Basal Ganglia. Steven McLoon Department of Neuroscience University of Minnesota
|
|
|
- Stewart Lane
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Basal Ganglia Steven McLoon Department of Neuroscience University of Minnesota 1
2 Course News Graduate School Discussion Wednesday, Nov 1, 11:00am MoosT with Paul Mermelstein (invite your friends) 2
3 Course News Coffee Hour Thursday, Nov 2, 9:30-10:30am Monday, Nov 6, 9:00-10:00am Surdyk s Café in Northrop Auditorium Stop by for a minute or an hour! 3
4 Is the nervous system really this simple? 4
5 Basal Ganglia Anatomy The basal ganglia consist of a number of nuclei in the basal region of the telencephalon, diencephalon and midbrain. The largest nuclei are: Striatum Caudate nucleus Putamen Nucleus accumbens Globus pallidus Subthalamic nucleus Substantia nigra 5
6 Basal Ganglia Anatomy The striatum is part of the telencephalon. The striatum is composed of three nuclei: caudate nucleus putamen nucleus accumbens Anatomically, the striatum is more like one nucleus divided by the internal capsule, which comes together in front of the internal capsule. 6
7 Striatum: caudate nucleus putamen nucleus accumbens 7
8 Basal Ganglia Anatomy The caudate nucleus follows the lateral ventricle. 8
9 caudate nucleus putamen 9
10 caudate nucleus putamen 10
11 caudate nucleus putamen 11
12 caudate nucleus putamen 12
13 caudate nucleus 13
14 Basal Ganglia Anatomy Globus pallidus is part of the telencephalon. Globus pallidus is positioned just medial to the putamen. Globus pallidus has two divisions: external (GPe) part of the internal basal ganglia circuitry internal (GPi) part of the basal ganglia output system 14
15 GPe GPi 15
16 Basal Ganglia Anatomy The subthalamic nucleus is part of the diencephalon. The subthalamic nucleus is positioned just below the thalamus and above the substantia nigra in the midbrain. 16
17 subthalamic nucleus 17
18 Basal Ganglia Anatomy The substantia nigra is part of the midbrain (mesencephalon). The substantia nigra is positioned just below the subthalamic nucleus, between the cerebral peduncle (anterior) and red nucleus (posterior). The substantia nigra has two parts: Pars compacta (SNc) part of the internal basal ganglia circuitry (pigmented & dopamenergic) Pars reticulata (SNr) part of the basal ganglia output system 18
19 subthalamic nucleus substantia nigra 19
20 SNc SNr 20
21 Basal Ganglia Circuitry The main input to the basal ganglia is from cortex and is to the striatum. The input from cortex uses glutamate as the transmitter and is excitatory. 21
22 Basal Ganglia Circuitry Different parts of the striatum serve different functions: caudate eye movements & cognition putamen limb, trunk & facial movement nuc. accumbens emotion, drive & desire 22
23 Basal Ganglia Circuitry Medium spiny neurons in the striatum send axons to most basal ganglia nuclei. Medium spiny neurons use GABA as the transmitter, which is inhibitory. 23
24 Basal Ganglia Circuitry Intrinsic circuits process the information. Almost every known neurotransmitter is used in intrinsic basal ganglia circuitry. 24
25 Basal Ganglia Circuitry The main basal ganglia output is from globus pallidus internal (Gpi) and substantia nigra pars reticulata (SNr). Basal ganglia connects to the ventral anterior and ventral lateral nuclei of thalamus. The output uses GABA and is inhibitory. 25
26 Basal Ganglia Pathology Degeneration of neurons in the basal ganglia can cause: reduced body movements (hypokinesia) increased body movement (hyperkinesia) Hypokinesia: akinesia impaired initiation of movements bradykinesia slower and reduced movements rigidity resistance when someone moves a resting limb Hyperkinesia include involuntary movements: chorea rapid movements athetosis slow writhing movements ballisim flailing limb movements 26
27 Basal Ganglia Pathology Basal ganglia pathologies also cause cognitive deficits and other neurological problems. 27
28 Parkinson s Disease Degeneration of the dopaminergic neurons in substantia nigra pars compacta (SNc) causes Parkinson s disease. 28
29 Parkinson s Disease Degeneration of the dopaminergic neurons in substantia nigra pars compacta (SNc) causes Parkinson s disease. 29
30 Parkinson s Disease Degeneration of the dopaminergic neurons in substantia nigra pars compacta (SNc) causes Parkinson s disease. 30
31 Parkinson s Disease Symptoms (hypokinesia): resting tremor, pronounced in the hands all muscles resist being moved by another person (rigidity) difficulty initiating movements (akinesia) and slower movements (bradykinesia) 31
32 Parkinson s Disease The onset is typically after 50 years of age. ~1% of those 60 and older have Parkinson s. Consumption of caffeine reduces the risk of Parkinson s 32
33 Parkinson s Disease Treatment is oral administration of L-DOPA; L-DOPA is a dopamine precursor that can cross the blood-brain barrier and is converted into dopamine within the striatum. 33
34 Parkinson s Disease Transplantation of embryonic midbrain tissue to the striatum is effective in eliminating Parkinson s in animals, and has been used in over 400 patients over the past 20 years. Current research is focused on turning stem cells into dopaminergic neurons for therapeutic cell replacement. 34
35 Parkinson s Disease MPTP was originally synthesized by a chemistry graduate student. He was synthesizing a synthetic morphine for recreational purposes, and MPTP was a major impurity in his chemical reaction. He self administered his drug, and within a few days he had Parkinson s disease. He was successfully treated with L-DOPA but died a few months later from a cocaine overdose. Autopsy showed that his SNc dopaminergic neurons were lost. Unfortunately, this experiment was repeated later in the San Francisco drug community. MPTP is now used in the laboratory to induce Parkinson s disease in animals for research purposes. 35
36 Huntington s Disease Degeneration of medium spiny neurons in the striatum causes Huntington s disease or Huntington s chorea. The main symptom is hyperkinesia: involuntary rapid, random movements of the trunk and limbs; writhing of the hands is common. Symptoms typically appear midlife, years of age. Huntington s disease is due to an inherited, dominant mutation. 36
37 Genes & Protein Synthesis Protein synthesis: The sequence of nucleotides in DNA (a gene) is used as a template for synthesis of messenger RNA (mrna) in the nucleus mrna is used as a template for synthesis of a protein in the cytoplasm. DNA (gene) > mrna > protein 37
38 Genes & Protein Synthesis DNA is a chain of four nucleotides. mrna is a chain of four slightly different nucleotides. Protein is a chain of amino acids. The sequence of three nucleotides in the mrna, a codon, specifies the amino acid to assemble into the protein being synthesized. Thus, the sequence of nucleotides in a gene (DNA) ultimately determines the sequence of amino acids in a protein. 38
39 Huntington s Disease Huntington s disease is due to an inherited, dominant mutation: Due to an abnormal repeat of the CAG nucleotides in the huntington gene. CAG encodes for the amino acid glutamine. The CAG repeats in the gene result in a polyglutamine sequence in the huntington protein. The huntington protein is expressed by medium spiny neurons in the striatum. The mutant protein kills medium spiny neurons over time. 39
40 40
41 Huntington s Disease 41
42 Deep Brain Stimulation (DBS) DBS is used to treat numerous motor diseases. Electrodes are implanted in the globus pallidus internis or subthalamic nucleus. The frequency and strength of the stimulus is determined empirically. The effect can be dramatic, particularly with Parkinson disease. 42
43 Deep Brain Stimulation (DBS) 43
Damage on one side.. (Notes) Just remember: Unilateral damage to basal ganglia causes contralateral symptoms.
 Lecture 20 - Basal Ganglia Basal Ganglia (Nolte 5 th Ed pp 464) Damage to the basal ganglia produces involuntary movements. Although the basal ganglia do not influence LMN directly (to cause this involuntary
Lecture 20 - Basal Ganglia Basal Ganglia (Nolte 5 th Ed pp 464) Damage to the basal ganglia produces involuntary movements. Although the basal ganglia do not influence LMN directly (to cause this involuntary
A. General features of the basal ganglia, one of our 3 major motor control centers:
 Reading: Waxman pp. 141-146 are not very helpful! Computer Resources: HyperBrain, Chapter 12 Dental Neuroanatomy Suzanne S. Stensaas, Ph.D. March 1, 2012 THE BASAL GANGLIA Objectives: 1. What are the main
Reading: Waxman pp. 141-146 are not very helpful! Computer Resources: HyperBrain, Chapter 12 Dental Neuroanatomy Suzanne S. Stensaas, Ph.D. March 1, 2012 THE BASAL GANGLIA Objectives: 1. What are the main
A. General features of the basal ganglia, one of our 3 major motor control centers:
 Reading: Waxman pp. 141-146 are not very helpful! Computer Resources: HyperBrain, Chapter 12 Dental Neuroanatomy Suzanne S. Stensaas, Ph.D. April 22, 2010 THE BASAL GANGLIA Objectives: 1. What are the
Reading: Waxman pp. 141-146 are not very helpful! Computer Resources: HyperBrain, Chapter 12 Dental Neuroanatomy Suzanne S. Stensaas, Ph.D. April 22, 2010 THE BASAL GANGLIA Objectives: 1. What are the
Basal Ganglia George R. Leichnetz, Ph.D.
 Basal Ganglia George R. Leichnetz, Ph.D. OBJECTIVES 1. To understand the brain structures which constitute the basal ganglia, and their interconnections 2. To understand the consequences (clinical manifestations)
Basal Ganglia George R. Leichnetz, Ph.D. OBJECTIVES 1. To understand the brain structures which constitute the basal ganglia, and their interconnections 2. To understand the consequences (clinical manifestations)
VL VA BASAL GANGLIA. FUNCTIONAl COMPONENTS. Function Component Deficits Start/initiation Basal Ganglia Spontan movements
 BASAL GANGLIA Chris Cohan, Ph.D. Dept. of Pathology/Anat Sci University at Buffalo I) Overview How do Basal Ganglia affect movement Basal ganglia enhance cortical motor activity and facilitate movement.
BASAL GANGLIA Chris Cohan, Ph.D. Dept. of Pathology/Anat Sci University at Buffalo I) Overview How do Basal Ganglia affect movement Basal ganglia enhance cortical motor activity and facilitate movement.
Making Things Happen 2: Motor Disorders
 Making Things Happen 2: Motor Disorders How Your Brain Works Prof. Jan Schnupp wschnupp@cityu.edu.hk HowYourBrainWorks.net On the Menu in This Lecture In the previous lecture we saw how motor cortex and
Making Things Happen 2: Motor Disorders How Your Brain Works Prof. Jan Schnupp wschnupp@cityu.edu.hk HowYourBrainWorks.net On the Menu in This Lecture In the previous lecture we saw how motor cortex and
Basal ganglia Sujata Sofat, class of 2009
 Basal ganglia Sujata Sofat, class of 2009 Basal ganglia Objectives Describe the function of the Basal Ganglia in movement Define the BG components and their locations Describe the motor loop of the BG
Basal ganglia Sujata Sofat, class of 2009 Basal ganglia Objectives Describe the function of the Basal Ganglia in movement Define the BG components and their locations Describe the motor loop of the BG
Anatomy of the basal ganglia. Dana Cohen Gonda Brain Research Center, room 410
 Anatomy of the basal ganglia Dana Cohen Gonda Brain Research Center, room 410 danacoh@gmail.com The basal ganglia The nuclei form a small minority of the brain s neuronal population. Little is known about
Anatomy of the basal ganglia Dana Cohen Gonda Brain Research Center, room 410 danacoh@gmail.com The basal ganglia The nuclei form a small minority of the brain s neuronal population. Little is known about
GBME graduate course. Chapter 43. The Basal Ganglia
 GBME graduate course Chapter 43. The Basal Ganglia Basal ganglia in history Parkinson s disease Huntington s disease Parkinson s disease 1817 Parkinson's disease (PD) is a degenerative disorder of the
GBME graduate course Chapter 43. The Basal Ganglia Basal ganglia in history Parkinson s disease Huntington s disease Parkinson s disease 1817 Parkinson's disease (PD) is a degenerative disorder of the
Lecture XIII. Brain Diseases I - Parkinsonism! Brain Diseases I!
 Lecture XIII. Brain Diseases I - Parkinsonism! Bio 3411! Wednesday!! Lecture XIII. Brain Diseases - I.! 1! Brain Diseases I! NEUROSCIENCE 5 th ed! Page!!Figure!!Feature! 408 18.9 A!!Substantia Nigra in
Lecture XIII. Brain Diseases I - Parkinsonism! Bio 3411! Wednesday!! Lecture XIII. Brain Diseases - I.! 1! Brain Diseases I! NEUROSCIENCE 5 th ed! Page!!Figure!!Feature! 408 18.9 A!!Substantia Nigra in
Basal Ganglia General Info
 Basal Ganglia General Info Neural clusters in peripheral nervous system are ganglia. In the central nervous system, they are called nuclei. Should be called Basal Nuclei but usually called Basal Ganglia.
Basal Ganglia General Info Neural clusters in peripheral nervous system are ganglia. In the central nervous system, they are called nuclei. Should be called Basal Nuclei but usually called Basal Ganglia.
COGNITIVE SCIENCE 107A. Motor Systems: Basal Ganglia. Jaime A. Pineda, Ph.D.
 COGNITIVE SCIENCE 107A Motor Systems: Basal Ganglia Jaime A. Pineda, Ph.D. Two major descending s Pyramidal vs. extrapyramidal Motor cortex Pyramidal system Pathway for voluntary movement Most fibers originate
COGNITIVE SCIENCE 107A Motor Systems: Basal Ganglia Jaime A. Pineda, Ph.D. Two major descending s Pyramidal vs. extrapyramidal Motor cortex Pyramidal system Pathway for voluntary movement Most fibers originate
Parkinsonism or Parkinson s Disease I. Symptoms: Main disorder of movement. Named after, an English physician who described the then known, in 1817.
 Parkinsonism or Parkinson s Disease I. Symptoms: Main disorder of movement. Named after, an English physician who described the then known, in 1817. Four (4) hallmark clinical signs: 1) Tremor: (Note -
Parkinsonism or Parkinson s Disease I. Symptoms: Main disorder of movement. Named after, an English physician who described the then known, in 1817. Four (4) hallmark clinical signs: 1) Tremor: (Note -
Dr. Farah Nabil Abbas. MBChB, MSc, PhD
 Dr. Farah Nabil Abbas MBChB, MSc, PhD The Basal Ganglia *Functions in association with motor cortex and corticospinal pathways. *Regarded as accessory motor system besides cerebellum. *Receive most of
Dr. Farah Nabil Abbas MBChB, MSc, PhD The Basal Ganglia *Functions in association with motor cortex and corticospinal pathways. *Regarded as accessory motor system besides cerebellum. *Receive most of
Strick Lecture 4 March 29, 2006 Page 1
 Strick Lecture 4 March 29, 2006 Page 1 Basal Ganglia OUTLINE- I. Structures included in the basal ganglia II. III. IV. Skeleton diagram of Basal Ganglia Loops with cortex Similarity with Cerebellar Loops
Strick Lecture 4 March 29, 2006 Page 1 Basal Ganglia OUTLINE- I. Structures included in the basal ganglia II. III. IV. Skeleton diagram of Basal Ganglia Loops with cortex Similarity with Cerebellar Loops
Connections of basal ganglia
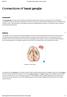 Connections of basal ganglia Introduction The basal ganglia, or basal nuclei, are areas of subcortical grey matter that play a prominent role in modulating movement, as well as cognitive and emotional
Connections of basal ganglia Introduction The basal ganglia, or basal nuclei, are areas of subcortical grey matter that play a prominent role in modulating movement, as well as cognitive and emotional
NS219: Basal Ganglia Anatomy
 NS219: Basal Ganglia Anatomy Human basal ganglia anatomy Analagous rodent basal ganglia nuclei Basal ganglia circuits: the classical model of direct and indirect pathways + Glutamate + - GABA - Gross anatomy
NS219: Basal Ganglia Anatomy Human basal ganglia anatomy Analagous rodent basal ganglia nuclei Basal ganglia circuits: the classical model of direct and indirect pathways + Glutamate + - GABA - Gross anatomy
Exam 2 PSYC Fall (2 points) Match a brain structure that is located closest to the following portions of the ventricular system
 Exam 2 PSYC 2022 Fall 1998 (2 points) What 2 nuclei are collectively called the striatum? (2 points) Match a brain structure that is located closest to the following portions of the ventricular system
Exam 2 PSYC 2022 Fall 1998 (2 points) What 2 nuclei are collectively called the striatum? (2 points) Match a brain structure that is located closest to the following portions of the ventricular system
Basal Ganglia. Introduction. Basal Ganglia at a Glance. Role of the BG
 Basal Ganglia Shepherd (2004) Chapter 9 Charles J. Wilson Instructor: Yoonsuck Choe; CPSC 644 Cortical Networks Introduction A set of nuclei in the forebrain and midbrain area in mammals, birds, and reptiles.
Basal Ganglia Shepherd (2004) Chapter 9 Charles J. Wilson Instructor: Yoonsuck Choe; CPSC 644 Cortical Networks Introduction A set of nuclei in the forebrain and midbrain area in mammals, birds, and reptiles.
Teach-SHEET Basal Ganglia
 Teach-SHEET Basal Ganglia Purves D, et al. Neuroscience, 5 th Ed., Sinauer Associates, 2012 Common organizational principles Basic Circuits or Loops: Motor loop concerned with learned movements (scaling
Teach-SHEET Basal Ganglia Purves D, et al. Neuroscience, 5 th Ed., Sinauer Associates, 2012 Common organizational principles Basic Circuits or Loops: Motor loop concerned with learned movements (scaling
The motor regulator. 1) Basal ganglia/nucleus
 The motor regulator 1) Basal ganglia/nucleus Neural structures involved in the control of movement Basal Ganglia - Components of the basal ganglia - Function of the basal ganglia - Connection and circuits
The motor regulator 1) Basal ganglia/nucleus Neural structures involved in the control of movement Basal Ganglia - Components of the basal ganglia - Function of the basal ganglia - Connection and circuits
For more information about how to cite these materials visit
 Author(s): Peter Hitchcock, PH.D., 2009 License: Unless otherwise noted, this material is made available under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Non-commercial Share Alike 3.0 License: http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-sa/3.0/
Author(s): Peter Hitchcock, PH.D., 2009 License: Unless otherwise noted, this material is made available under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Non-commercial Share Alike 3.0 License: http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-sa/3.0/
1/2/2019. Basal Ganglia & Cerebellum a quick overview. Outcomes you want to accomplish. MHD-Neuroanatomy Neuroscience Block. Basal ganglia review
 This power point is made available as an educational resource or study aid for your use only. This presentation may not be duplicated for others and should not be redistributed or posted anywhere on the
This power point is made available as an educational resource or study aid for your use only. This presentation may not be duplicated for others and should not be redistributed or posted anywhere on the
MOVEMENT OUTLINE. The Control of Movement: Muscles! Motor Reflexes Brain Mechanisms of Movement Mirror Neurons Disorders of Movement
 MOVEMENT 2 Dr. Steinmetz 3 OUTLINE The Control of Movement: Muscles! Motor Reflexes Brain Mechanisms of Movement Mirror Neurons Disorders of Movement Parkinson s Disease Huntington s Disease 1 4 TYPES
MOVEMENT 2 Dr. Steinmetz 3 OUTLINE The Control of Movement: Muscles! Motor Reflexes Brain Mechanisms of Movement Mirror Neurons Disorders of Movement Parkinson s Disease Huntington s Disease 1 4 TYPES
BASAL GANGLIA: A "pit stop" that integrates the movement, cognition and emotion.
 BASAL GANGLIA: A "pit stop" that integrates the movement, cognition and emotion. Poster No.: C-0795 Congress: ECR 2011 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: V. M. González Montaño, T. M. Zamorano Pozo, R.
BASAL GANGLIA: A "pit stop" that integrates the movement, cognition and emotion. Poster No.: C-0795 Congress: ECR 2011 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: V. M. González Montaño, T. M. Zamorano Pozo, R.
Movement Disorders. Psychology 372 Physiological Psychology. Background. Myasthenia Gravis. Many Types
 Background Movement Disorders Psychology 372 Physiological Psychology Steven E. Meier, Ph.D. Listen to the audio lecture while viewing these slides Early Studies Found some patients with progressive weakness
Background Movement Disorders Psychology 372 Physiological Psychology Steven E. Meier, Ph.D. Listen to the audio lecture while viewing these slides Early Studies Found some patients with progressive weakness
The Wonders of the Basal Ganglia
 Basal Ganglia The Wonders of the Basal Ganglia by Mackenzie Breton and Laura Strong /// https://kin450- neurophysiology.wikispaces.com/basal+ganglia Introduction The basal ganglia are a group of nuclei
Basal Ganglia The Wonders of the Basal Ganglia by Mackenzie Breton and Laura Strong /// https://kin450- neurophysiology.wikispaces.com/basal+ganglia Introduction The basal ganglia are a group of nuclei
Basal Ganglia. Today s lecture is about Basal Ganglia and it covers:
 Basal Ganglia Motor system is complex interaction between Lower motor neurons (spinal cord and brainstem circuits) and Upper motor neurons (pyramidal and extrapyramidal tracts) plus two main regulators
Basal Ganglia Motor system is complex interaction between Lower motor neurons (spinal cord and brainstem circuits) and Upper motor neurons (pyramidal and extrapyramidal tracts) plus two main regulators
MODULE 6: CEREBELLUM AND BASAL GANGLIA
 MODULE 6: CEREBELLUM AND BASAL GANGLIA This module will summarize the important neuroanatomical and key clinical concepts from Chapters 15 and 16 of the textbook for the course. The first part of this
MODULE 6: CEREBELLUM AND BASAL GANGLIA This module will summarize the important neuroanatomical and key clinical concepts from Chapters 15 and 16 of the textbook for the course. The first part of this
DISORDERS OF THE MOTOR SYSTEM. Jeanette J. Norden, Ph.D. Professor Emerita Vanderbilt University School of Medicine
 DISORDERS OF THE MOTOR SYSTEM Jeanette J. Norden, Ph.D. Professor Emerita Vanderbilt University School of Medicine THE MOTOR SYSTEM To understand disorders of the motor system, we need to review how a
DISORDERS OF THE MOTOR SYSTEM Jeanette J. Norden, Ph.D. Professor Emerita Vanderbilt University School of Medicine THE MOTOR SYSTEM To understand disorders of the motor system, we need to review how a
Study Guide Unit 2 Psych 2022, Fall 2003
 Study Guide Unit 2 Psych 2022, Fall 2003 Subcortical Anatomy 1. Be able to locate the following structures and be able to indicate whether they are located in the forebrain, diencephalon, midbrain, pons,
Study Guide Unit 2 Psych 2022, Fall 2003 Subcortical Anatomy 1. Be able to locate the following structures and be able to indicate whether they are located in the forebrain, diencephalon, midbrain, pons,
Computational cognitive neuroscience: 8. Motor Control and Reinforcement Learning
 1 Computational cognitive neuroscience: 8. Motor Control and Reinforcement Learning Lubica Beňušková Centre for Cognitive Science, FMFI Comenius University in Bratislava 2 Sensory-motor loop The essence
1 Computational cognitive neuroscience: 8. Motor Control and Reinforcement Learning Lubica Beňušková Centre for Cognitive Science, FMFI Comenius University in Bratislava 2 Sensory-motor loop The essence
PSY 315 Lecture 11 (2/23/2011) (Motor Control) Dr. Achtman PSY 215. Lecture 11 Topic: Motor System Chapter 8, pages
 Corrections: No Corrections Announcements: Exam #2 next Wednesday, March 2, 2011 Monday February 28, 2011 we will be going over the somatosensory system, and there will be time left in class to review
Corrections: No Corrections Announcements: Exam #2 next Wednesday, March 2, 2011 Monday February 28, 2011 we will be going over the somatosensory system, and there will be time left in class to review
UNIVERSITY OF JORDAN FACULTY OF MEDICINE DEPARTMENT OF PHYSIOLOGY & BIOCHEMISTRY NEUROPHYSIOLOGY (MEDICAL) Spring, 2014
 UNIVERSITY OF JORDAN FACULTY OF MEDICINE DEPARTMENT OF PHYSIOLOGY & BIOCHEMISTRY NEUROPHYSIOLOGY (MEDICAL) Spring, 2014 Textbook of Medical Physiology by: Guyton & Hall, 11 th edition 2006 Eman Al-Khateeb,
UNIVERSITY OF JORDAN FACULTY OF MEDICINE DEPARTMENT OF PHYSIOLOGY & BIOCHEMISTRY NEUROPHYSIOLOGY (MEDICAL) Spring, 2014 Textbook of Medical Physiology by: Guyton & Hall, 11 th edition 2006 Eman Al-Khateeb,
BASAL GANGLIA. Dr JAMILA EL MEDANY
 BASAL GANGLIA Dr JAMILA EL MEDANY OBJECTIVES At the end of the lecture, the student should be able to: Define basal ganglia and enumerate its components. Enumerate parts of Corpus Striatum and their important
BASAL GANGLIA Dr JAMILA EL MEDANY OBJECTIVES At the end of the lecture, the student should be able to: Define basal ganglia and enumerate its components. Enumerate parts of Corpus Striatum and their important
STRUCTURE AND CIRCUITS OF THE BASAL GANGLIA
 STRUCTURE AND CIRCUITS OF THE BASAL GANGLIA Rastislav Druga Department of Anatomy, Second Faculty of Medicine 2017 Basal ganglia Nucleus caudatus, putamen, globus pallidus (medialis et lateralis), ncl.
STRUCTURE AND CIRCUITS OF THE BASAL GANGLIA Rastislav Druga Department of Anatomy, Second Faculty of Medicine 2017 Basal ganglia Nucleus caudatus, putamen, globus pallidus (medialis et lateralis), ncl.
CN V! touch! pain! Touch! P/T!
 CN V! touch! pain! Touch! P/T! Visual Pathways! L! R! B! A! C! D! LT! E! F! RT! G! hypothalamospinal! and! ALS! Vestibular Pathways! 1. Posture/Balance!!falling! 2. Head Position! 3. Eye-Head Movements
CN V! touch! pain! Touch! P/T! Visual Pathways! L! R! B! A! C! D! LT! E! F! RT! G! hypothalamospinal! and! ALS! Vestibular Pathways! 1. Posture/Balance!!falling! 2. Head Position! 3. Eye-Head Movements
Biological Bases of Behavior. 8: Control of Movement
 Biological Bases of Behavior 8: Control of Movement m d Skeletal Muscle Movements of our body are accomplished by contraction of the skeletal muscles Flexion: contraction of a flexor muscle draws in a
Biological Bases of Behavior 8: Control of Movement m d Skeletal Muscle Movements of our body are accomplished by contraction of the skeletal muscles Flexion: contraction of a flexor muscle draws in a
Chapter 8. Control of movement
 Chapter 8 Control of movement 1st Type: Skeletal Muscle Skeletal Muscle: Ones that moves us Muscles contract, limb flex Flexion: a movement of a limb that tends to bend its joints, contraction of a flexor
Chapter 8 Control of movement 1st Type: Skeletal Muscle Skeletal Muscle: Ones that moves us Muscles contract, limb flex Flexion: a movement of a limb that tends to bend its joints, contraction of a flexor
Cheyenne 11/28 Neurological Disorders II. Transmissible Spongiform Encephalopathy
 Cheyenne 11/28 Neurological Disorders II Transmissible Spongiform Encephalopathy -E.g Bovine4 Spongiform Encephalopathy (BSE= mad cow disease), Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease, scrapie (animal only) -Sporadic:
Cheyenne 11/28 Neurological Disorders II Transmissible Spongiform Encephalopathy -E.g Bovine4 Spongiform Encephalopathy (BSE= mad cow disease), Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease, scrapie (animal only) -Sporadic:
Basal Nuclei (Ganglia)
 Doctor said he will not go deep within these slides because we will take them in physiology, so he will explain the anatomical structures, and he will go faster in the functions sheet in yellow Basal Nuclei
Doctor said he will not go deep within these slides because we will take them in physiology, so he will explain the anatomical structures, and he will go faster in the functions sheet in yellow Basal Nuclei
Motor System Hierarchy
 Motor Pathways Lectures Objectives Define the terms upper and lower motor neurons with examples. Describe the corticospinal (pyramidal) tract and the direct motor pathways from the cortex to the trunk
Motor Pathways Lectures Objectives Define the terms upper and lower motor neurons with examples. Describe the corticospinal (pyramidal) tract and the direct motor pathways from the cortex to the trunk
Systems Neuroscience Dan Kiper. Today: Wolfger von der Behrens
 Systems Neuroscience Dan Kiper Today: Wolfger von der Behrens wolfger@ini.ethz.ch 18.9.2018 Neurons Pyramidal neuron by Santiago Ramón y Cajal (1852-1934, Nobel prize with Camillo Golgi in 1906) Neurons
Systems Neuroscience Dan Kiper Today: Wolfger von der Behrens wolfger@ini.ethz.ch 18.9.2018 Neurons Pyramidal neuron by Santiago Ramón y Cajal (1852-1934, Nobel prize with Camillo Golgi in 1906) Neurons
Visualization and simulated animations of pathology and symptoms of Parkinson s disease
 Visualization and simulated animations of pathology and symptoms of Parkinson s disease Prof. Yifan HAN Email: bctycan@ust.hk 1. Introduction 2. Biochemistry of Parkinson s disease 3. Course Design 4.
Visualization and simulated animations of pathology and symptoms of Parkinson s disease Prof. Yifan HAN Email: bctycan@ust.hk 1. Introduction 2. Biochemistry of Parkinson s disease 3. Course Design 4.
First described by James Parkinson in his classic 1817 monograph, "An Essay on the Shaking Palsy"
 Parkinson's Disease First described by James Parkinson in his classic 1817 monograph, "An Essay on the Shaking Palsy" Parkinson s disease (PD) is a neurological disorder characterized by a progressive
Parkinson's Disease First described by James Parkinson in his classic 1817 monograph, "An Essay on the Shaking Palsy" Parkinson s disease (PD) is a neurological disorder characterized by a progressive
Brainstem. Steven McLoon Department of Neuroscience University of Minnesota
 Brainstem Steven McLoon Department of Neuroscience University of Minnesota 1 Course News Change in Lab Sequence Week of Oct 2 Lab 5 Week of Oct 9 Lab 4 2 Goal Today Know the regions of the brainstem. Know
Brainstem Steven McLoon Department of Neuroscience University of Minnesota 1 Course News Change in Lab Sequence Week of Oct 2 Lab 5 Week of Oct 9 Lab 4 2 Goal Today Know the regions of the brainstem. Know
nucleus accumbens septi hier-259 Nucleus+Accumbens birnlex_727
 Nucleus accumbens From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia Brain: Nucleus accumbens Nucleus accumbens visible in red. Latin NeuroNames MeSH NeuroLex ID nucleus accumbens septi hier-259 Nucleus+Accumbens birnlex_727
Nucleus accumbens From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia Brain: Nucleus accumbens Nucleus accumbens visible in red. Latin NeuroNames MeSH NeuroLex ID nucleus accumbens septi hier-259 Nucleus+Accumbens birnlex_727
Functional Distinctions
 Functional Distinctions FUNCTION COMPONENT DEFICITS Start Basal Ganglia Spontaneous Movements Move UMN/LMN Cerebral Cortex Brainstem, Spinal cord Roots/peripheral nerves Plan Cerebellum Ataxia Adjust Cerebellum
Functional Distinctions FUNCTION COMPONENT DEFICITS Start Basal Ganglia Spontaneous Movements Move UMN/LMN Cerebral Cortex Brainstem, Spinal cord Roots/peripheral nerves Plan Cerebellum Ataxia Adjust Cerebellum
Neurodegenerative Disease. April 12, Cunningham. Department of Neurosciences
 Neurodegenerative Disease April 12, 2017 Cunningham Department of Neurosciences NEURODEGENERATIVE DISEASE Any of a group of hereditary and sporadic conditions characterized by progressive dysfunction,
Neurodegenerative Disease April 12, 2017 Cunningham Department of Neurosciences NEURODEGENERATIVE DISEASE Any of a group of hereditary and sporadic conditions characterized by progressive dysfunction,
Basal nuclei, cerebellum and movement
 Basal nuclei, cerebellum and movement MSTN121 - Neurophysiology Session 9 Department of Myotherapy Basal Nuclei (Ganglia) Basal Nuclei (Ganglia) Role: Predict the effects of various actions, then make
Basal nuclei, cerebellum and movement MSTN121 - Neurophysiology Session 9 Department of Myotherapy Basal Nuclei (Ganglia) Basal Nuclei (Ganglia) Role: Predict the effects of various actions, then make
Course Calendar - Neuroscience
 2006-2007 Course Calendar - Neuroscience Meeting Hours for entire semester: Monday - Friday 1:00-2:20 p.m. Room 1200, COM August 28 August 29 August 30 August 31 September 1 Course introduction, Neurocytology:
2006-2007 Course Calendar - Neuroscience Meeting Hours for entire semester: Monday - Friday 1:00-2:20 p.m. Room 1200, COM August 28 August 29 August 30 August 31 September 1 Course introduction, Neurocytology:
Thalamus: VA VM, MD S N. GPi Superior colliculus. compacta reticulata
 . Putamen & Caudate Putamen & Caudate GPe Neocortex Thalamus: VA VM, MD S N GPi Superior colliculus compacta reticulata Substantia Nigra Pedunculopontine nuc. of midbrain ret.form. Satellites of the corpus
. Putamen & Caudate Putamen & Caudate GPe Neocortex Thalamus: VA VM, MD S N GPi Superior colliculus compacta reticulata Substantia Nigra Pedunculopontine nuc. of midbrain ret.form. Satellites of the corpus
Cell Migration II: CNS Cell Migration. Steven McLoon Department of Neuroscience University of Minnesota
 Cell Migration II: CNS Cell Migration Steven McLoon Department of Neuroscience University of Minnesota 1 Course News Coffee Hour Wednesday (Oct 18) 9:00-10:00am Surdyk s Café in Northrop Auditorium Stop
Cell Migration II: CNS Cell Migration Steven McLoon Department of Neuroscience University of Minnesota 1 Course News Coffee Hour Wednesday (Oct 18) 9:00-10:00am Surdyk s Café in Northrop Auditorium Stop
Making Every Little Bit Count: Parkinson s Disease. SHP Neurobiology of Development and Disease
 Making Every Little Bit Count: Parkinson s Disease SHP Neurobiology of Development and Disease Parkinson s Disease Initially described symptomatically by Dr. James Parkinson in 1817 in An Essay on the
Making Every Little Bit Count: Parkinson s Disease SHP Neurobiology of Development and Disease Parkinson s Disease Initially described symptomatically by Dr. James Parkinson in 1817 in An Essay on the
Lecture : Basal ganglia & Cerebellum By : Zaid Al-Ghnaneem
 Lecture : Basal ganglia & Cerebellum By : Zaid Al-Ghnaneem Some notes in the beginning : #1 : there is a slides file contains the sheet info as notes for those who love slides more than word papers. #2
Lecture : Basal ganglia & Cerebellum By : Zaid Al-Ghnaneem Some notes in the beginning : #1 : there is a slides file contains the sheet info as notes for those who love slides more than word papers. #2
神經解剖學 NEUROANATOMY BASAL NUCLEI 盧家鋒助理教授臺北醫學大學醫學系解剖學暨細胞生物學科臺北醫學大學醫學院轉譯影像研究中心.
 神經解剖學 NEUROANATOMY BASAL NUCLEI 盧家鋒助理教授臺北醫學大學醫學系解剖學暨細胞生物學科臺北醫學大學醫學院轉譯影像研究中心 http://www.ym.edu.tw/~cflu OUTLINE Components and Pathways of the Basal Nuclei Functions and Related Disorders of the Basal Nuclei
神經解剖學 NEUROANATOMY BASAL NUCLEI 盧家鋒助理教授臺北醫學大學醫學系解剖學暨細胞生物學科臺北醫學大學醫學院轉譯影像研究中心 http://www.ym.edu.tw/~cflu OUTLINE Components and Pathways of the Basal Nuclei Functions and Related Disorders of the Basal Nuclei
Deep Brain Stimulation Surgery for Parkinson s Disease
 Deep Brain Stimulation Surgery for Parkinson s Disease Demystifying Medicine 24 January 2012 Kareem A. Zaghloul, MD, PhD Staff Physician, Surgical Neurology Branch NINDS Surgery for Parkinson s Disease
Deep Brain Stimulation Surgery for Parkinson s Disease Demystifying Medicine 24 January 2012 Kareem A. Zaghloul, MD, PhD Staff Physician, Surgical Neurology Branch NINDS Surgery for Parkinson s Disease
2401 : Anatomy/Physiology
 Dr. Chris Doumen Week 7 2401 : Anatomy/Physiology The Cerebrum Central Nervous System TextBook Readings Pages 434-456 and 460-461 Make use of the figures in your textbook ; a picture is worth a thousand
Dr. Chris Doumen Week 7 2401 : Anatomy/Physiology The Cerebrum Central Nervous System TextBook Readings Pages 434-456 and 460-461 Make use of the figures in your textbook ; a picture is worth a thousand
Pathogenesis of Degenerative Diseases and Dementias. D r. Ali Eltayb ( U. of Omdurman. I ). M. Path (U. of Alexandria)
 Pathogenesis of Degenerative Diseases and Dementias D r. Ali Eltayb ( U. of Omdurman. I ). M. Path (U. of Alexandria) Dementias Defined: as the development of memory impairment and other cognitive deficits
Pathogenesis of Degenerative Diseases and Dementias D r. Ali Eltayb ( U. of Omdurman. I ). M. Path (U. of Alexandria) Dementias Defined: as the development of memory impairment and other cognitive deficits
14 - Central Nervous System. The Brain Taft College Human Physiology
 14 - Central Nervous System The Brain Taft College Human Physiology Development of the Brain The brain begins as a simple tube, a neural tube. The tube or chamber (ventricle) is filled with cerebrospinal
14 - Central Nervous System The Brain Taft College Human Physiology Development of the Brain The brain begins as a simple tube, a neural tube. The tube or chamber (ventricle) is filled with cerebrospinal
Prospective Memory as a Specific Form of Task Switching. Intention and Executive Control
 Prospective Memory as a Specific Form of Task Switching Intention and Executive Control Yehene E, Meiran N, Soroker N Taskalternationcostwithoutask alternation:measuringintentionality. A behavioral dissociation
Prospective Memory as a Specific Form of Task Switching Intention and Executive Control Yehene E, Meiran N, Soroker N Taskalternationcostwithoutask alternation:measuringintentionality. A behavioral dissociation
Course Calendar
 Clinical Neuroscience BMS 6706C Charles, Ph.D., Course Director charles.ouimet@med.fsu.edu (850) 644-2271 2004 2005 Course Calendar Click here to return to the syllabus Meeting Hours for entire semester:
Clinical Neuroscience BMS 6706C Charles, Ph.D., Course Director charles.ouimet@med.fsu.edu (850) 644-2271 2004 2005 Course Calendar Click here to return to the syllabus Meeting Hours for entire semester:
Huntington s Disease COGS 172
 Huntington s Disease COGS 172 Overview Part I: What is HD? - Clinical description and features - Genetic basis and neuropathology - Cell biology, mouse models and therapeutics Part II: HD as a model in
Huntington s Disease COGS 172 Overview Part I: What is HD? - Clinical description and features - Genetic basis and neuropathology - Cell biology, mouse models and therapeutics Part II: HD as a model in
Extrapyramidal Motor System. Basal Ganglia or Striatum. Basal Ganglia or Striatum 3/3/2010
 Extrapyramidal Motor System Basal Ganglia or Striatum Descending extrapyramidal paths receive input from other parts of motor system: From the cerebellum From the basal ganglia or corpus striatum Caudate
Extrapyramidal Motor System Basal Ganglia or Striatum Descending extrapyramidal paths receive input from other parts of motor system: From the cerebellum From the basal ganglia or corpus striatum Caudate
Kinematic Modeling in Parkinson s Disease
 Kinematic Modeling in Parkinson s Disease Alexander Hui Department of Bioengineering University of California, San Diego La Jolla, CA 92093 alexhui@ucsd.edu Abstract Parkinson s disease is a slowly progressing
Kinematic Modeling in Parkinson s Disease Alexander Hui Department of Bioengineering University of California, San Diego La Jolla, CA 92093 alexhui@ucsd.edu Abstract Parkinson s disease is a slowly progressing
The Central Nervous System
 The Central Nervous System Bởi: OpenStaxCollege The brain and the spinal cord are the central nervous system, and they represent the main organs of the nervous system. The spinal cord is a single structure,
The Central Nervous System Bởi: OpenStaxCollege The brain and the spinal cord are the central nervous system, and they represent the main organs of the nervous system. The spinal cord is a single structure,
Department of Neurology, Rigshospitalet, 9 Blegdamsvej, PAULSON, O.B. Involuntary Movements. Tohoku J. Exp. Med., 1990, 161,
 Tohoku J. Exp. Med., 1990, 161, Suppl., 21-27 Involuntary Movements OLAF B. PAULSON Department of Neurology, Rigshospitalet, 9 Blegdamsvej, DK-2100, Copenhagen, Denmark PAULSON, O.B. Involuntary Movements.
Tohoku J. Exp. Med., 1990, 161, Suppl., 21-27 Involuntary Movements OLAF B. PAULSON Department of Neurology, Rigshospitalet, 9 Blegdamsvej, DK-2100, Copenhagen, Denmark PAULSON, O.B. Involuntary Movements.
Cerebellum. Steven McLoon Department of Neuroscience University of Minnesota
 Cerebellum Steven McLoon Department of Neuroscience University of Minnesota 1 Anatomy of the Cerebellum The cerebellum has approximately half of all the neurons in the central nervous system. The cerebellum
Cerebellum Steven McLoon Department of Neuroscience University of Minnesota 1 Anatomy of the Cerebellum The cerebellum has approximately half of all the neurons in the central nervous system. The cerebellum
The Nervous System: Sensory and Motor Tracts of the Spinal Cord
 15 The Nervous System: Sensory and Motor Tracts of the Spinal Cord PowerPoint Lecture Presentations prepared by Steven Bassett Southeast Community College Lincoln, Nebraska Introduction Millions of sensory
15 The Nervous System: Sensory and Motor Tracts of the Spinal Cord PowerPoint Lecture Presentations prepared by Steven Bassett Southeast Community College Lincoln, Nebraska Introduction Millions of sensory
Movement Disorders Will Garrett, M.D Assistant Professor of Neurology
 Movement Disorders Will Garrett, M.D Assistant Professor of Neurology I. The Basal Ganglia The basal ganglia are composed of several structures including the caudate and putamen (collectively called the
Movement Disorders Will Garrett, M.D Assistant Professor of Neurology I. The Basal Ganglia The basal ganglia are composed of several structures including the caudate and putamen (collectively called the
Impact of the Secretome of Human Mesenchymal Stem Cells on Brain Structure and Animal Behavior in a Rat Model of Parkinson s Disease
 Impact of the Secretome of Human Mesenchymal Stem Cells on Brain Structure and Animal Behavior in a Rat Model of Parkinson s Disease FABIO G. TEIXEIRA,MIGUEL M.CARVALHO KRISHNA M. PANCHALINGAM ANA J.RODRIGUES
Impact of the Secretome of Human Mesenchymal Stem Cells on Brain Structure and Animal Behavior in a Rat Model of Parkinson s Disease FABIO G. TEIXEIRA,MIGUEL M.CARVALHO KRISHNA M. PANCHALINGAM ANA J.RODRIGUES
Brain anatomy and artificial intelligence. L. Andrew Coward Australian National University, Canberra, ACT 0200, Australia
 Brain anatomy and artificial intelligence L. Andrew Coward Australian National University, Canberra, ACT 0200, Australia The Fourth Conference on Artificial General Intelligence August 2011 Architectures
Brain anatomy and artificial intelligence L. Andrew Coward Australian National University, Canberra, ACT 0200, Australia The Fourth Conference on Artificial General Intelligence August 2011 Architectures
Overview of the Nervous System (some basic concepts) Steven McLoon Department of Neuroscience University of Minnesota
 Overview of the Nervous System (some basic concepts) Steven McLoon Department of Neuroscience University of Minnesota 1 Coffee Hour Tuesday (Sept 11) 10:00-11:00am Friday (Sept 14) 8:30-9:30am Surdyk s
Overview of the Nervous System (some basic concepts) Steven McLoon Department of Neuroscience University of Minnesota 1 Coffee Hour Tuesday (Sept 11) 10:00-11:00am Friday (Sept 14) 8:30-9:30am Surdyk s
The neurvous system senses, interprets, and responds to changes in the environment. Two types of cells makes this possible:
 NERVOUS SYSTEM The neurvous system senses, interprets, and responds to changes in the environment. Two types of cells makes this possible: the neuron and the supporting cells ("glial cells"). Neuron Neurons
NERVOUS SYSTEM The neurvous system senses, interprets, and responds to changes in the environment. Two types of cells makes this possible: the neuron and the supporting cells ("glial cells"). Neuron Neurons
Nsci 2100: Human Neuroanatomy 2017 Examination 3
 Name KEY Lab Section Nsci 2100: Human Neuroanatomy 2017 Examination 3 On this page, write your name and lab section. On your bubble answer sheet, enter your name (last name, space, first name), internet
Name KEY Lab Section Nsci 2100: Human Neuroanatomy 2017 Examination 3 On this page, write your name and lab section. On your bubble answer sheet, enter your name (last name, space, first name), internet
Chapter 3. Structure and Function of the Nervous System. Copyright (c) Allyn and Bacon 2004
 Chapter 3 Structure and Function of the Nervous System 1 Basic Features of the Nervous System Neuraxis: An imaginary line drawn through the center of the length of the central nervous system, from the
Chapter 3 Structure and Function of the Nervous System 1 Basic Features of the Nervous System Neuraxis: An imaginary line drawn through the center of the length of the central nervous system, from the
Brainstem: Midbrain. 1. Midbrain gross external anatomy 2. Internal structure of the midbrain:
 Brainstem: Midbrain 1. Midbrain gross external anatomy 2. Internal structure of the midbrain: cerebral peduncles tegmentum tectum (guadrigeminal plate) Midbrain Midbrain general features location between
Brainstem: Midbrain 1. Midbrain gross external anatomy 2. Internal structure of the midbrain: cerebral peduncles tegmentum tectum (guadrigeminal plate) Midbrain Midbrain general features location between
Neuroanatomy. Dr. Maha ELBeltagy. Assistant Professor of Anatomy Faculty of Medicine The University of Jordan
 Neuroanatomy Dr. Maha ELBeltagy Assistant Professor of Anatomy Faculty of Medicine The University of Jordan 2018 Prof Yousry 10/15/17 Types of brain fibers THE WHITE MATTER OF THE BRAIN The white matter
Neuroanatomy Dr. Maha ELBeltagy Assistant Professor of Anatomy Faculty of Medicine The University of Jordan 2018 Prof Yousry 10/15/17 Types of brain fibers THE WHITE MATTER OF THE BRAIN The white matter
The Neuroscience of Addiction: A mini-review
 The Neuroscience of Addiction: A mini-review Jim Morrill, MD, PhD MGH Charlestown HealthCare Center Massachusetts General Hospital Disclosures Neither I nor my spouse/partner has a relevant financial relationship
The Neuroscience of Addiction: A mini-review Jim Morrill, MD, PhD MGH Charlestown HealthCare Center Massachusetts General Hospital Disclosures Neither I nor my spouse/partner has a relevant financial relationship
A Grey Box Neural Network Model of Basal Ganglia for Gait Signal of Patients with Huntington Disease
 Basic and Clinical April 2016. Volume 7. Number 2 A Grey Box Neural Network Model of Basal Ganglia for Gait Signal of Patients with Huntington Disease Abbas Pourhedayat 1, Yashar Sarbaz 1* 1. Department
Basic and Clinical April 2016. Volume 7. Number 2 A Grey Box Neural Network Model of Basal Ganglia for Gait Signal of Patients with Huntington Disease Abbas Pourhedayat 1, Yashar Sarbaz 1* 1. Department
We are IntechOpen, the world s leading publisher of Open Access books Built by scientists, for scientists. International authors and editors
 We are IntechOpen, the world s leading publisher of Open Access books Built by scientists, for scientists 3,350 108,000 1.7 M Open access books available International authors and editors Downloads Our
We are IntechOpen, the world s leading publisher of Open Access books Built by scientists, for scientists 3,350 108,000 1.7 M Open access books available International authors and editors Downloads Our
The basal forebrain: Questions, chapter 29:
 The basal forebrain: Questions, chapter 29: 7) What is the "basal forebrain", and what is its involvement in Alzheimer' s Disease? The acetylcholine-containing neurons of the nucleus basalis of Meynart
The basal forebrain: Questions, chapter 29: 7) What is the "basal forebrain", and what is its involvement in Alzheimer' s Disease? The acetylcholine-containing neurons of the nucleus basalis of Meynart
Biological Bases of Behavior. 3: Structure of the Nervous System
 Biological Bases of Behavior 3: Structure of the Nervous System Neuroanatomy Terms The neuraxis is an imaginary line drawn through the spinal cord up to the front of the brain Anatomical directions are
Biological Bases of Behavior 3: Structure of the Nervous System Neuroanatomy Terms The neuraxis is an imaginary line drawn through the spinal cord up to the front of the brain Anatomical directions are
A Parkinson s Disease and related disorders
 A 3.5.2 Parkinson s Disease and related disorders 10 November 2016 Marinela Vavla marinela.vavla@kcl.ac.uk Learning objectives Basal ganglia: components and localization (inter)connections and functions
A 3.5.2 Parkinson s Disease and related disorders 10 November 2016 Marinela Vavla marinela.vavla@kcl.ac.uk Learning objectives Basal ganglia: components and localization (inter)connections and functions
DRUG TREATMENT OF PARKINSON S DISEASE. Mr. D.Raju, M.pharm, Lecturer
 DRUG TREATMENT OF PARKINSON S DISEASE Mr. D.Raju, M.pharm, Lecturer PARKINSON S DISEASE (parkinsonism) is a neurodegenerative disorder which affects t h e b a s a l g a n g l i a - and is associated with
DRUG TREATMENT OF PARKINSON S DISEASE Mr. D.Raju, M.pharm, Lecturer PARKINSON S DISEASE (parkinsonism) is a neurodegenerative disorder which affects t h e b a s a l g a n g l i a - and is associated with
Classes of Neurotransmitters. Neurotransmitters
 1 Drugs Outline 2 Neurotransmitters Agonists and Antagonists Cocaine & other dopamine agonists Alcohol & its effects / Marijuana & its effects Synthetic & Designer Drugs: Ecstasy 1 Classes of Neurotransmitters
1 Drugs Outline 2 Neurotransmitters Agonists and Antagonists Cocaine & other dopamine agonists Alcohol & its effects / Marijuana & its effects Synthetic & Designer Drugs: Ecstasy 1 Classes of Neurotransmitters
Visualization and Quantification of the Striato pallidonigral Fibers in Parkinson's Disease Using Diffusion Tensor Imaging
 Visualization and Quantification of the Striato pallidonigral Fibers in Parkinson's Disease Using Diffusion Tensor Imaging Yu Zhang, Katherine Wu, Shannon Buckley, Norbert Schuff On behalf of the Parkinson
Visualization and Quantification of the Striato pallidonigral Fibers in Parkinson's Disease Using Diffusion Tensor Imaging Yu Zhang, Katherine Wu, Shannon Buckley, Norbert Schuff On behalf of the Parkinson
1. The cerebellum coordinates fine movement through interactions with the following motor-associated areas:
 DENT/OBHS 131 2009 Take-home test 4 Week 6: Take-home test (2/11/09 close 2/18/09) 1. The cerebellum coordinates fine movement through interactions with the following motor-associated areas: Hypothalamus
DENT/OBHS 131 2009 Take-home test 4 Week 6: Take-home test (2/11/09 close 2/18/09) 1. The cerebellum coordinates fine movement through interactions with the following motor-associated areas: Hypothalamus
The Central Nervous System I. Chapter 12
 The Central Nervous System I Chapter 12 The Central Nervous System The Brain and Spinal Cord Contained within the Axial Skeleton Brain Regions and Organization Medical Scheme (4 regions) 1. Cerebral Hemispheres
The Central Nervous System I Chapter 12 The Central Nervous System The Brain and Spinal Cord Contained within the Axial Skeleton Brain Regions and Organization Medical Scheme (4 regions) 1. Cerebral Hemispheres
Cell Migration II: CNS Cell Migration. Steven McLoon Department of Neuroscience University of Minnesota
 Cell Migration II: CNS Cell Migration Steven McLoon Department of Neuroscience University of Minnesota 1 Hey! The major concepts discussed relative to neural crest cell migration apply to cell migration
Cell Migration II: CNS Cell Migration Steven McLoon Department of Neuroscience University of Minnesota 1 Hey! The major concepts discussed relative to neural crest cell migration apply to cell migration
PTA 106 Unit 1 Lecture 1B
 PTA 106 Unit 1 Lecture 1B Medulla Oblongata Cardiovascular Center: Regulates the rate and force of the heartbeat and the diameter of blood vessels Medullary Rhythmicity Area: adjusts the basic rhythm of
PTA 106 Unit 1 Lecture 1B Medulla Oblongata Cardiovascular Center: Regulates the rate and force of the heartbeat and the diameter of blood vessels Medullary Rhythmicity Area: adjusts the basic rhythm of
A3.1.7 Motor Control. 10 November 2016 Institute of Psychiatry,Psychology and Neuroscience Marinela Vavla
 A3.1.7 Motor Control 10 November 2016 Institute of Psychiatry,Psychology and Neuroscience Marinela Vavla marinela.vavla@kcl.ac.uk Learning objectives Motor systems: components & organization Spinal cord
A3.1.7 Motor Control 10 November 2016 Institute of Psychiatry,Psychology and Neuroscience Marinela Vavla marinela.vavla@kcl.ac.uk Learning objectives Motor systems: components & organization Spinal cord
10/3/2016. T1 Anatomical structures are clearly identified, white matter (which has a high fat content) appears bright.
 H2O -2 atoms of Hydrogen, 1 of Oxygen Hydrogen just has one single proton and orbited by one single electron Proton has a magnetic moment similar to the earths magnetic pole Also similar to earth in that
H2O -2 atoms of Hydrogen, 1 of Oxygen Hydrogen just has one single proton and orbited by one single electron Proton has a magnetic moment similar to the earths magnetic pole Also similar to earth in that
PETER PAZMANY CATHOLIC UNIVERSITY Consortium members SEMMELWEIS UNIVERSITY, DIALOG CAMPUS PUBLISHER
 PETER PAZMANY CATHOLIC UNIVERSITY SEMMELWEIS UNIVERSITY Development of Complex Curricula for Molecular Bionics and Infobionics Programs within a consortial* framework** Consortium leader PETER PAZMANY
PETER PAZMANY CATHOLIC UNIVERSITY SEMMELWEIS UNIVERSITY Development of Complex Curricula for Molecular Bionics and Infobionics Programs within a consortial* framework** Consortium leader PETER PAZMANY
Chapter 2: Studies of Human Learning and Memory. From Mechanisms of Memory, second edition By J. David Sweatt, Ph.D.
 Chapter 2: Studies of Human Learning and Memory From Mechanisms of Memory, second edition By J. David Sweatt, Ph.D. Medium Spiny Neuron A Current Conception of the major memory systems in the brain Figure
Chapter 2: Studies of Human Learning and Memory From Mechanisms of Memory, second edition By J. David Sweatt, Ph.D. Medium Spiny Neuron A Current Conception of the major memory systems in the brain Figure
Levodopa vs. deep brain stimulation: computational models of treatments for Parkinson's disease
 Levodopa vs. deep brain stimulation: computational models of treatments for Parkinson's disease Abstract Parkinson's disease (PD) is a neurodegenerative disease affecting the dopaminergic neurons of the
Levodopa vs. deep brain stimulation: computational models of treatments for Parkinson's disease Abstract Parkinson's disease (PD) is a neurodegenerative disease affecting the dopaminergic neurons of the
Modeling the interplay of short-term memory and the basal ganglia in sequence processing
 Neurocomputing 26}27 (1999) 687}692 Modeling the interplay of short-term memory and the basal ganglia in sequence processing Tomoki Fukai* Department of Electronics, Tokai University, Hiratsuka, Kanagawa
Neurocomputing 26}27 (1999) 687}692 Modeling the interplay of short-term memory and the basal ganglia in sequence processing Tomoki Fukai* Department of Electronics, Tokai University, Hiratsuka, Kanagawa
Organization of Motor Functions 4.
 Organization of Motor Functions 4. Dr. Attila Nagy 2018 Sensory-motor system Limbic cortex Structure Subcortical Motivational sub areas Frontal cortex Task Motivation Sequence Plan Tim e Ascending system
Organization of Motor Functions 4. Dr. Attila Nagy 2018 Sensory-motor system Limbic cortex Structure Subcortical Motivational sub areas Frontal cortex Task Motivation Sequence Plan Tim e Ascending system
Chapter 8. Parkinsonism. M.G.Rajanandh, Dept. of Pharmacy Practice, SRM College of Pharmacy, SRM University.
 Chapter 8 Parkinsonism M.G.Rajanandh, Dept. of Pharmacy Practice, SRM College of Pharmacy, SRM University. Definition of Parkinson s Disease Parkinson's disease is a progressive, neurodegenerative disease
Chapter 8 Parkinsonism M.G.Rajanandh, Dept. of Pharmacy Practice, SRM College of Pharmacy, SRM University. Definition of Parkinson s Disease Parkinson's disease is a progressive, neurodegenerative disease
