Dr Rodney Itaki Lecturer Anatomical Pathology Discipline. University of Papua New Guinea School of Medicine & Health Sciences Division of Pathology
|
|
|
- Norman York
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Fetal & Neonatal Pathology Dr Rodney Itaki Lecturer Anatomical Pathology Discipline University of Papua New Guinea School of Medicine & Health Sciences Division of Pathology
2 Self-Directed Reading Topics Intra-uterine growth retardation Definition, causes, diagnosis & complications. APGAR SCORE Tumor & tumor like lesions in the newborn (e.g. haemangioma) Immaturity of organ systems in the pre-term neonate: Lungs, kidneys, brain & liver Perinatal infections Transcervival (ascending) Transplacental (haematological) Common birth injuries Find out the common types of birth injuries at PMGH labor ward
3 Overview o Congenital malformations o Neonatal respiratory syndromes o Congenital heart diseases o Erythroblastosis fetalis haemolytic diseases of the new born o Inborn errors of metabolism o Phenylketoneuria o Galactosemia o Cystic fibrosis (mucoviscidosis)
4 Congenital Malformations Definitions: Define the following terms. Malformations intrinsic abnormalities occurring during development. Can affect single organ systems or multiple organs. Deformations arise later in fetal life. Represent alterations in form or structure from mechanical factors. Abnormalities in shape, form or position of body. Much less risk of transmission. Uterine constraint common cause, oligohydramnions, multiple fetus. Disruptions secondary destruction or interference with organ or body. Amniotic bands common cause. A sequence pattern of cascade of anomalies. Syndrome constellation of congenital anomalies pathologically related that cannot be explained on a basis of a single, localised initiating event. Agenesis, atresia, aplasia, hypoplasia, hyperplasia, hypertrophy or hypotrophy and dysplasia self directed reading.
5 Ref: Robins Pathological Basis of Diseases, 7 th Ed.
6 Study Guide Mechanisms of malformations Complex and poorly understood. Timing of prenatal teratogenic insult is important factor. Teratogens and genetic factors act at different levels affecting: Proper cell migration Cell proliferation Cellular interactions Cell-matrix interactions Programmed cell death (apoptosis) Hormonal influences Mechanical forces Describe the pathogenesis of congenital malformations self study.
7
8
9 Frequency of common malformations Ref: Ref: Robins Robins Pathological pathological Basis Basis of Diseases, of Diseases, 7 th Ed 6 th Ed.
10 PNG Picture - Frequency Ref: Birth Defects in PNG
11 Contd.. Ref: Birth Defects in PNG
12 Causes of Malformations REF: Robins Pathological Basis of Diseases, 6th Ed.
13 Neonatal Respiratory Distress Syndrome Common cause of RDS in the newborn is hyaline membrane disease. Underlying pathology lung immaturity. Common in pre-term neonates. Deficiency of pulmonary surfactant is the defect. There is alternating atelactasis and dilation of the alveoli causing hypoxemia & CO2 retention.
14 Pathophysiology of RDS Ref: Robins Pathological Basis of Diseases, 6 th Ed.
15 Transient Tachypnea of the Newborn (TTN) Also known as Type II RDS or Retained Lung Fluid
16 Etiology & Predisposing Factors C-section These infants do not have the fluid expelled from their airways as occurs in vaginal delivery Maternal Diabetes Increased chance of C-section Cord Compression Anesthesia
17 TTN Pathophysiology Primary problem = retained lung fluid Fluid not expelled from airways because of C-section Poor absorption of remaining fluid by pulmonary capillaries and lymphatics If retained fluid is in interstitial spaces, compliance decreased If retained fluid is in airways, airway resistance increased TTN can be restrictive, obstructive, or both! Fluid usually clears by itself after hours after birth
18 Persistent Pulmonary Hypertension Also known as Persistent Fetal Circulation -PPHN- -PFC-
19 Failure to make the transition from fetal to neonatal circulation or a reversion back to the condition where pulmonary artery pressure exceeds aortic pressure Results in R-L shunting across the D.A. and the Foramen Ovale
20 CONGENITAL HEART DISEASES
21 Relative Frequency of Lesions Ventricular septal defect Atrial septal defect (secundum) 6-8 Patent ductus arteriosus 6-8 Coarctation of aorta 5-7 Tetralogy of Fallot 5-7 Pulmonary valve stenosis 5-7 Aortic valve stenosis 4-7 Transposition of great arteries 3-5 Hypoplastic left ventricle 1-3 Hypoplastic right ventricle 1-3 Truncus arteriosus 1-2 Total anomalous pulm venous return 1-2 Tricuspid atresia 1-2 Double-outlet right ventricle 1-2 Others 5-10
22 Tetralogy of Fallot Cyanosis, especially in the adult, is the result of a small number of cardiac malformations well determined. One is much more frequent than the others. This malformation consists of a true anatomopathologic type represented by the following tetralogy: (1) Stenosis of the pulmonary artery; (2) Interventricular communication; (3) Deviation of the origin of the aorta to the right; and (4) Hypertrophy, almost always concentric in type, of the right ventricle. Failure of obliteration of the foramen ovale may occasionally be added in a wholly accessory manner. Fallot, Ètienne-Louis-Arthur. Contribution to the pathologic anatomy of morbus caeruleus (cardiac cyanosis). Marseilles Med. 1888; 25:
23 Tetralogy of Fallot VSD Over-riding aorta Pulmonary valve stenosis Right ventricular hypertrophy Significant cyanosis because of R-L shunt
24 Complete Transposition of the Great Vessels Pulmonary artery arises from left ventricle and Aorta arises from right ventricle R-L shunt through PDA, ASD, or VSD needs to be present for infant to survive until corrective surgery Balloon septostomy during cardiac catheterization
25 Truncus Arteriosus Aorta and pulmonary artery are the same vessel Large VSD Requires MAJOR surgical repair Mortality is 40-50%
26 Patent Ductus Arteriosus -PDA_ Failure of the D.A. to close at birth or a reopening of the D.A. after birth. Allows shunting between the pulmonary artery and the aorta
27 Occurrence 1 per 2000 term babies 30-50% of RDS babies
28 Etiology & Predisposing Factors Prematurity D.A. not as sensitive to increasing PaO2 Hypoxia Decreasing PaO2 allows it to re-open for up to three weeks after birth Thus, a PDA can occur in a premature infant who is NOT hypoxic or in a term baby who is hypoxic Worst case is a premature infant who is hypoxic!
29 Erythroblastosis Fetalis (Hemolytic Disease of the Newborn) Definition: haemolytic disease in the newborn caused by blood-group incompatibility between mother & child. (ABO and Rh) However, there are also non-immune causes. Sensitisation occurs in last trimester of pregnancy or during birth (absence of synciotrophoblast) Occurs in subsequent pregnancies. Not the first.
30 Pathogenesis of erythroblastosis Ref: Robins Pathological Basis of Diseases, 7 th Ed. Ref: Robins Pathological Basis of Diseases, 6 th Ed.
31 Non-Immune Causes Ref: Robins Pathological Basis of Diseases, 6 th Ed.
32 Inborn Errors of Metabolism Phenylketonuria Galactosemia Cystic fibrosis (Mucoviscidosis)
33 Clinical Symptomatology of Inborn Errors of Metabolism (IEM) in the Neonate or Infant Symptoms indicating possibility of an IEM (one or all) Infant becomes acutely ill after period of normal behavior and feeding; this may occur within hours or weeks Neonate or infant with seizures and/or hypotonia, especially if seizures are intractable Neonate or infant with an unusual odor Symptoms indicating strong possibility of an IEM, particularly when coupled with the above symptoms Persistent or recurrent vomiting Failure to thrive (failure to gain weight or weight loss) Apnea or respiratory distress (tachypnea) Jaundice or hepatomegaly Lethargy Coma (particularly intermittent) Unexplained hemorrhage Family history of neonatal deaths, or of similar illness, especially in siblings Parental consanguinity Sepsis (particularly Escherichia coli)
34 Inborn Errors of Metabolism of Acute Onset: Nonacidotic, Nonhyperammonemic Features Neurologic Features Predominant (Seizures, Hypotonia, Optic Abnormality) Glycine encephalopathy (nonketotic hyperglycinemia) Pyridoxine-responsive seizures Sulfite oxidase/santhine oxidase deficiency Peroxisomal disorders (Zellweger syndrome, neonatal adrenoleukodystrophy, infantile refsum disease) Jaundice Prominent Galactosemia Hereditary fructose intolerance Menkes kinky hair syndrome α 1 -antitrypsin deficiency Hypoglycemia (Nonketotic): Fatty acid oxidation defects (MCAD, LCAD, carnitine palmityl transferase, infantile form) Cardiomegaly Glycogen storage disease (type II phosphorylase kinase b deficiency 18 ) Fatty acid oxidation defects (LCAD) Hepatomegaly (Fatty): Fatty acid oxidation defects (MCAD, LCAD) Skeletal Muscle Weakness: Fatty acid oxidation defects (LCAD, SCAD, multiple acyl-coa dehydrogenase
35 Phenylketonuria Autosomal recessive disorder (must have 2 pair of the gene to express phenotypically i.e. homozygous) Molecular basis: severe lack of phenylalanine hydroxylase leading to increased levels of phenylalanine in the blood and PKU. Rising plasma levels of phenylalanine impair brain development. Phenylalanine hydroxylase converts phenylalanine to tyrosine.
36 Molecular Basis Deficiency of liver enzyme phenylalanine hydroxylase. Phenylalanine hydroxylase converts phenylalanine to tyrosine. Lack of enzyme results in increased level of phenylalanine. Phenylalanine essential amino acides cannot by synthesised by body. Therefore obtained in protein rich foods. Phenylalanine builds up to toxic levels manifested in clinical picture, esp. mental retardation.
37 Molecular basis Ref: Robins Pathological Basis of Diseases, 7 th Ed.
38 Galactosemia Autosomal recessive disorder Impaired galactose metabolism Many variants but common one is absent of a transferase enzyme in step 2 in galactose metabolism Lactose is major cabohydrate in breast milk. Lactose split into galactose & glucose. Glucose enters Krebs cycle. Galactose undergoes 3 step reaction before entering Krebs cycle.
39 PROTEIN GLYCOGEN FAT AMINO ACIDS FRUCTOSE GALACTOSE ORGANIC ACIDS GLUCOSE FREE FATTY ACIDS AMMONIA PYRUVATE LACTATE UREA CYCLE ACETYL CoA UREA KREBS CYCLE KETONES NADH ATP An integrated view of the metabolic pathways
40 Molecular basis lactose Splint into glucose & galactose Galacatose converted to glucose in 3 steps Major carbohydrate in mammalian milk Glucose enters Krebs cycle Galactose coverted to glucose in 3 reaction steps before entering Krebs cycle Enzyme (galactose- 1phosphate uridly transferase) in reaction 2 absent. Common variant As a result of transferase lack,galacatose-1-phosphate accumulates and deposited in various sites leading to clinical manifestations observed.
41 Cystic Fibrosis Primary defect is in the regulation of epithelial chloride transport by a chloride channel protein (CFTR) encoded by the cystic fibrosis gene. Various mutations & variants. Autosomal recessive disorder (must have 2 pairs of defective gene to express symptoms). Homozygous express symptoms. 2-4% of may be heterozygous.
42 Molecular basis Ref: Robins Pathological Basis of Diseaes, 7 th Ed
43 Ref: Robins Pathological Basis of Diseases, 7 th Ed.
44 Tumor Like Lesions Ref: Robins Pathological Basis of Diseases, 7 th Ed.
45 Malignant Tumors Only 2% of malignant tumors occur in infancy & childhood. Ref: Robins Pathological Basis of Diseases, 7 th Ed.
46 Genetic Markers of childhood tumors
47 Laboratory Diagnosis Prenatal screening for genetic defects Ultra-sound scan Screening tests in newborns Specific genetic markers for tumors UEC LFT
48 Laboratory Assessment of Neonates Suspected of Having an Inborn Error of Metabolism Routine Studies Special Studies Blood lactate and pyruvate Complete blood count and differential Plasma amino acids Plasma ammonia Plasma carnitine Plasma glucose Urine amino acids Plasma electrolytes and blood ph Urine organic acids Urine ketones Urine-reducing substances
49 Study Guide How is prenatal screening for genetic defects done? What is the appropriate sample to obtain to send to laboratory? What are the current neonatal screening tests available for screening inborn errors of metabolism? What complications can be expected in a newborn of a diabetic mother? What is the pathogenesis of these complications? How is diagnosis of cystic fibrosis confirmed? What is genetic counseling?
50 END Reference: Robins Pathological Basis of Diseases, 6 th & 7 th Ed. Download PDF copies of seminar notes at:
Screening for Critical Congenital Heart Disease
 Screening for Critical Congenital Heart Disease Caroline K. Lee, MD Pediatric Cardiology Disclosures I have no relevant financial relationships or conflicts of interest 1 Most Common Birth Defect Most
Screening for Critical Congenital Heart Disease Caroline K. Lee, MD Pediatric Cardiology Disclosures I have no relevant financial relationships or conflicts of interest 1 Most Common Birth Defect Most
CONGENITAL HEART DISEASE (CHD)
 CONGENITAL HEART DISEASE (CHD) DEFINITION It is the result of a structural or functional abnormality of the cardiovascular system at birth GENERAL FEATURES OF CHD Structural defects due to specific disturbance
CONGENITAL HEART DISEASE (CHD) DEFINITION It is the result of a structural or functional abnormality of the cardiovascular system at birth GENERAL FEATURES OF CHD Structural defects due to specific disturbance
Heart and Lungs. LUNG Coronal section demonstrates relationship of pulmonary parenchyma to heart and chest wall.
 Heart and Lungs Normal Sonographic Anatomy THORAX Axial and coronal sections demonstrate integrity of thorax, fetal breathing movements, and overall size and shape. LUNG Coronal section demonstrates relationship
Heart and Lungs Normal Sonographic Anatomy THORAX Axial and coronal sections demonstrate integrity of thorax, fetal breathing movements, and overall size and shape. LUNG Coronal section demonstrates relationship
Congenital Heart Defects
 Normal Heart Congenital Heart Defects 1. Patent Ductus Arteriosus The ductus arteriosus connects the main pulmonary artery to the aorta. In utero, it allows the blood leaving the right ventricle to bypass
Normal Heart Congenital Heart Defects 1. Patent Ductus Arteriosus The ductus arteriosus connects the main pulmonary artery to the aorta. In utero, it allows the blood leaving the right ventricle to bypass
Absent Pulmonary Valve Syndrome
 Absent Pulmonary Valve Syndrome Fact sheet on Absent Pulmonary Valve Syndrome In this condition, which has some similarities to Fallot's Tetralogy, there is a VSD with narrowing at the pulmonary valve.
Absent Pulmonary Valve Syndrome Fact sheet on Absent Pulmonary Valve Syndrome In this condition, which has some similarities to Fallot's Tetralogy, there is a VSD with narrowing at the pulmonary valve.
Anatomy & Physiology
 1 Anatomy & Physiology Heart is divided into four chambers, two atrias & two ventricles. Atrioventricular valves (tricuspid & mitral) separate the atria from ventricles. they open & close to control flow
1 Anatomy & Physiology Heart is divided into four chambers, two atrias & two ventricles. Atrioventricular valves (tricuspid & mitral) separate the atria from ventricles. they open & close to control flow
Neonatal Hypoglycemia. Presented By : Kamlah Olaimat 25\7\2010
 Neonatal Hypoglycemia Presented By : Kamlah Olaimat 25\7\2010 Definition The S.T.A.B.L.E. Program defines hypoglycemia as: Glucose delivery or availability is inadequate to meet glucose demand (Karlsen,
Neonatal Hypoglycemia Presented By : Kamlah Olaimat 25\7\2010 Definition The S.T.A.B.L.E. Program defines hypoglycemia as: Glucose delivery or availability is inadequate to meet glucose demand (Karlsen,
How to Recognize a Suspected Cardiac Defect in the Neonate
 Neonatal Nursing Education Brief: How to Recognize a Suspected Cardiac Defect in the Neonate https://www.seattlechildrens.org/healthcareprofessionals/education/continuing-medical-nursing-education/neonatalnursing-education-briefs/
Neonatal Nursing Education Brief: How to Recognize a Suspected Cardiac Defect in the Neonate https://www.seattlechildrens.org/healthcareprofessionals/education/continuing-medical-nursing-education/neonatalnursing-education-briefs/
Cardiovascular Pathophysiology: Right to Left Shunts aka Cyanotic Lesions
 Cardiovascular Pathophysiology: Right to Left Shunts aka Cyanotic Lesions Ismee A. Williams, MD, MS iib6@columbia.edu Pediatric Cardiology Learning Objectives To discuss the hemodynamic significance of
Cardiovascular Pathophysiology: Right to Left Shunts aka Cyanotic Lesions Ismee A. Williams, MD, MS iib6@columbia.edu Pediatric Cardiology Learning Objectives To discuss the hemodynamic significance of
Cardiovascular Pathophysiology: Right to Left Shunts aka Cyanotic Lesions Ismee A. Williams, MD, MS Pediatric Cardiology
 Cardiovascular Pathophysiology: Right to Left Shunts aka Cyanotic Lesions Ismee A. Williams, MD, MS iib6@columbia.edu Pediatric Cardiology Learning Objectives To discuss the hemodynamic significance of
Cardiovascular Pathophysiology: Right to Left Shunts aka Cyanotic Lesions Ismee A. Williams, MD, MS iib6@columbia.edu Pediatric Cardiology Learning Objectives To discuss the hemodynamic significance of
When is Risky to Apply Oxygen for Congenital Heart Disease 부천세종병원 소아청소년과최은영
 When is Risky to Apply Oxygen for Congenital Heart Disease 부천세종병원 소아청소년과최은영 The Korean Society of Cardiology COI Disclosure Eun-Young Choi The author have no financial conflicts of interest to disclose
When is Risky to Apply Oxygen for Congenital Heart Disease 부천세종병원 소아청소년과최은영 The Korean Society of Cardiology COI Disclosure Eun-Young Choi The author have no financial conflicts of interest to disclose
Index. cardiology.theclinics.com. Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type.
 Index Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A ACHD. See Adult congenital heart disease (ACHD) Adult congenital heart disease (ACHD), 503 512 across life span prevalence of, 504 506
Index Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A ACHD. See Adult congenital heart disease (ACHD) Adult congenital heart disease (ACHD), 503 512 across life span prevalence of, 504 506
Congenital Heart Disease: Physiology and Common Defects
 Congenital Heart Disease: Physiology and Common Defects Jamie S. Sutherell, M.D, M.Ed. Associate Professor, Pediatrics Division of Cardiology Director, Medical Student Education in Pediatrics Director,
Congenital Heart Disease: Physiology and Common Defects Jamie S. Sutherell, M.D, M.Ed. Associate Professor, Pediatrics Division of Cardiology Director, Medical Student Education in Pediatrics Director,
Metabolic Disorders. Chapter Thomson - Wadsworth
 Metabolic Disorders Chapter 28 1 Metabolic Disorders Inborn errors of metabolism group of diseases that affect a wide variety of metabolic processes; defective processing or transport of amino acids, fatty
Metabolic Disorders Chapter 28 1 Metabolic Disorders Inborn errors of metabolism group of diseases that affect a wide variety of metabolic processes; defective processing or transport of amino acids, fatty
Congenital Heart Disease
 Congenital Heart Disease Mohammed Alghamdi, MD, FRCPC, FAAP, FACC Associate Professor and Consultant Pediatric Cardiology, Cardiac Science King Fahad Cardiac Centre King Saud University INTRODUCTION CHD
Congenital Heart Disease Mohammed Alghamdi, MD, FRCPC, FAAP, FACC Associate Professor and Consultant Pediatric Cardiology, Cardiac Science King Fahad Cardiac Centre King Saud University INTRODUCTION CHD
PAEDIATRIC EMQs. Andrew A Mallick Paediatrics.info.
 PAEDIATRIC EMQs Andrew A Mallick Paediatrics.info www.paediatrics.info Paediatric EMQs Paediatrics.info First published in the United Kingdom in 2012. While the advice and information in this book is believed
PAEDIATRIC EMQs Andrew A Mallick Paediatrics.info www.paediatrics.info Paediatric EMQs Paediatrics.info First published in the United Kingdom in 2012. While the advice and information in this book is believed
"Lecture Index. 1) Heart Progenitors. 2) Cardiac Tube Formation. 3) Valvulogenesis and Chamber Formation. 4) Epicardium Development.
 "Lecture Index 1) Heart Progenitors. 2) Cardiac Tube Formation. 3) Valvulogenesis and Chamber Formation. 4) Epicardium Development. 5) Septation and Maturation. 6) Changes in Blood Flow during Development.
"Lecture Index 1) Heart Progenitors. 2) Cardiac Tube Formation. 3) Valvulogenesis and Chamber Formation. 4) Epicardium Development. 5) Septation and Maturation. 6) Changes in Blood Flow during Development.
Inborn Errors of Metabolism (IEM)
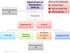 Clinical Presentation Inborn Errors of Metabolism (IEM) Click on the following: - Clinical Pearl - link to movie clip - link to picture Investigations Blood Work Urine No Acidosis NH 4 + Metabolic Acidosis
Clinical Presentation Inborn Errors of Metabolism (IEM) Click on the following: - Clinical Pearl - link to movie clip - link to picture Investigations Blood Work Urine No Acidosis NH 4 + Metabolic Acidosis
By Dickens ATURWANAHO & ORIBA DAN LANGOYA MAKchs, MBchB CONGENTAL HEART DISEASE
 By Dickens ATURWANAHO & ORIBA DAN LANGOYA MAKchs, MBchB CONGENTAL HEART DISEASE Introduction CHDs are abnormalities of the heart or great vessels that are present at birth. Common type of heart disease
By Dickens ATURWANAHO & ORIBA DAN LANGOYA MAKchs, MBchB CONGENTAL HEART DISEASE Introduction CHDs are abnormalities of the heart or great vessels that are present at birth. Common type of heart disease
Hypoglycaemia of the neonate. Dr. L.G. Lloyd Dept. Paediatrics
 Hypoglycaemia of the neonate Dr. L.G. Lloyd Dept. Paediatrics Why is glucose important? It provides 60-70% of energy needs Utilization obligatory by red blood cells, brain and kidney as major source of
Hypoglycaemia of the neonate Dr. L.G. Lloyd Dept. Paediatrics Why is glucose important? It provides 60-70% of energy needs Utilization obligatory by red blood cells, brain and kidney as major source of
Pathophysiology: Left To Right Shunts
 Pathophysiology: Left To Right Shunts Daphne T. Hsu, MD dh17@columbia.edu Learning Objectives Learn the relationships between pressure, blood flow, and resistance Review the transition from fetal to mature
Pathophysiology: Left To Right Shunts Daphne T. Hsu, MD dh17@columbia.edu Learning Objectives Learn the relationships between pressure, blood flow, and resistance Review the transition from fetal to mature
5.8 Congenital Heart Disease
 5.8 Congenital Heart Disease Congenital heart diseases (CHD) refer to structural or functional heart diseases, which are present at birth. Some of these lesions may be discovered later. prevalence of Chd
5.8 Congenital Heart Disease Congenital heart diseases (CHD) refer to structural or functional heart diseases, which are present at birth. Some of these lesions may be discovered later. prevalence of Chd
CYANOTIC CONGENITAL HEART DISEASES. PRESENTER: DR. Myra M. Koech Pediatric cardiologist MTRH/MU
 CYANOTIC CONGENITAL HEART DISEASES PRESENTER: DR. Myra M. Koech Pediatric cardiologist MTRH/MU DEFINITION Congenital heart diseases are defined as structural and functional problems of the heart that are
CYANOTIC CONGENITAL HEART DISEASES PRESENTER: DR. Myra M. Koech Pediatric cardiologist MTRH/MU DEFINITION Congenital heart diseases are defined as structural and functional problems of the heart that are
Slide 1. Slide 2. Slide 3 CONGENITAL HEART DISEASE. Papworth Hospital NHS Trust INTRODUCTION. Jakub Kadlec/Catherine Sudarshan INTRODUCTION
 Slide 1 CONGENITAL HEART DISEASE Jakub Kadlec/Catherine Sudarshan NHS Trust Slide 2 INTRODUCTION Most common congenital illness in the newborn Affects about 4 9 / 1000 full-term live births in the UK 1.5
Slide 1 CONGENITAL HEART DISEASE Jakub Kadlec/Catherine Sudarshan NHS Trust Slide 2 INTRODUCTION Most common congenital illness in the newborn Affects about 4 9 / 1000 full-term live births in the UK 1.5
The Fetal Cardiology Program
 The Fetal Cardiology Program at Texas Children s Fetal Center About the program Since the 1980s, Texas Children s Fetal Cardiology Program has provided comprehensive fetal cardiac care to expecting families
The Fetal Cardiology Program at Texas Children s Fetal Center About the program Since the 1980s, Texas Children s Fetal Cardiology Program has provided comprehensive fetal cardiac care to expecting families
Pathophysiology: Left To Right Shunts
 Pathophysiology: Left To Right Shunts Daphne T. Hsu, MD dh17@columbia.edu Learning Objectives Learn the relationships between pressure, blood flow, and resistance Review the transition from fetal to mature
Pathophysiology: Left To Right Shunts Daphne T. Hsu, MD dh17@columbia.edu Learning Objectives Learn the relationships between pressure, blood flow, and resistance Review the transition from fetal to mature
3/14/2011 MANAGEMENT OF NEWBORNS CARDIAC INTENSIVE CARE CONFERENCE FOR HEALTH PROFESSIONALS IRVINE, CA. MARCH 7, 2011 WITH HEART DEFECTS
 CONFERENCE FOR HEALTH PROFESSIONALS IRVINE, CA. MARCH 7, 2011 MANAGEMENT OF NEWBORNS WITH HEART DEFECTS A NTHONY C. CHANG, MD, MBA, MPH M E D I C AL D I RE C T OR, HEART I N S T I T U T E C H I LDRE N
CONFERENCE FOR HEALTH PROFESSIONALS IRVINE, CA. MARCH 7, 2011 MANAGEMENT OF NEWBORNS WITH HEART DEFECTS A NTHONY C. CHANG, MD, MBA, MPH M E D I C AL D I RE C T OR, HEART I N S T I T U T E C H I LDRE N
Patent ductus arteriosus PDA
 Patent ductus arteriosus PDA Is connecting between the aortic end just distal to the origin of the LT sub clavian artery& the pulmonary artery at its bifurcation. Female/male ratio is 2:1 and it is more
Patent ductus arteriosus PDA Is connecting between the aortic end just distal to the origin of the LT sub clavian artery& the pulmonary artery at its bifurcation. Female/male ratio is 2:1 and it is more
CongHeartDis.doc. Андрій Миколайович Лобода
 CongHeartDis.doc Андрій Миколайович Лобода 2015 Зміст 3 Зміст Зміст 4 A child with tetralogy of Fallot is most likely to exhibit: -Increased pulmonary blood flow -Increased pressure in the right ventricle
CongHeartDis.doc Андрій Миколайович Лобода 2015 Зміст 3 Зміст Зміст 4 A child with tetralogy of Fallot is most likely to exhibit: -Increased pulmonary blood flow -Increased pressure in the right ventricle
Foetal Cardiology: How to predict perinatal problems. Prof. I.Witters Prof.M.Gewillig UZ Leuven
 Foetal Cardiology: How to predict perinatal problems Prof. I.Witters Prof.M.Gewillig UZ Leuven Cardiopathies Incidence : 8-12 / 1000 births ( 1% ) Most frequent - Ventricle Septum Defect 20% - Atrium Septum
Foetal Cardiology: How to predict perinatal problems Prof. I.Witters Prof.M.Gewillig UZ Leuven Cardiopathies Incidence : 8-12 / 1000 births ( 1% ) Most frequent - Ventricle Septum Defect 20% - Atrium Septum
Standard of Newborn Care in the Age of Birth Plans. Stephanie Deal, MD Tiffany McKee-Garrett, MD
 Standard of Newborn Care in the Age of Birth Plans Stephanie Deal, MD Tiffany McKee-Garrett, MD Disclosure We have no relevant financial relationships with the manufacturers(s) of any commercial products(s)
Standard of Newborn Care in the Age of Birth Plans Stephanie Deal, MD Tiffany McKee-Garrett, MD Disclosure We have no relevant financial relationships with the manufacturers(s) of any commercial products(s)
Introduction. Pediatric Cardiology. General Appearance. Tools of Assessment. Auscultation. Vital Signs
 Introduction Pediatric Cardiology An introduction to the pediatric patient with heart disease: M-III Lecture Douglas R. Allen, M.D. Assistant Professor and Director of Community Pediatric Cardiology at
Introduction Pediatric Cardiology An introduction to the pediatric patient with heart disease: M-III Lecture Douglas R. Allen, M.D. Assistant Professor and Director of Community Pediatric Cardiology at
Cardiac Emergencies in Infants. Michael Luceri, DO
 Cardiac Emergencies in Infants Michael Luceri, DO October 7, 2017 I have no financial obligations or conflicts of interest to disclose. Objectives Understand the scope of congenital heart disease Recognize
Cardiac Emergencies in Infants Michael Luceri, DO October 7, 2017 I have no financial obligations or conflicts of interest to disclose. Objectives Understand the scope of congenital heart disease Recognize
Hypoglycemia. Objectives. Glucose Metabolism
 Hypoglycemia Instructor: Janet Mendis, MSN, RNC-NIC, CNS Outline: Janet Mendis, MSN, RNC-NIC, CNS Summer Morgan, MSN, RNC-NIC, CPNP UC San Diego Health System Objectives State the blood glucose level at
Hypoglycemia Instructor: Janet Mendis, MSN, RNC-NIC, CNS Outline: Janet Mendis, MSN, RNC-NIC, CNS Summer Morgan, MSN, RNC-NIC, CPNP UC San Diego Health System Objectives State the blood glucose level at
9/8/2009 < 1 1,2 3,4 5,6 7,8 9,10 11,12 13,14 15,16 17,18 > 18. Tetralogy of Fallot. Complex Congenital Heart Disease.
 Current Indications for Pediatric CTA S Bruce Greenberg Professor of Radiology Arkansas Children s Hospital University of Arkansas for Medical Sciences greenbergsbruce@uams.edu 45 40 35 30 25 20 15 10
Current Indications for Pediatric CTA S Bruce Greenberg Professor of Radiology Arkansas Children s Hospital University of Arkansas for Medical Sciences greenbergsbruce@uams.edu 45 40 35 30 25 20 15 10
Cardiology Competency Based Goals and Objectives
 Cardiology Competency Based Goals and Objectives COMPETENCY 1. Patient Care. Provide family centered patient care that is developmentally and age appropriate, compassionate, and effective for the treatment
Cardiology Competency Based Goals and Objectives COMPETENCY 1. Patient Care. Provide family centered patient care that is developmentally and age appropriate, compassionate, and effective for the treatment
Supplemental Information
 ARTICLE Supplemental Information SUPPLEMENTAL TABLE 6 Mosaic and Partial Trisomies Thirty-eight VLBW infants were identified with T13, of whom 2 had mosaic T13. T18 was reported for 128 infants, of whom
ARTICLE Supplemental Information SUPPLEMENTAL TABLE 6 Mosaic and Partial Trisomies Thirty-eight VLBW infants were identified with T13, of whom 2 had mosaic T13. T18 was reported for 128 infants, of whom
Notes: 1)Membranous part contribute in the formation of small portion in the septal cusp.
 Embryology 9 : Slide 16 : There is a sulcus between primitive ventricular and bulbis cordis that will disappear gradually and lead to the formation of one chamber which is called bulboventricular chamber.
Embryology 9 : Slide 16 : There is a sulcus between primitive ventricular and bulbis cordis that will disappear gradually and lead to the formation of one chamber which is called bulboventricular chamber.
INBORN ERRORS OF METABOLISM (IEM) IAP UG Teaching slides
 INBORN ERRORS OF METABOLISM (IEM) 1 OBJECTIVES What are IEMs? Categories When to suspect? History and clinical pointers Metabolic presentation Differential diagnosis Emergency and long term management
INBORN ERRORS OF METABOLISM (IEM) 1 OBJECTIVES What are IEMs? Categories When to suspect? History and clinical pointers Metabolic presentation Differential diagnosis Emergency and long term management
Congenital heart disease. By Dr Saima Ali Professor of pediatrics
 Congenital heart disease By Dr Saima Ali Professor of pediatrics What is the most striking clinical finding in this child? Learning objectives By the end of this lecture, final year student should be able
Congenital heart disease By Dr Saima Ali Professor of pediatrics What is the most striking clinical finding in this child? Learning objectives By the end of this lecture, final year student should be able
The Blue Baby. Network Stabilisation of the Term Infant Study Day 15 th March 2017 Joanna Behrsin
 The Blue Baby Network Stabilisation of the Term Infant Study Day 15 th March 2017 Joanna Behrsin Session Structure Definitions and assessment of cyanosis Causes of blue baby Structured approach to assessing
The Blue Baby Network Stabilisation of the Term Infant Study Day 15 th March 2017 Joanna Behrsin Session Structure Definitions and assessment of cyanosis Causes of blue baby Structured approach to assessing
Paediatrics Revision Session Cardiology. Emma Walker 7 th May 2016
 Paediatrics Revision Session Cardiology Emma Walker 7 th May 2016 Cardiovascular Examination! General:! Make it fun!! Change how you act depending on their age! Introduction! Introduce yourself & check
Paediatrics Revision Session Cardiology Emma Walker 7 th May 2016 Cardiovascular Examination! General:! Make it fun!! Change how you act depending on their age! Introduction! Introduce yourself & check
7 Medical Genetics. Hemoglobinopathies. Hemoglobinopathies. Protein and Gene Structure. and Biochemical Genetics
 SESSION 7 Medical Genetics Hemoglobinopathies and Biochemical Genetics J a v a d F a s a J a m s h i d i U n i v e r s i t y o f M e d i c a l S c i e n c e s, N o v e m b e r 2 0 1 7 Hemoglobinopathies
SESSION 7 Medical Genetics Hemoglobinopathies and Biochemical Genetics J a v a d F a s a J a m s h i d i U n i v e r s i t y o f M e d i c a l S c i e n c e s, N o v e m b e r 2 0 1 7 Hemoglobinopathies
Heart and Soul Evaluation of the Fetal Heart
 Heart and Soul Evaluation of the Fetal Heart Ivana M. Vettraino, M.D., M.B.A. Clinical Associate Professor, Michigan State University College of Human Medicine Objectives Review the embryology of the formation
Heart and Soul Evaluation of the Fetal Heart Ivana M. Vettraino, M.D., M.B.A. Clinical Associate Professor, Michigan State University College of Human Medicine Objectives Review the embryology of the formation
Notes by Sandra Dankwa 2009 HF- Heart Failure DS- Down Syndrome IE- Infective Endocarditis ET- Exercise Tolerance. Small VSD Symptoms -asymptomatic
 Congenital Heart Disease: Notes. Condition Pathology PC Ix Rx Ventricular septal defect (VSD) L R shuntsdefect anywhere in the ventricle, usually perimembranous (next to the tricuspid valve) 30% 1)small
Congenital Heart Disease: Notes. Condition Pathology PC Ix Rx Ventricular septal defect (VSD) L R shuntsdefect anywhere in the ventricle, usually perimembranous (next to the tricuspid valve) 30% 1)small
ULTRASOUND OF THE FETAL HEART
 ULTRASOUND OF THE FETAL HEART Cameron A. Manbeian, MD Disclosure Statement Today s faculty: Cameron Manbeian, MD does not have any relevant financial relationships with commercial interests or affiliations
ULTRASOUND OF THE FETAL HEART Cameron A. Manbeian, MD Disclosure Statement Today s faculty: Cameron Manbeian, MD does not have any relevant financial relationships with commercial interests or affiliations
September 26, 2012 Philip Stockwell, MD Lifespan CVI Assistant Professor of Medicine (Clinical)
 September 26, 2012 Philip Stockwell, MD Lifespan CVI Assistant Professor of Medicine (Clinical) Advances in cardiac surgery have created a new population of adult patients with repaired congenital heart
September 26, 2012 Philip Stockwell, MD Lifespan CVI Assistant Professor of Medicine (Clinical) Advances in cardiac surgery have created a new population of adult patients with repaired congenital heart
Cardiac Catheterization Cases Primary Cardiac Diagnoses Facility 12 month period from to PRIMARY DIAGNOSES (one per patient)
 PRIMARY DIAGNOSES (one per patient) Septal Defects ASD (Atrial Septal Defect) PFO (Patent Foramen Ovale) ASD, Secundum ASD, Sinus venosus ASD, Coronary sinus ASD, Common atrium (single atrium) VSD (Ventricular
PRIMARY DIAGNOSES (one per patient) Septal Defects ASD (Atrial Septal Defect) PFO (Patent Foramen Ovale) ASD, Secundum ASD, Sinus venosus ASD, Coronary sinus ASD, Common atrium (single atrium) VSD (Ventricular
Paediatric Clinical Chemistry
 Paediatric Clinical Chemistry Dr N Oosthuizen Dept Chemical Pathology UP 2011 Paediatric biochemistry The child is not a miniature adult Physiological development Immature organ systems Growing individual
Paediatric Clinical Chemistry Dr N Oosthuizen Dept Chemical Pathology UP 2011 Paediatric biochemistry The child is not a miniature adult Physiological development Immature organ systems Growing individual
Chapter 2 Cardiac Interpretation of Pediatric Chest X-Ray
 Chapter 2 Cardiac Interpretation of Pediatric Chest X-Ray Ra-id Abdulla and Douglas M. Luxenberg Key Facts The cardiac silhouette occupies 50 55% of the chest width on an anterior posterior chest X-ray
Chapter 2 Cardiac Interpretation of Pediatric Chest X-Ray Ra-id Abdulla and Douglas M. Luxenberg Key Facts The cardiac silhouette occupies 50 55% of the chest width on an anterior posterior chest X-ray
MEDICAL SCIENCES Vol.I -Adult Congenital Heart Disease: A Challenging Population - Khalid Aly Sorour
 ADULT CONGENITAL HEART DISEASE: A CHALLENGING POPULATION Khalid Aly Sorour Cairo University, Kasr elaini Hospital, Egypt Keywords: Congenital heart disease, adult survival, specialized care centers. Contents
ADULT CONGENITAL HEART DISEASE: A CHALLENGING POPULATION Khalid Aly Sorour Cairo University, Kasr elaini Hospital, Egypt Keywords: Congenital heart disease, adult survival, specialized care centers. Contents
Spectrum and age of presentation of significant congenital heart disease in KwaZulu Natal, South Africa
 Spectrum and age of presentation of significant congenital heart disease in KwaZulu Natal, South Africa EGM Hoosen, K Sprenger, H Dama, A Nzimela, M Adhikari KwaZulu Natal Population 10.3 million 3.3 million
Spectrum and age of presentation of significant congenital heart disease in KwaZulu Natal, South Africa EGM Hoosen, K Sprenger, H Dama, A Nzimela, M Adhikari KwaZulu Natal Population 10.3 million 3.3 million
Uptofate Study Summary
 CONGENITAL HEART DISEASE Uptofate Study Summary Acyanotic Atrial septal defect Ventricular septal defect Patent foramen ovale Patent ductus arteriosus Aortic coartation Pulmonary stenosis Cyanotic Tetralogy
CONGENITAL HEART DISEASE Uptofate Study Summary Acyanotic Atrial septal defect Ventricular septal defect Patent foramen ovale Patent ductus arteriosus Aortic coartation Pulmonary stenosis Cyanotic Tetralogy
Common Defects With Expected Adult Survival:
 Common Defects With Expected Adult Survival: Bicuspid aortic valve :Acyanotic Mitral valve prolapse Coarctation of aorta Pulmonary valve stenosis Atrial septal defect Patent ductus arteriosus (V.S.D.)
Common Defects With Expected Adult Survival: Bicuspid aortic valve :Acyanotic Mitral valve prolapse Coarctation of aorta Pulmonary valve stenosis Atrial septal defect Patent ductus arteriosus (V.S.D.)
AORTIC COARCTATION. Synonyms: - Coarctation of the aorta
 AORTIC COARCTATION Synonyms: - Coarctation of the aorta Definition: Aortic coarctation is a congenital narrowing of the aorta, usually located after the left subclavian artery, near the ductus or the ligamentum
AORTIC COARCTATION Synonyms: - Coarctation of the aorta Definition: Aortic coarctation is a congenital narrowing of the aorta, usually located after the left subclavian artery, near the ductus or the ligamentum
Pathophysiology. Tutorial 1 Genetic Diseases
 Pathophysiology Tutorial 1 Genetic Diseases ILOs Analyze genetic pedigrees and recognize the mode of inheritance of diseases. Differentiate between patterns of inheritance based on the type of the protein
Pathophysiology Tutorial 1 Genetic Diseases ILOs Analyze genetic pedigrees and recognize the mode of inheritance of diseases. Differentiate between patterns of inheritance based on the type of the protein
Pediatric Board Review Congenital Heart Disease. Steven H. Todman, M.D. Pediatric Cardiologist Louisiana State University
 Pediatric Board Review Congenital Heart Disease Steven H. Todman, M.D. Pediatric Cardiologist Louisiana State University Our Mission To discuss various types of congenital heart disease that are commonly
Pediatric Board Review Congenital Heart Disease Steven H. Todman, M.D. Pediatric Cardiologist Louisiana State University Our Mission To discuss various types of congenital heart disease that are commonly
Objectives Part 1. Objectives Part 2. Fetal Circulation Transition to Postnatal Circulation Normal Cardiac Anatomy Ductal Dependence and use of PGE1
 Cardiac Physiology Gia Marzano, AC PNP Pediatric Cardiac Surgery Rush Center for Congenital Heart Disease Rush University Medical Center Objectives Part 1 Fetal Circulation Transition to Postnatal Circulation
Cardiac Physiology Gia Marzano, AC PNP Pediatric Cardiac Surgery Rush Center for Congenital Heart Disease Rush University Medical Center Objectives Part 1 Fetal Circulation Transition to Postnatal Circulation
Coarctation of the aorta
 T H E P E D I A T R I C C A R D I A C S U R G E R Y I N Q U E S T R E P O R T Coarctation of the aorta In the normal heart, blood flows to the body through the aorta, which connects to the left ventricle
T H E P E D I A T R I C C A R D I A C S U R G E R Y I N Q U E S T R E P O R T Coarctation of the aorta In the normal heart, blood flows to the body through the aorta, which connects to the left ventricle
The blue baby. Case 4
 Case 4 The blue baby Mrs Smith has brought her baby to A&E because she says he has started turning blue. What are your immediate differential diagnoses? 1 Respiratory causes: Congenital respiratory disorder.
Case 4 The blue baby Mrs Smith has brought her baby to A&E because she says he has started turning blue. What are your immediate differential diagnoses? 1 Respiratory causes: Congenital respiratory disorder.
The spectrum and outcome of the. neonates with inborn errors of. metabolism at a tertiary care hospital
 The spectrum and outcome of the neonates with inborn errors of metabolism at a tertiary care hospital Dr. Sevim Ünal Neonatology Division, Ankara Children s Hematology Oncology Research Hospital, Ankara,
The spectrum and outcome of the neonates with inborn errors of metabolism at a tertiary care hospital Dr. Sevim Ünal Neonatology Division, Ankara Children s Hematology Oncology Research Hospital, Ankara,
Congenital heart disease: When to act and what to do?
 Leading Article Congenital heart disease: When to act and what to do? Duminda Samarasinghe 1 Sri Lanka Journal of Child Health, 2010; 39: 39-43 (Key words: Congenital heart disease) Congenital heart disease
Leading Article Congenital heart disease: When to act and what to do? Duminda Samarasinghe 1 Sri Lanka Journal of Child Health, 2010; 39: 39-43 (Key words: Congenital heart disease) Congenital heart disease
Transient malformations like PDA and PDA of prematurity were not considered. We have divided cardiac malformations in 2 groups:
 CARDIAC MALFORMATIONS DETECTED AT BIRTH Anwar Dudin-MD, Annie Rambaud-Cousson-MD, Mahmoud Nashashibi-MD Pediatric Department Makassed Hospital Jerusalem Diagnosis of congenital heart disease in the neonatal
CARDIAC MALFORMATIONS DETECTED AT BIRTH Anwar Dudin-MD, Annie Rambaud-Cousson-MD, Mahmoud Nashashibi-MD Pediatric Department Makassed Hospital Jerusalem Diagnosis of congenital heart disease in the neonatal
5/22/2013. Alan Zuckerman 1, Swapna Abhyankar 1, Tiffany Colarusso 2, Richard Olney 2, Kristin Burns 3, Marci Sontag 4
 Alan Zuckerman 1, Swapna Abhyankar 1, Tiffany Colarusso 2, Richard Olney 2, Kristin Burns 3, Marci Sontag 4 1 National Library of Medicine, NIH, Bethesda, MD, USA, 2 Centers for Disease Control and Prevention,
Alan Zuckerman 1, Swapna Abhyankar 1, Tiffany Colarusso 2, Richard Olney 2, Kristin Burns 3, Marci Sontag 4 1 National Library of Medicine, NIH, Bethesda, MD, USA, 2 Centers for Disease Control and Prevention,
Before we are Born: Fetal Diagnosis of Congenital Heart Disease
 Before we are Born: Fetal Diagnosis of Congenital Heart Disease Mohamed Sulaiman, MD Pediatric cardiologist Kidsheart: American Fetal & Children's Heart Center Dubai Healthcare City, Dubai-UAE First Pediatric
Before we are Born: Fetal Diagnosis of Congenital Heart Disease Mohamed Sulaiman, MD Pediatric cardiologist Kidsheart: American Fetal & Children's Heart Center Dubai Healthcare City, Dubai-UAE First Pediatric
A SURGEONS' GUIDE TO CARDIAC DIAGNOSIS
 A SURGEONS' GUIDE TO CARDIAC DIAGNOSIS PART II THE CLINICAL PICTURE DONALD N. ROSS B. Sc., M. B., CH. B., F. R. C. S. CONSULTANT THORACIC SURGEON GUY'S HOSPITAL, LONDON WITH 53 FIGURES Springer-Verlag
A SURGEONS' GUIDE TO CARDIAC DIAGNOSIS PART II THE CLINICAL PICTURE DONALD N. ROSS B. Sc., M. B., CH. B., F. R. C. S. CONSULTANT THORACIC SURGEON GUY'S HOSPITAL, LONDON WITH 53 FIGURES Springer-Verlag
2) VSD & PDA - Dr. Aso
 2) VSD & PDA - Dr. Aso Ventricular Septal Defect (VSD) Most common cardiac malformation 25-30 % Types of VSD: According to position perimembranous, inlet, muscular. According to size small, medium, large.
2) VSD & PDA - Dr. Aso Ventricular Septal Defect (VSD) Most common cardiac malformation 25-30 % Types of VSD: According to position perimembranous, inlet, muscular. According to size small, medium, large.
(f) "Birthing center" means any facility that is licensed by the Georgia Department of Community Health as a birthing center;
 Ga. Comp. R. & Regs. r. 511-5-5-.02 Definitions Rule 511-5-5-.02. Definitions (a) "Abnormal test result" is a test result from blood testing or physiologic monitoring that is outside the screening limits
Ga. Comp. R. & Regs. r. 511-5-5-.02 Definitions Rule 511-5-5-.02. Definitions (a) "Abnormal test result" is a test result from blood testing or physiologic monitoring that is outside the screening limits
Paediatric Cardiology. Acyanotic CHD. Prof F F Takawira
 Paediatric Cardiology Acyanotic CHD Prof F F Takawira Aetiology Chromosomal Down syndrome, T13, T18 Genetic syndromes (gene defects) Velo-Cardio-facial (22 del) Genetic syndromes (undefined aetiology)
Paediatric Cardiology Acyanotic CHD Prof F F Takawira Aetiology Chromosomal Down syndrome, T13, T18 Genetic syndromes (gene defects) Velo-Cardio-facial (22 del) Genetic syndromes (undefined aetiology)
The Chest X-ray for Cardiologists
 Mayo Clinic & British Cardiovascular Society at the Royal College of Physicians, London : 21-23-October 2013 Cases-Controversies-Updates 2013 The Chest X-ray for Cardiologists Michael Rubens Royal Brompton
Mayo Clinic & British Cardiovascular Society at the Royal College of Physicians, London : 21-23-October 2013 Cases-Controversies-Updates 2013 The Chest X-ray for Cardiologists Michael Rubens Royal Brompton
DEVELOPMENT OF THE CIRCULATORY SYSTEM L E C T U R E 5
 DEVELOPMENT OF THE CIRCULATORY SYSTEM L E C T U R E 5 REVIEW OF CARDIAC ANATOMY Heart 4 chambers Base and apex Valves Pericardial sac 3 layers: epi, myo, endo cardium Major blood vessels Aorta and its
DEVELOPMENT OF THE CIRCULATORY SYSTEM L E C T U R E 5 REVIEW OF CARDIAC ANATOMY Heart 4 chambers Base and apex Valves Pericardial sac 3 layers: epi, myo, endo cardium Major blood vessels Aorta and its
Critical Heart Disease in the Newborn. What you need to know
 Critical Heart Disease in the Newborn What you need to know DISCLOSURES Nothing to report OBJECTIVES DESCRIBE NEONATAL CARDIOVASCULAR PHYSIOLOGY RECOGNIZE NEONATAL CARDIAC EMERGENCIES FORMULATE TREATMENT
Critical Heart Disease in the Newborn What you need to know DISCLOSURES Nothing to report OBJECTIVES DESCRIBE NEONATAL CARDIOVASCULAR PHYSIOLOGY RECOGNIZE NEONATAL CARDIAC EMERGENCIES FORMULATE TREATMENT
APPROACH TO CARDIAC HISTORY TAKING. Index
 Christopher Cheung APPROACH TO CARDIAC HISTORY TAKING Index General Presentation...1 2 Table 1 Congenital Heart Conditions...2 Questions to Ask...2 Table 2 PQRSTAAA Mnemonic Approach to Chest Pain...3
Christopher Cheung APPROACH TO CARDIAC HISTORY TAKING Index General Presentation...1 2 Table 1 Congenital Heart Conditions...2 Questions to Ask...2 Table 2 PQRSTAAA Mnemonic Approach to Chest Pain...3
PREMATURITY/ESTIMATED GESTATIONAL AGE
 PREMATURITY/ESTIMATED GESTATIONAL AGE 765.21 < 24 completed weeks of gestation P07.21 Extreme immaturity of newborn, gestational age less than 23 completed weeks P07.22 Extreme immaturity of newborn, gestational
PREMATURITY/ESTIMATED GESTATIONAL AGE 765.21 < 24 completed weeks of gestation P07.21 Extreme immaturity of newborn, gestational age less than 23 completed weeks P07.22 Extreme immaturity of newborn, gestational
SURGICAL TREATMENT AND OUTCOME OF CONGENITAL HEART DISEASE
 SURGICAL TREATMENT AND OUTCOME OF CONGENITAL HEART DISEASE Mr. W. Brawn Birmingham Children s Hospital. Aims of surgery The aim of surgery in congenital heart disease is to correct or palliate the heart
SURGICAL TREATMENT AND OUTCOME OF CONGENITAL HEART DISEASE Mr. W. Brawn Birmingham Children s Hospital. Aims of surgery The aim of surgery in congenital heart disease is to correct or palliate the heart
Neonatal/Pediatric Cardiopulmonary Care. Persistent Pulmonary Hypertension of the Neonate (PPHN) PPHN. Other. Other Diseases
 Neonatal/Pediatric Cardiopulmonary Care Other Diseases Persistent Pulmonary Hypertension of the Neonate (PPHN) PPHN 3 Also known as Persistent Fetal Circulation (PFC) Seen most frequently in term, post-term
Neonatal/Pediatric Cardiopulmonary Care Other Diseases Persistent Pulmonary Hypertension of the Neonate (PPHN) PPHN 3 Also known as Persistent Fetal Circulation (PFC) Seen most frequently in term, post-term
24. An infant with recurrent pneumonia underwent a frontal chest radiograph (Fig 24-A) followed by
 24. An infant with recurrent pneumonia underwent a frontal chest radiograph (Fig 24-A) followed by diagnosis? ndings, what is the most likely A. Pulmonary sequestration B. Congenital pulmonary airway malformation
24. An infant with recurrent pneumonia underwent a frontal chest radiograph (Fig 24-A) followed by diagnosis? ndings, what is the most likely A. Pulmonary sequestration B. Congenital pulmonary airway malformation
Index. Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type.
 Index Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A Acid base balance pregnancy-related changes to, 640 Acquired heart disease, 731 Acute fatty liver of pregnancy (AFLP), 618 Acute kidney
Index Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A Acid base balance pregnancy-related changes to, 640 Acquired heart disease, 731 Acute fatty liver of pregnancy (AFLP), 618 Acute kidney
CCHD Screening with Pulse Oximetry: A Success Story!
 CCHD Screening with Pulse Oximetry: A Success Story! Nicole Spillane, MD Associate Director of Neonatology, HackensackUMC Hackensack Meridian Health Objective Recognize the contribution of pulse oximetry
CCHD Screening with Pulse Oximetry: A Success Story! Nicole Spillane, MD Associate Director of Neonatology, HackensackUMC Hackensack Meridian Health Objective Recognize the contribution of pulse oximetry
Suspected Metabolic Disease in the Newborn Period Acute Management "What do I do?" Barbara Marriage, PhD RD Abbott Nutrition
 Suspected Metabolic Disease in the Newborn Period Acute Management "What do I do?" Barbara Marriage, PhD RD Abbott Nutrition Introduction Review clinical findings that may be suspicious of a metabolic
Suspected Metabolic Disease in the Newborn Period Acute Management "What do I do?" Barbara Marriage, PhD RD Abbott Nutrition Introduction Review clinical findings that may be suspicious of a metabolic
Neonatal Cardiac Anomalies
 Objectives Neonatal Cardiac Anomalies Karen Knuth, RNC, MN, NNP-BC, ARNP Seattle Childrens Hospital What is CHD? Normal anatomy and circulation Clinical presentation: signs and symptoms Diagnostics Common
Objectives Neonatal Cardiac Anomalies Karen Knuth, RNC, MN, NNP-BC, ARNP Seattle Childrens Hospital What is CHD? Normal anatomy and circulation Clinical presentation: signs and symptoms Diagnostics Common
Infant Of Diabetic Mother(IDM)
 Infant Of Diabetic Mother(IDM) Sangram Satish Magar 1, Sanskriti Mirashi 2 1. M.D. Sch.(Kaumarbhrutya-Balrog) 2.Guide (Kaumarbhrutya-Balrog), L.R.P.Medical college,islampur,tal- Walwa, dist- Sangli, Maharashtra,
Infant Of Diabetic Mother(IDM) Sangram Satish Magar 1, Sanskriti Mirashi 2 1. M.D. Sch.(Kaumarbhrutya-Balrog) 2.Guide (Kaumarbhrutya-Balrog), L.R.P.Medical college,islampur,tal- Walwa, dist- Sangli, Maharashtra,
Appropriate Use Criteria for Initial Transthoracic Echocardiography in Outpatient Pediatric Cardiology (scores listed by Appropriate Use rating)
 Appropriate Use Criteria for Initial Transthoracic Echocardiography in Outpatient Pediatric Cardiology (scores listed by Appropriate Use rating) Table 1: Appropriate indications (median score 7-9) Indication
Appropriate Use Criteria for Initial Transthoracic Echocardiography in Outpatient Pediatric Cardiology (scores listed by Appropriate Use rating) Table 1: Appropriate indications (median score 7-9) Indication
Inborn Errors of Metabolism in the Emergency Department. Will Davies June 2014
 Inborn Errors of Metabolism in the Emergency Department Will Davies June 2014 Inborn Errors of Metabolism in the Emergency Department Overview Although individually rare, altogether they are 1:1000-2500
Inborn Errors of Metabolism in the Emergency Department Will Davies June 2014 Inborn Errors of Metabolism in the Emergency Department Overview Although individually rare, altogether they are 1:1000-2500
Pathological physiology of cardiovascular system Congenital heart diseases
 Pathological physiology of cardiovascular system Congenital heart diseases Rácz Oliver, Sedláková Eva Institute of Pathological Physiology, Medical School, P.J. Šafárik University Oliver Rácz, Eva Sedláková
Pathological physiology of cardiovascular system Congenital heart diseases Rácz Oliver, Sedláková Eva Institute of Pathological Physiology, Medical School, P.J. Šafárik University Oliver Rácz, Eva Sedláková
CONGENITAL HEART LESIONS ((C.H.L
 CONGENITAL HEART LESIONS ((C.H.L BY THE BOOKS: 0.8 IN FACT: 3-5% INCLUDING: - BICUSPID AORTIC VALVE MITRAL VALVE PROLAPSE LATE DIAGNOSIS - :INCREASED INCIDENCE IN ADULTS BETTER DIAGNOSIS IN INFANCY BETTER
CONGENITAL HEART LESIONS ((C.H.L BY THE BOOKS: 0.8 IN FACT: 3-5% INCLUDING: - BICUSPID AORTIC VALVE MITRAL VALVE PROLAPSE LATE DIAGNOSIS - :INCREASED INCIDENCE IN ADULTS BETTER DIAGNOSIS IN INFANCY BETTER
Approach to a baby with cyanosis
 Approach to a baby with cyanosis Objectives Cyanosis : types Differentials: cardiac vs. non cardiac Approach Case scenarios Cyanosis Greek word kuaneos meaning dark blue Bluish discolouration of skin,
Approach to a baby with cyanosis Objectives Cyanosis : types Differentials: cardiac vs. non cardiac Approach Case scenarios Cyanosis Greek word kuaneos meaning dark blue Bluish discolouration of skin,
Pathology. Congenital heart disease. congenital heart diseases. congenital heart diseases - etiology. lecture 7
 Pathology lecture 7 prof hab. n. med. Andrzej Marszałek Congenital heart disease congenital heart diseases Def.: anatomical anomalies present at delivery ambnormal embryogenesis 3. and 8. week of gestation
Pathology lecture 7 prof hab. n. med. Andrzej Marszałek Congenital heart disease congenital heart diseases Def.: anatomical anomalies present at delivery ambnormal embryogenesis 3. and 8. week of gestation
Clinicians and Facilities: RESOURCES WHEN CARING FOR WOMEN WITH ADULT CONGENITAL HEART DISEASE OR OTHER FORMS OF CARDIOVASCULAR DISEASE!!
 Clinicians and Facilities: RESOURCES WHEN CARING FOR WOMEN WITH ADULT CONGENITAL HEART DISEASE OR OTHER FORMS OF CARDIOVASCULAR DISEASE!! Abha'Khandelwal,'MD,'MS' 'Stanford'University'School'of'Medicine'
Clinicians and Facilities: RESOURCES WHEN CARING FOR WOMEN WITH ADULT CONGENITAL HEART DISEASE OR OTHER FORMS OF CARDIOVASCULAR DISEASE!! Abha'Khandelwal,'MD,'MS' 'Stanford'University'School'of'Medicine'
Lectures 4 Early fetal assessment, screening, ultrasound and treatment modalities during pregnancy. II. Asphyxia and Resuscitation (3 lectures)...
 Outline of a 2 year Neonatology educational course (80 lectures) PLUS 2 graduate level courses (GENETICS and BIOSTATISTICS & EPIDEMIOLOGY Approximate Percent in Examination I. Maternal-Fetal Medicine (6
Outline of a 2 year Neonatology educational course (80 lectures) PLUS 2 graduate level courses (GENETICS and BIOSTATISTICS & EPIDEMIOLOGY Approximate Percent in Examination I. Maternal-Fetal Medicine (6
The sinus venosus represent the venous end of the heart It receives 3 veins: 1- Common cardinal vein body wall 2- Umbilical vein from placenta 3-
 1 2 The sinus venosus represent the venous end of the heart It receives 3 veins: 1- Common cardinal vein body wall 2- Umbilical vein from placenta 3- Vitelline vein from yolk sac 3 However!!!!! The left
1 2 The sinus venosus represent the venous end of the heart It receives 3 veins: 1- Common cardinal vein body wall 2- Umbilical vein from placenta 3- Vitelline vein from yolk sac 3 However!!!!! The left
Pattern of Congenital Heart Disease A Hospital-Based Study *Sadiq Mohammed Al-Hamash MBChB, FICMS
 Pattern of Congenital Heart Disease A Hospital-Based Study *Sadiq Mohammed Al-Hamash MBChB, FICMS ABSTRACT Background: The congenital heart disease occurs in 0,8% of live births and they have a wide spectrum
Pattern of Congenital Heart Disease A Hospital-Based Study *Sadiq Mohammed Al-Hamash MBChB, FICMS ABSTRACT Background: The congenital heart disease occurs in 0,8% of live births and they have a wide spectrum
Congenital Heart Disease. CCCHD In WI. Critical Congenital Heart Disease. Why Screen? 4/20/2018. Early Detection = Better Outcomes
 Congenital Heart Disease A Positive Screen? What Does it Mean? A Review of Pulse Oximetry Screening for Critical Congenital Heart Disease Elizabeth Goetz MD MPH 8-10/1000 livebirths 3% of all infant mortality
Congenital Heart Disease A Positive Screen? What Does it Mean? A Review of Pulse Oximetry Screening for Critical Congenital Heart Disease Elizabeth Goetz MD MPH 8-10/1000 livebirths 3% of all infant mortality
Newborn Screen & Development Facts about the genetic diseases new since March 2006 (Excluding Cystic Fibrosis)
 Newborn Screen & Development Facts about the genetic diseases new since March 2006 (Excluding Cystic Fibrosis) 1) Argininosuccinic acidemia (ASA) a) Incidence: ~1 in 70,000 b) Deficiency in an enzyme of
Newborn Screen & Development Facts about the genetic diseases new since March 2006 (Excluding Cystic Fibrosis) 1) Argininosuccinic acidemia (ASA) a) Incidence: ~1 in 70,000 b) Deficiency in an enzyme of
Carnitine palmitoyl transferase 2 deficiency (CPT2) is a rare inherited disorder that occurs when
 CPT2 Deficiency Carnitine palmitoyl transferase 2 deficiency (CPT2) is a rare inherited disorder that occurs when the last step in the entry of fats into sac-like bodies called mitochondria is blocked.
CPT2 Deficiency Carnitine palmitoyl transferase 2 deficiency (CPT2) is a rare inherited disorder that occurs when the last step in the entry of fats into sac-like bodies called mitochondria is blocked.
PATENT DUCTUS ARTERIOSUS (PDA)
 PATENT DUCTUS ARTERIOSUS (PDA) It is a channel that connect the pulmonary artery with the descending aorta (isthumus part). It results from the persistence of patency of the fetal ductus arteriosus after
PATENT DUCTUS ARTERIOSUS (PDA) It is a channel that connect the pulmonary artery with the descending aorta (isthumus part). It results from the persistence of patency of the fetal ductus arteriosus after
Inborn Error Of Metabolism :
 Inborn Error Of Metabolism : Inborn Error Of Metabolism inborn error of metabolism are a large group of hereditary biochemical diseases in which specific gene mutation cause abnormal or missing proteins
Inborn Error Of Metabolism : Inborn Error Of Metabolism inborn error of metabolism are a large group of hereditary biochemical diseases in which specific gene mutation cause abnormal or missing proteins
Newborn Screening: Blood Spot Disorders
 Newborn Screening: Blood Spot Disorders Arizona s Newborn Screening Program Program Overview Panel of Disorders Disorder Descriptions Program Components Hospitals ADHS Lab ADHS Follow-up ADHS Billing Medical
Newborn Screening: Blood Spot Disorders Arizona s Newborn Screening Program Program Overview Panel of Disorders Disorder Descriptions Program Components Hospitals ADHS Lab ADHS Follow-up ADHS Billing Medical
: Provide cardiovascular preventive counseling to parents and patients with specific cardiac diseases about:
 Children s Hospital & Research Center Oakland Cardiology Primary Goals for this Rotation 5.13 GOAL: Prevention, Counseling and Screening (Cardiovascular). Understand the role of the pediatrician in preventing
Children s Hospital & Research Center Oakland Cardiology Primary Goals for this Rotation 5.13 GOAL: Prevention, Counseling and Screening (Cardiovascular). Understand the role of the pediatrician in preventing
The Fetal Care Center at NewYork-Presbyterian/ Weill Cornell Medicine
 The Fetal Care Center at NewYork-Presbyterian/ Weill Cornell Medicine Prompt and Personalized Care for Women with Complex Pregnancies A Team of Experts additional training in maternal and fetal complications
The Fetal Care Center at NewYork-Presbyterian/ Weill Cornell Medicine Prompt and Personalized Care for Women with Complex Pregnancies A Team of Experts additional training in maternal and fetal complications
