Magnetic resonance imaging assessment of temporomandibular joint soft tissue injuries of intracapsular condylar fracture,
|
|
|
- Tyler Chapman
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Available online at British Journal of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery 51 (2013) Magnetic resonance imaging assessment of temporomandibular joint soft tissue injuries of intracapsular condylar fracture, Yao Hui Yu a, Mei Hao Wang b, Shan Yong Zhang c,, Yi Ming Fang a,, Xing Hao Zhu a, Lu Lu Pan a, Chi Yang c, a Department of Oral & Maxillofacial Surgery, The First Affiliated Hospital of WenZhou Medical College, People s Republic of China b Department of Radiology, The First Affiliated Hospital of WenZhou Medical College, People s Republic of China c Department of Oral & Maxillofacial Surgery, Ninth People s Hospital, School of Stomatology, Shanghai JiaoTong University, People s Republic of China Accepted 29 March 2012 Available online 4 May 2012 Abstract We evaluated the soft tissue of the temporomandibular joint (TMJ) with magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) after intracapsular condylar fracture. Eighteen consecutive patients (19 TMJ) were diagnosed between 1 January 2010 and 30 October They were examined using bilateral sagittal and coronal MRI, which were obtained immediately after injury to assess the displacement of the disc, whether there was a tear in capsule or the retrodiscal tissue, and whether there was an effusion in the joint. On the affected side MRI showed disc displacement in 15 of 19, tears in the capsule in 9, and tears in the retrodiscal tissue in 16. All 19 had joint effusions. It also showed 2 joints with abnormalities on the unaffected side. We conclude that MRI is useful for diagnosis and for estimating the amount of damage to the TMJ, and is helpful in planning treatment The British Association of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgeons. Published by Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved. Keywords: Condyle fracture; Temporomandibular joint; Magnetic resonance imaging This study was supported by a grant from the Zhejiang Province Science and Technology Fund Project (2010C33G ). This study was supported by the Grant of Shanghai Leading Academic Discipline Project (Project Number. S30206), Grant from the National Natural Science Foundation of Shanghai No. 10ZR and Grant from Shanghai Municipal Bureau of Health (Grant No ). Corresponding author at: Department of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery, Ninth People s Hospital, Collage of Stomatology, Shanghai Jiao Tong University School of Medicine; Shanghai Key Laboratory of Stomatology & Shanghai Research Institute of Stomatology, No. 639, Zhi Zao Ju Rd, Shanghai, People s Republic of China. Corresponding author at: The First Affiliated Hospital of WenZhou Medical College, No. 2, Fu Xue Xiang Rd, WenZhou, People s Republic of China. Corresponding author at: Department of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery, Ninth People s Hospital, Collage of Stomatology, Shanghai Jiao Tong University School of Medicine; Shanghai Key Laboratory of Stomatology & Shanghai Research Institute of Stomatology, No. 639, Zhi Zao Ju Rd, Shanghai, People s Republic of China. addresses: zhangshanyong@126.com (S.Y. Zhang), yuyaohui1985@126.com (Y.M. Fang), yangchi63@hotmail.com (C. Yang) /$ see front matter 2012 The British Association of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgeons. Published by Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
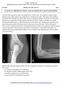
2 134 Y.H. Yu et al. / British Journal of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery 51 (2013) Introduction A fracture of the condyle of the temporomandibular joint (TMJ) has been described as the cause of severe changes in the soft tissue structures, and it can affect their functions. 1 Anatomical reduction has been beneficial for the biomechanical function of the TMJ, and reduces the number of complications of open surgery. 2 The degree and sites of soft tissue injuries as shown on MRI could provide detailed information when planning treatment. Several studies have characterised the damage to the soft tissues of the TMJ on MRI, including those to the disc, joint capsule, and retrodiscal tissues, and joint effusions, in patients with fractures of the condyle and subcondyle. 1 5 We know of only one study that has reported the MRI findings in the soft tissue structures of the TMJ after intracapsular condylar fracture, 2 and could find no paper that reported the extent of injury to the TMJ on the unaffected side. We have evaluated the soft tissue changes to the TMJ after intracapsular condylar fracture using MRI on the affected and unaffected sides. Patients and methods Patients Eighteen patients (19 TMJ) who visited the clinic at the First Affiliated Hospital of WenZhou Medical College, from 1 January 2010 to 30 October 2011 with unilateral or bilateral intracapsular condylar fractures that had been confirmed on computed tomography (CT) were examined by MRI. There were 11 men and 7 women (mean age 30 years, range 17 66). The right side was involved in 10 patients, the left in 7, and both sides in 1. Informed consent was obtained from all patients after we had explained the purpose of the scan. There were no contraindications. Inclusion criteria All 18 patients (19 TMJ) met the following inclusion criteria: a unilateral or bilateral intracapsular condylar fracture; no other fractures of the mandible or dentoalveolar injuries; the fracture had occurred within 3 14 days, 4 and the patient had no history of pain or dysfunction in the TMJ before the injury. The fractures were classified, based on the location of the fracture line. 6 Type A was a fracture with displacement of the medial parts of the condyle but maintaining vertical mandibular dimensions; type B affected the lateral condyle with reduction in mandibular height; and type M included high extracapsular fracture dislocations. Any patients who were pregnant, or had a pacemaker, cerebral aneurysm clips, metal implants, neurostimulators, hearing aids, or shrapnel, were excluded. MRI examination The TMJ were examined using a 1.5 T MR machine of Excite II supraconduction mode scanner (GE, USA). Both TMJ with the mouth both open and closed were examined with DUAL coil. The MRI scan followed this sequence: the transection plane was scanned to find the long axis of the condyle; the sagittal plane was then aligned perpendicular to this long axis, as the coronal plane paralleled the long axis. An oblique sagittal MRI was taken with T1-weighted image (WI) and diffusion (PD)-weighted image fast spin-echo (FSE) sequences. Oblique coronal MRI with T 1 and T 2 -weighted images and FSE sequences followed. The scanning variables of T 1 WI were FSE sequence: repetition time (TR), 440 ms; echo time (TE), 13.4/ef ms; number of excitations (NEX), 3. The variables of proton density weighted imaging (PDWI) were FSE sequence: TR, 2700 ms; TE, 13.4/ef ms; NEX, 3. The variables of T 2 WI were gradient echo (GRE) sequence: TR, 340 ms; TE, 15 ms; flip angle 20 ; NEX, 3. A slice of 2 mm in thickness with a skip of 0 mm, a matrix of pixels and field of view, 140 mm 140 mm were used. At least one of the investigators was present at all MRI to ensure that the quality of the images was good, and the subjects were instructed to keep the teeth in proper contact during the closed-mouth examinations. MRI evaluation The normal disc position was defined using the location of the posterior band of the disc at the superior (12 o clock) position relative to the top of the condyle in the glenoid fossa while in the closed-mouth position. 7 On the T1 and T2 weighted images, capsular tears in the TMJ and tears in the retrodiscal tissue were defined by the presence of a dotted, high-signal area. 5 The joint effusions were defined by a dotted, high-signal area on the diffusion weighted image, and the presence of a dotted, low-signal area on the T1 weighted image. 4 Haemarthrosis was defined by the presence of a dotted, high-signal area on the T1 and diffusion weighted images. 4 All MRI films were interpreted by a clinical specialist and a radiologist who were unaware of the clinical condition of the patient and who regularly evaluated injuries to the TMJ. Both judged the images separately and made similar evaluations. When they had different views, a third specialist evaluated the images. Results The 18 patients had 19 joints with intracapsular condylar fractures. Four joints were classified as type A fractures, 14 as type B fractures, and 1 as a type M fracture. Nineteen joints had the following soft tissue changes on MRI: disc displacement in 15/19 (Table 1), and the fractured condyle was also displaced in an anteroinferior direction (Fig. 1). Capsular tears were seen in 9/19 (Table 1), 6 of
3 Y.H. Yu et al. / British Journal of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery 51 (2013) Table 1 Findings on magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) of the temporomandibular joints with intracapsular condylar fractures. Data are number of patients. Findings on MRI No condylar fracture (n = 17) Disc displacement No 16 3 Yes 1 16 Capsule tear No Yes 9 Medial aspect 3 Lateral aspect 6 Retrodiscal tissue tear No 17 3 Yes 16 Joint effusion No 17 Joint effusion 19 Superior joint cavity 19 Inferior joint cavity 8 Haemarthrosis 16 Condylar injury No 16 Yes 1 19 Condylar fracture (n = 19) Fig. 2. T1 weighted coronal image showing the intracapsular condylar fracture, and the lateral side of the tear in the joint capsule (arrows). Fig. 1. Diffusion-weighted image showing that the fractured condyle (C) was displaced in an anteroinferior direction and an effusion (haemarthrosis) was present in both the superior and inferior joint cavities (arrows). The disc of the temporomandibular joint (D) was also displaced in the same direction as the fractured fragment. which were on the lateral side of the joint capsule and 3 on the medial side (Fig. 2). An MRI diagnosis of tears in the retrodiscal tissue was established in 16/19 TMJ (Table 1; Fig. 3). Joint effusion was a common finding in fractured TMJ, 8 of which were at the inferior joint cavity and 19 at the superior cavity (Table 1). Haemarthrosis was seen in 16/19 TMJ (Table 1; Fig. 1). TMJ with intracapsular condylar fractures showed signs of condylar injury on MRI in all (Table 1). Two joints had abnormal signs on non-affected sides, including 1 displaced disc and 1 condylar injury (Table 1; Fig. 4). Fig. 3. T1 weighted sagittal image showing that the fractured condyle (C) was displaced in an anteroinferior direction, and the tear in the retrodiscal tissue (arrows). Discussion On the basis of the classification, 6 4 were type A, 14 type B; and 1 type M. The intracapsular condylar fracture was caused by the external force to the condyle, the reaction of the joint nodules, the force from the lateral pterygoid muscle and the joint capsule and ligaments. We think that Neff s is the most popular method for diagnosis and classification of such fractures. 6 The amount of soft tissue injury around the TMJ in association with a condylar fracture is gradually being discussed in published papers. 1 5,7,8 Li et al. 8 acknowledged that damage to the disc and its attachment to the condylar head are
4 136 Y.H. Yu et al. / British Journal of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery 51 (2013) Fig. 4. T2 weighted coronal image showing strong signals (arrows) on the joint surface of the condylar process. important factors in the healing of condylar fractures. Zhang and He 9 and Laskin 10 discussed whether the displaced disc would play a critical part in early trauma-induced ankylosis of the TMJ. Chuong and Piper 11 reported a technique of open reduction of condylar fractures and stated that the TMJ disc was predictably dislocated, which emphasised that the disc should be simultaneously repositioned and repaired using microsurgical techniques. Takaku et al. 5 suggested that the disc should be correctly repositioned so that it could function, and repositioning of fragments to avoid malposition or malfunction of the disc from a contracture of the damaged capsule and retrodiscal tissue. We think, therefore, that the severity of damage to the disc, capsule, and retrodiscal tissue could be detected using MRI before treatment. It is beneficial in providing additional information and setting up a treatment regimen within the clinic. We have shown that the changes in TMJ soft tissue were mainly the result of disc displacements, joint effusions, abnormal retrodiscal tissues, and joint capsules. From an anatomical standpoint, the TMJ disc is between the glenoid fossa and the condyle, which can maintain the stability of the joint. The anterior or anteromedial displacement of the disc after injury to the TMJ has previously been reported. 1,5,10 Our results have shown 15 patients had displaced discs on MRI. The disc was located superiorly to the fragment of the condyle and was anteriorly and inferiorly displaced relative to the remaining condyle, 12 because the fragment was tightly pulled by the lateral pterygoid muscle. The capsular tear also had a critical role in the soft tissue injury of the TMJ. Gerhard et al. 13 reported that the capsular tear was found in 86% of all patients (type IV, V, or VI condylar fracture 14 ), and there was a important correlation between the degree of condylar injury and the capsular tear. Our study showed that only 9 of the intracapsular condylar fractures were associated with capsular tears seen on MRI. This is in accordance with results of other studies described by Takaku et al. 5 and Sullivan et al. 15 The lateral aspect of the capsule was affected more than the medial aspect. We thought that the force of the impact, traction from the lateral pterygoid muscle, and damage to the capsule by the bony spur, made it easier to tear the lateral capsule. These results correspond with the reports of other investigators who described tears in retrodiscal tissue as a common finding on MRI in patients with condylar injuries, the reported figures ranging from 39% to 74%. 2,5,15 Our figure was higher than that (16/19). The reported incidence of soft tissue injury to the TMJ varies among publications because different clinical and imaging criteria were used to diagnose such injuries. When the retrodiscal tissue was torn, the disc displaced more simply. There might be a parallel between severity of trauma and increased injury to the retrodiscal tissue. 1 Joint effusion after condylar fractures has been reported previously. 1,5,14,16 These authors suggested that an effusion into the TMJ was reflected by bleeding into the joint cavity caused by damage to capsule and retrodiscal tissue. 5 Takahashi et al. 16 thought that MRI evidence of joint effusion might serve as a marker for the detection of severe intra-articular damage to the TMJ after a condylar fracture. Gerhard et al. 13 reported that the finding of a significant relation between the degree of acute condylar injury and the MRI diagnosis of effusion could be compared with that of a previous report that the incidence of effusion in condylar fractures was significantly higher than when there was no condylar injury. Our results confirmed that joint effusions were present with most injuries to the TMJ, and haemarthrosis was found in 16 of 19. The superior joint cavity was affected in all cases, and the inferior in 8. This was similar to the previous report. 3 Most papers have ignored the condition of the unaffected side in unilateral condylar fractures of the TMJ before treatment, but we found that 2/19 had abnormal signs. We should therefore pay attention to the non-fractured sides when planning treatment and at follow-up for patients using MRI, to ascertain the problem early and treat it in a timely fashion. We conclude that MRI can detect the changes in the soft tissue of the TMJ that accompany intracapsular condylar fractures and may affect the non-fractured side, which is important in the planning of treatment. References 1. Wang P, Yang J, Yu Q. MR imaging assessment of temporomandibular joint soft tissue injuries in dislocated and nondislocated mandibular condylar fractures. American Journal of Neuroradiology 2009;30: Chen M, Yang C, He D, Zhang S, Jiang B. Soft tissue reduction during open treatment of intracapsular condylar fracture of the temporomandibular joint: our institution s experience. Journal of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery 2010;68:
5 Y.H. Yu et al. / British Journal of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery 51 (2013) Emshoff R, Rudisch A, Ennemoser T, Gerhard S. Magnetic resonance imaging findings of temporomandibular joint soft tissue changes in type V and VI condylar injuries. Journal of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery 2007;65: Jones JK, Van Sickels JE. A preliminary report of arthroscopic findings following acute condylar trauma. Journal of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery 1991;49: Takaku S, Yoshida M, Sano T, Toyoda T. Magnetic resonance images in patients with acute traumatic injury of the temporomandibular joint: a preliminary report. Journal of Cranio-Maxillo-Facial Surgery 1996;24: Hlawitschka M, Eckelt U. Assessment of patients treated for intracapsular fractures of the mandibular condyle by closed techniques. Journal of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery 2002;60: Drace JE, Enzmann DR. Defining the normal temporomandibular joint: closed-, partially open-, and open-mouth MR imaging of asymptomatic subjects. Radiology 1990;177: Li Z, Zhang W, Li ZB. The role of the disc in the healing of displaced subcondylar fracture in the growing period: an experimental study in rats. International Journal of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery 2010;39: Zhang Y, He DM. Clinical investigation of early post-traumatic temporomandibular joint ankylosis and the role of repositioning discs in treatment. International Journal of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery 2006;35: Laskin DM. Role of the meniscus in the enology of posttraumatic temporomandibular joint ankylosis. International Journal of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery 1978;7: Chuong R, Piper MA. Open reduction of condylar fractions of the mandible in conjunction with repair of discal injury: a preliminary report. Journal of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery 1988;46: Choi BH. Comparison of computed tomography imaging before and after functional treatment of bilateral condylar fractures in adults. International Journal of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery 1996;25: Gerhard S, Ennemoser T, Rudisch A, Emshoff R. Condylar injury: magnetic resonance imaging findings of temporomandibular joint softtissue changes. International Journal of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery 2007;36: Spiessl B, Schroll K. Classification of fractures of the condylar head and neck (in German). In: Nigst H, editor. Spezielle frakturen-und luxationslehre. Bd. I/II. Stuttgart: Thieme; p Sullivan S, Banghart PR, Anderson Q. Magnetic resonance imaging assessment of acute soft tissue injuries to the temporomandibular joint. Journal of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery 1995;53: Takahashi T, Ohtani M, Sano T, Ohnuki T, Kondoh T, Fukuda M. Magnetic resonance evidence of joint effusion of the temporomandibular joint after fractures of the mandibular condyle: a preliminary report. Cranio 2004;22:
The mandibular condyle fracture is a common mandibular
 ORIGINAL RESEARCH P. Wang J. Yang Q. Yu MR Imaging Assessment of Temporomandibular Joint Soft Tissue Injuries in Dislocated and Nondislocated Mandibular Condylar Fractures BACKGROUND AND PURPOSE: Evaluation
ORIGINAL RESEARCH P. Wang J. Yang Q. Yu MR Imaging Assessment of Temporomandibular Joint Soft Tissue Injuries in Dislocated and Nondislocated Mandibular Condylar Fractures BACKGROUND AND PURPOSE: Evaluation
Original Article Factors affecting the outcomes of non-surgical treatment for intracapsular condylar fractures
 Int J Clin Exp Med 2016;9(6):10847-10855 www.ijcem.com /ISSN:1940-5901/IJCEM0021362 Original Article Factors affecting the outcomes of non-surgical treatment for intracapsular condylar fractures Bao-Li
Int J Clin Exp Med 2016;9(6):10847-10855 www.ijcem.com /ISSN:1940-5901/IJCEM0021362 Original Article Factors affecting the outcomes of non-surgical treatment for intracapsular condylar fractures Bao-Li
Conventional radiograph verses CT for evaluation of sagittal fracture of mandibular condyle
 Case Report: Conventional radiograph verses CT for evaluation of sagittal fracture of mandibular condyle Dr Anjali Wadhwa, Dr Gaurav Shah, Dr Shweta Sharma, Dr Anand Bhatnagar, Dr Pallavi Malaviya NIMS
Case Report: Conventional radiograph verses CT for evaluation of sagittal fracture of mandibular condyle Dr Anjali Wadhwa, Dr Gaurav Shah, Dr Shweta Sharma, Dr Anand Bhatnagar, Dr Pallavi Malaviya NIMS
The Temporomandibular joint: Anatomy, Mechanics, Pathology. Aditya Bahel, DO
 The Temporomandibular joint: Anatomy, Mechanics, Pathology Aditya Bahel, DO Outline Anatomy Mechanics and function Indications for TMJ imaging MR Protocols and pitfalls Pathology Treatment options Anatomy
The Temporomandibular joint: Anatomy, Mechanics, Pathology Aditya Bahel, DO Outline Anatomy Mechanics and function Indications for TMJ imaging MR Protocols and pitfalls Pathology Treatment options Anatomy
Original Article Analysis of neurologic complications after modified temporomandibular joint disc anchorage surgery
 Int J Clin Exp Med 2017;10(3):5440-5444 www.ijcem.com /ISSN:1940-5901/IJCEM0041511 Original Article Analysis of neurologic complications after modified temporomandibular joint disc anchorage surgery Jin-Ze
Int J Clin Exp Med 2017;10(3):5440-5444 www.ijcem.com /ISSN:1940-5901/IJCEM0041511 Original Article Analysis of neurologic complications after modified temporomandibular joint disc anchorage surgery Jin-Ze
Anatomy and physiology of Temporomandibular Joint
 Anatomy and physiology of Temporomandibular Joint Temporomandibular joint (TMJ): It is the articulation of the condyle of the mandible, and the inter-articular disc; with the mandibular fossa (glenoid
Anatomy and physiology of Temporomandibular Joint Temporomandibular joint (TMJ): It is the articulation of the condyle of the mandible, and the inter-articular disc; with the mandibular fossa (glenoid
Journal of Cranio-Maxillo-Facial Surgery
 Journal of Cranio-Maxillo-Facial Surgery 42 (2014) 1078e1082 Contents lists available at SciVerse ScienceDirect Journal of Cranio-Maxillo-Facial Surgery journal homepage: www.jcmfs.com A retrospective
Journal of Cranio-Maxillo-Facial Surgery 42 (2014) 1078e1082 Contents lists available at SciVerse ScienceDirect Journal of Cranio-Maxillo-Facial Surgery journal homepage: www.jcmfs.com A retrospective
MRI imaging of the temporo-mandibular joint (TMJ) with regard to degeneration and disk displacement.
 MRI imaging of the temporo-mandibular joint (TMJ) with regard to degeneration and disk displacement. Poster No.: P-0023 Congress: ESSR 2015 Type: Educational Poster Authors: A. Hagenkord; Basel/CH Keywords:
MRI imaging of the temporo-mandibular joint (TMJ) with regard to degeneration and disk displacement. Poster No.: P-0023 Congress: ESSR 2015 Type: Educational Poster Authors: A. Hagenkord; Basel/CH Keywords:
FOR CMS (MEDICARE) MEMBERS ONLY NATIONAL COVERAGE DETERMINATION (NCD) FOR MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING:
 National Imaging Associates, Inc. Clinical guidelines TEMPOROMANDIBULAR JOINT (TMJ) MRI Original Date: May 23, 2003 Page 1 of 5 CPT Code: 70336 Last Review Date: May 2016 NCD 220.2 MRI Last Effective Date:
National Imaging Associates, Inc. Clinical guidelines TEMPOROMANDIBULAR JOINT (TMJ) MRI Original Date: May 23, 2003 Page 1 of 5 CPT Code: 70336 Last Review Date: May 2016 NCD 220.2 MRI Last Effective Date:
Temporomandibular Joint. Dr Noman ullah wazir
 Temporomandibular Joint Dr Noman ullah wazir Type of Joint TMJ is a Synovial joint between : The condylar head of the mandible. The mandibular fossa of squamous part of temporal bone. The joint cavity
Temporomandibular Joint Dr Noman ullah wazir Type of Joint TMJ is a Synovial joint between : The condylar head of the mandible. The mandibular fossa of squamous part of temporal bone. The joint cavity
CLINICAL PRESENTATION AND RADIOLOGY QUIZ QUESTION
 Donald L. Renfrew, MD Radiology Associates of the Fox Valley, 333 N. Commercial Street, Suite 100, Neenah, WI 54956 11/24/2012 Radiology Quiz of the Week # 100 Page 1 CLINICAL PRESENTATION AND RADIOLOGY
Donald L. Renfrew, MD Radiology Associates of the Fox Valley, 333 N. Commercial Street, Suite 100, Neenah, WI 54956 11/24/2012 Radiology Quiz of the Week # 100 Page 1 CLINICAL PRESENTATION AND RADIOLOGY
Neuroradiology MR Protocols
 Neuroradiology MR Protocols Brain protocols N 1: Brain MRI without contrast N 2: Pre- and post-contrast brain MRI N 3 is deleted N 4: Brain MRI without or pre-/post-contrast (seizure protocol) N 5: Pre-
Neuroradiology MR Protocols Brain protocols N 1: Brain MRI without contrast N 2: Pre- and post-contrast brain MRI N 3 is deleted N 4: Brain MRI without or pre-/post-contrast (seizure protocol) N 5: Pre-
Clinical Study Open Reduction of Subcondylar Fractures Using a New Retractor
 Plastic Surgery International Volume 2011, Article ID 421245, 5 pages doi:10.1155/2011/421245 Clinical Study Open Reduction of Subcondylar Fractures Using a New Retractor Akira Sugamata, 1 Naoki Yoshizawa,
Plastic Surgery International Volume 2011, Article ID 421245, 5 pages doi:10.1155/2011/421245 Clinical Study Open Reduction of Subcondylar Fractures Using a New Retractor Akira Sugamata, 1 Naoki Yoshizawa,
Meniscal Tears with Fragments Displaced: What you need to know.
 Meniscal Tears with Fragments Displaced: What you need to know. Poster No.: C-1339 Congress: ECR 2015 Type: Authors: Keywords: DOI: Educational Exhibit M. V. Ferrufino, A. Stroe, E. Cordoba, A. Dehesa,
Meniscal Tears with Fragments Displaced: What you need to know. Poster No.: C-1339 Congress: ECR 2015 Type: Authors: Keywords: DOI: Educational Exhibit M. V. Ferrufino, A. Stroe, E. Cordoba, A. Dehesa,
Modified Oblique Sagittal Magnetic Resonance Imaging of Rotator Cuff Tears: Comparison with Standard Oblique Sagittal Images
 Journal of Magnetics 22(3), 519-524 (2017) ISSN (Print) 1226-1750 ISSN (Online) 2233-6656 https://doi.org/10.4283/jmag.2017.22.3.519 Modified Oblique Sagittal Magnetic Resonance Imaging of Rotator Cuff
Journal of Magnetics 22(3), 519-524 (2017) ISSN (Print) 1226-1750 ISSN (Online) 2233-6656 https://doi.org/10.4283/jmag.2017.22.3.519 Modified Oblique Sagittal Magnetic Resonance Imaging of Rotator Cuff
This presentation is the intellectual property of the author. Contact them for permission to reprint and/or distribute.
 MRI of the Knee Jennifer Swart, M.D. Musculoskeletal Radiology South Texas Radiology Group Outline Coils, Patient Positioning Acquisition Parameters, Planes and Pulse Sequences Knee Arthrography Normal
MRI of the Knee Jennifer Swart, M.D. Musculoskeletal Radiology South Texas Radiology Group Outline Coils, Patient Positioning Acquisition Parameters, Planes and Pulse Sequences Knee Arthrography Normal
This presentation is the intellectual property of the author. Contact them at for permission to reprint and/or distribute.
 MRI of the Knee Jennifer Swart, M.D. Musculoskeletal Radiology South Texas Radiology Group Financial Disclosure Dr. Jennifer Swart has no relevant financial relationships with commercial interests to disclose.
MRI of the Knee Jennifer Swart, M.D. Musculoskeletal Radiology South Texas Radiology Group Financial Disclosure Dr. Jennifer Swart has no relevant financial relationships with commercial interests to disclose.
CLINICAL PRESENTATION AND RADIOLOGY QUIZ QUESTION
 Donald L. Renfrew, MD Radiology Associates of the Fox Valley, 333 N. Commercial Street, Suite 100, Neenah, WI 54956 10/6/2012 Radiology Quiz of the Week # 93 Page 1 CLINICAL PRESENTATION AND RADIOLOGY
Donald L. Renfrew, MD Radiology Associates of the Fox Valley, 333 N. Commercial Street, Suite 100, Neenah, WI 54956 10/6/2012 Radiology Quiz of the Week # 93 Page 1 CLINICAL PRESENTATION AND RADIOLOGY
EVALUATION OF LATERAL PTERYGOID MUSCLE IN TEMPOROMANDIBULAR DISORDER PATIENTS - A MRI STUDY. Part I
 EVALUATION OF LATERAL PTERYGOID MUSCLE IN TEMPOROMANDIBULAR DISORDER PATIENTS - A MRI STUDY Part I Authors : Dr. Amol S. Patil, BDS, MDS (ORTHODONTIA) Lecturer, Department of Orthodontics, Bharati Vidyapeeth
EVALUATION OF LATERAL PTERYGOID MUSCLE IN TEMPOROMANDIBULAR DISORDER PATIENTS - A MRI STUDY Part I Authors : Dr. Amol S. Patil, BDS, MDS (ORTHODONTIA) Lecturer, Department of Orthodontics, Bharati Vidyapeeth
Sensitivity and Specificity in Detection of Labral Tears with 3.0-T MRI of the Shoulder
 Magee and Williams MRI for Detection of Labral Tears Musculoskeletal Imaging Clinical Observations C M E D E N T U R I C L I M G I N G JR 2006; 187:1448 1452 0361 803X/06/1876 1448 merican Roentgen Ray
Magee and Williams MRI for Detection of Labral Tears Musculoskeletal Imaging Clinical Observations C M E D E N T U R I C L I M G I N G JR 2006; 187:1448 1452 0361 803X/06/1876 1448 merican Roentgen Ray
MRI of Bucket-Handle Te a rs of the Meniscus of the Knee 1
 MRI of ucket-handle Te a rs of the Meniscus of the Knee 1 Joon Yong Park, M.D., Young-uk Lee M.D., Eun-Chul Chung M.D., Hae-Won Park M.D., E u n - Kyung Youn M.D., Shin Ho Kook, M.D., Young Rae Lee, M.D.
MRI of ucket-handle Te a rs of the Meniscus of the Knee 1 Joon Yong Park, M.D., Young-uk Lee M.D., Eun-Chul Chung M.D., Hae-Won Park M.D., E u n - Kyung Youn M.D., Shin Ho Kook, M.D., Young Rae Lee, M.D.
Musculoskeletal MR Protocols
 Musculoskeletal MR Protocols Joint-based protocols MSK 1: Shoulder MRI MSK 1A: Shoulder MR arthrogram MSK 1AB: Shoulder MR arthrogram (instability protocol) MSK 2: Elbow MRI MSK 2A: Elbow MR arthrogram
Musculoskeletal MR Protocols Joint-based protocols MSK 1: Shoulder MRI MSK 1A: Shoulder MR arthrogram MSK 1AB: Shoulder MR arthrogram (instability protocol) MSK 2: Elbow MRI MSK 2A: Elbow MR arthrogram
NEURO PROTOCOLS MRI NEURO PROTOCOLS (SIEMENS SCANNERS)
 Page 1 NEURO PROTOCOLS Brain Stroke Brain Brain with contrast Brain for seizures Brain for MS Brain for Pineal gland Sella FAST Scan for hydrocephalus MRA/MRV Brain MRA carotids 8 th nerve Cranial nerves
Page 1 NEURO PROTOCOLS Brain Stroke Brain Brain with contrast Brain for seizures Brain for MS Brain for Pineal gland Sella FAST Scan for hydrocephalus MRA/MRV Brain MRA carotids 8 th nerve Cranial nerves
The Skull and Temporomandibular joint II Prof. Abdulameer Al-Nuaimi. E. mail:
 The Skull and Temporomandibular joint II Prof. Abdulameer Al-Nuaimi E-mail: a.al-nuaimi@sheffield.ac.uk E. mail: abdulameerh@yahoo.com Temporal fossa The temporal fossa is a depression on the temporal
The Skull and Temporomandibular joint II Prof. Abdulameer Al-Nuaimi E-mail: a.al-nuaimi@sheffield.ac.uk E. mail: abdulameerh@yahoo.com Temporal fossa The temporal fossa is a depression on the temporal
JMSCR Vol 05 Issue 01 Page January
 www.jmscr.igmpublication.org Impact Factor 5.244 Index Copernicus Value: 83.27 ISSN (e)-2347-176x ISSN (p) 2455-0450 DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.18535/jmscr/v5i1.28 Diagnostic Accuracy of Magnetic Resonance
www.jmscr.igmpublication.org Impact Factor 5.244 Index Copernicus Value: 83.27 ISSN (e)-2347-176x ISSN (p) 2455-0450 DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.18535/jmscr/v5i1.28 Diagnostic Accuracy of Magnetic Resonance
Imaging the Temporomandibular Joint in Pediatric Pa6ents
 Imaging the Temporomandibular Joint in Pediatric Pa6ents Arthur B. Meyers, MD Children s Hospital of Wisconsin/ Medical College of Wisconsin, Department of Radiology TMJ Pathology in Pediatrics Juvenile
Imaging the Temporomandibular Joint in Pediatric Pa6ents Arthur B. Meyers, MD Children s Hospital of Wisconsin/ Medical College of Wisconsin, Department of Radiology TMJ Pathology in Pediatrics Juvenile
Relationship between pain and effusion on magnetic resonance imaging in temporomandibular disorder patients
 Imaging Science in Dentistry 2014; 44: 293-9 http://dx.doi.org/10.5624/isd.2014.44.4.293 Relationship between pain and effusion on magnetic resonance imaging in temporomandibular disorder patients Ha-Na
Imaging Science in Dentistry 2014; 44: 293-9 http://dx.doi.org/10.5624/isd.2014.44.4.293 Relationship between pain and effusion on magnetic resonance imaging in temporomandibular disorder patients Ha-Na
Disk Displacement of the Temporomandibular Joint: Sonography Versus MR Imaging
 Rüdiger Emshoff 1 Siegfried Jank 1 Stefan Bertram 1 Ansgar Rudisch 2 Gerd Bodner 2 Received July 3, 2001; accepted after revision December 17, 2001. 1 Department of Oral and Maxillo-Facial Surgery, University
Rüdiger Emshoff 1 Siegfried Jank 1 Stefan Bertram 1 Ansgar Rudisch 2 Gerd Bodner 2 Received July 3, 2001; accepted after revision December 17, 2001. 1 Department of Oral and Maxillo-Facial Surgery, University
RECENT ADVANCES IN CLINICAL MR OF ARTICULAR CARTILAGE
 In Practice RECENT ADVANCES IN CLINICAL MR OF ARTICULAR CARTILAGE By Atsuya Watanabe, MD, PhD, Director, Advanced Diagnostic Imaging Center and Associate Professor, Department of Orthopedic Surgery, Teikyo
In Practice RECENT ADVANCES IN CLINICAL MR OF ARTICULAR CARTILAGE By Atsuya Watanabe, MD, PhD, Director, Advanced Diagnostic Imaging Center and Associate Professor, Department of Orthopedic Surgery, Teikyo
MRI evaluation of TMJ condylar angulations
 MRI evaluation of TMJ condylar angulations Poster No.: C-2272 Congress: ECR 2010 Type: Topic: Authors: Keywords: DOI: Scientific Exhibit Musculoskeletal M. Pregarz 1, C. Bodin 2 ; 1 Peschiera del Garda/IT,
MRI evaluation of TMJ condylar angulations Poster No.: C-2272 Congress: ECR 2010 Type: Topic: Authors: Keywords: DOI: Scientific Exhibit Musculoskeletal M. Pregarz 1, C. Bodin 2 ; 1 Peschiera del Garda/IT,
Temporomandibular Joint
 6 Temporomandibular Joint Most human bones are joined with one another. These connections of bones to each other are termed articulations or joints. Some joints are immovable as in the articulations of
6 Temporomandibular Joint Most human bones are joined with one another. These connections of bones to each other are termed articulations or joints. Some joints are immovable as in the articulations of
Role of magnetic resonance imaging in the evaluation of traumatic knee joint injuries
 Original Research Article Role of magnetic resonance imaging in the evaluation of traumatic knee joint injuries Dudhe Mahesh 1*, Rathi Varsha 2 1 Resident, 2 Professor, Department of Radio-Diagnosis, Grant
Original Research Article Role of magnetic resonance imaging in the evaluation of traumatic knee joint injuries Dudhe Mahesh 1*, Rathi Varsha 2 1 Resident, 2 Professor, Department of Radio-Diagnosis, Grant
Anterior shoulder instability: Evaluation using MR arthrography.
 Anterior shoulder instability: Evaluation using MR arthrography. Poster No.: C-2407 Congress: ECR 2016 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: C. Lord, I. Katsimilis, N. Purohit, V. T. Skiadas; Southampton/UK
Anterior shoulder instability: Evaluation using MR arthrography. Poster No.: C-2407 Congress: ECR 2016 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: C. Lord, I. Katsimilis, N. Purohit, V. T. Skiadas; Southampton/UK
Oral & Maxillofacial Surgery
 Chapter 2 Oral & Maxillofacial Surgery Ruchi Singhal 1 ; Virendra Singh 2 ; Amrish Bhagol* 1 Jaipur Dental College, Jaipur, India 2 Senior Professor, PGIDS, Rohtak, India Amrish Bhagol Condylar Fractures
Chapter 2 Oral & Maxillofacial Surgery Ruchi Singhal 1 ; Virendra Singh 2 ; Amrish Bhagol* 1 Jaipur Dental College, Jaipur, India 2 Senior Professor, PGIDS, Rohtak, India Amrish Bhagol Condylar Fractures
Post Traumatic Changes in TMJ Structure after unilateral Mandibular Fracture a Longitudinal MRI Study
 ORIGINAL RESEARCH www.ijcmr.com after unilateral Mandibular Fracture a Longitudinal MRI Study V. Senthilvelmurugan 1, U. Punitha Gnana Selvi 2, S. Rekha 3, P Nilofar Fathima 3 ABSTRACT Introduction: The
ORIGINAL RESEARCH www.ijcmr.com after unilateral Mandibular Fracture a Longitudinal MRI Study V. Senthilvelmurugan 1, U. Punitha Gnana Selvi 2, S. Rekha 3, P Nilofar Fathima 3 ABSTRACT Introduction: The
Post-graduate Student, Department of Oral and Maxillofacial Radiology, School of Dentistry, Isfahan University of Medical Sciences, Isfahan, Iran
 Journal section: Oral Surgery Publication Types: Research doi:10.4317/jced.53824 http://dx.doi.org/10.4317/jced.53824 Evaluation of orthognathic surgery on articular disc position and temporomandibular
Journal section: Oral Surgery Publication Types: Research doi:10.4317/jced.53824 http://dx.doi.org/10.4317/jced.53824 Evaluation of orthognathic surgery on articular disc position and temporomandibular
Navigation-Guided Lateral Gap Arthroplasty as the Treatment of Temporomandibular Joint Ankylosis
 CRANIOMAXILLOFACIAL DEFORMITIES/COSMETIC SURGERY Navigation-Guided Lateral Gap Arthroplasty as the Treatment of Temporomandibular Joint Ankylosis Haijun Gui, MD, DDS,* Jinyang Wu, DDS,y Steve G. F. Shen,
CRANIOMAXILLOFACIAL DEFORMITIES/COSMETIC SURGERY Navigation-Guided Lateral Gap Arthroplasty as the Treatment of Temporomandibular Joint Ankylosis Haijun Gui, MD, DDS,* Jinyang Wu, DDS,y Steve G. F. Shen,
Introduction to Occlusion and Mechanics of Mandibular Movement
 Introduction to Occlusion and Mechanics of Mandibular Movement Dr. Pauline Hayes Garrett Department of Endodontics, Prosthodontics, and Operative Dentistry University of Maryland, Baltimore Assigned reading
Introduction to Occlusion and Mechanics of Mandibular Movement Dr. Pauline Hayes Garrett Department of Endodontics, Prosthodontics, and Operative Dentistry University of Maryland, Baltimore Assigned reading
Meniscus T2 Relaxation Time at Various Stages of Knee Joint Degeneration
 Meniscus T2 Relaxation Time at Various Stages of Knee Joint Degeneration Richard Kijowski, Michael Fazio, Benjamin Beduhn, and Fang Liu Department of Radiology University of Wisconsin School of Medicine
Meniscus T2 Relaxation Time at Various Stages of Knee Joint Degeneration Richard Kijowski, Michael Fazio, Benjamin Beduhn, and Fang Liu Department of Radiology University of Wisconsin School of Medicine
KNEE ALIGNMENT SYSTEM (KAS) MRI Protocol
 KNEE ALIGNMENT SYSTEM (KAS) MRI Protocol Sample referral sticker Referral Sticker Insert here Corin 17 Bridge Street Pymble NSW Australia 2073 P: +61 (0)2 9497 7400 F: +61 (0)2 9497 7498 E: KAS.customerservice@coringroup.com
KNEE ALIGNMENT SYSTEM (KAS) MRI Protocol Sample referral sticker Referral Sticker Insert here Corin 17 Bridge Street Pymble NSW Australia 2073 P: +61 (0)2 9497 7400 F: +61 (0)2 9497 7498 E: KAS.customerservice@coringroup.com
Temporal region. temporal & infratemporal fossae. Zhou Hong Ying Dept. of Anatomy
 Temporal region temporal & infratemporal fossae Zhou Hong Ying Dept. of Anatomy Temporal region is divided by zygomatic arch into temporal & infratemporal fossae. Temporal Fossa Infratemporal fossa Temporal
Temporal region temporal & infratemporal fossae Zhou Hong Ying Dept. of Anatomy Temporal region is divided by zygomatic arch into temporal & infratemporal fossae. Temporal Fossa Infratemporal fossa Temporal
Muscles of mastication [part 1]
![Muscles of mastication [part 1] Muscles of mastication [part 1]](/thumbs/76/73586850.jpg) Muscles of mastication [part 1] In this lecture well have the muscles of mastication, neuromuscular function, and its relationship to the occlusion morphology. The fourth determinant of occlusion is the
Muscles of mastication [part 1] In this lecture well have the muscles of mastication, neuromuscular function, and its relationship to the occlusion morphology. The fourth determinant of occlusion is the
MRI of the Knee: Part 2 - menisci. Mark Anderson, M.D. University of Virginia Health System
 MRI of the Knee: Part 2 - menisci Mark Anderson, M.D. University of Virginia Health System Learning Objectives At the end of the presentation, each participant should be able to: describe the normal anatomy
MRI of the Knee: Part 2 - menisci Mark Anderson, M.D. University of Virginia Health System Learning Objectives At the end of the presentation, each participant should be able to: describe the normal anatomy
Orthopedic Hardware Imaging Part II: MRI v. Metal
 Orthopedic Hardware Imaging Trent Roth, MD And Lauren Ladd, MD Indiana University School of Medicine IU Health Physicians-Radiology Recap: Imaging Techniques Radiography Standard for initial and surveillance
Orthopedic Hardware Imaging Trent Roth, MD And Lauren Ladd, MD Indiana University School of Medicine IU Health Physicians-Radiology Recap: Imaging Techniques Radiography Standard for initial and surveillance
MRI of the Shoulder What to look for and how to find it? Dr. Eric Handley Musculoskeletal Radiologist Cherry Creek Imaging
 MRI of the Shoulder What to look for and how to find it? Dr. Eric Handley Musculoskeletal Radiologist Cherry Creek Imaging MRI of the Shoulder Benefits of Ultrasound: * Dynamic * Interactive real time
MRI of the Shoulder What to look for and how to find it? Dr. Eric Handley Musculoskeletal Radiologist Cherry Creek Imaging MRI of the Shoulder Benefits of Ultrasound: * Dynamic * Interactive real time
Why Talk About Technique? MRI of the Knee:
 Why Talk About Technique? MRI of the Knee: Part 1 - Imaging Techniques Mark Anderson, M.D. University of Virginia Health Sciences Center Charlottesville, Virginia Always had an interest teach our fellows
Why Talk About Technique? MRI of the Knee: Part 1 - Imaging Techniques Mark Anderson, M.D. University of Virginia Health Sciences Center Charlottesville, Virginia Always had an interest teach our fellows
The future of health is digital
 Dated: XX/XX/XXXX Name: XXXXXXXX XXXXXXXXXXX Birth Date: XX/XX/XXXX Date of scan: XX/XX/XXXX Examination of the anatomical volume: The following structures are reviewed and evaluated for bilateral symmetry,
Dated: XX/XX/XXXX Name: XXXXXXXX XXXXXXXXXXX Birth Date: XX/XX/XXXX Date of scan: XX/XX/XXXX Examination of the anatomical volume: The following structures are reviewed and evaluated for bilateral symmetry,
Imaging of Cervical Spine Trauma Tudor H Hughes, M.D.
 Imaging of Cervical Spine Trauma Tudor H Hughes, M.D. General Considerations Most spinal fractures are due to a single episode of major trauma. Fatigue fractures of the spine are unusual except in the
Imaging of Cervical Spine Trauma Tudor H Hughes, M.D. General Considerations Most spinal fractures are due to a single episode of major trauma. Fatigue fractures of the spine are unusual except in the
FieldStrength. Achieva 3.0T enables cutting-edge applications, best-in-class MSK images
 FieldStrength Publication for the Philips MRI Community Issue 33 December 2007 Achieva 3.0T enables cutting-edge applications, best-in-class MSK images Palo Alto Medical Clinic Sports Medicine Center employs
FieldStrength Publication for the Philips MRI Community Issue 33 December 2007 Achieva 3.0T enables cutting-edge applications, best-in-class MSK images Palo Alto Medical Clinic Sports Medicine Center employs
Original. Mamiko FUJIKURA 1, Keiichi NISHIKAWA 2 and Kazuyuki ARAKI 3
 Showa Univ J Med Sci 29 4, 415 423, December 2017 Original Magnetic Resonance Imaging Signal Intensities of the Temporomandibular Joint Articular Disc and Cortical Bone : Are These Measurements Valid for
Showa Univ J Med Sci 29 4, 415 423, December 2017 Original Magnetic Resonance Imaging Signal Intensities of the Temporomandibular Joint Articular Disc and Cortical Bone : Are These Measurements Valid for
Occlusion in complete denture
 Occlusion in complete denture Occlusion is a concept that is pertinent to all dental patients wheather they have their own teeth or not.it is a term used to describe the contact relationship between the
Occlusion in complete denture Occlusion is a concept that is pertinent to all dental patients wheather they have their own teeth or not.it is a term used to describe the contact relationship between the
Evaluation of Temporomandibular Joint Disk Displacement in Asymptomatic Volunteers Using Magnetic Resonance Imaging
 Int J Oral-Med Sci 14(1):21-27, 2015 21 Original Article Evaluation of Temporomandibular Joint Disk Displacement in Asymptomatic Volunteers Using Magnetic Resonance Imaging Takashi Uchida, 1,4 Osamu Komiyama,
Int J Oral-Med Sci 14(1):21-27, 2015 21 Original Article Evaluation of Temporomandibular Joint Disk Displacement in Asymptomatic Volunteers Using Magnetic Resonance Imaging Takashi Uchida, 1,4 Osamu Komiyama,
KEY WORDS: Disc Displacement; Effusion; Temporomandibular Joint; Magnetic Resonance Imaging
 Imaging Science in Dentistry 2013; 43: 245-51 http://dx.doi.org/10.5624/isd.2013.43.4.245 Relationship between anterior disc displacement with/without reduction and effusion in temporomandibular disorder
Imaging Science in Dentistry 2013; 43: 245-51 http://dx.doi.org/10.5624/isd.2013.43.4.245 Relationship between anterior disc displacement with/without reduction and effusion in temporomandibular disorder
CLINICAL PRESENTATION AND RADIOLOGY QUIZ QUESTION
 Donald L. Renfrew, MD Radiology Associates of the Fox Valley, 333 N. Commercial Street, Suite 100, Neenah, WI 54956 12/01/2012 Radiology Quiz of the Week # 101 Page 1 CLINICAL PRESENTATION AND RADIOLOGY
Donald L. Renfrew, MD Radiology Associates of the Fox Valley, 333 N. Commercial Street, Suite 100, Neenah, WI 54956 12/01/2012 Radiology Quiz of the Week # 101 Page 1 CLINICAL PRESENTATION AND RADIOLOGY
Comprehensive AOCMF Classification System. Cornelius CP, Kunz C, Prein J, Audigé L. Mandibular fractures Level-3 system (cases 22 to 33)
 Comprehensive AOCMF Classification System Cornelius CP, Kunz C, Prein J, Audigé L Mandibular fractures Level-3 system (cases 22 to 33) Case 22: Alvelolar process fracture Imaging: axial CT scan & 3D CT
Comprehensive AOCMF Classification System Cornelius CP, Kunz C, Prein J, Audigé L Mandibular fractures Level-3 system (cases 22 to 33) Case 22: Alvelolar process fracture Imaging: axial CT scan & 3D CT
Post-injury painful and locked knee
 H R J Post-injury painful and locked knee, p. 54-59 Clinical Case - Test Yourself Musculoskeletal Imaging Post-injury painful and locked knee Ioannis I. Daskalakis 1, 2, Apostolos H. Karantanas 1, 2 1
H R J Post-injury painful and locked knee, p. 54-59 Clinical Case - Test Yourself Musculoskeletal Imaging Post-injury painful and locked knee Ioannis I. Daskalakis 1, 2, Apostolos H. Karantanas 1, 2 1
Clinical details: Details of scan: CONE BEAM CT REPORT: Name: H. B. Gender: Reason for referral: Referred by:
 Name: H. B. Gender: Male DOB: 11/12/1950 Age: 64 Date taken: 16/11/2015 Date reported: 19/11/2015 Clinical details: Reason for referral: Referred by: Investigate symptoms related to left TMJ. Reconstructed
Name: H. B. Gender: Male DOB: 11/12/1950 Age: 64 Date taken: 16/11/2015 Date reported: 19/11/2015 Clinical details: Reason for referral: Referred by: Investigate symptoms related to left TMJ. Reconstructed
CLINICAL PRESENTATION AND RADIOLOGY QUIZ QUESTION
 Donald L. Renfrew, MD Radiology Associates of the Fox Valley, 333 N. Commercial Street, Suite 100, Neenah, WI 54956 10/13/2012 Radiology Quiz of the Week # 94 Page 1 CLINICAL PRESENTATION AND RADIOLOGY
Donald L. Renfrew, MD Radiology Associates of the Fox Valley, 333 N. Commercial Street, Suite 100, Neenah, WI 54956 10/13/2012 Radiology Quiz of the Week # 94 Page 1 CLINICAL PRESENTATION AND RADIOLOGY
External Distal Radius Fixator. Supplement to the 8 mm rod fixator system
 External Distal Radius Fixator. Supplement to the 8 mm rod fixator system Surgical technique This publication is not intended for distribution in the USA. Instruments and implants approved by the AO Foundation
External Distal Radius Fixator. Supplement to the 8 mm rod fixator system Surgical technique This publication is not intended for distribution in the USA. Instruments and implants approved by the AO Foundation
Original Report. The Reverse Segond Fracture: Association with a Tear of the Posterior Cruciate Ligament and Medial Meniscus
 Eva M. Escobedo 1 William J. Mills 2 John. Hunter 1 Received July 10, 2001; accepted after revision October 1, 2001. 1 Department of Radiology, University of Washington Harborview Medical enter, 325 Ninth
Eva M. Escobedo 1 William J. Mills 2 John. Hunter 1 Received July 10, 2001; accepted after revision October 1, 2001. 1 Department of Radiology, University of Washington Harborview Medical enter, 325 Ninth
 www.oralradiologists.com CONE BEAM CT REPORT CASE XXXX Patient information Patient Name: - Referring Doctor: - Patient DOB: - Scan Date: [Start date] Reason for Exam: Maxillary facial pain Doctor Notes:
www.oralradiologists.com CONE BEAM CT REPORT CASE XXXX Patient information Patient Name: - Referring Doctor: - Patient DOB: - Scan Date: [Start date] Reason for Exam: Maxillary facial pain Doctor Notes:
SURGICAL AND APPLIED ANATOMY
 Página 1 de 6 Copyright 2001 Lippincott Williams & Wilkins Bucholz, Robert W., Heckman, James D. Rockwood & Green's Fractures in Adults, 5th Edition SURGICAL AND APPLIED ANATOMY Part of "37 - HIP DISLOCATIONS
Página 1 de 6 Copyright 2001 Lippincott Williams & Wilkins Bucholz, Robert W., Heckman, James D. Rockwood & Green's Fractures in Adults, 5th Edition SURGICAL AND APPLIED ANATOMY Part of "37 - HIP DISLOCATIONS
Orthopaedic and Spine Institute 21 Spurs Lane, Suite 245, San Antonio, TX Tel#
 Orthopaedic and Spine Institute 21 Spurs Lane, Suite 245, San Antonio, TX 78240 www.saspine.com Tel# 210-487-7463 PATIENT GUIDE TO SHOULDER INSTABILITY LABRAL (BANKART) REPAIR / CAPSULAR SHIFT WHAT IS
Orthopaedic and Spine Institute 21 Spurs Lane, Suite 245, San Antonio, TX 78240 www.saspine.com Tel# 210-487-7463 PATIENT GUIDE TO SHOULDER INSTABILITY LABRAL (BANKART) REPAIR / CAPSULAR SHIFT WHAT IS
Imaging the musculoskeletal system. An Introduction
 Imaging the musculoskeletal system An Introduction Objectives Discuss: commonly used imaging modalities in the musculoskeletal system normal imaging anatomy in the extremities fracture description Imaging
Imaging the musculoskeletal system An Introduction Objectives Discuss: commonly used imaging modalities in the musculoskeletal system normal imaging anatomy in the extremities fracture description Imaging
Magnetic Resonance Angiography
 Magnetic Resonance Angiography 1 Magnetic Resonance Angiography exploits flow enhancement of GR sequences saturation of venous flow allows arterial visualization saturation of arterial flow allows venous
Magnetic Resonance Angiography 1 Magnetic Resonance Angiography exploits flow enhancement of GR sequences saturation of venous flow allows arterial visualization saturation of arterial flow allows venous
Tissue-engineered medical products Evaluation of anisotropic structure of articular cartilage using DT (Diffusion Tensor)-MR Imaging
 Provläsningsexemplar / Preview TECHNICAL REPORT ISO/TR 16379 First edition 2014-03-01 Tissue-engineered medical products Evaluation of anisotropic structure of articular cartilage using DT (Diffusion Tensor)-MR
Provläsningsexemplar / Preview TECHNICAL REPORT ISO/TR 16379 First edition 2014-03-01 Tissue-engineered medical products Evaluation of anisotropic structure of articular cartilage using DT (Diffusion Tensor)-MR
Shoulder Instability
 J F de Beer, K van Rooyen, D Bhatia Shoulder Instability INSTABILITY means that the shoulder dislocates completely (dislocation) or partially (subluxation). Anatomy The shoulder consists of a ball (humeral
J F de Beer, K van Rooyen, D Bhatia Shoulder Instability INSTABILITY means that the shoulder dislocates completely (dislocation) or partially (subluxation). Anatomy The shoulder consists of a ball (humeral
Use of Modified Retro-mandibular subparotid approach for treatment of Condylar fracture: a Technical note
 Original article: Use of Modified Retro-mandibular subparotid approach for treatment of Condylar fracture: a Technical note 1 DR.Sonal Anchlia, 2 DR.BIPIN.S.SADHWANI, 3 DR.ROHIT KUMAR, 4 Dr.Vipul 1Assistant
Original article: Use of Modified Retro-mandibular subparotid approach for treatment of Condylar fracture: a Technical note 1 DR.Sonal Anchlia, 2 DR.BIPIN.S.SADHWANI, 3 DR.ROHIT KUMAR, 4 Dr.Vipul 1Assistant
The examination of the temporomandibular joint on 1,5T magnetic resonance
 Prague Medical Report / Vol. 105 (2004) No. 1, p. 29 34 29) The examination of the temporomandibular joint on 1,5T magnetic resonance Peterová V. 1, Jirman R. 2, Mazánek J. 2, Seidl Z. 1 1 MR Department,
Prague Medical Report / Vol. 105 (2004) No. 1, p. 29 34 29) The examination of the temporomandibular joint on 1,5T magnetic resonance Peterová V. 1, Jirman R. 2, Mazánek J. 2, Seidl Z. 1 1 MR Department,
Patient ID. Case Conference. Physical Examination. Image examination. Treatment 2011/6/16
 Patient ID Case Conference R3 高逢駿 VS 徐郭堯 55 y/o female C.C.: recurrent right shoulder dislocation noted since falling down injury 2 years ago Came to ER because of dislocation for many times due to minor
Patient ID Case Conference R3 高逢駿 VS 徐郭堯 55 y/o female C.C.: recurrent right shoulder dislocation noted since falling down injury 2 years ago Came to ER because of dislocation for many times due to minor
and K n e e J o i n t Is the most complicated joint in the body!!!!
 K n e e J o i n t K n e e J o i n t Is the most complicated joint in the body!!!! 1-Consists of two condylar joints between: A-The medial and lateral condyles of the femur and The condyles of the tibia
K n e e J o i n t K n e e J o i n t Is the most complicated joint in the body!!!! 1-Consists of two condylar joints between: A-The medial and lateral condyles of the femur and The condyles of the tibia
CAN SOFT TISSUES STRUCTURES DIFFERENTIATE BETWEEN DYSPLASIA AND CAM-FAI OF THE HIP?
 CAN SOFT TISSUES STRUCTURES DIFFERENTIATE BETWEEN DYSPLASIA AND CAM-FAI OF THE HIP? A Le Bouthillier, KS Rakhra 1, PE Beaulé 2, RCB Foster 1 1 Department of Medical Imaging 2 Division of Orthopaedic Surgery
CAN SOFT TISSUES STRUCTURES DIFFERENTIATE BETWEEN DYSPLASIA AND CAM-FAI OF THE HIP? A Le Bouthillier, KS Rakhra 1, PE Beaulé 2, RCB Foster 1 1 Department of Medical Imaging 2 Division of Orthopaedic Surgery
Blair Radiology Exam Examination Packet
 Blair Radiology Exam Examination Packet This packet is made of up five sections: Examiner s Instructions, Applicant Requirements, Analysis Rubric, Overall Result and Comments and Exam Form. The Exam Form
Blair Radiology Exam Examination Packet This packet is made of up five sections: Examiner s Instructions, Applicant Requirements, Analysis Rubric, Overall Result and Comments and Exam Form. The Exam Form
TEMPORO-MANDIBULAR JOINT DISORDERS
 Disclaimer This movie is an educational resource only and should not be used to manage your dental health. All decisions about the management of TMJ Disorders must be made in conjunction with your Dental
Disclaimer This movie is an educational resource only and should not be used to manage your dental health. All decisions about the management of TMJ Disorders must be made in conjunction with your Dental
Certification Review. Module 28. Medical Coding. Radiology
 Module 28 is the study of x-rays, using radiant energy and other imaging techniques, such as resonance imaging or ultrasound, to diagnose illnesses and diseases. Vocabulary Barium enema (BE): lower gastrointestinal
Module 28 is the study of x-rays, using radiant energy and other imaging techniques, such as resonance imaging or ultrasound, to diagnose illnesses and diseases. Vocabulary Barium enema (BE): lower gastrointestinal
Arthroscopy / MRI Correlation Conference. Department of Radiology, Section of MSK Imaging Department of Orthopedic Surgery 7/19/16
 Arthroscopy / MRI Correlation Conference Department of Radiology, Section of MSK Imaging Department of Orthopedic Surgery 7/19/16 Case 1: 29 YOM with recurrent shoulder dislocations Glenoid Axial T1FS
Arthroscopy / MRI Correlation Conference Department of Radiology, Section of MSK Imaging Department of Orthopedic Surgery 7/19/16 Case 1: 29 YOM with recurrent shoulder dislocations Glenoid Axial T1FS
Temporomandibular Joint Clicking Noises Caused by a Multilocular Bone Cyst: A Case Report
 Temporomandibular Joint Clicking Noises Caused by a Multilocular Bone Cyst: A Case Report Abstract When diagnosing patients with temporomandibular disorder (TMD) symptoms, the possibility of unusual causes
Temporomandibular Joint Clicking Noises Caused by a Multilocular Bone Cyst: A Case Report Abstract When diagnosing patients with temporomandibular disorder (TMD) symptoms, the possibility of unusual causes
ULTRASOUND EVALUATION OF NORMAL AND ABNORMAL POSTERIOR CRUCIATE LIGAMENT - A PROSPECTIVE STUDY
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE ULTRASOUND EVALUATION OF NORMAL AND ABNORMAL POSTERIOR CRUCIATE LIGAMENT - A PROSPECTIVE STUDY Palle Lalitha, 1 M. Ch. Balaji Reddy, 1 K. Jagannath Reddy, 1 Vijaya Kumari 2 1 Department
ORIGINAL ARTICLE ULTRASOUND EVALUATION OF NORMAL AND ABNORMAL POSTERIOR CRUCIATE LIGAMENT - A PROSPECTIVE STUDY Palle Lalitha, 1 M. Ch. Balaji Reddy, 1 K. Jagannath Reddy, 1 Vijaya Kumari 2 1 Department
Posterior longitudinal ligament status in cervical spine bilateral facet dislocations
 Thomas Jefferson University Jefferson Digital Commons Department of Orthopaedic Surgery Faculty Papers Department of Orthopaedic Surgery November 2005 Posterior longitudinal ligament status in cervical
Thomas Jefferson University Jefferson Digital Commons Department of Orthopaedic Surgery Faculty Papers Department of Orthopaedic Surgery November 2005 Posterior longitudinal ligament status in cervical
Application of cone-beam computed tomography (CBCT) for diagnosis and management of mandibular condyle fractures
 Original Article Acharya et.al. for diagnosis and management of mandibular condyle fractures P Acharya 1, G Ren 2, MR Jaisani 1, A Dongol 1, RP Yadav 1, AK Mahat 1, F Dong 1 Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery
Original Article Acharya et.al. for diagnosis and management of mandibular condyle fractures P Acharya 1, G Ren 2, MR Jaisani 1, A Dongol 1, RP Yadav 1, AK Mahat 1, F Dong 1 Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery
Case Report. Orthognathic Correction of Class II Open Bite. Using the Piezoelectric System and MatrixORTHOGNATHIC Plating System.
 Case Report Orthognathic Correction of Class II Open Bite. Using the Piezoelectric System and MatrixORTHOGNATHIC Plating System. Orthognathic Correction of Class II Open Bite. Using the Piezoelectric System
Case Report Orthognathic Correction of Class II Open Bite. Using the Piezoelectric System and MatrixORTHOGNATHIC Plating System. Orthognathic Correction of Class II Open Bite. Using the Piezoelectric System
MRI KNEE WHAT TO SEE. Dr. SHEKHAR SRIVASTAV. Sr.Consultant KNEE & SHOULDER ARTHROSCOPY
 MRI KNEE WHAT TO SEE Dr. SHEKHAR SRIVASTAV Sr.Consultant KNEE & SHOULDER ARTHROSCOPY MRI KNEE - WHAT TO SEE MRI is the most accurate and frequently used diagnostic tool for evaluation of internal derangement
MRI KNEE WHAT TO SEE Dr. SHEKHAR SRIVASTAV Sr.Consultant KNEE & SHOULDER ARTHROSCOPY MRI KNEE - WHAT TO SEE MRI is the most accurate and frequently used diagnostic tool for evaluation of internal derangement
Web-based calibration of observers using MRI of the temporomandibular joint
 (2012) 41, 656 661 2012 The British Institute of Radiology http://dmfr.birjournals.org RESEARCH Web-based calibration of observers using MRI of the temporomandibular joint K Hellén-Halme*,1, L Hollender
(2012) 41, 656 661 2012 The British Institute of Radiology http://dmfr.birjournals.org RESEARCH Web-based calibration of observers using MRI of the temporomandibular joint K Hellén-Halme*,1, L Hollender
MR Advance Techniques. Vascular Imaging. Class II
 MR Advance Techniques Vascular Imaging Class II 1 Vascular Imaging There are several methods that can be used to evaluate the cardiovascular systems with the use of MRI. MRI will aloud to evaluate morphology
MR Advance Techniques Vascular Imaging Class II 1 Vascular Imaging There are several methods that can be used to evaluate the cardiovascular systems with the use of MRI. MRI will aloud to evaluate morphology
TRIFID MANDIBULAR CONDYLE: REPORT OF A RARE CASE
 TRIFID MANDIBULAR CONDYLE: REPORT OF A RARE CASE Khushboo Singh, MDS 1, Dr. Sujata Mohanty, MDS 2, Mahesh Verma, MDS, MBA, PhD 3, Sunita Gupta, MDS, MBA (HCA) 4, Sujoy Ghosh, MDS 5, and Meera Choudhary,
TRIFID MANDIBULAR CONDYLE: REPORT OF A RARE CASE Khushboo Singh, MDS 1, Dr. Sujata Mohanty, MDS 2, Mahesh Verma, MDS, MBA, PhD 3, Sunita Gupta, MDS, MBA (HCA) 4, Sujoy Ghosh, MDS 5, and Meera Choudhary,
Severe Posterior Open Bite by Posterior Folding of the Retrodiscal Tissue: A Case Report
 IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 14, Issue 10 Ver. V (Oct. 2015), PP 27-31 www.iosrjournals.org Severe Posterior Open Bite by Posterior
IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 14, Issue 10 Ver. V (Oct. 2015), PP 27-31 www.iosrjournals.org Severe Posterior Open Bite by Posterior
Usefulness of Unenhanced MRI and MR Arthrography of the Shoulder in Detection of Unstable Labral Tears
 Musculoskeletal Imaging Original Research Unenhanced MRI and MR rthrography for Unstable Labral Tears Musculoskeletal Imaging Original Research Thomas 1,2 T Keywords: labral tear, MRI, shoulder DOI:10.2214/JR.14.14262
Musculoskeletal Imaging Original Research Unenhanced MRI and MR rthrography for Unstable Labral Tears Musculoskeletal Imaging Original Research Thomas 1,2 T Keywords: labral tear, MRI, shoulder DOI:10.2214/JR.14.14262
ORIGINAL ARTICLE. ROLE OF MRI IN EVALUATION OF TRAUMATIC KNEE INJURIES Saurabh Chaudhuri, Priscilla Joshi, Mohit Goel
 ROLE OF MRI IN EVALUATION OF TRAUMATIC KNEE INJURIES Saurabh Chaudhuri, Priscilla Joshi, Mohit Goel 1. Associate Professor, Department of Radiodiagnosis & imaging, Bharati Vidyapeeth Medical College and
ROLE OF MRI IN EVALUATION OF TRAUMATIC KNEE INJURIES Saurabh Chaudhuri, Priscilla Joshi, Mohit Goel 1. Associate Professor, Department of Radiodiagnosis & imaging, Bharati Vidyapeeth Medical College and
Maxillofacial Injuries Practical Tips
 Saturday, October 29, 2016 Maxillofacial Injuries Practical Tips Suyash Mohan MD, PDCC THE ROOTS OF PENN RADIOLOGY RADIOLOGICAL Assistant Professor of Radiology Assistant Professor of Neurosurgery Neuroradiology
Saturday, October 29, 2016 Maxillofacial Injuries Practical Tips Suyash Mohan MD, PDCC THE ROOTS OF PENN RADIOLOGY RADIOLOGICAL Assistant Professor of Radiology Assistant Professor of Neurosurgery Neuroradiology
Artigo Original / Original Article
 Artigo Original / Original Article IJD ISSN:1806-146X Mandibular condyle morphology on panoramic radiographs of asymptomatic temporomandibular joints Christiano Oliveira 1 Renata Tarnoschi Bernardo 2 Ana
Artigo Original / Original Article IJD ISSN:1806-146X Mandibular condyle morphology on panoramic radiographs of asymptomatic temporomandibular joints Christiano Oliveira 1 Renata Tarnoschi Bernardo 2 Ana
Stability of Post Traumatic Osteochondritis Dissecans of the Knee: MR Imaging Findings
 Chin J Radiol 2005; 30: 199-204 199 Stability of Post Traumatic Osteochondritis Dissecans of the Knee: MR Imaging Findings YU-CHUNG HUNG 1 JON-KWAY HUANG 1,2 Department of Radiology 1, Mackay Memorial
Chin J Radiol 2005; 30: 199-204 199 Stability of Post Traumatic Osteochondritis Dissecans of the Knee: MR Imaging Findings YU-CHUNG HUNG 1 JON-KWAY HUANG 1,2 Department of Radiology 1, Mackay Memorial
FOR CMS (MEDICARE) MEMBERS ONLY NATIONAL COVERAGE DETERMINATION (NCD) FOR MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING:
 National Imaging Associates, Inc. Clinical guidelines BONE MARROW MRI Original Date: July 2008 Page 1 of 5 CPT Codes: 77084 Last Review Date: September 2014 NCD 220.2 MRI Last Effective Date: July 2011
National Imaging Associates, Inc. Clinical guidelines BONE MARROW MRI Original Date: July 2008 Page 1 of 5 CPT Codes: 77084 Last Review Date: September 2014 NCD 220.2 MRI Last Effective Date: July 2011
Total Prosthetic Replacement of the Temporomandibular Joint (TMJ)
 Total Prosthetic Replacement of the Temporomandibular Joint (TMJ) VERSION CONTROL Version: 2.0 Ratified by: Governing Body Date ratified: 13 November 2013 Name of originator/author: Name of responsible
Total Prosthetic Replacement of the Temporomandibular Joint (TMJ) VERSION CONTROL Version: 2.0 Ratified by: Governing Body Date ratified: 13 November 2013 Name of originator/author: Name of responsible
FOR CMS (MEDICARE) MEMBERS ONLY NATIONAL COVERAGE DETERMINATION (NCD) FOR MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING:
 National Imaging Associates, Inc. Clinical guidelines SINUS MRI Original Date: November 2007 Page 1 of 5 CPT Codes: 70540, 70542, 70543 Last Review Date: July 2014 NCD 220.2 MRI Last Effective Date: July
National Imaging Associates, Inc. Clinical guidelines SINUS MRI Original Date: November 2007 Page 1 of 5 CPT Codes: 70540, 70542, 70543 Last Review Date: July 2014 NCD 220.2 MRI Last Effective Date: July
The efficacy of anterior repositioning splint therapy studied by magnetic resonance imaging
 European Journal of Orthodontics 24 (2002) 343 352 2002 European Orthodontic Society The efficacy of anterior repositioning splint therapy studied by magnetic resonance imaging D. Eberhard*, H.-P. Bantleon*
European Journal of Orthodontics 24 (2002) 343 352 2002 European Orthodontic Society The efficacy of anterior repositioning splint therapy studied by magnetic resonance imaging D. Eberhard*, H.-P. Bantleon*
Surgical. Technique. AEQUALIS Spherical Base Glenoid. Shoulder Prosthesis.
 Surgical Technique Shoulder Prosthesis AEQUALIS Spherical Base Glenoid www.tornier.com CONTENTS CONTENTS 1. Subscapularis 2. Anterior capsule 3. Humeral protector 4. Inserting retractors 1. DESIGN FEATURES
Surgical Technique Shoulder Prosthesis AEQUALIS Spherical Base Glenoid www.tornier.com CONTENTS CONTENTS 1. Subscapularis 2. Anterior capsule 3. Humeral protector 4. Inserting retractors 1. DESIGN FEATURES
CT Findings of Traumatic Posterior Hip Dislocation after Reduction 1
 CT Findings of Traumatic Posterior Hip Dislocation after Reduction 1 Sung Kyoung Moon, M.D., Ji Seon Park, M.D., Wook Jin, M.D. 2, Kyung Nam Ryu, M.D. Purpose: To evaluate the CT images of reduced hips
CT Findings of Traumatic Posterior Hip Dislocation after Reduction 1 Sung Kyoung Moon, M.D., Ji Seon Park, M.D., Wook Jin, M.D. 2, Kyung Nam Ryu, M.D. Purpose: To evaluate the CT images of reduced hips
Comparative study of high resolusion ultrasonography and magnetic resonance imaging in diagnosing traumatic knee injuries & pathologies
 Original article: Comparative study of high resolusion ultrasonography and magnetic resonance imaging in diagnosing traumatic knee injuries & pathologies Dr. Rakesh Gujjar*, Dr. R. P. Bansal, Dr. Sandeep
Original article: Comparative study of high resolusion ultrasonography and magnetic resonance imaging in diagnosing traumatic knee injuries & pathologies Dr. Rakesh Gujjar*, Dr. R. P. Bansal, Dr. Sandeep
Dynamic High-Resolution Sonography Compared to Magnetic Resonance Imaging for Diagnosis of Temporomandibular Joint Disk Displacement
 ORIGINAL RESEARCH Dynamic High-Resolution Sonography Compared to Magnetic Resonance Imaging for Diagnosis of Temporomandibular Joint Disk Displacement Hadeel Habashi, MD, Ayelet Eran, MD, Israel Blumenfeld,
ORIGINAL RESEARCH Dynamic High-Resolution Sonography Compared to Magnetic Resonance Imaging for Diagnosis of Temporomandibular Joint Disk Displacement Hadeel Habashi, MD, Ayelet Eran, MD, Israel Blumenfeld,
A Rare Case of Cheerleader Syndrome, Case Report
 47 A Rare Case of Cheerleader Syndrome, Case Report Dr. Ayad AL mudarris, FIBMS (1) and Dr. Shifaa Hussain, MSc (2) (1)Head of Maxillofacial Surgical Department. Al Imamain Al Kadhemain Medical City; (2)
47 A Rare Case of Cheerleader Syndrome, Case Report Dr. Ayad AL mudarris, FIBMS (1) and Dr. Shifaa Hussain, MSc (2) (1)Head of Maxillofacial Surgical Department. Al Imamain Al Kadhemain Medical City; (2)
