopaedic procedures 20% of all surgeries at some centers Male:Female ratio - 2-4:1 Younger
Epidemiology 60-70/100,000 per year Meniscal Injury & Repair Arthroscopic Mensiscectomy One of the most common orthopaedic procedures 20% of all surgeries at some centers Male:Female ratio - 2-4:1 Younger
ADVANCED IMAGING OF THE KNEE
 MENISCAL ANATOMY ADVANCED IMAGING OF THE KNEE MENISCAL ABNORMALITIES MENISCAL FUNCTION MENISCAL FUNCTION load transmission shock absorption stability The menisci DO NOT function as primary stabilizers
MENISCAL ANATOMY ADVANCED IMAGING OF THE KNEE MENISCAL ABNORMALITIES MENISCAL FUNCTION MENISCAL FUNCTION load transmission shock absorption stability The menisci DO NOT function as primary stabilizers
Prevalence of Meniscal Radial Tears of the Knee Revealed by MRI After Surgery
 Downloaded from www.ajronline.org by 46.3.207.114 on 12/22/17 from IP address 46.3.207.114. Copyright RRS. For personal use only; all rights reserved Thomas Magee 1 Marc Shapiro David Williams Received
Downloaded from www.ajronline.org by 46.3.207.114 on 12/22/17 from IP address 46.3.207.114. Copyright RRS. For personal use only; all rights reserved Thomas Magee 1 Marc Shapiro David Williams Received
This presentation is the intellectual property of the author. Contact them for permission to reprint and/or distribute.
 MRI of the Knee Jennifer Swart, M.D. Musculoskeletal Radiology South Texas Radiology Group Outline Coils, Patient Positioning Acquisition Parameters, Planes and Pulse Sequences Knee Arthrography Normal
MRI of the Knee Jennifer Swart, M.D. Musculoskeletal Radiology South Texas Radiology Group Outline Coils, Patient Positioning Acquisition Parameters, Planes and Pulse Sequences Knee Arthrography Normal
This presentation is the intellectual property of the author. Contact them at for permission to reprint and/or distribute.
 MRI of the Knee Jennifer Swart, M.D. Musculoskeletal Radiology South Texas Radiology Group Financial Disclosure Dr. Jennifer Swart has no relevant financial relationships with commercial interests to disclose.
MRI of the Knee Jennifer Swart, M.D. Musculoskeletal Radiology South Texas Radiology Group Financial Disclosure Dr. Jennifer Swart has no relevant financial relationships with commercial interests to disclose.
Meniscal Root Tears: Evaluation, Imaging, and Repair Techniques
 Meniscal Root Tears: Evaluation, Imaging, and Repair Techniques R O B E R T N A S C I M E N TO, M D, M S C H I E F OF S P O RT S M E D I C I N E & SH O U L D E R S U R G E RY N E W TO N- W E L L E S L
Meniscal Root Tears: Evaluation, Imaging, and Repair Techniques R O B E R T N A S C I M E N TO, M D, M S C H I E F OF S P O RT S M E D I C I N E & SH O U L D E R S U R G E RY N E W TO N- W E L L E S L
Knee: Cruciate Ligaments
 72 Knee: Cruciate Ligaments R. Kent Sanders Sagittal oblique 2.5-mm sequences along the plane of the anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) typically yield three to four images of the ACL, with the first medial
72 Knee: Cruciate Ligaments R. Kent Sanders Sagittal oblique 2.5-mm sequences along the plane of the anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) typically yield three to four images of the ACL, with the first medial
Spectrum of meniscal lesions: An MR teaching atlas
 Spectrum of meniscal lesions: An MR teaching atlas Poster No.: C-2284 Congress: ECR 2010 Type: Educational Exhibit Topic: Musculoskeletal Authors: C. Leal, P. Alves, H. Tinto, J. Raposo, T. Bilhim, A.
Spectrum of meniscal lesions: An MR teaching atlas Poster No.: C-2284 Congress: ECR 2010 Type: Educational Exhibit Topic: Musculoskeletal Authors: C. Leal, P. Alves, H. Tinto, J. Raposo, T. Bilhim, A.
Spectrum of meniscal lesions: An MR teaching atlas
 Spectrum of meniscal lesions: An MR teaching atlas Poster No.: C-2284 Congress: ECR 2010 Type: Educational Exhibit Topic: Musculoskeletal - Joints Authors: C. Leal, P. Alves, H. A. M. R. Tinto, J. Raposo,
Spectrum of meniscal lesions: An MR teaching atlas Poster No.: C-2284 Congress: ECR 2010 Type: Educational Exhibit Topic: Musculoskeletal - Joints Authors: C. Leal, P. Alves, H. A. M. R. Tinto, J. Raposo,
Medical Diagnosis for Michael s Knee
 Medical Diagnosis for Michael s Knee Introduction The following report mainly concerns the diagnosis and treatment of the patient, Michael. Given that Michael s clinical problem surrounds an injury about
Medical Diagnosis for Michael s Knee Introduction The following report mainly concerns the diagnosis and treatment of the patient, Michael. Given that Michael s clinical problem surrounds an injury about
Rehab Considerations: Meniscus
 Rehab Considerations: Meniscus Steve Cox, PT, DPT Department of Orthopaedics School of Medicine University of Texas Health Science Center at San Antonio 1 -Anatomy/ Function/ Injuries -Treatment Options
Rehab Considerations: Meniscus Steve Cox, PT, DPT Department of Orthopaedics School of Medicine University of Texas Health Science Center at San Antonio 1 -Anatomy/ Function/ Injuries -Treatment Options
MENISCAL INJURIES. (copyright s h palmer 2009) MENISCAL FUNCTION
 (copyright s h palmer 2009) MENISCAL FUNCTION MENISCAL INJURIES Menisci are important for weight bearing, load distribution, joint stability and proprioception. Figure 1: A normal medial meniscus Any load
(copyright s h palmer 2009) MENISCAL FUNCTION MENISCAL INJURIES Menisci are important for weight bearing, load distribution, joint stability and proprioception. Figure 1: A normal medial meniscus Any load
Meniscus T2 Relaxation Time at Various Stages of Knee Joint Degeneration
 Meniscus T2 Relaxation Time at Various Stages of Knee Joint Degeneration Richard Kijowski, Michael Fazio, Benjamin Beduhn, and Fang Liu Department of Radiology University of Wisconsin School of Medicine
Meniscus T2 Relaxation Time at Various Stages of Knee Joint Degeneration Richard Kijowski, Michael Fazio, Benjamin Beduhn, and Fang Liu Department of Radiology University of Wisconsin School of Medicine
CMEArticle Clinics in diagnostic imaging (141)
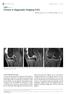 Singapore Med J 2012; 53(9) : 625 CMEArticle Clinics in diagnostic imaging (141) Hollie MY Lim 1, MBBS, FRCR, Wilfred CG Peh 1, FRCP, FRCR 1a 1b 1c Fig. 1 (a & b) Contiguous sagittal fat-suppressed PD-W
Singapore Med J 2012; 53(9) : 625 CMEArticle Clinics in diagnostic imaging (141) Hollie MY Lim 1, MBBS, FRCR, Wilfred CG Peh 1, FRCP, FRCR 1a 1b 1c Fig. 1 (a & b) Contiguous sagittal fat-suppressed PD-W
Role of Magnetic Resonance Imaging in Patients with Knee Trauma
 Original Research Article Role of Magnetic Resonance Imaging in Patients with Knee Trauma Bhautik Kapadia 1, Bhumika Suthar 2* 1 Associate Professor, 2 Assistant Professor, Department of Radiodiagnosis,
Original Research Article Role of Magnetic Resonance Imaging in Patients with Knee Trauma Bhautik Kapadia 1, Bhumika Suthar 2* 1 Associate Professor, 2 Assistant Professor, Department of Radiodiagnosis,
Original Report. The Reverse Segond Fracture: Association with a Tear of the Posterior Cruciate Ligament and Medial Meniscus
 Eva M. Escobedo 1 William J. Mills 2 John. Hunter 1 Received July 10, 2001; accepted after revision October 1, 2001. 1 Department of Radiology, University of Washington Harborview Medical enter, 325 Ninth
Eva M. Escobedo 1 William J. Mills 2 John. Hunter 1 Received July 10, 2001; accepted after revision October 1, 2001. 1 Department of Radiology, University of Washington Harborview Medical enter, 325 Ninth
What s your diagnosis?
 Case Study 58 A 61-year-old truck driver man presented with a valgus injury to the left knee joint when involved in a truck accident. What s your diagnosis? Diagnosis : Avulsion of Deep MCL The medial
Case Study 58 A 61-year-old truck driver man presented with a valgus injury to the left knee joint when involved in a truck accident. What s your diagnosis? Diagnosis : Avulsion of Deep MCL The medial
ORIGINAL ARTICLE. ROLE OF MRI IN EVALUATION OF TRAUMATIC KNEE INJURIES Saurabh Chaudhuri, Priscilla Joshi, Mohit Goel
 ROLE OF MRI IN EVALUATION OF TRAUMATIC KNEE INJURIES Saurabh Chaudhuri, Priscilla Joshi, Mohit Goel 1. Associate Professor, Department of Radiodiagnosis & imaging, Bharati Vidyapeeth Medical College and
ROLE OF MRI IN EVALUATION OF TRAUMATIC KNEE INJURIES Saurabh Chaudhuri, Priscilla Joshi, Mohit Goel 1. Associate Professor, Department of Radiodiagnosis & imaging, Bharati Vidyapeeth Medical College and
49 year old female with knee pain for several months after starting a new workout regimen. William Millard MSK Fellow
 49 year old female with knee pain for several months after starting a new workout regimen William Millard MSK Fellow DISCOID LATERAL MENISCUS Discoid lateral meniscus (DLM) Found in
49 year old female with knee pain for several months after starting a new workout regimen William Millard MSK Fellow DISCOID LATERAL MENISCUS Discoid lateral meniscus (DLM) Found in
Unlocking the locked Knee
 Unlocking the locked Knee Poster No.: P-0027 Congress: ESSR 2013 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: J. P. SINGH, S. Srivastava, S. S. BAIJAL ; Gurgaon, Delhi 1 1 2 1 2 NCR/IN, LUCKNOW, UTTAR PRADESH/IN
Unlocking the locked Knee Poster No.: P-0027 Congress: ESSR 2013 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: J. P. SINGH, S. Srivastava, S. S. BAIJAL ; Gurgaon, Delhi 1 1 2 1 2 NCR/IN, LUCKNOW, UTTAR PRADESH/IN
Anterior Cruciate Ligament Surgery
 Anatomy Anterior Cruciate Ligament Surgery Roger Ostrander, MD Andrews Institute Anatomy Anatomy Function Primary restraint to anterior tibial translation Secondary restraint to internal tibial rotation
Anatomy Anterior Cruciate Ligament Surgery Roger Ostrander, MD Andrews Institute Anatomy Anatomy Function Primary restraint to anterior tibial translation Secondary restraint to internal tibial rotation
Investigating the loading behaviour of intact and meniscectomy knee joints and the impact on surgical decisions
 Investigating the loading behaviour of intact and meniscectomy knee joints and the impact on surgical decisions M. S. Yeoman 1 1. Continuum Blue Limited, One Caspian Point, Caspian Way, CF10 4DQ, United
Investigating the loading behaviour of intact and meniscectomy knee joints and the impact on surgical decisions M. S. Yeoman 1 1. Continuum Blue Limited, One Caspian Point, Caspian Way, CF10 4DQ, United
The Meniscal Roots: Gross Anatomic Correlation with 3-T MRI Findings
 rody et al. Meniscal Root MRI Musculoskeletal Imaging Pictorial Essay Jeffrey M. rody 1 Michael J. Hulstyn 2 raden. Fleming 3 Glenn. Tung 1 rody JM, Hulstyn MJ, Fleming, Tung G Keywords: anatomy, knee,
rody et al. Meniscal Root MRI Musculoskeletal Imaging Pictorial Essay Jeffrey M. rody 1 Michael J. Hulstyn 2 raden. Fleming 3 Glenn. Tung 1 rody JM, Hulstyn MJ, Fleming, Tung G Keywords: anatomy, knee,
MRI grading of postero-lateral corner and anterior cruciate ligament injuries
 MRI grading of postero-lateral corner and anterior cruciate ligament injuries Poster No.: C-2533 Congress: ECR 2012 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: J. Lopes Dias, J. A. Sousa Pereira, L. Fernandes,
MRI grading of postero-lateral corner and anterior cruciate ligament injuries Poster No.: C-2533 Congress: ECR 2012 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: J. Lopes Dias, J. A. Sousa Pereira, L. Fernandes,
MRI Evaluation of Internal derangement of the Knee Joint - A PICTORIAL REVIEW
 MRI Evaluation of Internal derangement of the Knee Joint - A PICTORIAL REVIEW Poster No.: C-1386 Congress: ECR 2015 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: V. Nadaraja, F. Abubacker Sulaiman; Chennai/IN Keywords:
MRI Evaluation of Internal derangement of the Knee Joint - A PICTORIAL REVIEW Poster No.: C-1386 Congress: ECR 2015 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: V. Nadaraja, F. Abubacker Sulaiman; Chennai/IN Keywords:
ACL AND PCL INJURIES OF THE KNEE JOINT
 ACL AND PCL INJURIES OF THE KNEE JOINT Dr.KN Subramanian M.Ch Orth., FRCS (Tr & Orth), CCT Orth(UK) Consultant Orthopaedic Surgeon, Special interest: Orthopaedic Sports Injury, Shoulder and Knee Surgery,
ACL AND PCL INJURIES OF THE KNEE JOINT Dr.KN Subramanian M.Ch Orth., FRCS (Tr & Orth), CCT Orth(UK) Consultant Orthopaedic Surgeon, Special interest: Orthopaedic Sports Injury, Shoulder and Knee Surgery,
Discoid Medial Meniscus Tear, with a Literature Review of Treatments
 Case Report Knee Surg Relat Res 2017;29(3):237-242 https://doi.org/10.5792/ksrr.15.054 pissn 2234-0726 eissn 2234-2451 Knee Surgery & Related Research Discoid Medial Meniscus Tear, with a Literature Review
Case Report Knee Surg Relat Res 2017;29(3):237-242 https://doi.org/10.5792/ksrr.15.054 pissn 2234-0726 eissn 2234-2451 Knee Surgery & Related Research Discoid Medial Meniscus Tear, with a Literature Review
Meniscus Tears. Three bones meet to form your knee joint: your thighbone (femur), shinbone (tibia), and kneecap (patella).
 Meniscus Tears Information on meniscus tears is also available in Spanish: Desgarros de los meniscus (topic.cfm?topic=a00470) and Portuguese: Rupturas do menisco (topic.cfm?topic=a00754). Meniscus tears
Meniscus Tears Information on meniscus tears is also available in Spanish: Desgarros de los meniscus (topic.cfm?topic=a00470) and Portuguese: Rupturas do menisco (topic.cfm?topic=a00754). Meniscus tears
Medial Meniscal Root Tears: When to rehab? When to repair? When to debride. Christopher Betz, DO Orthopedics Sports Medicine Bristol, CT
 Medial Meniscal Root Tears: When to rehab? When to repair? When to debride Christopher Betz, DO Orthopedics Sports Medicine Bristol, CT Disclosure Consultant Mitek Smith and Nephew-biologic patch Good
Medial Meniscal Root Tears: When to rehab? When to repair? When to debride Christopher Betz, DO Orthopedics Sports Medicine Bristol, CT Disclosure Consultant Mitek Smith and Nephew-biologic patch Good
Stability of Post Traumatic Osteochondritis Dissecans of the Knee: MR Imaging Findings
 Chin J Radiol 2005; 30: 199-204 199 Stability of Post Traumatic Osteochondritis Dissecans of the Knee: MR Imaging Findings YU-CHUNG HUNG 1 JON-KWAY HUANG 1,2 Department of Radiology 1, Mackay Memorial
Chin J Radiol 2005; 30: 199-204 199 Stability of Post Traumatic Osteochondritis Dissecans of the Knee: MR Imaging Findings YU-CHUNG HUNG 1 JON-KWAY HUANG 1,2 Department of Radiology 1, Mackay Memorial
A comparison of arthroscopic diagnosis of ramp lesion and pre-operative MRI evaluation
 A comparison of arthroscopic diagnosis of ramp lesion and pre-operative MRI evaluation Yasuma S, Nozaki M, Kobayashi M, Kawanishi Y Yoshida M, Mitsui H, Nagaya Y, Iguchi H, Murakami H Department of Orthopaedic
A comparison of arthroscopic diagnosis of ramp lesion and pre-operative MRI evaluation Yasuma S, Nozaki M, Kobayashi M, Kawanishi Y Yoshida M, Mitsui H, Nagaya Y, Iguchi H, Murakami H Department of Orthopaedic
CLINICAL PRESENTATION AND RADIOLOGY QUIZ QUESTION
 Donald L. Renfrew, MD Radiology Associates of the Fox Valley, 333 N. Commercial Street, Suite 100, Neenah, WI 54956 12/01/2012 Radiology Quiz of the Week # 101 Page 1 CLINICAL PRESENTATION AND RADIOLOGY
Donald L. Renfrew, MD Radiology Associates of the Fox Valley, 333 N. Commercial Street, Suite 100, Neenah, WI 54956 12/01/2012 Radiology Quiz of the Week # 101 Page 1 CLINICAL PRESENTATION AND RADIOLOGY
Imaging the Athlete s Knee. Peter Lowry, MD Musculoskeletal Radiology University of Colorado
 Imaging the Athlete s Knee Peter Lowry, MD Musculoskeletal Radiology University of Colorado None Disclosures Knee Imaging: Radiographs Can be performed weight-bearing or non-weight-bearing View options
Imaging the Athlete s Knee Peter Lowry, MD Musculoskeletal Radiology University of Colorado None Disclosures Knee Imaging: Radiographs Can be performed weight-bearing or non-weight-bearing View options
2 A B Fig. 1. Lateral tibial condyle fracture with joint effusion in a 35-year-old man. Sagittal T2-weighted MRI shows a large amount of effusion
 1 2 1 1 1 2 A B Fig. 1. Lateral tibial condyle fracture with joint effusion in a 35-year-old man. Sagittal T2-weighted MRI shows a large amount of effusion (between arrowheads) in the suprapatellar pouch,
1 2 1 1 1 2 A B Fig. 1. Lateral tibial condyle fracture with joint effusion in a 35-year-old man. Sagittal T2-weighted MRI shows a large amount of effusion (between arrowheads) in the suprapatellar pouch,
Evaluation of Role of Magnetic Resonance Imaging in Knee Joint Injuries in Correlation with Arthroscopy
 Original Article Print ISSN: 2321-6379 Online ISSN: 2321-595X DOI: 10.17354/ijss/2017/442 Evaluation of Role of Magnetic Resonance Imaging in Knee Joint Injuries in Correlation with Arthroscopy T Sundara
Original Article Print ISSN: 2321-6379 Online ISSN: 2321-595X DOI: 10.17354/ijss/2017/442 Evaluation of Role of Magnetic Resonance Imaging in Knee Joint Injuries in Correlation with Arthroscopy T Sundara
Differential Diagnosis
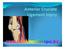 Case 31yo M who sustained an injury to L knee while playing Basketball approximately 2 weeks ago. He describes pivoting and hyperextending his knee, which swelled over the next few days. He now presents
Case 31yo M who sustained an injury to L knee while playing Basketball approximately 2 weeks ago. He describes pivoting and hyperextending his knee, which swelled over the next few days. He now presents
MR imaging of the knee in marathon runners before and after competition
 Skeletal Radiol (2001) 30:72 76 International Skeletal Society 2001 ARTICLE W. Krampla R. Mayrhofer J. Malcher K.H. Kristen M. Urban W. Hruby MR imaging of the knee in marathon runners before and after
Skeletal Radiol (2001) 30:72 76 International Skeletal Society 2001 ARTICLE W. Krampla R. Mayrhofer J. Malcher K.H. Kristen M. Urban W. Hruby MR imaging of the knee in marathon runners before and after
SOFT TISSUE INJURIES OF THE KNEE: Primary Care and Orthopaedic Management
 SOFT TISSUE INJURIES OF THE KNEE: Primary Care and Orthopaedic Management Gauguin Gamboa Australia has always been a nation where emphasis on health and fitness has resulted in an active population engaged
SOFT TISSUE INJURIES OF THE KNEE: Primary Care and Orthopaedic Management Gauguin Gamboa Australia has always been a nation where emphasis on health and fitness has resulted in an active population engaged
FAI syndrome with or without labral tear.
 Case This 16-year-old female, soccer athlete was treated for pain in the right groin previously. Now has acute onset of pain in the left hip. The pain was in the groin that was worse with activities. Diagnosis
Case This 16-year-old female, soccer athlete was treated for pain in the right groin previously. Now has acute onset of pain in the left hip. The pain was in the groin that was worse with activities. Diagnosis
Inside-Out Meniscal Repair Still the Gold Standard?
 Inside-Out Meniscal Repair Still the Gold Standard? ERIC BERKSON, MD MGH SPORTS MEDICINE TEAM PHYSICIAN, BOSTON RED SOX ASSISTANT PROFESSOR, HARVARD MEDICAL SCHOOL JULY 26, 2018 Disclosures Neither I nor
Inside-Out Meniscal Repair Still the Gold Standard? ERIC BERKSON, MD MGH SPORTS MEDICINE TEAM PHYSICIAN, BOSTON RED SOX ASSISTANT PROFESSOR, HARVARD MEDICAL SCHOOL JULY 26, 2018 Disclosures Neither I nor
Lesions of the Menisci of the Knee: Value of MR Imaging Criteria for Recognition of Unstable Lesions
 B. C. Vande Berg 1 P. Poilvache 2 F. Duchateau 1 F. E. Lecouvet 1 J. E. Dubuc 2 B. Maldague 1 J. Malghem 1 Received June 12, 2000; accepted after revision August 24, 2000. 1 Department of Radiology, Cliniques
B. C. Vande Berg 1 P. Poilvache 2 F. Duchateau 1 F. E. Lecouvet 1 J. E. Dubuc 2 B. Maldague 1 J. Malghem 1 Received June 12, 2000; accepted after revision August 24, 2000. 1 Department of Radiology, Cliniques
CLINICAL PRESENTATION AND RADIOLOGY QUIZ QUESTION
 Donald L. Renfrew, MD Radiology Associates of the Fox Valley, 333 N. Commercial Street, Suite 100, Neenah, WI 54956 11/24/2012 Radiology Quiz of the Week # 100 Page 1 CLINICAL PRESENTATION AND RADIOLOGY
Donald L. Renfrew, MD Radiology Associates of the Fox Valley, 333 N. Commercial Street, Suite 100, Neenah, WI 54956 11/24/2012 Radiology Quiz of the Week # 100 Page 1 CLINICAL PRESENTATION AND RADIOLOGY
Meniscal Tears: Role of Axial MRI Alone and in Combination with Other Imaging Planes
 Nefise Cagla Tarhan 1,2 Christine. Chung 1 urea Valeria Rosa Mohana-orges 1 Tudor Hughes 1 Donald Resnick 1 Received September 30, 2003; accepted after revision February 2, 2004. 1 Department of Radiology,
Nefise Cagla Tarhan 1,2 Christine. Chung 1 urea Valeria Rosa Mohana-orges 1 Tudor Hughes 1 Donald Resnick 1 Received September 30, 2003; accepted after revision February 2, 2004. 1 Department of Radiology,
Original Research Article
 ROLE OF IN INTERNAL DERANGEMENT OF KNEE JOINT IN CORRELATION WITH ARTHROSCOPY Onteddu Joji Reddy 1, Jamkhana Abdul Gafoor 2, Balla Suresh 3, Polysetty Obuleswar Prasad 4 1Professor and HOD, Department
ROLE OF IN INTERNAL DERANGEMENT OF KNEE JOINT IN CORRELATION WITH ARTHROSCOPY Onteddu Joji Reddy 1, Jamkhana Abdul Gafoor 2, Balla Suresh 3, Polysetty Obuleswar Prasad 4 1Professor and HOD, Department
MRI versus clinical examination for the diagnosis of meniscal and ligamentous injuries of kneee
 Original Research Article MRI versus clinical examination for the diagnosis of meniscal and ligamentous injuries of kneee Rakesh Gujjar *, R. P. Bansal, L. K. Gotecha, Raja Kollu Department of Radio-diagnosis
Original Research Article MRI versus clinical examination for the diagnosis of meniscal and ligamentous injuries of kneee Rakesh Gujjar *, R. P. Bansal, L. K. Gotecha, Raja Kollu Department of Radio-diagnosis
Medial Knee Osteoarthritis Precedes Medial Meniscal Posterior Root Tear with an Event of Painful Popping
 Medial Knee Osteoarthritis Precedes Medial Meniscal Posterior Root Tear with an Event of Painful Popping Dhong Won Lee, M.D, Ji Nam Kim, M.D., Jin Goo Kim, M.D., Ph.D. KonKuk University Medical Center
Medial Knee Osteoarthritis Precedes Medial Meniscal Posterior Root Tear with an Event of Painful Popping Dhong Won Lee, M.D, Ji Nam Kim, M.D., Jin Goo Kim, M.D., Ph.D. KonKuk University Medical Center
ACL Athletic Career. ACL Rupture - Warning Features Intensive pain Immediate swelling Locking Feel a Pop Dead leg Cannot continue to play
 FIMS Ambassador Tour to Eastern Europe, 2004 Belgrade, Serbia Montenegro Acute Knee Injuries - Controversies and Challenges Professor KM Chan OBE, JP President of FIMS Belgrade ACL Athletic Career ACL
FIMS Ambassador Tour to Eastern Europe, 2004 Belgrade, Serbia Montenegro Acute Knee Injuries - Controversies and Challenges Professor KM Chan OBE, JP President of FIMS Belgrade ACL Athletic Career ACL
Presenter: Mark Yeoman PhD Date: 19 October Research & Development, FEA, CFD, Material Selection, Testing & Assessment. Continuum Blue Ltd
 Research & Development, FEA, CFD, Material Selection, Testing & Assessment Investigating the loading behaviour of intact & meniscectomy knee joints & the impact on surgical decisions M S Yeoman PhD 1 1.
Research & Development, FEA, CFD, Material Selection, Testing & Assessment Investigating the loading behaviour of intact & meniscectomy knee joints & the impact on surgical decisions M S Yeoman PhD 1 1.
LATERAL MENISCUS SLOPE AND ITS CLINICAL RELEVANCE IN PATIENTS WITH A COMBINED ACL TEAR AND POSTERIOR TIBIA COMPRESSION
 LATERAL MENISCUS SLOPE AND ITS CLINICAL RELEVANCE IN PATIENTS WITH A COMBINED ACL TEAR AND POSTERIOR TIBIA COMPRESSION R. ŚMIGIELSKI, B. DOMINIK, U, ZDANOWICZ, Z. GAJEWSKI, K. SKIERBISZEWSKA, K. SIEWRUK,
LATERAL MENISCUS SLOPE AND ITS CLINICAL RELEVANCE IN PATIENTS WITH A COMBINED ACL TEAR AND POSTERIOR TIBIA COMPRESSION R. ŚMIGIELSKI, B. DOMINIK, U, ZDANOWICZ, Z. GAJEWSKI, K. SKIERBISZEWSKA, K. SIEWRUK,
and K n e e J o i n t Is the most complicated joint in the body!!!!
 K n e e J o i n t K n e e J o i n t Is the most complicated joint in the body!!!! 1-Consists of two condylar joints between: A-The medial and lateral condyles of the femur and The condyles of the tibia
K n e e J o i n t K n e e J o i n t Is the most complicated joint in the body!!!! 1-Consists of two condylar joints between: A-The medial and lateral condyles of the femur and The condyles of the tibia
ULTRASOUND EVALUATION OF NORMAL AND ABNORMAL POSTERIOR CRUCIATE LIGAMENT - A PROSPECTIVE STUDY
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE ULTRASOUND EVALUATION OF NORMAL AND ABNORMAL POSTERIOR CRUCIATE LIGAMENT - A PROSPECTIVE STUDY Palle Lalitha, 1 M. Ch. Balaji Reddy, 1 K. Jagannath Reddy, 1 Vijaya Kumari 2 1 Department
ORIGINAL ARTICLE ULTRASOUND EVALUATION OF NORMAL AND ABNORMAL POSTERIOR CRUCIATE LIGAMENT - A PROSPECTIVE STUDY Palle Lalitha, 1 M. Ch. Balaji Reddy, 1 K. Jagannath Reddy, 1 Vijaya Kumari 2 1 Department
FieldStrength. Achieva 3.0T enables cutting-edge applications, best-in-class MSK images
 FieldStrength Publication for the Philips MRI Community Issue 33 December 2007 Achieva 3.0T enables cutting-edge applications, best-in-class MSK images Palo Alto Medical Clinic Sports Medicine Center employs
FieldStrength Publication for the Philips MRI Community Issue 33 December 2007 Achieva 3.0T enables cutting-edge applications, best-in-class MSK images Palo Alto Medical Clinic Sports Medicine Center employs
Overview Ligament Injuries. Anatomy. Epidemiology Very commonly injured joint. ACL Injury 20/06/2016. Meniscus Tears. Patellofemoral Problems
 Overview Ligament Injuries Meniscus Tears Pankaj Sharma MBBS, FRCS (Tr & Orth) Consultant Orthopaedic Surgeon Manchester Royal Infirmary Patellofemoral Problems Knee Examination Anatomy Epidemiology Very
Overview Ligament Injuries Meniscus Tears Pankaj Sharma MBBS, FRCS (Tr & Orth) Consultant Orthopaedic Surgeon Manchester Royal Infirmary Patellofemoral Problems Knee Examination Anatomy Epidemiology Very
Medical Practice for Sports Injuries and Disorders of the Knee
 Sports-Related Injuries and Disorders Medical Practice for Sports Injuries and Disorders of the Knee JMAJ 48(1): 20 24, 2005 Hirotsugu MURATSU*, Masahiro KUROSAKA**, Tetsuji YAMAMOTO***, and Shinichi YOSHIDA****
Sports-Related Injuries and Disorders Medical Practice for Sports Injuries and Disorders of the Knee JMAJ 48(1): 20 24, 2005 Hirotsugu MURATSU*, Masahiro KUROSAKA**, Tetsuji YAMAMOTO***, and Shinichi YOSHIDA****
Comparative study of high resolusion ultrasonography and magnetic resonance imaging in diagnosing traumatic knee injuries & pathologies
 Original article: Comparative study of high resolusion ultrasonography and magnetic resonance imaging in diagnosing traumatic knee injuries & pathologies Dr. Rakesh Gujjar*, Dr. R. P. Bansal, Dr. Sandeep
Original article: Comparative study of high resolusion ultrasonography and magnetic resonance imaging in diagnosing traumatic knee injuries & pathologies Dr. Rakesh Gujjar*, Dr. R. P. Bansal, Dr. Sandeep
BASELINE QUESTIONNAIRE (SURGEON)
 SECTION A: STUDY INFORMATION Subject ID: - - Study Visit: Baseline Site Number: Date: / / Surgeon ID: SECTION B: INITIAL SURGEON HISTORY B1. Previous Knee Surgery: Yes No Not recorded B2. Number of Previous
SECTION A: STUDY INFORMATION Subject ID: - - Study Visit: Baseline Site Number: Date: / / Surgeon ID: SECTION B: INITIAL SURGEON HISTORY B1. Previous Knee Surgery: Yes No Not recorded B2. Number of Previous
A comparative study of MRI versus arthroscopic findings in ACL and meniscal injuries of the knee
 International Journal of Research in Orthopaedics Kulkarni OP et al. Int J Res Orthop. 2018 Mar;4(2):198-202 http://www.ijoro.org Original Research Article DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18203/issn.2455-4510.intjresorthop20180123
International Journal of Research in Orthopaedics Kulkarni OP et al. Int J Res Orthop. 2018 Mar;4(2):198-202 http://www.ijoro.org Original Research Article DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18203/issn.2455-4510.intjresorthop20180123
No Disclosures. Topics. Pediatric ACL Tears
 Knee Injuries in Skeletally Immature Athletes No Disclosures Zachary Stinson, M.D. 2 Topics ACL Tears and Tibial Eminence Fractures Meniscus Injuries Discoid Meniscus Osteochondritis Dessicans Patellar
Knee Injuries in Skeletally Immature Athletes No Disclosures Zachary Stinson, M.D. 2 Topics ACL Tears and Tibial Eminence Fractures Meniscus Injuries Discoid Meniscus Osteochondritis Dessicans Patellar
Imaging the Knee 17/10/2017. Friction syndrome Common in runners or cyclists Fluid between ITB and Lateral femoral condyle
 17/10/2017 Imaging the Knee Alicia M. Yochum RN, DC, DACBR, RMSK Iliotibial Band Syndrome Ligamentous Tears (ACL, PCL, MCL, LCL) Meniscal Tears Cartilage Degeneration Quadriceps/Patellar tendinosis Osteochondral
17/10/2017 Imaging the Knee Alicia M. Yochum RN, DC, DACBR, RMSK Iliotibial Band Syndrome Ligamentous Tears (ACL, PCL, MCL, LCL) Meniscal Tears Cartilage Degeneration Quadriceps/Patellar tendinosis Osteochondral
Priorities Forum Statement GUIDANCE
 Priorities Forum Statement Number 21 Subject Knee Arthroscopy including arthroscopic knee washouts Date of decision November 2016 Date refreshed March 2017 Date of review November 2018 Osteoarthritis of
Priorities Forum Statement Number 21 Subject Knee Arthroscopy including arthroscopic knee washouts Date of decision November 2016 Date refreshed March 2017 Date of review November 2018 Osteoarthritis of
Case Report Detached Anterior Horn of the Medial Meniscus Mimicking a Parameniscal Cyst
 Case Reports in Orthopedics Volume 2015, Article ID 706241, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2015/706241 Case Report Detached Anterior Horn of the Medial Meniscus Mimicking a Parameniscal Cyst Shoji Fukuta,
Case Reports in Orthopedics Volume 2015, Article ID 706241, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2015/706241 Case Report Detached Anterior Horn of the Medial Meniscus Mimicking a Parameniscal Cyst Shoji Fukuta,
The Impact of Age on Knee Injury Treatment
 The Impact of Age on Knee Injury Treatment Focus on the Meniscus Dr. Alvin J. Detterline, MD Sports Medicine and Orthopaedic Surgery Towson Orthopaedic Associates University of Maryland St. Joseph Medical
The Impact of Age on Knee Injury Treatment Focus on the Meniscus Dr. Alvin J. Detterline, MD Sports Medicine and Orthopaedic Surgery Towson Orthopaedic Associates University of Maryland St. Joseph Medical
B one contusion is a finding substantiated by magnetic
 592 ORIGINAL ARTICLE The appearance of kissing contusion in the acutely injured knee in the athletes I P Terzidis, A G Christodoulou, A L Ploumis, S R Metsovitis, M Koimtzis, P Givissis... See end of article
592 ORIGINAL ARTICLE The appearance of kissing contusion in the acutely injured knee in the athletes I P Terzidis, A G Christodoulou, A L Ploumis, S R Metsovitis, M Koimtzis, P Givissis... See end of article
Treatment of meniscal lesions and isolated lesions of the anterior cruciate ligament of the knee in adults
 QUICK REFERENCE GUIDE Treatment of meniscal s and isolated s of the anterior cruciate ligament of the knee in adults June 2008 AIM OF THE GUIDELINES To encourage good practices in the areas of meniscal
QUICK REFERENCE GUIDE Treatment of meniscal s and isolated s of the anterior cruciate ligament of the knee in adults June 2008 AIM OF THE GUIDELINES To encourage good practices in the areas of meniscal
Multi-ligamentous knee injuries - MRI injury patterns at a glance
 Multi-ligamentous knee injuries - MRI injury patterns at a glance Poster No.: P-0068 Congress: ESSR 2015 Type: Educational Poster Authors: A. Rastogi, D. Whelan, R. Martin, W. Mak, D. Pearce ; 1 1 1 2
Multi-ligamentous knee injuries - MRI injury patterns at a glance Poster No.: P-0068 Congress: ESSR 2015 Type: Educational Poster Authors: A. Rastogi, D. Whelan, R. Martin, W. Mak, D. Pearce ; 1 1 1 2
Arthroscopy / MRI Correlation Conference. Department of Radiology, Section of MSK Imaging Department of Orthopedic Surgery 7/19/16
 Arthroscopy / MRI Correlation Conference Department of Radiology, Section of MSK Imaging Department of Orthopedic Surgery 7/19/16 Case 1: 29 YOM with recurrent shoulder dislocations Glenoid Axial T1FS
Arthroscopy / MRI Correlation Conference Department of Radiology, Section of MSK Imaging Department of Orthopedic Surgery 7/19/16 Case 1: 29 YOM with recurrent shoulder dislocations Glenoid Axial T1FS
Meniscectomy to Repair: Roots, Ramps, Buckets, and Biologics. Charles A. Bush-Joseph, MD Rush University Medical Center Chicago, IL
 Meniscectomy to Repair: Roots, Ramps, Buckets, and Biologics Charles A. Bush-Joseph, MD Rush University Medical Center Chicago, IL Disclosures: None Orthopaedic Trends: Increase in physician education
Meniscectomy to Repair: Roots, Ramps, Buckets, and Biologics Charles A. Bush-Joseph, MD Rush University Medical Center Chicago, IL Disclosures: None Orthopaedic Trends: Increase in physician education
Case Report Double-Layered Lateral Meniscus Accompanied by Meniscocapsular Separation
 Case Reports in Orthopedics Volume 2015, Article ID 357463, 5 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2015/357463 Case Report Double-Layered Lateral Meniscus Accompanied by Meniscocapsular Separation Aki Fukuda,
Case Reports in Orthopedics Volume 2015, Article ID 357463, 5 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2015/357463 Case Report Double-Layered Lateral Meniscus Accompanied by Meniscocapsular Separation Aki Fukuda,
KNEE INJURIES IN SPORTS MEDICINE
 KNEE INJURIES IN SPORTS MEDICINE Irving Raphael, MD June 13, 2014 RSM Medical Associates Head Team Physician Syracuse University Outline Meniscal Injuries anatomy Exam Treatment ACL Injuries Etiology Physical
KNEE INJURIES IN SPORTS MEDICINE Irving Raphael, MD June 13, 2014 RSM Medical Associates Head Team Physician Syracuse University Outline Meniscal Injuries anatomy Exam Treatment ACL Injuries Etiology Physical
MY PATIENT HAS KNEE PAIN. David Levi, MD Chief, Division of Musculoskeletal l limaging Atlantic Medical Imaging
 MY PATIENT HAS KNEE PAIN David Levi, MD Chief, Division of Musculoskeletal l limaging Atlantic Medical Imaging Causes of knee pain Non traumatic Trauma Osteoarthritis Patellofemoral pain Menisci or ligaments
MY PATIENT HAS KNEE PAIN David Levi, MD Chief, Division of Musculoskeletal l limaging Atlantic Medical Imaging Causes of knee pain Non traumatic Trauma Osteoarthritis Patellofemoral pain Menisci or ligaments
Unicompartmental Knee Resurfacing
 Disclaimer This movie is an educational resource only and should not be used to manage knee pain. All decisions about the management of knee pain must be made in conjunction with your Physician or a licensed
Disclaimer This movie is an educational resource only and should not be used to manage knee pain. All decisions about the management of knee pain must be made in conjunction with your Physician or a licensed
MRI Diagnosis of Anterior Cruciate Ligament Tears: What is the Added Value of Oblique Sagittal Technique?
 Med. J. Cairo Univ., Vol. 85, No. 5, September: 1865-1872, 2017 www.medicaljournalofcairouniversity.net MRI Diagnosis of Anterior Cruciate Ligament Tears: What is the Added Value of Oblique Sagittal Technique?
Med. J. Cairo Univ., Vol. 85, No. 5, September: 1865-1872, 2017 www.medicaljournalofcairouniversity.net MRI Diagnosis of Anterior Cruciate Ligament Tears: What is the Added Value of Oblique Sagittal Technique?
Degeneratiivne menisk
 Degeneratiivne menisk Conflict of interest: none Microcirculation of the meniscus Age Dependent Inferior/Superior Geniculates Red zone peripheral 1/3 (3mm) Red/White zone Mid 1/3 (3-5mm) White zone Inner
Degeneratiivne menisk Conflict of interest: none Microcirculation of the meniscus Age Dependent Inferior/Superior Geniculates Red zone peripheral 1/3 (3mm) Red/White zone Mid 1/3 (3-5mm) White zone Inner
Disclosures. Background. Background
 Kinematic and Quantitative MR Imaging Evaluation of ACL Reconstructions Using the Mini-Two Incision Method Compared to the Anteromedial Portal Technique Drew A. Lansdown, MD Christina Allen, MD Samuel
Kinematic and Quantitative MR Imaging Evaluation of ACL Reconstructions Using the Mini-Two Incision Method Compared to the Anteromedial Portal Technique Drew A. Lansdown, MD Christina Allen, MD Samuel
CLINICAL ANALYSIS ON ARTHOSCOPIC MENISCAL REPAIR BY FAST-FIX SYSTEM
 CLINICAL ANALYSIS ON ARTHOSCOPIC MENISCAL REPAIR BY FAST-FIX SYSTEM Ashutosh Kumar Das, Liu Jun and Lu Hougen (Orthopaedics Department of Jingzhou Central hospital, Yangtze University) Jingzhou, Hubei,
CLINICAL ANALYSIS ON ARTHOSCOPIC MENISCAL REPAIR BY FAST-FIX SYSTEM Ashutosh Kumar Das, Liu Jun and Lu Hougen (Orthopaedics Department of Jingzhou Central hospital, Yangtze University) Jingzhou, Hubei,
Non-Surgical vs. Surgical Treatment of Meniscus Tears of the Knee
 Non-Surgical vs. Surgical Treatment of Meniscus Tears of the Knee Greg I. Nakamoto, MD FACP Section of Orthopedics and Sports Medicine Virginia Mason Medical Center CASE 1 45 y/o construction worker sent
Non-Surgical vs. Surgical Treatment of Meniscus Tears of the Knee Greg I. Nakamoto, MD FACP Section of Orthopedics and Sports Medicine Virginia Mason Medical Center CASE 1 45 y/o construction worker sent
OPERATIVE TREATMENT OF THE INTERCONDYLAR FRACTURE OF THE FEMUR
 OPERATIVE TREATMENT OF THE INTERCONDYLAR FRACTURE OF THE FEMUR S G Chee, K S Lam, B K Tay, N Balachandran SYNOPSIS Operative treatment of 28 intercondylar fractures of femur were done from 98 to 985. The
OPERATIVE TREATMENT OF THE INTERCONDYLAR FRACTURE OF THE FEMUR S G Chee, K S Lam, B K Tay, N Balachandran SYNOPSIS Operative treatment of 28 intercondylar fractures of femur were done from 98 to 985. The
Knee MRI Update Case Review 2009 Russell C. Fritz, M.D. National Orthopedic Imaging Associates San Francisco, CA
 Knee MRI Update Case Review 2009 Russell C. Fritz, M.D. National Orthopedic Imaging Associates San Francisco, CA Meniscal Tears -linear increased signal extending to an articular surface is the hallmark
Knee MRI Update Case Review 2009 Russell C. Fritz, M.D. National Orthopedic Imaging Associates San Francisco, CA Meniscal Tears -linear increased signal extending to an articular surface is the hallmark
New Evidence Suggests that Work Related Knee Pain with Degenerative Complications May Not Require Surgery
 4 th Quarter 2017 New Evidence Suggests that Work Related Knee Pain with Degenerative Complications May Not Require Surgery By: Michael Erdil MD, FACOEM Introduction It is estimated there are approximately
4 th Quarter 2017 New Evidence Suggests that Work Related Knee Pain with Degenerative Complications May Not Require Surgery By: Michael Erdil MD, FACOEM Introduction It is estimated there are approximately
Proximal tibial bony and meniscal slopes are higher in ACL injured subjects than controls: a comparative MRI study
 Proximal tibial bony and meniscal slopes are higher in ACL injured subjects than controls: a comparative MRI study Ashraf Elmansori, Timothy Lording, Raphaël Dumas, Khalifa Elmajri, Philippe Neyret, Sebastien
Proximal tibial bony and meniscal slopes are higher in ACL injured subjects than controls: a comparative MRI study Ashraf Elmansori, Timothy Lording, Raphaël Dumas, Khalifa Elmajri, Philippe Neyret, Sebastien
Anterior Tibial Translation Sign: Factors Affecting Interpretation of Anterior Cruciate Ligament Tear
 Anterior Tibial Translation Sign: Factors Affecting Interpretation of Anterior Cruciate Ligament Tear J Med Assoc Thai 2015; 98 (Suppl. 1): S57-S62 Full text. e-journal: http://www.jmatonline.com Numphung
Anterior Tibial Translation Sign: Factors Affecting Interpretation of Anterior Cruciate Ligament Tear J Med Assoc Thai 2015; 98 (Suppl. 1): S57-S62 Full text. e-journal: http://www.jmatonline.com Numphung
Meniscal Root Tears: A Silent Epidemic
 Meniscal Root Tears: A Silent Epidemic TRIA Orthopedic and Sports Medicine Conference February 9 th, 2018 Robert F. LaPrade, M.D., Ph.D. Chief Medical Officer Steadman Philippon Research Institute Co-Director,
Meniscal Root Tears: A Silent Epidemic TRIA Orthopedic and Sports Medicine Conference February 9 th, 2018 Robert F. LaPrade, M.D., Ph.D. Chief Medical Officer Steadman Philippon Research Institute Co-Director,
The occurrence and the consistency of the popliteomeniscal
 Popliteomeniscal Fascicle Tear: Diagnosis and Operative Technique Hong-Kwan Shin, M.D., Hee-Sung Lee, M.D., Young-Kuk Lee, M.D., Ki-Cheor Bae, M.D., Chul-Hyun Cho, M.D., and Kyung-Jae Lee, M.D. Abstract:
Popliteomeniscal Fascicle Tear: Diagnosis and Operative Technique Hong-Kwan Shin, M.D., Hee-Sung Lee, M.D., Young-Kuk Lee, M.D., Ki-Cheor Bae, M.D., Chul-Hyun Cho, M.D., and Kyung-Jae Lee, M.D. Abstract:
UNUSUAL ACL CASE: Tibial Eminence Fracture in a Female Collegiate Basketball Player
 UNUSUAL ACL CASE: Tibial Eminence Fracture in a Female Collegiate Basketball Player Cheri Drysdale, MEd,, ATC Margot Putukian,, MD Jeffery Bechler,, MD Princeton University How many of you have done an
UNUSUAL ACL CASE: Tibial Eminence Fracture in a Female Collegiate Basketball Player Cheri Drysdale, MEd,, ATC Margot Putukian,, MD Jeffery Bechler,, MD Princeton University How many of you have done an
The Knee. Prof. Oluwadiya Kehinde
 The Knee Prof. Oluwadiya Kehinde www.oluwadiya.sitesled.com The Knee: Introduction 3 bones: femur, tibia and patella 2 separate joints: tibiofemoral and patellofemoral. Function: i. Primarily a hinge joint,
The Knee Prof. Oluwadiya Kehinde www.oluwadiya.sitesled.com The Knee: Introduction 3 bones: femur, tibia and patella 2 separate joints: tibiofemoral and patellofemoral. Function: i. Primarily a hinge joint,
