Electrophysiology of Subthalamic Nucleus in Normal and Parkinson s Disease
|
|
|
- Bruno Park
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Continuing Medical Education 206 Electrophysiology of Subthalamic Nucleus in Normal and Parkinson s Disease Chun-Hwei Tai and Chung-Chin Kuo Abstract- Subthalamic nucleus (STN) has been known to play an important role in the regulation of cortico-basal ganglia-thalamo-cortical loop. STN neurons have pacemaking activitiy and their firing pattern can switch from spike mode to bursting mode when membrane potential becomes hyperpolarized. Recent study has shown that STN neurons show marked increase in burst and oscillatory activity during the dopaminedepleting state of Parkinson s disease (PD). This electrophysiological change in activity is now considered as an characterstic pathophysiological feature of PD. High frequency stimulation of STN can modify and normalize the activity of STN neurons in the pathophysiologial state. This electrophysiological treatment applied to STN, known as deep brain stimulation (DBS) clinically, ameliorates the symptoms of PD effectively, and is becoming a standard treatment in patients with advanced PD. This article would review the basic researches concerning electrical activities of STN and try to extend the basic knowledge into clinical applications. Key Words: Subthalamic nucleus, Cortical-basal ganglia loop, Electrophysiololgy, Motor control, Parkinson s disease, Deep brain stimulation From the Department of Neurology, College of Medicine and University Hospital, National Taiwan University, Taipei, Taiwan; Department of Physiology, College of Medicine, National Taiwan University, Taipei, Taiwan. Received April 17, Revised and Accepted April 24, Reprint requests and correspondence to: Chung-Chin Kuo, MD, PhD. Department of Neurology, National Taiwan University Hospital, No. 7, Chong-Shan S. Road, Taipei, Taiwan. cckuo@ha.mc.ntu.edu.tw
2 207 (subthalamic nucleus STN) STN STN (spike mode) (burst mode) STN glutamate STN (oscillation) STN STN STN STN STN STN Acta Neurol Taiwan 2006;15: (globus pallidus internus, GPi) (substantia nigra pars reticular, SNr) STN glutamatergic STN (ballism) STN cckuo@ha.mc.ntu.edu.tw
3 208 (rigidity) (bradykinesia) (parkinsonism) STN STN STN (deep brain stimulation, DBS) STN STN STN STN STN STN STN STN 9~15mm (substantia nigra) (interral capsule) (red nucleus) (medial lemniscus) (1) STN 560, mm 3 (2) subthalamic fasciculus ( STN globus pallidus) ansa lenticularis ( GPi thalamus) lenticular fasciculus ( GPi thalamus) nigrostriatal fibers SNc (3) STN diencephalic wall (thalamus). (hypothalamus) (4) STN glutamate projection neurons (5,6) STN GABA interneuron 7.5% (7) STN efferent fibers STN (striatum) (globus pallidus externus) (reciprocal interconnection) (1,8) STN afferent fibers (primary motor cortex) (supplementary motor area) (premotor area) (9) STN (substantia nigra pars compacta, SNc) (dopamine) (10) STN (11) STN STN
4 209 (12,13) STN STN STN 18~25 (regular 15 ~ 25%) (irrigular 55 ~ 65%) (bursting 15 ~ 50%) (14) (oscillatory) Kaneoke and Vitek 1996 (15) STN STN STN -35 ~ -50mV -40 ~ -60mV -60mV STN (16,17) STN STN STN -75 ~ -65mv T L (plateau potential) (18) STN (16) STN A STN B SNr 500 ms C D E F Percentages of STN neurons Normal 6-OHDA Burst Irregular Regular Percentages of SNr neurons Normal 6-OHDA Burst Irregular Regular. STN (A) STN (B) SNr (C) (D) STN SNr (E) (F) STN SNr
5 210 resurgent STN (16,19,20) (16,21) (Ik, Ca) h (Ih) -65 ~ -75mv T STN STN (thalamocortical neurons) acetylcholine, monoamine GABA STN STN GABA glutamate SNc STN dopamine GABA GPe GABAA receptor STN STN (17,22) pallidal fibers GABA STN GABA STN (23) STN glutamate A B C D A B C D. STN (A B) STN T (B C) L (C D)
6 211 STN STN AMPA STN (24,25) glutamate metabotropic recptors STN metabotropic receptor STN (26) SNc STN dopamine STN (27) STN dopamine D5 receptor (28) STN dopamine glutamate GABA STN (29) dopamine STN (28,30) STN glutamate bursting activity GABA STN Dopamine STN STN STN (31) STN 30% 50% STN (14,31,32) 200ms (33) STN somatotopy STN 2/3 STN STN (14,31,32) (direct pathway) (indirect pathway) (34) focused selection (motor pattern) (35) STN - STN STN glutamate GABA dopamine STN glutamate EPSP GPe GABA GABA IPSP glutamate dopamine STN STN STN glutamate, GABA dopamine STN STN glutamate
7 212. GPi SNR STN STN glutamate GPi SNr (1) STN GPe STN glutamate GPe GPe GABA GPe (synchronized oscillation) STN (36) STN GPe SNr STN GPe SNr (37,38) STN GPi SNr STN STN GPi SNr STN (39) STN GPi SNr (40) (41,42) indirect pathway STN (43)
8 213 SNc (Dopamine DA) (Levodopa) (44) STN DBS STN STN STN bursting activity oscillatory activity (11,45,46) DA STN STN Striatum GPe STN STN STN GPe (36) STN STN local field potential (LFP) (47) STN LFP <8Hz, 8~30 Hz >60Hz < 8 Hz 8~30 Hz (Bradykinesia) (Akinesia) 8~30 Hz >60Hz (47) STN (37,38) STN (high frequency stimulation HFS) STN STN (12,13) STN HFS A B C D. ON ON ON ON OFF OFF OFF OFF 10 sec STN ( 86%) STN [(A) (B)] STN ( 14%) [(C) (D)] ON OFF 130 Hz 60µ sec 500µ Amp
9 214 (Deep Brain Stimulation DBS) (48) ( 85Hz ) ( 100~185 Hz) STN (49) STN (50) HFS STN HFS HFS STN STN STN STN STN STN HFS STN STN 1. Parent A, Hazrati LN. Functional anatomy of the basal ganglia. II. The place of subthalamic nucleus and external pallidum in basal ganglia circuitry. Brain Res Brain Res Rev 1995;20: Hardman CD, Henderson JM, Finkelstein DI, et al. Comparison of the basal ganglia in rats, marmosets, macaques, baboons, and humans: volume and neuronal number for the output, internal relay, and striatal modulating nuclei. J Comp Neurol 2002;445: Yelnik J, Percheron G. Subthalamic neurons in primates: a quantitative and comparative analysis. Neuroscience 1979;4: Marchand R. Histogenesis of the subthalamic nucleus. Neuroscience 1987;21: Chang HT, Kita H, Kitai ST. The fine structure of the rat subthalamic nucleus: an electron microscopic study. J Comp Neurol 1983;221: Afsharpour S. Light microscopic analysis of Golgi-impregnated rat subthalamic neurons. J Comp Neurol 1985;236: Levesque JC, Parent A. GABAergic interneurons in human subthalamic nucleus. Mov Disord 2005;20: Feger J, Hassani OK, Mouroux M. The subthalamic nucleus and its connections. New electrophysiological and pharmacological data. Adv Neurol 1997;74: Nambu A, Tokuno H, Takada M. Functional significance of the cortico-subthalamo-pallidal hyperdirect pathway. Neurosci Res 2002;43: Francois C, Savy C, Jan C, et al. Dopaminergic innervation of the subthalamic nucleus in the normal state, in MPTPtreated monkeys, and in Parkinson s disease patients. J Comp Neurol 2000;425: Vila M, Perier C, Feger J, et al. Evolution of changes in neuronal activity in the subthalamic nucleus of rats with unilateral lesion of the substantia nigra assessed by metabolic and electrophysiological measurements. Eur J Neurosci 2000;12: Bergman H, Wichmann T, DeLong MR. Reversal of experimental parkinsonism by lesions of the subthalamic nucleus. Science 1990;249: Benazzouz A, Gross C, Feger J, et al. Reversal of rigidity and improvement in motor performance by subthalamic high-frequency stimulation in MPTP-treated monkeys. Eur J Neurosci 1993;5: Wichmann T, Bergman H, DeLong MR. The primate subthalamic nucleus. I. Functional properties in intact animals. J Neurophysiol 1994;72: Kaneoke Y, Vitek JL. Burst and oscillation as disparate neuronal properties. J Neurosci Methods 1996;68: Beurrier C, Congar P, Bioulac B, et al. Subthalamic nucleus neurons switch from single-spike activity to burst-firing
10 215 mode. J Neurosci 1999;19: Bevan MD, Wilson CJ, Bolam JP, et al. Equilibrium potential of GABA(A) current and implications for rebound burst firing in rat subthalamic neurons in vitro. J Neurophysiol 2000;83: Song WJ, Baba Y, Otsuka T, et al. Characterization of Ca(2+) channels in rat subthalamic nucleus neurons. J Neurophysiol 2000;84: Do MT, Bean BP. Subthreshold sodium currents and pacemaking of subthalamic neurons: modulation by slow inactivation. Neuron 2003;39: Do MT, Bean BP. Sodium currents in subthalamic nucleus neurons from Nav1.6-null mice. J Neurophysiol 2004;92: Wigmore MA, Lacey MG. A Kv3-like persistent, outwardly rectifying, Cs+-permeable, K+ current in rat subthalamic nucleus neurones. J Physiol 2000;527 Pt 3: Bevan MD, Wilson CJ. Mechanisms underlying spontaneous oscillation and rhythmic firing in rat subthalamic neurons. J Neurosci 1999;19: Bevan MD, Magill PJ, Hallworth NE, et al. Regulation of the timing and pattern of action potential generation in rat subthalamic neurons in vitro by GABA-A IPSPs. J Neurophysiol 2002;87: Otsuka T, Murakami F, Song WJ. Excitatory postsynaptic potentials trigger a plateau potential in rat subthalamic neurons at hyperpolarized states. J Neurophysiol 2001;86: Nakanishi H, Kita H, Kitai ST. An N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor mediated excitatory postsynaptic potential evoked in subthalamic neurons in an in vitro slice preparation of the rat. Neurosci Lett 1988;95: Awad-Granko H, Conn PJ. Activation of groups I or III metabotropic glutamate receptors inhibits excitatory transmission in the rat subthalamic nucleus. Neuropharmacology 2001;41: Kreiss DS, Mastropietro CW, Rawji SS, et al. The response of subthalamic nucleus neurons to dopamine receptor stimulation in a rodent model of Parkinson s disease. J Neurosci 1997;17: Baufreton J, Garret M, Rivera A, et al. D5 (not D1) dopamine receptors potentiate burst-firing in neurons of the subthalamic nucleus by modulating an L-type calcium conductance. J Neurosci 2003;23: Hassani OK, Feger J. Effects of intrasubthalamic injection of dopamine receptor agonists on subthalamic neurons in normal and 6-hydroxydopamine-lesioned rats: an electrophysiological and c-fos study. Neuroscience 1999;92: Tofighy A, Abbott A, Centonze D, et al. Excitation by dopamine of rat subthalamic nucleus neurones in vitro-a direct action with unconventional pharmacology. Neuroscience 2003;116: DeLong MR, Crutcher MD, Georgopoulos AP. Primate globus pallidus and subthalamic nucleus: functional organization. J Neurophysiol 1985;53: Bergman H, Wichmann T, Karmon B, et al. The primate subthalamic nucleus. II. Neuronal activity in the MPTP model of parkinsonism. J Neurophysiol 1994;72: Matsumura M, Kojima J, Gardiner TW, et al. Visual and oculomotor functions of monkey subthalamic nucleus. J Neurophysiol 1992;67: Alexander GE, Crutcher MD, DeLong MR. Basal gangliathalamocortical circuits: parallel substrates for motor, oculomotor, prefrontal and limbic functions. Prog Brain Res 1990;85: Mink JW. The basal ganglia: focused selection and inhibition of competing motor programs. Prog Neurobiol 1996; 50: Bevan MD, Magill PJ, Terman D, et al. Move to the rhythm: oscillations in the subthalamic nucleus-external globus pallidus network. Trends Neurosci 2002;25: Levy R, Ashby P, Hutchison WD, et al. Dependence of subthalamic nucleus oscillations on movement and dopamine in Parkinson s disease. Brain 2002;125: Levy R, Dostrovsky JO, Lang AE, et al. Effects of apomorphine on subthalamic nucleus and globus pallidus internus neurons in patients with Parkinson s disease. J Neurophysiol 2001;86: Rosales MG, Flores G, Hernandez S, et al. Activation of subthalamic neurons produces NMDA receptor-mediated dendritic dopamine release in substantia nigra pars reticulata: a microdialysis study in the rat. Brain Res 1994;645: Wichmann T, Bergman H, DeLong MR. The primate subthalamic nucleus. III. Changes in motor behavior and neuronal activity in the internal pallidum induced by subthalamic inactivation in the MPTP model of parkinsonism. J
11 216 Neurophysiol 1994;72: Dewey RB Jr, Jankovic J. Hemiballism-hemichorea. Clinical and pharmacologic findings in 21 patients. Arch Neurol 1989;46: Lee MS, Marsden CD. Movement disorders following lesions of the thalamus or subthalamic region. Mov Disord 1994;9: Dybdal D, Gale K. Postural and anticonvulsant effects of inhibition of the rat subthalamic nucleus. J Neurosci 2000; 20: Limousin P, Pollak P, Benazzouz A, et al. Effect of parkinsonian signs and symptoms of bilateral subthalamic nucleus stimulation. Lancet 1995;345: Magill PJ, Bolam JP, Bevan MD. Dopamine regulates the impact of the cerebral cortex on the subthalamic nucleusglobus pallidus network. Neuroscience 2001;106: Hutchison WD, Allan RJ, Opitz H, et al. Neurophysiological identification of the subthalamic nucleus in surgery for Parkinson s disease. Ann Neurol 1998;44: Brown P, Williams D. Basal ganglia local field potential activity: character and functional significance in the human. Clin Neurophysiol 2005;116: Benabid AL. Deep brain stimulation for Parkinson s disease. Curr Opin Neurobiol 2003;13: Krack P, Fraix V, Mendes A, et al. Postoperative management of subthalamic nucleus stimulation for Parkinson s disease. Mov Disord 2002;17 Suppl 3:S Tai CH, Boraud T, Bezard E, et al. Electrophysiological and metabolic evidence that high-frequency stimulation of the subthalamic nucleus bridles neuronal activity in the subthalamic nucleus and the substantia nigra reticulata. FASEB J 2003;17:
Parkinson s Disease and Cortico-Basal Ganglia Circuits
 Continuing Medical Education 213 Parkinson s Disease and Cortico-Basal Ganglia Circuits Ming-Kai Pan, Chun-Hwei Tai, Chung-Chin Kuo Abstract- Cortico-basal ganglia circuit model has been studied extensively
Continuing Medical Education 213 Parkinson s Disease and Cortico-Basal Ganglia Circuits Ming-Kai Pan, Chun-Hwei Tai, Chung-Chin Kuo Abstract- Cortico-basal ganglia circuit model has been studied extensively
Connections of basal ganglia
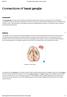 Connections of basal ganglia Introduction The basal ganglia, or basal nuclei, are areas of subcortical grey matter that play a prominent role in modulating movement, as well as cognitive and emotional
Connections of basal ganglia Introduction The basal ganglia, or basal nuclei, are areas of subcortical grey matter that play a prominent role in modulating movement, as well as cognitive and emotional
Basal Ganglia George R. Leichnetz, Ph.D.
 Basal Ganglia George R. Leichnetz, Ph.D. OBJECTIVES 1. To understand the brain structures which constitute the basal ganglia, and their interconnections 2. To understand the consequences (clinical manifestations)
Basal Ganglia George R. Leichnetz, Ph.D. OBJECTIVES 1. To understand the brain structures which constitute the basal ganglia, and their interconnections 2. To understand the consequences (clinical manifestations)
Anatomy of the basal ganglia. Dana Cohen Gonda Brain Research Center, room 410
 Anatomy of the basal ganglia Dana Cohen Gonda Brain Research Center, room 410 danacoh@gmail.com The basal ganglia The nuclei form a small minority of the brain s neuronal population. Little is known about
Anatomy of the basal ganglia Dana Cohen Gonda Brain Research Center, room 410 danacoh@gmail.com The basal ganglia The nuclei form a small minority of the brain s neuronal population. Little is known about
Damage on one side.. (Notes) Just remember: Unilateral damage to basal ganglia causes contralateral symptoms.
 Lecture 20 - Basal Ganglia Basal Ganglia (Nolte 5 th Ed pp 464) Damage to the basal ganglia produces involuntary movements. Although the basal ganglia do not influence LMN directly (to cause this involuntary
Lecture 20 - Basal Ganglia Basal Ganglia (Nolte 5 th Ed pp 464) Damage to the basal ganglia produces involuntary movements. Although the basal ganglia do not influence LMN directly (to cause this involuntary
GBME graduate course. Chapter 43. The Basal Ganglia
 GBME graduate course Chapter 43. The Basal Ganglia Basal ganglia in history Parkinson s disease Huntington s disease Parkinson s disease 1817 Parkinson's disease (PD) is a degenerative disorder of the
GBME graduate course Chapter 43. The Basal Ganglia Basal ganglia in history Parkinson s disease Huntington s disease Parkinson s disease 1817 Parkinson's disease (PD) is a degenerative disorder of the
COGNITIVE SCIENCE 107A. Motor Systems: Basal Ganglia. Jaime A. Pineda, Ph.D.
 COGNITIVE SCIENCE 107A Motor Systems: Basal Ganglia Jaime A. Pineda, Ph.D. Two major descending s Pyramidal vs. extrapyramidal Motor cortex Pyramidal system Pathway for voluntary movement Most fibers originate
COGNITIVE SCIENCE 107A Motor Systems: Basal Ganglia Jaime A. Pineda, Ph.D. Two major descending s Pyramidal vs. extrapyramidal Motor cortex Pyramidal system Pathway for voluntary movement Most fibers originate
Teach-SHEET Basal Ganglia
 Teach-SHEET Basal Ganglia Purves D, et al. Neuroscience, 5 th Ed., Sinauer Associates, 2012 Common organizational principles Basic Circuits or Loops: Motor loop concerned with learned movements (scaling
Teach-SHEET Basal Ganglia Purves D, et al. Neuroscience, 5 th Ed., Sinauer Associates, 2012 Common organizational principles Basic Circuits or Loops: Motor loop concerned with learned movements (scaling
Network Effects of Deep Brain Stimulation for Parkinson s Disease A Computational. Modeling Study. Karthik Kumaravelu
 Network Effects of Deep Brain Stimulation for Parkinson s Disease A Computational Modeling Study by Karthik Kumaravelu Department of Biomedical Engineering Duke University Date: Approved: Warren M. Grill,
Network Effects of Deep Brain Stimulation for Parkinson s Disease A Computational Modeling Study by Karthik Kumaravelu Department of Biomedical Engineering Duke University Date: Approved: Warren M. Grill,
Effects of nicotine on neuronal firing patterns in human subthalamic nucleus. Kim Scott Mentor: Henry Lester SURF seminar, January 15, 2009
 Effects of nicotine on neuronal firing patterns in human subthalamic nucleus Kim Scott Mentor: Henry Lester SURF seminar, January 15, 2009 Smoking tobacco protects against Parkinson s Disease (PD). Identical
Effects of nicotine on neuronal firing patterns in human subthalamic nucleus Kim Scott Mentor: Henry Lester SURF seminar, January 15, 2009 Smoking tobacco protects against Parkinson s Disease (PD). Identical
Modeling facilitation and inhibition of competing motor programs in basal ganglia subthalamic nucleus pallidal circuits
 Modeling facilitation and inhibition of competing motor programs in basal ganglia subthalamic nucleus pallidal circuits Leonid L. Rubchinsky*, Nancy Kopell, and Karen A. Sigvardt* *Center for Neuroscience
Modeling facilitation and inhibition of competing motor programs in basal ganglia subthalamic nucleus pallidal circuits Leonid L. Rubchinsky*, Nancy Kopell, and Karen A. Sigvardt* *Center for Neuroscience
Basal ganglia macrocircuits
 Tepper, Abercrombie & Bolam (Eds.) Progress in Brain Research, Vol. 160 ISSN 0079-6123 Copyright r 2007 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved CHAPTER 1 Basal ganglia macrocircuits J.M. Tepper 1,, E.D. Abercrombie
Tepper, Abercrombie & Bolam (Eds.) Progress in Brain Research, Vol. 160 ISSN 0079-6123 Copyright r 2007 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved CHAPTER 1 Basal ganglia macrocircuits J.M. Tepper 1,, E.D. Abercrombie
A. General features of the basal ganglia, one of our 3 major motor control centers:
 Reading: Waxman pp. 141-146 are not very helpful! Computer Resources: HyperBrain, Chapter 12 Dental Neuroanatomy Suzanne S. Stensaas, Ph.D. April 22, 2010 THE BASAL GANGLIA Objectives: 1. What are the
Reading: Waxman pp. 141-146 are not very helpful! Computer Resources: HyperBrain, Chapter 12 Dental Neuroanatomy Suzanne S. Stensaas, Ph.D. April 22, 2010 THE BASAL GANGLIA Objectives: 1. What are the
SYNCHRONIZATION OF PALLIDAL ACTIVITY IN THE MPTP PRIMATE MODEL OF PARKINSONISM IS NOT LIMITED TO OSCILLATORY ACTIVITY
 SYNCHRONIZATION OF PALLIDAL ACTIVITY IN THE MPTP PRIMATE MODEL OF PARKINSONISM IS NOT LIMITED TO OSCILLATORY ACTIVITY Gali Heimer, Izhar Bar-Gad, Joshua A. Goldberg and Hagai Bergman * 1. INTRODUCTION
SYNCHRONIZATION OF PALLIDAL ACTIVITY IN THE MPTP PRIMATE MODEL OF PARKINSONISM IS NOT LIMITED TO OSCILLATORY ACTIVITY Gali Heimer, Izhar Bar-Gad, Joshua A. Goldberg and Hagai Bergman * 1. INTRODUCTION
Basal ganglia Sujata Sofat, class of 2009
 Basal ganglia Sujata Sofat, class of 2009 Basal ganglia Objectives Describe the function of the Basal Ganglia in movement Define the BG components and their locations Describe the motor loop of the BG
Basal ganglia Sujata Sofat, class of 2009 Basal ganglia Objectives Describe the function of the Basal Ganglia in movement Define the BG components and their locations Describe the motor loop of the BG
A. General features of the basal ganglia, one of our 3 major motor control centers:
 Reading: Waxman pp. 141-146 are not very helpful! Computer Resources: HyperBrain, Chapter 12 Dental Neuroanatomy Suzanne S. Stensaas, Ph.D. March 1, 2012 THE BASAL GANGLIA Objectives: 1. What are the main
Reading: Waxman pp. 141-146 are not very helpful! Computer Resources: HyperBrain, Chapter 12 Dental Neuroanatomy Suzanne S. Stensaas, Ph.D. March 1, 2012 THE BASAL GANGLIA Objectives: 1. What are the main
Making Things Happen 2: Motor Disorders
 Making Things Happen 2: Motor Disorders How Your Brain Works Prof. Jan Schnupp wschnupp@cityu.edu.hk HowYourBrainWorks.net On the Menu in This Lecture In the previous lecture we saw how motor cortex and
Making Things Happen 2: Motor Disorders How Your Brain Works Prof. Jan Schnupp wschnupp@cityu.edu.hk HowYourBrainWorks.net On the Menu in This Lecture In the previous lecture we saw how motor cortex and
神經解剖學 NEUROANATOMY BASAL NUCLEI 盧家鋒助理教授臺北醫學大學醫學系解剖學暨細胞生物學科臺北醫學大學醫學院轉譯影像研究中心.
 神經解剖學 NEUROANATOMY BASAL NUCLEI 盧家鋒助理教授臺北醫學大學醫學系解剖學暨細胞生物學科臺北醫學大學醫學院轉譯影像研究中心 http://www.ym.edu.tw/~cflu OUTLINE Components and Pathways of the Basal Nuclei Functions and Related Disorders of the Basal Nuclei
神經解剖學 NEUROANATOMY BASAL NUCLEI 盧家鋒助理教授臺北醫學大學醫學系解剖學暨細胞生物學科臺北醫學大學醫學院轉譯影像研究中心 http://www.ym.edu.tw/~cflu OUTLINE Components and Pathways of the Basal Nuclei Functions and Related Disorders of the Basal Nuclei
Levodopa vs. deep brain stimulation: computational models of treatments for Parkinson's disease
 Levodopa vs. deep brain stimulation: computational models of treatments for Parkinson's disease Abstract Parkinson's disease (PD) is a neurodegenerative disease affecting the dopaminergic neurons of the
Levodopa vs. deep brain stimulation: computational models of treatments for Parkinson's disease Abstract Parkinson's disease (PD) is a neurodegenerative disease affecting the dopaminergic neurons of the
Down regulation of the HCN2 channel in rat models of Parkinson s disease
 Down regulation of the HCN2 channel in rat models of Parkinson s disease Abstract The basal ganglia is a key control centre involved with the regulation of movement. It is therefore a primary interest
Down regulation of the HCN2 channel in rat models of Parkinson s disease Abstract The basal ganglia is a key control centre involved with the regulation of movement. It is therefore a primary interest
Uncovering the mechanism(s) of deep brain stimulation
 Journal of Physics: Conference Series Uncovering the mechanism(s) of deep brain stimulation To cite this article: Li Gang et al 2005 J. Phys.: Conf. Ser. 13 336 View the article online for updates and
Journal of Physics: Conference Series Uncovering the mechanism(s) of deep brain stimulation To cite this article: Li Gang et al 2005 J. Phys.: Conf. Ser. 13 336 View the article online for updates and
The Wonders of the Basal Ganglia
 Basal Ganglia The Wonders of the Basal Ganglia by Mackenzie Breton and Laura Strong /// https://kin450- neurophysiology.wikispaces.com/basal+ganglia Introduction The basal ganglia are a group of nuclei
Basal Ganglia The Wonders of the Basal Ganglia by Mackenzie Breton and Laura Strong /// https://kin450- neurophysiology.wikispaces.com/basal+ganglia Introduction The basal ganglia are a group of nuclei
Basal Ganglia. Steven McLoon Department of Neuroscience University of Minnesota
 Basal Ganglia Steven McLoon Department of Neuroscience University of Minnesota 1 Course News Graduate School Discussion Wednesday, Nov 1, 11:00am MoosT 2-690 with Paul Mermelstein (invite your friends)
Basal Ganglia Steven McLoon Department of Neuroscience University of Minnesota 1 Course News Graduate School Discussion Wednesday, Nov 1, 11:00am MoosT 2-690 with Paul Mermelstein (invite your friends)
1/2/2019. Basal Ganglia & Cerebellum a quick overview. Outcomes you want to accomplish. MHD-Neuroanatomy Neuroscience Block. Basal ganglia review
 This power point is made available as an educational resource or study aid for your use only. This presentation may not be duplicated for others and should not be redistributed or posted anywhere on the
This power point is made available as an educational resource or study aid for your use only. This presentation may not be duplicated for others and should not be redistributed or posted anywhere on the
VL VA BASAL GANGLIA. FUNCTIONAl COMPONENTS. Function Component Deficits Start/initiation Basal Ganglia Spontan movements
 BASAL GANGLIA Chris Cohan, Ph.D. Dept. of Pathology/Anat Sci University at Buffalo I) Overview How do Basal Ganglia affect movement Basal ganglia enhance cortical motor activity and facilitate movement.
BASAL GANGLIA Chris Cohan, Ph.D. Dept. of Pathology/Anat Sci University at Buffalo I) Overview How do Basal Ganglia affect movement Basal ganglia enhance cortical motor activity and facilitate movement.
Modeling the interplay of short-term memory and the basal ganglia in sequence processing
 Neurocomputing 26}27 (1999) 687}692 Modeling the interplay of short-term memory and the basal ganglia in sequence processing Tomoki Fukai* Department of Electronics, Tokai University, Hiratsuka, Kanagawa
Neurocomputing 26}27 (1999) 687}692 Modeling the interplay of short-term memory and the basal ganglia in sequence processing Tomoki Fukai* Department of Electronics, Tokai University, Hiratsuka, Kanagawa
Computational cognitive neuroscience: 8. Motor Control and Reinforcement Learning
 1 Computational cognitive neuroscience: 8. Motor Control and Reinforcement Learning Lubica Beňušková Centre for Cognitive Science, FMFI Comenius University in Bratislava 2 Sensory-motor loop The essence
1 Computational cognitive neuroscience: 8. Motor Control and Reinforcement Learning Lubica Beňušková Centre for Cognitive Science, FMFI Comenius University in Bratislava 2 Sensory-motor loop The essence
NS219: Basal Ganglia Anatomy
 NS219: Basal Ganglia Anatomy Human basal ganglia anatomy Analagous rodent basal ganglia nuclei Basal ganglia circuits: the classical model of direct and indirect pathways + Glutamate + - GABA - Gross anatomy
NS219: Basal Ganglia Anatomy Human basal ganglia anatomy Analagous rodent basal ganglia nuclei Basal ganglia circuits: the classical model of direct and indirect pathways + Glutamate + - GABA - Gross anatomy
Functional interconnectivity between the globus pallidus and the subthalamic nucleus in the mouse brain slice
 J Physiol 567.3 (2005) pp 977 987 977 Functional interconnectivity between the globus pallidus and the subthalamic nucleus in the mouse brain slice K. C. Loucif 1,C.L.Wilson 1,2,R.Baig 1,M.G.Lacey 2 and
J Physiol 567.3 (2005) pp 977 987 977 Functional interconnectivity between the globus pallidus and the subthalamic nucleus in the mouse brain slice K. C. Loucif 1,C.L.Wilson 1,2,R.Baig 1,M.G.Lacey 2 and
Basal Ganglia. Introduction. Basal Ganglia at a Glance. Role of the BG
 Basal Ganglia Shepherd (2004) Chapter 9 Charles J. Wilson Instructor: Yoonsuck Choe; CPSC 644 Cortical Networks Introduction A set of nuclei in the forebrain and midbrain area in mammals, birds, and reptiles.
Basal Ganglia Shepherd (2004) Chapter 9 Charles J. Wilson Instructor: Yoonsuck Choe; CPSC 644 Cortical Networks Introduction A set of nuclei in the forebrain and midbrain area in mammals, birds, and reptiles.
Towards a Better Treatment of Parkinson's disease
 Loma Linda University TheScholarsRepository@LLU: Digital Archive of Research, Scholarship & Creative Works Loma Linda University Electronic Theses, Dissertations & Projects 3-2014 Towards a Better Treatment
Loma Linda University TheScholarsRepository@LLU: Digital Archive of Research, Scholarship & Creative Works Loma Linda University Electronic Theses, Dissertations & Projects 3-2014 Towards a Better Treatment
Dynamic Behaviour of a Spiking Model of Action Selection in the Basal Ganglia
 Dynamic Behaviour of a Spiking Model of Action Selection in the Basal Ganglia Terrence C. Stewart (tcstewar@uwaterloo.ca) Xuan Choo (fchoo@uwaterloo.ca) Chris Eliasmith (celiasmith@uwaterloo.ca) Centre
Dynamic Behaviour of a Spiking Model of Action Selection in the Basal Ganglia Terrence C. Stewart (tcstewar@uwaterloo.ca) Xuan Choo (fchoo@uwaterloo.ca) Chris Eliasmith (celiasmith@uwaterloo.ca) Centre
Stimulation of the Subthalamic Nucleus Changes the Firing Pattern of Pallidal Neurons
 1916 The Journal of Neuroscience, March 1, 2003 23(5):1916 1923 Stimulation of the Subthalamic Nucleus Changes the Firing Pattern of Pallidal Neurons Takao Hashimoto, 1,2 Christopher M. Elder, 1 Michael
1916 The Journal of Neuroscience, March 1, 2003 23(5):1916 1923 Stimulation of the Subthalamic Nucleus Changes the Firing Pattern of Pallidal Neurons Takao Hashimoto, 1,2 Christopher M. Elder, 1 Michael
Mahan Alavi. A thesis submitted in conformity with the requirements. for the Degree of Master of Science. Graduate Department of Physiology
 SPATIAL EXTENT OF BETA OSCILLATORY ACTIVITY IN AND BETWEEN THE SUBTHALAMIC NUCLEUS AND SUBSTANTIA NIGRA PARS RETICULATA OF PARKINSON S DISEASE PATIENTS by Mahan Alavi A thesis submitted in conformity with
SPATIAL EXTENT OF BETA OSCILLATORY ACTIVITY IN AND BETWEEN THE SUBTHALAMIC NUCLEUS AND SUBSTANTIA NIGRA PARS RETICULATA OF PARKINSON S DISEASE PATIENTS by Mahan Alavi A thesis submitted in conformity with
Whether deep brain stimulation can dramatically. Deep brain stimulation: How does it work?
 JERROLD L. VITEK, MD, PhD Director, Neuromodulation Research Center, Department of Neurosciences, Lerner Research Institute, Cleveland Clinic, Cleveland, OH Deep brain stimulation: How does it work? ABSTRACT
JERROLD L. VITEK, MD, PhD Director, Neuromodulation Research Center, Department of Neurosciences, Lerner Research Institute, Cleveland Clinic, Cleveland, OH Deep brain stimulation: How does it work? ABSTRACT
The motor regulator. 1) Basal ganglia/nucleus
 The motor regulator 1) Basal ganglia/nucleus Neural structures involved in the control of movement Basal Ganglia - Components of the basal ganglia - Function of the basal ganglia - Connection and circuits
The motor regulator 1) Basal ganglia/nucleus Neural structures involved in the control of movement Basal Ganglia - Components of the basal ganglia - Function of the basal ganglia - Connection and circuits
Network effects of subthalamic deep brain stimulation drive a unique mixture of responses in basal ganglia output
 Section: CECN Special Issue Proposed Associate Editor: Tomoki Fukai Network effects of subthalamic deep brain stimulation drive a unique mixture of responses in basal ganglia output Abbreviated title:
Section: CECN Special Issue Proposed Associate Editor: Tomoki Fukai Network effects of subthalamic deep brain stimulation drive a unique mixture of responses in basal ganglia output Abbreviated title:
Bifurcation analysis points towards the source of beta neuronal oscillations in Parkinson s disease
 2011 50th IEEE Conference on Decision and Control and European Control Conference (CDC-ECC) Orlando, FL, USA, December 12-15, 2011 Bifurcation analysis points towards the source of beta neuronal oscillations
2011 50th IEEE Conference on Decision and Control and European Control Conference (CDC-ECC) Orlando, FL, USA, December 12-15, 2011 Bifurcation analysis points towards the source of beta neuronal oscillations
Strick Lecture 4 March 29, 2006 Page 1
 Strick Lecture 4 March 29, 2006 Page 1 Basal Ganglia OUTLINE- I. Structures included in the basal ganglia II. III. IV. Skeleton diagram of Basal Ganglia Loops with cortex Similarity with Cerebellar Loops
Strick Lecture 4 March 29, 2006 Page 1 Basal Ganglia OUTLINE- I. Structures included in the basal ganglia II. III. IV. Skeleton diagram of Basal Ganglia Loops with cortex Similarity with Cerebellar Loops
Effects of Apomorphine on Subthalamic Nucleus and Globus Pallidus Internus Neurons in Patients With Parkinson s Disease
 Effects of Apomorphine on Subthalamic Nucleus and Globus Pallidus Internus Neurons in Patients With Parkinson s Disease R. LEVY, 1 J. O. DOSTROVSKY, 1,3 A. E. LANG, 3,4 E. SIME, 3 W. D. HUTCHISON, 1 3
Effects of Apomorphine on Subthalamic Nucleus and Globus Pallidus Internus Neurons in Patients With Parkinson s Disease R. LEVY, 1 J. O. DOSTROVSKY, 1,3 A. E. LANG, 3,4 E. SIME, 3 W. D. HUTCHISON, 1 3
Embryological origin of thalamus
 diencephalon Embryological origin of thalamus The diencephalon gives rise to the: Thalamus Epithalamus (pineal gland, habenula, paraventricular n.) Hypothalamus Subthalamus (Subthalamic nuclei) The Thalamus:
diencephalon Embryological origin of thalamus The diencephalon gives rise to the: Thalamus Epithalamus (pineal gland, habenula, paraventricular n.) Hypothalamus Subthalamus (Subthalamic nuclei) The Thalamus:
This manuscript version is distributed under the CC-BY-NC-ND (Creative Commons) license.
 This manuscript version is distributed under the CC-BY-NC-ND (Creative Commons) license. It has appeared in final form as: Van Albada SJ, Gray RT, Drysdale PM, Robinson PA. Mean-field modeling of the basal
This manuscript version is distributed under the CC-BY-NC-ND (Creative Commons) license. It has appeared in final form as: Van Albada SJ, Gray RT, Drysdale PM, Robinson PA. Mean-field modeling of the basal
Basal ganglia activity patterns in parkinsonism and computational modeling of their downstream effects
 Basal ganglia activity patterns in parkinsonism and computational modeling of their downstream effects Jonathan E. Rubin, University of Pittsburgh Cameron C. McIntyre, Cleveland Clinic Robert S Turner,
Basal ganglia activity patterns in parkinsonism and computational modeling of their downstream effects Jonathan E. Rubin, University of Pittsburgh Cameron C. McIntyre, Cleveland Clinic Robert S Turner,
Basal Ganglia. Today s lecture is about Basal Ganglia and it covers:
 Basal Ganglia Motor system is complex interaction between Lower motor neurons (spinal cord and brainstem circuits) and Upper motor neurons (pyramidal and extrapyramidal tracts) plus two main regulators
Basal Ganglia Motor system is complex interaction between Lower motor neurons (spinal cord and brainstem circuits) and Upper motor neurons (pyramidal and extrapyramidal tracts) plus two main regulators
Deep brain stimulation
 Cell Tissue Res (2004) 318: 275 288 DOI 10.1007/s00441-004-0936-0 REVIEW Sorin Breit. Jörg B. Schulz. Alim-Louis Benabid Deep brain stimulation Received: 30 January 2004 / Accepted: 1 June 2004 / Published
Cell Tissue Res (2004) 318: 275 288 DOI 10.1007/s00441-004-0936-0 REVIEW Sorin Breit. Jörg B. Schulz. Alim-Louis Benabid Deep brain stimulation Received: 30 January 2004 / Accepted: 1 June 2004 / Published
High-frequency stimulation produces a transient blockade of voltage-gated currents in subthalamic neurons.
 High-frequency stimulation produces a transient blockade of voltage-gated currents in subthalamic neurons. Corinne Beurrier, Bernard Bioulac, Jacques Audin, Constance Hammond To cite this version: Corinne
High-frequency stimulation produces a transient blockade of voltage-gated currents in subthalamic neurons. Corinne Beurrier, Bernard Bioulac, Jacques Audin, Constance Hammond To cite this version: Corinne
Basal Ganglia Anatomy, Physiology, and Function. NS201c
 Basal Ganglia Anatomy, Physiology, and Function NS201c Human Basal Ganglia Anatomy Basal Ganglia Circuits: The Classical Model of Direct and Indirect Pathway Function Motor Cortex Premotor Cortex + Glutamate
Basal Ganglia Anatomy, Physiology, and Function NS201c Human Basal Ganglia Anatomy Basal Ganglia Circuits: The Classical Model of Direct and Indirect Pathway Function Motor Cortex Premotor Cortex + Glutamate
Membrane Channel Interactions Underlying Rat Subthalamic Projection Neuron Rhythmic and Bursting Activity
 J Neurophysiol 95: 2352 2365, 2006. First published September 7, 2005; doi:10.1152/jn.00525.2005. Membrane Channel Interactions Underlying Rat Subthalamic Projection Neuron Rhythmic and Bursting Activity
J Neurophysiol 95: 2352 2365, 2006. First published September 7, 2005; doi:10.1152/jn.00525.2005. Membrane Channel Interactions Underlying Rat Subthalamic Projection Neuron Rhythmic and Bursting Activity
Basal Ganglia General Info
 Basal Ganglia General Info Neural clusters in peripheral nervous system are ganglia. In the central nervous system, they are called nuclei. Should be called Basal Nuclei but usually called Basal Ganglia.
Basal Ganglia General Info Neural clusters in peripheral nervous system are ganglia. In the central nervous system, they are called nuclei. Should be called Basal Nuclei but usually called Basal Ganglia.
We are IntechOpen, the world s leading publisher of Open Access books Built by scientists, for scientists. International authors and editors
 We are IntechOpen, the world s leading publisher of Open Access books Built by scientists, for scientists 4,100 116,000 120M Open access books available International authors and editors Downloads Our
We are IntechOpen, the world s leading publisher of Open Access books Built by scientists, for scientists 4,100 116,000 120M Open access books available International authors and editors Downloads Our
An Interactive Channel Model of the Basal Ganglia: Bifurcation Analysis Under Healthy and Parkinsonian Conditions
 Journal of Mathematical Neuroscience (2013) 3:14 DOI 10.1186/2190-8567-3-14 RESEARCH OpenAccess An Interactive Channel Model of the Basal Ganglia: Bifurcation Analysis Under Healthy and Parkinsonian Conditions
Journal of Mathematical Neuroscience (2013) 3:14 DOI 10.1186/2190-8567-3-14 RESEARCH OpenAccess An Interactive Channel Model of the Basal Ganglia: Bifurcation Analysis Under Healthy and Parkinsonian Conditions
The oscillatory activity in the Parkinsonian subthalamic nucleus investigated using the macro-electrodes for deep brain stimulation
 Clinical Neurophysiology 113 (2002) 1 6 www.elsevier.com/locate/clinph The oscillatory activity in the Parkinsonian subthalamic nucleus investigated using the macro-electrodes for deep brain stimulation
Clinical Neurophysiology 113 (2002) 1 6 www.elsevier.com/locate/clinph The oscillatory activity in the Parkinsonian subthalamic nucleus investigated using the macro-electrodes for deep brain stimulation
STRUCTURE AND CIRCUITS OF THE BASAL GANGLIA
 STRUCTURE AND CIRCUITS OF THE BASAL GANGLIA Rastislav Druga Department of Anatomy, Second Faculty of Medicine 2017 Basal ganglia Nucleus caudatus, putamen, globus pallidus (medialis et lateralis), ncl.
STRUCTURE AND CIRCUITS OF THE BASAL GANGLIA Rastislav Druga Department of Anatomy, Second Faculty of Medicine 2017 Basal ganglia Nucleus caudatus, putamen, globus pallidus (medialis et lateralis), ncl.
Deranged NMDAergic cortico-subthalamic transmission underlies parkinsonian motor deficits
 The Journal of Clinical Investigation Deranged NMDAergic cortico-subthalamic transmission underlies parkinsonian motor deficits Ming-Kai Pan, 1,2,3 Chun-Hwei Tai, 2 Wen-Chuan Liu, 2 Ju-Chun Pei, 4 Wen-Sung
The Journal of Clinical Investigation Deranged NMDAergic cortico-subthalamic transmission underlies parkinsonian motor deficits Ming-Kai Pan, 1,2,3 Chun-Hwei Tai, 2 Wen-Chuan Liu, 2 Ju-Chun Pei, 4 Wen-Sung
Visualization and simulated animations of pathology and symptoms of Parkinson s disease
 Visualization and simulated animations of pathology and symptoms of Parkinson s disease Prof. Yifan HAN Email: bctycan@ust.hk 1. Introduction 2. Biochemistry of Parkinson s disease 3. Course Design 4.
Visualization and simulated animations of pathology and symptoms of Parkinson s disease Prof. Yifan HAN Email: bctycan@ust.hk 1. Introduction 2. Biochemistry of Parkinson s disease 3. Course Design 4.
Short-Term Plasticity Shapes the Response to Simulated Normal and Parkinsonian Input Patterns in the Globus Pallidus
 The Journal of Neuroscience, June 15, 2002, 22(12):5164 5172 Short-Term Plasticity Shapes the Response to Simulated Normal and Parkinsonian Input Patterns in the Globus Pallidus Jesse E. Hanson and Dieter
The Journal of Neuroscience, June 15, 2002, 22(12):5164 5172 Short-Term Plasticity Shapes the Response to Simulated Normal and Parkinsonian Input Patterns in the Globus Pallidus Jesse E. Hanson and Dieter
Relationships between the Prefrontal Cortex and the Basal Ganglia in the Rat: Physiology of the Cortico-Nigral Circuits
 The Journal of Neuroscience, June 1, 1999, 19(11):4674 4681 Relationships between the Prefrontal Cortex and the Basal Ganglia in the Rat: Physiology of the Cortico-Nigral Circuits Nicolas Maurice, 1 Jean-Michel
The Journal of Neuroscience, June 1, 1999, 19(11):4674 4681 Relationships between the Prefrontal Cortex and the Basal Ganglia in the Rat: Physiology of the Cortico-Nigral Circuits Nicolas Maurice, 1 Jean-Michel
Gangli della Base: un network multifunzionale
 Gangli della Base: un network multifunzionale Prof. Giovanni Abbruzzese Centro per la Malattia di Parkinson e i Disordini del Movimento DiNOGMI, Università di Genova IRCCS AOU San Martino IST Basal Ganglia
Gangli della Base: un network multifunzionale Prof. Giovanni Abbruzzese Centro per la Malattia di Parkinson e i Disordini del Movimento DiNOGMI, Università di Genova IRCCS AOU San Martino IST Basal Ganglia
Supplementary Information for Decreased activity of single subthalamic nucleus neurons in Parkinson patients responding to placebo
 Supplementary Information for Decreased activity of single subthalamic nucleus neurons in Parkinson patients responding to placebo Fabrizio Benedetti, 1,2 Luana Colloca, 1,2 Elena Torre, 1 Michele Lanotte,
Supplementary Information for Decreased activity of single subthalamic nucleus neurons in Parkinson patients responding to placebo Fabrizio Benedetti, 1,2 Luana Colloca, 1,2 Elena Torre, 1 Michele Lanotte,
The basal ganglia (BG) are a group of nuclei located subcortically
 The Basal Ganglia and Disorders of Movement: Pathophysiological Mechanisms José A. Obeso, 1 María C. Rodríguez-Oroz, 1 Manuel Rodríguez, 4 Javier Arbizu, 2 and José M. Giménez-Amaya 3 Departments of 1
The Basal Ganglia and Disorders of Movement: Pathophysiological Mechanisms José A. Obeso, 1 María C. Rodríguez-Oroz, 1 Manuel Rodríguez, 4 Javier Arbizu, 2 and José M. Giménez-Amaya 3 Departments of 1
Motor System Hierarchy
 Motor Pathways Lectures Objectives Define the terms upper and lower motor neurons with examples. Describe the corticospinal (pyramidal) tract and the direct motor pathways from the cortex to the trunk
Motor Pathways Lectures Objectives Define the terms upper and lower motor neurons with examples. Describe the corticospinal (pyramidal) tract and the direct motor pathways from the cortex to the trunk
Deep Brain Stimulation: Surgical Process
 Deep Brain Stimulation: Surgical Process Kia Shahlaie, MD, PhD Assistant Professor Bronte Endowed Chair in Epilepsy Research Director of Functional Neurosurgery Minimally Invasive Neurosurgery Department
Deep Brain Stimulation: Surgical Process Kia Shahlaie, MD, PhD Assistant Professor Bronte Endowed Chair in Epilepsy Research Director of Functional Neurosurgery Minimally Invasive Neurosurgery Department
The Basal Ganglia and Motor Control
 NEURAL PLASTICITY VOLUME 10, NO. 1-2, 2003 The Basal Ganglia and Motor Control Henk J. Groenewegen Department ofanatomy, Research Institute Neurosciences Vrije Universiteit, Medical Center, Amsterdam,
NEURAL PLASTICITY VOLUME 10, NO. 1-2, 2003 The Basal Ganglia and Motor Control Henk J. Groenewegen Department ofanatomy, Research Institute Neurosciences Vrije Universiteit, Medical Center, Amsterdam,
Parkinsonism or Parkinson s Disease I. Symptoms: Main disorder of movement. Named after, an English physician who described the then known, in 1817.
 Parkinsonism or Parkinson s Disease I. Symptoms: Main disorder of movement. Named after, an English physician who described the then known, in 1817. Four (4) hallmark clinical signs: 1) Tremor: (Note -
Parkinsonism or Parkinson s Disease I. Symptoms: Main disorder of movement. Named after, an English physician who described the then known, in 1817. Four (4) hallmark clinical signs: 1) Tremor: (Note -
Afferent Control of Nigral Dopaminergic Neurons The Role of GABAergic Inputs
 In: Graybiel, A.M. et al., (Eds.) The Basal Ganglia VI, Kluwer Academic Publishers, Norwell, 2002 pp 641-651 Afferent Control of Nigral Dopaminergic Neurons The Role of GABAergic Inputs James M. Tepper,
In: Graybiel, A.M. et al., (Eds.) The Basal Ganglia VI, Kluwer Academic Publishers, Norwell, 2002 pp 641-651 Afferent Control of Nigral Dopaminergic Neurons The Role of GABAergic Inputs James M. Tepper,
Lecture XIII. Brain Diseases I - Parkinsonism! Brain Diseases I!
 Lecture XIII. Brain Diseases I - Parkinsonism! Bio 3411! Wednesday!! Lecture XIII. Brain Diseases - I.! 1! Brain Diseases I! NEUROSCIENCE 5 th ed! Page!!Figure!!Feature! 408 18.9 A!!Substantia Nigra in
Lecture XIII. Brain Diseases I - Parkinsonism! Bio 3411! Wednesday!! Lecture XIII. Brain Diseases - I.! 1! Brain Diseases I! NEUROSCIENCE 5 th ed! Page!!Figure!!Feature! 408 18.9 A!!Substantia Nigra in
The Basal Ganglia in Parkinson s Disease: Current Concepts and Unexplained Observations
 The Basal Ganglia in Parkinson s Disease: Current Concepts and Unexplained Observations Jose A. Obeso, PhD, MD, 1,2 Concepcio Marin, PhD, MD, 2,3 C. Rodriguez-Oroz, PhD, MD, 1,2 Javier Blesa, 1,2 B. Benitez-Temiño,
The Basal Ganglia in Parkinson s Disease: Current Concepts and Unexplained Observations Jose A. Obeso, PhD, MD, 1,2 Concepcio Marin, PhD, MD, 2,3 C. Rodriguez-Oroz, PhD, MD, 1,2 Javier Blesa, 1,2 B. Benitez-Temiño,
Mechanisms of Deep Brain Stimulation in Movement Disorders as Revealed by Changes in Stimulus Frequency
 Neurotherapeutics: The Journal of the American Society for Experimental NeuroTherapeutics Mechanisms of Deep Brain Stimulation in Movement Disorders as Revealed by Changes in Stimulus Frequency Merrill
Neurotherapeutics: The Journal of the American Society for Experimental NeuroTherapeutics Mechanisms of Deep Brain Stimulation in Movement Disorders as Revealed by Changes in Stimulus Frequency Merrill
The Response of Subthalamic Nucleus Neurons to Dopamine Receptor Stimulation in a Rodent Model of Parkinson s Disease
 The Journal of Neuroscience, September 1, 1997, 17(17):6807 6819 The Response of Subthalamic Nucleus Neurons to Dopamine Receptor Stimulation in a Rodent Model of Parkinson s Disease Deborah S. Kreiss,
The Journal of Neuroscience, September 1, 1997, 17(17):6807 6819 The Response of Subthalamic Nucleus Neurons to Dopamine Receptor Stimulation in a Rodent Model of Parkinson s Disease Deborah S. Kreiss,
Chapter 8. Control of movement
 Chapter 8 Control of movement 1st Type: Skeletal Muscle Skeletal Muscle: Ones that moves us Muscles contract, limb flex Flexion: a movement of a limb that tends to bend its joints, contraction of a flexor
Chapter 8 Control of movement 1st Type: Skeletal Muscle Skeletal Muscle: Ones that moves us Muscles contract, limb flex Flexion: a movement of a limb that tends to bend its joints, contraction of a flexor
Neurodegenerative Disease. April 12, Cunningham. Department of Neurosciences
 Neurodegenerative Disease April 12, 2017 Cunningham Department of Neurosciences NEURODEGENERATIVE DISEASE Any of a group of hereditary and sporadic conditions characterized by progressive dysfunction,
Neurodegenerative Disease April 12, 2017 Cunningham Department of Neurosciences NEURODEGENERATIVE DISEASE Any of a group of hereditary and sporadic conditions characterized by progressive dysfunction,
Microelectrode recording: lead point in STN-DBS surgery
 Acta Neurochir Suppl (2006) 99: 37 42 # Springer-Verlag 2006 Printed in Austria Microelectrode recording: lead point in STN-DBS surgery M. S. Kim 1, Y. T. Jung 1, J. H. Sim 1,S.J.Kim 2, J. W. Kim 3, and
Acta Neurochir Suppl (2006) 99: 37 42 # Springer-Verlag 2006 Printed in Austria Microelectrode recording: lead point in STN-DBS surgery M. S. Kim 1, Y. T. Jung 1, J. H. Sim 1,S.J.Kim 2, J. W. Kim 3, and
Basal Nuclei (Ganglia)
 Doctor said he will not go deep within these slides because we will take them in physiology, so he will explain the anatomical structures, and he will go faster in the functions sheet in yellow Basal Nuclei
Doctor said he will not go deep within these slides because we will take them in physiology, so he will explain the anatomical structures, and he will go faster in the functions sheet in yellow Basal Nuclei
Timing and direction selectivity of subthalamic and pallidal neurons in patients with Parkinson disease
 Exp Brain Res (2005) 162: 407 416 DOI 10.1007/s00221-004-2035-6 RESEARCH ARTICLE Ziv M. Williams Æ Joseph S. Neimat G. Rees Cosgrove Æ Emad N. Eskandar Timing and direction selectivity of subthalamic and
Exp Brain Res (2005) 162: 407 416 DOI 10.1007/s00221-004-2035-6 RESEARCH ARTICLE Ziv M. Williams Æ Joseph S. Neimat G. Rees Cosgrove Æ Emad N. Eskandar Timing and direction selectivity of subthalamic and
Park Yong Sook. Department of Medicine The Graduate School, Yonsei University
 Lesion of subthalamic nucleus in Parkinsonian rats: Effects of dopamine D1 and D2 receptor agonists on the neuronal activities of the substantia nigra pars reticulata Park Yong Sook Department of Medicine
Lesion of subthalamic nucleus in Parkinsonian rats: Effects of dopamine D1 and D2 receptor agonists on the neuronal activities of the substantia nigra pars reticulata Park Yong Sook Department of Medicine
UNIVERSITY OF JORDAN FACULTY OF MEDICINE DEPARTMENT OF PHYSIOLOGY & BIOCHEMISTRY NEUROPHYSIOLOGY (MEDICAL) Spring, 2014
 UNIVERSITY OF JORDAN FACULTY OF MEDICINE DEPARTMENT OF PHYSIOLOGY & BIOCHEMISTRY NEUROPHYSIOLOGY (MEDICAL) Spring, 2014 Textbook of Medical Physiology by: Guyton & Hall, 11 th edition 2006 Eman Al-Khateeb,
UNIVERSITY OF JORDAN FACULTY OF MEDICINE DEPARTMENT OF PHYSIOLOGY & BIOCHEMISTRY NEUROPHYSIOLOGY (MEDICAL) Spring, 2014 Textbook of Medical Physiology by: Guyton & Hall, 11 th edition 2006 Eman Al-Khateeb,
Neurobiology of Disease. Bertrand Degos, 1 Jean-Michel Deniau, 1 Anne-Marie Thierry, 2 Jacques Glowinski, 2 Laurent Pezard, 3 and Nicolas Maurice 1 1
 The Journal of Neuroscience, August 17, 2005 25(33):7687 7696 7687 Neurobiology of Disease Neuroleptic-Induced Catalepsy: Electrophysiological Mechanisms of Functional Recovery Induced by High- Frequency
The Journal of Neuroscience, August 17, 2005 25(33):7687 7696 7687 Neurobiology of Disease Neuroleptic-Induced Catalepsy: Electrophysiological Mechanisms of Functional Recovery Induced by High- Frequency
Beta and Tremor-Related Oscillations in the Motor Thalamus of Essential Tremor Patients
 IETF - WD Hutchison Feb 214 requesting $25, Beta and Tremor-Related Oscillations in the Motor Thalamus of Essential Tremor Patients 1. Specific aims of proposal The proposed study will examine beta oscillations
IETF - WD Hutchison Feb 214 requesting $25, Beta and Tremor-Related Oscillations in the Motor Thalamus of Essential Tremor Patients 1. Specific aims of proposal The proposed study will examine beta oscillations
For more information about how to cite these materials visit
 Author(s): Peter Hitchcock, PH.D., 2009 License: Unless otherwise noted, this material is made available under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Non-commercial Share Alike 3.0 License: http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-sa/3.0/
Author(s): Peter Hitchcock, PH.D., 2009 License: Unless otherwise noted, this material is made available under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Non-commercial Share Alike 3.0 License: http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-sa/3.0/
The control of spiking by synaptic input in striatal and pallidal neurons
 The control of spiking by synaptic input in striatal and pallidal neurons Dieter Jaeger Department of Biology, Emory University, Atlanta, GA 30322 Key words: Abstract: rat, slice, whole cell, dynamic current
The control of spiking by synaptic input in striatal and pallidal neurons Dieter Jaeger Department of Biology, Emory University, Atlanta, GA 30322 Key words: Abstract: rat, slice, whole cell, dynamic current
NEURAL CONTROL OF MOVEMENT: ENGINEERING THE RHYTHMS OF THE BRAIN
 NEURAL CONTROL OF MOVEMENT: ENGINEERING THE RHYTHMS OF THE BRAIN Madeleine Lowery School of Electrical and Electronic Engineering Centre for Biomedical Engineering University College Dublin Parkinson s
NEURAL CONTROL OF MOVEMENT: ENGINEERING THE RHYTHMS OF THE BRAIN Madeleine Lowery School of Electrical and Electronic Engineering Centre for Biomedical Engineering University College Dublin Parkinson s
Functional Neuroanatomy and Physiology for Movement Disorders
 Functional Neuroanatomy and Physiology for Movement Disorders Chang, Won Seok Division of Stereotactic and Functional Neurosurgery, Department of Neurosurgery, Brain Research Institute, Yonsei University
Functional Neuroanatomy and Physiology for Movement Disorders Chang, Won Seok Division of Stereotactic and Functional Neurosurgery, Department of Neurosurgery, Brain Research Institute, Yonsei University
SYSTEMS NEUROSCIENCE. Rachida Ammari 1,2,3, Bernard Bioulac 3,4, Liliana Garcia 3,4 and Constance Hammond 1,2 *
 SYSTEMS NEUROSCIENCE Original Research Article published: 13 June 211 doi: 1.3389/fnsys.211.43 The subthalamic nucleus becomes a generator of bursts in the dopamine-depleted state. Its high frequency stimulation
SYSTEMS NEUROSCIENCE Original Research Article published: 13 June 211 doi: 1.3389/fnsys.211.43 The subthalamic nucleus becomes a generator of bursts in the dopamine-depleted state. Its high frequency stimulation
This is a repository copy of Basal Ganglia. White Rose Research Online URL for this paper:
 This is a repository copy of. White Rose Research Online URL for this paper: http://eprints.whiterose.ac.uk/114159/ Version: Accepted Version Book Section: Prescott, A.J. orcid.org/0000-0003-4927-5390,
This is a repository copy of. White Rose Research Online URL for this paper: http://eprints.whiterose.ac.uk/114159/ Version: Accepted Version Book Section: Prescott, A.J. orcid.org/0000-0003-4927-5390,
Deep Brain Stimulation: Patient selection
 Deep Brain Stimulation: Patient selection Halim Fadil, MD Movement Disorders Neurologist Kane Hall Barry Neurology Bedford/Keller, TX 1991: Thalamic (Vim) DBS for tremor Benabid AL, et al. Lancet. 1991;337(8738):403-406.
Deep Brain Stimulation: Patient selection Halim Fadil, MD Movement Disorders Neurologist Kane Hall Barry Neurology Bedford/Keller, TX 1991: Thalamic (Vim) DBS for tremor Benabid AL, et al. Lancet. 1991;337(8738):403-406.
Basal ganglia output to the thalamus: still a paradox
 Basal ganglia output to the thalamus: still a paradox The MIT Faculty has made this article openly available. Please share how this access benefits you. Your story matters. Citation As Published Publisher
Basal ganglia output to the thalamus: still a paradox The MIT Faculty has made this article openly available. Please share how this access benefits you. Your story matters. Citation As Published Publisher
SYNAPTIC PLASTICITY IN BASAL GANGLIA OUTPUT NEURONS IN PARKINSON S DISEASE PATIENTS
 SYNAPTIC PLASTICITY IN BASAL GANGLIA OUTPUT NEURONS IN PARKINSON S DISEASE PATIENTS by Ian A. Prescott A thesis submitted in conformity with the requirements for the degree of Master of Science Graduate
SYNAPTIC PLASTICITY IN BASAL GANGLIA OUTPUT NEURONS IN PARKINSON S DISEASE PATIENTS by Ian A. Prescott A thesis submitted in conformity with the requirements for the degree of Master of Science Graduate
DBS efficacia, complicanze in cronico e nuovi orizzonti terapeutici
 DBS efficacia, complicanze in cronico e nuovi orizzonti terapeutici TECNICHE DI NEUROMODULAZIONE Invasiva: odeep Brain Stimulation Non Invasiva: o Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation (TMS) o Transcranial
DBS efficacia, complicanze in cronico e nuovi orizzonti terapeutici TECNICHE DI NEUROMODULAZIONE Invasiva: odeep Brain Stimulation Non Invasiva: o Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation (TMS) o Transcranial
Dr. Farah Nabil Abbas. MBChB, MSc, PhD
 Dr. Farah Nabil Abbas MBChB, MSc, PhD The Basal Ganglia *Functions in association with motor cortex and corticospinal pathways. *Regarded as accessory motor system besides cerebellum. *Receive most of
Dr. Farah Nabil Abbas MBChB, MSc, PhD The Basal Ganglia *Functions in association with motor cortex and corticospinal pathways. *Regarded as accessory motor system besides cerebellum. *Receive most of
COGNITIVE SCIENCE 107A. Sensory Physiology and the Thalamus. Jaime A. Pineda, Ph.D.
 COGNITIVE SCIENCE 107A Sensory Physiology and the Thalamus Jaime A. Pineda, Ph.D. Sensory Physiology Energies (light, sound, sensation, smell, taste) Pre neural apparatus (collects, filters, amplifies)
COGNITIVE SCIENCE 107A Sensory Physiology and the Thalamus Jaime A. Pineda, Ph.D. Sensory Physiology Energies (light, sound, sensation, smell, taste) Pre neural apparatus (collects, filters, amplifies)
Modulation of subthalamic T-type Ca 2+ channels remedies locomotor deficits in a rat model of Parkinson disease
 Research article Modulation of subthalamic T-type Ca 2+ channels remedies locomotor deficits in a rat model of Parkinson disease Chun-Hwei Tai, 1,2 Ya-Chin Yang, 3,4 Ming-Kai Pan, 1,2 Chen-Syuan Huang,
Research article Modulation of subthalamic T-type Ca 2+ channels remedies locomotor deficits in a rat model of Parkinson disease Chun-Hwei Tai, 1,2 Ya-Chin Yang, 3,4 Ming-Kai Pan, 1,2 Chen-Syuan Huang,
BASAL GANGLIA. Dr JAMILA EL MEDANY
 BASAL GANGLIA Dr JAMILA EL MEDANY OBJECTIVES At the end of the lecture, the student should be able to: Define basal ganglia and enumerate its components. Enumerate parts of Corpus Striatum and their important
BASAL GANGLIA Dr JAMILA EL MEDANY OBJECTIVES At the end of the lecture, the student should be able to: Define basal ganglia and enumerate its components. Enumerate parts of Corpus Striatum and their important
arxiv: v1 [math.fa] 18 Jun 2009
![arxiv: v1 [math.fa] 18 Jun 2009 arxiv: v1 [math.fa] 18 Jun 2009](/thumbs/93/111682225.jpg) Averaging Transformations of Synaptic Potentials on Networks H. R. Noori,a arxiv:0906.3404v1 [math.fa] 18 Jun 2009 Abstract a Interdisciplinary Center for Scientific Computing, University of Heidelberg,
Averaging Transformations of Synaptic Potentials on Networks H. R. Noori,a arxiv:0906.3404v1 [math.fa] 18 Jun 2009 Abstract a Interdisciplinary Center for Scientific Computing, University of Heidelberg,
Synchronizing activity of basal ganglia and pathophysiology of Parkinson s disease
 JNT-Suppl 70-0/5 For Author s Correction Only J Neural Transm (2006) [Suppl] 70: 1 4 # Springer-Verlag 2006 Synchronizing activity of basal ganglia and pathophysiology of Parkinson s disease G. Heimer
JNT-Suppl 70-0/5 For Author s Correction Only J Neural Transm (2006) [Suppl] 70: 1 4 # Springer-Verlag 2006 Synchronizing activity of basal ganglia and pathophysiology of Parkinson s disease G. Heimer
Biological Bases of Behavior. 8: Control of Movement
 Biological Bases of Behavior 8: Control of Movement m d Skeletal Muscle Movements of our body are accomplished by contraction of the skeletal muscles Flexion: contraction of a flexor muscle draws in a
Biological Bases of Behavior 8: Control of Movement m d Skeletal Muscle Movements of our body are accomplished by contraction of the skeletal muscles Flexion: contraction of a flexor muscle draws in a
Hold Your Horses: A Dynamic Computational Role for the Subthalamic Nucleus in Decision Making
 Frank 1 Hold Your Horses: A Dynamic Computational Role for the Subthalamic Nucleus in Decision Making Michael J. Frank Dept of Psychology and Program in Neuroscience University of Arizona 1503 E University
Frank 1 Hold Your Horses: A Dynamic Computational Role for the Subthalamic Nucleus in Decision Making Michael J. Frank Dept of Psychology and Program in Neuroscience University of Arizona 1503 E University
Lecture : Basal ganglia & Cerebellum By : Zaid Al-Ghnaneem
 Lecture : Basal ganglia & Cerebellum By : Zaid Al-Ghnaneem Some notes in the beginning : #1 : there is a slides file contains the sheet info as notes for those who love slides more than word papers. #2
Lecture : Basal ganglia & Cerebellum By : Zaid Al-Ghnaneem Some notes in the beginning : #1 : there is a slides file contains the sheet info as notes for those who love slides more than word papers. #2
Deep Brain Stimulation Surgery for Parkinson s Disease
 Deep Brain Stimulation Surgery for Parkinson s Disease Demystifying Medicine 24 January 2012 Kareem A. Zaghloul, MD, PhD Staff Physician, Surgical Neurology Branch NINDS Surgery for Parkinson s Disease
Deep Brain Stimulation Surgery for Parkinson s Disease Demystifying Medicine 24 January 2012 Kareem A. Zaghloul, MD, PhD Staff Physician, Surgical Neurology Branch NINDS Surgery for Parkinson s Disease
Cholinergic modulation of midbrain dopaminergic systems
 available at www.sciencedirect.com www.elsevier.com/locate/brainresrev Review Cholinergic modulation of midbrain dopaminergic systems J. Mena-Segovia a,, P. Winn b, J.P. Bolam a a MRC Anatomical Neuropharmacology
available at www.sciencedirect.com www.elsevier.com/locate/brainresrev Review Cholinergic modulation of midbrain dopaminergic systems J. Mena-Segovia a,, P. Winn b, J.P. Bolam a a MRC Anatomical Neuropharmacology
Subthalamic Nucleus Neurons Switch from Single-Spike Activity to Burst-Firing Mode
 The Journal of Neuroscience, January 15, 1999, 19(2):599 609 Subthalamic Nucleus Neurons Switch from Single-Spike Activity to Burst-Firing Mode Corinne Beurrier, 1 Patrice Congar, 2 Bernard Bioulac, 1
The Journal of Neuroscience, January 15, 1999, 19(2):599 609 Subthalamic Nucleus Neurons Switch from Single-Spike Activity to Burst-Firing Mode Corinne Beurrier, 1 Patrice Congar, 2 Bernard Bioulac, 1
