About Anxiety Disorders By Geraldine Merola Barton, Ph.D.
|
|
|
- Geoffrey Rose
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 About Anxiety Disorders by Geraldine Merola Barton, Ph.D. Page 1 About Anxiety Disorders By Geraldine Merola Barton, Ph.D. What is an Anxiety Disorder? Simply put, an anxiety disorder is too much of a good thing. Anxiety is one of many survival mechanisms that have helped our species survive. Anxiety signals us to pay attention and energizes us to react appropriately. Avoid that oncoming train! Keep your baby safe! Lock the door! Study for the exam! Look out! Anxiety makes life exciting. That sizzly feeling that makes you feel in the moment...there s nothing like it. But balance is key. Feeling too little anxiety, what stops you from blithely walking off a cliff? On the other hand, too much anxiety takes over your life and makes life miserable. Anxiety disorders are very common. In fact, they often run in families. They appear to be related to a combination of variables, including genetic predisposition, individual makeup, and environment. Anxiety disorders come in various shapes and sizes. With some types, you may feel anxious or keyed up most of the time, often without being able to say why. With Generalized anxiety disorder, you worry unrealistically, about far fetched things and out of proportion to the likelihood of their happening. With phobias, the anxiety is focused on an object (simple phobia) or situation (social phobia) and is so distressing that you go to great lengths to avoid the object. With panic disorder, the anxiety comes on as a sudden attack that is terrifying and immobilizing, feeling as though you are going crazy or dying. s are available, and they are often very effective. If you have symptoms of anxiety, it s a good idea to see your family physician to rule out a medical condition. The next step may be entering psychological treatment. Look for a psychologist who specializes in cognitive-behavioral therapy. Ask your psychologist if she/he is willing to work as a team, in the event that medication is prescribed, with your family physician or psychiatrist. Don t hesitate to discuss your thoughts about taking medication. Many people prefer to attempt psychotherapy first and only consider medication if absolutely necessary. If you see your psychiatrist first, ask if he/she does psychotherapy, or would be willing to refer you for psychotherapy while monitoring any medications.
2 About Anxiety Disorders by Geraldine Merola Barton, Ph.D. Page 2 Generalized Anxiety Disorder (GAD) Generalized anxiety disorder (GAD) is characterized by chronic, excessive, unrealistic worrying about imagined impending disasters. Individuals with GAD are often anticipating the worst about anything and everything. Typical topics of worry include their own or their family s health and safety, money, social interactions, or work. Individuals with generalized anxiety disorder usually know that their worrying is unrealistic or excessive to the situation, but can t seem to stop it. They experience physical symptoms such as feeling keyed up, muscle tension (tight chest, knots in the stomach, stiff neck, tight shoulders, etc.), trembling, headaches or irritability. The nervousness may result in lightheaded, out of breath, or nausea sensations. Individuals with GAD often startle more easily than others do. They may have a hard time relaxing or sleeping. They tend to feel fatigued and have trouble concentrating and remembering. For a mental health professional to diagnose GAD, an individual would have spent at least six months worrying excessively about a number of everyday problems. Although the worrying causes distress, people with mild GAD experience minimal impairment at home, in social settings, or at work. In severe cases, GAD can be emotionally painful and debilitating, interfering with daily activities and relationships. Often, people with GAD also suffer from depression. GAD comes on gradually and usually is first seen in childhood or adolescence. However, it can begin in adulthood. More women have GAD than men. Unlike many other anxiety disorders, people with GAD don't characteristically avoid certain situations as a result of their disorder. Cognitive-behavioral therapy and relaxation techniques can be highly effective treatment techniques. In some cases, medication is also indicated. Panic Disorder A panic attack is a singularly terrifying experience. It came over me out of nowhere. I was sitting in bed ready to lie down. Suddenly, I felt like I was choking. My heart started racing I thought it would pound out of my chest. I felt like I was dying. I could barely dial 911. By the time I got to the emergency room, the feelings had subsided, but I was terribly shaken. I didn t know what had happened to me. The hospital told me I was fine and sent me home. I had more episodes. I began to live with a feeling of dread and anxiety, always waiting for the next one. I thought I was going crazy. Finally, a psychologist told me I was having panic attacks. I was in the supermarket, in the check-out line. It hit me without warning. My heart was pounding, my body got clammy. I was shaking, I was terrified, I didn t know what
3 About Anxiety Disorders by Geraldine Merola Barton, Ph.D. Page 3 would happen or what I would do. I felt like I was going crazy, just losing control, a sense of doom. I had an urgent need to just get out of there. I left my groceries in the cart and ran out of the store. The next time I went to the store, I had another attack. After that, I was so afraid of having an attack that I tried to avoid stores. Then I started avoiding any place where escape was difficult. I began planning my life around avoiding attacks. My life became more and more restricted, until I was afraid to leave my house. These are descriptions of panic attacks, by individuals with panic disorder. A panic attack is different from what many people refer to as an anxiety attack, usually meaning they feel nervous and keyed up. A panic attack strikes out of nowhere, for no apparent reason. A panic attack may occur any time, even during the early phases of falling asleep. Your heart may pound. Your body may feel clammy or faint, and you may feel hot flushes or chills. Your hands may feel tingly or numb. You may experience chest pain or tightness. You may feel like you are smothering or choking. You may have a sense of unreality. You may feel like you are having a heart attack or dying. You may feel like you are going crazy or losing control. Usually, a panic attack lasts no longer than 10 minutes. For some individuals, panic attacks occur in a specific setting, such as in a mall or on a bridge, where escape is difficult. These settings may then be avoided, sometimes to the point where the individual feels unable to leave the safety of home. These individuals are said to have agoraphobia. For others, panic attacks can happen anywhere, even when relaxing. Each panic attack increases the feelings of dread and anxiety between episodes, worrying about when the next one will hit. People with panic attack often feel ashamed or crazy. Some people have just one or two panic attacks in their lives, often under times of stress or after a loss, without developing panic disorder. Panic disorder is more common in women than men. It often first shows up in young adulthood. Panic disorder may be accompanied by depression. Symptoms & of Panic Disorder Symptoms At least four of the following symptoms come on suddenly, creating a discrete period of intense fear or discomfort that peaks within 10 minutes. Palpitations, pounding heart or accelerated heart rate Sweating Trembling or shaking Sensations of shortness of breath or smothering Feeling of choking Chest pain or discomfort Nausea or abdominal distress Feeling dizzy, unsteady, lightheaded or faint Derealization (feelings of unreality) or depersonalization (being detached from oneself) Fear of losing control or going crazy Fear of dying Paresthesias (numbness or tingling sensations Chills or hot flushes
4 About Anxiety Disorders by Geraldine Merola Barton, Ph.D. Page 4 It s important to seek treatment as soon as possible, to prevent the disorder from becoming chronic and restricting your life. Research shows that 70 to 90 percent of people with panic disorder are helped by treatment. One effective treatment is a type of psychotherapy called cognitive-behavioral therapy. Cognitive-behavioral therapy helps patients take control of the panic attacks by viewing them differently and mastering strategies such as relaxation techniques. In addition, patients are helped to identify and change their non-productive thought patterns and behaviors. The phobias that often develop as a result of panic disorder (such as agoraphobia) can be helped by another cognitive-behavioral technique, exposure therapy, wherein the patient is very gradually exposed to the fearful situation until he or she becomes desensitized to it. Medication is often prescribed for panic disorder. In many cases, a combination of psychotherapy and medication is helpful. Significant improvement is often seen within eight weeks. Phobias A phobia is an extreme, irrational fear of a particular thing or situation. People with phobias realize the fear is irrational. However, because even the thought of facing the feared object or situation brings on severe anxiety, the feared stimulus is avoided. Avoiding only intensifies the fear, since the way to get over fears is to face them. Thus, the more it is avoided, the more fearful the stimulus becomes. No one knows just what causes phobias, but more than 1 in 10 people are known to have a phobia. Psychodynamic theories hold that phobias are the manifestation of an unconscious conflict. Behavior theories posit that the feared stimulus is paired with a traumatic event, and conditioning occurs. Phobias seem to run in families. They often first appear in adolescence or adulthood. About 20 percent of adult phobias vanish on their own. Childhood phobias usually, but not always, disappear over time. Specific Phobias Typically, people develop specific phobias of, for example, heights, flying, closed-in places, elevators, dogs, going over bridges, blood, or water. A phobia can subtly or dramatically alter one s life. I can t bring myself to drive over a bridge. When I have tried, it was a dreadful feeling. I felt panicked. My heart was pounding, my mind closed down I only wanted to get off that bridge. I couldn t distract myself or have a conversation. Now, I won t try at all. I just won t do it. I can t tell you exactly what frightens me about going over a bridge nothing realistic and I know it s silly to be afraid But I just can t do it. When I drove to New York from Maine, I got out a map and found all the bridges on the route. I plotted alternate routes that avoided bridges, even though it took hours longer to get to my destination. If the feared stimulus is avoidable, it may not seem necessary to seek treatment for the fear. Instead, an individual may make adjustments in her or his life, such as in the preceding case example of bridge phobia; and the phobia may cause little, or only occasional impairment in quality of life. Likewise, someone with an elevator phobia may simply take the stairs. Sometimes, important career or personal decisions are made to avoid a phobic situation. For example, a bridge phobic may not move to San Francisco; an elevator phobic would not work in the Empire State Building. An agoraphobic may find excuses not to leave home. In some cases, a feared object or situation is not so easy to plan a life around, and in fact, makes
5 About Anxiety Disorders by Geraldine Merola Barton, Ph.D. Page 5 exceedingly difficult what for most of us are only mildly anxiety-producing situations. An example would be social phobia, which is discussed later. Approximately 3 out of 4 people with a specific phobia can be helped with a kind of cognitivebehavioral therapy called desensitization therapy, in which patients are exposed to the frightening stimulus in very gradual phases, until it can be tolerated. Relaxation techniques are also helpful in reducing anxiety symptoms. There is no proven drug treatment to cure phobias. Medication is sometimes prescribed to help an individual face a feared stimulus, such as flying. Social Phobia I was terrified of running into someone I knew and not knowing what to say. When it happened, my mind would freeze up, I d have a hard time making eye contact, my body would feel clumsy. After such a meeting, I would agonize over the encounter for hours or days, obsessing over how I d made a fool of myself, like, why did I say such a stupid thing. "Asking someone for a date was excruciating. I was so afraid a woman would find me unattractive or ridiculous or intrusive, that I froze when I tried to approach someone. I would get sick to my stomach, my palms would get clammy, and my neck would flush... Then I was certain everyone was aware what was happening, which made it even worse. It was too embarrassing, so for a long time, I avoided the whole thing and just didn t date. The same thing would happen at parties, trying to talk to people. I couldn t make small talk, so I d avoid those kinds of settings. People with social phobia tend to overlook the social awkwardness of others, but exaggerate their own real and imagined faux pas. The physical giveaways of social embarrassment, such as clumsiness or blushing, may feel painfully embarrassing, and reinforce the perception that everyone is staring at me. If you have social phobia, you may be fine, even outgoing, with people you feel close to. The social discomfort may only be a problem in specific situations, such as in a group, giving a presentation, dating, dealing with authority figures; or, more rarely, using a public restroom, eating in front of others, or writing with others watching. Social phobia often runs in families. It often begins around early adolescence or even younger. It may be accompanied by depression or alcoholism. Many individuals with social phobia can be helped by cognitive-behavioral psychotherapy. Many other individuals respond best to psychotherapy plus medication. A therapist can help you learn to view social events differently; can help you acquire skills to overcome your fears of social situations; and can teach you anxiety management techniques, such as thought management and relaxation techniques.
6 About Anxiety Disorders by Geraldine Merola Barton, Ph.D. Page 6 Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder Obsessive-compulsive disorder, or OCD, is characterized by anxious thoughts or rituals that feel beyond your control. If you have OCD, you are plagued by persistent, unwelcome thoughts or images (obsessions), or by the urgent need to carry out certain ritualized behaviors (compulsions). If you resist carrying out the rituals, tension builds to the point of seeming unbearable. Carrying out the rituals results in temporary relief from the tension, but the behaviors are not pleasurable. "My life was taken over by the need to perform rituals, and by irrational thoughts that I couldn t shake. When going up stairs, I had to count the stairs. If I thought I had lost count, I had to start again. I had to take an even number of stairs. If it was going to be an odd number, I had to skip a step to make it even. I had to turn the lights on and off a certain number of times. I had to go back and check the stove over and over, because I worried I might have somehow left it on and the house would burn down. I knew I hadn t, yet I had to keep checking! The house had to be perfectly in order, or I couldn t rest. The tension was unbearable when I tried to resist the compulsions. I d have a terrible thought, like, What if I stab my wife with this knife. That s not something I d ever do, but thoughts like that would torment me. I had to keep washing my hands, to get rid of germs. I was fearful of contaminating myself or others. I knew the thoughts and the rituals were ridiculous, but I couldn t stop until I got treatment. Many healthy people experience some of these symptoms, such as needing to check things several times or having occasional odd and alarming thoughts. OCD is diagnosed when these symptoms are so frequent and intense that they result in significant loss of quality of life. OCD seems to run in families. It usually first shows up in adolescence or early adulthood, or sometimes in childhood. The course of OCD varies. Symptoms may come and go, they may ease over time, or they may grow progressively worse. As with other anxiety disorders, cognitive-behavioral psychotherapy and/or medication is the treatment of choice. Some individuals respond best to psychotherapy, others require medication, and many others to a combination. Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder (PTSD) can strike individuals who are involved in or witness lifethreatening events such as accidents, violent acts, wars and natural disasters. Among the symptoms of PTSD are: repeatedly reliving memories of the traumatic event during the day or in nightmares; feeling detached or numb; difficulty sleeping; nightmares; depressed mood; easy startle reflex; loss of interest in things that usually cause pleasure; difficulty feeling close or affectionate with others; and irritability. Reminders or anniversaries of the event can trigger the frightening memories, or flashbacks. A flashback can cause a momentary loss of touch with reality, wherein the individual experiences images, sounds, smells, or feelings as if the event is happening over again. PTSD generally begins within three months of the trauma, but it can emerge years later. It can last for just a few months, or develop into a chronic condition.
7 About Anxiety Disorders by Geraldine Merola Barton, Ph.D. Page 7 Cognitive-behavioral psychotherapy, along with relaxation training, can be extremely helpful in changing counter-productive behaviors, thoughts and reactions that contribute to PTSD symptoms. Medications such as antidepressants and anti-anxiety medications can ease some of the symptoms of PTSD, such as depression and insomnia, but does not cure PTSD. Family support is an important component of recovery.
Fortunately, panic disorder is one of the most treatable anxiety disorders. The illness can be controlled with medication and focused psychotherapy.
 Anxiety Disorders Anxiety disorders are the most common mental illness in America. More than 19 million Americans suffer from anxiety disorders, which include panic disorder, obsessive-compulsive disorder,
Anxiety Disorders Anxiety disorders are the most common mental illness in America. More than 19 million Americans suffer from anxiety disorders, which include panic disorder, obsessive-compulsive disorder,
Highs and Lows. Anxiety and Depression
 Highs and Lows Anxiety and Depression ANXIETY Anxiety is a normal reaction to stress and can actually be beneficial in some situations. For some people, however, anxiety can become excessive. However a
Highs and Lows Anxiety and Depression ANXIETY Anxiety is a normal reaction to stress and can actually be beneficial in some situations. For some people, however, anxiety can become excessive. However a
did you feel sad or depressed? did you feel sad or depressed for most of the day, nearly every day?
 Name: Age: Date: PDSQ This form asks you about emotions, moods, thoughts, and behaviors. For each question, circle YES in the column next to that question, if it describes how you have been acting, feeling,
Name: Age: Date: PDSQ This form asks you about emotions, moods, thoughts, and behaviors. For each question, circle YES in the column next to that question, if it describes how you have been acting, feeling,
TeensHealth.org A safe, private place to get doctor-approved information on health, emotions, and life. Anxiety Disorders. What Is Anxiety?
 TeensHealth.org A safe, private place to get doctor-approved information on health, emotions, and life. What Is Anxiety? Anxiety Disorders Liam had always looked out for his younger brother Sam. But whenever
TeensHealth.org A safe, private place to get doctor-approved information on health, emotions, and life. What Is Anxiety? Anxiety Disorders Liam had always looked out for his younger brother Sam. But whenever
Anxiety Quiz. Anxiety Quiz. Anxiety Quiz
 Child and Adolescent Mental Health Anxiety in Children & Adolescents Developed by Susan Ponting M.Ed., Registered Psychologist Outline 1. 2. Behaviours Often Seen in Children with Anxiety 3. Types of Anxiety
Child and Adolescent Mental Health Anxiety in Children & Adolescents Developed by Susan Ponting M.Ed., Registered Psychologist Outline 1. 2. Behaviours Often Seen in Children with Anxiety 3. Types of Anxiety
P A N A N X I E T Y C
 P A N A N X I E T Y C The terms panic attack and anxiety attack are used interchangeably, but they are not the same. Key characteristics distinguish one from the other, though they have several symptoms
P A N A N X I E T Y C The terms panic attack and anxiety attack are used interchangeably, but they are not the same. Key characteristics distinguish one from the other, though they have several symptoms
LIFE MENTAL HEALTH ANXIETY DISORDERS TREATMENT GUIDE
 ANXIETY DISORDERS TREATMENT GUIDE Anxiety Disorders Treatment Guide What is Panic Disorder? What is Agoraphobia? What is Generalised Anxiety Disorder? What is Social Phobia? What is Obsessive-Compulsive
ANXIETY DISORDERS TREATMENT GUIDE Anxiety Disorders Treatment Guide What is Panic Disorder? What is Agoraphobia? What is Generalised Anxiety Disorder? What is Social Phobia? What is Obsessive-Compulsive
Do you have sudden bursts of fear for no reason? Panic Disorder A R E A L I L L N E S S. Panic Disorcer NIH Publication No.
 Do you have sudden bursts of fear for no reason? A R E A L I L L N E S S Panic Disorder Panic Disorcer NIH Publication No. 00-4679 Does This Sound Like You? Do you have sudden bursts of fear for no reason?
Do you have sudden bursts of fear for no reason? A R E A L I L L N E S S Panic Disorder Panic Disorcer NIH Publication No. 00-4679 Does This Sound Like You? Do you have sudden bursts of fear for no reason?
Anxiety Attacks and Anxiety Disorders
 Anxiety Attacks and Anxiety Disorders Signs, Symptoms, and Treatment We all know what anxiety feels like. Your heart pounds before a big presentation or a tough exam. You get butterflies in your stomach
Anxiety Attacks and Anxiety Disorders Signs, Symptoms, and Treatment We all know what anxiety feels like. Your heart pounds before a big presentation or a tough exam. You get butterflies in your stomach
Anxiolytics and anxiety disorders. MUDr. Vítězslav Pálenský Dept. of Psychiatry, Masaryk University, Brno
 Anxiolytics and anxiety disorders MUDr. Vítězslav Pálenský Dept. of Psychiatry, Masaryk University, Brno Anxiety disorders 1. Panic disorders and agoraphobia 2. Specific phobia and social phobia 3. Obsessive
Anxiolytics and anxiety disorders MUDr. Vítězslav Pálenský Dept. of Psychiatry, Masaryk University, Brno Anxiety disorders 1. Panic disorders and agoraphobia 2. Specific phobia and social phobia 3. Obsessive
Anxiety Disorders Overview
 Anxiety Disorders Anxiety Disorders Overview What is anxiety? Categories of anxiety disorders Generalized Anxiety Disorder Panic Disorder Specific Phobia/Social Phobia Obsessive Compulsive Disorder DSM-IV
Anxiety Disorders Anxiety Disorders Overview What is anxiety? Categories of anxiety disorders Generalized Anxiety Disorder Panic Disorder Specific Phobia/Social Phobia Obsessive Compulsive Disorder DSM-IV
Welcome to Pine Street Family Practice s Podcasts!!
 Welcome to Pine Street Family Practice s Podcasts!! New Series of Podcasts A Few Topics Anxiety Diabetes Hypertension Dementia Obesity Nutrition What will the podcast review? Brief information on a health
Welcome to Pine Street Family Practice s Podcasts!! New Series of Podcasts A Few Topics Anxiety Diabetes Hypertension Dementia Obesity Nutrition What will the podcast review? Brief information on a health
OCD and Anxiety Disorders in Individuals with Down Syndrome
 OCD and Anxiety Disorders in Individuals with Down Syndrome Risk Factors, Interventions and Family Supports Khush Amaria, Clinical Psychologist CBT Associates, Toronto ON www.cbtassociates.com Objectives
OCD and Anxiety Disorders in Individuals with Down Syndrome Risk Factors, Interventions and Family Supports Khush Amaria, Clinical Psychologist CBT Associates, Toronto ON www.cbtassociates.com Objectives
Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder
 Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder Teena Jain 2017 Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder What is post-traumatic stress disorder, or PTSD? PTSD is a disorder that some people develop after experiencing a shocking,
Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder Teena Jain 2017 Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder What is post-traumatic stress disorder, or PTSD? PTSD is a disorder that some people develop after experiencing a shocking,
COUPLE & FAMILY INSTITUTE OF TRI-CITIES AMEN ADULT GENERAL SYMPTOM CHECKLIST
 COUPLE & FAMILY INSTITUTE OF TRI-CITIES AMEN ADULT GENERAL SYMPTOM CHECKLIST Please rate yourself on each symptom listed below. Please use the following scale: 0--------------------------1---------------------------2--------------------------3--------------------------4
COUPLE & FAMILY INSTITUTE OF TRI-CITIES AMEN ADULT GENERAL SYMPTOM CHECKLIST Please rate yourself on each symptom listed below. Please use the following scale: 0--------------------------1---------------------------2--------------------------3--------------------------4
Section 4 - Dealing with Anxious Thinking
 Section 4 - Dealing with Anxious Thinking How do we challenge our unhelpful thoughts? Anxiety may decrease if we closely examine how realistic and true our unhelpful/negative thoughts are. We may find
Section 4 - Dealing with Anxious Thinking How do we challenge our unhelpful thoughts? Anxiety may decrease if we closely examine how realistic and true our unhelpful/negative thoughts are. We may find
Anxiety in Children & Adolescents 4/1/2019. Mental Health America of Eastern Missouri. Addressing Anxiety and Depression In Children.
 Addressing Anxiety and Depression In Children 1 Mental Health America of Eastern Missouri Our Mission To promote mental health and to improve the care and treatment of persons with mental illness through
Addressing Anxiety and Depression In Children 1 Mental Health America of Eastern Missouri Our Mission To promote mental health and to improve the care and treatment of persons with mental illness through
ALLIANCE COMMUNITY HOSPITAL SLEEP DISORDERS CENTER PATIENT QUESTIONNAIRE/HISTORY PLEASE COMPLETE AND BRING WITH YOU ON THE NIGHT OF YOUR TEST.
 ALLIANCE COMMUNITY HOSPITAL SLEEP DISORDERS CENTER PATIENT QUESTIONNAIRE/HISTORY PLEASE COMPLETE AND BRING WITH YOU ON THE NIGHT OF YOUR TEST. NAME DATE: HEIGHT: WEIGHT: DOB: SEX: HOME PHONE #: REFERRING
ALLIANCE COMMUNITY HOSPITAL SLEEP DISORDERS CENTER PATIENT QUESTIONNAIRE/HISTORY PLEASE COMPLETE AND BRING WITH YOU ON THE NIGHT OF YOUR TEST. NAME DATE: HEIGHT: WEIGHT: DOB: SEX: HOME PHONE #: REFERRING
Mental Health ANXIETY
 Mental Health ANXIETY My experience over 90% have mental health issues a) If addicts don t get help, their chances of remaining sober aren t good b) Most common depression and anxiety c) Many addicts used
Mental Health ANXIETY My experience over 90% have mental health issues a) If addicts don t get help, their chances of remaining sober aren t good b) Most common depression and anxiety c) Many addicts used
FATIGUE ASSESSMENT SCALE
 WORKSHEET #1 FATIGUE ASSESSMENT SCALE Please indicate how true each statement has been for you during the past 7 days Not at all A little bit Some what Quite a lot Very much I feel fatigued I feel weak
WORKSHEET #1 FATIGUE ASSESSMENT SCALE Please indicate how true each statement has been for you during the past 7 days Not at all A little bit Some what Quite a lot Very much I feel fatigued I feel weak
Learning Targets: To identify characteristics & symptoms of Anxiety, OCD & PTSD To discuss what life is like for people with Anxiety, OCD & PTSD
 Anxiety, OCD & PTSD Learning Targets: To identify characteristics & symptoms of Anxiety, OCD & PTSD To discuss what life is like for people with Anxiety, OCD & PTSD Anxiety Based Disorders They are in
Anxiety, OCD & PTSD Learning Targets: To identify characteristics & symptoms of Anxiety, OCD & PTSD To discuss what life is like for people with Anxiety, OCD & PTSD Anxiety Based Disorders They are in
CNA Training Advisor
 CNA Training Advisor Volume 14 Issue No. 11 NOVEMBER 2016 Excessive, unrealistic worry about everyday tasks or events, or specific to certain objects or rituals, may indicate an anxiety disorder. Anxiety
CNA Training Advisor Volume 14 Issue No. 11 NOVEMBER 2016 Excessive, unrealistic worry about everyday tasks or events, or specific to certain objects or rituals, may indicate an anxiety disorder. Anxiety
How to Handle a Problem
 How to Handle a Problem Determine if it is temporary or persistent. Identify your problem. Determine whether it is temporary or persistent. If temporary If persistent How serious is it? Can you handle
How to Handle a Problem Determine if it is temporary or persistent. Identify your problem. Determine whether it is temporary or persistent. If temporary If persistent How serious is it? Can you handle
Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder
 Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder When Unwanted Thoughts or Irresistible Actions Take Over Teena Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder: When Unwanted Thoughts or Irresistible Actions Take Over Introduction Do you
Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder When Unwanted Thoughts or Irresistible Actions Take Over Teena Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder: When Unwanted Thoughts or Irresistible Actions Take Over Introduction Do you
Jonathan Haverkampf PANIC ATTACKS PANIC ATTACKS. Christian Jonathan Haverkampf MD
 Christian MD Panic attacks can be highly debilitating as they occur spontaneously and come with a dread of impending doom and often death. Their unpredictability and the strong feelings of anxiety can
Christian MD Panic attacks can be highly debilitating as they occur spontaneously and come with a dread of impending doom and often death. Their unpredictability and the strong feelings of anxiety can
A1a. Have you ever had a time in your life when you felt sad, blue, or depressed for two weeks or more in a row?
 PhenX Measure: General Psychiatric Assessment (#120100) PhenX Protocol: General Psychiatric Assessment - Adult (#120101) Date of Interview/Examination (MM/DD/YYYY): SECTION A: [Major Depressive Episode]
PhenX Measure: General Psychiatric Assessment (#120100) PhenX Protocol: General Psychiatric Assessment - Adult (#120101) Date of Interview/Examination (MM/DD/YYYY): SECTION A: [Major Depressive Episode]
Anxiety Disorders. Dr. Ameena S. Mu min, LPC Counseling Services- Nestor Hall 010
 Anxiety Disorders Dr. Ameena S. Mu min, LPC Counseling Services- Nestor Hall 010 Anxiety disorders are the most common mental illness in the U.S., affecting 40 million adults in the United States age 18
Anxiety Disorders Dr. Ameena S. Mu min, LPC Counseling Services- Nestor Hall 010 Anxiety disorders are the most common mental illness in the U.S., affecting 40 million adults in the United States age 18
Social Anxiety Disorder
 Social Anxiety Disorder More than Just Shyness Teena Social Anxiety Disorder: More than Just Shyness Introduction Are you extremely afraid of being judged by others? Are you very self-conscious in everyday
Social Anxiety Disorder More than Just Shyness Teena Social Anxiety Disorder: More than Just Shyness Introduction Are you extremely afraid of being judged by others? Are you very self-conscious in everyday
Anxiety and problem solving
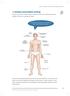 Anxiety and problem solving Anxiety is very common in ADHD, because it is diffi cult to relax with a restless body and racing thoughts. At night, worry may keep you awake. What physical sensations do you
Anxiety and problem solving Anxiety is very common in ADHD, because it is diffi cult to relax with a restless body and racing thoughts. At night, worry may keep you awake. What physical sensations do you
Specific Phobias. Symptoms
 ffl Specific Phobias Panic Disorder in Children and Adolescents Panic disorder is a common and treatable disorder. Children and adolescents with panic disorder Specific phobias are an overwhelming and
ffl Specific Phobias Panic Disorder in Children and Adolescents Panic disorder is a common and treatable disorder. Children and adolescents with panic disorder Specific phobias are an overwhelming and
PRISM SECTION 15 - STRESSFUL EVENTS
 START TIME : PRISM SECTION 15 - STRESSFUL EVENTS Statement I.1: These next questions are about difficult or stressful things that can happen to people. It may be hard to remember everything about these
START TIME : PRISM SECTION 15 - STRESSFUL EVENTS Statement I.1: These next questions are about difficult or stressful things that can happen to people. It may be hard to remember everything about these
Depression, Anxiety, and the Adolescent Athlete: Introduction to Identification and Treatment
 Depression, Anxiety, and the Adolescent Athlete: Introduction to Identification and Treatment Jamie E. Pardini, PhD Sports Medicine and Concussion Specialists Banner University Medical Center-Phoenix University
Depression, Anxiety, and the Adolescent Athlete: Introduction to Identification and Treatment Jamie E. Pardini, PhD Sports Medicine and Concussion Specialists Banner University Medical Center-Phoenix University
Panic. Information booklet. RDaSH leading the way with care
 Panic Information booklet RDaSH leading the way with care It is common to feel panicky from time to time. It could be because you think there is someone following you, you can t remember your words in
Panic Information booklet RDaSH leading the way with care It is common to feel panicky from time to time. It could be because you think there is someone following you, you can t remember your words in
A fact sheet produced by the Mental Health Information Service
 Anxiety what is it? A fact sheet produced by the Mental Health Information Service Anxiety is a natural reaction that everyone experiences - part of our fight or flight response - which helps us to be
Anxiety what is it? A fact sheet produced by the Mental Health Information Service Anxiety is a natural reaction that everyone experiences - part of our fight or flight response - which helps us to be
When Fear Overwhelms. Do you sometimes have sudden attacks. of fear that last for several minutes? Do you feel like you are having a
 Another type of medication called beta-blockers can help control some of the physical symptoms of panic disorder such as excessive sweating, a pounding heart, or dizziness.although beta blockers are not
Another type of medication called beta-blockers can help control some of the physical symptoms of panic disorder such as excessive sweating, a pounding heart, or dizziness.although beta blockers are not
AP PSYCH Unit 12.1 Abnormal Psychology Anxiety Disorders
 AP PSYCH Unit 12.1 Abnormal Psychology Anxiety Disorders Defining Psychological Disorders Abnormal Psychology At various moments, all of us feel, think or act the same way disturbed people do much of
AP PSYCH Unit 12.1 Abnormal Psychology Anxiety Disorders Defining Psychological Disorders Abnormal Psychology At various moments, all of us feel, think or act the same way disturbed people do much of
University Staff Counselling Service
 University Staff Counselling Service Anxiety and Panic What is anxiety? Anxiety is a normal emotional and physiological response to feeling threatened, ranging from mild uneasiness and worry to severe
University Staff Counselling Service Anxiety and Panic What is anxiety? Anxiety is a normal emotional and physiological response to feeling threatened, ranging from mild uneasiness and worry to severe
Answer Key for Case Studies. Grading for each case study. All Case Studies
 Answer Key for Case Studies Grading for each case study All Case Studies *give 5 points for listing at least four accurate symptoms of the disorder *give 3 points for listing 2 symptoms of the disorder
Answer Key for Case Studies Grading for each case study All Case Studies *give 5 points for listing at least four accurate symptoms of the disorder *give 3 points for listing 2 symptoms of the disorder
Seek, Test, Treat and Retain for Vulnerable Populations: Data Harmonization Measure
 Seek, Test, Treat and Retain for Vulnerable Populations: Measure MENTAL HEALTH Center for Epidemiologic Studies Depression Scale (CES-D) Reference: Radloff, L.S. (1977). The CES-D Scale: a self-report
Seek, Test, Treat and Retain for Vulnerable Populations: Measure MENTAL HEALTH Center for Epidemiologic Studies Depression Scale (CES-D) Reference: Radloff, L.S. (1977). The CES-D Scale: a self-report
Biopsychosocial Approach. considers combination of biological, psychological, and social factors as contributing to development of disorders
 Early Theories Abnormal behavior was evil spirits trying to get out, godlike powers, movement of stars Treatments: institutionalized, castration, drilling holes in skull, transfusion of animal blood, and
Early Theories Abnormal behavior was evil spirits trying to get out, godlike powers, movement of stars Treatments: institutionalized, castration, drilling holes in skull, transfusion of animal blood, and
Anxiety. Learn, think, do
 Anxiety Learn, think, do Anxiety disorders are the most common mental health problem in Australia. The Australian Bureau of Statistics reports that anxiety affects over 2 million people aged 16 85 years,
Anxiety Learn, think, do Anxiety disorders are the most common mental health problem in Australia. The Australian Bureau of Statistics reports that anxiety affects over 2 million people aged 16 85 years,
Teen Stress and Anxiety Wayne Hills Counseling Dept. June, 2017
 Teen Stress and Anxiety Wayne Hills Counseling Dept. June, 2017 True or False? 1. Even something positive, such as being selected for an award, can be stressful 2. The amount of stress you feel depends
Teen Stress and Anxiety Wayne Hills Counseling Dept. June, 2017 True or False? 1. Even something positive, such as being selected for an award, can be stressful 2. The amount of stress you feel depends
Post-traumatic Stress Disorder
 Parkland College A with Honors Projects Honors Program 2012 Post-traumatic Stress Disorder Nicole Smith Parkland College Recommended Citation Smith, Nicole, "Post-traumatic Stress Disorder" (2012). A with
Parkland College A with Honors Projects Honors Program 2012 Post-traumatic Stress Disorder Nicole Smith Parkland College Recommended Citation Smith, Nicole, "Post-traumatic Stress Disorder" (2012). A with
A NEW MOTHER S. emotions. Your guide to understanding maternal mental health
 A NEW MOTHER S emotions Your guide to understanding maternal mental health It is not your fault It is treatable Understanding Maternal Mental Health Life with a new baby is not always easy and the adjustment
A NEW MOTHER S emotions Your guide to understanding maternal mental health It is not your fault It is treatable Understanding Maternal Mental Health Life with a new baby is not always easy and the adjustment
Gray Matters 5/15/2017. Presentation Objectives. Definition. What You Need to Know About Aging and Anxiety
 Gray Matters What You Need to Know About Aging and Anxiety This presentation is made possible by a grant from the Extendicare Foundation Presentation Objectives Understand symptoms and risk factors of
Gray Matters What You Need to Know About Aging and Anxiety This presentation is made possible by a grant from the Extendicare Foundation Presentation Objectives Understand symptoms and risk factors of
EMOTIONAL SUPPORT ANIMAL (ESA) PSYCHOLOGICAL EVALUATION PART I: PERSONAL INFORMATION STREET ADDRESS CITY/STATE
 EMOTIONAL SUPPORT ANIMAL (ESA) PSYCHOLOGICAL EVALUATION PART I: PERSONAL INFORMATION FIRST NAME LAST NAME EMAIL PHONE # STREET ADDRESS CITY/STATE ZIP GENDER: MALE FEMALE TRANSGENER MARITAL STATUS: MARRIED
EMOTIONAL SUPPORT ANIMAL (ESA) PSYCHOLOGICAL EVALUATION PART I: PERSONAL INFORMATION FIRST NAME LAST NAME EMAIL PHONE # STREET ADDRESS CITY/STATE ZIP GENDER: MALE FEMALE TRANSGENER MARITAL STATUS: MARRIED
Aging Adults and Anxiety What You Need to Know. Behavioral Healthcare Options, Inc.
 Aging Adults and Anxiety What You Need to Know Behavioral Healthcare Options, Inc. You are Not Alone Anxiety is a common feeling. Almost everyone has felt it at one time or another, but those who suffer
Aging Adults and Anxiety What You Need to Know Behavioral Healthcare Options, Inc. You are Not Alone Anxiety is a common feeling. Almost everyone has felt it at one time or another, but those who suffer
PSYCHOLOGICAL DISORDERS
 PSYCHOLOGICAL DISORDERS 1. Anxiety Disorder a state of uneasiness that occurs in response to a vague or imagined danger a. Phobic Disorders b. Panic Disorders c. Generalized Anxiety Disorders d. Obsessive-Compulsive
PSYCHOLOGICAL DISORDERS 1. Anxiety Disorder a state of uneasiness that occurs in response to a vague or imagined danger a. Phobic Disorders b. Panic Disorders c. Generalized Anxiety Disorders d. Obsessive-Compulsive
Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder (OCD)
 Do you feel trapped in a pattern of unwanted and upsetting thoughts? A R E A L I L L N E S S Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder (OCD) Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder NIH Publication No. 00-4676 Does This Sound
Do you feel trapped in a pattern of unwanted and upsetting thoughts? A R E A L I L L N E S S Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder (OCD) Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder NIH Publication No. 00-4676 Does This Sound
Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder
 Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder "I was raped when I was 25 years old. For a long time, I spoke about the rape as though it was something that happened to someone else. I was very aware that it had happened
Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder "I was raped when I was 25 years old. For a long time, I spoke about the rape as though it was something that happened to someone else. I was very aware that it had happened
ANXIETY: SCREENING, DIFFERENTIAL DIAGNOSIS, TREATMENT MONITORING
 Psychiatry and Addictions Case Conference UW Medicine Psychiatry and Behavioral Sciences ANXIETY: SCREENING, DIFFERENTIAL DIAGNOSIS, TREATMENT MONITORING DEB COWLEY MD OCTOBER 20, 2016 OBJECTIVES At the
Psychiatry and Addictions Case Conference UW Medicine Psychiatry and Behavioral Sciences ANXIETY: SCREENING, DIFFERENTIAL DIAGNOSIS, TREATMENT MONITORING DEB COWLEY MD OCTOBER 20, 2016 OBJECTIVES At the
Some Common Mental Disorders in Young People Module 3B
 Some Common Mental Disorders in Young People Module 3B MENTAL ILLNESS AND TEENS About 70% of all mental illnesses can be diagnosed before 25 years of age When they start, most mental illnesses are mild
Some Common Mental Disorders in Young People Module 3B MENTAL ILLNESS AND TEENS About 70% of all mental illnesses can be diagnosed before 25 years of age When they start, most mental illnesses are mild
Stress & Mood Management. Managing Anxiety and Panic. Course Slides. Keeping Yourself Safe
 Course Slides Stress & Mood Management Managing Anxiety and Panic To obtain a copy of the course slides, log on to: www.inclusionthurrock.org Alternatively, email smm@sssft.nhs.uk. Please do not send any
Course Slides Stress & Mood Management Managing Anxiety and Panic To obtain a copy of the course slides, log on to: www.inclusionthurrock.org Alternatively, email smm@sssft.nhs.uk. Please do not send any
MAXIMIZING PERFORMANCE BY MINIMIZING ANXIETY RICHARD BOGIELSKI
 MAXIMIZING PERFORMANCE BY MINIMIZING ANXIETY RICHARD BOGIELSKI August 7, 2017 Anxiety Anxiety is a normal human experience Anxiety which interferes with functionality is the definition of dysfunction What
MAXIMIZING PERFORMANCE BY MINIMIZING ANXIETY RICHARD BOGIELSKI August 7, 2017 Anxiety Anxiety is a normal human experience Anxiety which interferes with functionality is the definition of dysfunction What
Who has Schizophrenia? What is Schizophrenia? 11/20/2013. Module 33. It is also one of the most misunderstood of all psychological disorders!
 What is Schizophrenia? Module 33 It is also one of the most misunderstood of all psychological disorders! Who has Schizophrenia? A middle-aged man walks the streets of New York with aluminum foil under
What is Schizophrenia? Module 33 It is also one of the most misunderstood of all psychological disorders! Who has Schizophrenia? A middle-aged man walks the streets of New York with aluminum foil under
Anxiety Disorders. Fear & Anxiety. Anxiety Disorder? 26/5/2014. J. H. Atkinson, M.D. Fear. Anxiety. An anxiety disorder is present when
 Anxiety s J. H. Atkinson, M.D. HIV Neurobehavioral Research Center University of California, San Diego Department of Psychiatry & Veterans Affairs Healthcare System, San Diego Materials courtesy of Dr.
Anxiety s J. H. Atkinson, M.D. HIV Neurobehavioral Research Center University of California, San Diego Department of Psychiatry & Veterans Affairs Healthcare System, San Diego Materials courtesy of Dr.
CBT Intake Form. Patient Name: Preferred Name: Last. First. Best contact phone number: address: Address:
 Patient Information CBT Intake Form Patient Name: Preferred Name: Last Date of Birth: _// Age: _ First MM DD YYYY Gender: Best contact phone number: Email address: _ Address: _ Primary Care Physician:
Patient Information CBT Intake Form Patient Name: Preferred Name: Last Date of Birth: _// Age: _ First MM DD YYYY Gender: Best contact phone number: Email address: _ Address: _ Primary Care Physician:
Psychological preparation for natural disasters
 Disaster Preparedness Psychological preparation for natural disasters Being psychologically prepared when a disaster is threatening can help people feel more confident, more in control and better able
Disaster Preparedness Psychological preparation for natural disasters Being psychologically prepared when a disaster is threatening can help people feel more confident, more in control and better able
Gray Matters What You Need To Know About Aging and Anxiety
 Gray Matters What You Need To Know About Aging and Anxiety This session is presented by a collaboration of Minnesota health plans working to improve antidepressant medication management in Minnesota. Thank
Gray Matters What You Need To Know About Aging and Anxiety This session is presented by a collaboration of Minnesota health plans working to improve antidepressant medication management in Minnesota. Thank
ObsessiveCompulsive. Disorder: When Unwanted Thoughts Take Over. Do you feel the need to check and. re-check things over and over?
 What is it like having OCD? I couldn t do anything without rituals. They invaded every aspect of my life. Counting really bogged me down. I would wash my hair three times as opposed to once because three
What is it like having OCD? I couldn t do anything without rituals. They invaded every aspect of my life. Counting really bogged me down. I would wash my hair three times as opposed to once because three
Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder
 When Unwanted Thoughts Take Over: Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder National Institute of Mental Health U.S. DEPARTMENT OF HEALTH AND HUMAN SERVICES National Institutes of Health National Institute of Mental
When Unwanted Thoughts Take Over: Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder National Institute of Mental Health U.S. DEPARTMENT OF HEALTH AND HUMAN SERVICES National Institutes of Health National Institute of Mental
Name That Disorder Psychological Disorders Name Date Period
 Name Date Period Directions: Read each case and do the following: 1) write the name of the psychological disorder that is the best diagnosis for that person next to Diagnosis 2) write the specific symptoms
Name Date Period Directions: Read each case and do the following: 1) write the name of the psychological disorder that is the best diagnosis for that person next to Diagnosis 2) write the specific symptoms
Post Traumatic Stress Disorder (PTSD) (PTSD)
 Post Traumatic Stress Disorder (PTSD) (PTSD) Reference: http://www.psychiatry.org/military Prevalence of PTSD One in five veterans of the Iraq and Afghanistan wars is diagnosed with PTSD. (http://www.psychiatry.org/military
Post Traumatic Stress Disorder (PTSD) (PTSD) Reference: http://www.psychiatry.org/military Prevalence of PTSD One in five veterans of the Iraq and Afghanistan wars is diagnosed with PTSD. (http://www.psychiatry.org/military
Anxiety, Stress and Health Disorders. Mr. Mattingly Abnormal Psychology
 Anxiety, Stress and Health Disorders Mr. Mattingly Abnormal Psychology What is Anxiety? Anxiety = state of apprehension, tension or worry AKA: Fearful Behavior Distinction: Adaptive Fear vs. Maladaptive
Anxiety, Stress and Health Disorders Mr. Mattingly Abnormal Psychology What is Anxiety? Anxiety = state of apprehension, tension or worry AKA: Fearful Behavior Distinction: Adaptive Fear vs. Maladaptive
Molly Faulkner, PhD, CNP, LISW UNM, Dept of Psychiatry and Behavioral Sciences Div of Community Behavioral Health
 Molly Faulkner, PhD, CNP, LISW UNM, Dept of Psychiatry and Behavioral Sciences Div of Community Behavioral Health What is anxiety? What causes anxiety? When is anxiety a problem? What is the size of the
Molly Faulkner, PhD, CNP, LISW UNM, Dept of Psychiatry and Behavioral Sciences Div of Community Behavioral Health What is anxiety? What causes anxiety? When is anxiety a problem? What is the size of the
1 anxiety and substance use
 1 anxiety and substance use anxiety and substance use 2 Contents Who is this booklet for and what does it do? 3 What is anxiety? 3 What is an anxiety disorder? 5 How common are anxiety disorders? 6 What
1 anxiety and substance use anxiety and substance use 2 Contents Who is this booklet for and what does it do? 3 What is anxiety? 3 What is an anxiety disorder? 5 How common are anxiety disorders? 6 What
a guide to living with ANXIETY Information provided by Mental Health Foundation
 www.mentalhealthireland.ie a guide to living with ANXIETY Information provided by Mental Health Foundation 1 a guide to living with anxiety about Mental Health Ireland (MHI) is a national voluntary organisation.
www.mentalhealthireland.ie a guide to living with ANXIETY Information provided by Mental Health Foundation 1 a guide to living with anxiety about Mental Health Ireland (MHI) is a national voluntary organisation.
KNOW WHAT CATEGORY ANY DISORDER FITS INTO
 KNOW WHAT CATEGORY ANY DISORDER FITS INTO Categories of Disorder: 1. Anxiety 2. Mood 3. Dissociative 4. Schizophrenia 5. Personality 6. Somatoform (Not in Book) 7. Facticious (Not in Book) Anxiety Disorders
KNOW WHAT CATEGORY ANY DISORDER FITS INTO Categories of Disorder: 1. Anxiety 2. Mood 3. Dissociative 4. Schizophrenia 5. Personality 6. Somatoform (Not in Book) 7. Facticious (Not in Book) Anxiety Disorders
Understanding Complex Trauma
 Understanding Complex Trauma Frightening events can have lasting effects Trauma and Homelessness Team Carswell House Dennistoun Glasgow G31 2HX Tel: 0141 232 0114 Fax: 0141 232 0131 General enquiries email:
Understanding Complex Trauma Frightening events can have lasting effects Trauma and Homelessness Team Carswell House Dennistoun Glasgow G31 2HX Tel: 0141 232 0114 Fax: 0141 232 0131 General enquiries email:
9.MEH.2.2 Design useful help- seeking strategies for depression and mental disorders.
 Essential Standard 9.MEH.2 Create help- seeking strategies for depression and mental disorders. Clarifying Objective 9.MEH.2.2 Design useful help- seeking strategies for depression and mental disorders.
Essential Standard 9.MEH.2 Create help- seeking strategies for depression and mental disorders. Clarifying Objective 9.MEH.2.2 Design useful help- seeking strategies for depression and mental disorders.
Depression/Anxiety Customer Care Packet
 Depression/Anxiety Customer Care Packet The following resources have been provided to you from the experts at eni Our 30 years of experience and our highly skilled, friendly and knowledgeable staff are
Depression/Anxiety Customer Care Packet The following resources have been provided to you from the experts at eni Our 30 years of experience and our highly skilled, friendly and knowledgeable staff are
What is Schizophrenia?
 What is Schizophrenia? Module 33 What symptoms would you expect this person to display? It is also one of the most misunderstood of all psychological disorders! 1 Who has Schizophrenia? A middle-aged man
What is Schizophrenia? Module 33 What symptoms would you expect this person to display? It is also one of the most misunderstood of all psychological disorders! 1 Who has Schizophrenia? A middle-aged man
MENTAL HEALTH AND OUR WORKPLACE CNLOPB SAFETY FORUM MAY 20 TH, 2015
 MENTAL HEALTH AND OUR WORKPLACE CNLOPB SAFETY FORUM MAY 20 TH, 2015 HOW MENTAL HEALTH AFFECTS OUR OFFSHORE WORKFORCE AND HOW WE CAN HELP OUR COWORKERS, FRIENDS AND FAMILY WHO MAY BE SUFFERING FROM A MENTAL
MENTAL HEALTH AND OUR WORKPLACE CNLOPB SAFETY FORUM MAY 20 TH, 2015 HOW MENTAL HEALTH AFFECTS OUR OFFSHORE WORKFORCE AND HOW WE CAN HELP OUR COWORKERS, FRIENDS AND FAMILY WHO MAY BE SUFFERING FROM A MENTAL
Anxiety Disorders. Phenomenology. Phenomenology. Dr. Boland: Anxiety Disorders. Mental Status Exam. General appearance Physical symptoms of anxiety
 Anxiety Disorders Phenomenology Phenomenology Mental Status Exam General appearance Physical symptoms of anxiety Emotional symptoms Thoughts Cognitive symptoms 1 Phenomenology Anxiety as Warning Signal
Anxiety Disorders Phenomenology Phenomenology Mental Status Exam General appearance Physical symptoms of anxiety Emotional symptoms Thoughts Cognitive symptoms 1 Phenomenology Anxiety as Warning Signal
Anxiety. DISORDERs? What ARE ANXIETY. What Are Anxiety Disorders? Physical Symptoms. Psychological Symptoms
 PRESENTS What ARE Anxiety s? w orry stress payments headache ANXIETY work bills What Are Anxiety Disorders? Individuals with an anxiety disorder can experience psychological or physical symptoms, or both.
PRESENTS What ARE Anxiety s? w orry stress payments headache ANXIETY work bills What Are Anxiety Disorders? Individuals with an anxiety disorder can experience psychological or physical symptoms, or both.
FMS Psychology, PLLC Adult Intake Form. Phone Number (Day): Phone Number (Evening):
 FMS Psychology, PLLC Adult Intake Form General Information: Name: Date of Birth: / / Age: Gender: Address: Phone Number (Day): Phone Number (Evening): Primary Care Physician: Highest Level of Formal Education:
FMS Psychology, PLLC Adult Intake Form General Information: Name: Date of Birth: / / Age: Gender: Address: Phone Number (Day): Phone Number (Evening): Primary Care Physician: Highest Level of Formal Education:
Be a Warrior, Not a Worrier: Anxiety Disorders in the Pediatric Setting
 Be a Warrior, Not a Worrier: Anxiety Disorders in the Pediatric Setting Ramon Solhkhah, M.D. Professor and Founding Chair, Department of Psychiatry & Behavioral Health Hackensack Meridian School of Medicine
Be a Warrior, Not a Worrier: Anxiety Disorders in the Pediatric Setting Ramon Solhkhah, M.D. Professor and Founding Chair, Department of Psychiatry & Behavioral Health Hackensack Meridian School of Medicine
Does anxiety cause some difficulty for a young person you know well? What challenges does this cause for the young person in the family or school?
 John Walker, Ph.D. Department of Clinical Health Psychology University of Manitoba Everyone has the emotions at times. Signal us to be careful. Help us to stay safe. Most children and adults have mild
John Walker, Ph.D. Department of Clinical Health Psychology University of Manitoba Everyone has the emotions at times. Signal us to be careful. Help us to stay safe. Most children and adults have mild
Panic Stations Module 2
 PANIC STATIONS Panic Stations Module 2 More about Panic Introduction 2 How do panic attacks happen? 2 How does panic disorder develop? 3 How is panic disorder maintained? 4 What can be done about panic
PANIC STATIONS Panic Stations Module 2 More about Panic Introduction 2 How do panic attacks happen? 2 How does panic disorder develop? 3 How is panic disorder maintained? 4 What can be done about panic
ADULT QUESTIONNAIRE. Date of Birth: Briefly describe the history and development of this issue from onset to present.
 ADULT QUESTIONNAIRE Name: Address: Preferred phone number to reach you: Is it okay to leave a message? Yes No (Please check one) Date of Birth: Reason(s) for seeking treatment at this time? Briefly describe
ADULT QUESTIONNAIRE Name: Address: Preferred phone number to reach you: Is it okay to leave a message? Yes No (Please check one) Date of Birth: Reason(s) for seeking treatment at this time? Briefly describe
EMOTIONAL SUPPORT ANIMAL (ESA) PSYCHOLOGICAL EVALUATION. Important Information
 EMOTIONAL SUPPORT ANIMAL (ESA) PSYCHOLOGICAL EVALUATION Important Information The primary purpose of an Emotional Support Animal (ESA) is to help his or her owner by decreasing symptoms that are associated
EMOTIONAL SUPPORT ANIMAL (ESA) PSYCHOLOGICAL EVALUATION Important Information The primary purpose of an Emotional Support Animal (ESA) is to help his or her owner by decreasing symptoms that are associated
WORD WALL. Write 3-5 sentences using as many words as you can from the list below.
 WORD WALL Write 3-5 sentences using as many words as you can from the list below. Suicide Phobia Bipolar Obsessive compulsive disorder(ocd) Anxiety Depression Mood Post traumatic stress disorder (PTSD)
WORD WALL Write 3-5 sentences using as many words as you can from the list below. Suicide Phobia Bipolar Obsessive compulsive disorder(ocd) Anxiety Depression Mood Post traumatic stress disorder (PTSD)
Your Anxious Child: What Parents Need to Know. Caryl Oris, MD
 Your Anxious Child: What Parents Need to Know Caryl Oris, MD What s Normal? n Normal developmental fears: n Separation Anxiety n Fear of the dark n Separation Anxiety n Fear is a physiological reaction
Your Anxious Child: What Parents Need to Know Caryl Oris, MD What s Normal? n Normal developmental fears: n Separation Anxiety n Fear of the dark n Separation Anxiety n Fear is a physiological reaction
Anxiety vs. Fear. Anxiety. Fear. Both involve physiological arousal. Both can be adaptive. Apprehension about a future threat
 Anxiety Disorders Anxiety vs. Fear Anxiety Apprehension about a future threat Fear Response to an immediate threat Both involve physiological arousal Sympathetic nervous system Both can be adaptive Fear
Anxiety Disorders Anxiety vs. Fear Anxiety Apprehension about a future threat Fear Response to an immediate threat Both involve physiological arousal Sympathetic nervous system Both can be adaptive Fear
Excerpted From "Staying Sober" By: Terence T. Gorski
 Excerpted From "Staying Sober" By: Terence T. Gorski With additions by: Lee Jamison When most people think about alcoholism or drug addiction they think only of the alcohol/drug-based symptoms and forget
Excerpted From "Staying Sober" By: Terence T. Gorski With additions by: Lee Jamison When most people think about alcoholism or drug addiction they think only of the alcohol/drug-based symptoms and forget
An Overview of Anxiety Disorders. Made available to ACT courtesy of Freedom From Fear. Jack D. Maser, Ph.D. National Institute of Mental Health
 An Overview of Anxiety Disorders Made available to ACT courtesy of Freedom From Fear Jack D. Maser, Ph.D. National Institute of Mental Health Fear and anxiety are a normal part of life, even adaptive in
An Overview of Anxiety Disorders Made available to ACT courtesy of Freedom From Fear Jack D. Maser, Ph.D. National Institute of Mental Health Fear and anxiety are a normal part of life, even adaptive in
DSM-IV-TR Diagnostic Criteria For Posttraumatic Stress Disorder
 DSM-IV-TR Diagnostic Criteria For Posttraumatic Stress Disorder PTSD When an individual who has been exposed to a traumatic event develops anxiety symptoms, re-experiencing of the event, and avoidance
DSM-IV-TR Diagnostic Criteria For Posttraumatic Stress Disorder PTSD When an individual who has been exposed to a traumatic event develops anxiety symptoms, re-experiencing of the event, and avoidance
Resources for Mental Health: Knowing Where to Look for Resources in Your Community
 Resources for Mental Health: Knowing Where to Look for Resources in Your Community April 28-29, 29, 2004 Paul Galonsky Mental Health Association in Delaware Mental Health Association In Delaware Founded
Resources for Mental Health: Knowing Where to Look for Resources in Your Community April 28-29, 29, 2004 Paul Galonsky Mental Health Association in Delaware Mental Health Association In Delaware Founded
CBT and Anxiety. Marjorie Rabiau, Ph.D. Pearl Lebovitch Clinical Day November 18, 2014
 CBT and Anxiety Marjorie Rabiau, Ph.D. Pearl Lebovitch Clinical Day November 18, 2014 Objectives Discuss effectiveness of CBT to treat anxiety Explain different CBT strategies to treat anxiety How to adapt
CBT and Anxiety Marjorie Rabiau, Ph.D. Pearl Lebovitch Clinical Day November 18, 2014 Objectives Discuss effectiveness of CBT to treat anxiety Explain different CBT strategies to treat anxiety How to adapt
INTERVIEWER INSTRUCTION: AFTER EACH YES RESPONSE, ASK R TO CHECK CORRESPONDING SITUATION IN BOOKLET.
 09/25/01 AGORAPHOBIA SECTION (AG) INTERVIEWER INSTRUCTION: AFTER EACH YES RESPONSE, ASK R TO CHECK CORRESPONDING SITUATION IN BOOKLET. *AG1. (RB, PG 12) Earlier you mentioned having a strong fear of things
09/25/01 AGORAPHOBIA SECTION (AG) INTERVIEWER INSTRUCTION: AFTER EACH YES RESPONSE, ASK R TO CHECK CORRESPONDING SITUATION IN BOOKLET. *AG1. (RB, PG 12) Earlier you mentioned having a strong fear of things
Controlling Worries and Habits
 THINK GOOD FEEL GOOD Controlling Worries and Habits We often have obsessional thoughts that go round and round in our heads. Sometimes these thoughts keep happening and are about worrying things like germs,
THINK GOOD FEEL GOOD Controlling Worries and Habits We often have obsessional thoughts that go round and round in our heads. Sometimes these thoughts keep happening and are about worrying things like germs,
COURSES ARTICLE - THERAPYTOOLS.US. Child Planning: A Treatment Planning Overview for Children with Phobias
 COURSES ARTICLE - THERAPYTOOLS.US Child Planning: A Treatment Planning Overview for Children with Phobias A Treatment Overview for Children with Phobias Duration: 3 hours Learning Objectives: Obtain a
COURSES ARTICLE - THERAPYTOOLS.US Child Planning: A Treatment Planning Overview for Children with Phobias A Treatment Overview for Children with Phobias Duration: 3 hours Learning Objectives: Obtain a
BRIEF PSYCHIATRIC SCREEN- ADOLESCENT
 BRIEF PSYCHIATRIC SCREEN- ADOLESCENT WILLIAM T. GOLDMAN, M.D. Adult and Pediatric Psychiatry Diplomate of the American Board of Psychiatry and Neurology 542 Silicon Dr. #100 Southlake, TX 76092 817/329-3300
BRIEF PSYCHIATRIC SCREEN- ADOLESCENT WILLIAM T. GOLDMAN, M.D. Adult and Pediatric Psychiatry Diplomate of the American Board of Psychiatry and Neurology 542 Silicon Dr. #100 Southlake, TX 76092 817/329-3300
Section VI, Module I: A Mental Health-Friendly Workplace Handouts
 Module I: Handout 1, Some Common Mental Illnesses Handout 2, A Mental Health- Friendly Workplace (Circle Diagram) Handout 3, What We Can Do To Counter Stigma Handout 4, Myths and s About People With Mental
Module I: Handout 1, Some Common Mental Illnesses Handout 2, A Mental Health- Friendly Workplace (Circle Diagram) Handout 3, What We Can Do To Counter Stigma Handout 4, Myths and s About People With Mental
Chapter 5 - Anxiety Disorders
 Chapter 5 - Anxiety Disorders I. PANIC DISORDER A. Description - with &without Agoraphobia 1. PD w/o Agora - panic attacks - feeling of imminent death - numerous symptoms (racing heart, sweating, dizziness)
Chapter 5 - Anxiety Disorders I. PANIC DISORDER A. Description - with &without Agoraphobia 1. PD w/o Agora - panic attacks - feeling of imminent death - numerous symptoms (racing heart, sweating, dizziness)
Fear and panic in humans with bilateral amygdala damage
 Fear and panic in humans with bilateral amygdala damage Justin S. Feinstein*, Colin Buzza*, Rene Hurlemann*, Robin L. Follmer, Nader S. Dahdaleh, William H. Coryell, Michael J. Welsh, Daniel Tranel, and
Fear and panic in humans with bilateral amygdala damage Justin S. Feinstein*, Colin Buzza*, Rene Hurlemann*, Robin L. Follmer, Nader S. Dahdaleh, William H. Coryell, Michael J. Welsh, Daniel Tranel, and
Generalized Anxiety Disorder:
 Generalized Anxiety Disorder: When Worry Gets Out of Control Are you extremely worried about everything in your life, even if there is little or no reason to worry? Are you very anxious about just getting
Generalized Anxiety Disorder: When Worry Gets Out of Control Are you extremely worried about everything in your life, even if there is little or no reason to worry? Are you very anxious about just getting
Non-epileptic attacks
 Non-epileptic attacks A short guide for patients and families Information for patients Neurology Psychotherapy Service What are non-epileptic attacks? Non-epileptic attacks are episodes in which people
Non-epileptic attacks A short guide for patients and families Information for patients Neurology Psychotherapy Service What are non-epileptic attacks? Non-epileptic attacks are episodes in which people
A report about. Anxiety. Easy Read summary
 A report about Anxiety Easy Read summary Mental Health Awareness Week 2014 This is an Easy Read summary of the Living with Anxiety report (2014). This report was written by the Mental Health Foundation.
A report about Anxiety Easy Read summary Mental Health Awareness Week 2014 This is an Easy Read summary of the Living with Anxiety report (2014). This report was written by the Mental Health Foundation.
Dr. Catherine Mancini and Laura Mishko
 Dr. Catherine Mancini and Laura Mishko Interviewing Depression, with case study Screening When it needs treatment Anxiety, with case study Screening When it needs treatment Observation Asking questions
Dr. Catherine Mancini and Laura Mishko Interviewing Depression, with case study Screening When it needs treatment Anxiety, with case study Screening When it needs treatment Observation Asking questions
