Case Reports Sirenomelia (symelia apus) with Potter s syndrome in connection with gestational diabetes mellitus: a case report and literature review
|
|
|
- Janel Peters
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Case Reports Sirenomelia (symelia apus) with Potter s syndrome in connection with gestational diabetes mellitus: a case report and literature review Al-Haggar M 1, Yahia S 1, Abdel-Hadi D 1, Grill F 2, *Al Kaissi A 2,3 1. Pediatrics Department, Genetic unit Mansoura University Children s Hospital, Mansoura, Egypt 2. Orthopaedic Hospital of Speising, Paediatric orthopaedic surgery, Speisinger Strasse 109, Vienna, Austria 3. Ludwig Boltzmann Institute of Osteology, at the Hanusch Hospital of WGKK and, AUVA Trauma Centre Meidling, 4th Medical Department, Hanusch Hospital Abstract We report one case of a fetus of sirenomelia sequence with Potters syndrome which showed oligohydramnios and symelia apus. The infant showed absent urinary tract and external genitalia, the legs were fused by skin and had separate bones associated with Potter s syndrome. The mother had a history of gestational diabetes mellitus. Key words: Sirenomelia; Potter s syndrome; Symelia apus; Gestational diabetes mellitus African Health Sciences 2010; 10(4): Introduction Sirenomelia, or the mermaid syndrome, is the most extreme example of the caudal regression syndrome. It invariably presents with lower limb fusion, sacral and pelvic bony anomalies, absent external genitalia, anal imperforation, and renal agenesis or dysgenesis. Because of the resultant oligohydramnios, these infants most often have Potter s facies and pulmonary hypoplasia. Prognosis is very poor because of the condition involves variable major anomalies, including bilateral renal agenesis, sacral agenesis and imperforate anus. Only four cases of a surviving infant with sirenomelia have been reported 1. Potter syndrome is usually fatal in the first few days of the patient s life; most often, the cause is pulmonary failure. Neonates with the potter sequence have an increased morbidity rate because of respiratory failure, pneumothorax, and acute renal failure during the neonatal period. Infants with Potter s facies have a flattened nose, receded chin, prominent epicanthal folds, and low-set abnormal ears. The case described *Correspondence author: Ali Al Kaissi Ludwig Boltzmann Institute of Osteology Hanusch Hospital of WGKK and AUVA Trauma Centre Meidling 4th Medical Department, Hanusch Hospital Heinrich Collin Strasse 30 A- Vienna, 1140 Austria ali.alkaissi@osteologie.at in this report shows the association of the abnormality with the syndrome described by Potter of renal agenesis, hypoplasia of the lungs, and a typical facies 1,2.The condition occurs predominantly in males, with a sex ratio of 2.7: 1 3. The sex of our foetus is a female. Most cases of caudal regression are sporadic or associated with gestational/maternal diabetes. The condition is thought to be part of a spectrum including imperforate anus, sacral agenesis and sirenomelia 4. Gestational diabetes mellitus is not a disease per se, but an abnormal plasma glucose level. Controversies still exist regarding gestational diabetes mellitus (GDM) and its prevalence, screening, clinical management and impact on maternal and infant outcomes 5-9. Clinical report A 42-week, 2450 gram term infant was born by a caesarean section to a primagravida mother 24- yearold- with a history of gestational diabetes mellitus. No family history of similar conditions (congenital anomalies) or consanguinity. Prenatal ultrasound showed marked oligohydramnios which was associated with marked restriction of the movement of lower limbs. Later on, just before labour, sonar showed absent bladder and kidneys, marked scoliosis to left side due to extensive vertebral malsegmentation. Elective caesarean section had been undertaken to avoid postmaturity. Examination of the infant revealed; the face showed all the features as described by Potter (flattening of the nose, African Health Sciences Vol 10 No 4 December
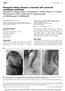
2 recession of the chin, soft flat ears, with apparent absence of the cartilage, and low positioning of the eras, the eyes showed hypertelorism (a wide interocular distance, and prominent epicanthal folds, forming a wide semicircle on each side of the nose and covering medial palpebral commissure) (fig 1). Figure 2: Sirenomelia (symelia apus): The lower limbs were joined together, the site of the fusion being along the postaxial of the limbs (being fused together in midline) Figure1: Examination of the infant revealed: the face showed all the features as described by Potter (flattening of the nose, recession of the chin, soft flat ears, with apparent absence of the cartilage, and low positioning of the eras, the eyes showed hypertelorism (a wide inter-ocular distance, and prominent epicanthal folds, forming a wide semicircle on each side of the nose and covering medial palpebral commissure). The pelvis was of small size and no external genitalia could be seen. The lower limbs were joined together, the site of the fusion being along the postaxial of the limbs (being fused together in midline) (fig 2). Cardiac examination was uneventful apart from ejection systolic murmur maximum on the second left interspace, echocardiographic evaluation revealed no structural anomaly but only haemodynamic abnormalities of persistent foetal circulation secondary to bilateral pulmonary hypoplasia. Radiologically there is hypoplasia of iliac bones, sacral agenesis causing effectively the development of severe spondylopelvic dissociation, multiple vertebral and rib malformation complex also showed the presence of both femora, and both tibiae with a single rudimentary and hypoplastic fibula impacted between the tibiae (arrow) (fig3). Figure 3. Anteroposterior radiograph of the axial and the appendicular skeleton showed hypoplasia of iliac bones, sacral agenesis causing effectively the development of severe spondylopelvic dissociation, multiple vertebral and rib malformation complex also showed the presence of both femora, tibiae with a single rudimentary and hypoplastic fibula impacted between the tibiae (arrow). 396 African Health Sciences Vol 10 No 4 December 2010
3 Apgar scores were 4, 7 at one and 5 minutes; patient was immediately transferred to neonatal intensive care unit and subjected to assisted ventilation. Postnatal ultrasound revealed absence of the bladder, ureters, and both kidneys. In the subsequent days patients developed deterioration of the ventilatory parameters; chest x-rays revealed air leak. Family refused autopsy studies. Cytogenetic analysis revealed a normal female fetus (46, XX). Discussion A malformation is a primary error of normal development or morphogenesis of an organ or tissue. All malformations are thus congenital or present at birth, although they may not be diagnosed until later, specially if microscopic or if internal organs are involved malformations may be single or multiple and may be of minor or major clinical significance. About 14% of newborns have a single minor malformation, 3% of newborns have a single major malformation and 0.7% of new born have multiple major malformations. The frequency of major malformations is even higher at conception (10-15%), but the majority of these fetuses are spontaneously aborted. a disruption (or secondary malformation) is a morphological defect due to breakdown of a previously normal organ or tissue. Disruptions can arise at any stage of gestation after initial morphogenesis. Similarly, deformations arise after the embryonic period and are alterations in shape caused by unusual mechanical forces. About 2% of newborns are affected, with multiple deformations in one-third. Malformations and deformations coexist, and there is an increased risk of deformation (8%) in the presence of a major congenital malformation, especially of the central nervous system or urinary tract. multifactorial inheritance is the commonest identifiable cause of congenital malformations followed by monogenic and chromosomal abnormalities. Thus, genetic disorders account for at least one-third of all congenital malformations of known aetiology.deformations are caused by any factor which restricts the mobility of the foetus such as oligohydramnios and so causes prolonged compression in an abnormal posture 10. Infants of diabetic mothers have two to three times the average incidence of congenital anomalies. These include neural tube defects, cardiac defects (transposition of the great vessels, coarctation of the aorta, VSD, ASD, cardiomyopathy), situs inversus, renal anomalies (hydronephrosis, renal agenesis, multicystic dysplastic kidney, duplication of the renal tracts), intestinal atresia, and forms of caudal regression including sacral agenesis 7,8. Lynch and Wright 9 reported a case where the mother had diabetes and the infant had sirenomelia with renal agenesis and an absent right radius. There was also a hypertrophic cardiomyopathy and a bicuspid pulmonary valve. Sirenomelia is thought to occur in about 1 in live births and may be more common in one of monozygotic twins. It bears resemblance to the mermaid Greek mythology.affected individuals exhibit a variable range of defects, including hypoplasia and or fusion of lower limbs, vertebral abnormalities, renal agenesis, imperforate anus, and anomalies of the genital organs 11. Previous reports described the extent of the malformation complex in association with sirenomelia. McCoy et al, 12 reported an unusual case with two normal kidneys. Perez-Aytes et al, 13 reported an unusual case where there appeared to be partial fusion of the lower limbs associated with absent feet, but other features of caudal regression and a single aberrant umbilical artery. Akbiyik et al., 14 reported male twins, one of which had sirenomelia and the other just an imperforate anus. Unfortunately zygosity was not established. Shonubi et al, 15 reported sirenomelia in 1 of 2 monochorionic twins. Duncan et al., 16 reviewed 445 cases ascertained for sacrococcygeal malformations and foundthat 12% had sirenomelia, 27% VATER association and 34% what they called the sacrococcygeal dysgenesis association. It was felt that these cases were aetiologically distinct from VATER association and sirenomelia cases. They had fewer anomalies per patient, a lower incidence of anatomical urinary tract anomalies (but a higher chance of neurogenic urinary problems), and a high incidence of CNS anomalies such as spina bifida and hydrocephalus. 28% of cases were born to diabetic mothers. Occasional cases have holoprosencephaly or cyclops 17,18 or craniorachischisis 19. Selig et al., 20 reported a family where three siblings and a maternal aunt had renal anomalies consistent with renal dysplasia (renal agenesis, cystic dysplastic kidneys, and urethral valves). A fourth sib had sirenomelia. Both parents had normal renal ultrasound examinations. Managoli et al., 21 reported a case with in addition good evidence of amniotic band disruption (midline disruption and adhesion of the lips by amniotic strings, a disrupted mandible, a bifid tongue, amputated fingers and African Health Sciences Vol 10 No 4 December
4 toes, hands attached to each other and to the chest wall in the midline at the sternum, feet that were attached to the symphysis in the midline by bands, body wall defects), and some other anomalies on examination and at PM (microphthalmia in one eye and megalocornea in the other, genitourinary hypoplasia, anal atresia, bicornuate uterus, no ovaries, hypoplastic lungs, an accessory spleen and an hypoplastic aorta. The sirenomelia (the legs were fused by skin and had separate bones) was in the fetal position. Guidera et al 22 reported a case of orthopaedic abnormalities and pelvic dysplasia, fused lower extremities, and osseous fusion of the calcanei, but with normal femurs, tibias, and fibulas. This patient also had significant cardiac and renal abnormalities. Stevenson et al. 23 reported in 1986 that the aetiology of sirenomelia was explained by vascular steal theory. They documented the common feature of a single large artery arising from high in the abdominal cavity, which they thought diverted nutrients from the caudal end of the embryo in a vascular steal phenomenon. The associated anomalies are variable and involved multiple organ systems. The most common anomalies include a single umbilical artery, malformation of urinary tract, lower gastrointestinal tract and external genitalia 24. In summary Sirenomelia sequence is classified into three groups according to the number of feet present 2. The most common of the three conditions is symelia apus, in which both legs are merged completely into a single lower extremity. In this condition both feet are absent or rudimentary. Symelia unipus shows a presentation of one foot, two femora, tibiae and fibulae. In symelia dipus, two distinct feet are present but are malrotated and resemble fins. Our case was compatible with symelia apus associated with Potter s syndrome. Careful diabetic control in the pre-conceptional period and the first eight weeks of pregnancy may lower the chances of congenital anomaly. Sells et al., 25 found that intellectual function in infants where mothers had been well controlled was not different from controls, whereas there was a correlation between delayed development and poor maternal diabetic control, or major congenital malformations in the infant. References 1. Duhamel B. From the mermaid to anal imperforation: The syndrome of caudal regression. Arch Dis Child 1961; 36: Sarpong S and Headings V. Sirenomelia accompanying exposure of the embryo to cocaine. South Med J 1992; 85: Murphy JJ, Fraser GC, Blair GK. Sirenomelia: The case of the surviving mermaid. J Pediatr Surg.1992 ; 27: Al Kaissi A, Klaushofer K, Grill F. Caudal regression syndrome and popliteal webbing in connection with maternal diabetes mellitus: a case report and literature review. Cases J. 2008; 19;1(1): Jarrett RJ. Gestational diabetes: anon-entity?. Br Med J. 1993; 306: Buekens P. Invited commentary: prenatal glucose screening and gestational diabetes. Am J Epidemiol. 2000; 152: Loffredo CA, Wilson PD, Ferencz C. Maternal diabetes: an independent risk factor for major cardiovascular malformations with increased mortality of affected infants. Teratology 2001; 64: PubMed. 8. Ylinen E, Wikstrom S. Increased risk of multicystic dysplastic kidney among babies of both pre-gestational and gestational diabetic mothers. Eur J Pediatr 2002; 161: PubMed. 9. Lynch SA, Wright C. Sirenomelia, limb reduction defects, cardiovascular malformation, renal agenesis in an infant born to a diabetic mother. Clin Dysmorphol 1997; 6:75-80 PubMed. 10. Maroteaux P, Le Merrer M Maladies osseuses de l enfant. 4 th edn. Medicine-Science, Flammarion, Paris Sadler T. W. Langman s Medical Embryology. 9th edition. Philadelphia. Lippincott Williams and Wilkins. 2004; McCoy MC, Chescheir NC, Kuller JA, et al. A fetus with sirenomelia, omphalocele, and meningomyelocele, but normal kidneys. Teratology 1994; 50: PubMed. 13. Perez-Aytes A, Montero L, Gomez J, Paya A. Single aberrant umbilical artery in a fetus with severe caudal defects: Sirenomelia or Caudal dysgenesis. Am J Med Genet 1997; 69: PubMed. 14. Akbiyik F, Balci S, Akkoyun I, Aktas D, Cakmak O. Type 1 sirenomelia in one of male twins, with imperforate anus in the other male twin. Clin Dysmorphol 2000; 9: PubMed. 15. Shonubi AM, Salami BA, Falade AG, Ejiwunmi AB. Sirenomelia in one of Nigerian 398 African Health Sciences Vol 10 No 4 December 2010
5 monochorionic twins. Afr J Med Med Sci 2002; 31: PubMed. 16. Duncan PA, Shapiro LR. Sirenomelia and VATER association: possible interrelated disorders with common embryologic pathogenesis. Dysmorph Clin Genet 1988; 2: PubMed. 17. Chen CP, Shih S-L, Liu FF, Jan SW. Cebocephaly, alobar holoprosencephaly, spina bifida, and sirenomelia in a stillbirth. J Med Genet 1997;34: PubMed. 18. Martinez-Frias ML, Garcia A, Bermejo EM. Cyclopia and Sirenomelia in a live born infant. J Med Genet 1998;35: Rodriguez JI, Palacios J. Craniorachischisis totalis and sirenomelia. Am J Med Genet 1992;43: PubMed. 20. Selig AM, Benacerraf B, Greene MF, et al. Renal dysplasia, megalocystis, and sirenomelia in four siblings. Teratology 1993;47:65-71 PubMed. 21. Managoli S, Chaturvedi P, Vilhekar KY, Iyenger J. Mermaid syndrome with amniotic band disruption. Indian J Pediatr 2003;70: PubMed. 22. Guidera KJ, Raney E, Ogden JA et al., Caudal regression: A review of seven cases, including the mermaid syndrome. J Pediatr Orthop 11 (1991), pp Stevenson RE, Phelan MC, Saul RA. Defects of the abdominal wall: association with vascular steal. Proc Gr Genet Center 1989;8:15-21 PubMed. 24. Stocker JT, Heifetz SA (1987) Sirenomelia: A morphological study of 33 cases and review of the literature. Perspect Pediatr Pathol 10: Sells CJ, Robinson NM, Brown Z, Knopp RH. Long-term developmental follow-up of infants of diabetic mothers. J Pediatr 1994;125:s9- s17 PubMed. African Health Sciences Vol 10 No 4 December
Supplemental Information
 ARTICLE Supplemental Information SUPPLEMENTAL TABLE 6 Mosaic and Partial Trisomies Thirty-eight VLBW infants were identified with T13, of whom 2 had mosaic T13. T18 was reported for 128 infants, of whom
ARTICLE Supplemental Information SUPPLEMENTAL TABLE 6 Mosaic and Partial Trisomies Thirty-eight VLBW infants were identified with T13, of whom 2 had mosaic T13. T18 was reported for 128 infants, of whom
Ultrasound Anomaly Details
 Appendix 2. Association of Copy Number Variants With Specific Ultrasonographically Detected Fetal Anomalies Ultrasound Anomaly Details Abdominal wall Bladder exstrophy Body-stalk anomaly Cloacal exstrophy
Appendix 2. Association of Copy Number Variants With Specific Ultrasonographically Detected Fetal Anomalies Ultrasound Anomaly Details Abdominal wall Bladder exstrophy Body-stalk anomaly Cloacal exstrophy
Obstetrics Content Outline Obstetrics - Fetal Abnormalities
 Obstetrics Content Outline Obstetrics - Fetal Abnormalities Effective February 2007 10 16% renal agenesis complete absence of the kidneys occurs when ureteric buds fail to develop Or degenerate before
Obstetrics Content Outline Obstetrics - Fetal Abnormalities Effective February 2007 10 16% renal agenesis complete absence of the kidneys occurs when ureteric buds fail to develop Or degenerate before
Pregestational and Gestational Diabetes
 Pregestational and Gestational Diabetes Francis S. Nuthalapaty, MD Greenville Health System University of South Carolina School of Medicine - Greenville Case History 30 year old black female presents to
Pregestational and Gestational Diabetes Francis S. Nuthalapaty, MD Greenville Health System University of South Carolina School of Medicine - Greenville Case History 30 year old black female presents to
Association Of Single Umbilical Artery With Common And Rare Congenital Malformations
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Pediatrics and Neonatology Volume 4 Number 1 Association Of Single Umbilical Artery With Common And Rare Congenital Malformations M Sur, S Nayler, R Muc Citation M Sur,
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Pediatrics and Neonatology Volume 4 Number 1 Association Of Single Umbilical Artery With Common And Rare Congenital Malformations M Sur, S Nayler, R Muc Citation M Sur,
Mermaid Syndrome- A Case Report
 Mermaid Syndrome- A Case Report Poster No.: R-0214 Congress: RANZCR-AOCR 2012 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: M. H. Mostofa Kamal, S. Al-Azad, S. Amin, A. S. M. Shahidul Hossain, M. Ali Kabir; Dhaka/BD
Mermaid Syndrome- A Case Report Poster No.: R-0214 Congress: RANZCR-AOCR 2012 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: M. H. Mostofa Kamal, S. Al-Azad, S. Amin, A. S. M. Shahidul Hossain, M. Ali Kabir; Dhaka/BD
Congenital Anomalies
 Congenital Anomalies Down Syndrome 7580 7580 DOWN''S SYNDROME Q900 Q90.0 : Trisomy 21, meiotic nondisjunction 7580 7580 DOWN''S SYNDROME Q901 Q90.1 : Trisomy 21, mosaicism (mitotic nondisjunction) 7580
Congenital Anomalies Down Syndrome 7580 7580 DOWN''S SYNDROME Q900 Q90.0 : Trisomy 21, meiotic nondisjunction 7580 7580 DOWN''S SYNDROME Q901 Q90.1 : Trisomy 21, mosaicism (mitotic nondisjunction) 7580
CAUDAL REGRESSION SYNDROME
 CAUDAL REGRESSION SYNDROME *Prateek Gehlot 1 and Jagdish Mandliya 2 1 Department of Radio-Diagnosis, R.D.Gardi Medical College,, Ujjain (MP). 2 Department of Pediatrics, R.D.Gardi Medical College, Ujjain
CAUDAL REGRESSION SYNDROME *Prateek Gehlot 1 and Jagdish Mandliya 2 1 Department of Radio-Diagnosis, R.D.Gardi Medical College,, Ujjain (MP). 2 Department of Pediatrics, R.D.Gardi Medical College, Ujjain
GU Ultrasound in First Trimester
 Fetal Renal Malformations: The Role of Ultrasound in Diagnosis & Management Outline 1. Renal Anomalies Urinary Tract Dilation Aberrant Early Development Defects Terminal Maturation Alfred Abuhamad, M.D.
Fetal Renal Malformations: The Role of Ultrasound in Diagnosis & Management Outline 1. Renal Anomalies Urinary Tract Dilation Aberrant Early Development Defects Terminal Maturation Alfred Abuhamad, M.D.
TERMINOLOGY. portion of a bone ossified from a primary center. portion of a bone ossified from a secondary center.
 Embryology APPENDICULAR SKELETON Consists of the pectoral and the pelvic girdles and the bones of the limbs. Beginning at the 4 th \ menstrual week primordial bone patterns evolve into cartilaginous bone
Embryology APPENDICULAR SKELETON Consists of the pectoral and the pelvic girdles and the bones of the limbs. Beginning at the 4 th \ menstrual week primordial bone patterns evolve into cartilaginous bone
Basic Training. ISUOG Basic Training The 20 Planes Approach to the Routine Mid Trimester Scan
 ISUOG The 20 Planes Approach to the Routine Mid Trimester Scan Learning objective At the end of the lecture you will be able to: Explain how to perform a structured routine examination, including measurements,
ISUOG The 20 Planes Approach to the Routine Mid Trimester Scan Learning objective At the end of the lecture you will be able to: Explain how to perform a structured routine examination, including measurements,
Chapter 6: Genitourinary and Gastrointestinal Systems 93
 Chapter 6: Genitourinary and Gastrointestinal Systems 93 Chapter 6 Genitourinary and Gastrointestinal Systems Embryology Three sets of excretory organs or kidneys develop in human embryos: Pronephros:
Chapter 6: Genitourinary and Gastrointestinal Systems 93 Chapter 6 Genitourinary and Gastrointestinal Systems Embryology Three sets of excretory organs or kidneys develop in human embryos: Pronephros:
Congenital Pediatric Anomalies: A Collection of Abdominal Scintigraphy Findings: An Imaging Atlas
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Nuclear Medicine Volume 5 Number 1 Congenital Pediatric Anomalies: A Collection of Abdominal Scintigraphy Findings: An Imaging Atlas V Vijayakumar, T Nishino Citation
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Nuclear Medicine Volume 5 Number 1 Congenital Pediatric Anomalies: A Collection of Abdominal Scintigraphy Findings: An Imaging Atlas V Vijayakumar, T Nishino Citation
The Fetal Care Center at NewYork-Presbyterian/ Weill Cornell Medicine
 The Fetal Care Center at NewYork-Presbyterian/ Weill Cornell Medicine Prompt and Personalized Care for Women with Complex Pregnancies A Team of Experts additional training in maternal and fetal complications
The Fetal Care Center at NewYork-Presbyterian/ Weill Cornell Medicine Prompt and Personalized Care for Women with Complex Pregnancies A Team of Experts additional training in maternal and fetal complications
A SMALL bony pelvic outlet was observed
 VOL. 121, No. SIZE OF PELVIC BONY OUTLET IN RENAL AGENESIS* By RICHARD A. FELLOWS, M.D.,t WALTER E. BERDON, M.D., and DAVID H. BAKER, M.D. A SMALL bony pelvic outlet was observed by Curranino2 and later
VOL. 121, No. SIZE OF PELVIC BONY OUTLET IN RENAL AGENESIS* By RICHARD A. FELLOWS, M.D.,t WALTER E. BERDON, M.D., and DAVID H. BAKER, M.D. A SMALL bony pelvic outlet was observed by Curranino2 and later
SPLIT NOTOCHORD SYNDROME ASSOCIATION. DR. Hasan Nugud Consultant Paediatric Surgeon
 SPLIT NOTOCHORD SYNDROME ASSOCIATION DR. Hasan Nugud Consultant Paediatric Surgeon CASE PRESENTATION :- New born baby, boy, referred to the paediatric surgical team at the age of 14 hours. Birth History
SPLIT NOTOCHORD SYNDROME ASSOCIATION DR. Hasan Nugud Consultant Paediatric Surgeon CASE PRESENTATION :- New born baby, boy, referred to the paediatric surgical team at the age of 14 hours. Birth History
APPROACH TO A DYSMORPHIC INDIVIDUAL. Denise LM Goh
 APPROACH TO A DYSMORPHIC INDIVIDUAL Denise LM Goh Contents The dysmorphic child Incidence of congenital anomalies Suspicion for diagnosis Approach to the dysmorphic child Problem analysis history hysical
APPROACH TO A DYSMORPHIC INDIVIDUAL Denise LM Goh Contents The dysmorphic child Incidence of congenital anomalies Suspicion for diagnosis Approach to the dysmorphic child Problem analysis history hysical
Neonatal Hypoglycemia. Presented By : Kamlah Olaimat 25\7\2010
 Neonatal Hypoglycemia Presented By : Kamlah Olaimat 25\7\2010 Definition The S.T.A.B.L.E. Program defines hypoglycemia as: Glucose delivery or availability is inadequate to meet glucose demand (Karlsen,
Neonatal Hypoglycemia Presented By : Kamlah Olaimat 25\7\2010 Definition The S.T.A.B.L.E. Program defines hypoglycemia as: Glucose delivery or availability is inadequate to meet glucose demand (Karlsen,
Urinary Tract Abnormalities
 Urinary Tract Abnormalities Dr Hennie Lombaard Senior Specialist Maternal and Fetal Medcine Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology Level 7 Pretoria Academic Hospital Pictures from The 18 to 23 weeks scan
Urinary Tract Abnormalities Dr Hennie Lombaard Senior Specialist Maternal and Fetal Medcine Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology Level 7 Pretoria Academic Hospital Pictures from The 18 to 23 weeks scan
VACTERL association: A Case Report of a congenital malformations Dr. Rinku Saini 1, Dr. Lovesh Saini 2, Dr. Priti Saini 3, Dr. R. N.
 VACTERL association: A Case Report of a congenital malformations Dr. Rinku Saini 1, Dr. Lovesh Saini 2, Dr. Priti Saini 3, Dr. R. N. Sehra 4 1 Assistant Professor, Department of Pediatric Medicine, S.M.S
VACTERL association: A Case Report of a congenital malformations Dr. Rinku Saini 1, Dr. Lovesh Saini 2, Dr. Priti Saini 3, Dr. R. N. Sehra 4 1 Assistant Professor, Department of Pediatric Medicine, S.M.S
A Very Unusual Case of a Dorsal Heteropagus Twin
 PRG A Very Unusual Case of a Dorsal Heteropagus Twin Nathan David P. Concepcion, MD 1, Bernard F. Laya, DO 1, Eduardo P. Manrique, MD 2 and Faith Caroline D. Bayabos, MD 1 1 Section of Pediatric Radiology,
PRG A Very Unusual Case of a Dorsal Heteropagus Twin Nathan David P. Concepcion, MD 1, Bernard F. Laya, DO 1, Eduardo P. Manrique, MD 2 and Faith Caroline D. Bayabos, MD 1 1 Section of Pediatric Radiology,
Kidneycentric. Follow this and additional works at:
 Washington University School of Medicine Digital Commons@Becker All Kidneycentric 2014 Renal Dysplasia Halana V. Whitehead Washington University School of Medicine in St. Louis Follow this and additional
Washington University School of Medicine Digital Commons@Becker All Kidneycentric 2014 Renal Dysplasia Halana V. Whitehead Washington University School of Medicine in St. Louis Follow this and additional
Basic Training. ISUOG Basic Training Examining the Upper Lip, Face & Profile
 ISUOG Examining the Upper Lip, Face & Profile Learning objectives At the end of the lecture you will be able to: Describe how to obtain the 3 planes required to assess the anatomy of the fetal face Recognise
ISUOG Examining the Upper Lip, Face & Profile Learning objectives At the end of the lecture you will be able to: Describe how to obtain the 3 planes required to assess the anatomy of the fetal face Recognise
Bench to Bassinet Pediatric Cardiac Genomics Consortium: CHD GENES Form 105: Congenital Extracardiac Findings Version: B - 11/01/2010
 Bench to Bassinet Pediatric Cardiac Genomics Consortium: CHD GENES Form 105: Congenital Extracardiac Findings Version: B - 11/01/2010 SECTION A: ADMINISTRATIVE INFORMATION A1. Study Identification Number:
Bench to Bassinet Pediatric Cardiac Genomics Consortium: CHD GENES Form 105: Congenital Extracardiac Findings Version: B - 11/01/2010 SECTION A: ADMINISTRATIVE INFORMATION A1. Study Identification Number:
Original Article. Associated Anomalies and Clinical Outcomes in Infants with Omphalocele: A Single-centre 10-year Review
 HK J Paediatr (new series) 2018;23:220-224 Original Article Associated Anomalies and Clinical Outcomes in Infants with Omphalocele: A Single-centre 10-year Review YY CHEE, MSC WONG, RMS WONG, KY WONG,
HK J Paediatr (new series) 2018;23:220-224 Original Article Associated Anomalies and Clinical Outcomes in Infants with Omphalocele: A Single-centre 10-year Review YY CHEE, MSC WONG, RMS WONG, KY WONG,
Sexual differentiation:
 Abnormal Development of Female Genitalia Dr. Maryam Fetal development of gonads, external genitalia, Mullerian ducts and Wolffian ducts can be disrupted at a variety of points, leading to a wide range
Abnormal Development of Female Genitalia Dr. Maryam Fetal development of gonads, external genitalia, Mullerian ducts and Wolffian ducts can be disrupted at a variety of points, leading to a wide range
Dysmorphology. Sue White. Diagnostic Dysmorphology, Aase. Victorian Clinical Genetics Services
 Dysmorphology Sue White www.rch.unimelb.edu.au/nets/handbook Diagnostic Dysmorphology, Aase Dysmorphology Assessment Algorithm no Are the features familial? yes Recognised syndrome yes no AD/XL syndrome
Dysmorphology Sue White www.rch.unimelb.edu.au/nets/handbook Diagnostic Dysmorphology, Aase Dysmorphology Assessment Algorithm no Are the features familial? yes Recognised syndrome yes no AD/XL syndrome
ISUOG Basic Training Distinguishing Between Normal and Abnormal Appearances of the Fetal Anatomy
 ISUOG Basic Training Distinguishing Between Normal and Abnormal Appearances of the Fetal Anatomy Reem S. Abu-Rustum, Lebanon Learning Objective At the end of the lecture you will be able to: Compare the
ISUOG Basic Training Distinguishing Between Normal and Abnormal Appearances of the Fetal Anatomy Reem S. Abu-Rustum, Lebanon Learning Objective At the end of the lecture you will be able to: Compare the
SWISS SOCIETY OF NEONATOLOGY. Cantrell s pentalogy: an unusual midline defect
 SWISS SOCIETY OF NEONATOLOGY Cantrell s pentalogy: an unusual midline defect October 2004 2 Cevey-Macherel MN, Meijboom EJ, Di Bernardo S, Truttmann AC, Division of Neonatology and Division of Pediatric
SWISS SOCIETY OF NEONATOLOGY Cantrell s pentalogy: an unusual midline defect October 2004 2 Cevey-Macherel MN, Meijboom EJ, Di Bernardo S, Truttmann AC, Division of Neonatology and Division of Pediatric
A. Definitions... CD-157. B. General Information... CD-158
 CD Part 10 Multiple Body System Disorders A. Definitions... CD-157 B. General Information... CD-158 C. Specific Listings and Residual Functional Capacity... CD-158 1. Listing 10.06: Non-Mosaic Down Syndrome
CD Part 10 Multiple Body System Disorders A. Definitions... CD-157 B. General Information... CD-158 C. Specific Listings and Residual Functional Capacity... CD-158 1. Listing 10.06: Non-Mosaic Down Syndrome
ISUOG Basic Training Distinguishing Between Normal and Abnormal Appearances of the Fetal Anatomy. Basic Training
 ISUOG Distinguishing Between Normal and Abnormal Appearances of the Fetal Anatomy Learning Objective At the end of the lecture you will be able to: Compare the differences between the ultrasound appearances
ISUOG Distinguishing Between Normal and Abnormal Appearances of the Fetal Anatomy Learning Objective At the end of the lecture you will be able to: Compare the differences between the ultrasound appearances
FETAL ICD-10 CODES QUICK REFERENCE GUIDE
 FETAL ICD-10 CODES QUICK REFERENCE GUIDE Page CONTENTS 1 Cardiac Anomalies 3 Chromosome Abnormalities 4 Central Nervous System Anomalies 5 Extremity Anomalies 6 Face / Neck Anomalies 7 Gastrointestinal
FETAL ICD-10 CODES QUICK REFERENCE GUIDE Page CONTENTS 1 Cardiac Anomalies 3 Chromosome Abnormalities 4 Central Nervous System Anomalies 5 Extremity Anomalies 6 Face / Neck Anomalies 7 Gastrointestinal
Heart and Lungs. LUNG Coronal section demonstrates relationship of pulmonary parenchyma to heart and chest wall.
 Heart and Lungs Normal Sonographic Anatomy THORAX Axial and coronal sections demonstrate integrity of thorax, fetal breathing movements, and overall size and shape. LUNG Coronal section demonstrates relationship
Heart and Lungs Normal Sonographic Anatomy THORAX Axial and coronal sections demonstrate integrity of thorax, fetal breathing movements, and overall size and shape. LUNG Coronal section demonstrates relationship
Genetics in Nephrology. Saeid Morovvati Associate Professor of BMSU Director of Biogene Laboratory
 Genetics in Nephrology Saeid Morovvati Associate Professor of BMSU Director of Biogene Laboratory Genetics in: A. Congenital Anomalies of the Kidney and Urinary Tract B. Cystic Diseases of the Kidney C.
Genetics in Nephrology Saeid Morovvati Associate Professor of BMSU Director of Biogene Laboratory Genetics in: A. Congenital Anomalies of the Kidney and Urinary Tract B. Cystic Diseases of the Kidney C.
Table S1. Number of patients dispensed a statin, by drug, during the 1 st trimester
 Supplementary material Table S1. Number of patients dispensed a statin, by drug, during the 1 st trimester Medication Count Overall 1152 Atorvastatin 538 Cerivastatin * Fluvastatin 47 Lovastatin 132 Pravastatin
Supplementary material Table S1. Number of patients dispensed a statin, by drug, during the 1 st trimester Medication Count Overall 1152 Atorvastatin 538 Cerivastatin * Fluvastatin 47 Lovastatin 132 Pravastatin
Elements of Dysmorphology I. Krzysztof Szczałuba
 Elements of Dysmorphology I Krzysztof Szczałuba 9.05.2016 Common definitions (1) Dysmorphology: recognition and study of birth defects (congenital malformations) and syndromes [David Smith, 1960] Malformation:
Elements of Dysmorphology I Krzysztof Szczałuba 9.05.2016 Common definitions (1) Dysmorphology: recognition and study of birth defects (congenital malformations) and syndromes [David Smith, 1960] Malformation:
Congenital anomalies of upper extremity - What Radiologist should know
 Congenital anomalies of upper extremity - What Radiologist should know Poster No.: C-0955 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: R. TUMMA, N. AHMED, V. Prasad; Hyderabad/IN Keywords: Congenital,
Congenital anomalies of upper extremity - What Radiologist should know Poster No.: C-0955 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: R. TUMMA, N. AHMED, V. Prasad; Hyderabad/IN Keywords: Congenital,
(i) Family 1. The male proband (1.III-1) from European descent was referred at
 1 Supplementary Note Clinical descriptions of families (i) Family 1. The male proband (1.III-1) from European descent was referred at age 14 because of scoliosis. He had normal development. Physical evaluation
1 Supplementary Note Clinical descriptions of families (i) Family 1. The male proband (1.III-1) from European descent was referred at age 14 because of scoliosis. He had normal development. Physical evaluation
The data were analysed using Fisher s exact test and the chi-squared test.
 Congenital malformations are a major cause of perinatal and neonatal death [1], both in developed and developing countries [2]. These malformations have multifactorial etiologies and 40% of cases are idiopathic
Congenital malformations are a major cause of perinatal and neonatal death [1], both in developed and developing countries [2]. These malformations have multifactorial etiologies and 40% of cases are idiopathic
Heart and Soul Evaluation of the Fetal Heart
 Heart and Soul Evaluation of the Fetal Heart Ivana M. Vettraino, M.D., M.B.A. Clinical Associate Professor, Michigan State University College of Human Medicine Objectives Review the embryology of the formation
Heart and Soul Evaluation of the Fetal Heart Ivana M. Vettraino, M.D., M.B.A. Clinical Associate Professor, Michigan State University College of Human Medicine Objectives Review the embryology of the formation
Fetal Urologic Anomalies
 Fetal Urologic Anomalies Kathryn Drennan, MD Elizabeth McKinney, MD MultiCare Regional Maternal-Fetal Medicine What you should know They are common Account for 15%-20% of all congenital anomalies Associated
Fetal Urologic Anomalies Kathryn Drennan, MD Elizabeth McKinney, MD MultiCare Regional Maternal-Fetal Medicine What you should know They are common Account for 15%-20% of all congenital anomalies Associated
CONGENITAL HEART DISEASE (CHD)
 CONGENITAL HEART DISEASE (CHD) DEFINITION It is the result of a structural or functional abnormality of the cardiovascular system at birth GENERAL FEATURES OF CHD Structural defects due to specific disturbance
CONGENITAL HEART DISEASE (CHD) DEFINITION It is the result of a structural or functional abnormality of the cardiovascular system at birth GENERAL FEATURES OF CHD Structural defects due to specific disturbance
ISUOG Basic Training Distinguishing between Normal & Abnormal Appearances of the Long Bones & Extremities. Basic Training
 ISUOG Basic Training Distinguishing between Normal & Abnormal Appearances of the Long Bones & Extremities Basic Training Learning objectives At the end of the lecture you will be able to: Describe how
ISUOG Basic Training Distinguishing between Normal & Abnormal Appearances of the Long Bones & Extremities Basic Training Learning objectives At the end of the lecture you will be able to: Describe how
Chapter 5 The Skeletal System
 Chapter 5 The Skeletal System The Skeletal System Parts of the skeletal system Bones (skeleton) Joints Cartilages Ligaments (bone to bone)(tendon=bone to muscle) Divided into two divisions Axial skeleton:
Chapter 5 The Skeletal System The Skeletal System Parts of the skeletal system Bones (skeleton) Joints Cartilages Ligaments (bone to bone)(tendon=bone to muscle) Divided into two divisions Axial skeleton:
Fetal Medicine. Case Presentations. Dr Ermos Nicolaou Fetal Medicine Unit Chris Hani Baragwanath Hospital. October 2003
 Case Presentations Dr Ermos Nicolaou Fetal Medicine Unit Chris Hani Baragwanath Hospital October 2003 Case 1 Ms A M 22year old P0 G1 Referred from Sebokeng Hospital at 36w for polyhydramnios On Ultrasound:
Case Presentations Dr Ermos Nicolaou Fetal Medicine Unit Chris Hani Baragwanath Hospital October 2003 Case 1 Ms A M 22year old P0 G1 Referred from Sebokeng Hospital at 36w for polyhydramnios On Ultrasound:
Prenatal Ultrasonographic Diagnosis of Proximal Focal Femoral Deficiency
 Prenatal Ultrasonographic Diagnosis of Proximal Focal Femoral Deficiency Ravi D Wadhwa, Madhusudan Dey, Anupam Kapur, Vipin Kumar Fetal Medicine Div, Department of Obstetric and Gynecology, Armed Forces
Prenatal Ultrasonographic Diagnosis of Proximal Focal Femoral Deficiency Ravi D Wadhwa, Madhusudan Dey, Anupam Kapur, Vipin Kumar Fetal Medicine Div, Department of Obstetric and Gynecology, Armed Forces
Unilateral renal agenesis does it matter?
 Clinical Research Facility Central Manchester University Hospitals NHS Foundation Trust Unilateral renal agenesis does it matter? Nicholas J A Webb BMedSci DM FRCP FRCPCH Honorary Professor of Paediatric
Clinical Research Facility Central Manchester University Hospitals NHS Foundation Trust Unilateral renal agenesis does it matter? Nicholas J A Webb BMedSci DM FRCP FRCPCH Honorary Professor of Paediatric
Complex Congenital Heart disease with Sacral Agenesis a Case Report
 International Journal of Anatomical Sciences 2011,2(1):1-6 1 Case Report Complex Congenital Heart disease with Sacral Agenesis a Case Report Srimathi, T. Department of Anatomy, Sri Ramachandra University,
International Journal of Anatomical Sciences 2011,2(1):1-6 1 Case Report Complex Congenital Heart disease with Sacral Agenesis a Case Report Srimathi, T. Department of Anatomy, Sri Ramachandra University,
I have no disclosures
 I have no disclosures Provide an overview of the spectrum of congenital upper extremity anomalies Describe the key imaging findings of these abnormalities Discuss the important clinical features of these
I have no disclosures Provide an overview of the spectrum of congenital upper extremity anomalies Describe the key imaging findings of these abnormalities Discuss the important clinical features of these
Table P-l. Summary of Dioxin-by-Covariate Interactions for. Selected Birth Defects
 Table P-l of Dioxin-by-Covariate Interactions for. Selected Birth Defects e) Table Reference: 8-21[bJ Interaction: Specific Delays in Development (Categ. DIOXIN by P-AGE, Categ. DIOXIN by C-TIHE) Exposure
Table P-l of Dioxin-by-Covariate Interactions for. Selected Birth Defects e) Table Reference: 8-21[bJ Interaction: Specific Delays in Development (Categ. DIOXIN by P-AGE, Categ. DIOXIN by C-TIHE) Exposure
RADPrimer Curriculum Breast Topics Covered Basic Intermediate 225
 Breast Anatomy & Normal Variants 11 Breast Imaging Modalities 13 BI RADS Lexicon 3 Mammography: Masses 9 Mammography: Calcifications 17 Mammography: Additional Findings 8 Ultrasound Features 10 Ultrasound
Breast Anatomy & Normal Variants 11 Breast Imaging Modalities 13 BI RADS Lexicon 3 Mammography: Masses 9 Mammography: Calcifications 17 Mammography: Additional Findings 8 Ultrasound Features 10 Ultrasound
Fetal Renal Malformations: The Role of Ultrasound in Diagnosis & Management
 Fetal Renal Malformations: The Role of Ultrasound in Diagnosis & Management 12 weeks Alfred Abuhamad, M.D. Eastern Virginia Medical School 13 weeks 2nd trimester Medullary pyramids Renal Sinus Cortex 2nd
Fetal Renal Malformations: The Role of Ultrasound in Diagnosis & Management 12 weeks Alfred Abuhamad, M.D. Eastern Virginia Medical School 13 weeks 2nd trimester Medullary pyramids Renal Sinus Cortex 2nd
Case Report Ipsilateral Hip Dysplasia in Patients with Sacral Hemiagenesis: A Report of Two Cases
 Case Reports in Orthopedics Volume 2015, Article ID 854151, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2015/854151 Case Report Ipsilateral Hip Dysplasia in Patients with Sacral Hemiagenesis: A Report of Two Cases
Case Reports in Orthopedics Volume 2015, Article ID 854151, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2015/854151 Case Report Ipsilateral Hip Dysplasia in Patients with Sacral Hemiagenesis: A Report of Two Cases
Congenital Digestive Malformation and Associated Anomalies
 EUROPEAN ACADEMIC RESEARCH Vol. VI, Issue 5/ August 2018 ISSN 2286-4822 www.euacademic.org Impact Factor: 3.4546 (UIF) DRJI Value: 5.9 (B+) Congenital Digestive Malformation and Associated Anomalies AUREL
EUROPEAN ACADEMIC RESEARCH Vol. VI, Issue 5/ August 2018 ISSN 2286-4822 www.euacademic.org Impact Factor: 3.4546 (UIF) DRJI Value: 5.9 (B+) Congenital Digestive Malformation and Associated Anomalies AUREL
Central nervous system. Obstetrics Content Outline Obstetrics - Fetal Abnormalities
 Obstetrics Content Outline Obstetrics - Fetal Abnormalities Many congenital malformations of the CNS result from incomplete closure of the neural tube Effective February 2007 10 16% the most common neural
Obstetrics Content Outline Obstetrics - Fetal Abnormalities Many congenital malformations of the CNS result from incomplete closure of the neural tube Effective February 2007 10 16% the most common neural
ISUOG Basic Training. Assessing the Neck & Chest Gihad Chalouhi, Lebanon
 ISUOG Basic Training Assessing the Neck & Chest Gihad Chalouhi, Lebanon Learning objectives 9 & 10 At the end of the lecture you will be able to: recognise the differences between the normal & most common
ISUOG Basic Training Assessing the Neck & Chest Gihad Chalouhi, Lebanon Learning objectives 9 & 10 At the end of the lecture you will be able to: recognise the differences between the normal & most common
AORTIC COARCTATION. Synonyms: - Coarctation of the aorta
 AORTIC COARCTATION Synonyms: - Coarctation of the aorta Definition: Aortic coarctation is a congenital narrowing of the aorta, usually located after the left subclavian artery, near the ductus or the ligamentum
AORTIC COARCTATION Synonyms: - Coarctation of the aorta Definition: Aortic coarctation is a congenital narrowing of the aorta, usually located after the left subclavian artery, near the ductus or the ligamentum
Chromosome 13. Introduction
 Chromosome 13 Chromosome Disorder Outreach Inc. (CDO) Technical genetic content provided by Dr. Iosif Lurie, M.D. Ph.D Medical Geneticist and CDO Medical Consultant/Advisor. Ideogram courtesy of the University
Chromosome 13 Chromosome Disorder Outreach Inc. (CDO) Technical genetic content provided by Dr. Iosif Lurie, M.D. Ph.D Medical Geneticist and CDO Medical Consultant/Advisor. Ideogram courtesy of the University
Normal and Abnormal Development of the Genital Tract. Dr.Raghad Abdul-Halim
 Normal and Abnormal Development of the Genital Tract Dr.Raghad Abdul-Halim objectives: Revision of embryology. Clinical presentation, investigations and clinical significance of most common developmental
Normal and Abnormal Development of the Genital Tract Dr.Raghad Abdul-Halim objectives: Revision of embryology. Clinical presentation, investigations and clinical significance of most common developmental
UNIT IX: GENETIC DISORDERS
 UNIT IX: GENETIC DISORDERS Younas Masih Lecturer New Life College Of Nursing Karachi 3/4/2016 1 Objectives By the end of this session the Learners will be able to, 1. Know the basic terms related genetics
UNIT IX: GENETIC DISORDERS Younas Masih Lecturer New Life College Of Nursing Karachi 3/4/2016 1 Objectives By the end of this session the Learners will be able to, 1. Know the basic terms related genetics
Research Article Spectrum of Congenital Anomalies among Surgical Patients at a Tertiary Care Centre over 4 Years
 Hindawi International Pediatrics Volume 2017, Article ID 4174573, 4 pages https://doi.org/10.1155/2017/4174573 Research Article Spectrum of Congenital Anomalies among Surgical Patients at a Tertiary Care
Hindawi International Pediatrics Volume 2017, Article ID 4174573, 4 pages https://doi.org/10.1155/2017/4174573 Research Article Spectrum of Congenital Anomalies among Surgical Patients at a Tertiary Care
3 Circulatory Pathways
 40 Chapter 3 Circulatory Pathways Systemic Arteries -Arteries carry blood away from the heart to the various organs of the body. -The aorta is the longest artery in the body; it branches to give rise to
40 Chapter 3 Circulatory Pathways Systemic Arteries -Arteries carry blood away from the heart to the various organs of the body. -The aorta is the longest artery in the body; it branches to give rise to
The Human Body. Lesson Goal. Lesson Objectives 9/10/2012. Provide a brief overview of body systems, anatomy, physiology, and topographic anatomy
 The Human Body Lesson Goal Provide a brief overview of body systems, anatomy, physiology, and topographic anatomy Medial Lateral Proximal Distal Superior Inferior Anterior Lesson Objectives Explain the
The Human Body Lesson Goal Provide a brief overview of body systems, anatomy, physiology, and topographic anatomy Medial Lateral Proximal Distal Superior Inferior Anterior Lesson Objectives Explain the
Why did this happen? Genetic and teratologic considerations in CHD Jennifer Kussmann, MS,CGC. The Children's Mercy Hospital, 2014.
 Why did this happen? Genetic and teratologic considerations in CHD Jennifer Kussmann, MS,CGC The Children's Mercy Hospital, 2014. 03/14 Risk factors Family history Maternal medical condition/ illness Monochorionic
Why did this happen? Genetic and teratologic considerations in CHD Jennifer Kussmann, MS,CGC The Children's Mercy Hospital, 2014. 03/14 Risk factors Family history Maternal medical condition/ illness Monochorionic
CNS Embryology 5th Menstrual Week (Dorsal View)
 Imaging of the Fetal Brain; Normal & Abnormal Alfred Abuhamad, M.D. Eastern Virginia Medical School CNS Embryology 5th Menstrual Week (Dorsal View) Day 20 from fertilization Neural plate formed in ectoderm
Imaging of the Fetal Brain; Normal & Abnormal Alfred Abuhamad, M.D. Eastern Virginia Medical School CNS Embryology 5th Menstrual Week (Dorsal View) Day 20 from fertilization Neural plate formed in ectoderm
CYANOTIC CONGENITAL HEART DISEASES. PRESENTER: DR. Myra M. Koech Pediatric cardiologist MTRH/MU
 CYANOTIC CONGENITAL HEART DISEASES PRESENTER: DR. Myra M. Koech Pediatric cardiologist MTRH/MU DEFINITION Congenital heart diseases are defined as structural and functional problems of the heart that are
CYANOTIC CONGENITAL HEART DISEASES PRESENTER: DR. Myra M. Koech Pediatric cardiologist MTRH/MU DEFINITION Congenital heart diseases are defined as structural and functional problems of the heart that are
The Fetal Cardiology Program
 The Fetal Cardiology Program at Texas Children s Fetal Center About the program Since the 1980s, Texas Children s Fetal Cardiology Program has provided comprehensive fetal cardiac care to expecting families
The Fetal Cardiology Program at Texas Children s Fetal Center About the program Since the 1980s, Texas Children s Fetal Cardiology Program has provided comprehensive fetal cardiac care to expecting families
Development of the Axial Skeleton and Limbs. Professor Alfred Cuschieri Department of Anatomy University of Malta
 Development of the Axial Skeleton and Limbs Professor Alfred Cuschieri Department of Anatomy University of Malta During the Fourth Week the Embryo Is Segmented. Each segment consists of: a segment of neural
Development of the Axial Skeleton and Limbs Professor Alfred Cuschieri Department of Anatomy University of Malta During the Fourth Week the Embryo Is Segmented. Each segment consists of: a segment of neural
Pregnancies complicated by diabetes. Marina Mickleson Nurse Practitioner Midwife CDE
 Pregnancies complicated by diabetes Marina Mickleson Nurse Practitioner Midwife CDE Two types Pre gestational Gestational diabetes Both types are on the increase Pre conception work up is imperative for
Pregnancies complicated by diabetes Marina Mickleson Nurse Practitioner Midwife CDE Two types Pre gestational Gestational diabetes Both types are on the increase Pre conception work up is imperative for
Fetal Tetralogy of Fallot
 36 Fetal Tetralogy of Fallot E.D. Bespalova, R.M. Gasanova, O.A.Pitirimova National Scientific and Practical Center of Cardiovascular Surgery, Moscow Elena D. Bespalova, MD Professor, Director Rena M,
36 Fetal Tetralogy of Fallot E.D. Bespalova, R.M. Gasanova, O.A.Pitirimova National Scientific and Practical Center of Cardiovascular Surgery, Moscow Elena D. Bespalova, MD Professor, Director Rena M,
APPENDIX 6 EPIDEMOLOGY OF CORNELIA DE LANGE SYNDROME
 APPENDIX 6 EPIDEMOLOGY OF CORNELIA DE LANGE SYNDROME Table 1. List of European registries contributing to the study: years of data, total number of births, prenatal diagnosis policy, followup of cases
APPENDIX 6 EPIDEMOLOGY OF CORNELIA DE LANGE SYNDROME Table 1. List of European registries contributing to the study: years of data, total number of births, prenatal diagnosis policy, followup of cases
SLOS? (Smith-Lemli-Opitz Syndrome) Dr E. P. Frohlich Sunninghill Hospital, Private Practice
 SLOS? (Smith-Lemli-Opitz Syndrome) Dr E. P. Frohlich Sunninghill Hospital, Private Practice Baby D Introduction SLOS is part of a heterogenic group of monogenically (AR, AD, XD) determined syndrome of
SLOS? (Smith-Lemli-Opitz Syndrome) Dr E. P. Frohlich Sunninghill Hospital, Private Practice Baby D Introduction SLOS is part of a heterogenic group of monogenically (AR, AD, XD) determined syndrome of
BIRTH DEFECTS IN MICHIGAN All Cases Reported and Processed by June 30, 2009
 MICHIGAN DEPARTMENT OF COMMUNITY HEALTH Division for Vital Records and Health Statistics MICHIGAN BIRTH DEFECTS SURVEILLANCE REGISTRY BIRTH DEFECTS IN MICHIGAN All Cases Reported and Processed by June
MICHIGAN DEPARTMENT OF COMMUNITY HEALTH Division for Vital Records and Health Statistics MICHIGAN BIRTH DEFECTS SURVEILLANCE REGISTRY BIRTH DEFECTS IN MICHIGAN All Cases Reported and Processed by June
ULTRASOUND OF THE FETAL HEART
 ULTRASOUND OF THE FETAL HEART Cameron A. Manbeian, MD Disclosure Statement Today s faculty: Cameron Manbeian, MD does not have any relevant financial relationships with commercial interests or affiliations
ULTRASOUND OF THE FETAL HEART Cameron A. Manbeian, MD Disclosure Statement Today s faculty: Cameron Manbeian, MD does not have any relevant financial relationships with commercial interests or affiliations
SWISS SOCIETY OF NEONATOLOGY. Yunis-Varon syndrome
 SWISS SOCIETY OF NEONATOLOGY Yunis-Varon syndrome January 2003 2 Heyland K, Hodler C, Bänziger O, Neonatology, University Children s Hospital of Zurich, Switzerland Swiss Society of Neonatology, Thomas
SWISS SOCIETY OF NEONATOLOGY Yunis-Varon syndrome January 2003 2 Heyland K, Hodler C, Bänziger O, Neonatology, University Children s Hospital of Zurich, Switzerland Swiss Society of Neonatology, Thomas
Hypoglycemia. Objectives. Glucose Metabolism
 Hypoglycemia Instructor: Janet Mendis, MSN, RNC-NIC, CNS Outline: Janet Mendis, MSN, RNC-NIC, CNS Summer Morgan, MSN, RNC-NIC, CPNP UC San Diego Health System Objectives State the blood glucose level at
Hypoglycemia Instructor: Janet Mendis, MSN, RNC-NIC, CNS Outline: Janet Mendis, MSN, RNC-NIC, CNS Summer Morgan, MSN, RNC-NIC, CPNP UC San Diego Health System Objectives State the blood glucose level at
Received 4 June 2013 Accepted 17 June 2014
 Short case report 133 Polycystic kidney disease in neonate with acrorenal mandibular syndrome Savithadevi G. Sanganalmatha a, Chandrasekhar R. Hedne a, Shankar S. Hiremath a, Shankaragoud B. Patil a, Jyothiprakash
Short case report 133 Polycystic kidney disease in neonate with acrorenal mandibular syndrome Savithadevi G. Sanganalmatha a, Chandrasekhar R. Hedne a, Shankar S. Hiremath a, Shankaragoud B. Patil a, Jyothiprakash
Skeletal System. Prof. Dr. Malak A. Al-yawer Department of Anatomy/Embryology Section
 Skeletal System Prof. Dr. Malak A. Al-yawer Department of Anatomy/Embryology Section Learning objectives At the end of this lecture, the medical student will be able to: State the embryonic origin of skeletal
Skeletal System Prof. Dr. Malak A. Al-yawer Department of Anatomy/Embryology Section Learning objectives At the end of this lecture, the medical student will be able to: State the embryonic origin of skeletal
Objectives See course web page for full objectives Read : , (not Bayes theorem section)
 An Approach to Birth Defects: Perspectives in Dysmorphology Cassatt children, Mary Cassatt Adam and Eve Romulus Vuia (1922) Elizabeth M. Petty, MD Associate Professor Molecular Medicine and Genetics epetty@umich.edu
An Approach to Birth Defects: Perspectives in Dysmorphology Cassatt children, Mary Cassatt Adam and Eve Romulus Vuia (1922) Elizabeth M. Petty, MD Associate Professor Molecular Medicine and Genetics epetty@umich.edu
Transient malformations like PDA and PDA of prematurity were not considered. We have divided cardiac malformations in 2 groups:
 CARDIAC MALFORMATIONS DETECTED AT BIRTH Anwar Dudin-MD, Annie Rambaud-Cousson-MD, Mahmoud Nashashibi-MD Pediatric Department Makassed Hospital Jerusalem Diagnosis of congenital heart disease in the neonatal
CARDIAC MALFORMATIONS DETECTED AT BIRTH Anwar Dudin-MD, Annie Rambaud-Cousson-MD, Mahmoud Nashashibi-MD Pediatric Department Makassed Hospital Jerusalem Diagnosis of congenital heart disease in the neonatal
Methods PEDIATRIC CARDIOLOGY
 1805 PEDIATRIC CARDIOLOGY Trends and Outcomes After Prenatal Diagnosis of Congenital Cardiac Malformations by Fetal Echocardiography in a Well Defined Birth Population, Atlanta, Georgia, 1990 1994 EDUARDO
1805 PEDIATRIC CARDIOLOGY Trends and Outcomes After Prenatal Diagnosis of Congenital Cardiac Malformations by Fetal Echocardiography in a Well Defined Birth Population, Atlanta, Georgia, 1990 1994 EDUARDO
Glossary of medical terms (grouped by affected system or organ)
 Glossary of medical terms (grouped by affected system or organ) Atrial septal defect (ASD) disorder of the heart that is present at birth involving a hole in the wall (septum) separating the two upper
Glossary of medical terms (grouped by affected system or organ) Atrial septal defect (ASD) disorder of the heart that is present at birth involving a hole in the wall (septum) separating the two upper
Arabian Gulf University Kingdom of Bahrain Year 5 Pediatrics 2 nd Week Dr. Zakariya Al-Akri Common and Uncommon Conditions
 Arabian Gulf University Kingdom of Bahrain Year 5 Pediatrics 2 nd Week Dr. Zakariya Al-Akri Common and Uncommon Conditions - Case (1): sunset eye appearance which occurs with increased intracranial pressure
Arabian Gulf University Kingdom of Bahrain Year 5 Pediatrics 2 nd Week Dr. Zakariya Al-Akri Common and Uncommon Conditions - Case (1): sunset eye appearance which occurs with increased intracranial pressure
ISUOG Basic Training. Examining Fetal Anatomy from Longitudinal Sections Titia Cohen-Overbeek, The Netherlands
 ISUOG Basic Training Examining Fetal Anatomy from Longitudinal Sections Titia Cohen-Overbeek, The Netherlands Learning objectives 2 & 3 At the end of the lecture you will be able to: describe how to obtain
ISUOG Basic Training Examining Fetal Anatomy from Longitudinal Sections Titia Cohen-Overbeek, The Netherlands Learning objectives 2 & 3 At the end of the lecture you will be able to: describe how to obtain
Renal ultrasonography not required in babies with isolated minor ear. anomalies
 ADC-FNN Online First, published on October 13, 2005 as 10.1136/adc.2005.083329 Renal ultrasonography not required in babies with isolated minor ear Corresponding author: S A Deshpande Royal Shrewsbury
ADC-FNN Online First, published on October 13, 2005 as 10.1136/adc.2005.083329 Renal ultrasonography not required in babies with isolated minor ear Corresponding author: S A Deshpande Royal Shrewsbury
Congenital Heart Disease
 Screening Programmes Fetal Anomaly Congenital Heart Disease Information for health professionals Publication date: April 2012 Review date: April 2013 Version 2 67 Congenital Heart Disease Information for
Screening Programmes Fetal Anomaly Congenital Heart Disease Information for health professionals Publication date: April 2012 Review date: April 2013 Version 2 67 Congenital Heart Disease Information for
Situs inversus. Dr praveena pulmonology- final year post graduate
 Situs inversus Dr praveena pulmonology- final year post graduate Definiton History Types Cause Clinical features Diagnosis Treatment Definition The term situs inversus is a short form of the latin phrase
Situs inversus Dr praveena pulmonology- final year post graduate Definiton History Types Cause Clinical features Diagnosis Treatment Definition The term situs inversus is a short form of the latin phrase
Dextrocardia in patients with Poland syndrome: Phenotypic characterization provides insight into the pathogenesis
 Dextrocardia in patients with Poland syndrome: Phenotypic characterization provides insight into the pathogenesis Anwar Baban Dipartimento Medico Chirurgico di Cardiologia Pediatrica. Ospedale Pediatrico
Dextrocardia in patients with Poland syndrome: Phenotypic characterization provides insight into the pathogenesis Anwar Baban Dipartimento Medico Chirurgico di Cardiologia Pediatrica. Ospedale Pediatrico
Radiological and pathologic findings of fetal renal cystic diseases and associated fetal syndromes: A pictorial review
 Radiological and pathologic findings of fetal renal cystic diseases and associated fetal syndromes: A pictorial review Poster No.: C-2835 Congress: ECR 2010 Type: Educational Exhibit Topic: Pediatric Authors:
Radiological and pathologic findings of fetal renal cystic diseases and associated fetal syndromes: A pictorial review Poster No.: C-2835 Congress: ECR 2010 Type: Educational Exhibit Topic: Pediatric Authors:
Supplementary Online Content
 Supplementary Online Content Honein MA, Dawson AL, Petersen E, et al; US Zika Pregnancy Registry Collaboration. Birth Defects Among Fetuses and Infants of US Women With Laboratory Evidence of Possible
Supplementary Online Content Honein MA, Dawson AL, Petersen E, et al; US Zika Pregnancy Registry Collaboration. Birth Defects Among Fetuses and Infants of US Women With Laboratory Evidence of Possible
Screening for Critical Congenital Heart Disease
 Screening for Critical Congenital Heart Disease Caroline K. Lee, MD Pediatric Cardiology Disclosures I have no relevant financial relationships or conflicts of interest 1 Most Common Birth Defect Most
Screening for Critical Congenital Heart Disease Caroline K. Lee, MD Pediatric Cardiology Disclosures I have no relevant financial relationships or conflicts of interest 1 Most Common Birth Defect Most
Parts of the skeletal system. Bones (skeleton) Joints Cartilages Ligaments (bone to bone)(tendon=bone to muscle)
 The Skeletal System The Skeletal System Parts of the skeletal system Bones (skeleton) Joints Cartilages Ligaments (bone to bone)(tendon=bone to muscle) Divided into two divisions Axial skeleton Appendicular
The Skeletal System The Skeletal System Parts of the skeletal system Bones (skeleton) Joints Cartilages Ligaments (bone to bone)(tendon=bone to muscle) Divided into two divisions Axial skeleton Appendicular
Welcome to ANAT 10A! What is Anatomy? Different levels of Anatomy The Language of Anatomy Pearson Education, Inc.
 Welcome to ANAT 10A! What is Anatomy? Different levels of Anatomy The Language of Anatomy Introduction Anatomy means to dissect: (ANAT 10A) The study of internal & external body structures The study of
Welcome to ANAT 10A! What is Anatomy? Different levels of Anatomy The Language of Anatomy Introduction Anatomy means to dissect: (ANAT 10A) The study of internal & external body structures The study of
Case MDCT 3D reconstructed features of posterior urethral valve
 Case 12688 MDCT 3D reconstructed features of posterior urethral valve Hidayatullah Hamidi Third year Resident of Radiology French medical institute for children Radiology Department; Kabul, Afghanistan;
Case 12688 MDCT 3D reconstructed features of posterior urethral valve Hidayatullah Hamidi Third year Resident of Radiology French medical institute for children Radiology Department; Kabul, Afghanistan;
Development of the urinary system
 Development of the urinary system WSO School of Biomedical Sciences, University of Hong Kong. 3 sets of kidneys developing in succession (temporally and spatially) : Pronephros ] Mesonephros ]- Intermediate
Development of the urinary system WSO School of Biomedical Sciences, University of Hong Kong. 3 sets of kidneys developing in succession (temporally and spatially) : Pronephros ] Mesonephros ]- Intermediate
intracranial anomalies
 Chapter 5: Fetal Central Nervous System 84 intracranial anomalies Hydrocephaly Dilatation of ventricular system secondary to an increase in the amount of CSF. Effects of hydrocephalus include flattening
Chapter 5: Fetal Central Nervous System 84 intracranial anomalies Hydrocephaly Dilatation of ventricular system secondary to an increase in the amount of CSF. Effects of hydrocephalus include flattening
HOW TO IMAGE AND DESCRIBE CONGENITAL LUNG MALFORMATIONS
 HOW TO IMAGE AND DESCRIBE CONGENITAL LUNG MALFORMATIONS Paul Thacker, MD Assistant Professor Departments of Radiology and Pediatrics Medical University of South Carolina DISCLOSURES I have no relevant
HOW TO IMAGE AND DESCRIBE CONGENITAL LUNG MALFORMATIONS Paul Thacker, MD Assistant Professor Departments of Radiology and Pediatrics Medical University of South Carolina DISCLOSURES I have no relevant
Case Report Agenesis of the Corpus Callosum and Skeletal Deformities in Two Unrelated Patients: Analysis via MRI and Radiography
 Case Reports in Orthopedics, Article ID 186973, 5 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2014/186973 Case Report Agenesis of the Corpus Callosum and Skeletal Deformities in Two Unrelated Patients: Analysis via
Case Reports in Orthopedics, Article ID 186973, 5 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2014/186973 Case Report Agenesis of the Corpus Callosum and Skeletal Deformities in Two Unrelated Patients: Analysis via
Grand Rounds Mullerian Anomalies. Sara Schaenzer, PGY-3 9/26/18
 Grand Rounds Mullerian Anomalies Sara Schaenzer, PGY-3 9/26/18 Background Congenital uterine anomalies occur in 2-4% of women Three times more common in women with recurrent pregnancy loss True incidence
Grand Rounds Mullerian Anomalies Sara Schaenzer, PGY-3 9/26/18 Background Congenital uterine anomalies occur in 2-4% of women Three times more common in women with recurrent pregnancy loss True incidence

