ASFYT Part I: The Skeletal System Module S4 (Leg Ankle and Foot)
|
|
|
- Mary McKenzie
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Mdule S4 (Leg Ankle and Ft) (1) OVERVIEW In this mdule, we ll explre the: Features f the leg & ft bnes Anatmy f the ankle & ft jints Mvements pssible at the ankle & ft Imprtant ligaments f the ankle & ft (2) BONES OF THE LEG Tw parallel lng bnes, the tibia and fibula, frm the regin f the lwer limb between the knee and the ankle (the tibia is medial, and the fibula is lateral) The tibia and fibula are cnnected by an intersseus membrane and articulate with each ther via the prximal, middle and distal tibifibular jints They frm a strnger and mre stable limb than thse f the frearm, but their jint structure allws less mvement The tibia articulates prximally with the femur t frm the mdified hinge jint f the knee, and distally with the talus bne f the ft t frm the hinge jint f the ankle The fibula des nt cntribute t the knee jint and merely helps stabilize the ankle jint Page 1 f 13 Jasn R. Brwn 2006
2 Mdule S4 (Leg Ankle and Ft) (3) FEATURES OF THE TIBIA The tibia receives the weight f the bdy frm the femur and transmits it t the ft It is secnd nly t the femur in size and strength At its brad prximal end are the cncave medial and lateral cndyles, which are separated by an irregular prjectin called the intercndylar eminence The tibial cndyles articulate with the crrespnding cndyles f the femur t frm the knee jint The inferir regin f the lateral tibial cndyle bears a facet that indicates the site f the prximal tibifibular jint Just inferir t the cndyles, the tibia's anterir surface displays the rugh tibial tubersity, where the patellar ligament attaches The anterir edge f the tibial shaft, which is triangular in crss sectin, is called the anterir crest Neither this crest nr the tibia's medial surface is cvered by muscles, s they can be felt just deep t the skin alng their entire length (the anguish f a "bumped" shin is an experience familiar t nearly everyne) Distally the tibia is flat where it articulates with the talus bne f the ft. Medial t that jint surface is an inferir prjectin, the medial mallelus ("little hammer"), which frms the medial bulge f the ankle The fibular ntch, n the lateral surface f the tibia, is part f the distal tibifibular jint Page 2 f 13 Jasn R. Brwn 2006
3 Mdule S4 (Leg Ankle and Ft) (4) FEATURES OF THE FIBULA The fibula ("pin") is a stick-like bne that des nt bear weight -- its shaft is heavily ridged and serves mainly as a site fr muscle attachment The prximal end f the fibula is called the head, which articulates with the lateral aspect f the tibia, and the distal end is the lateral mallelus, which articulates with the talus and frms the bvius bulge f the lateral ankle jint Hmestatic Imbalance A Ptt's fracture is a break that ccurs at the distal end f the fibula, the tibia, r bth, and is a cmmn sprts injury (5) BONES OF THE FOOT The ft has tw imprtant functins: 1. It supprts ur bdy weight, and 2. It acts as a lever t prpel the bdy frward when we walk and run A single bne culd serve bth purpses, but it wuld adapt prly t uneven grund -- segmentatin makes the ft mre pliable The ft includes the tarsal bnes, the metatarsal bnes, and the phalangeal bnes (r te bnes) Page 3 f 13 Jasn R. Brwn 2006
4 Mdule S4 (Leg Ankle and Ft) (6) TARSAL BONES The seven tarsal bnes frm the psterir half f the ft, and crrespnd t the carpal bnes f the hand Bdy weight is carried primarily by the tw largest, mst psterir tarsals: 1. the talus (ankle), which articulates with the tibia and fibula superirly, and 2. the calcaneus (heel bne), which frms the heel f the ft and carries the talus n its superir surface (the calcaneal tubersity is the part f the calcaneus that tuches the grund) The remaining tarsals, frm medial t lateral, are the: 3. Navicular (medial) 4. Medial cuneifrm 5. Intermediate cuneifrm 6. Lateral cuneifrm 7. Cubid (lateral) (7) METATARSAL BONES The metatarsal bnes are five small lng bnes that are numbered 1 t 5, beginning n the medial side f the ft (the great te side) The base f each metatarsal is prximal, while the head is distal Distally, where the metatarsals articulate with the prximal phalanges f the tes, the enlarged head f the first metatarsal frms the ball f the ft Page 4 f 13 Jasn R. Brwn 2006
5 Mdule S4 (Leg Ankle and Ft) The first metatarsal is shrt and thick, and its plantar surface rests n paired sesamid bnes (which play an imprtant rle in supprting bdy weight) (8) PHALANGES The 14 phalanges f the ft (tes) are a gd deal smaller than thse f the fingers and thus are less nimble, but their general structure and arrangement are the same Except fr the great te, there are three phalanges in each digit, which are identified as the prximal phalanx, the middle phalanx and the distal phalanx (the great te, r hallux, has nly prximal and distal phalanges) Phalanx is the singular; phalanges is plural As with the metatarsals, the base f each phalanx is prximal, while the head is distal (9) ARCHES OF THE FOOT The ft has three arches: 1. The medial lngitudinal arch curves well abve the grund; it riginates at the calcaneus, rises t the talus (the keystne f the arch), and then descends t the three medial metatarsals 2. The lateral lngitudinal arch is very lw; it elevates the lateral part f the ft just enugh t redistribute sme f the weight between the tw ends f the arch -- the calcaneus and the head f the fifth metatarsal (the cubid is the keystne bne f this arch) Page 5 f 13 Jasn R. Brwn 2006
6 Mdule S4 (Leg Ankle and Ft) 3. the transverse arch runs bliquely frm ne side f the ft t the ther, fllwing the line f the jints between the tarsals and metatarsals; the tw lngitudinal arches serve as pillars fr the transverse arch Tgether, the arches f the ft frm a half-dme that distributes abut half ur standing and walking weight t the heel bnes and half t the heads f the metatarsals, which accunts fr the ft s ability t bear the weight f the bdy The arches are maintained by the interlcking shapes f the ft bnes, by strng ligaments, and by the pull f sme tendns during muscle activity The ligaments and muscle tendns prvide a certain amunt f springiness, allwing the arches t give" r stretch slightly when weight is applied t the ft and spring back when the weight is remved (this makes walking and running mre ecnmical in terms f energy use than wuld therwise be the case) (10) HOMEOSTATIC IMBALANCE: FALLEN ARCHES Fallen arches (r flatfeet ) is a cnditin that ccurs when the arch r instep f the ft cllapses r tuches the standing surface. Can be structural (yu re brn with it) r functinal (yu ve lst it) Functinal flatfeet may result frm: prlnged standing (esp. if verweight) running n hard surfaces withut prper arch supprt temprary increase in elastin due t pregnancy Page 6 f 13 Jasn R. Brwn 2006
7 Mdule S4 (Leg Ankle and Ft) (11) PLANTAR FASCIA The plantar fascia is a dense layer f fibrus tissue n the plantar surface f the ft, which maintains and stabilizes the lngitudinal arches f the ft The plantar fascia attaches psterirly t the calcaneal tubersity and anterirly t the plantar plates f the metatarsphalangeal (MTP) jints and adjacent flexr tendns f the tes (12) WINDLASS MECHANISM The plantar fascia inserts int the flexr tendns, and gets pulled taut when the te jints are extended (as when rising nt the balls f the feet) As the plantar fascia becmes mre taut, the height f the arch increases and creates a mre rigid ft (13) HOMESTATIC IMBALANCE: PLANTAR FASCIITIS Plantar fasciitis is inflammatin f the plantar fascia, which usually results in lcalized pain under the calcaneus (the heel) Often the pain frm plantar fasciitis is mst severe in the mrning, when first standing, then subsides a bit, but then returns after prlnged standing r walking Plantar fasciitis is smetimes assciated with a rapid gain f weight, but is als seen in recreatinal athletes (especially runners); in these athletes, it is thught that the repetitive nature f the sprts causes the damage t the fibrus tissue that frms the arch f the ft Page 7 f 13 Jasn R. Brwn 2006
8 Mdule S4 (Leg Ankle and Ft) Treatment: Rest, Ice (use frzen water bttles), stretching the calf muscles, rthtics (14) TIBIOFIBULAR JOINTS Three tibifibular jints exist between the tibia and fibula The prximal tibifibular jint is lcated between the lateral cndyle f the tibia and the head f the fibula Classificatin: gliding synvial jint The middle tibifibular jint is created by the intersseus membrane uniting the shafts f the tibia and fibula Classificatin: slightly mvable fibrus jint the intersseus membrane hlds the tibia and fibula tgether s that they can grasp the talus between them at the ankle jint, as well as allw the frce f all muscle attachments that pull n the fibula t be transferred t the tibia t mve the leg at the knee jint The distal tibifibular jint is lcated between the medial side f the lateral mallelus f the fibula and the fibular ntch f the distal tibia Classificatin: slightly mvable fibrus jint The tibifibular jints allw superir and inferir glide f the fibula relative t the tibia (15) THE ANKLE JOINT The ankle jint is lcated between the trchlear surface f the dme f the talus and the rectangular cavity frmed by the distal end f the tibia and the malleli f the tibia and fibula Page 8 f 13 Jasn R. Brwn 2006
9 Mdule S4 (Leg Ankle and Ft) It resembles a mrtise jint (culd als be visualized as a nut within a wrench) It is classified as a freely mvable, synvial hinge jint (uniaxial) (16) MOTIONS ALLOWED AT THE ANKLE Drsiflexin (20 O ) and plantarflexin (50 O ) f the ft at the ankle jint within the sagittal plane arund a medilateral axis Reverse actin wuld be drsiflexin/plantarflexin f the leg at the ankle jint (ft fixed) (17) DELTOID LIGAMENT The deltid ligament is actually a set f several ligaments that fan ut frm the medial mallelus f the tibia t the medial side f the talus, calcaneus and navicular bnes; it limits eversin f the ft at the ankle jint Nte: the lateral mallelus f the fibula extends mre distally than the medial mallelus f the tibia, which helps limit excessive eversin f the ankle jint; this fact, in cnjunctin with the presence f the strng deltid ligament, makes eversin ankle sprains very uncmmn (18) LATERAL COLLATERAL LIGAMENT COMPLEX A cmplex f three ligaments that branch ut frm the lateral mallelus f the fibula and cllectively help t limit excessive inversin f the ankle Page 9 f 13 Jasn R. Brwn 2006
10 Mdule S4 (Leg Ankle and Ft) the anterir talfibular ligament attaches t the anterir talus, and is the mst cmmnly sprained ligament f the human bdy the psterir talfibular ligament attaches t the psterir talus the calcanefibular ligament attaches t the lateral surface f the calcaneus Nte: the medial mallelus f the tibia des nt extend distally enugh t prvide stability t the uter ankle, and therefre the lateral cllateral ligaments are the nly line f defense against inversin sprains f the ankle (19) OTHER STRUCTURES OF THE ANKLE Bursae (singular, bursa) and tendn sheaths, which help minimize frictin between the tendns and underlying bny structures, are prevalent thrughut the ankle jint Retinacula (singular, retinaculum) help t hld dwn the tendns that crss the ankle jint, preventing bwstringing f these tendns (20) SUBTALAR TARSAL JOINT The subtalar tarsal jint is the main tarsal jint f the ft, and is lcated between the talus and the calcaneus It is classified as a freely mvable, synvial gliding jint (uniaxial) (21) MOTIONS OF SUBTALAR TARSAL JOINTS Prnatin, which cnsists f: Eversin Page 10 f 13 Jasn R. Brwn 2006
11 Mdule S4 (Leg Ankle and Ft) Drsiflexin Abductin Supinatin, which cnsists f: Inversin Plantarflexin Adductin Nte: when weight-bearing, prnatin f the fts results in a visible drp in the arch (22) TRANSVERSE TARSAL JOINT The transverse tarsal jint is a cmpund jint cnsisting f: the talnavicular jint, between the talus and navicular bne the calcanecubid jint, between the calcaneus and cubid It is classified as a freely mvable, synvial gliding jint Mvements available at this jint include prnatin and supinatin (in cnjunctin with the subtalar jint) (23) TARSOMETATARSAL JOINTS There are five tarsmetatarsal (TMT) jints, which are lcated between the distal rw f tarsal bnes and the metatarsal bnes The 1 st thru 3 rd TMT jints are lcated between the 1-3 cuneifrms and the base f the 1 st thru 3 rd metatarsals The 4 th and 5 th TMT jints are lcated between the cubid and the base f the 4 th and 5 th metatarsals Page 11 f 13 Jasn R. Brwn 2006
12 Mdule S4 (Leg Ankle and Ft) They are all classified as freely mvable synvial, gliding jints The base f the 2nd metatarsal is set back further psterirly than the ther metatarsal bnes, causing it t be wedged between the 1st and 3rd cuneifrms; it is therefre the mst stable f the five TMT jints, and an imaginary line thrugh its crrespnding ray is knwn as the central stable pillar f the ft (24) INTERMETATARSAL JOINTS All five metatarsal bnes articulate with each ther prximally (at their bases) and distally (at their heads) All are freely mvable, gliding synvial jints Allw nn-axial gliding mtin f ne metatarsal relative t the adjacent metatarsal (25) METATARSOPHALANGEAL JOINTS The metatarsphalangeal (MTP) jints are lcated between the heads f the metatarsals and the bases f the prximal phalanges f the tes They are classified as freely mvable, synvial cndylid jints (biaxial) (26) The majr mtins allwed are: Flexin/Extensin within the sagittal plane arund a medilateral axis Abductin/Adductin within the transverse plane arund a vertical axis Page 12 f 13 Jasn R. Brwn 2006
13 Mdule S4 (Leg Ankle and Ft) Nte: the reference fr abductin/adductin is an imaginary line drawn thrugh the 2 nd te when it is in anatmic psitin Average Range f Mtin f MTP Jints Tes #2-5: Extensin (60 O ) / Flexin (40 O ) Big Te: Extensin (80 O ) / Flexin (40 O ) (27) INTERPHALANGEAL JOINTS The interphalangeal (IP) jints f the ft are lcated between the head f the mre prximal phalanx and the base f the mre distal phalanx The big te has ne IP jint between the prximal and distal phalanges f the big te Tes #2-5 have tw IP jints a prximal IP jint (PIP) between the prximal and middle phalanges, and a distal IP jint (DIP) between the middle and distal phalanges These jints are freely mvable, synvial hinge jints (uniaxial), allwing flexin and extensin within the sagittal plane arund a medilateral axis Page 13 f 13 Jasn R. Brwn 2006
ASFYT Part I: The Skeletal System S1: Intro to Kinesiology
 S1: Intr t Kinesilgy (1) Intr t Kinesilgy Majr Divisins f the Human Bdy Jints Between Majr Bdy Parts Describing Mvement in the Bdy True Mvement vs. Ging Alng fr the Ride Anatmic Psitin Directinal Terms
S1: Intr t Kinesilgy (1) Intr t Kinesilgy Majr Divisins f the Human Bdy Jints Between Majr Bdy Parts Describing Mvement in the Bdy True Mvement vs. Ging Alng fr the Ride Anatmic Psitin Directinal Terms
4.2 Joint and Movement Type
 TOPIC 4 MOVEMENT ANALYSIS 1 4.2 Jint and Mvement Type 4.2.1 - Outline the types f mvement f synvial jints The musculskeletal system is the arrangement f bnes, jints and muscles that permits mvement f the
TOPIC 4 MOVEMENT ANALYSIS 1 4.2 Jint and Mvement Type 4.2.1 - Outline the types f mvement f synvial jints The musculskeletal system is the arrangement f bnes, jints and muscles that permits mvement f the
Musculoskeletal MRI Protocols
 Musculskeletal MRI Prtcls Reviewed by: Lawrence Tang, MD Last Review Date: March 2018 Cntact: (866) 761-4200, ptin 1 *Nte t MR technlgists: Updates and new prtcls are underlined in this dcument. Please
Musculskeletal MRI Prtcls Reviewed by: Lawrence Tang, MD Last Review Date: March 2018 Cntact: (866) 761-4200, ptin 1 *Nte t MR technlgists: Updates and new prtcls are underlined in this dcument. Please
Knee Class Fremont Physical Therapy
 Fremnt Knee Facts The knee lses strength and stability after an injury. Stretching, strengthening and stability exercises are recmmended nt nly fr peple wh have injured their knees, but als t prevent injury.
Fremnt Knee Facts The knee lses strength and stability after an injury. Stretching, strengthening and stability exercises are recmmended nt nly fr peple wh have injured their knees, but als t prevent injury.
ASFYT Part I: The Skeletal System Module S3 (Joints)
 Mdule S3 (Jints) (1) Overview f Jints Classificatin f Jints Fibrus Jints Cartilaginus Jints Synvial Jints Factrs Determining the Stability f Synvial Jints Menisci and Articulating Discs Classificatin f
Mdule S3 (Jints) (1) Overview f Jints Classificatin f Jints Fibrus Jints Cartilaginus Jints Synvial Jints Factrs Determining the Stability f Synvial Jints Menisci and Articulating Discs Classificatin f
Hand Pain & Problems
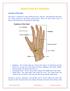 Anatmy f the hand: Hand Pain & Prblems The hand is cmpsed f many different bnes, muscles, and ligaments that allw fr a large amunt f mvement and dexterity. There are three majr types f bnes in the hand
Anatmy f the hand: Hand Pain & Prblems The hand is cmpsed f many different bnes, muscles, and ligaments that allw fr a large amunt f mvement and dexterity. There are three majr types f bnes in the hand
Musculoskeletal MRI Protocols
 Musculskeletal MRI Prtcls Reviewed by: Lawrence Tang, MD Last Review Date: July 2017 Cntact: (866) 761-4200, Optin 1 *Nte t MR technlgists: Marking updates and changes frm previus prtcls. Please pay extra
Musculskeletal MRI Prtcls Reviewed by: Lawrence Tang, MD Last Review Date: July 2017 Cntact: (866) 761-4200, Optin 1 *Nte t MR technlgists: Marking updates and changes frm previus prtcls. Please pay extra
Clarification of Terms
 Clarification of Terms The plantar aspect of the foot refers to the role or its bottom The dorsal aspect refers to the top or its superior portion The ankle and foot perform three main functions: 1. shock
Clarification of Terms The plantar aspect of the foot refers to the role or its bottom The dorsal aspect refers to the top or its superior portion The ankle and foot perform three main functions: 1. shock
BROCKTON AREA MULTI-SERVICES, INC. MEDICAL PROCEDURE GUIDE. Date(s) Reviewed/Revised:
 Page 1 f 6 Subject: Range f Mtin Exercises Date Develped: 4/2010 PROTOCOL FOR: All trained staff PURPOSE: Range f Mtin (ROM) exercises are very imprtant if an individual has t stay in bed r in a wheelchair.
Page 1 f 6 Subject: Range f Mtin Exercises Date Develped: 4/2010 PROTOCOL FOR: All trained staff PURPOSE: Range f Mtin (ROM) exercises are very imprtant if an individual has t stay in bed r in a wheelchair.
A foot x-ray series is required only if there is pain in the midfoot zone and any one of the following:
 RADIOGRAPHY OF THE ANKLE AND FOOT (OTTAWA ANKLE RULES) Clinical Practice Guideline January 2007 This guideline has been adapted frm the Ottawa Ankle Rules develped by Dr. Ian Stiell et al. Dr. Stiell received
RADIOGRAPHY OF THE ANKLE AND FOOT (OTTAWA ANKLE RULES) Clinical Practice Guideline January 2007 This guideline has been adapted frm the Ottawa Ankle Rules develped by Dr. Ian Stiell et al. Dr. Stiell received
ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY: SKELETAL SYSTEM
 FORBUSH HIGH SCHOOL ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY: SKELETAL SYSTEM GUIDE TO IDENTIFICATION Arranged by: M.Sewell Bnes and Prcesses t Knw Page 2 f 19 Cntents Bnes and prcesses needed t knw fr Anatmy:... 3 Be able
FORBUSH HIGH SCHOOL ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY: SKELETAL SYSTEM GUIDE TO IDENTIFICATION Arranged by: M.Sewell Bnes and Prcesses t Knw Page 2 f 19 Cntents Bnes and prcesses needed t knw fr Anatmy:... 3 Be able
The Lower Limb VII: The Ankle & Foot. Anatomy RHS 241 Lecture 7 Dr. Einas Al-Eisa
 The Lower Limb VII: The Ankle & Foot Anatomy RHS 241 Lecture 7 Dr. Einas Al-Eisa Ankle joint Synovial, hinge joint Allow movement of the foot in the sagittal plane only (1 degree of freedom): dorsiflexion:
The Lower Limb VII: The Ankle & Foot Anatomy RHS 241 Lecture 7 Dr. Einas Al-Eisa Ankle joint Synovial, hinge joint Allow movement of the foot in the sagittal plane only (1 degree of freedom): dorsiflexion:
Close to spine/ point of attachment
 Terms, Tissues and Imaging INTRODUCTION TO ANATOMY AND ANATOMICAL TERMINOLOGY 1. Anatmical Facts; islated bservatins r statements abut structures (bdy parts) r events (happenings) Anatmical cncepts; structures
Terms, Tissues and Imaging INTRODUCTION TO ANATOMY AND ANATOMICAL TERMINOLOGY 1. Anatmical Facts; islated bservatins r statements abut structures (bdy parts) r events (happenings) Anatmical cncepts; structures
Dear Medical Practitioner
 Dear Medical Practitiner The Western Australian Academy f Perfrming Arts (WAAPA) at Edith Cwan University (ECU) requires students applying fr certain curses t cnfirm their capacity t meet the physical
Dear Medical Practitiner The Western Australian Academy f Perfrming Arts (WAAPA) at Edith Cwan University (ECU) requires students applying fr certain curses t cnfirm their capacity t meet the physical
Chapter 37 The Skeletal and Muscular System:
 Chapter 37 The Skeletal and Muscular System: 3.5 Learning Objectives 3.5. Respnses in the human 1. Descriptin f the structure and functins f the skeletn. 2. Label the cmpnent parts f the axial and appendicular
Chapter 37 The Skeletal and Muscular System: 3.5 Learning Objectives 3.5. Respnses in the human 1. Descriptin f the structure and functins f the skeletn. 2. Label the cmpnent parts f the axial and appendicular
Copyright 2012 by The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved. McGraw-Hill/Irwin
 CHAPTER 8: THE LOWER EXTREMITY: KNEE, ANKLE, AND FOOT KINESIOLOGY Scientific Basis of Human Motion, 12 th edition Hamilton, Weimar & Luttgens Presentation Created by TK Koesterer, Ph.D., ATC Humboldt State
CHAPTER 8: THE LOWER EXTREMITY: KNEE, ANKLE, AND FOOT KINESIOLOGY Scientific Basis of Human Motion, 12 th edition Hamilton, Weimar & Luttgens Presentation Created by TK Koesterer, Ph.D., ATC Humboldt State
Getting Around Safely With Your Crutches (Partial Weight Bearing)
 OrthBethesda Therapy Services Getting Arund Safely With Yur Crutches (Partial Weight Bearing) Yur physician will decide whether yu are t be nn weight bearing, te-tuch weight bearing, partial weight bearing,
OrthBethesda Therapy Services Getting Arund Safely With Yur Crutches (Partial Weight Bearing) Yur physician will decide whether yu are t be nn weight bearing, te-tuch weight bearing, partial weight bearing,
Dr Nabil khouri MD. MSc. Ph.D
 Dr Nabil khouri MD. MSc. Ph.D Foot Anatomy The foot consists of 26 bones: 14 phalangeal, 5 metatarsal, and 7 tarsal. Toes are used to balance the body. Metatarsal Bones gives elasticity to the foot in
Dr Nabil khouri MD. MSc. Ph.D Foot Anatomy The foot consists of 26 bones: 14 phalangeal, 5 metatarsal, and 7 tarsal. Toes are used to balance the body. Metatarsal Bones gives elasticity to the foot in
Understanding your thumb osteoarthritis
 Understanding yur thumb stearthritis Intrductin The CMC jint is ne f the mst imprtant jints f the thumb and hand due t its wide range f mtin. Over time, the CMC jint is subject t large and repeated frces
Understanding yur thumb stearthritis Intrductin The CMC jint is ne f the mst imprtant jints f the thumb and hand due t its wide range f mtin. Over time, the CMC jint is subject t large and repeated frces
A Patient s Guide to Foot Anatomy
 A Patient s Guide to Foot Anatomy Introduction Our feet are constantly under stress. It's no wonder that 80 percent of us will have some sort of problem with our feet at some time or another. Many things
A Patient s Guide to Foot Anatomy Introduction Our feet are constantly under stress. It's no wonder that 80 percent of us will have some sort of problem with our feet at some time or another. Many things
FORCES IN THE KNEE JOINT DURING EXERCISE OF TIlE KNEE EXTENSORS 1
 10 THE AUSTRALIAN JOURNAL OF PHYSIOTHERAPY FORCES IN THE KNEE JOINT DURING EXERCISE OF TIlE KNEE EXTENSORS 1 R. S. HORSFIELD, B.SC., DIP.ED. (SYD.), M.PHYS. (U.N.S.W.), M.A.I.P., M.A.C.E. What frces arise
10 THE AUSTRALIAN JOURNAL OF PHYSIOTHERAPY FORCES IN THE KNEE JOINT DURING EXERCISE OF TIlE KNEE EXTENSORS 1 R. S. HORSFIELD, B.SC., DIP.ED. (SYD.), M.PHYS. (U.N.S.W.), M.A.I.P., M.A.C.E. What frces arise
Getting Around Safely With Your Crutches (Toe-Touch Weight Bearing)
 OrthBethesda Therapy Services Getting Arund Safely With Yur Crutches (Te-Tuch Weight Bearing) Yur physician will decide whether yu are t be nn weight bearing, te-tuch weight bearing, partial weight bearing,
OrthBethesda Therapy Services Getting Arund Safely With Yur Crutches (Te-Tuch Weight Bearing) Yur physician will decide whether yu are t be nn weight bearing, te-tuch weight bearing, partial weight bearing,
Introduction. The primary function of the ankle and foot is to absorb shock and impart thrust to the body during walking.
 The ankle 1 Introduction The primary function of the ankle and foot is to absorb shock and impart thrust to the body during walking. OSTEOLOGRY The term ankle refers primarily to the talocrural joint,
The ankle 1 Introduction The primary function of the ankle and foot is to absorb shock and impart thrust to the body during walking. OSTEOLOGRY The term ankle refers primarily to the talocrural joint,
Getting Around Safely With Your Crutches (Non Weight Bearing)
 OrthBethesda Therapy Services Getting Arund Safely With Yur Crutches (Nn Weight Bearing) Yur physician will decide whether yu are t be nn weight bearing, te-tuch weight bearing, partial weight bearing,
OrthBethesda Therapy Services Getting Arund Safely With Yur Crutches (Nn Weight Bearing) Yur physician will decide whether yu are t be nn weight bearing, te-tuch weight bearing, partial weight bearing,
Partial/Total Shoulder Arthroplasty POST-OPERATIVE PHYSICAL THERAPY PROTOCOL
 Partial/Ttal Shulder Arthrplasty POST-OPERATIVE PHYSICAL THERAPY PROTOCOL Rehabilitatin Precautins Sling shuld be wrn cntinuusly fr six weeks N internal rtatin (IR) x 12 weeks N crss chest adductin x 12
Partial/Ttal Shulder Arthrplasty POST-OPERATIVE PHYSICAL THERAPY PROTOCOL Rehabilitatin Precautins Sling shuld be wrn cntinuusly fr six weeks N internal rtatin (IR) x 12 weeks N crss chest adductin x 12
Section Three: The Leg, Ankle, and Foot Lecture: Review of Clinical Anatomy, Patterns of Dysfunction and Injury, and
 Section Three: The Leg, Ankle, and Foot Lecture: Review of Clinical Anatomy, Patterns of Dysfunction and Injury, and Treatment Implications for the Leg, Ankle, and Foot Levels I and II Demonstration and
Section Three: The Leg, Ankle, and Foot Lecture: Review of Clinical Anatomy, Patterns of Dysfunction and Injury, and Treatment Implications for the Leg, Ankle, and Foot Levels I and II Demonstration and
Materials Dissecting pan, dissecting kit, safety glasses, lab apron, pig heart, & gloves
 Heart Dissectin Intrductin Mammals have fur-chambered hearts and duble circulatin. The heart f a bird r mammal has tw atria and tw cmpletely separated ventricles. The dublelp circulatin is similar t amphibians
Heart Dissectin Intrductin Mammals have fur-chambered hearts and duble circulatin. The heart f a bird r mammal has tw atria and tw cmpletely separated ventricles. The dublelp circulatin is similar t amphibians
2019 Canada Winter Games Team NT Female Hockey Selection Camp August 16-19, 2018
 2019 Canada Winter Games Team NT Female Hckey Selectin Camp August 16-19, 2018 Strength and Cnditining Recmmendatins As discussed in the Call Fr Players letter, it is critical fr players t get their bdies
2019 Canada Winter Games Team NT Female Hckey Selectin Camp August 16-19, 2018 Strength and Cnditining Recmmendatins As discussed in the Call Fr Players letter, it is critical fr players t get their bdies
Main Menu. Ankle and Foot Joints click here. The Power is in Your Hands
 1 The Ankle and Foot Joints click here Main Menu Copyright HandsOn Therapy Schools 2009 K.8 http://www.handsonlineeducation.com/classes/k8/k8entry.htm[3/27/18, 1:40:03 PM] Ankle and Foot Joint 26 bones
1 The Ankle and Foot Joints click here Main Menu Copyright HandsOn Therapy Schools 2009 K.8 http://www.handsonlineeducation.com/classes/k8/k8entry.htm[3/27/18, 1:40:03 PM] Ankle and Foot Joint 26 bones
 P R E S E N T S Dr. Mufa T. Ghadiali is skilled in all aspects of General Surgery. His General Surgery Services include: General Surgery Advanced Laparoscopic Surgery Surgical Oncology Gastrointestinal
P R E S E N T S Dr. Mufa T. Ghadiali is skilled in all aspects of General Surgery. His General Surgery Services include: General Surgery Advanced Laparoscopic Surgery Surgical Oncology Gastrointestinal
Forensic Anthropology Lecture Notes. Week 3: Crime Scene Analysis, Trauma and Taphonomy
 Frensic Anthrplgy Lecture Ntes Week 3: Crime Scene Analysis, Trauma and Taphnmy Mdule 16: Blunt Frce Trauma What is Blunt Frce Trauma? Blunt frce trauma ccurs any time a frce impacts tissue ver a relatively
Frensic Anthrplgy Lecture Ntes Week 3: Crime Scene Analysis, Trauma and Taphnmy Mdule 16: Blunt Frce Trauma What is Blunt Frce Trauma? Blunt frce trauma ccurs any time a frce impacts tissue ver a relatively
Figure 7: Bones of the lower limb
 BONES OF THE APPENDICULAR SKELETON The appendicular skeleton is composed of the 126 bones of the appendages and the pectoral and pelvic girdles, which attach the limbs to the axial skeleton. Although the
BONES OF THE APPENDICULAR SKELETON The appendicular skeleton is composed of the 126 bones of the appendages and the pectoral and pelvic girdles, which attach the limbs to the axial skeleton. Although the
Postoperative Anterior Cruciate Ligament Reconstruction Care WITH meniscus repair:
 Pstperative Anterir Cruciate Ligament Recnstructin Care WITH meniscus repair: Imprtant Phne Numbers: - Please see the cntact infrmatin abve fr imprtant phne numbers t call. - If yu have cncerns after hurs,
Pstperative Anterir Cruciate Ligament Recnstructin Care WITH meniscus repair: Imprtant Phne Numbers: - Please see the cntact infrmatin abve fr imprtant phne numbers t call. - If yu have cncerns after hurs,
Anatomy of the lower limb
 Anatomy of the lower limb Arches & sole of the foot Dr. Hayder ARCHES OF THE FOOT The foot as a mechanical unit performs two major functions: - It acts as a pliable platform to support the body weigh during
Anatomy of the lower limb Arches & sole of the foot Dr. Hayder ARCHES OF THE FOOT The foot as a mechanical unit performs two major functions: - It acts as a pliable platform to support the body weigh during
FUNCTIONAL ANATOMY AND INJURY PREVENTION
 Functinal Anatmy and Injury preventin mdule FUNCTIONAL ANATOMY AND INJURY PREVENTION Australian Cllege f Sprt & Fitness 2014 Functinal Anatmy and Injury Preventin Mdule 1409C Page 1 f 216 Functinal Anatmy
Functinal Anatmy and Injury preventin mdule FUNCTIONAL ANATOMY AND INJURY PREVENTION Australian Cllege f Sprt & Fitness 2014 Functinal Anatmy and Injury Preventin Mdule 1409C Page 1 f 216 Functinal Anatmy
The Dance Hall by Vincent van Gogh,1888
 The Dance Hall by Vincent van Gogh,1888 Articulations of the pelvic girdle Lumbosacral joints, sacroiliac joints & pubic symphysis The remaining joints of the lower limb Hip joint Knee joint Tibiofibular
The Dance Hall by Vincent van Gogh,1888 Articulations of the pelvic girdle Lumbosacral joints, sacroiliac joints & pubic symphysis The remaining joints of the lower limb Hip joint Knee joint Tibiofibular
Hip joint Type: Articulating bones:
 Ana (242 ) Hip joint Type: Synovial, ball & socket Articulating bones: Formed between head of femur and lunate surface of acetabulum of hip bone. Capsule: it is a strong fibrous sleeve connecting the articulating
Ana (242 ) Hip joint Type: Synovial, ball & socket Articulating bones: Formed between head of femur and lunate surface of acetabulum of hip bone. Capsule: it is a strong fibrous sleeve connecting the articulating
CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM. Khaleel Alyahya, PhD, MEd King Saud University School of
 CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM Khaleel Alyahya, PhD, MEd King Saud University Schl f Medicine @khaleelya OBJECTIVES At the end f the lecture, students shuld be able t: Identify the cmpnents f the cardivascular
CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM Khaleel Alyahya, PhD, MEd King Saud University Schl f Medicine @khaleelya OBJECTIVES At the end f the lecture, students shuld be able t: Identify the cmpnents f the cardivascular
RETURN TO SPORT PROGRESSION: SOCCER
 1. The athlete must pass all functinal tests and/r be cleared by sprts medicine medical prvider befre beginning Return t Sccer Prtcl. 2. Recmmend pursuing Transitinal Therapy fr return t sprt activities
1. The athlete must pass all functinal tests and/r be cleared by sprts medicine medical prvider befre beginning Return t Sccer Prtcl. 2. Recmmend pursuing Transitinal Therapy fr return t sprt activities
Foot Anatomy. Midwest Bone & Joint Institute 2350 Royal Boulevard Suite 200 Elgin, IL Phone: Fax:
 A Patient s Guide to Foot Anatomy 2350 Royal Boulevard Suite 200 Elgin, IL 60123 Phone: 847.931.5300 Fax: 847.931.9072 DISCLAIMER: The information in this booklet is compiled from a variety of sources.
A Patient s Guide to Foot Anatomy 2350 Royal Boulevard Suite 200 Elgin, IL 60123 Phone: 847.931.5300 Fax: 847.931.9072 DISCLAIMER: The information in this booklet is compiled from a variety of sources.
Articulations or Joints
 Articulatins r Jints Bnes are cnnected t each ther by jints. The mst cmmn jint type is the diarthrsis f articulating jints, which has a fibrus cnnective tissue capsule (ligament), cntinuus with the peristeum
Articulatins r Jints Bnes are cnnected t each ther by jints. The mst cmmn jint type is the diarthrsis f articulating jints, which has a fibrus cnnective tissue capsule (ligament), cntinuus with the peristeum
10/12/2010. Upper Extremity. Pectoral (Shoulder) Girdle. Clavicle (collarbone) Skeletal System: Appendicular Skeleton
 Skeletal System: Appendicular Skeleton Pectoral girdle Pelvic girdle Upper limbs Lower limbs 8-1 Pectoral (Shoulder) Girdle Consists of scapula and clavicle Clavicle articulates with sternum (Sternoclavicular
Skeletal System: Appendicular Skeleton Pectoral girdle Pelvic girdle Upper limbs Lower limbs 8-1 Pectoral (Shoulder) Girdle Consists of scapula and clavicle Clavicle articulates with sternum (Sternoclavicular
Episode 1: Occult Fractures & Dislocations February, 2010
 Episde 1: Occult Fractures & Dislcatins February, 2010 Prepared by Lucas Chartier Mderated by Dr. Antn Helman Expert Guests: Dr. Arun Sayal & Dr. Nathalie Mamen Case 1: Occult hip fracture 67y.. wman with
Episde 1: Occult Fractures & Dislcatins February, 2010 Prepared by Lucas Chartier Mderated by Dr. Antn Helman Expert Guests: Dr. Arun Sayal & Dr. Nathalie Mamen Case 1: Occult hip fracture 67y.. wman with
INTRODUCTION TO THE CIRCULATORY SYSTEM
 INTRODUCTION TO THE CIRCULATORY SYSTEM What des bld d? 5. What makes this pssible? : In rder fr there t be an efficient exchange f xygen, waste and nutrients there must be a high surface area between the
INTRODUCTION TO THE CIRCULATORY SYSTEM What des bld d? 5. What makes this pssible? : In rder fr there t be an efficient exchange f xygen, waste and nutrients there must be a high surface area between the
DEESIDE NETBALL CLUB PLAYER S HANDBOOK. established 1979 INJURY PREVENTION GUIDELINES FOR NETBALL PLAYERS AND FIRST AID TREATMENTS
 DEESIDE NETBALL CLUB PLAYER S HANDBOOK established 1979 INJURY PREVENTION GUIDELINES FOR NETBALL PLAYERS AND FIRST AID TREATMENTS Affiliated t the Welsh Netball Assciatin Affiliated t England-Netball BE
DEESIDE NETBALL CLUB PLAYER S HANDBOOK established 1979 INJURY PREVENTION GUIDELINES FOR NETBALL PLAYERS AND FIRST AID TREATMENTS Affiliated t the Welsh Netball Assciatin Affiliated t England-Netball BE
RETURN TO SPORT PROGRESSION: FIELD HOCKEY
 1. The athlete must pass all functinal tests and/r be cleared by sprts medicine medical prvider befre beginning Return t Field Hckey Prtcl. 2. Recmmend pursuing Transitinal Therapy fr return t sprt activities
1. The athlete must pass all functinal tests and/r be cleared by sprts medicine medical prvider befre beginning Return t Field Hckey Prtcl. 2. Recmmend pursuing Transitinal Therapy fr return t sprt activities
Understanding Leg Anatomy and Function THE UPPER LEG
 Understanding Leg Anatomy and Function THE UPPER LEG The long thigh bone is the femur. It connects to the pelvis to form the hip joint and then extends down to meet the tibia (shin bone) at the knee joint.
Understanding Leg Anatomy and Function THE UPPER LEG The long thigh bone is the femur. It connects to the pelvis to form the hip joint and then extends down to meet the tibia (shin bone) at the knee joint.
Pectoral (Shoulder) Girdle
 Chapter 8 Skeletal System: Appendicular Skeleton Pectoral girdle Pelvic girdle Upper limbs Lower limbs 8-1 Pectoral (Shoulder) Girdle Consists of scapula and clavicle Clavicle articulates with sternum
Chapter 8 Skeletal System: Appendicular Skeleton Pectoral girdle Pelvic girdle Upper limbs Lower limbs 8-1 Pectoral (Shoulder) Girdle Consists of scapula and clavicle Clavicle articulates with sternum
 17.2 A-P Lower Leg Measure: A-P at mid-lower leg Protection: Apron draped over pelvis SID: 40 Table top No Tube Angle Film: 7 x17 I.D. down or diagonal 14 x 17 www.fisiokinesiterapia.biz A-P Lower Leg
17.2 A-P Lower Leg Measure: A-P at mid-lower leg Protection: Apron draped over pelvis SID: 40 Table top No Tube Angle Film: 7 x17 I.D. down or diagonal 14 x 17 www.fisiokinesiterapia.biz A-P Lower Leg
Tick fever is a cattle disease caused by any one of the following blood parasites:
 Tick fever Tick fever is a cattle disease caused by any ne f the fllwing bld parasites: Babesia bvis Babesia bigemina Anaplasma marginale These parasites are all transmitted by the cattle tick (Bphilus
Tick fever Tick fever is a cattle disease caused by any ne f the fllwing bld parasites: Babesia bvis Babesia bigemina Anaplasma marginale These parasites are all transmitted by the cattle tick (Bphilus
radiologymasterclass.co.uk
 http://radiologymasterclass.co.uk Hip X-ray anatomy - Normal AP (anterior-posterior) Shenton's line is formed by the medial edge of the femoral neck and the inferior edge of the superior pubic ramus Loss
http://radiologymasterclass.co.uk Hip X-ray anatomy - Normal AP (anterior-posterior) Shenton's line is formed by the medial edge of the femoral neck and the inferior edge of the superior pubic ramus Loss
Lecture 10. JOINTS of the FOOT. Dr Farooq Khan Aurakzai. Dated:
 Lecture 10 JOINTS of the FOOT. BY Dr Farooq Khan Aurakzai Dated: 20.02.2018 The joints of the foot are numerous. They are classified: A. Intertarsals B. Tarso metatarsals C. Intermetatarsals D. Metatarsophalangeal
Lecture 10 JOINTS of the FOOT. BY Dr Farooq Khan Aurakzai Dated: 20.02.2018 The joints of the foot are numerous. They are classified: A. Intertarsals B. Tarso metatarsals C. Intermetatarsals D. Metatarsophalangeal
Lower Extremity Amputation (LEA) Considerations / Issues
 Lwer Extremity Amputatin (LEA) Cnsideratins / Issues Prviding Te Fillers can be an advantageus resurce fr yur patient and business but it als cmes with certain cnsideratins. Please review this list belw
Lwer Extremity Amputatin (LEA) Cnsideratins / Issues Prviding Te Fillers can be an advantageus resurce fr yur patient and business but it als cmes with certain cnsideratins. Please review this list belw
o hold ankle (first uninvolved, then involved) o hold 4 seconds
 Prtcl fr Cx Technique Hands-On Prtins f Curses step by step instructins fr treating patients with Cx Distractin Decmpressin Adjustment & Manipulatin Prtcl I and II Instructins Lumbar Spine prepared by
Prtcl fr Cx Technique Hands-On Prtins f Curses step by step instructins fr treating patients with Cx Distractin Decmpressin Adjustment & Manipulatin Prtcl I and II Instructins Lumbar Spine prepared by
5 minutes: Attendance and Breath of Arrival. 50 minutes: Problem-Solving: Pelvis and Legs
 5 minutes: Attendance and Breath f Arrival 50 minutes: Prblem-Slving: Pelvis and Legs Punctuality- everybdy's time is precius: Be ready t learn by the start f class, we'll have yu ut f here n time Tardiness:
5 minutes: Attendance and Breath f Arrival 50 minutes: Prblem-Slving: Pelvis and Legs Punctuality- everybdy's time is precius: Be ready t learn by the start f class, we'll have yu ut f here n time Tardiness:
Dr.Israa H. Mohsen. Lecture 5. The vertebral column
 Anatomy Lecture 5 Dr.Israa H. Mohsen The vertebral column The vertebral column a flexible structure consisting of 33 vertebrae holds the head and torso upright, serves as an attachment point for the legs,
Anatomy Lecture 5 Dr.Israa H. Mohsen The vertebral column The vertebral column a flexible structure consisting of 33 vertebrae holds the head and torso upright, serves as an attachment point for the legs,
Leg. Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Associate Professor of Anatomy and Histology
 Leg Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Associate Professor of Anatomy and Histology Skin of the Leg Cutaneous Nerves Medially: The saphenous nerve, a branch of the femoral nerve supplies the skin on the medial surface
Leg Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Associate Professor of Anatomy and Histology Skin of the Leg Cutaneous Nerves Medially: The saphenous nerve, a branch of the femoral nerve supplies the skin on the medial surface
Biology 325 Fall 2003
 Name: pre-lab exercise due at beginning of your lab session Matching a. fibrous joints b. cartilaginous joints c. synovial joints 1. exhibit a joint cavity 2. types are sutures and syndesmoses 3. bones
Name: pre-lab exercise due at beginning of your lab session Matching a. fibrous joints b. cartilaginous joints c. synovial joints 1. exhibit a joint cavity 2. types are sutures and syndesmoses 3. bones
To learn the importance of cardiovascular exercise, to study the hamstring muscle and to practice basic martial arts kicks.
 Gal f 3 T learn the imprtance f cardivascular exercise, t study the hamstring muscle and t practice basic martial arts kicks. 3 3 Learning Objectives After participating in 3, students will: Understand
Gal f 3 T learn the imprtance f cardivascular exercise, t study the hamstring muscle and t practice basic martial arts kicks. 3 3 Learning Objectives After participating in 3, students will: Understand
musculoskeletal system anatomy muscles of foot sheet done by: dina sawadha & mohammad abukabeer
 musculoskeletal system anatomy muscles of foot sheet done by: dina sawadha & mohammad abukabeer Extensor retinaculum : A- superior extensor retinaculum (SER) : originates from the distal ends of the tibia
musculoskeletal system anatomy muscles of foot sheet done by: dina sawadha & mohammad abukabeer Extensor retinaculum : A- superior extensor retinaculum (SER) : originates from the distal ends of the tibia
Evidence-Based Examination of the Foot Presented by Alexis Wright, PT, PhD, DPT, FAAOMPT Practice Sessions/Skill Check-offs
 Evidence-Based Examination of the Foot Presented by Alexis Wright, PT, PhD, DPT, FAAOMPT Practice Sessions/Skill Check-offs Module Five: Movement Assessment of the Foot/Ankle (1 hour CEU Time) Skilled
Evidence-Based Examination of the Foot Presented by Alexis Wright, PT, PhD, DPT, FAAOMPT Practice Sessions/Skill Check-offs Module Five: Movement Assessment of the Foot/Ankle (1 hour CEU Time) Skilled
Chapter 8 The Skeletal System: The Appendicular Skeleton. Copyright 2009 John Wiley & Sons, Inc.
 Chapter 8 The Skeletal System: The Appendicular Skeleton Appendicular Skeleton It includes bones of the upper and lower limbs Girdles attach the limbs to the axial skeleton The pectoral girdle consists
Chapter 8 The Skeletal System: The Appendicular Skeleton Appendicular Skeleton It includes bones of the upper and lower limbs Girdles attach the limbs to the axial skeleton The pectoral girdle consists
5.1 Identify, describe the attachments of and deduce the actions of the muscles of the thigh:
 5.1 Identify, describe the attachments of and deduce the actions of the muscles of the thigh: Anterior group Proximal attachment Distal attachment Sartorius ASIS» Upper part of shaft tibia (middle surface)»
5.1 Identify, describe the attachments of and deduce the actions of the muscles of the thigh: Anterior group Proximal attachment Distal attachment Sartorius ASIS» Upper part of shaft tibia (middle surface)»
Copyright 2004, Yoshiyuki Shiratori. All right reserved.
 Ankle and Leg Evaluation 1. History Chief Complaint: A. What happened? B. Is it a sharp or dull pain? C. How long have you had the pain? D. Can you pinpoint the pain? E. Do you have any numbness or tingling?
Ankle and Leg Evaluation 1. History Chief Complaint: A. What happened? B. Is it a sharp or dull pain? C. How long have you had the pain? D. Can you pinpoint the pain? E. Do you have any numbness or tingling?
CHAPTER 8: THE BIOMECHANICS OF THE HUMAN LOWER EXTREMITY
 CHAPTER 8: THE BIOMECHANICS OF THE HUMAN LOWER EXTREMITY _ 1. The hip joint is the articulation between the and the. A. femur, acetabulum B. femur, spine C. femur, tibia _ 2. Which of the following is
CHAPTER 8: THE BIOMECHANICS OF THE HUMAN LOWER EXTREMITY _ 1. The hip joint is the articulation between the and the. A. femur, acetabulum B. femur, spine C. femur, tibia _ 2. Which of the following is
Introduction to Human Osteology Chapter 3: Hands and Feet
 Introduction to Human Osteology Chapter 3: Hands and Feet Roberta Hall Kenneth Beals Holm Neumann Georg Neumann Gwyn Madden Revised in 1978, 1984, and 2008 Bones of the Hand Eight carpal bones, in two
Introduction to Human Osteology Chapter 3: Hands and Feet Roberta Hall Kenneth Beals Holm Neumann Georg Neumann Gwyn Madden Revised in 1978, 1984, and 2008 Bones of the Hand Eight carpal bones, in two
Universal IC Attachment
 Universal IC Attachment www.preat.cm 800-232-7732 IC Universal Attachment Universal Male: 5.2mm length, 2mm Ø, 1mm nse Packaged Individually Indicatins: Esthetic partial dentures (n buccal clasp required)
Universal IC Attachment www.preat.cm 800-232-7732 IC Universal Attachment Universal Male: 5.2mm length, 2mm Ø, 1mm nse Packaged Individually Indicatins: Esthetic partial dentures (n buccal clasp required)
ANKLE JOINT ANATOMY 3. TALRSALS = (FOOT BONES) Fibula. Frances Daly MSc 1 CALCANEUS 2. TALUS 3. NAVICULAR 4. CUBOID 5.
 ANKLE JOINT ANATOMY The ankle joint is a synovial joint of the hinge type. The joint is formed by the distal end of the tibia and medial malleolus, the fibula and lateral malleolus and talus bone. It is
ANKLE JOINT ANATOMY The ankle joint is a synovial joint of the hinge type. The joint is formed by the distal end of the tibia and medial malleolus, the fibula and lateral malleolus and talus bone. It is
A. Incorrect! The appendicular skeleton includes bones of the shoulder, arm, hand, pelvis, leg and foot.
 Anatomy and Physiology - Problem Drill 08: The Skeletal System III No. 1 of 10 1. Which of the following statements about the appendicular skeleton is correct? A. The appendicular skeleton includes bones
Anatomy and Physiology - Problem Drill 08: The Skeletal System III No. 1 of 10 1. Which of the following statements about the appendicular skeleton is correct? A. The appendicular skeleton includes bones
حسام أبو عوض. - Ahmad. 1 P a g e
 - 9 حسام أبو عوض - - Ahmad 1 P a g e In the last lecture, we finished discussing the superficial part of the posterior compartment and the popliteus muscle of the deep layer[reminder: The entire posterior
- 9 حسام أبو عوض - - Ahmad 1 P a g e In the last lecture, we finished discussing the superficial part of the posterior compartment and the popliteus muscle of the deep layer[reminder: The entire posterior
Anatomy of Foot and Ankle
 Anatomy of Foot and Ankle Surface anatomy of the ankle & foot Surface anatomy of the ankle & foot Medial orientation point medial malleous sustentaculum tali tuberosity of navicular TA muscle TP muscle
Anatomy of Foot and Ankle Surface anatomy of the ankle & foot Surface anatomy of the ankle & foot Medial orientation point medial malleous sustentaculum tali tuberosity of navicular TA muscle TP muscle
Answers to Pre-Lab Quiz (p. 171) Answers to Activity Questions
 Answers to Pre-Lab Quiz (p. 171) 1. Holds bones together; allows the rigid skeleton some flexibility so that gross body movements can occur 2. c, amount of movement allowed by the joint 3. synovial 4.
Answers to Pre-Lab Quiz (p. 171) 1. Holds bones together; allows the rigid skeleton some flexibility so that gross body movements can occur 2. c, amount of movement allowed by the joint 3. synovial 4.
Referral Criteria: Inflammation of the Spine Feb
 Referral Criteria: Inflammatin f the Spine Feb 2019 1 5.7. Inflammatin f the Spine Backgrund Ankylsing spndylitis and axial spndylarthrpathy are fund in arund 0.3-1.2% f the ppulatin. Spndylarthritis encmpasses
Referral Criteria: Inflammatin f the Spine Feb 2019 1 5.7. Inflammatin f the Spine Backgrund Ankylsing spndylitis and axial spndylarthrpathy are fund in arund 0.3-1.2% f the ppulatin. Spndylarthritis encmpasses
The Skeletal System THE APPENDICULAR SKELETON
 The Skeletal System THE APPENDICULAR SKELETON The appendicular skeleton consists of the girdles and the skeleton of the limbs. The upper (anterior) limbs are attached to the pectoral (shoulder) girdle
The Skeletal System THE APPENDICULAR SKELETON The appendicular skeleton consists of the girdles and the skeleton of the limbs. The upper (anterior) limbs are attached to the pectoral (shoulder) girdle
The Cell Cycle & Cellular Division
 The Cell Cycle & Cellular Divisin Name: Perid: Date: I. Cell Divisin: All are derived frm preexisting cells (Cell Thery) is the prcess by which cells prduce new cells Cells grw in number, NOT in Smaller
The Cell Cycle & Cellular Divisin Name: Perid: Date: I. Cell Divisin: All are derived frm preexisting cells (Cell Thery) is the prcess by which cells prduce new cells Cells grw in number, NOT in Smaller
Chapter 13 Forensic Anthropology: What We Learn from Bones By the end of this chapter you will be able to:
 Chapter 13 Frensic Anthrplgy: What We Learn frm Bnes By the end f this chapter yu will be able t: Describe hw bne is frmed Distinguish between male and female skeletal remains Explain hw bnes cntain a
Chapter 13 Frensic Anthrplgy: What We Learn frm Bnes By the end f this chapter yu will be able t: Describe hw bne is frmed Distinguish between male and female skeletal remains Explain hw bnes cntain a
Initial Postoperative Knee Care Patella or Quadriceps Tendon Repairs: - Videos are available on Dr. Witty s website: drjeffreywitty.
 Initial Pstperative Knee Care Patella r Quadriceps Tendn Repairs: - Vides are available n Dr. Witty s website: drjeffreywitty.cm Imprtant Phne Numbers: - Please see the cntact infrmatin abve fr imprtant
Initial Pstperative Knee Care Patella r Quadriceps Tendn Repairs: - Vides are available n Dr. Witty s website: drjeffreywitty.cm Imprtant Phne Numbers: - Please see the cntact infrmatin abve fr imprtant
Year 2 MBChB Clinical Skills Session Examination of the Sensory System
 Year 2 MBChB Clinical Skills Sessin Examinatin f the Sensry System Reviewed & ratified by: Dr D Smith Cnsultant Neurlgist Dr R Davies Cnsultant Neurlgist Dr B Michael Neurlgy Clinical Lecturer Dr J Williamsn
Year 2 MBChB Clinical Skills Sessin Examinatin f the Sensry System Reviewed & ratified by: Dr D Smith Cnsultant Neurlgist Dr R Davies Cnsultant Neurlgist Dr B Michael Neurlgy Clinical Lecturer Dr J Williamsn
Therapeutic Foot Care Certificate Program Part I: Online Home Study Program
 Therapeutic Foot Care Certificate Program Part I: Online Home Study Program 1 Anatomy And Terminology Of The Lower Extremity Joan E. Edelstein, MA, PT, FISPO Associate Professor of Clinical Physical Therapy
Therapeutic Foot Care Certificate Program Part I: Online Home Study Program 1 Anatomy And Terminology Of The Lower Extremity Joan E. Edelstein, MA, PT, FISPO Associate Professor of Clinical Physical Therapy
Introduction. Lesson developed by: Heather Medema-Johnson, M.S, ATC, CSCS
 Updated DATE BSL PRO Lessn H35: Range f Mtin/Sit and Reach Lessn develped by: Heather Medema-Jhnsn, M.S, ATC, CSCS Intrductin A well-runded physical activity prgram is an integral part f a strng, verall
Updated DATE BSL PRO Lessn H35: Range f Mtin/Sit and Reach Lessn develped by: Heather Medema-Jhnsn, M.S, ATC, CSCS Intrductin A well-runded physical activity prgram is an integral part f a strng, verall
Active elbow motion is when your own muscles move the elbow back and forth.
 Initial Pstperative Shulder Care and Exercise: **Can be dne if a biceps tendesis has been perfrmed. If a biceps tendesis prcedure has been perfrmed, active elbw mtin is delayed up t 6 weeks. Please clarify
Initial Pstperative Shulder Care and Exercise: **Can be dne if a biceps tendesis has been perfrmed. If a biceps tendesis prcedure has been perfrmed, active elbw mtin is delayed up t 6 weeks. Please clarify
Post-Operative Instructions Shoulder Arthroscopy and SLAP Repair
 Laith M Jazrawi, MD Prfessr f Orthpedic Surgery Chief, Divisin f Sprts Medicine T 646-501-7223 Pst-Operative Instructins Shulder Arthrscpy and SLAP Repair Day f Surgery A. Relax. Diet as tlerated. B. Icing
Laith M Jazrawi, MD Prfessr f Orthpedic Surgery Chief, Divisin f Sprts Medicine T 646-501-7223 Pst-Operative Instructins Shulder Arthrscpy and SLAP Repair Day f Surgery A. Relax. Diet as tlerated. B. Icing
CMAC211. Session 3. Cupping Therapy. Chinese Medicine Department. Endeavour College of Natural Health endeavour.edu.au 1
 CMAC211 Sessin 3 Cupping Therapy Chinese Medicine Department Endeavur Cllege f Natural Health endeavur.edu.au 1 Pre Readings Bentley, B. (2013). Mending the fascia with mdern cupping. The Lantern, 10(3),
CMAC211 Sessin 3 Cupping Therapy Chinese Medicine Department Endeavur Cllege f Natural Health endeavur.edu.au 1 Pre Readings Bentley, B. (2013). Mending the fascia with mdern cupping. The Lantern, 10(3),
What Happens to the Paediatric Flat Foot? Peter J Briggs Freeman Hospital Newcastle upon Tyne
 What Happens to the Paediatric Flat Foot? Peter J Briggs Freeman Hospital Newcastle upon Tyne We don t know!! Population Studies 2300 children aged 4-13 years Shoe wearers Flat foot 8.6% Non-shoe wearers
What Happens to the Paediatric Flat Foot? Peter J Briggs Freeman Hospital Newcastle upon Tyne We don t know!! Population Studies 2300 children aged 4-13 years Shoe wearers Flat foot 8.6% Non-shoe wearers
Lumbar Spondylolysis/listhesis Rehabilitation Guideline
 Lumbar Spndyllysis/listhesis Rehabilitatin Guideline This rehabilitatin prgram is designed t return the individual t their activities as quickly and safely as pssible. It is designed fr rehabilitatin fllwing
Lumbar Spndyllysis/listhesis Rehabilitatin Guideline This rehabilitatin prgram is designed t return the individual t their activities as quickly and safely as pssible. It is designed fr rehabilitatin fllwing
Pelvic Girdle
 ARTICULATIONS OF LOWER EXTREMITY Pages 429-437 Pelvic Girdle formed by connection of the hip bones and the sacrum Sacroiliac Joints compound joints synovial joint - anterior, between the auricular surfaces
ARTICULATIONS OF LOWER EXTREMITY Pages 429-437 Pelvic Girdle formed by connection of the hip bones and the sacrum Sacroiliac Joints compound joints synovial joint - anterior, between the auricular surfaces
Chapter 20 The Heart
 Chapter 20 The Heart ANATOMY OF THE HEART The adult heart is apprximately the size f. The heart is lcated in the cavity, between. Base is directed, and the apex is directed. The membrane surrunding and
Chapter 20 The Heart ANATOMY OF THE HEART The adult heart is apprximately the size f. The heart is lcated in the cavity, between. Base is directed, and the apex is directed. The membrane surrunding and
You are not permitted to distribute this without prior written consent. Peripheral Nervous System Examination Upper + Lower Limbs
 Yu are nt permitted t distribute this withut prir written cnsent Peripheral Nervus System Examinatin Upper + Lwer Limbs Histry The patient may present with symptms that are purely sensry/mtr r mvement
Yu are nt permitted t distribute this withut prir written cnsent Peripheral Nervus System Examinatin Upper + Lwer Limbs Histry The patient may present with symptms that are purely sensry/mtr r mvement
The Leg. Prof. Oluwadiya KS
 The Leg Prof. Oluwadiya KS www.oluwadiya.sitesled.com Compartments of the leg 4 Four Compartments: 1. Anterior compartment Deep fibular nerve Dorsiflexes the foot and toes 2. Lateral Compartment Superficial
The Leg Prof. Oluwadiya KS www.oluwadiya.sitesled.com Compartments of the leg 4 Four Compartments: 1. Anterior compartment Deep fibular nerve Dorsiflexes the foot and toes 2. Lateral Compartment Superficial
To describe he knee joint, ligaments, structure & To list the main features of other lower limb joints
 To describe he knee joint, ligaments, structure & neurovascular supply To demonstrate the ankle joint anatomy To list the main features of other lower limb joints To list main groups of lymph nodes in
To describe he knee joint, ligaments, structure & neurovascular supply To demonstrate the ankle joint anatomy To list the main features of other lower limb joints To list main groups of lymph nodes in
Exercise 13. Articulations and Body Movements
 Exercise 13 Articulations and Body Movements Articulations Articulations, or joints, are points where a bone is connected to one or more other bones. Articulations hold the skeleton together. Articulations
Exercise 13 Articulations and Body Movements Articulations Articulations, or joints, are points where a bone is connected to one or more other bones. Articulations hold the skeleton together. Articulations
Understanding and Recognizing Anxiety
 Understanding and Recgnizing Anxiety Mst peple d nt recgnize their anxiety fr what it is, and instead think there is smething mre serius ging n. Myth: Reading, thinking, and learning abut anxiety will
Understanding and Recgnizing Anxiety Mst peple d nt recgnize their anxiety fr what it is, and instead think there is smething mre serius ging n. Myth: Reading, thinking, and learning abut anxiety will
These are medical emergencies that can cause death. If possible, remove OTFC from the mouth.
 MEDICATION GUIDE Oral Transmucsal Fentanyl Citrate (OTFC) CII (fentanyl citrate) ral transmucsal lzenge 200 mcg, 400 mcg, 600 mcg, 800 mcg, 1200 mcg, 1600 mcg IMPORTANT: D nt use Oral Transmucsal Fentanyl
MEDICATION GUIDE Oral Transmucsal Fentanyl Citrate (OTFC) CII (fentanyl citrate) ral transmucsal lzenge 200 mcg, 400 mcg, 600 mcg, 800 mcg, 1200 mcg, 1600 mcg IMPORTANT: D nt use Oral Transmucsal Fentanyl
9200 Calumet Avenue Sincer Jacob, PA-C Munster, IN Jessica Morin, ATC Deanna Cozzi, ATC
 DISCHARGE INSTRUCTIONS & PHYSICAL THERAPY PROTOCOL: Subacrmial Decmpressin, Glenhumeral Debridement, Distal Clavicle Resectin Recvery after shulder arthrscpy entails cntrlling swelling and discmfrt, return
DISCHARGE INSTRUCTIONS & PHYSICAL THERAPY PROTOCOL: Subacrmial Decmpressin, Glenhumeral Debridement, Distal Clavicle Resectin Recvery after shulder arthrscpy entails cntrlling swelling and discmfrt, return
Mitosis and Meiosis Lecture Notes
 Bilgy Mitsis and Meisis Lecture Ntes Name Per Learning Gals Quiz #6: December 6th Describe what happens during interphase Identify steps f mitsis/meisis by picture and functin Explain the diseases that
Bilgy Mitsis and Meisis Lecture Ntes Name Per Learning Gals Quiz #6: December 6th Describe what happens during interphase Identify steps f mitsis/meisis by picture and functin Explain the diseases that
Swindon Joint Strategic Needs Assessment Bulletin
 Swindn Jint Strategic Needs Assessment Bulletin Swindn Diabetes 2017 Key Pints: This JSNA gives health facts abut peple with diabetes r peple wh might get diabetes in Swindn. This helps us t plan fr medical
Swindn Jint Strategic Needs Assessment Bulletin Swindn Diabetes 2017 Key Pints: This JSNA gives health facts abut peple with diabetes r peple wh might get diabetes in Swindn. This helps us t plan fr medical
Principles of Anatomy and Physiology
 Principles of Anatomy and Physiology 14 th Edition CHAPTER 8 The Skeletal System: The Appendicular Skeleton The Appendicular Skeleton The 126 bones of the appendicular skeleton are primarily concerned
Principles of Anatomy and Physiology 14 th Edition CHAPTER 8 The Skeletal System: The Appendicular Skeleton The Appendicular Skeleton The 126 bones of the appendicular skeleton are primarily concerned
Foot. Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Associate Professor of Anatomy and Histology
 Foot Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Associate Professor of Anatomy and Histology Dorsum of the Foot Sole of the Foot Plantar aponeurosis It is a triangular thickening of deep fascia in the sole of the foot Attachments:
Foot Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Associate Professor of Anatomy and Histology Dorsum of the Foot Sole of the Foot Plantar aponeurosis It is a triangular thickening of deep fascia in the sole of the foot Attachments:
Chapter 8B. The Skeletal System: Appendicular Skeleton. The Appendicular Skeleton. Clavicle. Pectoral (Shoulder) Girdle
 The Appendicular Skeleton Chapter 8B The Skeletal System: Appendicular Skeleton 126 bones Pectoral (shoulder) girdle Pelvic (hip) girdle Upper limbs Lower limbs Functions primarily to facilitate movement
The Appendicular Skeleton Chapter 8B The Skeletal System: Appendicular Skeleton 126 bones Pectoral (shoulder) girdle Pelvic (hip) girdle Upper limbs Lower limbs Functions primarily to facilitate movement
