Role of Mri in Meniscal Tearsdr
|
|
|
- Simon Roy Green
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: , p-issn: Volume 16, Issue 3 Ver. III (March. 2017), PP Role of Mri in Meniscal Tearsdr Jeevika Mu 1,Dr L.Vinay Bhushan Reddy 2 1 Head Of Radiology Department, Jjmmc Davangere,India 2 Second Year Radiology Resident, Jjmmc Davangere,India Abstract: MR imaging provides information on soft tissue damage and has been accepted widely for the evaluation of internal knee derangements. Hence the purpose of this study was to evaluate the usefulness of MRI in the early and precise diagnosis and to study the meniscal anatomy, normal variants, types and incidence of injuries in menisci by MRI. Out of 43 patients the males (84%) are commonly affected than females (16%). Majority of the patients fall under the age group of years (48%). Among meniscal injuries medial meniscal tears (46.5%) were more common than lateral meniscus (37.2%), Grade III tears were common in both.among medial meniscus tear, The posterior horn (55%) was commonest site of involvement and the predominant type of tear was Horizontal and oblique (35%). Among lateral meniscus tear, the anterior horn (31.3%) was commonest site of involvement and the predominant type of tear was horizontal(31.3%). Interpretation And Conclusion : This prospective study consisting of 43 patients was performed in the Department of Radio-Diagnosis on patients referred from Orthopaedic department, Bapuji Hospital Davangere. They were evaluated with detailed clinical history and clinical examinations and were subsequently subjected to imaging of knee using 1.5 Tesla Philips Achieva machine using 8-channel SENSE knee coil. The following sequences were selected as required T1W coronal, PD Fat Sat Sagittal, STIR coronal, T2W axial. Methods : Normal Shape and Attachments of the Medial Meniscus- The Menisci are crescentic laminae that deepen the articulation of the tibial surfaces that receive the femur. Their peripheral attached borders are thick and convex, their free borders thin and concave. Their peripheral zone is vascularized by capillary loops from the fibrous capsule and synovial membrane, while their inner regions are avascular They are wedge-shaped, semilunar, fibrocartilage structures composed of thick collagen fibers primarily arranged circumferentially, with radial fibers extending from the capsule, between the circumferential fibers.[8]they cover 50% of the medial and 70% of the lateral surface of the tibial Plateau[9]Each meniscus is divided into an anterior horn, a body, and a posterior horn. These criteria are, first, contact of intrameniscal signal with the superior or the inferior surface of a meniscus (or with both surfaces) and, second, distortion of the normal appearance of a meniscus [7].To diagnose a meniscal tear using these criteria, it is essential to understand how normal variations in the shape of the menisci and their attachments compare with the MR appearance of a meniscal tear Mr Criteria For Diagnosing Meniscal Tears: To study the spectrum of MRI findings meniscal tears in traumatic knee. To correlate imaging findings with clinical examination findings.to identify the commonest derangement in meniscal tears Objectives: Keywords: (knee, meniscal anatomy, meniscal tear, MRI, normal variants) MRI is generally considered a valuable diagnostic tool when there is a history of knee trauma. MR imaging is the best modality for detecting meniscal tears. It is non invasive, fast can be done on an outpatient basis and is free of complications. I. Introduction Due to its anatomical configuration and because of its being the biggest joint of the human body, the knee is frequently subjected to direct trauma that can results in injuries of variable gravity[1]. MRI is a wellaccepted imaging Modality in the diagnostic workup of patients with knee complaints and has largely replaced diagnostic arthroscopy for this purpose MRI is capable of depicting soft tissue abnormalities, such as meniscal lesions[2]. When evaluating a knee MR examination we study the medial and lateral menisci first on the sagittal images and then on the coronal images because sagittal images are the Most useful in diagnosing meniscal tears Menisci should have low signal intensity on MR images because of their fibrocartilage composition, but they may have central globular or linear increased signal intensity secondary to internal mucinous degeneration [3] In addition, the menisci in asymptomatic children have a 66% frequency of internal signal on MRI and that signal is presumed to reflect normal vascularity [4]. Another proposed cause of increased intrameniscal signal is a DOI: / Page
2 meniscal contusion after acute trauma [5]. the diagnosis of meniscal contusion for menisci with Internal signal equal to fluid on T2-weighted images in patients with a recent episode of trauma Currently MR imaging is the best modality for meniscal tears and hence this study is undertaken to determine the Role of MRI in Meniscal tears. If high signal clearly disrupts an articular surface of the meniscus, it is a torn Meniscus.[18] Tears in the menisci result from acute trauma or repetitive trauma and progressive degeneration. Chronic repetitive trauma is common both in athletes and nonathletes with aging. Acute tears are usually due to athletic injuries, with crushing of the meniscus between the tibia and femoral condyles. Most tears extend from posterior to anterior. Chrondrocyte necrosis and increase in mucoid ground substance can lead to meniscal tears.[44 ]MRI is an established method of diagnosing meniscal tears with high sensitivity and Specificity.[19][20] In approximately 10% of cases, however, MRI findings are equivocal for the diagnosis of meniscal tear. Evaluation of the meniscus in these instances may be limited by partial volume averaging, truncation artifact, artifact From motion, meniscal degeneration, or normal anatomic structures abutting the meniscus.[21],[22],[23] Meniscal tears : Many variants of meniscus are seen. Commonest among them is the discoid meniscus. Discoid meniscus is an anatomical variant in which the meniscus is thickened and disc-shaped, covering a greater area of the tibial plateau than the normal semilunar meniscus.[12]although far more common on the lateral side, it is described for both lateral and medial menisci. Discoid menisci are arthroscopically classified by Watanabe et al as complete, incomplete and Wrisberg type.[13],[14]. Various MR imaging criteria have been proposed for the diagnosis.26 The most widely-used criterion is when three or more4 mm Thick consecutive sagittal images demonstrate continuity of the meniscus between the anterior and posterior horns.[15],[16 ] An abnormal, thickened, bow-tie appearance of the meniscus may also be suggestive.[17 ]Wrisberg variant of a discoid lateral meniscus.[18] This is a discoid meniscus that lacks attachments to the capsule via the normal struts or fascicles and lacks attachment to the tibia via the coronary or meniscotibial ligaments at the posterior horn of the meniscusa true meniscal flounce or fold represents a normal variant, provided there are no other associated indicators of meniscal pathology. The presence of a meniscal flounce is not associated with an increased prevalence of meniscaltears Meniscal Variants- The anterior horn of the medial meniscus is attached to the tibial Plateau anterior to the anterior cruciate ligament.[9].the anterior horn of the lateral meniscus has fibers of the ACL that extend into it at the anterior root attachment where it attaches to the Tibial plateau. The posterior horn of the medial meniscus attaches to the tibial plateau immediately anterior to the posterior cruciate ligament.the circumferential arrangement of the type I collagen fibers provides the meniscus with tensile strength most essential for its load bearingfunctions[10]the menisci transmit more than 50% of body weight in extension, and even more in flexion.[11] These are vertical longitudinal tears with displaced fragment. It occurs in about 10% of meniscal tears. Few characteristic signs are seen in this type Of tear which are described below. Absent bow tie sign: Only one body segment is seen instead of the normal two body segments present on the outermost sagittal images through the meniscus. Fragment in notch sign: A displaced meniscal fragment should always be found, most often in the intercondylar notch. It is seen more often in lateralbucket-handle tears,[27] and it has a sensitivity of 60% to 98% and specificity of73% to 82% for detecting bucket-handle tears[28],[29],[30],[31]. Double PCL sign: The displaced meniscal fragment can lie in front of the posterior cruciate ligament. Anterior flipped meniscus sign: The displaced fragment may flip over the anterior horn of the affected meniscus Bucket Handle Tear: Oblique and horizontal tear : It affects commonly the undersurface of the posterior horn of the medial meniscus. These are mostly degenerative in nature. Grade 1- Meniscal signal change is globular and do not communicate with articular surface. Grade 2- Meniscal signal change is linear, intrasubstance and do not communicate with articular surface. Grade 3 - Meniscal signal change that extends to the articular surface. 3a linear intrameniscal signal intensity abutting articular surface. 3b irregular signal intensity abutting articular surface. Grade 4 - Menisci are distorted in addition to signal changes similar to grade 3 Grading of meniscal tears[ 24],[25],[26]: DOI: / Page
3 Types Of Meniscal Tears Meniscocapular Tear Horizontal Cleavage Tear Flap Tear Radial/ Parrot Beak Tear Bucket Handle Tear Peripheral Tear A. Truncated triangle sign, B. Cleft sign, C. Marching cleft sign, D. Ghost meniscus sign Meniscal flap tear : A meniscal flap tear or displaced flap is the result of a short-segment, horizontal meniscal tear with either superior or inferior displacement of a meniscal fragment.[40] Meniscocapsular separation occurs when the meniscus detaches from the capsular attachments,[37 ]which is more common medially and usually is associated with other injuries.[38 ] Signs that have been described in meniscocapsular separation include displacement of the meniscus relative to the tibial margin, extension of the tear into the superior or inferior corner of the peripheral meniscus, and an irregular outer margin of the meniscus body on coronal images. Additional signs include increased distance between the meniscus and the MCL, or fluid between the meniscus and the MCL.[38],[39] Meniscocapsular separation : A root tear occurs at the tibial attachment or root of the meniscus, and it has been described only posteriorly. Meniscal extrusion is more pronounced and nearly four times as common with medial, as opposed to lateral meniscal root tears.[35] Lateral meniscal root tears are diagnosed when the posterior horn of the lateral meniscus does not cover the most medial aspect of the posterior lateral tibial plateau on at least one coronal image.[36] Root tear : The two most effective signs were the cleft and the truncated triangle signs. The use of only these two signs increased detection of radial Meniscal tears to 76%. The use of all four signs increased the detection rate for radialtears to 89%.[34] Radial tears of the meniscus are significant in that radial transection of the meniscus will completely disable the load-bearing function of the meniscus and will allow the meniscus to be extruded under axial loading.[32],[33] They are defined as vertical tears perpendicular to the free edge of the meniscus, characterized by blunting of both the anterior horn-body junction and blunting and elongation of the posterior horn body segment. Because the tearplane is in the anterior third of the meniscus, the posterior horn body segment is seen as exaggerated or elongated, a finding characteristic of radial Tears Keith W Harper et al. described show four signs for detecting radial meniscal tears.[34] Radial or transverse tears : Pitfalls in imaging of meniscal injuries[41]: Truncation artifacts are seen in the meniscus on sagittal images when using matrix and phase encoding in the superior-inferior (SI) direction. This subtle linear area of high signal intensity is commonly identified two pixels from the meniscal joint fluid interface. This defect can be easily recognized as it can be seen extending beyond the meniscal margins when images are optimally windowed. This artifact can be removed using or matrix and by switching the phase direction to the AP direction. Vacuum phenomenon is seen as irregular low intensity structure extending into the joint from the meniscal margin and can simulate discoid menisci or articular abnormalities in the joint. Magic angle phenomenon has been described with tendons and menisci when collagen fibers are oriented approximately 55 to the static magnetic field. At this angle, the interactions that contribute to T2 relaxation among water protons are nulled. This can result in increased signal intensity on the upper medial portion of the posterior horn of the lateral meniscus. This is particularly common with short TE sequences. Secondary Signs Of Meniscal Tear[42] : Useful in equivocal cases of meniscal tear. Meniscal/parameniscal cyst: This indirect MRI sign has a reported positive predictive value of 100% for the presence of meniscal tear at arthroscopy. 2. Joint effusion 3. MCL edema: This sign has nearly 100% specificity for the presence of adjacent Collateral ligament edema on MRI in relation to the presence of meniscal tear at arthroscopy. The sensitivity was higher for medial meniscal tears than for lateral meniscal tears, reflecting the closer apposition of the peripheral margin of the DOI: / Page
4 medial meniscus to the medial collateral ligament than of the lateral meniscus and lateral collateral ligament. 4. Subchondral marrow edema: This is seen immediately adjacent and parallel to the articular surface. associated with medial meniscal tears in more than 60% and lateral meniscal tears in almost 90% of cases. Findings On Physical Examination General findings include the following : Clicking Localised tenderness along the medial or lateral joint line or over the periphery of the meniscus. Locking of the knee in fixed flexion. Pseudo-locking which may be related to muscle spasm. Limping. All the patients referred with knee injuries following trauma. Cases of all age groups. Exclusion criteria : Patient having history of claustrophobia Patient having history of cardiac pacemakers, metallic foreign body and cochlear implants insitu. Methods : Imaging protocol: Technique Imaging will be done with 1.5 Tesla Philips Achieva Machine using 8 channel SENSE knee coil. Positioning - Imaging is done with full extension in neutral position. A small field of view (FOV) typically in the range cm Method-A prospective study consisting of 43 patients with traumatic knee joint is undertaken to study the spectrum of MRI findings in all consecutive cases of knee trauma referred from orthopaedic OPD of Bapuji Hospital, Davangere in a period of 1 years from November 2015 to November Inclusion criteria : To examine the lateral meniscus the examiner has to return the knee to full flexion and apply a medial rotation to the tibia prior to extending the knee once again. If pain occurs in first 30º of extension, indicates tear of posterior horn. Pain at 90º or above indicates tear in middle part or anterior horn The bounce test, McMurray s test and Apley s grind test can aid in the diagnosis of Meniscal injury McMurray test : The McMurray test is used to determine the presence of a meniscal tear. While the patient is supine on the exam table the examiner grasps the knee, placing one hand over the top of the knee with thumb over one joint line and index and middle finger over the opposite joint line. The examiner begins with the knee in full flexion and then medially and laterally rotates the tibia while paying attention for an audible click. The examiner then laterally rotates the tibia and extends the knee beyond 90. An audible click while performing this maneuver can indicate a torn meniscus Clinical tests for menisci :Out of total 43 patients with meniscal tears 20 (46.5%) were isolated medial meniscus tear, 16 (37.2%) were isolated lateral meniscus tear and 7 (16.3%) involved both menisci. Distribution of meniscal tears II. Results Data of 43 patients were analyzed in this study Following statistical methods were applied in the present study. 1. Descriptive statistics 2. Cross tables (contingency table analysis). a) T2W axial TE (100 MS), TR (5400 MS), FOV (160), Slice thickness (1-3 mm). b) PD fat sat sagittal TE (30 MS), TR (2500 MS), FOV (155), Slice thickness (3 mm). c) STIR coronal TE (60 MS), TR (3547 MS), FOV (150), Slice thickness(3 mm). d) mffe sagittal TE (9.2 MS), TR (934 MS), FOV (165), Slice thickness (1-3 mm). e) T1W coronal TE (7 MS), TR ( MS), FOV (150) Slice thickness (1mm). The following sequences will be selected as required. Distribution Of Meniscal Tears Site Of Tear Medial Meniscus Out of 20 patients with isolated medial meniscus tear, the posterior horn was commonest site of involvement occurring in 11 patients (55%) and the predominant type of tear was horizontal and oblique that occurred in 7 patients each (35%). Grade III tear were the commonest seen in 12 patient (60%) followed by grade II in 8 patients (40%). DOI: / Page
5 Type Of Tear- Medial Meniscus Medial Meniscus -Grades Lateral Menisci Site Out of 16 patients with isolated lateral meniscus tear the anterior horn was commonest site of involvement occurring in 5 patients (31.3%) and the predominant type of tear was horizontal and was seen in 5 patients (31.3%). Grade III tears were the commonest and were seen in 8 patients (50%) followed by grade II in 6 patients (37.5%). The commonest type of tear to involve the whole of meniscus both medial and lateral was horizontal tear and site was posterior horn. Grade III tear were commonest among both Types Of Tear Lateral Menisci correlation of meniscal tear with mcmurrays test Fig. 2: Sagittal MR Image of Superior and Inferior Popliteo meniscal Fascicles Fig. 1: Sagittal MR Image of Anterior and Posterior Meniscofemoral Ligaments Fig. 3: Transverse Meniscal Ligament On Axial MR Image Fig. 4 : Coronal MR image of discoid meniscus (B) Sagittal MR image of a normal lateral meniscus Fig. 5 : (A) Sagittal MR image of a normal medial meniscus Fig. 6: Wrisberg variant of discoid meniscus on sagittal MR Image no attachment of meniscus to capsule Fig. 7: Wavy Contour of Meniscal flounce on sagittal MR Image. Fig 9-pd sagittal image showing bucket handle tear of the lateral meniscus with displaced fragment seen in the posterior intercondylar region Fig 8-pd sagittal image showing horizontal tear of the body and posterior horn of medial meniscus Fig year-old man with complex tear of posterior horn of medial meniscus. Coronal proton density weighted image shows extensive distortion of meniscus Fig 10 -stir coronal image showing grade ii mcl tear with lateral sublaxation of body of medial meniscus FIG year-old woman with fraying and adjacent synovitis of lateral posterior root. A and B, Sagittal (A) and coronal (B) proton density weighted images show increased signal contacting surface of root (arrows). FIG year-old man with longitudinal tear (arrow). Sagittal proton density weighted image shows that tear extends to inferior surface of menisci. FIG year-old-boy with full-thickness peripheral longitudinal tear of posterior horn of lateral meniscus. A and B, Tear (arrows) is evident on proton density weighted image (A) but is more conspicuous as fluid cleft on T2 image (B).. FIG year-old boy with bucket-handle lateral meniscal tear. Sagittal proton density weighted image shows fragment flipped anteriorly (arrow) to abut anterior horn creating flipped meniscus sign. FIG year-old woman with bucket-handle medial meniscal tear. Midline sagittal proton density weighted image shows displaced central fragment (arrow) paralleling posterior cruciate ligament (PCL) creating double PCL sign. III. Conclusion 1. Vaz CES, Camargo OP de, Santana PJ de, Valezi AC. Accuracy of Magnetic Resonance In Identifying Traumatic 2. Intraarticular knee lesions. Clinics. 2005;60(6); Edwin H.G. Oei, Abida Z.Ginai, M.G. Myriam Hunink. MRI for Traumatic knee injury :A Review 4. Ravi Sohal Feb 26, 2009 what does an MRI Scan knee show? 5. Stoller DW. Magnetic Resonance Imaging in Orthopaedics and Sports Medicine. 3rd ed. Philadelphia: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins; Standring S. Gray s Anatomy. 39th ed. Philadelphia: Elsevier Ltd; p Anderson AF, Dome DC, Gautam S, Awh MH, Rennirt GW. Correlation of anthropometric measurements, 8. strength, anterior cruciate ligament size, and intercondylar notch characteristics to sex differences in 9. anteriorcruciate ligament tear rates. Am J Sports Med 2001;29(1): Chandrashekar N, Slauterbeck J, Hashemi J. Sexbased differences in the anthropometric characteristics of the 11. anterior cruciate ligament And Its relation to intercondylar notch geometry: a cadaveric study. Am J 12. Sports Med 2005; 33(10): Fox MG. MR Imaging of the Meniscus: Review, Current Trends, and Clinical Implications. 14. Radiol Clin N Am 2007;45: DOI: / Page
6 15. Rath E, Richmond JC. The menisci: basic science and advances in treatment. Br J Sports Med 2000;34(4): Fithian DC, Kelly MA, Mow VC. Material properties and structurefunction relationships in themenisci. Clin Orthop Relat 17. Res Mar 1990;(252): Harper KW, Helms CA, Lambert HS, Higgins LD. Radial meniscal tears: significance, incidence, and MR appearance. 19. AJR Am J Roentgenol 2005; 185(6): Rohren EM, Kosarek FJ, Helms CA. Discoid lateral meniscus and the frequency of meniscal tears. 21. Skeletal Radiol 2001;30: Samoto N, Kozuma M, Tokuhisa T, Kobayashi K. Diagnosis of the large medial meniscus of the knee on MR imaging. 23. Magn Reson Imaging2006;24: Rohren EM, Kosarek FJ, Helms CA. Discoid lateral meniscus and the frequency of meniscal tears. Skeletal Radiol ;30: Kelly BT, Green DW. Discoid lateral meniscus in children. Curr Opin Pediatr 2002;14: Helms CA, Major NM, Anderson MW, Kaplan PA, Helms RD. Musculoskeletal MRI. 2nd ed. Philadelphia: Saunders; Berquist TH. MRI of Musculoskeletal System. 5th ed. Philadelphia: Lippincott William & Wilkins; De Smet AA, Norris MA, Yandow DR, Quintana FA, Graf BK, Keene JS. MR diagnosis of meniscal tears of 30. the knee: importance of high signal in the meniscus that extends to the surface. AJR 1993;161: Rubin DA, Paletta GA. Current concepts and con troversies in meniscal imaging. Magn Reson Imaging 32. Clin N Am 2000;8: References [1]. The present study attempts to determine the role of magnetic resonance imaging in the evaluation meniscal tears. Knee joint being the largest and most complex weight bearing joint of the body is subject to damage because of its inherent structural complexity and the various types forces it is subjected to. In the setting of traumatic knee joint, MR imaging is the best noninvasive modality for the diagnosis of meniscal tears. Familiarity with the normal anatomy and common pit falls reduces errant interpretation but does not eliminate them entirely. MR imaging of [2]. knee is considered efficacious especially in the setting of indeterminate clinical findings and can stratify patients, guiding further surgical management. In the present study, 43 cases with history of trauma to knee joint were studied. [3]. The most common age group to be involved between years. The following pattern of meniscal tears were seen Among the meniscal injuries medial meniscal tears were more common and were seen in 20 patients (46.5%) than lateral meniscus. Grade III tears were common in both. [4]. Lee K, Siegel MJ, Lau DM, Hildebolt CF, Matava MJ. Anterior cruciate ligament tear: MR imaging based diagnosis in a paediatric population. Radiology 1999; 213: [5]. Helms CA, Major NM, Anderson MW, Kaplan PA, Helms RD. Musculoskeletal MRI. 2nd ed. Philadelphia: Saunders; 2008 [6]. Boyd KT, Myers PT. Meniscus preservation: rationale, repair techniques and results. Knee 2003;10:1 11. [7]. Messner K, Gao J. The menisci of the knee joint: anatomical and functional characteristics, and a rationale for clinicaltreatment. J Anat 1998;193: Harper KW, Helms CA, Lambert HS, Laurence D. Higgins. Radial Meniscal Tears: Significance, Incidence andmr Appearance. AJR 2005;185: [8]. Brody JM, Lin HM, Hulstyn MJ, Tung GA. Lateral meniscus root tear and meniscus extrusion with anterior cruciateligament tear. Radiology 2006; 239(3): [9]. Tuckman GA, Miller WJ, Remo JW, Fritts HM, Rozansky MI. Radial tears of the menisci: MR findings. AJR AmJ Roentgenol 1994;163(2): [10]. Rubin DA, Britton CA, Towers JD, Harner CD. Are MR imaging signs of meniscocapsular Separation valid? Radiology 1996;201(3): [11]. De Maeseneer M, Lenchik L, Starok M, Pedowitz R, Trudell D, Resnick D. Normal and abnormal medial meniscocapsular structures: MR Imaging and sonography in cadavers. AJR Am J Roentgenol 1998;171(4): [12]. De Maeseneer M, Shahabpour M, Vanderdood K, Von Roy F, Osteaux M. Medial meniscocapsular separation: MR imaging criteria and Diagnostic pitfalls. Eur J Radiol 2002;41(3): [13]. Ruff C, Weingardt J, Russ P, Kilcoyne R. MR imaging patterns of displaced meniscus injuries of the knee AJR 1998;170: [14]. Berquist TH. MRI of Musculoskeletal System. 5th ed. Philadelphia: Lippincott William & Wilkins; [15]. Bergin D, Hochberg H, Zoga AC, Qazi N, Parker L, Morrison WB. Indirect Soft-Tissue and Osseous Signs on Knee MRI of Surgically Proven Meniscal Tears AJR 2008; 191: [16]. Justice WW, Quinn SF. Error patterns in the MRI evaluation of menisci ofthe knee. Radiology 1995;196: [17]. De Smet AA, Graf BK. Meniscal tears missed on MRI: relationship to meniscal tear patterns and anterior cruciate ligaments tears. AJR 1994;162: [18]. Herman LJ, Beltran J. Pitfalls in MRI of the knee. Radiology 1988;167: [19]. Stroller DW, Martin C, Crues JV, Kaplan L, Mink JH. Meniscal Tears: pathological correlation with MR imaging. Radiology 1987;163: [20]. Mesgarzadeh M, Moyer R, Leder DS, Revesz G, Russoniello A, Bonakdarpour A, et al. MR imaging of knee: Expanded classification and pitfalls to the interpretation of meniscal tears. Radiographics 1993;13: [21]. Lotysch M, Mink J, Crues JV. Magnetic resonance imaging in the detection of meniscal injuries. Magnetic Resonance Imaging DOI: / Page
7 1986;4:185. [22]. Ruff C, Weingardt JP, Russ PD, Kilcoyne RF. MR imaging patterns of displaced meniscus injuries of the knee. AJR Am J Roentgenol 1998; 170(1):63 7. [23]. Vande Berg BC, Malghem J, Poilvache P, Maldaque B, Lecouvet FE. Meniscal tears with fragments displaced in notch and recesses of knee: MR imaging with arthroscopic comparison. Radiology 2005;234(3): [24]. Magee TH, Hinson GW. MRI of meniscal bucket-handle tears. Skeletal Radiol 1998;27(9): [25]. Ververidis AN, Verettas DA, Kazakos KJ, Tilkeridis CE, Chatzipapas CN. Meniscal bucket handle tears: a Retrospective study of arthroscopy and the relation to MRI. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc 2006;14(4): [26]. 29. Dorsay TA, Helms CA. Bucket-handle meniscal tears of the knee: sensitivity and specificity of MRI signs. [27]. Skeletal Radiol 2003;32(5):266 DOI: / Page
MENISCAL INJURY. Meniscus. Anterior Roots. Medial Meniscus. Lateral Meniscus. Posterior Roots. MRI and Arthroscopic Findings
 Meniscus Anterior Roots MENISCAL INJURY MRI and Arthroscopic Findings Medial Meniscus AH PH PH AH Lateral Meniscus Rawiwan Pattaweerakul Naresuan University Hospital Posterior Roots Meniscus Normal Meniscus
Meniscus Anterior Roots MENISCAL INJURY MRI and Arthroscopic Findings Medial Meniscus AH PH PH AH Lateral Meniscus Rawiwan Pattaweerakul Naresuan University Hospital Posterior Roots Meniscus Normal Meniscus
Meniscal Tears with Fragments Displaced: What you need to know.
 Meniscal Tears with Fragments Displaced: What you need to know. Poster No.: C-1339 Congress: ECR 2015 Type: Authors: Keywords: DOI: Educational Exhibit M. V. Ferrufino, A. Stroe, E. Cordoba, A. Dehesa,
Meniscal Tears with Fragments Displaced: What you need to know. Poster No.: C-1339 Congress: ECR 2015 Type: Authors: Keywords: DOI: Educational Exhibit M. V. Ferrufino, A. Stroe, E. Cordoba, A. Dehesa,
Post-injury painful and locked knee
 H R J Post-injury painful and locked knee, p. 54-59 Clinical Case - Test Yourself Musculoskeletal Imaging Post-injury painful and locked knee Ioannis I. Daskalakis 1, 2, Apostolos H. Karantanas 1, 2 1
H R J Post-injury painful and locked knee, p. 54-59 Clinical Case - Test Yourself Musculoskeletal Imaging Post-injury painful and locked knee Ioannis I. Daskalakis 1, 2, Apostolos H. Karantanas 1, 2 1
MRI of the Knee: Part 2 - menisci. Mark Anderson, M.D. University of Virginia Health System
 MRI of the Knee: Part 2 - menisci Mark Anderson, M.D. University of Virginia Health System Learning Objectives At the end of the presentation, each participant should be able to: describe the normal anatomy
MRI of the Knee: Part 2 - menisci Mark Anderson, M.D. University of Virginia Health System Learning Objectives At the end of the presentation, each participant should be able to: describe the normal anatomy
Role of magnetic resonance imaging in the evaluation of traumatic knee joint injuries
 Original Research Article Role of magnetic resonance imaging in the evaluation of traumatic knee joint injuries Dudhe Mahesh 1*, Rathi Varsha 2 1 Resident, 2 Professor, Department of Radio-Diagnosis, Grant
Original Research Article Role of magnetic resonance imaging in the evaluation of traumatic knee joint injuries Dudhe Mahesh 1*, Rathi Varsha 2 1 Resident, 2 Professor, Department of Radio-Diagnosis, Grant
Meniscal tears on 3T MR: Patterns, pearls and pitfalls
 Meniscal tears on 3T MR: Patterns, pearls and pitfalls Poster No.: C-2221 Congress: ECR 2010 Type: Educational Exhibit Topic: Musculoskeletal Authors: J. C. Kandathil; Singapore/SG Keywords: Knee injuries,
Meniscal tears on 3T MR: Patterns, pearls and pitfalls Poster No.: C-2221 Congress: ECR 2010 Type: Educational Exhibit Topic: Musculoskeletal Authors: J. C. Kandathil; Singapore/SG Keywords: Knee injuries,
Knee: Meniscus Back to Basics
 Knee: Meniscus Back to Basics Kyung Jin Suh kyungjin.suh@gmail.com Doctor Radiology, Daegu, KOREA Medial Lateral 7.7 10.2 11.6 9.6 10.6 mm Posterior > Anterior horn 10.6 mm Posterior = Anterior horn Medial
Knee: Meniscus Back to Basics Kyung Jin Suh kyungjin.suh@gmail.com Doctor Radiology, Daegu, KOREA Medial Lateral 7.7 10.2 11.6 9.6 10.6 mm Posterior > Anterior horn 10.6 mm Posterior = Anterior horn Medial
ADVANCED IMAGING OF THE KNEE
 MENISCAL ANATOMY ADVANCED IMAGING OF THE KNEE MENISCAL ABNORMALITIES MENISCAL FUNCTION MENISCAL FUNCTION load transmission shock absorption stability The menisci DO NOT function as primary stabilizers
MENISCAL ANATOMY ADVANCED IMAGING OF THE KNEE MENISCAL ABNORMALITIES MENISCAL FUNCTION MENISCAL FUNCTION load transmission shock absorption stability The menisci DO NOT function as primary stabilizers
MRI KNEE WHAT TO SEE. Dr. SHEKHAR SRIVASTAV. Sr.Consultant KNEE & SHOULDER ARTHROSCOPY
 MRI KNEE WHAT TO SEE Dr. SHEKHAR SRIVASTAV Sr.Consultant KNEE & SHOULDER ARTHROSCOPY MRI KNEE - WHAT TO SEE MRI is the most accurate and frequently used diagnostic tool for evaluation of internal derangement
MRI KNEE WHAT TO SEE Dr. SHEKHAR SRIVASTAV Sr.Consultant KNEE & SHOULDER ARTHROSCOPY MRI KNEE - WHAT TO SEE MRI is the most accurate and frequently used diagnostic tool for evaluation of internal derangement
Prevalence of Meniscal Radial Tears of the Knee Revealed by MRI After Surgery
 Downloaded from www.ajronline.org by 46.3.207.114 on 12/22/17 from IP address 46.3.207.114. Copyright RRS. For personal use only; all rights reserved Thomas Magee 1 Marc Shapiro David Williams Received
Downloaded from www.ajronline.org by 46.3.207.114 on 12/22/17 from IP address 46.3.207.114. Copyright RRS. For personal use only; all rights reserved Thomas Magee 1 Marc Shapiro David Williams Received
MRI of Bucket-Handle Te a rs of the Meniscus of the Knee 1
 MRI of ucket-handle Te a rs of the Meniscus of the Knee 1 Joon Yong Park, M.D., Young-uk Lee M.D., Eun-Chul Chung M.D., Hae-Won Park M.D., E u n - Kyung Youn M.D., Shin Ho Kook, M.D., Young Rae Lee, M.D.
MRI of ucket-handle Te a rs of the Meniscus of the Knee 1 Joon Yong Park, M.D., Young-uk Lee M.D., Eun-Chul Chung M.D., Hae-Won Park M.D., E u n - Kyung Youn M.D., Shin Ho Kook, M.D., Young Rae Lee, M.D.
Role of Magnetic Resonance Imaging in Patients with Knee Trauma
 Original Research Article Role of Magnetic Resonance Imaging in Patients with Knee Trauma Bhautik Kapadia 1, Bhumika Suthar 2* 1 Associate Professor, 2 Assistant Professor, Department of Radiodiagnosis,
Original Research Article Role of Magnetic Resonance Imaging in Patients with Knee Trauma Bhautik Kapadia 1, Bhumika Suthar 2* 1 Associate Professor, 2 Assistant Professor, Department of Radiodiagnosis,
a - CM EARTICLE Clinics in diagnostic imaging (139) !Medical Education Singapore Med J 2012; 53(4) CASE PRESENTATION
 !Medical Education Singapore Med J 2012; 53(4) 283 CM EARTICLE Clinics in diagnostic imaging (139) Wei Yang Liml, MBBS, FRCR, Nor Azam Mahmud2, MD, MMed, Wilfred CG Peh3, FRCP, FRCR a - - - Fig. 1 Sagittal
!Medical Education Singapore Med J 2012; 53(4) 283 CM EARTICLE Clinics in diagnostic imaging (139) Wei Yang Liml, MBBS, FRCR, Nor Azam Mahmud2, MD, MMed, Wilfred CG Peh3, FRCP, FRCR a - - - Fig. 1 Sagittal
This presentation is the intellectual property of the author. Contact them for permission to reprint and/or distribute.
 MRI of the Knee Jennifer Swart, M.D. Musculoskeletal Radiology South Texas Radiology Group Outline Coils, Patient Positioning Acquisition Parameters, Planes and Pulse Sequences Knee Arthrography Normal
MRI of the Knee Jennifer Swart, M.D. Musculoskeletal Radiology South Texas Radiology Group Outline Coils, Patient Positioning Acquisition Parameters, Planes and Pulse Sequences Knee Arthrography Normal
The Meniscus. History. Anatomy. Anatomy. Blood Supply. Attachments
 History The Meniscus W. Randall Schultz, MD, MS Austin, TX January 23, 2016 Meniscus originally thought to represent vestigial tissue 1883 first reported meniscal repair (Annandale) Total menisectomy treatment
History The Meniscus W. Randall Schultz, MD, MS Austin, TX January 23, 2016 Meniscus originally thought to represent vestigial tissue 1883 first reported meniscal repair (Annandale) Total menisectomy treatment
What is the most effective MRI specific findings for lateral meniscus posterior root tear in ACL injuries
 What is the most effective MRI specific findings for lateral meniscus posterior root tear in ACL injuries Kazuki Asai 1), Junsuke Nakase 1), Kengo Shimozaki 1), Kazu Toyooka 1), Hiroyuki Tsuchiya 1) 1)
What is the most effective MRI specific findings for lateral meniscus posterior root tear in ACL injuries Kazuki Asai 1), Junsuke Nakase 1), Kengo Shimozaki 1), Kazu Toyooka 1), Hiroyuki Tsuchiya 1) 1)
This presentation is the intellectual property of the author. Contact them at for permission to reprint and/or distribute.
 MRI of the Knee Jennifer Swart, M.D. Musculoskeletal Radiology South Texas Radiology Group Financial Disclosure Dr. Jennifer Swart has no relevant financial relationships with commercial interests to disclose.
MRI of the Knee Jennifer Swart, M.D. Musculoskeletal Radiology South Texas Radiology Group Financial Disclosure Dr. Jennifer Swart has no relevant financial relationships with commercial interests to disclose.
Lesions of the Menisci of the Knee: Value of MR Imaging Criteria for Recognition of Unstable Lesions
 B. C. Vande Berg 1 P. Poilvache 2 F. Duchateau 1 F. E. Lecouvet 1 J. E. Dubuc 2 B. Maldague 1 J. Malghem 1 Received June 12, 2000; accepted after revision August 24, 2000. 1 Department of Radiology, Cliniques
B. C. Vande Berg 1 P. Poilvache 2 F. Duchateau 1 F. E. Lecouvet 1 J. E. Dubuc 2 B. Maldague 1 J. Malghem 1 Received June 12, 2000; accepted after revision August 24, 2000. 1 Department of Radiology, Cliniques
The Egyptian Journal of Hospital Medicine (July 2018) Vol. 72 (10), Page
 The Egyptian Journal of Hospital Medicine (July 2018) Vol. 72 (10), Page 5490-5494 The Role of Ultrasound in Evaluation of Meniscal Injury Nada Sayed Mahdy*, Hossam Mousa Sakr, Allam Elsayed Allam Radiology
The Egyptian Journal of Hospital Medicine (July 2018) Vol. 72 (10), Page 5490-5494 The Role of Ultrasound in Evaluation of Meniscal Injury Nada Sayed Mahdy*, Hossam Mousa Sakr, Allam Elsayed Allam Radiology
Spectrum of meniscal lesions: An MR teaching atlas
 Spectrum of meniscal lesions: An MR teaching atlas Poster No.: C-2284 Congress: ECR 2010 Type: Educational Exhibit Topic: Musculoskeletal - Joints Authors: C. Leal, P. Alves, H. A. M. R. Tinto, J. Raposo,
Spectrum of meniscal lesions: An MR teaching atlas Poster No.: C-2284 Congress: ECR 2010 Type: Educational Exhibit Topic: Musculoskeletal - Joints Authors: C. Leal, P. Alves, H. A. M. R. Tinto, J. Raposo,
Spectrum of meniscal lesions: An MR teaching atlas
 Spectrum of meniscal lesions: An MR teaching atlas Poster No.: C-2284 Congress: ECR 2010 Type: Educational Exhibit Topic: Musculoskeletal Authors: C. Leal, P. Alves, H. Tinto, J. Raposo, T. Bilhim, A.
Spectrum of meniscal lesions: An MR teaching atlas Poster No.: C-2284 Congress: ECR 2010 Type: Educational Exhibit Topic: Musculoskeletal Authors: C. Leal, P. Alves, H. Tinto, J. Raposo, T. Bilhim, A.
ORIGINAL ARTICLE. ROLE OF MRI IN EVALUATION OF TRAUMATIC KNEE INJURIES Saurabh Chaudhuri, Priscilla Joshi, Mohit Goel
 ROLE OF MRI IN EVALUATION OF TRAUMATIC KNEE INJURIES Saurabh Chaudhuri, Priscilla Joshi, Mohit Goel 1. Associate Professor, Department of Radiodiagnosis & imaging, Bharati Vidyapeeth Medical College and
ROLE OF MRI IN EVALUATION OF TRAUMATIC KNEE INJURIES Saurabh Chaudhuri, Priscilla Joshi, Mohit Goel 1. Associate Professor, Department of Radiodiagnosis & imaging, Bharati Vidyapeeth Medical College and
JMSCR Vol 05 Issue 01 Page January
 www.jmscr.igmpublication.org Impact Factor 5.244 Index Copernicus Value: 83.27 ISSN (e)-2347-176x ISSN (p) 2455-0450 DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.18535/jmscr/v5i1.28 Diagnostic Accuracy of Magnetic Resonance
www.jmscr.igmpublication.org Impact Factor 5.244 Index Copernicus Value: 83.27 ISSN (e)-2347-176x ISSN (p) 2455-0450 DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.18535/jmscr/v5i1.28 Diagnostic Accuracy of Magnetic Resonance
MRI Evaluation of Internal derangement of the Knee Joint - A PICTORIAL REVIEW
 MRI Evaluation of Internal derangement of the Knee Joint - A PICTORIAL REVIEW Poster No.: C-1386 Congress: ECR 2015 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: V. Nadaraja, F. Abubacker Sulaiman; Chennai/IN Keywords:
MRI Evaluation of Internal derangement of the Knee Joint - A PICTORIAL REVIEW Poster No.: C-1386 Congress: ECR 2015 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: V. Nadaraja, F. Abubacker Sulaiman; Chennai/IN Keywords:
Original Research Article
 ROLE OF IN INTERNAL DERANGEMENT OF KNEE JOINT IN CORRELATION WITH ARTHROSCOPY Onteddu Joji Reddy 1, Jamkhana Abdul Gafoor 2, Balla Suresh 3, Polysetty Obuleswar Prasad 4 1Professor and HOD, Department
ROLE OF IN INTERNAL DERANGEMENT OF KNEE JOINT IN CORRELATION WITH ARTHROSCOPY Onteddu Joji Reddy 1, Jamkhana Abdul Gafoor 2, Balla Suresh 3, Polysetty Obuleswar Prasad 4 1Professor and HOD, Department
Do Not Fall on Your Knees - Recognizing Common and Uncommon Pitfalls that May Simulate Meniscal Tears
 Do Not Fall on Your Knees - Recognizing Common and Uncommon Pitfalls that May Simulate Meniscal Tears Poster No.: C-1146 Congress: ECR 2016 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: P. Musa Aguiar, J. Goncalves,
Do Not Fall on Your Knees - Recognizing Common and Uncommon Pitfalls that May Simulate Meniscal Tears Poster No.: C-1146 Congress: ECR 2016 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: P. Musa Aguiar, J. Goncalves,
Epidemiology. Meniscal Injury & Repair. Meniscus Anatomy. Meniscus Anatomy
 Epidemiology 60-70/100,000 per year Meniscal Injury & Repair Arthroscopic Mensiscectomy One of the most common orthopaedic procedures 20% of all surgeries at some centers Male:Female ratio - 2-4:1 Younger
Epidemiology 60-70/100,000 per year Meniscal Injury & Repair Arthroscopic Mensiscectomy One of the most common orthopaedic procedures 20% of all surgeries at some centers Male:Female ratio - 2-4:1 Younger
Knee: Cruciate Ligaments
 72 Knee: Cruciate Ligaments R. Kent Sanders Sagittal oblique 2.5-mm sequences along the plane of the anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) typically yield three to four images of the ACL, with the first medial
72 Knee: Cruciate Ligaments R. Kent Sanders Sagittal oblique 2.5-mm sequences along the plane of the anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) typically yield three to four images of the ACL, with the first medial
Imaging the Athlete s Knee. Peter Lowry, MD Musculoskeletal Radiology University of Colorado
 Imaging the Athlete s Knee Peter Lowry, MD Musculoskeletal Radiology University of Colorado None Disclosures Knee Imaging: Radiographs Can be performed weight-bearing or non-weight-bearing View options
Imaging the Athlete s Knee Peter Lowry, MD Musculoskeletal Radiology University of Colorado None Disclosures Knee Imaging: Radiographs Can be performed weight-bearing or non-weight-bearing View options
Stability of Post Traumatic Osteochondritis Dissecans of the Knee: MR Imaging Findings
 Chin J Radiol 2005; 30: 199-204 199 Stability of Post Traumatic Osteochondritis Dissecans of the Knee: MR Imaging Findings YU-CHUNG HUNG 1 JON-KWAY HUANG 1,2 Department of Radiology 1, Mackay Memorial
Chin J Radiol 2005; 30: 199-204 199 Stability of Post Traumatic Osteochondritis Dissecans of the Knee: MR Imaging Findings YU-CHUNG HUNG 1 JON-KWAY HUANG 1,2 Department of Radiology 1, Mackay Memorial
Unlocking the locked Knee
 Unlocking the locked Knee Poster No.: P-0027 Congress: ESSR 2013 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: J. P. SINGH, S. Srivastava, S. S. BAIJAL ; Gurgaon, Delhi 1 1 2 1 2 NCR/IN, LUCKNOW, UTTAR PRADESH/IN
Unlocking the locked Knee Poster No.: P-0027 Congress: ESSR 2013 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: J. P. SINGH, S. Srivastava, S. S. BAIJAL ; Gurgaon, Delhi 1 1 2 1 2 NCR/IN, LUCKNOW, UTTAR PRADESH/IN
A comparative study of MRI versus arthroscopic findings in ACL and meniscal injuries of the knee
 International Journal of Research in Orthopaedics Kulkarni OP et al. Int J Res Orthop. 2018 Mar;4(2):198-202 http://www.ijoro.org Original Research Article DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18203/issn.2455-4510.intjresorthop20180123
International Journal of Research in Orthopaedics Kulkarni OP et al. Int J Res Orthop. 2018 Mar;4(2):198-202 http://www.ijoro.org Original Research Article DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18203/issn.2455-4510.intjresorthop20180123
Comparative study of high resolusion ultrasonography and magnetic resonance imaging in diagnosing traumatic knee injuries & pathologies
 Original article: Comparative study of high resolusion ultrasonography and magnetic resonance imaging in diagnosing traumatic knee injuries & pathologies Dr. Rakesh Gujjar*, Dr. R. P. Bansal, Dr. Sandeep
Original article: Comparative study of high resolusion ultrasonography and magnetic resonance imaging in diagnosing traumatic knee injuries & pathologies Dr. Rakesh Gujjar*, Dr. R. P. Bansal, Dr. Sandeep
Diagnostic accuracy of Magnetic Resonance Imaging in assessment of Meniscal and ACL tear: Correlation with arthroscopy
 Open Access Original Article Diagnostic accuracy of Magnetic Resonance Imaging in assessment of Meniscal and ACL tear: Correlation with arthroscopy Jamal Yaqoob 1, Muhammad Shahbaz Alam 2, Nadeem Khalid
Open Access Original Article Diagnostic accuracy of Magnetic Resonance Imaging in assessment of Meniscal and ACL tear: Correlation with arthroscopy Jamal Yaqoob 1, Muhammad Shahbaz Alam 2, Nadeem Khalid
and K n e e J o i n t Is the most complicated joint in the body!!!!
 K n e e J o i n t K n e e J o i n t Is the most complicated joint in the body!!!! 1-Consists of two condylar joints between: A-The medial and lateral condyles of the femur and The condyles of the tibia
K n e e J o i n t K n e e J o i n t Is the most complicated joint in the body!!!! 1-Consists of two condylar joints between: A-The medial and lateral condyles of the femur and The condyles of the tibia
MRI grading of postero-lateral corner and anterior cruciate ligament injuries
 MRI grading of postero-lateral corner and anterior cruciate ligament injuries Poster No.: C-2533 Congress: ECR 2012 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: J. Lopes Dias, J. A. Sousa Pereira, L. Fernandes,
MRI grading of postero-lateral corner and anterior cruciate ligament injuries Poster No.: C-2533 Congress: ECR 2012 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: J. Lopes Dias, J. A. Sousa Pereira, L. Fernandes,
49 year old female with knee pain for several months after starting a new workout regimen. William Millard MSK Fellow
 49 year old female with knee pain for several months after starting a new workout regimen William Millard MSK Fellow DISCOID LATERAL MENISCUS Discoid lateral meniscus (DLM) Found in
49 year old female with knee pain for several months after starting a new workout regimen William Millard MSK Fellow DISCOID LATERAL MENISCUS Discoid lateral meniscus (DLM) Found in
Original Research Article. Atul Bucha 1, Sunita Dashottar 2 *, Surabhi Sharma 2, Preeth Pany 2, Rushabh Bhikhanhai Suthar 2
 International Journal of Advances in Medicine http://www.ijmedicine.com pissn 2349-3925 eissn 2349-3933 Original Research Article DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18203/2349-3933.ijam20184747 A study to evaluate
International Journal of Advances in Medicine http://www.ijmedicine.com pissn 2349-3925 eissn 2349-3933 Original Research Article DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18203/2349-3933.ijam20184747 A study to evaluate
Clinics in diagnostic imaging (177)
 Singapore Med J 2017; 58(5): 241-245 doi: 10.11622/smedj.2017038 CMEArticle Clinics in diagnostic imaging (177) Poh Lye Paul See, MBBS, FRCR Fig. 1 Sagittal proton density (PD)-weighted fast spin-echo
Singapore Med J 2017; 58(5): 241-245 doi: 10.11622/smedj.2017038 CMEArticle Clinics in diagnostic imaging (177) Poh Lye Paul See, MBBS, FRCR Fig. 1 Sagittal proton density (PD)-weighted fast spin-echo
Evaluation of Role of Magnetic Resonance Imaging in Knee Joint Injuries in Correlation with Arthroscopy
 Original Article Print ISSN: 2321-6379 Online ISSN: 2321-595X DOI: 10.17354/ijss/2017/442 Evaluation of Role of Magnetic Resonance Imaging in Knee Joint Injuries in Correlation with Arthroscopy T Sundara
Original Article Print ISSN: 2321-6379 Online ISSN: 2321-595X DOI: 10.17354/ijss/2017/442 Evaluation of Role of Magnetic Resonance Imaging in Knee Joint Injuries in Correlation with Arthroscopy T Sundara
MR Imaging Based Diagnosis of Anterior Cruciate Ligament Tears in Patients with Internal Derangement of Knee
 DOI: 10.7860/IJARS/2017/26026:2263 Radiology Section Original Article MR Imaging Based Diagnosis of Anterior Cruciate Ligament Tears in Patients with Internal Derangement of Knee Hemanth Purigali Naganna,
DOI: 10.7860/IJARS/2017/26026:2263 Radiology Section Original Article MR Imaging Based Diagnosis of Anterior Cruciate Ligament Tears in Patients with Internal Derangement of Knee Hemanth Purigali Naganna,
Meniscal Tears: Role of Axial MRI Alone and in Combination with Other Imaging Planes
 Nefise Cagla Tarhan 1,2 Christine. Chung 1 urea Valeria Rosa Mohana-orges 1 Tudor Hughes 1 Donald Resnick 1 Received September 30, 2003; accepted after revision February 2, 2004. 1 Department of Radiology,
Nefise Cagla Tarhan 1,2 Christine. Chung 1 urea Valeria Rosa Mohana-orges 1 Tudor Hughes 1 Donald Resnick 1 Received September 30, 2003; accepted after revision February 2, 2004. 1 Department of Radiology,
MR Imaging of a Posterior Root Tear of the Medial Meniscus: Diagnostic Accuracy of Various Tear Configurations and
 MR Imaging of a Posterior Root Tear of the Medial Meniscus: Diagnostic Accuracy of Various Tear Configurations and Associated Knee Abnormalities 1 Hyang Mi Lee, M.D., Jae Chan Shim, M.D., Jin Goo Kim,
MR Imaging of a Posterior Root Tear of the Medial Meniscus: Diagnostic Accuracy of Various Tear Configurations and Associated Knee Abnormalities 1 Hyang Mi Lee, M.D., Jae Chan Shim, M.D., Jin Goo Kim,
ULTRASOUND EVALUATION OF NORMAL AND ABNORMAL POSTERIOR CRUCIATE LIGAMENT - A PROSPECTIVE STUDY
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE ULTRASOUND EVALUATION OF NORMAL AND ABNORMAL POSTERIOR CRUCIATE LIGAMENT - A PROSPECTIVE STUDY Palle Lalitha, 1 M. Ch. Balaji Reddy, 1 K. Jagannath Reddy, 1 Vijaya Kumari 2 1 Department
ORIGINAL ARTICLE ULTRASOUND EVALUATION OF NORMAL AND ABNORMAL POSTERIOR CRUCIATE LIGAMENT - A PROSPECTIVE STUDY Palle Lalitha, 1 M. Ch. Balaji Reddy, 1 K. Jagannath Reddy, 1 Vijaya Kumari 2 1 Department
MRI versus clinical examination for the diagnosis of meniscal and ligamentous injuries of kneee
 Original Research Article MRI versus clinical examination for the diagnosis of meniscal and ligamentous injuries of kneee Rakesh Gujjar *, R. P. Bansal, L. K. Gotecha, Raja Kollu Department of Radio-diagnosis
Original Research Article MRI versus clinical examination for the diagnosis of meniscal and ligamentous injuries of kneee Rakesh Gujjar *, R. P. Bansal, L. K. Gotecha, Raja Kollu Department of Radio-diagnosis
Learning Objectives. Meniscal Injuries of the Knee. Meniscal Anatomy. Medial Meniscus. Chock Block Shape. Lateral Meniscus
 Meniscal Injuries of the Knee Learning Objectives Edward P. Mulligan, MS, PT, SCS, ATC VP, National Director of Clinical Education HealthSouth Corporation Grapevine, TX Clinical Instructor University of
Meniscal Injuries of the Knee Learning Objectives Edward P. Mulligan, MS, PT, SCS, ATC VP, National Director of Clinical Education HealthSouth Corporation Grapevine, TX Clinical Instructor University of
Differential Diagnosis
 Case 31yo M who sustained an injury to L knee while playing Basketball approximately 2 weeks ago. He describes pivoting and hyperextending his knee, which swelled over the next few days. He now presents
Case 31yo M who sustained an injury to L knee while playing Basketball approximately 2 weeks ago. He describes pivoting and hyperextending his knee, which swelled over the next few days. He now presents
MRI of the Knee: Part 4 - normal variants that may simulate disease. Mark Anderson, M.D. University of Virginia
 MRI of the Knee: Part 4 - normal variants that may simulate disease Mark Anderson, M.D. University of Virginia discuss the most common normal variants in the pediatric knee that may simulate pathology
MRI of the Knee: Part 4 - normal variants that may simulate disease Mark Anderson, M.D. University of Virginia discuss the most common normal variants in the pediatric knee that may simulate pathology
Traumatic and non-traumatic isolated horizontal meniscal tears of the knee in patients less than 40 years of age
 DOI 10.1007/s00590-012-1028-6 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Traumatic and non-traumatic isolated horizontal meniscal tears of the knee in patients less than 40 years of age Jung-Ryul Kim Byung-Guk Kim Jin-Woo Kim Jin-Hyun
DOI 10.1007/s00590-012-1028-6 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Traumatic and non-traumatic isolated horizontal meniscal tears of the knee in patients less than 40 years of age Jung-Ryul Kim Byung-Guk Kim Jin-Woo Kim Jin-Hyun
The Meniscal Roots: Gross Anatomic Correlation with 3-T MRI Findings
 rody et al. Meniscal Root MRI Musculoskeletal Imaging Pictorial Essay Jeffrey M. rody 1 Michael J. Hulstyn 2 raden. Fleming 3 Glenn. Tung 1 rody JM, Hulstyn MJ, Fleming, Tung G Keywords: anatomy, knee,
rody et al. Meniscal Root MRI Musculoskeletal Imaging Pictorial Essay Jeffrey M. rody 1 Michael J. Hulstyn 2 raden. Fleming 3 Glenn. Tung 1 rody JM, Hulstyn MJ, Fleming, Tung G Keywords: anatomy, knee,
MR imaging of the knee in marathon runners before and after competition
 Skeletal Radiol (2001) 30:72 76 International Skeletal Society 2001 ARTICLE W. Krampla R. Mayrhofer J. Malcher K.H. Kristen M. Urban W. Hruby MR imaging of the knee in marathon runners before and after
Skeletal Radiol (2001) 30:72 76 International Skeletal Society 2001 ARTICLE W. Krampla R. Mayrhofer J. Malcher K.H. Kristen M. Urban W. Hruby MR imaging of the knee in marathon runners before and after
FieldStrength. Achieva 3.0T enables cutting-edge applications, best-in-class MSK images
 FieldStrength Publication for the Philips MRI Community Issue 33 December 2007 Achieva 3.0T enables cutting-edge applications, best-in-class MSK images Palo Alto Medical Clinic Sports Medicine Center employs
FieldStrength Publication for the Philips MRI Community Issue 33 December 2007 Achieva 3.0T enables cutting-edge applications, best-in-class MSK images Palo Alto Medical Clinic Sports Medicine Center employs
Knee Joint Anatomy 101
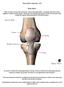 Knee Joint Anatomy 101 Bone Basics There are three bones at the knee joint femur, tibia and patella commonly referred to as the thighbone, shinbone and kneecap. The fibula is not typically associated with
Knee Joint Anatomy 101 Bone Basics There are three bones at the knee joint femur, tibia and patella commonly referred to as the thighbone, shinbone and kneecap. The fibula is not typically associated with
What s your diagnosis?
 Case Study 58 A 61-year-old truck driver man presented with a valgus injury to the left knee joint when involved in a truck accident. What s your diagnosis? Diagnosis : Avulsion of Deep MCL The medial
Case Study 58 A 61-year-old truck driver man presented with a valgus injury to the left knee joint when involved in a truck accident. What s your diagnosis? Diagnosis : Avulsion of Deep MCL The medial
Viviane Khoury, MD. Assistant Professor Department of Radiology University of Pennsylvania
 U Penn Diagnostic Imaging: On the Cape Chatham, MA July 11-15, 2016 Viviane Khoury, MD Assistant Professor Department of Radiology University of Pennsylvania Hip imaging has changed in recent years: new
U Penn Diagnostic Imaging: On the Cape Chatham, MA July 11-15, 2016 Viviane Khoury, MD Assistant Professor Department of Radiology University of Pennsylvania Hip imaging has changed in recent years: new
Benjamin E. Plotkin, M.D., Vishal K. Agarwal, M.D., and Rajeev Varma, M.D.
 Stump Entrapment of the Torn Anterior Cruciate Ligament Benjamin E. Plotkin, M.D., Vishal K. Agarwal, M.D., and Rajeev Varma, M.D. Citation: Plotkin BE, Agarwal VK, Varma R. Stump Entrapment of the Torn
Stump Entrapment of the Torn Anterior Cruciate Ligament Benjamin E. Plotkin, M.D., Vishal K. Agarwal, M.D., and Rajeev Varma, M.D. Citation: Plotkin BE, Agarwal VK, Varma R. Stump Entrapment of the Torn
LATERAL MENISCUS SLOPE AND ITS CLINICAL RELEVANCE IN PATIENTS WITH A COMBINED ACL TEAR AND POSTERIOR TIBIA COMPRESSION
 LATERAL MENISCUS SLOPE AND ITS CLINICAL RELEVANCE IN PATIENTS WITH A COMBINED ACL TEAR AND POSTERIOR TIBIA COMPRESSION R. ŚMIGIELSKI, B. DOMINIK, U, ZDANOWICZ, Z. GAJEWSKI, K. SKIERBISZEWSKA, K. SIEWRUK,
LATERAL MENISCUS SLOPE AND ITS CLINICAL RELEVANCE IN PATIENTS WITH A COMBINED ACL TEAR AND POSTERIOR TIBIA COMPRESSION R. ŚMIGIELSKI, B. DOMINIK, U, ZDANOWICZ, Z. GAJEWSKI, K. SKIERBISZEWSKA, K. SIEWRUK,
Imaging the Knee 17/10/2017. Friction syndrome Common in runners or cyclists Fluid between ITB and Lateral femoral condyle
 17/10/2017 Imaging the Knee Alicia M. Yochum RN, DC, DACBR, RMSK Iliotibial Band Syndrome Ligamentous Tears (ACL, PCL, MCL, LCL) Meniscal Tears Cartilage Degeneration Quadriceps/Patellar tendinosis Osteochondral
17/10/2017 Imaging the Knee Alicia M. Yochum RN, DC, DACBR, RMSK Iliotibial Band Syndrome Ligamentous Tears (ACL, PCL, MCL, LCL) Meniscal Tears Cartilage Degeneration Quadriceps/Patellar tendinosis Osteochondral
The Knee. Prof. Oluwadiya Kehinde
 The Knee Prof. Oluwadiya Kehinde www.oluwadiya.sitesled.com The Knee: Introduction 3 bones: femur, tibia and patella 2 separate joints: tibiofemoral and patellofemoral. Function: i. Primarily a hinge joint,
The Knee Prof. Oluwadiya Kehinde www.oluwadiya.sitesled.com The Knee: Introduction 3 bones: femur, tibia and patella 2 separate joints: tibiofemoral and patellofemoral. Function: i. Primarily a hinge joint,
MRI Diagnosis of Anterior Cruciate Ligament Tears: What is the Added Value of Oblique Sagittal Technique?
 Med. J. Cairo Univ., Vol. 85, No. 5, September: 1865-1872, 2017 www.medicaljournalofcairouniversity.net MRI Diagnosis of Anterior Cruciate Ligament Tears: What is the Added Value of Oblique Sagittal Technique?
Med. J. Cairo Univ., Vol. 85, No. 5, September: 1865-1872, 2017 www.medicaljournalofcairouniversity.net MRI Diagnosis of Anterior Cruciate Ligament Tears: What is the Added Value of Oblique Sagittal Technique?
Medical Diagnosis for Michael s Knee
 Medical Diagnosis for Michael s Knee Introduction The following report mainly concerns the diagnosis and treatment of the patient, Michael. Given that Michael s clinical problem surrounds an injury about
Medical Diagnosis for Michael s Knee Introduction The following report mainly concerns the diagnosis and treatment of the patient, Michael. Given that Michael s clinical problem surrounds an injury about
CLINICAL PRESENTATION AND RADIOLOGY QUIZ QUESTION
 Donald L. Renfrew, MD Radiology Associates of the Fox Valley, 333 N. Commercial Street, Suite 100, Neenah, WI 54956 12/01/2012 Radiology Quiz of the Week # 101 Page 1 CLINICAL PRESENTATION AND RADIOLOGY
Donald L. Renfrew, MD Radiology Associates of the Fox Valley, 333 N. Commercial Street, Suite 100, Neenah, WI 54956 12/01/2012 Radiology Quiz of the Week # 101 Page 1 CLINICAL PRESENTATION AND RADIOLOGY
RECENT ADVANCES IN CLINICAL MR OF ARTICULAR CARTILAGE
 In Practice RECENT ADVANCES IN CLINICAL MR OF ARTICULAR CARTILAGE By Atsuya Watanabe, MD, PhD, Director, Advanced Diagnostic Imaging Center and Associate Professor, Department of Orthopedic Surgery, Teikyo
In Practice RECENT ADVANCES IN CLINICAL MR OF ARTICULAR CARTILAGE By Atsuya Watanabe, MD, PhD, Director, Advanced Diagnostic Imaging Center and Associate Professor, Department of Orthopedic Surgery, Teikyo
Comparative study of sensitivity and specificity of MRI versus GNRB to detect ACL complete and partial tears
 Comparative study of sensitivity and specificity of MRI versus GNRB to detect ACL complete and partial tears Anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) tears are difficult to diagnose and treat (DeFranco). The preoperative
Comparative study of sensitivity and specificity of MRI versus GNRB to detect ACL complete and partial tears Anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) tears are difficult to diagnose and treat (DeFranco). The preoperative
Causation Review - Meniscal Tears.
 Causation Review - Meniscal Tears. Classification Of Meniscal Tears Of The Knee And The Evidence That Certain Tears Are Degenerative In Origin; Including The Relationship Of Meniscal Tears To Knee Osteoarthritis.
Causation Review - Meniscal Tears. Classification Of Meniscal Tears Of The Knee And The Evidence That Certain Tears Are Degenerative In Origin; Including The Relationship Of Meniscal Tears To Knee Osteoarthritis.
ESMRMB. School of MRI Advanced MR Imaging of the Musculoskeletal System. November 10-12, 2016 Menton/FR
 School of MRI 2016 Advanced MR Imaging of the Musculoskeletal System November 10-12, 2016 Menton/FR Topic 5 Knee L. Sconfienza io@lucasconfienza.it THE KNEE Luca Maria Sconfienza, MD PhD Unit of Diagnostic
School of MRI 2016 Advanced MR Imaging of the Musculoskeletal System November 10-12, 2016 Menton/FR Topic 5 Knee L. Sconfienza io@lucasconfienza.it THE KNEE Luca Maria Sconfienza, MD PhD Unit of Diagnostic
MENISCAL INJURIES. (copyright s h palmer 2009) MENISCAL FUNCTION
 (copyright s h palmer 2009) MENISCAL FUNCTION MENISCAL INJURIES Menisci are important for weight bearing, load distribution, joint stability and proprioception. Figure 1: A normal medial meniscus Any load
(copyright s h palmer 2009) MENISCAL FUNCTION MENISCAL INJURIES Menisci are important for weight bearing, load distribution, joint stability and proprioception. Figure 1: A normal medial meniscus Any load
On Field Assessment and Management of Acute Knee Injuries: A Physiotherapist s Perspective
 On Field Assessment and Management of Acute Knee Injuries: A Physiotherapist s Perspective Jessica Condliffe Physiotherapist / Clinic Manager TBI Health Wellington Presentation Outline Knee anatomy review
On Field Assessment and Management of Acute Knee Injuries: A Physiotherapist s Perspective Jessica Condliffe Physiotherapist / Clinic Manager TBI Health Wellington Presentation Outline Knee anatomy review
Posttraumatic subchondral bone contusions and fractures of the talotibial joint: Occurrence of kissing lesions
 KISSING CONTUSIONS CHAPTER 7 Posttraumatic subchondral bone contusions and fractures of the talotibial joint: Occurrence of kissing lesions Elizabeth S. Sijbrandij 1, Ad P.G. van Gils 1, Jan Willem K.
KISSING CONTUSIONS CHAPTER 7 Posttraumatic subchondral bone contusions and fractures of the talotibial joint: Occurrence of kissing lesions Elizabeth S. Sijbrandij 1, Ad P.G. van Gils 1, Jan Willem K.
2 A B Fig. 1. Lateral tibial condyle fracture with joint effusion in a 35-year-old man. Sagittal T2-weighted MRI shows a large amount of effusion
 1 2 1 1 1 2 A B Fig. 1. Lateral tibial condyle fracture with joint effusion in a 35-year-old man. Sagittal T2-weighted MRI shows a large amount of effusion (between arrowheads) in the suprapatellar pouch,
1 2 1 1 1 2 A B Fig. 1. Lateral tibial condyle fracture with joint effusion in a 35-year-old man. Sagittal T2-weighted MRI shows a large amount of effusion (between arrowheads) in the suprapatellar pouch,
A comparison of arthroscopic diagnosis of ramp lesion and pre-operative MRI evaluation
 A comparison of arthroscopic diagnosis of ramp lesion and pre-operative MRI evaluation Yasuma S, Nozaki M, Kobayashi M, Kawanishi Y Yoshida M, Mitsui H, Nagaya Y, Iguchi H, Murakami H Department of Orthopaedic
A comparison of arthroscopic diagnosis of ramp lesion and pre-operative MRI evaluation Yasuma S, Nozaki M, Kobayashi M, Kawanishi Y Yoshida M, Mitsui H, Nagaya Y, Iguchi H, Murakami H Department of Orthopaedic
Rehab Considerations: Meniscus
 Rehab Considerations: Meniscus Steve Cox, PT, DPT Department of Orthopaedics School of Medicine University of Texas Health Science Center at San Antonio 1 -Anatomy/ Function/ Injuries -Treatment Options
Rehab Considerations: Meniscus Steve Cox, PT, DPT Department of Orthopaedics School of Medicine University of Texas Health Science Center at San Antonio 1 -Anatomy/ Function/ Injuries -Treatment Options
MRI of ligaments. Ligament biomechanics Spine Shoulder Elbow Hand/wrist Pelvis/hip Knee Foot/ankle
 MRI of ligaments Chang Ho Kang M.D. Korea University Anam Hospital Spine Shoulder Elbow Hand/wrist Pelvis/hip Knee Foot/ankle Introduction Ligament Fibrous connective tissue Attaches bone to bone Holds
MRI of ligaments Chang Ho Kang M.D. Korea University Anam Hospital Spine Shoulder Elbow Hand/wrist Pelvis/hip Knee Foot/ankle Introduction Ligament Fibrous connective tissue Attaches bone to bone Holds
Knee MRI Update Case Review 2009 Russell C. Fritz, M.D. National Orthopedic Imaging Associates San Francisco, CA
 Knee MRI Update Case Review 2009 Russell C. Fritz, M.D. National Orthopedic Imaging Associates San Francisco, CA Meniscal Tears -linear increased signal extending to an articular surface is the hallmark
Knee MRI Update Case Review 2009 Russell C. Fritz, M.D. National Orthopedic Imaging Associates San Francisco, CA Meniscal Tears -linear increased signal extending to an articular surface is the hallmark
Available online at
 Original Research Article Evaluation of knee joint by MRI in 65 patients Gulamus sibtain asad *, Himanshu Singla, Ankit vasoya, P. J. Jhala 2 2 nd year Resident, 2 Professor Radiology Department, SBKS
Original Research Article Evaluation of knee joint by MRI in 65 patients Gulamus sibtain asad *, Himanshu Singla, Ankit vasoya, P. J. Jhala 2 2 nd year Resident, 2 Professor Radiology Department, SBKS
THE NEW ZEALAND MEDICAL JOURNAL
 THE NEW ZEALAND MEDICAL JOURNAL Vol 118 No 1209 ISSN 1175 8716 Reliability of magnetic resonance imaging for traumatic injury of the knee Keith Winters, Russell Tregonning Abstract Background: Magnetic
THE NEW ZEALAND MEDICAL JOURNAL Vol 118 No 1209 ISSN 1175 8716 Reliability of magnetic resonance imaging for traumatic injury of the knee Keith Winters, Russell Tregonning Abstract Background: Magnetic
Magnetic Resonance Imaging of Knee Trauma: Biomechanical Approach
 Topics in Magnetic Resonance Imaging 14(2): 161 178 2003 Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, Inc., Philadelphia Magnetic Resonance Imaging of Knee Trauma: Biomechanical Approach William E. Palmer, M.D. Summary:
Topics in Magnetic Resonance Imaging 14(2): 161 178 2003 Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, Inc., Philadelphia Magnetic Resonance Imaging of Knee Trauma: Biomechanical Approach William E. Palmer, M.D. Summary:
Tears of the knee menisci frequently occur not. Is There a Role for Sonography in the Diagnosis of Tears of the Knee Menisci?
 Is There a Role for Sonography in the Diagnosis of Tears of the Knee Menisci? Roberto Azzoni, MD, Paolo Cabitza, MD Orthopedic and Trauma Surgery Department, Policlinico San Donato Institute, University
Is There a Role for Sonography in the Diagnosis of Tears of the Knee Menisci? Roberto Azzoni, MD, Paolo Cabitza, MD Orthopedic and Trauma Surgery Department, Policlinico San Donato Institute, University
Meniscal Root Tears: Evaluation, Imaging, and Repair Techniques
 Meniscal Root Tears: Evaluation, Imaging, and Repair Techniques R O B E R T N A S C I M E N TO, M D, M S C H I E F OF S P O RT S M E D I C I N E & SH O U L D E R S U R G E RY N E W TO N- W E L L E S L
Meniscal Root Tears: Evaluation, Imaging, and Repair Techniques R O B E R T N A S C I M E N TO, M D, M S C H I E F OF S P O RT S M E D I C I N E & SH O U L D E R S U R G E RY N E W TO N- W E L L E S L
BASELINE QUESTIONNAIRE (SURGEON)
 SECTION A: STUDY INFORMATION Subject ID: - - Study Visit: Baseline Site Number: Date: / / Surgeon ID: SECTION B: INITIAL SURGEON HISTORY B1. Previous Knee Surgery: Yes No Not recorded B2. Number of Previous
SECTION A: STUDY INFORMATION Subject ID: - - Study Visit: Baseline Site Number: Date: / / Surgeon ID: SECTION B: INITIAL SURGEON HISTORY B1. Previous Knee Surgery: Yes No Not recorded B2. Number of Previous
The Knee. Tibio-Femoral
 The Knee Tibio-Femoral Osteology Distal Femur with Proximal Tibia Largest Joint Cavity in the Body A modified hinge joint with significant passive rotation Technically, one degree of freedom (Flexion/Extension)
The Knee Tibio-Femoral Osteology Distal Femur with Proximal Tibia Largest Joint Cavity in the Body A modified hinge joint with significant passive rotation Technically, one degree of freedom (Flexion/Extension)
Original Report. The Reverse Segond Fracture: Association with a Tear of the Posterior Cruciate Ligament and Medial Meniscus
 Eva M. Escobedo 1 William J. Mills 2 John. Hunter 1 Received July 10, 2001; accepted after revision October 1, 2001. 1 Department of Radiology, University of Washington Harborview Medical enter, 325 Ninth
Eva M. Escobedo 1 William J. Mills 2 John. Hunter 1 Received July 10, 2001; accepted after revision October 1, 2001. 1 Department of Radiology, University of Washington Harborview Medical enter, 325 Ninth
(Alternate title) Evaluation of Meniscal Extrusion with Posterior Root Disruption and Repair using Ultrasound
 Evaluation of lateral meniscal position with weight bearing: Ultrasonography to measure extrusion with intact, torn and repaired posterior root attachments (Alternate title) Evaluation of Meniscal Extrusion
Evaluation of lateral meniscal position with weight bearing: Ultrasonography to measure extrusion with intact, torn and repaired posterior root attachments (Alternate title) Evaluation of Meniscal Extrusion
Case Report: Knee MR Imaging of Haemarthrosis in a Case of Haemophilia A
 Clinical > Pediatric Imaging Case Report: Knee MR Imaging of Haemarthrosis in a Case of Haemophilia A M. A. Weber, J. K. Kloth University Hospital Heidelberg, Department of Diagnostic and Interventional
Clinical > Pediatric Imaging Case Report: Knee MR Imaging of Haemarthrosis in a Case of Haemophilia A M. A. Weber, J. K. Kloth University Hospital Heidelberg, Department of Diagnostic and Interventional
Please differentiate an internal derangement from an external knee injury.
 Knee Orthopaedic Tests Sports and Knee Injuries James J. Lehman, DC, MBA, DABCO University of Bridgeport College of Chiropractic Knee Injury Strain, Sprain, Internal Derangement Anatomy of the Knee Please
Knee Orthopaedic Tests Sports and Knee Injuries James J. Lehman, DC, MBA, DABCO University of Bridgeport College of Chiropractic Knee Injury Strain, Sprain, Internal Derangement Anatomy of the Knee Please
FAI syndrome with or without labral tear.
 Case This 16-year-old female, soccer athlete was treated for pain in the right groin previously. Now has acute onset of pain in the left hip. The pain was in the groin that was worse with activities. Diagnosis
Case This 16-year-old female, soccer athlete was treated for pain in the right groin previously. Now has acute onset of pain in the left hip. The pain was in the groin that was worse with activities. Diagnosis
Medial Knee Osteoarthritis Precedes Medial Meniscal Posterior Root Tear with an Event of Painful Popping
 Medial Knee Osteoarthritis Precedes Medial Meniscal Posterior Root Tear with an Event of Painful Popping Dhong Won Lee, M.D, Ji Nam Kim, M.D., Jin Goo Kim, M.D., Ph.D. KonKuk University Medical Center
Medial Knee Osteoarthritis Precedes Medial Meniscal Posterior Root Tear with an Event of Painful Popping Dhong Won Lee, M.D, Ji Nam Kim, M.D., Jin Goo Kim, M.D., Ph.D. KonKuk University Medical Center
Proximal tibial bony and meniscal slopes are higher in ACL injured subjects than controls: a comparative MRI study
 Proximal tibial bony and meniscal slopes are higher in ACL injured subjects than controls: a comparative MRI study Ashraf Elmansori, Timothy Lording, Raphaël Dumas, Khalifa Elmajri, Philippe Neyret, Sebastien
Proximal tibial bony and meniscal slopes are higher in ACL injured subjects than controls: a comparative MRI study Ashraf Elmansori, Timothy Lording, Raphaël Dumas, Khalifa Elmajri, Philippe Neyret, Sebastien
Discoid Medial Meniscus Tear, with a Literature Review of Treatments
 Case Report Knee Surg Relat Res 2017;29(3):237-242 https://doi.org/10.5792/ksrr.15.054 pissn 2234-0726 eissn 2234-2451 Knee Surgery & Related Research Discoid Medial Meniscus Tear, with a Literature Review
Case Report Knee Surg Relat Res 2017;29(3):237-242 https://doi.org/10.5792/ksrr.15.054 pissn 2234-0726 eissn 2234-2451 Knee Surgery & Related Research Discoid Medial Meniscus Tear, with a Literature Review
Multi-ligamentous knee injuries - MRI injury patterns at a glance
 Multi-ligamentous knee injuries - MRI injury patterns at a glance Poster No.: P-0068 Congress: ESSR 2015 Type: Educational Poster Authors: A. Rastogi, D. Whelan, R. Martin, W. Mak, D. Pearce ; 1 1 1 2
Multi-ligamentous knee injuries - MRI injury patterns at a glance Poster No.: P-0068 Congress: ESSR 2015 Type: Educational Poster Authors: A. Rastogi, D. Whelan, R. Martin, W. Mak, D. Pearce ; 1 1 1 2
HAGL lesion of the shoulder
 HAGL lesion of the shoulder A 24 year old rugby player presented to an orthopaedic surgeon with a history of dislocation of the left shoulder. It reduced spontaneously and again later during the same match.
HAGL lesion of the shoulder A 24 year old rugby player presented to an orthopaedic surgeon with a history of dislocation of the left shoulder. It reduced spontaneously and again later during the same match.
Accuracy of Magnetic Resonance Imaging of the Knee and Unjustified Surgery
 CLINICAL ORTHOPAEDICS AND RELATED RESEARCH Number 0, pp. 000 000 2006 Lippincott Williams & Wilkins Accuracy of Magnetic Resonance Imaging of the Knee and Unjustified Surgery Peleg Ben-Galim, MD*; Ely
CLINICAL ORTHOPAEDICS AND RELATED RESEARCH Number 0, pp. 000 000 2006 Lippincott Williams & Wilkins Accuracy of Magnetic Resonance Imaging of the Knee and Unjustified Surgery Peleg Ben-Galim, MD*; Ely
4/28/2010. Fractures. Normal Bone and Normal Ossification Bone Terms. Epiphysis Epiphyseal Plate (physis) Metaphysis
 Fractures Normal Bone and Normal Ossification Bone Terms Epiphysis Epiphyseal Plate (physis) Metaphysis Diaphysis 1 Fracture Classifications A. Longitudinal B. Transverse C. Oblique D. Spiral E. Incomplete
Fractures Normal Bone and Normal Ossification Bone Terms Epiphysis Epiphyseal Plate (physis) Metaphysis Diaphysis 1 Fracture Classifications A. Longitudinal B. Transverse C. Oblique D. Spiral E. Incomplete
Meniscus T2 Relaxation Time at Various Stages of Knee Joint Degeneration
 Meniscus T2 Relaxation Time at Various Stages of Knee Joint Degeneration Richard Kijowski, Michael Fazio, Benjamin Beduhn, and Fang Liu Department of Radiology University of Wisconsin School of Medicine
Meniscus T2 Relaxation Time at Various Stages of Knee Joint Degeneration Richard Kijowski, Michael Fazio, Benjamin Beduhn, and Fang Liu Department of Radiology University of Wisconsin School of Medicine
UCLA UCLA Previously Published Works
 UCLA UCLA Previously Published Works Title MR-IMAGING OF TIBIAL COLLATERAL LIGAMENT INJURY - COMPARISON WITH CLINICAL EXAMINATION Permalink https://escholarship.org/uc/item/2bs9g934 Journal SKELETAL RADIOLOGY,
UCLA UCLA Previously Published Works Title MR-IMAGING OF TIBIAL COLLATERAL LIGAMENT INJURY - COMPARISON WITH CLINICAL EXAMINATION Permalink https://escholarship.org/uc/item/2bs9g934 Journal SKELETAL RADIOLOGY,
Medical Practice for Sports Injuries and Disorders of the Knee
 Sports-Related Injuries and Disorders Medical Practice for Sports Injuries and Disorders of the Knee JMAJ 48(1): 20 24, 2005 Hirotsugu MURATSU*, Masahiro KUROSAKA**, Tetsuji YAMAMOTO***, and Shinichi YOSHIDA****
Sports-Related Injuries and Disorders Medical Practice for Sports Injuries and Disorders of the Knee JMAJ 48(1): 20 24, 2005 Hirotsugu MURATSU*, Masahiro KUROSAKA**, Tetsuji YAMAMOTO***, and Shinichi YOSHIDA****
KNEE INJURIES IN SPORTS MEDICINE
 KNEE INJURIES IN SPORTS MEDICINE Irving Raphael, MD June 13, 2014 RSM Medical Associates Head Team Physician Syracuse University Outline Meniscal Injuries anatomy Exam Treatment ACL Injuries Etiology Physical
KNEE INJURIES IN SPORTS MEDICINE Irving Raphael, MD June 13, 2014 RSM Medical Associates Head Team Physician Syracuse University Outline Meniscal Injuries anatomy Exam Treatment ACL Injuries Etiology Physical
Knee Joint Assessment and General View
 Knee Joint Assessment and General View Done by; Mshari S. Alghadier BSc Physical Therapy RHPT 366 m.alghadier@sau.edu.sa http://faculty.sau.edu.sa/m.alghadier/ Functional anatomy The knee is the largest
Knee Joint Assessment and General View Done by; Mshari S. Alghadier BSc Physical Therapy RHPT 366 m.alghadier@sau.edu.sa http://faculty.sau.edu.sa/m.alghadier/ Functional anatomy The knee is the largest
B one contusion is a finding substantiated by magnetic
 592 ORIGINAL ARTICLE The appearance of kissing contusion in the acutely injured knee in the athletes I P Terzidis, A G Christodoulou, A L Ploumis, S R Metsovitis, M Koimtzis, P Givissis... See end of article
592 ORIGINAL ARTICLE The appearance of kissing contusion in the acutely injured knee in the athletes I P Terzidis, A G Christodoulou, A L Ploumis, S R Metsovitis, M Koimtzis, P Givissis... See end of article
