Dysplasia Epiphysealis Hemimelica or Trevor s Disease: A Case Report
|
|
|
- Sophie Shepherd
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Chin J Radiol 2001; 26: CASE REPORT Dysplasia Epiphysealis Hemimelica or Trevor s Disease: A Case Report YIH-HUIE LIN 1 YI-JIUN CHOU 2 LEE-REN YEH 1 CLEMENT K.H. CHEN 1 HUAY-BAN PAN 1 CHIEN-FANG YANG 1 Departments of Radiology 1, Orthopedics 2, Kaohsiung Veterans General Hospital, Kaohsiung, Taiwan Trevor s disease, or dysplasia epiphysealis hemimelica (DEH), is an uncommon skeletal developmental disorder representing an osteochondroma arising from 1 or more epiphyses. We present the case of a 21-year-old female who had suffered from a hard protruding mass of the right ankle for more than 10 years. It was mistakenly thought to be posttraumatic osseous fragments by a local practitioner since her childhood. However, DEH was diagnosed with the characteristic image findings and proven by the pathology report after an operation. Review of the related literature shows that this disease is rare in Taiwan. The imaging studies, which are helpful in making a correct diagnosis and proper preoperative plan, are also discussed. Key words: Trevor s disease, Dysplasia epiphysealis hemimelica, Epiphysis, Osteochondroma Reprint requests to: Dr. Clement K. H. Chen Department of Radiology, Kaohsiung Veterans General Hospital, 386 Ta-Chung 1st Rd. Kaohsiung 813, Taiwan, R.O.C. Trevor s disease is a rare developmental lesion that is histologically identical to an osteochondroma affecting 1 or more epiphyses. The reported incidence is 1 in 1,000,000 [1]. Historically, it has been referred to by many names. It was originally described as a tarsomegalie in 1926 by Mouchet and Belot [2]. Trevor described 10 patients in 1950 and used the name tarso-epiphyseal aclasis, and this abnormality is also commonly referred to as Trevor's disease [3]. In 1956, Fairbank reported on 14 patients and renamed the condition as the currently used term, dysplasia epiphysealis hemimelica (DEH) [4]. DEH usually becomes evident in children and young adults. It is more common in men than in women in a ratio of approximately 3 to 1 [1]. There is no definite evidence that it is hereditary [7, 10], and no cases of malignant transformation have been reported [5, 7, 8]. Typically, clinical manifestations include swelling and, less commonly, pain and deformity. The common sites of involvement are the distal tibia and femur. Upper extremity involvement is rarely reported [5, 10-12]. The disease is usually restricted to the medial or lateral side of the limb (hemimelic). Herein we report a case of DEH with a typical location and imaging findings. A history of trauma at an early age, however, misled the local practitioner to the diagnosis of fracture fragments. To the best of our knowledge, only 1 case has been reported in Taiwan [9]. By introducing this case, we hope to inform clinicians of its specific imaging findings. In addition to conventional imaging examinations, a three-dimensional (3D) reconstruction computed tomography (CT) scan was also used for this case.
2 216 Trevor s disease 1a 1b 1c Figure 1. Serial lateral radiographs of right ankle in the case of Trevor s disease discloses progressive enlargement and confluence of the bony masses. a. At 3 years old, small faint osseous bodies over the medial aspect of the hind foot were noted (arrows), which were interpreted as posttraumatic bone fragments then. b. At 10 years old, confluences of the osseous bodies with tarsal bones (arrows) were found. c. At 21 years old, confluence and enlargement of the bony mass resulted in hind foot valgus. CASE REPORT A 21-year-old woman was admitted to our hospital because of right ankle bony mass for more than 10 years. She had had a lesion over the right medial ankle since she was 3 years old, which had been noted after an accident. The mass became progressively larger as she grew up. There was no associated painful disability or marked tenderness except for occasional aching pain. Ankle radiographs were taken twice (Fig. 1a, b), and she was diagnosed as posttraumatic dislocation or large displaced osseous fragments. No specific treatment was given during these years. Some doctors suggested that she continue observation and clinical assessment until she reached skeletal maturity. Because of the unpleasant appearance, she was eager to resolve the problem, and admission was arranged for further evaluation and treatment. Physical examination revealed a palpable hard mass about 8 8 cm 2 over the right medial malleolar area with limited eversion and inversion of the ankle. Valgus deformity with mild lateral rotation of the ankle and mild muscle atrophy on the right were also noted. Bilateral lower limbs were of equal length. Plain radiographs showed a prominently enlarged medial malleolar osseous mass filling the medial space of the right hindfoot (Fig. 1c). On spiral computed tomography scan with 3D shaded surface display (SSD) reconstruction, a confluent ossific mass was found which had a lobulated appearance and communicated from the marrow with the underlying epiphysis and adjacent bones (Fig. 2). Subsequent magnetic resonance scan for preoperative evaluation of the soft tissue and cartilage demonstrated a bony mass protrusion with marrow continuity from the medial aspect of the distal tibial platform, medial malleolus, talus, and also the navicular bone (Fig. 3). The mass had normal cortical and trabecular signal intensity with incomplete confluence, and was localized over the medial aspect of the right ankle and hindfoot. The resultant enlargement of the medial malleolus and talus caused compression and displacement of the surrounding soft tissue and valgus deformity of the right ankle. The medial tendons, including the posterior tibialis tendon, flexor digitorum longus, and flexor hallucis longus, were preserved. Degenerative change of the right ankle joint with thinning of the articular cartilage was evident. According to the radiographic findings, a preliminary diagnosis of Trevor's disease was made, and excision was performed. A bony mass
3 Trevor s disease 217 2b 2a Figure 2. Craniocaudal a. and lateral b. projections of the 3D reconstructed CT images, shaded surface display (SSD), well delineate the lesion for surgical planning (arrows and *). with cartilage caps over the medial malleolus and talus medial site was found during the operation. It was removed with an oscillating saw, and the deltoid ligament was repaired and re-attached to the bony surface. The postoperative condition was stable, and the patient was discharged with good wound healing. On pathologic examination, the lesion consisted of multiple pieces of bony tissue. The surface was capped by cartilage and covered by fibrous tissue with endochondral ossification. This finding is consistent with dysplasia epiphysealis hemimelica. DISCUSSION The etiology of DEH is still unclear. In Trevor's report, he believed that the lesion was congenital and was related to an insult during the formation of the limb bud [3]. Fairbank believed the process to be a true dysplasia or faulty growth of part of the epiphysis itself [4]. Typically, the disease occurs over the epiphysis or the tarsal or flat bones, in a single lower extremity. The ankle is most commonly affected. Although asymmetrical involvement has been reported [13], the lesions typically affect only one side of the joint, with the medial side affected twice as frequently as the lateral [6]. There may be single lesion or multiple lesions; 2/3 of patients have multiple lesions [1, 5, 11, 12]. This leads to designation of a localized form (monostotic involvement), a classic form (more than 1 area of osseous involvement in a single Figure 3. Axial (a, TR/TE/excitation=550/11/2) T1- weighted MR images (Signa 1.5T, GE Medical system) of the ankle demonstrate osteochondromas arising from the talus and navicular with marrow continuity and protruding osseous mass (*). extremity), and a generalized or severe form (involvement of an entire single extremity) [14]. The localized form of DEH usually affects bones of the hindfoot or ankle. The classic form shows characteristic hemimelic distribution and accounts for more than 2/3 of cases. It typically involves more than one epiphysis within a single lower extremity, especially around the knee and
4 218 Trevor s disease ankle (talus, distal femoral, and distal tibial epiphyses). In the generalized or severe form, the entire lower extremity may be involved. The affected location in our patient was over the right medial ankle, which is the most common site reported. The involved range was the classic form. In our patient s history, plain films were taken twice. One was taken at the age of 3 just after the accident, and small faint osseous bodies can be observed (Fig. 1a). The other was taken when she was about 10 years old; multiple ossified masses can be noted protruding from the medial malleolus, talus, and navicular bone (Fig. 1b). The latest film taken in our hospital shows that all the separate ossifications join to give a lobular appearance with valgus deformity of the ankle joint (Fig. 1c). These radiographic findings have been well described in multiple reports [5, 6]. The lesion is often not visible on plain radiographs initially, as it may not begin to ossify. Once mineralization has begins, it appears as at a secondary ossification center. In infant or young child, small, multifocal, irregular ossifications are seen adjacent to 1 side of an ossifying epiphysis (or carpal or tarsal bone). The adjacent metaphysis may be widened. Subsequently, the ossifications become confluent with the adjacent bone, eventually appearing as a lobulated osseous mass protruding from the epiphysis (or carpal or tarsal bone) [15]. The final appearance resembles that of osteochondroma with the affected area (or areas) remaining large and irregular. Premature closure of the physis may occur along with its consequence of limb deformity and limb length discrepancy. The articular surface is often irregular and, combined with the angular deformity, frequently results in premature secondary osteoarthritis. At an early stage, this finding may be confused with either loose bodies or synovial osteochondromatosis. Synovial osteochondromatosis occurs primarily in later adulthood and is extremely rare in children. A misdiagnosis of loose bodies was previously made for our patient due to her traumatic history. But, subsequent examinations allowed us to make the definite diagnosis because bony fragments should not enlarge as a patient grows up. CT is used to assess the continuity of the lobulated mass with the underlying epiphysis. It also demonstrates similar attenuation of tissue between the two structures, both composed of cartilage and osteoid. However, the relationship in different section planes is better evaluated with MR imaging. In addition to conventional CT imaging, we further studied this case with 3D reconstruction. The appearance of the mass and the 3-dimensional relationships between the lesion and adjacent bones (distal tibia, talus, and navicular) were observed more clearly in the reconstructed images (Fig. 2). MR imaging is extremely useful for identifying the extent of epiphyseal involvement, joint deformity, and the effect on surrounding soft tissue, as with osteochondromas at other sites. Details of the unossified cartilaginous mass and the status of the articular and meniscal cartilage and growth plate are optimally assessed with MR imaging. The lesion and involved epiphyseal cartilage have similar signal intensities, with intermediate signal intensity on T1-weighted and high signal intensity on T2-weighted MR images. Areas of low signal intensity on T1- and T2- weighted images indicate areas of calcification or ossification that increase as the lesion and patient's skeletal maturity progress. Often there is a clear plane of separation between the lesion and the normal epiphysis. Complete skeletal maturity of our patient was noted at admission, and the lesion was shown to be totally ossified with marrow continuity to adjacent bones on MR imaging. According to the findings on her early radiographs, we believe that the cartilaginous component and the separated plane between the accessory ossification center and the normal epiphysis could have been observed if she had been examined at a younger age. According to the pathology report, the lesion is a lobulated mass protruding from the epiphysis with a cartilaginous cap. The lesion is sometimes indistinguishable from the normal epiphysis. Its histologic features are identical to those of an osteochondroma, consisting of a base of normal bone and hyaline cartilage with abundant enchondral ossification. The histologic findings support Trevor s hypothesis that the disease is a result of abnormal cellular activity at the cartilaginous ossification center. The normal cartilage sequence follows an orderly fashion of cell proliferation, maturation, senescence, and disintegration that does not occur in DEH. Trevor used the term aclasis in describing this failure of normal cellular breakdown. Biopsy is typically not necessary because of diagnostic radiologic features. However, a
5 Trevor s disease 219 skeletal survey should be performed to exclude additional areas of involvement, particularly of the lower extremities. Surveillance and clinical assessment are usually continued until the patient reaches skeletal maturity. Surgical intervention is more frequently required for these lesions than for solitary osteochondromas because the epiphyseal location is often associated with pain, deformity, or loss of normal mechanical function [11]. Excision, even incomplete resection, may result in a reduction of symptoms. Surgery is often directed at improving joint congruity to lessen subsequent development of secondary osteoarthritis; thus, treatment at an early stage of disease improves the outcome [3, 11]. Corrective osteotomies may also be needed to treat residual deformities. The prognosis of this disease is generally good. It is reported that plain films supplemented with MRI provide the greatest diagnostic information in cases of DEH. Though MRI is helpful in defining the site and extent of the osteocartilaginous mass and providing detailed images of the associated joint deformity, we think it is not routinely required. If there isn t much cartilaginous, component the exact location and extent of lesion can be fully evaluated by CT imaging. With 3D reconstruction, the lesion can be seen through the covering soft tissue from any direction without excision. SUMMARY Clinicians must be aware of DEH if a patient has a growing hard mass over one side of single lower extremity. Imaging can help to make a correct diagnosis. If bony fragments are suspected, a subsequent imaging examination will be helpful. CT and MR can show the relationship between the lesion and the underlying bone marrow or surrounding soft tissue. MRI is not needed as a routine examination especially when the patient has passed puberty. Sectional and reconstructed 3D CT can be used for making a proper evaluation and surgical plan. REFERENCE 1. Wynne-Davis R, Hall CM, Apley AG. Dysplasia epiphysealis hemimelica. In: Wynne-Davis R, Hall CM, Apley AG, Eds. Atlas of skeletal dysplasias. New York, NY: Churchill Livingstone, 1985; Mouchet A, Belot J. La tarsomegalie. J Radiol Electrol 1926; 10: Trevor D. Tarso-epiphyseal aclasis, a congenital error of epiphysial development. J Bone Joint Surg Br 1950; 32: Fairbank TJ. Dysplasia epiphysealis hemimelica (tarsoepiphyseal aclasis). J Bone Joint Surg Br 1956; 32: Azouz EM, Slomic AM, Marton D, Rigault P, Finidori G. The variable manifestations of dysplasia epiphysealis hemimelica. Pediatr Radiol 1985; 15: Silverman FN. Dysplasia epiphysealis hemimelica. Semin Roentgenol 1989; 24: Hensinger RN, Cowell HR, Ramsey PL, Leopold RG. Familial dysplasia epiphysealis hemimelica associated with chondromas and osteochondromas. Report of a kindred with variable presentations. J Bone Joint Surg Am 1974; 56: Schmidt MB, Lomasney LM. Radiologic case study. Trevor disease: dysplasia epiphysealis hemimelica. Orthopedics 1994; 17: Hon-Ming Ma, Jason Shih-Chia Liu. Dysplasia epiphysealis hemimelica: report of an unusual case- A four years follow-up. J0rthop Surg ROC 1998; 15: Cruz-Conde R, Amaya S, Valdivia P, Hernandez M, Calvo M. Dysplasia epiphysealis hemimelica. J Pediatr Orthop 1984; 4: Rao SB, Roy DR. Dysplasia epiphysealis hemimelica. Upper limb involvement with associated osteochondroma. Clin Orthop 1994; 307: Lamesch A. Dysplasia epiphysealis hemimelica of the carpal bones. Report of a case and review of the literature. J Bone and Joint Surg Am 1983; 65: Heilbronner DM. Asymmetric dysplasia epiphysealis hemimelica. Orthopedics 1988; 11: Pritchard DJ, Lunke RJ, Taylor WF, et al. Chondrosarcoma: A clinicopathologic and statistical analysis. Cancer 1980; 45: Kettelkamp DB, Campbell CJ, Bonfiglio M. Dysplasia epiphysealis hemimelica. A report of fifteen cases and a review of the literature. J Bone Joint Surg Am 1966; 48: 746
6 220 Trevor s disease
Citation Acta medica Nagasakiensia. 1997, 42
 NAOSITE: Nagasaki University's Ac Title Author(s) Dysplasia Epiphysealis Hemimelica o Uetani, Masataka; Hashmi, Rashid; H Hayashi, Tomayoshi Citation Acta medica Nagasakiensia. 1997, 42 Issue Date 1997-12-20
NAOSITE: Nagasaki University's Ac Title Author(s) Dysplasia Epiphysealis Hemimelica o Uetani, Masataka; Hashmi, Rashid; H Hayashi, Tomayoshi Citation Acta medica Nagasakiensia. 1997, 42 Issue Date 1997-12-20
Hip Joint Trevor Disease: Literature Review and a Case Report
 http:// ijp.mums.ac.ir Case Report (Pages: 6809-6814) Hip Joint Trevor Disease: Literature Review and a Case Report Mohammad Hallaj Moghadam 1, *Ali Parsa 2,3, Mohammad Hassani 4, Maryam Mirzaie 5, Reza
http:// ijp.mums.ac.ir Case Report (Pages: 6809-6814) Hip Joint Trevor Disease: Literature Review and a Case Report Mohammad Hallaj Moghadam 1, *Ali Parsa 2,3, Mohammad Hassani 4, Maryam Mirzaie 5, Reza
Dysplasia Epiphysealis Hemimelica of the Acetabulum
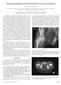 Dysplasia Epiphysealis Hemimelica of the Acetabulum A REPORT OF TWO CASES* BY DAVID L. SKAGGS, M.D., CHARLES N. MOON, M.D., ROBERT M. KAY, M.D., LOS ANGELES, CALIFORNIA, AND HAMLET A. PETERSON, M.D., ROCHESTER,
Dysplasia Epiphysealis Hemimelica of the Acetabulum A REPORT OF TWO CASES* BY DAVID L. SKAGGS, M.D., CHARLES N. MOON, M.D., ROBERT M. KAY, M.D., LOS ANGELES, CALIFORNIA, AND HAMLET A. PETERSON, M.D., ROCHESTER,
Advertisement. Osteochondroma
 Advertisement Osteochondroma An osteochondroma is a benign (noncancerous) tumor that develops during childhood or adolescence. It is an abnormal growth that forms on the surface of a bone near the growth
Advertisement Osteochondroma An osteochondroma is a benign (noncancerous) tumor that develops during childhood or adolescence. It is an abnormal growth that forms on the surface of a bone near the growth
DYSPLASIA EPIPHYSEALIS HEMIMELICA OF THE DISTAL ULNA: A CASE REPORT AND REVIEW OF THE LITERATURE
 272 EUROPEAN JOURNAL OF MEDICAL RESEARCH June 18, 2009 Eur J Med Res (2009) 14: 272-276 I. Holzapfel Publishers 2009 DYSPLASIA EPIPHYSEALIS HEMIMELICA OF THE DISTAL ULNA: A CASE REPORT AND REVIEW OF THE
272 EUROPEAN JOURNAL OF MEDICAL RESEARCH June 18, 2009 Eur J Med Res (2009) 14: 272-276 I. Holzapfel Publishers 2009 DYSPLASIA EPIPHYSEALIS HEMIMELICA OF THE DISTAL ULNA: A CASE REPORT AND REVIEW OF THE
Lower Extremity Alignment: Genu Varum / Valgum
 Lower Extremity Alignment: Genu Varum / Valgum Arthur B Meyers, MD Nemours Children s Hospital & Health System Associate Professor of Radiology, University of Central Florida Clinical Associate Professor
Lower Extremity Alignment: Genu Varum / Valgum Arthur B Meyers, MD Nemours Children s Hospital & Health System Associate Professor of Radiology, University of Central Florida Clinical Associate Professor
Case. 15 Y old boy presented with pain in the foot. No history of injury or any constitutional symptoms. Your diagnosis?
 Case 15 Y old boy presented with pain in the foot. No history of injury or any constitutional symptoms Your diagnosis? Diagnosis: Calcaneo-navicular tarsal coalition. C sign Talar beaking Ant eaters nose
Case 15 Y old boy presented with pain in the foot. No history of injury or any constitutional symptoms Your diagnosis? Diagnosis: Calcaneo-navicular tarsal coalition. C sign Talar beaking Ant eaters nose
Magnetic resonance imaging of femoral head development in roentgenographically normal patients
 Skeletal Radiol (1985) 14:159-163 Skeletal Radiology Magnetic resonance imaging of femoral head development in roentgenographically normal patients Peter J. Littrup, M.D. 1, Alex M. Aisen, M.D. 2, Ethan
Skeletal Radiol (1985) 14:159-163 Skeletal Radiology Magnetic resonance imaging of femoral head development in roentgenographically normal patients Peter J. Littrup, M.D. 1, Alex M. Aisen, M.D. 2, Ethan
CLINICAL PRESENTATION AND RADIOLOGY QUIZ QUESTION
 Donald L. Renfrew, MD Radiology Associates of the Fox Valley, 333 N. Commercial Street, Suite 100, Neenah, WI 54956 11/24/2012 Radiology Quiz of the Week # 100 Page 1 CLINICAL PRESENTATION AND RADIOLOGY
Donald L. Renfrew, MD Radiology Associates of the Fox Valley, 333 N. Commercial Street, Suite 100, Neenah, WI 54956 11/24/2012 Radiology Quiz of the Week # 100 Page 1 CLINICAL PRESENTATION AND RADIOLOGY
Case Report Trevor s Disease: A Literature Review regarding Classification, Treatment, and Prognosis apropos of a Case
 Case Reports in Orthopedics, Article ID 940360, 8 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2014/940360 Case Report Trevor s Disease: A Literature Review regarding Classification, Treatment, and Prognosis apropos
Case Reports in Orthopedics, Article ID 940360, 8 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2014/940360 Case Report Trevor s Disease: A Literature Review regarding Classification, Treatment, and Prognosis apropos
Avascular Necrosis of the Foot. Dr. Hema Choudur MD, FRCPC Associate Professor. Dept. of Radiology. McMaster University, Hamilton, Canada.
 Avascular Necrosis of the Foot Dr. Hema Choudur MD, FRCPC Associate Professor. Dept. of Radiology. McMaster University, Hamilton, Canada. Avascular Necrosis: Pathophysiology Ischemia to the bone from oxygen
Avascular Necrosis of the Foot Dr. Hema Choudur MD, FRCPC Associate Professor. Dept. of Radiology. McMaster University, Hamilton, Canada. Avascular Necrosis: Pathophysiology Ischemia to the bone from oxygen
Chapter 5 The Skeletal System
 Chapter 5 The Skeletal System The Skeletal System Parts of the skeletal system Bones (skeleton) Joints Cartilages Ligaments (bone to bone)(tendon=bone to muscle) Divided into two divisions Axial skeleton:
Chapter 5 The Skeletal System The Skeletal System Parts of the skeletal system Bones (skeleton) Joints Cartilages Ligaments (bone to bone)(tendon=bone to muscle) Divided into two divisions Axial skeleton:
Intracapsular and para- articular chondroma of knee: a report of four cases and review of the literature
 Intracapsular and para- articular chondroma of knee: a report of four cases and review of the literature Milan Samardziski, Marta Foteva, Aleksandar Adamov, George Zafiroski University Clinic for Orthopaedic
Intracapsular and para- articular chondroma of knee: a report of four cases and review of the literature Milan Samardziski, Marta Foteva, Aleksandar Adamov, George Zafiroski University Clinic for Orthopaedic
Ethan M. Braunstein, M.D. 1, Steven A. Goldstein, Ph.D. 2, Janet Ku, M.S. 2, Patrick Smith, M.D. 2, and Larry S. Matthews, M.D. 2
 Skeletal Radiol (1986) 15:27-31 Skeletal Radiology Computed tomography and plain radiography in experimental fracture healing Ethan M. Braunstein, M.D. 1, Steven A. Goldstein, Ph.D. 2, Janet Ku, M.S. 2,
Skeletal Radiol (1986) 15:27-31 Skeletal Radiology Computed tomography and plain radiography in experimental fracture healing Ethan M. Braunstein, M.D. 1, Steven A. Goldstein, Ph.D. 2, Janet Ku, M.S. 2,
4/28/2010. Fractures. Normal Bone and Normal Ossification Bone Terms. Epiphysis Epiphyseal Plate (physis) Metaphysis
 Fractures Normal Bone and Normal Ossification Bone Terms Epiphysis Epiphyseal Plate (physis) Metaphysis Diaphysis 1 Fracture Classifications A. Longitudinal B. Transverse C. Oblique D. Spiral E. Incomplete
Fractures Normal Bone and Normal Ossification Bone Terms Epiphysis Epiphyseal Plate (physis) Metaphysis Diaphysis 1 Fracture Classifications A. Longitudinal B. Transverse C. Oblique D. Spiral E. Incomplete
PEM GUIDE CHILDHOOD FRACTURES
 PEM GUIDE CHILDHOOD FRACTURES INTRODUCTION Skeletal injuries account for 10-15% of all injuries in children; 20% of those are fractures, 3 out of 4 fractures affect the physis or growth plate. Always consider
PEM GUIDE CHILDHOOD FRACTURES INTRODUCTION Skeletal injuries account for 10-15% of all injuries in children; 20% of those are fractures, 3 out of 4 fractures affect the physis or growth plate. Always consider
Case Report Extraosseous Intra-Articular Osteochondroma
 Case Reports in Orthopedics Volume 2013, Article ID 181862, 5 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2013/181862 Case Report Extraosseous Intra-Articular Osteochondroma Pragash Mohanen, 1,2 Kumaresan Palania
Case Reports in Orthopedics Volume 2013, Article ID 181862, 5 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2013/181862 Case Report Extraosseous Intra-Articular Osteochondroma Pragash Mohanen, 1,2 Kumaresan Palania
Case Report Painful Os Peroneum Syndrome: Underdiagnosed Condition in the Lateral Midfoot Pain
 Case Reports in Radiology Volume 2016, Article ID 8739362, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2016/8739362 Case Report Painful Os Peroneum Syndrome: Underdiagnosed Condition in the Lateral Midfoot Pain
Case Reports in Radiology Volume 2016, Article ID 8739362, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2016/8739362 Case Report Painful Os Peroneum Syndrome: Underdiagnosed Condition in the Lateral Midfoot Pain
CASE REPORT GIANT OSTEOCHONDRAL LOOSE BODY OF THE KNEE JOINT
 Journal of Musculoskeletal Research, Vol. 4, No. 2 (2000) 145 149 World Scientific Publishing Company ORIGINAL CASE REPORT ARTICLES GIANT OSTEOCHONDRAL LOOSE BODY OF THE KNEE JOINT Mustafa Yel *,, Mustafa
Journal of Musculoskeletal Research, Vol. 4, No. 2 (2000) 145 149 World Scientific Publishing Company ORIGINAL CASE REPORT ARTICLES GIANT OSTEOCHONDRAL LOOSE BODY OF THE KNEE JOINT Mustafa Yel *,, Mustafa
THE Salter-Harris classification is a radiologic
 Advanced Emergency Nursing Journal Vol. 29, No. 1, pp. 10 19 Copyright c 2007 Wolters Kluwer Health Lippincott Williams & Wilkins Radiology R O U N D S Column Editor: Jonathan Lee Salter-Harris Fractures
Advanced Emergency Nursing Journal Vol. 29, No. 1, pp. 10 19 Copyright c 2007 Wolters Kluwer Health Lippincott Williams & Wilkins Radiology R O U N D S Column Editor: Jonathan Lee Salter-Harris Fractures
MRI of the Knee: Part 4 - normal variants that may simulate disease. Mark Anderson, M.D. University of Virginia
 MRI of the Knee: Part 4 - normal variants that may simulate disease Mark Anderson, M.D. University of Virginia discuss the most common normal variants in the pediatric knee that may simulate pathology
MRI of the Knee: Part 4 - normal variants that may simulate disease Mark Anderson, M.D. University of Virginia discuss the most common normal variants in the pediatric knee that may simulate pathology
The Skeletal System PART A
 5 The Skeletal System PART A PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Jerry L. Cook, Sam Houston University ESSENTIALS OF HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY EIGHTH EDITION ELAINE N. MARIEB The Skeletal System
5 The Skeletal System PART A PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Jerry L. Cook, Sam Houston University ESSENTIALS OF HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY EIGHTH EDITION ELAINE N. MARIEB The Skeletal System
Osteomyelitis in infancy and childhood: A clinical and diagnostic overview M. Mearadji
 Osteomyelitis in infancy and childhood: A clinical and diagnostic overview M. Mearadji International Foundation for Pediatric Imaging Aid Introduction Osteomyelitis is a relative common disease in infancy
Osteomyelitis in infancy and childhood: A clinical and diagnostic overview M. Mearadji International Foundation for Pediatric Imaging Aid Introduction Osteomyelitis is a relative common disease in infancy
MRI of Pediatric Ankle and Foot. Mahesh Thapa, MD Associate Professor Seattle Children s University of Washington School of Medicine
 MRI of Pediatric Ankle and Foot Mahesh Thapa, MD Associate Professor Seattle Children s University of Washington School of Medicine Disclosures Under contract with Lippincott Williams and Wilkins (LWW)
MRI of Pediatric Ankle and Foot Mahesh Thapa, MD Associate Professor Seattle Children s University of Washington School of Medicine Disclosures Under contract with Lippincott Williams and Wilkins (LWW)
Pediatric Fractures. Objectives. Epiphyseal Complex. Anatomy and Physiology. Ligaments. Bony matrix
 1 Pediatric Fractures Nicholas White, MD Assistant Professor of Pediatrics Eastern Virginia Medical School Attending, Pediatric Emergency Department Children s Hospital of The King s Daughters Objectives
1 Pediatric Fractures Nicholas White, MD Assistant Professor of Pediatrics Eastern Virginia Medical School Attending, Pediatric Emergency Department Children s Hospital of The King s Daughters Objectives
Physeal Fractures and Growth Arrest
 Physeal Fractures and Growth Arrest Raymond W. Liu, M.D. Victor M. Goldberg Master Clinician-Scientist in Orthopaedics Rainbow Babies and Children s Hospital Case Western Reserve University Outline General
Physeal Fractures and Growth Arrest Raymond W. Liu, M.D. Victor M. Goldberg Master Clinician-Scientist in Orthopaedics Rainbow Babies and Children s Hospital Case Western Reserve University Outline General
Treatment of malunited fractures of the ankle
 Treatment of malunited fractures of the ankle A LONG-TERM FOLLOW-UP OF RECONSTRUCTIVE SURGERY I. I. Reidsma, P. A. Nolte, R. K. Marti, E. L. F. B. Raaymakers From Academic Medical Center, Amsterdam, Netherlands
Treatment of malunited fractures of the ankle A LONG-TERM FOLLOW-UP OF RECONSTRUCTIVE SURGERY I. I. Reidsma, P. A. Nolte, R. K. Marti, E. L. F. B. Raaymakers From Academic Medical Center, Amsterdam, Netherlands
MARK D. MURPHEY MD, FACR. Physician-in-Chief, AIRP. Chief, Musculoskeletal Imaging
 ALPHABET SOUP AND CYSTIC LESIONS OF THE BONE MARK D. MURPHEY MD, FACR Physician-in-Chief, AIRP Chief, Musculoskeletal Imaging ALPHABET SOUP AND CYSTIC LESIONS OF THE BONE Giant cell tumor (GCT) Unicameral
ALPHABET SOUP AND CYSTIC LESIONS OF THE BONE MARK D. MURPHEY MD, FACR Physician-in-Chief, AIRP Chief, Musculoskeletal Imaging ALPHABET SOUP AND CYSTIC LESIONS OF THE BONE Giant cell tumor (GCT) Unicameral
What s your diagnosis?
 Case Study 58 A 61-year-old truck driver man presented with a valgus injury to the left knee joint when involved in a truck accident. What s your diagnosis? Diagnosis : Avulsion of Deep MCL The medial
Case Study 58 A 61-year-old truck driver man presented with a valgus injury to the left knee joint when involved in a truck accident. What s your diagnosis? Diagnosis : Avulsion of Deep MCL The medial
11/4/2018 SUBTLETIES OF LOWER EXTREMITY TRAUMA IMAGING SPEAKER DISCLOSURES
 SUBTLETIES OF LOWER EXTREMITY TRAUMA IMAGING Charles S. Resnik, M.D. Professor of Radiology University of Maryland School of Medicine Upon completion of this presentation, participants will be better able
SUBTLETIES OF LOWER EXTREMITY TRAUMA IMAGING Charles S. Resnik, M.D. Professor of Radiology University of Maryland School of Medicine Upon completion of this presentation, participants will be better able
Friday Teaching. Bones
 Friday Teaching Bones Regarding slipped femoral capital epiphysis It represents Salter Harris type V injury 20% are bilateral There is slight widening of the joint space Slip is typically posteromedial
Friday Teaching Bones Regarding slipped femoral capital epiphysis It represents Salter Harris type V injury 20% are bilateral There is slight widening of the joint space Slip is typically posteromedial
Original Report. The Reverse Segond Fracture: Association with a Tear of the Posterior Cruciate Ligament and Medial Meniscus
 Eva M. Escobedo 1 William J. Mills 2 John. Hunter 1 Received July 10, 2001; accepted after revision October 1, 2001. 1 Department of Radiology, University of Washington Harborview Medical enter, 325 Ninth
Eva M. Escobedo 1 William J. Mills 2 John. Hunter 1 Received July 10, 2001; accepted after revision October 1, 2001. 1 Department of Radiology, University of Washington Harborview Medical enter, 325 Ninth
Skeletally Immature Athletes Ununited Osteochondral Fractures of the Distal Fibula
 Chronic, Painful Ankle Instability in Skeletally Immature Athletes Ununited Osteochondral Fractures of the Distal Fibula Brian D. Busconi,* MD, and Arthur M. Pappas, MD From the Department of Orthopedics
Chronic, Painful Ankle Instability in Skeletally Immature Athletes Ununited Osteochondral Fractures of the Distal Fibula Brian D. Busconi,* MD, and Arthur M. Pappas, MD From the Department of Orthopedics
Knee Contusions and Stress Injuries. Laura W. Bancroft, M.D.
 Knee Contusions and Stress Injuries Laura W. Bancroft, M.D. Objectives Review 5 types of contusion patterns Pivot shift Dashboard Hyperextension Clip Lateral patellar dislocation Demonstrate various stress
Knee Contusions and Stress Injuries Laura W. Bancroft, M.D. Objectives Review 5 types of contusion patterns Pivot shift Dashboard Hyperextension Clip Lateral patellar dislocation Demonstrate various stress
Tarsal Coalition On MR
 Tarsal Coalition On MR By William Renner, M.D. This and other topics will be discussed in Tarsal coalition is a congenital anomaly with fusion of the tarsal bones. The fusion may be bony, fibrous or cartilaginous.
Tarsal Coalition On MR By William Renner, M.D. This and other topics will be discussed in Tarsal coalition is a congenital anomaly with fusion of the tarsal bones. The fusion may be bony, fibrous or cartilaginous.
.org. Ankle Fractures (Broken Ankle) Anatomy
 Ankle Fractures (Broken Ankle) Page ( 1 ) A broken ankle is also known as an ankle fracture. This means that one or more of the bones that make up the ankle joint are broken. A fractured ankle can range
Ankle Fractures (Broken Ankle) Page ( 1 ) A broken ankle is also known as an ankle fracture. This means that one or more of the bones that make up the ankle joint are broken. A fractured ankle can range
Childhood Fractures. Incomplete fractures more common. Ligaments stronger than bone. Tendons stronger than bone. Fractures may be pathologic
 Childhood Fractures Incomplete fractures more common Plastic bowing Torus / Buckle Greenstick Ligaments stronger than bone Fracture patterns different Physeal injury, not dislocation Tendons stronger than
Childhood Fractures Incomplete fractures more common Plastic bowing Torus / Buckle Greenstick Ligaments stronger than bone Fracture patterns different Physeal injury, not dislocation Tendons stronger than
EPIPHYSEAL PLATE IN FEMUR
 Reviewing: Epiphyseal Plates (younger skeletons) eventually will disappear. Bones grow lengthwise up and down from each plate, and in a circular collar like fashion around the diaphysis. These plates will
Reviewing: Epiphyseal Plates (younger skeletons) eventually will disappear. Bones grow lengthwise up and down from each plate, and in a circular collar like fashion around the diaphysis. These plates will
CLINICAL PRESENTATION AND RADIOLOGY QUIZ QUESTION
 Donald L. Renfrew, MD Radiology Associates of the Fox Valley, 333 N. Commercial Street, Suite 100, Neenah, WI 54956 12/08/2012 Radiology Quiz of the Week # 102 Page 1 CLINICAL PRESENTATION AND RADIOLOGY
Donald L. Renfrew, MD Radiology Associates of the Fox Valley, 333 N. Commercial Street, Suite 100, Neenah, WI 54956 12/08/2012 Radiology Quiz of the Week # 102 Page 1 CLINICAL PRESENTATION AND RADIOLOGY
The Skeletal System PART A. PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College
 PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College The Skeletal System 5 PART A The Skeletal System Parts of the skeletal system Bones (skeleton) Joints
PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College The Skeletal System 5 PART A The Skeletal System Parts of the skeletal system Bones (skeleton) Joints
The scapula is located on the back side of the ribcage and helps provide part of the shoulder joint and movement for the arms.
 The scapula is located on the back side of the ribcage and helps provide part of the shoulder joint and movement for the arms. Scapula Humerus (Upper Arm Bone) Radius and Ulna Radius on Top Ulna on Bottom
The scapula is located on the back side of the ribcage and helps provide part of the shoulder joint and movement for the arms. Scapula Humerus (Upper Arm Bone) Radius and Ulna Radius on Top Ulna on Bottom
Physeal injuries of the ankle joint constitute 11% of all
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Outcome of Physeal and Epiphyseal Injuries of the Distal Tibia With Intra-Articular Involvement Savvas P. Nenopoulos, MD, Vasilios A. Papavasiliou, MD, and Athanasios V. Papavasiliou,
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Outcome of Physeal and Epiphyseal Injuries of the Distal Tibia With Intra-Articular Involvement Savvas P. Nenopoulos, MD, Vasilios A. Papavasiliou, MD, and Athanasios V. Papavasiliou,
Monostotic Paget s Disease: A Case Report
 Chin J Radiol 2002; 27: 117-121 117 CASE REPORT Monostotic Paget s Disease: A Case Report CHI-CHEN HOU 1 CHI WEI LO 2 JINN-MING CHANG 1 CHING-CHERNG TZENG 3 Department of Diagnostic Radiology 1, Orthopedics
Chin J Radiol 2002; 27: 117-121 117 CASE REPORT Monostotic Paget s Disease: A Case Report CHI-CHEN HOU 1 CHI WEI LO 2 JINN-MING CHANG 1 CHING-CHERNG TZENG 3 Department of Diagnostic Radiology 1, Orthopedics
Results of Calcaneal Osteotomy & Flexor Digitorum Longus transfer in Stage II Acquired Flatfoot Deformity
 Results of Calcaneal Osteotomy & Flexor Digitorum Longus transfer in Stage II Acquired Flatfoot Deformity Mr Amit Chauhan Mr Prasad Karpe Ms Maire-claire Killen Mr Rajiv Limaye University Hospital of North
Results of Calcaneal Osteotomy & Flexor Digitorum Longus transfer in Stage II Acquired Flatfoot Deformity Mr Amit Chauhan Mr Prasad Karpe Ms Maire-claire Killen Mr Rajiv Limaye University Hospital of North
SKELETAL SYSTEM. Introduction Notes (pt 1)
 SKELETAL SYSTEM Introduction Notes (pt 1) I. INTRODUCTION 1. Bones include active, living tissues: bone tissue, cartilage, dense connective tissue, blood, and nervous tissue. 2. Bones: support and protect
SKELETAL SYSTEM Introduction Notes (pt 1) I. INTRODUCTION 1. Bones include active, living tissues: bone tissue, cartilage, dense connective tissue, blood, and nervous tissue. 2. Bones: support and protect
Pellegrini-Stieda Syndrome: Report Of Two Cases. M Akinkunmi, S Vijayvargiya, C Prakash, M Kayode, G Awosanya
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Radiology Volume 12 Number 2 M Akinkunmi, S Vijayvargiya, C Prakash, M Kayode, G Awosanya Citation M Akinkunmi, S Vijayvargiya, C Prakash, M Kayode, G Awosanya.. The Internet
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Radiology Volume 12 Number 2 M Akinkunmi, S Vijayvargiya, C Prakash, M Kayode, G Awosanya Citation M Akinkunmi, S Vijayvargiya, C Prakash, M Kayode, G Awosanya.. The Internet
Physeal Growth Plate Fractures: Implications for the Pediatric Athlete
 Physeal Growth Plate Fractures: Implications for the Pediatric Athlete Tara J. Clark, Lindsey E. Eberman, and Michelle A. Cleary Abstract: Pediatric musculoskeletal trauma accounts for most childhood injuries.
Physeal Growth Plate Fractures: Implications for the Pediatric Athlete Tara J. Clark, Lindsey E. Eberman, and Michelle A. Cleary Abstract: Pediatric musculoskeletal trauma accounts for most childhood injuries.
Skeletal System. Chapter 6.1 Human Anatomy & Physiology
 Skeletal System Chapter 6.1 Human Anatomy & Physiology Overview of Skeletal System Bones Joints Skeletal System Cartilage Tendons (bone to muscle) Ligaments (bone to bone) Function of the Skeletal System
Skeletal System Chapter 6.1 Human Anatomy & Physiology Overview of Skeletal System Bones Joints Skeletal System Cartilage Tendons (bone to muscle) Ligaments (bone to bone) Function of the Skeletal System
Isolated congenital anterolateral bowing of the fibula : A case report with 24 years follow-up
 Acta Orthop. Belg., 2009, 75, 842-846 CASE REPORT Isolated congenital anterolateral bowing of the fibula : A case report with 24 years follow-up Karolien LELIEFELD, Hans VAN DER SLUIJS, Ibo VAN DER HAVEN
Acta Orthop. Belg., 2009, 75, 842-846 CASE REPORT Isolated congenital anterolateral bowing of the fibula : A case report with 24 years follow-up Karolien LELIEFELD, Hans VAN DER SLUIJS, Ibo VAN DER HAVEN
«Foot & Ankle Surgery» 04. Sept THE PAINFUL FLATFOOT. Norman Espinosa, MD
 THE PAINFUL FLATFOOT Norman Espinosa, MD Department of Orthopaedics University of Zurich Balgrist Switzerland www.balgrist.ch WHAT TO DO? INTRINSIC > EXTRINSIC ETIOLOGIES Repetitive microtrauma combined
THE PAINFUL FLATFOOT Norman Espinosa, MD Department of Orthopaedics University of Zurich Balgrist Switzerland www.balgrist.ch WHAT TO DO? INTRINSIC > EXTRINSIC ETIOLOGIES Repetitive microtrauma combined
Figure ) The area that causes the lengthwise growth of a long bone is indicated by letter. Diff: 2 Page Ref:
 Essentials of Anatomy and Physiology, 9e (Marieb) Chapter 5 The Skeletal System Short Answer Figure 5.1 Using Figure 5.1, identify the following: 1) Spongy bone is indicated by letter. Diff: 1 Page Ref:
Essentials of Anatomy and Physiology, 9e (Marieb) Chapter 5 The Skeletal System Short Answer Figure 5.1 Using Figure 5.1, identify the following: 1) Spongy bone is indicated by letter. Diff: 1 Page Ref:
A Patient s Guide to Flatfoot Deformity (Pes Planus) in Children
 A Patient s Guide to Flatfoot Deformity (Pes Planus) in Children 2350 Royal Boulevard Suite 200 Elgin, IL 60123 Phone: 847.931.5300 Fax: 847.931.9072 DISCLAIMER: The information in this booklet is compiled
A Patient s Guide to Flatfoot Deformity (Pes Planus) in Children 2350 Royal Boulevard Suite 200 Elgin, IL 60123 Phone: 847.931.5300 Fax: 847.931.9072 DISCLAIMER: The information in this booklet is compiled
Current Thinking of the Osteochondroses. Diego Jaramillo, M.D., M.P.H. Department of Radiology Stanford Children s Hospital
 Current Thinking of the Osteochondroses Diego Jaramillo, M.D., M.P.H. Department of Radiology Stanford Children s Hospital What is an osteochondrosis? Abnormal endochondral ossification and epiphyseal
Current Thinking of the Osteochondroses Diego Jaramillo, M.D., M.P.H. Department of Radiology Stanford Children s Hospital What is an osteochondrosis? Abnormal endochondral ossification and epiphyseal
OSSEOUS TISSUE & BONE STRUCTURE PART I: OVERVIEW & COMPONENTS
 OSSEOUS TISSUE & BONE STRUCTURE PART I: OVERVIEW & COMPONENTS The Skeletal System Skeletal system includes: bones of the skeleton, cartilages, ligaments, and connective tissues What are the functions of
OSSEOUS TISSUE & BONE STRUCTURE PART I: OVERVIEW & COMPONENTS The Skeletal System Skeletal system includes: bones of the skeleton, cartilages, ligaments, and connective tissues What are the functions of
Fractures of the Ankle Region in the Skeletally Immature Patient. The Salter Classification is Worthless!!
 Fractures of the Ankle Region in the Skeletally Immature Patient. The Salter Classification is Worthless!! Kaye E Wilkins D.V.M,M.D. President's Council/Dielmann Chair in Pediatric Orthopedics Professor
Fractures of the Ankle Region in the Skeletally Immature Patient. The Salter Classification is Worthless!! Kaye E Wilkins D.V.M,M.D. President's Council/Dielmann Chair in Pediatric Orthopedics Professor
General osteology. General anatomy of the human skeleton. Development and classification of bones. The bone as a multifunctional organ.
 General osteology. General anatomy of the human skeleton. Development and classification of bones. The bone as a multifunctional organ. Composed by Natalia Leonidovna Svintsitskaya, Associate professor
General osteology. General anatomy of the human skeleton. Development and classification of bones. The bone as a multifunctional organ. Composed by Natalia Leonidovna Svintsitskaya, Associate professor
Interesting Case Series. Ganglion Cyst of the Peroneus Longus
 Interesting Case Series Ganglion Cyst of the Peroneus Longus Andrew A. Marano, BA, Paul J. Therattil, MD, Dare V. Ajibade, MD, PhD, MPH, and Ramazi O. Datiashvili, MD, PhD Division of Plastic and Reconstructive
Interesting Case Series Ganglion Cyst of the Peroneus Longus Andrew A. Marano, BA, Paul J. Therattil, MD, Dare V. Ajibade, MD, PhD, MPH, and Ramazi O. Datiashvili, MD, PhD Division of Plastic and Reconstructive
Evaluation of Pediatric Foot Pain
 May 2006 Evaluation of Pediatric Foot Pain John Flibotte, Harvard Medical School Year III Our Patient AP is a 10 year old boy with chronic R foot pain 2 Anatomy of the Foot Manusov EG, et al. (1996), Part
May 2006 Evaluation of Pediatric Foot Pain John Flibotte, Harvard Medical School Year III Our Patient AP is a 10 year old boy with chronic R foot pain 2 Anatomy of the Foot Manusov EG, et al. (1996), Part
CLINICAL PRESENTATION AND RADIOLOGY QUIZ QUESTION
 Donald L. Renfrew, MD Radiology Associates of the Fox Valley, 333 N. Commercial Street, Suite 100, Neenah, WI 54956 12/29/2012 Radiology Quiz of the Week # 105 Page 1 CLINICAL PRESENTATION AND RADIOLOGY
Donald L. Renfrew, MD Radiology Associates of the Fox Valley, 333 N. Commercial Street, Suite 100, Neenah, WI 54956 12/29/2012 Radiology Quiz of the Week # 105 Page 1 CLINICAL PRESENTATION AND RADIOLOGY
Apply this knowledge into proper management strategies and referrals
 1 2 3 Lower Extremity Injuries Jason Kennedy, M.D. Disclosures I have no financial/ industry disclosures. Objectives Identify common lower extremity injury patterns in the child and adolescent Apply this
1 2 3 Lower Extremity Injuries Jason Kennedy, M.D. Disclosures I have no financial/ industry disclosures. Objectives Identify common lower extremity injury patterns in the child and adolescent Apply this
CT Findings of Traumatic Posterior Hip Dislocation after Reduction 1
 CT Findings of Traumatic Posterior Hip Dislocation after Reduction 1 Sung Kyoung Moon, M.D., Ji Seon Park, M.D., Wook Jin, M.D. 2, Kyung Nam Ryu, M.D. Purpose: To evaluate the CT images of reduced hips
CT Findings of Traumatic Posterior Hip Dislocation after Reduction 1 Sung Kyoung Moon, M.D., Ji Seon Park, M.D., Wook Jin, M.D. 2, Kyung Nam Ryu, M.D. Purpose: To evaluate the CT images of reduced hips
Unilateral osteonecrosis. imaging findings
 Skeletal Radiol (2001) 30:643 647 DOI 10.1007/s002560100423 CASE REPORT F. Abascal L. Cerezal F. del Piñal R. García-Valtuille A. García-Valtuille A. Canga J. Torcida Unilateral osteonecrosis in a patient
Skeletal Radiol (2001) 30:643 647 DOI 10.1007/s002560100423 CASE REPORT F. Abascal L. Cerezal F. del Piñal R. García-Valtuille A. García-Valtuille A. Canga J. Torcida Unilateral osteonecrosis in a patient
Section 4: Tarsal Coalitions
 Case H (Figure 2): PedCat CBCT transverse plane reconstruction of right Lisfranc midfoot dislocation compared to normal left foot. Clinical Relevance of the PedCat Study: The weight bearing CBCT study
Case H (Figure 2): PedCat CBCT transverse plane reconstruction of right Lisfranc midfoot dislocation compared to normal left foot. Clinical Relevance of the PedCat Study: The weight bearing CBCT study
SALTER HARRIS FRACTURES:
 SALTER HARRIS FRACTURES: DO THESE LIL GUYS SPRAIN OR BREAK? Process of growth Begins in utero Continues until the end of puberty Linear growth Result of multiplication of chondrocytes in the epiphyses
SALTER HARRIS FRACTURES: DO THESE LIL GUYS SPRAIN OR BREAK? Process of growth Begins in utero Continues until the end of puberty Linear growth Result of multiplication of chondrocytes in the epiphyses
COPYRIGHT 2004 BY THE JOURNAL OF BONE AND JOINT SURGERY, INCORPORATED
 84 COPYRIGHT 2004 BY THE JOURNAL BONE AND JOINT SURGERY, INCORPORATED Radiographic Evaluation of Pathological Bone Lesions: Current Spectrum of Disease and Approach to Diagnosis BY BENJAMIN G. DOMB, MD,
84 COPYRIGHT 2004 BY THE JOURNAL BONE AND JOINT SURGERY, INCORPORATED Radiographic Evaluation of Pathological Bone Lesions: Current Spectrum of Disease and Approach to Diagnosis BY BENJAMIN G. DOMB, MD,
Case Avulsion fracture of the tibial tubercle in an adolescent
 Case 14039 Avulsion fracture of the tibial tubercle in an adolescent Charlotte Vanhoenacker 1, Kris Van Crombrugge 2, Lieven Tack 2, Filip Vanhoenacker 2, 3, 4 1: Leuven University Hospital, Department
Case 14039 Avulsion fracture of the tibial tubercle in an adolescent Charlotte Vanhoenacker 1, Kris Van Crombrugge 2, Lieven Tack 2, Filip Vanhoenacker 2, 3, 4 1: Leuven University Hospital, Department
Bones. The division of bones anatomically is : long, short, irregular, flat and sesamoid.
 Bones Osteocytes : Are responsible for maintenance of bones Present in lacunae, and send processes. Unable to divide. The division of bones anatomically is : long, short, irregular, flat and sesamoid.
Bones Osteocytes : Are responsible for maintenance of bones Present in lacunae, and send processes. Unable to divide. The division of bones anatomically is : long, short, irregular, flat and sesamoid.
KNEE DISLOCATION. The most common injury will be an anterior dislocation, and this usually results from a hyperextension mechanism.
 KNEE DISLOCATION Introduction Dislocation of the knee is a severe injury associated with major soft tissue injury and a high incidence of damage to the popliteal artery. There is displacement of the tibia
KNEE DISLOCATION Introduction Dislocation of the knee is a severe injury associated with major soft tissue injury and a high incidence of damage to the popliteal artery. There is displacement of the tibia
General Concepts. Growth Around the Knee. Topics. Evaluation
 General Concepts Knee Injuries in Skeletally Immature Athletes Zachary Stinson, M.D. Increased rate and ability of healing Higher strength of ligaments compared to growth plates Continued growth Children
General Concepts Knee Injuries in Skeletally Immature Athletes Zachary Stinson, M.D. Increased rate and ability of healing Higher strength of ligaments compared to growth plates Continued growth Children
PAINFUL SESAMOID OF THE GREAT TOE Dr Vasu Pai ANATOMICAL CONSIDERATION. At the big toe MTP joint: Tibial sesamoid (medial) & fibular (lateral)
 PAINFUL SESAMOID OF THE GREAT TOE Dr Vasu Pai ANATOMICAL CONSIDERATION At the big toe MTP joint: Tibial sesamoid (medial) & fibular (lateral) They are contained within the tendons of Flexor Hallucis Brevis
PAINFUL SESAMOID OF THE GREAT TOE Dr Vasu Pai ANATOMICAL CONSIDERATION At the big toe MTP joint: Tibial sesamoid (medial) & fibular (lateral) They are contained within the tendons of Flexor Hallucis Brevis
Imaging the musculoskeletal system. An Introduction
 Imaging the musculoskeletal system An Introduction Objectives Discuss: commonly used imaging modalities in the musculoskeletal system normal imaging anatomy in the extremities fracture description Imaging
Imaging the musculoskeletal system An Introduction Objectives Discuss: commonly used imaging modalities in the musculoskeletal system normal imaging anatomy in the extremities fracture description Imaging
Primary bone tumors > metastases from other sites Primary bone tumors widely range -from benign to malignant. Classified according to the normal cell
 Primary bone tumors > metastases from other sites Primary bone tumors widely range -from benign to malignant. Classified according to the normal cell counterpart and line of differentiation. Among the
Primary bone tumors > metastases from other sites Primary bone tumors widely range -from benign to malignant. Classified according to the normal cell counterpart and line of differentiation. Among the
Aetiology: Pressure of Distal intermetatarsal ligament against common digital nerve. Lumbar radiculopathy Instability MTPJ joint or inflammatory MPJ
 MORTON S NEUROMA 80% III web space (next common is II). Never occurs in III or IV Common in females in fifties Aetiology: Pressure of Distal intermetatarsal ligament against common digital nerve Rule out
MORTON S NEUROMA 80% III web space (next common is II). Never occurs in III or IV Common in females in fifties Aetiology: Pressure of Distal intermetatarsal ligament against common digital nerve Rule out
Bursa Formation and Synovial Chondrometaplasia Associated with Osteochondromas
 Bursa Formation and Synovial Chondrometaplasia Associated with Osteochondromas ANITA M. BORGES, M. D., ANDREW G. HUVOS, M. D., AND JULIUS SMITH, M. D. Borges, Anita M., Huvos, Andrew G., and Smith, Julius:
Bursa Formation and Synovial Chondrometaplasia Associated with Osteochondromas ANITA M. BORGES, M. D., ANDREW G. HUVOS, M. D., AND JULIUS SMITH, M. D. Borges, Anita M., Huvos, Andrew G., and Smith, Julius:
Will She Still Make the WNBA? Sports Injuries & Fractures
 Will She Still Make the WNBA? Sports Injuries & Fractures Aharon Z. Gladstein MD Pediatric Orthopaedic Surgery Pediatric Sports Medicine Sports Injuries Chronic (overuse) Acute Who can be treated in PCP
Will She Still Make the WNBA? Sports Injuries & Fractures Aharon Z. Gladstein MD Pediatric Orthopaedic Surgery Pediatric Sports Medicine Sports Injuries Chronic (overuse) Acute Who can be treated in PCP
The Radiology Assistant : Bone tumor - well-defined osteolytic tumors and tumor-like lesions
 Bone tumor - well-defined osteolytic tumors and tumor-like lesions Henk Jan van der Woude and Robin Smithuis Radiology department of the Onze Lieve Vrouwe Gasthuis, Amsterdam and the Rijnland hospital,
Bone tumor - well-defined osteolytic tumors and tumor-like lesions Henk Jan van der Woude and Robin Smithuis Radiology department of the Onze Lieve Vrouwe Gasthuis, Amsterdam and the Rijnland hospital,
Review relevant anatomy of the foot and ankle. Learn the approach to examining the foot and ankle
 Objectives Review relevant anatomy of the foot and ankle Learn the approach to examining the foot and ankle Learn the basics of diagnosis and treatment of ankle sprains Overview of other common causes
Objectives Review relevant anatomy of the foot and ankle Learn the approach to examining the foot and ankle Learn the basics of diagnosis and treatment of ankle sprains Overview of other common causes
Ankle Valgus in Cerebral Palsy
 Ankle Valgus in Cerebral Palsy Freeman Miller Contents Introduction... 2 Natural History... 2 Treatment... 3 Diagnostic Evaluations... 3 Indications for Intervention... 3 Outcome of Treatment... 5 Complications
Ankle Valgus in Cerebral Palsy Freeman Miller Contents Introduction... 2 Natural History... 2 Treatment... 3 Diagnostic Evaluations... 3 Indications for Intervention... 3 Outcome of Treatment... 5 Complications
OSTEOPHYTOSIS OF THE FEMORAL HEAD AND NECK
 908 RDIOLOGIC VIGNETTE OSTEOPHYTOSIS OF THE FEMORL HED ND NECK DONLD RESNICK Osteophytes are frequently considered the most characteristic abnormality of degenerative joint disease. In patients with osteoarthritis,
908 RDIOLOGIC VIGNETTE OSTEOPHYTOSIS OF THE FEMORL HED ND NECK DONLD RESNICK Osteophytes are frequently considered the most characteristic abnormality of degenerative joint disease. In patients with osteoarthritis,
Magnetic Resonance Atlas of Skeletal Development of the Knee
 Magnetic Resonance Atlas of Skeletal Development of the Knee A Standard of Reference Andrew T. Pennock, MD James D. Bomar, MPH Rady Children s Hospital, San Diego University of California, San Diego 2
Magnetic Resonance Atlas of Skeletal Development of the Knee A Standard of Reference Andrew T. Pennock, MD James D. Bomar, MPH Rady Children s Hospital, San Diego University of California, San Diego 2
Brothers with genu recurvatum
 Short Communication Brothers with genu recurvatum Naoto Saito a, *, Keiji Tensyo b, Hiroshi Horiuchi b, Kaoru Aoki b, Seneki Kobayashi b, Hiroyuki Kato b, and Tomoki Kosho c adepartment of Applied Physical
Short Communication Brothers with genu recurvatum Naoto Saito a, *, Keiji Tensyo b, Hiroshi Horiuchi b, Kaoru Aoki b, Seneki Kobayashi b, Hiroyuki Kato b, and Tomoki Kosho c adepartment of Applied Physical
BCCH Emergency Department LOWER LIMB INJURIES Resource pack
 1 BCCH Emergency Department LOWER LIMB INJURIES Resource pack Developed by: Rena Heathcote RN. 2 Knee Injuries The knee joint consists of a variety of structures including: 3 bones (excluding the patella)
1 BCCH Emergency Department LOWER LIMB INJURIES Resource pack Developed by: Rena Heathcote RN. 2 Knee Injuries The knee joint consists of a variety of structures including: 3 bones (excluding the patella)
Extraarticular Lateral Ankle Impingement
 Extraarticular Lateral Ankle Impingement Poster No.: C-1282 Congress: ECR 2016 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: C. Cevikol; Keywords: Trauma, Diagnostic procedure, MR, CT, Musculoskeletal system, Musculoskeletal
Extraarticular Lateral Ankle Impingement Poster No.: C-1282 Congress: ECR 2016 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: C. Cevikol; Keywords: Trauma, Diagnostic procedure, MR, CT, Musculoskeletal system, Musculoskeletal
Common Orthopaedic Injuries in Children
 Common Orthopaedic Injuries in Children Rakesh P. Mashru, M.D. Division of Orthopaedic Trauma Cooper University Hospital Cooper Medical School of Rowan University December 1, 2017 1 Learning Objectives
Common Orthopaedic Injuries in Children Rakesh P. Mashru, M.D. Division of Orthopaedic Trauma Cooper University Hospital Cooper Medical School of Rowan University December 1, 2017 1 Learning Objectives
Imaging of Ankle and Foot pain
 Imaging of Ankle and Foot pain Pramot Tanutit, M.D. Department of Radiology Faculty of Medicine, Prince of Songkla University 1 Outlines Plain film: anatomy Common causes of ankle and foot pain Exclude:
Imaging of Ankle and Foot pain Pramot Tanutit, M.D. Department of Radiology Faculty of Medicine, Prince of Songkla University 1 Outlines Plain film: anatomy Common causes of ankle and foot pain Exclude:
COURSE TITLE: Skeletal Anatomy and Fractures of the Lower Arm, Wrist, and Hand
 COURSE DESCRIPTION Few parts of the human body are required to pivot, rotate, abduct, and adduct like the wrist and hand. The intricate and complicated movements of the arm, wrist, and hand exist partly
COURSE DESCRIPTION Few parts of the human body are required to pivot, rotate, abduct, and adduct like the wrist and hand. The intricate and complicated movements of the arm, wrist, and hand exist partly
Priorities Forum Statement GUIDANCE
 Priorities Forum Statement Number 21 Subject Knee Arthroscopy including arthroscopic knee washouts Date of decision November 2016 Date refreshed March 2017 Date of review November 2018 Osteoarthritis of
Priorities Forum Statement Number 21 Subject Knee Arthroscopy including arthroscopic knee washouts Date of decision November 2016 Date refreshed March 2017 Date of review November 2018 Osteoarthritis of
The Skeletal System 5PART F. PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College
 PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College The Skeletal System 5PART F Joints Articulations of bones Functions of joints Hold bones together Allow
PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College The Skeletal System 5PART F Joints Articulations of bones Functions of joints Hold bones together Allow
What is bone? Specialized form of connective tissue: mineralized collagen matrix, therefore very rigid and strong while still retaining some degree of
 Bone What is bone? Specialized form of connective tissue: mineralized collagen matrix, therefore very rigid and strong while still retaining some degree of flexibility Other types of connective tissue:
Bone What is bone? Specialized form of connective tissue: mineralized collagen matrix, therefore very rigid and strong while still retaining some degree of flexibility Other types of connective tissue:
Stage-I osteochondritis dissecans versus normal variants of ossification in the knee in children
 Pediatr Radiol (2005) 35: 880 886 DOI 10.1007/s00247-005-1507-6 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Kathleen Gebarski Ramiro J. Hernandez Stage-I osteochondritis dissecans versus normal variants of ossification in the knee
Pediatr Radiol (2005) 35: 880 886 DOI 10.1007/s00247-005-1507-6 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Kathleen Gebarski Ramiro J. Hernandez Stage-I osteochondritis dissecans versus normal variants of ossification in the knee
Microanatomy, Physiology of Bone & Joints
 Microanatomy, Physiology of Bone & Joints The Skeleton There are 206 bones in the human body. The bones that are required in this syllabus are the cranium, mandible, clavicle, sternum, scapula, ribs, humerous,
Microanatomy, Physiology of Bone & Joints The Skeleton There are 206 bones in the human body. The bones that are required in this syllabus are the cranium, mandible, clavicle, sternum, scapula, ribs, humerous,
Treatment Outcomes of Triplane and Tillaux Fractures of the Ankle in Adolescence
 Original Article Clinics in Orthopedic Surgery 2010;2:34-38 doi:10.4055/cios.2010.2.1.34 Treatment Outcomes of Triplane and Tillaux Fractures of the Ankle in Adolescence Jung Ryul Kim, MD, Kwang Hun Song,
Original Article Clinics in Orthopedic Surgery 2010;2:34-38 doi:10.4055/cios.2010.2.1.34 Treatment Outcomes of Triplane and Tillaux Fractures of the Ankle in Adolescence Jung Ryul Kim, MD, Kwang Hun Song,
2017 SAFSA CONGRESS PROGRAMME
 2017 SAFSA CONGRESS PROGRAMME THURSDAY, MAY 25 07h45 07h55: WELCOME & INTRODUCTIONS Forefoot I: Hallux Valgus and Lesser Toes (08h00-10h00 Lectures) 08h00 08h30: Surgical Management of Hallux Valgus Rippstein,
2017 SAFSA CONGRESS PROGRAMME THURSDAY, MAY 25 07h45 07h55: WELCOME & INTRODUCTIONS Forefoot I: Hallux Valgus and Lesser Toes (08h00-10h00 Lectures) 08h00 08h30: Surgical Management of Hallux Valgus Rippstein,
PowerPoint Lecture Slides. Prepared by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College. The Skeletal System Pearson Education, Inc.
 PowerPoint Lecture Slides Prepared by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College CHAPTER 5 The Skeletal System 2012 Pearson Education, Inc. Title Classification of Bones and Gross Anatomy
PowerPoint Lecture Slides Prepared by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College CHAPTER 5 The Skeletal System 2012 Pearson Education, Inc. Title Classification of Bones and Gross Anatomy
The skeleton consists of: Bones: special connective tissue, hard. Cartilage: special connective tissue, less hard than bones. Joints: joint is the
 The skeleton consists of: Bones: special connective tissue, hard. Cartilage: special connective tissue, less hard than bones. Joints: joint is the location at witch two bones make contact, whereas ligaments
The skeleton consists of: Bones: special connective tissue, hard. Cartilage: special connective tissue, less hard than bones. Joints: joint is the location at witch two bones make contact, whereas ligaments
Lecture (10) Bone Fractures. Resources: - Lecture by dr.alboukai - Diagnostic imaging book
 Lecture (10) Bone Fractures Hanan Alsalman Hanan Alrabiah Reem Aljurayyad Ayshah Almahboob Ghadeer Alwuhyad Khawlah AlOthman Dalal Alqadi Suliman Alshammari Maha AlKubaidan Rawabi Alghamdi Resources: -
Lecture (10) Bone Fractures Hanan Alsalman Hanan Alrabiah Reem Aljurayyad Ayshah Almahboob Ghadeer Alwuhyad Khawlah AlOthman Dalal Alqadi Suliman Alshammari Maha AlKubaidan Rawabi Alghamdi Resources: -
Ultrasound Evaluation of Posteromedial Ankle Pathology. Andrew C Cordle, M.D., Ph.D. 9/21/2018
 Ultrasound Evaluation of Posteromedial Ankle Pathology Andrew C Cordle, M.D., Ph.D. 9/21/2018 Overview: Pathology of the Posteromedial Ankle Flexor Tendon Pathology Accessory Navicular Bone Pathology Tarsal
Ultrasound Evaluation of Posteromedial Ankle Pathology Andrew C Cordle, M.D., Ph.D. 9/21/2018 Overview: Pathology of the Posteromedial Ankle Flexor Tendon Pathology Accessory Navicular Bone Pathology Tarsal
Differential Diagnosis
 Case 31yo M who sustained an injury to L knee while playing Basketball approximately 2 weeks ago. He describes pivoting and hyperextending his knee, which swelled over the next few days. He now presents
Case 31yo M who sustained an injury to L knee while playing Basketball approximately 2 weeks ago. He describes pivoting and hyperextending his knee, which swelled over the next few days. He now presents
Correction of Traumatic Ankle Valgus and Procurvatum using the Taylor Spatial Frame: A Case Report
 The Foot and Ankle Online Journal Official publication of the International Foot & Ankle Foundation Correction of Traumatic Ankle Valgus and Procurvatum using the Taylor Spatial Frame: A Case Report by
The Foot and Ankle Online Journal Official publication of the International Foot & Ankle Foundation Correction of Traumatic Ankle Valgus and Procurvatum using the Taylor Spatial Frame: A Case Report by
Post test for O&P 2 Hrs CE. The Exam
 Post test for O&P 2 Hrs CE The Exam This examination is taken in "open book" format. That means you are free to answer the questions after research or discussion with your fellow workers. We feel this
Post test for O&P 2 Hrs CE The Exam This examination is taken in "open book" format. That means you are free to answer the questions after research or discussion with your fellow workers. We feel this
