The motor regulator. 1) Basal ganglia/nucleus
|
|
|
- Matthew Sharp
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 The motor regulator 1) Basal ganglia/nucleus
2 Neural structures involved in the control of movement
3 Basal Ganglia - Components of the basal ganglia - Function of the basal ganglia - Connection and circuits - Functional circuitry of the basal ganglia e.g., direct and indirect pathways, transmitters - Symptoms and disorders discussed
4 Parts
5 Atlas Fig. 6-37
6 Atlas Fig. 6-36
7 Atlas Fig. 6-35
8 Atlas Fig. 6-34
9
10 Atlas Fig. 6-32
11 Atlas Fig. 6-32
12 Function of the basal ganglia
13 Direct = Dark grey Red Blue Light grey Indirect = Dark grey Green Blue Light grey Text Fig. 26-9
14 Medium spiny neuron projections
15 Neurons of the basal ganglia
16 Connections and circuits
17 Connections and circuits
18 Motor Loop
19 Visuomotor Loop
20 Executive Loop Dorsomedial
21 Motivational Loop
22 Functional loops
23 Text Fig A,B
24 _ + + Text Fig A,B
25 Text Fig C,D
26 + + _ + Text Fig C,D +
27 Modulators (associated nuclei)
28 Modulators (associated nuclei) - Subthalamic Nucleus????? - Nigral Complex - Parabrachial Pontine Reticular Formation - Zona inserta - Ventral Basal Nuclei
29 Modulators (associated nuclei) - Subthalamic Nucleus????? - Nigral Complex - Parabrachial Pontine Reticular Formation - Zona inserta - Ventral Basal Nuclei
30 Nigral modulation glu R EPSP DA Direct transmission
31 Direct transmission vs. modulation glu DA Almost No direct effect of DA
32 Direct transmission vs. modulation Striatal medium spiny neuron glu R enhanced or diminished response DA D1-Rs in the direct pathway: 1) increase GluR phosphorylation 2) alters ionic conductances to amplify cortical input Modulation
33 Direct transmission vs. modulation Striatal medium spiny neuron glu R enhanced or diminished response DA D2-Rs in the indirect pathway: 1) increase GluR phosphorylation 2) alters ionic conductances to dampen cortical input Modulation
34 Direct and Indirect Pathways (Including the Substantia Nigra Text Fig A,B
35 Motor behavior is determined by the balance between direct/indirect striatal outputs Hypokinetic disorders insufficient direct pathway output excess indirect pathway output
36 Corticostriatial Striatopallidal Pallidothalammic Thalamocortical Corticospinal, Corticonuclear Text Fig A,B
37 Text Fig A,B
38 Motor behavior is determined by the balance between direct/indirect striatal outputs Hypokinetic disorders insufficient direct pathway output excess indirect pathway output Hyperkinetic disorders excess direct pathway output insufficient indirect pathway output
39 Corticostriatal, Corticosubthalamic Striatopallidal Pallidosubthalamic Subthalamopallidal Pallidothalamic Thalamocortical Corticospinal, Corticonuclear Text Fig C,D
40 Hyperkinetic symptoms (Choreatic symptoms) Involuntary (unwanted) movements Chorea (dance-like) Ballismus Dystonia (torsion spasm) Athetosis (changeable or writhing movements) Choreoathetosis athetotic dystonia
41 Basal Ganglia disorders
42 Parkinson s disease Michael J. Fox Muhammad Ali Striatum Pathophysiology Primary: loss of nigrostriatal DA projection SNc
43 Human midbrain Parkinson s disease Normal
44 Loss of Dopaminergic Nigral Connections Text Fig C,D
45 Parkinson s disease
46 Parkinson s disease Symptoms Motoric Tremor (~4-5 Hz, resting) Bradykinesia Rigidity Loss of postural reflexes Depression Dementia
47 Parkinson s disease Treatment L-DOPA This is initially effective, but after 5-10 years, 50% of patients develop DOPAinduced dyskinesia.
48 Parkinson s disease L-DOPA Treatment This is initially effective, but after 5-10 years, 50% of patients develop DOPAinduced dyskinesia. Deep brain stimulation The indirect pathway is increased in Parkinson s. This parkinsonian patient has bilateral STN stimulating electrodes: high frequency stimulation inactivates the STN.
49 Parkinson s disease L-DOPA Treatment This is initially effective, but after 5-10 years, 50% of patients develop DOPA-induced dyskinesia. Deep brain stimulation SN or subthalamic nucleus (STN)/ globus pallidus interna (GPi) high frequency stimulation inactivates the STN or GPi.
50 Parkinson s disease L-DOPA Treatment Deep brain stimulation Novel treatments Anti cholinergic, anti AMPA, & A2
51 Hyperkinetic disorders: choreatic syndromes Causes: 1. Huntington s chorea Genetic (autosomal dominant) 2. Dystonia 3. Tardive dyskinesia 4. DOPA-induced dyskinesia 5. Hemiballismus 6. Tourette s syndrome Genetic or idiopathic Chronic neuroleptic use Parkinson s therapy Unilateral vascular accident, typically subthalamic nucleus Excessive D2-subtype DA receptor expression(?)
52 Choreatic symptoms Involuntary (unwanted) movements Chorea (dance-like) Athetosis (changeable or writhing movements) Dystonia (torsion spasm)
53 Hyperkinetic disorders: choreatic syndromes Huntington s disease Dystonia Tardive dyskinesia DOPA-induced dyskinesia Hemiballismus Tourette s syndrome
54 Huntington s disease Pathophysiology Atrophy of striatum Loss of striatal GABAergic neurons Neuropathological sequence start, rostral and medial then caudal and lateral absentmindedness, irritability, depression, clumsiness, and sudden falls. Choreiform
55 Huntington s disease pathology Huntington s Normal
56 Huntington s disease
57 Huntington s disease Choreatic gait Symptoms Early motor signs chorea (brief, involuntary movements) dystonia (abnormal postures) Dystonic movements
58 Huntington s disease Cognitive abnormalities Executive function (complex tasks) Recent and remote memory (poor retrieval) Psychiatric changes Depression Psychosis Later decline Immobility Weight loss Death within years (often from pneumonia)
59 Etiology of Huntington s disease Huntingtin mutation Mutation near 5 end contains >>CAG repeats Produces protein with excess glutamines near NH 2 terminus Why cell death? Not yet certain Excitotoxicity? Glutamate acting via NMDA receptors can kill medium spiny neurons; glutamate antagonists block
60 Hyperkinetic disorders: choreatic syndromes Huntington s disease Cervical dystonia (torticollis) Dystonia Tardive dyskinesia DOPA-induced dyskinesia After botulinum toxin Hemiballismus Tourette s syndrome
61 Hyperkinetic disorders: choreatic syndromes Huntington s disease Dystonia Tardive dyskinesia DOPA-induced dyskinesia Hemiballismus Axial (thoracic and/or lumbar) dystonia Tourette s syndrome
62 Hyperkinetic disorders: choreatic syndromes Huntington s disease Dystonia Tardive dyskinesia DOPA-induced dyskinesia Hemiballismus Tourette s syndrome
63 Hyperkinetic disorders: choreatic syndromes Huntington s disease Dystonia Tardive dyskinesia *DOPA-induced dyskinesia Hemiballismus Tourette s syndrome *50% of PD patients on L-DOPA will develop DOPA dyskinesia
64 Hyperkinetic disorders: choreatic syndromes Huntington s disease Dystonia Tardive dyskinesia DOPA-induced dyskinesia Hemiballismus Tourette s syndrome
65 Hyperkinetic disorders: choreatic syndromes Huntington s disease Dystonia Tardive dyskinesia DOPA-induced dyskinesia Hemiballismus unilateral STN stroke Tourette s syndrome After treatment with the D2-R blocker sulpiride
66 Atlas Fig. 8-33A,B
67 Sydenham Chorea
Basal Ganglia. Today s lecture is about Basal Ganglia and it covers:
 Basal Ganglia Motor system is complex interaction between Lower motor neurons (spinal cord and brainstem circuits) and Upper motor neurons (pyramidal and extrapyramidal tracts) plus two main regulators
Basal Ganglia Motor system is complex interaction between Lower motor neurons (spinal cord and brainstem circuits) and Upper motor neurons (pyramidal and extrapyramidal tracts) plus two main regulators
A. General features of the basal ganglia, one of our 3 major motor control centers:
 Reading: Waxman pp. 141-146 are not very helpful! Computer Resources: HyperBrain, Chapter 12 Dental Neuroanatomy Suzanne S. Stensaas, Ph.D. March 1, 2012 THE BASAL GANGLIA Objectives: 1. What are the main
Reading: Waxman pp. 141-146 are not very helpful! Computer Resources: HyperBrain, Chapter 12 Dental Neuroanatomy Suzanne S. Stensaas, Ph.D. March 1, 2012 THE BASAL GANGLIA Objectives: 1. What are the main
A. General features of the basal ganglia, one of our 3 major motor control centers:
 Reading: Waxman pp. 141-146 are not very helpful! Computer Resources: HyperBrain, Chapter 12 Dental Neuroanatomy Suzanne S. Stensaas, Ph.D. April 22, 2010 THE BASAL GANGLIA Objectives: 1. What are the
Reading: Waxman pp. 141-146 are not very helpful! Computer Resources: HyperBrain, Chapter 12 Dental Neuroanatomy Suzanne S. Stensaas, Ph.D. April 22, 2010 THE BASAL GANGLIA Objectives: 1. What are the
VL VA BASAL GANGLIA. FUNCTIONAl COMPONENTS. Function Component Deficits Start/initiation Basal Ganglia Spontan movements
 BASAL GANGLIA Chris Cohan, Ph.D. Dept. of Pathology/Anat Sci University at Buffalo I) Overview How do Basal Ganglia affect movement Basal ganglia enhance cortical motor activity and facilitate movement.
BASAL GANGLIA Chris Cohan, Ph.D. Dept. of Pathology/Anat Sci University at Buffalo I) Overview How do Basal Ganglia affect movement Basal ganglia enhance cortical motor activity and facilitate movement.
Making Things Happen 2: Motor Disorders
 Making Things Happen 2: Motor Disorders How Your Brain Works Prof. Jan Schnupp wschnupp@cityu.edu.hk HowYourBrainWorks.net On the Menu in This Lecture In the previous lecture we saw how motor cortex and
Making Things Happen 2: Motor Disorders How Your Brain Works Prof. Jan Schnupp wschnupp@cityu.edu.hk HowYourBrainWorks.net On the Menu in This Lecture In the previous lecture we saw how motor cortex and
Connections of basal ganglia
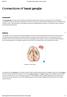 Connections of basal ganglia Introduction The basal ganglia, or basal nuclei, are areas of subcortical grey matter that play a prominent role in modulating movement, as well as cognitive and emotional
Connections of basal ganglia Introduction The basal ganglia, or basal nuclei, are areas of subcortical grey matter that play a prominent role in modulating movement, as well as cognitive and emotional
Basal ganglia Sujata Sofat, class of 2009
 Basal ganglia Sujata Sofat, class of 2009 Basal ganglia Objectives Describe the function of the Basal Ganglia in movement Define the BG components and their locations Describe the motor loop of the BG
Basal ganglia Sujata Sofat, class of 2009 Basal ganglia Objectives Describe the function of the Basal Ganglia in movement Define the BG components and their locations Describe the motor loop of the BG
Basal Ganglia. Steven McLoon Department of Neuroscience University of Minnesota
 Basal Ganglia Steven McLoon Department of Neuroscience University of Minnesota 1 Course News Graduate School Discussion Wednesday, Nov 1, 11:00am MoosT 2-690 with Paul Mermelstein (invite your friends)
Basal Ganglia Steven McLoon Department of Neuroscience University of Minnesota 1 Course News Graduate School Discussion Wednesday, Nov 1, 11:00am MoosT 2-690 with Paul Mermelstein (invite your friends)
神經解剖學 NEUROANATOMY BASAL NUCLEI 盧家鋒助理教授臺北醫學大學醫學系解剖學暨細胞生物學科臺北醫學大學醫學院轉譯影像研究中心.
 神經解剖學 NEUROANATOMY BASAL NUCLEI 盧家鋒助理教授臺北醫學大學醫學系解剖學暨細胞生物學科臺北醫學大學醫學院轉譯影像研究中心 http://www.ym.edu.tw/~cflu OUTLINE Components and Pathways of the Basal Nuclei Functions and Related Disorders of the Basal Nuclei
神經解剖學 NEUROANATOMY BASAL NUCLEI 盧家鋒助理教授臺北醫學大學醫學系解剖學暨細胞生物學科臺北醫學大學醫學院轉譯影像研究中心 http://www.ym.edu.tw/~cflu OUTLINE Components and Pathways of the Basal Nuclei Functions and Related Disorders of the Basal Nuclei
COGNITIVE SCIENCE 107A. Motor Systems: Basal Ganglia. Jaime A. Pineda, Ph.D.
 COGNITIVE SCIENCE 107A Motor Systems: Basal Ganglia Jaime A. Pineda, Ph.D. Two major descending s Pyramidal vs. extrapyramidal Motor cortex Pyramidal system Pathway for voluntary movement Most fibers originate
COGNITIVE SCIENCE 107A Motor Systems: Basal Ganglia Jaime A. Pineda, Ph.D. Two major descending s Pyramidal vs. extrapyramidal Motor cortex Pyramidal system Pathway for voluntary movement Most fibers originate
Damage on one side.. (Notes) Just remember: Unilateral damage to basal ganglia causes contralateral symptoms.
 Lecture 20 - Basal Ganglia Basal Ganglia (Nolte 5 th Ed pp 464) Damage to the basal ganglia produces involuntary movements. Although the basal ganglia do not influence LMN directly (to cause this involuntary
Lecture 20 - Basal Ganglia Basal Ganglia (Nolte 5 th Ed pp 464) Damage to the basal ganglia produces involuntary movements. Although the basal ganglia do not influence LMN directly (to cause this involuntary
Lecture XIII. Brain Diseases I - Parkinsonism! Brain Diseases I!
 Lecture XIII. Brain Diseases I - Parkinsonism! Bio 3411! Wednesday!! Lecture XIII. Brain Diseases - I.! 1! Brain Diseases I! NEUROSCIENCE 5 th ed! Page!!Figure!!Feature! 408 18.9 A!!Substantia Nigra in
Lecture XIII. Brain Diseases I - Parkinsonism! Bio 3411! Wednesday!! Lecture XIII. Brain Diseases - I.! 1! Brain Diseases I! NEUROSCIENCE 5 th ed! Page!!Figure!!Feature! 408 18.9 A!!Substantia Nigra in
Neurodegenerative Disease. April 12, Cunningham. Department of Neurosciences
 Neurodegenerative Disease April 12, 2017 Cunningham Department of Neurosciences NEURODEGENERATIVE DISEASE Any of a group of hereditary and sporadic conditions characterized by progressive dysfunction,
Neurodegenerative Disease April 12, 2017 Cunningham Department of Neurosciences NEURODEGENERATIVE DISEASE Any of a group of hereditary and sporadic conditions characterized by progressive dysfunction,
Basal Ganglia George R. Leichnetz, Ph.D.
 Basal Ganglia George R. Leichnetz, Ph.D. OBJECTIVES 1. To understand the brain structures which constitute the basal ganglia, and their interconnections 2. To understand the consequences (clinical manifestations)
Basal Ganglia George R. Leichnetz, Ph.D. OBJECTIVES 1. To understand the brain structures which constitute the basal ganglia, and their interconnections 2. To understand the consequences (clinical manifestations)
Movement Disorders Will Garrett, M.D Assistant Professor of Neurology
 Movement Disorders Will Garrett, M.D Assistant Professor of Neurology I. The Basal Ganglia The basal ganglia are composed of several structures including the caudate and putamen (collectively called the
Movement Disorders Will Garrett, M.D Assistant Professor of Neurology I. The Basal Ganglia The basal ganglia are composed of several structures including the caudate and putamen (collectively called the
Anatomy of the basal ganglia. Dana Cohen Gonda Brain Research Center, room 410
 Anatomy of the basal ganglia Dana Cohen Gonda Brain Research Center, room 410 danacoh@gmail.com The basal ganglia The nuclei form a small minority of the brain s neuronal population. Little is known about
Anatomy of the basal ganglia Dana Cohen Gonda Brain Research Center, room 410 danacoh@gmail.com The basal ganglia The nuclei form a small minority of the brain s neuronal population. Little is known about
Strick Lecture 4 March 29, 2006 Page 1
 Strick Lecture 4 March 29, 2006 Page 1 Basal Ganglia OUTLINE- I. Structures included in the basal ganglia II. III. IV. Skeleton diagram of Basal Ganglia Loops with cortex Similarity with Cerebellar Loops
Strick Lecture 4 March 29, 2006 Page 1 Basal Ganglia OUTLINE- I. Structures included in the basal ganglia II. III. IV. Skeleton diagram of Basal Ganglia Loops with cortex Similarity with Cerebellar Loops
Teach-SHEET Basal Ganglia
 Teach-SHEET Basal Ganglia Purves D, et al. Neuroscience, 5 th Ed., Sinauer Associates, 2012 Common organizational principles Basic Circuits or Loops: Motor loop concerned with learned movements (scaling
Teach-SHEET Basal Ganglia Purves D, et al. Neuroscience, 5 th Ed., Sinauer Associates, 2012 Common organizational principles Basic Circuits or Loops: Motor loop concerned with learned movements (scaling
GBME graduate course. Chapter 43. The Basal Ganglia
 GBME graduate course Chapter 43. The Basal Ganglia Basal ganglia in history Parkinson s disease Huntington s disease Parkinson s disease 1817 Parkinson's disease (PD) is a degenerative disorder of the
GBME graduate course Chapter 43. The Basal Ganglia Basal ganglia in history Parkinson s disease Huntington s disease Parkinson s disease 1817 Parkinson's disease (PD) is a degenerative disorder of the
UNIVERSITY OF JORDAN FACULTY OF MEDICINE DEPARTMENT OF PHYSIOLOGY & BIOCHEMISTRY NEUROPHYSIOLOGY (MEDICAL) Spring, 2014
 UNIVERSITY OF JORDAN FACULTY OF MEDICINE DEPARTMENT OF PHYSIOLOGY & BIOCHEMISTRY NEUROPHYSIOLOGY (MEDICAL) Spring, 2014 Textbook of Medical Physiology by: Guyton & Hall, 11 th edition 2006 Eman Al-Khateeb,
UNIVERSITY OF JORDAN FACULTY OF MEDICINE DEPARTMENT OF PHYSIOLOGY & BIOCHEMISTRY NEUROPHYSIOLOGY (MEDICAL) Spring, 2014 Textbook of Medical Physiology by: Guyton & Hall, 11 th edition 2006 Eman Al-Khateeb,
DISORDERS OF THE MOTOR SYSTEM. Jeanette J. Norden, Ph.D. Professor Emerita Vanderbilt University School of Medicine
 DISORDERS OF THE MOTOR SYSTEM Jeanette J. Norden, Ph.D. Professor Emerita Vanderbilt University School of Medicine THE MOTOR SYSTEM To understand disorders of the motor system, we need to review how a
DISORDERS OF THE MOTOR SYSTEM Jeanette J. Norden, Ph.D. Professor Emerita Vanderbilt University School of Medicine THE MOTOR SYSTEM To understand disorders of the motor system, we need to review how a
CN V! touch! pain! Touch! P/T!
 CN V! touch! pain! Touch! P/T! Visual Pathways! L! R! B! A! C! D! LT! E! F! RT! G! hypothalamospinal! and! ALS! Vestibular Pathways! 1. Posture/Balance!!falling! 2. Head Position! 3. Eye-Head Movements
CN V! touch! pain! Touch! P/T! Visual Pathways! L! R! B! A! C! D! LT! E! F! RT! G! hypothalamospinal! and! ALS! Vestibular Pathways! 1. Posture/Balance!!falling! 2. Head Position! 3. Eye-Head Movements
A Parkinson s Disease and related disorders
 A 3.5.2 Parkinson s Disease and related disorders 10 November 2016 Marinela Vavla marinela.vavla@kcl.ac.uk Learning objectives Basal ganglia: components and localization (inter)connections and functions
A 3.5.2 Parkinson s Disease and related disorders 10 November 2016 Marinela Vavla marinela.vavla@kcl.ac.uk Learning objectives Basal ganglia: components and localization (inter)connections and functions
The Wonders of the Basal Ganglia
 Basal Ganglia The Wonders of the Basal Ganglia by Mackenzie Breton and Laura Strong /// https://kin450- neurophysiology.wikispaces.com/basal+ganglia Introduction The basal ganglia are a group of nuclei
Basal Ganglia The Wonders of the Basal Ganglia by Mackenzie Breton and Laura Strong /// https://kin450- neurophysiology.wikispaces.com/basal+ganglia Introduction The basal ganglia are a group of nuclei
Movement disorders. Dr Rick Leventer Royal Children s Hospital
 Movement disorders Dr Rick Leventer Royal Children s Hospital richard.leventer@rch.org.au Movement disorders! conditions that affect the speed, fluency, quality, and ease of movement! usually affect TONE
Movement disorders Dr Rick Leventer Royal Children s Hospital richard.leventer@rch.org.au Movement disorders! conditions that affect the speed, fluency, quality, and ease of movement! usually affect TONE
NS219: Basal Ganglia Anatomy
 NS219: Basal Ganglia Anatomy Human basal ganglia anatomy Analagous rodent basal ganglia nuclei Basal ganglia circuits: the classical model of direct and indirect pathways + Glutamate + - GABA - Gross anatomy
NS219: Basal Ganglia Anatomy Human basal ganglia anatomy Analagous rodent basal ganglia nuclei Basal ganglia circuits: the classical model of direct and indirect pathways + Glutamate + - GABA - Gross anatomy
Functional Distinctions
 Functional Distinctions FUNCTION COMPONENT DEFICITS Start Basal Ganglia Spontaneous Movements Move UMN/LMN Cerebral Cortex Brainstem, Spinal cord Roots/peripheral nerves Plan Cerebellum Ataxia Adjust Cerebellum
Functional Distinctions FUNCTION COMPONENT DEFICITS Start Basal Ganglia Spontaneous Movements Move UMN/LMN Cerebral Cortex Brainstem, Spinal cord Roots/peripheral nerves Plan Cerebellum Ataxia Adjust Cerebellum
First described by James Parkinson in his classic 1817 monograph, "An Essay on the Shaking Palsy"
 Parkinson's Disease First described by James Parkinson in his classic 1817 monograph, "An Essay on the Shaking Palsy" Parkinson s disease (PD) is a neurological disorder characterized by a progressive
Parkinson's Disease First described by James Parkinson in his classic 1817 monograph, "An Essay on the Shaking Palsy" Parkinson s disease (PD) is a neurological disorder characterized by a progressive
Department of Neurology, Rigshospitalet, 9 Blegdamsvej, PAULSON, O.B. Involuntary Movements. Tohoku J. Exp. Med., 1990, 161,
 Tohoku J. Exp. Med., 1990, 161, Suppl., 21-27 Involuntary Movements OLAF B. PAULSON Department of Neurology, Rigshospitalet, 9 Blegdamsvej, DK-2100, Copenhagen, Denmark PAULSON, O.B. Involuntary Movements.
Tohoku J. Exp. Med., 1990, 161, Suppl., 21-27 Involuntary Movements OLAF B. PAULSON Department of Neurology, Rigshospitalet, 9 Blegdamsvej, DK-2100, Copenhagen, Denmark PAULSON, O.B. Involuntary Movements.
MODULE 6: CEREBELLUM AND BASAL GANGLIA
 MODULE 6: CEREBELLUM AND BASAL GANGLIA This module will summarize the important neuroanatomical and key clinical concepts from Chapters 15 and 16 of the textbook for the course. The first part of this
MODULE 6: CEREBELLUM AND BASAL GANGLIA This module will summarize the important neuroanatomical and key clinical concepts from Chapters 15 and 16 of the textbook for the course. The first part of this
Huntington s Disease COGS 172
 Huntington s Disease COGS 172 Overview Part I: What is HD? - Clinical description and features - Genetic basis and neuropathology - Cell biology, mouse models and therapeutics Part II: HD as a model in
Huntington s Disease COGS 172 Overview Part I: What is HD? - Clinical description and features - Genetic basis and neuropathology - Cell biology, mouse models and therapeutics Part II: HD as a model in
Deep Brain Stimulation: Surgical Process
 Deep Brain Stimulation: Surgical Process Kia Shahlaie, MD, PhD Assistant Professor Bronte Endowed Chair in Epilepsy Research Director of Functional Neurosurgery Minimally Invasive Neurosurgery Department
Deep Brain Stimulation: Surgical Process Kia Shahlaie, MD, PhD Assistant Professor Bronte Endowed Chair in Epilepsy Research Director of Functional Neurosurgery Minimally Invasive Neurosurgery Department
Extrapyramidal Motor System. Basal Ganglia or Striatum. Basal Ganglia or Striatum 3/3/2010
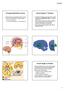 Extrapyramidal Motor System Basal Ganglia or Striatum Descending extrapyramidal paths receive input from other parts of motor system: From the cerebellum From the basal ganglia or corpus striatum Caudate
Extrapyramidal Motor System Basal Ganglia or Striatum Descending extrapyramidal paths receive input from other parts of motor system: From the cerebellum From the basal ganglia or corpus striatum Caudate
Professor Tim Anderson
 Professor Tim Anderson Neurologist University of Otago Christchurch 11:00-11:55 WS #91: Shakes Jerks and Spasms - Recognition and Differential Diagnosis 12:05-13:00 WS #102: Shakes Jerks and Spasms - Recognition
Professor Tim Anderson Neurologist University of Otago Christchurch 11:00-11:55 WS #91: Shakes Jerks and Spasms - Recognition and Differential Diagnosis 12:05-13:00 WS #102: Shakes Jerks and Spasms - Recognition
Parkinsonism or Parkinson s Disease I. Symptoms: Main disorder of movement. Named after, an English physician who described the then known, in 1817.
 Parkinsonism or Parkinson s Disease I. Symptoms: Main disorder of movement. Named after, an English physician who described the then known, in 1817. Four (4) hallmark clinical signs: 1) Tremor: (Note -
Parkinsonism or Parkinson s Disease I. Symptoms: Main disorder of movement. Named after, an English physician who described the then known, in 1817. Four (4) hallmark clinical signs: 1) Tremor: (Note -
Movement Disorders. Psychology 372 Physiological Psychology. Background. Myasthenia Gravis. Many Types
 Background Movement Disorders Psychology 372 Physiological Psychology Steven E. Meier, Ph.D. Listen to the audio lecture while viewing these slides Early Studies Found some patients with progressive weakness
Background Movement Disorders Psychology 372 Physiological Psychology Steven E. Meier, Ph.D. Listen to the audio lecture while viewing these slides Early Studies Found some patients with progressive weakness
Dr. Farah Nabil Abbas. MBChB, MSc, PhD
 Dr. Farah Nabil Abbas MBChB, MSc, PhD The Basal Ganglia *Functions in association with motor cortex and corticospinal pathways. *Regarded as accessory motor system besides cerebellum. *Receive most of
Dr. Farah Nabil Abbas MBChB, MSc, PhD The Basal Ganglia *Functions in association with motor cortex and corticospinal pathways. *Regarded as accessory motor system besides cerebellum. *Receive most of
Chapter 8. Control of movement
 Chapter 8 Control of movement 1st Type: Skeletal Muscle Skeletal Muscle: Ones that moves us Muscles contract, limb flex Flexion: a movement of a limb that tends to bend its joints, contraction of a flexor
Chapter 8 Control of movement 1st Type: Skeletal Muscle Skeletal Muscle: Ones that moves us Muscles contract, limb flex Flexion: a movement of a limb that tends to bend its joints, contraction of a flexor
1. The cerebellum coordinates fine movement through interactions with the following motor-associated areas:
 DENT/OBHS 131 2009 Take-home test 4 Week 6: Take-home test (2/11/09 close 2/18/09) 1. The cerebellum coordinates fine movement through interactions with the following motor-associated areas: Hypothalamus
DENT/OBHS 131 2009 Take-home test 4 Week 6: Take-home test (2/11/09 close 2/18/09) 1. The cerebellum coordinates fine movement through interactions with the following motor-associated areas: Hypothalamus
Professor Tim Anderson
 Professor Tim Anderson Neurologist University of Otago Christchurch 11:00-11:55 WS #91: Shakes Jerks and Spasms - Recognition and Differential Diagnosis 12:05-13:00 WS #102: Shakes Jerks and Spasms - Recognition
Professor Tim Anderson Neurologist University of Otago Christchurch 11:00-11:55 WS #91: Shakes Jerks and Spasms - Recognition and Differential Diagnosis 12:05-13:00 WS #102: Shakes Jerks and Spasms - Recognition
Pathogenesis of Degenerative Diseases and Dementias. D r. Ali Eltayb ( U. of Omdurman. I ). M. Path (U. of Alexandria)
 Pathogenesis of Degenerative Diseases and Dementias D r. Ali Eltayb ( U. of Omdurman. I ). M. Path (U. of Alexandria) Dementias Defined: as the development of memory impairment and other cognitive deficits
Pathogenesis of Degenerative Diseases and Dementias D r. Ali Eltayb ( U. of Omdurman. I ). M. Path (U. of Alexandria) Dementias Defined: as the development of memory impairment and other cognitive deficits
STRUCTURE AND CIRCUITS OF THE BASAL GANGLIA
 STRUCTURE AND CIRCUITS OF THE BASAL GANGLIA Rastislav Druga Department of Anatomy, Second Faculty of Medicine 2017 Basal ganglia Nucleus caudatus, putamen, globus pallidus (medialis et lateralis), ncl.
STRUCTURE AND CIRCUITS OF THE BASAL GANGLIA Rastislav Druga Department of Anatomy, Second Faculty of Medicine 2017 Basal ganglia Nucleus caudatus, putamen, globus pallidus (medialis et lateralis), ncl.
An approach to movement disorders. Kailash Bhatia, DM, FRCP Professor of Clinical Neurology Institute of Neurology Queen Square, London
 An approach to movement disorders Kailash Bhatia, DM, FRCP Professor of Clinical Neurology Institute of Neurology Queen Square, London Neurology Diagnosis Two main questions: What parts of the nervous
An approach to movement disorders Kailash Bhatia, DM, FRCP Professor of Clinical Neurology Institute of Neurology Queen Square, London Neurology Diagnosis Two main questions: What parts of the nervous
Motor System Hierarchy
 Motor Pathways Lectures Objectives Define the terms upper and lower motor neurons with examples. Describe the corticospinal (pyramidal) tract and the direct motor pathways from the cortex to the trunk
Motor Pathways Lectures Objectives Define the terms upper and lower motor neurons with examples. Describe the corticospinal (pyramidal) tract and the direct motor pathways from the cortex to the trunk
Visualization and simulated animations of pathology and symptoms of Parkinson s disease
 Visualization and simulated animations of pathology and symptoms of Parkinson s disease Prof. Yifan HAN Email: bctycan@ust.hk 1. Introduction 2. Biochemistry of Parkinson s disease 3. Course Design 4.
Visualization and simulated animations of pathology and symptoms of Parkinson s disease Prof. Yifan HAN Email: bctycan@ust.hk 1. Introduction 2. Biochemistry of Parkinson s disease 3. Course Design 4.
Deep Brain Stimulation. Is It Right for You?
 Deep Brain Stimulation Is It Right for You? Northwestern Medicine Deep Brain Stimulation What is DBS? Northwestern Medicine Central DuPage Hospital is a regional destination for the treatment of movement
Deep Brain Stimulation Is It Right for You? Northwestern Medicine Deep Brain Stimulation What is DBS? Northwestern Medicine Central DuPage Hospital is a regional destination for the treatment of movement
Gangli della Base: un network multifunzionale
 Gangli della Base: un network multifunzionale Prof. Giovanni Abbruzzese Centro per la Malattia di Parkinson e i Disordini del Movimento DiNOGMI, Università di Genova IRCCS AOU San Martino IST Basal Ganglia
Gangli della Base: un network multifunzionale Prof. Giovanni Abbruzzese Centro per la Malattia di Parkinson e i Disordini del Movimento DiNOGMI, Università di Genova IRCCS AOU San Martino IST Basal Ganglia
Basal Ganglia. Introduction. Basal Ganglia at a Glance. Role of the BG
 Basal Ganglia Shepherd (2004) Chapter 9 Charles J. Wilson Instructor: Yoonsuck Choe; CPSC 644 Cortical Networks Introduction A set of nuclei in the forebrain and midbrain area in mammals, birds, and reptiles.
Basal Ganglia Shepherd (2004) Chapter 9 Charles J. Wilson Instructor: Yoonsuck Choe; CPSC 644 Cortical Networks Introduction A set of nuclei in the forebrain and midbrain area in mammals, birds, and reptiles.
Organization of Motor Functions 4.
 Organization of Motor Functions 4. Dr. Attila Nagy 2018 Sensory-motor system Limbic cortex Structure Subcortical Motivational sub areas Frontal cortex Task Motivation Sequence Plan Tim e Ascending system
Organization of Motor Functions 4. Dr. Attila Nagy 2018 Sensory-motor system Limbic cortex Structure Subcortical Motivational sub areas Frontal cortex Task Motivation Sequence Plan Tim e Ascending system
Deep Brain Stimulation: Patient selection
 Deep Brain Stimulation: Patient selection Halim Fadil, MD Movement Disorders Neurologist Kane Hall Barry Neurology Bedford/Keller, TX 1991: Thalamic (Vim) DBS for tremor Benabid AL, et al. Lancet. 1991;337(8738):403-406.
Deep Brain Stimulation: Patient selection Halim Fadil, MD Movement Disorders Neurologist Kane Hall Barry Neurology Bedford/Keller, TX 1991: Thalamic (Vim) DBS for tremor Benabid AL, et al. Lancet. 1991;337(8738):403-406.
Clinical Features and Treatment of Parkinson s Disease
 Clinical Features and Treatment of Parkinson s Disease Richard Camicioli, MD, FRCPC Cognitive and Movement Disorders Department of Medicine University of Alberta 1 Objectives To review the diagnosis and
Clinical Features and Treatment of Parkinson s Disease Richard Camicioli, MD, FRCPC Cognitive and Movement Disorders Department of Medicine University of Alberta 1 Objectives To review the diagnosis and
Part 1 Parkinson s Disease. COGS 172: Brain Disorders and Cogni5on
 Part 1 Parkinson s Disease COGS 172: Brain Disorders and Cogni5on Background: Neuroanatomy of the motor system Note: Given short time to the final the details of the anatomy will not be in the exam, but
Part 1 Parkinson s Disease COGS 172: Brain Disorders and Cogni5on Background: Neuroanatomy of the motor system Note: Given short time to the final the details of the anatomy will not be in the exam, but
Deep Brain Stimulation for Parkinson s Disease & Essential Tremor
 Deep Brain Stimulation for Parkinson s Disease & Essential Tremor Albert Fenoy, MD Assistant Professor University of Texas at Houston, Health Science Center Current US Approvals Essential Tremor and Parkinsonian
Deep Brain Stimulation for Parkinson s Disease & Essential Tremor Albert Fenoy, MD Assistant Professor University of Texas at Houston, Health Science Center Current US Approvals Essential Tremor and Parkinsonian
Basal nuclei, cerebellum and movement
 Basal nuclei, cerebellum and movement MSTN121 - Neurophysiology Session 9 Department of Myotherapy Basal Nuclei (Ganglia) Basal Nuclei (Ganglia) Role: Predict the effects of various actions, then make
Basal nuclei, cerebellum and movement MSTN121 - Neurophysiology Session 9 Department of Myotherapy Basal Nuclei (Ganglia) Basal Nuclei (Ganglia) Role: Predict the effects of various actions, then make
Deep Brain Stimulation: Indications and Ethical Applications
 Deep Brain Stimulation Overview Kara D. Beasley, DO, MBe, FACOS Boulder Neurosurgical and Spine Associates (303) 562-1372 Deep Brain Stimulation: Indications and Ethical Applications Instrument of Change
Deep Brain Stimulation Overview Kara D. Beasley, DO, MBe, FACOS Boulder Neurosurgical and Spine Associates (303) 562-1372 Deep Brain Stimulation: Indications and Ethical Applications Instrument of Change
Parts of the motor circuits
 MOVEMENT DISORDERS Parts of the motor circuits cortical centers: there are centers in all the cortical lobes subcortical centers: caudate nucleus putamen pallidum subthalamical nucleus (Luys) nucleus ruber
MOVEMENT DISORDERS Parts of the motor circuits cortical centers: there are centers in all the cortical lobes subcortical centers: caudate nucleus putamen pallidum subthalamical nucleus (Luys) nucleus ruber
ASHI691: Why We Fall Apart: The Neuroscience and Neurophysiology of Aging. Dr. Olav E. Krigolson Lecture 5: PARKINSONS DISEASE
 ASHI691: Why We Fall Apart: The Neuroscience and Neurophysiology of Aging Dr. Olav E. Krigolson krigolson@uvic.ca Lecture 5: PARKINSONS DISEASE The Basal Ganglia Primary motor cortex Execution of movement
ASHI691: Why We Fall Apart: The Neuroscience and Neurophysiology of Aging Dr. Olav E. Krigolson krigolson@uvic.ca Lecture 5: PARKINSONS DISEASE The Basal Ganglia Primary motor cortex Execution of movement
Disorders of Movement M A R T I N H A R L E Y N E U R O L O G Y
 Disorders of Movement M A R T I N H A R L E Y N E U R O L O G Y Educational Objectives Improved history taking in patients with movement disorders. Develop a systematic approach to observing and describing
Disorders of Movement M A R T I N H A R L E Y N E U R O L O G Y Educational Objectives Improved history taking in patients with movement disorders. Develop a systematic approach to observing and describing
How to Effectively Manage the Motor Symptoms of HD
 How to Effectively Manage the Motor Symptoms of HD Yvette Bordelon, MD, PhD Associate Clinical Professor of Neurology David Geffen School of Medicine at UCLA The information provided by speakers in workshops,
How to Effectively Manage the Motor Symptoms of HD Yvette Bordelon, MD, PhD Associate Clinical Professor of Neurology David Geffen School of Medicine at UCLA The information provided by speakers in workshops,
DEEP BRAIN STIMULATION
 DEEP BRAIN STIMULATION Non-Discrimination Statement and Multi-Language Interpreter Services information are located at the end of this document. Coverage for services, procedures, medical devices and drugs
DEEP BRAIN STIMULATION Non-Discrimination Statement and Multi-Language Interpreter Services information are located at the end of this document. Coverage for services, procedures, medical devices and drugs
Cheyenne 11/28 Neurological Disorders II. Transmissible Spongiform Encephalopathy
 Cheyenne 11/28 Neurological Disorders II Transmissible Spongiform Encephalopathy -E.g Bovine4 Spongiform Encephalopathy (BSE= mad cow disease), Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease, scrapie (animal only) -Sporadic:
Cheyenne 11/28 Neurological Disorders II Transmissible Spongiform Encephalopathy -E.g Bovine4 Spongiform Encephalopathy (BSE= mad cow disease), Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease, scrapie (animal only) -Sporadic:
symptoms of Parkinson s disease EXCEPT.
 M. Angele Theard, M.D Asst. Professor, Washington University, St. Louis, MO Quiz team; Shobana Rajan, M.D; Suneeta Gollapudy, MD; Verghese Cherian, M.D, M. Angele Theard, MD This quiz is being published
M. Angele Theard, M.D Asst. Professor, Washington University, St. Louis, MO Quiz team; Shobana Rajan, M.D; Suneeta Gollapudy, MD; Verghese Cherian, M.D, M. Angele Theard, MD This quiz is being published
DRUG TREATMENT OF PARKINSON S DISEASE. Mr. D.Raju, M.pharm, Lecturer
 DRUG TREATMENT OF PARKINSON S DISEASE Mr. D.Raju, M.pharm, Lecturer PARKINSON S DISEASE (parkinsonism) is a neurodegenerative disorder which affects t h e b a s a l g a n g l i a - and is associated with
DRUG TREATMENT OF PARKINSON S DISEASE Mr. D.Raju, M.pharm, Lecturer PARKINSON S DISEASE (parkinsonism) is a neurodegenerative disorder which affects t h e b a s a l g a n g l i a - and is associated with
Deep Brain Stimulation Surgery for Parkinson s Disease
 Deep Brain Stimulation Surgery for Parkinson s Disease Demystifying Medicine 24 January 2012 Kareem A. Zaghloul, MD, PhD Staff Physician, Surgical Neurology Branch NINDS Surgery for Parkinson s Disease
Deep Brain Stimulation Surgery for Parkinson s Disease Demystifying Medicine 24 January 2012 Kareem A. Zaghloul, MD, PhD Staff Physician, Surgical Neurology Branch NINDS Surgery for Parkinson s Disease
PARKINSON S DISEASE: current aspects of ETIOLOGY, DIAGNOSIS and TREATMENT. Dilek Ince Gunal, MD Assoc. Prof
 PARKINSON S DISEASE: current aspects of ETIOLOGY, DIAGNOSIS and TREATMENT Dilek Ince Gunal, MD Assoc. Prof Definition Clinical symptoms: Pathogenesis: Etiology: Neurodegenerative syndrome with chronic,
PARKINSON S DISEASE: current aspects of ETIOLOGY, DIAGNOSIS and TREATMENT Dilek Ince Gunal, MD Assoc. Prof Definition Clinical symptoms: Pathogenesis: Etiology: Neurodegenerative syndrome with chronic,
Mechanisms of L-DOPA-induced dyskinesia in Parkinson s Disease M. Angela Cenci
 Mechanisms of L-DOPA-induced Dyskinesia in Parkinson s Disease 1 Prof., MD, PhD Professor of Experimental Medical Research Basal Ganglia Pathophysiology Unit Lund University, Lund (Sweden) Parkinson s
Mechanisms of L-DOPA-induced Dyskinesia in Parkinson s Disease 1 Prof., MD, PhD Professor of Experimental Medical Research Basal Ganglia Pathophysiology Unit Lund University, Lund (Sweden) Parkinson s
Basal Nuclei (Ganglia)
 Doctor said he will not go deep within these slides because we will take them in physiology, so he will explain the anatomical structures, and he will go faster in the functions sheet in yellow Basal Nuclei
Doctor said he will not go deep within these slides because we will take them in physiology, so he will explain the anatomical structures, and he will go faster in the functions sheet in yellow Basal Nuclei
Table of Contents. Preface... xi. Part I: Introduction to Movement Disorders
 Table of Contents Visit www.healthreferenceseries.com to view A Contents Guide to the Health Reference Series, a listing of more than 14,000 topics and the volumes in which they are covered. Preface...
Table of Contents Visit www.healthreferenceseries.com to view A Contents Guide to the Health Reference Series, a listing of more than 14,000 topics and the volumes in which they are covered. Preface...
Biological Bases of Behavior. 8: Control of Movement
 Biological Bases of Behavior 8: Control of Movement m d Skeletal Muscle Movements of our body are accomplished by contraction of the skeletal muscles Flexion: contraction of a flexor muscle draws in a
Biological Bases of Behavior 8: Control of Movement m d Skeletal Muscle Movements of our body are accomplished by contraction of the skeletal muscles Flexion: contraction of a flexor muscle draws in a
Basal Ganglia General Info
 Basal Ganglia General Info Neural clusters in peripheral nervous system are ganglia. In the central nervous system, they are called nuclei. Should be called Basal Nuclei but usually called Basal Ganglia.
Basal Ganglia General Info Neural clusters in peripheral nervous system are ganglia. In the central nervous system, they are called nuclei. Should be called Basal Nuclei but usually called Basal Ganglia.
MOVEMENT OUTLINE. The Control of Movement: Muscles! Motor Reflexes Brain Mechanisms of Movement Mirror Neurons Disorders of Movement
 MOVEMENT 2 Dr. Steinmetz 3 OUTLINE The Control of Movement: Muscles! Motor Reflexes Brain Mechanisms of Movement Mirror Neurons Disorders of Movement Parkinson s Disease Huntington s Disease 1 4 TYPES
MOVEMENT 2 Dr. Steinmetz 3 OUTLINE The Control of Movement: Muscles! Motor Reflexes Brain Mechanisms of Movement Mirror Neurons Disorders of Movement Parkinson s Disease Huntington s Disease 1 4 TYPES
A3.1.7 Motor Control. 10 November 2016 Institute of Psychiatry,Psychology and Neuroscience Marinela Vavla
 A3.1.7 Motor Control 10 November 2016 Institute of Psychiatry,Psychology and Neuroscience Marinela Vavla marinela.vavla@kcl.ac.uk Learning objectives Motor systems: components & organization Spinal cord
A3.1.7 Motor Control 10 November 2016 Institute of Psychiatry,Psychology and Neuroscience Marinela Vavla marinela.vavla@kcl.ac.uk Learning objectives Motor systems: components & organization Spinal cord
Basal Ganglia Anatomy, Physiology, and Function. NS201c
 Basal Ganglia Anatomy, Physiology, and Function NS201c Human Basal Ganglia Anatomy Basal Ganglia Circuits: The Classical Model of Direct and Indirect Pathway Function Motor Cortex Premotor Cortex + Glutamate
Basal Ganglia Anatomy, Physiology, and Function NS201c Human Basal Ganglia Anatomy Basal Ganglia Circuits: The Classical Model of Direct and Indirect Pathway Function Motor Cortex Premotor Cortex + Glutamate
EMERGING TREATMENTS FOR PARKINSON S DISEASE
 EMERGING TREATMENTS FOR PARKINSON S DISEASE Katerina Markopoulou, MD, PhD Director Neurodegenerative Diseases Program Department of Neurology NorthShore University HealthSystem Clinical Assistant Professor
EMERGING TREATMENTS FOR PARKINSON S DISEASE Katerina Markopoulou, MD, PhD Director Neurodegenerative Diseases Program Department of Neurology NorthShore University HealthSystem Clinical Assistant Professor
Making Every Little Bit Count: Parkinson s Disease. SHP Neurobiology of Development and Disease
 Making Every Little Bit Count: Parkinson s Disease SHP Neurobiology of Development and Disease Parkinson s Disease Initially described symptomatically by Dr. James Parkinson in 1817 in An Essay on the
Making Every Little Bit Count: Parkinson s Disease SHP Neurobiology of Development and Disease Parkinson s Disease Initially described symptomatically by Dr. James Parkinson in 1817 in An Essay on the
See Policy CPT/HCPCS CODE section below for any prior authorization requirements
 Effective Date: 1/1/2019 Section: SUR Policy No: 395 1/1/19 Medical Policy Committee Approved Date: 8/17; 2/18; 12/18 Medical Officer Date APPLIES TO: Medicare Only See Policy CPT/HCPCS CODE section below
Effective Date: 1/1/2019 Section: SUR Policy No: 395 1/1/19 Medical Policy Committee Approved Date: 8/17; 2/18; 12/18 Medical Officer Date APPLIES TO: Medicare Only See Policy CPT/HCPCS CODE section below
BASAL GANGLIA. Dr JAMILA EL MEDANY
 BASAL GANGLIA Dr JAMILA EL MEDANY OBJECTIVES At the end of the lecture, the student should be able to: Define basal ganglia and enumerate its components. Enumerate parts of Corpus Striatum and their important
BASAL GANGLIA Dr JAMILA EL MEDANY OBJECTIVES At the end of the lecture, the student should be able to: Define basal ganglia and enumerate its components. Enumerate parts of Corpus Striatum and their important
PACEMAKERS ARE NOT JUST FOR THE HEART! Ab Siadati MD
 PACEMAKERS ARE NOT JUST FOR THE HEART! Ab Siadati MD WHAT IS DEEP BRAIN STIMULATION? WHY SHOULD YOU CONSIDER DBS SURGERY FOR YOUR PATIENTS? HOW DOES DBS WORK? DBS electrical stimulation overrides abnormal
PACEMAKERS ARE NOT JUST FOR THE HEART! Ab Siadati MD WHAT IS DEEP BRAIN STIMULATION? WHY SHOULD YOU CONSIDER DBS SURGERY FOR YOUR PATIENTS? HOW DOES DBS WORK? DBS electrical stimulation overrides abnormal
Punit Agrawal, DO Clinical Assistant Professor of Neurology Division of Movement Disorders OSU Department of Neurology
 Deep Brain Stimulation for Movement Disorders Punit Agrawal, DO Clinical Assistant Professor of Neurology Division of Movement Disorders OSU Department of Neurology History of DBS 1 History of DBS 1987
Deep Brain Stimulation for Movement Disorders Punit Agrawal, DO Clinical Assistant Professor of Neurology Division of Movement Disorders OSU Department of Neurology History of DBS 1 History of DBS 1987
Phenomenology of Movement Disorders
 Phenomenology of Movement Disorders Raja Mehanna MD Anatomical reasoning Anatomical reasoning Phenomenological reasoning Abnormal movement Hypokinetic Hyperkinetic Ataxia Video 1 But there is a tremor!
Phenomenology of Movement Disorders Raja Mehanna MD Anatomical reasoning Anatomical reasoning Phenomenological reasoning Abnormal movement Hypokinetic Hyperkinetic Ataxia Video 1 But there is a tremor!
Identification number: TÁMOP /1/A
 Manifestation of Novel Social Challenges of the European Union in the Teaching Material of Medical Biotechnology Master s Programmes at the University of Pécs and at the University of Debrecen Identification
Manifestation of Novel Social Challenges of the European Union in the Teaching Material of Medical Biotechnology Master s Programmes at the University of Pécs and at the University of Debrecen Identification
Moving fast or moving slow: an overview of Movement Disorders
 Moving fast or moving slow: an overview of Movement Disorders Mini Medical School October 25, 2018 Heather Rigby, MD, FRCPC 2014 MFMER slide-1 2014 MFMER slide-2 Basal Ganglia Dysfunction - Movement Disorders
Moving fast or moving slow: an overview of Movement Disorders Mini Medical School October 25, 2018 Heather Rigby, MD, FRCPC 2014 MFMER slide-1 2014 MFMER slide-2 Basal Ganglia Dysfunction - Movement Disorders
Neuroscience 410 Huntington Disease - Clinical. March 18, 2008
 Neuroscience 410 March 20, 2007 W. R. Wayne Martin, MD, FRCPC Division of Neurology University of Alberta inherited neurodegenerative disorder autosomal dominant 100% penetrance age of onset: 35-45 yr
Neuroscience 410 March 20, 2007 W. R. Wayne Martin, MD, FRCPC Division of Neurology University of Alberta inherited neurodegenerative disorder autosomal dominant 100% penetrance age of onset: 35-45 yr
The Basal Ganglia in Parkinson s Disease: Current Concepts and Unexplained Observations
 The Basal Ganglia in Parkinson s Disease: Current Concepts and Unexplained Observations Jose A. Obeso, PhD, MD, 1,2 Concepcio Marin, PhD, MD, 2,3 C. Rodriguez-Oroz, PhD, MD, 1,2 Javier Blesa, 1,2 B. Benitez-Temiño,
The Basal Ganglia in Parkinson s Disease: Current Concepts and Unexplained Observations Jose A. Obeso, PhD, MD, 1,2 Concepcio Marin, PhD, MD, 2,3 C. Rodriguez-Oroz, PhD, MD, 1,2 Javier Blesa, 1,2 B. Benitez-Temiño,
Chapter 8. Parkinsonism. M.G.Rajanandh, Dept. of Pharmacy Practice, SRM College of Pharmacy, SRM University.
 Chapter 8 Parkinsonism M.G.Rajanandh, Dept. of Pharmacy Practice, SRM College of Pharmacy, SRM University. Definition of Parkinson s Disease Parkinson's disease is a progressive, neurodegenerative disease
Chapter 8 Parkinsonism M.G.Rajanandh, Dept. of Pharmacy Practice, SRM College of Pharmacy, SRM University. Definition of Parkinson s Disease Parkinson's disease is a progressive, neurodegenerative disease
Dystonia: Title. A real pain in the neck. in All the Wrong Places
 Focus on CME at the University of Western Ontario Dystonia: Title in All the Wrong Places A real pain in the neck By Mandar Jog, MD, FRCPC and; Mary Jenkins, MD, FRCPC What is dystonia? Dystonia is a neurologic
Focus on CME at the University of Western Ontario Dystonia: Title in All the Wrong Places A real pain in the neck By Mandar Jog, MD, FRCPC and; Mary Jenkins, MD, FRCPC What is dystonia? Dystonia is a neurologic
Childhood Movement Disorders Alessandro Capuano, MD, PhD Federica Graziola, MD
 Childhood Movement Disorders Alessandro Capuano, MD, PhD Federica Graziola, MD Movement Disorders Center Department of Neuroscience Bambino Gesù Pediatric Hospital, Rome Two categories: Approach to diagnosis
Childhood Movement Disorders Alessandro Capuano, MD, PhD Federica Graziola, MD Movement Disorders Center Department of Neuroscience Bambino Gesù Pediatric Hospital, Rome Two categories: Approach to diagnosis
Study Guide Unit 2 Psych 2022, Fall 2003
 Study Guide Unit 2 Psych 2022, Fall 2003 Subcortical Anatomy 1. Be able to locate the following structures and be able to indicate whether they are located in the forebrain, diencephalon, midbrain, pons,
Study Guide Unit 2 Psych 2022, Fall 2003 Subcortical Anatomy 1. Be able to locate the following structures and be able to indicate whether they are located in the forebrain, diencephalon, midbrain, pons,
III./3.1. Movement disorders with akinetic rigid symptoms
 III./3.1. Movement disorders with akinetic rigid symptoms III./3.1.1. Parkinson s disease Parkinson s disease (PD) is the second most common neurodegenerative disorder worldwide after Alzheimer s disease.
III./3.1. Movement disorders with akinetic rigid symptoms III./3.1.1. Parkinson s disease Parkinson s disease (PD) is the second most common neurodegenerative disorder worldwide after Alzheimer s disease.
Computational cognitive neuroscience: 8. Motor Control and Reinforcement Learning
 1 Computational cognitive neuroscience: 8. Motor Control and Reinforcement Learning Lubica Beňušková Centre for Cognitive Science, FMFI Comenius University in Bratislava 2 Sensory-motor loop The essence
1 Computational cognitive neuroscience: 8. Motor Control and Reinforcement Learning Lubica Beňušková Centre for Cognitive Science, FMFI Comenius University in Bratislava 2 Sensory-motor loop The essence
nucleus accumbens septi hier-259 Nucleus+Accumbens birnlex_727
 Nucleus accumbens From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia Brain: Nucleus accumbens Nucleus accumbens visible in red. Latin NeuroNames MeSH NeuroLex ID nucleus accumbens septi hier-259 Nucleus+Accumbens birnlex_727
Nucleus accumbens From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia Brain: Nucleus accumbens Nucleus accumbens visible in red. Latin NeuroNames MeSH NeuroLex ID nucleus accumbens septi hier-259 Nucleus+Accumbens birnlex_727
Indications. DBS for Tremor. What is the PSA? 6/08/2014. Tremor. 1. Tremor. 2. Gait freezing/postural instability. 3. Motor fluctuations
 Indications Deep brain stimulation for Parkinson s disease A Tailored Approach 1. Tremor 2. Gait freezing/postural instability Wesley Thevathasan FRACP DPhil.Oxf 3. Motor fluctuations Consultant Neurologist,
Indications Deep brain stimulation for Parkinson s disease A Tailored Approach 1. Tremor 2. Gait freezing/postural instability Wesley Thevathasan FRACP DPhil.Oxf 3. Motor fluctuations Consultant Neurologist,
Parkinson's Disease KP Update
 Parkinson's Disease KP Update Andrew Imbus, PA-C Neurology, Movement Disorders Kaiser Permanente, Los Angeles Medical Center No disclosures "I often say now I don't have any choice whether or not I have
Parkinson's Disease KP Update Andrew Imbus, PA-C Neurology, Movement Disorders Kaiser Permanente, Los Angeles Medical Center No disclosures "I often say now I don't have any choice whether or not I have
Network Effects of Deep Brain Stimulation for Parkinson s Disease A Computational. Modeling Study. Karthik Kumaravelu
 Network Effects of Deep Brain Stimulation for Parkinson s Disease A Computational Modeling Study by Karthik Kumaravelu Department of Biomedical Engineering Duke University Date: Approved: Warren M. Grill,
Network Effects of Deep Brain Stimulation for Parkinson s Disease A Computational Modeling Study by Karthik Kumaravelu Department of Biomedical Engineering Duke University Date: Approved: Warren M. Grill,
2401 : Anatomy/Physiology
 Dr. Chris Doumen Week 7 2401 : Anatomy/Physiology The Cerebrum Central Nervous System TextBook Readings Pages 434-456 and 460-461 Make use of the figures in your textbook ; a picture is worth a thousand
Dr. Chris Doumen Week 7 2401 : Anatomy/Physiology The Cerebrum Central Nervous System TextBook Readings Pages 434-456 and 460-461 Make use of the figures in your textbook ; a picture is worth a thousand
Deep Brain Stimulation (DBS)
 Deep Brain Stimulation (DBS) [For the list of services and procedures that need preauthorization, please refer to www.mcs.com.pr go to Comunicados a Proveedores, and click Cartas Circulares.] Medical Policy:
Deep Brain Stimulation (DBS) [For the list of services and procedures that need preauthorization, please refer to www.mcs.com.pr go to Comunicados a Proveedores, and click Cartas Circulares.] Medical Policy:
Neuroanatomy. Dr. Maha ELBeltagy. Assistant Professor of Anatomy Faculty of Medicine The University of Jordan
 Neuroanatomy Dr. Maha ELBeltagy Assistant Professor of Anatomy Faculty of Medicine The University of Jordan 2018 Prof Yousry 10/15/17 Types of brain fibers THE WHITE MATTER OF THE BRAIN The white matter
Neuroanatomy Dr. Maha ELBeltagy Assistant Professor of Anatomy Faculty of Medicine The University of Jordan 2018 Prof Yousry 10/15/17 Types of brain fibers THE WHITE MATTER OF THE BRAIN The white matter
Basal ganglia macrocircuits
 Tepper, Abercrombie & Bolam (Eds.) Progress in Brain Research, Vol. 160 ISSN 0079-6123 Copyright r 2007 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved CHAPTER 1 Basal ganglia macrocircuits J.M. Tepper 1,, E.D. Abercrombie
Tepper, Abercrombie & Bolam (Eds.) Progress in Brain Research, Vol. 160 ISSN 0079-6123 Copyright r 2007 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved CHAPTER 1 Basal ganglia macrocircuits J.M. Tepper 1,, E.D. Abercrombie
Exam 2 PSYC Fall (2 points) Match a brain structure that is located closest to the following portions of the ventricular system
 Exam 2 PSYC 2022 Fall 1998 (2 points) What 2 nuclei are collectively called the striatum? (2 points) Match a brain structure that is located closest to the following portions of the ventricular system
Exam 2 PSYC 2022 Fall 1998 (2 points) What 2 nuclei are collectively called the striatum? (2 points) Match a brain structure that is located closest to the following portions of the ventricular system
10/13/2017. Disclosures. Deep Brain Stimulation in the Treatment of Movement Disorders. Deep Brain Stimulation: Objectives.
 Deep Brain Stimulation in the Treatment of Movement Disorders Disclosures None Eleanor K Orehek, M.D. Movement Disorders Specialist Noran Neurological Clinic 1 2 Objectives To provide an overview of deep
Deep Brain Stimulation in the Treatment of Movement Disorders Disclosures None Eleanor K Orehek, M.D. Movement Disorders Specialist Noran Neurological Clinic 1 2 Objectives To provide an overview of deep
