Ultrasound of the Shoulder: Asymptomatic Findings in Men
|
|
|
- Georgina Melton
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Musculoskeletal Imaging Original Research Girish et al. Shoulder Ultrasound Findings Musculoskeletal Imaging Original Research Gandikota Girish 1 Lucas G. Lobo 1 Jon A. Jacobson 1 Yoav Morag 1 Bruce Miller 2 David A. Jamadar 1 Girish G, Lobo LG, Jacobson JA, Morag Y, Miller B, Jamadar DA Keywords: asymptomatic findings, musculoskeletal ultrasound, shoulder DOI: /AJR Received April 3, 2011; accepted after revision May 26, Department of Radiology, University of Michigan Hospitals, 1500 E Medical Center Dr, Ann Arbor, MI Address correspondence to G. Girish (ggirish@med.umich.edu). 2 Department of Orthopedic Surgery, University of Michigan Hospitals, Ann Arbor, MI. WEB This is a Web exclusive article. AJR 2011; 197:W713 W X/11/1974 W713 American Roentgen Ray Society Ultrasound of the Shoulder: Asymptomatic Findings in Men OBJECTIVE. The purpose of this study was to examine the range and prevalence of asymp tomatic findings at sonography of the shoulder. MATERIALS AND METHODS. The study sample comprised 51 consecutively enrolled subjects who had no symptoms in either shoulder. Ultrasound of one shoulder per patient was performed by a musculoskeletal sonographer according to a defined protocol that included imaging of the rotator cuff, tendon of the long head of the biceps brachii muscle, subacromial-subdeltoid bursa, acromioclavicular joint, and posterior labrum. The shoulder imaged was determined at random. The 51 scans were retrospectively analyzed by three fellowship-trained musculoskeletal radiologists in consensus, and pathologic findings were recorded. Subtle or questionable findings of mild tendinosis, bursal prominence, and mild osteoarthritis were not recorded. RESULTS. Twenty-five right and 26 left shoulders were imaged. The subject age range was years. Ultrasound showed subacromial-subdeltoid bursal thickening in 78% (40/51) of the subjects, acromioclavicular joint osteoarthritis in 65% (33/51), supraspinatus tendinosis in 39% (20/51), subscapularis tendinosis in 25% (13/51), partial-thickness tear of the bursal side of the supraspinatus tendon in 22% (11/51), and posterior glenoid labral abnormality in 14% (7/51). All other findings had a prevalence of 10% or less. CONCLUSION. Asymptomatic shoulder abnormalities were found in 96% of the subjects. The most common were subacromial-subdeltoid bursal thickening, acromioclavicular joint osteoarthritis, and supraspinatus tendinosis. Ultrasound findings should be interpreted closely with clinical findings to determine the cause of symptoms. U ltrasound of the shoulder is accepted as the investigation of choice for rotator cuff abnormality in many centers around the world [1 3]. It is also one of the most commonly performed studies among all diagnostic musculoskeletal ultrasound examinations. Study results [3, 4] have indicated that the sensitivity and specificity of ultrasound equal those of MRI in assessment of the rotator cuff. Several advantages of ultrasound are availability, cost-effectiveness, and patient preference for ultrasound evaluation over MRI [5]. Dynamic imaging and immediate patient feedback are other advantages of ultrasound. However, ultrasound is heavily operator dependent, and thorough training of the operator is essential to guarantee high sensitivity and specificity of the diagnostic information obtained. Incidentally findings of asymptomatic rotator cuff tears have been made at MRI [6 10], ultrasound [11 17], and cadaveric studies [18 21]. A complete routine shoulder examination involves assessment of rotator cuff and surrounding structures [22]. To our knowledge, there have been no peer-reviewed reports of asymptomatic shoulder findings at ultrasound examinations that include the entire anatomy of the shoulder, that is, the rotator cuff and all nearby structures. The purpose of this study was to describe the prevalence of asympto matic findings at shoulder ultrasound and highlight the spectrum of asymptomatic shoulder abnormalities that may be encountered at sonographic examinations. Awareness of the range of asymptomatic shoulder abnormalities is essential to gaining perspective on the clinical importance of such findings in diagnosis and patient care. Materials and Methods Institutional review board approval was obtained before the study, and patient consent was obtained. W713
2 Girish et al. The patient sample consisted of 51 consecutively registered men without symptoms who were recruited as a part of a wider study of bone density in the first half of These patients had gone to the orthopedic clinic because of knee problems. All subjects were men because women were excluded from the study to avoid postmenopausal effects on humeral bone density. All subjects included in the study reported no symptoms, trauma, or treatment involving either shoulder as determined by a sport medicine trained orthopedic shoulder surgeon. No subject had a history of systemic inflammatory disease. Medical records, including reports of other imaging studies, were reviewed. All scans were performed according to a routine shoulder protocol with a 12-MHz linear-array high-frequency transducer (model iu-22, Philips Healthcare). Scans were performed by one of two musculoskeletal sonographers (each with more than 5 years of musculoskeletal scanning experience), and both static images and cine clips were recorded. The sonographer who performed the scan was blinded to the subject s dominant side, and a single randomly determined shoulder was scanned per patient. The routine shoulder ultrasound protocol at our institution included evaluation of the rotator cuff and the tendon of the long head of the biceps brachii muscle in the long and short axes and of the subacromial-subdeltoid bursa, acromioclavicular joint, and posterior labrum. Dynamic assessment for subacromial impingement and subluxation and dislocation of the long head of the biceps brachii was also performed. Shoulder ultrasound static images and cine clips were retrospectively reviewed by three musculoskeletal radiologists fellowship trained in obtaining and evaluating musculoskeletal ultrasound images; each had more than 5 years of musculoskeletal scanning experience. Only definitive sonographic abnormalities agreed on by the three musculoskeletal radiologists in consensus were included in the study. The ultrasound diagnoses of pathologic findings were based on the following criteria. Full-thickness tear was defined as discontinuity of the tendon fibers resulting in communication between the articular and bursal surfaces appearing as a hypoechoic or anechoic defect. Supraspinatus tears extending 2.5 cm or more posterior to the biceps tendon in the transverse view were regarded as tears extending into the infraspinatus. Partial-thickness tear was defined as partial tear of the tendon fibers involving either the bursal or the articular surface that appeared as a focal hypoechoic or anechoic defect not traversing the entire tendon thickness. Tendinosis was defined as tendon thickening associated with abnormal echogenicity and loss of the normal fibrillar echotexture of the tendon evaluated subjectively by consensus. Atrophy was defined as increased TABLE 1: Prevalence of Asymptomatic Shoulder Ultrasound Findings (n = 51) Finding Prevalence (%) Supraspinatus Full-thickness tear 10 (5) Partial-thickness tear, articular 4 (2) Partial-thickness tear, bursal 22 (11) Tendinosis 39 (20) Calcification 4 (2) Infraspinatus Full-thickness tear 4 (2) Tendinosis 10 (5) Subscapularis Tendinosis 25 (13) Partial-thickness tear 10 (5) Calcification 4 (2) Teres minor atrophy 8 (4) Biceps brachii Tendinosis 4 (2) Full-thickness tear 2 (1) Fluid distention of sheath 2 (1) Subluxation or dislocation 6 (3) Subacromial-subdeltoid bursal thickening 78 (40) Subacromial impingement 6 (3) Acromioclavicular osteoarthritis 65 (33) Posterior labrum abnormality 14 (7) Note Values in parentheses are number of cases. muscle echogenicity and decreased size. Calcification was defined as echogenic focus with or without posterior acoustic shadowing. Biceps brachii long head subluxation was defined as biceps partially medial to the bicipital groove location. Biceps brachii long head dislocation was defined as biceps tendon completely out of the bicipital groove. Biceps brachii long head tendon tear was defined as discontinuity and absence of biceps tendon in the bicipital groove. Distention of the biceps brachii tendon sheath was defined as hypoechoic or anechoic fluid or hypoechoic soft tissue surrounding the biceps tendon. Subacromial-subdeltoid bursal thickening was defined as focal or diffuse bursal thickening of more than 2-mm transverse thickness with associated hypoechogenicity with or without bursal fluid [23]. Subacromial impingement was defined as pooling of subacromial-subdeltoid bursal content just lateral to the acromion at dynamic shoulder abduction evaluation [24]. Acromioclavicular osteoarthritis was defined as the presence of osteophytes with associated articular surface irregularity with or without joint effusion or capsular thickening. Posterior glenoid labral abnormality was defined as abnormal hypoechogenicity or anechoic cleft. In an attempt to increase specificity and eliminate false-positive diagnoses, questionable or mild cases of tendinosis, osteoarthritis, bursal surface or articular surface fraying, possible bursal thickening, and partial-thickness tears of the biceps brachii long head tendon were excluded from analysis. Results The study group consisted of 51 men (average age, 56 years; range, years) who did not have shoulder symptoms. Twenty-five ultrasound examinations were performed on the right shoulder and 26 on the left. Of these examinations, 25 were performed on the dominant side and 22 on the nondominant side; four subjects were ambidextrous. Abnormalities were found at ultrasound in 96% (49/51) of the subjects. Of the two studies with normal findings, one was performed on the dominant side and the other on the nondominant side. The prevalence of the findings is shown in Table 1. Rotator Cuff Asymptomatic rotator cuff (supraspinatus, infraspinatus, subscapularis, and teres minor) W714
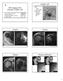
3 Shoulder Ultrasound Findings A B Fig year-old man with asymptomatic full-thickness supraspinatus tear. A and B, Long-axis (A) and short-axis (B) ultrasound images in expected location of supraspinatus tendon show complete full-thickness tear of supraspinatus tendon (between stars). GT = greater tuberosity, B = tendon of long head of biceps brachii muscle. Fig year-old man with asymptomatic partial-thickness tear of bursal surface of supraspinatus tendon. Long-axis ultrasound image of supraspinatus tendon shows predominately hypoechoic bursal surface tear (box). Articular fibers deep to bursal surface tear are intact. SST = supraspinatus tendon, GT = greater tuberosity. abnormality (tear, tendinosis, calcification, atrophy) was noted in 75% (38/51) of the shoulders. Supraspinatus tendon abnormality was found in 65% (33/51) of the subjects; 10% (5/51) of these men had a full-thickness tear (Fig. 1). All the full-thickness tears were located at the distal attachment site of the tendon and involved the anterior fibers. Two of the tears extended posteriorly to involve the posterior fibers of the supraspinatus tendon. Three of the full-thickness tears of the supraspinatus tendon were found on the dominant side and two on the nondominant side. The supraspinatus tendon had partial-thickness tears in 24% (12/51) of subjects, and nearly all (92%, 11/12) were partial-thickness tears of the bursal surface (Fig. 2). One subject had tears of both the bursal and articular surfaces, which did not communicate. One subject had a partial-thickness tear involving only the articular surface (Fig. 3). All but one of the supraspinatus tendon tears were associated with subacromial-subdeltoid bursal thickening. Thirty-nine percent (20/51) of the subjects had supraspinatus tendinosis (Fig. 4). Calcification was seen in 4% (2/51) of supraspinatus tendons (Fig. 5). Infraspinatus tendon abnormality was found in a small minority of the cases and was always associated with supraspinatus abnormalities in this study. Ten percent (5/51) of subjects had tendinosis, and 4% (2/51) had full-thickness tears. Both of these cases of full- thickness infraspinatus tendon tears were associated with full-thickness tears of the adjacent supraspinatus tendon. With regard to the subscapularis tendon, no full-thickness tears were encountered. Ten percent (5/51) of subjects had a partialthickness tear of the subscapularis. Twentyfive percent (13/51) of subjects had subscapularis tendinosis (Fig. 6). Tendon calcification was seen in 4% (2/51) of subjects. Teres minor atrophy was found in 8% (4/51) of the subjects (Fig. 7) and was independent of Fig year-old man with asymptomatic partial-thickness tear of articular surface of supraspinatus tendon. Long-axis ultrasound image of supraspinatus tendon shows hypoechoic articular surface tear (between stars) and intact bursal fibers overlying articular surface tear. SST = supraspinatus tendon, C = cartilage, GT = greater tuberosity. adjacent infraspinatus abnormalities. No teres minor tendon tears, tendinosis, or calcification were identified. Biceps Brachii Long Head Tendinosis of the biceps brachii long head was found in 4% (2/51) and full-thickness complete tendon tear in 2% (1/51) of subjects (Fig. 8). The only full-thickness tear of the biceps tendon was in a nondominant shoulder. Fluid and soft-tissue distention of the biceps brachii tendon sheath was found in 2% (1/51) of subjects. Medial subluxation of the biceps brachii long head tendon was found in 4% (2/51) (Fig. 9) and medial dislocation with an empty bicipital groove in 2% (1/51) of the men. All cases of medial subluxation of the biceps brachii long head tendon were associated with an adjacent partial-thickness tear of the subscapularis tendon involving the superior fibers of the subscapularis. Supraspinatus tendon tear was seen in the one case of full-thickness biceps brachii W715
4 Girish et al. Fig year-old man with supraspinatus tendinosis. Long-axis ultrasound image of supraspinatus tendon shows thickening and hypoechogenicity of tendon with loss of normal fibrillar echotexture. SST = supraspinatus tendon, GT = greater tuberosity. tendon tear (100%) and the two cases of medial biceps subluxation (50%). Subacromial-Subdeltoid Bursa Ultrasound images showed thickening of the subacromial-subdeltoid bursa in 78% (40/51) of subjects (Fig. 10). Seven of these men had associated fluid in the bursa. Subacromial impingement was found in 6% (3/51) of subjects (Fig. 11). Supraspinatus tendon tears were seen in 40% (16/40) of subjects with subacromial-subdeltoid bursal thickening. Acromioclavicular Joint Sixty-five percent (33/51) of the shoulders imaged had osteoarthritis of the acromioclavicular joint (Fig. 12). Posterior Glenoid Labrum The posterior glenoid labrum was found to be abnormal in 14% (7/51) of subjects. Fig year-old man with asymptomatic supraspinatus tendon calcification. A and B, Long-axis ultrasound image of supraspinatus tendon (SST) (A) and anteroposterior external rotation radiograph (B) obtained as part of original bone density study show calcification (arrow) within tendon. GT = greater tuberosity. Discussion Our study results show the variety of incidental asymptomatic abnormal findings in the shoulder on ultrasound scans. Asymptomatic shoulder abnormalities were found in 96% of subjects. The most common were subacromial-subdeltoid bursal thickening (78%), acromioclavicular joint osteoarthritis (65%), and supraspinatus (39%) and subscapularis (25%) tendinosis. A With regard to asymptomatic rotator cuff abnormalities, we found the rate of fullthickness tears of the supraspinatus tendon in our study to be 9.8%, slightly higher than the B Fig year-old man with asymptomatic subscapularis tendinosis. Shortaxis ultrasound image of subscapularis tendon (SUB) shows heterogeneity and hypoechoic thickening (arrows) of superior fibers of subscapularis tendon. LT = lesser tuberosity. Fig year-old man with asymptomatic teres minor muscle atrophy. Shortaxis ultrasound image of teres minor and infraspinatus (IST) musculature shows loss of volume and increase in echogenicity of teres minor (circle) in keeping with teres minor atrophy. W716
5 Shoulder Ultrasound Findings A B Fig year-old man with asymptomatic full-thickness tear of tendon of long head biceps brachii muscle. A and B, Long-axis (A) and short-axis (B) ultrasound images (in relation to bicipital groove) show complete absence of biceps brachii long head tendon with residual fluid (arrows) in bicipital groove. GT = greater tuberosity. Fig year-old man with asymptomatic medial subluxation of biceps brachii tendon. Short-axis ultrasound image of long head of biceps brachii tendon shows medial subluxation of biceps tendon (B) from bicipital groove (arrow) overlying lesser tuberosity (LT). GT = greater tuberosity. 7.6% reported by Moosmayer et al. [25] and 6% reported by Schibany et al. [14] and lower than the 21.7% reported in a meta-analysis of cadaveric studies by Reilly et al. [26]. Other authors, such as Sher et al. [10], found a higher rate of full-thickness tears, close to 15%, likely because of an older population. Their sample included subjects as old as 88 years, and 90% of the tears were found in subjects older than 60 years. None of our subjects was older than 70 years, and the mean age was 56 years. We did not identify any full-thickness supraspinatus tendon tears in the 40- to 50-year-old group. Two (4%) full-thickness tears supraspinatus were in the 51- to 60-year-old group. Three full-thickness tears (6%) were found in the 61- to 70-year-old group, in keeping with the findings noted by Moosmayer et al. in the same age group. This increase in prevalence of tears with increasing age is consistent with findings in other studies [13, 16, 27]. The literature on the presence and quantification of asymptomatic partial-thickness rotator cuff tears is scant. Milgrom et al. [11] documented a 17.2% frequency of partial-thickness supraspinatus tears. We found partial-thickness supraspinatus tears in 24% of the subjects, a rate slightly higher possibly owing to patient selection or improved technology and use of high-frequency transducers. Partial-thickness supraspinatus tears were overwhelmingly more common on the bursal surface, 85% of partial-thickness tears having bursal surface involvement. We did not find any reports of comprehensive evaluations of partial-thickness tears with which to compare our data. We found that asymptomatic full-thickness tears were uncommonly found outside the supraspinatus tendon; this findings is consistent with those of other studies [14, 15, 25]. Two of our subjects had full-thickness tears of the infraspinatus tendon, both of which were associated with a supraspinatus tear. No subject had a full-thickness tear of the subscapularis tendon. Another finding in Fig year-old man with asymptomatic subacromial-subdeltoid bursal thickening. Long-axis ultrasound image of supraspinatus tendon (SST) in shows subacromial-subdeltoid bursal thickening (arrows) between supraspinatus and deltoid muscles. GT = greater tuberosity. the rotator cuff was four cases (8%) of teres minor atrophy. Friend et al. [28] found teres minor atrophy in 3% of cases and theorized that this asymptomatic finding may be due to variations in teres minor innervation. With regard to the long head of the biceps brachii tendon, one full-thickness tear was identified in this study. We did not find documentation of this type of asymptomatic tear in the peer-reviewed literature. The supraspinatus tendon was also torn in this subject. We found subacromial-subdeltoid bursal thickening in 78% of subjects; only 14% of thickened areas contained bursal fluid. This result suggests that an isolated finding of subacromial-subdeltoid bursal abnormality is not an indicator of symptomatic subacromial external impingement. A study by Oschman et al. [13] showed that 4% of subjects who had no symptoms had the changes of subacromialsubdeltoid bursitis, although asymptomatic effusion was seen in 36% of overhead-throwing athletes [12]. Among the cases of full-thickness W717
6 Girish et al. Fig year-old man with asymptomatic subacromial impingement. Ultrasound image over lateral acromion in coronal plane with shoulder in active abduction shows pooling of fluid in subacromial-subdeltoid bursa (arrows) between acromion and greater tuberosity. tear of the supraspinatus tendon in our study, we found that 40% were associated with subacromial-subdeltoid bursal effusion. The presence of bursal effusion in a similar population ranged from none reported by Tempelhof et al. [15] through 34.3% in a study by Moosmayer et al. [25] to 100% reported by Needell et al. [8]. Of our cases of bursal thickening or fluid accumulation, 40% were associated with supraspinatus tear. We also found three cases (6%) of impingement, all of which were asymptomatic. The high rate of osteoarthritis of the acromioclavicular joint (65%) in our study is not unexpected because of the age of our subjects. Fialka et al. [27] found that the acromioclavicular joint often has degenerative changes by the third decade of life. Because ultrasound is sensitive to cortical irregularity, detection of early asymptomatic degenerative change is likely. We acknowledge several possible limitations of this study. The sample was not representative of the general population because all of the subjects were men recruited at a sports medicine clinic and had problems remote to the shoulder. However, the subjects were recruited into the study by a shoulder surgeon after a careful history and clinical examination of both shoulders, and shoulders exhibiting any symptoms were excluded. Because the cases were asymptomatic, there was no surgical confirmation or clinical follow-up. To compensate for this limitation, only obvious abnormal ultrasound findings interpreted in consensus by all three radiologists were included. We understand that there is also the possibility of recall bias of the patient sample with regard to the absence of previous symptoms. A current absence of symptoms does not exclude the development of symptoms at a later date. Radiographs were not available in all cases. When radiographs were available, only an anteroposterior view was obtained. Consensus reading of the images was performed, but because specificity was believed most important, we believe this method was reasonable. Conclusion Asymptomatic shoulder abnormalities were found in 96% of subjects years old. The most common abnormalities were subacromial-subdeltoid bursal thickening, acromioclavicular joint osteoarthritis, and supraspinatus tendinosis. Our results in the absence of symptoms suggest that when symptoms are present, ultrasound findings should be interpreted closely with clinical findings to determine the cause. Acknowledgments We thank Brian Robertson, Tracy Boon, and Theresa Guckian Kijek for their work and support. References 1. Prickett WD, Teefey SA, Galatz LM, Calfee RP, Middleton WD, Yamaguchi K. Accuracy of ultrasound imaging of the rotator cuff in shoulders that are painful postoperatively. J Bone Joint Surg Am 2003; 85: Teefey SA, Hasan SA, Middleton WD, Patel M, Wright RW, Yamaguchi K. Ultrasonography of the rotator cuff: a comparison of ultrasonographic and arthroscopic findings in one hundred consecutive cases. J Bone Joint Surg Am 2000; 82: Teefey SA, Rubin DA, Middleton WD, Hildebolt CF, Leibold RA, Yamaguchi K. Detection and quantification of rotator cuff tears: comparison of ultrasonographic, magnetic resonance imaging, and arthroscopic findings in seventy-one consecutive cases. J Bone Joint Surg Am 2004; 86: Fig year-old man with asymptomatic acromioclavicular osteoarthritis. Ultrasound image of acromioclavicular joint (box) shows osteophyte formation and cortical irregularity of articular surface. Clavicle is on left side of image and acromion on right. 4. Vlychou M, Dailiana Z, Fotiadou A, Papanagiotou M, Fezoulidis IV, Malizos K. Symptomatic partial rotator cuff tears: diagnostic performance of ultrasound and magnetic resonance imaging with surgical correlation. Acta Radiol 2009; 50: Middleton WD, Payne WT, Teefey SA, Hildebolt CF, Rubin DA, Yamaguchi K. Sonography and MRI of the shoulder: comparison of patient satisfaction. AJR 2004; 183: Chandnani V, Ho C, Gerharter J, et al. MR findings in asymptomatic shoulders: a blind analysis using symptomatic shoulders as controls. Clin Imaging 1992; 16: Miniaci A, Dowdy PA, Willits KR, Vellet AD. Magnetic resonance imaging evaluation of the rotator cuff tendons in the asymptomatic shoulder. Am J Sports Med 1995; 23: Needell SD, Zlatkin MB, Sher JS, Murphy BJ, Uribe JW. MR imaging of the rotator cuff: peritendinous and bone abnormalities in an asymptomatic population. AJR 1996; 166: Neumann CH, Holt RG, Steinbach LS, Jahnke AH Jr, Petersen SA. MR imaging of the shoulder: appearance of the supraspinatus tendon in asymptomatic volunteers. AJR 1992; 158: Sher JS, Uribe JW, Posada A, Murphy BJ, Zlatkin MB. Abnormal findings on magnetic resonance images of asymptomatic shoulders. J Bone Joint Surg Am 1995; 77: Milgrom C, Schaffler M, Gilbert S, van Holsbeeck M. Rotator-cuff changes in asymptomatic adults: the effect of age, hand dominance and gender. J Bone Joint Surg Br 1995; 77: Ocguder DA, Tosun O, Bektaser B, Cicek N, Ipek A, Bozkurt M. Ultrasonographic evaluation of the shoulder in asymptomatic overhead athletes. Acta Orthop Belg 2010; 76: Oschman Z, Janse van Rensburg C, Boraine H, Owen R. Ultrasound study of the asymptomatic shoulder in patients with a confirmed rotator cuff tear in the opposite shoulder. South Afr J Sports W718
7 Shoulder Ultrasound Findings Med 2007; 19:23 28 tor cuff: a radiological and pathological necropsy Shoulder impingement syndrome: sonographic 14. Schibany N, Zehetgruber H, Kainberger F, et al. survey. J Bone Joint Surg Br 1964; 46: evaluation. Radiology 1990; 176: Rotator cuff tears in asymptomatic individuals: a 19. Keyes EL. Anatomical observations on senile 25. Moosmayer S, Smith HJ, Tariq R, Larmo A. Prev- clinical and ultrasonographic screening study. changes in the shoulder. J Bone Joint Surg Am alence and characteristics of asymptomatic tears Eur J Radiol 2004; 51: ; 17: of the rotator cuff: an ultrasonographic and clini- 15. Tempelhof S, Rupp S, Seil R. Age-related prevalence of rotator cuff tears in asymptomatic shoulders. J Shoulder Elbow Surg 1999; 8: Worland RL, Lee D, Orozco CG. SozaRex F, Keenan J. Correlation of age, acromial morphology, and rotator cuff tear pathology diagnosed by ultrasound in asymptomatic patients. J South Orthop Assoc 2003; 12: Yamamoto A, Takagishi K, Kobayashi T, Shitara H, Osawa T. Factors involved in the presence of symptoms associated with rotator cuff tears: a comparison of asymptomatic and symptomatic rotator cuff tears in the general population. J Shoulder Elbow Surg 2011 Mar 29 [Epub ahead of print] 18. Cotton RE, Rideout DF. Tears of the humeral rota- 20. Ozaki J, Fujimoto S, Nakagawa Y, Masuhara K, Tamai S. Tears of the rotator cuff of the shoulder associated with pathological changes in the acromion: a study in cadavera. J Bone Joint Surg Am 1988; 70: Skinner HA. Anatomical considerations relative to rupture of the supraspinatus tendon. J Bone Joint Surg Br 1937; 19: Jamadar DA, Jacobson JA, Caoili EM, et al. Musculoskeletal sonography technique: focused versus comprehensive evaluation. AJR 2008; 190: van Holsbeeck M, Strouse PJ. Sonography of the shoulder: evaluation of the subacromial-subdeltoid bursa. AJR 1993; 160: Farin PU, Jaroma H, Harju A, Soimakallio S. cal study. J Bone Joint Surg Br 2009; 91: Reilly P, Macleod I, Macfarlane R, Windley J, Emery RJ. Dead men and radiologists don t lie: a review of cadaveric and radiological studies of rotator cuff tear prevalence. Ann R Coll Surg Engl 2006; 88: Fialka C, Krestan CR, Stampfl P, Trieb K, Aharinejad S, Vecsei V. Visualization of intraarticular structures of the acromioclavicular joint in an ex vivo model using a dedicated MRI protocol. AJR 2005; 185: Friend J, Francis S, McCulloch J, Ecker J, Breidahl W, McMenamin P. Teres minor innervation in the context of isolated muscle atrophy. Surg Radiol Anat 2010; 32: W719
Rotator Cuff and Biceps Pathology
 Rotator Cuff and Biceps Pathology Jon A. Jacobson, M.D. Professor of Radiology Director, Division of Musculoskeletal Radiology University of Michigan Disclosures: Consultant: Bioclinica Advisory Board:
Rotator Cuff and Biceps Pathology Jon A. Jacobson, M.D. Professor of Radiology Director, Division of Musculoskeletal Radiology University of Michigan Disclosures: Consultant: Bioclinica Advisory Board:
Ultrasound of the Shoulder
 Ultrasound of the Shoulder Patrick Battaglia, DC, DACBR Logan University, Department of Radiology Outline Review ultrasound appearance of NMSK tissues Present indications for ultrasound of the shoulder.
Ultrasound of the Shoulder Patrick Battaglia, DC, DACBR Logan University, Department of Radiology Outline Review ultrasound appearance of NMSK tissues Present indications for ultrasound of the shoulder.
US finding of the shoulder (with live demonstration) 인제의대상계백병원 안재기
 US finding of the shoulder (with live demonstration) 인제의대상계백병원 안재기 Shoulder US Biceps tendon & Rotator Cuff Long Head of Biceps Tendon Subscapularis tendon Supraspinatus tendon Infraspinatus tendon Teres
US finding of the shoulder (with live demonstration) 인제의대상계백병원 안재기 Shoulder US Biceps tendon & Rotator Cuff Long Head of Biceps Tendon Subscapularis tendon Supraspinatus tendon Infraspinatus tendon Teres
Ultrasound assessment of most frequent shoulder disorders
 Ultrasound assessment of most frequent shoulder disorders Poster No.: C-2026 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: S. P. Ivanoski; Ohrid/MK Keywords: Trauma, Athletic injuries, Arthritides,
Ultrasound assessment of most frequent shoulder disorders Poster No.: C-2026 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: S. P. Ivanoski; Ohrid/MK Keywords: Trauma, Athletic injuries, Arthritides,
DISTINGUISHING BETWEEN ACUTE AND CHRONIC ROTATOR CUFF INJURIES IN WORKERS COMPENSATION PATIENTS
 DISTINGUISHING BETWEEN ACUTE AND CHRONIC ROTATOR CUFF INJURIES IN WORKERS COMPENSATION PATIENTS Lyndon B. Gross M.D. Ph.D. The Orthopedic Center of St. Louis SHOULDER PAIN Third most common musculoskeletal
DISTINGUISHING BETWEEN ACUTE AND CHRONIC ROTATOR CUFF INJURIES IN WORKERS COMPENSATION PATIENTS Lyndon B. Gross M.D. Ph.D. The Orthopedic Center of St. Louis SHOULDER PAIN Third most common musculoskeletal
Common Applications for Sonography and Guided Intervention: Shoulder
 Common Applications for Sonography and Guided Intervention: Shoulder Jon A. Jacobson, M.D. Professor of Radiology Director, Division of Musculoskeletal Radiology University of Michigan Disclosures: Consultant:
Common Applications for Sonography and Guided Intervention: Shoulder Jon A. Jacobson, M.D. Professor of Radiology Director, Division of Musculoskeletal Radiology University of Michigan Disclosures: Consultant:
The demographic and morphological features of rotator cuff disease: A comparison of asymptomatic and symptomatic shoulders
 Washington University School of Medicine Digital Commons@Becker Open Access Publications 8-1-2006 The demographic and morphological features of rotator cuff disease: A comparison of asymptomatic and symptomatic
Washington University School of Medicine Digital Commons@Becker Open Access Publications 8-1-2006 The demographic and morphological features of rotator cuff disease: A comparison of asymptomatic and symptomatic
Adress correspondence and reprint requests to Hyun Seok Song, M.D. Department of Orthopedic Surgery, St.Paul s Hospital, The Catholic University of
 Adress correspondence and reprint requests to Hyun Seok Song, M.D. Department of Orthopedic Surgery, St.Paul s Hospital, The Catholic University of Korea 620-56 Jeonnong-dong, Dongdaemun-gu, Seoul, Korea
Adress correspondence and reprint requests to Hyun Seok Song, M.D. Department of Orthopedic Surgery, St.Paul s Hospital, The Catholic University of Korea 620-56 Jeonnong-dong, Dongdaemun-gu, Seoul, Korea
Original Research Article
 Original Research Article Study of Rotator Cuff Disorders by Ultrasound with Magnetic Resonance Imaging Correlation Hemanth Purigali Naganna 1, Shashikumar Mysore Rangaswamy 2, Jaganathan 3, Nanjaraj Chakenalli
Original Research Article Study of Rotator Cuff Disorders by Ultrasound with Magnetic Resonance Imaging Correlation Hemanth Purigali Naganna 1, Shashikumar Mysore Rangaswamy 2, Jaganathan 3, Nanjaraj Chakenalli
Musculoskeletal Ultrasound. Technical Guidelines SHOULDER
 Musculoskeletal Ultrasound Technical Guidelines SHOULDER 1 Although patient s positioning for shoulder US varies widely across different Countries and Institutions reflecting multifaceted opinions and
Musculoskeletal Ultrasound Technical Guidelines SHOULDER 1 Although patient s positioning for shoulder US varies widely across different Countries and Institutions reflecting multifaceted opinions and
Detection and Measurement of Rotator Cuff Tears with Sonography: Analysis of Diagnostic Errors
 Musculoskeletal Imaging Teefey et al. Detection of Rotator Cuff Tears with Sonography Sharlene A. Teefey 1 William D. Middleton 1 William T. Payne 2 Ken Yamaguchi 3 Teefey SA, Middleton WD, Payne WT, Yamaguchi
Musculoskeletal Imaging Teefey et al. Detection of Rotator Cuff Tears with Sonography Sharlene A. Teefey 1 William D. Middleton 1 William T. Payne 2 Ken Yamaguchi 3 Teefey SA, Middleton WD, Payne WT, Yamaguchi
Ultrasound Guided Therapeutic Injections in the Treatment of Shoulder Pain: A Multimedia Review
 Ultrasound Guided Therapeutic Injections in the Treatment of Shoulder Pain: A Multimedia Review Poster No.: P-0127 Congress: ESSR 2015 Type: Educational Poster Authors: A. Karsandas, J. Tuckett, R. Sinha,
Ultrasound Guided Therapeutic Injections in the Treatment of Shoulder Pain: A Multimedia Review Poster No.: P-0127 Congress: ESSR 2015 Type: Educational Poster Authors: A. Karsandas, J. Tuckett, R. Sinha,
Comparison of the results of ultrasonographic evaluation and arthroscopy in patients scheduled for surgery of the supraspinatus tendon rupture
 Comparison of the results of ultrasonographic evaluation and arthroscopy in patients scheduled for surgery of the supraspinatus tendon rupture Cemille Görmeli, a Gökay Görmeli, b Cüneyt Yücesoy, c Baybars
Comparison of the results of ultrasonographic evaluation and arthroscopy in patients scheduled for surgery of the supraspinatus tendon rupture Cemille Görmeli, a Gökay Görmeli, b Cüneyt Yücesoy, c Baybars
Dynamic Sonography Evaluation of Shoulder Impingement Syndrome
 Sonography of Shoulder Impingement Syndrome Musculoskeletal Imaging Clinical Observations A C M E D E N T U R I C A L I M A G I N G AJR 2006; 187:216 220 0361 803X/06/1871 216 American Roentgen Ray Society
Sonography of Shoulder Impingement Syndrome Musculoskeletal Imaging Clinical Observations A C M E D E N T U R I C A L I M A G I N G AJR 2006; 187:216 220 0361 803X/06/1871 216 American Roentgen Ray Society
Ultrasound study of the asymptomatic shoulder in patients with a confirmed rotator cuff tear in the opposite shoulder
 original research ARTICLE Ultrasound study of the asymptomatic shoulder in patients with a confirmed rotator cuff tear in the opposite shoulder Z Oschman (MB ChB, DCH, MSc (Sports Medicine)) 1 C Janse
original research ARTICLE Ultrasound study of the asymptomatic shoulder in patients with a confirmed rotator cuff tear in the opposite shoulder Z Oschman (MB ChB, DCH, MSc (Sports Medicine)) 1 C Janse
Sonographic Differences in the Appearance of Acute and Chronic Full-Thickness Rotator Cuff Tears
 Sonographic Differences in the Appearance of Acute and Chronic Full-Thickness Rotator Cuff Tears Sharlene A. Teefey, MD, William D. Middleton, MD, Gregory S. Bauer, MD, Charles F. Hildebolt, DDS, PhD,
Sonographic Differences in the Appearance of Acute and Chronic Full-Thickness Rotator Cuff Tears Sharlene A. Teefey, MD, William D. Middleton, MD, Gregory S. Bauer, MD, Charles F. Hildebolt, DDS, PhD,
MRI SHOULDER WHAT TO SEE
 MRI SHOULDER WHAT TO SEE DR SHEKHAR SRIVASTAV Sr. Consultant- Knee & Shoulder Arthroscopy Sant Parmanand Hospital Normal Anatomy Normal Shoulder MRI Coronal Oblique Sagital Oblique Axial Cuts Normal Coronal
MRI SHOULDER WHAT TO SEE DR SHEKHAR SRIVASTAV Sr. Consultant- Knee & Shoulder Arthroscopy Sant Parmanand Hospital Normal Anatomy Normal Shoulder MRI Coronal Oblique Sagital Oblique Axial Cuts Normal Coronal
The Upper Limb II. Anatomy RHS 241 Lecture 11 Dr. Einas Al-Eisa
 The Upper Limb II Anatomy RHS 241 Lecture 11 Dr. Einas Al-Eisa Sternoclavicular joint Double joint.? Each side separated by intercalating articular disc Grasp the mid-portion of your clavicle on one side
The Upper Limb II Anatomy RHS 241 Lecture 11 Dr. Einas Al-Eisa Sternoclavicular joint Double joint.? Each side separated by intercalating articular disc Grasp the mid-portion of your clavicle on one side
MRI of the Shoulder What to look for and how to find it? Dr. Eric Handley Musculoskeletal Radiologist Cherry Creek Imaging
 MRI of the Shoulder What to look for and how to find it? Dr. Eric Handley Musculoskeletal Radiologist Cherry Creek Imaging MRI of the Shoulder Benefits of Ultrasound: * Dynamic * Interactive real time
MRI of the Shoulder What to look for and how to find it? Dr. Eric Handley Musculoskeletal Radiologist Cherry Creek Imaging MRI of the Shoulder Benefits of Ultrasound: * Dynamic * Interactive real time
Radiographs of the shoulders of 84 asymptomatic
 The relationship of age, gender, and degenerative changes observed on radiographs of the shoulder in asymptomatic individuals S. Bonsell, A. W. Pearsall IV, R. J. Heitman, C. A. Helms, N. M. Major, K.
The relationship of age, gender, and degenerative changes observed on radiographs of the shoulder in asymptomatic individuals S. Bonsell, A. W. Pearsall IV, R. J. Heitman, C. A. Helms, N. M. Major, K.
Imaging. Ultrasound imaging for the rheumatologist XLIV. Ultrasound of the shoulder in healthy individuals
 Imaging Ultrasound imaging for the rheumatologist XLIV. Ultrasound of the shoulder in healthy individuals A. Iagnocco 1, E. Filippucci 2, G. Sakellariou 3, F. Ceccarelli 1, L. Di Geso 2, L. Carli 4, L.
Imaging Ultrasound imaging for the rheumatologist XLIV. Ultrasound of the shoulder in healthy individuals A. Iagnocco 1, E. Filippucci 2, G. Sakellariou 3, F. Ceccarelli 1, L. Di Geso 2, L. Carli 4, L.
Case study # 6 Sharon P
 Patient is a morbidly obese 70 year old female presenting with left shoulder pain after a severe fall. Patient is in moderate to severe pain with extremely limited range of motion due to extensive shoulder
Patient is a morbidly obese 70 year old female presenting with left shoulder pain after a severe fall. Patient is in moderate to severe pain with extremely limited range of motion due to extensive shoulder
Ultrasonography of the Rotator Cuff
 Ultrasonography of the Rotator Cuff A COMPARISON OF ULTRASONOGRAPHIC AND ARTHROSCOPIC FINDINGS IN ONE HUNDRED CONSECUTIVE CASES* BY SHARLENE A. TEEFEY, M.D., S. ASHFAQ HASAN, M.D., WILLIAM D. MIDDLETON,
Ultrasonography of the Rotator Cuff A COMPARISON OF ULTRASONOGRAPHIC AND ARTHROSCOPIC FINDINGS IN ONE HUNDRED CONSECUTIVE CASES* BY SHARLENE A. TEEFEY, M.D., S. ASHFAQ HASAN, M.D., WILLIAM D. MIDDLETON,
Ultrasonographic Evaluation of Painful Shoulder joint in rural population
 Original article: Ultrasonographic Evaluation of Painful Shoulder joint in rural population Dr. Pankaj Garg*, Dr. V.N. Marathe, Dr. S. G. Gandage, Dr.S.G.Kachewar Department of Radiology, Rural Medical
Original article: Ultrasonographic Evaluation of Painful Shoulder joint in rural population Dr. Pankaj Garg*, Dr. V.N. Marathe, Dr. S. G. Gandage, Dr.S.G.Kachewar Department of Radiology, Rural Medical
A Prospective Comparative Study of High Resolution Ultrasound and MRI in the Diagnosis of Rotator Cuff Tears in a Tertiary Hospital of North India
 Signature: Pol J Radiol, 2016; 81: 491-497 DOI: 10.12659/PJR.897830 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Received: 2016.01.29 Accepted: 2016.03.15 Published: 2016.10.19 Authors Contribution: A Study Design B Data Collection
Signature: Pol J Radiol, 2016; 81: 491-497 DOI: 10.12659/PJR.897830 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Received: 2016.01.29 Accepted: 2016.03.15 Published: 2016.10.19 Authors Contribution: A Study Design B Data Collection
What can Imaging tell us?
 What can Imaging tell us? David Connell FRANZCR, FFSEM (UK) Assoc Professor Dept of Medicine, Nursing & Healthcare Monash University, Melbourne, Australia Assoc Professor Sport & Exercise Medicine Research
What can Imaging tell us? David Connell FRANZCR, FFSEM (UK) Assoc Professor Dept of Medicine, Nursing & Healthcare Monash University, Melbourne, Australia Assoc Professor Sport & Exercise Medicine Research
FUNCTIONAL ANATOMY OF SHOULDER JOINT
 FUNCTIONAL ANATOMY OF SHOULDER JOINT ARTICULATION Articulation is between: The rounded head of the Glenoid cavity humerus and The shallow, pear-shaped glenoid cavity of the scapula. 2 The articular surfaces
FUNCTIONAL ANATOMY OF SHOULDER JOINT ARTICULATION Articulation is between: The rounded head of the Glenoid cavity humerus and The shallow, pear-shaped glenoid cavity of the scapula. 2 The articular surfaces
Ultrasound of Shoulder Pathology and Intervention 서울대학교병원재활의학과 김기원
 Ultrasound of Shoulder Pathology and Intervention 서울대학교병원재활의학과 김기원 Ultrasound for Shoulder Disorder Advantage Dynamic evaluation Immediate clinical correlation + Intervention Weakness Diagnostic accuracy?
Ultrasound of Shoulder Pathology and Intervention 서울대학교병원재활의학과 김기원 Ultrasound for Shoulder Disorder Advantage Dynamic evaluation Immediate clinical correlation + Intervention Weakness Diagnostic accuracy?
IMAGING OF ROTATOR CUFF PATHOLOGY- IS ULTRASOUND AS GOOD AS MRI
 IMAGING OF ROTATOR CUFF PATHOLOGY- IS ULTRASOUND AS GOOD AS MRI Vinoth Alagappan 1, Nirmal Kumar Prabhu 2, Srikanth Moorthy 3, Sreekumar Karumathil Pullara 4, Rajesh Kanann Ramesh 5, Nazar P. K 6, Chinmay
IMAGING OF ROTATOR CUFF PATHOLOGY- IS ULTRASOUND AS GOOD AS MRI Vinoth Alagappan 1, Nirmal Kumar Prabhu 2, Srikanth Moorthy 3, Sreekumar Karumathil Pullara 4, Rajesh Kanann Ramesh 5, Nazar P. K 6, Chinmay
Pediatric Musculoskeletal Ultrasound: Cases reviewed and lessons learned
 Pediatric Musculoskeletal Ultrasound: Cases reviewed and lessons learned Jessica Leschied, MD Sections of Pediatric and Musculoskeletal Radiology C.S. Mott Children s Hospital University of Michigan Ann
Pediatric Musculoskeletal Ultrasound: Cases reviewed and lessons learned Jessica Leschied, MD Sections of Pediatric and Musculoskeletal Radiology C.S. Mott Children s Hospital University of Michigan Ann
Office-based Versus Radiologist-based Ultrasonography for the Diagnosis of Rotator Cuff Tears
 Article ID: WMC003756 ISSN 2046-1690 Office-based Versus Radiologist-based Ultrasonography for the Diagnosis of Rotator Cuff Tears Corresponding Author: Mr. Chetan S Modi, Shoulder and Elbow Fellow, Toronto
Article ID: WMC003756 ISSN 2046-1690 Office-based Versus Radiologist-based Ultrasonography for the Diagnosis of Rotator Cuff Tears Corresponding Author: Mr. Chetan S Modi, Shoulder and Elbow Fellow, Toronto
The Role of Sonography in Differentiating Full Versus Partial Distal Biceps Tendon Tears: Correlation With Surgical Findings
 Musculoskeletal Imaging Original Research Da Gama Lobo et al. Sonography in Biceps Tendon Tears Musculoskeletal Imaging Original Research Lucas Da Gama Lobo 1,2 David P. Fessell 1 Bruce S. Miller 1,3 Aine
Musculoskeletal Imaging Original Research Da Gama Lobo et al. Sonography in Biceps Tendon Tears Musculoskeletal Imaging Original Research Lucas Da Gama Lobo 1,2 David P. Fessell 1 Bruce S. Miller 1,3 Aine
The Shoulder. Anatomy and Injuries PSK 4U Unit 3, Day 4
 The Shoulder Anatomy and Injuries PSK 4U Unit 3, Day 4 Shoulder Girdle Shoulder Complex is the most mobile joint in the body. Scapula Clavicle Sternum Humerus Rib cage/thorax Shoulder Girdle It also includes
The Shoulder Anatomy and Injuries PSK 4U Unit 3, Day 4 Shoulder Girdle Shoulder Complex is the most mobile joint in the body. Scapula Clavicle Sternum Humerus Rib cage/thorax Shoulder Girdle It also includes
The Shoulder. Systematically scanning the shoulder provides extremely useful diagnostic information. The Shoulder
 1 ! The most ACCESSIBLE to sonographic exam! The most MOBILE and VULNERABLE extremity AND Systematically scanning the shoulder provides extremely useful diagnostic information! The Goal for this section
1 ! The most ACCESSIBLE to sonographic exam! The most MOBILE and VULNERABLE extremity AND Systematically scanning the shoulder provides extremely useful diagnostic information! The Goal for this section
MUSCLES OF SHOULDER REGION
 Dr Jamila EL Medany OBJECTIVES At the end of the lecture, students should: List the name of muscles of the shoulder region. Describe the anatomy of muscles of shoulder region regarding: attachments of
Dr Jamila EL Medany OBJECTIVES At the end of the lecture, students should: List the name of muscles of the shoulder region. Describe the anatomy of muscles of shoulder region regarding: attachments of
ROTATOR CUFF DISORDERS/IMPINGEMENT
 ROTATOR CUFF DISORDERS/IMPINGEMENT Dr.KN Subramanian M.Ch Orth., FRCS (Tr & Orth), CCT Orth(UK) Consultant Orthopaedic Surgeon, Special interest: Orthopaedic Sports Injury, Shoulder and Knee Surgery, SPARSH
ROTATOR CUFF DISORDERS/IMPINGEMENT Dr.KN Subramanian M.Ch Orth., FRCS (Tr & Orth), CCT Orth(UK) Consultant Orthopaedic Surgeon, Special interest: Orthopaedic Sports Injury, Shoulder and Knee Surgery, SPARSH
CLINICAL ARTICLE. Abstract. Diagnostic applications of shoulder sonography Rotator cuff tears
 Page 66 / SA ORTHOPAEDIC JOURNAL Autumn 2011 Vol 10 No 1 C L I N I C A L A RT I C L E Ultrasound and the shoulder surgeon Joe de Beer MBChB, MMed (Ortho) Karin van Rooyen MBChB Hans van der Bracht MD Cape
Page 66 / SA ORTHOPAEDIC JOURNAL Autumn 2011 Vol 10 No 1 C L I N I C A L A RT I C L E Ultrasound and the shoulder surgeon Joe de Beer MBChB, MMed (Ortho) Karin van Rooyen MBChB Hans van der Bracht MD Cape
AMSER Case of the Month January 2019
 AMSER Case of the Month January 2019 55 yo female presenting with 1 year of shoulder pain without prior trauma Nicholas Bertha, MS4 Drexel University College of Medicine Brandon Schooley, MD Allegheny
AMSER Case of the Month January 2019 55 yo female presenting with 1 year of shoulder pain without prior trauma Nicholas Bertha, MS4 Drexel University College of Medicine Brandon Schooley, MD Allegheny
Role of Magnetic Resonance Imaging in Internal Derangement of Shoulder
 IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 15, Issue 5 Ver. I (May. 2016), PP 22-26 www.iosrjournals.org Role of Magnetic Resonance Imaging in Internal
IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 15, Issue 5 Ver. I (May. 2016), PP 22-26 www.iosrjournals.org Role of Magnetic Resonance Imaging in Internal
Superior Labrum Anterior Posterior lesions: ultrasound evaluation
 Superior Labrum Anterior Posterior lesions: ultrasound evaluation Poster No.: C-0472 Congress: ECR 2017 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: D. Belyaev; Yaroslavl/RU Keywords: Trauma, Arthrography, Ultrasound,
Superior Labrum Anterior Posterior lesions: ultrasound evaluation Poster No.: C-0472 Congress: ECR 2017 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: D. Belyaev; Yaroslavl/RU Keywords: Trauma, Arthrography, Ultrasound,
The use of Ultrasound of the shoulder as a screening method for rotator cuff tear; A single institution experience
 The use of Ultrasound of the shoulder as a screening method for rotator cuff tear; A single institution experience Poster No.: C-0596 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: R. A. Ahyad, Z.
The use of Ultrasound of the shoulder as a screening method for rotator cuff tear; A single institution experience Poster No.: C-0596 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: R. A. Ahyad, Z.
Greater Trochanter: Anatomy and Pathology
 Greater Trochanter: Anatomy and Pathology Jon A. Jacobson, M.D. Professor of Radiology Director, Division of Musculoskeletal Radiology University of Michigan Disclosures: Consultant: Bioclinica Book Royalties:
Greater Trochanter: Anatomy and Pathology Jon A. Jacobson, M.D. Professor of Radiology Director, Division of Musculoskeletal Radiology University of Michigan Disclosures: Consultant: Bioclinica Book Royalties:
Conflict of Interest. New Strategies in Rotator Cuff Repair. Objectives. Learner Outcome
 Conflict of Interest New Strategies in Rotator Cuff Repair Sheri Lankford, BSN, CNOR I hereby certify that, to the best of my knowledge, no aspect of my current personal or professional situation might
Conflict of Interest New Strategies in Rotator Cuff Repair Sheri Lankford, BSN, CNOR I hereby certify that, to the best of my knowledge, no aspect of my current personal or professional situation might
APPROPRIATE USE GUIDELINES
 APPROPRIATE USE GUIDELINES Appropriateness of Advanced Imaging Procedures (MRI, CT, Bone Scan/PET) in Patients with Shoulder Pain CDI QUALITY INSTITUTE: PROVIDER LED ENTITY (PLE) Compiled by Rob Liddell,
APPROPRIATE USE GUIDELINES Appropriateness of Advanced Imaging Procedures (MRI, CT, Bone Scan/PET) in Patients with Shoulder Pain CDI QUALITY INSTITUTE: PROVIDER LED ENTITY (PLE) Compiled by Rob Liddell,
Musculoskeletal Imaging Clinical Observations
 MRI of Internal Impingement of the Shoulder Musculoskeletal Imaging Clinical Observations Eddie L. Giaroli 1 Nancy M. Major Laurence D. Higgins Giaroli EL, Major NM, Higgins LD DOI:10.2214/AJR.04.0971
MRI of Internal Impingement of the Shoulder Musculoskeletal Imaging Clinical Observations Eddie L. Giaroli 1 Nancy M. Major Laurence D. Higgins Giaroli EL, Major NM, Higgins LD DOI:10.2214/AJR.04.0971
SHOULDER IMPINGEMENT / ROTATOR CUFF TENDONITIS / SUBACROMIAL BURSITIS
 SHOULDER IMPINGEMENT / ROTATOR CUFF TENDONITIS / SUBACROMIAL BURSITIS The terms impingement, rotator cuff tendonitis, and subacromial bursitis, all refer to a spectrum of the same condition. Anatomy The
SHOULDER IMPINGEMENT / ROTATOR CUFF TENDONITIS / SUBACROMIAL BURSITIS The terms impingement, rotator cuff tendonitis, and subacromial bursitis, all refer to a spectrum of the same condition. Anatomy The
Shoulder ultrasonography performed by orthopedic surgeons increases efficiency in diagnosis of rotator cuff tears
 Chiu et al. Journal of Orthopaedic Surgery and Research (2017) 12:63 DOI 10.1186/s13018-017-0565-4 RESEARCH ARTICLE Shoulder ultrasonography performed by orthopedic surgeons increases efficiency in diagnosis
Chiu et al. Journal of Orthopaedic Surgery and Research (2017) 12:63 DOI 10.1186/s13018-017-0565-4 RESEARCH ARTICLE Shoulder ultrasonography performed by orthopedic surgeons increases efficiency in diagnosis
Sensitivity and Specificity in Detection of Labral Tears with 3.0-T MRI of the Shoulder
 Magee and Williams MRI for Detection of Labral Tears Musculoskeletal Imaging Clinical Observations C M E D E N T U R I C L I M G I N G JR 2006; 187:1448 1452 0361 803X/06/1876 1448 merican Roentgen Ray
Magee and Williams MRI for Detection of Labral Tears Musculoskeletal Imaging Clinical Observations C M E D E N T U R I C L I M G I N G JR 2006; 187:1448 1452 0361 803X/06/1876 1448 merican Roentgen Ray
2015 OPSC Annual Convention. syllabus. February 4-8, 2015 Hyatt Regency Mission Bay San Diego, California
 2015 OPSC Annual Convention syllabus February 4-8, 2015 Hyatt Regency Mission Bay San Diego, California THURSDAY, FEBRUARY 5, 2015: 3:30pm - 4:30pm The Shoulder: 2 View or Not 2 View * Presented by Alexandra
2015 OPSC Annual Convention syllabus February 4-8, 2015 Hyatt Regency Mission Bay San Diego, California THURSDAY, FEBRUARY 5, 2015: 3:30pm - 4:30pm The Shoulder: 2 View or Not 2 View * Presented by Alexandra
SHOULDER PROBLEMS & ARTHROSCOPIC MANAGEMENT
 SHOULDER PROBLEMS & ARTHROSCOPIC MANAGEMENT DR.SHEKHAR SRIVASTAV Sr. Consultant-KNEE & SHOULDER Arthroscopy Sant Parmanand Hospital,Delhi Peculiarities of Shoulder Elegant piece of machinery It has the
SHOULDER PROBLEMS & ARTHROSCOPIC MANAGEMENT DR.SHEKHAR SRIVASTAV Sr. Consultant-KNEE & SHOULDER Arthroscopy Sant Parmanand Hospital,Delhi Peculiarities of Shoulder Elegant piece of machinery It has the
Ultrasound-Guided Shoulder Injections 인제대학교일산백병원 재활의학과 임길병
 Ultrasound-Guided Shoulder Injections 인제대학교일산백병원 재활의학과 임길병 How to improve needle visibility Advantages of Ultrasound in Procedures Real-time imaging Avoids radiation exposure But, interventions without
Ultrasound-Guided Shoulder Injections 인제대학교일산백병원 재활의학과 임길병 How to improve needle visibility Advantages of Ultrasound in Procedures Real-time imaging Avoids radiation exposure But, interventions without
Rotator Cuff Injuries: Is Ultrasound Enough? A Correlation with MRI
 DOI: 10.7860/IJARS/2017/28116:2279 Radiology Section Original Article Rotator Cuff Injuries: Is Ultrasound Enough? A Correlation with MRI Vishal Dhirenbhai Thakker, Dipu Bhuyan, Manali Arora, Mohsina Islam
DOI: 10.7860/IJARS/2017/28116:2279 Radiology Section Original Article Rotator Cuff Injuries: Is Ultrasound Enough? A Correlation with MRI Vishal Dhirenbhai Thakker, Dipu Bhuyan, Manali Arora, Mohsina Islam
Sonographic Findings of Adductor Insertion Avulsion Syndrome With Magnetic Resonance Imaging Correlation
 Case Report Sonographic Findings of Adductor Insertion Avulsion Syndrome With Magnetic Resonance Imaging Correlation Jennifer S. Weaver, MD, Jon A. Jacobson, MD, David A. Jamadar, MBBS, Curtis W. Hayes,
Case Report Sonographic Findings of Adductor Insertion Avulsion Syndrome With Magnetic Resonance Imaging Correlation Jennifer S. Weaver, MD, Jon A. Jacobson, MD, David A. Jamadar, MBBS, Curtis W. Hayes,
Comparative Study of MRI and Operative Findings in Rotator Cuff Tears. University of Medical Sciences, Iran. Medical Sciences, Iran.
 Comparative Study of MRI and Operative Findings in Rotator Cuff s Mohammad Hossein Daghighi 1, Alireza Rouhani 2, Masoud oureisa 3, Ali Sadighi 4, Farnaz Hafez Quran 5 *, Masoumeh Ahmadi Mohtasham 5 1.
Comparative Study of MRI and Operative Findings in Rotator Cuff s Mohammad Hossein Daghighi 1, Alireza Rouhani 2, Masoud oureisa 3, Ali Sadighi 4, Farnaz Hafez Quran 5 *, Masoumeh Ahmadi Mohtasham 5 1.
A prospective comparative study of high resolution ultrasound and MRI in the diagnosis of rotator cuff tears
 International Journal of Current Research in Medical Sciences ISSN: 2454-5716 P-ISJN: A4372-3064, E -ISJN: A4372-3061 www.ijcrims.com Original Research Article Volume 4, Issue 12-2018 DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.22192/ijcrms.2018.04.12.013
International Journal of Current Research in Medical Sciences ISSN: 2454-5716 P-ISJN: A4372-3064, E -ISJN: A4372-3061 www.ijcrims.com Original Research Article Volume 4, Issue 12-2018 DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.22192/ijcrms.2018.04.12.013
The Shoulder CLINICAL PERSPECTIVE. Colm McMahon and Corrie Yablon SUMMARY OF KEY POINTS CHAPTER OUTLINE CHAPTER
 CHPTER 24 The Shoulder Colm McMahon and Corrie Yablon SUMMRY OF KEY POINTS In the diagnosis of full-thickness rotator cuff tears, Understanding of optimal patient positioning, probe ultrasound is of comparable
CHPTER 24 The Shoulder Colm McMahon and Corrie Yablon SUMMRY OF KEY POINTS In the diagnosis of full-thickness rotator cuff tears, Understanding of optimal patient positioning, probe ultrasound is of comparable
Evidence Based Approach to Shoulder Injections
 Evidence Based Approach to Shoulder Injections Bradley Sandella, DO Christiana Care Sports Medicine Joseph Straight, MD First State Orthopaedics Objectives Relevant Anatomy Indications for injections Injection
Evidence Based Approach to Shoulder Injections Bradley Sandella, DO Christiana Care Sports Medicine Joseph Straight, MD First State Orthopaedics Objectives Relevant Anatomy Indications for injections Injection
Ultrasound of the Hip: Anatomy, Pathology, and Procedures
 Ultrasound of the Hip: Anatomy, Pathology, and Procedures Jon A. Jacobson, M.D. Professor of Radiology Director, Division of Musculoskeletal Radiology University of Michigan Outline Hip Joint Native hip
Ultrasound of the Hip: Anatomy, Pathology, and Procedures Jon A. Jacobson, M.D. Professor of Radiology Director, Division of Musculoskeletal Radiology University of Michigan Outline Hip Joint Native hip
11/13/2017. Disclosures: The Irreparable Rotator Cuff. I am a consultant for Arhtrex, Inc and Endo Pharmaceuticals.
 Massive Rotator Cuff Tears without Arthritis THE CASE FOR SUPERIOR CAPSULAR RECONSTRUCTION MICHAEL GARCIA, MD NOVEMBER 4, 2017 FLORIDA ORTHOPAEDIC INSTITUTE Disclosures: I am a consultant for Arhtrex,
Massive Rotator Cuff Tears without Arthritis THE CASE FOR SUPERIOR CAPSULAR RECONSTRUCTION MICHAEL GARCIA, MD NOVEMBER 4, 2017 FLORIDA ORTHOPAEDIC INSTITUTE Disclosures: I am a consultant for Arhtrex,
The shoulder in a production line: clinical and ultrasound study
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE The shoulder in a production line: clinical and ultrasound study Ernesto Youiti Maeda 1, Milton Helfenstein Jr. 1, João Eduardo Barile Ascencio 2, Daniel Feldman 1 ABSTRACT Introduction:
ORIGINAL ARTICLE The shoulder in a production line: clinical and ultrasound study Ernesto Youiti Maeda 1, Milton Helfenstein Jr. 1, João Eduardo Barile Ascencio 2, Daniel Feldman 1 ABSTRACT Introduction:
Calcific Tendinitis of the Long Head of the Biceps Brachii Distal to the Glenohumeral Joint: Plain Film
 1011 Calcific Tendinitis of the Long Head of the Biceps Brachii Distal to the Glenohumeral Joint: Plain Film Radiographic Findings Amy Beth Goldman1 Calcific tendinitis is a painful condition related to
1011 Calcific Tendinitis of the Long Head of the Biceps Brachii Distal to the Glenohumeral Joint: Plain Film Radiographic Findings Amy Beth Goldman1 Calcific tendinitis is a painful condition related to
Rotator cuff. MR Imaging of the Shoulder: Rotator Cuff. Trauma. Trauma. Trauma. Tendon calcification. Acute. Degenerative. Trauma Calcific tendinitis
 Rotator cuff MR Imaging of the Shoulder: Rotator Cuff Dr. Mini N. Pathria M.D., FRCP(C) Department of Radiology University of California School of Medicine San Diego, California Acute Trauma Calcific tendinitis
Rotator cuff MR Imaging of the Shoulder: Rotator Cuff Dr. Mini N. Pathria M.D., FRCP(C) Department of Radiology University of California School of Medicine San Diego, California Acute Trauma Calcific tendinitis
Case 27 Clinical Presentation
 53 Case 27 Clinical Presentation 40-year-old man presents with acute shoulder pain and normal findings on radiographs. 54 RadCases Musculoskeletal Radiology Imaging Findings (,) Coronal images of the shoulder
53 Case 27 Clinical Presentation 40-year-old man presents with acute shoulder pain and normal findings on radiographs. 54 RadCases Musculoskeletal Radiology Imaging Findings (,) Coronal images of the shoulder
Review shoulder anatomy Review the physical exam of the shoulder Discuss some common causes of acute shoulder pain Discuss some common causes of
 Review shoulder anatomy Review the physical exam of the shoulder Discuss some common causes of acute shoulder pain Discuss some common causes of chronic shoulder pain Review with some case questions Bones:
Review shoulder anatomy Review the physical exam of the shoulder Discuss some common causes of acute shoulder pain Discuss some common causes of chronic shoulder pain Review with some case questions Bones:
Shoulder Ultrasonography as a Diagnostic Tool for Rotator Cuff Disease
 Shoulder Ultrasonography as a Diagnostic Tool for Rotator Cuff Disease Jay D Keener, MD Associate Professor Shoulder and Elbow Service Washington University Disclosure No relevant financial disclosures
Shoulder Ultrasonography as a Diagnostic Tool for Rotator Cuff Disease Jay D Keener, MD Associate Professor Shoulder and Elbow Service Washington University Disclosure No relevant financial disclosures
The Shoulder. By Patrick Ryan, Bobby Law, Jack Beaty, Alex Newhouse and Chuck Nelson
 The Shoulder By Patrick Ryan, Bobby Law, Jack Beaty, Alex Newhouse and Chuck Nelson Learning Objectives/Agenda Review the anatomy of the shoulder Describe the main diseases of the shoulder Describe the
The Shoulder By Patrick Ryan, Bobby Law, Jack Beaty, Alex Newhouse and Chuck Nelson Learning Objectives/Agenda Review the anatomy of the shoulder Describe the main diseases of the shoulder Describe the
SHOULDER PAIN. A Real Pain in the Neck. Michael Wolk, MD Northeastern Rehabilitation Associates October 31, 2017
 SHOULDER PAIN A Real Pain in the Neck Michael Wolk, MD Northeastern Rehabilitation Associates October 31, 2017 THE SHOULDER JOINT (S) 1. glenohumeral 2. suprahumeral 3. acromioclavicular 4. scapulocostal
SHOULDER PAIN A Real Pain in the Neck Michael Wolk, MD Northeastern Rehabilitation Associates October 31, 2017 THE SHOULDER JOINT (S) 1. glenohumeral 2. suprahumeral 3. acromioclavicular 4. scapulocostal
Index. Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type.
 Magn Reson Imaging Clin N Am 12 (2004) 185 189 Index Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A Acromioclavicular joint, MR imaging findings concerning, 161 Acromion, types of, 77 79
Magn Reson Imaging Clin N Am 12 (2004) 185 189 Index Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A Acromioclavicular joint, MR imaging findings concerning, 161 Acromion, types of, 77 79
Shoulder joint Assessment and General View
 Shoulder joint Assessment and General View Done by; Mshari S. Alghadier BSc Physical Therapy RHPT 366 m.alghadier@sau.edu.sa http://faculty.sau.edu.sa/m.alghadier/ Functional anatomy The shoulder contains
Shoulder joint Assessment and General View Done by; Mshari S. Alghadier BSc Physical Therapy RHPT 366 m.alghadier@sau.edu.sa http://faculty.sau.edu.sa/m.alghadier/ Functional anatomy The shoulder contains
Anatomical Considerations/ Pathophysiology The shoulder is the most mobile joint in the body. : Three bones:
 Introduction Musculoskeletal training is generally underrepresented in medical training and residency curriculums. There is a general deficit in musculoskeletal knowledge amongst current medical students,
Introduction Musculoskeletal training is generally underrepresented in medical training and residency curriculums. There is a general deficit in musculoskeletal knowledge amongst current medical students,
International Journal of Health Sciences and Research ISSN:
 International Journal of Health Sciences and Research www.ijhsr.org ISSN: 2249-9571 Original Research Article Correlation between High Resolution Ultrasonography and MRI in Rotator Cuff Tear Diagnosis
International Journal of Health Sciences and Research www.ijhsr.org ISSN: 2249-9571 Original Research Article Correlation between High Resolution Ultrasonography and MRI in Rotator Cuff Tear Diagnosis
Provider Led Entity. CDI Quality Institute PLE Shoulder AUC 05/22/2018
 Provider Led Entity CDI Quality Institute PLE Shoulder AUC 05/22/2018 Appropriateness of advanced imaging procedures* in patients with shoulder pain and the following clinical presentations: *Including
Provider Led Entity CDI Quality Institute PLE Shoulder AUC 05/22/2018 Appropriateness of advanced imaging procedures* in patients with shoulder pain and the following clinical presentations: *Including
1. The coordinated action of a scapular upward rotation and humeral abduction is known as the:
 1 1. The coordinated action of a scapular upward rotation and humeral abduction is known as the: a. Carrying angle of the arm b. Scapulohumeral rhythm c. Glenohumeral capsular pattern d. Abduction resistance
1 1. The coordinated action of a scapular upward rotation and humeral abduction is known as the: a. Carrying angle of the arm b. Scapulohumeral rhythm c. Glenohumeral capsular pattern d. Abduction resistance
Ultrasound of the Knee
 Ultrasound of the Knee Jon A. Jacobson, M.D. Professor of Radiology Director, Division of Musculoskeletal Radiology University of Michigan Disclosures: Consultant: Bioclinica Book Royalties: Elsevier Advisory
Ultrasound of the Knee Jon A. Jacobson, M.D. Professor of Radiology Director, Division of Musculoskeletal Radiology University of Michigan Disclosures: Consultant: Bioclinica Book Royalties: Elsevier Advisory
UPPER EXTREMITY INJURIES. Recognizing common injuries to the upper extremity
 UPPER EXTREMITY INJURIES Recognizing common injuries to the upper extremity ANATOMY BONES Clavicle Scapula Spine of the scapula Acromion process Glenoid fossa/cavity Humerus Epicondyles ANATOMY BONES Ulna
UPPER EXTREMITY INJURIES Recognizing common injuries to the upper extremity ANATOMY BONES Clavicle Scapula Spine of the scapula Acromion process Glenoid fossa/cavity Humerus Epicondyles ANATOMY BONES Ulna
Introduction. Al Kindy Col Med J 2012; Vol. 8 No. 1 P: 63
 Ultrasound of the Rotator Cuff: A Comparison of Ultrasonographic and Physical Examination Finding in Seventy Consecutive Cases *Mohammed S. Al- Iedani, F.I.C.M.S. * Ghadeer H. Majeed, F.I.C.M.S. ** Tamer
Ultrasound of the Rotator Cuff: A Comparison of Ultrasonographic and Physical Examination Finding in Seventy Consecutive Cases *Mohammed S. Al- Iedani, F.I.C.M.S. * Ghadeer H. Majeed, F.I.C.M.S. ** Tamer
JMSCR Vol 06 Issue 02 Page February 2018
 www.jmscr.igmpublication.org Impact Factor (SJIF): 6.379 Index Copernicus Value: 71.58 ISSN (e)-2347-176x ISSN (p) 2455-0450 DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.18535/jmscr/v6i2.03 Clinical Presentation and Spectrum
www.jmscr.igmpublication.org Impact Factor (SJIF): 6.379 Index Copernicus Value: 71.58 ISSN (e)-2347-176x ISSN (p) 2455-0450 DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.18535/jmscr/v6i2.03 Clinical Presentation and Spectrum
Sonographic Findings of Pectoralis Major Tears With Surgical, Clinical, and Magnetic Resonance Imaging Correlation in 6 Patients
 Article Sonographic Findings of Pectoralis Major Tears With Surgical, Clinical, and Magnetic Resonance Imaging Correlation in 6 Patients Jennifer S. Weaver, MD, Jon A. Jacobson, MD, David A. Jamadar, MBBS,
Article Sonographic Findings of Pectoralis Major Tears With Surgical, Clinical, and Magnetic Resonance Imaging Correlation in 6 Patients Jennifer S. Weaver, MD, Jon A. Jacobson, MD, David A. Jamadar, MBBS,
Musculoskeletal Sonography: Important Imaging Pitfalls
 Musculoskeletal Imaging Pictorial Essay Jamadar et al. Pitfalls in Musculoskeletal Sonography Musculoskeletal Imaging Pictorial Essay Downloaded from www.ajronline.org by 37.44.196.16 on 11/30/17 from
Musculoskeletal Imaging Pictorial Essay Jamadar et al. Pitfalls in Musculoskeletal Sonography Musculoskeletal Imaging Pictorial Essay Downloaded from www.ajronline.org by 37.44.196.16 on 11/30/17 from
Chronic Shoulder Disorders
 Chronic Shoulder Disorders Dr. Mustafa Elsingergy Consultant orthopedic surgeon Dallah Hospita Prof. Mamoun Kremli Almaarefa Medical College Contents INTRINSIC Shoulder Pain Due to causes in the shoulder
Chronic Shoulder Disorders Dr. Mustafa Elsingergy Consultant orthopedic surgeon Dallah Hospita Prof. Mamoun Kremli Almaarefa Medical College Contents INTRINSIC Shoulder Pain Due to causes in the shoulder
THE TENDONS OF THE supraspinatus, infraspinatus,
 1162 ORIGINAL ARTICLE The Validity of the Lag Signs in Diagnosing Full-Thickness Tears of the Rotator Cuff: A Preliminary Investigation Caroline A. Miller, MSc, Gail A. Forrester, MSc, Jeremy S. Lewis,
1162 ORIGINAL ARTICLE The Validity of the Lag Signs in Diagnosing Full-Thickness Tears of the Rotator Cuff: A Preliminary Investigation Caroline A. Miller, MSc, Gail A. Forrester, MSc, Jeremy S. Lewis,
Role and Correlation of High Resolution Ultrasound and Magnetic Resonance Imaging in Evaluation of Patients with Shoulder Pain
 Signature: Pol J Radiol, 2017; 82: 410-417 DOI: 10.12659/PJR.901540 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Received: 2016.09.13 Accepted: 2016.11.10 Published: 2017.07.28 Authors Contribution: A Study Design B Data Collection
Signature: Pol J Radiol, 2017; 82: 410-417 DOI: 10.12659/PJR.901540 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Received: 2016.09.13 Accepted: 2016.11.10 Published: 2017.07.28 Authors Contribution: A Study Design B Data Collection
Tendinosis & Subacromial Impingement Syndrome. Gene Desepoli, LMT, D.C.
 Tendinosis & Subacromial Impingement Syndrome Gene Desepoli, LMT, D.C. What is the shoulder joint? Shoulder joint or shoulder region? There is an interrelatedness of all moving parts of the shoulder and
Tendinosis & Subacromial Impingement Syndrome Gene Desepoli, LMT, D.C. What is the shoulder joint? Shoulder joint or shoulder region? There is an interrelatedness of all moving parts of the shoulder and
Shoulder Arthroscopy. Dr. J.J.A.M. van Raaij. NOV Jaarvergadering Den Bosch 25 jan 2018
 Shoulder Arthroscopy Dr. J.J.A.M. van Raaij NOV Jaarvergadering Den Bosch 25 jan 2018 No disclosures Disclosure Shoulder Instability Traumatic anterior Traumatic posterior Acquired atraumatic Multidirectional
Shoulder Arthroscopy Dr. J.J.A.M. van Raaij NOV Jaarvergadering Den Bosch 25 jan 2018 No disclosures Disclosure Shoulder Instability Traumatic anterior Traumatic posterior Acquired atraumatic Multidirectional
Shoulder Joint Examination. Shoulder Joint Examination. Inspection. Inspection Palpation Movement. Look Feel Move
 Shoulder Joint Examination History Cuff Examination Instability Examination AC Joint Examination Biceps Tendon Examination Superior Labrum Examination Shoulder Joint Examination Inspection Palpation Movement
Shoulder Joint Examination History Cuff Examination Instability Examination AC Joint Examination Biceps Tendon Examination Superior Labrum Examination Shoulder Joint Examination Inspection Palpation Movement
WORKPLACE SAFETY AND INSURANCE APPEALS TRIBUNAL DECISION NO. 3231/16
 WORKPLACE SAFETY AND INSURANCE APPEALS TRIBUNAL DECISION NO. 3231/16 BEFORE: S. Peckover: Vice-Chair HEARING: December 12, 2016 at Toronto Written DATE OF DECISION: December 20, 2016 NEUTRAL CITATION:
WORKPLACE SAFETY AND INSURANCE APPEALS TRIBUNAL DECISION NO. 3231/16 BEFORE: S. Peckover: Vice-Chair HEARING: December 12, 2016 at Toronto Written DATE OF DECISION: December 20, 2016 NEUTRAL CITATION:
Usefulness of musculoskeletal ultrasonography for treatment of shoulder pain
 CONTINUING EDUCTION COLUMN pissn 1975-8456 / eissn 2093-5951 http://dx.doi.org/10.5124/jkma.2016.59.3.205 견관절통증의치료에서근골격초음파의유용성 정웅교 고려대학교의과대학정형외과학교실 Usefulness of musculoskeletal ultrasonography for treatment
CONTINUING EDUCTION COLUMN pissn 1975-8456 / eissn 2093-5951 http://dx.doi.org/10.5124/jkma.2016.59.3.205 견관절통증의치료에서근골격초음파의유용성 정웅교 고려대학교의과대학정형외과학교실 Usefulness of musculoskeletal ultrasonography for treatment
WORKPLACE SAFETY AND INSURANCE APPEALS TRIBUNAL DECISION NO. 2134/16
 WORKPLACE SAFETY AND INSURANCE APPEALS TRIBUNAL DECISION NO. 2134/16 BEFORE: S. Peckover: Vice-Chair HEARING: August 24, 2016 at Toronto Written DATE OF DECISION: September 21, 2016 NEUTRAL CITATION: 2016
WORKPLACE SAFETY AND INSURANCE APPEALS TRIBUNAL DECISION NO. 2134/16 BEFORE: S. Peckover: Vice-Chair HEARING: August 24, 2016 at Toronto Written DATE OF DECISION: September 21, 2016 NEUTRAL CITATION: 2016
SYMPOSIUM: TRIBUTE TO DR. ANTHONY F. DEPALMA, FIRST EDITOR-IN-CHIEF
 Clin Orthop Relat Res (2008) 466:543 551 DOI 10.1007/s11999-007-0103-5 SYMPOSIUM: TRIBUTE TO DR. ANTHONY F. DEPALMA, FIRST EDITOR-IN-CHIEF OF CLINICAL ORTHOPAEDICS AND RELATED RESEARCH The Classic Surgical
Clin Orthop Relat Res (2008) 466:543 551 DOI 10.1007/s11999-007-0103-5 SYMPOSIUM: TRIBUTE TO DR. ANTHONY F. DEPALMA, FIRST EDITOR-IN-CHIEF OF CLINICAL ORTHOPAEDICS AND RELATED RESEARCH The Classic Surgical
Rotator cuff injuries are commonly attributed to repetitive
 [ Orthopaedics ] Massive Rotator Cuff Tear in an Adolescent Athlete: A Case Report Kimberly A. Turman, MD,* Mark W. Anderson, MD, and Mark D. Miller, MD Full-thickness rotator cuff tears in the young athlete
[ Orthopaedics ] Massive Rotator Cuff Tear in an Adolescent Athlete: A Case Report Kimberly A. Turman, MD,* Mark W. Anderson, MD, and Mark D. Miller, MD Full-thickness rotator cuff tears in the young athlete
Imaging of the shoulder
 ISBN: PPI201402DC4571 WWW.BOTICA.COM.VE ISSN: 2443-4388 Imaging of the shoulder ABSTRACT It is difficult to precisely define which imaging method is the gold standard in the evolution of numerous problems
ISBN: PPI201402DC4571 WWW.BOTICA.COM.VE ISSN: 2443-4388 Imaging of the shoulder ABSTRACT It is difficult to precisely define which imaging method is the gold standard in the evolution of numerous problems
Original Report. Sonography of Ankle Tendon Impingement with Surgical Correlation
 Downloaded from www.ajronline.org by 162.158.89.91 on 08/23/18 from IP address 162.158.89.91. Copyright RRS. For personal use only; all rights reserved Monisha Shetty 1 David P. Fessell 1 John E. Femino
Downloaded from www.ajronline.org by 162.158.89.91 on 08/23/18 from IP address 162.158.89.91. Copyright RRS. For personal use only; all rights reserved Monisha Shetty 1 David P. Fessell 1 John E. Femino
Sports Medicine: Shoulder Arthrography. Christine B. Chung, M.D. Professor of Radiology Musculoskeletal Division UCSD and VA Healthcare System
 Sports Medicine: Shoulder Arthrography Christine B. Chung, M.D. Professor of Radiology Musculoskeletal Division UCSD and VA Healthcare System Disclosure Off-label use for gadolinium Pediatric Sports Injuries
Sports Medicine: Shoulder Arthrography Christine B. Chung, M.D. Professor of Radiology Musculoskeletal Division UCSD and VA Healthcare System Disclosure Off-label use for gadolinium Pediatric Sports Injuries
Massive Rotator Cuff Tears. Rafael M. Williams, MD
 Massive Rotator Cuff Tears Rafael M. Williams, MD Rotator Cuff MRI MRI Small / Partial Thickness Medium Tear Arthroscopic View Massive Tear Fatty Atrophy Arthroscopic View MassiveTears Tear is > 5cm
Massive Rotator Cuff Tears Rafael M. Williams, MD Rotator Cuff MRI MRI Small / Partial Thickness Medium Tear Arthroscopic View Massive Tear Fatty Atrophy Arthroscopic View MassiveTears Tear is > 5cm
Acromioplasty. Surgical Indications and Considerations
 1 Acromioplasty Surgical Indications and Considerations Anatomical Considerations: Any abnormality that disrupts the intricate relationship within the subacromial space may lead to impingement. Both intrinsic
1 Acromioplasty Surgical Indications and Considerations Anatomical Considerations: Any abnormality that disrupts the intricate relationship within the subacromial space may lead to impingement. Both intrinsic
Ultrasonographic Evaluation of the Shoulder in Elite Wheelchair Tennis Players
 Journal of Sport Rehabilitation, 2010, 1-12 2010 Human Kinetics, Inc. Ultrasonographic Evaluation of the Shoulder in Elite Wheelchair Tennis Players In-Ho Jeon, Hemanshu Kochhar, Jong-Min Lee, Hee-Soo
Journal of Sport Rehabilitation, 2010, 1-12 2010 Human Kinetics, Inc. Ultrasonographic Evaluation of the Shoulder in Elite Wheelchair Tennis Players In-Ho Jeon, Hemanshu Kochhar, Jong-Min Lee, Hee-Soo
I (and/or my co-authors) have something to disclose.
 Shoulder Anatomy And Biomechanics Nikhil N Verma, MD Director of Sports Medicine Professor, Department of Orthopedics Rush University Team Physician, Chicago White Sox and Bulls I (and/or my co-authors)
Shoulder Anatomy And Biomechanics Nikhil N Verma, MD Director of Sports Medicine Professor, Department of Orthopedics Rush University Team Physician, Chicago White Sox and Bulls I (and/or my co-authors)
Musculoskeletal Ultrasound Fundamentals
 Fundamentals Benjamin D. Levine, M.D. Associate Professor of Radiology Musculoskeletal Imaging Dept. of Radiological Sciences UCLA Health System I. Image Optimization II. Image Interpretation Artifacts
Fundamentals Benjamin D. Levine, M.D. Associate Professor of Radiology Musculoskeletal Imaging Dept. of Radiological Sciences UCLA Health System I. Image Optimization II. Image Interpretation Artifacts
Partial Thickness Rotator Cuff Tears: All-Inside Repair of PASTA Lesions in Athletes
 Partial Thickness Rotator Cuff Tears: All-Inside Repair of PASTA Lesions in Athletes Thomas M. DeBerardino, MD Associate Professor, UConn Health Center Team Physician, Orthopaedic Consultant UConn Huskie
Partial Thickness Rotator Cuff Tears: All-Inside Repair of PASTA Lesions in Athletes Thomas M. DeBerardino, MD Associate Professor, UConn Health Center Team Physician, Orthopaedic Consultant UConn Huskie
