DYNAMIC ANALYSIS OF THE HUMAN KNEE
|
|
|
- Myles Burke
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 122 Vol. 14 No. 3 June 2002 DYNAMIC ANALYSIS OF THE HUMAN KNEE R. TARLOCHAN,' S. RAMESH,' AND B. M. HILLBERRY 2 ' Department of Mechanical Engineering, University Tenaga Nasional, Selangor, Malaysia. 2Department of Mechanical Engineering, Purdue University, IN, USA. ABSTRACT Biomed. Eng. Appl. Basis Commun : Downloaded from The objective of this paper is to present a dynamic analysis of the human knee for various activities such as walking and stair ascending/descending. The results of this work is significant as it can used as inputs to joint simulators for artificial Fttjoint NWsf study, Y for rehabilitation purposes and to some extend applied to sports biomechanics. In the present esrt work an experimental study consisting of a motion sensor and a force plate Wivi was used c?r^ to capture t the r3teinor#o motion of subjects afst and to provide ground force reactions data that will serve su as inptis inputs to rt the tyre model. wndel Subjects.i. j bis in the years old bracket performed activities such as walking, stairs ascending nt'1ing and descending. descerdm,g..7h This age bracket was chosen because most of patients with knee-related c-rc1atedproblerrts problems are found in 'n this age r ' group. Some of the results from the present work correlated with that r Q of l# published literurur. literature. However, ffa# the present analysis was based on a more comprehensive model of f the 7 knee, ; which makes m<tk?s flee the results more realistic to the actual mechanical behavior of the lower limb. Biomed Eng Appl Basis Comm, 2002 (June); 14: INTRODUCTION The functions of the lower limb are to support body weight, provide movement and to maintain stability of the entire body. The knee joint is the largest and the most complex joint in the body. The importance of this joint to the mobility and stability of the human body cannot be denied. In addition, many sports injuries and arthritis are related to the knee joint. Hence this joint has been studied extensively for decades. Numerous models have been developed to gain a better understanding of the knee joint and motion [1]. Several knee simulators were designed to further understand the behavior of the knee and to evaluate knee replacement components [2]. In general the knee joint has been modeled as a spatial movement with rotations and translations in two and three-dimension [1]. In the force analysis, very few models were developed that takes into ac- Received: April 26, 2002; Accepted: June 10, 2002 Correspondence: Dr. S. Ramesh Department of Mechanical Engineering, University Tenaga Nasional, Km-7 Jalan Kajang-Puchong, Kajang, Selangor, Malaysia. rameshjit@uniten.edu.my count all vital structures of the joint, such as the patello-femoral and tibio-femoral joints, menisci, articular-surfaces and the cruciate ligaments structures [1]. Lacking of these vital structures in model predictions can lead to inaccurate results. In addition, a single dynamic model that consists of both the tibio-femoral and patello-femoral joints and anatomical structures like menisci and ligaments has yet to be developed with proper contact conditions and surface geometry. The understanding of the behavior of the knee not only highlight the importance of this joint but also assist the prosthetic industry in designing, developing and evaluating artificial knee replacement joints and rehabilitation centers in developing and correcting locomotion deficiency in patients that have abnormal motion patterns. The objective of this work was to study the dynamic motion of the knee by adopting and improving existing models. The analysis incorporates most of the vital structures of the knee joint and a multi rigid open chain system [3] was employed to determine the inverse dynamics of the system. 2. METHODS 2.1 Modeling -26-
2 BIOMEDICAL ENGINEERING- APPLICATIONS, BASIS & COMMUNICATIONS 123 Biomed. Eng. Appl. Basis Commun : Downloaded from V. Fa. FEMORAL FRAME Fig. 1. Open chain system to describe the motion of the knee joint [3]. To describe the motion of the tibio-femoral, modifications of the inverse kinematics of a three-cylindric robot developed by Pennock and Vierstra [4, 5] was used (Fig. 1). Since a cylindric joint permits rotation and translation, combinations of three of these joints describes the motion of the knee in three-dimension. Basically, a cylindric joint is the kinematic equivalent of a revolute joint and a prismatic joint sharing the same axis and has two degrees of freedom (Fig. 1). For a typical link, there are two Cartesian reference frames attached to the link namely the body frame denoted by F; and the joint frame denoted by Ci. The frames F0 and F3 are referred to as the base frame and the end effector frame, respectively (Fig. 1). The equations used to derive the displacements are well documented [4, 5] and expressed in terms of dual-number algebra and (3x3) dual-number transformation matrices. An example of a dual algebra representation is the dual unit vector U that can be written as: U, U= U2 U3 U1 +U,, s U2 + Uz s U3 +U3 s where the subscript number 1, 2 and 3 are the reference system directions analogous to the x, y and z Cartesian reference system. The real parts of the dual algebra are direction cosines and are re?resented by U1, U2 and U3, whereas the dual parts U,, U2 and U3 (1) are the components of the moment of the line about the origin. The symbol, s, designates exclusively the dual unit having the properties s = 0. Details of the formulation and mathematical derivation employed in the present work are described elsewhere [6]. For the patello-femoral joint, the model developed by Rullkoeter [7] was used. In this model, the open chain system used is similar to that proposed by Grood and Suntay [8]. The prediction of external moments and forces were based on the analytical technique proposed by Pennock and Yang [3] to derive and solve for the dynamic equations of a multi rigid body open chain system. The analytical technique is based on Newtonian mechanics with screw calculus. This technique provides very concise expression for the description of the forces and moments of a rigid body in general motion and allow the freedom of choosing a body reference frame with any point as its origin on the geometric constraints imposed on the body [3]. The derivation and solutions of this technique are based on dual number algebra and (3x3) dual matrix, consistent with that used for the kinematics analysis. The external moments and forces at the patello-femoral joints were assumed zero [9]. In the present study, the knee joint analysis was extended to the formulation of a three-dimensional mathematical dynamic model of a general three body segmented articulating knee joint [6]. This formulation was applied to investigate the relative dynamic motions between the femur-tibia-patella as well as the -27-
3 124 ligaments, muscles and contact forces developed in the joint while taking into account the geometry of the articulating surfaces and the appropriate constitutive behavior of the ligaments. The articulating surfaces are modeled as rigid and non-deformable. On the other hand, the femoral articulating surfaces are modeled as spheres whereas the articulating surfaces of the tibia and patellar facets are modeled as planes. By assuming the above geometrical shapes for the surfaces, point contacts are assumed on each medial and lateral articulating surfaces. The locations of the contact points are assumed based from studies conducted by Rahman [10]. In the present study, twelve nonlinear spring elements are modeled as ligaments to represent the different ligamentous and the capsular tissue posterior of the knee joint. For the kinematic and force analysis of the lower extremity, transformation matrices that provide information on the relative orientation of one segment with respect to another are important. In human motion studies, the most frequently used method for measuring human movement involves certain markers being placed on the subject's skin surface. These markers are generally used to represent the underlying bone movement although doubts exist on the accuracy of this technique. However in the present work, the method developed by Andriacchi et al. [I I ] was employed to determine the motion of the underlying bone. In general, this method uses a set of cluster points uniformly distributed on the limb segment. Each point or marker is assigned a mass, and the center of mass and inertia tensor of this system of cluster points is determined. From the inertia tensor, eigenvalues and eigenvectors are used to define a coordinate frame as well as providing means of studying the contribution of the skin motion. 2.2 Experimental Study Experimental study was carried out to provide inputs into the models. Four subjects were chosen in the age bracket of years. This age bracket was chosen since this age bracket has a high percentage of patients with related lower limb problem [6]. The devices used in this study were an Optotrak and a force plate. The Optotrak is a three-dimensional motion system that measures the motion in space by using infra red light emitting markers. The force plate provides the reaction forces, moments and center of pressure when a load is applied to the plate. The data from the motion sensor was used in determining the joint motion, velocity and acceleration of the limb segment via numerical differentiation. The data from the force plate along with the data from the motion sensor was used in determining the external forces and moments. The types of activities performed in this study were level walking, ascending and descending stairs. Vol. 14 No. 3 June RESULTS AND DISCUSSION The important parameters in describing the knee are kinematic and force distribution in three dimension. Nonetheless, the knee flexion extension angles (Fig. 2), adduction - abduction moments (Fig. 3) and the contact forces at the condyles (Fig. 4) are the important parameters worth discussing. The knee flexionextension is the main motion of the knee joint. The adduction-abduction moment is the main moment used in stabilizing the knee in the support phase of the gait, whereas the contact forces are the actual forces that contribute to the stress distribution on the articulating surfaces. The data presented here is for level walking since it is the most significant activity in gait analysis. For the knee flexion and extension angles (Fig. 2), the waveform is very similar to that reported in literature [12]. Slight variations however do exist and are attributed to variability in parameters such as age, sex, walking speed and natural responses of subjects. The average pattern of the flexion/extension is biphasic where a slight flexion followed by an extension during the stance phase and a large flexion accompanied by extension in the swing phase. As the heel strikes the ground, the knee flexes slightly before the quadriceps muscles contract to extent the knee to achieve support and stability of the limb during the stance phase. As the limb approaches the end of the stance phase the activation of the flexor muscles become dominant in flexing the legs and hence providing the forward propulsion of the body. At this time the limb is entering the swing phase where the flexion of the knee joint reaches its maximum value before the quadriceps muscles activate to extend the knee preparing for the next stance phase. Therefore this completes one gait cycle (Fig. 2) and the cycle continues for the entire gait. The external moments when compared with that of reported by other researchers [12] differs in magnitude but not in the general waveform as depicted in Fig. 3. Some shifts in the curve were expected due to different muscular activation in the subjects. This is because the external moments are balanced in a dynamic % Gait Fig. 2. Knee flexion-extension angle for a complete gait cycle. -28-
4 BIOMEDICAL ENGINEERING- APPLICATIONS, BASIS & COMMUNICATIONS sense by an equal an opposite internal moments. Muscles, ligaments and contact forces generate these internal moments, although the muscles are the primary structure contributing to these moments. The adductor moment is the largest compared to the flexion and rotation moment since it is used to stabilize the knee during the support phase. This compresses the medial compartment of the knee and stretches the lateral soft tissue. Internal-external moments in the transverse plane are also important in providing stability to the knee joint. This stability is due to the contribution of the ligaments. The kinematic and external forces and moments calculated from this study were very consistent with that reported in the literature [12]. The model of the knee develop in the present work has provided a satisfactory prediction of the motions and the moments. The model predictions are not intended as a substitute for accurate studies of the biomechanical aspect of the knee due to variations exist between subjects. However, the current model proved to be effective in providing reliable predictions of the knee kinematics and external moments with regards to normal and abnormal gait. On the other hand the waveform obtained for the contact forces for the tibio-femoral joint were not in agreement with published values [13]. This discrepancy in the results could be attributed to the way the Time (seq Fig. 3 Knee adduction - abduction moment (Nm) against time. 7 4 Force to Body Weight 3 Ratio Time (sec( Fig. 4 Tibio-femoral contact forces. Rmedial Rlateral knee joint was modeled, the assumptions made and the solution method used. As mentioned earlier the knee joint was modeled taking into consideration the twelve ligaments with different stiffness. In addition, the muscular activation assumptions used [6] can also result in different outputs. Nonetheless, the present work affirmed that the medial compartment of the tibial plateau experiences a larger contact force than the lateral compartment (Fig. 4). This could be attributed to the adduction moment that compresses the medial compartment of the knee joint as reflected in Fig. 3. In this study several assumptions were made to reduce the indeterminacy of the system. Future recommendations to the model include developing a more comprehensive and complex model that takes into account the menisci and the deformability of the articular cartilage. Besides this optimization algorithm can be used to converge to a solution due to the highly nonlinear behavior of the system. Optimization is also important to some extend to better predict muscle and bone attachment behaviour. 4. CONCLUSIONS In the present work, the model developed and approach taken was to best mimic the anatomical behavior of the knee. This was done by inclusion of vital structures and better analytical and experimental techniques. The current model proved to be effective in providing reliable predictions of the knee kinematics and external moments with regards to normal and abnormal gait. Insight information of the knee behaviour was gained and the results obtained from this study could serve as a source for clinical and component development usage. It is envisage that this model can be expanded to the area of sports biomechanics where ways to reduce athlete's injuries can be studied. ACKNOWLEDGEMENT Rameshjit Tarlochan would like to thank the Biomedical Engineering Department of Purdue University USA for providing the financial support in carrying out this research. REFERENCES 1. M. S. Hefzy and T. D. V. Cooke, "Review of Knee Models: 1996 Update," Applied Mechanics Review, 49 (1996) S. W. Peter, "A Knee Simulating Machine for Performance Evaluation of Total Knee Replacements," J ofbiomechanics, 30 (1997) G. R. Pennock and A. T. Yang, "Dynamic Analysis -29-
5 126 of a Multi-Rigid Body Open Chain System," Journal of Mechanism, Transmission, and Automation in Design, 105 (1983 ) G. R. Pennock and B. C. Vierstra, "The Inverse Kinematics of a Three Cylindric Robot," International Journal of Robotics and Research, 9 (1990) G. R. Pennock and K. J. Clark, "An Anatomical Based Coordinate System for the Description of the Kinematics Displacement in the Human Knee," Journal ofbiomechanics, 23 (1990) R. Tarlochan, "Lower Limb Biomechanical Analysis," Master Thesis, Purdue University (2001). 7. P. J. Rullkoeter, "A Graphical and Quantitative Method for Determining Joint Surface Contact under Dynamic Loading Conditions," Master's Thesis, Purdue University, (1992) pp E. S. Grood and W. I. Suntay, "A Joint Coordinate System for the Clinical Description of Three- Dimensional Motions: Application to the Knee," Journal of Biomechanical Engineering, 105 (1983) Vol. 14 No. 3 June M. S. Hefzy and H. Yang, "Three-Dimensional Anatomical Model of the Human Patello-Femoral.Joint to Determine Motions and Contact Characteristics," Journal of Biomedical Engineering, 15 (1993) E. M. A. Rahmen and M. S. Hefzy, "Three - Dimensional Dynamic Behavior of the Human Knee Joint under Impact Loading," Journal of Medical Engineering and Physics, 20 (1998) T. P. Andriachi, E. J. Alexander, M. K. Toney, C. Dyrby and J. Sum, "A Point Cluster Method for In- Vivo Motion Analysis: Applied to a Study of Knee Kinematics," Journal of Biomechanical Engineering, 120 (1999) J. Apkarian, S. Naumann and B. Cairns, "A Three - Dimensional Kinematic and Dynamic Model of the Lower Limb," Journal of Biomechanics, 22 (1989) A. Seireg and R. J. Arvikar, "The Prediction of Muscular Load Sharing and Joint Forces in the Lower Extremities During Walking," Journal of Biomechanics, 8 (1975)
TOTAL KNEE ARTHROPLASTY (TKA)
 TOTAL KNEE ARTHROPLASTY (TKA) 1 Anatomy, Biomechanics, and Design 2 Femur Medial and lateral condyles Convex, asymmetric Medial larger than lateral 3 Tibia Tibial plateau Medial tibial condyle: concave
TOTAL KNEE ARTHROPLASTY (TKA) 1 Anatomy, Biomechanics, and Design 2 Femur Medial and lateral condyles Convex, asymmetric Medial larger than lateral 3 Tibia Tibial plateau Medial tibial condyle: concave
Discrepancies in Knee Joint Moments Using Common Anatomical Frames Defined by Different Palpable Landmarks
 Journal of Applied Biomechanics, 2008, 24, 185-190 2008 Human Kinetics, Inc. Discrepancies in Knee Joint Moments Using Common Anatomical Frames Defined by Different Palpable Landmarks Dominic Thewlis,
Journal of Applied Biomechanics, 2008, 24, 185-190 2008 Human Kinetics, Inc. Discrepancies in Knee Joint Moments Using Common Anatomical Frames Defined by Different Palpable Landmarks Dominic Thewlis,
CONTROL OF THE BOUNDARY CONDITIONS OF A DYNAMIC KNEE SIMULATOR
 CONTROL OF THE BOUNDARY CONDITIONS OF A DYNAMIC KNEE SIMULATOR J. Tiré 1, J. Victor 2, P. De Baets 3 and M.A. Verstraete 2 1 Ghent University, Belgium 2 Ghent University, Department of Physical Medicine
CONTROL OF THE BOUNDARY CONDITIONS OF A DYNAMIC KNEE SIMULATOR J. Tiré 1, J. Victor 2, P. De Baets 3 and M.A. Verstraete 2 1 Ghent University, Belgium 2 Ghent University, Department of Physical Medicine
Biomechanics of the Knee. Valerie Nuñez SpR Frimley Park Hospital
 Biomechanics of the Knee Valerie Nuñez SpR Frimley Park Hospital Knee Biomechanics Kinematics Range of Motion Joint Motion Kinetics Knee Stabilisers Joint Forces Axes The Mechanical Stresses to which
Biomechanics of the Knee Valerie Nuñez SpR Frimley Park Hospital Knee Biomechanics Kinematics Range of Motion Joint Motion Kinetics Knee Stabilisers Joint Forces Axes The Mechanical Stresses to which
Q: What is the relationship between muscle forces and EMG data that we have collected?
 FAQs ABOUT OPENSIM Q: What is the relationship between muscle forces and EMG data that we have collected? A: Muscle models in OpenSim generate force based on three parameters: activation, muscle fiber
FAQs ABOUT OPENSIM Q: What is the relationship between muscle forces and EMG data that we have collected? A: Muscle models in OpenSim generate force based on three parameters: activation, muscle fiber
A Kinematic Assessment of Knee Prosthesis from Fluoroscopy Images
 Memoirs of the Faculty of Engineering, Kyushu University, Vol. 68, No. 1, March 2008 A Kinematic Assessment of Knee Prosthesis from Fluoroscopy Images by Mohammad Abrar HOSSAIN *, Michihiko FUKUNAGA and
Memoirs of the Faculty of Engineering, Kyushu University, Vol. 68, No. 1, March 2008 A Kinematic Assessment of Knee Prosthesis from Fluoroscopy Images by Mohammad Abrar HOSSAIN *, Michihiko FUKUNAGA and
One hundred and ten individuals participated in this study
 Purpose The purpose of this study was to compare gait characteristics in an asymptomatic population of younger and older adults to older OA patients of different severities Hypothesis(es) The following
Purpose The purpose of this study was to compare gait characteristics in an asymptomatic population of younger and older adults to older OA patients of different severities Hypothesis(es) The following
The Knee. Tibio-Femoral
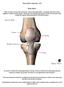
 The Knee Tibio-Femoral Osteology Distal Femur with Proximal Tibia Largest Joint Cavity in the Body A modified hinge joint with significant passive rotation Technically, one degree of freedom (Flexion/Extension)
The Knee Tibio-Femoral Osteology Distal Femur with Proximal Tibia Largest Joint Cavity in the Body A modified hinge joint with significant passive rotation Technically, one degree of freedom (Flexion/Extension)
The Knee. Two Joints: Tibiofemoral. Patellofemoral
 Evaluating the Knee The Knee Two Joints: Tibiofemoral Patellofemoral HISTORY Remember the questions from lecture #2? Girth OBSERVATION TibioFemoral Alignment What are the consequences of faulty alignment?
Evaluating the Knee The Knee Two Joints: Tibiofemoral Patellofemoral HISTORY Remember the questions from lecture #2? Girth OBSERVATION TibioFemoral Alignment What are the consequences of faulty alignment?
Computational Investigation of the Creep Behaviour of Human Knee Joint under Realistic Loading and Contact Boundary Conditions
 Computational Investigation of the Creep Behaviour of Human Knee Joint under Realistic Loading and Contact Boundary Conditions Qingen Meng 1, Zhongmin Jin 1,2, Ruth Wilcox 1, John Fisher 1. 1 Institute
Computational Investigation of the Creep Behaviour of Human Knee Joint under Realistic Loading and Contact Boundary Conditions Qingen Meng 1, Zhongmin Jin 1,2, Ruth Wilcox 1, John Fisher 1. 1 Institute
Do Persons with PFP. PFJ Loading? Biomechanical Factors Contributing to Patellomoral Pain: The Dynamic Q Angle. Patellofemoral Pain: A Critical Review
 Biomechanical Factors Contributing to Patellomoral Pain: The Dynamic Q Angle Division Biokinesiology & Physical Therapy Co Director, oratory University of Southern California Movement Performance Institute
Biomechanical Factors Contributing to Patellomoral Pain: The Dynamic Q Angle Division Biokinesiology & Physical Therapy Co Director, oratory University of Southern California Movement Performance Institute
CHAPTER 8: THE BIOMECHANICS OF THE HUMAN LOWER EXTREMITY
 CHAPTER 8: THE BIOMECHANICS OF THE HUMAN LOWER EXTREMITY _ 1. The hip joint is the articulation between the and the. A. femur, acetabulum B. femur, spine C. femur, tibia _ 2. Which of the following is
CHAPTER 8: THE BIOMECHANICS OF THE HUMAN LOWER EXTREMITY _ 1. The hip joint is the articulation between the and the. A. femur, acetabulum B. femur, spine C. femur, tibia _ 2. Which of the following is
OPEN KNEE: CAPACITY TO REPRODUCE ANTERIOR CRUCIATE LIGAMENT DEFORMATIONS
 OPEN KNEE: CAPACITY TO REPRODUCE ANTERIOR CRUCIATE LIGAMENT DEFORMATIONS A. Erdemir1,2 and S. Sibole3 1. ABSTRACT Simulation-based explorations of the knee have commonly relied on finite element analysis.
OPEN KNEE: CAPACITY TO REPRODUCE ANTERIOR CRUCIATE LIGAMENT DEFORMATIONS A. Erdemir1,2 and S. Sibole3 1. ABSTRACT Simulation-based explorations of the knee have commonly relied on finite element analysis.
MOTION MODELING OF THE HUMAN LOWER LIMB, SUPPORTED BY ORTHOSES
 11th International DAAAM Baltic Conference "INDUSTRIA ENGINEERING - 0- April 016, Tallinn, Estonia MOTION MODEING OF THE HUMAN OWER IMB, SUPPORTED BY ORTHOSES Krokhaleva, N.; Turchinovich, N.; Ovchinnikov,
11th International DAAAM Baltic Conference "INDUSTRIA ENGINEERING - 0- April 016, Tallinn, Estonia MOTION MODEING OF THE HUMAN OWER IMB, SUPPORTED BY ORTHOSES Krokhaleva, N.; Turchinovich, N.; Ovchinnikov,
Knee Joint Anatomy 101
 Knee Joint Anatomy 101 Bone Basics There are three bones at the knee joint femur, tibia and patella commonly referred to as the thighbone, shinbone and kneecap. The fibula is not typically associated with
Knee Joint Anatomy 101 Bone Basics There are three bones at the knee joint femur, tibia and patella commonly referred to as the thighbone, shinbone and kneecap. The fibula is not typically associated with
BIOMECHANICAL MECHANISMS FOR DAMAGE: RETRIEVAL ANALYSIS AND COMPUTATIONAL WEAR PREDICTIONS IN TOTAL KNEE REPLACEMENTS
 Journal of Mechanics in Medicine and Biology Vol. 5, No. 3 (2005) 469 475 c World Scientific Publishing Company BIOMECHANICAL MECHANISMS FOR DAMAGE: RETRIEVAL ANALYSIS AND COMPUTATIONAL WEAR PREDICTIONS
Journal of Mechanics in Medicine and Biology Vol. 5, No. 3 (2005) 469 475 c World Scientific Publishing Company BIOMECHANICAL MECHANISMS FOR DAMAGE: RETRIEVAL ANALYSIS AND COMPUTATIONAL WEAR PREDICTIONS
What is Kinesiology? Basic Biomechanics. Mechanics
 What is Kinesiology? The study of movement, but this definition is too broad Brings together anatomy, physiology, physics, geometry and relates them to human movement Lippert pg 3 Basic Biomechanics the
What is Kinesiology? The study of movement, but this definition is too broad Brings together anatomy, physiology, physics, geometry and relates them to human movement Lippert pg 3 Basic Biomechanics the
Knee Joint Assessment and General View
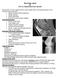
 Knee Joint Assessment and General View Done by; Mshari S. Alghadier BSc Physical Therapy RHPT 366 m.alghadier@sau.edu.sa http://faculty.sau.edu.sa/m.alghadier/ Functional anatomy The knee is the largest
Knee Joint Assessment and General View Done by; Mshari S. Alghadier BSc Physical Therapy RHPT 366 m.alghadier@sau.edu.sa http://faculty.sau.edu.sa/m.alghadier/ Functional anatomy The knee is the largest
CONTRIBUTING SURGEON. Barry Waldman, MD Director, Center for Joint Preservation and Replacement Sinai Hospital of Baltimore Baltimore, MD
 CONTRIBUTING SURGEON Barry Waldman, MD Director, Center for Joint Preservation and Replacement Sinai Hospital of Baltimore Baltimore, MD System Overview The EPIK Uni is designed to ease the use of the
CONTRIBUTING SURGEON Barry Waldman, MD Director, Center for Joint Preservation and Replacement Sinai Hospital of Baltimore Baltimore, MD System Overview The EPIK Uni is designed to ease the use of the
Biomechanics of. Knee Replacement. Mujda Hakime, Paul Malcolm
 Biomechanics of Knee Replacement Mujda Hakime, Paul Malcolm 1 Table of contents Knee Anatomy Movements of the Knee Knee conditions leading to knee replacement Materials Alignment and Joint Loading Knee
Biomechanics of Knee Replacement Mujda Hakime, Paul Malcolm 1 Table of contents Knee Anatomy Movements of the Knee Knee conditions leading to knee replacement Materials Alignment and Joint Loading Knee
Knee Android Model Reproducing Internal-External Rotation with Screw-Home Movement of the Human Knee
 Journal of Robotics, Networking and Artificial Life, Vol. 3, No. 2 (September 2016), 69-73 Knee Android Model Reproducing Internal-External Rotation with Screw-Home Movement of the Human Knee Daichi Yamauchi,
Journal of Robotics, Networking and Artificial Life, Vol. 3, No. 2 (September 2016), 69-73 Knee Android Model Reproducing Internal-External Rotation with Screw-Home Movement of the Human Knee Daichi Yamauchi,
Estimation of Complex Anatomical Joint Motions Using a Spatial Goniometer
 Estimation of Complex Anatomical Joint Motions Using a Spatial Goniometer V. A. Dung Cai *, Philippe Bidaud *, Vincent Hayward *, and Florian Gosselin * UPMC Univ Paris 06, Institut des Systèmes Intelligents
Estimation of Complex Anatomical Joint Motions Using a Spatial Goniometer V. A. Dung Cai *, Philippe Bidaud *, Vincent Hayward *, and Florian Gosselin * UPMC Univ Paris 06, Institut des Systèmes Intelligents
The Knee. Prof. Oluwadiya Kehinde
 The Knee Prof. Oluwadiya Kehinde www.oluwadiya.sitesled.com The Knee: Introduction 3 bones: femur, tibia and patella 2 separate joints: tibiofemoral and patellofemoral. Function: i. Primarily a hinge joint,
The Knee Prof. Oluwadiya Kehinde www.oluwadiya.sitesled.com The Knee: Introduction 3 bones: femur, tibia and patella 2 separate joints: tibiofemoral and patellofemoral. Function: i. Primarily a hinge joint,
Investigating the loading behaviour of intact and meniscectomy knee joints and the impact on surgical decisions
 Investigating the loading behaviour of intact and meniscectomy knee joints and the impact on surgical decisions M. S. Yeoman 1 1. Continuum Blue Limited, One Caspian Point, Caspian Way, CF10 4DQ, United
Investigating the loading behaviour of intact and meniscectomy knee joints and the impact on surgical decisions M. S. Yeoman 1 1. Continuum Blue Limited, One Caspian Point, Caspian Way, CF10 4DQ, United
HIGH FLEXION IN CONTEMPORARY TOTAL KNEE DESIGN: A PRECURSOR OF UHMWPE DAMAGE? A FINITE ELEMENT STUDY
 HIGH FLEXION IN CONTEMPORARY TOTAL KNEE DESIGN: A PRECURSOR OF UHMWPE DAMAGE? A FINITE ELEMENT STUDY Orthopaedic Research Laboratories Cleveland, Ohio Edward A. Morra, M.S.M.E. A. Seth Greenwald, D.Phil.(Oxon)
HIGH FLEXION IN CONTEMPORARY TOTAL KNEE DESIGN: A PRECURSOR OF UHMWPE DAMAGE? A FINITE ELEMENT STUDY Orthopaedic Research Laboratories Cleveland, Ohio Edward A. Morra, M.S.M.E. A. Seth Greenwald, D.Phil.(Oxon)
A Strain-Energy Model of Passive Knee Kinematics for the Study of Surgical Implantation Strategies
 IN:Springer Lecture Notes in Computer Science 1935 A Strain-Energy Model of Passive Knee Kinematics for the Study of Surgical Implantation Strategies E. Chen R. E. Ellis J. T. Bryant Computing and Information
IN:Springer Lecture Notes in Computer Science 1935 A Strain-Energy Model of Passive Knee Kinematics for the Study of Surgical Implantation Strategies E. Chen R. E. Ellis J. T. Bryant Computing and Information
To describe he knee joint, ligaments, structure & To list the main features of other lower limb joints
 To describe he knee joint, ligaments, structure & neurovascular supply To demonstrate the ankle joint anatomy To list the main features of other lower limb joints To list main groups of lymph nodes in
To describe he knee joint, ligaments, structure & neurovascular supply To demonstrate the ankle joint anatomy To list the main features of other lower limb joints To list main groups of lymph nodes in
Medial Patellofemoral Ligament Reconstruction Guidelines Brian Grawe Protocol
 Medial Patellofemoral Ligament Reconstruction Guidelines Brian Grawe Protocol Progression is based on healing constraints, functional progression specific to the patient. Phases and time frames are designed
Medial Patellofemoral Ligament Reconstruction Guidelines Brian Grawe Protocol Progression is based on healing constraints, functional progression specific to the patient. Phases and time frames are designed
Modeling And Biomechanical Analysis Of Human Knee Joint
 Modeling And Biomechanical Analysis Of Human Knee Joint V Jeevan Kumar 1, P Satish Reddy 2,N Guru Murthy 3 PG Student, Assoc. Professor, Asst Professor Prasiddha College of Engg & Tech, Amalapuram jvankaya@yahoo.in,
Modeling And Biomechanical Analysis Of Human Knee Joint V Jeevan Kumar 1, P Satish Reddy 2,N Guru Murthy 3 PG Student, Assoc. Professor, Asst Professor Prasiddha College of Engg & Tech, Amalapuram jvankaya@yahoo.in,
Myology of the Knee. PTA 105 Kinesiology
 Myology of the Knee PTA 105 Kinesiology Objectives Describe the planes of motion and axes of rotation of the knee joint Visualize the origins and insertions of the muscles about the knee List the innervations
Myology of the Knee PTA 105 Kinesiology Objectives Describe the planes of motion and axes of rotation of the knee joint Visualize the origins and insertions of the muscles about the knee List the innervations
ChiroCredit.com Presents Biomechanics: Focus on
 ChiroCredit.com Presents Biomechanics: Focus on the Knee Presented by: Ivo Waerlop, DC Shawn Allen, DC 1 Focus on The Knee 2 Pertinent Anatomy Femur Tibia Fibula Patella Prepatellar bursa Infrapatellar
ChiroCredit.com Presents Biomechanics: Focus on the Knee Presented by: Ivo Waerlop, DC Shawn Allen, DC 1 Focus on The Knee 2 Pertinent Anatomy Femur Tibia Fibula Patella Prepatellar bursa Infrapatellar
EMG-Driven Human Model for Orthosis Control
 EMG-Driven Human Model for Orthosis Control Christian Fleischer, Günter Hommel Institute for Computer Engineering and Microelectronics Berlin University of Technology, Germany {fleischer, hommel}@cs.tu-berlin.de
EMG-Driven Human Model for Orthosis Control Christian Fleischer, Günter Hommel Institute for Computer Engineering and Microelectronics Berlin University of Technology, Germany {fleischer, hommel}@cs.tu-berlin.de
FINITE ELEMENT MODELING OF HUMAN KNEE JOINT - MENISCUS UNDER COMPRESSIVE LOAD
 FINITE ELEMENT MODELING OF HUMAN KNEE JOINT - MENISCUS UNDER COMPRESSIVE LOAD 1 PRAVEEN KUMAR S, 2 RAMESH KANDADAI 1 PG Student (CAD Program), 2 Visiting Professor Department of Mechanical Engineering,
FINITE ELEMENT MODELING OF HUMAN KNEE JOINT - MENISCUS UNDER COMPRESSIVE LOAD 1 PRAVEEN KUMAR S, 2 RAMESH KANDADAI 1 PG Student (CAD Program), 2 Visiting Professor Department of Mechanical Engineering,
Partial Knee Replacement
 Partial Knee Replacement A partial knee replacement removes damaged cartilage from the knee and replaces it with prosthetic implants. Unlike a total knee replacement, which removes all of the cartilage,
Partial Knee Replacement A partial knee replacement removes damaged cartilage from the knee and replaces it with prosthetic implants. Unlike a total knee replacement, which removes all of the cartilage,
ANATOMIC. Navigated Surgical Technique 4 in 1 TO.G.GB.016/1.0
 ANATOMIC Navigated Surgical Technique 4 in 1 TO.G.GB.016/1.0 SCREEN LAYOUT Take screenshot Surgical step Dynamic navigation zone Information area and buttons 2 SCREEN LAYOUT Indicates action when yellow
ANATOMIC Navigated Surgical Technique 4 in 1 TO.G.GB.016/1.0 SCREEN LAYOUT Take screenshot Surgical step Dynamic navigation zone Information area and buttons 2 SCREEN LAYOUT Indicates action when yellow
The Knee Joint By Prof. Dr. Muhammad Imran Qureshi
 The Knee Joint By Prof. Dr. Muhammad Imran Qureshi Structurally, it is the Largest and the most complex joint in the body because of the functions that it performs: Allows mobility (flexion/extension)
The Knee Joint By Prof. Dr. Muhammad Imran Qureshi Structurally, it is the Largest and the most complex joint in the body because of the functions that it performs: Allows mobility (flexion/extension)
Retrieved from DalSpace, the institutional repository of Dalhousie University
 Retrieved from DalSpace, the institutional repository of Dalhousie University https://dalspace.library.dal.ca/handle/10222/72293 Version: Post-print Publisher s version: Wilson, Janie L. Astephen, Michael
Retrieved from DalSpace, the institutional repository of Dalhousie University https://dalspace.library.dal.ca/handle/10222/72293 Version: Post-print Publisher s version: Wilson, Janie L. Astephen, Michael
Takashi Fukaya, 1 Hirotaka Mutsuzaki, 2 Hirofumi Ida, 3 and Yasuyoshi Wadano Introduction
 Rehabilitation Research and Practice Volume 2012, Article ID 586348, 6 pages doi:10.1155/2012/586348 Research Article Two Different Protocols for Knee Joint Motion Analyses in the Stance Phase of Gait:
Rehabilitation Research and Practice Volume 2012, Article ID 586348, 6 pages doi:10.1155/2012/586348 Research Article Two Different Protocols for Knee Joint Motion Analyses in the Stance Phase of Gait:
3. Examination of Knee Kinematics In Vitro
 3. Examination of Knee Kinematics In Vitro 3.1 Introduction This chapter details two in vitro studies that were conducted to better understand the kinematic behavior of the knee. First, the role of graft
3. Examination of Knee Kinematics In Vitro 3.1 Introduction This chapter details two in vitro studies that were conducted to better understand the kinematic behavior of the knee. First, the role of graft
NZQA Expiring unit standard 7026 version 4 Page 1 of 7. Apply knowledge of functional anatomy and biomechanics
 Page 1 of 7 Title Apply knowledge of functional anatomy and biomechanics Level 5 Credits 5 Purpose People credited with this unit standard are able to: apply knowledge of human anatomy relevant to exercise
Page 1 of 7 Title Apply knowledge of functional anatomy and biomechanics Level 5 Credits 5 Purpose People credited with this unit standard are able to: apply knowledge of human anatomy relevant to exercise
ACL Rehabilitation and Return To Play
 ACL Rehabilitation and Return To Play Seth Gasser, MD Director of Sports Medicine Florida Orthopaedic Institute Introduction Return to Play: the point in recovery from an injury when a person is safely
ACL Rehabilitation and Return To Play Seth Gasser, MD Director of Sports Medicine Florida Orthopaedic Institute Introduction Return to Play: the point in recovery from an injury when a person is safely
Sports Rehabilitation & Performance Center Medial Patellofemoral Ligament Reconstruction Guidelines * Follow physician s modifications as prescribed
 The following MPFL guidelines were developed by the Sports Rehabilitation and Performance Center team at Hospital for Special Surgery. Progression is based on healing constraints, functional progression
The following MPFL guidelines were developed by the Sports Rehabilitation and Performance Center team at Hospital for Special Surgery. Progression is based on healing constraints, functional progression
FUSE TECHNICAL REPORT
 FUSE TECHNICAL REPORT 1 / 16 Contents Page 3 Page 4 Page 8 Page 10 Page 13 Page 16 Introduction FUSE Accuracy Validation Testing LBD Risk Score Model Details FUSE Risk Score Implementation Details FUSE
FUSE TECHNICAL REPORT 1 / 16 Contents Page 3 Page 4 Page 8 Page 10 Page 13 Page 16 Introduction FUSE Accuracy Validation Testing LBD Risk Score Model Details FUSE Risk Score Implementation Details FUSE
Re-establishing establishing Neuromuscular
 Re-establishing establishing Neuromuscular Control Why is NMC Critical? What is NMC? Physiology of Mechanoreceptors Elements of NMC Lower-Extremity Techniques Upper-Extremity Techniques Readings Chapter
Re-establishing establishing Neuromuscular Control Why is NMC Critical? What is NMC? Physiology of Mechanoreceptors Elements of NMC Lower-Extremity Techniques Upper-Extremity Techniques Readings Chapter
Rehabilitation Guidelines for Meniscal Repair
 Rehabilitation Guidelines for Meniscal Repair The knee is the body's largest joint, and the place where the femur, tibia, and patella meet to form a hinge-like joint. These bones are supported by a large
Rehabilitation Guidelines for Meniscal Repair The knee is the body's largest joint, and the place where the femur, tibia, and patella meet to form a hinge-like joint. These bones are supported by a large
PARTIAL KNEE REPLACEMENT
 PARTIAL KNEE REPLACEMENT A partial knee replacement removes damaged cartilage from the knee and replaces it with prosthetic implants. Unlike a total knee replacement, which removes all of the cartilage,
PARTIAL KNEE REPLACEMENT A partial knee replacement removes damaged cartilage from the knee and replaces it with prosthetic implants. Unlike a total knee replacement, which removes all of the cartilage,
Arthritic history is similar to that of the hip. Add history of give way and locking, swelling
 KNEE VASU PAI Arthritic history is similar to that of the hip. Add history of give way and locking, swelling INJURY MECHANISM When How Sequence Progress Disability IKDC Activity I - Strenuous activity
KNEE VASU PAI Arthritic history is similar to that of the hip. Add history of give way and locking, swelling INJURY MECHANISM When How Sequence Progress Disability IKDC Activity I - Strenuous activity
Evolution. Medial-Pivot Knee System The Bi-Cruciate-Substituting Knee. Key Aspects
 Evolution Medial-Pivot Knee System The Bi-Cruciate-Substituting Knee Key Aspects MicroPort s EVOLUTION Medial-Pivot Knee System was designed to recreate the natural anatomy that is lost during a total
Evolution Medial-Pivot Knee System The Bi-Cruciate-Substituting Knee Key Aspects MicroPort s EVOLUTION Medial-Pivot Knee System was designed to recreate the natural anatomy that is lost during a total
Modeling of human knee joint and finite element analysis of landing impact motion
 ISSN 1746-7659, England, UK Journal of Information and Computing Science Vol. 13, No. 1, 2018, pp.044-048 Modeling of human knee joint and finite element analysis of landing impact motion Bao Chunyu 1,3,Meng
ISSN 1746-7659, England, UK Journal of Information and Computing Science Vol. 13, No. 1, 2018, pp.044-048 Modeling of human knee joint and finite element analysis of landing impact motion Bao Chunyu 1,3,Meng
About the Simulation of the Human Knee Joint for Walking Locomotion
 About the Simulation of the Human Knee Joint for Walking Locomotion Dragos Popa*, Daniela Tarnita**, Danut Tarnita***, Iulian Iordachita**** * The University of Craiova, Calea Bucuresti 165, Craiova, Romania,
About the Simulation of the Human Knee Joint for Walking Locomotion Dragos Popa*, Daniela Tarnita**, Danut Tarnita***, Iulian Iordachita**** * The University of Craiova, Calea Bucuresti 165, Craiova, Romania,
Stephen R Smith Northeast Nebraska Orthopaedics PC. Ligament Preserving Techniques in Total Knee Arthroplasty
 Stephen R Smith Northeast Nebraska Orthopaedics PC Ligament Preserving Techniques in Total Knee Arthroplasty 10-15% have Fair to poor Results? Why? The complication rate is 2.567% If It happens To You
Stephen R Smith Northeast Nebraska Orthopaedics PC Ligament Preserving Techniques in Total Knee Arthroplasty 10-15% have Fair to poor Results? Why? The complication rate is 2.567% If It happens To You
Rehabilitation Guidelines for Anterior Cruciate Ligament (ACL) Reconstruction
 Rehabilitation Guidelines for Anterior Cruciate Ligament (ACL) Reconstruction The knee is the body's largest joint, and the place where the femur, tibia, and patella meet to form a hinge-like joint. These
Rehabilitation Guidelines for Anterior Cruciate Ligament (ACL) Reconstruction The knee is the body's largest joint, and the place where the femur, tibia, and patella meet to form a hinge-like joint. These
Total Knee Replacement
 Total Knee Replacement A total knee replacement, also known as total knee arthroplasty, involves removing damaged portions of the knee, and capping the bony surfaces with man-made prosthetic implants.
Total Knee Replacement A total knee replacement, also known as total knee arthroplasty, involves removing damaged portions of the knee, and capping the bony surfaces with man-made prosthetic implants.
6 th International Conference on Trends in Agricultural Engineering 7-9 September 2016, Prague, Czech Republic
 MEASUREMENT OF PRESSURE DISTRIBUTION IN KNEE JOINT REPLACEMENT J. Volf 1, V. Novák 1, V. Ryzhenko 1, D. Novák 2 1 Faculty of Engineering, Czech University of Life Sciences Prague, Czech Republic 2 Faculty
MEASUREMENT OF PRESSURE DISTRIBUTION IN KNEE JOINT REPLACEMENT J. Volf 1, V. Novák 1, V. Ryzhenko 1, D. Novák 2 1 Faculty of Engineering, Czech University of Life Sciences Prague, Czech Republic 2 Faculty
SKELETAL KINEMATICS OF THE ANTERIOR CRUCIATE LIGAMENT DEFICIENT KNEE WITH AND WITHOUT FUNCTIONAL BRACES
 SKELETAL KINEMATICS OF THE ANTERIOR CRUCIATE LIGAMENT DEFICIENT KNEE WITH AND WITHOUT FUNCTIONAL BRACES Dan K. Ramsey 1, Mario Lamontagne, Per F.Wretenberg 3 and Gunnar Németh 1 School of Human Kinetics,
SKELETAL KINEMATICS OF THE ANTERIOR CRUCIATE LIGAMENT DEFICIENT KNEE WITH AND WITHOUT FUNCTIONAL BRACES Dan K. Ramsey 1, Mario Lamontagne, Per F.Wretenberg 3 and Gunnar Németh 1 School of Human Kinetics,
ATTUNE Knee System: Stability in Total Knee Replacement
 ATTUNE Knee System: Stability in Total Knee Replacement Chadd Clary, PhD Staff Engineer DePuy Synthes Joint Reconstruction Young and active total knee replacement (TKR) patients demand a knee that feels
ATTUNE Knee System: Stability in Total Knee Replacement Chadd Clary, PhD Staff Engineer DePuy Synthes Joint Reconstruction Young and active total knee replacement (TKR) patients demand a knee that feels
Lecture 2. Statics & Dynamics of Rigid Bodies: Human body 30 August 2018
 Lecture 2. Statics & Dynamics of Rigid Bodies: Human body 30 August 2018 Wannapong Triampo, Ph.D. Static forces of Human Body Equilibrium and Stability Stability of bodies. Equilibrium and Stability Fulcrum
Lecture 2. Statics & Dynamics of Rigid Bodies: Human body 30 August 2018 Wannapong Triampo, Ph.D. Static forces of Human Body Equilibrium and Stability Stability of bodies. Equilibrium and Stability Fulcrum
Evaluation of Gait Mechanics Using Computerized Plantar Surface Pressure Analysis and it s Relation to Common Musculoskeletal Problems
 Evaluation of Gait Mechanics Using Computerized Plantar Surface Pressure Analysis and it s Relation to Common Musculoskeletal Problems Laws of Physics effecting gait Ground Reaction Forces Friction Stored
Evaluation of Gait Mechanics Using Computerized Plantar Surface Pressure Analysis and it s Relation to Common Musculoskeletal Problems Laws of Physics effecting gait Ground Reaction Forces Friction Stored
CHANGES IN LOWER-LIMB MUSCLE FORCES WITH PROPHYLACTIC KNEE BRACING DURING LANDING AND STOP-JUMP TASKS
 CHANGES IN LOWER-LIMB MUSCLE FORCES WITH PROPHYLACTIC KNEE BRACING DURING LANDING AND STOP-JUMP TASKS Katie Ewing 1, Rezaul Begg 2, Peter Lee 1 Department of Mechanical Engineering, University of Melbourne,
CHANGES IN LOWER-LIMB MUSCLE FORCES WITH PROPHYLACTIC KNEE BRACING DURING LANDING AND STOP-JUMP TASKS Katie Ewing 1, Rezaul Begg 2, Peter Lee 1 Department of Mechanical Engineering, University of Melbourne,
Rehabilitation Protocol:
 Rehabilitation Protocol: Patellofemoral resurfacing: Osteochondral Autograft Transplantation (OATS), Autologous Chondrocyte Implantation (ACI) and Microfracture Department of Orthopaedic Surgery Lahey
Rehabilitation Protocol: Patellofemoral resurfacing: Osteochondral Autograft Transplantation (OATS), Autologous Chondrocyte Implantation (ACI) and Microfracture Department of Orthopaedic Surgery Lahey
Biokinesiology of the Ankle Complex
 Rehabilitation Considerations Following Ankle Fracture: Impact on Gait & Closed Kinetic Chain Function Disclosures David Nolan, PT, DPT, MS, OCS, SCS, CSCS I have no actual or potential conflict of interest
Rehabilitation Considerations Following Ankle Fracture: Impact on Gait & Closed Kinetic Chain Function Disclosures David Nolan, PT, DPT, MS, OCS, SCS, CSCS I have no actual or potential conflict of interest
Post Operative Total Hip Replacement Protocol Brian J. White, MD
 Post Operative Total Hip Replacement Protocol Brian J. White, MD www.western-ortho.com The intent of this protocol is to provide guidelines for progression of rehabilitation. It is not intended to serve
Post Operative Total Hip Replacement Protocol Brian J. White, MD www.western-ortho.com The intent of this protocol is to provide guidelines for progression of rehabilitation. It is not intended to serve
Iliotibial Band Strain and Force in. Retrospective Iliotibial Band Syndrome. Aspiring Kid, PhD
 Iliotibial Band Strain and Force in Female Runners With and Without Retrospective Iliotibial Band Syndrome Aspiring Kid, PhD FUNCTION OF ILIOTIBIAL BAND Proximally: lateral hip stabilizer Helps prevent
Iliotibial Band Strain and Force in Female Runners With and Without Retrospective Iliotibial Band Syndrome Aspiring Kid, PhD FUNCTION OF ILIOTIBIAL BAND Proximally: lateral hip stabilizer Helps prevent
BIOMECHANICS AND CONTEXT OF ACUTE KNEE INJURIES. Uwe Kersting MiniModule Idræt Biomekanik 2. Objectives
 BIOMECHANICS AND CONTEXT OF ACUTE KNEE INJURIES Uwe Kersting MiniModule 06 2011 Idræt Biomekanik 2 1 Objectives Know about the static and dynamic organisation of the knee joint (anatomy & function) Be
BIOMECHANICS AND CONTEXT OF ACUTE KNEE INJURIES Uwe Kersting MiniModule 06 2011 Idræt Biomekanik 2 1 Objectives Know about the static and dynamic organisation of the knee joint (anatomy & function) Be
Life Science Journal 2014;11(12) Surface Modification and Software Design of Customized Knee Joint
 Surface Modification and Software Design of Customized Knee Joint Chin YU Wang 1*, Chien Fen Huang 2, Yi-Lin Liou 1 1 Department of Mechanical Engineering, Cheng Shiu University 2 Department of Physical
Surface Modification and Software Design of Customized Knee Joint Chin YU Wang 1*, Chien Fen Huang 2, Yi-Lin Liou 1 1 Department of Mechanical Engineering, Cheng Shiu University 2 Department of Physical
Balanced Body Movement Principles
 Balanced Body Movement Principles How the Body Works and How to Train it. Module 3: Lower Body Strength and Power Developing Strength, Endurance and Power The lower body is our primary source of strength,
Balanced Body Movement Principles How the Body Works and How to Train it. Module 3: Lower Body Strength and Power Developing Strength, Endurance and Power The lower body is our primary source of strength,
The Effect of Lateral Meniscal Root Injuries on the Stability of the Anterior Cruciate Ligament Deficient Knee
 The Effect of Lateral Meniscal Root Injuries on the Stability of the Anterior Cruciate Ligament Deficient Knee Charles Vega 1, Jebran Haddad 1, Jerry Alexander 2, Jonathan Gold 2, Theodore Shybut 1, Philip
The Effect of Lateral Meniscal Root Injuries on the Stability of the Anterior Cruciate Ligament Deficient Knee Charles Vega 1, Jebran Haddad 1, Jerry Alexander 2, Jonathan Gold 2, Theodore Shybut 1, Philip
OTM Lecture Gait and Somatic Dysfunction of the Lower Extremity
 OTM Lecture Gait and Somatic Dysfunction of the Lower Extremity Somatic Dysfunction Tenderness Asymmetry Range of Motion Tissue Texture Changes Any one of which must be present to diagnosis somatic dysfunction.
OTM Lecture Gait and Somatic Dysfunction of the Lower Extremity Somatic Dysfunction Tenderness Asymmetry Range of Motion Tissue Texture Changes Any one of which must be present to diagnosis somatic dysfunction.
Knee Ligament Function 3 properties allow ligaments mechanical functions to limit motion: Attachment Location
 29 muscles attach Lumbar Spine Muscles Transversospinalis group Rotatores Interspinales Intertransversarii Semispinalis Multifidus Erector spinae Iliocostalis Longissimus Spinalis Quadratus lumborum Latissimus
29 muscles attach Lumbar Spine Muscles Transversospinalis group Rotatores Interspinales Intertransversarii Semispinalis Multifidus Erector spinae Iliocostalis Longissimus Spinalis Quadratus lumborum Latissimus
Parameters of kinaesthesis during gaits derived from an ultrasound-based measuring system
 Modelling in Medicine and Biology VIII 171 Parameters of kinaesthesis during gaits derived from an ultrasound-based measuring system R. M. Kiss Department of Structures, Budapest University of Technology
Modelling in Medicine and Biology VIII 171 Parameters of kinaesthesis during gaits derived from an ultrasound-based measuring system R. M. Kiss Department of Structures, Budapest University of Technology
IDENTIFICATION OF INTERNAL LOADS AT THE SELECTED JOINTS AND VALIDATION OF A BIOMECHANICAL MODEL DURING PERFORMANCE OF THE HANDSPRING FRONT SOMERSAULT
 IDENTIFICATION OF INTERNAL LOADS AT THE SELECTED JOINTS AND VALIDATION OF A BIOMECHANICAL MODEL DURING PERFORMANCE OF THE HANDSPRING FRONT SOMERSAULT Adam CZAPLICKI *, Krzysztof DZIEWIECKI **, Tomasz SACEWICZ
IDENTIFICATION OF INTERNAL LOADS AT THE SELECTED JOINTS AND VALIDATION OF A BIOMECHANICAL MODEL DURING PERFORMANCE OF THE HANDSPRING FRONT SOMERSAULT Adam CZAPLICKI *, Krzysztof DZIEWIECKI **, Tomasz SACEWICZ
[ICESTM-2018] ISSN Impact Factor
![[ICESTM-2018] ISSN Impact Factor [ICESTM-2018] ISSN Impact Factor](/thumbs/88/117546298.jpg) GLOBAL JOURNAL OF ENGINEERING SCIENCE AND RESEARCHES MODELING AND FINITE ELEMENT ANALYSIS OF KNEE JOINT PROSTHESIS U.D.S.Prathap varma *1,S.Rajesh 2, B.Suresh Kumar 3 & P.Rama Murthy Raju 4 *1 M.TechScholar,
GLOBAL JOURNAL OF ENGINEERING SCIENCE AND RESEARCHES MODELING AND FINITE ELEMENT ANALYSIS OF KNEE JOINT PROSTHESIS U.D.S.Prathap varma *1,S.Rajesh 2, B.Suresh Kumar 3 & P.Rama Murthy Raju 4 *1 M.TechScholar,
Accurate Estimation of Mechanical Load on the Musculoskeletal System Using Biomechanics Modelling
 Accurate Estimation of Mechanical Load on the Musculoskeletal System Using Biomechanics Modelling António Veloso, Sílvia Cabral, Filipa João, Vera Moniz-Pereira, http://neuromechanics.fmh.ulisboa.pt/ Biomechanics
Accurate Estimation of Mechanical Load on the Musculoskeletal System Using Biomechanics Modelling António Veloso, Sílvia Cabral, Filipa João, Vera Moniz-Pereira, http://neuromechanics.fmh.ulisboa.pt/ Biomechanics
Revolution. Unicompartmental Knee System
 Revolution Unicompartmental Knee System While Total Knee Arthroplasty (TKA) is one of the most predictable procedures in orthopedic surgery, many patients undergoing TKA are in fact excellent candidates
Revolution Unicompartmental Knee System While Total Knee Arthroplasty (TKA) is one of the most predictable procedures in orthopedic surgery, many patients undergoing TKA are in fact excellent candidates
Copyright 2012 by The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved. McGraw-Hill/Irwin
 CHAPTER 8: THE LOWER EXTREMITY: KNEE, ANKLE, AND FOOT KINESIOLOGY Scientific Basis of Human Motion, 12 th edition Hamilton, Weimar & Luttgens Presentation Created by TK Koesterer, Ph.D., ATC Humboldt State
CHAPTER 8: THE LOWER EXTREMITY: KNEE, ANKLE, AND FOOT KINESIOLOGY Scientific Basis of Human Motion, 12 th edition Hamilton, Weimar & Luttgens Presentation Created by TK Koesterer, Ph.D., ATC Humboldt State
Knee Capsular Disorder. ICD-9-CM: Stiffness in joint of lower leg, not elsewhere classified
 1 Knee Capsular Disorder "Knee Capsulitis" ICD-9-CM: 719.56 Stiffness in joint of lower leg, not elsewhere classified Diagnostic Criteria History: Physical Exam: Stiffness Aching with prolonged weight
1 Knee Capsular Disorder "Knee Capsulitis" ICD-9-CM: 719.56 Stiffness in joint of lower leg, not elsewhere classified Diagnostic Criteria History: Physical Exam: Stiffness Aching with prolonged weight
Introduction to Biomechanical Analysis
 Introduction to Biomechanical Analysis LEARNING OBJECTIVES: At the end of this laboratory exercise the student will be able to: Identify forces used during activities Identify moments used during activities
Introduction to Biomechanical Analysis LEARNING OBJECTIVES: At the end of this laboratory exercise the student will be able to: Identify forces used during activities Identify moments used during activities
The Pelvic Equilibrium Theory Part 2
 The Pelvic Equilibrium Theory Part 2 Understanding the abnormal motion patterns associated with The Pelvic Equilibrium Theory and Leg length Inequality. Aims of this section! To discuss the abnormal motion
The Pelvic Equilibrium Theory Part 2 Understanding the abnormal motion patterns associated with The Pelvic Equilibrium Theory and Leg length Inequality. Aims of this section! To discuss the abnormal motion
Multiapical Deformities p. 97 Osteotomy Concepts and Frontal Plane Realignment p. 99 Angulation Correction Axis (ACA) p. 99 Bisector Lines p.
 Normal Lower Limb Alignment and Joint Orientation p. 1 Mechanical and Anatomic Bone Axes p. 1 Joint Center Points p. 5 Joint Orientation Lines p. 5 Ankle p. 5 Knee p. 5 Hip p. 8 Joint Orientation Angles
Normal Lower Limb Alignment and Joint Orientation p. 1 Mechanical and Anatomic Bone Axes p. 1 Joint Center Points p. 5 Joint Orientation Lines p. 5 Ankle p. 5 Knee p. 5 Hip p. 8 Joint Orientation Angles
ACL AND PCL INJURIES OF THE KNEE JOINT
 ACL AND PCL INJURIES OF THE KNEE JOINT Dr.KN Subramanian M.Ch Orth., FRCS (Tr & Orth), CCT Orth(UK) Consultant Orthopaedic Surgeon, Special interest: Orthopaedic Sports Injury, Shoulder and Knee Surgery,
ACL AND PCL INJURIES OF THE KNEE JOINT Dr.KN Subramanian M.Ch Orth., FRCS (Tr & Orth), CCT Orth(UK) Consultant Orthopaedic Surgeon, Special interest: Orthopaedic Sports Injury, Shoulder and Knee Surgery,
Total Hip Replacement Rehabilitation: Progression and Restrictions
 Total Hip Replacement Rehabilitation: Progression and Restrictions The success of total hip replacement (THR) is a result of predictable pain relief, improvements in quality of life, and restoration of
Total Hip Replacement Rehabilitation: Progression and Restrictions The success of total hip replacement (THR) is a result of predictable pain relief, improvements in quality of life, and restoration of
Femoral Condyle Rehabilitation Guidelines
 Femoral Condyle Rehabilitation Guidelines PHASE I - PROTECTION PHASE (WEEKS 0-6) Brace: Protect healing tissue from load and shear forces Decrease pain and effusion Restore full passive knee extension
Femoral Condyle Rehabilitation Guidelines PHASE I - PROTECTION PHASE (WEEKS 0-6) Brace: Protect healing tissue from load and shear forces Decrease pain and effusion Restore full passive knee extension
Biomechanics of Skeletal Muscle and the Musculoskeletal System
 Biomechanics of Skeletal Muscle and the Musculoskeletal System Hamill & Knutzen (Ch 3) Nordin & Frankel (Ch 5), or Hall (Ch. 6) Muscle Properties Ø Irritability Ø Muscle has the capability of receiving
Biomechanics of Skeletal Muscle and the Musculoskeletal System Hamill & Knutzen (Ch 3) Nordin & Frankel (Ch 5), or Hall (Ch. 6) Muscle Properties Ø Irritability Ø Muscle has the capability of receiving
Hip Arthroscopy Protocol
 The intent of this protocol is to provide guidelines for progression of rehabilitation, it is not intended to serve as a substitute for clinical decision making. Progression through each phase of rehabilitation
The intent of this protocol is to provide guidelines for progression of rehabilitation, it is not intended to serve as a substitute for clinical decision making. Progression through each phase of rehabilitation
ACL Athletic Career. ACL Rupture - Warning Features Intensive pain Immediate swelling Locking Feel a Pop Dead leg Cannot continue to play
 FIMS Ambassador Tour to Eastern Europe, 2004 Belgrade, Serbia Montenegro Acute Knee Injuries - Controversies and Challenges Professor KM Chan OBE, JP President of FIMS Belgrade ACL Athletic Career ACL
FIMS Ambassador Tour to Eastern Europe, 2004 Belgrade, Serbia Montenegro Acute Knee Injuries - Controversies and Challenges Professor KM Chan OBE, JP President of FIMS Belgrade ACL Athletic Career ACL
An Inverse Kinematics Model For Post-operative Knee
 An Inverse Kinematics Model For Post-operative Knee Ligament Parameters Estimation From Knee Motion Elvis C. S. Chen 1 and Randy E. Ellis 1,2 1 School of Computing, Queen s University, Canada chene@cs.queensu.ca
An Inverse Kinematics Model For Post-operative Knee Ligament Parameters Estimation From Knee Motion Elvis C. S. Chen 1 and Randy E. Ellis 1,2 1 School of Computing, Queen s University, Canada chene@cs.queensu.ca
APPLICATION OF THE MOVEMENT SYSTEMS MODEL TO THE MANAGEMENT COMMON HIP PATHOLOGIES
 APPLICATION OF THE MOVEMENT SYSTEMS MODEL TO THE MANAGEMENT COMMON HIP PATHOLOGIES Tracy Porter, PT, DPT Des Moines University Department of Physical Therapy Objectives Review current literature related
APPLICATION OF THE MOVEMENT SYSTEMS MODEL TO THE MANAGEMENT COMMON HIP PATHOLOGIES Tracy Porter, PT, DPT Des Moines University Department of Physical Therapy Objectives Review current literature related
CLASSIFICATION OF MOBILE BEARING KNEE DESIGN: MOBILITY AND CONSTRAINT
 CLASSIFICATION OF MOBILE BEAING KNEE DESIGN: MOBILITY AND CONSTAINT Orthopaedic esearch Laboratories Lutheran Hospital Cleveland Clinic Health System Christine S. Heim, B.Sc. Paul. D. Postak, B.Sc. Nicholas
CLASSIFICATION OF MOBILE BEAING KNEE DESIGN: MOBILITY AND CONSTAINT Orthopaedic esearch Laboratories Lutheran Hospital Cleveland Clinic Health System Christine S. Heim, B.Sc. Paul. D. Postak, B.Sc. Nicholas
Meniscus Repair Rehabilitation Protocol
 Brian E. Camilleri, DO 2610 Enterprise Dr Anderson, IN 46013 Phone: (765) 683-4400 Fax: (765) 642-7903 www.ciocenter.com Meniscus Repair Rehabilitation Protocol The intent of this protocol is to provide
Brian E. Camilleri, DO 2610 Enterprise Dr Anderson, IN 46013 Phone: (765) 683-4400 Fax: (765) 642-7903 www.ciocenter.com Meniscus Repair Rehabilitation Protocol The intent of this protocol is to provide
Post-Operative Meniscus Repair Protocol Brian J.White, MD
 Post-Operative Meniscus Repair Protocol Brian J.White, MD www.western-ortho.com (This protocol should be used with combined a ACL Reconstruction and meniscus repair) The intent of this protocol is to provide
Post-Operative Meniscus Repair Protocol Brian J.White, MD www.western-ortho.com (This protocol should be used with combined a ACL Reconstruction and meniscus repair) The intent of this protocol is to provide
Concurrent Prediction of Muscle Force and Cartilage Stress during Movement
 MUSCULOSKELETAL BIOMECHANICS RESEARCH LAB Concurrent Prediction of Muscle Force and Cartilage Stress during Movement Trent M. Guess, PhD University of Missouri-Kansas City, Kansas City, MO RPI-NSF Workshop
MUSCULOSKELETAL BIOMECHANICS RESEARCH LAB Concurrent Prediction of Muscle Force and Cartilage Stress during Movement Trent M. Guess, PhD University of Missouri-Kansas City, Kansas City, MO RPI-NSF Workshop
The virtual morphology and the main movements of the human neck simulations used for car crash studies
 IOP Conference Series: Materials Science and Engineering PAPER OPEN ACCESS The virtual morphology and the main movements of the human neck simulations used for car crash studies Related content - Stochastic
IOP Conference Series: Materials Science and Engineering PAPER OPEN ACCESS The virtual morphology and the main movements of the human neck simulations used for car crash studies Related content - Stochastic
Investigation of Human Whole Body Motion Using a Three-Dimensional Neuromusculoskeletal Model
 Investigation of Human Whole Body Motion Using a Three-Dimensional Neuromusculoskeletal Model 1 Akinori Nagano, 2 Senshi Fukashiro, 1 Ryutaro Himeno a-nagano@riken.jp, fukashiro@idaten.c.u-tokyo.ac.jp,
Investigation of Human Whole Body Motion Using a Three-Dimensional Neuromusculoskeletal Model 1 Akinori Nagano, 2 Senshi Fukashiro, 1 Ryutaro Himeno a-nagano@riken.jp, fukashiro@idaten.c.u-tokyo.ac.jp,
Presenter: Mark Yeoman PhD Date: 19 October Research & Development, FEA, CFD, Material Selection, Testing & Assessment. Continuum Blue Ltd
 Research & Development, FEA, CFD, Material Selection, Testing & Assessment Investigating the loading behaviour of intact & meniscectomy knee joints & the impact on surgical decisions M S Yeoman PhD 1 1.
Research & Development, FEA, CFD, Material Selection, Testing & Assessment Investigating the loading behaviour of intact & meniscectomy knee joints & the impact on surgical decisions M S Yeoman PhD 1 1.
Evaluation Of Contact Pressure On Total Surface Bearing And Patellar Tendon Bearing Sockets During Stair Ascent And
 Evaluation Of Contact Pressure On Total Surface Bearing And Patellar Tendon Bearing Sockets During Stair Ascent And Descent Koji Totoribe, Etsuo Chosa, MD, PhD, Xin Zhao, MD, PhD, Go Yamako, PhD, Shinji
Evaluation Of Contact Pressure On Total Surface Bearing And Patellar Tendon Bearing Sockets During Stair Ascent And Descent Koji Totoribe, Etsuo Chosa, MD, PhD, Xin Zhao, MD, PhD, Go Yamako, PhD, Shinji
Effect of Speed and Experience on Kinetic and Kinematic Factors During Exercise on a Stair-Climbing Machine
 Journal of Sport Rehabilitation, 1996, 5, 224-233 O 1996 Human Kinetics Publishers, Inc. Effect of Speed and Experience on Kinetic and Kinematic Factors During Exercise on a Stair-Climbing Machine Jiping
Journal of Sport Rehabilitation, 1996, 5, 224-233 O 1996 Human Kinetics Publishers, Inc. Effect of Speed and Experience on Kinetic and Kinematic Factors During Exercise on a Stair-Climbing Machine Jiping
Unicompartmental Knee Resurfacing
 Disclaimer This movie is an educational resource only and should not be used to manage knee pain. All decisions about the management of knee pain must be made in conjunction with your Physician or a licensed
Disclaimer This movie is an educational resource only and should not be used to manage knee pain. All decisions about the management of knee pain must be made in conjunction with your Physician or a licensed
NexGen Legacy LPS-Flex Knee. Brochure
 NexGen Legacy LPS-Flex Knee Brochure What postoperative range of motion can your TKA patients expect? For patients with the ability and desire to perform For patients with the ability high-flexion activities,
NexGen Legacy LPS-Flex Knee Brochure What postoperative range of motion can your TKA patients expect? For patients with the ability and desire to perform For patients with the ability high-flexion activities,
JOINT RULER. Surgical Technique For Knee Joint JRReplacement
 JR JOINT RULER Surgical Technique For Knee Joint JRReplacement INTRODUCTION The Joint Ruler * is designed to help reduce the incidence of flexion, extension, and patellofemoral joint problems by allowing
JR JOINT RULER Surgical Technique For Knee Joint JRReplacement INTRODUCTION The Joint Ruler * is designed to help reduce the incidence of flexion, extension, and patellofemoral joint problems by allowing
Masterclass. Tips and tricks for a successful outcome. E. Verhaven, M. Thaeter. September 15th, 2012, Brussels
 Masterclass Tips and tricks for a successful outcome September 15th, 2012, Brussels E. Verhaven, M. Thaeter Belgium St. Nikolaus-Hospital Orthopaedics & Traumatology Ultimate Goal of TKR Normal alignment
Masterclass Tips and tricks for a successful outcome September 15th, 2012, Brussels E. Verhaven, M. Thaeter Belgium St. Nikolaus-Hospital Orthopaedics & Traumatology Ultimate Goal of TKR Normal alignment
